В статье мы расскажем, как исправить ошибку (код состояния) 500 со стороны пользователя и администратора сайта, а также подробно разберём, что такое ошибка запроса 500.
Что такое внутренняя ошибка сервера 500
Код ошибки 5хх говорит о том, что браузер отправил запрос корректно, но сервер не смог его обработать. Что значит ошибка 500? Это проблема сервера, причину которой он не может распознать.
Сообщение об ошибке сопровождается описанием. Самые популярные варианты:
- Внутренняя ошибка сервера 500,
- Ошибка 500 Internal Server Error,
- Временная ошибка (500),
- Внутренняя ошибка сервера,
- 500 ошибка сервера,
- Внутренняя ошибка HTTP 500,
- Произошла непредвиденная ошибка,
- Ошибка 500,
- HTTP status 500 internal server error (перевод ― HTTP статус 500 внутренняя ошибка сервера).
Дизайн и описание ошибки 500 может быть любым, так как каждый владелец сайта может создать свою версию страницы. Например, так выглядит страница с ошибкой на REG.RU:
Как ошибка 500 влияет на SEO-продвижение
Для продвижения сайта в поисковых системах используются поисковые роботы. Они сканируют страницы сайта, проверяя их доступность. Если страница работает корректно, роботы анализируют её содержимое. После этого формируются поисковые запросы, по которым можно найти ресурс в поиске.
Когда поисковый робот сканирует страницу с ошибкой 500, он не изменяет её статус в течение суток. В течение этого времени администратор может исправить ошибку. Если робот перейдёт на страницу и снова столкнётся с ошибкой, он исключит эту страницу из поисковой выдачи.
Проверить, осталась ли страница на прежних позициях, можно с помощью Google Search Console. Если робот исключил страницу из поисковой выдачи, её можно добавить снова.
Код ошибки 500: причины
Если сервер вернул ошибку 500, это могло случиться из-за настроек на web-хостинге или проблем с кодом сайта. Самые распространённые причины:
- ошибки в файле .htaccess,
- неподходящая версия PHP,
- некорректные права на файлы и каталоги,
- большое количество запущенных процессов,
- большие скрипты,
- несовместимые или устаревшие плагины.
Решить проблему с сервером можно только на стороне владельца веб-ресурса. Однако пользователь тоже может выполнить несколько действий, чтобы продолжить работу на сайте.
Что делать, если вы пользователь
Если на определённом ресурсе часто возникает ошибка 500, вы можете связаться с владельцем сайта по инструкции.
Перезагрузите страницу
Удаленный сервер возвращает ошибку не только из-за серьёзных проблем на сервере. Иногда 500 ошибка сервера может быть вызвана небольшими перегрузками сайта.
Чтобы устранить ошибку, перезагрузите страницу с помощью сочетания клавиш:
- на ПК — F5,
- на ноутбуке — Fn + F5,
- на устройствах от Apple — Cmd + R.
Обратите внимание! Если вы приобретаете товары в интернет-магазине и при оформлении заказа появляется 500 Internal Server Error (перевод — внутренняя ошибка сервера), при перезагрузке страницы может создаться несколько заказов. Поэтому сначала проверьте, оформился ли ваш предыдущий заказ. Если нет, попробуйте оформить заказ заново.
Очистите кэш и cookies браузера
Кэш и cookies сохраняют данные посещаемых сайтов и данные аутентификаций, чтобы в будущем загружать веб-ресурсы быстрее. Если на ресурсе уже был статус ошибки 500, при повторном входе на сайт может загружаться старая версия страницы с ошибкой из кэша, хотя на самом деле страница уже работает. Очистить кэш и куки браузера вам поможет инструкция.
Если ни одно из этих действий не решило проблему, значит, некорректно работает сам сервер сайта. Вернитесь на страницу позже, как только владелец решит проблему.
Что делать, если вы владелец сайта
В большинстве случаев устранить проблему может только владелец сайта. Как правило, ошибка связана с проблемами в коде. Реже проблемы могут быть на физическом сервере хостинг-провайдера.
Ниже рассмотрим самые популярные причины и способы решения.
Ошибки в файле .htaccess
Неверные правила в файле .htaccess — частая причина возникновения ошибки. Чтобы это проверить, найдите .htaccess в файлах сайта и переименуйте его (например, в test). Так директивы, прописанные в файле, не повлияют на работу сервера. Если сайт заработал, переименуйте файл обратно в .htaccess и найдите ошибку в директивах. Если вы самостоятельно вносили изменения в .htaccess, закомментируйте новые строки и проверьте доступность сайта.Также может помочь замена текущего файла .htaccess на стандартный в зависимости от CMS.
Найти директиву с ошибкой можно с помощью онлайн-тестировщика. Введите содержимое .htaccess и ссылку на сайт, начиная с https://. Затем нажмите Test:
Произошла непредвиденная ошибка
На экране появится отчёт. Если в .htaccess есть ошибки, они будут выделены красным цветом:
500 ошибка nginx
Активирована устаревшая версия PHP
Устаревшие версии PHP не получают обновления безопасности, работают медленнее и могут вызывать проблемы с плагинами и скриптами. Возможно, для работы вашего веб-ресурса нужна более новая версия PHP. Попробуйте сменить версию PHP на другую по инструкции.
Установлены некорректные права на файлы и каталоги сайта
В большинстве случаев корректными правами для каталогов являются «755», для файлов — «644». Проверьте, правильно ли они установлены, и при необходимости измените права на файлы и папки.
Запущено максимальное количество процессов
На тарифах виртуального хостинга REG.RU установлены ограничения на количество одновременно запущенных процессов. Например, на тарифах линейки «Эконом» установлено ограничение в 18 одновременно запущенных процессов, на тарифах «+Мощность» ― 48 процессов. Если лимит превышен, новый процесс не запускается и возникает системная ошибка 500.
Такое большое число одновременных процессов может складываться из CRON-заданий, частых подключений с помощью почтовых клиентов по протоколу IMAP, подключения по FTP или других процессов.
Чтобы проверить количество процессов, подключитесь по SSH. Выполните команду:
ps aux | grep [u]1234567 |wc -lВместо u1234567 укажите ваш логин хостинга: Как узнать логин хостинга.
Чтобы посмотреть, какие процессы запущены, введите команду:
Вместо u1234567 укажите логин услуги хостинга.
Командная строка отобразит запущенные процессы:
Код ошибки 500
Где:
- u1234567 — логин услуги хостинга,
- 40522 — PID процесса,
- S — приоритет процесса,
- /usr/libexec/sftp-server — название процесса.
Процесс можно завершить командой kill, например:
Вместо 40522 укажите PID процесса.
Чтобы решить проблему, вы также можете:
- увеличить интервал запуска заданий CRON,
- ограничить количество IMAP-соединений в настройках почтового клиента. Подробнее в статье Ограничение IMAP-соединений,
- проанализировать запущенные процессы самостоятельно или обратившись за помощью к разработчикам сайта.
Если вам не удалось самостоятельно устранить ошибку 500, обратитесь в техподдержку.
Скрипты работают слишком медленно
На каждом виртуальном хостинге есть ограничения на время выполнения скрипта. Если за установленное время скрипт не успевает выполниться, возникает ошибка сервера 500. Для решения проблемы обратитесь к разработчику сайта и оптимизируйте скрипты. Если оптимизировать нельзя, перейдите на более мощный вид сервера.
У пользователей VPS есть возможность увеличить максимальное использование оперативной памяти на процесс, но лучше делать скрипты меньшего размера.
Ошибка 500 на сайте, созданном на WordPress
WordPress предлагает много плагинов для создания хорошего сайта. Они значительно расширяют возможности CMS. Однако они же могут нарушать работу сайта и вызывать ошибку 500. Вызвать ошибку могут как недавно установленные плагины, так и старые.
Для начала проверьте, нужно ли обновить плагины. Часто устаревшие плагины перестают работать и вызывают проблемы работы сайта. Если все плагины обновлены, но 500 Internal Server Error остаётся, отключите все плагины, чтобы убедиться, что именно они мешают работе сайта. Как только станет понятно, что виноват один из плагинов, отключайте их по очереди, пока не найдёте тот, который нарушает работу сервера.
Как отключить плагин в WordPress
- 1.
-
2.
Перейдите во вкладку «Плагины» ― «Установленные».
-
3.
Нажмите Деактивировать у плагина, который, как вам кажется, повлиял на работу сайта:
Если все ваши действия не решили проблему или вы не уверены в своих технических знаниях, обратитесь к службе технической поддержки. Сообщите время обнаружения проблемы и опишите все действия, которые вы предприняли перед обращением. Специалисты сделают детальную проверку настроек вашего сайта и при необходимости обратятся к администраторам сервера на стороне хостинг-провайдера.
Что это? Ошибка 500 – это то, что препятствует открытию той или иной страницы сайта. Вместо ожидаемой, например, статьи, перед пользователем возникает фраза Internal Server Error 500. Она сообщает о проблемах ресурса с подключением к серверу.
Как исправить? Устранить ошибку можно как со стороны пользователя сайта, так и его владельца. В первом случае способы не гарантируют на 100 %, что Error 500 моментально пропадает, но попробовать стоит. Больше возможностей в этом плане у собственника ресурса.
