When a website fails to load, it’s simply annoying. It’s important to understand, though, why that happened so you know how to fix it.
The 4xx family of status codes is the one we’re investigating here as they relate to invalid or corrupt requests from the client. Specifically, we’ll take a closer look at the 400 Bad Request error: what this error means, what causes it as well as some specific steps to fix the issue.
- What is 400 Bad Request Error?
- What Causes a 400 Bad Request Error
- 400 Bad Request Error: What Does It Look Like?
- How to Fix 400 Bad Request Error
Check out our video guide to fixing 400 errors:
What is a 400 Bad Request Error?
A 400 Bad Request, also known as a 400 error or HTTP error 400, is perceived by the server as a generic client error and it is returned when the server determines the error doesn’t fall in any of the other status code categories.
The key concept to understand here is that the 400 Bad Request error is something that has to do with the submitted request from the client before it is even processed by the server.
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) defines the 400 Bad Request as:
The 400 (Bad Request) status code indicates that the server cannot or will not process the request due to something that is perceived to be a client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing).
What Causes the HTTP 400 Bad Request Error?
There are various root causes that can trigger the 400 Bad Request error and, even if this error isn’t specific to any particular browser or OS (operating system), the fixes do vary slightly.
1. URL String Syntax Error
The HTTP error 400 can occur due to incorrectly typed URL, malformed syntax, or a URL that contains illegal characters.
This is surprisingly easy to do by mistake and can happen if a URL has been encoding incorrectly. The following link is an example of a URL containing characters the server won’t be able to process, hence a 400 Bad Request error is triggered.
https://twitter.com/share?lang=en&text=Example%20of%20malformed%%20characters%20in%20URL
Note the extra % character immediately after the word malformed in the URL. A properly encoded space should be %20 and not %%20. This is what the result looks like in the Chrome browser.
An illegal character can also trigger a 400 Bad request error. The following URL contains a { character, which is not allowed. Therefore, it results in the same type of error.
https://twitter.com/share?lang=en&text=Example%20of%20malformed{%20characters%20in%20URL
2. Corrupted Browser Cache & Cookies
Even if the URL is 100% correct, the 400 Bad Request error can still occur because of corrupted files in the browser cache or problems with expired/corrupted browser cookies.
You may have encountered a 400 Bad Request error when trying to access the admin area of your WordPress site some time after your last log in. That’s happening because of the way the cookie handling your login authentication data may have gotten corrupted and can’t successfully authenticate you as a valid user with admin privileges. This will then result in the connection being refused and a 400 Bad Request error is triggered.
3. DNS Lookup Cache
The 400 Bad Request can happen when the DNS data stored locally is out of sync with registered DNS information.
All domain names are aliases for IP addresses. You can think of an IP address as a phone number “always calling” a specific server you want to connect to. When you first visit a website, a process called “name resolution” takes place and that’s when the domain name resolves to the specific IP address of the server.
To speed things up, these details are stored locally on your computer in the local DNS cache so the name resolution process doesn’t have to be done for every single visit for a given website. This is similar to how the browser cache works for HTML, CSS, JavaScript, media, and other files.
4. File Size Too Large
A 400 Bad Request can also occur when you try to upload a file to a website that’s too large for the upload request to be fulfilled. This is strictly related to the file size limit of the server and will vary based on how it has been set up.
Until now, we’ve focused on the 400 Bad Request error being triggered only due to client-side issues.
5. Generic Server Error
This error can sometimes be triggered because of server-side issues as well. Specifically, a 400 status code could indicate a general problem with the server, a server glitch, or other unspecified temporary issues.
If this happens when trying to connect to a third-party website, it’s really outside of your control and your best shot is to try refreshing the browser and check at regular intervals whether the issue has been fixed by the site owners.
One thing you can do to verify the issue is a server-side issue is to try loading the website on different browsers. If you want to go the extra mile, test it on an entirely different machine/device to rule out system-specific problems.
When you can’t connect to the site via any other browsers, computers, operating systems, or other devices then it’s likely to be a server-side issue. If you’d like, you can reach out to the site owner and let them know which OS, browser, and versions you were using when experienced the issue.
400 Bad Request Error: What Does It Look Like?
Most of the time a 400 Bad Request is related to client-side issues. We already saw what a 400 Bad Request error looks like in the Chrome browser.
But what about the other browsers?
400 Bad Request in Firefox
400 Bad Request in Safari
400 Bad Request in Microsoft Edge
As you can see, all browsers return a generic and unhelpful 400 status code message. It seems you’re pretty much left alone for finding a solution to the problem. In Firefox and Safari, it’s not even clear a 400 Bad Request error has occurred at all as the browser window is completely blank!
Fortunately, we’ve put together a series of simple steps you can take to fix the 400 Bad Request error. Let’s take a closer look at each one of these in the next section!
400 Bad Request (Glossary):
The 400 Bad Request Error is an HTTP response status code
that indicates the server was unable to process (understand) the request sent by the client due to incorrect syntax, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing.
How to Fix 400 Bad Request Error?
Complete the steps outlined in this section to help diagnose and correct a 400 Bad Request.
The proposed solutions include:
- 1. Check the Submitted URL
- 2. Clear Browser Cache
- 3. Clear Browser Cookies
- 4. File Upload Exceeds Server Limit
- 5. Clear DNS Cache
- 6. Deactivate Browser Extensions
Before digging deeper on the different ways to fix the 400 Bad Request error, you may notice that several steps involve flushing locally cached data.
It’s true that if your computer didn’t cache any files or data at all, there would probably be significantly less connection error issues.
However, the benefits of caching files/data are well documented and the web browsing experience would certainly suffer if caching techniques weren’t used by browsers. When it comes to Edge Caching, for example, you can reduce by more than 50% the time required to deliver full pages to browsers.
It all comes down to a compromise between optimization and user experience, where websites try to load as quickly as possible but can occasionally be prone to errors such as a 400 Bad Request without any warning.
1. Check the Submitted URL
As this is one of the most common reasons for a 400 Bad Request error let’s start with an obvious culprit, the URL string itself. It can be very easy to include unwanted characters in the URL when entering it manually in the browser.
Check that the domain name and specific page you’re trying to access are spelled and typed correctly. Also, make sure they’re separated with forward slashes. If the URL contains special characters, make sure they have been encoded correctly and are legal URL characters.
For long URLs, you might find it easier and less error-prone, to use an online URL encoder/decoder. These type of utilities should also be able to detect illegal characters automatically in the URL as well.
Once you’re sure the URL is correct, try to access it again in the browser. If you’re still getting the 400 Bad Request error it’s time to clear some cache!
2. Clear Browser Cache
If any locally stored website files have been corrupted this can cause a 400 Bad Request error to be returned instead of the expected website content.
This includes all types of files a website needs to properly run such as:
- HTML
- JavaScript
- Text/config files
- CSS
- Media (images, videos, audio)
- Data files (XML, JSON)
These files are stored locally on your computer by the browser when the website is originally visited.
To fix this, the browser cache needs to be cleared.
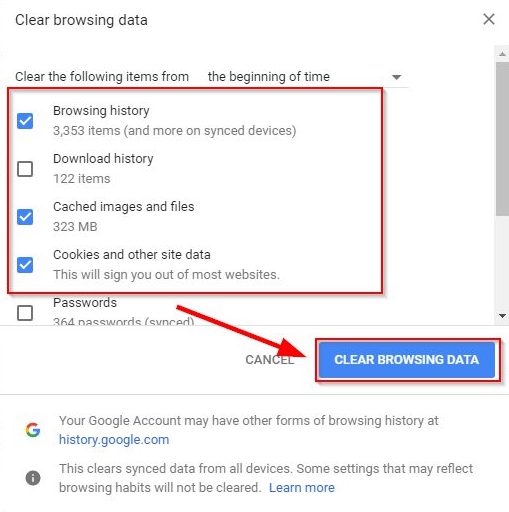
In Chrome, click on the three-dotted icon on the right-hand corner and select the More Tools > Clear Browsing Data from the popup menu.
