Configuration
- Ubuntu Server 11.10 64 bit
- Amazon AWS, Ec2, hosted on the cloud
- t1.micro instance
Before I write anything else, I’d like to state that I’ve checked both nginx 502 bad gateway and Nginx + PHP-FPM 502 Bad Gateway threads, which unfortunately haven’t helped me in this regard.
The issue appears to be rather common: a misconfiguration of nginx or php-fpm can lead to a 502 Bad Gateway error, which is something that I haven’t been able to get rid of. Note that this appears even when I go to my domain root, without specifying any particular directory.
I’m running an Amazon EC2 webserver, with port 9000 enabled, port 80 open, etc.
The question in particular is, how can I get rid of this nasty error? Or, better yet, how can I get php5-fpm to actually work.
What I Have Attempted so Far
Mostly consistent editing of configuration files, notably php-fpm.conf and nginx.conf.
i. php-fpm.conf
I’ve added the following, which hasn’t quite helped much:
;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Fpm Start ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;
;pm.start_servers = 20
;pm.min_spare_servers = 5
;pm.max_spare_servers = 35
Now, afterward I tried including my configuration files:
include=/etc/php5/fpm/*.conf
Which only screwed me even further.
Full Configuration
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; FPM Configuration ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; All relative paths in this configuration file are relative to PHP's install
; prefix (/usr). This prefix can be dynamicaly changed by using the
; '-p' argument from the command line.
; Include one or more files. If glob(3) exists, it is used to include a bunch of
; files from a glob(3) pattern. This directive can be used everywhere in the
; file.
; Relative path can also be used. They will be prefixed by:
; - the global prefix if it's been set (-p arguement)
; - /usr otherwise
;include=/etc/php5/fpm/*.conf
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Global Options ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
[global]
; Pid file
; Note: the default prefix is /var
; Default Value: none
pid = /var/run/php5-fpm.pid
; Error log file
; Note: the default prefix is /var
; Default Value: log/php-fpm.log
error_log = /var/log/php5-fpm.log
; Log level
; Possible Values: alert, error, warning, notice, debug
; Default Value: notice
log_level = notice
; If this number of child processes exit with SIGSEGV or SIGBUS within the time
; interval set by emergency_restart_interval then FPM will restart. A value
; of '0' means 'Off'.
; Default Value: 0
;emergency_restart_threshold = 0
; Interval of time used by emergency_restart_interval to determine when
; a graceful restart will be initiated. This can be useful to work around
; accidental corruptions in an accelerator's shared memory.
; Available Units: s(econds), m(inutes), h(ours), or d(ays)
; Default Unit: seconds
; Default Value: 0
emergency_restart_interval = 0
; Time limit for child processes to wait for a reaction on signals from master.
; Available units: s(econds), m(inutes), h(ours), or d(ays)
; Default Unit: seconds
; Default Value: 0
;process_control_timeout = 0
; Send FPM to background. Set to 'no' to keep FPM in foreground for debugging.
; Default Value: yes
daemonize = no
;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Fpm Start ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;
;pm.start_servers = 20
;pm.min_spare_servers = 5
;pm.max_spare_servers = 35
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Pool Definitions ;
;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
; Multiple pools of child processes may be started with different listening
; ports and different management options. The name of the pool will be
; used in logs and stats. There is no limitation on the number of pools which
; FPM can handle. Your system will tell you anyway :)
; To configure the pools it is recommended to have one .conf file per
; pool in the following directory:
include=/etc/php5/fpm/pool.d/*.conf
ii. nginx.conf
In all honesty this configuration is a smattering of a few websites I’ve visited, but I can tell you that before this 502 Bad Gateway business, the server was running fine (without PHP working. Period.).
The issue primarily lies in the fact that something is terribly, terribly wrong. And now, when I try to do a service php5-fpm restart, it hangs in what I’m guessing is an infinite loop or something, which I can’t even CTRL—C out of.
Full Configuration
user www-data;
worker_processes 1;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 64;
# multi_accept on;
}
http {
##
# Basic Settings
##
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush off;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
# server_tokens off;
# server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;
# server_name_in_redirect off;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
##
# Logging Settings
##
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
##
# Gzip Settings
##
gzip on;
gzip_disable "msie6";
# gzip_vary on;
# gzip_proxied any;
# gzip_comp_level 6;
# gzip_buffers 16 8k;
# gzip_http_version 1.1;
# gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/x-javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript;
##
# Virtual Host Configs
##
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
server {
listen 80;
server_name ec2-xx-xx-xx-xx.compute-x.amazonaws.com;
location ~ ^(.+.php)(.*)$ {
root /home/wayvac/public;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php5-fpm.pid;
#fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; #Un-comment this and comment "fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php-fpm/php-fpm.sock;" if you are not using php-fpm.
fastcgi_index index.php;
set $document_root2 $document_root;
if ($document_root2 ~ "^(.*\\).*?[\\|/]../(.*)$") { set $document_root2 $1$2; }
if ($document_root2 ~ "^(.*\\).*?[\\|/]../(.*)$") { set $document_root2 $1$2; }
if ($document_root2 ~ "^(.*\\).*?[\\|/]../(.*)$") { set $document_root2 $1$2; }
if ($document_root2 ~ "^(.*\\).*?[\\|/]../(.*)$") { set $document_root2 $1$2; }
if ($document_root2 ~ "^(.*\\).*?[\\|/]../(.*)$") { set $document_root2 $1$2; }
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+.php)(.*)$;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root2$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info;
fastcgi_param PATH_TRANSLATED $document_root2$fastcgi_path_info;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param DOCUMENT_ROOT $document_root2;
}
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
location / {
root /home/wayvac/public;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
}
location ~* .(?:ico|css|js|gif|jpe?g|png)$ {
# Some basic cache-control for static files to be sent to the browser
expires max;
add_header Pragma public;
add_header Cache-Control "public, must-revalidate, proxy-revalidate";
}
#include drop.conf;
#include php.conf;
}
}
Editor’s note: php-fpm uses the term “master” to describe its primary process. Datadog does not use this term. Within this blog post, we will refer to this as “primary,” except for the sake of clarity in instances where we must reference a specific process name.
This post is part of a series on troubleshooting NGINX 502 Bad Gateway errors. If you’re not using PHP-FPM, check out our other article on troubleshooting NGINX 502s with Gunicorn as a backend.
PHP-FastCGI Process Manager (PHP-FPM) is a daemon for handling web server requests for PHP applications. In production, PHP-FPM is often deployed behind an NGINX web server. NGINX proxies web requests and passes them on to PHP-FPM worker processes that execute the PHP application.
NGINX will return a 502 Bad Gateway error if it can’t successfully proxy a request to PHP-FPM, or if PHP-FPM fails to respond. In this post, we’ll examine some common causes of 502 errors in the NGINX/PHP-FPM stack, and we’ll provide guidance on where you can find information that can help you resolve these errors.
Explore the metrics, logs, and traces behind NGINX 502 Bad Gateway errors using Datadog.
Some possible causes of 502s
In this section, we’ll describe how the following conditions can cause NGINX to return a 502 error:
- PHP-FPM is not running
- NGINX can’t communicate with PHP-FPM
- PHP-FPM is timing out
If NGINX is unable to communicate with PHP-FPM for any of these reasons, it will respond with a 502 error, noting this in its access log (/var/log/nginx/access.log) as shown in this example:
access.log
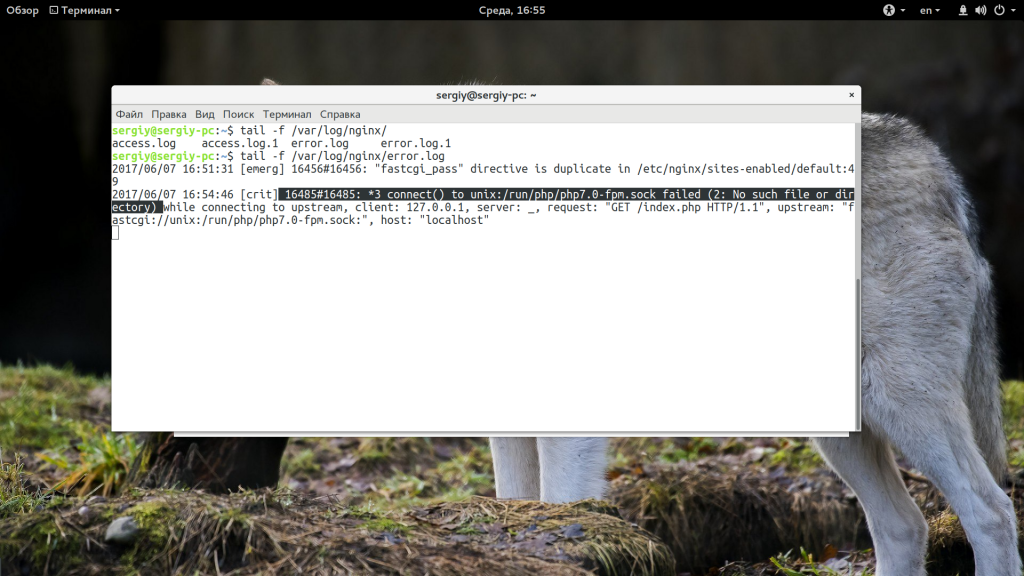
127.0.0.1 - - [31/Jan/2020:18:30:55 +0000] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 502 182 "-" "curl/7.58.0"NGINX’s access log doesn’t explain the cause of a 502 error, but you can consult its error log (/var/log/nginx/error.log) to learn more. For example, here is a corresponding entry in the NGINX error log that shows that the cause of the 502 error is that the socket doesn’t exist, possibly because PHP-FPM isn’t running. (In the next section, we’ll look at how to detect and correct this problem.)
error.log
2020/01/31 18:30:55 [crit] 13617#13617: *557 connect() to unix:/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock failed (2: No such file or directory) while connecting to upstream, client: 127.0.0.1, server: localhost, request: "GET / HTTP/1.1", upstream: "fastcgi://unix:/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock:", host: "localhost"PHP-FPM isn’t running
Note: This section includes a process name that uses the term “master.” Except when referring to specific processes, this article uses the term “primary” instead.