В статье рассказывается:
- Что значит код ошибки 500
- Основные причины возникновения ошибки 500
- Текст и внешний вид ошибки
- Советы по исправлению ошибки 500 для пользователя
- Рекомендации по исправлению ошибки 500 для владельца сайта
-
Пройди тест и узнай, какая сфера тебе подходит:
айти, дизайн или маркетинг.Бесплатно от Geekbrains
Значение 500 является кодом положения протокола НТТР. Из-за чего появляется ошибка 500? Происходит это потому, что случилась неисправность конфигурации сервера или пришёл сигнал о том, что компонент отказал. Когда возникает эта ошибка, программное обеспечение продолжает работать, но из-за серьёзных внутренних нарушений запросы обрабатываются некорректно.
Ошибка 500 значит, что пользовательский запрос неправильно переводится в действие. По этой причине возникают проблемы во время работы с сайтом. Нужно как можно скорее понять, из-за чего именно появилась ошибка, и устранить её.
Оповещение о том, что произошла ошибка 500, имеет текстовое описание. Наиболее частые варианты:
- Ошибка 500.
- Внутренняя ошибка сервера 500.
- Ошибка 500 Internal Server Error.
- Временная ошибка (500).
- Внутренняя ошибка сервера.
- 500 ошибка сервера.
- Внутренняя ошибка HTTP 500.
- Произошла непредвиденная ошибка.
- HTTP status 500 internal server error (перевод ― HTTP статус 500 внутренняя ошибка сервера).
Скачать файл
Визуальный вид и текстовое сопровождение ошибки могут отличаться у каждого пользователя, потому что версии страницы могут быть разными.
Вероятность столкнуться с такой неприятностью есть при работе с любым веб-ресурсом, браузером или устройством. Главное, понимать, что эта ошибка, как и другие, которые начинаются на цифру 5, является промахом разработчиков или администратора сайта и вашей вины в этом нет.
Основные причины возникновения ошибки 500
Мы уже выяснили, что данная ошибка появляется, когда сервер не смог обработать запрос, совершённый пользователем, в результате чего человек не может открыть ресурс, а поисковые системы с ним взаимодействовать. Проблему обязательно нужно устранить, но для начала следует найти причину её появления, среди которых может быть:
- Неправильный синтаксис файла .htaccess – это файл, в котором можно менять настройки при работе с веб-сервером Apache и корректировать его функционирование (управлять различными перенаправлениями, правами доступа к данным, опциями PHP, задавать собственные страницы ошибок и прочее).
- Неполадки в сценариях сайта, которые отвечают за дополнительные возможности и визуальные эффекты.
- Недостаточно оперативной памяти, чтобы выполнить скрипт.
- Ошибки в коде CMS, системы управления наполнением ресурса. В большинстве случаев (80 %) причиной являются конфликтующие плагины.
Текст и внешний вид ошибки
Вы узнали, что означает ошибка 500, теперь пришло время перейти к более подробному разбору возможных причин её появления. Иногда разобраться с этим вопросом можно и без помощи специалиста.
Вид ошибки может отличаться. Это зависит от того, из-за чего она возникла. Наиболее распространенные причины можно узнать по тому, как отображается ошибка и какой текст её сопровождает.
Internal Server Error
Данный вид ошибки – сигнал о том, что есть проблемы с файлом .htaccess (к примеру, он был неправильно настроен). Чтобы понять, действительно ли дело в .htaccess, добавьте к его названию в конце цифру один. Сделать это поможет FTP-клиент (например, FileZilla) или файловый менеджер на вашем хостинге (в Timeweb есть подобный, и он очень простой в использовании). После этой манипуляции попробуйте заново открыть сайт. Если ошибка не выскочила, значит, вы нашли, из-за чего она появилась.
Топ-30 самых востребованных и высокооплачиваемых профессий 2023
Поможет разобраться в актуальной ситуации на рынке труда
Подборка 50+ ресурсов об IT-сфере
Только лучшие телеграм-каналы, каналы Youtube, подкасты, форумы и многое другое для того, чтобы узнавать новое про IT
ТОП 50+ сервисов и приложений от Geekbrains
Безопасные и надежные программы для работы в наши дни
Уже скачали 18731
HTTP ERROR 500 или пустая страница
Подобное означает, что причина в сценариях сайта. Но надо уточнить насчёт пустой страницы, что это не только признак внутренней ошибки 500 в сервере.
Предлагаем детальнее разобраться с пустой страницей, обращаясь к инструментам разработчика. Через браузерную панель пользователь получает уведомления об ошибках и другую информацию (время запуска сайта, html-элементы и прочее).
Каким образом открывается панель разработчика? Для начала нажмите F12 (это подходит для большинства браузеров на Windows). Если вы пользуетесь Google Chrome на macOS, то вам нужно использовать сочетание кнопок Cmd+Opt+J. В случае Safari на macOS нужна комбинация Cmd+Opt+C, но перед тем, как её нажать, включите «Меню разработки» в разделе «Настройки» -> «Продвинутые».
Есть ещё один способ открыть панель разработчика: кликнуть правой кнопкой мыши в любом месте сайта и в открывшемся контекстном меню выбрать «Посмотреть код». После этого откройте вкладку «Сеть» (или Network) и посмотрите, какое значение указано в строке «Статус». Если дело в ошибке 500, то будет стоять эта цифра.
Советы по исправлению ошибки 500 для пользователя
Для начала расскажем, на что лучше не тратить своё время. Данная ошибка связана с сервером, поэтому делать что-то со стороны клиента (перезагружать роутер, менять браузер, переустанавливать программу) смысла нет.
- Заново откройте сайт
Ошибка 500 может появиться не только из-за серьёзных проблем с сервером, но и по причине временной перегрузки сайта. Перезагрузить страницу можно с помощью клавиш: на ПК — F5, ноутбуке — Fn + F5, на устройствах от Apple — Cmd + R.

Читайте также
- Очистите кэш и cookies браузера
Кэш и cookies нужны для того, чтобы при повторном открытии страницы не нужно было заново прогружать все данные, то есть они сохраняют информацию с первого посещения, за счёт чего в следующий раз сайт открывается быстрее.
Если на сервере была ошибка, то даже если её уже устранили, из-за кэша может открываться старая версия страницы с этой неполадкой.
Если ничего из этого вам не помогло, то остаётся ждать, когда владелец решит эту проблему, и вернуться на сайт позже.
- Обратитесь к владельцу сайта
Когда, например, в интернет-магазине часто всплывает ошибка 500, можно связаться с его владельцем. Информация с контактными данными, как правило, находится либо внизу страницы, либо в разделе «Контакты».
Чаще всего информация закрытая, но есть форма для обратной связи. Однако не факт, что вы получите ответ. Если нужные данные вы не нашли или ответа так и нет, можно воспользоваться такими вариантами: через Whois, хостинг-провайдера или регистратора домена, с помощью сторонних сервисов.
Рекомендации по исправлению ошибки 500 для владельца сайта
Стоит учитывать большое количество факторов: движок, на котором работает ваш сайт, на каком он хостинге расположен, какие недавние изменения были внесены. Как бы там ни было, зачастую универсальные методы убирают ошибку 500. Желательно попробовать все варианты, которые подойдут под специфику вашего ресурса.
- Устраните неполадки в синтаксисе файла .htaccess
Выше мы уже рассказывали, как понять, в нём ошибка или нет. Попробуйте изменить имя документа, к примеру, на .htaccess_, и заново открыть сайт. Если ошибка не вылезла, значит, дело всё-таки в .htaccess. Проанализируйте синтаксис документа на наличие лишних символов или опечаток. Если вы сохраняли прошлую версию настроек, то надо попробовать её вернуть, чтобы проверить, будет ли ошибка.
В некоторых случаях может помочь закомментирование строки Options в .htaccess – вставить # в её начале. Если ничего не поменялось, проделайте то же самое с другими строками, а потом по очереди убирайте # и смотрите на результат.
После изменения файла .htaccess надо проверить, сохранилось ли оно. Иногда хостер может выставить на документ права, которые мешают его менять. В этой ситуации вы можете скачать файл .htaccess к себе на устройство, открыть и отредактировать его в любом текстовом документе и залить обратно, заменив старую версию.
Точный инструмент «Колесо компетенций»
Для детального самоанализа по выбору IT-профессии
Список грубых ошибок в IT, из-за которых сразу увольняют
Об этом мало кто рассказывает, но это должен знать каждый
Мини-тест из 11 вопросов от нашего личного психолога
Вы сразу поймете, что в данный момент тормозит ваш успех
Регистрируйтесь на бесплатный интенсив, чтобы за 3 часа начать разбираться в IT лучше 90% новичков.
Только до 13 февраля
Осталось 17 мест
- Обновите РНР
Версии РНР, которые уже устарели, не поддерживают обновления безопасности, хуже работают и из-за них может быть некорректная работа плагинов и сценариев.
Может, для того, чтобы ваш сайт работал без перебоев, вам надо просто обновить РНР.
- Настройте права для CGL-скриптов
Одним из методов устранения ошибки 500 на сайте является выставление прав для CGL-скриптов. Если такие сценарии у вас есть, то их папки и файлы должны иметь такое право доступа: 0755 (drwxr-xr-x), которое даёт возможность менять их только владельцу, а остальные могут их лишь открывать и активировать. Когда на скриптах стоит другое право доступа, это может привести к появлению ошибки 500.
