- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
Hello All,
I am trying to connect to my exchange server via PowerShell. When I ran the following PS command:
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName Exch01 -Credential SAMOAdmin -Authentication Default
I got the following error:
Enter-PSSession : Connecting to remote server failed with the following error message : The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the re
quest. Verify that the service on the destination is running and is accepting requests. Consult the logs and documentation for the WS-Management service
running on the destination, most commonly IIS or WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM service, run the following command on the destination to analyzWinRM service is started on Exchange server. Any thoughts?
| title | description | author | audience | ms.topic | ms.author | manager | localization_priority | ms.custom | search.appverid | appliesto | ms.date | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Connecting to the remote server failed when start Management Shell or Console |
Connecting to the remote server failed with the following error message when you start the Exchange Management Shell or the Exchange Management Console. |
simonxjx |
ITPro |
troubleshooting |
v-six |
dcscontentpm |
Normal |
|
MET150 |
|
3/31/2022 |
«Connecting to the remote server failed with the following error message» error when you start the Exchange Management Shell or the Exchange Management Console
Symptoms
When you try to start the Microsoft Exchange Management Shell (EMS) or the Microsoft Exchange Management Console (EMC) on a server that is running Microsoft Exchange Server, you receive one of the following error messages:
-
Error message 1
Connecting to remote server failed with the following error message: The WinRM client cannot process the request. It cannot determine the content type of the HTTP response from the destination computer. The content type is absent or invalid. For more information, see the about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
-
Error message 2
Connecting to remote server failed with the following error message: The WinRM client sent a request to an HTTP server and got a response saying the requested HTTP URL was not available. This is usually returned by a HTTP server that does not support the WS-Management protocol. For more information, see the about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
-
Error message 3
Connecting to remote server failed with the following error message: The WinRM client received an HTTP server error status (500), but the remote service did not include any other information about the cause of the failure. For more information, see the about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic. It was running the command ‘Discover-ExchangeServer -UseWIA $true -SuppressError $true’.
-
Error message 4
Connecting to remote server failed with the following error message: The connection to the specified remote host was refused. Verify that the WS-Management service is running on the remote host and configured to listen for requests on the correct port and HTTP URL. For more information, see the about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
-
Error message 5
Connecting to remote server failed with the following error message: The WinRM client received an HTTP status code of 403 from the remote WS-Management service.
-
Error message 6
Connecting to the remote server failed with the following error message: The WinRM client sent a request to an HTTP server and got a response saying the requested HTTP URL was not available. This is usually returned by a HTTP server that does not support the WS-Management protocol.
-
Error message 7
Connecting to remote server failed with the following error message: The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the request. Verify that the service on the destination is running and is accepting requests. Consult the logs and documentation for the WS-Management service running on the destination, most commonly IIS or WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM service, run the following command on the destination to analyze and configure the WinRM service:
-
Error message 8
Connecting to remote server failed with the following error message: The WS-Management service does not support the request.
-
Error message 9
Connecting to remote server failed with the following error message: The WinRM client cannot process the request. The WinRM client tried to use Kerberos authentication mechanism, but the destination computer.
Resolution
To resolve these problems, run the «Exchange Management Troubleshooter» (EMTshooter).
About the EMT shooter
The EMTshooter runs on the local (target) Exchange server and tries to identify potential problems that affect the management tools that are connected to it.
The troubleshooter runs in two stages. First, it examines the IIS Default Web Site, the PowerShell vdir, and other critical areas to identify known causes of connection problems. If the tool identifies a problem that affects one of the pre-check processes, it makes a recommendation to resolve the problem. If the pre-checks pass, the troubleshooter tries to connect to the server exactly like the management tools would connect. If that connection attempt still causes a WinRM-style error, the troubleshooter tries compare that error to a list of stored strings that are collected from related support cases. If a match is found, the troubleshooter displays the known causes of that error in the CMD window.
The following screen shot shows how this display might appear.
:::image type=»content» source=»media/connecting-remote-server-failed/emt-shooter.png» alt-text=»Screenshot of how this display might appear.»:::
The EMTshooter logs events in the «Microsoft-Exchange-Troubleshooters/Operational» event log. All results that are displayed in the CMD window are also logged in the event log to create a record.
