Настройка во время выполнения
Поведение этих функций зависит от установок в php.ini.
| Имя | По умолчанию | Место изменения | Список изменений |
|---|---|---|---|
| error_reporting | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| display_errors | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| display_startup_errors | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL |
До PHP 8.0.0 значение по умолчанию было "0".
|
| log_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| log_errors_max_len | «1024» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| ignore_repeated_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| ignore_repeated_source | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| report_memleaks | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| track_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | Объявлено устаревшим в PHP 7.2.0, удалено в PHP 8.0.0. |
| html_errors | «1» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| xmlrpc_errors | «0» | PHP_INI_SYSTEM | |
| xmlrpc_error_number | «0» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| docref_root | «» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| docref_ext | «» | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_prepend_string | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_append_string | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_log | NULL | PHP_INI_ALL | |
| error_log_mode | 0o644 | PHP_INI_ALL | Доступно, начиная с PHP 8.2.0 |
| syslog.facility | «LOG_USER» | PHP_INI_SYSTEM | Доступно, начиная с PHP 7.3.0. |
| syslog.filter | «no-ctrl» | PHP_INI_ALL | Доступно, начиная с PHP 7.3.0. |
| syslog.ident | «php» | PHP_INI_SYSTEM | Доступно, начиная с PHP 7.3.0. |
Для подробного описания констант
PHP_INI_*, обратитесь к разделу Где могут быть установлены параметры конфигурации.
Краткое разъяснение конфигурационных
директив.
-
error_reporting
int -
Задаёт уровень протоколирования ошибки. Параметр может быть либо числом,
представляющим битовое поле, либо именованной константой.
Соответствующие уровни и константы приведены в разделе
Предопределённые константы,
а также в php.ini. Для установки настройки во время выполнения используйте функцию
error_reporting(). Смотрите также описание директивы
display_errors.Значение по умолчанию равно
E_ALL.До PHP 8.0.0 значение по умолчанию было:
E_ALL&
~E_NOTICE&
~E_STRICT&
~E_DEPRECATED
При этой настройке не отображаются уровни ошибокE_NOTICE,
E_STRICTиE_DEPRECATED.Замечание:
PHP-константы за пределами PHPИспользование PHP-констант за пределами PHP, например в файле
httpd.conf, не имеет смысла, так как в таких случаях требуются
целочисленные значения (int). Более того, с течением времени будут
добавляться новые уровни ошибок, а максимальное значение константы
E_ALLсоответственно будет расти. Поэтому в месте, где
предполагается указатьE_ALL, лучше задать большое целое число,
чтобы перекрыть все возможные битовые поля. Таким числом может быть, например,
2147483647(оно включит все возможные ошибки, не
толькоE_ALL). -
display_errors
string -
Эта настройка определяет, требуется ли выводить ошибки на экран вместе
с остальным выводом, либо ошибки должны быть скрыты от пользователя.Значение
"stderr"посылает ошибки в потокstderr
вместоstdout.Замечание:
Эта функциональность предназначена только для разработки и не должен использоваться в
готовых производственных системах (например, системах, имеющих доступ в интернет).Замечание:
Несмотря на то, что display_errors может быть установлена во время выполнения
(функцией ini_set()), это ни на что не повлияет, если в скрипте есть
фатальные ошибки. Это обусловлено тем, что ожидаемые действия программы во время
выполнения не получат управления (не будут выполняться). -
display_startup_errors
bool -
Даже если display_errors включена, ошибки, возникающие во время запуска PHP, не будут
отображаться. Настойчиво рекомендуем включать директиву display_startup_errors только
для отладки. -
log_errors
bool -
Отвечает за выбор журнала, в котором будут сохраняться сообщения об ошибках. Это
может быть журнал сервера или error_log.
Применимость этой настройки зависит от конкретного сервера.Замечание:
Настоятельно рекомендуем при работе на готовых работающих
web сайтах протоколировать ошибки там, где они отображаются. -
log_errors_max_len
int -
Задание максимальной длины log_errors в байтах. В
error_log добавляется информация
об источнике. Значение по умолчанию 1024. Установка значения в 0
позволяет снять ограничение на длину log_errors. Это ограничение
распространяется на записываемые в журнал ошибки, на отображаемые ошибки,
а также на $php_errormsg, но не на явно вызываемые функции,
такие как error_log().Если используется int, значение измеряется байтами. Вы также можете использовать сокращённую запись, которая описана в этом разделе FAQ.
-
ignore_repeated_errors
bool -
Не заносить в журнал повторяющиеся ошибки. Ошибка считается
повторяющейся, если происходит в том же файле и в той же строке, и если настройка
ignore_repeated_source выключена. -
ignore_repeated_source
bool -
Игнорировать источник ошибок при пропуске повторяющихся сообщений. Когда
эта настройка включена, повторяющиеся сообщения об ошибках не будут
заноситься в журнал вне зависимости от того, в каких файлах и строках они происходят. -
report_memleaks
bool -
Если настройка включена (по умолчанию), будет формироваться отчёт об утечках памяти,
зафиксированных менеджером памяти Zend. На POSIX платформах этот отчёт будет
направляться в поток stderr. На Windows платформах он будет посылаться в отладчик
функцией OutputDebugString(), просмотреть отчёт в этом случае можно с помощью утилит,
вроде » DbgView. Эта настройка имеет
смысл в сборках, предназначенных для отладки. При этом
E_WARNINGдолжна быть включена в список error_reporting. -
track_errors
bool -
Если включена, последняя произошедшая ошибка будет первой в переменной
$php_errormsg. -
html_errors
bool -
Если разрешена, сообщения об ошибках будут включать теги HTML. Формат для
HTML-ошибок производит нажимаемые ссылки, ведущие на описание ошибки, либо
функии, в которой она произошла. За такие ссылки ответственны
docref_root и
docref_ext.Если запрещена, то ошибки будут выдаваться простым текстом, без форматирования.
-
xmlrpc_errors
bool -
Если включена, то нормальное оповещение об ошибках отключается и, вместо него,
ошибки выводятся в формате XML-RPC. -
xmlrpc_error_number
int -
Используется в качестве значения XML-RPC элемента faultCode.
