In my dynamic web project in eclipse, I have jQuery in my js source folder. For some reason, Eclipse is not handling it correctly and interpreting many lines as errors in the standard jQuery file (even though I have the javascript development tools installed).
Can I turn off the error checking on the jQuery file (and that file only)? I still want it to detect errors as usual, but ignore anything in jQuery.js.
asked Nov 26, 2010 at 4:00
4
It looks like eclipse has changed a bit,
but the following method which worked for me seems very close to the old one.
The solution consists of 2 steps:
-
First you have to update Eclipse’s preferences (
Window > Preferences):Make sure that you check both
Manual&Buildnext to theValidatoryou need
(in my case — a javascript one). -
Last you should change your project’s Validators:
Click on
Client-side JavaScript Settings(or any other validator you need):The explanation is clear but basically what you should do is as follows:
Click on
Add Exclude Group..., select it and then click onAdd rule....
Then pickFolder or file name(note that there are other options), and specify your file/folder.
You should be able to verify that its working by deleting the existing errors/warnings,
and then left-click your project and select the Validate option.
This setting can be committed into source control as well.
answered Nov 26, 2010 at 11:41
Gábor LiptákGábor Lipták
9,6082 gold badges57 silver badges112 bronze badges
8
Perform these steps to solve this(This will disable eclipse validation for Javascript):
1. Go to Eclipse > preference > Javascript> validators > Errors/Warnings
2. Uncheck «Enable JavaScript semantic validation».
If you have messed around with the javascript settings in your projects, then restore everything to default first for all the projects that u have changed. After that, follow the steps.
answered Feb 6, 2013 at 4:30
MandarkMandark
751 silver badge5 bronze badges
I had javascript errors seen on jquery mobile file on an Android Phonegap project. I simply removed the file from the project and add it afterwards. It works now.
answered Jul 4, 2013 at 14:25
danpopdanpop
95912 silver badges25 bronze badges
Not sure if it’ll work for all.
But what i did was select the unnecessary errors in ‘problems’ tab of eclipse, Rclick and Delete.
Eclipse stopped showing the error..
answered Jun 21, 2017 at 3:48
One way is that :
1.remove javascript -> validator -> errors/warning.
2.remove project -> .project file -> javascript command
3.It is important,too! delete js file and import again.
answered Feb 6, 2013 at 17:26
With eclipse Luna I was getting this as well. I did a right click on jquery.jqGrid.min.js and selected ‘Validate’. It then validated fine and the errors went away.
answered Apr 22, 2015 at 18:02
This isn’t for the «current project» (per the exact question), but it is applicable in a more general sense…
Just close the project!
This should be obvious, but it went right over my head at first. I had no idea the project was «open» by default just because it was «imported». The ui in Eclipse should be tweaked at bit to make this more clear. Apparently, unless you realized this, all of those projects you see listed are «open» by Eclipse and therefore part of whatever processing it is doing, including listing errors (even when you switch «working sets», etc).
To be explicit, in the project explorer, right-click on that project making a mess of your errors list and lighting up with an nasty «!» on it, then select «close project». When you want to work on it again, simply right click on it and select «open project».
If you have a working set selected, which it belongs to, it will disappear entirely when you close it. Deselecting all working sets, gives you the entire list of projects that Eclipse knows about. In this view, you’ll see how the icon on the project changes to denote being open vs closed.
I’m having a lot of parser errors from eclipse but I don’t have these errors when I compile the code. How can I ignore them?
Illidanek
9981 gold badge18 silver badges32 bronze badges
asked Jul 18, 2012 at 17:11
2
In the Indigo version of the CDT:
Project Settings -> C/C++ General -> Code Analysis
You can enable/disable specific errors and warnings, as well as customize inclusion and exclusion patterns for those warnings.
