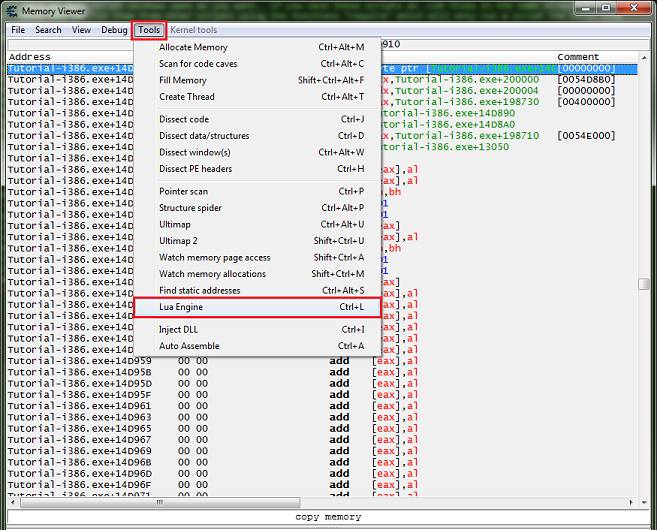
Writing a Script
You need to have the Memory Viewer window open and go to «Tools->Auto Assemble» or hit CTRL+A to open the Auto assemble window. When you click «Execute» the code is not actually executed, but assembled into machine code. The code is actually executed when you overwrite existing game code and the game executes it in the normal course of playing or when you call CREATETHREAD.
Writing an address or label followed by a colon will do one of two opposite things. If the label is known, i.e. it is an address or if there is a defined symbol or memory has been allocated with that name, the assembler will move to that address for assembling the following code. If the label is unknown, it must have been passed to LABEL(name) (or you will get an error) and the value of that label will be set to the current position where code is set to be assembled.
Simple Example — Example showing ALLOC, LABEL, REGISTERSYMBOL and CREATETHREAD.
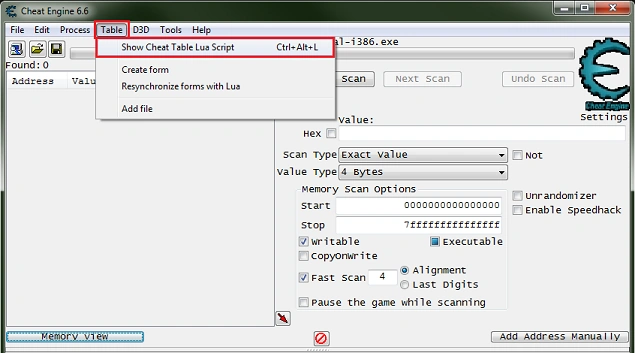
Assigning a Script to a CheatTable
Scripts assigned to cheat tables usually have two sections, «[ENABLE]» and «[DISABLE]». Code before «[ENABLE]» will be assembled every time the script is enabled OR disabled. The code in the «[ENABLE]» section will be assembled (not executed) when the entry is checked and the code in the «[DISABLE]» section will be assembled when the entry is unchecked.
You will generally alloc memory in [ENABLE] and overwrite existing instructions inside the process you have opened to jump to your code where you can modify values and jump back. You will then dealloc the memory and put the original instructions back when disabling.
To assign it to your cheat table, click on «File->Assign to current cheat table» and close the window because to edit the table script you have to double-click on the «<script>» value in your table.
Serious Sam 3 BFE Example — Example showing ENABLE and DISABLE
Injecting a DLL
loadlibrary(name) can be used to load a dll and register it’s symbols for
use by your assembly code. Note that you should not put quotes around the DLL name. Here’s an example:
LoadLibrary Example
General Information
Auto assemble allows you to write assembler code at different locations using a script. It can be found in the memory view part of cheat engine under extra.
See Auto Assembler Commands for a full list of all Auto Assembler commands.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| AOBSCAN(name, xx xx xx xx xx) | Scans the memory for the given array of byte and sets the result to the symbol named «name» |
| AOBSCANMODULE(name, moduleName, xx xx xx xx xx) | Scans the memory of a specific module for the given array of byte and sets the result to the symbol names «name» |
| AOBSCANREGION(name, Sadd$, Fadd$, xx xx xx) | Will scan the specific range from start address to finish addressfor the given AOB and labels it with the given name |
| ALLOC(allocName, sizeInBytes, Optional: AllocateNearThisAddress) | Allocates a certain amount of memory and defines the specified name in the script. If AllocateNearThisAddress is specified CE will try to allocate the memory near that address. This is useful for 64-bit targets where the jump distance could be bigger than 2GB otherwise |
| DEALLOC(allocName) | Deallocates a block of memory allocated with Alloc. It always gets executed last, no matter where it is positioned in the code, and only actually frees the memory when all allocations have been freed. Only usable in a script designed as a cheat table. (e.g used for the disable cheat) |
| CREATETHREAD(address) | Will spawn a thread in the process at the specified address |
| DEFINE(name,whatever) | Creates a token with the specified name that will be replaced with the text of whatever |
| FULLACCESS(address,size,preferedsize) | Makes a memory region at the specified address and at least «size» bytes readable, writable and executable |
| GLOBALALLOC(name,size) | Allocates a certain amount of memory and registers the specified name. Using GlobalAlloc in other scripts will then not allocate the memory again, but reuse the already existing memory. (Or allocate it anyhow if found it wasn’t allocated yet) |
| INCLUDE(filename) | Includes another auto assembler file at that spot |
| LABEL(labelName) | Enables the word labelName to be used as an address |
| LOADBINARY(address,filename) | Loads a binary file at the specified address |
| LOADLIBRARY(filename) | Injects the specified DLL into the target process |
| READMEM(address,size) | Writes the memory at the specified address with the specified size to the current location |
| REGISTERSYMBOL(symbolName) | Adds a symbol to the user-defined symbol list so cheat tables and the memory browser can use that name instead of a address (The symbol has to be declared in the script when using it) |
| UNREGISTERSYMBOL(symbolName) | Removes a symbol from the user-defined symbol list. No error will occur if the symbol doesn’t exist. |
Value Notation
Normally everything is written as hexadecimal in auto assembler, but there are ways to override this so you can input decimal values, and even floating point values.
for example, a integer value of 100 can be written in hex as 64, but you can also write it as #100, or as (int)100
for floating point value like 100.1 you can use (float)100.1
and for a double, you could use (double)100.1
NOTE:Use ‘dq (double)100.1’ instead of ‘dd’!
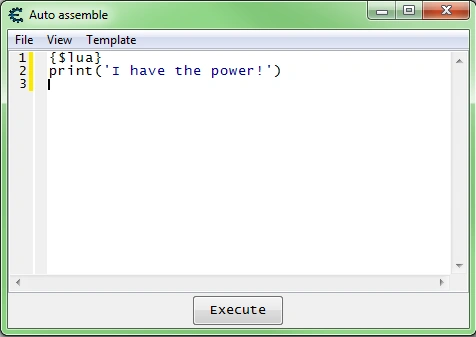
{$lua}
Auto assembler scripts support section written in Lua.You can start such a section using the {$lua} keyword, and end it with {$asm}.
The return value of such a function (if it returns a value at all) will be interpreted as normal auto assembler commands.
When syntax checking, the lua sections get executed. To make sure your lua script behaves properly in those situations, check the «syntaxcheck» boolean. If it’s true, then do not make permanent changes.
e.g:
if syntaxcheck then return end
Of course, if your script is meant to generate code, do make it return code so that it passes the initial syntax check. (e.g label definitions etc…)
Examples
Basic Example
00451029: jmp 00410000 nop nop nop 00410000: mov [00580120],esi mov [esi+80],ebx xor eax,eax jmp 00451031
Example using LABEL
label(mylabel) 00451029: jmp 00410000 nop nop nop mylabel: 00410000: mov [00580120],esi mov [esi+80],ebx xor eax,eax jmp mylabel
Example using ALLOC
alloc(alloc1,4) 00451029: jmp 00410000 nop nop nop 00410000: mov [alloc1],esi mov [esi+80],ebx xor eax,eax jmp 00451031
Example using ALLOC and LABEL
alloc(alloc1,4) label(mylabel) 00451029: jmp 00410000 nop nop nop mylabel: 00410000: mov [alloc1],esi mov [esi+80],ebx xor eax,eax jmp mylabel
Example using FULLACCESS
FULLACCESS(00400800,4) //00400800 is usually read only non executable data, this makes it writeable and executable 00451029: jmp 00410000 nop nop nop 00410000: mov [00400800],esi mov [esi+80],ebx xor eax,eax jmp 00451031
Example using DEFINE
DEFINE(clear_eax,xor eax,eax) 00400500: clear_eax
Example using READMEM
alloc(x,16) alloc(script,2048) script: mov eax,[x] mov edx,[x+c] ret x: readmem(00410000,16) //place the contents of address 00410000 at the address of X
See also
- Assembler
- Tutorials
Writing a Script
You need to have the Memory Viewer window open and go to «Tools->Auto Assemble» or hit CTRL+A to open the Auto assemble window. When you click «Execute» the code is not actually executed, but assembled into machine code. The code is actually executed when you overwrite existing game code and the game executes it in the normal course of playing or when you call CREATETHREAD.
Writing an address or label followed by a colon will do one of two opposite things. If the label is known, i.e. it is an address or if there is a defined symbol or memory has been allocated with that name, the assembler will move to that address for assembling the following code. If the label is unknown, it must have been passed to LABEL(name) (or you will get an error) and the value of that label will be set to the current position where code is set to be assembled.
Simple Example — Example showing ALLOC, LABEL, REGISTERSYMBOL and CREATETHREAD.
Assigning a Script to a CheatTable
Scripts assigned to cheat tables usually have two sections, «[ENABLE]» and «[DISABLE]». Code before «[ENABLE]» will be assembled every time the script is enabled OR disabled. The code in the «[ENABLE]» section will be assembled (not executed) when the entry is checked and the code in the «[DISABLE]» section will be assembled when the entry is unchecked.
You will generally alloc memory in [ENABLE] and overwrite existing instructions inside the process you have opened to jump to your code where you can modify values and jump back. You will then dealloc the memory and put the original instructions back when disabling.
To assign it to your cheat table, click on «File->Assign to current cheat table» and close the window because to edit the table script you have to double-click on the «<script>» value in your table.
Serious Sam 3 BFE Example — Example showing ENABLE and DISABLE
Injecting a DLL
loadlibrary(name) can be used to load a dll and register it’s symbols for
use by your assembly code. Note that you should not put quotes around the DLL name. Here’s an example:
LoadLibrary Example
General Information
Auto assemble allows you to write assembler code at different locations using a script. It can be found in the memory view part of cheat engine under extra.
See Auto Assembler Commands for a full list of all Auto Assembler commands.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| AOBSCAN(name, xx xx xx xx xx) | Scans the memory for the given array of byte and sets the result to the symbol named «name» |
| AOBSCANMODULE(name, moduleName, xx xx xx xx xx) | Scans the memory of a specific module for the given array of byte and sets the result to the symbol names «name» |
| AOBSCANREGION(name, Sadd$, Fadd$, xx xx xx) | Will scan the specific range from start address to finish addressfor the given AOB and labels it with the given name |
| ALLOC(allocName, sizeInBytes, Optional: AllocateNearThisAddress) | Allocates a certain amount of memory and defines the specified name in the script. If AllocateNearThisAddress is specified CE will try to allocate the memory near that address. This is useful for 64-bit targets where the jump distance could be bigger than 2GB otherwise |
| DEALLOC(allocName) | Deallocates a block of memory allocated with Alloc. It always gets executed last, no matter where it is positioned in the code, and only actually frees the memory when all allocations have been freed. Only usable in a script designed as a cheat table. (e.g used for the disable cheat) |
| CREATETHREAD(address) | Will spawn a thread in the process at the specified address |
| DEFINE(name,whatever) | Creates a token with the specified name that will be replaced with the text of whatever |
| FULLACCESS(address,size,preferedsize) | Makes a memory region at the specified address and at least «size» bytes readable, writable and executable |
| GLOBALALLOC(name,size) | Allocates a certain amount of memory and registers the specified name. Using GlobalAlloc in other scripts will then not allocate the memory again, but reuse the already existing memory. (Or allocate it anyhow if found it wasn’t allocated yet) |
| INCLUDE(filename) | Includes another auto assembler file at that spot |
| LABEL(labelName) | Enables the word labelName to be used as an address |
| LOADBINARY(address,filename) | Loads a binary file at the specified address |
| LOADLIBRARY(filename) | Injects the specified DLL into the target process |
| READMEM(address,size) | Writes the memory at the specified address with the specified size to the current location |
| REGISTERSYMBOL(symbolName) | Adds a symbol to the user-defined symbol list so cheat tables and the memory browser can use that name instead of a address (The symbol has to be declared in the script when using it) |
| UNREGISTERSYMBOL(symbolName) | Removes a symbol from the user-defined symbol list. No error will occur if the symbol doesn’t exist. |
Value Notation
Normally everything is written as hexadecimal in auto assembler, but there are ways to override this so you can input decimal values, and even floating point values.
for example, a integer value of 100 can be written in hex as 64, but you can also write it as #100, or as (int)100
for floating point value like 100.1 you can use (float)100.1
and for a double, you could use (double)100.1
NOTE:Use ‘dq (double)100.1’ instead of ‘dd’!
{$lua}
Auto assembler scripts support section written in Lua.You can start such a section using the {$lua} keyword, and end it with {$asm}.
The return value of such a function (if it returns a value at all) will be interpreted as normal auto assembler commands.
When syntax checking, the lua sections get executed. To make sure your lua script behaves properly in those situations, check the «syntaxcheck» boolean. If it’s true, then do not make permanent changes.
e.g:
if syntaxcheck then return end
Of course, if your script is meant to generate code, do make it return code so that it passes the initial syntax check. (e.g label definitions etc…)
Examples
Basic Example
00451029: jmp 00410000 nop nop nop 00410000: mov [00580120],esi mov [esi+80],ebx xor eax,eax jmp 00451031
Example using LABEL
label(mylabel) 00451029: jmp 00410000 nop nop nop mylabel: 00410000: mov [00580120],esi mov [esi+80],ebx xor eax,eax jmp mylabel
Example using ALLOC
alloc(alloc1,4) 00451029: jmp 00410000 nop nop nop 00410000: mov [alloc1],esi mov [esi+80],ebx xor eax,eax jmp 00451031
Example using ALLOC and LABEL
alloc(alloc1,4) label(mylabel) 00451029: jmp 00410000 nop nop nop mylabel: 00410000: mov [alloc1],esi mov [esi+80],ebx xor eax,eax jmp mylabel
Example using FULLACCESS
FULLACCESS(00400800,4) //00400800 is usually read only non executable data, this makes it writeable and executable 00451029: jmp 00410000 nop nop nop 00410000: mov [00400800],esi mov [esi+80],ebx xor eax,eax jmp 00451031
Example using DEFINE
DEFINE(clear_eax,xor eax,eax) 00400500: clear_eax
Example using READMEM
alloc(x,16) alloc(script,2048) script: mov eax,[x] mov edx,[x+c] ret x: readmem(00410000,16) //place the contents of address 00410000 at the address of X
See also
- Assembler
- Tutorials
Содержание
- Учимся работать с Cheat Engine
- Изменение значений в игре
- Включение SpeedHack
- Вопросы и ответы
Если вы хотите поиграть в компьютерные игры не совсем честно, но не знаете как это сделать, тогда данная статья именно для вас. Сегодня мы расскажем вам, как можно взломать различные игры с помощью специализированного софта. Делать это мы будем с помощью Cheat Engine.
Скачать последнюю версию Cheat Engine
Сразу же хотим обратить внимание на тот факт, что в некоторых случаях при использовании указанной программы вы можете получить бан. Поэтому лучше всего сперва проверить работоспособность взлома на каком-то новом аккаунте, который будет не жалко в случае чего потерять.
Рассматриваемая нами программа для взлома весьма функциональна. С помощью нее можно выполнять множество различных задач. Но для большинства из них потребуется определенный багаж знаний, например опыт работы с HEX (Хекс). Мы не будем нагружать вас различными терминами и поучениями, поэтому просто расскажем вам об общих приемах и способах применения Cheat Engine.
Изменение значений в игре
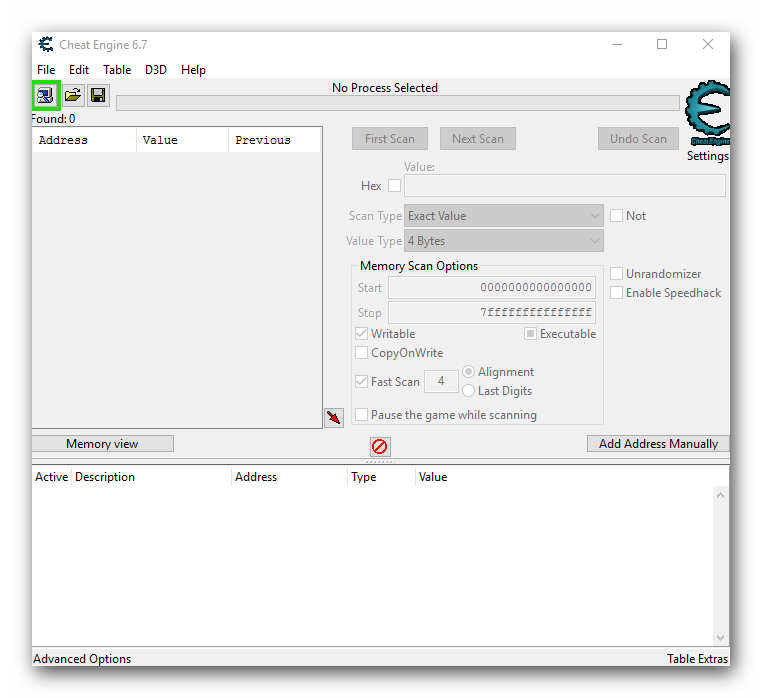
Данная функция является самой популярной из всего арсенала Cheat Engine. Она позволяет изменить нужным образом практически любое значение в игре. Это может быть здоровье, броня, количество боеприпасов, денег, координаты персонажа и многое другое. Вы должны понимать, что использование данной функции далеко не всегда завершается успешно. Причиной неудачи может быть как ваша ошибка, так и надежная защита игры (если рассматривать онлайн-проекты). Тем не менее попытаться взломать показатели вы все же можете. Вот что нужно сделать:
- Загружаем с официального сайта Cheat Engine, после чего устанавливаем ее на компьютер либо ноутбук, а после этого запускаем.
- Вы увидите на рабочем столе следующую картину.
- Теперь следует запустить клиент с игрой либо открыть таковую в браузере (если речь идет о веб-приложениях).
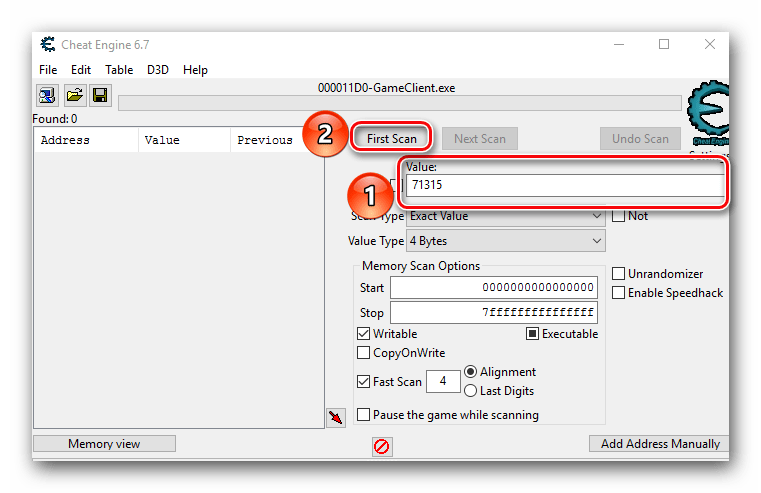
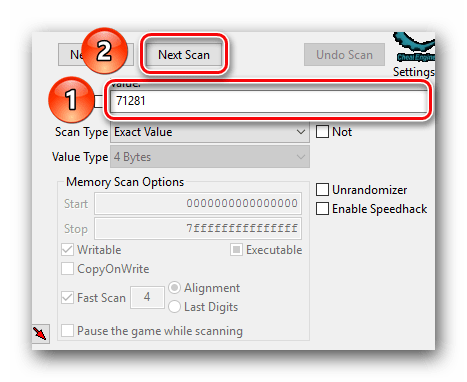
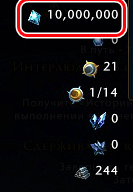
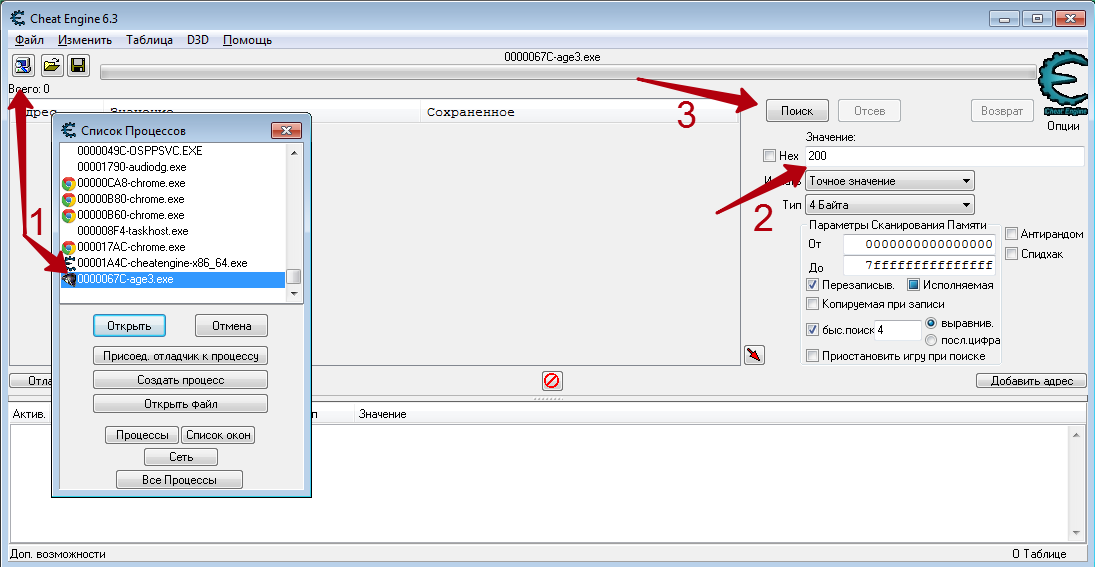
- После того, как игра будет запущена, необходимо определиться с тем, показатель чего именно вы хотите изменить. К примеру, это какая-то валюта. Смотрим в инвентарь и запоминаем ее текущее значение. В приведенном ниже примере данное значение равняется 71 315.
