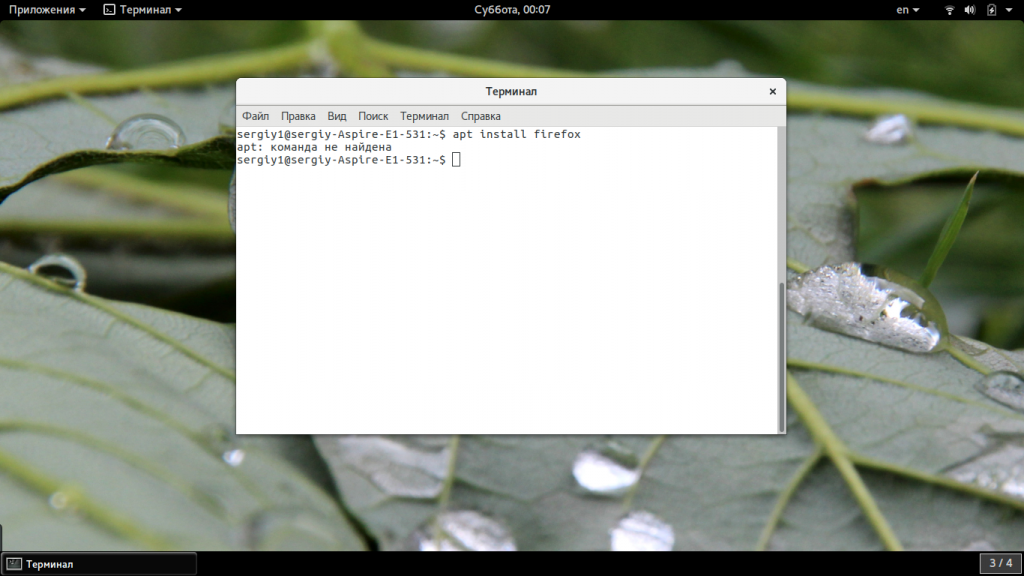
Очень важно уточнить, что большинство пользователей, получающих эту ошибку, не получают настоящую системную ошибку, а используют дистрибутив Linux с другим менеджером пакетов, отличным от apt. Обычно это вызвано ошибкой на стороне пользователя.
В большинстве случаев пользователям, сталкивающимся с этим сообщением, просто нужно использовать правильный менеджер пакетов для своего дистрибутива Linux.
Менеджеры пакетов apt или apt-get используются дистрибутивами Linux на основе Debian, такими как Ubuntu.
Если вы используете другой дистрибутив Linux, такой как CentOS, вам нужно использовать менеджер пакетов yum вместо apt. Если вы используете Fedora, используйте менеджер пакетов dnf.
Пользователи SUSE должны использовать менеджер пакетов zypp.
Если вы используете дистрибутив Linux, такой как Debian или Ubuntu, и у вас возникает ошибка «apt command not found», продолжайте читать ниже. Первый раздел этого документа предназначен для пользователей Ubuntu; инструкции для пользователей Debian можно найти во втором разделе.
Исправление ошибки «apt command not found» в Ubuntu Linux
В этом руководстве я предполагаю, что по какой-то причине внешний интерфейс диспетчера пакетов apt был удален из вашей системы.
В приведенных ниже инструкциях описаны все шаги по установке последней версии пакета apt для Ubuntu.
Для начала перейдите по этой ссылке https://packages.ubuntu.com/ и прокрутите страницу вниз, чтобы найти раздел поиска.
Введите apt в поле ключевого слова, выберите правильный выпуск Ubuntu и нажмите кнопку «Поиск», как указано стрелками на снимке экрана ниже.
Прокрутите начальную страницу вниз и нажмите ссылку на пакет apt, как показано на следующем рисунке.
Прокрутите вниз начальную страницу. Внизу вы найдете ссылки для каждой архитектуры; нажмите правильный для вашей системы.
Чтобы завершить загрузку apt, нажмите на ссылку для скачивания.
После загрузки пакета установите его с помощью dpkg, как показано ниже. Важно уточнить, что 1.6.12ubuntu0.2_amd64 необходимо заменить на ту версию и архитектуру, которые вы скачали.
sudo dpkg -i apt_1.6.12ubuntu0.2_amd64.deb
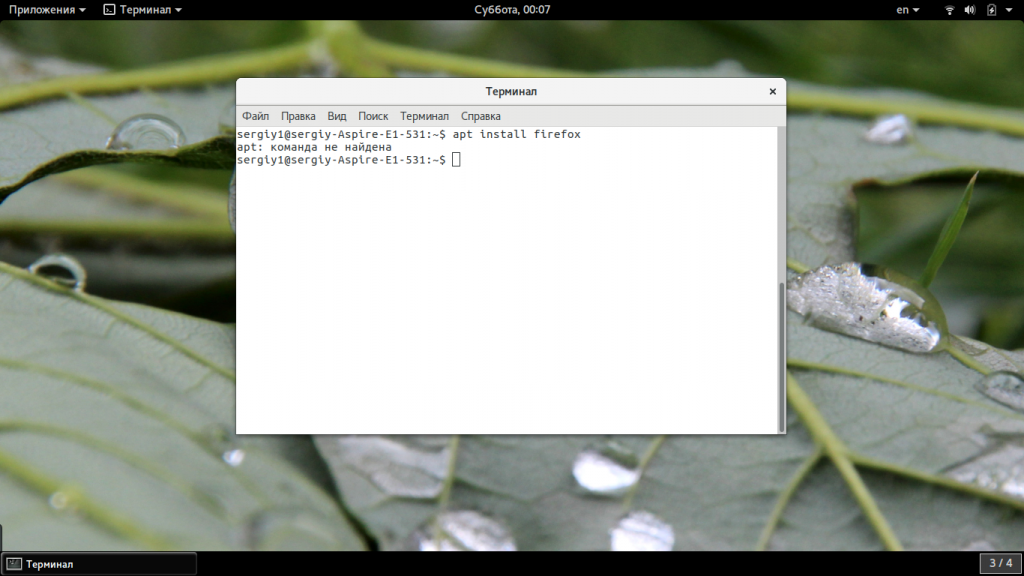
Протестируйте apt еще раз, чтобы проверить, работает ли он сейчас.
Если это все еще не работает, возможно, проблема связана с переменной окружения $PATH.