If you get a large number of «Type ‘TYPE’ could not be resolved» errors, perhaps you need to make sure Eclipse can find all your code and libraries. You might want to check:
C/C++ General -> Paths and Symbols
answered Jul 18, 2012 at 18:23
SovermanSoverman
1,1351 gold badge9 silver badges16 bronze badges
1
Under Settings you can selectively turn off and on which errors it reports, and how it displays them.
answered Jul 18, 2012 at 17:18
Andrew TomazosAndrew Tomazos
64.6k36 gold badges180 silver badges309 bronze badges
1 ]
- Windows—>preferences—>type «anno» you will find annotation
- Navigate(scroll) to warning section , uncheck vertical ruler and rest
if you wish
other method
- 2] go to project explorer right click any project you wish to
disable/turn off warnings or such - —>properties —> c/c++ settings—>tool settings—>search your compiler c or C++ and —> navigate to warning section—-uncheck
all (/any checked)
——> build project and Voila warnings gone
answered Sep 11, 2013 at 21:40
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.annotation.inheritNullAnnotations=disabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.annotation.missingNonNullByDefaultAnnotation=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.annotation.nonnull=org.eclipse.jdt.annotation.NonNull
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.annotation.nonnull.secondary=
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.annotation.nonnullbydefault=org.eclipse.jdt.annotation.NonNullByDefault
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.annotation.nonnullbydefault.secondary=
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.annotation.nullable=org.eclipse.jdt.annotation.Nullable
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.annotation.nullable.secondary=
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.annotation.nullanalysis=disabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.codegen.inlineJsrBytecode=enabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.codegen.methodParameters=do not generate
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.codegen.unusedLocal=preserve
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.debug.lineNumber=generate
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.debug.localVariable=generate
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.debug.sourceFile=generate
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.APILeak=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.annotationSuperInterface=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.assertIdentifier=error
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.autoboxing=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.comparingIdentical=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.deadCode=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.deprecation=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.deprecationInDeprecatedCode=disabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.deprecationWhenOverridingDeprecatedMethod=disabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.discouragedReference=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.emptyStatement=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.enumIdentifier=error
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.explicitlyClosedAutoCloseable=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.fallthroughCase=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.fatalOptionalError=disabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.fieldHiding=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.finalParameterBound=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.finallyBlockNotCompletingNormally=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.forbiddenReference=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.hiddenCatchBlock=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.includeNullInfoFromAsserts=disabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.incompatibleNonInheritedInterfaceMethod=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.incompleteEnumSwitch=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.indirectStaticAccess=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.localVariableHiding=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.methodWithConstructorName=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.missingDefaultCase=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.missingDeprecatedAnnotation=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.missingEnumCaseDespiteDefault=disabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.missingHashCodeMethod=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.missingOverrideAnnotation=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.missingOverrideAnnotationForInterfaceMethodImplementation=enabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.missingSerialVersion=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.missingSynchronizedOnInheritedMethod=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.noEffectAssignment=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.noImplicitStringConversion=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.nonExternalizedStringLiteral=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.nonnullParameterAnnotationDropped=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.nonnullTypeVariableFromLegacyInvocation=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.nullAnnotationInferenceConflict=error
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.nullReference=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.nullSpecViolation=error
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.nullUncheckedConversion=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.overridingPackageDefaultMethod=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.parameterAssignment=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.pessimisticNullAnalysisForFreeTypeVariables=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.possibleAccidentalBooleanAssignment=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.potentialNullReference=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.potentiallyUnclosedCloseable=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.rawTypeReference=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.redundantNullAnnotation=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.redundantNullCheck=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.redundantSpecificationOfTypeArguments=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.redundantSuperinterface=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.reportMethodCanBePotentiallyStatic=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.reportMethodCanBeStatic=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.specialParameterHidingField=disabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.staticAccessReceiver=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.suppressOptionalErrors=disabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.suppressWarnings=enabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.syntacticNullAnalysisForFields=disabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.syntheticAccessEmulation=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.terminalDeprecation=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.typeParameterHiding=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unavoidableGenericTypeProblems=enabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.uncheckedTypeOperation=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unclosedCloseable=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.undocumentedEmptyBlock=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unhandledWarningToken=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unlikelyCollectionMethodArgumentType=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unlikelyCollectionMethodArgumentTypeStrict=disabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unlikelyEqualsArgumentType=info
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unnecessaryElse=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unnecessaryTypeCheck=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unqualifiedFieldAccess=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedDeclaredThrownException=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedDeclaredThrownExceptionExemptExceptionAndThrowable=enabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedDeclaredThrownExceptionIncludeDocCommentReference=enabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedDeclaredThrownExceptionWhenOverriding=disabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedExceptionParameter=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedImport=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedLabel=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedLocal=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedObjectAllocation=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedParameter=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedParameterIncludeDocCommentReference=enabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedParameterWhenImplementingAbstract=disabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedParameterWhenOverridingConcrete=disabled
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedPrivateMember=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedTypeParameter=ignore
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.unusedWarningToken=warning
org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.varargsArgumentNeedCast=warning
So for the missing serial version Id warning, you can set org.eclipse.jdt.core.compiler.problem.missingSerialVersion=ignore
You might want to trigger a full build to update those diagnostics in your project (alt+shift+b, full)
It looks like eclipse has changed a bit,
but the following method which worked for me seems very close to the old one.
