Download Article
Download Article
Are you bored of the plain white text on black background in cmd? If yes then read on to know how to change the text colour and the background colour.
-
1
Press windows + R to open run.
-
2
Type ‘cmd’ (without the quotes) and click ok.
Advertisement
-
3
Type color z to get the list of all colors and numbers or letters assigned for them. The first letter/number in the command is the colour of the background and the second is the colour of the text.
-
4
Type color letter/number to change the text color. Use the letter/number for the color you want. e.g. Type ‘color 6’ to have yellow text, ‘color 4’ to have red text, ‘color A’ to have light green text etc. ( Ignore all quotes )
-
5
To change the colour of the text as well as the background, type ‘color ce’ ( without the quotes ) to have light yellow text on a light red background or any other combination.
Advertisement
-
1
Open Command Prompt.
-
2
Right-click on the top.
-
3
Click on Properties.
-
4
Go to the Colors tab.
-
5
Select text or background and edit the color values.
- Play around with the combinations!
-
6
Click ok to apply changes.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
Can I color certain letters or words?
Yes. Right click on the tab or image, then go to properties, then go to color and you can change the background color and the letters.
-
Question
How do I do this in a specific batch file?
Flashlight
Community Answer
Simply type the same command line code you used into the batch before echoing.
-
Question
How do I change my command prompt color to a rainbow color?
CaTsArEsOcUtE
Community Answer
I do not think there is a way to change it to rainbow color.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
List of Possible Colors
- 0 = Black
- 1 = Blue
- 2 = Green
- 3 = Aqua
- 4 = Red
- 5 = Purple
- 6 = Yellow
- 7 = White
- 8 = Gray
- 9 = Light Blue
- A = Light Green
- B = Light Aqua
- C = Light Red
- D = Light Purple
- E = Light Yellow
- F = Bright White
-
Be careful of the spellings of ‘color’ and do not type ‘colour’. Otherwise it will not work.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 405,699 times.
Is this article up to date?
Download Article
Download Article
Are you bored of the plain white text on black background in cmd? If yes then read on to know how to change the text colour and the background colour.
-
1
Press windows + R to open run.
-
2
Type ‘cmd’ (without the quotes) and click ok.
Advertisement
-
3
Type color z to get the list of all colors and numbers or letters assigned for them. The first letter/number in the command is the colour of the background and the second is the colour of the text.
-
4
Type color letter/number to change the text color. Use the letter/number for the color you want. e.g. Type ‘color 6’ to have yellow text, ‘color 4’ to have red text, ‘color A’ to have light green text etc. ( Ignore all quotes )
-
5
To change the colour of the text as well as the background, type ‘color ce’ ( without the quotes ) to have light yellow text on a light red background or any other combination.
Advertisement
-
1
Open Command Prompt.
-
2
Right-click on the top.
-
3
Click on Properties.
-
4
Go to the Colors tab.
-
5
Select text or background and edit the color values.
- Play around with the combinations!
-
6
Click ok to apply changes.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
Can I color certain letters or words?
Yes. Right click on the tab or image, then go to properties, then go to color and you can change the background color and the letters.
-
Question
How do I do this in a specific batch file?
Flashlight
Community Answer
Simply type the same command line code you used into the batch before echoing.
-
Question
How do I change my command prompt color to a rainbow color?
CaTsArEsOcUtE
Community Answer
I do not think there is a way to change it to rainbow color.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
List of Possible Colors
- 0 = Black
- 1 = Blue
- 2 = Green
- 3 = Aqua
- 4 = Red
- 5 = Purple
- 6 = Yellow
- 7 = White
- 8 = Gray
- 9 = Light Blue
- A = Light Green
- B = Light Aqua
- C = Light Red
- D = Light Purple
- E = Light Yellow
- F = Bright White
-
Be careful of the spellings of ‘color’ and do not type ‘colour’. Otherwise it will not work.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 405,699 times.
Is this article up to date?
Загрузить PDF
Загрузить PDF
Вам надоело постоянно видеть стандартный белый текст на черном фоне в командной строке? Если да, тогда читайте дальше, чтобы узнать, как изменить цвет текста и фона.
Шаги
-
1
Нажмите сочетание клавиш Windows + R для открытия окна «Выполнить».
-
2
Введите cmd и нажмите «OK».
-
3
Введите color z, чтобы получить список всех цветов и цифры или буквы, которые им соответствуют. Первые буква/цифра — это цвет фона, а вторая — цвет текста.
-
4
Введите букву/цифру цвета, чтобы изменить цвет текста. Например, введите color 6, чтобы получился желтый текст, color 4 для красного цвета, color A для изменения текста в светло-зеленую окраску и так далее.
-
5
Для изменения цвета текста, а также его фона, введите color ce, чтобы получился светло-желтый текст на светло-красном фоне, или любую другую комбинацию. Первая буква/цифра обозначает цвет фона, а вторая соотносится с цветом текста.
Реклама
-
1
Запустите командную строку.
-
2
Щелкните сверху правой кнопкой мыши.
-
3
Выберите «Свойства».
-
4
Перейдите на вкладку «Цвета».
-
5
Выберите свойства текста или фона и отредактируйте цветовые значения.
- Поэкспериментируйте с различными комбинациями!
-
6
Щелкните по кнопке «OK» для сохранения изменений.
Реклама
Список возможных расцветок
- 0 = Черный
- 1 = Синий
- 2 = Зеленый
- 3 = Аквамарин
- 4 = Красный
- 5 = Фиолетовый
- 6 = Желтый
- 7 = Белый
- 8 = Серый
- 9 = Светло-голубой
- A = Светло-зеленый
- В = Светлый аквамарин
- С = Светло-красный
- D = Светло-фиолетовый
- E = Светло-желтый
- F = Ярко-белый
Советы
- Будьте осторожны в правописании слова «color» и не введите по ошибке «colour». В противном случае изменения не сработают.
Реклама
Об этой статье
Эту страницу просматривали 82 212 раз.
Была ли эта статья полезной?
I wanted to to print one single line in a different color.
Use ANSI Escape Sequences.
Windows before 10 — no native support for ANSI colors on the console
For Windows version below 10, the Windows command console doesn’t support output coloring by default. You could install either Cmder, ConEmu, ANSICON or Mintty (used by default in GitBash and Cygwin) to add coloring support to your Windows command console.
Windows 10 — Command Line Colors
Starting from Windows 10 the Windows console support ANSI Escape Sequences and some colors by default. The feature shipped with the Threshold 2 Update in Nov 2015.
MSDN Documentation
Update (05-2019): The ColorTool enables you to change the color scheme of the console. It’s part of the Microsoft Terminal project.
Demo
Batch Command
The win10colors.cmd was written by Michele Locati:
The text below is stripped of special characters and will not work. You must copy it from here.
@echo off
cls
echo [101;93m STYLES [0m
echo ^<ESC^>[0m [0mReset[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[1m [1mBold[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[4m [4mUnderline[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[7m [7mInverse[0m
echo.
echo [101;93m NORMAL FOREGROUND COLORS [0m
echo ^<ESC^>[30m [30mBlack[0m (black)
echo ^<ESC^>[31m [31mRed[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[32m [32mGreen[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[33m [33mYellow[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[34m [34mBlue[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[35m [35mMagenta[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[36m [36mCyan[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[37m [37mWhite[0m
echo.
echo [101;93m NORMAL BACKGROUND COLORS [0m
echo ^<ESC^>[40m [40mBlack[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[41m [41mRed[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[42m [42mGreen[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[43m [43mYellow[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[44m [44mBlue[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[45m [45mMagenta[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[46m [46mCyan[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[47m [47mWhite[0m (white)
echo.
echo [101;93m STRONG FOREGROUND COLORS [0m
echo ^<ESC^>[90m [90mWhite[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[91m [91mRed[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[92m [92mGreen[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[93m [93mYellow[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[94m [94mBlue[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[95m [95mMagenta[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[96m [96mCyan[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[97m [97mWhite[0m
echo.
echo [101;93m STRONG BACKGROUND COLORS [0m
echo ^<ESC^>[100m [100mBlack[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[101m [101mRed[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[102m [102mGreen[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[103m [103mYellow[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[104m [104mBlue[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[105m [105mMagenta[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[106m [106mCyan[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[107m [107mWhite[0m
echo.
echo [101;93m COMBINATIONS [0m
echo ^<ESC^>[31m [31mred foreground color[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[7m [7minverse foreground ^<-^> background[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[7;31m [7;31minverse red foreground color[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[7m and nested ^<ESC^>[31m [7mbefore [31mnested[0m
echo ^<ESC^>[31m and nested ^<ESC^>[7m [31mbefore [7mnested[0m
Qwerty
27.3k21 gold badges107 silver badges129 bronze badges
answered Jul 27, 2016 at 15:22
Jens A. KochJens A. Koch
38.9k13 gold badges110 silver badges137 bronze badges
20
This isn’t a great answer, but if you know the target workstation has Powershell you can do something like this (assuming BAT / CMD script):
CALL:ECHORED "Print me in red!"
:ECHORED
%Windir%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0Powershell.exe write-host -foregroundcolor Red %1
goto:eof
Edit: (now simpler!)
It’s an old answer but I figured I’d clarify & simplify a bit
PowerShell is now included in all versions of Windows since 7. Therefore the syntax for this answer can be shortened to a simpler form:
- the path doesn’t need to be specified since it should be in the environment variable already.
- unambiguous commands can be abbreviated. For example you can:
- use
-foreinstead of-foregroundcolor - use
-backinstead of-backgroundcolor
- use
- the command can also basically be used ‘inline‘ in place of
echo
(rather than creating a separate batch file as above).
Example:
powershell write-host -fore Cyan This is Cyan text
powershell write-host -back Red This is Red background
More Information:
The complete list of colors and more information is available in the
— PowerShell Documentation for Write-Host
ashleedawg
19.8k7 gold badges70 silver badges103 bronze badges
answered Aug 4, 2011 at 13:30
IainIain
10.3k16 gold badges56 silver badges62 bronze badges
5
This is a self-compiled bat/.net hybrid (should be saved as .BAT) that can be used on any system that have installed .net framework (it’s a rare thing to see an windows without .NET framework even for the oldest XP/2003 installations) . It uses jscript.net compiler to create an exe capable to print strings with different background/foreground color only for the current line.