- Проверьте файлы CGL-скриптов
У правильных сценариев окончание строк в формате Unix (n), а не Windows (rn). Для сохранения корректного варианта нужно загружать код (в большинстве хостингов) по FTP в режиме ASCII. Если вы не помните, какие ранее были настройки, заново добавьте сценарии и посмотрите, появится или нет ошибка 500. К тому же CGL-скрипты могут быть причиной неправильных HTTP‑заголовков ответа. В данном варианте вы сможете заметить ошибку в логах.
- Проверьте плагины
Причина может скрываться в плагинах, которые вы недавно установили.
Нередко встречается такое, что отдельные элементы сайта или плагины не могут работать совместно друг с другом. Данная проблема становится причиной не только того, что сайт выдаёт ошибку 500, но и возникновения других неполадок на сервере. Если модели были установлены или обновлены не так давно, то можно попробовать их отключить через панель администратора. Есть вероятность, что после этого могут всплыть другие неполадки, но если ошибка 500 исчезла, значит, дело было в конфликте плагинов или компонентов.
- Проверьте лог ошибок
Более точный анализ проводится с помощью логов. Если объяснять простым языком, то лог – это своеобразный журнал, в котором хранится информация об ошибках, направленных запросах, подключениях, действий с документами и так далее. Так как данных в логах очень много, они делятся на категории, чтобы было проще найти то, что нужно.
Если в последнее время вы как-то меняли сайт, то это могло стать причиной появления ошибки с кодом состояния 500. Зайдите в логи и проверьте, нет ли там информации о проблемах. Если ошибки высветились, то надо их изучить и отменить последние изменения.
Как правило, хостеры предоставляют информацию о том, где найти логи и как их открыть с панели управления. Данные об этом есть в разделе помощи FAQ (frequently asked questions — часто задаваемые вопросы) на сайте хостинга.
- Оптимизируйте сценарии
Если написанные сценарии долго грузятся или вообще не могут запуститься из-за нехватки ресурсов, проанализируйте их содержимое. Может, код надо оптимизировать, чтобы он стал легче и быстрее загружался. Нередко сценариям недостаточно ресурсов при работе с виртуальным хостингом. У них есть жёсткий лимит на память, чтобы каждый пользователь имел равные возможности во время пребывания на выбранном сайте.
Разделите скрипты на части и проверьте каждый на эффективность их деятельности. Если вы обнаружили в коде много ненужных вызовов либо необходимый объём памяти постоянно растёт, нужно обязательно проработать эти моменты.
- Увеличьте объём оперативной памяти сервера
Встречаются ситуации, когда даже после оптимизации сценариев они продолжают занимать много памяти. Чтобы решить эту проблему, придётся начать пользоваться более дорогим пакетом обслуживания, который предлагает хостинг.
Либо, если есть вариант увеличить объём памяти, прибегнуть к нему. К тому же вы не будете платить за те функции, которые не нужны вашему ресурсу.
Если вы испробовали все возможные варианты, но ничего не помогло, лучше обратиться за помощью к службе технической поддержки. Укажите время, когда вылезла ошибка, и подробно расскажите, что пытались предпринять для её устранения. Специалисты подробно изучат настройки сайта и, если потребуется, обратятся к управляющим сервера на стороне хостинг-провайдера.

Читайте также
Ошибка выполнения запроса 500 является обобщенным кодом состояния НТТР, который говорит о том, что на сервере произошла какая-то неполадка, но более точно описать проблему сервер не может. Так что первым делом нужно узнать, что послужило причиной возникновения ошибки, и только после этого заниматься её устранением.
The dreaded 500 internal server error. It always seems to come at the most inopportune time and you’re suddenly left scrambling to figure out how to get your WordPress site back online. Trust us, we’ve all been there. Other errors that behave similarly that you might have also seen include the frightening error establishing a database connection and the dreaded white screen of death. But from the moment your site goes down, you’re losing visitors and customers. Not to mention it simply looks bad for your brand.
Today we’re going to dive into the 500 internal server error and walk you through some ways to get your site back online quickly. Read more below about what causes this error and what you can do to prevent it in the future.
- What is a 500 internal server error?
- How to fix the 500 internal server error
500 Internal Server Error (Most Common Causes):
500 Internal server error in WordPress can be caused by many things. If you’re experiencing one, there’s a high chance one (or more) of the following elements is causing the issue:
- Browser Cache.
- Incorrect database login credentials.
- Corrupted database.
- Corrupted files in your WordPress installation.
- Issues with your database server.
- Corrupted WordPress core files.
- Corrupted .htaccess file and PHP memory limit.
- Issues with third-party plugins and themes.
- PHP timing out or fatal PHP errors with third-party plugins.
- Wrong file and folder permissions.
- Exhausted PHP memory limit on your server
- Corrupted or broken .htaccess file.
- Errors in CGI and Perl script.
Check Out Our Ultimate Guide to Fixing the 500 Internal Server Error
What is a 500 Internal Server Error?
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) defines the 500 Internal Server Error as:
The 500 (Internal Server Error) status code indicates that the server encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request.
When you visit a website your browser sends a request over to the server where the site is hosted. The server takes this request, processes it, and sends back the requested resources (PHP, HTML, CSS, etc.) along with an HTTP header. The HTTP also includes what they call an HTTP status code. A status code is a way to notify you about the status of the request. It could be a 200 status code which means “Everything is OK” or a 500 status code which means something has gone wrong.
There are a lot of different types of 500 status error codes (500, 501, 502, 503, 504, etc.) and they all mean something different. In this case, a 500 internal server error indicates that the server encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request (RFC 7231, section 6.6.1).
500 Internal Server Error Variations
Due to the various web servers, operating systems, and browsers, a 500 internal server error can present itself in a number of different ways. But they are all communicating the same thing. Below are just a couple of the many different variations you might see on the web:
-
- “500 Internal Server Error”
- “HTTP 500”
- “Internal Server Error”
- “HTTP 500 – Internal Server Error”
- “500 Error”
- “HTTP Error 500”
- “500 – Internal Server Error”
- “500 Internal Server Error. Sorry something went wrong.”
- “500. That’s an error. There was an error. Please try again later. That’s all we know.”
- “The website cannot display the page – HTTP 500.”
- “Is currently unable to handle this request. HTTP ERROR 500.”
You might also see this message accompanying it:
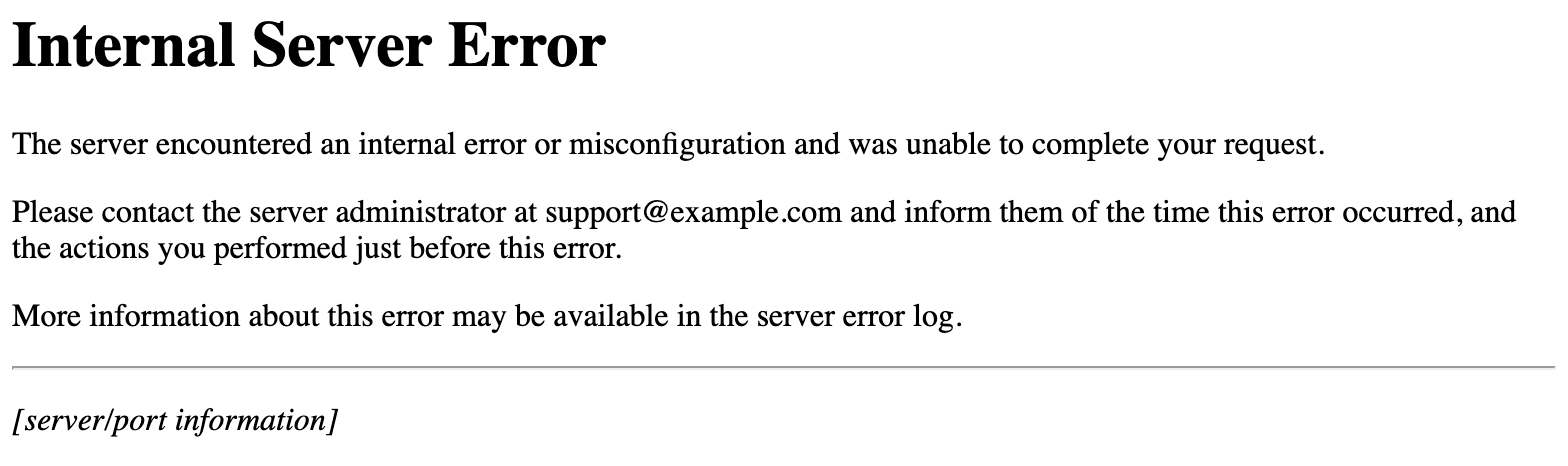
The server encountered an internal error or misconfiguration and was unable to complete your request. Please contact the server administrator, [email protected] and inform them of the time the error occurred, and anything you might have done that may have caused the error. More information about this error may be available in the server error log.
Other times, you might simply see a blank white screen. When dealing with 500 internal server errors, this is actually quite common in browsers like Firefox and Safari.
Bigger brands might even have their own custom 500 internal server error messages, such as this one from Airbnb.
Here is another creative 500 server error example from the folks over at readme.
Even the mighty YouTube isn’t safe from 500 internal server errors.
If it’s an IIS 7.0 (Windows) or higher server, they have additional HTTP status codes to more closely indicate the cause of the 500 error:
- 500.0 – Module or ISAPI error occurred.
- 500.11 – Application is shutting down on the web server.
- 500.12 – Application is busy restarting on the web server.
- 500.13 – Web server is too busy.
- 500.15 – Direct requests for global.asax are not allowed.