The solution consists of 2 steps:
-
First you have to update Eclipse’s preferences (
Window > Preferences):Make sure that you check both
Manual&Buildnext to theValidatoryou need
(in my case — a javascript one). -
Last you should change your project’s Validators:
Click on
Client-side JavaScript Settings(or any other validator you need):The explanation is clear but basically what you should do is as follows:
Click on
Add Exclude Group..., select it and then click onAdd rule....
Then pickFolder or file name(note that there are other options), and specify your file/folder.
You should be able to verify that its working by deleting the existing errors/warnings,
and then left-click your project and select the Validate option.
This setting can be committed into source control as well.
Friday, September 30, 2022

There is a project from a guy called ‘tarlog’ that made a plugin for eclipse at this google code site: http://code.google.com/p/tarlog-plugins/downloads/detail?name=tarlog.eclipse.plugins_1.4.2.jar&can=2&q=
It has some other features for eclipse, amongst which is Ctrl++ and Ctrl+- to change the font size, it’s frickin’ awesome.
Monday, October 17, 2022

You can simply achieve your goal by doing this
accept=».txt»
<input ui-jq="filestyle" type="file" nv-file-select="" accept=".txt" uploader="uploader" data-icon="false" data-classButton="btn btn-default" data-classInput="form-control inline v-middle input-s" multiple>
more information
Thursday, September 22, 2022

You could use sed for something that simple:
printf "line 1nLine 2nLine 3n" | sed '$ ! s/$/ && /'
Output
line 1 &&
Line 2 &&
Line 3
Monday, August 1, 2022

Puuh — just when I had given up I accidentally found this:
Try this: Right click on Eclipse’s
toolbar and choose «Customize this
perspective» option. You will see a
dialog box, and on «Shortcuts» tab
choose «New» from «Submenus:»
droplist.Find «PHP» in the left pane and check
the checkbox next to it. It will
enable both «PHP File» and «PHP
Project» in «New» menu of your
perspective. You can do the same to
other file editors as well. (HTML,
CSS,….
http://dev.eclipse.org/newslists/news.eclipse.tools.pdt/msg00228.html
Friday, October 21, 2022

Only authorized users can answer the search term. Please sign in first, or register a free account.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged :
jquery
eclipse
ide
While Lint can often find real errors that must be fixed, it also flags issues that may or may not be a problem depending on the context. If you’ve manually verified that an issue is not a problem, you may want to mark the issue as verified such that lint does not keep pointing it out.
In Source
You can suppress lint issues directly in the source code. This has the advantage that you filter only this specific occurrence of the lint issue (that you’ve presumably manually verified), not all occurrences of a particular issue type, or all occurrences in a file.
With Annotations
In .java files, you can suppress issues with the @SuppressLint annotations. You supply the lint issue id as the argument to the annotations.
For example
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
public void onGlobalLayout() {
....
You can also suppress more than one issue using a comma separated list:
@SuppressLint({"NewApi","StringFormatInvalid"})
In both Android Studio and Eclipse you can easily suppress lint issues directly without having to write the annotation yourself. Just invoke the quickfix for the warning, and one of the options will be to ignore the issue with an annotation; this will annotate either the local declaration, or the method, or the class, or the field, depending on the location of the error. (Some screenshots of this in action in Eclipse is shown here.)
In .xml files, you suppress issues with the special tools:ignore attribute instead.
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
....
<LinearLayout
tools:ignore="MergeRootFrame"
...
Tip: You can supply a comma separated list of issue id’s, or the special value «all» to indicate all issues.