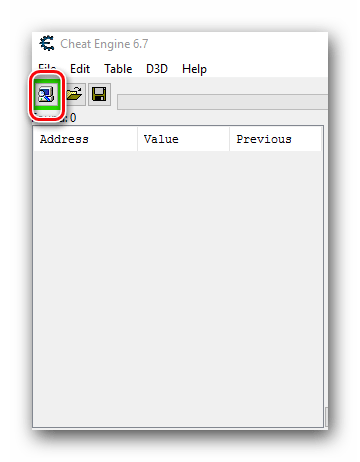
- Теперь снова возвращаемся к запущенной Cheat Engine. Необходимо в главном окне найти кнопку с изображением компьютера. До первого нажатия эта кнопка будет с мигающей обводкой. Нажимаем на нее один раз левой кнопкой мыши.
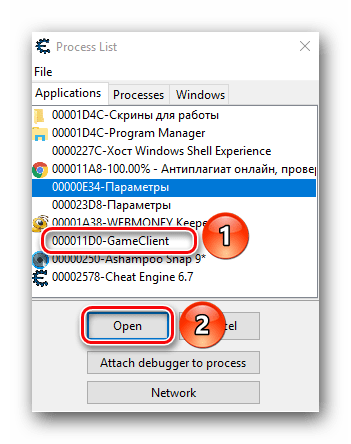
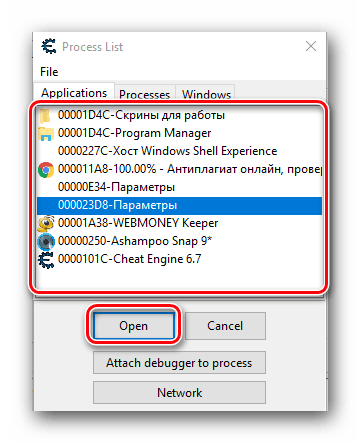
- В результате на экране появится окно меньших размеров со списком запущенных приложений. Из подобного списка вам нужно выделить ту строчку левой кнопки мыши, которая отвечает за игру. Ориентироваться можно по иконке слева от названия, а если таковая отсутствует, то по самому имени приложения. Как правило, имя содержит название приложения либо слово «GameClient». Выбрав нужную позицию, следует нажать на кнопку «Open», которая располагается немного ниже.
- Кроме того, выбрать нужную игру можно также из списка процессов или открытых окон. Для этого нужно просто перейти в одну из вкладок с соответствующим названием вверху.
- Когда игра будет выбрана из списка, программе потребуется буквально пару секунд, чтобы провести так называемую инъекцию библиотек. Если ей это удастся, то в самом верху главного окна Cheat Engine будет отображено название приложения, которое вы выбрали ранее.
- Теперь можно приступить непосредственно к поиску нужного значения и его дальнейшему редактированию. Для этого в поле с названием «Value» вводим значение, которое мы ранее запомнили и которое хотим изменить. В нашем случае это 71 315.
- Далее нажимаем кнопку «First Scan», которая находится выше поля ввода.
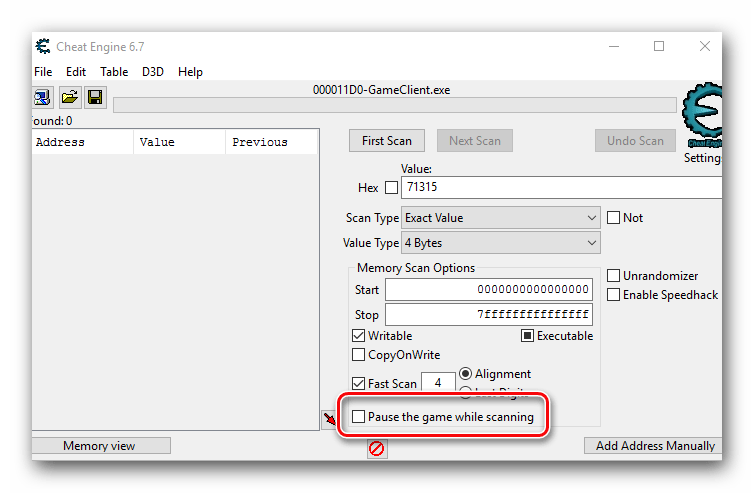
- Чтобы результаты поиска получились более точными, можно установить опцию паузы в игре во время сканирования. Делать это не обязательно, но в некоторых случаях помогает сузить перечень вариантов. Чтобы включить данную функцию, достаточно поставить отметку в чекбокс напротив соответствующей строки. Ее мы отметили на изображении ниже.
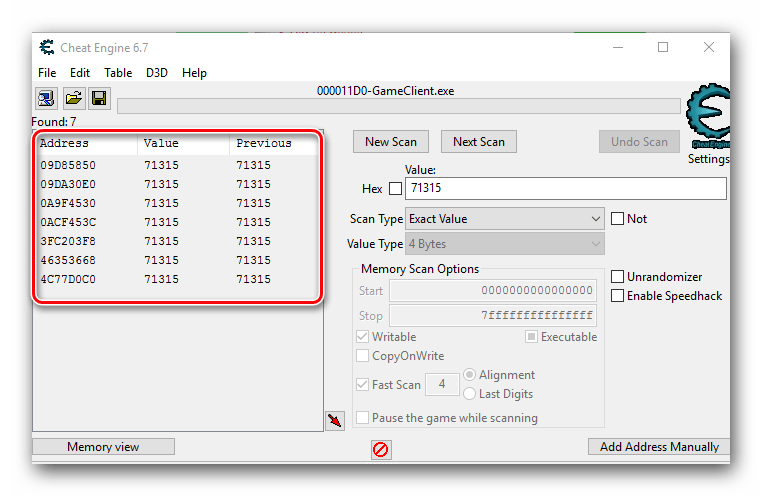
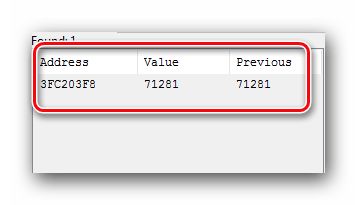
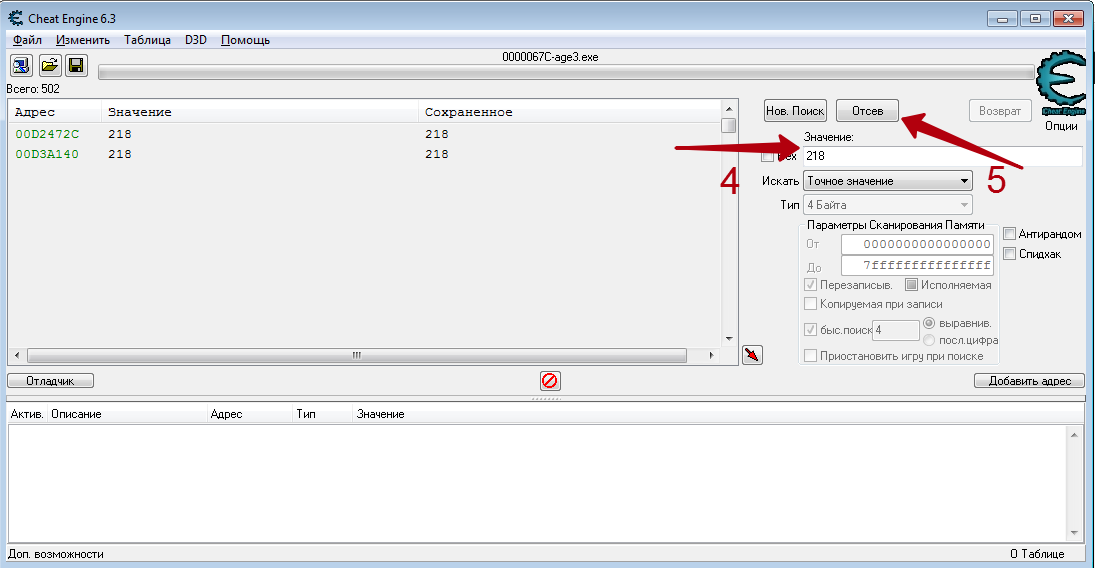
- Нажав на кнопку «First Scan», вы увидите спустя короткий промежуток времени все найденные результаты в левой части программы в виде своеобразного списка.
- За искомое значение отвечает лишь один адрес. Поэтому необходимо отсеять лишние. Для этого нужно вернуться в игру и изменить числовое значение валюты, жизней или того, что вы хотите изменить. Если это какая-то валюта, то достаточно просто что-либо купить или продать. Не важно, в какую сторону изменится значение. В примере после манипуляций у нас получилось число 71 281.
- Возвращаемся снова к Cheat Engine. В строке «Value», куда ранее мы вписывали значение 71 315, теперь указываем новое число — 71 281. Проделав это, жмем кнопку «Next Scan». Она находится немного выше строчки ввода.
- При самых хороших раскладах вы увидите в списке значений лишь одну нужную строчку. Если же таких будет несколько, то необходимо повторить предыдущий пункт еще раз. Имеется в виду смена значения в игре, ввод нового числа в поле «Value» и повторный поиск через «Next Scan». В нашем случае все получилось с первого раза.
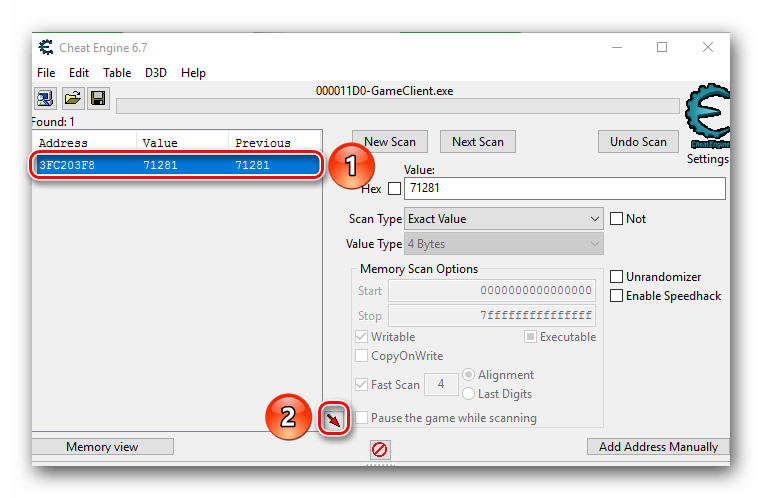
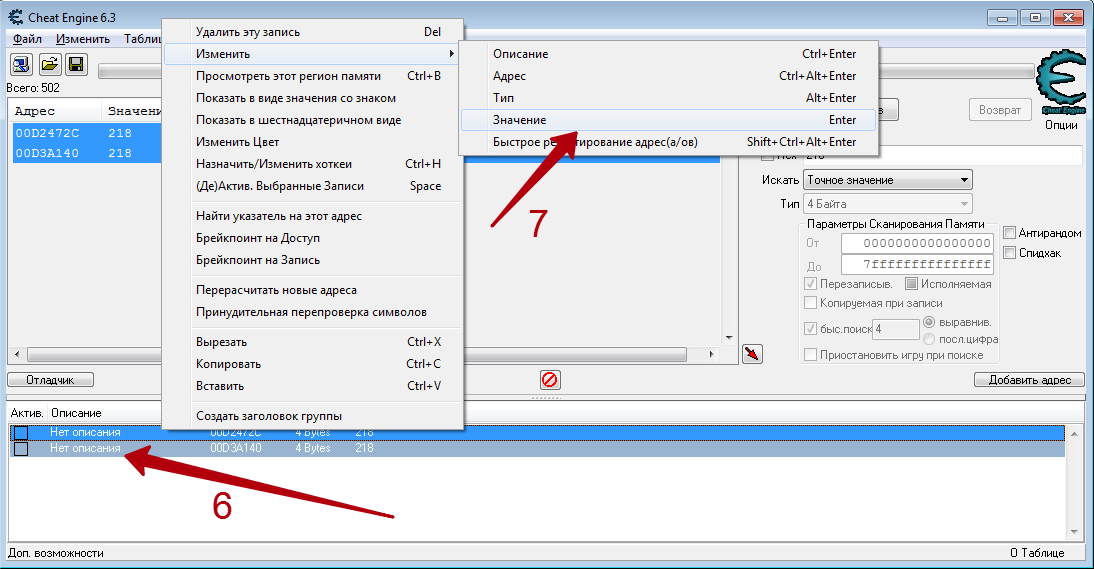
- Выделяем найденный адрес одиночным нажатием левой кнопкой мыши. После этого нажимаем на кнопку с красной стрелкой. Ее мы отметили на скриншоте ниже.
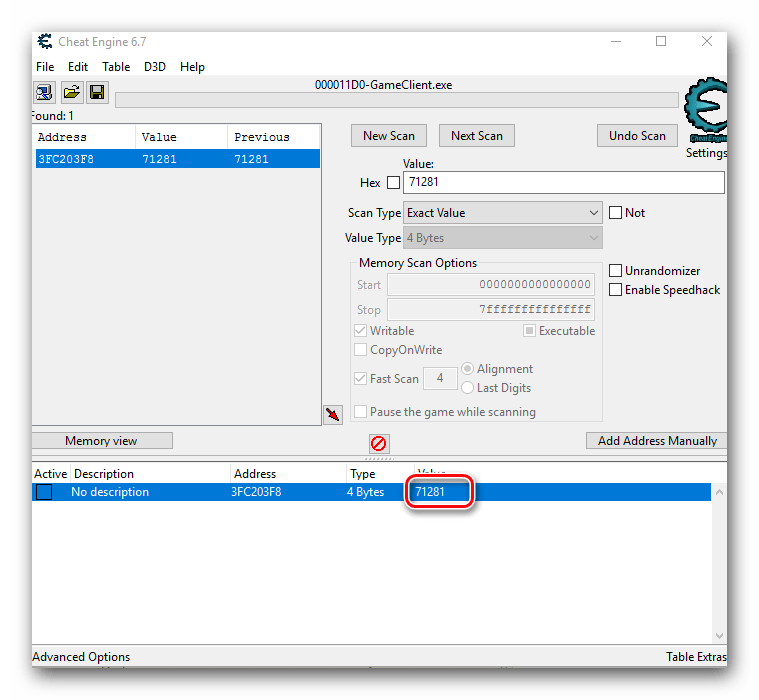
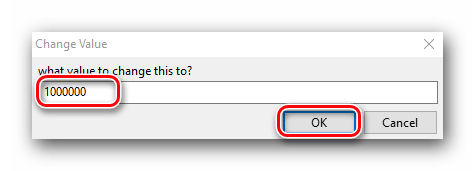
- Выбранный адрес переместится в нижнюю часть окна программы, где можно производить дальнейшие правки. Для изменения значения кликаем два раза левой кнопкой мышки на той части строки, где находятся цифры.
- Появится маленькое окошко с единственным полем для ввода. В нем пишем то значение, которое вы хотите получить. К примеру вы хотите 1 000 000 денег. Именно данное число и пишем. Подтверждаем действия нажатием кнопки «OK» в этом же окне.
- Возвращаемся обратно к игре. Если все сделано верно, то изменения тут же вступят в силу. Вы увидите примерно следующую картину.
- В некоторых случаях необходимо еще раз изменить числовое значение в игре (купить, продать и так далее) для того, чтобы новый параметр вступил в силу.
Вот собственно и вся методология поиска и изменения нужного параметра. Мы советуем при сканировании и отсеве параметров не менять настройки программы по умолчанию. Для этого необходимы более глубокие знания. А без них вы попросту не сможете добиться желаемого результата.
Важно помнить, что при работе с онлайн-играми далеко не всегда получится проделать описанные выше манипуляции. Виной всему защита, которую нынче стараются установить практически везде, даже в браузерные проекты. Если у вас что-либо не получается, то это не значит, что всему виной ваши ошибки. Возможно, это установленная защита не дает подключиться Cheat Engine к игре, вследствие чего на экране могут возникнуть различные ошибки. Кроме того, часто встречаются ситуации, когда поменять значения выходит лишь на уровне клиента. Это значит что отображаться будет введенное вами значение, но сервер по факту увидит лишь настоящие цифры. Это также заслуга системы защиты.
Включение SpeedHack
SpeedHack — это изменение скорости движения, стрельбы, полета и прочих параметров в игре. С помощью Cheat Engine сделать это абсолютно несложно.
- Заходим в ту игру, в которой нужно изменить скорость.
- Далее снова возвращаемся к ранее запущенному Cheat Engine. Жмем на кнопку в виде компьютера с лупой в левом верхнем углу. О ней мы упоминали в предыдущем разделе.
- Выбираем из появившегося списка свою игру. Чтобы она появилась в данном перечне, ее необходимо предварительно запустить. Выбрав приложение, жмем кнопку «Open».
- Если защита позволит программе подключиться к игре, то вы не увидите на экране никакого сообщения. В верхней части окна лишь отобразится название подключенного приложения.
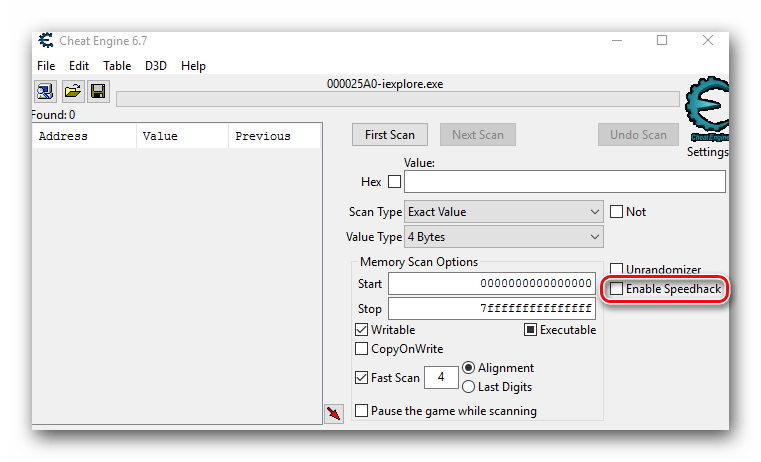
- С правой стороны окна Cheat Engine вы найдете строчку «Enable Speedhack». Ставим отметку в чекбоксе рядом с данной строчкой.
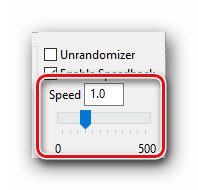
- Если попытка включения завершится успехом, вы увидите ниже появившуюся строчку для ввода и ползунок. Изменить скорость можно как в большую сторону, так и вовсе опустить ее до нуля. Для этого нужно ввести в строчку нужное значение скорости либо выставить его с помощью ползунка путем перетягивания последнего.
- Для того чтобы изменения вступили в силу, нужно нажать кнопку «Apply» после того, как выбрали нужную скорость.
- После этого ваша скорость в игре изменится. В некоторых случаях увеличивается скорость не только ваша, но и всего происходящего в игровом мире. Кроме того, иногда сервер не успевает обрабатывать подобные запросы, в результате чего возникают некие рывки и подергивания. Это связано с защитой игры и обойти это, к сожалению, никак нельзя.
- Если вам необходимо отключить Speedhack, то достаточно просто закрыть Cheat Engine или снять галочку напротив строки в окне программы.
Вот таким нехитрым образом можно в игре быстро бегать, стрелять и проводить прочие действия.
На этом данная статья подходит к концу. Мы рассказали вам об основных и самых востребованных функциях CheatEngine. Но это не значит, что программа больше ни на что не способна. На самом деле, ее возможности очень велики (составление трейнеров, работа с хексом, подмена пакетов и так далее). Но для этого потребуются куда большие знания, а пояснять подобные манипуляции понятным всем языком не так-то просто. Надеемся, у вас получится достигнуть поставленных целей. А если вам нужна будет консультация или совет — милости просим в комментарии к этой статье.