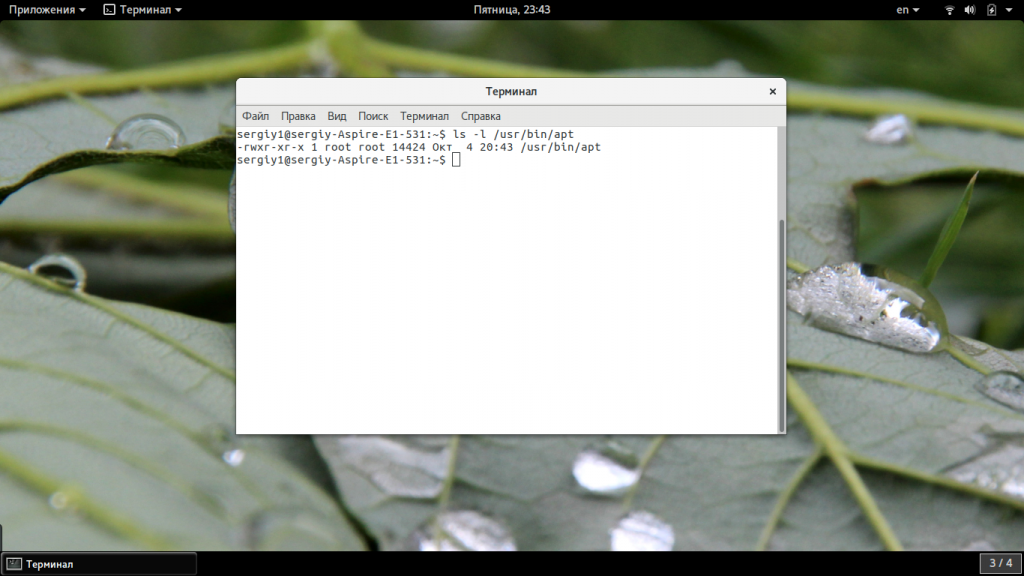
Чтобы подтвердить это, сначала проверьте, где находится двоичный файл apt. Вы можете использовать команду whereis, как показано в следующем примере.
whereis apt
Как видите, двоичный файл находится в каталоге двоичных файлов /usr/bin (/usr/bin/apt).
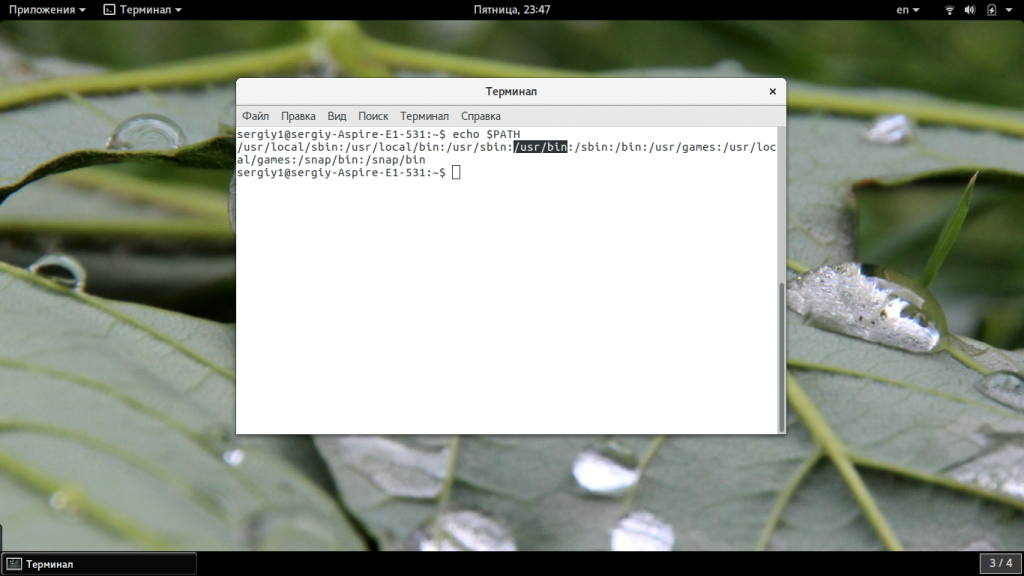
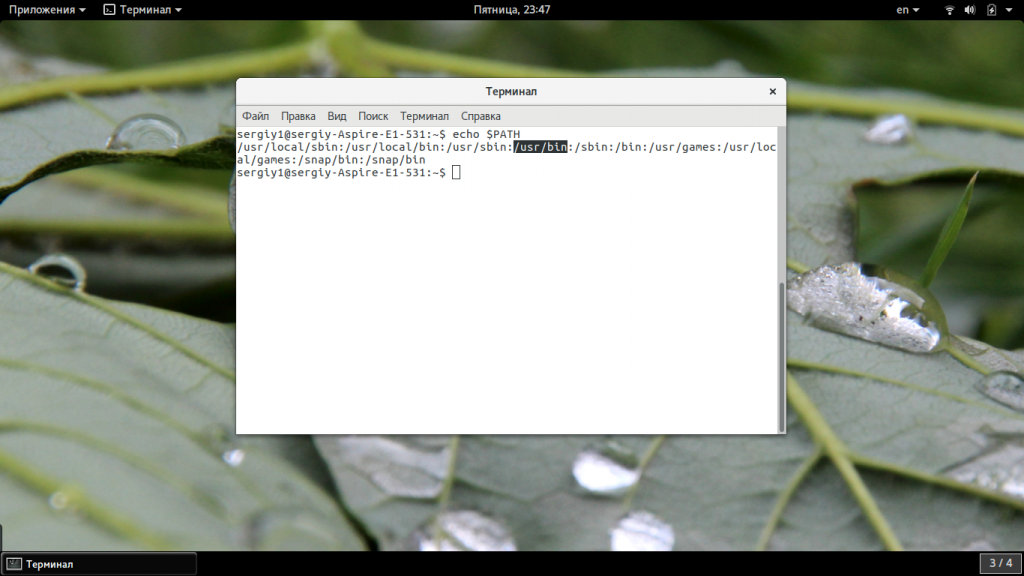
Чтобы подтвердить, включен ли путь в ваши переменные среды $PATH, используйте команду echo, за которой следует переменная среды, которую вы хотите проверить ($PATH).
echo $PATH
Как видите, каждый путь отделяется двоеточием. Если в вашем случае путь /usr/bin не включен, добавьте его с помощью команды экспорта, как показано на следующем рисунке, а затем снова проверьте apt.
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/bin
Если после экспорта пути менеджер пакетов apt работает правильно, вы нашли проблему. Но экспорт пути из командной строки — это только временное исправление без сохранения после перезагрузки системы или смены сеанса.
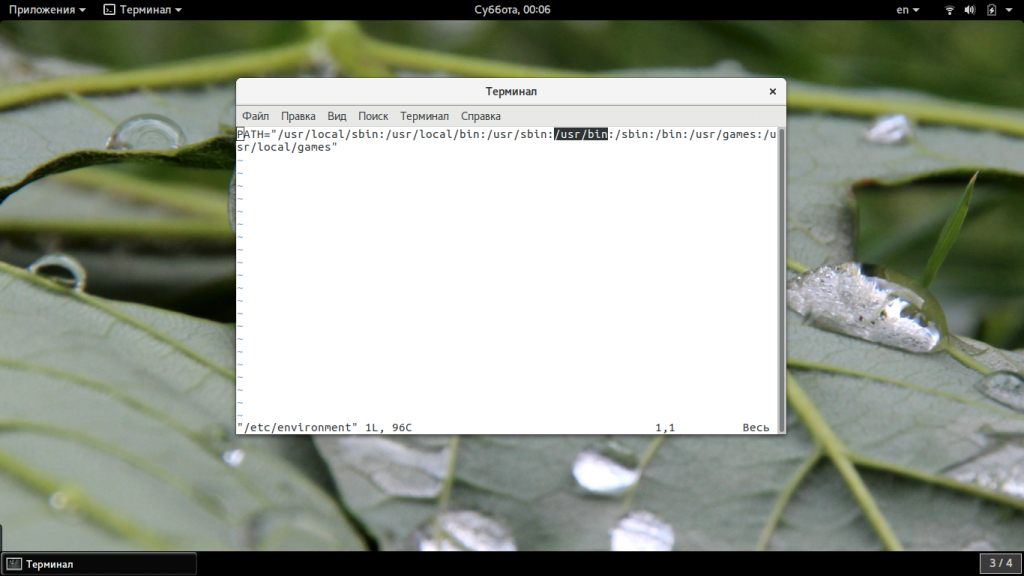
Чтобы сделать это решение постоянным, откройте файл. bashrc в вашем домашнем каталоге с помощью текстового редактора, такого как nano или vi.
nano .bashrc
В конце файла добавьте следующую строку.
export PATH="$PATH:/usr/bin"
Закрой. bashrc сохраните изменения и обновите переменную среды пути, выполнив следующую команду.
source .bashrc
Теперь команда apt должна работать.