In Source: With Comments
In recent versions of lint, you can also use a special line comment on the line above the error to suppress a warning.
In .java and .gradle files, use a comment line this (where again the issue id can be a comma separated list of id’s). You can prefix the id with «AndroidLint», which is allowed for consistency with the way IntelliJ disables inspections in comments.)
//noinspection AndroidLintSdCardPath
String path = "/sdcard/legacy.txt";
In XML files, the comment should look like this:
<!--suppress AndroidLintHardcodedText -->
(Again, you can supply a comma separated list of issue ids instead of a single id.)
In Build File: With Gradle Configuration
In Gradle files, you can specify a lintOptions configuration where you can disable id’s, enable id’s, as well as change the severity of issue id’s (including to «ignore» to disable them).
android {
lintOptions {
disable 'TypographyFractions','TypographyQuotes'
...
}
}
From Command Line
The lint command has three commands for controlling which checks are performed: --enable, --disable and --check (see the overview document for more details on these flags). However, these must be specified each time you run lint. This is similar to the lintOptions for Gradle above.
Config File: lint.xml
To persistently configure which rules are run, you can create a file named lint.xml in the root directory of your project (next to the manifest file). Lint will automatically look at this file and use it to ignore warnings. Gradle, Android Studio and Eclipse will also use this configuration file if present. Note that when you use Eclipse to suppress errors, it automatically creates this file for you, so you can use Eclipse to ignore warnings and then check in the resulting configuration file such that for example build server lint runs will ignore warnings you’ve manually verified.
Here’s a sample lint.xml file (the comments are obviously not needed; I’ve added them here to explain what each line does)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<lint>
<!-- Disable the given check in this project -->
<issue id="IconMissingDensityFolder" severity="ignore" />
<!-- Ignore the ObsoleteLayoutParam issue in the given files -->
<issue id="ObsoleteLayoutParam">
<ignore path="res/layout/activation.xml" />
<ignore path="res/layout-xlarge/activation.xml" />
<!-- Ignore the UselessLeaf issue in the given file -->
<issue id="UselessLeaf">
<ignore path="res/layout/main.xml" />
<!-- Change the severity of hardcoded strings to "error" -->
<issue id="HardcodedText" severity="error" />
</lint>
In recent versions of lint (Gradle plugin 0.9+, SDK Tools 27+, Android Studio 0.5+) you can use a globbing pattern for the path:
<issue id="ObsoleteLayoutParam">
<ignore path="res/**/activation.xml" />
You can also specify a full regular expression, by using a regexp attribute instead of path:
<ignore regexp="res/.*/activation.xml" />
You can also use «all» as the issue id if you want to apply settings for all issues.
Finally, as of Android Studio 0.9 and Gradle plugin 0.14.+ you can use a regular expression to match the error message as well:
<ignore regexp="Invalid package reference in library; not included in Android: java.* Referenced from " />
Issue Id’s
The issue identifiers used to suppress issues as shown above (IconMissingDensityFolder, ObsoleteLayoutParam etc) are the issue ids, which are included in the error output from the lint command:
Warning: The resource R.drawable.robot appears to be unused [UnusedResources]
You can also look up the lint ids with the lint --show command (for full details) or lint --list (for a brief summary):
$ lint --list
...
"ContentDescription": Ensures that image widgets provide a contentDescription
"DuplicateIncludedIds": Checks for duplicate ids across layouts that are
combined with include tags
"DuplicateIds": Checks for duplicate ids within a single layout
"StateListReachable": Looks for unreachable states in a <selector>
"InefficientWeight": Looks for inefficient weight declarations in
LinearLayouts
"NestedWeights": Looks for nested layout weights, which are costly
...
This lint configuration file apply to the current project, as well as any library projects included into this project. If you want to also have a «global» configuration used for all projects, you can create an additional global file and then invoke lint with the --config flag:
--config <filename> Use the given configuration file to determine whether
issues are enabled or disabled. If a project contains
a lint.xml file, then this config file will be used
as a fallback.
From Android Studio
You can configure lint severities from the global inspections menu. However, these will only be used inside Studio itself. If you want the Gradle command line build and other users to see your altered severities, use a lint.xml file or a Gradle lintOptions configuration instead.