-
docref_root
string -
Новый формат ошибок содержит ссылку на страницу с описанием ошибки или
функции, вызвавшей эту ошибку. Можно разместить копию
описаний ошибок и функций локально и задать ini директиве значение
URL этой копии. Если, например, локальная копия описаний доступна по
адресу"/manual/", достаточно прописать
docref_root=/manual/. Дополнительно, необходимо
задать значение директиве docref_ext, отвечающей за соответствие
расширений файлов файлам описаний вашей локальной копии,
docref_ext=.html. Также возможно использование
внешних ссылок. Например,
docref_root=http://manual/en/или
docref_root="http://landonize.it/?how=url&theme=classic&filter=Landon
&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.php.net%2F"В большинстве случаев вам потребуется, чтобы значение docref_root оканчивалось
слешем"/". Тем не менее, бывают случаи, когда
это не требуется (смотрите выше, второй пример).Замечание:
Эта функциональность предназначена только для разработки, так как он облегчает
поиск описаний функций и ошибок. Не используйте его в готовых
производственных системах (например, имеющих доступ в интернет). -
docref_ext
string -
Смотрите docref_root.
Замечание:
Значение docref_ext должно начинаться с точки
".". -
error_prepend_string
string -
Строка, которая будет выводиться непосредственно перед сообщением об ошибке.
Используется только тогда, когда на экране отображается сообщение об ошибке.
Основная цель — добавить дополнительную HTML-разметку к сообщению об ошибке. -
error_append_string
string -
Строка, которая будет выводиться после сообщения об ошибке.
Используется только тогда, когда на экране отображается сообщение об ошибке.
Основная цель — добавить дополнительную HTML-разметку к сообщению об ошибке. -
error_log
string -
Имя файла, в который будут добавляться сообщения об ошибках. Файл
должен быть открыт для записи пользователем веб-сервера. Если
используется специальное значениеsyslog, то
сообщения будут посылаться в системный журнал. На Unix-системах это
syslog(3), на Windows NT — журнал событий. Смотрите также: syslog().
Если директива не задана, ошибки будут направляться в SAPI журналы.
Например, это могут быть журналы ошибок Apache или поток
stderrкомандной строки CLI.
Смотрите также функцию error_log(). -
error_log_mode
int -
Режим файла, описанного в error_log.
-
syslog.facility
string -
Указывает, какой тип программы регистрирует сообщение.
Действует только в том случае, если опция error_log установлена в «syslog». -
syslog.filter
string -
Указывает тип фильтра для фильтрации регистрируемых сообщений.
Разрешённые символы передаются без изменений; все остальные записываются в шестнадцатеричном представлении с префиксомx.-
all– строка будет разделена
на символы новой строки и все символы будут переданы без изменений
-
ascii– строка будет разделена
на символы новой строки, а любые непечатаемые 7-битные символы ASCII будут экранированы
-
no-ctrl– строка будет разделена
на символы новой строки, а любые непечатаемые символы будут экранированы
-
raw– все символы передаются в системный
журнал без изменений, без разделения на новые строки (идентично PHP до 7.3)
Параметр влияет на ведение журнала через error_log установленного в «syslog» и вызовы syslog().
Замечание:
Тип фильтра
rawдоступен начиная с PHP 7.3.8 и PHP 7.4.0.
Директива не поддерживается в Windows.
-
-
syslog.ident
string -
Определяет строку идентификатора, которая добавляется к каждому сообщению.
Действует только в том случае, если опция error_log установлена в «syslog».
cjakeman at bcs dot org ¶
13 years ago
Using
<?php ini_set('display_errors', 1); ?>
at the top of your script will not catch any parse errors. A missing ")" or ";" will still lead to a blank page.
This is because the entire script is parsed before any of it is executed. If you are unable to change php.ini and set
display_errors On
then there is a possible solution suggested under error_reporting:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
ini_set("display_errors", 1);
include("file_with_errors.php");
?>
[Modified by moderator]
You should also consider setting error_reporting = -1 in your php.ini and display_errors = On if you are in development mode to see all fatal/parse errors or set error_log to your desired file to log errors instead of display_errors in production (this requires log_errors to be turned on).
ohcc at 163 dot com ¶
6 years ago
If you set the error_log directive to a relative path, it is a path relative to the document root rather than php's containing folder.
iio7 at protonmail dot com ¶
1 year ago
It's important to note that when display_errors is "on", PHP will send a HTTP 200 OK status code even when there is an error. This is not a mistake or a wrong behavior, but is because you're asking PHP to output normal HTML, i.e. the error message, to the browser.
When display_errors is set to "off", PHP will send a HTTP 500 Internal Server Error, and let the web server handle it from there. If the web server is setup to intercept FastCGI errors (in case of NGINX), it will display the 500 error page it has setup. If the web server cannot intercept FastCGI errors, or it isn't setup to do it, an empty screen will be displayed in the browser (the famous white screen of death).
If you need a custom error page but cannot intercept PHP errors on the web server you're using, you can use PHPs custom error and exception handling mechanism. If you combine that with output buffering you can prevent any output to reach the client before the error/exception occurs. Just remember that parse errors are compile time errors that cannot be handled by a custom handler, use "php -l foo.php" from the terminal to check for parse errors before putting your files on production.
Roger ¶
3 years ago
When `error_log` is set to a file path, log messages will automatically be prefixed with timestamp [DD-MMM-YYYY HH:MM:SS UTC]. This appears to be hard-coded, with no formatting options.
php dot net at sp-in dot dk ¶
8 years ago
There does not appear to be a way to set a tag / ident / program for log entries in the ini file when using error_log=syslog. When I test locally, "apache2" is used.
However, calling openlog() with an ident parameter early in your script (or using an auto_prepend_file) will make PHP use that value for all subsequent log entries. closelog() will restore the original tag.
This can be done for setting facility as well, although the original value does not seem to be restored by closelog().
jaymore at gmail dot com ¶
6 years ago
Document says
So in place of E_ALL consider using a larger value to cover all bit fields from now and well into the future, a numeric value like 2147483647 (includes all errors, not just E_ALL).
But it is better to set "-1" as the E_ALL value.
For example, in httpd.conf or .htaccess, use
php_value error_reporting -1
to report all kind of error without be worried by the PHP version.
В этом руководстве мы расскажем о различных способах того, как в PHP включить вывод ошибок. Мы также обсудим, как записывать ошибки в журнал (лог).