Как исправить ошибку «команда apt не найдена» в Debian Linux
Чтобы пользователи Debian могли исправить эту ошибку, сначала перейдите по ссылке https://www.debian.org/distrib/packages#search_packages и прокрутите вниз, чтобы найти раздел поиска.
В поле ключевого слова введите apt, выберите правильный дистрибутив Debian и нажмите кнопку «Поиск».
Вы будете перенаправлены на страницу со списком пакетов. Нажмите на ссылку пакета apt, относящуюся к вашей версии Debian.
Прокрутите начальную страницу вниз и выберите правильную архитектуру для вашей системы.
После перенаправления на страницу зеркал нажмите любое из них, чтобы начать загрузку пакета.
В некоторых случаях ваш браузер может помешать вам загрузить пакет. Разрешить загрузку пакета.
После того, как вы получите пакет с помощью менеджера пакетов dpkg, установите его, как показано ниже. Помните, что 2.2.4_amd64 необходимо заменить на фактическую версию/архитектуру, которую вы загружаете.
sudo dpkg -i apt_2.2.4_amd64.deb
Теперь команда apt должна работать. Если это все еще не работает, возможно, проблема связана с переменной окружения $PATH.
Во-первых, проверьте, где находится двоичный файл apt. Вы можете использовать команду whereis, как показано в следующем примере.
whereis apt
Как видите, бинарник находится в каталоге /usr/bin (/usr/bin/apt).
Чтобы узнать, включен ли путь в ваши переменные среды, используйте команду echo, за которой следует переменная среды, которую вы хотите проверить (в данном случае $PATH).
echo $PATH
Как видите, каждый путь отделяется двоеточием. Если в вашем случае путь /usr/bin не включен, добавьте его с помощью команды экспорта, как показано ниже, а затем снова проверьте apt.
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/bin
Если после экспорта пути менеджер пакетов apt работает, вы нашли проблему. Но экспорт пути из командной строки — это только временное исправление без последствий после перезагрузки или смены сеанса.
Чтобы сделать это исправление постоянным, откройте файл. bashrc в вашем домашнем каталоге с помощью текстового редактора.
nano .bashrc
В конце файла добавьте следующую строку.
export PATH="$PATH:/usr/bin"
Закрой. bashrc сохраните изменения и обновите переменную среды пути, выполнив следующую команду.
source .bashrc
Это все; Я надеюсь, что эти шаги решат вашу проблему.
Вывод
Наиболее распространенной причиной появления этого сообщения об ошибке является неправильное использование менеджера пакетов, не совместимого с установленным дистрибутивом Linux. В большинстве случаев это ошибка со стороны пользователя. Но если пользователь пытается правильно использовать менеджер пакетов apt в совместимом дистрибутиве Linux, его установка или исправление пути, как описано в этом руководстве, весьма вероятно решит проблему, если только это не является следствием неправильной установки или более серьезный системный сбой. Все возможные решения, описанные ранее, довольно легко реализуются любым пользователем Linux, независимо от уровня знаний. Для этого требуется только использование менеджера пакетов dpkg или исправление пути.
Большое спасибо за чтение этой статьи; Я надеюсь, что это было полезно для решения проблемы. Продолжайте следить за нами для получения дополнительных советов и руководств.
Apt-get — это пакетный менеджер, который используется по умолчанию в семействе дистрибутивов Debian и Ubuntu. Учитывая, что это пакетный менеджер, один из почти самых основных пакетов системы, то логично, что программа должна присутствовать в каждом дистрибутиве. Но все же некоторые пользователи встречаются с ошибкой apt get command not found.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим почему возникает такая ошибка, как это вообще может быть и как исправить apt get команда не найдена.
Фактически это сообщение об ошибке означает как раз то, что оно нам сообщает, команда, которую вы пытаетесь выполнить не найдена в системе. Она либо еще не была установлена, либо была удалена. Но все это звучит очень странно в отношении к менеджеру пакетов. Рассмотрим основные причины возникновения ошибки:
- Одна из самых очевидных причин, получения ошибки «apt get не найдена» в том, что у вас не Ubuntu. Этот пакетный менеджер используется только в дистрибутивах Linux, основанных на Debian. Системы Red Hat, CentOS, Fedora, OpenSUSE, CoreOS, Cloud Linux, ArchLlinux и другие таковыми не являются. Они имеют собственный пакетный менеджер, у каждой свой и именно его нужно использовать для установки пакетов, а не искать apt.
- Если вы используете команду apt, а не apt-get, то, возможно, у вас старый дистрибутив, который не поддерживает такого синтаксиса, используйте apt-get;
- Вторая причина в том что вы случайно или намерено удалили пакет Apt. Его больше нет в системе поэтому система и не может его найти;
- Третья причина, может быть в невозможности обнаружения программы. Утилита apt есть в системе и исправно работает, но вы повредили переменную среды PATH и теперь система не ищет исполняемые файлы в той папке где находится apt.
Теперь рассмотрим как решить проблему. Это очень просто.
Как исправить apt get команда не найдена?
