Ошибка 412 относится, как к обычному пользователю, так и к вебмастеру. Только, если речь идет о простом пользователе – особо делать нечего, т.к. все зависит от администратора сайта. Разберемся, что означает данная ошибка, когда она возникает и при каких условиях, а также как исправить ошибку 412 Precondition Failed.
Что такое «Ошибка 412 Precondition Failed» и когда она возникает?
Ошибка 412 Precondition Failed (Error 412 Precondition Failed) – это уведомление со стороны HTTP, которое указывает на то, что доступ к ресурсу был отклонен. Ресурсом может быть не только сайт в целом, но и отдельные элементы: изображения, аудио и видео контент, отдельные скрипты или плагины.
Следует отметить, что ошибка 412 Precondition Failed возникает в двух случаях: в клиентском браузере и на стороне администратора сайта. В первом случае, если вы уверены, что сайт должен открываться – следует почистить куки в вашем браузере. Во втором – скорее всего вы выполняли изменения на сайте. Часто, ошибка 412 возникает у администраторов, сервер которых использует систему Windows.
Для администратора сайта: причины ошибки 412
- Ошибка 412 возникает после изменений на сайте, часто изменения глобальные. Для примера, вы решили изменить код сайта, чтобы установить водяные знаки на все изображения в постах сайта. При редактировании поста может возникнуть ошибка 412. Данный случай связан с Windows Live Writer. Система выдает ошибку 412 Precondition Failed – не выполнено предварительное условие.
- При использовании Windows Server 2008 в пакете Standart SP 1 в журнале вы можете обнаружить ошибку 412. Связано это может быть не только с изменениями на самом сайте, но и банально – смена железа. Обновление в SP 2 скорее всего ничего не решит. Что делать и как исправить ошибку 412 вебмастеру читаем в следующем разделе.
- Изменения с помощью плагинов и изменения в теме сайта. При изменении дизайна сайта пакетом через административную панель, например, на WordPress. Т.е. вы приобрели пакет шаблона и попытались установить новую тему. Также и с плагинами. К слову, часто плагин WP Super Cache приводит к возникновению ошибки 412, причем не только на видимой пользователю части, но и в административной. При этом, это результат конфликта между настройками кеширования на самом сервере, и настройками установленного плагина.
Причины ошибки 412 со стороны пользователя
Со стороны пользователя ошибка возникает только в одном случае – сбой в браузере. Скорее всего, почти все сайты, которые вы раньше открывали, перестанут работать. Если проблема только с одним сайтом – это не ваша проблема. Все просто.
Как исправить ошибку 412 Precondition Failed?
Меньше всего действий нужно предпринимать со стороны пользователя. Именно поэтому, начнем список с решений для обычного пользователя. Кстати, в выдаче Google есть сайт, на котором любая ошибка, даже ошибка 404, лечится чисткой реестра или переустановкой системы Windows. Ребят, это полная чушь. В решении ошибки 412 никаких манипуляций с системой со стороны пользователя делать не стоит.
Исправление ошибки 412 обычному пользователю
Как уже упоминалось выше, если при входе на сайт вы видите ошибку 412, не паникуйте. В первую очередь, пробуйте самое простое – перезапустите ваш браузер. Не помогло? В этом случае нужно почистить куки. Обычно пользователи годами этого не делают. Можно почистить сразу все браузеры с помощью программы CCleaner – программа бесплатная. Просто скачайте, установите и в разделе чистки выполните очистку, пользуясь подсказками.
Как почистить куки без программ, чтобы удалить ошибку 412 в браузере? Перечислим несколько популярных браузеров и пути для поиска функции в программе. Внимание: удаляются все данные сайтов, включая сохраненные пароли (если удалять комплексом куки, историю, автозаполнение и т.д.).
Opera. Нажимаем на иконку Оперы в левом верхнем углу, затем ищем «Настройки». Затем выбираем пункты: Безопасность – Все файлы cookies – выбираем все – нажимаем удалить.
Google Chrome. В новой пустой вкладке нажимаем комбинацию клавиш – Shift+Ctrl+Del. Ставим все галочки, выбираем время «Очистить за все время» и удаляем.
Mozilla Firefox. В правом верхнем углу есть три полоски (нажимаем) и ищем пункт «Настройки». Вы увидите страницу, где в левой колонке нужно выбрать «Приватность и Защита» — нажимаем. Смотрим раздел «Куки и данные сайтов» и нажимаем там «Удалить данные». Подтверждаем – «Удалить».
Что делать администратору сайта?
- В первом случае, который описан выше, попробуйте просто восстановить сайт из резервной копии. Обычно, любой уважающий себя хостинг, делает ежедневные резервные копии. Это можно сделать, если вы сделали много правок на сайте и не знаете, какая именно правка или какие изменения вызвали ошибку. Совет на будущее – сделали правку, проверили сайт. Ошибка 412 Precondition Failed уйдет после восстановления из резервной копии. На всякий случай, восстановить нужно, как сайт, так и БД.
- Если ошибка 412 возникла на системе Windows Server 2008, можно переустановить систему. Но более удачное решение – установить Update Если у вас стоит SP 1, обновление до SP 2 ничего не изменит. Чтобы исправить ошибку 412 также можно просто переустановить систему с нуля. Данные манипуляции следует делать, если вы на 100% уверены, что ошибка не связана с последними изменениями на сайте, которые вы делали.
- В случае обнаружения ошибки 412 на сайте нужно сразу пройти в консоль Google. Проверьте, какие страницы привели первоначально к сбою. Возможно, если ошибка возникла давно, эти страницы выпали из поиска. Это грустно. Придется поработать. Начните с отката изменений, например, удалите последние плагины. Параллельно нужно тестировать сайт на разных устройствах.