@if (@X)==(@Y) @end /* JScript comment
@echo off
setlocal
for /f "tokens=* delims=" %%v in ('dir /b /s /a:-d /o:-n "%SystemRoot%Microsoft.NETFramework*jsc.exe"') do (
set "jsc=%%v"
)
if not exist "%~n0.exe" (
"%jsc%" /nologo /out:"%~n0.exe" "%~dpsfnx0"
)
%~n0.exe %*
endlocal & exit /b %errorlevel%
*/
import System;
var arguments:String[] = Environment.GetCommandLineArgs();
var newLine = false;
var output = "";
var foregroundColor = Console.ForegroundColor;
var backgroundColor = Console.BackgroundColor;
var evaluate = false;
var currentBackground=Console.BackgroundColor;
var currentForeground=Console.ForegroundColor;
//http://stackoverflow.com/a/24294348/388389
var jsEscapes = {
'n': 'n',
'r': 'r',
't': 't',
'f': 'f',
'v': 'v',
'b': 'b'
};
function decodeJsEscape(_, hex0, hex1, octal, other) {
var hex = hex0 || hex1;
if (hex) { return String.fromCharCode(parseInt(hex, 16)); }
if (octal) { return String.fromCharCode(parseInt(octal, 8)); }
return jsEscapes[other] || other;
}
function decodeJsString(s) {
return s.replace(
// Matches an escape sequence with UTF-16 in group 1, single byte hex in group 2,
// octal in group 3, and arbitrary other single-character escapes in group 4.
/\(?:u([0-9A-Fa-f]{4})|x([0-9A-Fa-f]{2})|([0-3][0-7]{0,2}|[4-7][0-7]?)|(.))/g,
decodeJsEscape);
}
function printHelp( ) {
print( arguments[0] + " -s string [-f foreground] [-b background] [-n] [-e]" );
print( " " );
print( " string String to be printed" );
print( " foreground Foreground color - a " );
print( " number between 0 and 15." );
print( " background Background color - a " );
print( " number between 0 and 15." );
print( " -n Indicates if a new line should" );
print( " be written at the end of the ");
print( " string(by default - no)." );
print( " -e Evaluates special character " );
print( " sequences like \n\b\r and etc ");
print( "" );
print( "Colors :" );
for ( var c = 0 ; c < 16 ; c++ ) {
Console.BackgroundColor = c;
Console.Write( " " );
Console.BackgroundColor=currentBackground;
Console.Write( "-"+c );
Console.WriteLine( "" );
}
Console.BackgroundColor=currentBackground;
}
function errorChecker( e:Error ) {
if ( e.message == "Input string was not in a correct format." ) {
print( "the color parameters should be numbers between 0 and 15" );
Environment.Exit( 1 );
} else if (e.message == "Index was outside the bounds of the array.") {
print( "invalid arguments" );
Environment.Exit( 2 );
} else {
print ( "Error Message: " + e.message );
print ( "Error Code: " + ( e.number & 0xFFFF ) );
print ( "Error Name: " + e.name );
Environment.Exit( 666 );
}
}
function numberChecker( i:Int32 ){
if( i > 15 || i < 0 ) {
print("the color parameters should be numbers between 0 and 15");
Environment.Exit(1);
}
}
if ( arguments.length == 1 || arguments[1].toLowerCase() == "-help" || arguments[1].toLowerCase() == "-help" ) {
printHelp();
Environment.Exit(0);
}
for (var arg = 1; arg <= arguments.length-1; arg++ ) {
if ( arguments[arg].toLowerCase() == "-n" ) {
newLine=true;
}
if ( arguments[arg].toLowerCase() == "-e" ) {
evaluate=true;
}
if ( arguments[arg].toLowerCase() == "-s" ) {
output=arguments[arg+1];
}
if ( arguments[arg].toLowerCase() == "-b" ) {
try {
backgroundColor=Int32.Parse( arguments[arg+1] );
} catch(e) {
errorChecker(e);
}
}
if ( arguments[arg].toLowerCase() == "-f" ) {
try {
foregroundColor=Int32.Parse(arguments[arg+1]);
} catch(e) {
errorChecker(e);
}
}
}
Console.BackgroundColor = backgroundColor ;
Console.ForegroundColor = foregroundColor ;
if ( evaluate ) {
output=decodeJsString(output);
}
if ( newLine ) {
Console.WriteLine(output);
} else {
Console.Write(output);
}
Console.BackgroundColor = currentBackground;
Console.ForegroundColor = currentForeground;
Here’s the help message:
Example:
coloroutput.bat -s "aanbbnu0025cc" -b 10 -f 3 -n -e
You can also find this script here.
You can also check carlos’ color function -> http://www.dostips.com/forum/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=4453
answered Jan 31, 2015 at 10:53
npocmakanpocmaka
54.6k18 gold badges147 silver badges184 bronze badges
2
Windows 10 — TH2 and above:
(a.k.a. Version 1511, build 10586, release 2015-11-10)
At Command Prompt:
echo ^[[32m HI ^[[0m
Using the actual keys: echo Ctrl+[[32m HI Ctrl+[[0mEnter
You should see a green «HI» below it.
Code numbers can be found here:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ANSI_escape_code#Colors
Notepad:
To save this into notepad, you can type ESC into it using: Alt+027 with the numpad, then the [32m part. Another trick when I was on a laptop, redirect the line above into a file to get started, then cut and paste:
echo echo ^[[32m HI ^[[0m >> batch_file.cmd
answered Oct 5, 2018 at 20:06
Gringo SuaveGringo Suave
29k6 gold badges85 silver badges75 bronze badges
5
You can just creates files with the name of the word to print, uses findstr which can print in color, and then erases the file. Try this example:
@echo off
SETLOCAL EnableDelayedExpansion
for /F "tokens=1,2 delims=#" %%a in ('"prompt #$H#$E# & echo on & for %%b in (1) do rem"') do (
set "DEL=%%a"
)
call :ColorText 0a "green"
call :ColorText 0C "red"
call :ColorText 0b "cyan"
echo(
call :ColorText 19 "blue"
call :ColorText 2F "white"
call :ColorText 4e "yellow"
goto :eof
:ColorText
echo off
<nul set /p ".=%DEL%" > "%~2"
findstr /v /a:%1 /R "^$" "%~2" nul
del "%~2" > nul 2>&1
goto :eof
Run color /? to get a list of colors.
answered Apr 15, 2014 at 0:09
TutankhamenTutankhamen
3,5021 gold badge30 silver badges37 bronze badges
11
You could use ANSICON to enable ANSI terminal codes in older versions of Windows. There are 32 and 64 bit versions that I have used in Windows XP and Windows 7.
Gringo Suave
29k6 gold badges85 silver badges75 bronze badges
answered Jan 19, 2012 at 3:49
Bryan AshBryan Ash
4,3203 gold badges40 silver badges57 bronze badges
3
I was annoyed by the lack of proper coloring in cmd too, so I went ahead and created cmdcolor. It’s just an stdout proxy, which looks for a limited set of ANSI/VT100 control sequences (in other words, like in bash), i.e. echo 33[31m RED 33[0m DEFAULT | cmdcolor.exe.
Usage and downloads.
answered Feb 13, 2014 at 11:59
Alec MevAlec Mev
4,5034 gold badges29 silver badges44 bronze badges
4
I looked at this because I wanted to introduce some simple text colors to a Win7 Batch file. This is what I came up with. Thanks for your help.
@echo off
cls && color 08
rem .... the following line creates a [DEL] [ASCII 8] [Backspace] character to use later
rem .... All this to remove [:]
for /F "tokens=1,2 delims=#" %%a in ('"prompt #$H#$E# & echo on & for %%b in (1) do rem"') do (set "DEL=%%a")
echo.
<nul set /p="("
call :PainText 09 "BLUE is cold" && <nul set /p=") ("
call :PainText 02 "GREEN is earth" && <nul set /p=") ("
call :PainText F0 "BLACK is night" && <nul set /p=")"
echo.
<nul set /p="("
call :PainText 04 "RED is blood" && <nul set /p=") ("
call :PainText 0e "YELLOW is pee" && <nul set /p=") ("
call :PainText 0F "WHITE all colors"&& <nul set /p=")"
goto :end
:PainText
<nul set /p "=%DEL%" > "%~2"
findstr /v /a:%1 /R "+" "%~2" nul
del "%~2" > nul
goto :eof
:end
echo.
pause
answered Feb 9, 2015 at 5:00
0
There is an accepted answer with more than 250 upvotes already. The reason I am still contributing is that the escape character required for echoing is not accepted by many editors (I am using, e.g., MS Code) and all other solutions require some third-party (non-Windows-default) pieces of software.
The work-around with using only plain batch commands is using PROMPT instead of ECHO. The PROMPT command accepts the escape character in an any-editor-friendly way as a $Echaracter sequence. (Simply replace the Esc in the ASCII Escape codes) with $E.
Here is a demo code:
@ECHO OFF
:: Do not pollute environment with the %prompt.bak% variable
:: ! forgetting ENDLOCAL at the end of the batch leads to prompt corruption
SETLOCAL
:: Old prompt settings backup
SET prompt.bak=%PROMPT%
:: Entering the "ECHO"-like section
:: Forcing prompt to display after every command (see below)
ECHO ON
:: Setting the prompt using the ANSI Escape sequence(s)
:: - Always start with $E[1A, otherwise the text would appear on a next line
:: - Then the decorated text follows
:: - And it all ends with $E30;40m, which makes the following command invisible
:: - assuming default background color of the screen
@ PROMPT $E[1A$E[30;42mHELLO$E[30;40m
:: An "empty" command that forces the prompt to display.
:: The word "rem" is displayed along with the prompt text but is made invisible
rem
:: Just another text to display
@ PROMPT $E[1A$E[33;41mWORLD$E[30;40m
rem
:: Leaving the "ECHO"-like section
@ECHO OFF
:: Or a more readable version utilizing the cursor manipulation ASCII ESC sequences
:: the initial sequence
PROMPT $E[1A
:: formating commands
PROMPT %PROMPT%$E[32;44m
:: the text
PROMPT %PROMPT%This is an "ECHO"ed text...