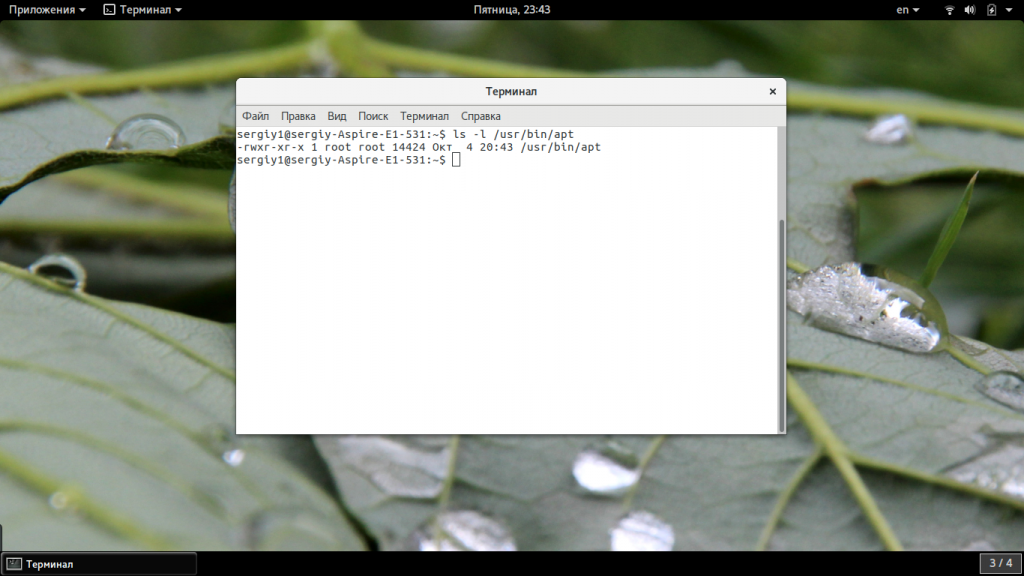
Поскольку вторая причина предполагает меньше действий, нам нужно сначала проверить ее. Обычно исполняемые файлы apt находятся в каталоге /usr/bin. Сначала посмотрим есть ли такой файл в той папке:
ls -l /usr/bin/apt-get
Если файл есть, то вы увидите что-то похожее как на снимке выше. Также обратите внимания на права. Для пользователя, группы и остальных должен быть выставлен флаг «x» означающий исполнение. Если же его нет, то apt придется переустановить. Если права отличаются от приведенных выше, а именно «-rwxr-xr-x», то их тоже нужно исправить, добавим для всех категорий флаг исполняемости:
chmod +x /usr/bin/apt-get
Если предыдущие варианты не сработали проверим содержимое переменной среды PATH:
echo $PATH
Вы должны увидеть в ней ссылку на /usr/bin. Если такой строчки нет, то проблема была здесь, а строчку нужно добавить в конец:
export PATH=текущее_содержимое:/usr/bin
Например:
export PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/bin:/snap/bin
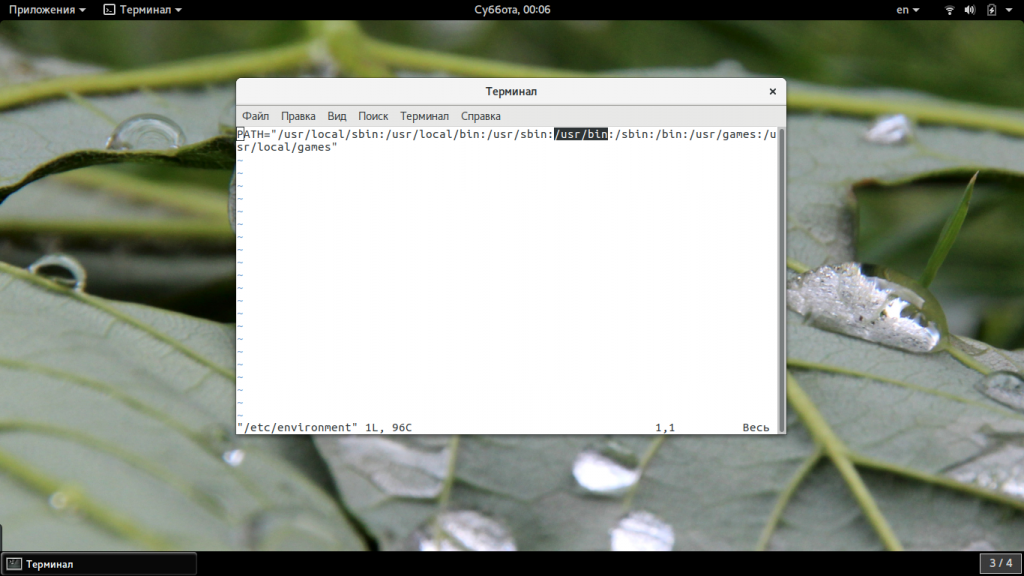
Если вы вносили изменения в файл /etc/profile, и переменная PATH сломалась из-за этого, то нужно внести исправления и в этот файл.
Последний вариант, если ничего не помогло, это переустановить утилиту. Мы просто скачаем ее из официального сайта и установим в систему. Только нужно выбирать версию для своей операционной системы. Вы можете скачать пакет с помощью браузера или таких команд:
Для Ubuntu Xenial:
wget http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/a/apt/apt_1.2.15ubuntu0.2_i386.deb
Для Ubuntu Yakkety:
wget http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/a/apt/apt_1.3.3_i386.deb
Теперь осталось установить загруженный пакет:
sudo dpkg -i apt*
Готово, после этого ошибка apt get command not found должна исчезнуть и вы сможете нормально работать со своими пакетами.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели почему не работает apt get, из-за чего возникает ошибка apt get команда не найдена, а также как ее решить. Надеюсь, приведенная здесь информация была полезной для вас.
Статья распространяется под лицензией Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 при копировании материала ссылка на источник обязательна .
Об авторе
Основатель и администратор сайта losst.ru, увлекаюсь открытым программным обеспечением и операционной системой Linux. В качестве основной ОС сейчас использую Ubuntu. Кроме Linux, интересуюсь всем, что связано с информационными технологиями и современной наукой.
Starting in Ubuntu 14.04, there is a command in Ubuntu called just
apt, which didn’t exist when this question was originally asked. The
aptcommand provides a convenient subset of the functionality of
various otherapt-commands (e.g.,apt-get,apt-cache), with
colorized display and progress bars. Although theaptcommand does
not support all the same actions and options asapt-get, it may often be used in place ofapt-get. See Fsando’s answer for
details.
APT is a suite of utilities, including a database of information about what packages are available from where.
APT is not a single command. Rather, it provides several commands.
The most commonly used APT command is apt-get. That’s what you should probably be using.
To update information about what packages are available and from where (which you should do before attempting to upgrade or install any packages with apt-get), run:
sudo apt-get update
To upgrade packages (i.e., «update your system»), run:
sudo apt-get upgrade
To upgrade packages, including packages that require uninstalled packages to be installed, or installed packages to be removed, run this (but be careful—it’s best to pay attention to what will be added or removed):
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
To install one or more packages, run this, replacing ... with the list of packages you want to install (if you want to install more than one package, put spaces between the package names):
sudo apt-get install ...
To remove one or more packages (i.e., to uninstall it), run:
sudo apt-get remove ...
To remove a package and also remove its systemwide configuration files (but not its per-user configuration files, which reside in users’ home directories), run:
sudo apt-get purge ...
To remove packages that were installed automatically because other packages needed them, but which now are no longer needed, run:
sudo apt-get autoremove
To do that, and also remove their global configuration files»
sudo apt-get --purge autoremove
To reinstall a package, run:
sudo apt-get --reinstall install ...
To reinstall a package and delete its systemwide configuration files while doing so:
sudo apt-get --purge --reinstall install ...
To delete cached package installer (.deb) files (which does not remove any packages, but will make it so they have to be fetched over the network again to be reinstalled):
sudo apt-get clean
To deleted cached package installer files, but only for packages that are unlikely to be needed again (i.e., those that are so old they’ve been removed from the servers, as of last time sudo apt-get update was run):
sudo apt-get autoclean
That was just a brief overview. It does not capture all possible uses of apt-get, plus there are a number of other utilities provided in the APT suite, such as apt-cache for examining information about installed and available packages.
You can learn more by reading the apt-get and apt manual pages.

Debian Linux and Linux distributions based on Debian employ the APT package management system. APT configures, builds, and installs software from a variety of sources, including the internet, a LAN server, or a CD-ROM. It can make the process of installing and uninstalling software on a Linux machine much easier.
APT is a package management toolset made up of several commands, rather than a single command. Apt-get and apt-cache are two of the most regularly used APT commands.
When you try to run apt-get commands on your own Linux computer or a server, you may get an “apt-get: command not found” error. This article will help you understand a few possible causes and how to rapidly resolve them.
What is the apt-get command?
A command-line program for installing, updating, and uninstalling Linux packages is apt-get. It obtains information about the packages, as well as their dependencies, from trusted sources to install or delete them.