Если вам интересна тема взлома игр и использования читов, рекомендуем ознакомиться со списком софта, который в этом поможет.
Подробнее: Программы-аналоги ArtMoney
Еще статьи по данной теме:
Помогла ли Вам статья?
Привет юный хацкер! Сегодня мы с тобой напишем свой первый чит с помощью Cheat Engine. Для примера я взял популярную в кругах молодежи игру — Among us. В этом уроке мы разберем основы — поиск адреса, его изменение, типы адресов и многое другое. Садись по удобнее, заваривай кофе. Мы начинаем!
Шаг 1. Учимся правильно искать адреса.
Итак, после того, как выбрали для себя игру, делаем самое легкое в нашей работе — выбираем процесс . Тут не нужно иметь ученую степень по математике, достаточно просто тыкнуть сюда Посмотреть вложение 105409 и откроется окно с выбором процесса, кликаем по иконке нашей игры. Вуаля! Теперь можем начинать «потеть».
С самого начала мы видим окошкоПосмотреть вложение 105411 куда можно вбить значение и кучу не понятных(для кого-то) параметров. В строке (Value) мы будем писать значения и искать их адреса в памяти. Memory Scan Options нас сейчас особо не интересует. Итак, прежде чем выполнить поиск определимся с тем, что мы ищем. Я буду искать значение скорости в параметрах комнаты. Для этого я смотрю чему равно значение скорости в комнате сейчас, а оно равно 1. Я вбиваю его в поиск и жму First Scan. Затем, меняю его и нажимаю кнопку Next Scan, это называется отсеивание. И вот незадача! Нашего значения здесь нет??? Конечно нет, ведь мы не выбрали Value Type, в случае с нашем значением (Value Type) = Float, т.к значение скорости десятичное, но это не всегда так, по умолчанию значения Чит Энджин ставит 4 Bytes, это целое значение. Опять-же, это ситуативно. Нажимаем кнопку New Scan, чтобы начать заново. Пишем значения скорости 1, меняем его в настройках комнаты на любое другое, например — 1,75. Делая всё по тому-же принципу я нахожу один адрес.
Посмотреть вложение 105415
Изменив его значение, значение в параметре комнаты изменилось, а значит это то что нам нужно. Теперь, когда зайдете в другую комнату у вас будет Speedhack. А это значит, что мы написали свой первый чит! Да, после перезагрузки игры и многих других факторов, адрес пропадет и придется искать снова, но не отчаивайтесь, это очень легко, к тому-же это всего-лишь основы. Удачи!
Ну вот, как-то так.
Посмотреть вложение 105416
List of CE specific functions and variables:
Contents
- 1 TrainerOrigin
- 2 process
- 3 getCEVersion
- 4 activateProtection
- 5 fullAccess
- 6 loadTable
- 7 saveTable
- 8 readBytes
- 9 writeBytes
- 10 readSmallInteger
- 11 readInteger
- 12 readQword
- 13 readPointer
- 14 readFloat
- 15 readDouble
- 16 readString
- 17 writeSmallInteger
- 18 writeInteger
- 19 writeQword
- 20 writeFloat
- 21 writeDouble
- 22 writeString
- 23 readBytesLocal
- 24 readIntegerLocal
- 25 readQwordLocal
- 26 readPointerLocal
- 27 readFloatLocal
- 28 readDoubleLocal
- 29 readStringLocal
- 30 writeIntegerLocal
- 31 writeQwordLocal
- 32 writeFloatLocal
- 33 writeDoubleLocal
- 34 writeStringLocal
- 35 writeBytesLocal
- 36 wordToByteTable
- 37 dwordToByteTable
- 38 qwordToByteTable
- 39 floatToByteTable
- 40 doubleToByteTable
- 41 stringToByteTable
- 42 wideStringToByteTable
- 43 byteTableToWord
- 44 byteTableToDword
- 45 byteTableToQword
- 46 byteTableToFloat
- 47 byteTableToDouble
- 48 byteTableToString
- 49 byteTableToWideString
- 50 bOr
- 51 bXor
- 52 bAnd
- 53 bShl
- 54 bShr
- 55 bNot
- 56 writeRegionToFile
- 57 readRegionFromFile
- 58 resetLuaState
- 59 createRef
- 60 getRef
- 61 destroyRef
- 62 reloadSettingsFromRegistry
- 63 getTranslationFolder
- 64 loadPOFile
- 65 translate
- 66 translateID
- 67 ansiToUtf8
- 68 utf8ToAnsi
- 69 enumModules
- 70 getAddress
- 71 getSymbolInfo
- 72 getModuleSize
- 73 reinitializeSymbolhandler
- 74 reinitializeDotNetSymbolhandler
- 75 errorOnLookupFailure
- 76 generateAPIHookScript
- 77 autoAssemble
- 78 registerAutoAssemblerCommand
- 79 unregisterAutoAssemblerCommand
- 80 registerSymbolLookupCallback
- 81 unregisterSymbolLookupCallback
- 82 registerAddressLookupCallback
- 83 unregisterAddressLookupCallback
- 84 registerStructureDissectOverride
- 85 unregisterStructureDissectOverride
- 86 registerStructureNameLookup
- 87 unregisterStructureNameLookup
- 88 registerAssembler
- 89 unregisterAssembler
- 90 registerAutoAssemblerPrologue
- 91 unregisterAutoAssemblerPrologue
- 92 showMessage
- 93 inputQuery
- 94 messageDialog
- 95 sleep
- 96 getProcesslist
- 97 getWindowlist
- 98 getThreadlist
- 99 onOpenProcess
- 100 getOpenedProcessID
- 101 getProcessIDFromProcessName
- 102 openProcess
- 103 setPointerSize
- 104 pause
- 105 unpause
- 106 getPixel
- 107 getMousePos
- 108 setMousePos
- 109 isKeyPressed
- 110 keyDown
- 111 keyUp
- 112 doKeyPress
- 113 shortCutToText
- 114 textToShortCut
- 115 convertKeyComboToString
- 116 outputDebugString
- 117 shellExecute
- 118 getTickCount
- 119 processMessages
- 120 inMainThread
- 121 integerToUserData
- 122 userDataToInteger
- 123 synchronize
- 124 checkSynchronize
- 125 writeToClipboard
- 126 readFromClipboard
- 127 speedhack_setSpeed
- 128 speedhack_getSpeed
- 129 injectDLL
- 130 loadPlugin
- 131 registerCustomTypeLua
- 132 registerCustomTypeAutoAssembler
- 133 onAutoGuess
- 134 closeCE
- 135 hideAllCEWindows
- 136 unhideMainCEwindow
- 137 getAutoAttachList
- 138 AOBScan
- 139 allocateSharedMemory
- 140 getForegroundProcess
- 141 findWindow
- 142 getWindow
- 143 getWindowCaption
- 144 getWindowClassName
- 145 getWindowProcessID
- 146 getForegroundWindow
- 147 sendMessage
- 148 hookWndProc
- 149 unhookWndProc
- 150 cheatEngineIs64Bit
- 151 targetIs64Bit
- 152 getCheatEngineDir
- 153 disassemble
- 154 splitDisassembledString
- 155 getInstructionSize
- 156 getPreviousOpcode
- 157 beep
- 158 playSound
- 159 speak
- 160 speakEnglish
- 161 getUserRegistryEnvironmentVariable
- 162 setUserRegistryEnvironmentVariable
- 163 broadcastEnvironmentUpdate
- 164 stringToMD5String
- 165 getFormCount
- 166 getForm
- 167 registerFormAddNotification
- 168 unregisterFormAddNotification
- 169 getSettingsForm
- 170 getMemoryViewForm
- 171 getMainForm
- 172 getLuaEngine
- 173 getApplication
- 174 getAddressList
- 175 getFreezeTimer
- 176 getUpdateTimer
- 177 setGlobalKeyPollInterval
- 178 setGlobalDelayBetweenHotkeyActivation
- 179 getPropertyList
- 180 setProperty
- 181 getProperty
- 182 setMethodProperty
- 183 getMethodProperty
- 184 registerSymbol
- 185 unregisterSymbol
- 186 getNameFromAddress
- 187 inModule
- 188 inSystemModule
- 189 getCommonModuleList
- 190 debugging
- 190.1 debug variables
- 190.2 Debug related routines
- 190.3 createProcess
- 190.4 debugProcess
- 190.5 debug_isDebugging
- 190.6 debug_getCurrentDebuggerInterface
- 190.7 debug_canBreak
- 190.8 debug_isBroken
- 190.9 debug_getBreakpointList
- 190.10 debug_addThreadToNoBreakList
- 190.11 debug_removeThreadFromNoBreakList
- 190.12 debug_setBreakpoint
- 190.13 debug_removeBreakpoint
- 190.14 debug_continueFromBreakpoint
- 190.15 debug_getXMMPointer
- 190.16 debug_setLastBranchRecording
- 190.17 debug_getMaxLastBranchRecord
- 190.18 debug_getLastBranchRecord
- 190.19 debug_getContext
- 190.20 debug_updateGUI
- 190.21 detachIfPossible
- 190.22 getComment
- 190.23 setComment
- 190.24 getHeader
- 190.25 setHeader
- 190.26 registerBinUtil
- 191 class helper functions
- 191.1 inheritsFromObject
- 191.2 inheritsFromComponent
- 191.3 inheritsFromControl
- 191.4 inheritsFromWinControl
- 191.5 createClass
- 192 Class definitions
- 192.1 Object
- 192.2 Component
- 192.3 Control
- 192.4 GraphicsObject
- 192.5 Region
- 192.6 WinControl
- 192.7 MenuItem
- 192.8 Menu
- 192.9 MainMenu
- 192.10 PopupMenu
- 192.11 Strings
- 192.12 Stringlist
- 192.13 Application
- 192.14 Form
- 192.15 CEForm
- 192.16 GraphicControl
- 192.17 PaintBox
- 192.18 Label
- 192.19 Splitter
- 192.20 Panel
- 192.21 Image
- 192.22 Edit
- 192.23 Memo
- 192.24 ButtonControl
- 192.25 Button
- 192.26 CheckBox
- 192.27 ToggleBox
- 192.28 GroupBox
- 192.29 RadioGroup
- 192.30 ListBox
- 192.31 Calendar
- 192.32 ComboBox
- 192.33 ProgressBar
- 192.34 TrackBar
- 192.35 CollectionItem
- 192.36 ListColumn
- 192.37 Collection
- 192.38 ListColumns
- 192.39 ListItem
- 192.40 ListItems
- 192.41 Listview
- 192.42 TreeNode
- 192.43 TreeNodes
- 192.44 Treeview
- 192.45 Timer
- 192.46 CustomControl
- 192.47 Canvas
- 192.48 Pen
- 192.49 Brush
- 192.50 Font
- 192.51 Graphic
- 192.52 RasterImage
- 192.53 Bitmap
- 192.54 PortableNetworkGraphic
- 192.55 JpegImage
- 192.56 Picture
- 192.57 GenericHotkey
- 192.58 CommonDialog
- 192.59 FindDialog
- 192.60 FileDialog
- 192.61 OpenDialog
- 192.62 SaveDialog
- 192.63 SelectDirectoryDialog
- 192.64 Stream
- 192.65 MemoryStream
- 192.66 FileStream
- 192.67 StringStream
- 192.68 TableFile
- 192.69 xmplayer
- 192.70 CheatComponent
- 192.71 MemoryRecordHotkey
- 192.72 MemoryRecord
- 192.73 Addresslist
- 192.74 MemScan
- 192.75 createFoundList
- 192.76 Memoryview
- 192.77 DisassemblerviewLine
- 192.78 Disassemblerview
- 192.79 Hexadecimal
- 192.80 Thread
- 192.81 StructureFrm
- 192.82 structColumn
- 192.83 structGroup
- 192.84 structure
- 192.85 StructureElement
- 192.86 supportCheatEngine
- 192.87 fuckCheatEngine
- 192.87.1 Following are some more internal functions for Cheat Engine
- 192.88 dbk_initialize
- 192.89 dbk_useKernelmodeOpenProcess
- 192.90 dbk_useKernelmodeProcessMemoryAccess
- 192.91 dbk_WriteProcessMemory
- 192.92 dbk_useKernelmodeQueryMemoryRegions
- 192.93 dbk_getPEProcess
- 192.94 dbk_getPEThread
- 192.95 dbk_readMSR
- 192.96 dbk_writeMSR
- 192.97 dbk_executeKernelMemory
- 192.98 dbvm_initialize
- 192.99 dbvm_readMSR
- 192.100 dbvm_writeMSR
- 192.101 dbk_getCR0
- 192.102 dbk_getCR3
- 192.103 dbk_getCR4
- 192.104 dbk_getPhysicalAddress
- 192.105 dbk_writesIgnoreWriteProtection
- 192.106 dbvm_getCR4
- 192.107 onAPIPointerChange
- 192.108 setAPIPointer
- 192.109 dbk_NtOpenProcess
- 192.110 dbvm_block_interrupts
- 192.111 dbvm_raise_privilege
- 192.112 dbvm_restore_interrupts
- 192.113 dbvm_changeselectors
- 192.114 D3DHOOK
- 192.115 D3DHook_Texture
- 192.116 D3DHook_FontMap
- 192.117 D3DHook_RenderObject
- 192.118 D3DHook_Sprite
- 192.119 D3Dhook_TextContainer
- 192.120 Disassembler
- 192.121 DissectCode
- 192.122 RIPRelativeScanner
- 192.123 LuaPipe
- 192.124 LuaPipeClient
- 192.125 LuaPipeServer
- 192.126 openLuaServer
- 192.127 Settings class
- 192.127.1 global functions
- 192.128 getSettings
- 192.129 SymbolList class
- 192.130 createSymbolList
- 192.131 deleteSymbol
- 192.132 deleteSymbol
- 192.133 register
- 192.134 unregister
- 192.135 Pagecontrol
- 192.136 TabSheet
- 193 Links
TrainerOrigin[edit]
- TrainerOrigin
- A variable that contains the path of the trainer that launched cheat engine (Only set when launched as a trainer)
process[edit]
- process
- A variable that contains the main modulename of the currently opened process
getCEVersion[edit]
- getCEVersion()
- Returns a floating point value specifying the version of cheat engine
activateProtection[edit]
- activateProtection()
- Prevents basic memory scanners from opening the cheat engine process
fullAccess[edit]
- fullAccess(address,size)
- Changes the protection of a block of memory to writable and executable
loadTable[edit]
- loadTable(filename, merge OPTIONAL)
- Loads a .ct or .cetrainer. If merge is provided and set to true it will not clear the old table
saveTable[edit]
- saveTable(filename, protect OPTIONAL)
- Saves the current table. If protect is provided and set to true and the filename has the ‘.CETRAINER’ extension, it will protect it from reading normally
Note: Addresses can be strings, if a string they will get interpreted by ce’s symbolhandler.
readBytes[edit]
- readBytes(address,bytecount, ReturnAsTable )
- returns the bytes at the given address. If ReturnAsTable is true it will return a table instead of multiple bytes Reads the bytes at the given address and returns a table containing the read out bytes
writeBytes[edit]
- writeBytes(address, x,x,x,x,…)
- writeBytes(address, table)
- Write the given bytes to the given address.
readSmallInteger[edit]
- readSmallInteger(address)
- Reads a 16-bit integer from the specified address
readInteger[edit]
- readInteger(address)
- Reads a 32-bit integer from the specified address
readQword[edit]
- readQword(address)
- Reads a 64-bit integer from the specified address
readPointer[edit]
- readPointer(address)
- In a 64-bit target this equals readQword, in a 32-bit target readInteger()
readFloat[edit]
- readFloat(address)
- Reads a single precision floating point value from the specified address
readDouble[edit]
- readDouble(address)
- Reads a double precision floating point value from the specified address
readString[edit]
- readString(address, maxlength, widechar OPTIONAL)
- Reads a string till it encounters a 0-terminator. Maxlength is just so you won’t freeze for too long, set to 6000 if you don’t care too much. Set WideChar to true if it is encoded using a widechar formatting.
writeSmallInteger[edit]
- writeSmallInteger(address,value)
- Writes a 16-bit integer to the specified address. Returns true on success.
writeInteger[edit]
- writeInteger(address,value)
- Writes a 32-bit integer to the specified address. Returns true on success.
writeQword[edit]
- writeQword(address, value)
- Write a 64-bit integer to the specified address
writeFloat[edit]
- writeFloat(address,value)
- Writes a single precision floating point to the specified address. Returns true on success
writeDouble[edit]
- writeDouble(address,value)
- Writes a double precision floating point to the specified address. Returns true on success
writeString[edit]
- writeString(address,text, widechar OPTIONAL)
- Write a string to the specified address. Returns true on success. Set WideChar to true if it is encoded using a widechar formatting.
readBytesLocal[edit]
- readBytesLocal(address,bytecount, ReturnAsTable)
- See readBytes but then it’s for Cheat engine’s memory
readIntegerLocal[edit]
- readIntegerLocal(address)
- Reads an integer from the specified address in CE’s memory
readQwordLocal[edit]
- readQwordLocal(address)
- Reads a 64-bit integer from the specified address in CE’s memory
readPointerLocal[edit]
- readPointerLocal(address)
- ReadQwordLocal/ReadIntegerLocal depending on the cheat engine build
readFloatLocal[edit]
- readFloatLocal(address)
- Reads a single precision floating point value from the specified address in CE’s memory
readDoubleLocal[edit]
- readDoubleLocal(address)
- Reads a double precision floating point value from the specified address in CE’s memory
readStringLocal[edit]
- readStringLocal(address, maxlength, widechar OPTIONAL)
- Reads a string from CE’s memory till it encounters a 0-terminator. Maxlength is just so you won’t freeze for too long, set to 6000 if you don’t care too much. Set WideChar to true if it is encoded using a widechar formatting
writeIntegerLocal[edit]
- writeIntegerLocal(address,value)
- Writes an integer to the specified address in CE’s memory. Returns true on success
writeQwordLocal[edit]
- writeQwordLocal(address,value)
- Writes a 64-bit integer to the specified address in CE’s memory. Returns true on success
writeFloatLocal[edit]
- writeFloatLocal(address,value)
- Writes a single precision floating point to the specified address in CE’s memory. Returns true on success
writeDoubleLocal[edit]
- writeDoubleLocal(address,value)
- Writes a double precision floating point to the specified address in CE’s memory. Returns true on success
writeStringLocal[edit]
- writeStringLocal(address,string, widechar OPTIONAL)
- Write a string to CE’s memory at the specified address. Returns true on success. Set WideChar to true if it is encoded using a widechar formatting.
writeBytesLocal[edit]
- writeBytesLocal(address, x,x,x,x,…)
- writeBytesLocal(address, table, , count)
- See writeBytes but then it’s for Cheat Engine’s memory.
wordToByteTable[edit]
- wordToByteTable(number)
- Converts a word to a bytetable
dwordToByteTable[edit]
- dwordToByteTable(number)
- Converts a dword to a bytetable
qwordToByteTable[edit]
- qwordToByteTable(number)
- Converts a qword to a bytetable
floatToByteTable[edit]
- floatToByteTable(number)
- Converts a float to a bytetable
doubleToByteTable[edit]
- doubleToByteTable(number)
- Converts a double to a bytetable
stringToByteTable[edit]
- stringToByteTable(string)
- Converts a string to a bytetable
wideStringToByteTable[edit]
- wideStringToByteTable(string)
- Converts a string to a widestring and converts that to a bytetable
byteTableToWord[edit]
- byteTableToWord(table)
- Converts a bytetable to a word
byteTableToDword[edit]
- byteTableToDword(table)
- Converts a bytetable to a dword
byteTableToQword[edit]
- byteTableToQword(table)
- Converts a bytetable to a qword
byteTableToFloat[edit]
- byteTableToFloat(table)
- Converts a bytetable to a float
byteTableToDouble[edit]
- byteTableToDouble(table)
- Converts a bytetable to a double
byteTableToString[edit]
- byteTableToString(table)
- Converts a bytetable to a string
byteTableToWideString[edit]
- byteTableToWideString(table)
- Converts a bytetable to a widestring and converts that to a string
bOr[edit]
- bOr(int1, int2)
- Binary Or
bXor[edit]
- bXor(int1, int2)
- Binary Xor
bAnd[edit]
- bAnd(int1, int2)
- Binary And
bShl[edit]
- bShl(int, int2)
- Binary shift leftP
bShr[edit]
- bShr(int, int2)
- Binary shift right
bNot[edit]
- bNot(int)
- Binary not
writeRegionToFile[edit]
- writeRegionToFile(filename, sourceaddress,size)
- Writes the given region to a file. Returns the number of bytes written
readRegionFromFile[edit]
- readRegionFromFile(filename, destinationaddress)
- Reads a file from memory and writes the contents of that file to the specified address
resetLuaState[edit]
- resetLuaState()
- This will create a new lua state that will be used. (Does not destroy the old one, so memory leak)
createRef[edit]
- createRef(…)
- Returns an integer reference that you can use with getRef. Useful for objects that can only store integers and need to reference lua objects. (Component.Tag…)
getRef[edit]
- getRef(integer)
- Returns whatever the reference points out
destroyRef[edit]
- destroyRef(integer)
- Removes the reference.
reloadSettingsFromRegistry[edit]
- reloadSettingsFromRegistry()
- This will cause cheat engine to reload the settings from the registry and apply them
getTranslationFolder[edit]
- getTranslationFolder()
- Returns the path of the current translation files. Empty if there is no translation going on
loadPOFile[edit]
- loadPOFile(path)
- Loads a ‘.PO’ file used for translation
translate[edit]
- translate(string)
- Returns a translation of the string. Returns the same string if it can’t be found
translateID[edit]
- translateID(translationid — string, originalstring — string OPTIONAL)
- Returns a translation of the string id
ansiToUtf8[edit]
- ansiToUtf8(string)
- Converts a string in Ansi encoding to UTF8
utf8ToAnsi[edit]
- utf8ToAnsi(string)
- Converts a string in UTF8 encoding to Ansi
Note: GUI components mainly show in UTF8, some other functions use Ansi, try to find out which ones…
enumModules[edit]
- enumModules(processid OPTIONAL)
- Returns a table containing information about each module in the current process, or the specified processid Each entry is a table with fields
- Name: String containing the modulename
- Address: Integer representing the address the module is loaded
- Is64Bit: Boolean set to true if it’s a 64-bit module
- PathToFile: String to the location this module is loaded
getAddress[edit]
- getAddress(string, local OPTIONAL)
- returns the address of a symbol. Can be a modulename or an export. set Local to true if you wish to querry the symboltable of the ce process
getSymbolInfo[edit]
- getSymbolInfo(symbolname)
- Returns a table as defined by the SymbolList class object (modulename, searchkey, address, size)
getModuleSize[edit]
- getModuleSize(modulename)
- Returns the size of a given module (Use getAddress to get the base address)
reinitializeSymbolhandler[edit]
- reinitializeSymbolhandler(waittilldone : BOOLEAN OPTIONAL, default=TRUE)
- reinitializes the symbolhandler. E.g when new modules have been loaded
reinitializeDotNetSymbolhandler[edit]
- reinitializeDotNetSymbolhandler(modulename OPTIONAL)
- Reinitializes only the DotNet part of the symbol list. (E.g After an ILCode has been JITed) (6.4+)
errorOnLookupFailure[edit]
- errorOnLookupFailure(state)
- If set to true (default) address lookups in stringform will raise an error if it can not be looked up. This includes symbolnames that are not defined and pointers that are bad. If set to false it will return 0 in those cases (Useful for pointers that don’t work 100% of the time) 6.4+:Returns the original state
generateAPIHookScript[edit]
- generateAPIHookScript(address, addresstojumpto, addresstogetnewcalladdress OPT)
- Generates an auto assembler script which will hook the given address when executed
autoAssemble[edit]
- autoAssemble(text, targetself OPTIONAL)
- runs the auto assembler with the given text. Returns true on success (if targetself is set it will assemble into Cheat Engine itself)
registerAutoAssemblerCommand[edit]
- registerAutoAssemblerCommand(command, function(parameters, syntaxcheckonly))
- Registers an auto assembler command to call the specified function. The command will be replaced by the string this function returns when executed. The function can be called twice. Once for syntax check and symbol lookup(1), and the second time for actual execution by the assembler(2) if it has not been removed in phase1.