Как быстро показать все ошибки PHP
Самый быстрый способ отобразить все ошибки и предупреждения php — добавить эти строки в файл PHP:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
Что именно делают эти строки?
Функция ini_set попытается переопределить конфигурацию, найденную в вашем ini-файле PHP.
Display_errors и display_startup_errors — это только две из доступных директив. Директива display_errors определяет, будут ли ошибки отображаться для пользователя. Обычно директива dispay_errors не должна использоваться для “боевого” режима работы сайта, а должна использоваться только для разработки.
display_startup_errors — это отдельная директива, потому что display_errors не обрабатывает ошибки, которые будут встречаться во время запуска PHP. Список директив, которые могут быть переопределены функцией ini_set, находится в официальной документации .
К сожалению, эти две директивы не смогут отображать синтаксические ошибки, такие как пропущенные точки с запятой или отсутствующие фигурные скобки.
Отображение ошибок PHP через настройки в php.ini
Если ошибки в браузере по-прежнему не отображаются, то добавьте директиву:
display_errors = on
Директиву display_errors следует добавить в ini-файл PHP. Она отобразит все ошибки, включая синтаксические ошибки, которые невозможно отобразить, просто вызвав функцию ini_set в коде PHP.
Актуальный INI-файл можно найти в выводе функции phpinfo (). Он помечен как “загруженный файл конфигурации” (“loaded configuration file”).
Отображать ошибки PHP через настройки в .htaccess
Включить или выключить отображение ошибок можно и с помощью файла .htaccess, расположенного в каталоге сайта.
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
.htaccess также имеет директивы для display_startup_errors и display_errors.
Вы можете настроить display_errors в .htaccess или в вашем файле PHP.ini. Однако многие хостинг-провайдеры не разрешают вам изменять ваш файл PHP.ini для включения display_errors.
В файле .htaccess также можно включить настраиваемый журнал ошибок, если папка журнала или файл журнала доступны для записи. Файл журнала может быть относительным путем к месту расположения .htaccess или абсолютным путем, например /var/www/html/website/public/logs.
php_value error_log logs/all_errors.log
Включить подробные предупреждения и уведомления
Иногда предупреждения приводят к некоторым фатальным ошибкам в определенных условиях. Скрыть ошибки, но отображать только предупреждающие (warning) сообщения можно вот так:
error_reporting(E_WARNING);
Для отображения предупреждений и уведомлений укажите «E_WARNING | E_NOTICE».
Также можно указать E_ERROR, E_WARNING, E_PARSE и E_NOTICE в качестве аргументов. Чтобы сообщить обо всех ошибках, кроме уведомлений, укажите «E_ALL & ~ E_NOTICE», где E_ALL обозначает все возможные параметры функции error_reporting.
Более подробно о функции error_reporting ()
Функция сообщения об ошибках — это встроенная функция PHP, которая позволяет разработчикам контролировать, какие ошибки будут отображаться. Помните, что в PHP ini есть директива error_reporting, которая будет задана этой функцией во время выполнения.
error_reporting(0);
Для удаления всех ошибок, предупреждений, сообщений и уведомлений передайте в функцию error_reporting ноль. Можно сразу отключить сообщения отчетов в ini-файле PHP или в .htaccess:
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);
PHP позволяет использовать переменные, даже если они не объявлены. Это не стандартная практика, поскольку необъявленные переменные будут вызывать проблемы для приложения, если они используются в циклах и условиях.
Иногда это также происходит потому, что объявленная переменная имеет другое написание, чем переменная, используемая для условий или циклов. Когда E_NOTICE передается в функцию error_reporting, эти необъявленные переменные будут отображаться.
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);
Функция сообщения об ошибках позволяет вам фильтровать, какие ошибки могут отображаться. Символ «~» означает «нет», поэтому параметр ~ E_NOTICE означает не показывать уведомления. Обратите внимание на символы «&» и «|» между возможными параметрами. Символ «&» означает «верно для всех», в то время как символ «|» представляет любой из них, если он истинен. Эти два символа имеют одинаковое значение в условиях PHP OR и AND.
error_reporting(E_ALL);
error_reporting(-1);
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
Эти три строки кода делают одно и то же, они будут отображать все ошибки PHP. Error_reporting(E_ALL) наиболее широко используется разработчиками для отображения ошибок, потому что он более читабелен и понятен.
Включить ошибки php в файл с помощью функции error_log ()
У сайта на хостинге сообщения об ошибках не должны показываться конечным пользователям, но эта информация все равно должна быть записана в журнал (лог).
Простой способ использовать файлы журналов — использовать функцию error_log, которая принимает четыре параметра. Единственный обязательный параметр — это первый параметр, который содержит подробную информацию об ошибке или о том, что нужно регистрировать. Тип, назначение и заголовок являются необязательными параметрами.
error_log("There is something wrong!", 0);
Параметр type, если он не определен, будет по умолчанию равен 0, что означает, что эта информация журнала будет добавлена к любому файлу журнала, определенному на веб-сервере.
error_log("Email this error to someone!", 1, "someone@mydomain.com");
Параметр 1 отправит журнал ошибок на почтовый ящик, указанный в третьем параметре. Чтобы эта функция работала, PHP ini должен иметь правильную конфигурацию SMTP, чтобы иметь возможность отправлять электронные письма. Эти SMTP-директивы ini включают хост, тип шифрования, имя пользователя, пароль и порт. Этот вид отчетов рекомендуется использовать для самых критичных ошибок.
error_log("Write this error down to a file!", 3, "logs/my-errors.log");
Для записи сообщений в отдельный файл необходимо использовать тип 3. Третий параметр будет служить местоположением файла журнала и должен быть доступен для записи веб-сервером. Расположение файла журнала может быть относительным путем к тому, где этот код вызывается, или абсолютным путем.
Журнал ошибок PHP через конфигурацию веб-сервера
Лучший способ регистрировать ошибки — это определить их в файле конфигурации веб-сервера.
Однако в этом случае вам нужно попросить администратора сервера добавить следующие строки в конфигурацию.
Пример для Apache:
ErrorLog "/var/log/apache2/my-website-error.log"
В nginx директива называется error_log.
error_log /var/log/nginx/my-website-error.log;
Теперь вы знаете, как в PHP включить отображение ошибок. Надеемся, что эта информация была вам полезна.