- 500.19 – Configuration data is invalid.
- 500.21 – Module not recognized.
- 500.22 – An ASP.NET httpModules configuration does not apply in Managed Pipeline mode.
- 500.23 – An ASP.NET httpHandlers configuration does not apply in Managed Pipeline mode.
- 500.24 – An ASP.NET impersonation configuration does not apply in Managed Pipeline mode.
- 500.50 – A rewrite error occurred during RQ_BEGIN_REQUEST notification handling. A configuration or inbound rule execution error occurred.
- 500.51 – A rewrite error occurred during GL_PRE_BEGIN_REQUEST notification handling. A global configuration or global rule execution error occurred.
- 500.52 – A rewrite error occurred during RQ_SEND_RESPONSE notification handling. An outbound rule execution occurred.
- 500.53 – A rewrite error occurred during RQ_RELEASE_REQUEST_STATE notification handling. An outbound rule execution error occurred. The rule is configured to be executed before the output user cache gets updated.
500.100 – Internal ASP error.
500 Errors Impact on SEO
Unlike 503 errors, which are used for WordPress maintenance mode and tell Google to check back at a later time, a 500 error can have a negative impact on SEO if not fixed right away. If your site is only down for say 10 minutes and it’s being crawled consistently a lot of times the crawler will simply get the page delivered from cache. Or Google might not even have a chance to re-crawl it before it’s back up. In this scenario, you’re completely fine.
However, if the site is down for an extended period of time, say 6+ hours, then Google might see the 500 error as a site level issue that needs to be addressed. This could impact your rankings. If you’re worried about repeat 500 errors you should figure out why they are happening to begin with. Some of the solutions below can help.
How to Fix the 500 Internal Server Error
Where should you start troubleshooting when you see a 500 internal server error on your WordPress site? Sometimes you might not even know where to begin. Typically 500 errors are on the server itself, but from our experience, these errors originate from two things, the first is user error (client-side issue), and the second is that there is a problem with the server. So we’ll dive into a little of both.
This is never not annoying 😖 pic.twitter.com/pPKxbkvI9K
— Dare Obasanjo 🐀 (@Carnage4Life) September 26, 2019
Check out these common causes and ways to fix the 500 internal server error and get back up and running in no time.
1. Try Reloading the Page
This might seem a little obvious to some, but one of the easiest and first things you should try when encountering a 500 internal server error is to simply wait a minute or so and reload the page (F5 or Ctrl + F5). It could be that the host or server is simply overloaded and the site will come right back. While you’re waiting, you could also quickly try a different browser to rule that out as an issue.
Another thing you can do is to paste the website into downforeveryoneorjustme.com. This website will tell you if the site is down or if it’s a problem on your side. A tool like this checks the HTTP status code that is returned from the server. If it’s anything other than a 200 “Everything is OK” then it will return a down indication.
We’ve also noticed that sometimes this can occur immediately after you update a plugin or theme on your WordPress site. Typically this is on hosts that aren’t set up properly. What happens is they experience a temporary timeout right afterward. However, things usually resolve themselves in a couple of seconds and therefore refreshing is all you need to do.
2. Clear Your Browser Cache
Clearing your browser cache is always another good troubleshooting step before diving into deeper debugging on your site. Below are instructions on how to clear cache in the various browsers:
- How to Force Refresh a Single Page for All Browsers
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Google Chrome
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Mozilla Firefox
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Safari
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Internet Explorer
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Microsoft Edge
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Opera
3. Check Your Server Logs
You should also take advantage of your error logs. If you’re a Kinsta client, you can easily see errors in the log viewer in the MyKinsta dashboard. This can help you quickly narrow down the issue, especially if it’s resulting from a plugin on your site.
If your host doesn’t have a logging tool, you can also enable WordPress debugging mode by adding the following code to your wp-config.php file to enable logging:
define( 'WP_DEBUG', true );
define( 'WP_DEBUG_LOG', true );
define( 'WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', false );The logs are typically located in the /wp-content directory. Others, like here at Kinsta might have a dedicated folder called “logs”.
You can also check the log files in Apache and Nginx, which are commonly located here:
- Apache: /var/log/apache2/error.log
- Nginx: /var/log/nginx/error.log
If you’re a Kinsta client you can also take advantage of our analytics tool to get a breakdown of the total number of 500 errors and see how often and when they are occurring. This can help you troubleshoot if this is an ongoing issue, or perhaps something that has resolved itself.
If the 500 error is displaying because of a fatal PHP error, you can also try enabling PHP error reporting. Simply add the following code to the file throwing the error. Typically you can narrow down the file in the console tab of Google Chrome DevTools.
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);And you might need to also modify your php.ini file with the following:
display_errors = on4. Error Establishing a Database Connection
500 internal server errors can also occur from a database connection error. Depending upon your browser you might see different errors. But both will generate a 500 HTTP status code regardless in your server logs.
Below is an example of what an “error establishing a database connection” message looks like your browser. The entire page is blank because no data can be retrieved to render the page, as the connection is not working properly. Not only does this break the front-end of your site, but it will also prevent you from accessing your WordPress dashboard.
So why exactly does this happen? Well, here are a few common reasons below.
- The most common issue is that your database login credentials are incorrect. Your WordPress site uses separate login information to connect to its MySQL database.
- Your WordPress database is corrupted. With so many moving parts with themes, plugins, and users constantly deleting and installing them, sometimes databases get corrupted. This can be due to a missing or individually corrupted table, or perhaps some information was deleted by accident.
- You may have corrupt files in your WordPress installation. This can even happen sometimes due to hackers.
- Issues with your database server. A number of things could be wrong on the web hosts end, such as the database being overloaded from a traffic spike or unresponsive from too many concurrent connections. This is actually quite common with shared hosts as they are utilizing the same resources for a lot of users on the same servers.
Check out our in-depth post on how to fix the error establishing a database connection in WordPress.
5. Check Your Plugins and Themes
Third-party plugins and themes can easily cause 500 internal server errors. We’ve seen all types cause them here at Kinsta, from slider plugins to ad rotator plugins. A lot of times you should see the error immediately after installing something new or running an update. This is one reason why we always recommend utilizing a staging environment for updates or at least running updates one by one. Otherwise, if you encounter a 500 internal server error you’re suddenly scrambling to figure out which one caused it.
A few ways you can troubleshoot this is by deactivating all your plugins. Remember, you won’t lose any data if you simply deactivate a plugin. If you can still access your admin, a quick way to do this is to browse to “Plugins” and select “Deactivate” from the bulk actions menu. This will disable all of your plugins.
If this fixes the issue you’ll need to find the culprit. Start activating them one by one, reloading the site after each activation. When you see the 500 internal server error return, you’ve found the misbehaving plugin. You can then reach out to the plugin developer for help or post a support ticket in the WordPress repository.
If you can’t login to WordPress admin you can FTP into your server and rename your plugins folder to something like plugins_old. Then check your site again. If it works, then you will need to test each plugin one by one. Rename your plugin folder back to “plugins” and then rename each plugin folder inside of if it, one by one, until you find it. You could also try to replicate this on a staging site first.
Always makes sure your plugins, themes, and WordPress core are up to date. And check to ensure you are running a supported version of PHP. If it turns out to be a conflict with bad code in a plugin, you might need to bring in a WordPress developer to fix the issue.
6. Reinstall WordPress Core
Sometimes WordPress core files can get corrupted, especially on older sites. It’s actually quite easy to re-upload just the core of WordPress without impacting your plugins or themes. We have an in-depth guide with 5 different ways to reinstall WordPress. And of course, make sure to take a backup before proceeding. Skip to one of the sections below:
- How to reinstall WordPress from the WordPress dashboard while preserving existing content
- How to manually reinstall WordPress via FTP while preserving existing content
- How to manually reinstall WordPress via WP-CLI while preserving existing content
7. Permissions Error
A permissions error with a file or folder on your server can also cause a 500 internal server error to occur. Here are some typical recommendations for permissions when it comes to file and folder permissions in WordPress:
- All files should be 644 (-rw-r–r–) or 640.
- All directories should be 755 (drwxr-xr-x) or 750.
- No directories should ever be given 777, even upload directories.
- Hardening: wp-config.php could also be set to 440 or 400 to prevent other users on the server from reading it.
See the WordPress Codex article on changing file permissions for a more in-depth explanation.
You can easily see your file permissions with an FTP client (as seen below). You could also reach out to your WordPress host support team and ask them to quickly GREP file permissions on your folders and files to ensure they’re setup properly.
8. PHP Memory Limit
A 500 internal server error could also be caused by exhausting the PHP memory limit on your server. You could try increasing the limit. Follow the instructions below on how to change this limit in cPanel, Apache, your php.ini file, and wp-config.php file.
Increase PHP Memory Limit in cPanel
If you’re running on a host that uses cPanel, you can easily change this from the UI. Under Software click on “Select PHP Version.”
Click on “Switch to PHP Options.”
You can then click on the memory_limit attribute and change its value. Then click on “Save.”
Increase PHP Memory Limit in Apache
The .htaccess file is a special hidden file that contains various settings you can use to modify the server behavior, right down to a directory specific level. First login to your site via FTP or SSH, take a look at your root directory and see if there is a .htaccess file there.
