You probably have an anonymous user ''@'localhost' or ''@'127.0.0.1'.
As per the manual:
When multiple matches are possible, the server must determine which of
them to use. It resolves this issue as follows: (…)
- When a client attempts to connect, the server looks through the rows [of table mysql.user] in sorted order.
- The server uses the first row that matches the client host name and user name.
(…)
The server uses sorting rules that order rows with the most-specific Host values first.
Literal host names [such as ‘localhost’] and IP addresses are the most specific.
Therefore such an anonymous user would «mask» any other user like '[any_username]'@'%' when connecting from localhost.
'bill'@'localhost' does match 'bill'@'%', but would match (e.g.) ''@'localhost' beforehands.
The recommended solution is to drop this anonymous user (this is usually a good thing to do anyways).
Below edits are mostly irrelevant to the main question. These are only meant to answer some questions raised in other comments within this thread.
Edit 1
Authenticating as 'bill'@'%' through a socket.
root@myhost:/home/mysql-5.5.16-linux2.6-x86_64# ./mysql -ubill -ppass --socket=/tmp/mysql-5.5.sock
Welcome to the MySQL monitor (...)
mysql> SELECT user, host FROM mysql.user;
+------+-----------+
| user | host |
+------+-----------+
| bill | % |
| root | 127.0.0.1 |
| root | ::1 |
| root | localhost |
+------+-----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> SELECT USER(), CURRENT_USER();
+----------------+----------------+
| USER() | CURRENT_USER() |
+----------------+----------------+
| bill@localhost | bill@% |
+----------------+----------------+
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
mysql> SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'skip_networking';
+-----------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-----------------+-------+
| skip_networking | ON |
+-----------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Edit 2
Exact same setup, except I re-activated networking, and I now create an anonymous user ''@'localhost'.
root@myhost:/home/mysql-5.5.16-linux2.6-x86_64# ./mysql
Welcome to the MySQL monitor (...)
mysql> CREATE USER ''@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'anotherpass';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> Bye
root@myhost:/home/mysql-5.5.16-linux2.6-x86_64# ./mysql -ubill -ppass
--socket=/tmp/mysql-5.5.sock
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'bill'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
root@myhost:/home/mysql-5.5.16-linux2.6-x86_64# ./mysql -ubill -ppass
-h127.0.0.1 --protocol=TCP
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'bill'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
root@myhost:/home/mysql-5.5.16-linux2.6-x86_64# ./mysql -ubill -ppass
-hlocalhost --protocol=TCP
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'bill'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
Edit 3
Same situation as in edit 2, now providing the anonymous user’s password.
root@myhost:/home/mysql-5.5.16-linux2.6-x86_64# ./mysql -ubill -panotherpass -hlocalhost
Welcome to the MySQL monitor (...)
mysql> SELECT USER(), CURRENT_USER();
+----------------+----------------+
| USER() | CURRENT_USER() |
+----------------+----------------+
| bill@localhost | @localhost |
+----------------+----------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
Conclusion 1, from edit 1: One can authenticate as 'bill'@'%'through a socket.
Conclusion 2, from edit 2: Whether one connects through TCP or through a socket has no impact on the authentication process (except one cannot connect as anyone else but 'something'@'localhost' through a socket, obviously).
Conclusion 3, from edit 3: Although I specified -ubill, I have been granted access as an anonymous user. This is because of the «sorting rules» advised above. Notice that in most default installations, a no-password, anonymous user exists (and should be secured/removed).
Дата: 25.11.2013
Автор: Василий Лукьянчиков , vl (at) sqlinfo (dot) ru
Статистика форума SQLinfo показывает, что одной из наиболее популярных проблем является ошибка mysql №1045 (ошибка доступа).
Текст ошибки содержит имя пользователя, которому отказано в доступе, компьютер, с которого производилось подключение, а также ключевое слово YES или NO, которые показывают использовался ли при этом пароль или была попытка выполнить подключение с пустым паролем.