Introduction
PHP is a server-side scripting language used in web development. As a scripting language, PHP is used to write code (or scripts) to perform tasks. If a script encounters an error, PHP can generate an error to a log file.
In this tutorial, learn how to enable PHP Error Reporting to display all warnings. We also dive into creating an error log file in PHP.

What is a PHP Error?
A PHP error occurs when there is an issue within the PHP code. Even something simple can cause an error, such as using incorrect syntax or forgetting a semicolon, which prompts a notice. Or, the cause may be more complex, such as calling an improper variable, which can lead to a fatal error that crashes your system.
If you do not see errors, you may need to enable error reporting.
To enable error reporting in PHP, edit your PHP code file, and add the following lines:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL);
?>You can also use the ini_set command to enable error reporting:
<?php
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
?>Edit php.ini to Enable PHP Error Reporting
If you have set your PHP code to display errors and they are still not visible, you may need to make a change in your php.ini file.
On Linux distributions, the file is usually located in /etc/php.ini folder.
Open php.ini in a text editor.
Then, edit the display_errors line to On.
This is an example of the correction in a text editor:

Edit .htaccess File to turn on Error Reporting
The .htaccess file, which acts as a master configuration file, is usually found in the root or public directory. The dot at the beginning means it’s hidden. If you’re using a file manager, you’ll need to edit the settings to see the hidden files.
Open the .htaccess file for editing, and add the following:
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors onIf these values are already listed, make sure they’re set to on.
Save the file and exit.
Other Useful Commands
To display only the fatal warning and parse errors, use the following:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ERROR | E_WARNING | E_PARSE);
?>You can add any other error types you need. Just separate them with the pipe | symbol.
This list contains all the predefined constants for PHP error types.
One useful feature is the “not” symbol.
To exclude a particular error type from reporting:
<?php
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE)
?>In this example, the output displays all errors except for notice errors.
How to Turn Off PHP Error Reporting
To turn off or disable error reporting in PHP, set the value to zero. For example, use the code snippet:
<?php
error_reporting(0);
?>How to Create an Error Log File in PHP
Error logs are valuable resources when dealing with PHP issues.
To display PHP error logs, edit the .htaccess file by adding the following:
php_value error_log logs/all_errors.logIf you don’t have access to the .htaccess file, you can edit the httpd.conf or apache2.conf file directly.
This log is typically stored in the /var/log/httpd/ or /var/log/apache2/ directory.
To enable error logging, edit your version of the file and add the following:
ErrorLog “/var/log/apache2/website-name-error.log”You may substitute httpd for apache2 if needed. Likewise, if you’re using nginx, you can use that directory for the error log.
How to Display PHP Errors on a Webpage
Error logs are valuable resources when dealing with PHP issues.
To display PHP error logs, edit the .htaccess file by adding the following:
php_value error_log logs/all_errors.logIf you don’t have access to the file, you can edit the httpd.conf or apache2.conf file directly.
This log is typically stored in the /var/log/httpd/ or /var/log/apache2/ directory.
To enable error logging, edit your version of the file and add the following:
ErrorLog “/var/log/apache2/website-name-error.log”You may substitute httpd for apache2 if needed. Likewise, if you’re using nginx, you can use that directory for the error log.
Conclusion
This tutorial has provided you with multiple alternatives to enable and show all PHP errors and warnings. By receiving error notifications quickly and accurately, you can improve the ability to troubleshoot PHP issues. If you are implementing new features, installing a new PHP-based app, or trying to locate a bug on your website, it is important to know which PHP version your web server is running before taking any steps.
During the execution of a PHP application, it can generate a wide range of warnings and errors. For developers seeking to troubleshoot a misbehaving application, being able to check these errors is critical. Developers, on the other hand, frequently encounter difficulties when attempting to display errors from their PHP applications. Instead, their applications simply stop working.
First and foremost, you should be aware that with PHP, some errors prevent the script from being executed. Some errors, on the other hand, just display error messages with a warning. Then you’ll learn how to use PHP to show or hide all error reporting.
In PHP, there are four types of errors:
- Notice Error – When attempting to access an undefined index in a PHP code, an error occurs. The execution of the PHP code is not halted by the notice error. It just alerts you to the fact that there is an issue.
- Warning Error – The most common causes of warning errors are omitting a file or invoking a function with improper parameters. It’s comparable to seeing a mistake, but it doesn’t stop the PHP code from running. It just serves as a reminder that the script has a flaw.
- Fatal Error – When undefined functions and classes are called in a PHP code, a fatal error occurs. The PHP code is stopped and an error message is displayed when a fatal error occurs.
- Parse Error – When a syntax issue occurs in the script, it is referred to as a parse error. The execution of the PHP code is also stopped when a parse error occurs, and an error message is displayed.
You’ve come to the right place if you’re having troubles with your PHP web application and need to see all of the errors and warnings. We’ll go through all of the different ways to activate PHP errors and warnings in this tutorial.
- To Show All PHP Errors
- .htaccess Configuration to Show PHP Errors
- Enable Detailed Warnings and Notices
- In-depth with the error_reporting() function
- Use error_log() Function to Log PHP Error
- Use Web Server Configuration to Log PHP Errors
- Collect PHP Errors using Atatus
1. To Show All PHP Errors
Adding these lines to your PHP code file is the quickest way to output all PHP errors and warnings:
ini_set ('display_errors', 1);
ini_set ('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting (E_ALL);The ini_set() function will attempt to override the PHP ini file’s configuration.
The display_errors and display_startup_errors directives are just two of the options.
- The display_errors directive determines whether or not the errors are visible to the user. After development, the dispay_errors directive should usually be disabled.
- The display_startup_errors directive, on the other hand, is separate since display errors do not handle errors that occur during PHP’s startup sequence.
The official documentation contains a list of directives that can be overridden by the ini_set() function. Unfortunately, parsing problems such as missing semicolons or curly brackets will not be displayed by these two directives. The PHP ini configuration must be changed in this scenario.
To display all errors, including parsing errors, in xampp, make the following changes to the php.ini example file and restart the apache server.
display_errors = onIn the PHP.ini file, set the display errors directive to turn on. It will show all errors that can’t be seen by just calling the ini_set() function, such as syntax and parsing errors.
2. .htaccess Configuration to Show PHP Errors
The directory files are normally accessible to developers. The .htaccess file in the project’s root or public directory can also be used to enable or disable the directive for displaying PHP errors.