The most popular apt-get commands are as follows:
- sudo apt-get install (to install a package)
- sudo apt-get remove (package removal)
- sudo apt-get update (for updating a package)
- sudo apt-get upgrade (for upgrading a package)
- apt-get help (to know more about a command )
In this case, sudo is used to provide you with superuser security privileges.
What Causes the ‘sudo apt-get command not found’ Error on macOS?
When your Terminal displays the message ‘command not found,’ it signifies that the command isn’t accessible. All commands and features linked to that utility will not operate if the program or utility is not installed on your system.
We all know that the Terminal commands on Linux and macOS are nearly identical. However, this does not imply that both Linux and macOS will use the same package managers and tools for installation and management. Finally, the APT commands are not supported on macOS.
Alternatives of APT for macOS
APT commands are used in Terminal to download, update, and upgrade software. This option, however, is only available for a few Debian Linux distributions. As a result, there are just a few options for macOS that function in the same way as APT. These alternatives do the same functions as APT but with a few additional/improved capabilities.
How to solve the apt-get command not found an error?
This apt-get command not found error is solved using the following solutions:
- Check your Linux distribution
- Check apt path for its binary
- Reinstall apt using dpkg
- Using the Correct Package Manager
- Downloading the Latest APT Package
- Installing Homebrew in macOS
- Installing MacPorts in macOS
- Make sure You Are Connected to AWS
- Try to set the Software-properties-common Plan
- Run the Environment Variables
- Try to Update Ubuntu Repositories (Debian and Ubuntu)
- Reinstall the Operating System
- For CentOS
Let us go through them one by one:
Solution 1: Check your Linux distribution
There are around a thousand Linux distributions (or Linux distros) available at any given time. They may be set up and adjusted for a variety of devices (desktops, laptops, servers, tablets, etc).
They can be presented in a form that is appropriate for a particular culture. They can also be created specifically for usage on a web-based service (Amazon Linux AMI).
Only a few Linux distributions are mature enough to be deemed major. Almost everyone will base their release on one of the “majors,” each of which has its own set of standard packages (package manager like apt included).
By default, only Debian and Ubuntu-based distributions utilize apt.
You may use the command cat /etc/*-release or one of a few different methods to see if your distribution has apt beneath the hood.
If you’re copying terminal commands from a tutorial, we recommend looking for one that’s compatible with your Linux system.
A typical issue for AWS users that utilize Amazon Linux images on their servers is “apt-get: command not found.” Keep in mind that Amazon Linux was originally based on CentOS, then diverged, yet yum remains the default package manager.
Solution 2: Check apt path for its binary
The message apt-get: command is not found mac means that the system can’t find apt-get in its path. Manually verifying that the route is in place is the logical solution.
To discover where the system expects the apt-get binary to be, type the following command in the terminal: locate apt-get
The resulting output should resemble the image below or include the following string: /usr/bin/apt-get

If the command gives you no results, you don’t have the “apt” package installed. You’ll have to manually install it using a.deb file.
Solution 3: Reinstall apt using dpkg
To do so, you’ll need to download the corresponding .deb package for your OS version. Go to one of Ubuntu’s Archive Mirrors if you’re using it. In this scenario, go to http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/. and look under “/pool/main/a/apt/” for a list of.deb packages. Choose the option that best fits your architecture (and64/i386).
After it has finished downloading, use the following command to install the apt DEB file:
sudo dpkg -i /path/to/apt_deb_file.debRemember to substitute the path to the file you just downloaded for “/path/to/apt deb file.deb.”
Solution 4: Using the Correct Package Manager
The first step in resolving the issue is to use the apt-get command to install the necessary Linux distributions. Avoid downloading any of the following files that APT does not support:
- CentOS
- openSUSE
- RHEL
- Arch
- macOS X
- Fedora
Yum is the default package manager in Linux distributions including Fedora, CentOS, and RHEL. To use Yum to install them, use the following command:
$ sudo yum install <packagename>Homebrew is the default package manager for macOS X. You may utilize it by typing the following command:
$ brew install tmuxFor Arch Linux, you must use the Pacman package manager, which may be found here:
$ packman -S tmux Solution 5: Downloading the Latest APT Package
Another option for resolving this problem is to get the most recent APT package for your system. You must download the .deb file according to your system architecture, which might be either 32-bit or 64-bit.
The.deb file may be found in the “/etc/apt/sources.list” file. This file contains relevant links for package installation and upgrades. Running the command “$cat /etc/apt/sources.list” will reveal the downloading source.
Visit the “/pool/main/a/apt/” directory under the downloading source, find the.deb files relevant to your architecture and then download it. After downloading the file, use the dpkg command to install it —
$ sudo dpkg -i apt_1.9.3_i386.debSolution 6: Installing Homebrew in macOS
The apt-get tool is used to install packages on Linux computers. For the Mac, homebrew is the equivalent. Most people are familiar with it because of the package manager.
Packages are installed in their directory by Homebrew, which then symbolic links their files into /user/local. Follow the instructions below to install homebrew and run the command to install packages:
- To open Spotlight, hold down the Command key and press Space, then type Terminal and press Enter.
- To begin, use the following command to install the Xcode command-line tool:
xcode-select --install- After installing the Xcode tool, execute or copy the following command to install Homebrew on macOS:
ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"- For confirmation, the installation will ask for the Return (Enter) key and password.
- For properly installing the utility, you will receive an installation success message.
- Type the following command in Homebrew to install any package you want:
brew install name- The package will be installed successfully on your system using the brew command.
Solution 7: Installing MacPorts in macOS
MacPorts is a piece of software that allows you to compile, install, and manage open source applications. Any needed dependencies for the port that the user is trying to install will be installed automatically by MacPorts.
It’s simple to use; with just one command, you may install, download, or build a program or library. Upgrades and uninstalls for installed ports are also available through MacPorts. You may install it by carefully following the procedures below:
- Open the App Store from the Dock and type Xcode into the search bar. Install Xcode by clicking Get. Because the file is about 6GB in size, it will take some time to install. It will prompt you for your App Store account’s username and password.
- By launching the program from the App Store or Dock and selecting the Agree button, you can agree to Xcode’s terms. To consent to the agreements, use the following command in Terminal:
sudo xcodebuild -license - To install the Xcode command-line tool, hold the Command key and press Space to launch Spotlight. Then enter Terminal and execute the following command:
xcode-select --install - Now, for your operating system, download MacPorts.
- To install apt-get, follow the on-screen instructions and supply the password if prompted.
- Restart Terminal when the installation is complete and run the following command:
sudo port selfupdate
If the notice ‘Updating MacPorts base sources using rsync’ appears, MacPorts has been installed. However, if you don’t see this message, you’ll need to reinstall it properly.
- Using the command “
sudo port install name” you may now install any package.
The package name in the command can be the name of the software you’re trying to install on your Mac.
Solution 8: Make sure You Are Connected to AWS
If you are new to RDP/AWS services, this is the best approach for you. Make sure you’re connected to AWS by going to the AWS Page and clicking on your instances. To finish “SSH,” press Connect and follow the on-screen instructions. When you’re finished, try using the apt command in AWS.
Solution 9: Try to set the Software-properties-common Plan
To begin, open your “Terminal” and type the following command: ”sudo apt-get install software-properties-common”. Then press Enter
You must wait till the procedure is finished.
