| description | title | ms.date | f1_keywords | helpviewer_keywords | ms.assetid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Compiler Error CS0019 |
Compiler Error CS0019 |
07/20/2015 |
CS0019 |
CS0019 |
5a25be41-535b-4850-a230-9a385e01fd20 |
Compiler Error CS0019
Operator ‘operator’ cannot be applied to operands of type ‘type’ and ‘type’
A binary operator is applied to data types that do not support it. For example, you cannot use the || operator on strings, you cannot use +, -, <, or > operators on bool variables, and you cannot use the == operator with a struct type unless the type explicitly overloads that operator.
You can overload an operator to make it support operands of certain types. For more information, see Operator overloading.
Example 1
In the following example, CS0019 is generated in three places because bool in C# is not convertible to int. CS0019 is also generated when the subtraction operator - is applied to a string. The addition operator + can be used with string operands because that operator is overloaded by the String class to perform string concatenation.
static void Main() { bool result = true; if (result > 0) //CS0019 { // Do something. } int i = 1; // You cannot compare an integer and a boolean value. if (i == true) //CS0019 { //Do something... } string s = "Just try to subtract me."; float f = 100 - s; // CS0019 }
Example 2
In the following example, conditional logic must be specified outside the xref:System.Diagnostics.ConditionalAttribute. You can pass only one predefined symbol to the xref:System.Diagnostics.ConditionalAttribute.
The following sample generates CS0019:
// CS0019_a.cs // compile with: /target:library using System.Diagnostics; public class MyClass { [ConditionalAttribute("DEBUG" || "TRACE")] // CS0019 public void TestMethod() {} // OK [ConditionalAttribute("DEBUG"), ConditionalAttribute("TRACE")] public void TestMethod2() {} }
See also
- C# operators
This program is in response to the assignment:
«Create a method named Sum() that accepts any number of integer parameters and
displays their sum. Write a Main() method that demonstrates that the Sum() method works correctly when passed one, three, five, or an array of ten integers. Save the program as UsingSum.cs.»
from Microsoft® Visual C#® 2008, An Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming, 3e, Joyce Farrell
My code in the «//step 1:» part is getting the CS0019 error, which states that it cannot be applied to operands of type bool and int.
I highly suspect there are also other problems with this code, but it’s a great improvement over what I had four hours ago…
using System;
public class UsingSum
{
public static void Main()
{
Sum();
}
public static void Sum()
{
// Step 1: Addition of one, three, five
bool q, r, s;
int firstTotal, n, o, p;
string k, l, m;
Console.Write("Type the number 1: ");
k = Console.ReadLine();
n = Convert.ToInt32(k);
q = Convert.ToBoolean(k);
Console.WriteLine();
if (q == 1)
Console.WriteLine("Input accepted.");
else if (!(q == 1))
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: You didn't type the number 1. Please try again.");
Console.Write("Type the number 1: ");
k = Console.ReadLine();
n = Convert.ToInt32(k);
q = Convert.ToBoolean(k);
}
}
Console.Write("Type the number 3: ");
l = Console.ReadLine();
r = Convert.ToBoolean(l);
o = Convert.ToInt32(l);
Console.WriteLine();
if (r <= 2 || r >= 4)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: You didn't type the number 3. Please try again.");
Console.Write("Type the number 3: ");
l = Console.ReadLine();
r = Convert.ToBoolean(l);
o = Convert.ToInt32(l);
}
else
if (r = 3)
Console.WriteLine("Input accepted.");
Console.Write("Type the number 5: ");
m = Console.ReadLine();
p = Convert.ToInt32(m);
s = Convert.ToBoolean(m);
Console.WriteLine();
if (s <= 4 || s >= 6)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: You didn't type the number 5. Please try again.");
Console.Write("Type the number 5: ");
m = Console.ReadLine();
p = Convert.ToInt32(m);
s = Convert.ToBoolean(m);
}
else
if (s = 5)
Console.WriteLine("Input accepted.");
firstTotal = n + o + p;
Console.WriteLine("{0} + {1} + {2} = {3}", n, o, p, firstTotal);
// Step 2: Entering integers for array[10]
int a, arrayTotal, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, unlimited;
Console.Write("Enter first integer for addition: ");
a = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter second integer for addition: ");
b = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter third integer for addition: ");
c = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter forth integer for addition: ");
d = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter fifth integer for addition: ");
e = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter sixth integer for addition: ");
f = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter seventh integer for addition: ");
g = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter eighth integer for addition: ");
h = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter ninth integer for addition: ");
i = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.Write("Enter tenth integer for addition: ");
j = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
arrayTotal = a + b + c + d + e + f + g + h + i +j;
Console.WriteLine("The total of {0} + {1} + {2} + {3} + {4} + {5} + {6} + {7} + {8} + {9} = {10}",
a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, arrayTotal);
// Step 3: Unlimited array addition
int[] arrayTwo;
int total, y;
string ADD, x;
while(Console.Write("Enter an integer for addition, or type ADD to calculate the sum: "))
{
x = Console.ReadLine();
y = Convert.ToInt32(x);
if (x == ADD)
Console.WriteLine("Calculating the total sum");
}
for (y = 0; y < arrayTwo.Length; ++y)
{
total = arrayTwo[y] + arrayTwo[y];
++arrayTwo[y];
Console.WriteLine("========================");
Console.WriteLine("=/n= The total is: {0} =/n=", total);
Console.WriteLine("========================");
}
}
}
|
Slavormund 0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 18.09.2020 Сообщений: 31 |
||||
|
1 |
||||
|
25.01.2021, 19:55. Показов 5014. Ответов 4 Метки нет (Все метки)
Я не понимаю в чем проблема,вроде подобное уже делал,но не могу понять Ошибка:
__________________
0 |
|
randok 612 / 392 / 187 Регистрация: 28.11.2019 Сообщений: 852 |
||||||||||||||||
|
25.01.2021, 19:58 |
2 |
|||||||||||||||
|
Решение
замените на
И вот тут будет ошибка
Если конечно Abs это не какой-то ваш метод.