This will display the Clear browsing data window. In here, you’ll want to make sure the Cached images and files option is checked and then click on the Clear data button to clear the browser cache.
You can also choose to delete recent files for a specific time range via the Time range dropdown. However, to make sure all potentially corrupted files are removed we recommend deleting all locally stored files by selecting the All time option.
If you’re using an alternative browser, check this guide for clearing the browser cache for all the major browsers (Mozilla Firefox, Safari, Internet Explorer, Microsoft Edge, Opera).
3. Clear Browser Cookies
If clearing your browser cache didn’t work, then it’s time to delete the cookies too. A single website can use dozens of different cookies. If just one of them is expired or becomes corrupted, then it can be enough to trigger a 400 Bad Request.
To clear your cookies in Chrome, open up the Clear browsing data window by clicking the icon with the three dots in the top-right corner and select More Tools > Clear Browsing Data from the popup menu.
Make sure the Cookies and other site data is checked and select All time for the date range option to delete all current website cookies.
Once done, try loading the website which returned the 400 Bad Request error again. Assuming the site uses cookies, clearing them out from your browser could fix the issue as it’s often associated with corrupt or expired cookies.
To clear cookies in browsers other than Chrome please read this guide here.
4. File Upload Exceeds Server Limit
If you’re trying to upload a file to a website that’s exceeding the server file size limit, you’ll encounter a 400 Bad Request error.
You can test this out by uploading a smaller file first. If this is successful then the initial file is probably too large and you’ll need to find some way to reduce it before uploading it again.
This will depend on the type of file you’re trying to upload but there are plenty of resources available online that can help to compress large images, video, and audio files.
5. Clear DNS Cache
Another common cause of a 400 Bad Request is when local DNS lookup data becomes either corrupted or out-of-date.
Local DNS data isn’t stored by the browser but by the operating system itself. We have put together a detailed guide to clear the DNS cache for Windows and macOS operating systems.
6. Deactivate Browser Extensions
If you have browser extensions installed that affect website cookies then these could actually be the culprit here. Try temporarily disabling them to see if it makes a difference before trying to connect to the website again.
You may not have considered this could be an issue, but it’s certainly worth a try if you’ve exhausted all other options.
Experiencing a 400 Bad Request error? Check out our detailed guide on how to fix it once and for all! ❌🦊Click to Tweet
Summary
If you’re experiencing a 400 Bad Request error there are several actions you can perform to try and fix the issue.
In the vast majority of possible scenarios, a 400 Bad Request is a client-side issue caused by the submitted request to the server or a local caching issue. The solutions outlined in this article are easy to implement by anyone with minimal technical knowledge. You should be able to get your website working again in no time!
On occasions, though, a 400 Bad Request status code could hint to a generic server issue. This can be quickly diagnosed by testing the given site on different devices. If you suspect this to be a server-side error, there’s not much you can do other than keep trying to load the site at regular intervals and inform the site admin.
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275 PoPs worldwide
Test it yourself with $20 off your first month of Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
Ошибка 400 Bad Request – это код ответа HTTP, который означает, что сервер не смог обработать запрос, отправленный клиентом из-за неверного синтаксиса. Подобные коды ответа HTTP отражают сложные взаимоотношения между клиентом, веб-приложением, сервером, а также зачастую сразу несколькими сторонними веб-сервисами. Из-за этого поиск причины появления ошибки может быть затруднён даже внутри контролируемой среды разработки.
В этой статье мы разберём, что значит ошибка 400 Bad Request (переводится как «Неверный запрос»), и как ее исправить
- На стороне сервера или на стороне клиента?
- Начните с тщательного резервного копирования приложения
- Диагностика ошибки 400 Bad Request
- Исправление проблем на стороне клиента
- Проверьте запрошенный URL
- Очистите соответствующие куки
- Загрузка файла меньшего размера
- Выйдите и войдите
- Отладка на распространённых платформах
- Откатите последние изменения
- Удалите новые расширения, модули или плагины
- Проверьте непреднамеренные изменения в базе данных
- Поиск проблем на стороне сервера
- Проверка на неверные заголовки HTTP
- Просмотрите логи
- Отладьте код приложения или скриптов
Все коды ответа HTTP из категории 4xx считаются ошибками на стороне клиента. Несмотря на это, появление ошибки 4xx не обязательно означает, что проблема как-то связана с клиентом, под которым понимается веб-браузер или устройство, используемое для доступа к приложению. Зачастую, если вы пытаетесь диагностировать проблему со своим приложением, можно сразу игнорировать большую часть клиентского кода и компонентов, таких как HTML, каскадные таблицы стилей (CSS), клиентский код JavaScript и т.п. Это также применимо не только к сайтам. Многие приложения для смартфонов, которые имеют современный пользовательский интерфейс, представляют собой веб-приложения.
С другой стороны, ошибка 400 Bad Request означает, что запрос, присланный клиентом, был неверным по той или иной причине. Пользовательский клиент может попытаться загрузить слишком большой файл, запрос может быть неверно сформирован, заголовки HTTP запроса могут быть неверными и так далее.
Мы рассмотрим некоторые из этих сценариев (и потенциальные решения) ниже. Но имейте в виду: мы не можем однозначно исключить ни клиент, ни сервер в качестве источника проблемы. В этих случаях сервер является сетевым объектом, генерирующим ошибку 400 Bad Request и возвращающим её как код ответа HTTP клиенту, но возможно именно клиент ответственен за возникновение проблемы.
Важно сделать полный бэкап вашего приложения, базы данных и т.п. прежде, чем вносить какие-либо правки или изменения в систему. Ещё лучше, если есть возможность создать полную копию приложения на дополнительном промежуточном сервере, который недоступен публично.
Подобный подход обеспечит чистую тестовую площадку, на которой можно отрабатывать все возможные сценарии и потенциальные изменения, чтобы исправить или иную проблему без угрозы безопасности или целостности вашего «живого» приложения.
Ошибка 400 Bad Request означает, что сервер (удалённый компьютер) не может обработать запрос, отправленный клиентом (браузером), вследствие проблемы, которая трактуется сервером как проблема на стороне клиента.
Существует множество сценариев, в которых ошибка 400 Bad Request может появляться в приложении. Ниже представлены некоторые наиболее вероятные случаи:
- Клиент случайно (или намеренно) отправляет информацию, перехватываемую маршрутизатором ложных запросов. Некоторые веб-приложения ищут особые заголовки HTTP, чтобы обрабатывать запросы и удостовериться в том, что клиент не предпринимает ничего зловредного. Если ожидаемый заголовок HTTP не найден или неверен, то ошибка 400 Bad Request – возможный результат.
- Клиент может загружать слишком большой файл. Большинство серверов или приложений имеют лимит на размер загружаемого файла, Это предотвращает засорение канала и других ресурсов сервера. Во многих случаях сервер выдаст ошибку 400 Bad Request, когда файл слишком большой и поэтому запрос не может быть выполнен.
- Клиент запрашивает неверный URL. Если клиент посылает запрос к неверному URL (неверно составленному), это может привести к возникновению ошибки 400 Bad Request.