Вообще, ошибка 412 у вебмастера возникает ввиду не аккуратного редактирования кода, поэтому всегда делайте резервную копию перед любыми правками. Если остались вопросы – напишите в комментариях, отвечаю быстро. До связи.
The HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
412 Precondition Failed client error response code
indicates that access to the target resource has been denied. This happens with
conditional requests on methods other than GET or
HEAD when the condition defined by the
If-Unmodified-Since or If-None-Match headers is not
fulfilled. In that case, the request, usually an upload or a modification of a resource,
cannot be made and this error response is sent back.
Status
Examples
ETag: "33a64df551425fcc55e4d42a148795d9f25f89d4"
ETag: W/"0815"
Avoiding mid-air collisions
With the help of the ETag and the If-Match headers, you
can detect mid-air edit collisions.
For example, when editing MDN, the current wiki content is hashed and put into an
Etag in the response:
ETag: "33a64df551425fcc55e4d42a148795d9f25f89d4"
When saving changes to a wiki page (posting data), the POST request
will contain the If-Match header containing the ETag
values to check freshness against.
If-Match: "33a64df551425fcc55e4d42a148795d9f25f89d4"
If the hashes don’t match, it means that the document has been edited in-between and a
412 Precondition Failed error is thrown.
Specifications
| Specification |
|---|
| HTTP Semantics # status.412 |
Browser compatibility
BCD tables only load in the browser
The information below has been pulled from MDN’s GitHub (https://github.com/mdn/browser-compat-data).
See also
It is unclear to me when you should and should not return a HTTP 412: Precondition Failed, error for a web service? I am thinking of using it when validating data. For example, if a client POST’s XML data and that data is missing a required data element, then responding with a 412 and a description of the error.
Does that align with the spirit of responding with an HTTP 412, or should something else be used (e.g. another http error code or web application exception)?
Elias Zamaria
93.8k31 gold badges113 silver badges145 bronze badges
asked Mar 20, 2011 at 15:40
2
If you look at RFC 2616 you’ll see a number of request headers that can be used to apply conditions to a request:
If-Match
If-Modified-Since
If-None-Match
If-Range
If-Unmodified-Since
These headers contain ‘preconditions’, allowing the client to tell the server to only complete the request if certain conditions are met. For example, you use a PUT request to update the state of a resource, but you only want the PUT to be actioned if the resource has not been modified by someone else since your most recent GET.
The response status code 412 (Precondition Failed) is typically used when these preconditions fail.
Your example sounds like an invalid request (i.e. the client has submitted data that is invalid because of missing values). A status code of 400 (Bad Request) is more appropriate here IMO.
answered Mar 20, 2011 at 15:57
joelittlejohnjoelittlejohn
11.5k2 gold badges40 silver badges54 bronze badges
1
412 is reserved for cases where the request is conditional, and the condition isn’t met.
For your use case, 422 Unprocessable Entity is a good match.
answered Mar 20, 2011 at 16:47
Julian ReschkeJulian Reschke
39.2k8 gold badges92 silver badges96 bronze badges
4
Your best bet would be to avoid 412. In practice most web services that I’ve used send a 400 code (Bad Request). A lot of frameworks have built-in support for 400 too and your clients will appreciate a more common error code. Often times, especially with REST interfaces, a simple «message» or «error» element is returned with a description.
answered Mar 20, 2011 at 15:46
Matt BishopMatt Bishop
1,0006 silver badges18 bronze badges
3
- Overview
- The Basics
- The Details
- 400, 401 & 404
- 412 Precondition Failed
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
- 500 Internal Server Error
- 502 Naughty Gateway
- 503 Planned Downtime
- The Gory Details
- Duplicate Checks
- Building Tolerance into Your Application
- There’s Errors and Then There’s Errors
- Error Simulation
- Real-time Error Simulation
- Delayed Error Simulation
- More Information About Errors
1. Overview
One of the great values that Cheddar provides is its simplified error reporting. We’ve done all we can to eliminate the error handling hassles that come with online billing and subscription management. Payment gateways can have hundreds of unique error codes. In the real world, you’ll only see a tiny fraction of them and most of those will be the ones you want (e.g. invalid credit card expiration date). We’ve narrowed it down for you. Here it is.
2. The Basics
First of all, the basics. Errors reported by the API look something like this:
XML
<error id="12345" code="422" auxCode="5003">
Credit card type is not accepted
</error>
JSON
{
"error": {
"id": 12345,
"code": 422,
"auxCode": "5003",
"message": "Credit card type is not accepted"
}
}
If the customer does not exist yet, only the error node will be returned. If the customer already exists, the error node will be embedded in the customer response, like so:
<customers>
<errors>
<error id="1235" code="422" auxCode="6000">The transaction was declined</error>
</errors>
<customer id="d665b62a-0fc9-102d-844d-94789ca76f11" code="YOUR_CODE">
<firstName>Example</firstName>
<lastName>Customer</lastName>
.
.
.
Cheddar exposes errors, and in some cases additional information about errors, to you in the admin GUI under Reports->Errors
3. The Details
Cheddar breaks up errors into categories for you based on HTTP status code. The HTTP status code is produced in the response header and the code attribute of the error node corresponds to that same HTTP status code. Here’s a list of the status codes that Cheddar produces:
- 400 Bad Request: The request was invalid.
- 401 Not Authorized: Authentication credentials were missing or incorrect or you are not authorized to use the requested resource.
- 404 Not Found: The URI requested is invalid or the resource requested, such as a user, does not exist.
- 412 Precondition Failed: The request contains POST data that is in an invalid format or required parameters are missing.
- 422 Unprocessable Entity: A error occurred during processing. Please fix the error and try again.