Note: The callback function can return multiple values. If the function returns nil, and as secondary parameter a string, this will make the auto assembler fail with that error.
- Nil, String: Will raise an error with the given string
- MultilineString: Replaces the line in the script with the given strings.
unregisterAutoAssemblerCommand[edit]
- unregisterAutoAssemblerCommand(command)
- Removes the callback.
registerSymbolLookupCallback[edit]
- registerSymbolLookupCallback(function(string) : integer, location) : ID 6.4+
- Registers a function to be called when a a symbol is parsed Location determines at what part of the symbol lookup the function is called.
- The function should return an Integer with the corresponding address if the callback found it. Nil or 0 if you didn’t.
- slStart: The very start of a symbol lookup. Before tokenization
- slNotInt: Called when it has been determined it’s not a hexadecimal only string. Before tokenization
- The following locations can be called multiple times for one string as they are called for each token and appended token
- slNotModule: Called when it has been determined the current token is not a modulename
- slNotUserdefinedSymbol: Called when it has been determined it’s not a userdefined symbol
- slNotSymbol: Called when it has been determined it’s not a symbol in the symbollist
- slFailure: Called when it has no clue what the given string is
Note: slNotSymbol and slFailure are similar, but failure comes only if there’s no token after the current token that can be concatenated. Else slNotSymbol will loop several times till all tokens make up the full string
unregisterSymbolLookupCallback[edit]
- unregisterSymbolLookupCallback(ID)
- Removes the callback.
registerAddressLookupCallback[edit]
- registerAddressLookupCallback(function(integer) : string) : ID
- Registers a function to be called when the name of an address is requested
unregisterAddressLookupCallback[edit]
- unregisterAddressLookupCallback(ID)
- Removes the callback.
registerStructureDissectOverride[edit]
- registerStructureDissectOverride(function(structure, baseaddress) : table)
- Registers a function to be called whenever the structure dissect window when the user chooses to let cheat engine guess the structure for them.
- Use the structure object to fill it in
- Return true if you have filled it in, or false or nil if you did not
Tip: Use inputQuery to ask the user the size if your function doesn’t do that automatically
unregisterStructureDissectOverride[edit]
- unregisterStructureDissectOverride(ID)
- Removes the callback.
registerStructureNameLookup[edit]
- registerStructureNameLookup(function(address) : name, address OPTIONAL)
- Registers a function to be called when dissect data asks the user for the name of a new structure define. If you have code that can look up the name of a structure, and perhaps also the real starting point, you can use this to improve the data dissection.
unregisterStructureNameLookup[edit]
- unregisterStructureNameLookup(ID)
- Removes the callback.
registerAssembler[edit]
- registerAssembler(function(address, instruction) : bytetable)
- Registers a function to be called when the single line assembler is invoked to convert an instruction to a list of bytes
- Return a bytetable with the specific bytes, or nil if you wish to let another function, or the original x86 assembler to assemble it
unregisterAssembler[edit]
- unregisterAssembler(ID)
- Unregisters the registered assembler
registerAutoAssemblerPrologue[edit]
- registerAutoAssemblerPrologue(function(script, syntaxcheck))
- Registers a function to be called when the auto assembler is about to parse an auto assembler script. The script you get is after the [ENABLE] and [DISABLE] tags have been used to strip the script to the according one, but before comment stripping and trimming has occured.
- Script is a Strings object which when changed has direct effect to the script.
unregisterAutoAssemblerPrologue[edit]
- unregisterAutoAssemblerPrologue(ID)
- Removes the callback.
showMessage[edit]
- showMessage(text)
- shows a messagebox with the given text
inputQuery[edit]
- inputQuery(caption, prompt, initialstring)
- Shows a dialog where the user can input a string. This function returns the given string, or nil on cancel CE6.4+
messageDialog[edit]
- messageDialog(text, type, buttons…)
- pops up a messagebox with a specific icon/sound with the specified buttons (mbok, mbyes, ….)
sleep[edit]
- sleep(milliseconds)
- pauses for the number of specified milliseconds (1000= 1 sec…)
getProcesslist[edit]
- getProcesslist()
- getProcesslist(Strings)
- Returns a table with the process list (pid — name ), if ‘Strings’ is not set.
- If ‘Strings’ is set fills a Strings inherited object with the process list of the system.
- Format: %x-pidname
getWindowlist[edit]
- getWindowlist()
- getWindowlist(Strings)
- Returns a table with the window list (pid — window caption), if ‘Strings’ is not set.
- If ‘Strings’ is set fills a Strings inherited object with the top-window list of the system.
- Format: %x-windowcaption
getThreadlist[edit]
- getThreadlist(List)
- fills a List object with the threadlist of the currently opened process.
- Format: %x
onOpenProcess[edit]
- function onOpenProcess(processid)
- If this function is defined it will be called whenever cheat engine opens a process.
Note: The the same process might be opened multiple times in a row internally
Note 2: This function is called before attachment is fully done. You can call reinitializeSymbolhandler() to force the open to complete, but it will slow down process opens. Alternatively, you could launch a timer which will run when the opening has finished.
getOpenedProcessID[edit]
- getOpenedProcessID()
- Returns the currently opened process. If none is open, returns 0
getProcessIDFromProcessName[edit]
- getProcessIDFromProcessName(name)
- returns a processid
openProcess[edit]
- openProcess(processid)
- causes cheat engine to open the given processid
- openProcess(processname)
- causes cheat engine to find and open the given process
setPointerSize[edit]
- setPointerSize(size)
- Sets the size cheat engine will deal with pointers in bytes. (Some 64-bit processes can only use 32-bit addresses)
pause[edit]
- pause()
- pauses the current opened process
unpause[edit]
- unpause()
- resumes the current opened process
getPixel[edit]
- getPixel(x, y)
- returns the rgb value of the pixel at the specific screen coordinate
getMousePos[edit]
- getMousePos
- returns the x,y coordinates of the mouse
setMousePos[edit]
- setMousePos(x,y)
- sets the mouse position
isKeyPressed[edit]
- isKeyPressed(key)
- returns true if the specified key is currently pressed
keyDown[edit]
- keyDown(key)
- causes the key to go into down state
keyUp[edit]
- keyUp(key)
- causes the key to go up
doKeyPress[edit]
- doKeyPress(key)
- simulates a key press
shortCutToText[edit]
- shortCutToText(shortcut)
- Returns the textual representation of the given shortut value (integer) (6.4+)
textToShortCut[edit]
- textToShortCut(shortcutstring)
- Returns an shortcut integer that the given string represents. (6.4+)
convertKeyComboToString[edit]
- convertKeyComboToString(key1,…)
- convertKeyComboToString({key1,…})
- Returns a string representation of the given keys like the hotkey handler does
outputDebugString[edit]
- outputDebugString(text)
- Outputs a message using the windows OutputDebugString message. You can use tools like dbgview to read this. Useful for testing situations where the GUI freezes
shellExecute[edit]
- shellExecute(command, parameters OPTIONAL, folder OPTIONAL, showcommand OPTIONAL)
- Executes a given command
getTickCount[edit]
- getTickCount()
- Returns the current tickcount since windows was started. Each tick is one millisecond
processMessages[edit]
- processMessages()
- Lets the main eventhandler process the new messages (allows for new button clicks)
inMainThread[edit]
- inMainThread()
- Returns true if the current code is running inside the main thread (6.4+)
integerToUserData[edit]
- integerToUserData(int)
- Converts a given integer to a userdata variable
userDataToInteger[edit]
- userDataToInteger(UserDataVar)
- Converts a given userdata variable to an integer
synchronize[edit]
- synchronize(function(…), …)
- Calls the given function from the main thread. Returns the return value of the given function
checkSynchronize[edit]
- checkSynchronize()
- Calls this from an infinite loop in the main thread when using threading and synchronize calls. This will execute any queued synchronize calls
writeToClipboard[edit]
- writeToClipboard(text)
- Writes the given text to the clipboard
readFromClipboard[edit]
- readFromClipboard()
- Reads the text from the clipboard
speedhack_setSpeed[edit]
- speedhack_setSpeed(speed)
- Enables the speedhack if needed and sets the specific speed
speedhack_getSpeed[edit]
- speedhack_getSpeed()
- Returns the last set speed
injectDLL[edit]
- injectDLL(filename)
- Injects a dll, and returns true on success
loadPlugin[edit]
- loadPlugin(dllnameorpath)
- Loads the given plugin. Returns nil on failure. On success returns a value of 0 or greater
registerCustomTypeLua[edit]
- registerCustomTypeLua(typename, bytecount, bytestovaluefunction, valuetobytesfunction, isFloat)
- Registers a Custom type based on lua functions.
- The bytes to value function should be defined as «function bytestovalue (b1,b2,b3,b4)» and return an integer as result.
- The value to bytes function should be defined as «function valuetobytes (integer)» and return the bytes it should write.
registerCustomTypeAutoAssembler[edit]
- registerCustomTypeAutoAssembler(script)
- Registers a custom type based on an auto assembler script. The script must allocate an «ConvertRoutine» and «ConvertBackRoutine».
onAutoGuess[edit]
- onAutoGuess(function)
- Registers an function to be called whenever autoguess is used to predict a variable type.
- function override (address, ceguess): Return the variable type you want it to be. If no change, just return ceguess.
closeCE[edit]
- closeCE()
- just closes ce
hideAllCEWindows[edit]
- hideAllCEWindows()
- makes all normal ce windows invisible (e.g trainer table)
unhideMainCEwindow[edit]
- unhideMainCEwindow()
- shows the main cheat engine window
getAutoAttachList[edit]
- getAutoAttachList()
- returns the AutoAttach StringList object. It can be controlled with the stringlist_ routines (it’s not recommended to destroy this list object)
AOBScan[edit]
- AOBScan(x, x, x, x, …)
- AOBScan(aobstring, protectionflags OPTIONAL, alignmenttype OPTIONAL, alignmentparam HALFOPTIONAL)
- scans the currently opened process and returns a StringList object containing all the results. don’t forget to free this list when done.
- Bytevalue of higher than 255 or anything not an integer will be seen as a wildcard.
- protectionflags is a string:
- Add a + to indicate that flag MUST be set and a — to indicate that that flag MUST NOT be set. (* sets it to don’t care)
- X = Executable
- W = Writable memory
- C = Copy On Write.
Examples:
+W-C = Writable memory exluding copy on write and doesn't care about the Executable flag +X-C-W = Find readonly executable memory +W = Finds all writable memory and don't care about copy on write or execute "" = Find everything (is the same as "*X*C*W" )
- alignmenttype is an integer:
- 0 = No alignment check
- 1 = Address must be dividable by alignmentparam
- 2 = Address must end with alignmentparam
- alignmentparam is a string which either holds the value the addresses must be dividable by or what the last digits of the address must be.
Regarding eventhandlers. You can initialize them using both a string of a functionname or the function itself.
If initialized using a function itself it won’t be able to get saved in the table.
allocateSharedMemory[edit]
- allocateSharedMemory(name, size)
- Creates a shared memory object of the given size if it doesn’t exist yet. If size is not given and there is no shared region with this name then the default size of 4096 is used.
- It then maps this shared memory block into the currently targeted process. It returns the address of mapped region in the target process.
getForegroundProcess[edit]
- getForegroundProcess()
- Returns the processID of the process that is currently on top.
findWindow[edit]
- findWindow(classname OPTIONAL, caption OPTIONAL): windowhandle
- Finds a window with the given classname and/or windowname.
getWindow[edit]
- getWindow(windowhandle, command) : windowhandle
- Gets a specific window based on the given window (Check MSDN getWindow for the command description).
getWindowCaption[edit]
- getWindowCaption(windowhandle) : string
- Returns the caption of the window.
getWindowClassName[edit]
- getWindowClassName(windowhandle) : string
- Returns the classname of the window.
getWindowProcessID[edit]
- getWindowProcessID(windowhandle) : processid
- Returns the processid of the process this window belongs to.
getForegroundWindow[edit]
- getForegroundWindow() : windowhandle
- Returns the windowhandle of the topmost window.
sendMessage[edit]
- sendMessage(hwnd, msg, wparam, lparam) : result
- Sends a message to a window. Those that wish to use it, should know how to use it (and fill in the msg id’s yourself).
hookWndProc[edit]
- hookWndProc(hwnd, function(hwnd, msg, wparam, lparam), async) : result
- Hooks a window’s wndproc procedure. The given function will receive all functions.
- Return 0 to say you handled it. 1 to let the default windows handler deal with it.
- Or anything else, to let the original handler deal with it.
- Besides the return value, you can also return hWnd, Msg, lParam and wParam, modified, or nil for the original value.
- Set ASYNC to true if you don’t want to run this in the CE GUI. (faster, but you can’t touch GUI objects).
unhookWndProc[edit]
- unhookWndProc(hwnd)
- Call this when done with the hook.
- Not calling this function will result in the process window behaving badly when you exit CE.
cheatEngineIs64Bit[edit]
- cheatEngineIs64Bit()
- Returns true if CE is 64-bit, false if 32-bit
targetIs64Bit[edit]
- targetIs64Bit()
- Returns true if the target process is 64-bit, false if 32-bit
getCheatEngineDir[edit]
- getCheatEngineDir()
- Returns the folder Cheat Engine is located at
disassemble[edit]
- disassemble(address)
- Disassembles the given address and returns a string in the format of «address — bytes — opcode : extra»
splitDisassembledString[edit]
- splitDisassembledString(disassembledstring)
- Returns 4 strings. The address, bytes, opcode and extra field
getInstructionSize[edit]
- getInstructionSize(address)
- Returns the size of an instruction (basically it disassembles the instruction and returns the number of bytes for you)
getPreviousOpcode[edit]
- getPreviousOpcode(address)
- Returns the address of the previous opcode (this is just an estimated guess)
beep[edit]
- beep()
- Plays the fabulous beep/ping sound!
playSound[edit]
- playSound(stream, waittilldone OPTIONAL)
- Plays the given memorystream containing a .WAV formatted memory object. If waittilldone is true the script will stop executing till the sound has stopped
- playSound(tablefile, waittilldone OPTIONAL)
- Takes the memorystream from the tablefile and plays it.
- There are two tablefiles predeclared inside cheat engine «Activate» and «Deactivate» . You are free to use or override them
speak[edit]
- speak(text, waittilldone OPTIONAL)
- Speaks a given text.
- If waitTillDone is true the thread it’s in will be frozen till it is done
- speak(text, flags)
- Speaks a given text using the given flags.
speakEnglish[edit]
- speakEnglish(text, waittilldone OPTIONAL)
- Will try the English voice by wrapping the given text into an XML statement specifying the English voice.
- It’ll not say anything, if no English language is present on your computer.
getUserRegistryEnvironmentVariable[edit]
- getUserRegistryEnvironmentVariable(name)
- Returns the environment variable stored in the user registry environment
setUserRegistryEnvironmentVariable[edit]
- setUserRegistryEnvironmentVariable(name, string)
- Sets the environment variable stored in the user registry environment
broadcastEnvironmentUpdate[edit]
- broadcastEnvironmentUpdate()
- Call this when you’ve changed the environment variables in the registry. This will cause at least the shell to update so you don’t have to reboot. (It’s always recommended to reboot though)
stringToMD5String[edit]
- stringToMD5String(string)
- Returns an md5 hash string from the provided string
getFormCount[edit]
- getFormCount()
- Returns the total number of forms assigned to the main CE application
getForm[edit]
- getForm(index)
- Returns the form at the specific index
registerFormAddNotification[edit]
- registerFormAddNotification(function(form)): object
- Registers a function to be called when a form is attached to ce’s form list. This is useful for extentions that add new functionality to certain existing forms.
- It returns an object that you can use with unregisterFormAddNotification.
unregisterFormAddNotification[edit]
- unregisterFormAddNotification(object)
getSettingsForm[edit]
- getSettingsForm()
- Returns the main settings form
getMemoryViewForm[edit]
- getMemoryViewForm()
- Returns the main memoryview form class object which can be accessed using the Form_ class methods and the methods of the classes it inherits from. There can be multiple memory views, but this will only find the original/base
getMainForm[edit]
- getMainForm()
- Returns the main form class object which can be accessed using the Form_ class methods and the methods of the classes it inherits from
getLuaEngine[edit]
- getLuaEngine()
- Returns the lua engine form object (Creates it if needed)
getApplication[edit]
- getApplication()
- Returns the application object. (the titlebar)
getAddressList[edit]
- getAddressList()
- Returns the cheat table addresslist object
getFreezeTimer[edit]
- getFreezeTimer()
- Returns the freeze timer object
getUpdateTimer[edit]
- getUpdateTimer()
- Returns the update timer object
setGlobalKeyPollInterval[edit]
- setGlobalKeyPollInterval(integer)
- Sets the global keypoll interval. The interval determines the speed of how often CE checks if a key has been pressed or not.
- Lower is more accurate, but eats more cpu power
setGlobalDelayBetweenHotkeyActivation[edit]
- setGlobalDelayBetweenHotkeyActivation(integer)
- Sets the minimum delay between the activation of the same hotey in milliseconds. Affects all hotkeys that do not set their own minimum delay
undefined property functions. Not all properties of all classes have been explicitly exposed to lua, but if you know the name of a property of a specific class you can still access them (assuming they are declared as published in the pascal class declaration)
getPropertyList[edit]
- getPropertyList(class)
- Returns a stringlist object containing all the published properties of the specified class: (free the list when done)
- Note: not all classed with properties have ‘published’ properties. E.g: stringlist)
setProperty[edit]
- setProperty(class, propertyname, propertyvalue)
- Sets the value of a published property of a class: (Won’t work for method properties)
getProperty[edit]
- getProperty(class, propertyname)
- Gets the value of a published property of a class: (Won’t work for method properties)
setMethodProperty[edit]
- setMethodProperty(class, propertyname, function)
- Sets the method property to the specific function
getMethodProperty[edit]
- getMethodProperty(Class, propertyname)
- Returns a function you can use to call the original function
registerSymbol[edit]
- registerSymbol(symbolname, address, OPTIONAL donotsave)
- Registers a userdefined symbol. If donotsave is true this symbol will not get saved when the table is saved
unregisterSymbol[edit]
- unregisterSymbol(symbolname)
- Unregisters a userdefined symbol.
getNameFromAddress[edit]
- getNameFromAddress(address)
- Returns the given address as a string. Registered symbolname, modulename+offset, or just a hexadecimal string depending on what address
inModule[edit]
- inModule(address)
- returns true if the given address is inside a module
inSystemModule[edit]
- inSystemModule(address)
- returns true if the given address is inside a system module
getCommonModuleList[edit]
- getCommonModuleList
- Returns the commonModuleList stringlist. (Do not free this one)
debugging[edit]
debug variables[edit]
- EFLAGS
- 32-bit: EAX, EBX, ECX, EDX, EDI, ESP, EBP, ESP, EIP
- 64-bit: RAX, EBX, RBX, RDX, RDI, RSP, RBP, RSP, RIP, R8, R9, R10, R11, R12, R13, R14, R15
[edit]
- function debugger_onBreakpoint()
- When a breaking breakpoint hits (that includes single stepping) and the lua function debugger_onBreakpoint() is defined it will be called and the global variables EAX, EBX, …. will be filled in
- Return 0 if you want the userinterface to be updated and anything else if not (e.g: You continued from the breakpoint in your script)
createProcess[edit]
- createProcess(path, parameters OPTIONAL, debug OPTIONAL, breakonentrypoint OPTIONAL)
- Creates a process. If debug is true it will be created using the windows debugger and if breakonentry is true it will cause a breakpoint to occur on entrypoint.
debugProcess[edit]
- debugProcess(interface OPTIONAL)
- starts the debugger for the currently opened process (won’t ask the user).