Things to remember
-
Depending on your current settings, you may have to adjust the execution policy on your computer to run the troubleshooter by using one of the following commands:
-
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
-
Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted
[!IMPORTANT]
Remember to revert to the usual settings after you run the troubleshooter.
-
-
You must run this version of the troubleshooter on the server that is running Exchange Server that the management tools do not connect to.
-
In order to run the troubleshooter, you must have the user rights to log on locally to the Exchange server. This is a current requirement of the tool. Additionally, you must have the user rights to run Windows PowerShell.
How to install EMTshooter
To install the EMT shooter, follow these steps:
- Download the troubleshooter compressed file that has a .zip filename extension from here.
- Extract the four files that are included in the .zip file into a folder, and then rename the file extensions to .ps1.
- Run EMTshooter.ps1 from a standard (and local) Windows PowerShell window.
References
For more information about the problems that are processed by EMTshooter and the causes of some of those problems, see the following Exchange Team Blog articles:
Troubleshooting Exchange 2010 Management Tools startup issues
Resolving WinRM errors and Exchange 2010 Management tools startup failures
I am receiving the following error when I try to connect exchange online from powershell.
[ps.outlook.com] Connecting to remote server failed with the following error message : The WinRM client cannot process the request because the server name cannot be resolved. For more information, see the about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
+ CategoryInfo : OpenError: (System.Manageme....RemoteRunspace:RemoteRunspace) [], PSRemotingTransportException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : PSSessionOpenFailed
I am using below command to connect Office 365 using remote PowerShell:
$365Logon = Get-Credential $Session = New-PSSession -ConfigurationName Microsoft.Exchange -ConnectionUri https://outlook.office365.com/powershell-liveid/ -Credential $365Logon -Authentication Basic -AllowRedirection Import-PSSession $Session
Solution 1: Run as Administrator
To troubleshoot the error message “Connecting to remote server failed with the following error message: The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the request”, You have to run the Windows PowerShell with elevated privilege ( right click the Windows PowerShell and click “Run as Administrator”).
Solution 2: Connect Office 365 via Proxy Server
This issue also can occur if the Windows PowerShell remoting is affected by proxy settings. To resolve this problem, use proxy setting options in your remote command. The following settings are available: ProxyAccessType, ProxyAuthentication, ProxyCredential
To set these options for a particular command, use the following procedure:
1. Use the ProxyAccessType, ProxyAuthentication, and ProxyCredential parameters of the New-PSSessionOption cmdlet to create a session option object with the proxy settings for your enterprise. Save the option object is a variable.
2. Use the variable that contains the option object as the value of the SessionOption parameter of a New-PSSession command.
$365Logon = Get-Credential $proxyOptions = New-PSSessionOption -ProxyAccessType IEConfig $Session = New-PSSession -ConfigurationName Microsoft.Exchange -ConnectionUri https://outlook.office365.com/powershell-liveid/ -Credential $365Logon -Authentication Basic -AllowRedirection -SessionOption $proxyOptions Import-PSSession $Session
For more detailed information: please refer to the HOW TO CONFIGURE REMOTING WITH A PROXY SERVER section in the following article: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd347642.aspx
Source : https://community.office365.com/en-us/f/148/t/19593
I’ve had two annoying PowerShell errors today, both for the same server:
Enter-PSSession : Connecting to remote server server-a.rcmtech.co.uk failed with the following error message : The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the request. Verify that the service on the destination is running and is accepting requests. Consult the logs and documentation for the WS-Management service running on the destination, most commonly IIS or WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM service, run the following command on the destination to analyze and configure the WinRM service: "winrm quickconfig". For more information, see the about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
The standard “internet” response to this is to open an Administrator command prompt and run
winrm qc
(or winrm quickconfig). Or open an Administrator PowerShell prompt and run:
Enable-PSRemoting
But these are quite annoying solutions if you know that it should be working, and indeed is working on all your other servers, because you’ve configured it via Group Policy! There’s no harm in running the commands anyway, but most likely they’ll just come back and say “already configured” or words to that effect.