Типичные примеры:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES) — сервер MySQL
— сообщает, что была неудачная попытка подключения с локальной машины пользователя с именем root и
— не пустым паролем.
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO) — отказано в
— доступе с локальной машины пользователю с именем root при попытке подключения с пустым паролем.
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO) — отказано в
— доступе с локальной машины пользователю с именем ODBC при попытке подключения с пустым паролем.
Причина возникновения ошибки 1045
Как ни банально, но единственная причина это неправильная комбинация пользователя и пароля. Обратите внимание, речь идет о комбинации пользователь и пароль, а не имя пользователя и пароль. Это очень важный момент, так как в MySQL пользователь характеризуется двумя параметрами: именем и хостом, с которого он может обращаться. Синтаксически записывается как ‘имя пользователя’@’имя хоста’.
Таким образом, причина возникновения MySQL error 1045 — неправильная комбинация трех параметров: имени пользователя, хоста и пароля.
В качестве имени хоста могут выступать ip адреса, доменные имена, ключевые слова (например, localhost для обозначения локальной машины) и групповые символы (например, % для обозначения любого компьютера кроме локального). Подробный синтаксис смотрите в документации
Замечание: Важно понимать, что в базе не существует просто пользователя с заданным именем (например, root), а существует или пользователь с именем root, имеющий право подключаться с заданного хоста (например, root@localhost) или даже несколько разных пользователей с именем root (root@127.0.0.1, root@webew.ru, root@’мой домашний ip’ и т.д.) каждый со своим паролем и правами.
Примеры.
1) Если вы не указали в явном виде имя хоста
GRANT ALL ON publications.* TO ‘ODBC’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘newpass’;
то у вас будет создан пользователь ‘ODBC’@’%’ и при попытке подключения с локальной машины вы получите ошибку:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
так как пользователя ‘ODBC’@’localhost’ у вас не существует.
2) Другой первопричиной ошибки mysql 1045 может быть неправильное использование кавычек.
CREATE USER ‘new_user@localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘mypass’; — будет создан пользователь ‘new_user@localhost’@’%’
Правильно имя пользователя и хоста нужно заключать в кавычки отдельно, т.е. ‘имя пользователя’@’имя хоста’
3) Неочевидный вариант. IP адрес 127.0.0.1 в имени хоста соответствует ключевому слову localhost. С одной стороны, root@localhost и ‘root’@’127.0.0.1’ это синонимы, с другой, можно создать двух пользователей с разными паролями. И при подключении будет выбран тот, который распологается в таблице привелегий (mysql.user) раньше.
4) Аккаунт с пустым именем пользователя трактуется сервером MySQL как анонимный, т.е. позволяет подключаться пользователю с произвольным именем или без указания имени.
Например, вы создали пользователя »@localhost с пустым паролем, чтобы каждый мог подключиться к базе. Однако, если при подключении вы укажите пароль отличный от пустого, то получите ошибку 1045. Как говорилось ранее, нужно совпадение трех параметров: имени пользователя, хоста и пароля, а пароль в данном случае не совпадает с тем, что в базе.
Что делать?
Во-первых, нужно убедиться, что вы используете правильные имя пользователя и пароль. Для этого нужно подключиться к MySQL с правами администратора (если ошибка 1045 не дает такой возможности, то нужно перезапустить сервер MySQL в режиме —skip-grant-tables), посмотреть содержимое таблицы user служебной базы mysql, в которой хранится информация о пользователях, и при необходимости отредактировать её.
Пример.