- Клиент использует недействительные или устаревшие куки. Это возможно, так как локальные куки в браузере являются идентификатором сессии. Если токен конкретной сессии совпадает с токеном запроса от другого клиента, то сервер/приложение может интерпретировать это как злонамеренный акт и выдать код ошибки 400 Bad Request.
Устранение ошибки 400 Bad Request (попробуйте позже) лучше начать с исправления на стороне клиента. Вот несколько советов, что следует попробовать в браузере или на устройстве, которые выдают ошибку.
Наиболее частой причиной ошибки 400 Bad Request является банальный ввод некорректного URL. Доменные имена (например, internet-technologies.ru) нечувствительны к регистру, поэтому ссылка, написанная в смешанном регистре, такая как interNET-technologies.RU работает так же, как и нормальная версия в нижнем регистре internet-technologies.ru. Но части URL, которые расположены после доменного имени, чувствительными к регистру. Кроме случаев, когда приложение/сервер специально осуществляет предварительную обработку всех URL и переводит их в нижний регистр перед исполнением запроса.
Важно проверять URL на неподходящие специальные символы, которых в нем не должно быть. Если сервер получает некорректный URL, он выдаст ответ в виде ошибки 400 Bad Request.
Одной из потенциальных причин возникновения ошибки 400 Bad Request являются некорректные или дублирующие локальные куки. Файлы куки в HTTP – это небольшие фрагменты данных, хранящиеся на локальном устройстве, которые используются сайтами и веб-приложениями для «запоминания» конкретного браузера или устройства. Большинство современных веб-приложений использует куки для хранения данных, специфичных для браузера или пользователя, идентифицируя клиента и позволяя делать следующие визиты быстрее и проще.
Но куки, хранящие информацию сессии о вашем аккаунте или устройстве, могут конфликтовать с другим токеном сессии от другого пользователя, выдавая кому-то из вас (или вам обоим) ошибку 400 Bad Request.
В большинстве случаев достаточно рассматривать только ваше приложение в отношении файлов куки, которые относятся к сайту или веб-приложению, выдающему ошибку 400 Bad Request.
Куки хранятся по принципу доменного имени веб-приложения, поэтому можно удалить только те куки, которые соответствуют домену сайта, сохранив остальные куки не тронутыми. Но если вы не знакомы с ручным удалением определённых файлов куки, гораздо проще и безопаснее очистить сразу все файлы куки.
Это можно сделать разными способами в зависимости от браузера, который вы используете:
- Google Chrome;
- Internet Explorer;
- Microsoft Edge;
- Mozilla Firefox;
- Safari.
Если вы получаете ошибку 400 Bad Request при загрузке какого-либо файла, попробуйте корректность работы на меньшем по размеру файле, Это включает в себя и «загрузки» файлов, которые не загружаются с вашего локального компьютера. Даже файлы, отправленные с других компьютеров, считаются «загрузками» с точки зрения веб-сервера, на котором работает ваше приложение.
Попробуйте выйти из системы и войти обратно. Если вы недавно очистили файлы куки в браузере, это приводит к автоматическому выходу из системы при следующей загрузке страницы. Попробуйте просто войти обратно, чтобы посмотреть, заработала ли система корректно.
Также приложение может столкнуться с проблемой, связанной с вашей предыдущей сессией, являющейся лишь строкой, которую сервер посылает клиенту, чтобы идентифицировать клиента при будущих запросах. Как и в случае с другими данными, токен сессии (или строка сессии) хранится локально на вашем устройстве в файлах куки и передаётся клиентом на сервер при каждом запросе. Если сервер решает, что токен сессии некорректен или скомпрометирован, вы можете получить ошибку 400 Bad Request.
В большинстве веб-приложений выход повторный вход приводит к перегенерации локального токена сессии.
Если вы используете на сервере распространённые пакеты программ, которые выдают ошибку 400 Bad Request, изучите стабильность и функциональность этих платформ. Наиболее распространённые системы управления контентом, такие как WordPress, Joomla! и Drupal, хорошо протестированы в своих базовых версиях. Но как только вы начинаете изменять используемые ими расширения PHP, очень легко спровоцировать непредвиденные проблемы, которые выльются в ошибку 400 Bad Request.
Если вы обновили систему управления контентом непосредственно перед появлением ошибки 400 Bad Request, рассмотрите возможность отката к предыдущей версии, которая была установлена, как самый быстрый и простой способ убрать ошибку 400 bad request.
Аналогично, любые расширения или модули, которые были обновлены, могут вызывать ошибки на стороне сервера, поэтому откат к предыдущим версиям этих расширений также может помочь.
Но в некоторых случаях CMS не предоставляют возможности отката к предыдущим версиям. Так обычно происходит с популярными платформами, поэтому не бойтесь, если вы не можете найти простой способ вернуться к использованию старой версии той или иной программной платформы.
В зависимости от конкретной CMS, которую использует приложение, имена этих компонентов будут различаться. Но во всех системах они служат одной и той же цели: улучшение возможностей платформы относительно её стандартной функциональности.
При этом имейте в виду, что расширения могут так или иначе получать полный контроль над системой, вносить изменения в код PHP, HTML, CSS, JavaScript или базу данных. Поэтому мудрым решением может быть удаление любых новых расширений, которые были недавно добавлены.
Даже если удалили расширение через панель управления CMS, это не гарантирует, что внесенные им изменения были полностью отменены. Это касается многих расширений WordPress, которым предоставляется полный доступ к базе данных.
Расширение может изменить записи в базе данных, которые «не принадлежат» ему, а созданы и управляются другими расширениями (или даже самой CMS). В подобных случаях модуль может не знать, как откатить назад изменения, внесенные в записи базы данных.
Я лично сталкивался с такими случаями несколько раз. Поэтому лучшим путём будет открыть базу данных и вручную просмотреть таблицы и записи, которые могли быть изменены расширением.
Если вы уверены, что ошибка 400 Bad Request не связана с CMS, вот некоторые дополнительные советы, которые могут помочь найти проблему на стороне сервера.
Ошибка, которую вы получаете от приложения, является результатом недостающих или некорректных специальных заголовков HTTP, которые ожидает получить приложение или сервер. В подобных случаях нужно проанализировать заголовки HTTP, которые отправляются на сторону сервера.
Почти любое веб-приложение будет вести логи на стороне сервера. Они представляют собой историю того, что делало приложение. Например, какие страницы были запрошены, к каким серверам оно обращалось, какие результаты предоставлялись из базы данных и т.п.
Логи сервера относятся к оборудованию, на котором выполняется приложение, и зачастую представляют собой детали о статусе подключённых сервисов или даже о самом сервере. Поищите в интернете “логи [ИМЯ_ПЛАТФОРМЫ]”, если вы используете CMS, или “логи [ЯЗЫК_ПРОГРАММИРОВАНИЯ]” и “логи [ОПЕРАЦИОННАЯ_СИСТЕМА]”, если у вас собственное приложение, чтобы получить подробную информацию по поиску логов.
Если это не помогло, проблема может быть в исходном коде, который выполняется внутри приложения. Попытайтесь диагностировать, откуда может исходить проблема, отлаживая приложение вручную и параллельно просматривая логи приложения и сервера.
Создайте копию всего приложения на локальном устройстве для разработки и пошагово повторите тот сценарий, который приводил к возникновению ошибки 400 Bad Request. А затем просмотрите код приложения в тот момент, когда что-то пойдёт не так.
Независимо от причины возникновения ошибки, даже если вам удалось исправить её в этот раз, появление в вашем приложении такой проблемы — это сигнал для того, чтобы внедрить инструмент обработки ошибок, который поможет автоматически обнаруживать их и оповещать в момент возникновения.