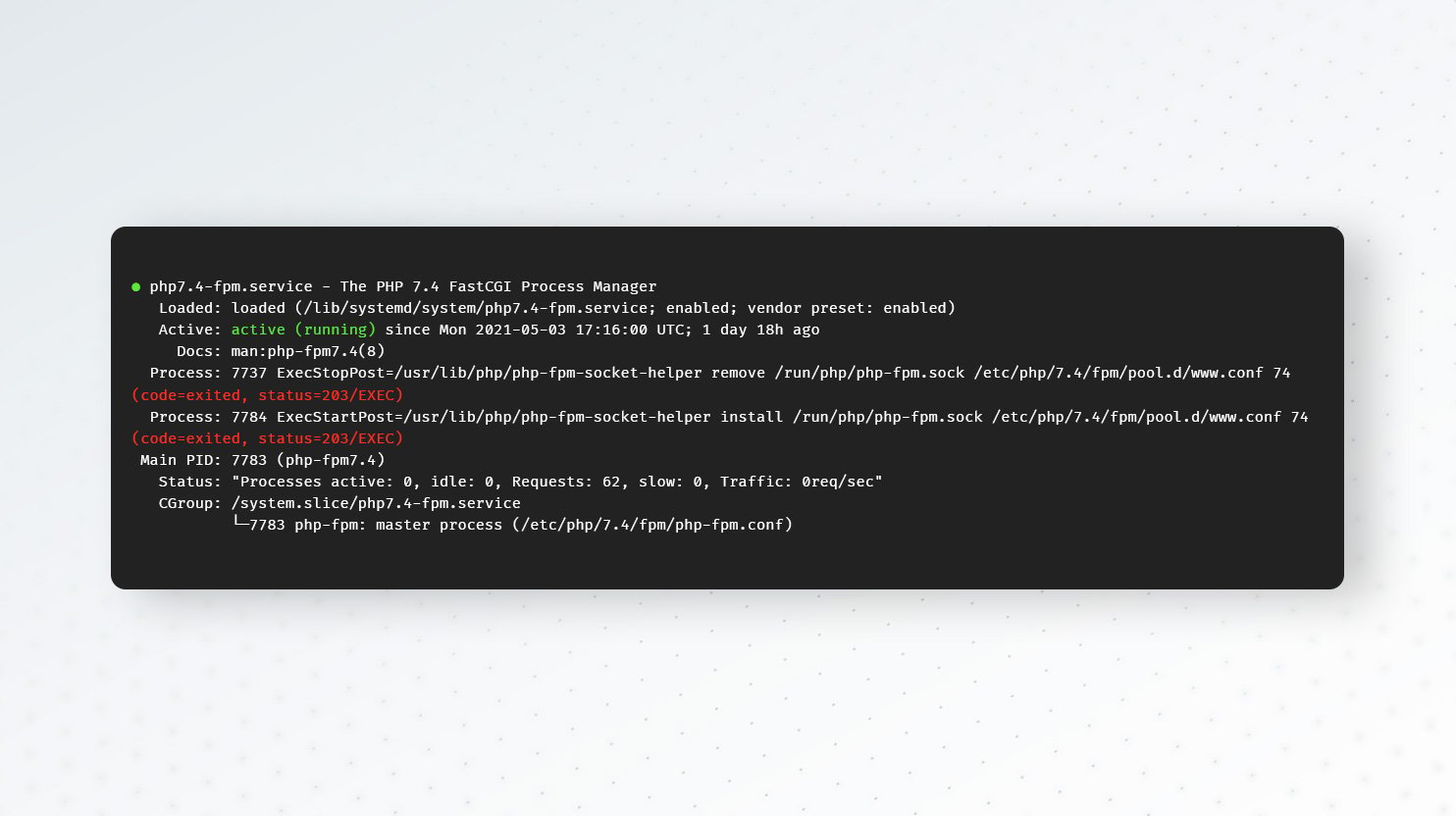
If PHP-FPM isn’t running, NGINX will return a 502 error for any request meant to reach the PHP application. If you’re seeing 502s, first check to confirm that PHP-FPM is running. For example, on a Linux host, you can use a ps command like this one to look for running PHP-FPM processes:
PHP-FPM organizes its worker processes in groups called pools. The sample output below shows that the PHP-FPM primary process is running, as are two worker processes in the default pool (named www):
root 29852 0.0 2.2 435484 22396 ? Ssl 16:27 0:00 php-fpm: master process (/etc/php/7.2/fpm/php-fpm.conf)
www-data 29873 0.0 1.5 438112 15220 ? Sl 16:27 0:00 php-fpm: pool www
www-data 29874 0.0 1.6 438112 16976 ? Sl 16:27 0:00 php-fpm: pool wwwIf the output of the ps command doesn’t show any PHP-FPM primary or pool processes, you’ll need to get PHP-FPM running to resolve the 502 errors.
In a production environment, you should consider using systemd to run PHP-FPM as a service. This can make your PHP application more reliable and scalable, since the PHP-FPM daemon will automatically start serving your PHP app when your server starts or when a new instance launches. PHP-FPM is included in the PHP source code, so you can add PHP-FPM as a systemd service when you configure PHP.
Once your PHP-FPM project is configured as a service, you can use the following command to ensure that it starts automatically when your server starts up:
sudo systemctl enable php7.2-fpm.serviceThen you can use the list-unit-files command to see information about your service:
sudo systemctl list-unit-files | grep -E 'php[^fpm]*fpm'On a PHP 7.2 server that has PHP-FPM installed (even if it is not running), the output of this command will be:
php7.2-fpm.service enabledTo see information about your PHP-FPM service, use this command:
sudo systemctl is-active php7.2-fpm.serviceThis command should return an output of active. If it doesn’t, you can start the service with:
sudo service php7.2-fpm startNGINX can’t access the socket
When PHP-FPM starts, it creates one or more TCP or Unix sockets to communicate with the NGINX web server. PHP-FPM’s worker processes use these sockets to listen for requests from NGINX.
To determine whether a 502 error was caused by a socket misconfiguration, confirm that PHP-FPM and NGINX are configured to use the same socket. PHP-FPM uses a separate configuration file for each worker process pool; these files are located at /etc/php/7.2/fpm/pool.d/. Each pool’s socket is defined in a listen directive in the pool’s configuration file. For example, the listen directive below configures a pool named mypool to use a Unix socket located at /run/php/mypool.sock:
mypool.conf
listen = /run/php/mypool.sockIf NGINX can’t access the socket for a particular pool, you can determine which worker pool is involved in the issue by checking which socket is named in the NGINX error log entry. For example, if PHP-FPM had failed to start the mypool worker pool, NGINX would return a 502 and its error log entry would include:
error.log
connect() to unix:/run/php/mypool.sock failed (2: No such file or directory)Check your nginx.conf file to ensure that the relevant location block specifies the same socket. The example below contains an include directive that loads some general configuration information for PHP-FPM, and a fastcgi_pass directive that specifies the same Unix socket named in the mypool.conf file, above.
nginx.conf
location / {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/mypool.sock;
}Unix sockets are subject to Unix file system permissions. The PHP-FPM pool’s configuration file specifies the mode and ownership of the socket, as shown here:
www.conf
listen.owner = www-data
listen.group = www-data
listen.mode = 0660Make sure these permissions allow the user and group running NGINX to access the socket. If the permissions on the socket are incorrect, NGINX will log a 502 error in its access log, and a message like the one shown below in its error log:
error.log
2020/02/20 17:12:03 [crit] 3059#3059: *4 connect() to unix:/run/php/mypool.sock failed (13: Permission denied) while connecting to upstream, client: 127.0.0.1, server: localhost, request: "GET / HTTP/1.1", upstream: "fastcgi://unix:/run/php/mypool.sock:", host: "localhost"Note that the default values of listen.owner and listen.group match the default owner and group running NGINX, and listen.mode defaults to 0660. Using these defaults, NGINX should be able to access the socket.
If PHP-FPM is listening on a TCP socket, the pool conifguration’s listen directive will have a value in the form of address:port, as shown below:
Just as with a Unix socket, you can prevent 502 errors by confirming that the location of this socket matches the one specified in the NGINX configuration.
PHP-FPM is timing out
If your application is taking too long to respond, your users will experience a timeout error. If PHP-FPM’s timeout—which is set in the pool configuration’s request_terminate_timeout directive (and defaults to 20 seconds)—is less than NGINX’s timeout (which defaults to 60 seconds), NGINX will respond with a 502 error. The NGINX error log shown below indicates that its upstream process—which is PHP-FPM—closed the connection before sending a valid response. In other words, this is the error log we see when PHP-FPM times out:
error.log
2020/02/20 17:17:12 [error] 3059#3059: *29 recv() failed (104: Connection reset by peer) while reading response header from upstream, client: 127.0.0.1, server: localhost, request: "GET / HTTP/1.1", upstream: "fastcgi://unix:/run/php/mypool.sock:", host: "localhost"In this case, the PHP-FPM log (which by default is located at /var/log/php7.2-fpm.log) shows a correlated message which provides further information:
php7.2-fpm.log
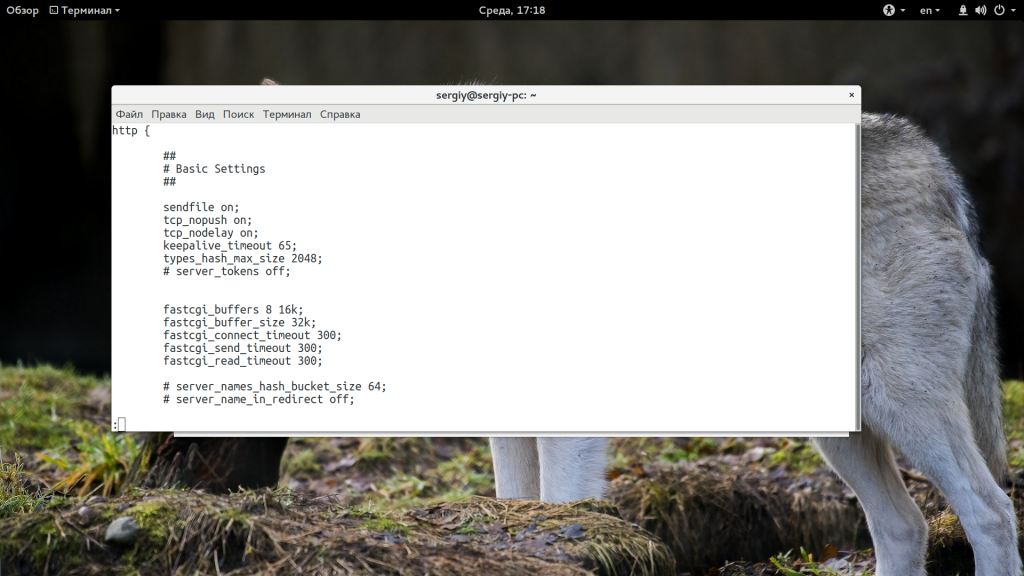
[20-Feb-2020 17:17:12] WARNING: [pool mypool] child 2120, script '/var/www/html/index.php' (request: "GET /index.php") execution timed out (25.755070 sec), terminatingYou can raise PHP-FPM’s timeout setting by editing the pool’s configuration file, but this could cause another issue: NGINX may time out before receiving a response from PHP-FPM. The default NGINX timeout is 60 seconds; if you’ve raised your PHP-FPM timeout above 60 seconds, NGINX will return a 504 Gateway Timeout error if your PHP application hasn’t responded in time. You can prevent this by also raising your NGINX timeout. In the example below, we’ve raised the timeout value to 90 seconds by adding the fastcgi_read_timeout item to the http block of /etc/nginx/nginx.conf:
nginx.conf
http {
...
fastcgi_buffers 8 16k;
fastcgi_buffer_size 32k;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 90;
fastcgi_send_timeout 90;
fastcgi_read_timeout 90;
}Reload your NGINX configuration to apply this change:
Next, to determine why PHP-FPM timed out, you can collect logs and application performance monitoring (APM) data that can reveal causes of latency within and outside your application.