1 |
|
1483 / 880 / 321 Регистрация: 17.05.2015 Сообщений: 3,351 |
|
|
25.01.2021, 20:01 |
3 |
|
if (((a = 1) && (b = 2)) = — оператор присваивания
1 |
|
0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 18.09.2020 Сообщений: 31 |
|
|
25.01.2021, 20:06 [ТС] |
4 |
|
с Abs нет ошибки, я использовал using static System.Math; чтобы не вызывать каждый раз класс Math (вроде правильно объяснил)
0 |
|
612 / 392 / 187 Регистрация: 28.11.2019 Сообщений: 852 |
|
|
25.01.2021, 20:13 |
5 |
|
чтобы не вызывать каждый раз класс Math Я понял мысль, но лучше так не делать, вносит сумятицу при чтении кода. Вот я не посмотрел на юзинги и сразу в глаза бросился этот Abs. В общем, уводит внимание от привычного написания метода.
0 |
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
Hi,
I want to compare two <T> elements as in the simple code below:
class MyList<T>
{
public T Data = default(T);
private MyList<T> Next;
public void Insert(T item)
{
if (item == Data) // compiler errror CS0019
return;
}
}
I’ve tried IEqualityComparer<T> and to overload the operator but it doesn’t solve my problem.
Thanks for any help.
Answers
-
Operators are actually «static» class members; they are not base class or interface members. Therefore, you cannot invoke them in a «generic» way.
Use the .Equals() method instead of ==.
Another way to do this, which constrains T to implement IEqualityComparer is as follows. This might be more efficient for T that are value types as I believe that the Object.Equals(object) above will cause boxing of value types. This will ensure that the «strongly typed» IEqualityComparer.Equals(T) is used):
Code Block
class MyList<T> where T : IEqualityComparer<T>
{
public T Data = default(T);
private MyList<T> Next;
public void Insert(T item)
{
if (item.Equals(Data))
return;
}
}
C# Compiler Error Message
Operator ‘{0}’ cannot be applied to operands of type ‘{1}’ and ‘{2}’
Reason for the Error
You would usually get this error when you are using an operator that doesn’t support a specific data type. Below are some of the cases when you will receive this error.
- When you use bool and think, it works as integer.
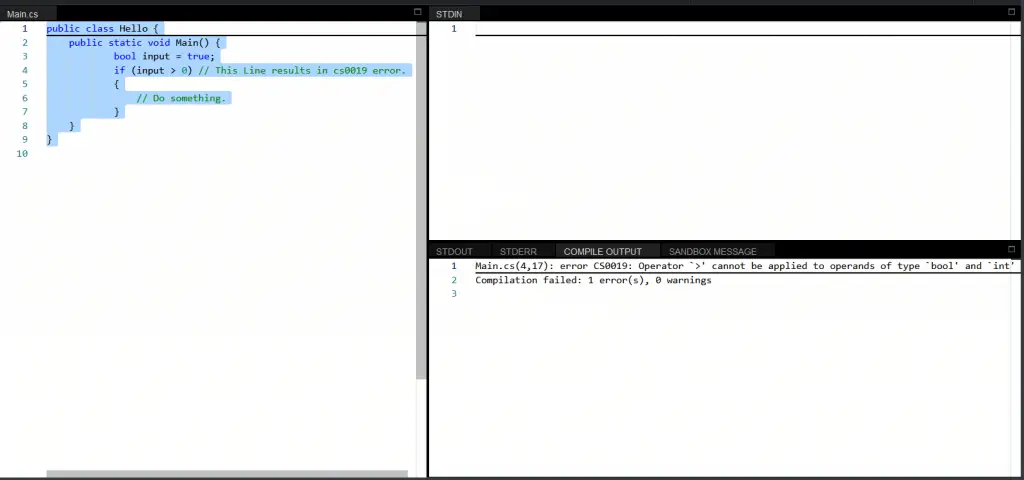
public class Hello {
public static void Main() {
bool input = true;
if (input > 0) // This Line results in cs0019 error.
{
// Do something.
}
}
}
Error CS0019 Operator ‘>’ cannot be applied to operands of type ‘bool’ and ‘int’ ConsoleApp1 C:UsersSenthilsourcereposConsoleApp1ConsoleApp1Program.cs 6 Active
- When you compare an int with boolean
namespace ClassLibrary
{
public class DeveloperPublish
{
public static void Main()
{
int input = 1;
if (input == true)
{
}
}
}
}
You will receive the below error.
Error CS0019 Operator ‘==’ cannot be applied to operands of type ‘int’ and ‘bool’ ConsoleApp1 C:UsersSenthilsourcereposConsoleApp1ConsoleApp1Program.cs 8 Active
Some of the Other common scenarios that would result with this error includes
- When you use || operator on strings
- When you use +,- on boolean.
- When you use == with structs
Solution
To fix the error, ensure that you revisit the logic and ensure that the right operator is used for the operands in your .NET application.

 Сообщение было отмечено Slavormund как решение
Сообщение было отмечено Slavormund как решение