If there is you can edit that file to add the necessary code for increasing the PHP memory limit. Most likely it is set at 64M or below, you can try increasing this value.
php_value memory_limit 128MIncrease PHP Memory Limit in php.ini File
If the above doesn’t work for you might try editing your php.ini file. Log in to your site via FTP or SSH, go to your site’s root directory and open or create a php.ini file.
If the file was already there, search for the three settings and modify them if necessary. If you just created the file, or the settings are nowhere to be found you can paste the code below. You can modify of course the values to meet your needs.
memory_limit = 128MSome shared hosts might also require that you add the suPHP directive in your .htaccess file for the above php.ini file settings to work. To do this, edit your .htaccess file, also located at the root of your site, and add the following code towards the top of the file:
<IfModule mod_suphp.c>
suPHP_ConfigPath /home/yourusername/public_html
</IfModule>If the above didn’t work for you, it could be that your host has the global settings locked down and instead have it configured to utilize .user.ini files. To edit your .user.ini file, login to your site via FTP or SSH, go to your site’s root directory and open or create a .user.ini file. You can then paste in the following code:
memory_limit = 128MIncrease PHP Memory Limit in wp-config.php
The last option is not one we are fans of, but if all else fails you can give it a go. First, log in to your site via FTP or SSH, and locate your wp-config.php file, which is typically in the root of your site.
Add the following code to the top of your wp-config.php file:
define('WP_MEMORY_LIMIT', '128M');You can also ask your host if you’re running into memory limit issues. We utilize the Kinsta APM tool and other troubleshooting methods here at Kinsta to help clients narrow down what plugin, query, or script might be exhausting the limit. You can also use your own custom New Relic key from your own license.
9. Problem With Your .htaccess File
Kinsta only uses Nginx, but if you’re using a WordPress host that is running Apache, it could very well be that your .htaccess file has a problem or has become corrupted. Follow the steps below to recreate a new one from scratch.
First, log in to your site via FTP or SSH, and rename your .htaccess file to .htaccess_old.
Normally to recreate this file you can simply re-save your permalinks in WordPress. However, if you’re in the middle of a 500 internal server error you most likely can’t access your WordPress admin, so this isn’t an option. Therefore you can create a new .htaccess file and input the following contents. Then upload it to your server.
# BEGIN WordPress
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index.php$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.php [L]
</IfModule>
# END WordPressSee the WordPress Codex for more examples, such as a default .htaccess file for multisite.
10. Coding or Syntax Errors in Your CGI/Perl Script
500 errors being caused by errors in CGI and Perl is a lot less common than it used to be. Although it’s still worth mentioning, especially for those using cPanel where there are a lot of one-click CGI scripts still being used. As AEM on Stack Overflow says:
CGI has been replaced by a vast variety of web programming technologies, including PHP, various Apache extensions like mod_perl, Java of various flavors and frameworks including Java EE, Struts, Spring, etc, Python-based frameworks like Django, Ruby on Rails and many other Ruby frameworks, and various Microsoft technologies.
Here are a few tips when working with CGI scripts:
- When editing, always used a plain text editor, such as Atom, Sublime, or Notepad++. This ensures they remain in ASCII format.
- Ensure correct permissions of chmod 755 are used on CGI scripts and directories.
- Upload your CGI scripts in ASCII mode (which you can select in your FTP editor) into the cgi-bin directory on your server.
- Confirm that the Perl modules you require for your script are installed and supported.
11. Server Issue (Check With Your Host)
Finally, because 500 internal server errors can also occur from PHP timing out or fatal PHP errors with third-party plugins, you can always check with your WordPress host. Sometimes these errors can be difficult to troubleshoot without an expert. Here are just a few common examples of some errors that trigger 500 HTTP status codes on the server that might have you scratching your head.
PHP message: PHP Fatal error: Uncaught Error: Call to undefined function mysql_error()...PHP message: PHP Fatal error: Uncaught Error: Cannot use object of type WP_Error as array in /www/folder/web/shared/content/plugins/plugin/functions.php:525We monitor all client’s sites here at Kinsta and are automatically notified when these types of errors occur. This allows us to be pro-active and start fixing the issue right away. We also utilize LXD managed hosts and orchestrated LXC software containers for each site. This means that every WordPress site is housed in its own isolated container, which has all of the software resources required to run it (Linux, Nginx, PHP, MySQL). The resources are 100% private and are not shared with anyone else or even your own sites.
PHP timeouts could also occur from the lack of PHP workers, although typically these cause 504 errors, not 500 errors. These determine how many simultaneous requests your site can handle at a given time. To put it simply, each uncached request for your website is handled by a PHP Worker.
When PHP workers are already busy on a site, they start to build up a queue. Once you’ve reached your limit of PHP workers, the queue starts to push out older requests which could result in 500 errors or incomplete requests. Read our in-depth article about PHP workers.
Monitor Your Site
If you’re worried about these types of errors happening on your site in the future, you can also utilize a tool like updown.io to monitor and notify you immediately if they occur. It periodically sends an HTTP HEAD request to the URL of your choice. You can simply use your homepage. The tool allows you to set check frequencies of:
- 15 seconds
- 30 seconds
- 1 minute
- 2 minutes
- 5 minutes
- 10 minutes
It will send you an email if and when your site goes down. Here is an example below.
This can be especially useful if you’re trying to debug a faulty plugin or are on a shared host, who tend to overcrowd their servers. This can give you proof of how often your site might actually be doing down (even during the middle of the night).
That’s why we always recommend going with an application, database, and managed WordPress host (like Kinsta).
Make sure to check out our post that explores the top 9 reasons to choose managed WordPress hosting.
Summary
500 internal server errors are always frustrating, but hopefully, now you know a few additional ways to troubleshoot them to quickly get your site back up and running. Remember, typically these types of errors are caused by third-party plugins, fatal PHP errors, database connection issues, problems with your .htaccess file or PHP memory limits, and sometimes PHP timeouts.
Was there anything we missed? Perhaps you have another tip on troubleshooting 500 internal server errors. If so, let us know below in the comments.
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275 PoPs worldwide
Test it yourself with $20 off your first month of Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
Troubleshooting an HTTP 500 internal server error is like solving a mystery.
You don’t know what exactly happened or why it happened — all you know is that something’s wrong and you need to fix it.
To guide you through the hassle of troubleshooting the dreaded HTTP 500 internal server error, let’s go over what it exactly means and its most common causes and solutions.
An HTTP 500 internal server error is a general error message. It covers unexpected issues that don’t fit into existing error codes. HTTP 500 errors are difficult to troubleshoot because a range of issues on the server side can trigger them.
Here are some examples of what a 500 error page might look like in your browser:
Image Source
Image Source
HTTP 500
HTTP 500 errors aren’t problems with your computer, browser, or internet connection. Instead, they’re a generic response that catches any unexplainable server error. You’ll see the HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) 500 Internal Server Error when your server issue doesn’t fit another error code.
Other Common Error Codes
HTTP codes show you how your web browser and website communicate. These are some other common error codes you might see on your website:
HTTP 200
This is a standard status code for websites that are performing well.
HTTP 301
This is the code for permanent redirects. For example, say you have two site pages about widgets with duplicate information and one gets more traffic than the other. It makes sense to redirect the low-traffic page to the high-traffic page to improve SEO for your site.
HTTP 302
This code is for temporary redirects. This is for situations where you want to send users to an alternate page for a short amount of time.
HTTP 304
This code shows up when the website you’re requesting hasn’t seen an update since your last visit.
HTTP 403
This code comes from the server when you’re trying to access a restricted URL.
HTTP 404
A 404 code tells your users that your server can’t find that page they requested with their browser. 404 errors are common, and some sites use this to their advantage.
HTTP 405
This is an HTTP response status code error. It tells you that a web browser wants to access your web page and your server has rejected that specific HTTP method. This means that the browser can’t access the requested web page.
HTTP 410
This is a permanent code that tells site visitors that the page they’re looking for doesn’t exist.
HTTP 413
This code appears when a user tries to upload a file that exceeds the server’s file size limit.
HTTP 429
This error is a server response to stop sending requests because of overloaded resources. This code might show up if your site needs to make too many API calls to meet a request.
HTTP 503
This code tells users that the server is temporarily unable to load the page they’re looking for.
Check out this post for a comprehensive overview of error codes.
Potential Causes of a 500 Internal Server Error
A 500 internal server error is, as the name implies, a general problem with the website’s server. More than likely, this means there’s an issue or temporary glitch with the website’s programming.
Some potential causes of a 500 internal server error include:
Corrupted or Broken .Htaccess File
A .htaccess file is a text file with important server instructions. These instructions tell your software to enable or disable specific functions. They might help you protect passwords in a directory or restrict user access.
There are many ways to corrupt a .htaccess file. It can happen during plugin installation, file configuration, or while you are working on your server.
A Permissions Error
Permission errors come with file protection. Permissions errors might be bugs, user mistakes, or networking problems. Usually, this error means that the user isn’t allowed to perform the action they’re trying.
Faulty Third-Party Plugins or Themes
To increase user features and functionality, you might add a third-party theme or plugin to your website. These plugins can be great for your site, but they can also impact site security, bugs, and performance.
These plugins and themes are often created by individuals or small groups. This can be challenging because they may need more time to address bug fixes and vulnerabilities.
Exceeding the PHP Memory Limit
PHP is a server-side scripting language embedded in HTML. PHP is for managing content, databases, session tracking, and more. Each PHP process uses memory, and your hosting account has a limit for each one of these processes.
If a website needs more than this memory limit, you may see an HTTP 500 error.