SELECT user,host,password FROM mysql.user;
+—————+——————+——————————————-+
| user | host | password |
+—————+——————+——————————————-+
| root | house-f26710394 | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B |
| aa | localhost | *196BDEDE2AE4F84CA44C47D54D78478C7E2BD7B7 |
| test | localhost | |
| new_user | % | |
| | % | *D7D6F58029EDE62070BA204436DE23AC54D8BD8A |
| new@localhost | % | *ADD102DFD6933E93BCAD95E311360EC45494AA6E |
| root | localhost | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B |
+—————+——————+——————————————-+
Если изначально была ошибка:
-
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
значит вы указывали при подключении неверный пароль, так как пользователь root@localhost существует. Сам пароль храниться в зашифрованном виде и его нельзя узнать, можно лишь задать новый
SET PASSWORD FOR root@localhost=PASSWORD(‘новый пароль’);
-
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
в данном случае в таблице привилегий отсутствует пользователь ‘ODBC’@’localhost’. Его нужно создать, используя команды GRANT, CREATE USER и SET PASSWORD.
Экзотический пример. Устанавливаете новый пароль для root@localhost в режиме —skip-grant-tables, однако после перезагрузки сервера по прежнему возникает ошибка при подключении через консольный клиент:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
Оказалось, что было установлено два сервера MySQL, настроенных на один порт.
phpmyadmin
При открытии в браузере phpmyadmin получаете сообщение:
Error
MySQL said:
#1045 — Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: NO)
Connection for controluser as defined in your configuration failed.
phpMyAdmin tried to connect to the MySQL server, and the server rejected the connection. You should check the host, username and password in your configuration and make sure that they correspond to the information given by the administrator of the MySQL server.
Ни логина, ни пароля вы не вводили, да и пхпадмин их нигде требовал, сразу выдавая сообщение об ошибке. Причина в том, что данные для авторизации берутся из конфигурационного файла config.inc.php Необходимо заменить в нем строчки
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘user’] = ‘root’; // MySQL user
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘password’] = »; // MySQL password (only needed
на
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘user’] = ‘ЛОГИН’;
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘password’] = ‘ПАРОЛЬ’
Установка новой версии
Устанавливаете новую версию MySQL, но в конце при завершении конфигурации выпадает ошибка:
ERROR Nr. 1045
Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO)
Это происходит потому, что ранее у вас стоял MySQL, который вы удалили без сноса самих баз. Если вы не помните старый пароль и вам нужны эти данные, то выполните установку новой версии без смены пароля, а потом смените пароль вручную через режим —skip-grant-tables.
P.S. Статья написана по материалам форума SQLinfo, т.е. в ней описаны не все потенциально возможные случаи возникновения ошибки mysql №1045, а только те, что обсуждались на форуме. Если ваш случай не рассмотрен в статье, то задавайте вопрос на форуме SQLinfo
Вам ответят, а статья будет расширена.
Дата публикации: 25.11.2013
© Все права на данную статью принадлежат порталу SQLInfo.ru. Перепечатка в интернет-изданиях разрешается только с указанием автора и прямой ссылки на оригинальную статью. Перепечатка в бумажных изданиях допускается только с разрешения редакции.
Server errors are annoying, especially when they are cryptic like “sql error 1045 sqlstate 28000″.
The message contains some error codes.
But, what’s the real problem here?
At Bobcares, we help website owners resolve complex errors like “sql error 1045 sqlstate 28000“ as part of our Outsourced Hosting Support services.
Today, let’s discuss the top 5 reasons for this error and we fix them.
‘SQL error 1045 sqlstate 28000’ – What this means?
Before we move on to the reasons for this error, let’s first get an idea of this error.
Website owners face this error when querying data from the SQL server.
For instance, the complete error message looks like this:
SQLSTATE[28000] [1045] Access denied for user 'user'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
This error shows that the MySQL server disallows the user to connect to it from localhost or 127.0.0.1.
‘SQL error 1045 sqlstate 28000’ – Causes & Fixes
In our experience managing servers, we’ll see the major causes of this error and how our Dedicated Support Engineers fix it.
1) Typo in username and password
This is the most common reason for the error “sql error 1045 sqlstate 28000″.
Users may type wrong username and password while connecting to the database.
Therefore, SQL server can’t identify the authenticity of the account.
Solution
In such cases, we help website owners reset the database user password.