To suppress an error, open the issue in the editor and run the quickfix/intentions action (Ctrl/Cmd F1) and select Suppress which will use annotations, attributes or comments to disable the issue.
From Eclipse
If you’re using the Eclipse Lint plugin, you can suppress errors directly from the Lint Window. There are three separate ignore levels:
- Always ignore. This completely suppresses the given warning. Use this for warnings you never want flagged.
- Ignore in project. This will ignore this warning in the current project (and any library projects referenced from this project).
- Ignore in file. This will ignore this warning anywhere in the current file, but not in any other files.
- (Ignore warnings within a class, method or even for a specific variable declaration, using annotations or attributes: See this document for more information.)
You can also access these from the quickfix menu in XML editors, and the first two from the Global Options dialog and from the Project Options dialog.
Project and file specific warnings are written into lint.xml files into the projects, so command line and build server lint runs will pick these up.
Whenever you write a Java class in Eclipse which implements java.io.Serializable interface, you’ll get this warning:
The serializable class XXXX does not declare a static final serialVersionUID field of type long
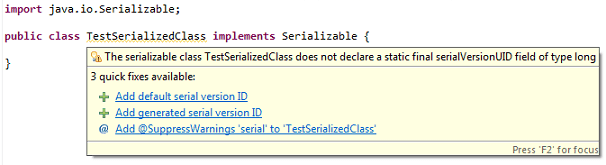
Why do we need serialVersionUID?
Whenever we implement java.io.Serializable interface, we explicitly tell JVM that this class can be serialized. Meaning, we might convert object of this class into byte streams and write it into a file or send it to another JVM through network.
Now when Java objects use serialization to save state in files, or as blobs in databases, the potential arises that the version of a class reading the data is different than the version that wrote the data.
Thus the serialVersionUID provides a versioning mechanism to Java class so that the same class format is used in reading (de-serialization) and writing (serialization) of objects.
But in most of the cases, you will not need this field. You will not have more than one versions of class file which creates issues in deserialization. And that’s why most of the time I skip adding a serialVersionUID version number.
How to ignore serialVersionUID warning
In Eclipse, you can permanently mute the serialVersionUID warning by:
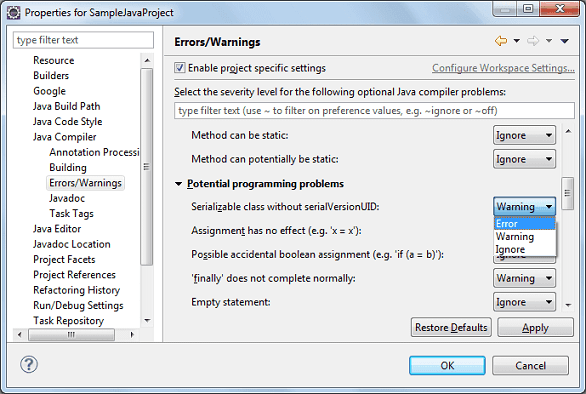
1. To ignore warning for specific eclipse project:
- Right click on Project, select Properties from context menu (Shortcut: Alt+Enter)
- Go to Java Compiler > Errors/Warnings
- Under Potential programming problems section, change Serializable class without serialVersionUID: to Ignore
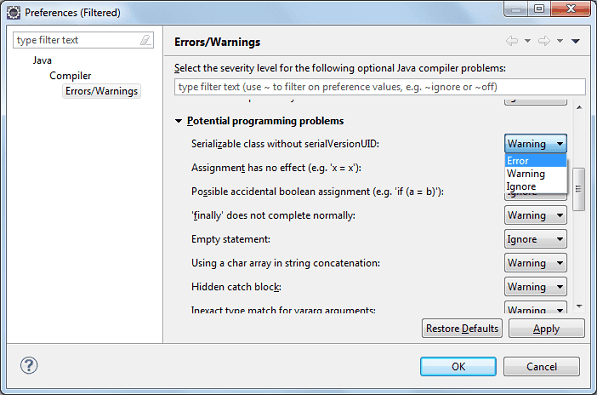
Or you may want to ignore this warning at workspace level.
2. To ignore warning at workspace level:
- Go to menu Windows > Preferences
- Navigate to Java > Compiler > Errors/Warnings
- Under Potential programming problems section, change Serializable class without serialVersionUID: to Ignore
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||