HTTP Error 500 Browser Compatibility
Most businesses design their websites for maximum browser compatibility. This means that your website is easy to access and use on any browser or operating system. But your site may work perfectly in one browser and have issues or errors in others.
Because HTTP 500 is a catch-all error, you can see this error on any browser and in any operating system.
How an HTTP 500 Error Might Appear
This error can come up on any site you try to visit on a browser. Because it’s such a common error, there are many ways to communicate this code.
- Internal server error
- The page isn’t working
- 500 Internal Server Error
- 500 Server Error
- 500. That’s an error.
- HTTP 500.0 — Internal Server Error
- Error 500
- Error code: 500
- The server returned a 500 Internal Server Error
- Temporary Error (500)
How to Fix a 500 Internal Server Error
Unlike other server-side errors like a 502 code, a 500 internal server error is it doesn’t immediately tell you what the problem is, nor does it tell you how to fix it. If the error persists for too long on your site, it could even negatively impact your SEO.
So, let’s dive into some solutions so you can try to fix the issue.
If You’re Trying to Load a Page with a 500 Internal Server Error:
1. Refresh the page.
This might seem obvious, but if it’s a temporary loading issue, you might find success if you refresh the page. Before trying anything else in this list, reload the page and see what happens.
2. Come back later.
Since the error is on the server side, I’m willing to bet the website owners are working as quickly as possible to resolve the issue. Give it a few minutes or up to an hour or so, and then reload the URL and see if the development team has fixed the issue.
3. Delete your browser’s cookies.
If clearing the browser history doesn’t work, you might try deleting your browser’s cookies. If the cookies are associated with the error-prone webpage, deleting the cookies might help reload the page.
4. Paste your URL into the website «Down for Everyone or Just Me.»
Head to downforeveryoneorjustme.com and paste in the URL where you’re seeing the internal server error. You’ll either be told that the website is only down for you, or that the website is down for everyone.
If the 500 Internal Server Error is on Your Own Website:
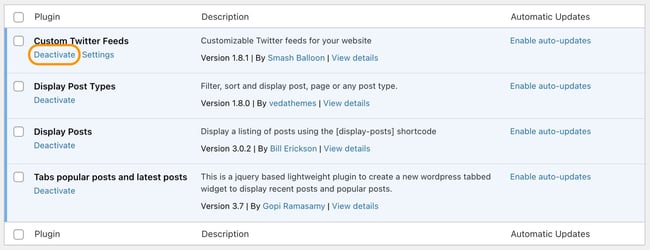
1. Deactivate a plugin or theme.
Newly activated software, add-ons, or third-party scripts might be conflicting with your current server configuration. To determine this, try (carefully) deactivating or uninstalling your software add-ons one at a time to identify what exactly is causing the internal server error.
If you run a WordPress website, this is easy to do with plugins. From your dashboard, choose Plugins > Installed Plugins, then deactivate the first plugin. If the error resolves, you know this plugin is part of the issue. Reactivate the first plugin, then repeat this deactivate-reactivate process one at a time for all plugins to determine which ones are causing your error.
Alternatively, if you just upgraded your software, your current plugins or themes might not be compatible with the new upgrade. Deactivating plugins or themes one at a time until the error disappears is the best way to find the root cause of your problem.
2. Use a plugin like WP Debugging to identify the issue.
If your site is powered by WordPress and you’re comfortable with WordPress debugging processes, consider installing a plugin to help you identify the issue with your server.
The debug plugin WP Debugging, for instance, helps you figure out exactly what’s wrong with your site, which will result in a speedier fix.
Image Source
3. Ensure your PHP setup is configured correctly.
If the issue is related to a PHP timeout, consider creating timeout rules or error handling in your script to resolve the issue. Here’s a full list of php.ini directives to configure your PHP setup.
Additionally, wrong permissions on a file or folder that has a script, like a PHP or CGI script, won’t allow the script to run. Check your permissions and make sure you set them correctly on your server.
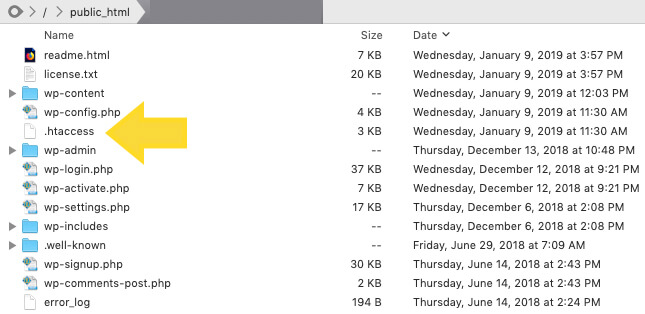
4. Check the code for your site’s .htaccess file.
Incorrect coding or improper structure with your .htaccess file could be the reason you’re seeing the 500 internal error. The .htaccess file helps you manage how long resources should be stored in a browser’s cache. Try editing the file if you’re seeing a 500 internal server error.
To locate your .htaccess file, access your website files through a file manager like cPanel or via FTP/SFTP. The file will probably be located in your public_html directory. There’s a good chance your server will hide this file from view by default and you’ll need to toggle hidden files on to see it.
Image Source
Coding errors in .htaccess and custom scripts can also cause an HTTP 500 internal server error.
5. Ensure your new software is installed correctly.
Finally, check to see if your recently installed or upgraded software actually failed to install or upgrade. To refresh your software, check the vendor’s website for instructions.
Last Resort: Ask a Server Administrator for Help
If troubleshooting popular software problems or debugging server-side scripts doesn’t fix your HTTP 500 internal server error, you should read about the most common causes for this type of issue in your server’s documentation — an HTTP 500 internal server error can occur in different operating systems for a multitude of reasons.
You can also ask your service provider to access your error logs and find evidence of the root cause of your problem.
Internal server errors are irritating because they’re unhelpful — it’s basically the web server’s way of saying, «Eh, I’m not sure.» Hopefully, one of the above steps will resolve the problem so you can get back to life as usual.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in October 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
HTTP status codes provide information about whether an online request was successful, and if not, what the error is. But the error messages aren’t always clear. This is especially the case for the “500 Internal Server Error.” This message indicates that an error has occurred during connection to the server and that the requested page cannot be accessed. However, it won’t tell you exactly why this is the case. Fortunately, there are different methods for finding the cause. We point out typical error sources and give tips on what to do if you encounter the HTTP error 500.
Contents
- What does the internal server error mean?
- What are the causes of error 500?
- How can website operators fix the 500 Internal Server Error?
- How should internet users respond to an HTTP error 500?
$1 Domain Names
Register great TLDs for less than $1 for the first year.
Why wait? Grab your favorite domain name today!
Matching email
SSL certificate
24/7/365 support
What does the internal server error mean?
Using status codes, the web server tells an internet user’s browser (client) whether a request (i.e. accessing a website) was successful or not. If the browser receives the 200 status code, it knows that everything went well. However, the user never sees this message since the requested content appears instead. The situation is different with the 400 and 500 status codes. While the former indicate client errors, the latter are server-related. The Internal Server Error 500 is a collective status code for server errors. Therefore, at first glance, it is not possible to determine where the error actually lies. The user only knows that the server has reported an unexpected error.
However, if the server has installed Microsoft Internet Information Services (Microsoft IIS), the error code will be specified. Decimal places indicate the cause of the error in more detail:
- 500.0: Module or ISAPI error occurred.
- 500.11: Application is shutting down on the web server.
- 500.12: Application is busy restarting on the web server.
- 500.13: Web server is too busy.
- 500.15: Direct requests for global.asax are not allowed.
- 500.19: Configuration data is invalid.
- 500.21: Module not recognized.
- 500.22: An ASP.NET httpModules configuration does not apply in Managed Pipeline mode.
- 500.23: An ASP.NET httpHandlers configuration does not apply in Managed Pipeline mode.
- 500.24: An ASP.NET impersonation configuration does not apply in Managed Pipeline mode.
- 500.50: A rewrite error occurred during RQ_BEGIN_REQUEST notification handling. A configuration or inbound rule execution error occurred.
- 500.51: A rewrite error occurred during GL_PRE_BEGIN_REQUEST notification handling. A global configuration or global rule execution error occurred.
- 500.52: A rewrite error occurred during RQ_SEND_RESPONSE notification handling. An outbound rule execution occurred.
- 500.53: A rewrite error occurred during RQ_RELEASE_REQUEST_STATE notification handling. An outbound rule execution error occurred. The rule is configured to be executed before the output user cache gets updated.
- 500.100: Internal ASP error.
What are the causes of error 500?
The “Internal Server Error” can occur when the request is processed by the web server. The collective status code includes everything unplanned that can happen on the server and prevent the website from being loaded. The server error 500 probably happens because an error has occurred in the configuration of the web server. Here is a selection of typical error sources:
- Permission error: The permissions of the main files and folders are not set correctly.
- PHP timeout: The script tries to access an external resource and experiences a timeout.
- Incorrect code in .htaccess: The structure in a .htaccess file could be wrong.
- Error in syntax or code in CGI/Perl scripts: In some cases, scripts are incorrect. Paths, especially, can be misaligned.
- PHP memory limit: A process exceeds memory and therefore cannot be executed correctly.
In the case of WordPress sites or other content management systems, installing a faulty or incompatible extension can also be the cause. Plugins and themes – especially from third-party providers – can affect the entire website.
How can website operators fix the 500 Internal Server Error?