- interface:
- 0=default
- 1=windows debug
- 2=VEHDebug
- 3=Kerneldebug
debug_isDebugging[edit]
- debug_isDebugging()
- Returns true if the debugger has been started
debug_getCurrentDebuggerInterface[edit]
- debug_getCurrentDebuggerInterface()
- Returns the current debuggerinterface used (1=windows, 2=VEH 3=Kernel, nil=no debugging active)
debug_canBreak[edit]
- debug_canBreak()
- Returns true if there is a possibility the target can stop on a breakpoint. 6.4+
debug_isBroken[edit]
- debug_isBroken()
- Returns true if the debugger is currently halted on a thread
debug_getBreakpointList[edit]
- debug_getBreakpointList()
- Returns a lua table containing all the breakpoint addresses
debug_addThreadToNoBreakList[edit]
- debug_addThreadToNoBreakList(threadid)
- This will cause breakpoints on the provided thread to be ignored
debug_removeThreadFromNoBreakList[edit]
- debug_removeThreadFromNoBreakList(threadid)
- removed the threadid from the list
debug_setBreakpoint[edit]
- debug_setBreakpoint(address, size OPTIONAL, trigger OPTIONAL, breakpointmethod OPTIONAL, functiontocall() OPTIONAL)
- debug_setBreakpoint(address, size OPTIONAL, trigger OPTIONAL, functiontocall() OPTIONAL)
- debug_setBreakpoint(address, functiontocall() OPTIONAL)
- sets a breakpoint of a specific size at the given address. if trigger is bptExecute then size is ignored. If trigger is ignored then it will be of type bptExecute, which obviously also ignores the size then as well.
debug_removeBreakpoint[edit]
- debug_removeBreakpoint(address)
- if the given address is a part of a breakpoint it will be removed
debug_continueFromBreakpoint[edit]
- debug_continueFromBreakpoint(continueMethod)
- if the debugger is currently waiting to continue you can continue with this. Valid parameters are :co_run (just continue), co_stepinto(when on top of a call, follow it), co_stepover (when on top of a call run till after the call).
debug_getXMMPointer[edit]
- debug_getXMMPointer(xmmregnr)
- Returns the address of the specified xmm register of the thread that is currently broken.
- This is a LOCAL Cheat Engine address. Use Local memory access functions to read and modify xmmregnr can be 0 to 15 (0 to 7 on 32-bit).
The following routines describe last branch recording.
These functions only work when kernelmode debugging is used and using windows XP (vista and later work less
effective or not at all because the operating system interferes.
Might also be intel specific. A dbvm upgrade in the future might make this work for windows vista and later)
debug_setLastBranchRecording[edit]
- debug_setLastBranchRecording(boolean)
- When set the Kernel debugger will try to record the last branch(es) taken before a breakpoint happens
debug_getMaxLastBranchRecord[edit]
- debug_getMaxLastBranchRecord()
- Returns the maximum branch record your cpu can store (-1 if none)
debug_getLastBranchRecord[edit]
- debug_getLastBranchRecord(index)
- Returns the value of the Last Branch Record at the given index (when handling a breakpoint)
- function debugger_onModuleLoad(modulename, baseaddress)
- this routine is called when a module is loaded. Only works for the windows debugger.
- Return 1 if you want to cause the debugger to break.
Changing registers:
When the debugger is waiting to continue you can change the register variables. When you continue those register values will be set in the thread’s context.
If the target is currently stopped on a breakpoint, but not done through an onBreakpoint function. The context won’t be set.
You can get and set the context back with these functions before execution continues»
debug_getContext[edit]
- debug_getContext(BOOL extraregs)
- Fills the global variables for the regular registers.
- If extraregs is true, it will also set FP0 to FP7 and XMM0 to XMM15.
debug_updateGUI[edit]
- debug_updateGUI()
- Will refresh the userinterface to reflect the new context if the debugger was broken.
detachIfPossible[edit]
- detachIfPossible()
- Detaches the debugger from the target process (if it was attached).
[edit]
- getComment(address)
- Gets the userdefined comment at the specified address.
[edit]
- setComment(address, text)
- Sets a userdefined comment at the specifried address. %s is used to display the autoguess value if there is one.
[edit]
- getHeader(address)
- Gets the userdefined header at the specified address.
[edit]
- setHeader(address)
- Sets the userdefined header at the specified address.
registerBinUtil[edit]
- registerBinUtil(config)
- Registers a binutils toolset with CE (for assembling and disassembling in other cpu instruction sets)
- config is a table containing several fields that describe the tools, and lets you specify extra parameters
- Name: The displayed name in the binutils menu in memview.
- Description: The description for this toolset.
- Architecture: used by the objdump -m<architecture> (required).
- ASParam: extra parameters to pass on to AS (optional).
- LDParam: extra parameters to pass on to LD.
- OBJDUMPParam: extra parameters to pass on to OBJDUMP.
- OnDisassemble: a lua function that gets called each time an address is disassembled. The return value will be passed on to OBJDUMP.
- Path: filepath to the binutils set.
- Prefix: prefix (e.g: «arm-linux-androideabi-«).
- DisassemblerCommentChar: Depending on which target you’re disassembling, the comment character can be different. (ARM=»;» x86=’#’ ).
class helper functions[edit]
inheritsFromObject[edit]
- inheritsFromObject(object)
- Returns true if given any class.
inheritsFromComponent[edit]
- inheritsFromComponent(object)
- Returns true if the given object inherits from the Component class.
inheritsFromControl[edit]
- inheritsFromControl(object)
- Returns true if the given object inherits from the Control class.
inheritsFromWinControl[edit]
- inheritsFromWinControl(object)
- Returns true if the given object inherits from the WinControl class.
createClass[edit]
- createClass(classname)
- Creates an object of the specified class: (Assuming it’s a registered class and has a default constructor).
Class definitions[edit]
Object[edit]
Object class: (Inheritance: )
Properties:
ClassName: String - The name of class: (Read only)
Methods:
getClassName(): Returns the classname destroy(): Destroys the object
Component[edit]
Component class: (Inheritance: Object)
Properties:
ComponentCount: Integer - Number of child components . Readonly Component[int]: Component - Array containing the child components. Starts at 0. Readonly ComponentByName[string]: Component - Returns a component based on the name. Readonly Name: string - The name of the component Tag: integer - Free to use storage space. (Useful for id's) Owner: Component - Returns the owner of this object. Nil if it has none
Methods:
getComponentCount() : Returns the number of components attached to his component getComponent(index) : Returns the specific component findComponentByName(name) : Returns the component with this name getName() : Return the name setName(newname) : Changes the name getTag() : Sets an integer value. You can use this for ID's setTag(tagvalue) : Get the tag value getOwner() : Returns the owner of this component
Control[edit]
Control class: (Inheritance: Component—>Object)
Properties:
Caption: string - The text of a control Top : integer - The x position Left : integer - The y position Width : integer - The width of the control Height : integer - The height of the control ClientWidth: integer - The usable width inside the control (minus the borders) ClientHeight: integer - The usable height the control (minus the borders) Align: AlignmentOption - Alignment of the control Enabled: boolean - Determines if the object is usable or greyed out Visible: boolean - Determines if the object is visible or not Color: ColorDefinition/RGBInteger - The color of the object. Does not affect the caption Parent: WinControl - The owner of this control PopupMenu: PopupMenu - The popup menu that shows when rightclicking the control Font: Font - The font class associated with the control OnClick: function - The function to call when a button is pressed
Methods:
getLeft() setLeft(integer) getTop() setTop(integer) getWidth() setWidth(integer) getHeight() setHeight() setCaption(caption) : sets the text on a control. All the GUI objects fall in this category getCaption() : Returns the text of the control setPosition(x,y): sets the x and y position of the object base don the top left position (relative to the client array of the owner object) getPosition(): returns the x and y position of the object (relative to the client array of the owner object) setSize(width,height) : Sets the width and height of the control getSize() : Gets the size of the control setAlign(alignmentoption): sets the alignment of the control getAlign(alignmentoption): gets the alignment of the control getEnabled() : gets the enabled state of the control setEnabled(boolean) : Sets the enabled state of the control getVisible() : gets the visible state of the control setVisible(boolean) : sets the visible state of the control getColor() : gets the color setColor(rgb) : Sets the color getParent() : Returns nil or an object that inherits from the Wincontrol class setParent(wincontrol) : Sets the parent for this control getPopupMenu() setPopupMenu() getFont(): Returns the Font object of this object setFont(): Assigns a new font object. (Not recommended to use. Change the font object that's already there if you wish to change fonts) repaint(): Invalidates the graphical area of the control and forces and update update() : Only updates the invalidated areas setOnClick(functionnameorstring) : Sets the onclick routine getOnClick(): Gets the onclick function doClick(): Executes the current function under onClick
GraphicsObject[edit]
GraphicsObject class: (Inheritance: Object)
Region[edit]
Region class: (Inheritance: GraphicsObject—>Object)
createRegion(): Creates an empty region.
Methods:
addRectangle(x1, y1, x2, y2): Adds a rectangle to the region
addPolygon(tablewithcoordinates): Adds an array of 2D locations. (example : {{0,0},{100,100}, {0,100}} for a triangle )
WinControl[edit]
WinControl class: (Inheritance: Control—>Component—>Object)
Properties:
DoubleBuffered: boolean - Graphical updates will go to a offscreen bitmap which will then be shown on the screen instead of directly to the screen.
May reduce flickering.
ControlCount : integer - The number of child controls of this wincontrol
Control[] : Control - Array to access a child control
OnEnter : function - Function to be called when the WinControl gains focus
OnExit : function - Function to be called when the WinControl loses focus
Methods:
getControlCount() Returns the number of Controls attached to this class getControl(index) : Returns a WinControl class object getControlAtPos(x,y): Gets the control at the given x,y position relative to the wincontrol's position canFocus(): returns true if the object can be focused focused(): returns boolean true when focused setFocus(): tries to set keyboard focus the object setShape(Region): Sets the region object as the new shape for this wincontrol setShape(Bitmap): setOnEnter(function) : Sets an onEnter event. (Triggered on focus enter) getOnEnter() setOnExit(function) : Sets an onExit event. (Triggered on lost focus) getOnExit()
[edit]
MenuItem class: (Inheritance: Component—>Object)
createMenuItem(ownermenu) : Creates a menu item that gets added to the owner menu
Properties:
Caption : String - Text of the menu item Shortcut : string - Shortcut in textform to trigger the menuitem Count : integer - Number of children attached to this menuitem Menu: Menu - The menu this item resides in Parent: MenuItem - The menuitem this item hangs under MenuIndex: integer - The position this menu item is in it's parent Item[] : Array to access each child menuitem [] : Item[] OnClick: Function to call when the menu item is activated
Methods:
getCaption() : Gets the caption of the menu item
setCaption(caption) : Sets the caption of the menu item
getShortcut(): Returns the shortcut for this menu item
setShortcut(shortcut): Sets the shortcut for this menuitem. A shortcut is a string in the form of ("ctrl+x")
getCount()
getItem(index) : Returns the menuitem object at the given index
add(menuitem) : Adds a menuItem as a submenu item
insert(index, menuitem): Adds a menuItem as a submenu item at the given index
delete(index)
setOnClick(function) : Sets an onClick event
getOnClick()
doClick(): Executes the onClick method if one is assigned
[edit]
Menu class: (Inheritance: Component—>Object)
Properties:
Items : MenuItem - The base MenuItem class of this menu (readonly)
Methods:
getItems() : Returns the main MenuItem of this Menu
MainMenu[edit]
MainMenu class: (Inheritance: Menu—>Component—>Object)
createMainMenu(form)
The main menu is the menu at the top of a window.
[edit]
PopupMenu class: (Inheritance: Menu—>Component—>Object)
createPopupMenu(owner)
The popup menu is the menu that pops up when showing the (rightclick) context of an control
Strings[edit]
Strings class: (Inheritance : Object) (Mostly an abstract class)
Properties:
Text : String - All the strings in one string Count: Integer - The number of strings in this list String[]: String - Array to access one specific string in the list [] = String[]
Methods:
clear() : Deletes all strings in the list add(string) : adds a string to the list delete(index) : Deletes a string from the list getText() : Returns all the strings as one big string setText() : Sets the strings of the given strings object to the given text (can be multiline) indexOf(string): Returns the index of the specified string. Returns -1 if not found insert(index, string): Inserts a string at a specific spot moving the items after it getCount(): Returns the number is strings in the list remove(string); Removes the given string from the list loadFromFile(filename) : Load the strings from a textfile saveToFile(filename) : Save the strings to a textfile getString(index) : gets the string at the given index setString(index, string) : Replaces the string at the given index
Stringlist[edit]
Stringlist class: (Inheritance : Strings—>Object)
createStringlist() : Creates a stringlist class object (for whatever reason, lua strings are probably easier to use)
Properties:
Duplicates : DuplicatesType - Determines how duplicates should be handled Sorted : boolean - Determines if the list should be sorted CaseSensitive: boolean - Determines if the list is case sensitive or not.
Methods:
getDuplicates() : returns the duplicates property setDuplicates(Duplicates) : Sets the duplicates property (dupIgnore, dupAccept, dupError) getSorted() : returns true if the list has the sorted property setSorted(boolean) : Sets the sorted property getCaseSensitive() : Returns true if the case sensitive property is set setCaseSensitive(boolean): Sets the case sensitive property
Application[edit]
Application class: (Inheritance: CustomApplication—>Component—>Object)
Properties:
Title: The title of cheat engine in the bar
Methods:
bringToFront(): Shows the cheat engine app
Form[edit]
Form class: (Inheritance: ScrollingWinControl—>CustomControl—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
Properties:
AllowDropFiles: boolean - Allows files to be dragged into the form
ModalResult: integer - The current ModalResult value of the form. Note: When this value gets set the modal form will close
Menu: MainMenu - The main menu of the form
OnClose: function(sender) - The function to call when the form gets closed
OnDropFiles: function(sender, {filenames}) - Called when files are dragged on top of the form. Filenames is an arraytable with the files
Methods:
centerScreen(); : Places the form at the center of the screen
hide() : Hide the form
show() : show the form
close(): Closes the form. Without an onClose this will be the same as hide
bringToFront(): Brings the form to the foreground
showModal() : show the form and wait for it to close and get the close result
isForegroundWindow(): returns true if the specified form has focus
setOnClose(function) : function (sender) : Return a CloseAction to determine how to close the window
getOnClose() : Returns the function
getMenu() : Returns the mainmenu object of this form
setMenu(mainmenu)
setBorderStyle( borderstyle): Sets the borderstyle of the window
getBorderStyle()
printToRasterImage(rasterimage): Draws the contents of the form to a rasterimage class object
dragNow(): Call this on mousedown on any object if you wish that the mousemove will drag the whole form arround.
Useful for borderless windows (Dragging will stop when the mouse button is released)
CEForm[edit]
CEForm class: (Inheritance: Form—>ScrollingWinControl—>CustomControl—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createForm(visible OPT): creates a CEForm class object(window) and returns the pointer for it. Visible is default true but can be changed createFormFromFile(filename): Returns the generated CEform
Properties:
DoNotSaveInTable: boolean - Set this if you do not wish to save the forms in the table
Methods:
saveToFile(filename): Saves a userdefined form getDoNotSaveInTable(): Returns the DoNotSaveInTable property setDoNotSaveInTable(boolean): Sets the DoNotSaveInTable property
GraphicControl[edit]
GraphicControl class: (Inheritance: Control—>Component—>Object)
Properties:
Canvas: Canvas - The canvas for rendering this control
Methods:
getCanvas() : Returns the Canvas object for the given object that has inherited from customControl
PaintBox[edit]
PaintBox class: (Inheritance: GraphicControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createPaintBox(owner): Creates a Paintbox class object
Label[edit]
Label class: (Inheritance: GraphicControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createLabel(owner): Creates a Label class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
Splitter[edit]
Splitter class: (Inheritance: CustomControl—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createSplitter(owner): Creates a Splitter class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
Panel[edit]
Panel class: (Inheritance: CustomControl—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createPanel(owner): Creates a Panel class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
Properties:
Alignment: alignment BevelInner: panelBevel BevelOuter: panelBevel BevelWidth: Integer FullRepaint: boolean
Methods:
getAlignment() : gets the alignment property setAlignment(alignment) : sets the alignment property getBevelInner() setBevelInner(PanelBevel) getBevelOuter() setBevelOuter(PanelBevel) getBevelWidth() setBevelWidth(BevelWidth) getFullRepaint() setFullRepaint(boolean)
Image[edit]
Image class: (Inheritance: GraphicControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createImage(owner): Creates an Image class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
Properties:
Canvas: Canvas - The canvas object to access the picture of the image Transparent: boolean - Determines if some parts of the picture are see through (usually based on the bottomleft corner) Stretch: boolean - Determines if the picture gets stretched when rendered in the image component Picture: Picture - The picture to render
Methods:
loadImageFromFile(filename) getStretch() setStretch(boolean) getTransparent() setTransparent(boolean) getCanvas() setPicture(picture) getPicture() : Returns the Picture object of this image
Edit[edit]
Edit class: (Inheritance: WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createEdit(owner): Creates an Edit class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
Properties:
Text: string - The current contents of the editfield OnChange: function - The function to call when the editfield is changed
Methods:
clear() selectAll() clearSelection() copyToClipboard() cutToClipboard() pasteFromClipboard() onChange(function)
Memo[edit]
Memo class: (Inheritance: Edit—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createMemo(owner): Creates a Memo class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
Properties:
Lines: Strings - Strings object for this memo WordWrap: boolean - Set if words at the end of the control should go to the next line WantTabs: Boolean - Set if tabs will add a tab to the memo. False if tab will go to the next control WantReturns: Boolean - Set if returns will send a event or not Scrollbars: Scrollstyle - Set the type of ascrollbars to show (ssNone, ssHorizontal, ssVertical, ssBoth, ssAutoHorizontal, ssAutoVertical, ssAutoBoth)
Methods:
append(string) getLines() : returns a Strings class getWordWrap() setWordWrap(boolean) getWantTabs() setWantTabs(boolean) getWantReturns() setWantReturns(boolean) getScrollbars() setScrollbars(scrollbarenumtype) : Sets the scrollbars. Horizontal only takes affect when wordwrap is disabled valid enum types: ssNone : No scrollbars ssHorizontal: Has a horizontal scrollbar ssVertical: Has a vertical scrollbar ssBoth: Has both scrollbars ssAutoHorizontal: Same as above but only shows when there actually is something to scroll for ssAutoVertical: " " " " ... ssAutoBoth: " " " " ...
ButtonControl[edit]
ButtonControl class: (Inheritance: WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
Button[edit]
Button class: (Inheritance: ButtonControl—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createButton(owner): Creates a Button class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
Properties:
ModalResult: ModalResult - The result this button will give the modalform when clicked
Methods:
getModalResult(button) setModalResult(button, mr)
CheckBox[edit]
CheckBox class: (Inheritance: ButtonControl—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createCheckBox(owner): Creates a CheckBox class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
Properties:
Checked: boolean - True if checked AllowGrayed: boolean - True if it can have 3 states. True/False/None State: checkboxstate - The state. (cbUnchecked=0, cbChecked=1, cbGrayed=2) OnChange: function - Function to call when the state it changed
Methods:
getAllowGrayed() setAllowGrayed(boolean) getState(): Returns a state for the checkbox. (cbUnchecked, cbChecked, cbGrayed) setState(boolean): Sets the state of the checkbox onChange(function)
ToggleBox[edit]
ToggleBox class: (Inheritance: CheckBox—>ButtonControl—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createToggleBox(owner): Creates a ToggleBox class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
GroupBox[edit]
GroupBox class: (Inheritance: WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createGroupBox(owner): Creates a GroupBox class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
RadioGroup[edit]
RadioGroup class: (Inheritance: GroupBox—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createRadioGroup(owner): Creates a RadioGroup class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
Properties:
Items: Strings - Strings derived object containings all the items in the list Columns: Integer - The number of columns to split the items into ItemIndex: Integer - The currently selected item OnClick: Called when the control is clicked
Methods:
getRows(): Returns the number of rows getItems(): Returns a Strings object getColumns(): Returns the nuber of columns setColumns(integer) getItemIndex() setItemIndex(integer) setOnClick(function) getOnClick()
ListBox[edit]
ListBox class: (Inheritance: WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createListBox(owner): Creates a ListBox class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
Properties:
MultiSelect: boolean - When set to true you can select multiple items Items: Strings - Strings derived object containings all the items in the list Selected[] - Returns true if the given line is selected. Use Items.Count-1 to find out the max index ItemIndex: integer - Get selected index. -1 is nothing selected Canvas: Canvas - The canvas object used to render on the object
Methods:
clear() clearSelection() : Deselects all items in the list selectAll(): Selects all items in the list getItems(): Returns a strings object setItems(Strings): sets a strings object to the listbox getItemIndex() setItemIndex(integer) getCanvas()
Calendar[edit]
Calendar class: (Inheritance: WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createCalendar(owner): Creates a Calendar class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl. Valid date is between "September 14, 1752" and "December 31, 9999".