:: new line; 2000 is to move to the left "a lot"
PROMPT %PROMPT%$E[1B$E[2000D
:: formating commands fro the next line
PROMPT %PROMPT%$E[33;47m
:: the text (new line)
PROMPT %PROMPT%...spreading over two lines
:: the closing sequence
PROMPT %PROMPT%$E[30;40m
:: Looks like this without the intermediate comments:
:: PROMPT $E[1A
:: PROMPT %PROMPT%$E[32;44m
:: PROMPT %PROMPT%This is an "ECHO"ed text...
:: PROMPT %PROMPT%$E[1B$E[2000D
:: PROMPT %PROMPT%$E[33;47m
:: PROMPT %PROMPT%...spreading over two lines
:: PROMPT %PROMPT%$E[30;40m
:: show it all at once!
ECHO ON
rem
@ECHO OFF
:: End of "ECHO"-ing
:: Setting prompt back to its original value
:: - We prepend the settings with $E[37;40m in case
:: the original prompt settings do not specify color
:: (as they don't by default).
:: - If they do, the $E[37;40m will become overridden, anyway.
:: ! It is important to write this command
:: as it is with `ENDLOCAL` and in the `&` form.
ENDLOCAL & PROMPT $E[37;40m%prompt.bak%
EXIT /B 0
NOTE: The only drawback is that this technique collides with user cmd color settings (color command or settings) if not known explicitly.
— Hope this helps as thi is the only solution acceptable for me for the reasons mentioned at the beginning. —
EDIT:
Based on comments, I am enclosing another snippet inspired by @Jeb. It:
- Shows how to obtain and use the «Esc» character runtime (rather than entering it to an editor) (Jeb’s solution)
- Uses «native»
ECHOcommand(s) - So it does not affect local
PROMPTvalue - Demonstrates that coloring the
ECHOoutput inevitably affectPROMPTcolor so the color must be reset, anyway
@ECHO OFF
:: ! To observe color effects on prompt below in this script
:: run the script from a fresh cmd window with no custom
:: prompt settings
:: Only not to pollute the environment with the %e% variable (see below)
:: Not needed because of the `PROMPT` variable
SETLOCAL
:: Parsing the `escape` character (ASCII 27) to a %e% variable
:: Use %e% in place of `Esc` in the [http://ascii-table.com/ansi-escape-sequences.php]
FOR /F "delims=#" %%E IN ('"prompt #$E# & FOR %%E IN (1) DO rem"') DO SET "e=%%E"
:: Demonstrate that prompt did not get corrupted by the previous FOR
ECHO ON
rem : After for
@ECHO OFF
:: Some fancy ASCII ESC staff
ECHO [ ]
FOR /L %%G IN (1,1,10) DO (
TIMEOUT /T 1 > NUL
ECHO %e%[1A%e%[%%GC%e%[31;43m.
ECHO %e%[1A%e%[11C%e%[37;40m]
)
:: ECHO another decorated text
:: - notice the `%e%[30C` cursor positioning sequence
:: for the sake of the "After ECHO" test below
ECHO %e%[1A%e%[13C%e%[32;47mHELLO WORLD%e%[30C
:: Demonstrate that prompt did not get corrupted by ECHOing
:: neither does the cursor positioning take effect.
:: ! But the color settings do.
ECHO ON
rem : After ECHO
@ECHO OFF
ENDLOCAL
:: Demonstrate that color settings do not reset
:: even when out of the SETLOCAL scope
ECHO ON
rem : After ENDLOCAL
@ECHO OFF
:: Reset the `PROMPT` color
:: - `PROMPT` itself is untouched so we did not need to backup it.
:: - Still ECHOING in color apparently collide with user color cmd settings (if any).
:: ! Resetting `PROMPT` color this way extends the `PROMPT`
:: by the initial `$E[37;40m` sequence every time the script runs.
:: - Better solution then would be to end every (or last) `ECHO` command
:: with the `%e%[37;40m` sequence and avoid setting `PROMPT` altogether.
:: which makes this technique preferable to the previous one (before EDIT)
:: - I am keeping it this way only to be able to
:: demonstrate the `ECHO` color effects on the `PROMPT` above.
PROMPT $E[37;40m%PROMPT%
ECHO ON
rem : After PROMPT color reset
@ECHO OFF
EXIT /B 0
answered Jan 23, 2020 at 8:42
PavDubPavDub
1211 silver badge5 bronze badges
10
I’m adding an answer to address an issue noted in some comments above: that inline ansi color codes can misbehave when inside a FOR loop (actually, within any parenthesized block of code). The .bat code below demonstrates (1) the use of inline color codes, (2) the color failure that can occur when inline color codes are used in a FOR loop or within a parenthesized block of code, and (3) a solution to the problem. When the .bat code executes, tests 2 and 3 demonstrate the colorcode failure, and test 4 shows no failure because it implements the solution.
[EDIT 2020-04-07: I found another solution that’s presumably more efficient than calling a subroutine. Enclose the FINDSTR phrase in parentheses, as in the following line:
echo success | (findstr /R success)
ENDEDIT]
Note: In my (limited) experience, the color code problem manifests only after input is piped to FINDSTR inside the block of code. That’s how the following .bat reproduces the problem. It’s possible the color code problem is more general than after piping to FINDSTR. If someone can explain the nature of the problem, and if there’s a better way to solve it, I’d appreciate it.
@goto :main
:resetANSI
EXIT /B
rem The resetANSI subroutine is used to fix the colorcode
rem bug, even though it appears to do nothing.
:main
@echo off
setlocal EnableDelayedExpansion
rem Define some useful colorcode vars:
for /F "delims=#" %%E in ('"prompt #$E# & for %%E in (1) do rem"') do set "ESCchar=%%E"
set "green=%ESCchar%[92m"
set "yellow=%ESCchar%[93m"
set "magenta=%ESCchar%[95m"
set "cyan=%ESCchar%[96m"
set "white=%ESCchar%[97m"
set "black=%ESCchar%[30m"
echo %white%Test 1 is NOT in a FOR loop nor within parentheses, and color works right.
echo %yellow%[Test 1] %green%This is Green, %magenta%this is Magenta, and %yellow%this is Yellow.
echo %Next, the string 'success' will be piped to FINDSTR...
echo success | findstr /R success
echo %magenta%This is magenta and FINDSTR found and displayed 'success'.%yellow%
echo %green%This is green.
echo %cyan%Test 1 completed.
echo %white%Test 2 is within parentheses, and color stops working after the pipe to FINDSTR.
( echo %yellow%[Test 2] %green%This is Green, %magenta%this is Magenta, and %yellow%this is Yellow.
echo %Next, the string 'success' will be piped to FINDSTR...
echo success | findstr /R success
echo %magenta%This is supposed to be magenta and FINDSTR found and displayed 'success'.
echo %green%This is supposed to be green.
)
echo %cyan%Test 2 completed.
echo %white%Test 3 is within a FOR loop, and color stops working after the pipe to FINDSTR.
for /L %%G in (3,1,3) do (
echo %yellow%[Test %%G] %green%This is Green, %magenta%this is Magenta, and %yellow%this is Yellow.
echo %Next, the string 'success' will be piped to FINDSTR...
echo success | findstr /R success
echo %magenta%This is supposed to be magenta and FINDSTR found and displayed 'success'.
echo %green%This is supposed to be green.
)
echo %cyan%Test 3 completed.
echo %white%Test 4 is in a FOR loop but color works right because subroutine :resetANSI is
echo called after the pipe to FINDSTR, before the next color code is used.
for /L %%G in (4,1,4) do (
echo %yellow%[Test %%G] %green%This is Green, %magenta%this is Magenta, and %yellow%this is Yellow.
echo %Next, the string 'success' will be piped to FINDSTR...
echo success | findstr /R success
call :resetANSI
echo %magenta%This is magenta and FINDSTR found and displayed 'success'.
echo %green%This is green.
)
echo %cyan%Test 4 completed.%white%
EXIT /B
answered Mar 26, 2020 at 11:12
An option for non windows 10 users that doesn’t require calling labels, avoiding the delays that go with doing so.
Below is a macro verison of a findstr colorprint routine
usage — where BF is replaced with the hex digit values of the background / Foreground colors:
%Col%{BF}{«string to print»}
@Echo off & CD "%TEMP%"
For /F "tokens=1,2 delims=#" %%a in ('"prompt #$H#$E# & echo on & for %%b in (1) do rem"') do (set "DEL=%%a")
Set "Col=For %%l in (1 2)Do if %%l==2 (Set "_Str="&(For /F "tokens=1,2 Delims={}" %%G in ("!oline!")Do Set "C_Out=%%G" & Set "_Str=%%~H")&(For %%s in (!_Str!)Do Set ".Str=%%s")&( <nul set /p ".=%DEL%" > "!_Str!" )&( findstr /v /a:!C_Out! /R "^$" "!_Str!" nul )&( del " !_Str!" > nul 2>&1 ))Else Set Oline="
Setlocal EnableDelayedExpansion
rem /* concatenation of multiple macro expansions requires the macro to be expanded within it's own code block. */
(%Col%{02}{"green on black,"}) & (%Col%{10}{black on blue})
Echo/& (%Col%{04}{red on black}) & (%Col%{34}{" red on blue"})
Goto :Eof
A more robust version of the macro replete with error handling.