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on.htaccess has directives for display_startup_errors and display_errors, similar to what will be added to the PHP code to show PHP errors. The benefit of displaying or silencing error messages in this way is that development and production can have separate .htaccess files, with production suppressing error displays.
You may want to adjust display_errors in .htaccess or your PHP.ini file depending on which files you have access to and how you handle deployments and server configurations. Many hosting companies won’t let you change the PHP.ini file to enable display errors.
3. Enable Detailed Warnings and Notices
Warnings that appear to not affect the application at first might sometimes result in fatal errors under certain circumstances. These warnings must be fixed because they indicate that the application will not function normally in certain circumstances. If these warnings result in a large number of errors, it would be more practical to hide the errors and only display the warning messages.
error_reporting(E_WARNING);Showing warnings and hiding errors are as simple as adding a single line of code for a developer. The parameter for the error reporting function will be “E_WARNING | E_NOTICE” to display warnings and notifications. As bitwise operators, the error reporting function can accept E_ERROR, E_WARNING, E_PARSE, and E_NOTICE parameters.
For ease of reference, these constants are also detailed in the online PHP Manual.
To report all errors except notices, use the option «E_ALL & E_NOTICE,» where E_ALL refers to all of the error reporting function’s potential parameters.
4. In-depth with the error_reporting() Function
One of the first results when you browser «PHP errors» is a link to the error_reporting() function documentation.
The PHP error_reporting() function allows developers to choose which and how many errors should be displayed in their applications. Remember that this function will set the error reporting directive in the PHP ini configuration during runtime.
error_reporting(0);The value zero should be supplied to the error_reporting() function to delete all errors, warnings, parse messages, and notices. This line of code would be impractical to include in each of the PHP files. It is preferable to disable report messages in the PHP ini file or the .htaccess file.
error_reporting(-1);An integer value is also passed as an input to the error_reporting() function. In PHP, we may use this method to display errors. In PHP, there are many different types of errors. All PHP errors are represented by the -1 level. Even with new levels and constants, passing the value -1 will work in future PHP versions.
error_reporting(E_NOTICE);Variables can be used even if they aren’t declared in PHP. This isn’t recommended because undeclared variables can create issues in the application when they’re utilized in loops and conditions.
This can also happen when the stated variable is spelled differently than the variable used in conditions or loops. These undeclared variables will be displayed in the web application if E_NOTICE is supplied in the error_reporting() function.
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE);You can filter which errors are displayed using the error_reporting() function. The “~” character stands for “not” or “no,” hence the parameter ~E_NOTICE indicates that notices should not be displayed.
In the code, keep an eye out for the letters «&» and «|.» The “&” symbol stands for “true for all,” whereas the “|” character stands for “true for either.” In PHP, these two characters have the same meaning: OR and AND.
5. Use error_log() Function to Log PHP Error
Error messages must not be displayed to end-users during production, but they must be logged for tracing purposes. The best approach to keep track of these error messages in a live web application is to keep track of them in log files.
The error_log() function, which accepts four parameters, provides a simple way to use log files. The first parameter, which contains information about the log errors or what should be logged, is the only one that must be provided. This function’s type, destination, and header parameters are all optional.
error_log("Whoosh!!! Something is wrong!", 0);If the type option is not specified, it defaults to 0, which means that this log information will be appended to the web server’s log file.
error_log("Email this error to Justin!", 1, "Justin@mydomain.com");The error logs supplied in the third parameter will be emailed using the type 1 parameter. To use this feature, the PHP ini must have a valid SMTP configuration to send emails.
Host, encryption type, username, password, and port are among the SMTP ini directives. This kind of error reporting is recommended for logging or notifying errors that must be corrected as soon as possible.
error_log("Write this error down to a file!", 3, "logs/php-errors.log");Type 3 must be used to log messages in a different file established by the web server’s configuration. The third parameter specifies the log file’s location, which must be writable by the webserver. The log file’s location might be either a relative or absolute library to where this code is invoked.
You can also refer to the error_log() function documentation to know more.
6. Use Web Server Configuration to Log PHP Errors
The ideal technique to record errors is to define them in the web server configuration file, rather than modifying parameters in the .htaccess or adding lines in the PHP code to show errors.
ErrorLog "/var/log/apache2/my-website-error.log"These files must be added to the virtual host of a specific HTML page or application in Apache, which is commonly found in the sites-available folder in Ubuntu or the httpd-vhosts file in Windows.
error_log /var/log/nginx/my-website-error.log;The directive is just called error_log() in Nginx, as it is in Apache. The log files for both Apache and Nginx web servers must be writable by the webserver. Fortunately, the folders for the log files of these two web servers are already writable after installation.
7. Collect PHP Errors using Atatus
Atatus is an Application Performance Management (APM) solution that collects all requests to your PHP applications without requiring you to change your source code. However, the tool does more than just keep track of your application’s performance. Atatus’ ability to automatically gather all unhandled errors in your PHP application is one of its best features.
To fix PHP exceptions, gather all necessary information such as class, message, URL, request agent, version, and so on. Every PHP error is logged and captured with a full stack trace, with the precise line of source code marked, to make bug fixes easy.
Read the guide to know more about PHP Performance Monitoring.
All errors are automatically logged and structured in Atatus so that they can be easily viewed. Not only will Atatus show you what errors have happened, but it will also examine where and why they occurred. The logs also display the time and number of occurrences, making it much easier to focus on which issue to address.
Start your 14-day free trial of Atatus, right now!!!
Summary
When there is an issue with the PHP code, a PHP error occurs. Even something as simple as incorrect syntax or forgetting a semicolon can result in an error, prompting a notification. Alternatively, the cause could be more complicated, such as invoking an incorrect variable, which can result in a fatal error and cause your system to crash.
This tutorial has shown you several ways to enable and display all PHP errors and warnings. You can boost your ability to debug PHP issues by receiving error notifications fast and precisely.
Let us know what you think about displaying PHP errors in the below comment section.
Хостинг-провайдеры нередко отключают или блокируют вывод всех ошибок и предупреждений. Такие ограничения вводятся не просто так. Дело в том, что на рабочих серверах крайне не рекомендуется держать ошибки в открытом доступе. Информация о неисправностях может стать «наживкой» для злоумышленников.