Collect and analyze your logs
To troubleshoot application errors, you can collect your logs and send them to a log management service. In addition to the NGINX logs we examined above, PHP can log errors and other events that might be valuable to you. See our PHP logging guide for more information.
When you bring your PHP and NGINX logs into a log management service, combined with logs from relevant technologies like caching servers and databases, you can analyze logs from throughout your web stack in a single platform.
Collect APM data from your web stack
APM can help you identify bottlenecks and resolve issues, like 502 errors, which affect the performance of your app. The screenshot below shows NGINX’s APM data visualized in Datadog. This view summarizes request volume, error rates, and latency for an NGINX-based service and helps you investigate performance problems like 502 errors.
200 OK
The faster you can diagnose and resolve your application’s 502 errors, the better. Datadog allows you to analyze metrics, traces, logs, and network performance data from across your infrastructure. If you’re already a Datadog customer, you can start monitoring NGINX, PHP-FPM, and more than
600 other technologies. If you don’t yet have a Datadog account, sign up for a 14-day free trial and get started in minutes.
"My WordPress site is getting lot of bad gateways when trying to edit the back end. Please fix."
Recently, we were contacted by a customer who was getting PHP 502 bad gateway error when trying to update his website.
In our role as Technical Support Services for web hosting companies, configuring and managing the web servers for best performance, is a major task we do.
Resolving web server errors forms a part of this service. Today, we’ll see how we fix 502 gateway errors in our customers’ servers.
What is PHP 502 bad gateway error?
A gateway in a server denotes a connection point between two services in it. Gateway errors happen when front-end web server does not get a response from back-end web server.
502 gateway error usually happens in these scenarios: Nginx or Apache is front-end web server & Apache, PHP-FPM or other services is in back-end.
When the front-end server is unable to establish a proper connection to the back-end server, the websites served by these web server starts showing PHP 502 bad gateway errors.
The easiest way to resolve this error is to restart the services. But that is only a band-aid fix and you will soon find the same error recurring in your sites.
In the servers that we manage, we examine the service related logs and website logs to figure out what exactly is causing this error, and then proceed to fix it.
PHP 502 bad gateway error – Major causes
In our experience dealing with gateway errors, we’ve come across a number of causes that turn out to be the culprits behind the error.
1. Service errors
The first step we do is to verify the status of the back-end service. If the service is not running or not giving the desired results, gateway errors pop up.
That back-end service can be Apache, PHP-FPM or other services such as Perl, Python, etc. 502 errors also occur when the service is overloaded or keeps crashing.
2. Configuration issues
Most often, even if the back-end service is in running status, it may not be configured adequately to serve the front-end web server purpose.
Certain websites are very demanding and with huge traffic. But the website specific service configuration may not be adequate to handle this demand.
If the configuration is not proper, services such as PHP-FPM or Nginx can time out handling the web server requests. This leads to PHP 502 bad gateway errors.
3. Mod-security restrictions
Mod-security is a web application firewall (WAF) configured to protect websites from attacks. This WAF is configured based on rules that filter incoming traffic.
Some of these rules can create unwanted complications and disrupt the service functioning. We have noticed 502 gateway errors in websites due to some messy Mod-security rules.
4. Cloudflare settings
Cloudflare is a CDN service that offers DDOS protection to websites. But for sites with too many redirects, this causes 502 errors at times, if not configured correctly.
5. Port or permission issues
In a gateway setup, there would be two services connecting to each other. These services would be running in separate ports.
For instance, in a server where reverse proxy is configured, Nginx (front-end server) would be listening on port 80 and Apache (back-end server) would be on port 8080.
These ports can be further changed for security reasons. If the ports are not allowed for connections in the server firewall, the connectivity can fail and lead to gateway errors.
Services such as PHP-FPM can also be configured to bind to socket files in the server. If the ownership, permissions or path to the socket file in the configuration file is improper, errors can occur.
6. Software bugs
In cases where custom software or some third party applications are configured as back-end services, any bugs in these software can lead to 502 errors.
7. High server load
Server load can spike when the website traffic is high or when a DOS attack occurs to the server. Peak traffic or malware files in the server can contribute to this high server load.
Certain 3rd party applications or not optimised website code can hog the server resources such as CPU and memory, and cause high load. This can lead to timeout issues and website errors.
Solutions for PHP 502 bad gateway error
Finding the root cause of the 502 error and resolving it, is the key to prevent intermittent website down times. The solution for the error varies based on the issue noted in the logs.
- In cases where the underlying service itself is not running, our primary focus is to figure out the problem and fix the service. This is done with the help of service or application or website logs.
- If the service is working fine, but logs show timeout errors, then we increase the execution time, buffer size and timeout settings of the service or application. But this value should not be increased blindly, as it can hog the server resources.
- The configuration file for the service is examined and settings such as socket path, port, user and group etc. are confirmed to be correct. Reviewing the website specific settings is also vital to pinpoint the issue.
- The port connectivity, firewall rule or related socket file is checked and proper access rights and permissions are granted for its functioning.
- Problem aspects such as APC cache, Cloudflare settings, redirect rules, mod-security configuration, etc. are reviewed, and issues, if any, are sorted out.
- To prevent a single process from hogging the entire server memory, we set memory limits of processes and services and tweak them to use the maximum allotted memory for that service.
- At times, a problematic web code or a query can tie up the resources, take a lot of time to complete execution, and cause errors. We identify such problem-makers and take actions to fix them.
- We review the number of processes configured for services such as PHP-FPM and Nginx or Apache. By tweaking these process count to the ideal values supported by server resources, we ensure that service errors are fixed.
Conclusion
Today we’ve discussed how our Support Engineers fix PHP 502 bad gateway in the servers we manage, and ensure error-free websites for our customers.
In our customers’ servers, monitoring the server resources periodically and conducting periodic server audits and tweaks enable us to prevent such bad gateway errors to a great extent.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
SEE SERVER ADMIN PLANS
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
Nginx is one of the fast performing web servers on the internet. Nginx and php-fpm are the most used combinations on the internet to server PHP websites. Sometimes we came across a very bad Nginx 502 Bad Gateway error generated by Nginx server and it is not very easy to identify the problem and fix. Here are some quick solutions to fix Nginx 502 Bad Gateway error on a web-server.
Contents
- 1 How Nginx 502 Bad Gateway Error happens and what is its connection with php-fpm
- 1.1 Nginx 502 Bad Gateway Error with PHP-FPM
- 1.2 Php-fpm is not communicating with Nginx and causing a 502 Bad Gateway Error
- 1.3 502 Bad Gateway Error due to Nginx is timing out
- 1.4 502 Bad Gateway Error due to PHP-FPM is timing out
- 2 Nginx 502 Bad Gateway Error when Nginx as Proxy for Apache
- 3 Nginx with other services/apps and 502 Bad Gateway Error
How Nginx 502 Bad Gateway Error happens and what is its connection with php-fpm
Common 502 errors include the following messages from Nginx server
- “502 Bad Gateway”
- “502 Bad Gateway NGINX”
- “502 Proxy Error”
- “502 Service Temporarily Overloaded”
- “Error 502”
- “HTTP Error 502 – Bad Gateway”
- “HTTP 502 Bad Gateway”
These errors point to the same situation of Nginx server and the error came across below situations
- Nginx server running with php-fpm service
- Nginx is running as a reverse proxy to Apache server
- Nginx running as a gateway to other services like Python, Ruby, etc.
- Bad configuration of cache or timeout.
Now the error says there is a “BAD GATEWAY”. That means Nginx server is trying to communicate to another service through a gateway and it is not getting any answer from that gateway. This is Nginx 502 Bad Gateway error situation.
So Nginx and another service (Apache, php-fpm, other services) running. Both are communicating through a gateway and Nginx is not getting any answer from the gateway. To solve 502 Bad Gateway Error the other service running with Nginx must answer through the gateway.
Usually, this happens due to a misconfiguration in the configuration files of the server. Or the other service is not running properly with Nginx. So to solve this problem a two-step check is required.
- Step 1: Check the other server status, whether it is running perfectly, is it giving the desired output?
- Step 2: Is the configuration correct? Is the second service configured to answer the gateway perfectly?
Nginx 502 Bad Gateway Error with PHP-FPM
The problem occurs due to the following conditions
- PHP-FPM won’t get started
- PHP-FPM not running
- NGINX can’t communicate with PHP-FPM server
- NGINX is timing out
- PHP-FPM is timing out with requests
Check whether php-fpm is running or not
service php-fpm status
or
systemctl status php-fpm.service
will tell you about the current situation of php-fpm server
Just restart the php-fpm server to solve this problem
service php-fpm restart
or
systemctl restart php-fpm.service
for php5 the name of service may be php5-fpm, for PHP 7 it may be php7.0-fpm or php7.1-fpm or php7.2-fpm check accordingly.
Php-fpm is not communicating with Nginx and causing a 502 Bad Gateway Error
This is caused due to the misconfiguration of the php-fpm server or the misconfiguration of Nginx server.
Check the following configuration files in the worker pool configuration (the file is in /etc/php/fpm/pool.d/www.conf, this may vary with installation) and verify these lines ( www-data is the owner of the web server process, that is nginx)
user = www-data
group = www-data
listen = /var/run/php7-fpm.sock
listen.owner = www-data
listen.group = www-datathen restart the php-fpm service.
If the Nginx server and php-fpm are running and still getting a 502 Bad Gateway error then it is the problem with communicating the gateway. The problem is happening due to the misconfiguration in the file /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default, by default or the file name in the name of the website called /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/mywebsite.com.conf
Look at the segment where the fastcgi_pass configuration. It must be the same as the listen in the above configuration
location ~ .php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php7-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_nam$
include fastcgi_params;
}See
listen = /var/run/php7-fpm.sock
and
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php7-fpm.sock
must be the same.
Then restart both Nginx and php-fpm servers. Now check the website whether it is serving properly.
502 Bad Gateway Error due to Nginx is timing out
if php-fpm is running and serving the requests properly then there will be a chance of Nginx is timing out. That is php-fpm do not respond to NGINX in a timely manner will cause a 502 because NGINX couldn’t wait any longer for a response from php-fpm.
In this case, increasing the maximum execution time of the application and NGINX’s timeout window would be the best solution.
To get this we need two changes:
First, increase the maximum execution time of the php-fpm server. To do this open PHP-FPM’s configuration file
sudo nano /etc/php7/fpm/php.ini
find the following line and increase the number to a higher value. Usually 60 or 120.
max_execution_time = 30
The value depends upon the expected execution time of the application running in the php-fpm server. Add some extra buffer time to get rid of the situation again.
Exceptionally large execution time will affect the server performance and it may lead to a dead server process in the memory.