@Echo off & PUSHD "%TEMP%"
rem /* Macro Definitions */
(Set n=^^^
%= macro newline Do not modify =%
)
(Set LF=^
%= linefeed. Do not modify =%)
If "!![" == "[" (
Echo/%%COL%% macro must be defined prior to delayed expansion being enabled
Goto :end
)
For /F "tokens=1,2 delims=#" %%a in ('"prompt #$H#$E# & echo on & for %%b in (1) do rem"') do (set "DEL=%%a")
rem /* %hCol% - Alternate color macro; escaped for use in COL macro. No error checking. Usage: (%hCol:?=HEXVALUE%Output String) */
Set "hCol=For %%o in (1 2)Do if %%o==2 (^<nul set /p ".=%DEL%" ^> "!os!" ^& findstr /v /a:? /R "^$" "!os!" nul ^& del "!os!" ^> nul 2^>^&1 )Else Set os="
rem /* %TB% - used with substitution within COL macro to format help output; not fit for general use, */
Set "TB=^&^< nul Set /P "=.%DEL%!TAB!"^&"
rem /* %COL% - main color output macro. Usage: (%COL%{[a-f0-9][a-f0-9]}{String to Print}) */
Set COL=Set "_v=1"^&Set "Oline="^& For %%l in (1 2)Do if %%l==2 (%n%
If not "!Oline!" == "" (%n%
Set "_Str="%n%
For /F "tokens=1,2 Delims={}" %%G in ("!oline!")Do (%n%
Set "Hex=%%G"%n%
Set "_Str=%%~H"%n%
)%n%
Echo/!Hex!^|findstr /RX "[0-9a-fA-F][0-9a-fA-F]" ^> nul ^|^| (Echo/^&(%hCol:?=04%Invalid - )%TB%(%hCol:?=06%Bad Hex value.)%TB%(%hCol:?=01%%%COL%%{!Hex!}{!_Str!})%TB:TAB=LF%(%hCol:?=02%!Usage!)^&Set "_Str="^&Set "_v=0")%n%
If not "!_Str!" == "" (%n%
^<nul set /p ".=%DEL%" ^> "!_Str!"%n%
findstr /v /a:!Hex! /R "^$" "!_Str!" nul %n%
del "!_Str!" ^> nul 2^>^&1%n%
)Else If not !_v! EQU 0 (%n%
Echo/^&(%hCol:?=04%Invalid -)%TB%(%hCol:?=06%Arg 2 absent.)%TB%(%hCol:?=01%%%COL%%!Oline!)%TB:TAB=LF%(%hCol:?=04%Input is required for output string.)%TB:TAB=LF%(%hCol:?=02%!Usage!)%n%
)%n%
)Else (Echo/^&(%hCol:?=04%Invalid -)%TB%(%hCol:?=06%No Args)%TB:TAB=!TAB!!TAB!%(%hCol:?=01%%%COL%%!Oline!)%TB:TAB=LF%(%hCol:?=02%!Usage!))%n%
)Else Set Oline=
Set "usage=%%COL%%{[a-f0-9][a-f0-9]}{String to Print}"
For /F eol^=^%LF%%LF%^ delims^= %%A in ('forfiles /p "%~dp0." /m "%~nx0" /c "cmd /c echo(0x09"') do Set "TAB=%%A"
rem /* removes escaping from macros to enable use outside of COL macro */
Set "hCol=%hCol:^=%"
Set "TB=%TB:^=%"
Setlocal EnableDelayedExpansion
rem /* usage examples */
(%COL%{02}{"green on black,"}) & (%COL%{10}{"black on blue"})
Echo/
(%COL%{04}{"red on black"}) & (%COL%{34}{" red on blue"})&(%COL%{40}{"black on red"})
Echo/& %COL%{03}{Demonstration of error handling-}
rem /* error handling */
Echo/%TB:TAB=!LF! % %hCol:?=20%Example 1 - No args
%COL%
Echo/%TB:TAB=!LF! % %hCol:?=20%Example 2 - Missing 2nd Arg
%COL%{ff}
Echo/%TB:TAB=!LF! % %hCol:?=20%Example 3 - Invalid hex value for 1st Arg
%COL%{HF}{string}
Echo/%TB:TAB=!LF! % %hCol:?=0d%Done
:end
POPD
Goto :Eof
answered Nov 24, 2020 at 19:07
T3RR0RT3RR0R
2,6863 gold badges10 silver badges25 bronze badges
The following code consists of two parts. If it is convenient for you too, there is also a .txt format in this .cmd file, below the «double» line (====).
::adonios77
::This is a .cmd file
@ECHO OFF
TITLE Colored Command Prompt echoes HELP
mode con: cols=55 lines=47
CLS
COLOR 0f
echo [93m
ECHO This is just help, as optical example,
ECHO when make or modify colorful command prompt echoes.
ECHO.
ECHO More info in Source:
ECHO [4m[94mhttps://stackoverflow.com/questions/2048509/how-to-echo-with-different-colors-in-the-windows-command-line[0m
ECHO.
ECHO [0mESC[0m "Text" Default colours Text[0m
ECHO [7mESC[7m "Text" Inversed Back-Fore colors[0m
ECHO [101mESC[101m "Text" in Red Background[0m
ECHO [91mESC[91m "Text" in Red Foreground)[0m
echo.
echo To make an ESC special character, (ASCII Escape code)
echo open or edit a .txt or .bat or .cmd file,
echo (hold)L-Alt and (type)027 in NumPad)
echo Or, in Command Prompt, (can't copy/paste special char.)
echo just press Ctrl+[
echo (it should look like: "echo ^[[33m'Text'^[[0m")
echo.
echo STYLES
echo [0mESC[0m Reset[0m
echo [1mESC[1m Bold [90m*This is not work for me[0m
echo [4mESC[4m Underline[0m
echo [7mESC[7m[0m Inverse
echo.
echo COLORS# Foreground-Background (color /? HEX) && echo.
echo [90mDark[0m / [100mLight[0m
echo Fore-Back / Fore-Back
echo Black * [100m[30m30[0m-[4m[40m40 [0m (0) / (8) [90m90[0m-[100m100 [0m
echo Red [31m31[0m-[41m41 [0m (4) / (C) [91m91[0m-[101m101 [0m
echo Green [32m32[0m-[42m42 [0m (2) / (A) [92m92[0m-[102m102 [0m
echo Yellow [33m33[0m-[90m[43m43 [0m (6) / (E) [93m93[0m-[90m[103m103 [0m
echo Blue [34m34[0m-[44m44 [0m (1) / (9) [94m94[0m-[104m104 [0m
echo Magenta [35m35[0m-[45m45 [0m (5) / (D) [95m95[0m-[105m105 [0m
echo Cyan [36m36[0m-[46m46 [0m (3) / (B) [96m96[0m-[106m106 [0m
echo White * [37m37[0m-[47m47 [0m (7) / (F) [97m97[0m-[7;97m107 [0m
echo.
echo Note: use ESC[0m at the end of (every) line.
echo.
echo COMBINATIONS
echo [7;91mESC[7;91m inverse red foreground color ESC[0m[0m
echo.
ECHO. && PAUSE
exit
============================================================
:: This is a .txt file.
This is just help, as optical example,
when make or modify colorful command prompt echoes.
More info in Source:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2048509/how-to-echo-with-different-colors-in-the-windows-command-line
To make an ESC special character, (),
open or edit a .txt or .bat or .cmd file,
(hold)L-Alt and (type)027 in NumPad)
STYLES
[0m Reset
[1m Bold
[4m Underline
[7m Inverse
COLORS# (Foreground-Background)
Dark / Light
Fore-Back / Fore-Back
Black 30-40 (0) / (8) 90-100
Red 31-41 (4) / (C) 91-101
Green 32-42 (2) / (A) 92-102
Yellow 33-43 (6) / (E) 93-103
Blue 34-44 (1) / (9) 94-104
Magenta 35-45 (5) / (D) 95-105
Cyan 36-46 (3) / (B) 96-106
White 37-47 (7) / (F) 97-107
COMBINATIONS
ESC[7;31m inverse red foreground color 0m
Note: use ESC[0m at the end of (every) line.
examples:
@ECHO OFF
ECHO Default Text
ECHO [7m"Text" Inversed Back-Fore colors (7m)[0m
ECHO [101m"Text" in Red Background (101m)[0m
ECHO [91m"Text" in Red Foreground (91m)[0m
============================================================
Also, I figured out that with this way can be change the way the Command Prompt looks like, temporarily or permanently.
The following TEXT code is an example of:
This is a .txt file. Antony's examples: prompt $Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$S $T$_ $P$_$G gives something like that: ==================== 19:53:02,73 C:Windowssystem32 > For All Users & Permanent: (if there is space between characters, must double quoted [""]) SETX PROMPT /M $Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$S$S$T$_$_$S$P$_$G$S gives something like that: ==================== 9:01:23,17 C:Windowssystem32 > NOTE: Variables created or modified by SETX will be available at the next logon session.
Now let’s give colors to the above examples. The result in the image above.
COLORED PROMPT examples:
For only the current User:
prompt $E[91m$E[40m$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$S $T$E[93m$_ $P$_$G$E[0m
or
For All Users and Permanently:
SETX PROMPT /M $E[91m$E[40m$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$Q$S$S$T$E[93m$_$_$S$P$_$G$S$E[0m
answered Sep 22, 2020 at 12:24
Solution for changing the foreground and background colors and writing without new lines.
It does not create any temporary files.
No special editors are required, so Notepad can be used for editing.
The first parameter for the :color subroutine is the color code, the rest of the (optional) parameters are the text to display. If the last parameter is $ then a new line is written at the end.
The color codes are the same as for the color command.
The :echo subroutine can be used to display a text without new line (unlike regular echo).