Ultimate Guide to Understanding HTTP Status Codes – 400 Series

400 series request codes deal with malformed and unserviceable requests from a user-agent. Whenever a 400 series is encountered the problem is usually on the client side.
Issues with a user-agent client can range from requesting resources that are no longer available (by mis-typing a URI) or even the server reacting to requests fitting a security-attack signature.
The most common is the 404 – document not found. 404 Document Not Found is returned when a resource is requested the web-server cannot find:
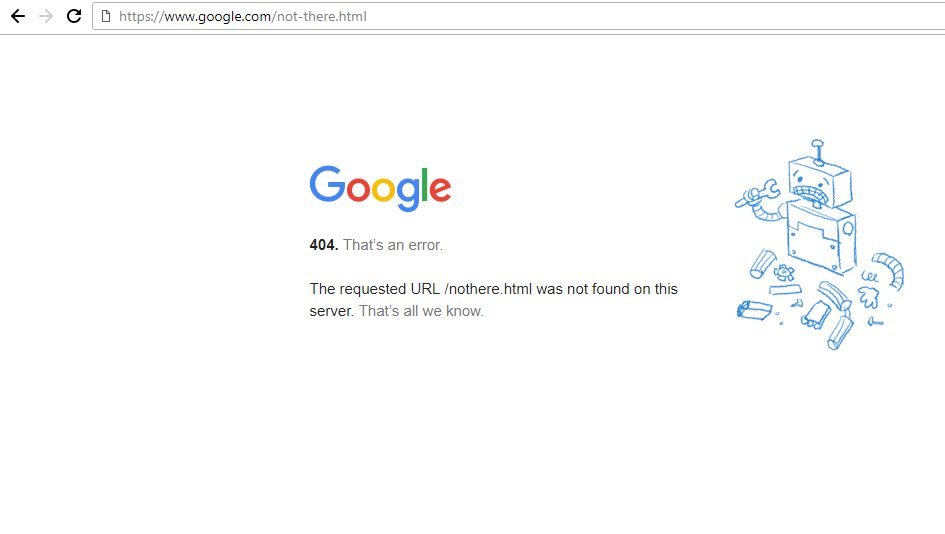
404 Document not Found when mistyping a URL
Let’s go over the most common and interesting 404 series response codes in a little more detail.
400 – Bad Request
400 Bad Request is (usually) the result of a user-agent sending something in the request a web-server could not process. Let’s generate a 400 Bad Request to understand what can cause this error.
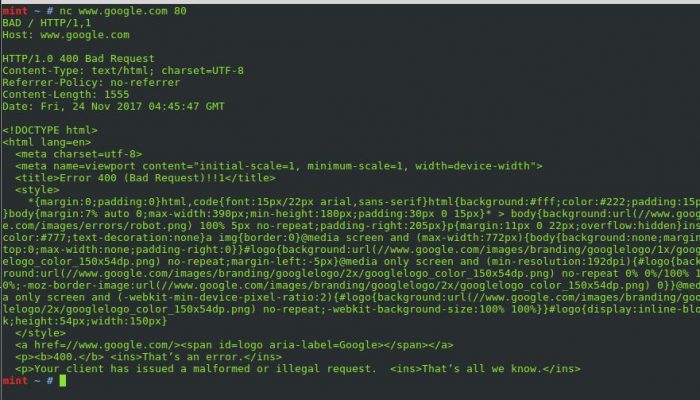
We will go old-school on Linux and use a tool called netcat. Netcat can be used for sending raw data over sockets. After all, HTTP requests are just that – raw text.
First, let’s send a legitimate HEAD Request to google:
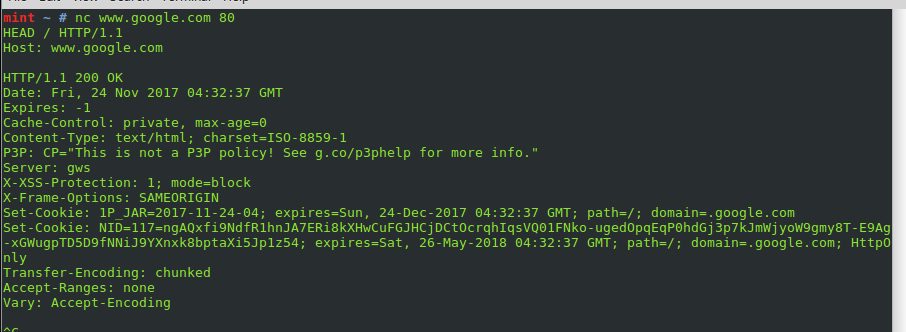
The web-server responded with 200.
Let’s force a 400 – Bad Request:
We purposfully sent a request the server could not understand – let’s look at the request method used:
mint ~ # nc www.google.com 80
BAD / HTTP/1,1
Host: www.google.com
The web-server could not process the method: BAD
It’s unlikely a modern web browser would send malformed requests like depicted above. However, if you’re using a custom developed HTTP application like a web-scraper, it’s time to debug.
Following the procedures below will resolve most all 400 Bad Request Errors.
1. Check The URL
If clicking on a link it is quite possible the web-author made a typo. Examine the entire URL paying particular attention to the path, document title, and query-string portions.
2. Clear all Cookies and Cache
Clearing the browser cache will solve 80% of 400 Bad Request Codes. Following these steps is a good universal fix for a lot of 400 Status Codes, too.
- clear all cookies and browsing history
- re-try the request
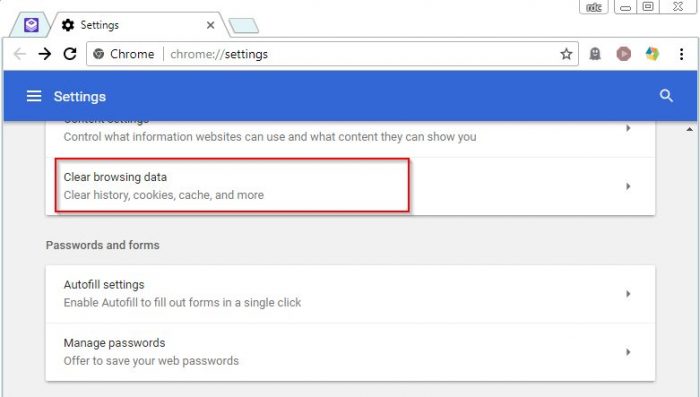
Let’s see how this is done with Chrome:
- Go into Settings
- Go to Advanced
- Click “Clear Browsing Data”
- Select the following options
Clearing all cookies and browsing history will assure anything cached and/or corrupted (like cookies) are gone. More than likely this will fix your issues with most 400 Bad Request Codes
3. File Upload Size
The problem could very well be a back-end script itself, uploading too large of a file or a file with an incorrect media type.
- If the 400 bad request presents itself while uploading a file, try a smaller file.
- Make sure the file-type is acceptable. 2.
- If uploading an image try both jpeg and png formats.
- If an uploading a document usually text files .txt and Microsoft Word files are permitted.
4. Malformed Headers
Malformed headers would be a pretty low-level issue and could very well leave the web-application itself at fault.
Using the HTTPFox plugin with Firefox we can watch the entire HTTP transaction for anything looking out of the ordinary.