Second, edit the NGINX config
sudo nano /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
add the following within the HTTP block to increase timeout windows, buffers, and buffer sizes:
http {
...
fastcgi_buffers 8 16k;
fastcgi_buffer_size 32k;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
}
Save the changes to the file and exit. Now restart Nginx and php-fpm
service php-fpm restart
or
systemctl restart php-fpm.service and
service nginx restart
systemctl restart nginx.service
502 Bad Gateway Error due to PHP-FPM is timing out
if the php-fpm server is timing out upon execution of an exceptionally long PHP script or the script is blocked by a large MySQL query process then these solutions may not work. In that situation, you could temporarily extend PHP’s execution time limit by invoking the set_time_limit() function from within the PHP application, but if you are continuously reaching into the execution timeout limit then as a long-term solution like profiling or increasing PHP-FPM’s timeout may be more appropriate to get rid of a 502 error more safely. These things must be done after an extensive research of the execution time of the corresponding PHP function or MySQL query. Take a look at the memory and system load during the execution is a must for a smooth operation of this server.
Nginx 502 Bad Gateway Error when Nginx as Proxy for Apache
In this situation, the gateway service is Apache and the Nginx is a proxy for Apache. If apache server dies or it’s not well configured, it can cause this 502 Bad Gateway error. How to fix the apache error? Most of the times, restarting apache web server will get rid of this, but you must check the log files to know why exactly this was caused.
Nginx with other services/apps and 502 Bad Gateway Error
In this situation, the app is gone not responding. Try restarting the other service behind Nginx server and check the logs created by the application to find the exact reason why a 502 Error happened.
Check the status codes HTTP Status Codes on W3C for more details.
HTTP 504 Gateway Timeout and HTTP 502 Bad Gateway errors are the most common server errors for WordPress website visitors and owners. In my previous article, we’ve already discussed the causes of a 504 Gateway Timeout error and possible solutions for it. In this article, we’ll come to understand what a 502 Bad Gateway error is, talk about the reasons for a 502 Bad Gateway error, and explore some tips for troubleshooting this type of errors.
What does 502 Bad Gateway mean?
Before we define what a 502 Bad Gateway error is, let’s deep-dive into server infrastructure and find out the meaning of some terms, like web server, proxy server or gateway, and upstream server.
Let’s first discuss how hosting a modern web application works. For this we need three actors:
- The web application
- The gateway
- The web server
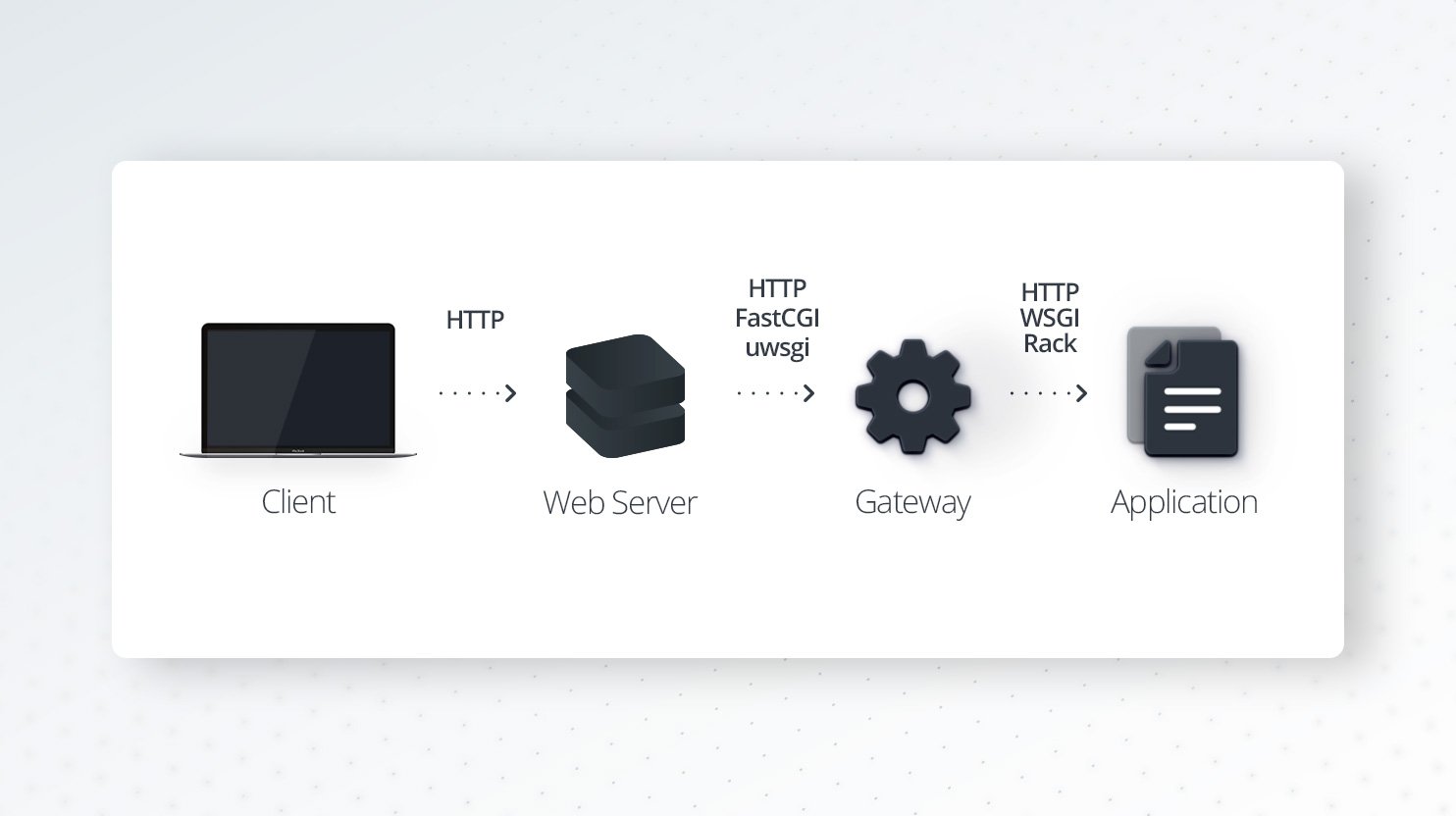
In the picture below you can see the PHP modern web application workflow.
A web application is application software that can be coded in different programming languages and can use specific frameworks or libraries. It typically has tools to handle HTTP requests. For your WordPress website, the web application is your WordPress installation which is coded in PHP.
The gateway sits between a web server (Nginx, Apache) and a web application. It accepts requests from a web server and translates them for a web application. The exact definition of a gateway is somewhat fluid. Some call themselves process managers, some call themselves HTTP servers.
Here’s what the common functionality of a gateway entails:
- Listening for requests (HTTP, FastCGI, uWSGI, and more)
- Translating requests to application code
- Spawning multiple processes and/or threads of applications
- Monitoring spawned processes
- Loading balance requests between processes
- Reporting/logging
PHP-FPM (PHP-FastCGI Process Manager) is the gateway for PHP. It is an implementation of FastCGI and will listen for FastCGI requests from a web server.
FastCGI is a binary protocol for interfacing interactive programs with a web server. CGI (Common Gateway Interface) is a web technology and protocol which describes a way for a web server to communicate with external applications, e.g. PHP. CGI is an interface between the web server and the dynamic web content that is generated by web applications that are written in different programming languages, such as PHP, Python, etc. FastCGI is an improved version of CGI.
A modern way to run PHP applications is to use PHP-FPM. Before PHP-FPM, PHP was commonly run directly in Apache, there was no need for a gateway. Apache’s PHP module loaded PHP directly, allowing PHP to be run in line with any processed files.
The web server generally hosts multiple sites, serves static files, proxies requests to other processes, performs load balancing and HTTP caching. The most popular web servers are Apache and Nginx. Apache used to be the most widespread web server until Nginx became more popular.
At 10Web we support LEMP stack, which is similar to LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP), except Apache is replaced with Nginx. What happens when you open your WordPress website hosted by 10Web in your browser? The web server, in this case, Nginx, accepts a request and relays it to PHP-FPM, which in turn interprets the PHP code. The response is relayed back, finally reaching the client. In this case, Ngnix acts like a proxy server which in most cases is called an edge server. The server behind the proxy server is called upstream or origin server. In this case, PHP-FPM acts as an upstream server.
Now that we fully understood the above-mentioned terms, let’s finally understand what the 502 Bad Gateway error is.
What is a 502 Bad Gateway error?
We face a 502 Bad Gateway error when the web server acts as a proxy server and receives an invalid response from the upstream server. A 502 Bad Gateway error indicates that the proxy server, which is the edge server, was not able to get a valid response from the upstream server, which is the origin server. When you see a 502 Bad Gateway error it means that something is wrong with the upstream server. This can happen because of various reasons which we’ll cover in this article.
The different forms of 502 errors
A 502 Bad Gateway error can appear in different ways depending on the operating system, web browser, and device. Here’s how it looks most of the time:
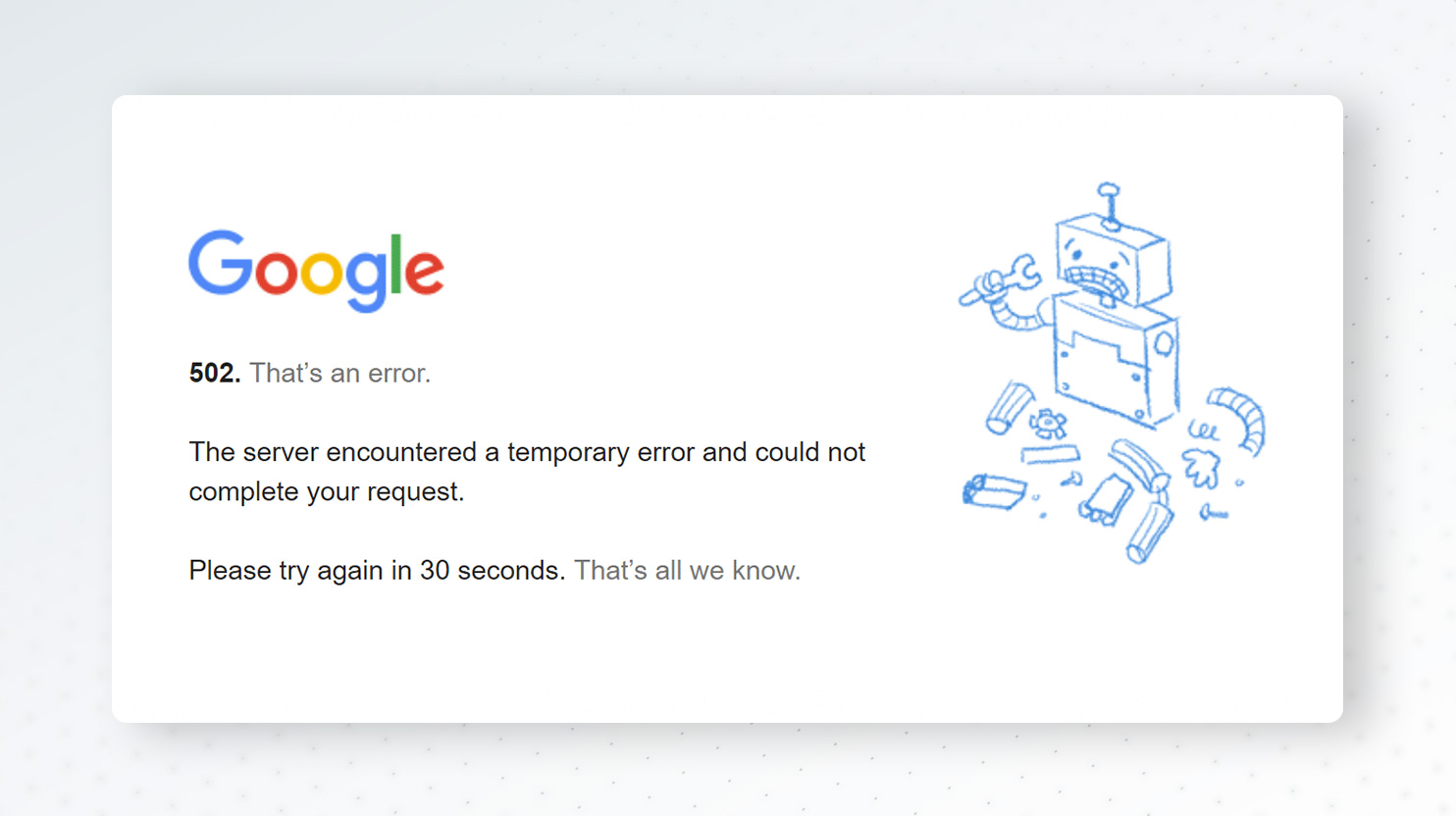
Some websites customize 502 Bad Gateway pages. Here’s Google’s:
Platforms can also change the message of the error. So you can encounter different messages for the same error but they all have the same meaning:
- 502 Bad Gateway
- HTTP Error 502 Bad Gateway
- Error 502
- HTTP 502
- HTTP Error 502 – Bad Gateway
- 502 Proxy Error
- 502 Server Error: The server encountered a temporary error and could not complete your request.