Properties:
Date: string - current date of the Calendar, format: yyyy-mm-dd DateTime: number - days since December 30, 1899
Methods:
getDateLocalFormat - returns current date of the Calendar, format: ShortDateFormat from OS local settings
ComboBox[edit]
ComboBox class: (Inheritance: WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createComboBox(owner): Creates a ComboBox class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
Properties:
Items: Strings - Strings derived object containings all the items in the list ItemIndex: integer - Get selected index. -1 is nothing selected Canvas: Canvas - The canvas object used to render on the object
Methods:
clear() getItems() setItems() getItemIndex() setItemIndex(integer) getCanvas()
ProgressBar[edit]
ProgressBar class: (Inheritance: WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createProgressBar(owner): Creates a ProgressBar class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
Properties:
Min: integer - The minimum positionvalue the progressbar can have (default 0) Max: integer - The maximum positionvalue the progressbar can have (default 100 Position: integer - The position of the progressbar Step: integer- The stepsize to step by when stepIt() is called
Methods:
stepIt() - Increase position with "Step" size stepBy(integer) - increase the position by the given integer value getMax() - returns the Max property setMax(integer) - sets the max property getMin() - returns the min property setMin(integer)- sets the min property getPosition() - returns the current position setPosition(integer) - sets the current position
TrackBar[edit]
TrackBar class: (Inheritance: WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createTrackBar(owner): Creates a TrackBar class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
Properties:
Min: integer - Minimal value for the trackbar Max: integer - Maximum value for the trackbar Position: integer - The current position OnChange: function - Function to call when
Methods:
getMax() setMax(integer) getMin(trackbar) setMin(trackbar, integer) getPosition(progressbar) setPosition(progressbar, integer) getOnChange(function) setOnChange()
CollectionItem[edit]
CollectionItem class: (Inheritance: Object)
Base class for some higher level classes. Often used for columns
Properties:
ID: integer Index: integer - The index in the array this item belong to DisplayName: string
Methods:
getID() getIndex() setIndex() getDisplayName() setDisplayName()
ListColumn[edit]
ListColumn class: (Inheritance: CollectionItem—>Object)
Properties:
AutoSize: boolean Caption: string MaxWidth: integer MinWidth: integer Width: integer Visible: boolean
Methods:
getAutosize() setAutosize(boolean) getCaption() setCaption(caption) getMaxWidth() setMaxWidth(width) getMinWidth() setMinWidth(width) getWidth() setWidth(width)
Collection[edit]
Collection class: (Inheritance: TObject)
Properties:
Count: integer
Methods:
clear(collection) getCount(collection) delete(collection, index)
ListColumns[edit]
ListColumns class: (Inheritance: Collection—>Object)
Properties:
Columns[]: Array to access a column [] = Columns[]
Methods:
add(): Returns a new ListColumn object getColumn(index): Returns a ListColumn object; setColumn(index, listcolumns): Sets a ListColumn object (not recommended, use add instead)
ListItem[edit]
ListItem class: (Inheritance: TObject)
Properties:
Caption: boolean - The text of this listitem Checked: boolean - Determines if the checkbox is checked (if it has a checkbox) SubItems: Strings - The Strings object that hold the subitems Selected: boolean - Returns true if selected Index: integer - The index in the Items object of the owner of this listitem (readonly) Owner: ListItems - The ListItems object that owns this ListItem (readonly)
Methods:
delete() getCaption() : Returns the first columns string of the listitem setCaption(string) : Sets the first column string of the listitem getChecked() : Returns true if the listitem is checked setChecked(boolean): Sets the checkbox of the listbox to the given state getSubItems(): Returns a Strings object makeVisible(partial): Scrolls the listview so this item becomes visible (Cheat Engine 6.4 and later)
ListItems[edit]
ListItems class: (Inheritance: TObject)
Properties:
Count : Integer - The number of ListItems this object holds (Normally read only, but writable if OwnerData is true in the listview) Item[]: ListItem[] - Array to access each ListItem object [] = Item[]
Methods:
clear() getCount() getItem(integer) : Return the listitem object at the given index add(): Returns a new ListItem object
Listview[edit]
Listview class: (Inheritance: WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createListView(owner): Creates a ListView class object which belongs to the given owner. Owner can be any object inherited from WinControl
Properties:
Columns: ListColumns - The Listcolumns object of the listview (Readonly)
Items: ListItems - The ListItems objects of the listview
ItemIndex: integer - The currently selected index in the Items object (-1 if nothing is selected)
Selected: ListItem - The currently selected listitem (nil if nothing is selected)
Canvas: Canvas - The canvas object used to render the listview (Readonly)
AutoWidthLastColumn: Boolean - When set to true the last column will resize when the control resizes
HideSelection: Boolean - When set to true the selection will not hide when the focus leaves the control
RowSelect: Boolean - When set to true the whole row will be selected instead of just the first column
OwnerData: Boolean - When set to true the listview will call the onData function for every line being displayed.
Use Items.Count to set the number of virtual lines.
OnData: function(sender, ListItem) - Called when a listview with OwnerData true renders a line
Methods:
clear() getColumns() : ListColumns - Returns a ListColumns object getItems(): ListItems - Returns a ListItems object getItemIndex(): integer - Returns the currently selected index in the Items object setItemIndex(index: integer)- Sets the current itemindex getCanvas() : Canvas - Returns the canvas object used to render the listview
TreeNode[edit]
TreeNode class: (Inheritance: TObject)
Properties:
Text: string - The text of the treenode Parent: Treenode - The treenode this object is a child of. (can be nil) (ReadOnly) Level: Integer - The level this node is at HasChildren: boolean - Set to true if it has children, or you wish it to have an expand sign Expanded: boolean - Set to true if it has been expanded Count : Integer - The number of children this node has Items[]: Treenode - Array to access the child nodes of this node [] = Items[] Index: Integer - The index based on the parent AbsoluteIndex: Integer - The index based on the TreeView's Treenodes object (Items) Selected: Boolean - Set to true if currently selected MultiSelected: Boolean - Set to true if selected as well, but not the main selected object Data: Pointer - Space to store 4 or 8 bytes depending on which version of CE is used
Methods:
delete() deleteChildren() makeVisible() expand(recursive:boolean=TRUE OPTIONAL) : Expands the given node collapse(recursive:boolean=TRUE OPTIONAL) : collapses the given node getNextSibling(): Returns the treenode object that's behind this treenode on the same level add(text:string): Returns a Treenode object that is a child of the treenode used to create it
TreeNodes[edit]
TreeNodes class: (Inheritance: TObject)
Properties:
Count : Integer - The total number of Treenodes this object has Item[]: TreeNode - Array to access each node [] = Item[]
Methods:
clear() getCount() getItem(integer) : Return the TreeNode object at the given index (based on the TreeView's Treenodes) add(text:string): Returns a new root Treenode object insert(treenode, string): Returns a new treenode object that has been inserted before the given treenode insertBehind(treenode, string): Returns a new treenode object that has been inserted after the given treenode
Treeview[edit]
Treeview class: (Inheritance: CustomControl—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createTreeView(owner)
Properties:
Items: TreeNodes - The Treenodes object of the treeview (ReadOnly) Selected: TreeNode - The currently selected treenode
Methods:
getItems() getSelected() setSelected() fullCollapse() : Collapses all the nodes, including the children's nodes fullExpand() : Expands all the nodes and all their children saveToFile(filename): Saves the contents of the treeview to disk
Timer[edit]
Timer class: (Inheritance: Component—>Object)
createTimer(owner OPT, enabled OPT): Creates a timer object. If enabled is not given it will be enabled by default (will start as soon as an onTimer event has been assigned)
Owner may be nil, but you will be responsible for destroying it instead of being the responsibility of the owner object)
Properties:
Interval: integer - The number of milliseconds (1000=1 second) between executions Enabled: boolean OnTimer: function(timer) - The function to call when the timer triggers
Methods:
getInterval() setInterval(interval) : Sets the speed on how often the timer should trigger. In milliseconds (1000=1 second) getOnTimer() setOnTimer(function(timer)) getEnabled() setEnabled(boolean)
CustomControl[edit]
CustomControl class: (CustomControl—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
Properties:
Canvas : The canvas object for drawing on the control/. Readonly
Methods:
getCanvas() : Returns the Canvas object for the given object that has inherited from customControl
Canvas[edit]
Canvas class: (Inheritance: CustomCanvas—>Object)
Properties:
Brush: Brush - The brush object Pen: Pen - The pen object Font: Font - The font object Width: integer - Width of the canvas Height: integer - Height of the canvas
Methods:
getBrush(): Returns the brush object of this canvas
getPen(): Returns the pen object of this canvas
getFont(): Returns the font object of this canvas
getWidth()
getHeight()
getPenPosition()
setPenPosition(x,y)
clear() - Clears the canvas
line(sourcex, sourcey, destinationx, destinationy)
lineTo(destinationx, destinationy)
rect(x1,y1,x2,y2)
fillRect(x1,y1,x2,y2)
textOut(x,y, text)
getTextWidth(text)
getTextHeight(text)
getPixel(x,y)
setPixel(x,y,color)
floodFill(x,y)
ellipse(x1,y1,x2,y2)
gradientFill(x1,y1,x2,y2, startcolor, stopcolor, direction) : Gradient fills a rectangle.
Direction can be 0 or 1. 0=Vertical 1=Horizontal
copyRect(dest_x1,dest_y1,dest_x2,dest_y2, sourceCanvas, source_x1,source_y1,source_x2,source_y2) : Draws an image from one source to another. Useful in cases of doublebuffering.
draw(x,y, graphic) : Draw the image of a specific Graphic class
getClipRect() : Returns a table containing the fields Left, Top, Right and Bottom, which define the invalidated region of the graphical object. Use this to only render what needs to be rendered in the onPaint event of objects.
Pen[edit]
Pen class: (Inheritance: CustomPen—>CanvasHelper—>Object)
Properties:
Color: Integer - The color of the pen Width: integer - Thickness of the pen
Methods:
getColor() setColor(color) getWidth() setWidth(width)
Brush[edit]
Brush class: (Inheritance: CustomBrush—>CanvasHelper—>Object)
Properties:
Color : Integer
Methods:
getColor() setColor()
Font[edit]
Font class: (Inheritance: CustomFont—>CanvasHelper—>Object)
createFont(): Returns a font object (default initialized based on the main ce window)
Properties:
Name: string Size: integer Color: integer
Methods:
getName(): Gets the fontname of the font setName(string): Sets the fontname of the font getSize(): Gets the size of the font setSize(integer): Sets the size of the font getColor(): Gets the color of the font setColor(integer): Sets the color of the font assign(font): Copies the contents of the font given as parameter to this font
Graphic[edit]
Graphic class: (Inheritance: Object) : Abstract class
Properties:
Width: integer Height: integer Transparent: boolean
Methods:
getWidth(graphic): Gets the current width in pixels of this graphics object setWidth(graphic, width): Sets thw width in pixels getHeight(graphic) setHeight(graphic, height)
RasterImage[edit]
RasterImage class: (Inheritance: Graphic—>Object) : Base class for some graphical controls
Properties:
Canvas: Canvas PixelFormat: PixelFormat - the pixelformat for this image. Will clear the current image if it had one. Supported pixelformats: pf1bit, pf4bit, pf8bit, pf15bit, pf16bit, pf24bit, pf32bit (recommended) TransparentColor: integer
Methods:
getCanvas(): Returns the Canvas object for this image getPixelFormat(): Returns the current pixelformat getPixelFormat(pixelformat): Sets the pixelformat for this image. Will clear the current image if it had one. Supported pixelformats: pf1bit, pf4bit, pf8bit, pf15bit, pf16bit, pf24bit, pf32bit (recommended) setTransparentColor(integer): Sets the color that will be rendered as transparent when drawn getTransparentColor(): Returns the color set to be transparent
Bitmap[edit]
Bitmap class: (Inheritance: CustomBitmap—>RasterImage—>Graphic—>Object) : Bitmap based Graphic object
createBitmap(width, height) - Returns a Bitmap object
PortableNetworkGraphic[edit]
PortableNetworkGraphic Class: (Inheritence: CustomBitmap—>RasterImage—>Graphic—>Object)
createPNG(width, height) - Returns a PortableNetworkGraphic object
JpegImage[edit]
JpegImage Class: (Inheritence: CustomBitmap—>RasterImage—>Graphic—>Object)
createJpeg(width, height) - Returns a Jpeg object
Picture[edit]
Picture class: (Inheritance: Object) : Container for the Graphic class
createPicture() : Returns a empty picture object
Properties:
Graphic PNG Bitmap Jpeg
Methods:
loadFromFile(filename) saveToFile(filename) loadFromStream(stream, originalextension OPTIONAL) : Loads a picture from a stream. Note that the stream position must be set to the start of the picture assign(sourcepicture) getGraphic() : Gets the Graphic object of this picture getPNG(): Returns a PortableNetworkGraphic Class object (Can be used from scratch) getBitmap(): Returns a Bitmap Class object (Can be used from scratch) getJpeg(): Returns a JpegImage Class object (Picture must be initialized with a jpeg file first)
GenericHotkey[edit]
GenericHotkey class: (Inheritance: Object)
createHotkey(function, keys, ...) : returns an initialized GenericHotkey class object. Maximum of 5 keys
createHotkey(function, {keys, ...}) : ^
Properties:
DelayBetweenActivate: integer - Interval in milliseconds that determines the minimum time between hotkey activations. If 0, the global delay is used onHotkey: The function to call when the hotkey is pressed
Methods:
getKeys() setKeys(key, ....) setOnHotkey(table) getOnHotkey
CommonDialog[edit]
CommonDialog class: (Inheritance: Object)
Properties: OnShow: function(sender) OnClose: function(sender) Title: string - The caption at top of the dialog Methods: Execute() : Shows the dialog and return true/false depending on the dialog
FindDialog[edit]
FindDialog class: (Inheritance: CommonDialog—>Component—>Object)
Properties:
FindText: String - The text the user wishes to find
Options: Enum - Find Options
{ frDown, frFindNext, frHideMatchCase, frHideWholeWord,
frHideUpDown, frMatchCase, frDisableMatchCase, frDisableUpDown,
frDisableWholeWord, frReplace, frReplaceAll, frWholeWord, frShowHelp,
frEntireScope, frHideEntireScope, frPromptOnReplace, frHidePromptOnReplace }
OnFind: function (sender) - Called when the find button has been clicked
OnHelp: function (sender) - Called when the help button is visible (see Options) and clicked
Methods:
-
FileDialog[edit]
FileDialog class: (Inheritance: CommonDialog—>Component—>Object)
Properties:
DefaultExt: string - When not using filters this will be the default extention used if no extension is given Files: Strings - Stringlist containing all selected files if multiple files are selected FileName: string - The filename that was selected Filter: string - A filter formatted string FilterIndex: integer - The index of which filter to use InitialDir: string - Sets the folder the filedialog will show first
Methods:
-
OpenDialog[edit]
OpenDialog class: (Inheritance: FileDialog—>CommonDialog—>Component—>Object)
createOpenDialog(owner) : Creates an opendialog object
Properties:
Options: String
A string formatted as "[param1, param2, param3]" to set OpenDialogs options
Valid parameters are:
ofReadOnly,
ofOverwritePrompt : if selected file exists shows a message, that file will be overwritten
ofHideReadOnly : hide read only file
ofNoChangeDir : do not change current directory
ofShowHelp : show a help button
ofNoValidate
ofAllowMultiSelect : allow multiselection
ofExtensionDifferent
ofPathMustExist : shows an error message if selected path does not exist
ofFileMustExist : shows an error message if selected file does not exist
ofCreatePrompt
ofShareAware
ofNoReadOnlyReturn : do not return filenames that are readonly
ofNoTestFileCreate
ofNoNetworkButton
ofNoLongNames
ofOldStyleDialog
ofNoDereferenceLinks : do not expand filenames
ofEnableIncludeNotify
ofEnableSizing : dialog can be resized, e.g. via the mouse
ofDontAddToRecent : do not add the path to the history list
ofForceShowHidden : show hidden files
ofViewDetail : details are OS and interface dependent
ofAutoPreview : details are OS and interface dependent
Methods:
-
SaveDialog[edit]
SaveDialog class: (Inheritance: OpenDialog—>FileDialog—>CommonDialog—>Component—>Object)
createSaveDialog(owner)
SelectDirectoryDialog[edit]
SelectDirectoryDialog class: (Inheritance: OpenDialog—>FileDialog—>CommonDialog—>Component—>Object)
createSelectDirectoryDialog(owner)
Stream[edit]
Stream class: (Inheritance: Object)
Properties:
Size: integer Position: integer
Methods:
copyFrom(stream, count) - Copies count bytes from the given stream to this stream read(count): bytetable - Returns a bytetable containing the bytes of the stream. This increases the position write(bytetable, count OPTIONAL)- Writes the given bytetable to the stream
MemoryStream[edit]
MemoryStream class: (Inheritance: Stream—>Object)
createMemoryStream()
Properties:
Memory: Integer - The address in Cheat Engine's memory this stream is loaded (READONLY, tends to change)
Methods:
loadFromFile(filename) : Replaces the contents in the memory stream with the contents of a file on disk saveToFile(filename) : Writes the contents of the memory stream to the specified file
FileStream[edit]
FileStream class: (Inheritance: HandleStream—>Stream—>Object)
createFileStream(filename, mode)
StringStream[edit]
StringStream class: (Inheritance: Stream—>Object)
createStringStream(string)
Properties:
DataString: The internal string
TableFile[edit]
TableFile class: (Inheritance: Object)
findTableFile(filename): Returns the TableFile class object for the saved file
Properties:
Name: string Stream: MemoryStream
Methods:
saveToFile(filename) getData() : Gets a MemoryStream object
xmplayer[edit]
xmplayer class: (Inheritance: Object)
The xmplayer class has already been defined as xmplayer, no need to create it manually
Properties:
IsPlaying: boolean - Indicator that the xmplayer is currently playing a xm file Initialized: boolean - Indicator that the xmplayer is actually actively loaded in memory
Methods:
setVolume(int) playXM(filename, OPTIONAL noloop) playXM(tablefile, OPTIONAL noloop) playXM(Stream, OPTIONAL noloop) pause() resume() stop()
CheatComponent[edit]
CheatComponent class: (Inheritance: WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
The cheatcomponent class is the component used in Cheat Engine 5.x trainers Most people will probably want to design their own components but for those that don't know much coding and use the autogenerated trainer this will be used
Properties:
Color: Integer - background color Textcolor: integer - text color Activationcolor: integer - The textcolor to show when activated is true Activated: boolean - Toggles between the ActivationColor and the TextColor Editleft:integer - The x position of the optional edit field Editwidth: integer - the width of the optional edit field Editvalue:string - The string of the optional edit field Hotkey:string read - The hotkeypart of the cheat line Description:string - Description part of the cheat line Hotkeyleft: integer - The x position of the hotkey line Descriptionleft:integer - The x position of the Description line ShowHotkey: boolean - Decides if the hotkey label should be shown HasEditBox: boolean - Decides if the editbox should be shown HasCheckbox: boolean - Decides if the checkbox should be shown Font: Font - The font to use to render the text
Methods:
-
MemoryRecordHotkey[edit]
MemoryRecordHotkey class: (Inheritance: Object)
The memoryrecord hotkey class is mainly readonly with the exception of the event properties to be used to automatically create trainers Use the genreric hotkey class if you wish to create your own hotkeys
Properties:
Owner: MemoryRecord - The memoryrecord this hotkey belongs to (ReadOnly) ID: integer - Unique id of this hotkey (ReadOnly) Description: string - The description of this hotkey (ReadOnly) HotkeyString: string - The hotkey formatted as a string (ReadOnly) OnHotkey: function(sender) - Function to be called when a hotkey has just been pressed OnPostHotkey: function(sender) - Function to be called when a hotkey has been pressed and the action has been performed
Methods:
doHotkey: Executes the hotkey as if it got triggered by the keyboard
MemoryRecord[edit]
MemoryRecord class: (Inheritance: Object)
The memoryrecord objects are the entries you see in the addresslist
Properties:
ID: Integer - Unique ID
Index: Integer - The index ID for this record. 0 is top. (ReadOnly)
Description: string- The description of the memory record
Address: string - Get/set the interpretable address string. Useful for simple address settings.