Are your website visitors only seeing the 500 server error? As an operator, you should tackle the problem quickly because not only will this scare off your visitors, but it could also mean that Google will lower your ranking. Before you take action, first check whether your server is still running. If not, contact your hosting provider as soon as possible.
If there is an internal error, the first step is to view the log files. For Linux servers, the collection of error messages should be found at /var/log/httpd/error_log. It makes sense to reload the website to reproduce the HTTP error 500 code and observe how the log file is being created. This will help you find the source of the error quite quickly. Also consider which changes were made shortly before. In many cases, incorrectly programmed or incompatible plugins are the cause of error messages.
Errors can also occur if you have not set permissions correctly for important files. In general, there are three types of rights:
- Read (r)
- Write (w)
- Execute (x)
These permissions can be assigned for three different user types:
- Owner of the file
- Group of users
- All others
The rights are specified either in the abbreviations r, w, and x, or in corresponding numerical values: 4 for read, 2 for write, and 1 for execute. They are added for each user type and specified one after the other: rwxr-xr-x (rwx for the owner, r-x for the group, and r-x for all others) or 755. This configuration (755) should be the default setting. If the permission assignment is set differently, an error may occur. You can change this with a command:
If this change does not solve the problem, you can also release all rights for each group for test purposes:
But only use this setting to locate the problem. Any user is allowed to rewrite the file, which is understandably a security risk.
Next, check (if distributing the rights didn’t produce the error message) if your scripts are running correctly. Sometimes errors occur because the script files have been moved, renamed, or deleted. Also check the .htaccess file: even a syntax error – no matter how small – can cause an internal server error. An equally common error is incorrectly formatting the .htaccess file. This must be created in ASCII or ANSI format, not in Unicode. Therefore, write the file in a text editor such as Notepad, Notepad++, or Sublime Text, and not in a word processing program such as Microsoft Word. To test whether the file is responsible for the error, you can temporarily rename it and reload the website. The server now won’t access .htaccess when loading the website. If you no longer receive the error message, you can repair the file or create a new one.
A timeout can also lead to an error message. In this case, it isn’t a web server error, but rather an interrupted connection to an external source. Are PHP scripts on your website set to access resources from other servers? Perhaps the resource is no longer available or server communication is down for some other reason. One way to eliminate this source of error is of course to not make your site dependent on external resources. If this is not possible, you can increase the time limit of your script. It also makes sense to implement efficient error handling so that errors in the PHP script can be detected more accurately.
Could it be that the memory is overloaded? The memory limit determines how much memory a process may use. If more RAM is needed than is available, this could result in an internal server error. You can increase the limit as a temporary solution. To do this, add a command like this to php.ini:
In this example, you would set the memory provided to 512MB. Note, however, that your hosting provider will only allow you a certain PHP script limit within the package that you’ve booked. If you enter a higher value, the web server will ignore it. Raising the limit is only a temporary solution: once your site is up and running again, you should look for the reason for the high RAM usage. There is a high probability that the error can be found in the code of your website.
If none of these methods offer you a solution, it is a good idea to contact your hosting provider. Before doing so, you can check the status of the servers: many hosting service providers will report the status of their servers via a status page or inform users via social media if a problem has occurred.
Tip
IONOS also has a status page where the hosting service’s customers are informed about current problems.
How should internet users respond to an HTTP error 500?
As a website visitor, there is little you can do if you encounter an internal server error. The web server on which the target website is located has an incorrect configuration. This means that there is no error in your PC settings or the network connection settings. Therefore, the easiest solution for you as an internet user is usually to reload the page again later. On the one hand, it is possible that the webmaster has already corrected the error. This is very likely, especially with large providers. On the other hand, it could be that you’re trying to access the website at an inconvenient time for the web server. If you’ve chosen the exact moment that the service is rebooting, the error message will be displayed even though everything is going to plan.
Note
If you are confronted with the error message when ordering online, you must not reload the webpage, since you can’t see where the error occurred. It could be that the confirmation page failed to load, but the system has already accepted your order. Refreshing the page could therefore lead to a duplicate order.
It is also possible that an extreme increase in page views has brought the server down all of a sudden. This problem is usually solved within a few seconds – unless the website is permanently overloaded. If you still receive the error message after refreshing the page, you should first clear your browser’s cache. The browser may not actually reload the website, but use its internal memory instead. After emptying the cache, try again to access the website.
If the “500 Internal Server Error” is still being displayed, you simply have no other choice, but to wait for the website operator to solve the problem. There is, however, a little trick you can use in order to access the contents of the website. If you are not dependent on the latest state of the (functioning) page, you can access the Google cache. If you enter the command cache: followed by the relevant URL in the Google search bar, you can access an earlier – hopefully still working – version of the website. However, you won’t really be surfing the page, you will only be navigating within the copy on the Google server.
If you have to go back even further in the past, it may be worth taking a look at the Wayback Machine. There you can sometimes find older versions of websites that are even decades old.
If the website you want to visit is not accessible for a longer time, you can of course contact the webmaster. They may not even know that visitors are unable to access their site, which is why they will be grateful to be told.

HTTP 503 (Service Unavailable): meaning and troubleshooting
It’s very likely that you’ve stumbled on the ‘HTTP Error 503 The service is unavailable’ notification or something similar during your daily browsing. The error message appears whenever a web server can’t display the website that the user is trying to access. There are many reasons for these notifications, just as there are many solutions. It’s your responsibility as the website operator to…
HTTP 503 (Service Unavailable): meaning and troubleshooting

HTTP 400: Bad Request explained
Internet users are often confronted with error messages. HTTP status codes can be especially annoying, and even more so if you don’t understand what they mean. The message ‘HTTP 400 – Bad Request’ is a mystery for many internet users, but luckily it can be solved in most cases. We explain what the error message means and how to fix the error.
HTTP 400: Bad Request explained

HTTP 504 (Gateway Timeout): How to fix an error 504
If the error message ‘HTTP 504 Gateway Timeout’ appears when you attempt to open a website, it means that the allowed time for responding to browser queries has been exceeded. A lot of the time the culprit is not the web server itself, but instead some other component of the server, i.e. a gateway, which is integral to the path of communication. What does 504 gateway timeout mean? How can you fix…
HTTP 504 (Gateway Timeout): How to fix an error 504
How to fix a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)
The infamous blue screen of death usually shows up without any warning. It’s an important indicator of internal problems with hardware, software, or drivers. If Windows can no longer be run as a result of such a problem, then the forced shutdown takes place in the form of a blue screen containing an error message. This may cause unsaved files and documents to be lost. The most important thing with…
How to fix a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)

SMTP error 550: how to fix “Requested action not taken: mailbox unavailable” and other SMTP 550 error messages
If you want to send a message with your e-mail client and the sending fails, you’ll receive a corresponding error message from the server, including an SMTP status code. For example, the message “550 Requested action not taken: mailbox unavailable” means that the targeted address couldn’t be reached. Since this problem can have various causes, even more possible solutions exist, some of which you…
SMTP error 550: how to fix “Requested action not taken: mailbox unavailable” and other SMTP 550 error messages
The error 500 can prevent you from accessing a page or website. When this error occurs, in fact, the server sends an HTTP error 500 status code to the browser to communicate a generic problem that prevents you from reaching the requested address.
When error 500 prevents you from reaching a site, the solution is to try again later when the problem has been resolved.
But what if error 500 occurs on your site? There are several checks you can do to try and fix it as soon as possible, so you won’t have a negative impact on your site visits and, more importantly, sales.
In this article,500 error: how to solve it, we’ll see what kind of problem is behind a 500 error. We’ll look at the possible causes and see what solutions you can implement to quickly fix the error and get your site back online.
To top it off, we will also see how to get around the error 500 in case you are not the owner of the site, but just want to access a temporarily unreachable resource.
What is Error 500?
The definition of Error 500 given by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) is as follows:
Status code 500 (Internal Server Error) indicates that the server encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request. (RFC7231)
So let’s start in order, what is an HTTP status code?
To allow us to reach an address, the browser must send a request to the server on which the site is hosted. The server, in response, returns a code to communicate the outcome of the request.
HTTP status codes are composed of 3 digits, the first of which indicates the category:
1XX: status codes starting with 1 are the informational ones. They indicate that the request has been received and they have yet to process it.
2XX: these codes are the confirmation codes, meaning that the request has been received and processed.
3XX: these are the redirection codes that are used when a resource has been moved temporarily (redirect 302) or permanently (as in the case of redirect 301)
4XX: these codes indicate client errors, such as error 403 and error 404 indicating a resource not found.
5XX: this is the category of server errors. It includes error 502 bad gateway, 504 gateway time-out and error 508, as well as error 500.
So these are the five categories of standard HTTP status codes. Then there are other codes that are always in decimal form and provide further details about the status of the request.
An example is given by Microsoft IIS (Internet Information Services) servers which in the case of error 500 allow getting more specific about the causes of the error.
- 500.0: the error is in a module or in ISAPI
- 500.11: one of the applications on the server is about to be stopped.
- 500.12: an application is about to restart.