So the fix (for me) for the above error was to check what IP addresses the listener was listening on using:
netstat -aon | find "5985"
where 5985 is the default port used by WinRM. You should see the system process (ID 4) listening on 0.0.0.0 like this:
TCP 0.0.0.0:5985 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 4
However on my problem server it was listening on 127.0.0.1. This can be confirmed using:
netsh http show iplisten
and you’ll only see 127.0.0.1 in the list.
On the problem server itself you’ll find that using:
Enter-PSSession -Computername localhost
works, whereas:
Enter-PSSession -Computername server-a.rcmtech.co.uk
does not.
localhost is the name for the loopback address 127.0.0.1 whereas the fully qualified server name will give you the IP address of the server as seen from your network.
The fix for this is to delete the loopback address from the http listener, which then makes it listen on all valid addresses:
netsh http delete iplisten 127.0.0.1.
Check what addresses it is now listening on (plus the port) by using:
winrm e winrm/config/listener
Problem solved. Or not, I then got this error:
Enter-PSSession : Connecting to remote server server-a.rcmtech.co.uk failed with the following error message : The WinRM client sent a request to an HTTP server and got a response saying the requested HTTP URL was not available. This is usually returned by a HTTP server that does not support the WS-Management protocol. For more information, see the about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
Which it turns out can be caused by having IPv6 enabled on the server.
In the netstat output (see above) I also had some IPv6 addresses showing as listening on port 5985.
I don’t use IPv6 but it’s on by default in Windows and will auto-assign itself a link local address (starts with fe80:). So I disabled IPv6 and the error went away. There’s also a workaround using the hosts file if you don’t want to disable IPv6.
Update
This might also be caused because you have the following group policy configured:
Computer ConfigurationPoliciesAdministrative TemplatesWindows ComponentsWindows Remote ManagementWinRM ServiceAllow remote server management through WinRM
And in the settings for that policy, you only have a * in the box for IPv4, and nothing in the box for IPv6. Add a * in the IPv6 box too.
I have two Windows 7 Computers.
Can Not Connect to remote PowerShell and getting this error message
invoke-command -computername XXXXXX -scriptblock {
get-process} -credential administrator
[XXXXXXX] Connecting to remote server XXXXXX failed with the
following error message : The WinRM client cannot process the request. If the
authentication scheme is different from Kerberos, or if the client computer is
not joined to a domain, then HTTPS transport must be used or the destination
machine must be added to the TrustedHosts configuration setting. Use winrm.cmd
to configure TrustedHosts. Note that computers in the TrustedHosts list might
not be authenticated. You can get more information about that by running the
following command: winrm help config. For more information, see the
about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
+ CategoryInfo : OpenError: XXXXXX [], PSRemotingT
ransportException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : ServerNotTrusted,PSSessionStateBroken
PS C:windowssystem32>
PS C:UsersAdministrator> Invoke-Command -ComputerName XXXX -ScriptBlock {get-process} -credential administrator
[XXXXXX] Connecting to remote server XXXXX failed with the following
error message : The client cannot connect to the destination specified in the
request. Verify that the service on the destination is running and is accepting
requests. Consult the logs and documentation for the WS-Management service running
on the destination, most commonly IIS or WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM
service, run the following command on the destination to analyze and configure the
WinRM service: «winrm quickconfig». For more information, see the
about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
+ CategoryInfo : OpenError: (XXXXX:String) [], PSRemotingTranspo
rtException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : CannotConnect,PSSessionStateBroken
# Outbound connection is fine as I can connect to different machine from here. However Incoming Connection Does not work
# Have Tried Multiple Things like «Enable-PSRemoting -Force». and it starts Perfectly.
# And since I have put the machine in workgroup run the command as well «Set-Item wsman:localhostclienttrustedhosts *» (This runs successfully as well)