OffsetCount: integer - The number of offsets. Set to 0 for a normal address
Offset[]: integer - Array to access each offset
CurrentAddress: integer - The address the memoryrecord points to
Type: ValueType - The variable type of this record. See vtByte to vtCustom
If the type is vtString then the following properties are available:
String.Size: Number of characters in the string
String.Unicode: boolean
If the type is vtBinary then the following properties are available
Binary.Startbit: First bit to start reading from
Binary.Size: Number of bits
If the type is vtByteArray then the following properties are available
Aob.Size: Number of bytes
CustomTypeName: String - If the type is vtCustomType this will contain the name of the CustomType
Script: String - If the type is vtAutoAssembler this will contain the auto assembler script
Value: string - The value in stringform.
Selected: boolean - Set to true if selected (ReadOnly)
Active: boolean - Set to true to activate/freeze, false to deactivate/unfreeze
Color: integer
ShowAsHex: boolean - Self explanatory
ShowAsSigned: boolean - Self explanatory
AllowIncrease: boolean - Allow value increasing, unfreeze will reset it to false
AllowDecrease: boolean - Allow value decreasing, unfreeze will reset it to false
Count: Number of children
Child[index]: Array to access the child records
[index] = Child[index]
HotkeyCount: integer - Number of hotkeys attached to this memory record
Hotkey[]: Array to index the hotkeys
OnActivate: function(memoryrecord,before,currentstate):boolean - The function to call when the memoryrecord will change (or changed) Active to true.
If before is true, not returning true will cause the activation to stop.
OnDeactivate: function(memoryrecord,before,currentstate):boolean - The function to call when the memoryrecord will change (or changed) Active to false.
If before is true, not returning true will cause the deactivation to stop.
OnDestroy: function() - Called when the memoryrecord is destroyed.
DontSave: boolean - Don't save this memoryrecord and it's children
Methods:
getDescription() setDescription() getAddress(): Returns the interpretable addressstring of this record. If it is a pointer, it returns a second result as a table filled with the offsets setAddress(string): Sets the interpretable address string, and if offsets are provided make it a pointer getOffsetCount(): Returns the number of offsets for this memoryrecord setOffsetCount(integer): Lets you set the number of offsets getOffset(index): Gets the offset at the given index setOffset(index, value): Sets the offset at the given index getCurrentAddress(): Returns the current address as an integer (the final result of the interpretable address and pointer offsets) appendToEntry(memrec): Appends the current memory record to the given memory record getHotkey(index): Returns the hotkey from the hotkey array getHotkeyByID(integer): Returns the hotkey with the given id
Addresslist[edit]
Addresslist class: (Inheritance: Panel—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
Properties:
Count: Integer - The number of records in the table SelCount: integer- The number of records that are selected SelectedRecord: MemoryRecord - The main selected record MemoryRecord[]: MemoryRecord - Array to access the individial memory records [] = MemoryRecord - Default accessor
Methods:
getCount() getMemoryRecord(index) getMemoryRecordByDescription(description): returns a MemoryRecord object getMemoryRecordByID(ID) createMemoryRecord(): creates an generic cheat table entry and add it to the list getSelectedRecords(): Returns a table containing all the selected records doDescriptionChange(): Will show the GUI window to change the description of the selected entry doAddressChange(): Will show the GUI window to change the address of the selected entry doTypeChange(): Will show the GUI window to change the type of the selected entries doValueChange(): Will show the GUI window to change the value of the selected entries getSelectedRecord(): Gets the main selected memoryrecord setSelectedRecord(memrec): Sets the currently selected memoryrecord. This will unselect all other entries
MemScan[edit]
MemScan class: (Inheritance: Object)
getCurrentMemscan(): Returns the current memory scan object. If tabs are used the current tab's memscan object createMemScan(progressbar OPTIONAL): Returns a new MemScan class object
Properties:
OnScanDone: function(memscan) - Set a function to be called when the scan has finished FoundList: FoundList - The foundlist currently attached to this memscan object OnlyOneResult: boolean - If this is set to true memscan will stop scanning after having found the first result, and written the address to "Result" Result: Integer - If OnlyOneResult is used this will contain the address after a scan has finished
Methods:
firstScan(scanoption, vartype, roundingtype, input1, input2 ,startAddress ,stopAddress ,protectionflags ,alignmenttype, "alignmentparam", isHexadecimalInput, isNotABinaryString, isunicodescan, iscasesensitive);
Does an initial scan.
memscan: The MemScan object created with createMemScan
scanOption: Defines what type of scan is done. Valid values for firstscan are:
soUnknownValue: Unknown initial value scan
soExactValue: Exact Value scan
soValueBetween: Value between scan
soBiggerThan: Bigger than ... scan
soSmallerThan: smaller than ... scan
vartype: Defines the variable type. Valid variable types are:
vtByte
vtWord 2 bytes
vtDword 4 bytes
vtQword 8 bytes
vtSingle float
vtDouble
vtString
vtByteArray
vtGrouped
vtBinary
vtAll
roundingtype: Defined the way scans for exact value floating points are handled
rtRounded: Normal rounded scans. If exact value = "3" then it includes 3.0 to 3.49999999. If exact value is "3.0" it includes 3.00 to 3.0499999999
rtTruncated: Truncated algorithm. If exact value = "3" then it includes 3.0 to 3.99999999. If exact value is "3.0" it includes 3.00 to 3.099999999
rtExtremerounded: Rounded Extreme. If exact value = "3" then it includes 2.0000001 to 3.99999999. If exact value is "3.0" it includes 2.900000001 to 3.099999999
input1: If required by the scanoption this is a string of the given variable type
input2: If requires by the scanoption this is the secondary input
startAddress: The start address to scan from. You want to set this to 0
stopAddress : The address the scan should stop at. (You want to set this to 0xffffffffffffffff)
protectionflags: See aobscan about protectionflags
alignmenttype: Scan alignment type. Valid options are:
fsmNotAligned: No alignment check
fsmAligned : The address must be dividable by the value in alignmentparam
fsmLastDigits: The last digits of the address must end with the digits provided by alignmentparam
alignmentparam: String that holds the alignment parameter.
isHexadecimalInput: When true this will handle the input field as a hexadecimal string else decimal
isNotABinaryString: When true and the varType is vtBinary this will handle the input field as a decimal instead of a binary string
isunicodescan: When true and the vartype is vtString this will do a unicode (utf16) string scan else normal utf8 string
iscasesensitive: When true and the vartype is vtString this check if the case matches
nextScan(scanoption, roundingtype, input1,input2, isHexadecimalInput, isNotABinaryString, isunicodescan, iscasesensitive, ispercentagescan, savedresultname OPTIONAL);
Does a next scan based on the current addresslist and values of the previous scan or values of a saved scan
memscan: The MemScan object that has previously done a first scan
scanoption:
soExactValue: Exact Value scan
soValueBetween: Value between scan
soBiggerThan: Bigger than ... scan
soSmallerThan: smaller than ... scan
soIncreasedValue: Increased value scan
soIncreasedValueBy: Increased value by scan
soDecreasedValue: Decreased value scan
soDecreasedValueBy: Decreased value by scan
soChanged: Changed value scan
soUnchanged: Unchanged value scan
roundingtype: Defined the way scans for exact value floating points are handled
rtRounded: Normal rounded scans. If exact value = "3" then it includes 3.0 to 3.49999999. If exact value is "3.0" it includes 3.00 to 3.0499999999
rtTruncated: Truncated algoritm. If exact value = "3" then it includes 3.0 to 3.99999999. If exact value is "3.0" it includes 3.00 to 3.099999999
rtExtremerounded: Rounded Extreme. If exact value = "3" then it includes 2.0000001 to 3.99999999. If exact value is "3.0" it includes 2.900000001 to 3.099999999
input1: If required by the scanoption this is a string of the given variable type
input2: If requires by the scanoption this is the secondary input
isHexadecimalInput: When true this will handle the input field as a hexadecimal string else decimal
isNotABinaryString: When true and the varType is vtBinary this will handle the input field as a decimal instead of a binary string
isunicodescan: When true and the vartype is vtString this will do a unicode (utf16) string scan else normal utf8 string
iscasesensitive: When true and the vartype is vtString this check if the case matches
ispercentage: When true and the scanoption is of type soValueBetween, soIncreasedValueBy or soDecreasedValueBy will cause CE to do a precentage scan instead of a normal value scan
savedResultName: String that holds the name of a saved result list that should be compared against. First scan is called "FIRST"
newScan(): Clears the current results
waitTillDone(): Waits for the memscan thread(s) to finish scanning. Always use this
saveCurrentResults(name): Save the current scanresults to a unique name for this memscan. This save can be used to compare against in a subsequent next scan
getAttachedFoundlist(): Returns a FoundList object if one is attached to this scanresults. Returns nil otherwise
setOnlyOneResult(state): If set to true before you start a scan, this will cause the scanner to only return one result. Note that it does not work with a foundlist
getOnlyResult(): Only works if returnOnlyOneResult is true. Returns nil if not found, else returns the address that was found (integer)
- FoundList
- The foundlist is an object that opens the current memscan’s result file and provides an interface for reading out the addresses.
createFoundList[edit]
- createFoundList(memscan)
Properties:
Count: integer Address[index]: Value[index]:
Methods:
initialize(): Call this when a memscan has finished scanning. This will open the results for reading deinitialize(): Release the results getCount() getAddress(index): Returns the address as a string getValue(index): Returs the value as a string
Memoryview[edit]
Memoryview class: (Inheritance: Form—>ScrollingWinControl—>CustomControl—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
createMemoryView() - Creates a new memoryview window. This window will not receive debug events. Use getMemoryViewForm() function to get the main memoryview window
Properties:
DisassemblerView: The disassemblerview class of this memoryview object HexadecimalView: The hexadecimalview class of this memoryview object
Methods:
-
DisassemblerviewLine[edit]
DisassemblerviewLine class: (Inheritance: Object)
Properties:
Address: The current address of this line Owner: The Disassemblerview that owns this line
Methods:
-
Disassemblerview[edit]
Disassemblerview class: (Inheritance: Panel—>CustomControl—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
The visual disassembler used on the memory view window
Properties:
SelectedAddress: integer - The currently selected address in the disassemblerview SelectedAddress2: integer - The secondary selected address in the disassemblerview TopAddress: Integer - The first address to show ShowJumplines: boolean - Determines if the jumplines should be shown OnSelectionChange: function(sender, address, address2) - Function to call when the selection has changed OnExtraLineRender: function(sender, Address, AboveInstruction, Selected): RasterImage OPTIONAL, x OPTIONAL, y OPTIONAL Function to call when you wish to provide the disassembler view with an extra image containing data you wish to show. This function is called once to get an image to show above the instruction, and once to get an image to show under the instruction and optional comments. The image for both calls must be different objects as rendering will only be done when both calls have been completed Sender is a DisassemblerviewLine object. If no coordinates are given the image will be centered above/below the instruction.
Methods:
-
Hexadecimal[edit]
Hexadecimal class: (Inheritance: Panel—>CustomControl—>WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
The visual hexadecimal object used on the memory view window
Properties:
OnAddressChange(hexadecimalview, function): function(hexadecimalview, address) OnByteSelect(hexadecimalview, function): function(hexadecimalview, address, address2)
Methods:
-
Thread[edit]
Thread class: (Inheritance: Object)
createNativeThread(function(Thread,...), ...): Executes the given function in another thread using the systems thread mechanism The function returns the Thread class object function declaration: function (Thread, ...)
Properties:
name: string - This name will be shown when the thread terminated abnormally
Methods:
freeOnTerminate(state): When set to true the thread object will free itself when the function ends (default=true) Note: Use this only from inside the thread function as the thread might have already terminated and freed itself when called synchronize(function(thread, ...), ...): Called from inside the thread. This wil cause the tread to get the main thread to execute the given function and wait for it to finish. Usually for GUI access Returns the return value of the given function waitfor(): Waits for the given thread to finish (Not recommended to call this from inside the thread itself)
StructureFrm[edit]
StructureFrm class: (Inheritance: Object)
createStructureForm(address)
Properties:
Column[index]: structColumn - Fetches a structColumn object from the structure form Group[index]: structGroup - Fetches a structGroup object from the structure form Methods: structChange(): Forces a refresh addColumn(): Adds a new column in the currently focuses group and returns it's structColumn object addGroup(): Adds a new group and returns the structGroup object
structColumn[edit]
structColumn class: (Inheritance: Object)
Properties:
Address: integer - The current address AddressText: string - Gets/sets the visual address Focused: boolean - Gets/sets the focused state
Methods:
focus(): focuses the current column
structGroup[edit]
structGroup class: (Inheritance: Object)
Properties:
name: string - gets the current name box: Groupbox - Gets the groupbox object columnCount: integer- Gets the number of columns in the group columns[index]: structColumn - Returns the specific structColumn object
Methods:
addColumns(): Adds a new columns to the specific group and returns it's structColumn objecy
structure[edit]
structure class: (Inheritance: Object)
getStructureCount(): Returns the number of Global structures. (Global structures are the visible structures) getStructure(index): Returns the Structure object at the given index createStructure(name): Returns an empty structure object (Not yet added to the Global list. Call structure.addToGlobalStructureList manually)
Properties:
Name: String - The name of the structure Size: Integer - The number of bytes between the last element and the start. ReadOnly Count: Integer - Number of elements in the structure. ReadOnly Element[]: structureElement - Returns the structure element at the given index. Readonly
Methods:
getName(): Returns the name setName(name): Sets the name getElement(index): Returns a structureElement object (Changing offsets can change the index) getElementByOffset(offset): Returns a structureElement object where the specified offset is at least the requested offset addElement(): Adds a new blank structureElement and returns it autoGuess(baseaddresstoguessfrom, offset, size) fillFromDotNetAddress(address, changeName): Fills the structure with the layout gathered from querying .NET. If changeName is true, the structure will take the name of the .NET class. (6.4+) beginUpdate(): Call this when you want to make multiple updates to a structure. It will speed up the update process endUpdate(): Call this when done addToGlobalStructureList(): Add this to the list of structures for the user to select from. (Global structures will get saved to the table) removeFromGlobalStructureList(): Remove from the list of structures.
StructureElement[edit]
StructureElement class: (Inheritance: Object)
Properties:
Owner: structure - The structure this element belongs to. Readonly Offset: integer - The offset of this element Name: string - The name of this element Vartype: integer - The variable type of this element ChildStruct: structure - If not nil this element is a pointer to the structure defined here ChildStructStart: integer - The number of bytes inside the provided childstruct. (E.g: It might point to offset 10 of a certain structure) Bytesize: integer - The number of bytes of this element. Readonly for basic types, writable for types that require a defined length like strings and array of bytes
Methods:
getOwnerStructure(): Returns the structure this element belongs to getOffset(): Returns the offset of this element setOffset(offset): Sets the offset of this element getName(): Returns the name of this element setName(name): Sets the name of this element (tip: Leave blank if you only want to set the name of the variable) getVartype(): Returns the variable type of this element (check Variable types in defines.lua) setVartype(vartype) getChildStruct() setChildStruct(structure) getChildStructStart() setChildStructStart(offset) getBytesize(): Gets the bytesize of the element. Usually returns the size of the type, except for string and aob setBytesize(size): sets the bytesize for types that are affected (string, aob)
supportCheatEngine[edit]
- supportCheatEngine(attachwindow, hasclosebutton, width, height, position ,yoururl OPTIONAL, extraparameters OPTIONAL, percentageshown OPTIONAL)
- Will show an advertising window which will help keep the development of Cheat Engine going.
- If you provide your own url it will be shown Up to 75% of the time.
- attachwindow: form : The form that the ad is attached to
- hasclosebutton: boolean : If true the window will have a border an a close button at top
- width, height: integer : The client width and height of the window.
- Prefered formats: 120×600, 160×600, 300×250, 468×60, 728×90, But you are free to use different formats.
- width, height: integer : The client width and height of the window.
- Position: integer/enum: The place of the window
- 0=Top
- 1=Right
- 2=Bottom
- 3=left
- Yoururl: string: The url you want to show. When given instead of showing CE’s ads 100% it will show your url up to 75%.
-
- You can use it for your own income, or for updating users about new versions of your trainer or whatever you feel like
- Extraparameters: string: are url request parameters you can add to the default parameters (e.g trainername=mytrainer for tracking purposes).
- PercentageShown: You can change the default of 75% to a smaller value like 50%.
fuckCheatEngine[edit]
- fuckCheatEngine()
- Removes the ad window if it was showing
Following are some more internal functions for Cheat Engine[edit]
dbk_initialize[edit]
- dbk_initialize()
- Returns true if the dbk driver is loaded in memory. False if it failed for whatever reason (e.g 64-bit and not booted with unsigned driver support)
dbk_useKernelmodeOpenProcess[edit]
- dbk_useKernelmodeOpenProcess()
- Switches the internal pointer of the OpenProcess api to dbk_OpenProcess
dbk_useKernelmodeProcessMemoryAccess[edit]
- dbk_useKernelmodeProcessMemoryAccess()
- Switches the internal pointer to the ReadProcessMemory and WriteProcessMemory apis to dbk_ReadProcessMemory and
dbk_WriteProcessMemory[edit]
- dbk_WriteProcessMemory
- —
dbk_useKernelmodeQueryMemoryRegions[edit]
- dbk_useKernelmodeQueryMemoryRegions()
- Switches the internal pointer to the QueryVirtualMemory api to dbk_QueryVirtualMemory
dbk_getPEProcess[edit]
- dbk_getPEProcess(processid)
- Returns the pointer of the EProcess structure of the selected processid
dbk_getPEThread[edit]
- dbk_getPEThread(threadid)
- Gets the pointer to the EThread structure
dbk_readMSR[edit]
- dbk_readMSR(msr)
- Reads the msr
dbk_writeMSR[edit]
- dbk_writeMSR(msr, msrvalue)
- Writes the msr
dbk_executeKernelMemory[edit]
- dbk_executeKernelMemory(address, parameter)
- Executes a routine from kernelmode (e.g a routine written there with auto assembler) parameter can be a value or an address. It’s up to your code how it’s handled
dbvm_initialize[edit]
- dbvm_initialize(offloados OPTIONAL)
- Initializes the dbvm functions (dbk_initialize also calls this) offloados is a boolean that when set will offload the system onto dbvm if it’s not yet running (and only IF the dbk driver is loaded)
dbvm_readMSR[edit]
- dbvm_readMSR(msr)
- See dbk_readMSR
dbvm_writeMSR[edit]
- dbvm_writeMSR(msr, value)
- See dbk_writeMSR
dbk_getCR0[edit]
- dbk_getCR0()
- Returns Control Register 0
dbk_getCR3[edit]
- dbk_getCR3()
- Returns Control Register 3 of the currently opened process
dbk_getCR4[edit]
- dbk_getCR4()
- Returns Control Register 4
dbk_getPhysicalAddress[edit]
- dbk_getPhysicalAddress(address)
- Returns the physical address of the given address
dbk_writesIgnoreWriteProtection[edit]
- dbk_writesIgnoreWriteProtection(state)
- Set to true if you do not wish to initiate copy-on-write behaviour
dbvm_getCR4[edit]
- dbvm_getCR4()
- Returns the real Control Register 4 state
onAPIPointerChange[edit]
- onAPIPointerChange(function)
- Registers a callback when an api pointer is changed (can happen when the user clicks ok in settings, or when dbk_use*** is used. Does
NOT happen when setAPIPointer is called)
setAPIPointer[edit]
- setAPIPointer(functionid, address)
- Sets the pointer of the given api to the given address. The address can be a predefined address set at initialization by Cheat Engine, or an address you got from an autoassembler script or injected dll (When Cheat Engine itself was targeted)
functionid:
0: OpenProcess
Known compatible address defines:
windows_OpenProcess
dbk_OpenProcess
1: ReadProcessMemory
Known compatible address defines:
windows_ReadProcessMemory
dbk_ReadProcessMemory
dbk_ReadPhysicalMemory
dbvm_ReadPhysicalMemory
2: WriteProcessMemory
Known compatible address defines:
windows_WriteProcessMemory
dbk_WriteProcessMemory
dbk_WritePhysicalMemory
dbvm_WritePhysicalMemory
3: VirtualQueryEx
Known compatible address defines:
windows_VirtualQueryEx
dbk_VirtualQueryEx
VirtualQueryExPhysical
Extra variables defined:
dbk_NtOpenProcess[edit]
- dbk_NtOpenProcess
- Address of the NtOpenProcess implementation in DBK32
The dbvm_ addresses should only be used with auto assembler scripts injected into Cheat Engine
dbvm_block_interrupts[edit]
- dbvm_block_interrupts
- Address of function dbvm_block_interrupts: DWORD; stdcall;
dbvm_raise_privilege[edit]
- dbvm_raise_privilege
- Address of function dbvm_raise_privilege: DWORD; stdcall;
dbvm_restore_interrupts[edit]
- dbvm_restore_interrupts
- Address of function dbvm_restore_interrupts: DWORD; stdcall;
dbvm_changeselectors[edit]
- dbvm_changeselectors
- Address of function dbvm_changeselectors(cs,ss,ds,es,fs,gs: dword): DWORD; stdcall;
D3DHOOK[edit]
D3DHOOK class: (Inheritance: Object)
The d3dhook functions provide a method to render graphics and text inside the game, as long as it is running in directx9, 10 or 11
createD3DHook(textureandcommandlistsize OPTIONAL, hookmessages OPTIONAL): Hooks direct3d and allocates a buffer with given size for storage of for the rendercommand list hookmessages defines if you want to hook the windows message handler for the direct3d window. The d3dhook_onClick function makes use of that If no size is provided 16MB is used and hookmessages is true Note: You can call this only once for a process It returns a d3dhook object
Properties:
Width: Integer: The width of the screen (readonly)
Height: integer: The height of the screen (readonly)
DisabledZBuffer: boolean: Set this to true if you don't want previously rendered walls to overlap a newly rendered object (e.g map is rendered first, then the players are rendered)
WireframeMode: boolean: Set this to true if you don't want the faces of 3d objects to be filled
MouseClip: boolean: Set this if to true if you have one of those games where your mouse can go outside of the gamewindow and you don't want that.