При этом в процессе разработки сайтов и скриптов, очень важно отслеживать возникающие предупреждения. Знать о сбоях и неисправностях также важно и системным администраторам — это позволяет предотвратить проблемы на сайте или сервере.
Самый оптимальный вариант — не просто скрыть показ ошибок, но и настроить запись о них в логах. Это позволит отслеживать предупреждения и не подвергать сервер угрозе.
В статье мы расскажем, как включить и отключить через .htaccess вывод ошибок php, а также двумя другими способами — через скрипт PHP и через файл php.ini.
Обратите внимание: в некоторых случаях изменение настроек вывода возможно только через обращение в техническую поддержку хостинга.
Через .htaccess
Перейдите в каталог сайта и откройте файл .htaccess.
Вариант 1. Чтобы включить вывод, добавьте следующие строки:
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag html_errors onЧтобы отключить ошибки PHP htaccess, введите команду:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors off
php_flag html_errors offТакже выключить .htaccess display errors можно командой:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors off
php_flag html_errors off
php_value docref_root 0
php_value docref_ext 0Через логи PHP
Если вам нужно проверить или выключить ошибки только в определенных файлах, это можно сделать с помощью вызова PHP-функций.
Вариант 1. Чтобы включить вывод, используйте команду error_reporting. В зависимости от типа ошибок, которые вы хотите увидеть, подставьте нужное значение. Например, команда для вывода всех ошибок будет выглядеть так:
А для всех типов, исключая тип Notice, так:
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE)Чтобы отключить вывод, введите команду:
Чтобы отключить логирование повторяющихся ошибок, введите:
# disable repeated error logging
php_flag ignore_repeated_errors on
php_flag ignore_repeated_source onВариант 2. Чтобы проверить конкретный кусок кода, подойдет команда ниже. В зависимости от типа ошибок, которые вы хотите увидеть, в скобках подставьте нужное значение. Например, команда для вывода всех ошибок будет выглядеть так:
ini_set('display_errors', 'On')
error_reporting(E_ALL)После этого в консоли введите:
ini_set('display_errors', 'Off')Вариант 3. Ещё один из вариантов подключения через скрипт:
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors onДля отключения укажите:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors offВариант 4. Чтобы настроить вывод с логированием через конфигурацию веб-сервера, введите:
- для Apache —
ErrorLog «/var/log/apache2/my-website-error.log», - для Nginx —
error_log /var/log/nginx/my-website-error.log.
Подробнее о других аргументах читайте в документации на официальном сайте php.net.
Через файл php.ini
Настроить отслеживание также можно через файл php.ini. Этот вариант подойдет, когда отображение или скрытие ошибок нужно настроить для всего сайта или кода. Обратите внимание: возможность настройки через файл php.ini есть не у всех, поскольку некоторые хостинг-провайдеры частично или полностью закрывают доступ к файлу.
Вариант 1. Если у вас есть доступ, включить вывод можно командой:
После этого нужно перезагрузить сервер:
sudo apachectl -k gracefulВариант 2. Чтобы включить вывод, используйте команду error_reporting. В зависимости от типа ошибок, которые вы хотите увидеть, после знака = подставьте нужное значение. Например, команда для вывода всех ошибок будет выглядеть так:
error_reporting = E_ALL
display_errors OnПосле ввода перезагрузите сервер:
sudo apachectl -k gracefulЧтобы скрыть отображение, во второй строке команды укажите Оff вместо On:
Теперь вы знаете, как настроить не только через PHP и php.ini, но и через htaccess отображение ошибок.
I still vividly remember the first time I learned about PHP error handling.
It was in my fourth year of programming, my second with PHP, and I’d applied for a developer position at a local agency. The application required me to send in a code sample (GitHub as we know it didn’t exist back then) so I zipped and sent a simple custom CMS I’d created the previous year.
The email I got back from the person reviewing the code still chills my bones to this day.
«I was a bit worried about your project, but once I turned error reporting off, I see it actually works pretty well».
That was the first time I searched «PHP error reporting», discovered how to enable it, and died inside when I saw the stream of errors that were hidden from me before.
PHP errors and error reporting are something that many developers new to the language might miss initially. This is because, on many PHP based web server installations, PHP errors may be suppressed by default. This means that no one sees or is even aware of these errors.
For this reason, it’s a good idea to know where and how to enable them, especially for your local development environment. This helps you pick up errors in your code early on.
If you Google «PHP errors» one of the first results you will see is a link to the error_reporting function documentation.
This function allows you to both set the level of PHP error reporting, when your PHP script (or collection of scripts) runs, or retrieve the current level of PHP error reporting, as defined by your PHP configuration.
The error_reporting function accepts a single parameter, an integer, which indicates which level of reporting to allow. Passing nothing as a parameter simply returns the current level set.
There is a long list of possible values you can pass as a parameter, but we’ll dive into those later.
For now it’s important to know that each possible value also exists as a PHP predefined constant. So for example, the constant E_ERROR has the value of 1. This means you could either pass 1, or E_ERROR to the error_reporting function, and get the same result.
As a quick example, if we create a php_error_test.php PHP script file, we can see the current error reporting level set, as well as set it to a new level.
<?php
// echo the current error reporting level
echo error_reporting();
<?php
// report all Fatal run-time errors.
echo error_reporting(1);
Error reporting configuration
Using the error_reporting function in this way is great when you just want to see any errors related to the piece of code you’re currently working on.
But it would be better to control which errors are being reported on in your local development environment, and log them somewhere logical, to be able to review as you code. This can be done inside the PHP initialization (or php.ini) file.
The php.ini file is responsible for configuring all the aspects of PHP’s behavior. In it you can set things like how much memory to allocate to PHP scripts, what size file uploads to allow, and what error_reporting level(s) you want for your environment.