- 500 Internal Server Error: Something is broken. Please post in the support forum so the Cheddar team can investigate.
- 502 Bad Gateway: Communication with the payment gateway failed. Try again later.
- 503 Service Unavailable: Cheddar is temporarily offline for maintenance. Try again later.
An accompanying message will explain the error in greater detail.
400, 401 & 404
400, 401 and 404 usually result from something you can fix pretty quickly in your app. Once you do, an instance of that error shouldn’t happen again. The accompanying error message will tell you exactly what you need to know. There might be more information in the error report.
The 412
The 412 Precondition Failed error is special. Your customer may have entered some data that has gotten past your own input filtering and validation. If this happens, an error will be produced and the auxCode attribute of the error node will give you the info you need. Here’s an example of a 412 error:
<error id="12345" code="412" auxCode="firstName:isEmpty">
A value is required
</error>
This error would be produced if you tried to create a new customer without a firstName value. The auxCode attribute contains the field name and the error type separated by a colon :. Refer to the API Documentation for information about field requirements and formats. More information about the fields that failed validation can be found in the error report.
This error will also be produced if your customer attempts to add a tracked item or change to a pricing plan in a way that doesn’t align with item or plan limits you’ve set in Cheddar. For example, if you’ve set a hard limit for a tracked item of 100 and customer attempts to use more than that number, when your system attempts to set the quantity to 101 on the customer’s upcoming bill, Cheddar will return a 412 error with the aux code attribute of quantity:notLessThanOrEqual. You can utilize these errors to control access to certain features of your website and to prompt the customer to upgrade their plan. For more information, see Using Item Quantity Restrictions for Upselling.
The 422
The 422 Unprocessable Entity is similar to the 412 error in that it is due to an error in input but it is related to payment data only. This error will be produced if all data passes Cheddar’s validation and is sent to the payment gateway for processing which in turn rejects the data. When this happens, the auxCode will tell you everything you need to know. The content of the error message, while somewhat simple, is fit for human consumption but you might wish to change it. There might be more information in the error report.
500 (Oops)
We hope to never see a 500 error but we’re human so it’s possible. If a 500 is produced, it means that Cheddar goofed. Whenever a 500 happens, red flags wave and buzzers and bells ring around here. Rest assured, we’re on top of it. See Building Tolerance into Your Application.
502 Naughty Gateway
When a 502 happens, it means that Cheddar was either unable to communicate with your gateway or the gateway did something extra screwy that Cheddar’s never seen before. If we can prevent it from happening again, we will but sometimes the internet breaks and there’s nothing that Cheddar can do about it. Sad but true. There might be more information in the error report.
503 Planned Downtime
HTTP status 503 will be returned when the system is in a maintenance state. This situation is temporary and should last only a short time. See Building Tolerance into Your Application.
4. The Gory Details
Here’s where Cheddar translates what it receives from your gateway into something useful and stuffs it into the auxCode attribute. As always, you may find more information in your error log. While interacting with a gateway, Cheddar can produce the following codes:
| Code | AuxCode | Message | (Some) Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 | 1000 | An unrecognized gateway error occured | This is a fallback position for Cheddar. Cheddar got something from a gateway that it doesn’t recognize but probably should. This should never happen but in this reality, it does. |
| 400 | 1001 | The record already exists | Cheddar tried to create a record at the gateway but the record already exists. This should never happen but we live in an imperfect world. |
| 500 | 1002 | Invalid communication | Cheddar said something to the gateway that it didn’t like. This should never happen but, yeah, sometimes it does. |
| 500 | 1003 | Record not found | Cheddar tried to use a gateway record that doesn’t exist. This should never happen but things get misplaced on occassion. |
| 401 | 2000 | The gateway configuration is incompatible | Something is wrong with the config in Cheddar. It is most likely a problem with the gateway API credentials provided to Cheddar. |
| 401 | 2001 | The configuration at the gateway is incompatible | Something is wrong with the config at the gateway. You’ll probably want to call the gateway to find out what. You may be able to find more information in your error log. |
| 401 | 2002 | Authentication to the gateway failed | Cheddar tried to talk to the gateway but something went wrong during authentication. This is usually due to invalid credentials provided to Cheddar or the gateway password was changed. |
| 401 | 2003 | The gateway has denied access | Cheddar was denied access to your gateway account. Try calling your gateway provider. |
| 401 | 2004 | The gateway does not support the requested action. | You made a request that is not supported by your gateway. |
| 502 | 3000 | The response from the gateway was not recognized | The gateway responded to Cheddar’s advances in an undocumented way. |
| 502 | 4000 | The connection to the gateway failed. Please try again later. | The tubes are broke! Maybe the gateway is down. Maybe there’s something wrong with Cheddar’s connection to the interwebs. Probably temporary. |
| 422 | 5000 | There was an error processing the transaction | This is a fallback position for Cheddar when the gateway responds with a code that means error but is very unlikely to occur. |
| 422 | 5001 | Credit card number is invalid | The credit card number passed all of the sophisticated validation that Cheddar puts it through but the gateway still doesn’t like it. |
| 422 | 5002 | Expiration date is invalid | The date passed validation in Cheddar but the gateway doesn’t like it. It’s probably just the wrong expiration date for the credit card provided. |
| 422 | 5003 | Credit card type is not accepted | Your gateway account isn’t setup to accept this credit card type. Typically, only visa and mastercard are accepted. You might accept more. Check with your gateway. |
| 422 | 5004 | The transaction is not voidable | A void was attempted but the transaction doesn’t meet the criteria for a void. |
| 422 | 5005 | The transaction is not refundable | A refund was attempted but the transaction doesn’t meet the criteria for a refund. |
| 422 | 6000 | The transaction was declined | Often, payment gateways don’t specify why a credit card is declined. This usually means that the credit balance isn’t sufficient for the transaction. The only way to find out why a decline like this occurred is for the cardholder to contact their bank. |
| 422 | 6001 | The transaction was declined due to AVS mismatch | The transaction failed Address Verification Service («AVS») checks. Your gateway may be configured to decline the transaction. |
| 422 | 6002 | The transaction was declined due to card code verification failure | The little 3 or 4 digit number (CCV or CCV2) is invalid. |
| 422 | 6003 | The transaction was declined due to insufficient funds | This is rare but sometimes the gateway can returns a definitive response that means the payment method used does not have a sufficient balance to cover the amount of the transaction |
| 422 | 6004 | Credit card number is invalid | The same as 5001 except this is a declined condition rather than an error condition |
| 422 | 6005 | Credit card type is not accepted | The same as 5003 except this is a declined condition rather than an error condition |
| 422 | 6006 | The transaction was declined — contact support | The transaction has been determined to be fraudulent. This could be the result of a third party fraud filter. |
| 422 | 6007 | Credit card is expired | The same as 5002 except this is a declined condition rather than an error condition |
| 422 | 7000 | The transaction failed for an unknown reason | Whoa. This should never happen |
5. Duplicate Checks
The following API endpoints include a check for duplicate POST requests:
customers/newcustomers/editcustomers/edit-subscriptioncustomers/add-chargeinvoices/new
A duplicate identical POST request sent to any of these endpoints within a window of 10 seconds is considered to be invalid and will receive a 400 status response with auxCode=duplicate. A request is considered a duplicate if it contains the same POST parameters with the same values as a previous request, no more no less.