- 502 Bad Gateway NGINX
- 502. That’s an error. The server encountered a temporary error and could not complete your request. Please try again in 30 seconds. That’s all we know.
What are the reasons behind the 502 Bad Gateway error?
The 5xx status codes indicate that there are problems with the server, and 502 is not an exception. For some reason, the proxy server can’t get a response or a valid response from the upstream server. In your WordPress website with Nginx/PHP-FPM stack, a 502 error can happen when PHP-FPM is not running or Nginx can’t communicate with PHP-FPM for some reason. This case should be checked by your hosting provider. Another reason could be PHP-FPM timeout issues, which we’ll discuss down the line.
Any misunderstanding between Nginx and PHP-FPM can lead to a 502 Bad Gateway error. Though these errors are connected to server-side issues, there are some tips for troubleshooting on the client side.
Let’s go over both client- and server-side troubleshooting.
How to Troubleshoot a 502 error message
Here are some very simple ways of fixing 502 Bad Gateway errors from the client side.
Reload the page
The first thing you should do is reload the page and wait for a minute. If the 502 Bad Gateway error disappears, it means there was a temporary problem with the upstream server or the networking between servers. If the error remains, check if the site is down for everyone. You can use Is it down right now? for this. If the site is up for everyone except you, open the site on another browser or in private mode.
Clear browser cache
Another easy tip is to clear the browser cache. If the error disappears after cleaning cache, it means that there was a temporary problem that has been resolved, but because of cache, you kept seeing the 502 Bad Gateway error template, instead of your website. If the error remains, try the next tip.
Flush DNS cache
The 502 Bad Gateway error can occur because of DNS issues. Operating systems, such as Linux, Windows, and macOS save name resolution information in the form of a DNS cache. In many cases clearing the DNS cache can solve a 502 Bad Gateway error. Here are the commands which you can use for flushing DNS cache on Windows, MacOs, and Linux.
Use this command to flush cache on Windows:
ipconfig /flushdns
On macOS, you should open the terminal and type:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
There’s no message after processing this command, but you can add your own by running the command like this:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder; dns cleared successfully
Things are different in Linux, as different Linux distributions use different DNS services. Some of them are NSCD (Name Service Caching Daemon), dnsmasq, and BIND (Berkeley Internet Name Domain). For an NSCD DNS cache:
sudo /etc/init.d/nscd restart
For a dnsmasq DNS cache:
sudo /etc/init.d/dnsmasq restart
For a BIND DNS cache:
sudo /etc/init.d/named restart sudo rndc restart sudo rndc exec
If the terminal asks for your password, just enter it.
Change DNS servers
You can also try to temporarily change your DNS servers. More information about changing DNS servers can be found in this article: Change your DNS servers settings.
If you’re using Cloudflare
Cloudflare returns a Cloudflare-branded HTTP 502 error when your origin web server responds with a standard HTTP 502 bad gateway:
This means that something is wrong with your origin server and you can try to use the above-described tips to fix the issue.
If the 502 error is from Cloudflare, the page looks like this:
If the error contains the word “Cloudflare,” the problem comes from Cloudflare, otherwise, it is from the origin server. In the first case, you can contact Cloudflare support, and in the second case, you can follow the described tips. If nothing helps, contact your hosting provider. You can read more about Cloudflare 5xx errors in the article Troubleshooting Cloudflare 5XX errors.
We’ve discussed some client-side tips which can help you troubleshoot a 502 Bad Gateway error. Now let’s see what you can do on the server-side.
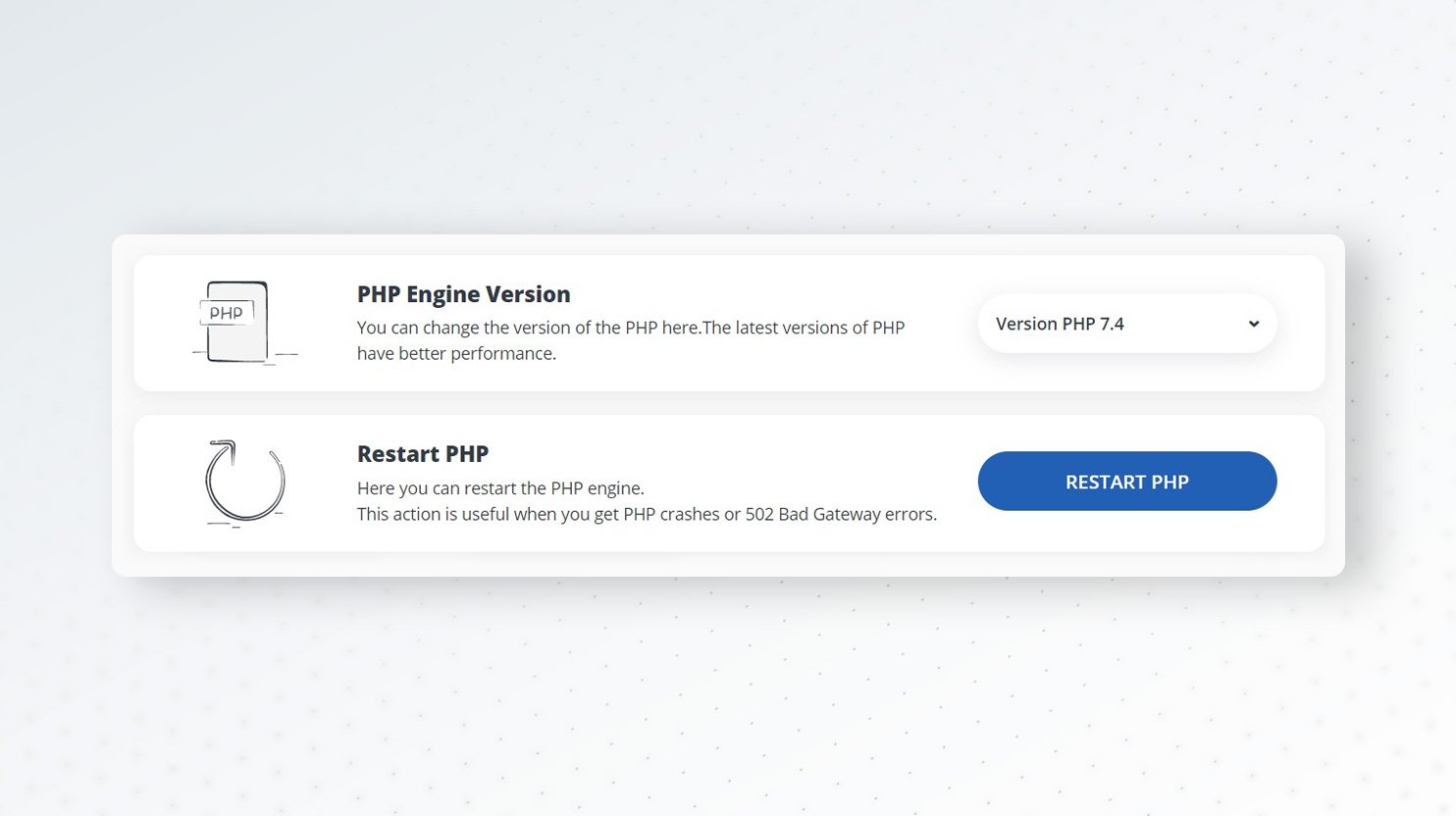
Restart PHP
The very first step is to restart your PHP. With 10Web, you can do this by going to Hosting Services > Tools and clicking the blue “Restart PHP” button.
If your hosting doesn’t provide an interface for restarting PHP, ask them to do it for you.