@echo off
call :color 4
call :echo Red foreground
call :color 7 " and "
call :color 4f
echo Red background
call :color
echo Back to normal
call :color 70 "Black "
call :color 1 "Blue "
call :color 2 "Green "
call :color 3 "Aqua "
call :color 4 "Red "
call :color 5 "Purple "
call :color 6 "Yellow "
call :color 7 "White "
call :color 8 "Gray "
call :color 9 "LightBlue" $
call :color a "LightGreen "
call :color b "LightAqua "
call :color c "LightRed "
call :color d "LightPurple "
call :color e "LightYellow "
call :color f "BrightWhite " $
call :color 1f Blue back
call :color 2f Green back
call :color 3f Aqua back
call :color 4f Red back
call :color 5f Purple back
call :color 6f Yellow back
call :color 7f White back
call :color 8f Gray back
call :color 9f "LightBlue back" $
call :color a0 LightGreen back
call :color b0 LightAqua back
call :color c0 LightRed back
call :color d0 LightPurple back
call :color e0 LightYellow back
call :color f0 LightWhite back $
call :color
echo %ESC%[4mUnderline%ESC%[0m.
pause
goto :eof
:: Displays a text without new line at the end (unlike echo)
:echo
@<nul set /p ="%*"
@goto :eof
:: Change color to the first parameter (same codes as for the color command)
:: And display the other parameters (write $ at the end for new line)
:color
@echo off
IF [%ESC%] == [] for /F %%a in ('echo prompt $E ^| cmd') do set "ESC=%%a"
SET color=0%1
IF [%color%] == [0] SET color=07
SET fore=%color:~-1%
SET back=%color:~-2,1%
SET color=%ESC%[
if %fore% LEQ 7 (
if %fore% == 0 SET color=%ESC%[30
if %fore% == 1 SET color=%ESC%[34
if %fore% == 2 SET color=%ESC%[32
if %fore% == 3 SET color=%ESC%[36
if %fore% == 4 SET color=%ESC%[31
if %fore% == 5 SET color=%ESC%[35
if %fore% == 6 SET color=%ESC%[33
if %fore% == 7 SET color=%ESC%[37
) ELSE (
if %fore% == 8 SET color=%ESC%[90
if %fore% == 9 SET color=%ESC%[94
if /i %fore% == a SET color=%ESC%[92
if /i %fore% == b SET color=%ESC%[96
if /i %fore% == c SET color=%ESC%[91
if /i %fore% == d SET color=%ESC%[95
if /i %fore% == e SET color=%ESC%[93
if /i %fore% == f SET color=%ESC%[97
)
if %back% == 0 (SET color=%color%;40) ELSE (
if %back% == 1 SET color=%color%;44
if %back% == 2 SET color=%color%;42
if %back% == 3 SET color=%color%;46
if %back% == 4 SET color=%color%;41
if %back% == 5 SET color=%color%;45
if %back% == 6 SET color=%color%;43
if %back% == 7 SET color=%color%;47
if %back% == 8 SET color=%color%;100
if %back% == 9 SET color=%color%;104
if /i %back% == a SET color=%color%;102
if /i %back% == b SET color=%color%;106
if /i %back% == c SET color=%color%;101
if /i %back% == d SET color=%color%;105
if /i %back% == e SET color=%color%;103
if /i %back% == f SET color=%color%;107
)
SET color=%color%m
:repeatcolor
if [%2] NEQ [$] SET color=%color%%~2
shift
if [%2] NEQ [] if [%2] NEQ [$] SET color=%color% & goto :repeatcolor
if [%2] EQU [$] (echo %color%) else (<nul set /p ="%color%")
goto :eof
answered Mar 4, 2021 at 0:44
Cosmin RusCosmin Rus
3242 silver badges7 bronze badges
A fast alternative to color efficiently with cmd batch since Windows XP by using PowerShell as a subprocess linked to the console output through a named pipe. It can be done with FindStr too, but PowerShell offers more options and seems quicker.
The main interest in keeping PowerShell as a subprocess, using a pipe to communicate, is that the display is far more faster than launching PowerShell or FindStr for each line to display.
Other good points :
- No need for temporary files
- Echoing though a pipe permits the display of the full ASCII table without bothering escapes.
- Works fine with fd redirection. To color only stderr as example, or to redirect to a file / other process.
Here is a sample code for doing that :
::
:: Launch a PowerShell child process in the background linked to the console and
:: earing through named pipe PowerShellCon_%PID%
::
:: Parameters :
:: [ PID ] : Console Process ID used as an identifier for the named pipe, launcher PID by default.
:: [ timeout ] : Subprocess max life in seconds, 300 by default. If -1, the subprocess
:: will not terminate while the process %PID% is still alive.
:: Return :
:: 0 if the child PowerShell has been successfully launched and the named pipe is available.
:: 1 if it fails.
:: 2 if we can't get a PID.
:: 3 if PowerShell is not present or doesn't work.
::
:LaunchPowerShellSubProcess
SET LOCALV_PID=
SET LOCALV_TIMEOUT=300
IF NOT "%~1" == "" SET LOCALV_PID=%~1
IF NOT "%~2" == "" SET LOCALV_TIMEOUT=%~2
powershell -command "$_" 2>&1 >NUL
IF NOT "!ERRORLEVEL!" == "0" EXIT /B 3
IF "!LOCALV_PID!" == "" (
FOR /F %%P IN ('powershell -command "$parentId=(Get-WmiObject Win32_Process -Filter ProcessId=$PID).ParentProcessId; write-host (Get-WmiObject Win32_Process -Filter ProcessId=$parentId).ParentProcessId;"') DO (
SET LOCALV_PID=%%P
)
)
IF "!LOCALV_PID!" == "" EXIT /B 2
START /B powershell -command "$cmdPID=$PID; Start-Job -ArgumentList $cmdPID -ScriptBlock { $ProcessActive = $true; $timeout=!LOCALV_TIMEOUT!; while((!LOCALV_TIMEOUT! -eq -1 -or $timeout -gt 0) -and $ProcessActive) { Start-Sleep -s 1; $timeout-=1; $ProcessActive = Get-Process -id !LOCALV_PID! -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue; } if ($timeout -eq 0 -or ^! $ProcessActive) { Stop-Process -Id $args; } } | Out-Null ; $npipeServer = new-object System.IO.Pipes.NamedPipeServerStream('PowerShellCon_!LOCALV_PID!', [System.IO.Pipes.PipeDirection]::In); Try { $npipeServer.WaitForConnection(); $pipeReader = new-object System.IO.StreamReader($npipeServer); while(($msg = $pipeReader.ReadLine()) -notmatch 'QUIT') { $disp='write-host '+$msg+';'; invoke-expression($disp); $npipeServer.Disconnect(); $npipeServer.WaitForConnection(); }; } Finally { $npipeServer.Dispose(); }" 2>NUL
SET /A LOCALV_TRY=20 >NUL
:LaunchPowerShellSubProcess_WaitForPipe
powershell -nop -c "& {sleep -m 50}"
SET /A LOCALV_TRY=!LOCALV_TRY! - 1 >NUL
IF NOT "!LOCALV_TRY!" == "0" cmd /C "ECHO -NoNewLine|MORE 1>\.pipePowerShellCon_!LOCALV_PID!" 2>NUL || GOTO:LaunchPowerShellSubProcess_WaitForPipe
IF "!LOCALV_TRY!" == "0" EXIT /B 1
EXIT /B 0
This «code» is written with delayed expansion ON but can be rewrite to work without it. There is many security points to consider, do not use it directly in the wild.
How to use it :
@ECHO OFF
SETLOCAL ENABLEEXTENSIONS
IF ERRORLEVEL 1 (
ECHO Extension inapplicable
EXIT /B 1
)
::
SETLOCAL ENABLEDELAYEDEXPANSION
IF ERRORLEVEL 1 (
ECHO Expansion inapplicable
EXIT /B 1
)
CALL:LaunchPowerShellSubProcess
IF NOT ERRORLEVEL 0 EXIT /B 1
CALL:Color Cyan "I write this in Cyan"
CALL:Blue "I write this in Blue"
CALL:Green "And this in green"
CALL:Red -nonewline "And mix Red"
CALL:Yellow "with Yellow"
CALL:Green "And not need to trouble with ()<>&|;,%""^ and so on..."
EXIT /B 0
:Color
ECHO -foregroundcolor %*>\.pipePowerShellCon_!LOCALV_PID!
ECHO[|SET /P=>NUL
GOTO:EOF
:Blue
ECHO -foregroundcolor Blue %*>\.pipePowerShellCon_!LOCALV_PID!
ECHO[|SET /P=>NUL
GOTO:EOF
:Green
ECHO -foregroundcolor Green %*>\.pipePowerShellCon_!LOCALV_PID!
ECHO[|SET /P=>NUL
GOTO:EOF
:Red
ECHO -foregroundcolor Red %*>\.pipePowerShellCon_!LOCALV_PID!
ECHO[|SET /P=>NUL
GOTO:EOF
:Yellow
ECHO -foregroundcolor Yellow %*>\.pipePowerShellCon_!LOCALV_PID!
ECHO[|SET /P=>NUL
GOTO:EOF
::
:: Launch a PowerShell child process in the background linked to the console and
:: earing through named pipe PowerShellCon_%PID%
::
:: Parameters :
:: [ PID ] : Console Process ID used as an identifier for the named pipe, launcher PID by default.
:: [ timeout ] : Subprocess max life in seconds, 300 by default. If -1, the subprocess
:: will not terminate while the process %PID% is still alive.
:: Return :
:: 0 if the child PowerShell has been successfully launched and the named pipe is available.
:: 1 if it fails.
:: 2 if we can't get a PID.
:: 3 if PowerShell is not present or doesn't work.
::
:LaunchPowerShellSubProcess
SET LOCALV_PID=
SET LOCALV_TIMEOUT=300
IF NOT "%~1" == "" SET LOCALV_PID=%~1
IF NOT "%~2" == "" SET LOCALV_TIMEOUT=%~2
powershell -command "$_" 2>&1 >NUL
IF NOT "!ERRORLEVEL!" == "0" EXIT /B 3
IF "!LOCALV_PID!" == "" (
FOR /F %%P IN ('powershell -command "$parentId=(Get-WmiObject Win32_Process -Filter ProcessId=$PID).ParentProcessId; write-host (Get-WmiObject Win32_Process -Filter ProcessId=$parentId).ParentProcessId;"') DO (
SET LOCALV_PID=%%P
)
)
IF "!LOCALV_PID!" == "" EXIT /B 2
START /B powershell -command "$cmdPID=$PID; Start-Job -ArgumentList $cmdPID -ScriptBlock { $ProcessActive = $true; $timeout=!LOCALV_TIMEOUT!; while((!LOCALV_TIMEOUT! -eq -1 -or $timeout -gt 0) -and $ProcessActive) { Start-Sleep -s 1; $timeout-=1; $ProcessActive = Get-Process -id !LOCALV_PID! -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue; } if ($timeout -eq 0 -or ^! $ProcessActive) { Stop-Process -Id $args; } } | Out-Null ; $npipeServer = new-object System.IO.Pipes.NamedPipeServerStream('PowerShellCon_!LOCALV_PID!', [System.IO.Pipes.PipeDirection]::In); Try { $npipeServer.WaitForConnection(); $pipeReader = new-object System.IO.StreamReader($npipeServer); while(($msg = $pipeReader.ReadLine()) -notmatch 'QUIT') { $disp='write-host '+$msg+';'; invoke-expression($disp); $npipeServer.Disconnect(); $npipeServer.WaitForConnection(); }; } Finally { $npipeServer.Dispose(); }" 2>NUL
SET /A LOCALV_TRY=20 >NUL
:LaunchPowerShellSubProcess_WaitForPipe
powershell -nop -c "& {sleep -m 50}"
SET /A LOCALV_TRY=!LOCALV_TRY! - 1 >NUL
IF NOT "!LOCALV_TRY!" == "0" cmd /C "ECHO -NoNewLine|MORE 1>\.pipePowerShellCon_!LOCALV_PID!" 2>NUL || GOTO:LaunchPowerShellSubProcess_WaitForPipe
IF "!LOCALV_TRY!" == "0" EXIT /B 1
EXIT /B 0
Link to my original answer on the same topic.
answered Mar 12, 2021 at 18:07
Zilog80Zilog80
2,5072 gold badges15 silver badges20 bronze badges
2
An advanced Macro for handling Cursor Color, Position and properties For Windows 10.