6. Building Fault Tolerance into Your Application
The interwebs aren’t perfect. It’s important to tolerate its quirks and nuances so that your application doesn’t freak out in the event of a failure. Here’s a guide to the general types of failures that can occur and how you can develop your integration to tolerate them:
- When Cheddar has been taken offline intentionally the API will return a simple error response with HTTP status=503. When your app experiences a 503 response, you should consider this temporary and handle the event appropriately. We don’t often have intentional downtime where a 503 is necessary but sometimes there’s no way around it. In the case of planned downtime, you can expect to be notified in advance. You can test this with Error Simulation.
- It’s possible that Cheddar will return a 500 HTTP status in the event of an unknown failure within Cheddar’s processing of any API request. Again, this scenario should be considered temporary. You can test this with Error Simulation.
- Connection failure or timeout. Your app’s HTTP library should provide a mechanism for detecting a connection failure so that your app logic can behave accordingly.
- Read failure or timeout. This can happen when connection to Cheddar is successful and the request is sent but your app does not receive a response from Cheddar. Your app’s HTTP library should provide a mechanism for detecting a read failure so that your app logic can behave accordingly.
To keep things simple, you might consider a broad stroke solution for all of the above scenarios. Perhaps deferring to an expired cached customer status or limiting access to your app during this period would be appropriate. In short, it’s up to you to decide how your app should behave under these conditions.
7. There’s Errors and Then There’s Errors
Errors can occur in one of two general ways. In one, the entire action requested failed. In the other, some portion of the action was successful and then something failed. The first example is very simple. The bulk of errors are of this type:
<error id="1234" code="422" auxCode="6000">
The transaction was declined
</error>
The second example is a little more complicated but only because it combines a standard xml response with embedded errors. For example, a customer is created and subscribed to a pricing plan with a setup fee. When Cheddar tries to run the setup fee invoice transaction, the transaction is declined.
<customers>
<errors>
<error id="1235" code="422" auxCode="6000">The transaction was declined</error>
</errors>
<customer id="d665b62a-0fc9-102d-844d-94789ca76f11" code="YOUR_CODE">
<firstName>Example</firstName>
<lastName>Customer</lastName>
.
.
.
<subscriptions>
<subscription id="2b13dc42-0fca-102d-844d-94789ca76f11">
<invoices>
<invoice id="2bb6bb24-0fca-102d-844d-94789ca76f39">
<type>setup</type>
.
.
.
<transactions>
<transaction id="2d237e5c-0fca-102d-844d-94789ca76f11">
.
.
.
<response>declined</response>
<responseReason>The transaction was declined</responseReason>
.
.
.
</transaction>
</transactions>
</invoice>
.
.
.
</invoices>
</subscription>
</subscription>
</customer>
</customers>
8. Error Simulation
You can simulate all of the payment gateway related errors that Cheddar can return by using a customer’s credit card billing address postal code (or API parameter ccZip) in a specific way. The error codes that can be simulated are listed in the AUXCODE column of the table here.
Error simulation is only enabled when your payment processor is in simulation mode. As soon as you setup a live payment processor, error simulation is disabled.
There are two ways of simulating these errors: real-time errors, and delayed errors.
8.1 Real-time Error Simulation
Real-time errors are those that occur when a customer’s credit card is initially validated. This occurs when a new customer is subscribed to a paid plan or when a customer’s credit card information is changed. If the POST data passes Cheddar’s validation and Cheddar will need to interact with the gateway, the error simulation occurs. In order to trigger the error simulation, the customer’s billing postal code must be sent in the following format: 0XXXX, where XXXX is one of the AUXCODE’s listed here.
8.2 Delayed Error Simulation
Delayed errors occur after a customer’s credit card information is successfully validated and a subsequently generated transaction fails. This could happen, for example, if the setup charge for the subscribed plan is $100 and the customer’s credit card only has a balance of $50. In this case, the credit card will validate successfully because it has a positive available balance but the transaction for the setup charge will fail because the balance on the card is not sufficient. Simulated delayed errors are triggered in a way similar to real-time simulated errors. The only difference is that the customer’s billing postal code must be sent in the following format: 9XXXX (note the 9 instead of 0), where XXXX is one of the AUXCODE’s listed here.