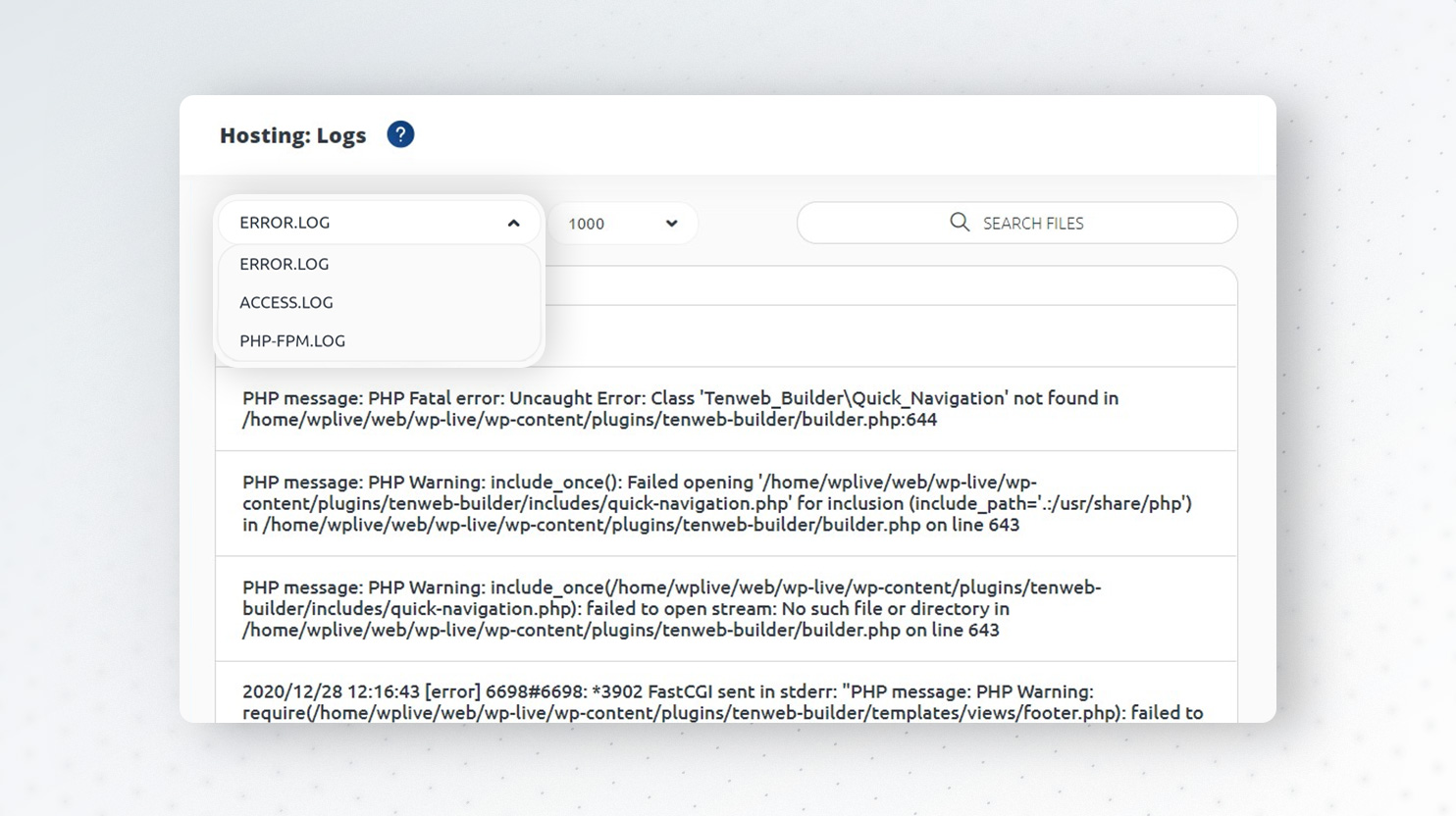
Check logs
Checking your server error logs can give you very useful information about 502 Bad Gateway errors. With 10Web, you can easily check server logs by going to Hosting Services > Logs.
If you have access to your file system, you can check server logs. In the case of the Nginx web server, you can find logs here:
/var/log/nginx
In the case of Apache web server, the logs are in this repository:
/var/log/apache2
Improper firewall configuration
Improper firewall configuration can lead to 502 Bad Gateway errors. A firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls the incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. It typically establishes a barrier between a trusted network and an untrusted network.
There can be cases that some awkward firewall settings can consider safe and valid content malicious and, consequently, cut off traffic which in turn cause 502 Bad Gateway errors. Check your firewall configuration to reveal any improper configs.
Third-party plugins & themes
Non-optimal codes in WordPress plugins and themes can also cause 502 errors. So, check your plugins and theme. If you have access to your WordPress admin, deactivate all your plugins, and if the error disappears it means that there is at least one guilty plugin. Then activate them one by one to find the guilty ones. If your WordPress admin area can’t be reached because of the error but you have access to your WordPress files, just rename the plugins directory in wp-content. It will deactivate all plugins. And again start activating them one by one.
If the problem isn’t the plugins, that is deactivating all plugins or renaming plugins directory doesn’t change anything, try to temporarily change your theme to WordPress’s default theme. Once you find the bad plugins or theme, connect to the respective support team and describe the issue.
And don’t forget to keep your plugins, theme, and WordPress core up-to-date. This will help you avoid many problems, including 502 errors.
Restart PHP-FPM service
You will get a 502 error if the PHP-FPM service is inactive or not running on your server. If you have access to your hosting, you can check this by running one of the following commands. For SysVinit:
sudo service php7.4-fpm status
For SystemD:
sudo systemctl status php7.4-fpm
If the service is active and running, the output of the command should be like this:
If the status is not Active: active(running), try restarting PHP-FPM service to resolve the error using one of the following commands. For SysVinit:
sudo service php7.4-fpm restart
For SystemD:
sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
Timeout issues
The 502 error can be caused by a PHP-FPM timeout. If your application is taking too long to respond, your users will experience a timeout error. If the PHP-FPM timeout is less than Nginx timeout, Nginx will return a 502 Bad Gateway error. To avoid this, you can increase PHP-FPM timeout if you have access to your server.
PHP-FPM timeout is set in pool configuration which is
request_terminate_timeout
The default value for this directive is 20 seconds. If you don’t have access to your server, ask your hosting provider to check it. To avoid getting 504 errors after increasing PHP-FPM timeout which can be because of Nginx timeout, the default is 60 seconds, you can increase fastcgi_read_timeout directive in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf file. Don’t forget to reload the Nginx server after changing the directive:
nginx -s reload
PHP execution time errors can also lead to 502 Bad Gateway errors. To avoid this, you can increase the PHP configs, such as max_exexution_time and max_input_time.
If you have your server access, just change these directives in your php.ini file. If not, ask your hosting provider to do it for you.
FAQs
What is the difference between a 404 error and a 502?
A 404 Not Found error occurs when content can’t be found by the web server. A 502 Bad Gateway error happens when the proxy server can’t get any response or gets an invalid response from the upstream server. You come across 404 when requested content was removed or doesn’t exist. You see 502 errors when there is an issue with the upstream or origin server or a communication issue between proxy and upstream servers.
What is the difference between 502, 503, and 504 error messages on websites?
You got a 502 Bad Gateway error when the proxy server doesn’t get a valid response from the upstream or origin server. 504 Gateway Timeout error happens when the server which is acting as a proxy server can’t receive a timely response from the upstream server. 503 Service Unavailable error indicates that the server is not ready to handle the request, this happens when the server is down for maintenance or is overloaded.
Do 502 errors have any impact on website rankings?
The 502 Bad gateway error can have a major impact on website rankings. You don’t have to worry about a negative impact on SEO if the error lasts a few minutes. If the page is being crawled during this time, the crawler can load it from the cache. But you do need to worry if this error lasts for a few hours. In that case, Google will see the 502 error which can negatively impact your rankings.
What can I do when PHP is working in the command line but returns a 502 error in the browser?
502 error happens because of bad communication between proxy and upstream servers. When you’re running PHP in the command line you don’t need a web server, PHP works for you directly. To find out the reasons for 502 errors, read the above-described tips.
Conclusion
Now you have a complete understanding of what 502 errors are and why they appear on your website. We’ve discussed the various possible reasons for these errors and described many troubleshooting approaches that’ll help you find a solution.
That was all for now. Feel free to leave a comment and let us know if we managed to provide a suitable way for you to troubleshoot your bag gateway error!
Начинающие веб-мастера и системные администраторы временами сталкиваются с ошибкой 502 bad gateway nginx. Nginx — это не просто один из лучших веб-серверов, в то же время, он проектировался как отличный прокси. Логически можно предположить, что эта ошибка возникает, когда что-то не так со шлюзом.
И необязательно чтобы вы использовали Nginx в качестве прокси для доступа к сети. Нет, для работы большинства сайтов требуется генерация динамического контента, например, на php. Поэтому Nginx часто выступает в прокси для Apache или php-fpm. В этой статье мы рассмотрим что означает 502 bad gateway Nginx, как исправить ее.
Как и следует из названия, эта ошибка значит, что Nginx попытался связаться со шлюзом и у него ничего не вышло. Например, запросы от пользователей принимает Nginx, поскольку он работает быстро и потребляет мало ресурсов, а за генерацию контента отвечает php-fpm. Если сервис php-fpm во время обработки запроса получил какую-либо ошибку и не вернул результата, или же он вообще отключен и Nginx не может получить к нему доступ мы получим такую ошибку.
Вот основные причины:
- Nginx используется в качестве прокси для Apache или php-fpm, но эти сервисы не запущены;
- Nginx используется качестве прокси для php-fpm, но параметры доступа к сокету неверно настроены;
- Неверно настроены значения размера буфера и таймаута для php-fpm в nginx.conf;
- Ошибки в конфигурации Nginx.