- 500.13: server overload
- 500.15: request for global.asax file not allowed
- 500.19: configuration data is not valid
- 500.21: one of the modules was not recognized
- 500.22: the configuration of an HTTP module of an ASP.NET web application is not valid in Managed Pipeline mode
- 500.23: the configuration of an HTTP handlers element of an ASP.NET web application is not valid in Managed Pipeline mode
- 500.24: problems with the configuration of an identity change in Managed Pipeline mode
- 500.50: there was a rewrite error when processing the RQ_BEGIN_REQUEST message
- 500.51: there was a rewrite error while processing GL_PRE_BEGIN_REQUEST message
- 500.52: there was a rewriting error while processing the message RQ_SEND_RESPONSE
- 500.53: there was a rewriting error while processing the message RQ_RELEASE_REQUEST_STATE
- 500.100: the error occurred within the ASP application.
Error 500 can occur in a number of ways, here are some of the most common variations you may come across:
- 500 Internal Server Error
- HTTP 500 Internal Error
- HTTP Error 500
- Internal Server Error
- The website cannot display the page
- HTTP 500 – Internal Server Error
- Internal Server Error 500
- 500 Error
- 500 Server Error
- 500 Internal Server Error. Sorry something went wrong.
- Temporary Error (500)
- Server Error 500 internal
- Error 500 HTTP
- Error 500 Internal Server Error
- HTTP Error 500
- An error occurred during data request (500)
The error message can change from one server to another and on different browsers. In the screenshot below you can see an example of the error on Google Chrome.
Other browsers, such as Firefox, however, may also simply show you a white screen like this.
Causes of error 500
Error 500 can result from several causes ranging from an error in the .htaccess file to server unavailability due to maintenance. In this paragraph, we will examine some of the most common causes that can generate this type of error. In the next one, instead, we’re going to see how to proceed step by step to solve it.
Errors in the file .htaccess
The .htaccess file is used to insert directives for Apache servers. For example, you can use the .htaccess file to implement 301 redirects.
The presence of an error, such as an incorrect command or even a syntax or writing error, within this file, can cause the server to respond with an error 500.
Permissions errors
Permissions can be set for all files and folders on the server. This determines which users are granted permissions to read, write and execute files.
For example regarding permissions for WordPress files and folders you should use the following permissions:
- 644 or 640 for files
- 755 or 750 for folders.
An error in permissions can be the cause of a 500 error.
Problems with a script
An error in the syntax or code of a script, but also in the path setting can cause a 500 error. Also, you may have problems with Perl scripts if they were loaded in binary mode instead of ASCII, or if the necessary modules were not installed.
Problems with the server
Error 500 may be due to problems with the server, for example, if there is an overload on the server or due to maintenance. In these cases, you can wait and try to reload the page after some time or contact your provider.
Compatibility problems with plugins and themes
When using a CMS with extensions, plugins, or themes, a common situation you might find yourself in is a 500 error right after installing one of these components.
To quickly figure out if the cause of the 500 error is a plugin you can disable all of them temporarily. You can do this directly from the dashboard, but if you can’t log in, there are other methods as well, which we’ll see later in the section on Error 500 solutions.
Problems with WordPress core files
Although error 500 is not directly related to the platform you’re using, there are cases where the problem can stem from the CMS files.
For example, in the case of WordPress, it is possible that the core files have been damaged and need to be restored. In this case, you’ll have to proceed to reinstall WordPress without losing the content you’ve created so far.
Keep in mind that it is essential to make a backup before proceeding, to avoid losing your content.
Database problems
A 500 error can result from a problem with the database. Among the most common causes for which you may find yourself having your site down are:
- wrong credentials to access the database
- corrupted database
- database server overload.
PHP memory limit
If a script exceeds the memory threshold, the process is inhibited and you may be faced with a 500 error.
500 error: how to solve it
In addition to looking at the possible causes, we just saw there are other checks we can do to determine the origin of error 500. First, let’s start by analyzing the log files, and then see how to practically fix the common problems we saw earlier.
Check the log files
The cause of error 500 may not fit into the list of common causes we just reviewed. That’s why one of the first things to do is to go and check the server’s error logs or logs.
Access the site’s files, for example through the cPanel file manager, and look for a file like this “error_log”:
With WordPress you can also enable debug mode by adding this code to the wp-config.php file:
define( 'WP_DEBUG', true ); define( 'WP_DEBUG_LOG', true ); define( 'WP_DEBUG_DISPLAY', false );
Check file and folder permissions
You should make sure that files and folders on the server have proper permissions. For example in the case of WordPress, files should have permissions 644 or 640, while folders should be 755 or 750.
You can check and possibly change the file permissions in several ways. For example, you can use the cPanel file manager. With all our shared hosting plan, WordPress hosting, VPS cloud hosting and dedicated servers you can conveniently manage your site files from the file manager.
Next to each file, you’ll see a column that says Permissions and indicates the permissions of the file. In this example, all files are set to 644 and folders to 755.
If you want to change the permissions just click on the number corresponding to the file you want to change, type the new code and click on Save as you see in this screenshot:
You can also change file permissions with an FTP client. For example, you can see how to do it with Filezilla, in our guide dedicated to one of the most used FTP clients.
HTTP error 500 and problems with the .htaccess file
As we said before, one of the causes of an internal server error can be an error in the .htaccess file.
To check if the .htaccess file is the cause, all you have to do is rename it temporarily. You can always do this using the file manager or by accessing the server via FTP.
If you use cPanel’s file manager and can’t find the file, you’ll have to check the settings and make sure the Show hidden files (dotfiles) option is enabled.
Once you have located the .htaccess file, simply rename it and see if the error 500 has been resolved.
If the error 500 no longer appears after renaming the .htaccess file, you will need to locate and correct the error in it. After that, you can rename the file back to its original name (.htaccess).
Change PHP memory limit
If one of the active processes on your site is exceeding the PHP memory limit, you may see an error 500.
In this case, you can change the memory limit to see if this is the cause of the error. There are several ways to do this, one of the easiest is to proceed directly from cPanel.
After logging into cPanel click on Select PHP version from the Software section.
This tool allows us to change the PHP version and modify the memory limit.
Click on the Options tab and scroll down to memory_limit, then set the PHP memory limit according to the options the drop-down menu allows you.
Deactivate plugins
Sometimes activating a new plugin or theme can cause a 500 error. To figure out if the cause of the error is a plugin you can temporarily disable all plugins and see if the error gets resolved.
You can deactivate WordPress plugins in several ways: from the dashboard, through the control panel (or via FTP), but also using phpMyAdmin or through WP-CLI.
After deactivating all plugins check if the 500 error has been resolved. In this case, you will have to reactivate the plugins one by one and check if the error reoccurs to find the responsible plugin.
Disable plugins from the dashboard
The easiest way to deactivate all plugins is to do it directly from the dashboard:
- check the box to select all plugins
- from the Group Actions drop-down menu choose Deactivate
- then click on Apply button and all plugins will be deactivated.
If you can’t access the dashboard there are other ways to disable plugins.
Disable plugins from file manager
You can disable all plugins by simply renaming the folder that contains them. You can access your site files from cPanel file manager or by using an FTP client like Filezilla.
Usually the path to the plugins folder is this: /public_html/wp-content/plugins. Rename it, as you see in this example and check if error 500 still occurs.
After that you’ll have to rename the folder again, using the original name and you’ll be able to manually reactivate plugins from the WordPress dashboard.
Disable plugins with phpMyAdmin
We can use phpMyAdmin to deactivate plugins directly from the database. In this case, remember that before making changes to the database it is always wise to create a backup.
To deactivate plugins we just need to open the wp_options table and edit the active_plugins record inserting a:0:{} inside the option_value.
You can follow the procedure step by step in our guide to phpMyAdmin for WordPress.
Disable plugins with WP-CLI
WP-CLI allows us to manage our WordPress installations from the command line. With one command you can deactivate all plugins:
wp plugin deactivate --allAlso in this case you can check if the error depends on one of the plugins and go to reactivate them one by one from the dashboard.
Contact support
If you can’t find the cause of the error 500, you can always contact support, indicate the checks you have already done and find a solution to the problem with support.
Alternatively, if you want to entrust the technical management of the site to a team of professionals, you can consider switching to a managed WordPress solution. In this way, the resolution of errors of this type, as well as the maintenance operations of your site will be entrusted to experienced hands.
How to solve as a user
The solutions we have seen can be applied in case the error 500 occurs on your site.
If, on the other hand, error 500 appears on the site you are trying to visit, there is little you can do.
Since this is a server-side error, it does not depend on your connection or the device you are using. In fact, if you try to it access from another device or browser, you will find yourself facing the same error.
You can try to check the status of the site with a free service like Down for Everyone or Just Me that allows you to understand if the site is online or not.
In such cases, then, you just have to wait and try to connect to the site again later. If you need to access the content of the page, you can always take advantage of the Google cache to access the version of the site stored in the search engine cache.
Conclusion
As we have seen in this article,500 error: how to solve it, the error 500 is a server error that occurs when something goes wrong and makes it impossible to reach the desired site.
Since it is a generic error, the browser doesn’t offer more information about what caused the problem, it just shows the HTTP error 500 status code, or in other cases, it just shows you a blank screen. For this reason, the only way to solve it is to rule out possible causes one by one.
In this article, we’ve seen what the most common causes of error 500 are, and we’ve looked at possible ways to fix it in case the problem occurs on your site. If, on the other hand, you come across the error while you visit a site, there’s a little trick you can use to still access the resources you were looking for.
Have you ever seen an error 500 on your site? How did you solve it? Let me know in the comments below if the solutions in this article helped you solve it or if you had to use some other method, so we can add more solutions to help out our readers.