For older Ubuntu, follow the command: “sudo apt-get mount python-software-properties”
Solution 10: Run the Environment Variables
If you’re still having trouble with the sudo apt-get command not found error, try the following command: “~/$[YOURUSER]/.bashrc”
Execute the following command in the next step: “sudo /usr/bin/apt-get update”
Once you’ve completed the preceding procedures, check to see whether the problem has been fixed. If it hasn’t, try using a root account and repeat the steps above. If you’re having trouble, try running the command listed here: “sudo find / -name ‘apt-get”
Solution 11: Try to Update Ubuntu Repositories (Debian and Ubuntu)
To update your database, go through the following steps:
- To begin, open your Terminal and type the following instructions, pressing Enter after each one:”sudo apt-get update” is a command.
- After that, wait until the operation is completed to see whether the sudo apt-get command not found error has been fixed.
Solution 12: Reinstall the Operating System
If the solutions listed above haven’t worked, the quickest alternative is to reinstall the operating system. On a server, just re-imaging the server will give you a fresh start. This may solve the issue.
Make sure that the sudo access keyword is used correctly in all of the commands. The apt-get problem might occur if your system administrator refuses to let you use the apt-get command.
Before you reinstall, make a backup of your data and settings.
Solution 13: For CentOS
The default package manager is “Yum,” therefore try the command “sudo yum install packagename>.”
To avoid an error, use the following command to get the rpmforge-release package:
wget http://packages.sw.be/rpmforge-release /rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.e15.rf.i386.rpmFinally, type the instructions listed below for package verification and installation:
sudo rpm –import http://apt.sw.be/RPM-GPG-KEY.dag.txt
rpm -K rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.e15.rf.i386.rpm
sudo rpm -I rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.e15.rf.i386.rpmConclusion
That is all there is to it. I’ve done my best to offer you all of the available solutions to the sudo apt-get command not found the issue. Hopefully, one of the options suggested above successfully resolves your issue.
Содержание
- Ошибка apt-get command not found
- Что значит apt get команда не найдена?
- Как исправить apt get команда не найдена?
- Выводы
- 🇦🇮 Как исправить ‘add-apt-repository command not found’в Ubuntu и Debian
- Что такое Personal Package Archive
- Добавление нового PPA (Personal Package Archive) в Ubuntu
- Исправить add-apt-repository: ошибка команды не найдена
- Установка пакета в Debian / Ubuntu LTS
- Установка пакета в Ubuntu 13.10 и старше
- apt-get command not found in Linux
- What is the apt-get command?
- What is the apt-get command not found?
- Operating System Not Supportive
- Package Not Available
- How to solve the apt-get command not found an error?
- 1) Using the Correct Package Manager
- 2) Downloading the Latest APT Package
- 3) Reinstalling the OS
- Why is the «apt» command not found?
- 4 Answers 4
- Ошибка apt-get command not found
- Что значит apt get команда не найдена?
- Как исправить apt get команда не найдена?
- Выводы
Ошибка apt-get command not found
В этой статье мы рассмотрим почему возникает такая ошибка, как это вообще может быть и как исправить apt get команда не найдена.
Что значит apt get команда не найдена?
Фактически это сообщение об ошибке означает как раз то, что оно нам сообщает, команда, которую вы пытаетесь выполнить не найдена в системе. Она либо еще не была установлена, либо была удалена. Но все это звучит очень странно в отношении к менеджеру пакетов. Рассмотрим основные причины возникновения ошибки:
Теперь рассмотрим как решить проблему. Это очень просто.
Как исправить apt get команда не найдена?
Поскольку вторая причина предполагает меньше действий, нам нужно сначала проверить ее. Обычно исполняемые файлы apt находятся в каталоге /usr/bin. Сначала посмотрим есть ли такой файл в той папке:
Если файл есть, то вы увидите что-то похожее как на снимке выше. Также обратите внимания на права. Для пользователя, группы и остальных должен быть выставлен флаг «x» означающий исполнение. Если же его нет, то apt придется переустановить. Если права отличаются от приведенных выше, а именно «-rwxr-xr-x», то их тоже нужно исправить, добавим для всех категорий флаг исполняемости:
Если предыдущие варианты не сработали проверим содержимое переменной среды PATH:
Вы должны увидеть в ней ссылку на /usr/bin. Если такой строчки нет, то проблема была здесь, а строчку нужно добавить в конец:
Если вы вносили изменения в файл /etc/profile, и переменная PATH сломалась из-за этого, то нужно внести исправления и в этот файл.
Последний вариант, если ничего не помогло, это переустановить утилиту. Мы просто скачаем ее из официального сайта и установим в систему. Только нужно выбирать версию для своей операционной системы. Вы можете скачать пакет с помощью браузера или таких команд:
Для Ubuntu Yakkety:
Теперь осталось установить загруженный пакет:
Готово, после этого ошибка apt get command not found должна исчезнуть и вы сможете нормально работать со своими пакетами.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели почему не работает apt get, из-за чего возникает ошибка apt get команда не найдена, а также как ее решить. Надеюсь, приведенная здесь информация была полезной для вас.
Источник
🇦🇮 Как исправить ‘add-apt-repository command not found’в Ubuntu и Debian
В некоторых случаях в Linux Mint, Linux Lite, Zorin OS, Elementary OS и других дистрибутивах на основе Ubuntu, а также в Ubuntu и Debian вы увидите ошибку, что команда add-apt-repository отсутствует.
Из этого руководства вы узнаете, как быстро исправить ошибку «command add-apt-repository not found» в Debian, Ubuntu и других дистрибутивах Linux на основе Debian.
Что такое Personal Package Archive
PPA – это веб-адрес личного репозитория.
Репозиторий представляет собой набор файлов, которые содержат информацию о различном программном обеспечении, его версиях и некоторых других деталях, таких как контрольная сумма.
Каждая версия Ubuntu имеет собственный официальный набор из четырех репозиториев.
Наиболее распространенный способ установки программного обеспечения в Ubuntu или Debian, если пакет еще не находится в официальном репозитории, – это использование PPA (Personal Package Archive).
add-apt-repository – это утилита командной строки для добавления PPA (Personal Package Archive) в Ubuntu и Debian Linux.
Добавление нового PPA (Personal Package Archive) в Ubuntu
Если вы хотите добавить новый репозиторий PPA, вам нужно будет использовать команду add-apt-repository:
Исправить add-apt-repository: ошибка команды не найдена
Таким образом, команда add-apt-repository в более новых системах находится под общим свойством software-properties пакета, и вам необходимо сначала установить этот пакет, чтобы установить add-apt-repository.
Установка пакета в Debian / Ubuntu LTS
Если вы используете Debian / Ubuntu LTS, такие как системы 18.04, 16.04 и 14.04, то установите пакет software-properties-common для получения команды add-apt-repository.
Примечание. Если вы видите сообщение об ошибке, в котором говорится, что пакет software-properties-common не найден, вам нужно запустить sudo apt-get update и затем попытаться установить его снова.
Установка пакета в Ubuntu 13.10 и старше
Если вы используете Ubuntu v13.10 или более раннюю, команда add-apt-repository доступна в пакете python-software-properties.
Поэтому вместо этого установите этот пакет, используя команду apt-get
После того, как вы установили software-properties-common или python-software-properties в зависимости от вашей системы, вы можете удобно использовать команды add-apt-repository или apt-add-repository для добавления PPA.
Давайте попробуем добавить пример PPA, ранее упомянутый в этом руководстве:
Надеюсь, это помогло вам решить ваши проблемы с PPA.