Как исправить ошибку 502 bad gateway Nginx
1. Анализ логов и перезапуск
Чтобы исправить ошибку нужно выяснить что случилось со шлюзом. Лучший способ сделать это — посмотреть логи Nginx, там обязательно должно быть что-то написано и намного подробнее, чем в выводе браузера:
tail -f /var/log/nginx/error.log
Это уже должно дать вам некоторые подсказки что делать дальше. Еще в первую очередь не помешает проверить файл конфигурации Nginx на ошибки:
nginx -t
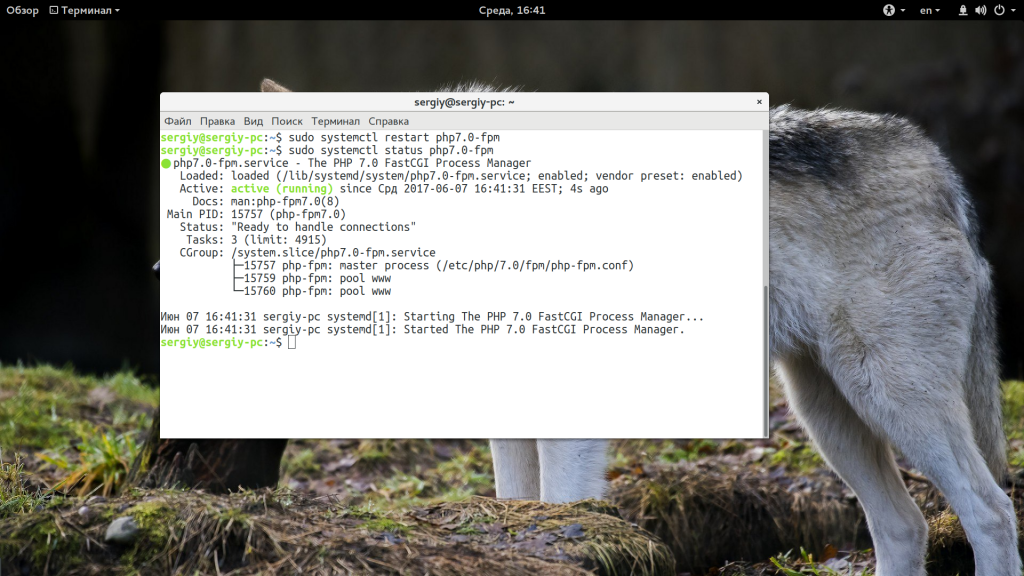
Допустим, у нас в качестве шлюза для генерации динамического содержимого используется php-fpm. Тогда нужно проверить запущен ли вообще этот сервис:
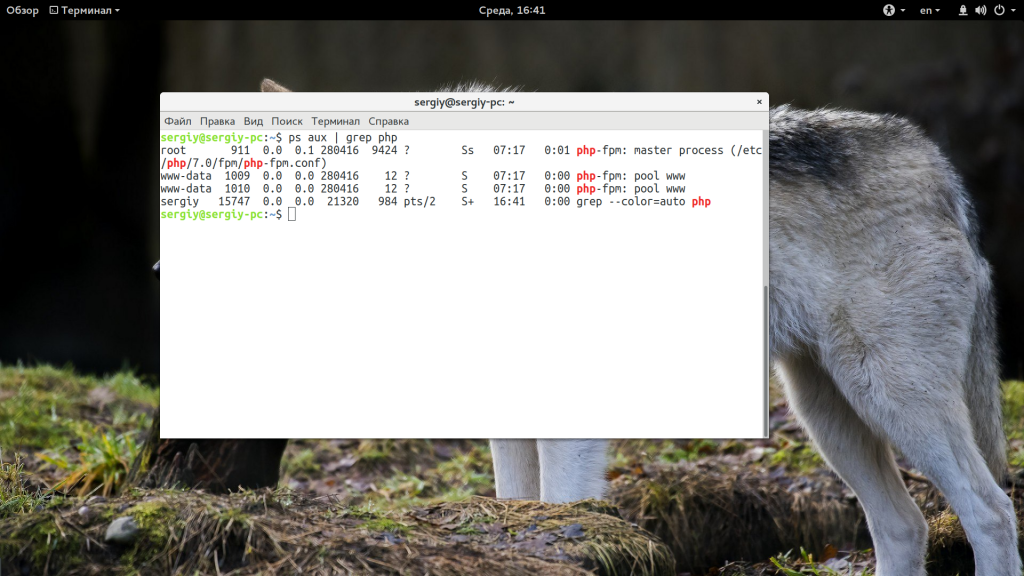
ps aux | grep php
Если все процессы уже запущены, попробуйте перезапустить их с помощью systemd:
sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
Если процесс остановлен, то его нужно запустить:
sudo systemctl start php-fpm
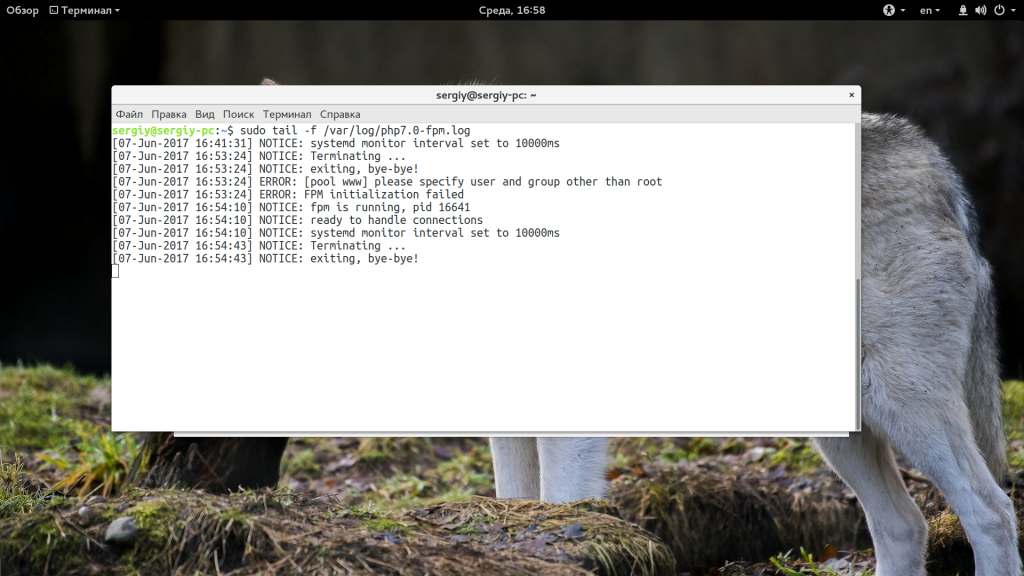
Это самая распространенная причина, вызывающая ошибку 502 Bad Gateway и обычно после перезапуска сервиса все будет работать, вам осталось выяснить только почему он завершился. В этом вам может помочь просмотр лога php-fpm:
sudo tail -f /var/log/php7.0-fpm.log
Но если такой рецепт не помог, и ошибка 502 bad gateway nginx нужно идти дальше. Внимательно пересмотрите лог, возможно, там уже есть ответ.
2. Доступность php-fpm и владелец
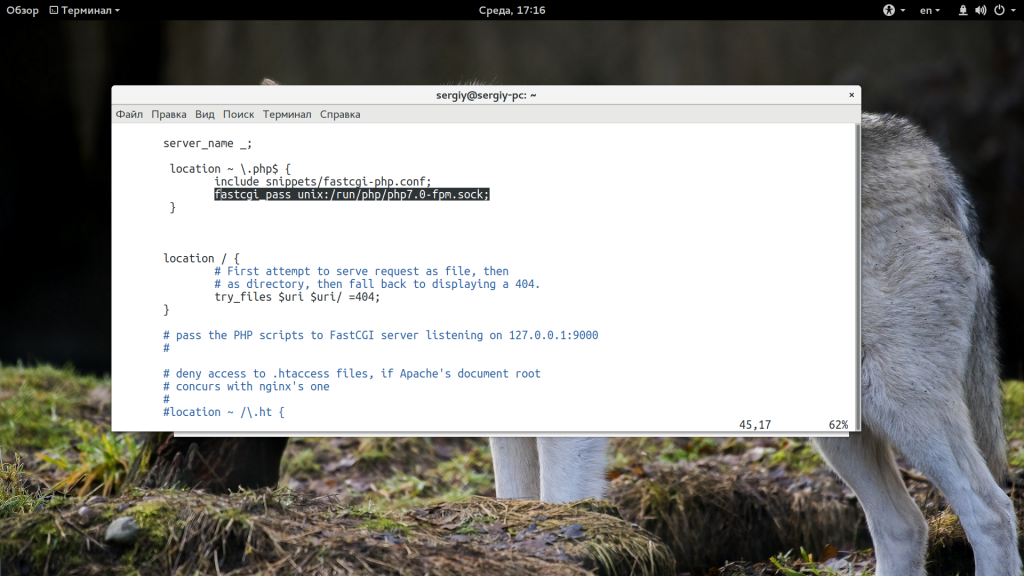
Также эта ошибка может возникать при проблемах доступа к файлу сокета php-fpm, например, когда этот файл называется по другому или для него выставлены неверные права. Сначала убедитесь, что в конфигурационном файле /etc/nginx/nginx.conf указан правильный адрес файла сокета php-fpm:
location ~ .php$ {
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php7.0-fpm.sock;
include fastcgi_params;
}
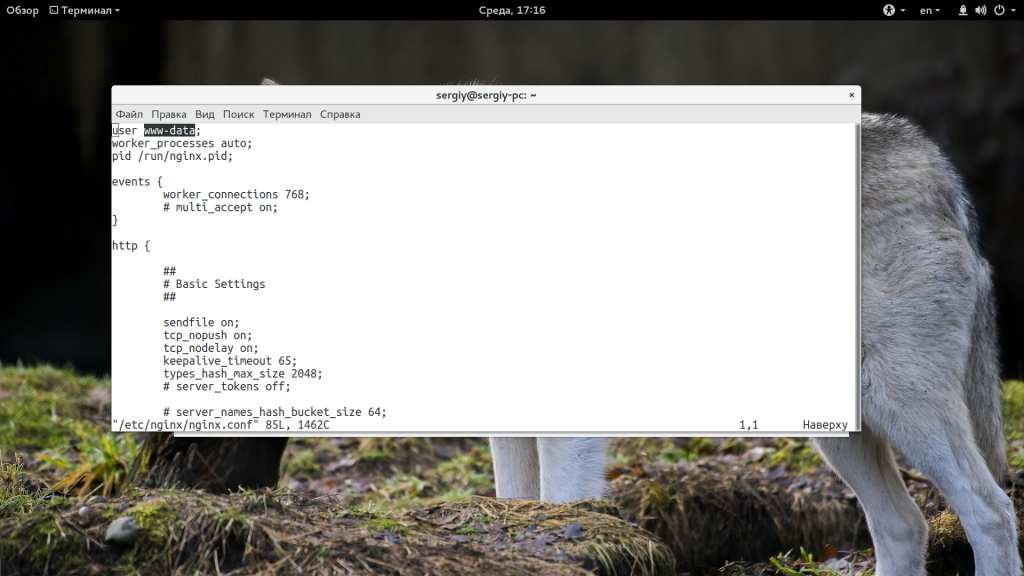
Файл /var/run/php7.0-fpm.sock должен действительно существовать в файловой системе. Дальше нужно убедиться, что у сокета правильный владелец, это должен быть тот же пользователь, от имени которого запускается Nginx, группа тоже должна соответствовать. Откройте файл /etc/php7.0/fpm/pool.d/www.conf и найдите строчки user и group. Они должны иметь такое же значение, как строчка user в конфиге nginx.conf:
listen = /var/run/php7.0-fpm.sock
listen.owner = www-data
listen.group = www-data
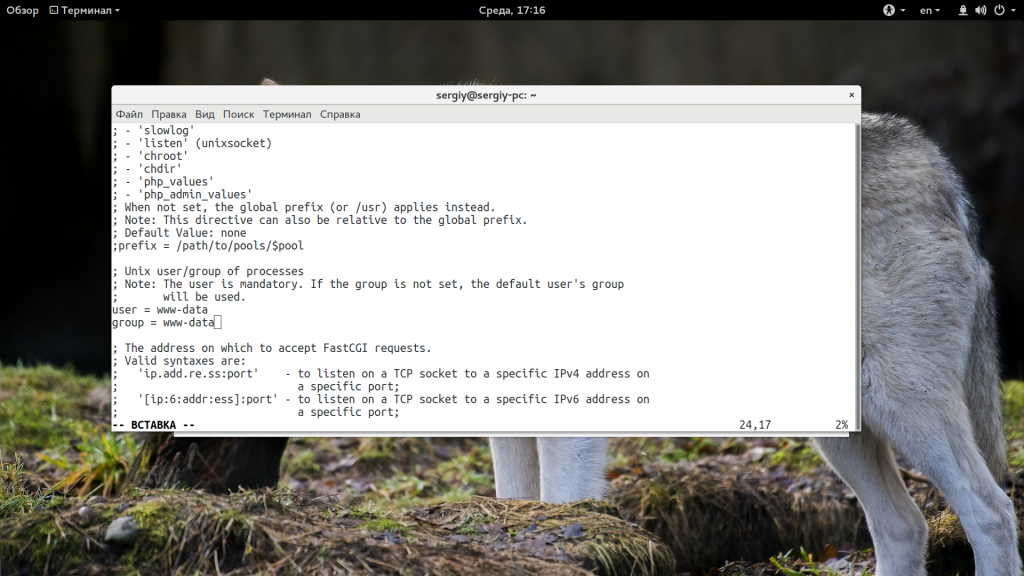
После того как выставите правильные параметры, перезапустите сервисы:
sudo service php5-fpm restart
$ sudo service nginx restart
3. Время отклика и размер буфера
Возможно, размер буфера и время ожидания ответа от fastcgi настроены неверно и программа просто не успевает обработать большой запрос. Попробуйте увеличить такие параметры в /etc/nginx/nginx.conf. Если таких строк не существует, добавьте их в блок http, как здесь:
sudo vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
http {
...
fastcgi_buffers 8 16k;
fastcgi_buffer_size 32k;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
...