Please refer to the help and usage examples for information on usage.
Supports and Shows examples of:
- Cursor Positioning
- Absolute
- Relative to last Cursor Position ; left right by n columns ; up down by n lines
- Combinations of Relative and Absolute Position.
- Show / Hide Cursor
- Cursor Graphics properties [ Color ; Foreground and Background ]
- Same line multicolor output
- Easily chain multiple VT graphics sequences.
- Clearing of all text on a line from a given position.
- Deletion of a number of characters to the right of the cursor on the current line.
- Optionally Save the Cursor position at the time of expansion as independent Y and X values.
- /Save Cursor position storing component of the macro adpated from Jeb’s answer here
- NEW: Switching between Screen buffers.
Edit:
I’ve included below the final usage example a command line that uses
VT codes to achieve the same result as that example, to illustrate the
difference in readability when using multiple Terminal sequences in
the same Cursor output.NOTES On changing Buffers:
Cursor position is tied to the active buffer; It is not availale when switching to an alternate buffer.
When reverting to the main buffer:
The cursor position originally occupied in the main buffer is restored, and the content of the alternate buffer is discarded.
::: Cout cursor Macro. Author: T3RRY ::: Filename: Cout.bat
::: OS requirement: Windows 10
::: Purpose: Facilitate advanced console display output with the easy use of Virtual terminal codes
::: Uses a macro function to effect display without users needing to memorise or learn specific
::: virtual terminal sequences.
::: Enables output of text in 255 bit color at absolute or relative Y;X positions.
::: Allows cursor to be hidden or shown during and after text output. See help for more info.
@Echo off & Setlocal EnableExtensions
============================================== :# Usage
If not "%~1" == "" Echo/%~1.|findstr /LIC:"/?" > nul && (
If "%~2" == "" (Cls & Mode 1000,50 & Color 30)
If "%~2" == "Usage" ( Color 04 & ( Echo/n|choice /n /C:o 2> nul ) & timeout /T 5 > nul )
If "%~2" == "DE" ( Color 04 & Echo/ --- Delayed expansion detected^^^! Must not be enabled prior to calling %~n0 ---&( Echo/n|choice /n /C:o 2> nul ))
If not Exist "%TEMP%%~n0helpfile.~tmp" (For /F "Delims=" %%G in ('Type "%~f0"^| Findstr.exe /BLIC:":::" 2^> nul ')Do (
For /F "Tokens=2* Delims=[]" %%v in ("%%G")Do Echo(^|%%v^|
))>"%TEMP%%~n0helpfile.~tmp"
Type "%TEMP%%~n0helpfile.~tmp" | More
timeout /T 60 > nul
Color 07
If "%~2" == "DE" (Exit)Else Exit /B 1
)
If "!![" == "[" Call "%~f0" "/?" "DE"
:::[=====================================================================================================================]
:::[ cout /? ]
:::[ %COUT% Cursor output macro. ]
:::[ * Valid Args for COUT: {/Y:Argvalue} {/X:Argvalue} {/S:Argvalue} {/C:Argvalue} ]
:::[ - Args Must be encased in curly braces. Arg order does not matter ; Each Arg is optional. ]
:::[ * Valid Switches for COUT: /Save /Alt /Main ]
:::[ /Save - Stores the Y and X position at the start of the current expansion to .lY and .lX variables ]
:::[ /Alt - Switch console to alternate screen Buffer. Persists until /Main switch is used. ]
:::[ /Main - Restore console to main screen Buffer. Console default is the main buffer. ]
:::[ ]
:::[ USAGE: ]
:::[ * ArgValue Options ; '#' is an integer: ]
:::[ {/Y:up|down|#} {/Y:up#|down#|#} {/Y:#up|#down|#} {/X:left|right|#} {/X:left#|right#|#} {/X:#left|#right|#} ]
:::[ * note: {/Y:option} {/X:option} - 1 option only per Arg. ]
:::[ - directions: 'up' 'down' 'left' 'right' are relative to the cursors last position. ]
:::[ - /Y and /X options - #direction or direction#: ]
:::[ Positions the cursor a number of cells from the current position in the given direction. ]
:::[ Example; To move the cursor 5 rows up in the same column, without displaying any new text: ]
:::[ %COUT%{/Y:5up} ]
:::[ - '#' (Absolute position) is the column number {/X:#} or row number {/Y:#} the cursor ]
:::[ * Integers for absolute positions contained in variables must be Expanded: {/Y:%varname%} ]
:::[ is to be positioned at, allowing cursor position to be set on single or multiple axis. ]
:::[ * Absolute Y and X positions capped at line and column maximum of the console display. ]
:::[ * Exceeding the maximum Y positions the cursor at the start of the last line in the console display. ]
:::[ * Exceeding the maximum X positions the cursor at the start of the next line ]
:::[ ]
:::[ {/S:Output String} {/S:(-)Output String} {/S:Output String(+)} {/S:Output String(K)} {/S:Output String(.#.)} ]
:::[ * note: (-) Hide or (+) Show the Cursor during output of the string. ]
:::[ (K) Clears the row of text from the position (K) occurs. ]
:::[ Example; Delete 5 characters from the current row to the right of the curser: ]
:::[ %COUT%{/S:(.5.)} ]
:::[ {/C:VTcode} {/C:VTcode-VTcode} {/C:VTcode-VTcode-VTcode} ]
:::[ * note: Chain multiple graphics rendition codes using '-' ]
:::[ See: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/console/console-virtual-terminal-sequences#text-formatting ]
:::[ See also: https://www.rapidtables.com/web/color/RGB_Color.html ]
:::[=====================================================================================================================]
============================================== :# PreScript variable definitions
rem /* generate Vitual Terminal Escape Control .Character */
For /F %%a in ( 'Echo prompt $E ^| cmd' )Do Set "E=%%a"
rem /* https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/console/console-virtual-terminal-sequences */
(Set n=^^^
%= Newline variable for macro definitions. DO NOT MODIFY this line or above 2 lines. =%)
================== :# Screen Dimensions [Customise columns,lines using the mode command.]
Mode 160,38 & Cls
rem /* Get screen dimensions [lines] [columns]. Must be done before delayed expansion is enabled. */
For /F "tokens=1,2 Delims=:" %%G in ('Mode')Do For %%b in (%%H)Do For %%a in (%%G)Do Set "%%a=%%b"
rem /* NON ENGLISH VERSION USERS: You will need to manually set Columns and lines for their desired console size */
If not defined columns (Set "columns=100"& Set "lines=30")
rem /* Cursor position codes - https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/console/console-virtual-terminal-sequences#simple-cursor-positioning */
Set "left=D"&Set "right=C"&Set "up=A"&set "down=B"
For /L %%n in (1 1 %lines%)Do (Set "%%ndown=[%%nB"&Set "down%%n=[%%nB"& set "%%nup=[%%nA"&Set "up%%n=[%%nA")
For /L %%n in (1 1 %columns%)Do (Set "%%nleft=[%%nD"&Set "left%%n=[%%nD"&set "%%nright=[%%nC"&set "right%%n=[%%nC")
%= Catch Args =%Set COUT=For %%n in (1 2)Do If %%n==2 ( %n%
%= Test No Args =%If "!Args!" == "" (CLS^&Echo/Usage Error. Args Required. ^& Call "%~f0" "/?" "Usage" ^|^| Exit /B 1) %n%
%= Test Braces Used =%If "!Args:}=!" == "!Args!" (CLS^&Echo/Usage Error. Args must be enclosed in curly braces ^& Call "%~f0" "/?" "Usage" ^|^| Exit /B 1) %n%
%= Reset macro =%Set ".Y=" ^& Set ".X=" ^& Set ".Str=" ^& Set ".C=" %n%
%= internal vars =%Set "Arg1=" ^& Set "Arg2=" ^& Set "Arg3=" ^& Set "Arg4=" %n%
%= Split Args. =%For /F "Tokens=1,2,3,4 Delims={}" %%1 in ("!Args!")Do ( %n%
%= Substring =%Set "Arg1=%%~1" %n%
%= modification =%Set "Arg2=%%~2" %n%
%= identifies Args =%Set "Arg3=%%~3" %n%
%= during handling. =%Set "Arg4=%%~4" %n%
%= =%) %n%
%= Check /Save switch =%If not "!Args:/Save=!" == "!Args!" (%n%
%= Reset Cursor Save =%Set ".Cpos=" ^&Set ".Char="%n%
%= 10 char max; Repeat =%For /L %%l in (2 1 12)Do (%n%
%= until R returned =%If not "!.Char!" == "R" (%n%
%= from esc[6n =%^<nul set /p "=%E%[6n" %n%
%= Redirects to =%FOR /L %%z in (1 1 %%l) DO pause ^< CON ^> NUL%n%
%= prevent blocking =%Set ".Char=;"%n%
%= script execution =%for /F "tokens=1 skip=1 delims=*" %%C in ('"REPLACE /W ? . < con"') DO (Set ".Char=%%C")%n%
%= Append string w.out R =%If "!.Cpos!" == "" (Set ".Cpos=!.Char!")Else (set ".Cpos=!.Cpos!!.Char:R=!") %n%
%= =%)%n%
%= =%)%n%
%= Split Captured Pos =%For /F "tokens=1,2 Delims=;" %%X in ("!.Cpos!")Do Set ".lY=%%X" ^& Set ".LX=%%Y" %n%