For example, in cPanel servers, we reset the database user password from Databases > Mysql databases > Current Users.
Mysql databases option in cPanel
Also, for database driven websites like WordPress, Magento, etc., we update the new database username and password in the website configuration files.
For example, in the Magento application, we update the database name, username and password in the “app/etc/local.xml” file.
In some cases, website owners get errors like this:
SQLSTATE[28000] [1045] Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
This is because, the root session don’t know the password of mysql root user.
And, it can be probably a mis-typed password during the initial setup.
Here, our Hosting Engineers reset the admin/root password after starting the MySQL in safe mode.
For example, we use the below command to reset the root password in safe mode.
update user set password=PASSWORD("YOURPASSWORDHERE") where User='root';2) Accessing from wrong host
MySQL uses host based restrictions for user access to enhance security.
In other words, MySQL allows user access only from hosts defined in the MySQL user table.
So, any access from remote machines whose hostnames are not defined in this user table will bounce with the error “sql error 1045 sqlstate 28000”
Solution
First, our Hosting Engineers check whether the remote host is allowed in the MySQL user table.
If not, we add the hostname of the remote machine in the MySQL user table.
For instance, we use the below command to add a host in the MySQL user table.
update user set host='hostname' where user='username';Here, hostname is the hostname of the remote machine, and username is the MySQL user.
We’ve seen cases where server owners use wildcards(%) in host field which gives universal access to this user.
But, this is not a good practice as there is a security risk that user can access the database from any hosts.
In addition to that, due to security concerns, we always disable accessing root user from remote machines.
[You don’t have to be a MySQL expert to keep your websites online. We have experienced MySQL admins available 24/7.]
3) User doesn’t exist
Similarly, this error “sql error 1045 sqlstate 28000” occurs when the user trying to access the database doesn’t exist on the MySQL server.
For example, if you access MySQL using a testuser that doesn’t exist, you can see the following error.
# mysql -u testuser -p Enter password: ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'testuser'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
Solution
In such cases, our Support Engineers first check whether the user exists in the MySQL user table.
If not, we check the user’s requirement to access the database and if it is valid, we create a user with that username.
4) Existence of Anonymous users
Website owners face this error when there are anonymous MySQL users like ”@localhost or ”@127.0.0.1.
That is, when a client tries to connect to the database, the MySQL server looks through the rows in the user table in a sorted order.
The server uses the first row that matches the most specific username and hostname.
So, here the anonymous user (‘ ‘@localhost) precedes any other users like ‘user’@localhost when connecting from localhost.
And, use the anonymous user password to connect to the server.
Finally, the result is “sql error 1045 sqlstate 28000“.
Solution
Our Hosting Engineers check the MySQL user table and remove the anonymous user account.
For example, we use the below command to remove the anonymous user from MySQL.
delete from user where User = ' ';5) Insufficient privileges
Likewise, insufficient privileges for the user to access the database can also result in this error.
Solution
In such cases, we assign proper access rights for the user to access the database.
For example, in cPanel servers, we manage user privileges from:
cPanel > Mysql databases > Current databases > Privileged users > Click on the database user.
Granting user privileges in cPanel
[Struggling with database user permissions and privileges? Our MySQL Experts are here for your help.]
Conclusion
In short, “sql error 1045 sqlstate 28000” may occur due to insufficient database privileges, wrong username or password, etc. Today we’ve discussed the top 5 reasons for this error and how our Dedicated Support Engineers fix it.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
SEE SERVER ADMIN PLANS
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
Одной из наиболее популярных проблем является ошибка mysql №1045 (ошибка доступа).
Текст ошибки содержит имя пользователя, которому отказано в доступе, компьютер, с которого производилось подключение, а также ключевое слово YES или NO, которые показывают использовался ли при этом пароль или была попытка выполнить подключение с пустым паролем.
Типичные примеры:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES) — сервер MySQL сообщает, что была неудачная попытка подключения с локальной машины пользователя с именем root и не пустым паролем.