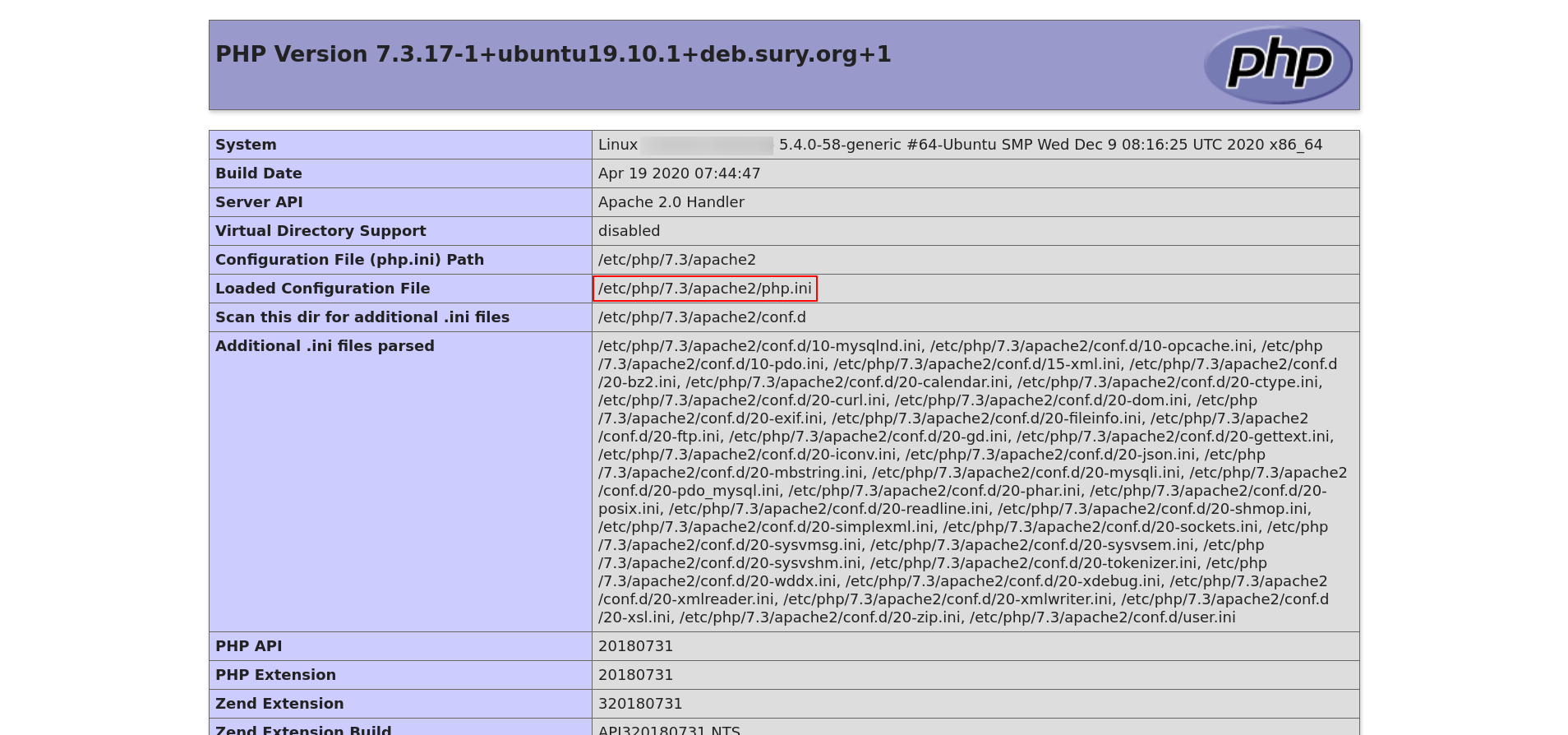
If you’re not sure where your php.ini file is located, one way to find out is to create a PHP script which uses the phpinfo function. This function will output all the information relative to your PHP install.
<?php
phpinfo();As you can see from my phpinfo, my current php.ini file is located at /etc/php/7.3/apache2/php.ini.
Once you’ve found your php.ini file, open it in your editor of choice, and search for the section called ‘Error handling and logging’. Here’s where the fun begins!
Error reporting directives
The first thing you’ll see in that section is a section of comments which include a detailed description of all the Error Level Constants. This is great, because you’ll be using them later on to set your error reporting levels.
Fortunately these constants are also documented in the online PHP Manual, for ease of reference.
Below this list is a second list of Common Values. This shows you how to set some commonly used sets of error reporting value combinations, including the default values, the suggested value for a development environment, and the suggested values for a production environment.
; Common Values:
; E_ALL (Show all errors, warnings and notices including coding standards.)
; E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE (Show all errors, except for notices)
; E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT (Show all errors, except for notices and coding standards warnings.)
; E_COMPILE_ERROR|E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR|E_ERROR|E_CORE_ERROR (Show only errors)
; Default Value: E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED
; Development Value: E_ALL
; Production Value: E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICTFinally, at the bottom of all the comments is the current value of your error_reporting level. For local development, I’d suggest setting it to E_ALL, so as to see all errors.
error_reporting = E_ALLThis is usually one of the first things I set when I set up a new development environment. That way I’ll see any and all errors that are reported.
After the error_reporting directive, there are some additional directives you can set. As before, the php.ini file includes descriptions of each directive, but I’ll give a brief description of the important ones below.
The display_errors directive allows you to toggle whether PHP outputs the errors or not. I usually have this set to On, so I can see errors as they happen.
display_errors=OnThe display_startup_errors allows for the same On/Off toggling of errors that may occur during PHP’s startup sequence. These are typically errors in your PHP or web server configuration, not specifically your code. It’s recommended to leave this Off, unless you’re debugging a problem and you aren’t sure what’s causing it.
The log_errors directive tells PHP whether or not to log errors to an error log file. This is always On by default, and is recommended.
The rest of the directives can be left as the default, except for maybe the error_log directive, which allows you to specify where to log the errors, if log_errors is on. By default it will log the errors wherever your web server has defined them to be logged.
Custom error logging
I use the Apache web server on Ubuntu, and my project-specific virtual host configurations use the following to determine the location for the error log.
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/project-error.logThis means it will log to the default Apache log directory, which is /var/log/apache2, under a file called project-error.log. Usually I replace project with the name of the web project it relates to.
So, depending on your local development environment you may need to tweak this to suit your needs. Alternatively, if you can’t change this at the web server level, you can set it at the php.ini level to a specific location.
error_log = /path/to/php.logIt is worth noting that this will log all PHP errors to this file, and if you’re working on multiple projects that might not be ideal. However, always knowing to check that one file for errors might work better for you, so your mileage may vary.
Find and fix those errors
If you’ve recently started coding in PHP, and you decide to turn error reporting on, be prepared to deal with the fallout from your existing code. You may see some things you didn’t expect, and need to fix.