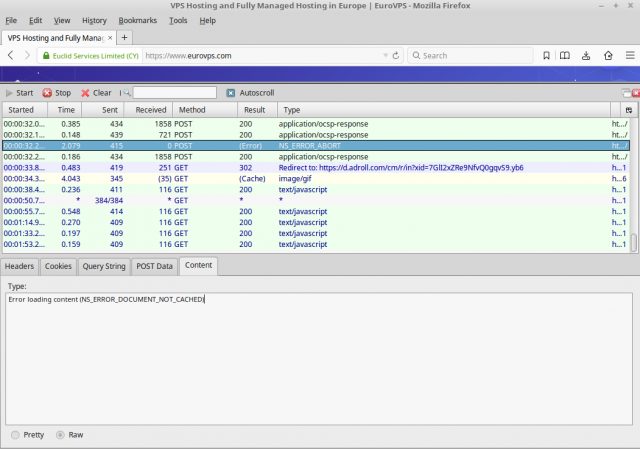
Looks as if I need to clear the cache on my web-browser. Pretty simple to diagnose with HTTPFox.
5. Update Your Web Browser and Disable Plugins
Like anything HTTP goes through versions and revisions. If your browser is out of date it could very well be sending antiquated headers and requests.
Also, try removing or disabling all plug-ins and extensions. Trying the same request in another web browser can assist in isolating issues as well.
6. Check Your Internet Connection
A bad Internet Connection can cause data to be corrupted at lower layers, thus sending malformed data to the web server.
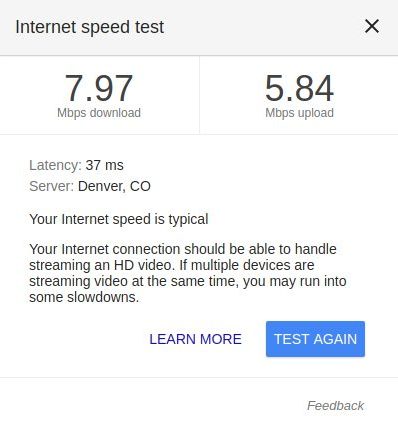
Using a good Internet Speed Test utility can help troubleshoot any issues with an Internet connection. Try running the utility 5 or 6 times for comparison.
7. Try Logging Out
If using a web application with user-based authentication and sessions try logging out and then clearing the browser cache.
401 – Unauthorized
401 Unauthorized is returned when a web server requests credentials for a secured document.
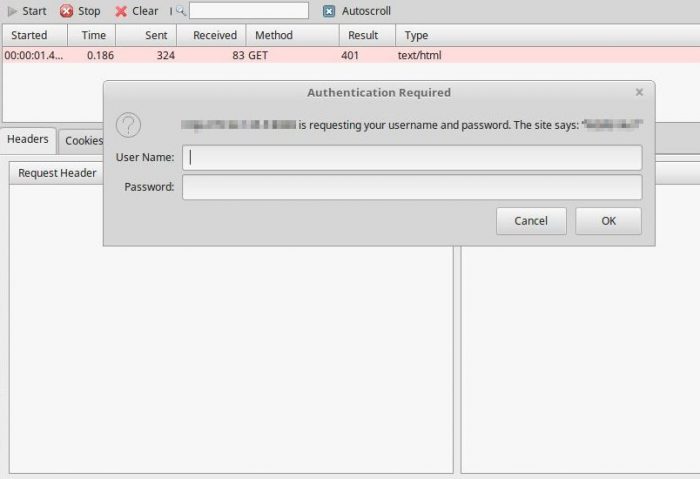
The HTTP Response will be 200 upon valid credentials being supplied
403 – Forbidden
403 Forbidden is usually one of four things:
- directory listings are not permitted
- currently authenticated user does not have sufficient permissions
- the web-server process has inadequate permissions
- requesting address has been banned
Directory Listing Not Permitted
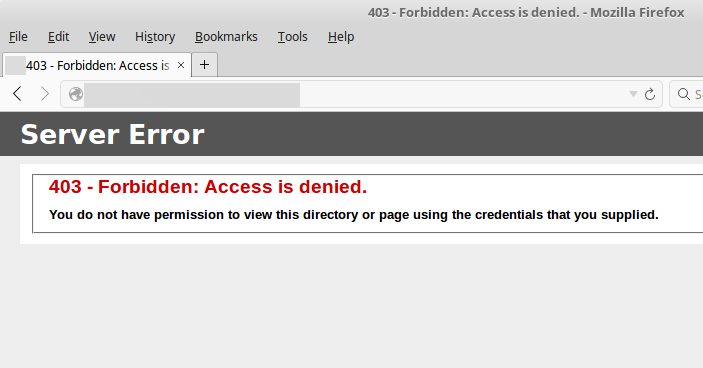
Shows 403 Forbidden when trying to access a directory listing
IIS Showing Directory Permissions are not granted to unauthenticated users. The simplest method is to put an index file in the directory. Otherwise, directory listings to unauthenticated users will need to be explicitly set.
Authenticated User Does Not Have Permissions
The best method in this situation is making a group for all users who need access to a resource. Give this group the necessary permissions at the filesystem level. Then add permitted users to the group.
Web Server Process Does Not Have Sufficient Permissions
We are unable to access the test.php page in the webroot in /var/www/html. So first we need to:
-
check permissions to the webroot:
-
assign the www-data group to the webroot and give read + execute permissions:
mint# ls -ld /var/www/html/ drwx------ 3 root root 4096 Nov 24 03:47 /var/www/html/the /usr/var/html/ directory is owned by the root user and root group with no access to any other user.
To fix a permissions issue like this, we need to modify permissions to the directory:
mint# chgrp -R www-data /var/www/html mint# chmod 750 /var/www/html mint# chmod g+rx /var/www/html/test.php mint html # chmod g-w /var/www/html/test.php mint# ls -ld /var/www/html/ drwxrw---- 3 root www-data 4096 Nov 24 03:47 /var/www/html/ mint# ls -l /var/www/html/test.php -rwxr-x--- 1 root www-data 91 Nov 16 06:52 /var/www/html/test.php
A little theory on how the problem was fixed:
- change the owning group of the webroot to www-data
- give proper permissions to the web-root for the www-data group. directory should be read and execute
- give read and execute permissions to test.php for the www-data group
For best security practice the www-data group should not have write permissions on files and folders. However, some content management systems or special purpose scripts may need write access by the web-server process
Denying write permissions to files and folders can provide a higher layer of security in the event a web-application flaw is leveraged by an attacker to modify content, delete files, or add files.
Permissions, as mentioned above, are for a production environment. But can be somewhat restrictive for development stages.
Since we took away write permissions to the directory and to test.php only root can add and edit files. This is good in production – we are 100% sure the web-process cannot write to and create files if a script is compromised.
However, this is very impractical for development. In a staging environment, it would be best to put developers in the www-data group. Then give them write permissions to the web-root and all its files. This is a good example of why modern DevOps keeps staging and production segmented.
Another common scenario for a 403 Forbidden Status may be an IP Address or IP Range being banned in a .htaccess file by the server Administrator.
404 – Not Found
404 Not Found means the web-server could not find a requested resource. When encountering a 404 error a few things can be done:
-
check spelling of host, domain, path, and document
-
check case of file and path. Linux and Unix web-servers (unless configured differently) usually distinquish case, with tradition of using all lowercase for each.
-
use Google to find an alternative URL to the resource
-
try getting a cached page from google
Using Advances Google Operators
Many times I have been able to locate a document with expired links (resulting in a 404) using a Google query similar to the one above. Listing of Advanced Google Operators
Try Getting the Same Resource From Google’s Cache
Using advanced Google Operators and Google’s Cache you may be able to find the resource even if it has been taken down.
405 – Method Not allowed
A 405 Method Not Allowed is presented when attempting a request method that is unpermitted by the web-server.