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO) — отказано в доступе с локальной машины пользователю с именем root при попытке подключения с пустым паролем.
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO) — отказано в доступе с локальной машины пользователю с именем ODBC при попытке подключения с пустым паролем.
Причина возникновения ошибки 1045
Как ни банально, но единственная причина это неправильная комбинация пользователя и пароля. Обратите внимание, речь идет о комбинации пользователь и пароль, а не имя пользователя и пароль. Это очень важный момент, так как в MySQL пользователь характеризуется двумя параметрами: именем и хостом, с которого он может обращаться. Синтаксически записывается как ‘имя пользователя’@’имя хоста’.
Таким образом, причина возникновения MySQL error 1045 — неправильная комбинация трех параметров: имени пользователя, хоста и пароля.
В качестве имени хоста могут выступать ip адреса, доменные имена, ключевые слова (например, localhost для обозначения локальной машины) и групповые символы (например, % для обозначения любого компьютера кроме локального). Подробный синтаксис смотрите в документации
Замечание: Важно понимать, что в базе не существует просто пользователя с заданным именем (например, root), а существует или пользователь с именем root, имеющий право подключаться с заданного хоста (например, root@localhost) или даже несколько разных пользователей с именем root (root@127.0.0.1, root@webew.ru, root@’мой домашний ip’ и т.д.) каждый со своим паролем и правами.
Примеры.
1) Если вы не указали в явном виде имя хоста
GRANT ALL ON publications.* TO ‘ODBC’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘newpass’;
то у вас будет создан пользователь ‘ODBC’@’%’ и при попытке подключения с локальной машины вы получите ошибку:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
так как пользователя ‘ODBC’@’localhost’ у вас не существует.
2) Другой первопричиной ошибки mysql 1045 может быть неправильное использование кавычек.
CREATE USER ‘new_user@localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘mypass’; — будет создан пользователь ‘new_user@localhost’@’%’
Правильно имя пользователя и хоста нужно заключать в кавычки отдельно, т.е. ‘имя пользователя’@’имя хоста’
3) Неочевидный вариант. IP адрес 127.0.0.1 в имени хоста соответствует ключевому слову localhost. С одной стороны, root@localhost и ‘root’@’127.0.0.1’ это синонимы, с другой, можно создать двух пользователей с разными паролями. И при подключении будет выбран тот, который распологается в таблице привелегий (mysql.user) раньше.
4) Аккаунт с пустым именем пользователя трактуется сервером MySQL как анонимный, т.е. позволяет подключаться пользователю с произвольным именем или без указания имени. Например, вы создали пользователя »@localhost с пустым паролем, чтобы каждый мог подключиться к базе. Однако, если при подключении вы укажите пароль отличный от пустого, то получите ошибку 1045. Как говорилось ранее, нужно совпадение трех параметров: имени пользователя, хоста и пароля, а пароль в данном случае не совпадает с тем, что в базе.
Что делать?
Во-первых, нужно убедиться, что вы используете правильные имя пользователя и пароль. Для этого нужно подключиться к MySQL с правами администратора (если ошибка 1045 не дает такой возможности, то нужно перезапустить сервер MySQL в режиме —skip-grant-tables), посмотреть содержимое таблицы user служебной базы mysql, в которой хранится информация о пользователях, и при необходимости отредактировать её.
Пример.
SELECT user,host,password FROM mysql.user;
+—————+—————————+—————————————————————————-+
| user | host | password |
+—————+—————————+—————————————————————————-+
| root | house-f26710394 | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B |
| aa | localhost | *196BDEDE2AE4F84CA44C47D54D78478C7E2BD7B7 |
| test | localhost | |
| new_user | % | |
| | % | *D7D6F58029EDE62070BA204436DE23AC54D8BD8A |
| new@localhost | % | *ADD102DFD6933E93BCAD95E311360EC45494AA6E |
| root | localhost | *81F5E21E35407D884A6CD4A731AEBFB6AF209E1B |
+—————+—————————+——————————————————————————+
Если изначально была ошибка:
-
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
значит вы указывали при подключении неверный пароль, так как пользователь root@localhost существует. Сам пароль храниться в зашифрованном виде и его нельзя узнать, можно лишь задать новый
SET PASSWORD FOR root@localhost=PASSWORD(‘новый пароль’);
-
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘ODBC’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)
в данном случае в таблице привилегий отсутствует пользователь ‘ODBC’@’localhost’. Его нужно создать, используя команды GRANT, CREATE USER и SET PASSWORD.