The advantage though, is now that you know how to turn it all on at the server level, you can make sure you see these errors when they happen, and deal with them before someone else sees them!
Oh, and if you were wondering, the errors I was referring to at the start of this post were related to the fact that I was defining constants incorrectly, by not adding quotes around the constant name.
define(CONSTANT, 'Hello world.');PHP allowed (and might still allow) this, but it would trigger a notice.
Notice: Use of undefined constant CONSTANT - assumed 'CONSTANT' This notice was triggered every time I defined a constant, which for that project was about 8 or 9 times. Not great for someone to see 8 or 9 notices at the top of each page…
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
- Способы включения и отключения вывода ошибок PHP
- Через .htaccess
- Через логи PHP
- Через файл php.ini
Как правило, хостинг-провайдеры отключают или блокируют показ ошибок PHP. Подобные ограничения вводятся потому что информацией об ошибках могут воспользоваться злоумышленники. Поэтому на рабочих серверах нежелательно включать вывод ошибок на экран.
При разработке сайтов и скриптов крайне важно отслеживать возникающие проблемы. Также эта информация нужна и системным администраторам, чтобы своевременно предотвращать сбои в работе сайта и сервера.
Лучшим вариантом будет отключить вывод ошибок на экран и настроить отображение ошибок в логах. Так вы сможете отслеживать возникающие проблемы, не подвергая сервер угрозе.
В статье мы расскажем, как отключить или включить отображение ошибок PHP при помощи .htaccess, через скрипт PHP и с помощью файла php ini.
Обратите внимание: в некоторых случаях изменить настройки вывода можно только через обращение в техническую поддержку.
Способы включения и отключения вывода ошибок PHP
Через .htaccess
Перейдите в корневую папку сайта. Путь к корневой папке можно посмотреть в разделе «Хостинг» > «Сайты» в колонке «Папка»:
Открыть папку можно в разделе «Хостинг» > «Файловый менеджер». Другой способ перейти к папке: в разделе «Хостинг» > «Сайты» в колонке «Операции» нажмите Открыть папку.
В корневой папке откройте файл .htaccess. Если файла не существует, создайте его.
Чтобы вывести ошибки, добавьте в файл следующие строки:
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag html_errors on
Чтобы отключить ошибки PHP, добавьте в файл строки:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors off
php_flag html_errors off
Так же отключить отображение PHP error можно используя строки:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors off
php_flag html_errors off
php_value docref_root 0
php_value docref_ext 0
Через логи PHP
Проверить или скрыть ошибки в определенных файлах можно при помощи вызова PHP-функций.
Способ 1. Для вывода ошибок используйте функцию error_reporting. Пропишите необходимое вам значение в зависимости от того, какие ошибки вы хотите увидеть.
- Функция для вывода всех ошибок:
error_reporting(E_ALL)
- Функция для вывода всех ошибок, за исключением типа Notice:
error_reporting(E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE)
- Отключение вывода:
error_reporting(0)
- Отключение логирования повторяющихся ошибок:
# disable repeated error logging
php_flag ignore_repeated_errors on
php_flag ignore_repeated_source on
Способ 2. Этот метод подойдет для проверки конкретной части кода. Пропишите необходимое вам значение в зависимости от того, какие типы ошибок вы хотите увидеть.
Команда для вывода всех ошибок выглядит следующим образом:
ini_set(‘display_errors’, ‘On’)
error_reporting(E_ALL)
После этого добавьте:
ini_set(‘display_errors’, ‘Off’)
Способ 3. Другой вариант включения вывода ошибок через скрипт:
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
Для отключения добавьте строки:
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors off
Способ 4. Для подключения вывода с логированием через конфигурацию веб-сервера введите:
- для Apache:
ErrorLog «/var/log/apache2/my-website-error.log»,
- для Nginx:
error_log /var/log/nginx/my-website-error.log.
Подробнее о других аргументах вы можете прочитать в документации PHP на официальном сайте php.net.
Через файл php.ini
Включить отслеживание ошибок можно с помощью файла php.ini. Такой способ подойдет тем, кто хочет отобразить или скрыть ошибки для всего сайта или кода.
Важно! Настройка отслеживания ошибок через файл php.ini есть не у всех, так как некоторые хостинг-провайдеры частично или полностью закрывают доступ к файлу.
Способ 1. Показать все ошибки можно добавив в php.ini строку:
display_errors = on
После этого перезагрузите сервер:
sudo apachectl -k graceful
Способ 2. Включить вывод ошибок можно при помощи error_reporting. После знака «=» пропишите необходимое вам значение в зависимости от того, какие типы ошибок вы хотите увидеть.
Чтобы вывести все ошибки, добавьте следующие строки:
error_reporting = E_ALL
display_errors On
После перезагрузите веб-сервер:
sudo apachectl -k graceful
Чтобы скрыть отображение ошибок, добавьте строки:
error_reporting = E_ALL
display_errors Off
Теперь вы знаете, как можно включить и отключить вывод ошибок PHP.
Нет кода без ошибок. Как говорят, на ошибках учатся. Ну, а мы сегодня научимся включать и отключать вывод ошибок в PHP.
Если вы видите белый экран, вместо какого-либо ожидаемого результата, значит скорее всего в вашем коде произошла ошибка. Посмотрите, если в ответе сервера пришёл статус ошибки, например 500, но при этом на экране ничего нет, то вам нужно включить вывод ошибок.
Включить ошибки в PHP
Включение ошибок и предупреждений в php-скрипте
Для того, чтобы включить ошибки прямо в скрипте, перед выполняемым кодом напишите следующее:
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
После этого обновите страницу, сообщение об ошибке должно отобразиться. Вы также можете включить ошибки и предупреждения на уровне сервера.
Включение ошибок и предупреждений в файле .htaccess
Если у вас есть доступ к редактированию файла .htaccess, то пропишите в нём следующие строки:
php_value display_errors 1 php_value display_startup_errors 1 php_value error_reporting E_ALL
После этого перезапустите Apache.
Включение ошибок и предупреждений в файле php.ini
Конечно же, можно настроить отображение ошибок в конфигурационном файле PHP. Для этого, добавить в файл php.ini следующее:
error_reporting = E_ALL display_errors = On display_startup_errors = On
После этого перезапустите PHP.