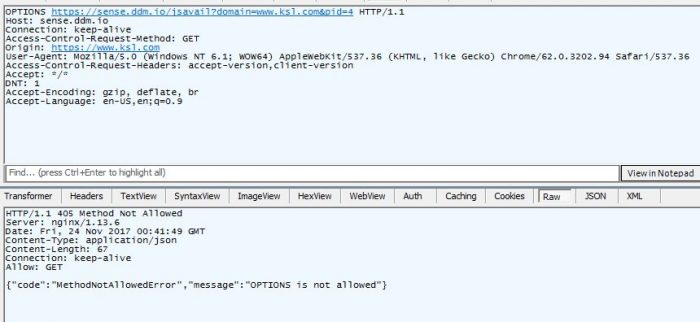
OPTIONS Request Not Allowed
406 – Not Acceptable
406 Not Acceptable will be given when the user-agent and client cannot establish acceptable content/encoding types or character-sets.
When resolving a 406 Status Code using a tool like HTTPFox is necessary.
Header values sent by the client to look over include:
- Accept:
- Accept-Charset
- Accept-Encoding
- Accept-Languages
A modern web-browser will never experience this issue. If it does, try upgrading your web-browser to later version.
407 – Proxy Authentication Required
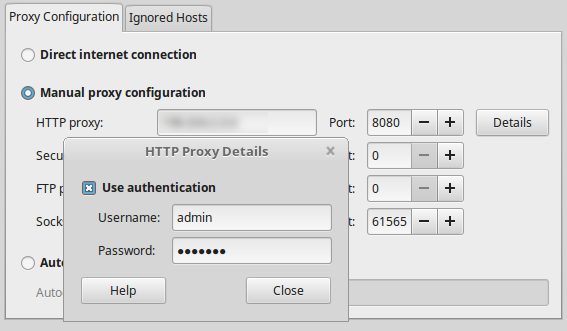
407 Proxy Authentication Required will usually mean the user-agent needs to provide credentials to access a proxy server.
408 – Request Timeout
This status code will usually result from latency between your computer and the web-server.
To assist in resolving 408 Request Timeout Errors:
- try another website to make sure it is not the server infrastructure
- make sure no other downloads are running saturating your bandwidth
- reconnect to your WiFi
- reboot your router
- try an Internet Speed Test
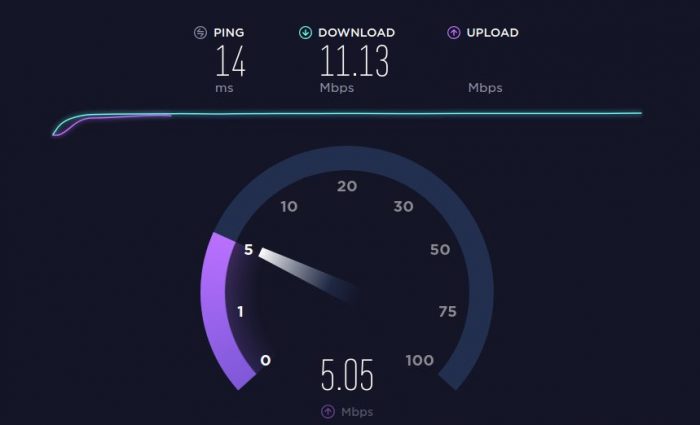
If able to connect to another website fine, it is probably a remote network. If an Internet Speed Test is showing latency the problem could be your ISP or LAN.
Speedtest.net offers a great and free online app for testing Internet connection speeds. The app will check upload speed, download speed, and latency. Speedtest.net Speed Testing App Online
429 – Too Many Requests
429 will usually mean rate limiting has been enabled on the server. Rate limiting will only allow a certain amount of requests in an allotted amount of time.
When recieving 429 – Too Many Requests the user-agent will be blocked for a time period, usually by IP address.
To bypass 429 and 403 restricted errors try using Tor Browser
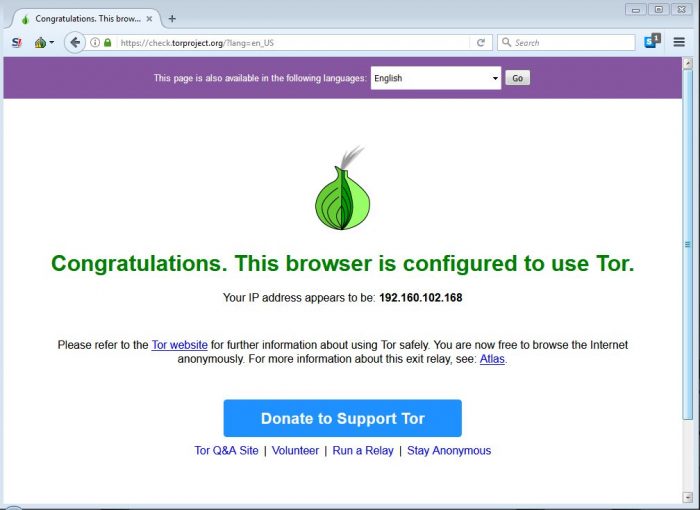
TOR Browser can be used obfuscate your IP address
451 – Unavailable for Legal Reasons
451 could be seen when a web-page violates copyrights, trademarks, intellectual property laws, or has been deemed a threat to national security.

Sample of a website seized by US Law Enforcement

Read More
- 400
- Errors
- HTTP

What is Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) anyway?
Ultimate Guide to Understanding HTTP Status Codes 500 – Internal Service Error
Ultimate Guide Understanding HTTP Status Codes – 300 Series
Интернет ― это сложная схема взаимодействия устройств. Между компьютером и сервером сайта легко могут появиться проблемы с сетью: код ошибки 400, 406, 410. В этой статье мы рассмотрим ошибку 400.
Что значит ошибка 400
Все ошибки, которые начинаются на 4, говорят о том, что проблема на стороне пользователя.
Ошибка 400 bad request переводится как «плохой запрос». Она возникает тогда, когда браузер пользователя отправляет некорректный запрос серверу, на котором находится сайт.
Чаще всего проблема действительно обнаруживается на стороне пользователя, но бывают и исключения, когда проблема на стороне провайдера или владельца сайта.
Причины появления ошибки 400
- Ссылка на страницу была некорректной. Если в ссылке была допущена опечатка, сайт, как правило, выдаёт ошибку 404: «Страница не найдена». Опечатку в запросе может сделать сам пользователь, который вводит URL-адрес вручную, а также владелец сайта, который размещает ссылку на странице.
- Используются устаревшие файлы cookies.
- Пользователь загружает на сайт слишком большой файл.
- Антивирус или брандмауэр блокирует сайт.
- На компьютере есть вирус, который блокирует доступ к сайту.
- Проблемы на стороне интернет-провайдера.
Как исправить ошибку 400
Перед тем как заниматься серьёзной настройкой устройства, проверьте правильность написания URL-адреса. Если ссылка была скопирована с сайта, попробуйте найти нужную страницу по ключевым словам. Как только вы найдёте правильную ссылку, сайт заработает.
Если причина не в этом, переходите к другим настройкам, которые описаны ниже.
Очистите файлы cookies и кэш браузера
Файлы куки и кэш созданы для того, чтобы запоминать сайты и персональные данные пользователя. За счёт этой памяти ускоряется процесс повторной загрузки страницы. Но cookies и кэш, которые хранят данные предыдущей сессии, могут конфликтовать с другим токеном сессии. Это приведёт к ошибке 400 Bad Request.
Очистите кэш браузера по инструкции и попробуйте зайти на страницу заново.
