I have the following source from the Text Accelerated C++. When I attempt to compile the source file I get the following compilation error listed below. I’m a novice of the C++ language so your assistance would be appreciated.
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
#include <ios>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
struct Student_info {
string name;
double midterm, final;
vector<double> homework;
};
double median(vector<double>);
double grade(const Student_info&);
double grade(double, double, double);
double grade(double, double, const vector<double>&);
istream& read_hw(istream&, vector<double>&);
istream& read(istream&, Student_info&);
bool compare(const Student_info&, Student_info&);
int main() {
vector<Student_info> students;
Student_info record;
string::size_type maxlen = 0;
while(read(cin, record)) {
maxlen = max(maxlen, record.name.size());
students.push_back(record);
}
sort(students.begin(), students.end(), compare);
for(vector<Student_info>::size_type i = 0;
i != students.size(); ++i) {
cout << students[i].name << string(maxlen + 1 - students[i].name.size(), ' ');
try {
double final_grade = grade(students[i]);
streamsize prec = cout.precision();
cout << setprecision(3) << final_grade
<< setprecision(prec);
} catch(domain_error& e) {
cout << e.what();
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
double median(vector<double> vec) {
typedef vector<double>::size_type vec_sz;
vec_sz size = vec.size();
if(size == 0)
throw domain_error("median of an empty vector");
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end());
vec_sz mid = size/2;
return size%2 == 0 ? (vec[mid] + vec[mid - 1])/2 : vec[mid];
}
double grade(const Student_info& s) {
return grade(s.midterm, s.final, s.homework);
}
double grade(double midterm, double final, double homework) {
return 0.2*midterm + 0.4*final + 0.4*homework;
}
double grade(double midterm, double final, const vector<double>& hw) {
if(hw.size() == 0)
throw domain_error("student has done no homework");
return grade(midterm, final, median(hw));
}
istream& read_hw(istream& in, vector<double>& hw) {
if(in) {
hw.clear();
double x;
while(in >> x)
hw.push_back(x);
in.clear();
}
return in;
}
istream& read(istream& is, Student_info& s) {
is >> s.name >> s.midterm >> s.final;
read_hw(is, s.homework);
return is;
}
bool compare(const Student_info& x, const Student_info& y) {
return x.name < y.name;
}
binding of reference to type ‘Student_info’ to a value of type ‘const Student_info’ drops qualifiers compute_grades_rev-b
line 125, external location: /usr/include/c++/4.2.1/bits/stl_algo.h C/C++ Problem
Here is the code from stl_algo.h:
template<typename _Tp, typename _Compare>
inline const _Tp&
__median(const _Tp& __a, const _Tp& __b, const _Tp& __c, _Compare __comp)
{
// concept requirements
__glibcxx_function_requires(_BinaryFunctionConcept<_Compare,bool,_Tp,_Tp>)
if (__comp(__a, __b))
if (__comp(__b, __c))
return __b;
else if (__comp(__a, __c))
return __c;
else
return __a;
else if (__comp(__a, __c))
return __a;
else if (__comp(__b, __c))
return __c;
else
return __b;
}
I change the declaration of the compare function from:
bool compare(const Student_info&, Student_info&);
bool compare(const Student_info, Student_info);
Now it compiles.
why does the following throw this error:
IntelliSense: qualifiers dropped in binding reference of type
«string &» to initializer of type «const string»
.h
class A
{
public:
wstring& GetTitle() const;
private:
wstring title;
};
.cpp
wstring& GetTitle() const
{
return this->title;
}
If i remove the const word, it stops complaining, and yet i have never made any changes to the variable?
asked May 10, 2015 at 0:50
Jimmyt1988Jimmyt1988
20k40 gold badges129 silver badges229 bronze badges
4
By returning a non-const reference to a member of your class, you are giving the caller access to the object as if it’s non const. But GetTitle, being a const function, does not have the right to grant that access.