# Infact WinRM QuickConfig does not work.
# And have tried with and without firewall. and also applied Multiple hotfixes but did not resolve the issue
Please advise
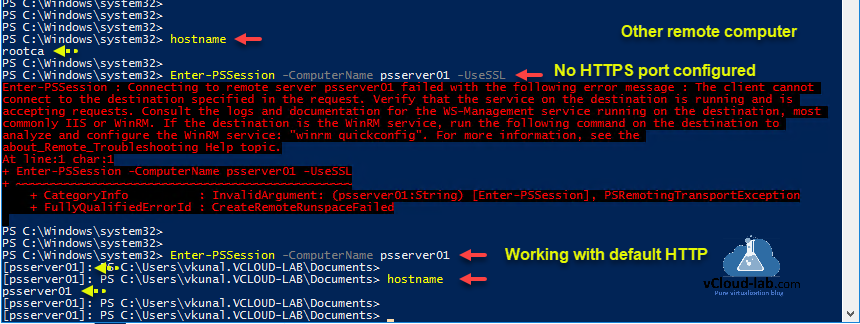
This is a step by step guide and will show you how to use HTTPS port and self signed SSL certificate while using Powershell Remoting. On the PSRemoting regards I had already written one article in the past POWERSHELL PS REMOTING BETWEEN STANDALONE WORKGROUP COMPUTERS, When you use WinRM PSRemoting, it uses default HTTP 5985 port for connection and SSL is not used, If I try to use Enter-PSSession command with -UseSSL syntax which Indicates that it will use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol to establish a connection to the remote computer. WS-Management encrypts all Windows PowerShell content transmitted over the network. If you use this parameter, but SSL is not configured, the command fails with below error.
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <FQDN_IP> -UseSSL
Enter-PSSession : Connecting to remote server psserver01 failed with the following error message : The client cannot
connect to the destination specified in the request. Verify that the service on the destination is running and is
accepting requests. Consult the logs and documentation for the WS-Management service running on the destination, most
commonly IIS or WinRM. If the destination is the WinRM service, run the following command on the destination to
analyze and configure the WinRM service: «winrm quickconfig». For more information, see the
about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
At line:1 char:1
+ Enter-PSSession -ComputerName psserver01 -UseSSL
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : InvalidArgument: (psserver01:String) [Enter-PSSession], PSRemotingTransportException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : CreateRemoteRunspaceFailed
Series
POWERSHELL PS REMOTING BETWEEN STANDALONE WORKGROUP COMPUTERS
PowerShell remoting over HTTPS using self-signed SSL certificate
Configure Powershell WinRM to use OpenSSL generated Self-Signed certificate
Powershell WinRM HTTPs CA signed certificate configuration
Powershell Generate Self-signed certificate with Self-Signed Root CA Signer
The -UseSSL parameter is an additional protection that sends the data across an HTTPS connection instead of an HTTP connection. If I don’t use -UseSSL parameter everything is successful as you can see on below screenshot.
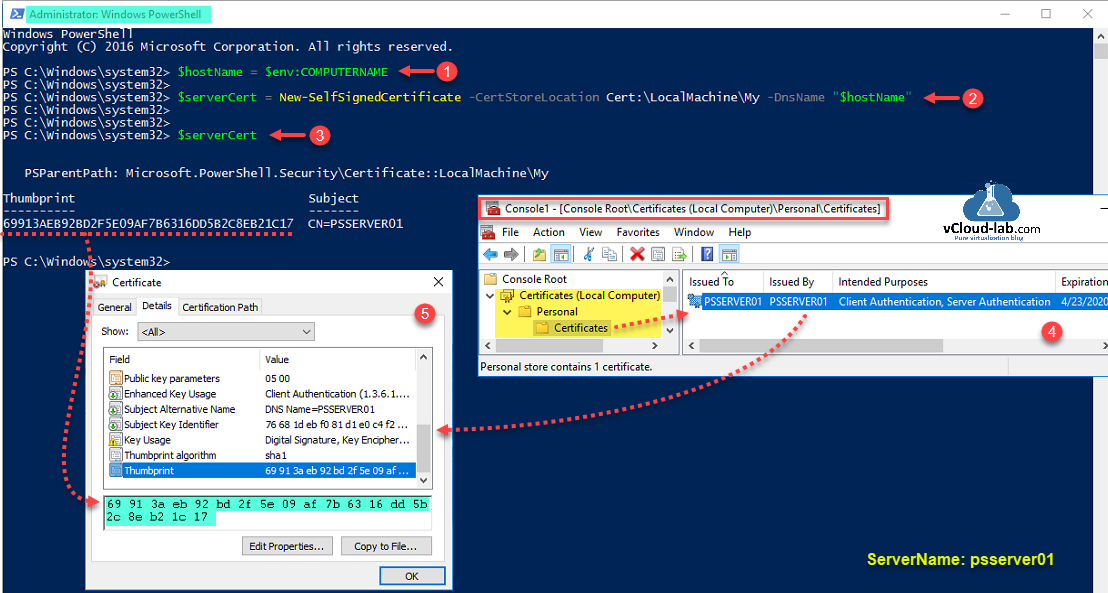
To start configuring SSL certificate, first step is requirement of certificate, which can be self signed or CA certificate. As this is a Lab proof of concept (POC), I am using powershell command to create one cert, Dns name should be matching current hostname as DNSName for self-signed certificate.