Экзотический пример. Устанавливаете новый пароль для root@localhost в режиме —skip-grant-tables, однако после перезагрузки сервера по прежнему возникает ошибка при подключении через консольный клиент:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: YES)Оказалось, что было установлено два сервера MySQL, настроенных на один порт.
phpmyadmin
При открытии в браузере phpmyadmin получаете сообщение:
Error
MySQL said:#1045 — Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: NO)
Connection for controluser as defined in your configuration failed.
phpMyAdmin tried to connect to the MySQL server, and the server rejected the connection. You should check the host, username and password in your configuration and make sure that they correspond to the information given by the administrator of the MySQL server.
Ни логина, ни пароля вы не вводили, да и пхпадмин их нигде требовал, сразу выдавая сообщение об ошибке. Причина в том, что данные для авторизации берутся из конфигурационного файла config.inc.php Необходимо заменить в нем строчки
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘user’] = ‘root’; // MySQL user
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘password’] = »; // MySQL password (only needed
на
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘user’] = ‘ЛОГИН’;
$cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘password’] = ‘ПАРОЛЬ’
Установка новой версии
Устанавливаете новую версию MySQL, но в конце при завершении конфигурации выпадает ошибка:
ERROR Nr. 1045
Access denied for user ‘root’@‘localhost’ (using password: NO)
Это происходит потому, что ранее у вас стоял MySQL, который вы удалили без сноса самих баз. Если вы не помните старый пароль и вам нужны эти данные, то выполните установку новой версии без смены пароля
I just installed a fresh copy of Ubuntu 10.04.2 LTS on a new machine. I logged into MySQL as root:
david@server1:~$ mysql -u root -p123
I created a new user called repl. I left host blank, so the new user can may have access from any location.
mysql> CREATE USER 'repl' IDENTIFIED BY '123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
I checked the user table to verify the new user repl was properly created.
mysql> select host, user, password from mysql.user;
+-----------+------------------+-------------------------------------------+
| host | user | password |
+-----------+------------------+-------------------------------------------+
| localhost | root | *23AE809DDACAF96AF0FD78ED04B6A265E05AA257 |
| server1 | root | *23AE809DDACAF96AF0FD78ED04B6A265E05AA257 |
| 127.0.0.1 | root | *23AE809DDACAF96AF0FD78ED04B6A265E05AA257 |
| ::1 | root | *23AE809DDACAF96AF0FD78ED04B6A265E05AA257 |
| localhost | | |
| server1 | | |
| localhost | debian-sys-maint | *27F00A6BAAE5070BCEF92DF91805028725C30188 |
| % | repl | *23AE809DDACAF96AF0FD78ED04B6A265E05AA257 |
+-----------+------------------+-------------------------------------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
I then exit, try to login as user repl, but access is denied.
david@server1:~$ mysql -u repl -p123
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'repl'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
david@server1:~$ mysql -urepl -p123
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'repl'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
david@server1:~$
Why is access denied?
asked Mar 28, 2013 at 19:44
1
The reason you could not login as repl@'%' has to do with MySQL’s user authentication protocol. It does not cover patterns of users as one would believe.
Look at how you tried to logged in
mysql -u repl -p123
Since you did not specify an IP address, mysql assumes host is localhost and tries to connect via the socket file. This is why the error message says Access denied for user 'repl'@'localhost' (using password: YES).