%= End of Pos /Save =%)%n%
%= Begin Arg =%For %%i in (1 2 3 4)Do For %%S in (Y X C S)Do If not "!Arg%%i!" == "" ( %n%
%= Processing. 4 Args =%If not "!Arg%%i:/%%S:=!" == "!Arg%%i!" ( %n%
%= Flagged with Y X C S =%Set "Arg%%i=!Arg%%i:/%%S:=!" %n%
%= Strip /Flag In Arg# =%For %%v in ("!Arg%%i!")Do ( %n%
%= /Y Lines Arg handling =%If "%%S" == "Y" ( %n%
%= Test if arg is variable =%If Not "!%%~v!" == "" ( %n%
%= assign down / up value =%Set ".Y=%E%!%%~v!" %n%
%= -OR- =%)Else ( %n%
%= assign using operation =%Set /A ".Y=!Arg%%i!" %n%
%= to allow use of offsets; =%If !.Y! GEQ !Lines! (Set /A ".Y=Lines-1") %n%
%= constrained to console =%Set ".Y=%E%[!.Y!d" %n%
%= maximum lines. =%)) %n%
%= /X Cols Arg handling =%If "%%S" == "X" ( %n%
%= processing follows same =%If Not "!%%~v!" == "" ( %n%
%= logic as /Y; =%Set ".X=%E%!%%~v!" %n%
%= except if Columns =%)Else ( %n%
%= exceed console max =%Set /A ".X=!Arg%%i!" %n%
%= columns line wrapping =%If !.X! GEQ !Columns! (Set ".X=1"^& Set ".Y=%E%!Down!") %n%
%= is effected. =%Set ".X=%E%[!.X!G" %n%
%= =%)) %n%
%= /C Color Arg Handling. %If "%%S" == "C" ( %n%
%= Substituition =%Set ".C=%E%[!Arg%%i!" %n%
%= replaces '-' with VT =%Set ".C=!.C:-=m%E%[!" %n%
%= chain - mE[ =%Set ".C=!.C!m" %n%
%= =%) %n%
%= /S String Arg Handle =%If "%%S" == "S" ( %n%
%= Substitute Sub-Args =%Set ".Str=!Arg%%i!" %n%
%= (-) hide cursor =%Set ".Str=!.Str:(-)=%E%[?25l!" %n%
%= (+) show cursor =%Set ".Str=!.Str:(+)=%E%[?25h!" %n%
%= (K) clear line =%Set ".Str=!.Str:(K)=%E%[K!" %n%
%= (.#.) delete # of =%Set ".Str=!.Str:(.=%E%[!" %n%
%= characters =%Set ".Str=!.Str:.)=P!" %n%
%= =%) %n%
%= End Arg Handling =%))) %n%
%= /Main /Alt Switch =%If not "!Args:/Main=!" == "!Args!" ( %n%
%= handling for =%^< nul Set /P "=%E%[?1049l!.Y!!.X!!.C!!.Str!%E%[0m" %n%
%= switching console =%)Else If not "!Args:/Alt=!" == "!Args!" ( %n%
%= buffers. No Switch =%^< nul Set /P "=%E%[?1049h!.Y!!.X!!.C!!.Str!%E%[0m" %n%
%= outputs to current =%)Else ( ^< nul Set /P "=!.Y!!.X!!.C!!.Str!%E%[0m" ) %n%
%= buffer. =%)Else Set Args=
rem /* Simple subsecond delay macro. Uses call to a non existentent label # number of times to delay script execution. */
For /F "tokens=1,2 delims==" %%G in ('wmic cpu get maxclockspeed /format:value')Do Set /A "%%G=%%H/20" 2> nul
If not defined Maxclockspeed Set "Maxclockspeed=200"
Set "Hash=#"& Set "delay=(If "!Hash!" == "#" (Set /A "Delay.len=Maxclockspeed")Else Set "Delay.len=#")& For /L %%i in (1 1 !Delay.Len!)Do call :[_false-label_] 2> Nul"
============================================== :# Script Body [Demo]
rem /* Enable Delayed Expansion after macro definiton in order to expand macro. */
Setlocal EnableDelayedExpansion & CD "%TEMP%"
rem /* Usage examples */
%COUT%{/X:10}{/Y:5}{/C:34}{"/S:(-)hello there^^^!"}
%Delay%
rem /* Example use of mixed foreground / background color and other graphics rendition properties */
%COUT%{"/C:31-1-4-48;2;0;80;130"}{/S:Bye for now.}{/Y:down}
%Delay%
%COUT%{/Y:up}{/C:35}{/S:again}{/X:16}
%Delay%
%COUT%{"/S:(K)^_^"}{/X:right}{/C:32}{/Y:down} /Save
%Delay%
rem /* Switch to Alternate screen buffer: /Alt */
%COUT%{"/S:(-)(K)o_o"}{/X:.lX+1}{/Y:6}{/C:33}{/Y:down} /Alt
%Delay%
%COUT%{"/S:Don't worry, they'll be back"}{/Y:down}{/X:15left}{/C:7-31}
rem /* Cursor position is tied to the active console buffer. The contents of the Alternate buffer are discarded when reverting to the Main buffer. */
%Delay%
rem /* Return to Main screen buffer: /Main */
%COUT%{/X:3left}{/Y:5up}{"/S:That's all folks."} /Save /Main
rem /* Cursor position is tied to the active console buffer. */
%Delay%
rem /* restore cursor position /Save .lX value with +7 offset ; Overwrite all and delete 6 following characters:(.6.) ; restore cursor: (+) */
%COUT%{/X:10left}{/S:How(.6.)(+)}{/C:32}
rem /* The same as the above line using VT codes manually. */
::: <nul Set /P "=%E%[10D%E%[32mHow%E%[6P%E%[?25l"
%Delay%
%COUT%{/Y:100}
Endlocal
Goto :eof
An alternate version of the above macro that uses a structure for arg handling that is simpler and has better readability can be found here.
answered Jan 22, 2021 at 13:43
T3RR0RT3RR0R
2,6863 gold badges10 silver badges25 bronze badges
I just converted from Win 7 Home to Win 10 Pro and wanted to replace the batch I call from other batches to echo info in color. Reviewing what is discussed above I use the following which will directly replace my previous batch. NOTE the addition of «~» to the message so that messages with spaces may be used. Instead of remembering codes I use letters for the colors I needed.
If %2 contains spaces requires «…»
%1 Strong Colors on black: R=Red G=GREEN Y=YELLOW W=WHITE
ECHO OFF
IF "%1"=="R" ECHO ^[91m%~2[0m
IF "%1"=="G" ECHO ^[92m%~2[0m
IF "%1"=="Y" ECHO ^[93m%~2[0m
IF "%1"=="W" ECHO ^[97m%~2[0m
answered Apr 28, 2020 at 14:51
for me i found some solutions: it is a working solution
@echo off
title a game for youtube
explorer "https://thepythoncoding.blogspot.com/2020/11/how-to-echo-with-different-colors-in.html"
SETLOCAL EnableDelayedExpansion
for /F "tokens=1,2 delims=#" %%a in ('"prompt #$H#$E# & echo on & for %%b in (1) do rem"') do (
set "DEL=%%a"
)
echo say the name of the colors, don't read
call :ColorText 0a "blue"
call :ColorText 0C "green"
call :ColorText 0b "red"
echo(
call :ColorText 19 "yellow"
call :ColorText 2F "black"
call :ColorText 4e "white"
goto :Beginoffile
:ColorText
echo off
<nul set /p ".=%DEL%" > "%~2"
findstr /v /a:%1 /R "^$" "%~2" nul
del "%~2" > nul 2>&1
goto :eof
:Beginoffile
answered Nov 4, 2020 at 20:17
Kais TounsiKais Tounsi
6924 silver badges8 bronze badges
Put the following lines into a file called ColourText.bas on your desktop.
Imports System
Imports System.IO
Imports System.Runtime.InteropServices
Imports Microsoft.Win32
Public Module MyApplication
Public Declare Function GetStdHandle Lib "kernel32" Alias "GetStdHandle" (ByVal nStdHandle As Long) As Long
Public Declare Function SetConsoleTextAttribute Lib "kernel32" Alias "SetConsoleTextAttribute" (ByVal hConsoleOutput As Long, ByVal wAttributes As Long) As Long
Public Const STD_ERROR_HANDLE = -12&
Public Const STD_INPUT_HANDLE = -10&
Public Const STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE = -11&
Sub Main()
Dim hOut as Long
Dim Ret as Long
Dim Colour As Long
Dim Colour1 As Long
Dim Text As String
hOut = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE)
Colour = CLng("&h" & Split(Command(), " ")(0))
Colour1 = Clng("&h" & Split(Command(), " ")(1))
Text = Mid(Command(), 7)
Ret = SetConsoleTextAttribute(hOut, Colour)
Console.Out.WriteLine(text)
Ret = SetConsoleTextAttribute(hOut, Colour1)
End Sub
End Module
Save it and type the following in a command prompt.
"C:WindowsMicrosoft.NETFrameworkv4.0.30319vbc.exe" /target:exe /out:"%userprofile%desktopColourText.exe" "%userprofile%desktopColourText.bas" /verbose
A file called ColourText.exe will appear on your desktop. Move it to the Windows folder.
To use you must use two character codes to set colour eg 01 not 1.
ColourText ColourOfText ColourOfTextWhenFinished Text
EG To set blue on white by not passing any text, then red on white text, finishing with blue on grey.
ColourText F1 F1
ColourText F2 71 This is green on white
or
ColourText F1 F1
cls
ColourText F4 F4
Echo Hello
Echo Hello today
ColourText F1 F1
Also the CLS command becomes interesting. Color command without parameters resets all colours to startup colours.
To get the colour code add the following numbers together. Use Calculator in programmers mode. These are hex numbers. They can be added together eg Red + Blue + FG Intensity = 13 = D. As 10+ wasn’t used the background will be black. Colour codes MUST be two characters, eg 08 not 8.
FOREGROUND_RED = &H4 ' text color contains red.
FOREGROUND_INTENSITY = &H8 ' text color is intensified.
FOREGROUND_GREEN = &H2 ' text color contains green.
FOREGROUND_BLUE = &H1 ' text color contains blue.
BACKGROUND_BLUE = &H10 ' background color contains blue.
BACKGROUND_GREEN = &H20 ' background color contains green.
BACKGROUND_INTENSITY = &H80 ' background color is intensified.