$hostName = $env:COMPUTERNAME
$serverCert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:LocalMachineMy -DnsName $hostName
Verify the thumbprint of the newly created certificate, it is located under Local machine personal certificate store.
$serverCert
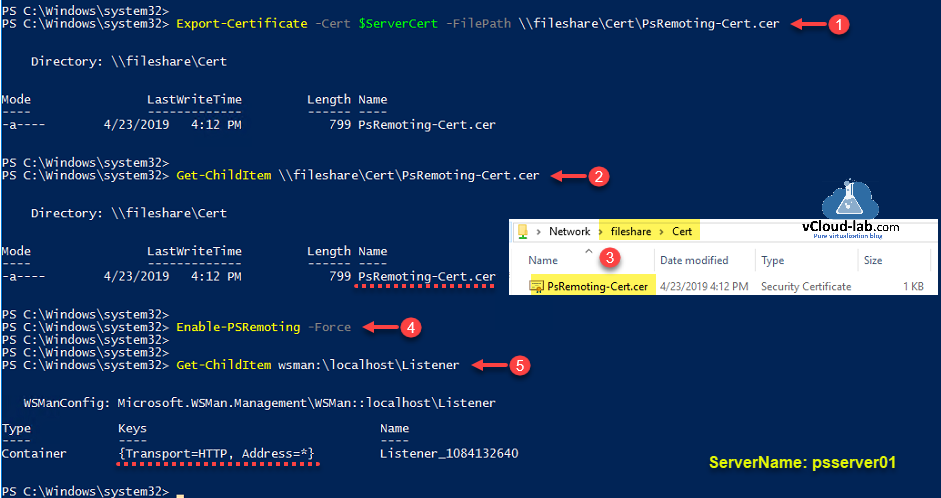
Creation of self signed SSL certificate is successful and it will be needed on the last steps, I am exporting it on remote share drive using below command.
Export-Certificate -Cert $serverCert -FilePath \filesharecertPsRemoting-Cert.cer
Next verify and check on fileshare for exported certificate that is exported successfully.
Get-ChildItem \fileshareCertPsRemoting-Cert.cer
You can enable powershell remoting now, Although this command might not be required to run on newer version of windows OS, because remoting is by default enabled.
Enable-PSRemoting -Force
Running above command will update WinRM for remote management, WinRM service type will set and change to delayed auto start and it will be started, and in the last
It creates a WinRM listener on https://* to accept WS-Man requests to any IP for this machine, we will start working on it
Default TCP ports for Powershell Remoting are HTTP — 5985 and HTTPS — 5986. You will always find one default listener (PS-Remoting endpoint) created with name {Transport=HTTPs, Address=*}. Below command helps to view the listener, it is located under PSDrive WsMan.