Если нет, или у вас есть другие вопросы, оставьте нам комментарий под статьей.
Источник
apt-get command not found in Linux
The APT (Advanced Package Tools) is a package manager used for managing packages of Debian-based operating systems and its derivatives, such as Ubuntu. APT can be used to install, update the OS and remove applications. While working with APT a common error that is encountered is “apt-get command not found”.
This error occurs when you are trying to install other operating systems that do not support APT. Using the command with the appropriate operating systems will solve the issue.
In this article, we will delve into the details of this error and its solutions.
What is the apt-get command?
The apt-get is a command-line tool used for installing, upgrading, and deleting a Linux package. It fetches information about the packages from authenticated sources to install or remove them, along with their dependencies.
The most common commands under apt-get are as follows –
Here, sudo is used for providing you with the security privileges of a superuser.
What is the apt-get command not found?
As mentioned earlier, when you try to install or modify a package on Linux with the apt-get command, you might receive this error. It may look something like this –
Let us see the reasons behind this problem.
Operating System Not Supportive
The apt-get command only works on Debian, Ubuntu, and its derivatives. If you are trying to install rpm-based operating systems such as Fedora, RHEL and CentOS, the command will not work. As a result, you will receive the error.
Distributions that support apt-get
To find out the Linux distribution name, type in the following command –
Package Not Available
If you are using an operating system that is compatible with the apt-get command, then check the availability of the APT. Type in the command locate apt-get to check whether it is installed in your system. The command must return the following output –
If no output is returned, it means that the APT package is not installed. You have to manually install it to get things working for you.
How to solve the apt-get command not found an error?
This apt-get command not found error using the following method:
1) Using the Correct Package Manager
Distributions such as Fedora, CentOS, and RHEL use Yum as their default package manager. Type in the following command to install them using Yum –
macOS X uses Homebrew as their default package manager. You can use it by running the command below –
For Arch Linux, you have to use the Pacman package manager like this –
2) Downloading the Latest APT Package
3) Reinstalling the OS
After installing the APT package, check the /usr/bin/ directory to ensure if it had properly installed. If the file is empty, then run the locate apt-get command again. If no result is shown, there is no alternative but to reinstall the operating system. This might fix the problem.
Make sure all the commands are properly using the sudo access keyword. The apt-get error may arise if the system administrator is not letting you execute the apt-get command on your system.
Источник
Why is the «apt» command not found?
What does this error mean? The apt command is not working, and I’ve lost the Software Center.
4 Answers 4
APT is a suite of utilities, including a database of information about what packages are available from where.
APT is not a single command. Rather, it provides several commands.
To update information about what packages are available and from where (which you should do before attempting to upgrade or install any packages with apt-get ), run:
To upgrade packages (i.e., «update your system»), run:
To upgrade packages, including packages that require uninstalled packages to be installed, or installed packages to be removed, run this (but be careful—it’s best to pay attention to what will be added or removed):
To remove one or more packages (i.e., to uninstall it), run:
To remove a package and also remove its systemwide configuration files (but not its per-user configuration files, which reside in users’ home directories), run:
To remove packages that were installed automatically because other packages needed them, but which now are no longer needed, run:
To do that, and also remove their global configuration files»
To reinstall a package, run:
To reinstall a package and delete its systemwide configuration files while doing so:
To deleted cached package installer files, but only for packages that are unlikely to be needed again (i.e., those that are so old they’ve been removed from the servers, as of last time sudo apt-get update was run):
You can learn more by reading the apt-get and apt manual pages.
Источник
Ошибка apt-get command not found
В этой статье мы рассмотрим почему возникает такая ошибка, как это вообще может быть и как исправить apt get команда не найдена.
Что значит apt get команда не найдена?
Фактически это сообщение об ошибке означает как раз то, что оно нам сообщает, команда, которую вы пытаетесь выполнить не найдена в системе. Она либо еще не была установлена, либо была удалена. Но все это звучит очень странно в отношении к менеджеру пакетов. Рассмотрим основные причины возникновения ошибки:
Теперь рассмотрим как решить проблему. Это очень просто.
Как исправить apt get команда не найдена?
Поскольку вторая причина предполагает меньше действий, нам нужно сначала проверить ее. Обычно исполняемые файлы apt находятся в каталоге /usr/bin. Сначала посмотрим есть ли такой файл в той папке:
Если файл есть, то вы увидите что-то похожее как на снимке выше. Также обратите внимания на права. Для пользователя, группы и остальных должен быть выставлен флаг «x» означающий исполнение. Если же его нет, то apt придется переустановить. Если права отличаются от приведенных выше, а именно «-rwxr-xr-x», то их тоже нужно исправить, добавим для всех категорий флаг исполняемости:
chmod +x /usr/bin/apt-get
Если предыдущие варианты не сработали проверим содержимое переменной среды PATH:
Вы должны увидеть в ней ссылку на /usr/bin. Если такой строчки нет, то проблема была здесь, а строчку нужно добавить в конец:
Если вы вносили изменения в файл /etc/profile, и переменная PATH сломалась из-за этого, то нужно внести исправления и в этот файл.
Последний вариант, если ничего не помогло, это переустановить утилиту. Мы просто скачаем ее из официального сайта и установим в систему. Только нужно выбирать версию для своей операционной системы. Вы можете скачать пакет с помощью браузера или таких команд:
Для Ubuntu Yakkety:
Теперь осталось установить загруженный пакет:
Готово, после этого ошибка apt get command not found должна исчезнуть и вы сможете нормально работать со своими пакетами.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели почему не работает apt get, из-за чего возникает ошибка apt get команда не найдена, а также как ее решить. Надеюсь, приведенная здесь информация была полезной для вас.
Источник
APT, otherwise known as Advanced Packaging Tool, is a package management system used by Debian based Linux distros to configure, compile and install software from the internet.
It makes installing software extremely easy as all you have to do is type a command and hit enter. However, APT in itself isn’t a single command but more like a package of tools users can use to manage programs on their Linux computers.
In this article, we’re looking at apt-get command not found errors on Linux and Mac and how you can fix them.
Also read: Debian vs Ubuntu: Which Linux distro should you pick?
How to fix apt-get command not found on Linux?
If you’re on a Linux machine, follow these steps to resolve your error.
Check your Linux distro
As we’ve mentioned above, not all Linux distros use apt-get by default to fetch and install programs. Distros have their own choice of package managers, and depending on which one you’re using, you might have to use something else such as yum or zypper.
Here’s a list of popular Linux distros and the package managers they use.
| Distro | Package management system | Package Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Red Hat Linux | RPM-based | yum/dnf |
| Fedora | RPM-based | yum/dnf |
| CentOS | RPM-based | yum/dnf |
| Amazon Linux | RPM-based | yum/dnf |
| openSUSE | RPM-based | zypper (for CLI) YaST (for GUI) |
| Debian | DEB-based | apt/apt-get |
| Ubuntu | DEB-based | apt/apt-get |
| Kali Linux | DEB-based | apt/apt-get |
| Arch Linux | Pacman-based | pacman |
| Gentoo | Portage-based | portage |
| Slackware | SlackPKG | pkgtool/slackpkg |
Check APT path
If you’re getting this error, the chances are that either APT isn’t installed or is in some other location other than the default path.
Type the command below to check the path of the APT binary.
locate apt-getIf the command outputs something similar to the screenshot above, you’ve got APT installed. If there’s no output, you need to reinstall APT.