}
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели 502 bad gateway nginx что это значит и как исправить эту ошибку. Как видите, может быть достаточно много причин ее возникновения, но решить все достаточно просто если внимательно посмотреть логи и понять в чем там действительно проблема. Надеюсь, информация была полезной для вас.
Статья распространяется под лицензией Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 при копировании материала ссылка на источник обязательна .
Об авторе
Основатель и администратор сайта losst.ru, увлекаюсь открытым программным обеспечением и операционной системой Linux. В качестве основной ОС сейчас использую Ubuntu. Кроме Linux, интересуюсь всем, что связано с информационными технологиями и современной наукой.
Ошибка 502 при открытии сайта может появиться неожиданно. В этой статье мы расскажем, что значит код ошибки 502 и что может сделать пользователь и владелец сайта, чтобы её исправить.
Ошибка 502 Bad Gateway: что значит
Файлы любого сайта находятся на физическом сервере. Чтобы их получить и отобразить веб-ресурс на компьютере, браузер делает запрос на сервер. Если он по какой-либо причине не передал файлы, появляется ошибка 500-511.
Ошибка 502 Bad Gateway возникает при неправильной работе прокси-сервера, DNS-сервера и чаще всего сервера, на котором размещён сайт. Проблема может распространяться как на весь ресурс, так и на отдельные страницы. Это зависит от характера проблемы. Существуют разновидности 502 ошибки: Bad Gateway Nginx, Bad Gateway Apache. Об их отличиях мы расскажем ниже. Также эта ошибка может иметь формулировки:
- Bad Gateway: Registered endpoint failed to handle the request, Temporary Error (502),
- Error 502,
- Bad 502 Gateway,
- 502 Error,
- 502. That’s an error,
- 502 Service Temporarily Overloaded,
- 502 Server Error: The server encountered a temporary error and could not complete your request,
- 502 – Web server received an invalid response while acting as a gateway or proxy server,
- 502 Bad Gateway Nginx,
- 502 Proxy Error,
- HTTP 502,
- HTTP Error 502 Bad Gateway.
Что значит плохой шлюз: ошибка 502
Причины возникновения ошибки 502 Bad Gateway
-
Первая и основная причина ― перегрузка сервера. Перегрузка может быть вызвана несколькими проблемами:
- Большое количество посетителей одновременно. Веб-ресурс может посещать ограниченное количество посетителей. Сколько человек может посетить сайт зависит от возможностей сервера (размера оперативной памяти) и настроек, которые сделал создатель ресурса. Если по какой-либо причине на сайт зайдёт больше пользователей, чем запланировано, сервис может не справиться и страница выдаст код 502. Такое случается при рекламных акциях и распродажах в интернет-магазинах.
- Атака хакеров или DDoS-атака. Эта проблема связана с предыдущей причиной перегрузки. Хакер имитирует большой наплыв пользователей, из-за чего сервер выходит из строя. Такие атаки могут быть использованы для снижения продаж.
- Плохая оптимизация сайта. Настройки ресурса сделаны так, что маленькое количество посетителей генерирует много запросов. В этом случае нужно оптимизировать работу сервера с пользовательскими запросами.
- Второй причиной возникновения кода 502 могут явиться ошибки РНР. Если для расширения функционала сайта в панель управления были добавлены некорректно настроенные плагины, они могут выдавать проблемы в своей работе. Вместе с ними ошибку покажет и сайт целиком. Также если код сайта написан неправильно, запросы могут давать отрицательный результат.
- Ошибка браузера. Проблема может быть на стороне пользователя, если у него установлены расширения, которые нарушают соединение с сервером сайта.
Чем отличается ошибка 502 Bad Gateway Nginx
Между браузером и сервером может стоять веб-сервер. Он используется для снижения нагрузки на сервер, аутентификации пользователей и многого другого. Самые популярные программы для создания веб-сервера ― Nginx и Apache. Так как веб-сервер является посредником между браузером и сервером, то именно он будет оповещать пользователя о проблеме. Поэтому в зависимости от веб-сервера в сообщении вы можете увидеть надпись Bad Gateway Nginx или Bad Gateway Apache. При этом причины возникновения проблемы одинаковы.
Как исправить ошибку 502
Что делать, если вы пользователь
- Перезагрузите страницу, если проблема была вызвана наплывом посетителей. Возможно, через некоторое время посетители уйдут со страницы и вы сможете увидеть контент.
- Попробуйте зайти на другой веб-ресурс. Если вы можете зайти на другой сайт, значит проблема на стороне владельца ресурса и вы ничего не можете сделать. Вернитесь на страницу позже, когда администратор восстановит доступ.
- Проверьте подключение к интернету. Из-за низкой скорости или нестабильности соединения браузер может не получать данные с сервера.
- Запустите браузер в режиме «Инкогнито». В режиме «Инкогнито» браузер работает с базовыми настройками. Если вам удалось зайти на веб-ресурс в этом режиме, значит одно из ваших расширений браузера мешает соединению. Это расширение нужно отключить.
- Почистите файлы cookies. Если при повторном входе на сайт всё равно отображается ошибка 502, очистите кэш браузера. Возможно, доступ уже восстановлен, но ваш браузер обращается к старой версии страницы из кэша.
- Очистите кэш DNS. DNS-кэш — это временная база данных вашего компьютера, которая хранит записи обо всех последних посещениях и попытках посещений веб-сайтов и их IP-адресах. Кэш позволяет ускорить вход на часто посещаемые веб-ресурсы. Если у сайта изменились DNS, а данные из кэша отправляют на старый IP-адрес, в браузере появится код 502. После очистки браузер начнёт обращаться к новому IP-адресу.
Как очистить кэш DNS
В зависимости от вашей операционной системы очистите кэш по одной из инструкций.
- Откройте командную строку. Для этого введите в поисковую строку «Командная строка» и выберите появившееся приложение:
- Введите команду:
ipconfig /flushdns
- Дождитесь сообщения об очистке кэша:
- Откройте терминал клавишами Ctrl+Alt+T.
- Введите команду:
Для Ubuntu:
sudo service network-manager restart
Для других дистрибутивов:
sudo /etc/init.d/nscd restart
- Войдите в терминал. Для этого нажмите клавиши Command + Space. Введите Терминал и нажмите на найденное приложение.
- Введите команду:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
Готово, вы очистили кеш DNS. Попробуйте заново зайти на сайт.
Что делать, если вы владелец сайта
Проверьте количество свободной памяти. Это можно сделать двумя способами.
Способ 1 ― введите команду top в командной строке сервера:
Mem ― вся оперативная память.
Swap ― раздел подкачки.
Посмотрите на строку Mem ― free. Это количество свободного места на сервере. Если там указано маленькое число, ошибка 502 Bad Gateway появляется из-за нехватки памяти. Увеличьте количество оперативной памяти и проблема пропадёт. Также в результатах можно будет увидеть, какую нагрузку на сервер даёт каждый отдельный процесс.
Способ 2 ― введите команду free -m.
Mem ― вся оперативная память.
Swap ― раздел подкачки.
В строке Mem ― free показано свободное место на сервере. Если там маленькое число, увеличьте количество оперативной памяти.
Проверьте логи сервера. Если проблема возникла в момент каких-либо обновлений на сайте, проверьте журнал изменений, чтобы отменить те доработки, которые нарушили функциональность сервера. Также в логах можно увидеть DDos-атаку. Если дело в нехватке памяти, в логах отобразится ошибка OOM (out of memory).
Проверьте плагины в WordPress. Если ваш сайт создан на WordPress, некоторые плагины и темы могут нарушать работу сервера.
-
1.
Войдите в панель управления WordPress. Если вы пользуетесь услугой REG.Site, войти в панель управления CMS можно прямо из Личного кабинета.
-
2.
Перейдите во вкладку «Плагины» ― «Установленные».
-
3.
Нажмите Деактивировать у плагина, который, как вам кажется, повлиял на работу сайта:
Можно сразу отключить все плагины, чтобы убедиться, что один из них влияет на работу сервера. И далее по очереди включайте плагины, пока не найдёте конкретный плагин-виновник.
Проверьте, как работают вспомогательные службы, например MySQL и Memcached. Иногда они могут стать причиной 502 ошибки.
Свяжитесь со службой поддержки своего хостинг-провайдера. Если ничего из вышеперечисленного не помогло, обратитесь к службе поддержки и подробно опишите проблему и действия, которые вы предприняли до обращения. Действуйте по одной из инструкций ниже.
Сайт находится на виртуальном хостинге REG.RU
Если вы столкнулись с единичными случаями возникновения 502 ошибки, можете проигнорировать их.
Если код 502 возникает регулярно, напишите заявку в службу поддержки. В заявке укажите:
- Точное московское время наблюдения проблемы.
- Название сайта, на котором была замечена проблема.
- Если ошибка отображается не сразу, а после определённых действий (добавление изображения, отправка формы с сайта, импорт файлов), подробно опишите порядок действий, по которому мы сможем воспроизвести проблему.
- Если для воспроизведения проблемы необходимо авторизоваться в административной части сайта, предоставьте логин и пароль для доступа.
Сайт находится на VPS REG.RU
Чаще всего на VPS используется связка: Nginx + бэкенд-сервер (Apache, PHP-FPM, Gunicorn, NodeJS). Ошибка 502 возникает в случае, если Nginx не может получить ответ от этих сервисов.
Клиенты с VPS сталкиваются с «502 Bad Gateway», когда:
- какой-то из сервисов выключен. Перезапустите веб-сервер Apache, PHP-FPM либо другой сервис, с которым работает Nginx;
- между Nginx и бэкенд-сервером некорректно настроена связь. Например, Nginx производит обращение к порту 8080, а веб-сервер Apache «слушает» на 8081. В этом случае необходимо скорректировать настройки веб-сервера.
Если вам не удалось самостоятельно устранить ошибку 502, обратитесь в техподдержку. В заявке укажите:
- Точное московское время наблюдения проблемы.
- Название сайта, на котором была замечена проблема.
- Если ошибка отображается не сразу, а после определённых действий (добавление изображения, отправка формы с сайта, импорт файлов), подробно опишите порядок действий, по которому мы сможем воспроизвести проблему.
- Если для воспроизведения проблемы необходимо авторизоваться в административной части сайта, предоставьте логин и пароль для доступа.