OnClick: function(d3dhook_sprite, x, y)
A function to be called when clicked on an sprite (excluding the mouse)
x and y are coordinates in the sprite object. If sprites overlap the highest zorder sprite will be given. It does NOT care if a transparent part is clicked or not
Note: If you set this it can cause a slowdown in the game if there are a lot of sprites and you press the left button a lot
OnKeyDown: function(virtualkey, char)
function(vkey, char): boolean
A function to be called when a key is pressed in the game window (Not compatible with DirectInput8)
Return false if you do not wish this key event to pass down to the game
Methods:
beginUpdate(): Use this function when you intent to update multiple sprites,textcontainers or textures. Otherwise artifacts may occur (sprite 1 might be drawn at the new location while sprite 2 might still be at the old location when a frame is rendered) endUpdate(): When done updating, call this function to apply the changes enableConsole(virtualkey): Adds a (lua)console to the specific game. The given key will bring it up (0xc0=tilde) createTexture(filename): Returns a d3dhook_texture object createTexture(picture, transparentColor OPTIONAL): Returns a d3dhook_texture object if the picture is not a transparent image the transparentcolor parameter can be used to make one of it's colors transparent createFontmap(font): Returns a d3dhook_fontmap object created from the given font createSprite(d3dhook_texture): returns a d3dhook_sprite object that uses the given texture for rendering createTextContainer(d3dhook_fontmap, x, y, text): Returns a d3dhook_textContainer object
D3DHook_Texture[edit]
D3DHook_Texture class: (Inheritance: Object)
This class controls the texture in memory. Without a sprite to use it, it won’t show
Properties:
Height: integer (ReadOnly) Width: integer (ReadOnly)
Methods:
loadTextureByPicture(picture)
D3DHook_FontMap[edit]
D3DHook_FontMap class: (Inheritance: D3DHook_Texture—>Object)
A fontmap is a texture that contains extra data regarding the characters. This class is used by the textcontainer
Current implementation only supports 96 characters (character 32 to 127)
Properties:
-
Methods:
changeFont(font): Changes the fontmap to the selected font getTextWidth(string): Returns the width of the given string in pixels
D3DHook_RenderObject[edit]
D3DHook_RenderObject class: (Inheritance: Object)
The renderobject is the abstract class used to control in what manner objects are rendered.
The sprite and TextContainer classed inherit from this
Properties:
X: Float - The x-coordinate of the object on the screen Y: Float - The y-coordinate of the object on the screen CenterX: Float - X coordinate inside the object. It defines the rotation spot and affects the X position CenterY: Float - Y " " Rotation: Float - Rotation value in degrees (0 and 360 are the same) Alphablend: Float - Alphablend value. 1.0 is fully visible, 0.0=invisible Visible: boolean - Set to false to hide the object ZOrder: integer - Determines if the object will be shown in front or behind another object
Methods:
-
D3DHook_Sprite[edit]
D3DHook_Sprite class: (Inheritance: D3DHook_RenderObject—>Object)
A d3dhook_sprite class is a visible texture on the screen.
Properties:
Width: Integer - The width of the sprite in pixels. Default is the initial texture width Height: Integer - The height of the sprite in pixels. Default is the initial texture height Texture: d3dhook_texture - The texture to show on the screen
Methods:
-
D3Dhook_TextContainer[edit]
D3Dhook_TextContainer class: (Inheritance: D3DHook_RenderObject—>Object)
A d3dhook_sprite class draws a piece of text on the screen based on the used fontmap.
While you could use a texture with the text, updating a texture in memory is slow. So if you wish to do a lot of text updates, use a textcontainer
Properties:
FontMap: The D3DHook_FontMap object to use for rendering text Text: The text to render
Methods:
-
Disassembler[edit]
Disassembler class: (Inheritance: Object)
createDisassembler() - Creates a disassembler object that can be used to disassemble an instruction and at the same time get more data
getDefaultDisassembler() - Returns the default disassembler object used by a lot of ce's disassembler routines
getVisibleDisassembler() - Returns the disassembler used by the disassemblerview. Special codes are: {H}=Hex value {R}=Register {S}=Symbol {N}=Nothing special
registerGlobalDisassembleOverride(function(sender: Disassembler, address: integer, LastDisassembleData: Table): opcode, description): Same as
Disassembler.OnDisassembleOverride, but does it for all disassemblers, including newly created ones. Tip: Check the sender to see if you should use syntax
highlighting codes or not
This function returns an ID you can pass on to unregisterGlobalDisassembleOverride() 6.4+
unregisterGlobalDisassembleOverride(id)
Properties:
LastDisassembleData: Table OnDisassembleOverride: function(sender: Disassembler, address: integer, LastDisassembleData: Table): opcode, description syntaxhighlighting: boolean: This property is set if the syntax highlighting codes are accepted or not
Methods:
disassemble(address): Disassembles the given instruction and returns the opcode. It also fills in a LastDisassembleData record
decodeLastParametersToString(): Returns the unedited "Comments" information. Does not display userdefined comments
getLastDisassembleData(): Returns the LastDisassembleData table.
The table is build-up as follow:
address: integer - The address that was disassembled
opcode: string - The opcode without parameters
parameters: string - The parameters
description: string - The description of this opcode
bytes: table - A table containing the bytes this instruction consists of (1.. )
modrmValueType: DisAssemblerValueType - Defines the type of the modrmValue field (dvtNone=0, dvtAddress=1, dvtValue=2)
modrmValue: Integer - The value that the modrm specified. modrmValueType defines what kind of value
parameterValueType: DisAssemblerValueType
parameterValue: Integer - The value that the parameter part specified
isJump: boolean - Set to true if the disassembled instruction can change the EIP/RIP (not ret)
isCall: boolean - Set to true if it's a Call
isRet: boolean - Set to true if it's a Ret
isConditionalJump: boolean - Set to true if it's a conditional jump
DissectCode[edit]
DissectCode class: (Inheritance: Object)
getDissectCode(): Creates or returns the current code DissectCode object
Properties:
-
Methods:
clear(): Clears all data dissect(modulename): Dissects the memory of a module dissect(base,size): Dissect the specified memory region addReference(fromAddress, ToAddress, type, OPTIONAL isstring): Adds a reference. Type can be jtCall, jtUnconditional, jtConditional, jtMemory In case of jtMemory setting isstring to true will add it to the referenced strings list deleteReference(fromAddress, ToAddress) getReferences(address): Returns a table containing the addresses that reference this address and the type getReferencedStrings(): Returns a table of addresses and their strings that have been referenced. Use getReferences to find out which addresses that are getReferencedFunctions(): Returns a table of functions that have been referenced. Use getReferences to find out which callers that are saveToFile(filename) loadFromFile(filename)
RIPRelativeScanner[edit]
RIPRelativeScanner class: (Inheritance: Object)
createRipRelativeScanner(modulename): Creates a RIP relative scanner. This will scan the provided module for RIP relative instructions which you can use for whatever you like
Properties:
Count: integer - The number of instructions found that have a RIP relative address Address[]: integer - An array to access the results. The address is the address of the RIP relative offset in the instruction
Methods:
-
LuaPipe[edit]
LuaPipe class: (Inheritance: Object)
Abstract class that LuaPipeServer and LuaPipeclient inherit from. It implements the data transmission methods
Properties:
Connected: boolean: True if the pipe is connected
Methods:
lock(): Acquire a lick on this pipe till unlock is called. If lock can not be acquired, wait. Recursive calls are allowed unlock() writeBytes(ByteTable, size OPTIONAL): Writes the provided byte table to the pipe. if size is not provided, the whole table is sent. Returns the number of bytes sent, or nil on failure readBytes(size: integer): returns a byte table from the pipe, or nil on failure readDouble(): Read a double from the pipe, nil on failure readFloat(): Read a float from the pipe, nil on failure readQword(): Read an 8 byte value from the pipe, nil on failure readDword(): Read a 4 byte value from the pipe, nil on failure readWord(): Read a 2 byte value from the pipe, nil on failure readByte(): Read a byte from the pipe, nil on failure readString(size: integer): Reads a string from the pipe, nil on failure. (Can support 0-byte chars) readWideString(size: integer): Reads a widestring from the pipe, nil on failure writeDouble(v: double): Writes a double to the pipe. Returns the number of bytes sent, nil on failure writeFloat(v: single): writes a float to the pipe. Returns the number of bytes sent, nil on failure writeQword(v: qword): writes an 8 byte value to the pipe. Returns the number of bytes sent, nil on failure writeDword(v: dword): writes a 4 byte value to the pipe. Returns the number of bytes sent, nil on failure writeWord(v: word): writes a word to the pipe. Returns the number of bytes sent, nil on failure writeByte(v: byte): writes a byte to the pipe. Returns the number of bytes sent, nil on failure writeString(str: string; include0terminator: boolean OPTIONAL); Writes a string to the pipe. If include0terminator is false or not provided it will not write the 0 terminator byte. Returns the number of bytes written, or nil on failure writeWideString(str: widestring; include0terminator: boolean OPTIONAL); Writes a widestring to the pipe. If include0terminator is false or not provided it will not write the 0 terminator bytes. Returns the number of bytes written, or nil on failure
LuaPipeClient[edit]
LuaPipeClient class: (Inheritance: LuaPipe—>Object)
Class implementing a client that connects to a pipe
connectToPipe(pipename): Returns a LuaPipeClient connected to the given pipename. Nil if the connection fails
Properties:
-
Methods:
-
LuaPipeServer[edit]
LuaPipeServer class: (Inheritance: LuaPipe—>Object)
Class launching the server side of a pipe
createPipe(pipename, inputsize OPTIONAL, outputsize OPTIONAL): Creates a LuaPipeServer which can be connected to by a pipe client. InputSize and Outputsize define buffers how much data can be in the specific buffer before the writer halts. Default input and output size is 4096 for both
Properties:
valid: boolean - Returns true if the pipe has been created properly. False on failure (e.g wrong pipename)
Methods:
acceptConnection() - Waits for a client to connect to this pipe (Warning: Freezes the thread this is executed in)
openLuaServer[edit]
- openLuaServer(Name)
- Opens a pipe with the given name. The LuaClient dll needs this name to connect to ce
LuaClient.dll functions:
- BOOL CELUA_Initialize(char *name)
- Initializes
- UINT_PTR CELUA_ExecuteFunction(char *luacode, UINT_PTR parameter)
- This function executes a lua function with parameters (parameter) and with the luacode as body Parameter will be treated as an integer
In short:
function(parameter)
<luacode>
end
The return value of this function is the return value of the lua function (integer)
Settings class[edit]
This class can be used to read out and set settings of cheat engine and of plugins, and store your own data
global functions[edit]
getSettings[edit]
- getSettings(path Optional)
- Returns a settings object. If path is nil it will points to the Cheat Engine main settings (Registry) . If name is provides the settings currently accessed will be the one at the subkey provided
- Note: Keep in mind that it returns a new object each call, even if he same name is used multiple times
- Properties:
- Path: string — Gets/Sets the current subkey (nil if main)
- Value[]: A table access into the settings. e.g: Value[«Count»]=12
- Methods:
- —
- Properties:
SymbolList class[edit]
This class can be used to look up an address to a symbolname, and a symbolname to an address
It can also be registered with the internal symbol handler of cheat engine
This class makes use of a special «Symbol» table construction that contains size and optionally other data
- Symbol Table:
- modulename: string
- searchkey: string
- address: integer
- symbolsize: integer
Global functions
createSymbolList[edit]
- createSymbolList()
- Creates an empty symbollist.
- Properties:
- —
- Methods:
- clear():
- getSymbolFromAddress(address): Searches the list for the given address. The address does not have to match the exact address. As long as it falls withing the range
- getSymbolFromString(searchkey):
- addSymbol(modulename, searchkey, address, symbolsize, skipAddressToSymbolLookup OPTIONAL, extradata OPTIONAL): Adds a symbol to the symbollist
- extradata is a table which can be used to fill in a return type and parameters for function calls. It has the following fields:
-
- returntype: string
- parameters: string
-
- extradata is a table which can be used to fill in a return type and parameters for function calls. It has the following fields:
- Properties:
deleteSymbol[edit]
- deleteSymbol(searchkey)
- —
deleteSymbol[edit]
- deleteSymbol(address)
- —
register[edit]
- register()
- Registers the current symbol list with the symbol handler
unregister[edit]
- unregister()
- Unregisters the current symbol list from the symbol handler
Pagecontrol[edit]
Pagecontrol class: (WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
This is an object that can hold multiple pages
Global functions
- createPageControl(owner)
-
- Properties:
- ShowTabs: boolean — Shows the tabs
- TabIndex: integer — Gets and sets the current tab
- ActivePage: TabSheet — Returns the current tabsheet.
- PageCount: integer — Gets the number of pages
- Page[]: TabSheet — Get a specific page (TabSheet)
- Methods:
- addTab(): TabSheet — Creates a new TabSheet
- Properties:
TabSheet[edit]
TabSheet class: (WinControl—>Control—>Component—>Object)
Part of a page control. This object can contain other objects
Properties:
TabIndex: integer - the current index in the pagelist of the owning pagecontrol
Methods:
-
Links[edit]
- Help File
- Back
- Next
Lua interaction is done a few ways in Cheat Engine.
- You have the Lua Engine that you can access from the memory view form by selecting Tools then selecting Lua Engine. You can debug the scripts written here by setting a breakpoint by clicking next to the line numbers. This is mostly used for testing since it is not saved with the cheat table in any way. Also it is easy to do a lot of work and then have CE crash losing it all, so make sure to grab this autorun script. One other useful feature is that you can return a table and CE will attempt to print it for you whereas lua’s default for print is to do nothing and tostring just returns something like table: 0000000004195640
- There is a lua script associated with your cheat table that you access from the Cheat Engine main form menu by selecting Table then select Show Cheat Table Lua Script. This is the script that CE (settings dependent) prompts you to execute when you open a CT/CETrainer file with a lua script. You can also load and execute other lua scripts from here.
- There is the luaCall Auto Assembler command, that you pass a single line Lua script to (you can use ; for new lines!). You can open an auto assembler form from the memory viewer Tools->Auto Assemble menu option (shortcut `Ctrl+A`) or from the Cheat Engine main form by pressing Ctrl+Alt+A.
-
luaCall(print('I have the power!'))
-
- Then there is making use of the {$lua} tag in an Auto Assembler script. See previous luaCall description for how to open the AA form.
- Note this code is executed before any of the AA code, and that’s for the following purpose:
- If you return a string from the {$lua} tag it will be treated as Auto Assembly code in the location of that lua block. And yes, you can return a string that contains another lua block but you have to do something like
return "{$lua}nprint('hi')n{$asm}"since CE seems to want the {$…} tags without whitespace but actually having it without whitespace in a multiline string (
[[like this]]
) causes the original lua block to be terminated prematurely
- If you return a string from the {$lua} tag it will be treated as Auto Assembly code in the location of that lua block. And yes, you can return a string that contains another lua block but you have to do something like
- With this (since CE 6.7) you have access to the memrec and syntaxcheck variables, memrec is the memory record the script is in (can be nil when assigning the script to the table or executing the code without assigning it) while syntaxcheck is true if Cheat Engine is running the script to check the syntax of the AA code (such as when editing the script) and false when it’s actually enabling the memory record script.
{$lua} -- code before either enable/disable section runs for both just like with AA code if syntaxcheck then return end if memrec then print(memrec.Description) end -- the check is not really necessary but it is technically correct to have it ------------------------------ ENABLE ------------------------------ -- yes [ENABLE]/[DISABLE] are valid inside of a lua block [ENABLE] ------------------------------ DISABLE ------------------------------ [DISABLE]
Lua Engine
The Lua Engine form contains a text box for lua’s standard output (print calls use the standard output) as well as an interactive script box that you can directly execute lua script. You can open or save scripts from here.
Cheat table lua script
From the Cheat Engine main form press Ctrl+Alt+L, to open the cheat table lua script form.
This script is associated with the cheat table. By default when opening a cheat table file Cheat Engine will prompt you that the table has a table lua script and asking you if you want to execute it.
Note: You can change what Cheat Engine does with the cheat table Lua script in the Cheat Engine general settings.
From the cheat table lua script form menu you can select file then select new window to open new script windows.
Script windows
You can debug the scripts written here by setting a breakpoint by clicking next to the line numbers.
You can have as many script windows open as you want, simply click File then New Window. If you save these scripts as lua files in the same directory as your cheat table or any directory included in the
package.path
string. You can run them from other scripts using lua’s require, which will only run a script the first time it’s required (or if package.loaded.filename is set to nil), and dofile, which will run a script every time you call it. Note that you do not use the extension with require, «.lua» is assumed, but you do need it with dofile.
Code:
require(‘Script1’)
dofile(‘Script1.lua’)
require(‘Script1’)
Output:
Script1 Executing…
Script1 Executing…
—
—
Script1 Executing…
See also
- Lua
- Tutorials
- Auto Assembler Basics
External links
- www.lua.org
- github.com/rjpcomputing/luaforwindows
- wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Lua
- lua.org — Getting started
- lua-users.org — Tutorial directory
Syntax Highlighter
- pinetools.com/syntax-highlighter
Cheat Engine– полезнейшая программа в арсенале любого геймера. Изменить внутренние параметры игры и «создать» себе нужное количество игрового золота, боеприпасов или любых других ресурсов в несколько кликов мышки, вот предназначение этой программы. К сожалению, у многих игроков при первом использовании возникают вопросы, как ею правильно пользоваться, поэтому мы написали для вас подробною инструкцию, как пользоваться Cheat Engine.
Инструкция будет показана на примере старой доброй игры Age of Empires III, где мы «наколдуем» себе пару миллионов игровых монет. Итак, для начала скачайте последнюю версию cheat engine и запустите сначала ее, а затем игру.
Делай раз
Запустим какую-нибудь миссию в игре и увидим, что золота у нас не так что бы уж очень много – 200.
Запомним это значение и откроем через alt+tab окно с нашей программой. Здесь вам нужно будет выбрать игровой процесс (1), в строку поиска ввести искомое значение (2) и нажать кнопку “Поиск” (3).
В этот момент Cheat Engine просканирует память игры на предмет наличия этого значения. Скорее всего, в результате вы получите огромное количество результатов и понять какой именно отвечает за наше золото будет непросто.
Делай два
Поэтому возвращаемся к игре и отправим поселенцев заработать немного денег, что бы изменить их количество.
Переключаемся опять к cheat engine, вводим в строку поиска новое значение (4) и запускаем повторное сканирование кнопкой “Отсев” (5), что бы программа искала изменение значений только среди результатов первого сканирования.
Как видите, результатов осталось всего два. Выберете их мышкой, щелкните правой клавишей и нажмите “Добавить выбранные адреса в таблицу”.
Делай три
Теперь в таблице выберете эти два значения, нажмите на них правой кнопкой мыши и проследуйте по пути “Изменить ” – “Значение”.
И устанавливайте нужное вам. Например, 10000. Теперь возвращайтесь в игру, и вуаля – теперь количество золота у вас равно десяти тысячам. Таким же образом вы можете изменять любые другие значения в любых играх. Удачи в экспериментах!
Твитнуть
Поделиться
Плюсануть
Поделиться
Программа предназначенная для взлома игр. Позволяет искать в памяти многих запущенных приложений какие то конкретные значения (патронов, жизней, очков), изменяя данные значения в памяти — меняем их в игре.
Для удобства позволяет сохранять таблицы адресов таких значений, давая возможность игрокам создавать некое подобие трейнеров в среде Cheat Engine.
Установка:
1) Распаковать архив.
2) Запустить CheatEngine74.exe и следовать инструкциям установщика.
Установка русификатора:
1) Скопировать содержимое папки «RUS» в корневую папку с установленной программой Cheat Engine
2) При первом запуске Cheat Engine появиться окно с предложением выбрать язык программы.
Выберите «Russian» и нажмите «Ok». Перезапустите Cheat Engine.
Если по каким-либо причинам окно выбора языка не появилось, то зайдите в настройки Cheat Engine.
Выберите меню «Languages», затемы выберите «Russian» и нажмите кнопку «Select Language». Перезапустите Cheat Engine.
Старые версии Cheat Engine:
Спойлер
Свежие таблицы для игр вы сможете найти здесь.