BACKGROUND_RED = &H40 ' background color contains red.
answered Jan 1, 2017 at 21:55
1
To get this working on Windows 10, you can enable this flag: ENABLE_VIRTUAL_TERMINAL_PROCESSING.
With this registry key you can set this by default
[HKCUConsole] VirtualTerminalLevel dword 0x1
answered Jul 12, 2017 at 10:16
An alternative is to use NodeJS.
Here is an example:
const os = require('os');
const colors = require('colors');
console.log("Operative System:".green,os.type(),os.release());
console.log("Uptime:".blue,os.uptime());
And this is the result:
answered Feb 10, 2019 at 21:51
JosemJosem
3587 silver badges14 bronze badges
1
Setting color to the log statements in powershell is not a big deal friend.
you can use -ForegroundColor parameter.
To write a confirmation message.
Write-Host "Process executed Successfully...." -ForegroundColor Magenta
To write an error message.
Write-Host "Sorry an unexpected error occurred.." -ForegroundColor Red
To write a progress message.
Write-Host "Working under pocess..." -ForegroundColor Green
answered Apr 15, 2020 at 5:48
ajeshajesh
3105 silver badges7 bronze badges
call :color_echo "blue" "blue txt"
call :color_echo "red" "red txt"
echo "white txt"
REM : https://www.robvanderwoude.com/ansi.php
:color_echo
@echo off
set "color=%~1"
set "txt=%~2"
set ESC=
set black=%ESC%[30m
set red=%ESC%[31m
set green=%ESC%[32m
set yellow=%ESC%[33m
set blue=%ESC%[34m
set magenta=%ESC%[35m
set cyan=%ESC%[36m
set white=%ESC%[37m
if "%~1" == "black" set "color=!black!"
if "%~1" == "red" set "color=!red!"
if "%~1" == "green" set "color=!green!"
if "%~1" == "yellow" set "color=!yellow!"
if "%~1" == "blue" set "color=!blue!"
if "%~1" == "magenta" set "color=!magenta!"
if "%~1" == "cyan" set "color=!cyan!"
if "%~1" == "white" set "color=!white!"
echo | set /p="!color!!txt!"
echo.
REM : return to standard white color
echo | set /p="!white!"
REM : exiting the function only
EXIT /B 0
answered Apr 25, 2020 at 8:37
1
Easiest way is make a system call to powershell like this :
s=os.system('powershell Write-Host "I am so bored with this. Work already" -ForegroundColor Blue')
otherwise :
←[94mPff
answered Mar 20, 2021 at 15:18
Gediz GÜRSUGediz GÜRSU
4374 silver badges12 bronze badges
You can use the color command to change the color of the whole console
Color 0F
Is black and white
Color 0A
Is black and green
dawsnap
93410 silver badges21 bronze badges
answered Jan 21, 2013 at 21:13
3
Color is an inbuilt command found inside the Windows Command Processor (cmd.exe), that is used for changing the colors for the console’s foreground and background. By default, the console has white foreground color and black background color (07 color code). The command is generally used either to personalize the aesthetics of the console window, or the make the colors more appropriate for Dim or Dark Displays (ex. TN panels). In this article, we will learn about the color command and will also take a look at the various uses it offers.
Description of the Command :
Type the command – color /? in the Command Prompt.
It sets the default console foreground and background colors.
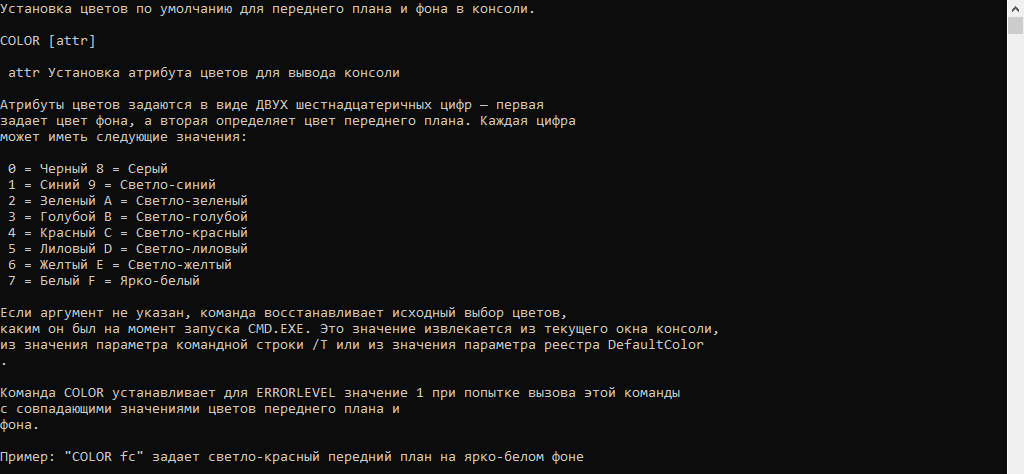
COLOR [attr] attr - Specifies the color attribute of console output.
Color attributes are specified by two hex digits –
- First corresponds to the background.
- Second corresponds to the foreground.
Using the Command :
The command takes in input 2 hexadecimal digits (2nd digit optional) where the first digit corresponds to the background color and the second digit corresponds to the foreground color.
Syntax :
Color (Background)(Foreground)
If the first digit is only provided, then only the foreground color changes. Each digit can have any of the values in hexadecimal codepoint (0 – f) where each one corresponds to a unique color. The digit to color correspondence is as follows –
0 = Black 8 = Gray 1 = Blue 9 = Light Blue 2 = Green A = Light Green 3 = Aqua B = Light Aqua 4 = Red C = Light Red 5 = Purple D = Light Purple 6 = Yellow E = Light Yellow 7 = White F = Bright White
Syntax :
Color 1F
It will produce bright White on Dark Blue. Any combination of the above set of digits could be used, except for the special case in which the foreground and the background color is the same (Ex. color FF or color 33). In that case no color change occurs, and the value of %ERRORLEVEL% changes to 1. If the command is executed without providing any parameters, then the command will restore the color to which cmd.exe initially started as.
- Changing Only The Foreground Color :
Syntax :
Color (Hex_digit)
(Hex_digit) is a digit (or character) within the hexadecimal range, i.e. it should belong in the range 0-F.
Example :
We will change the foreground color to Yellow (6).Before :
After :
It is clear from the above images that after executing the command Color 6, the color of the foreground changes from white to yellow.
- Changing the Color of Background And Foreground :
For changing the color of the foreground and the background of the console window, the color attributes are specified by 2 of the previously mentioned hex digits.Syntax :
color (Back_Hex_digit)(Fore_hex_digit)
Back_Hex_digit and Fore_hex_digit are hexadecimal digits used to determine the color of the background and foreground respectively. In the following example, we will change the background color to grey (7) and foreground color to light green (a).
Before :
After :
- 13.02.2020
- 15 468
- 0
- 04.10.2021
- 42
- 41
- 1
- Содержание статьи
- Описание
- Синтаксис
- Параметры
- Примечания
- Примеры использования
- Справочная информация
- Добавить комментарий
Описание
COLOR — Изменяет цвет текста и фона в окне командной строки для текущего сеанса.
Эта команда поддерживается только в CMD.EXE и не доступна в PowerShell.
Синтаксис
color> [тф]Где т — цвет текста
ф — цвет фона
Параметры
В следующей таблице перечислены допустимые шестнадцатеричные числа, которые можно задать в качестве значений параметров т и ф.
| Параметр | Описание |
|---|---|
| 0 | Черный |
| 1 | Синий |
| 2 | Зеленый |
| 3 | Голубой |
| 4 | Красный |
| 5 | Сиреневый |
| 6 | Желтый |
| 7 | Белый |
| 8 | Серый |
| 9 | Светло-синий |
| A | Светло-зеленый |
| B | Светло-голубой |
| C | Светло-красный |
| D | Светло-сиреневый |
| E | Светло-желтый |
| F | Яркий белый |
| /? | Выводит справочную информацию в командной строке. |
Примечания
- Чтобы задать стандартные цвета в окне командной строки, щелкните левый верхний угол этого окна, выберите команду Умолчания, перейдите к вкладке Цвета и укажите цвета для параметров Текст на экране и Фон экрана.
- Для изменения цветов окна командной строки в текущем сеансе можно воспользоваться командой cmd /t:тф.
- Если цвета текста и фона совпадают, команда color устанавливает значение параметра ERRORLEVEL в единицу (1).
Примеры использования
Чтобы изменить цвет текста на красный, а цвет фона на белый в окне командной строки, введите следующую команду:
color FCЧтобы вернуть все настройки, которые были по-умолчанию наберите команду без параметров:
colorСправочная информация
Всем привет! Сегодня я расскажу как изменить цвет фона и шрифта командной строки (CMD) Windows.
Изменение цвета текста и фона в окне командной строки для текущего сеанса. Выполненная без параметров команда color восстанавливает стандартные цвета текста и фона в окне командной строки.
Синтаксис
color [тф]
Параметры
тф — Изменение цвета текста (т) и фона (ф).
В следующей таблице перечислены допустимые шестнадцатеричные числа, которые можно задать в качестве значений параметров т и ф.
| Цвет | Значение |
| Черный | 0 |
| Синий | 1 |
| Зеленый | 2 |
| Голубой | 3 |
| Красный | 4 |
| Сиреневый | 5 |
| Желтый | 6 |
| Белый | 7 |
| Серый | 8 |
| Светло-синий | 9 |
| Светло-зеленый | A |
| Светло-голубой | B |
| Светло-красный | C |
| Светло-сиреневый | D |
| Светло-желтый | E |
| Яркий белый | F |
/? Отображение справки в командной строке.
Описание
Чтобы задать стандартные цвета в окне командной строки, щелкните левый верхний угол этого окна, выберите команду «Умолчания», перейдите к вкладке «Цвета» и укажите цвета для параметров «Текст на экране» и «Фон экрана».
Для изменения цветов окна командной строки в текущем сеансе можно воспользоваться командой cmd /t:тф.
Если цвета текста и фона совпадают, команда color устанавливает значение параметра ERRORLEVEL в единицу (1).
Пример
Чтобы изменить цвет текста на красный, а цвет фона на белый в окне командной строки, введите следующую команду:
color FC
Posted in WINDOWS and tagged cmd.