A good use of delayed error simulation is to test your app’s behavior during the various error conditions when Cheddar automatically runs a recurring transaction.
9. More Information About Errors
Detailed information not conveyed via error messages in the GUI and API can be found in the error report. The error report can be found under Reports->Errors or here. Basic information is given via the API error node:
<error id="12345" code="401" auxCode="2001">
The configuration at the gateway is incompatible
</error>
The error report will show you the details specific to your gateway. Maybe something like this:
The configuration at the gateway is incompatible
* 33:Phone is required.
* message:Phone is required.
View Plans and Pricing or Get Started with Cheddar now →
| Error Number: | HTTP Error 412 | |
| Error Name: | Precondition Failed | |
| Error Description: | A certain configuration is required for this file to be delivered, but the browser client has not set this up. | |
| Developer: | Microsoft Corporation | |
| Software: | Windows Operating System | |
| Applies to: | Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10, 11 |
File corruption, missing, or deleted Precondition Failed files can result in Edge errors. As a first troubleshootiong step, most PC professionals will attempt to replace the applicable version of the Windows 10 file. After the problem file is replaced, running a registry scan can help clean up any invalid Precondition Failed, file extension, or other file path references which could have been affected from a previous malware infection.
Common Precondition Failed Error Messages
Issues related to Precondition Failed and Edge:
- «Error: Precondition Failed.»
- «Precondition Failed moved or missing.»
- «Not found: Precondition Failed.»
- «Failure to load Precondition Failed.»
- «Module missing: failed to register Precondition Failed»
- «Runtime Error — Precondition Failed.»
- «Precondition Failed cannot load.»
Precondition Failed-related problems, sometimes related to Edge, occur during startup / shutdown, while a Precondition Failed-related program is running, or rarely during Windows install process. Notating when Precondition Failed errors happen is paramount in finding the cause of the Edge-related problems and reporting them to Microsoft Corporation for help.
Precondition Failed Issue Origins
Most Precondition Failed problems stem from a missing or corrupt Precondition Failed, virus infection, or invalid Windows registry entries associated with Edge.
Chiefly, complications of Precondition Failed due to:
- Corrupt Windows registry keys associated with Precondition Failed / Edge.
- Precondition Failed file corrupted from malware infection.
- Another program maliciously or mistakenly deleted Precondition Failed-related files.
- Precondition Failed is in conflict with another program (shared file).
- Corrupt download or incomplete installation of Edge software.
Product by Solvusoft
Download Now
WinThruster 2022 — Scan your PC for computer errors.
Compatible with Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, Vista, XP and 2000
Optional Offer for WinThruster by Solvusoft | EULA | Privacy Policy | Terms | Uninstall
Browser Status Codes Knowledgebase
Article ID:
120630
Article Author:
Last Updated:
Popularity:
star rating here
Download Now (Error Fix)
Содержание
Составили подробный классификатор кодов состояния HTTP. Добавляйте в закладки, чтобы был под рукой, когда понадобится.
Что такое код ответа HTTP
Когда посетитель переходит по ссылке на сайт или вбивает её в поисковую строку вручную, отправляется запрос на сервер. Сервер обрабатывает этот запрос и выдаёт ответ — трехзначный цифровой код HTTP от 100 до 510. По коду ответа можно понять реакцию сервера на запрос.
Первая цифра в ответе обозначает класс состояния, другие две — причину, по которой мог появиться такой ответ.
Как проверить код состояния страницы
Проверить коды ответа сервера можно вручную с помощью браузера и в панелях веб‑мастеров: Яндекс.Вебмастер и Google Search Console.
В браузере
Для примера возьмём Google Chrome.
-
Откройте панель разработчика в браузере клавишей F12, комбинацией клавиш Ctrl + Shift + I или в меню браузера → «Дополнительные инструменты» → «Инструменты разработчика». Подробнее об этом рассказывали в статье «Как открыть исходный код страницы».