Get-ChildItem wsman:localhostListener
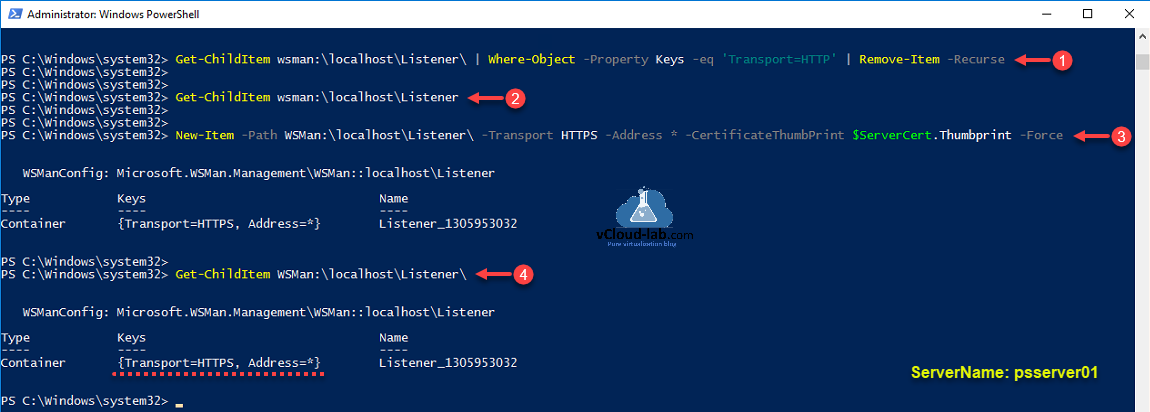
I am going to remove this default HTTP listener. for security reason I will only use HTTPS port to connect. HTTPS can coexist with HTTP.
Get-ChildItem wsman:localhostListener | Where-Object -Property Keys -eq ‘Transport=HTTP’ | Remove-Item -Recurse
Re-verify that no listener is available, running below command again.
Get-ChildItem wsman:localhostListener
Create a new listener with previously created SSL certificate.
New-Item -Path WSMan:localhostListener -Transport HTTPS -Address * -CertificateThumbPrint $serverCert.Thumbprint -Force
Rerun the command to verify new setting on the listener, There should be new HTTPS listener created.
Get-ChildItem wsman:localhostListener
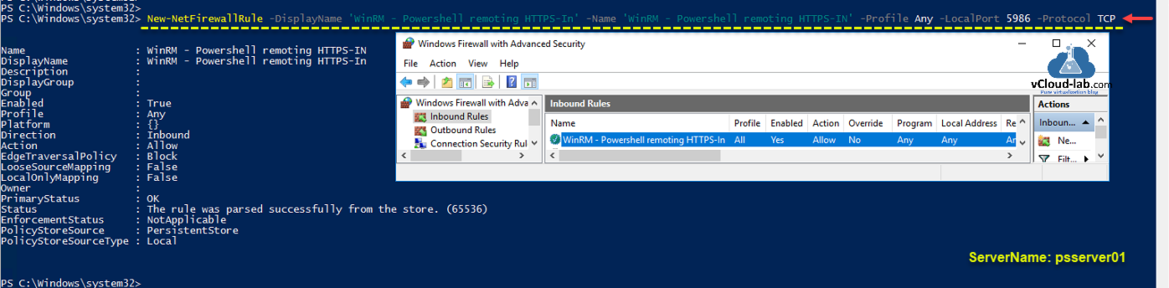
Although I have disabled firewall completely on my lab server, but in case windows software Firewall is enabled in your environment on the server, you will need to create a new rule in firewall to allow traffic through TCP port number 5986. It will be Inbound rule for Windows Remote Management via WS-Management. [TCP 5986].
New-NetFirewallRule -Displayname ‘WinRM — Powershell remoting HTTPS-In’ -Name ‘WinRM — Powershell remoting HTTPS-In’ -Profile Any -LocalPort 5986 -Protocol TCP
You can verify the same on Windows Firewall with Advanced Security, Inbound rules settings.
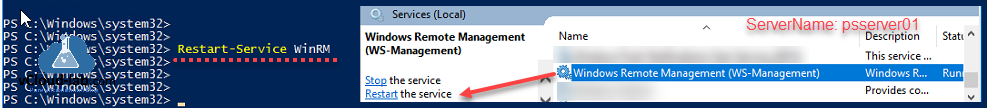
Although restarting WinRM service is not required, but still restart it using command to take effect, you can also use Services.msc — Windows Remote Management (WS-Management).