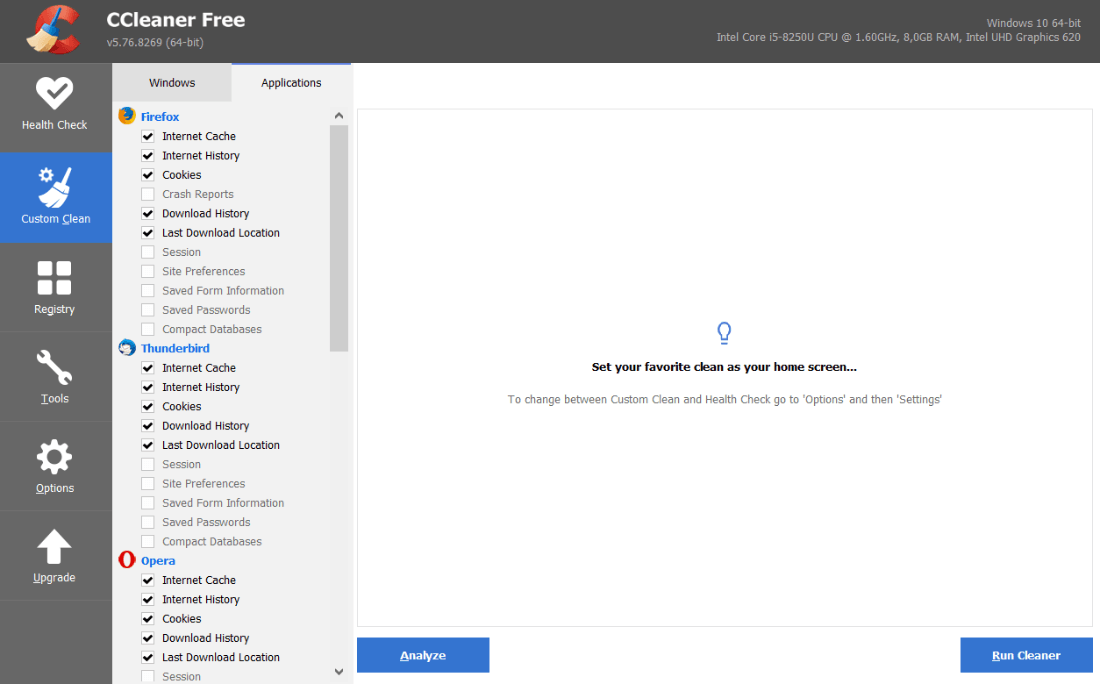
Очистить кэш и куки можно не только вручную, но и с помощью программ CCleaner и Advanced SystemCare.
CCleaner ― эффективное решение для оптимизации работы системы. За пару кликов можно очистить кэш и cookies в нескольких браузерах одновременно. Также можно быстро почистить все временные файлы, которые могут замедлять работу системы. Интуитивный интерфейс не требует специальных знаний:
Ещё одним популярным приложением для оптимизации ПК является Advanced SystemCare. Эта программа поможет удалить ненужные файлы, очистить реестр, ускорить работу системы, освободить память и место на диске. Также она может контролировать безопасность просмотра веб-страниц, защищая конфиденциальные данные, блокируя вредоносные веб-сайты и предотвращая майнинг криптовалюты.
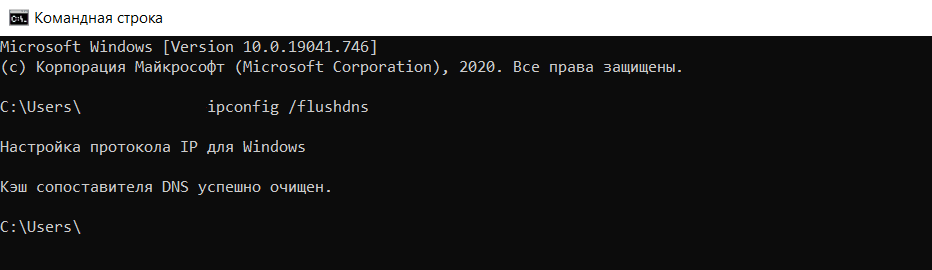
Очистите кэш DNS
DNS-кэш — это временная база данных вашего компьютера, которая хранит IP-адреса часто посещаемых веб-сайтов. Такая база данных ускоряет связь с сервером.
Вы можете изменить DNS, однако данные из кэша отправляют на старый IP-адрес. После очистки браузер начнёт обращаться к новому IP-адресу. Чаще всего проблема несоответствия DNS приводит к ошибке 502, но также может появиться ошибка 400.
В зависимости от вашей операционной системы очистите кэш по одной из инструкций.
-
1.
Откройте командную строку. Для этого введите в поисковую строку «Командная строка» и выберите появившееся приложение:
- 2.
-
3.
Дождитесь сообщения об очистке кэша:
-
1.
Откройте терминал клавишами Ctrl+Alt+T.
-
2.
Введите команду:
Для Ubuntu:
sudo service network-manager restartДля других дистрибутивов:
sudo /etc/init.d/nscd restart
-
1.
Войдите в терминал. Для этого нажмите клавиши Command + Space. Введите Терминал и нажмите на найденное приложение.
-
2.
Введите команду:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
Готово, вы очистили кэш DNS. Попробуйте заново зайти на сайт.
Измените настройки антивируса и брандмауэра
Нарушать соединение с сервером может брандмауэр или антивирус. Чтобы проверить, мешает ли соединению один из них, временно отключите ваш антивирус и брандмауэр. Если страница заработала, нужно менять настройки одного из них.
Как отключить брандмауэр на Windows 7/10
Брандмауэр ― межсетевой экран, стена, которая защищает компьютер от вторжений и от утечки информации в сеть. Многие антивирусы имеют межсетевой экран. В этом случае брандмауэр можно выключить, чтобы он не нарушал соединения с сайтами. Если в антивирусе нет межсетевого экрана, не отключайте брандмауэр без особой причины.
Чтобы отключить брандмауэр на Windows 7/10:
-
1.
В левом нижнем углу экрана нажмите на иконку Лупы.
-
2.
Перейдите во вкладку «Приложения» и выберите Панель управления:
-
3.
Нажмите на Брандмауэр Защитника Windows:
-
4.
В левом меню нажмите на Включение и отключение брандмауэра Защитника Windows:
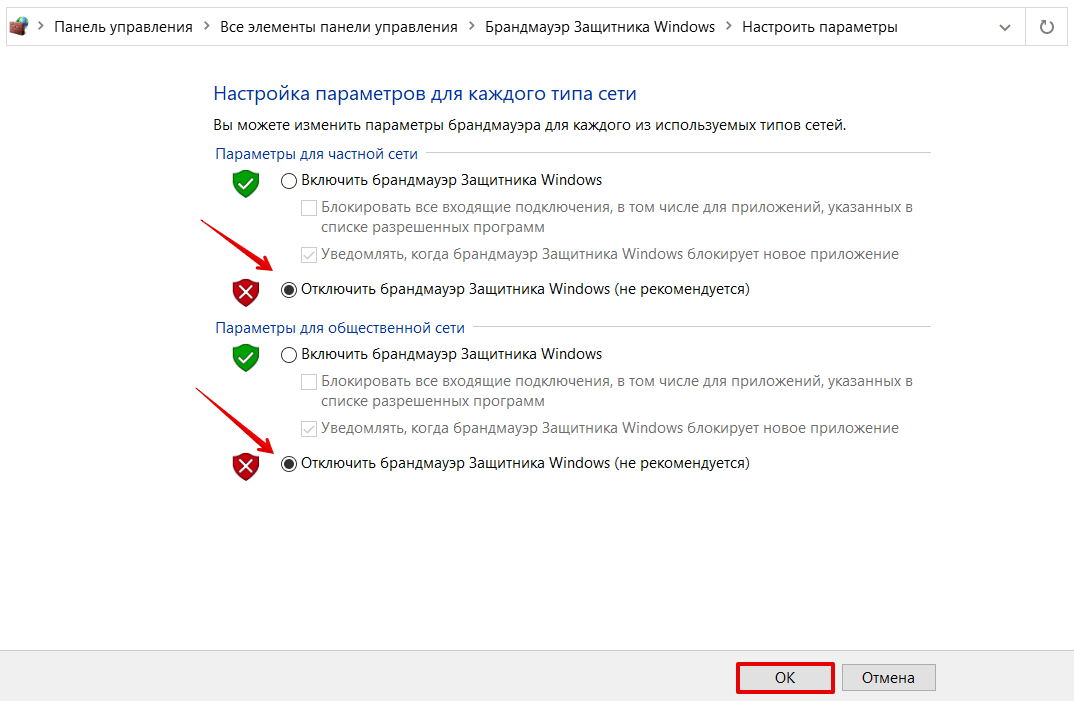
-
5.