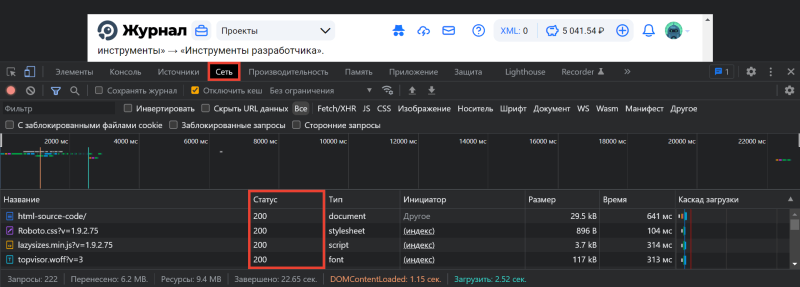
-
Переключитесь на вкладку «Сеть» в Инструментах разработчика и обновите страницу:
В Яндекс.Вебмастере
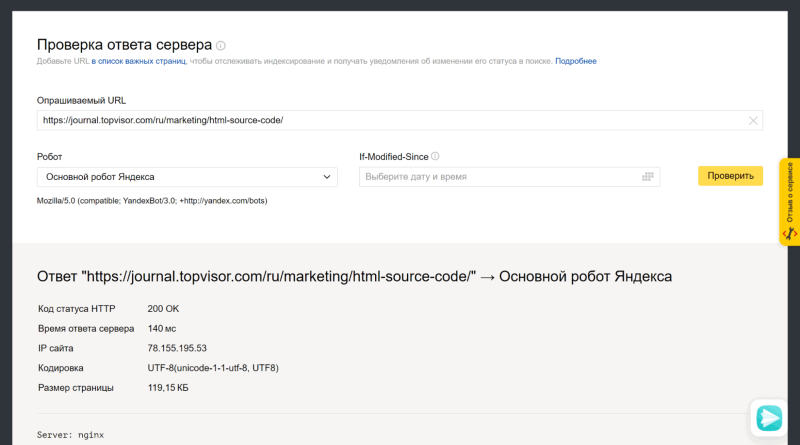
Откройте инструмент «Проверка ответа сервера» в Вебмастере. Введите URL в специальное поле и нажмите кнопку «Проверить»:
Как добавить сайт в Яндекс.Вебмастер и другие сервисы Яндекса
В Google Search Console
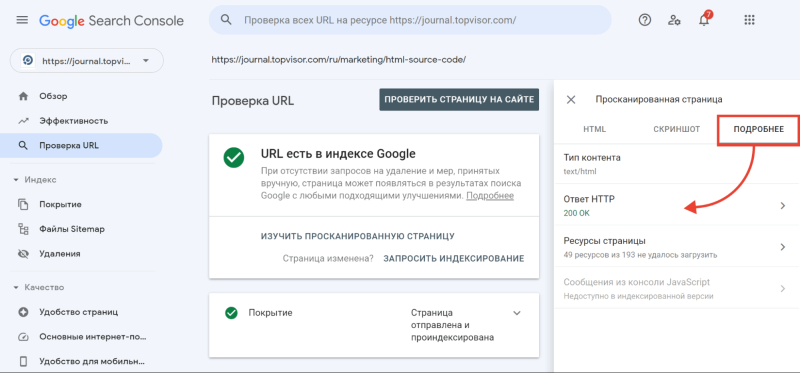
Чтобы посмотреть код ответа сервера в GSC, перейдите в инструмент проверки URL — он находится в самом верху панели:
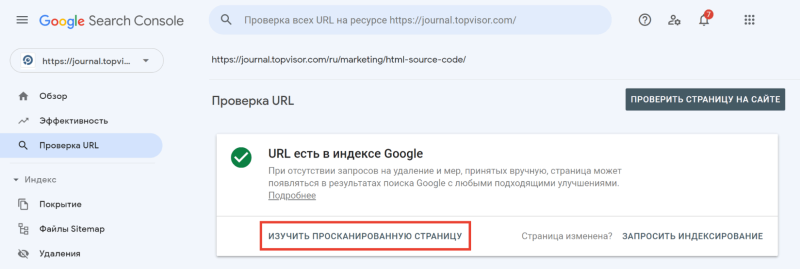
Введите ссылку на страницу, которую хотите проверить, и нажмите Enter. В результатах проверки нажмите на «Изучить просканированную страницу» в блоке «URL есть в индексе Google».
А затем в открывшемся окне перейдите на вкладку «Подробнее»:
Теперь расскажем подробнее про все классы кодов состояния HTTP.
1* класс кодов (информационные сообщения)
Это системный класс кодов, который только информирует о процессе передачи запроса. Такие ответы не являются ошибкой, хотя и могут отображаться в браузере как Error Code.
100 Continue
Этот ответ сообщает, что полученные сведения о запросе устраивают сервер и клиент может продолжать отправлять данные. Такой ответ может требоваться клиенту, если на сервер отправляется большой объём данных.
101 Switching Protocols
Сервер одобрил переключение типа протокола, которое запросил пользователь, и в настоящий момент выполняет действие.
102 Processing
Запрос принят — он находится в обработке, и на это понадобится чуть больше времени.
103 Checkpoint
Контрольная точка — используется в запросах для возобновления после прерывания запросов POST или PUT.
POST отправляет данные на сервер, PUT создает новый ресурс или заменяет существующий данными, представленными в теле запроса.
Разница между ними в том, что PUT работает без изменений: повторное его применение даёт такой же результат, что и в первый раз, а вот повторный вызов одного и того же метода POST часто меняет данные.
Пример — оформленный несколько раз интернет‑заказ. Такое часто происходит как раз по причине неоднократного использования запроса PUT.
105 Name Not Resolved
Не удается преобразовать DNS‑адрес сервера — это означает ошибку в службе DNS. Эта служба преобразует IP‑адреса в знакомые нам доменные имена.
2* класс кодов (успешно обработанные запросы)
Эти коды информируют об успешности принятия и обработки запроса. Также сервер может передать заголовки или тело сообщений.
200 ОК
Все хорошо — HTTP‑запрос успешно обработан (не ошибка).
201 Created
Создано — транзакция успешна, сформирован новый ресурс или документ.
202 Accepted
Принято — запрос принят, но ещё не обработан.
203 Non‑Authoritative Information
Информация не авторитетна — запрос успешно обработан, но передаваемая информация была взята не из первичного источника (данные могут быть устаревшими).
204 No Content
Нет содержимого — запрос успешно обработан, однако в ответе только заголовки без контента сообщения. Не нужно обновлять содержимое документа, но можно применить к нему полученные метаданные.
205 Reset Content
Сбросить содержимое. Запрос успешно обработан — но нужно сбросить введенные данные. Страницу можно не обновлять.
206 Partial Content
Частичное содержимое. Сервер успешно обработал часть GET‑запроса, а другую часть вернул.
GET — метод для чтения данных с сайта. Он говорит серверу, что клиент хочет прочитать какой‑то документ.
Представим интернет‑магазин и страницы каталога. Фильтры, которые выбирает пользователь, передаются благодаря методу GET. GET‑запрос работает с получением данных, а POST‑запрос нужен для отправки данных.
При работе с подобными ответами следует уделить внимание кэшированию.
207 Multi‑Status
Успешно выполнено несколько операций — сервер передал результаты выполнения нескольких независимых операций. Они появятся в виде XML‑документа с объектом multistatus.