One would think repl@'%' would allow repl@localhost. According to how MySQL perform user authentication, that will simply never happen. Would doing this help ?
mysql -u repl -p123 -h127.0.0.1
Believe it or not, mysql would attempt repl@localhost again. Why? The mysql client sees 127.0.0.1 and tries the socket file again.
Try it like this:
mysql -u repl -p123 -h127.0.0.1 --protocol=tcp
This would force the mysql client to user the TCP/IP protocol explicitly. It would then have no choice but to user repl@'%'.
answered Mar 28, 2013 at 20:40
RolandoMySQLDBARolandoMySQLDBA
177k32 gold badges307 silver badges505 bronze badges
0
You should issue for localhost specific to it.
GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'repl'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '123';
And try connecting.
answered Mar 29, 2013 at 5:40
MannojMannoj
1,4992 gold badges14 silver badges34 bronze badges
The problem is these two accounts, added by default.
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.5/en/default-privileges.html
+-----------+------------------+-------------------------------------------+
| host | user | password |
+-----------+------------------+-------------------------------------------+
| localhost | | |
| server1 | | |
+-----------+------------------+-------------------------------------------+
A blank user name is a wildcard, so no matter what account you use, it matches this user if MySQL thinks you’re connecting from localhost or your local server name (server1 in this case)… since they have no password, any password you try is wrong. User authentication only tries the first match, so the user you created never gets noticed when your host is localhost (or your server name).
Delete these two from the mysql.user table and then FLUSH PRIVILEGES;.
Or, the mysql_secure_installation script can do this for you, although I tend to prefer doing things manually.
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.5/en/mysql-secure-installation.html
answered Mar 30, 2013 at 2:02
Michael — sqlbotMichael — sqlbot
22.2k2 gold badges46 silver badges75 bronze badges
Database may not be configured yet just issue a no-arg call:
mysql <enter>
Server version: xxx
Copyright (c) xxx
Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement.
Mysql [(none)]>
If Mysql must be set a root password, you can use
mysql_secure_installation
answered Apr 18, 2020 at 7:45
Make sure that all fields in the connector are set up with the correct details
host = «localhost»,
user = «CorrectUser»,
passwd = «coRrectPasswd»,
database = «CorreCTDB»
Check for upper and lowercase errors as well — 1045 is not a Syntax error, but has to do with incorrect details in the connector
answered Dec 13, 2019 at 22:59
This could be an issue with corruption of your mysql database. Tables inside mysql database like user table can get corrupt and may cause issued.
Please do a check on those
myisamchk /var/lib/mysql/mysql/ *.MYI
Usually while checking or fixing myisam tables we would like to take mysql down first. If this problem is still not solve please try this out aswell.
If they are corrupt then you can fix them using
myisamchk —silent —force —fast /path/table-name.MYI
Thanks,
Masood
answered Mar 31, 2013 at 17:25
After completing the installation of a local host server, if you try to access the phpMyAdmin, then you may encounter MySQL error 1045 (28000) access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: YES). This error primarily comes into action when the local host is not assigned with complete accessing authority or may be the password that is facilitated is incorrect. If these things will be happening then you may come across this error. But, you need not worry, in this article you will be guided properly to find a way around for avoiding & solving MySQL error 1045 (28000): access denied for user.
Image will appear as shown below;
By following the below mentioned steps, you can easily troubleshoot MySQL error 1045 SQLstate 28000 access denied for user. So, just follow them one-by-one to resolve such error.
Step 1: Open MySQL console
With the help of WAMP, do left click on your WAMP icon positioned at the bottom right area of the screen of your desktop and go to MySQL console.
But this part can be ignored if you already have the correct password;
- First of all, type: use mysql
- Next, hit the enter
- Set password for MySQL: Update mysql.user
Step 2: Set Password= PASSWORD (Enter Your Password Here)
Where User=”root”
- Replace your password with your chosen password
- After that, you need to hit the Enter
- Wash out the Priviliges
- Now, click on Exit
- Again hit the Enter
Step 3: Open config.inc.php file situated in files of local server and edit it.