Restart-Service WinRM
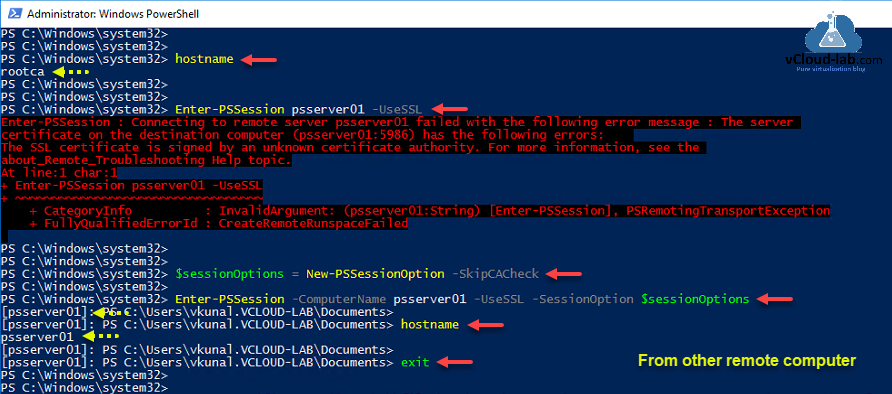
On the other computer from where you want to try remote use command Enter-PSSession <ComputerName> -UseSSL, it might fail again, it will show another error message. As we removed default listener in earlier commands, remoting will not even work without -UseSSL syntax.
Enter-PSSession : Connecting to remote server psserver01 failed with the following error message : The server
certificate on the destination computer (psserver01:5986) has the following errors:
The SSL certificate is signed by an unknown certificate authority. For more information, see the
about_Remote_Troubleshooting Help topic.
At line:1 char:1
+ Enter-PSSession adserver001 -UseSSL
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : InvalidArgument: (adserver001:String) [Enter-PSSession], PSRemotingTransportException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : CreateRemoteRunspaceFailed
This error is receiving because certificate is self signed and not trusted, for a testing purpose we can skip certificate check to test PSRemoting as below.
$sessionOptions = New-PSSessionOption -SkipCACheck
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <FQDN_HostName> -UseSSL -SessionOption $sessionOptions
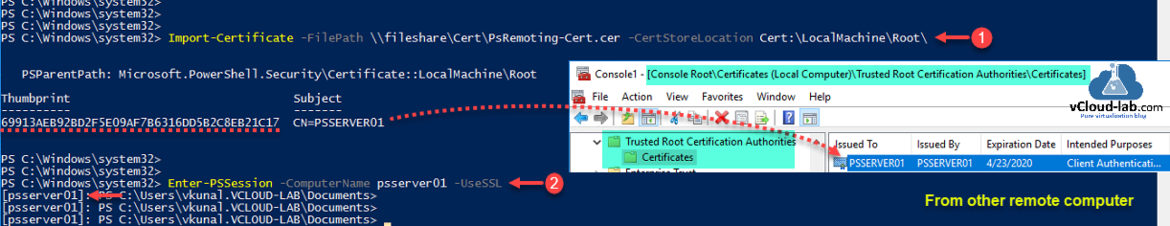
Above command add one line to the script, to avoid it, if you have admin access you can trust the self-signed cert, you will need it to import to Trusted Root Certification Authorities, run command.
Import-Certificate -FilePath \fileshareCertPsRemoting-Cert.cer -CertStoreLocation Cert:LocalMachineroot
Once imported verifiy the certificate thumbprint and try psremoting.
Enter-PSSession -Computername <FQDN> -UseSSL
Useful Articles
Generate new self-signed certificates for ESXi using OpenSSL
Push SSL certificates to client computers using Group Policy
Replacing a default ESXi certificate with a CA-Signed certificate
Troubleshooting replacing a corrupted certificate on Esxi server
How to import default vCenter server appliance VMCA root certificate and refresh CA certificate on ESXi
How to replace default vCenter VMCA certificate with Microsoft CA signed certificate