Installing APT from scratch
Another quick solution is to install APT from scratch and avoid jumping through any hoops.
Step 1: First up, we need the deb file for the APT package. Head over to this link and click on the latest version of the APT package. In this case, it’s apt_2.3.6_amd64.deb
Step 2: Once you’ve downloaded the package, run the following command to install the package file. Make sure to add the correct path to the downloaded deb file.
sudo dpkg -i path/to/deb/the_deb_file.debThe APT commands should work just fine now.
Reinstall the OS
If the above methods don’t work, you’re going to have to reinstall the entire OS. Make sure to install an OS that uses APT as its default package manager, such as Ubuntu or Linux Mint.
Also read: Syntax error near unexpected token: 3 Fixes
How to fix apt-get command not found on macOS?
You’re seeing the ‘command not found’ error on your mac because macOS doesn’t use the APT package for installing or updating programs. However, there are macOS alternatives available for APT, the most popular one being Homebrew.
Here’s how you can install Homebrew on macOS.
Step 1: Hold the Command key and press Space to open Spotlight. Type terminal and hit enter.
Step 2: Now install Xcode command-line tool using the following command
xcode-select --install
Step 3: Now, we can install Homebrew using the command below.
ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
Wait for the installation to finish. You may be prompted for your password during the process.
Once Homebrew is installed, you can install packages using this command.
brew install <package name>Also read: How to add a user to a group in Linux?
Someone who writes/edits/shoots/hosts all things tech and when he’s not, streams himself racing virtual cars.
You can contact him here: [email protected]
The Sudo: apt-get: Command not Found Error usually occurs on macOS and on Linux. It prevents users from executing certain commands that might not be executed because some libraries aren’t available. Therefore, we suggest that you try to check if your Distribution includes APT and follow the solutions that we have listed below.
Fixing the Sudo: apt-get: command not found Error:
Method 1: Using Homebrew In MacOS
Although apt-get is limited to Linux for installation of packages you can use its alternative/equivalent on Mac which is known as “Homebrew”. Follow the steps below in order to do so:
- Press the “Command + Space” keys together to launch the “Spotlight”, type in “Terminal” and press the “Enter” key.
Terminal - Then type in the following command and press the “Enter” button:
xcode-select –install
- Now, to install “Homebrew” type in or copy the following command and press the “Enter” button:
ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)"
- Once the installation is complete, you can now use the following command to install any program/package:
brew install "Name"
Method 2: Using MacPorts On MacOS
This software can be used for the installation and compilation of other packages/software. Proceed with the steps below:
- Launch the “App Store”, type in “Xcode” in the search bar and click “Get”.
- Once installed by follow the on-screen instructions, launch it, and click “Agree”.
- Now, press the “Command + Space” keys together, type in “Terminal” and press “Enter”.
- Next type in the following command and press “Enter” afterwards.
xcode-select –install
- Now, head over to the MacPorts website from here and download it for your “OS”.
- Launch the file after downloading it and “Install” it by following the on-screen instructions.
- Restart the terminal afterwards and then type in the following:
sudo port selfupdate
- Press “Enter” and now you should be able to use the following command to install any package:
sudo port install name
Method 3: Check If You Have APT Installed
For apt commands to work you must first have its library/package installed. For this, you can check it by heading over to your terminal, and there type the below-mentioned command. Press the “Enter” key afterwards.
locate apt-get
If you have the package installed, you will see the following line of code:
/usr/bin/apt-get
Else, it means that you do not have it installed.
Method 4: Reinstalling APT Through dpkg
Follow the steps below to reinstall APT:
- To start with head over to the archive by pressing here.
- Then navigate to the following path:
pool/main/a/apt/
- Here you will see a lot of files with “.deb format”, choose the one according to your architecture.
- Download it and then install it through the following command:
sudo dpkg -i "Path of File"
- Write the path of your file and then run it on your system. Once done then check to see if the Sudo: apt-get: Command not Found problem got solved.
Method 5: Ensuring That You Are Connected to the AWS
If you are a beginner at RDP/AWS services, then this is the most suitable fix for you. Ensure that you are connected to your AWS Instance, for this head over to the AWS service page, and navigate to your instances. Click “Connect” and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the “SSH”. Once that is done, you should be able to use the apt command in your AWS.
Method 6: Using Correct Package Manager
Based on the distribution being used, you need to use the commands that are supported and appropriate for your machine. For example, if you are using an Amazon Linux, you need to use “yum” instead of “apt-get” as they are based on “Fedora”. macOS by default uses “brew” while Arch Linux uses “packman”, you can also try using “amazon-Linux-extras”.
Method 7: Updating Ubuntu Repositories (Ubuntu and Debian)
To update your databases, proceed with the steps below:
- First, launch your “Terminal”, then type in the following command and press the “Enter” button:
sudo apt-get update
- Wait for the process to be completed and then check if the Sudo: apt-get: Command not Found error got removed.
Method 8: Setting Up Software-properties-common Plan
- Launch your “Terminal”, here type in the following command and press the “Enter” button:
sudo apt-get install software-properties-common
- Now, wait for the process to get completed.
- You can use the following command for older Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get mount python-software-properties
Method 9: Adding In APT
Follow the steps below to install the latest version of Wine on Ubuntu which should resolve the issue:
- Launch your “Terminal”, then type in the following command and hit the “Enter” button afterwards.
sudo apt-add-repository ‘deb https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/ubuntu/ bionic major’
- Wait for some time until the process gets completed.
To install LibreOffice:
- Launch your “Terminal”, type in the following commands in sequence, and then press “Enter” afterwards.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:libreoffice/ppa sudo apt update apt install LibreOffice
- Wait for the process to get completed and then see if the Sudo: apt-get: Command not Found problem still persists or not.
Method 10: For CentOS
Your OS’s default package manager is “Yum” so you can try using the command mentioned below:
sudo yum install <packagename>
But you might encounter an error this way for which you can try downloading the rpmforge-release package using the command below:
wget http://packages.sw.be/rpmforge-release /rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.e15.rf.i386.rpm
Next, type in the following commands sequence wise to verify and install the package:
sudo rpm –import http://apt.sw.be/RPM-GPG-KEY.dag.txt rpm -K rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.e15.rf.i386.rpm sudo rpm -I rpmforge-release-0.5.3-1.e15.rf.i386.rpm
Now you should be able to use the install command that you were getting errors on earlier.
Method 11: Running the Environment Variables
If you are sure that your default package installer command is apt-get and still getting the error code, then you can try running the following command:
~/$[YOURUSER]/.bashrc
Next, execute the following command:
sudo /usr/bin/apt-get update
Now check to see if your issue is resolved, if not, then try with a “root” account and repeat the above steps. If that did not work either, then try running the following command:
sudo find / -name ‘apt-get’
Method 12: Reinstalling OS
If none of these methods worked for you then you should try reinstalling your operating system. Doing so will help you get through the error easily. As something might have gone wrong during the installation procedure for the first time due to which you are not able to fully access what should normally be available to you. Before a clean reinstallation, you need to make a complete backup of your data and then proceed with the reinstallation. For reinstalling Ubuntu, you can try copying everything to your HDD from the USB drive, you can also try performing a system repair which might work out or you can install the APT package as mentioned in the steps above.
Follow the aforementioned methods in order to get through the error successfully but in case you have more queries in this regard feel free to Contact Us.