226 IM Used
Успешно обработан IM‑заголовок (специальный заголовок, который отправляется клиентом и используется для передачи состояния HTTP).
3* класс кодов (перенаправление на другой адрес)
Эти коды информируют, что для достижения успешной операции нужно будет сделать другой запрос, возможно, по другому URL.
300 Multiple Choices
Множественный выбор — сервер выдает список нескольких возможных вариантов перенаправления (максимум — 5). Можно выбрать один из них.
301 Moved Permanently
Окончательно перемещено — страница перемещена на другой URL, который указан в поле Location.
302 Found/Moved
Временно перемещено — страница временно перенесена на другой URL, который указан в поле Location.
303 See Other
Ищите другую страницу — страница не найдена по данному URL, поэтому смотрите страницу по другому URL, используя метод GET.
304 Not Modified
Модификаций не было — с момента последнего визита клиента изменений не было.
305 Use Proxy
Используйте прокси — запрос к нужному ресурсу можно сделать только через прокси‑сервер, URL которого указан в поле Location заголовка.
306 Unused
Зарезервировано. Код в настоящий момент не используется.
307 Temporary Redirect
Временное перенаправление — запрашиваемый ресурс временно доступен по другому URL.
Этот код имеет ту же семантику, что код ответа 302 Found, за исключением того, что агент пользователя не должен изменять используемый метод HTTP: если в первом запросе использовался POST, то во втором запросе также должен использоваться POST.
308 Resume Incomplete
Перемещено полностью (навсегда) — запрашиваемая страница была перенесена на новый URL, указанный в поле Location заголовка. Метод запроса (GET/POST) менять не разрешается.
4* класс кодов (ошибки на стороне клиента)
Эти коды указывают на ошибки со стороны клиентов.
400 Bad Request
Неверный запрос — запрос клиента не может быть обработан, так как есть синтаксическая ошибка (возможно, опечатка).
401 Unauthorized
Не пройдена авторизация — запрос ещё в обработке, но доступа нет, так как пользователь не авторизован.
Для доступа к запрашиваемому ресурсу клиент должен представиться, послав запрос, включив при этом в заголовок сообщения поле Authorization.
402 Payment Required
Требуется оплата — зарезервировано для использования в будущем. Код предусмотрен для платных пользовательских сервисов, а не для хостинговых компаний.
403 Forbidden
Запрещено — запрос принят, но не будет обработан, так как у клиента недостаточно прав. Может возникнуть, когда пользователь хочет открыть системные файлы (robots, htaccess) или не прошёл авторизацию.
404 Not Found
Не найдено — запрашиваемая страница не обнаружена. Сервер принял запрос, но не нашёл ресурса по указанному URL (возможно, была ошибка в URL или страница была перемещена).
405 Method Not Allowed
Метод не разрешён — запрос был сделан методом, который не поддерживается данным ресурсом. Сервер должен предложить доступные методы решения в заголовке Allow.
406 Not Acceptable
Некорректный запрос — неподдерживаемый поисковиком формат запроса (поисковый робот не поддерживает кодировку или язык).
407 Proxy Authentication Required
Нужно пройти аутентификацию прокси — ответ аналогичен коду 401, только нужно аутентифицировать прокси‑сервер.
408 Request Timeout
Тайм‑аут запроса — запрос клиента занял слишком много времени. На каждом сайте существует свое время тайм‑аута — проверьте интернет‑соединение и просто обновите страницу.
409 Conflict
Конфликт (что‑то пошло не так) — запрос не может быть выполнен из‑за конфликтного обращения к ресурсу (несовместимость двух запросов).
410 Gone
Недоступно — ресурс раньше был размещён по указанному URL, но сейчас удалён и недоступен (серверу неизвестно месторасположение).
411 Length Required
Добавьте длины — сервер отклоняет отправляемый запрос, так как длина заголовка не определена, и он не находит значение Content‑Length.
Нужно исправить заголовки на сервере, и в следующий раз робот сможет проиндексировать страницу.
412 Precondition Failed
Предварительное условие не выполнено — стоит проверить правильность HTTP‑заголовков данного запроса.
413 Request Entity Too Large
Превышен размер запроса — перелимит максимального размера запроса, принимаемого сервером. Браузеры поддерживают запросы от 2 до 8 килобайт.
414 Request‑URI Too Long
Превышена длина запроса — сервер не может обработать запрос из‑за длинного URL. Такая ошибка может возникнуть, например, когда клиент пытается передать чересчур длинные параметры через метод GET, а не POST.
415 Unsupported Media Type
Формат не поддерживается — сервер не может принять запрос, так как данные подгружаются в некорректном формате, и сервер разрывает соединение.
416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable
Диапазон не поддерживается — ошибка возникает в случаях, когда в самом HTTP‑заголовке прописывается некорректный байтовый диапазон.
Корректного диапазона в необходимом документе может просто не быть, или есть опечатка в синтаксисе.
417 Expectation Failed
Ожидания не оправдались — прокси некорректно идентифицировал содержимое поля «Expect: 100‑Continue».
418 I’m a teapot
Первоапрельская шутка разработчиков в 1998 году. В расшифровке звучит как «я не приготовлю вам кофе, потому что я чайник». Не используется в работе.
422 Unprocessable Entity
Объект не обработан — сервер принял запрос, но в нём есть логическая ошибка. Стоит посмотреть в сторону семантики сайта.
423 Locked
Закрыто — ресурс заблокирован для выбранного HTTP‑метода. Можно перезагрузить роутер и компьютер. А также использовать только статистический IP.
424 Failed Dependency
Неуспешная зависимость — сервер не может обработать запрос, так как один из зависимых ресурсов заблокирован.