Make use of a text editor like Notepa++ to open config.inc.php file.
- Switch to My Computer> C Drive> (Folder Of Local Server MAMP/XAMPP/WAMP)> APPS> PHPMYADMIN> Config.inc.php
- Locate this line of code: $cfg [‘Servers’][$i][‘password’] = “; //MySQL password
- Make alteration with the freshly created password from step 2.
- Click save
Step 4: Access phpMyAdmin
You can make access of phpMyAdmin by switching to the http://localhost/phpMyAdmin/
After finishing all the steps above hopefully you will be able to access the database with no issue. Even after trying all these steps, if you are still getting error 1045 mysql 28000 access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ Windows then ty the below solution.
Fully Automated Solution To Solve Access Denied For User ‘Root’@’Localhost’ (Using Password: No)
If the above stated solution does not help you to get rid of error 1045 MySQL 28000 access denied for user MySQL then you can try MySQL Repair Tool. This software is the most reliable tool to repair corrupted and damaged database files along with the several MySQL database errors and issues.
Apart from that, it can easily recovers stored procedures, views, indexes, tables, unique/primary keys etc. without any backup. So, you need to just download & install this excellent program to fix MySQL error 1045 SQLstate 28000 access denied for user and other issues easily.

STEPS TO SOLVE ERROR 1045 (28000):
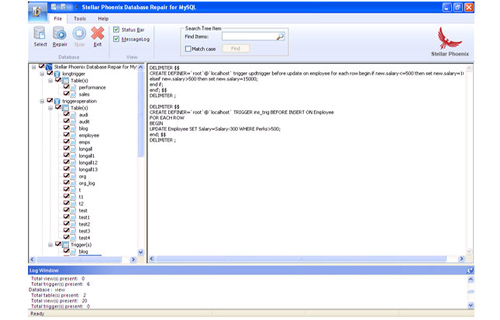
Step 1: Start with Stellar Phoenix Database Repair for MySQL . Software and you can see the main interface as shown below.
Step 2: Click on ‘Select’ button & then select ‘Repair corrupt database which is stored at default location of MySQL’ option to select your database from default location and then click.
Step 3: The left pane shows the preview of database and its component in a tree like structure after completing scanning process.
Step 4: After previewing your database, to start repair process click ‘Repair’ button in file menu on the main user interface. Stellar Phoenix Database Repair for MySQL dialog box appears. Click Yes.
Step 5: After successful completion of the process, a message box is displayed as ‘repair process finished successfully’. Click ‘OK’ to close the message box.
The FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
How Do I Troubleshoot MySQL?
In order to troubleshooting problems starting with MySQL server, you need to follow the below steps:
- Check the error log to see why the server does not start.
- Make sure that the server knows where to find the data directory.
- Specify any special options needed by the storage engines that you are using.
- Ensure that a server can access the data directory.
How Do I Access Root MySQL?
To access root MySQL, you have to create the MySQL databases & users
- At the command line, log in to MySQLas the root user: MySQL -u root -p.
- Next, type the MySQL rootpassword, and then hit the Enter.
- Type q to exit the MySQL
- To log in to MySQLas the user you just created, type the following command. …
- At last, type the user’s password, and then press Enter.
Bottom Line
Now you have learned that how to bypass the error 1045 MySQL 28000 access denied for user MySQL further.
In the above section of this post, I have mentioned the different approaches to fix this issue. But if you want the easiest & fastest way to resolve this error then you can go with the MySQL Repair Tool.
If you liked this article, then do not forget to share it with your friends and family members.

Jacob Martin is a technology enthusiast having experience of more than 4 years with great interest in database administration. He is expertise in related subjects like SQL database, Access, Oracle & others. Jacob has Master of Science (M.S) degree from the University of Dallas. He loves to write and provide solutions to people on database repair. Apart from this, he also loves to visit different countries in free time.

WRITE FOR US