В блоках «Параметры для частной сети» и «Параметры для общественной сети» отметьте пункт Отключить брандмауэр Защитника Windows. Нажмите OK:
Готово, вы отключили брандмауэр.
Проверка на вирусы
Вирусы на устройстве могут нарушать связь с сайтами. Отсканируйте систему антивирусной программой. Когда вирус будет найден, удалите его и перезагрузите устройство. Если вируса нет, попробуйте другой способ.
Обновите драйверы сетевых устройств
Устаревшее ПО на сетевых устройствах может генерировать неверные запросы. Установите новые драйверы для сетевого соединения.
Уменьшите размер файла
Несмотря на то что ошибки 4xx в основном вызваны проблемами на устройстве пользователя, бывают случаи, когда ошибка связана с сервером. 400 ошибка сервера возникает, когда пользователь загружает слишком большой файл на ресурс.
Создатели сайта иногда ставят ограничения на файлы, которые загружают пользователи, чтобы не занимать много места на своём сервере. Если у вас появляется ошибка 400 при загрузке файла, то, скорее всего, он больше, чем требует владелец веб-ресурса. Попробуйте уменьшить вес файла и загрузите его снова.
Проблема на стороне интернет-провайдера
Попробуйте загрузить другой веб-сайт. Если ошибка сохраняется, значит проблема может быть связана с нарушением работы сетевого оборудования. Чтобы её исправить попробуйте перезагрузить сетевое оборудование (модем, маршрутизатор) и само устройство.
Если и это не помогло, обратитесь к своему интернет-провайдеру. Максимально полно опишите проблему и действия, которые вы предпринимали. Опишите, какая у вас операционная система и браузер, используете ли брандмауэр и прокси-сервер, очистили ли вы кэш и куки, проверили ли устройство на вирусы.
Для владельца сайта
Если вы увидели, что ваш сайт выдаёт ошибку 400, проделайте все вышеперечисленные действия. Вполне возможно, что у ваших клиентов всё отображается правильно. Очень редко, но случается, что проблема всё-таки с сервером, на котором находится сайт. В этом случае обратитесь к хостинг-провайдеру, чтобы найти ошибку в настройках.
A HyperText Transfer Protocol Bad Request 400 indicates a client error. When the client sends an invalid request to the server, the server issues an HTTP status code 400. A high number of 400 errors can negatively affect the usability of websites, and is usually caused by an incorrectly entered URL. [1]
Background
The 400 (Bad Request) status code indicates that the server cannot or will not process the request due to something that is perceived to be a client error.[2] In response to an invalid request, the server should issue the exact 4xx code in the case of an unsuccessful request.
Common Causes
A 400 Bad Request error is usually the result of entering the wrong URL in the browser address window, or by making mistakes in a link’s address when linking from page to page.
How to fix 400 Errors
- Check that the entered URL is correct: The URL and link syntax should be correct, and the target URL should exist. You can use Ryte’s Website Success to crawl a website and ensure all link targets are a 200 Success code.
- Clear your DNS Cache: The errors might be being displayed as your computer is storing outdated DNS records. Execute ipconfig/flushdns from a Command Prompt to do this.
- Clear your browser cache: Another reason could be that your cached version of the page is still suffering from the 400 status code error. In your browser’s History, you can clear your cache that would resolve this problem.
- Clear your browser’s cookies: While you’re there in your browser’s History, you could also clear your cookies. This is the best practice when you’re getting a Bad Request error on a Google site or service.
List of all 4xx status codes
Errors with the status code 4xx are listed below:
* 400 bad request: All errors with the status code 4xx indicate an invalid request from a client to a server.
* 401 unauthorized: This request to the server requires the client to authorize. This is usually done by logging in. If a user still wants to access the password-protected resource, the status code 401 (unauthorized) appears with a note on what to do.
* 402 payment required: This status code is for future use. It will indicate that you have to pay a fee in order to view the content, and that it will only be visible after payment.
* 403 forbidden: Access is denied even with valid login data. This can happen for example when a site is requested with HTTP, but is configured with HTTPS.
* 404 not found: One of the most frequently displayed status codes is the 404-error. It is used to indicate that a requested link does not exist. If the error page displays a different HTTP status code to 404, this results in a soft 404 error.
* 405 method not allowed: The request was made using the wrong request method. The required method, such as GET or POST is explained by the response within the error code.
* 406 not acceptable: In this case, the format requested by the client cannot be issued by the server. The content type is available in the server response.
* 407 proxy authentication required: Similar to status code 401, the server requests authentication by the client, in this case in relation to the proxy server being used.
* 405 request time-out: This code is displayed if the client could not send a complete request in the time period defined by the server.
* 409 conflict: This request by the client is rejected by the server because it was submitted under a false assumption. This status code may get output if the resource has changed.
* 410 gone: If the user receives this status code, it means that the resource is no longer available and/or has been deleted.
* 411 length required: If this code appears, the content length needs to be specified in the header to process the client request.
* 412 precondition failed: In this case, the prerequisite has been defined in the request, which does not apply. (for example, an if match)
* 413 request entity too large: This indicates that the request was too big to be processed by the server in question. The server response may include the instruction to try again later.
* 414 request-URI too long: The server cannot respond because the URI is too long. This is usually caused by too many redirects.
* 415 unsupported media type: This request cannot be answered because the media type is not available.
* 416 request range not satisfiable: This error code indicates that a portion of the requested resource is no longer available or invalid.
* 417 expectation failed: This code will be output if the “expect” field of the header specifies a particular request that the server that cannot fulfill.
* 422 unprocessable entity: This code indicates that the request cannot be processed. This could be caused by semantic errors, but not media type errors as is the case with 415.
* 423 locked: The requested resource is temporarily locked and not accessible.
* 424 failed dependency: If this status code is issued, two requests were made. The second request depended on the first, but was unsuccessful.
* 426 upgrade required: In order for the server to handle this request, the client must use TLS 1.0.
* 428 precondition required: Preconditions must be fulfilled In order to execute this request successfully.
* 429 too many requests: This code is issued by the server if it received too many requests from a client within a certain period of time. This may occur, for example, if an SEO tool queries too many keywords on Google within a short period of time.
* 431 request header fields too large: If the length of the header field or the entire header has been exceeded, this status code appears.
References
- ↑ RFC2616-sec10 w3.org Accessed on June 12, 2019
- ↑ RFC 2731 Section 6.5.1. 400 Bad Request Accessed on June 12, 2019
Web Links
- status code definitions by w3.org
- How to deal with 404 error pages