Выполнение запроса напрямую зависит от успешности выполнения другой операции, и если она не будет успешно завершена, то вся обработка запроса будет прервана.
425 Unordered Collection
Неверный порядок в коллекции — ошибка возникает, если клиент указал номер элемента в неупорядоченном списке или запросил несколько элементов в порядке, отличном от серверного.
426 Upgrade Required
Нужно обновление — в заголовке ответа нужно корректно сформировать поля Upgrade и Connection.
Этот ответ возникает, когда серверу требуется обновление до SSL‑протокола, но клиент не имеет его поддержки.
428 Precondition Required
Нужно предварительное условие — сервер просит внести в запрос информацию о предварительных условиях обработки данных, чтобы выдавать корректную информацию по итогу.
429 Too Many Requests
Слишком много запросов — отправлено слишком много запросов за короткое время. Это может указывать, например, на попытку DDoS‑атаки, для защиты от которой запросы блокируются.
431 Request Header Fields Too Large
Превышена длина заголовков — сервер может и не отвечать этим кодом, вместо этого он может просто сбросить соединение.
Исправляется это с помощью сокращения заголовков и повторной отправки запроса.
434 Requested Host Unavailable
Адрес запрашиваемой страницы недоступен.
444 No Response
Нет ответа — код отображается в лог‑файлах, чтобы подтвердить, что сервер никак не отреагировал на запрос пользователя и прервал соединение. Возвращается только сервером nginx.
Nginx — программное обеспечение с открытым исходным кодом. Его используют для создания веб‑серверов, а также в качестве почтового или обратного прокси‑сервера. Nginx решает проблему падения производительности из‑за роста трафика.
449 Retry With
Повторите попытку — ошибка говорит о необходимости скорректировать запрос и повторить его снова. Причиной становятся неверно указанные параметры (возможно, недостаточно данных).
450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls
Заблокировано родительским контролем — говорит о том, что с компьютера попытались зайти на заблокированный ресурс. Избежать этой ошибки можно изменением параметров системы родительского контроля.
451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
Недоступно по юридическим причинам — доступ к ресурсу закрыт, например, по требованию органов государственной власти или по требованию правообладателя в случае нарушения авторских прав.
456 Unrecoverable Error
Неустранимая ошибка — при обработке запроса возникла ошибка, которая вызывает некорректируемые сбои в таблицах баз данных.
499 Client Closed Request
Запрос закрыт клиентом — нестандартный код, используемый nginx в ситуациях, когда клиент закрыл соединение, пока nginx обрабатывал запрос.
5* класс кодов (ошибки на стороне сервера)
Эти коды указывают на ошибки со стороны серверов.
При использовании всех методов, кроме HEAD, сервер должен вернуть в теле сообщения гипертекстовое пояснение для пользователя. И его можно использовать в работе.
500 Internal Server Error
Внутренняя ошибка сервера — сервер столкнулся с неким условием, из‑за которого не может выполнить запрос.
Проверяйте, корректно ли указаны директивы в системных файлах (особенно htaccess) и нет ли ошибки прав доступа к файлам. Обратите внимание на ошибки внутри скриптов и их медленную работу.
501 Not Implemented
Не выполнено — код отдается, когда сам сервер не может идентифицировать метод запроса.
Сами вы эту ошибку не исправите. Устранить её может только сервер.
502 Bad Gateway
Ошибка шлюза — появляется, когда сервер, выступая в роли шлюза или прокси‑сервера, получил ответное сообщение от вышестоящего сервера о несоответствии протоколов.
Актуально исключительно для прокси и шлюзовых конфигураций.
503 Service Unavailable
Временно не доступен — сервер временно не имеет возможности обрабатывать запросы по техническим причинам (обслуживание, перегрузка и прочее).
В поле Retry‑After заголовка сервер укажет время, через которое можно повторить запрос.
504 Gateway Timeout
Тайм‑аут шлюза — сервер, выступая в роли шлюза или прокси‑сервера, не получил ответа от вышестоящего сервера в нужное время.
Исправить эту ошибку самостоятельно не получится. Здесь дело в прокси, часто — в веб‑сервере.
Первым делом просто обновите веб‑страницу. Если это не помогло, нужно почистить DNS‑кэш. Для этого нажмите горячие клавиши Windows+R и введите команду cmd (Control+пробел). В открывшемся окне укажите команду ipconfig / flushdns и подтвердите её нажатием Enter.
505 HTTP Version Not Supported
Сервер не поддерживает версию протокола — отсутствует поддержка текущей версии HTTP‑протокола. Нужно обеспечить клиента и сервер одинаковой версией.
506 Variant Also Negotiates
Неуспешные переговоры — с такой ошибкой сталкиваются, если сервер изначально настроен неправильно. По причине ошибочной конфигурации выбранный вариант указывает сам на себя, из‑за чего процесс и прерывается.
507 Insufficient Storage
Не хватает места для хранения — серверу недостаточно места в хранилище. Нужно либо расчистить место, либо увеличить доступное пространство.
508 Loop Detected
Обнаружен цикл — ошибка означает провал запроса и выполняемой операции в целом.
509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded
Превышена пропускная способность — используется при чрезмерном потреблении трафика. Владельцу площадки следует обратиться к своему хостинг‑провайдеру.
510 Not Extended
Не продлён — ошибка говорит, что на сервере отсутствует нужное для клиента расширение. Чтобы исправить проблему, надо убрать часть неподдерживаемого расширения из запроса или добавить поддержку на сервер.
511 Network Authentication Required
Требуется аутентификация — ошибка генерируется сервером‑посредником, к примеру, сервером интернет‑провайдера, если нужно ввести пароль для получения доступа к сети через платную точку доступа.