For example:
A a;
string& b = a.GetTitle(); // Allows control over original variable
answered May 10, 2015 at 0:54
Benjamin LindleyBenjamin Lindley
101k9 gold badges199 silver badges271 bronze badges
4
You can add const before the reference that would resolve the conflict as well, i.e. const wstring& GetTitle() const; and likewise for the .cpp file.
answered Aug 16, 2022 at 5:43
Hello i am getting the following error can someone give me a little help:
main.cpp: In constructor ‘ChessBoardArray::ConstRow::ConstRow(const ?>ChessBoardArray&, int)’: main.cpp:26:52: error: binding reference of type ‘ChessBoardArray&’ to ‘const ChessBoardArray’ discards qualifiers ConstRow(const ChessBoardArray &a, int i): board(a), row(i) {}
^
My code:
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
class ChessBoardArray {
protected:
class Row {
private:
ChessBoardArray &board;
int row;
public:
Row(ChessBoardArray &a, int i) : board(a), row(i) {}
int &operator[](int i) const {
return board.select(row, i);
}
};
class ConstRow {
private:
ChessBoardArray &board;
int row;
public:
ConstRow(const ChessBoardArray &a, int i): board(a), row(i) {}
int operator[](int i) const{
return board.select(row, i);
}
};
////public
public:
ChessBoardArray(unsigned int size = 0, unsigned int base = 0) {
data_size = pow(size, size) / 2 + size / 2;
data = new int[data_size];
this->base = base;
this->size = size;
}
ChessBoardArray(const ChessBoardArray &a) {
this->data = a.data;
this->size = a.size;
this->base = a.base;
}
~ChessBoardArray() {
delete[] data;
}
int &select(int i, int j){
return data[loc(i, j)];
}
int select(int i, int j) const {
return data[loc(i, j)];
}
const Row operator[](int i) {
return Row(*this, i);
}
const ConstRow operator [] (int i) const{
return ConstRow(*this, i);
}
private:
int *data;
int data_size;
int size;
int base;
unsigned int loc(int i, int j) const throw(out_of_range) {
int s = i + j;
if (i > size || i < 1 || j > size || j < 1)
throw out_of_range("Out of range cordinates!");
else if (!s % 2)
throw out_of_range("This is cell is black!");
else {
s = (i + 1) / 2 + (j - 1) / 2 * size + (0 ? j % 2 : j / 2 * 2 + 1);
return s;
}
}
};
int main() {
ChessBoardArray a(4, 1); // size 4x4, rows and columns numbered from 1
a[3][1] = 42;
a[4][4] = 17;
try { a[2][1] = 7; }
catch(out_of_range &e) { cout << "a[2][1] is black" << endl; }
try { cout << a[1][2] << endl; }
catch(out_of_range &e) { cout << "and so is a[1][2]" << endl; }
return 0;
}
|
nofx 8 / 8 / 5 Регистрация: 28.10.2012 Сообщений: 135 |
||||
|
1 |
||||
|
16.01.2017, 01:15. Показов 6631. Ответов 5 Метки нет (Все метки)
есть public метод класса с квалификатором const тип _ships — QMultiMap
Помогите разобраться, как исправить ошибку? Где именно теряется квалификатор? Миниатюры
__________________
0 |
|
nofx 8 / 8 / 5 Регистрация: 28.10.2012 Сообщений: 135 |
||||
|
16.01.2017, 01:21 [ТС] |
2 |
|||
|
вот определение _ships
0 |
|
retmas Жарю без масла 867 / 749 / 225 Регистрация: 13.01.2012 Сообщений: 1,702 |
||||||||
|
16.01.2017, 09:23 |
3 |
|||||||
|
последняя строка вывода компиля на вашем изображении намекает.
а должно быть
0 |
|
8 / 8 / 5 Регистрация: 28.10.2012 Сообщений: 135 |
|
|
16.01.2017, 12:15 [ТС] |
4 |
|
Ship& operator=(const Ship&) — а разве обязательно c конст, допускают и без. Я решил открыть мой проект в студии (через плагин). В студии все собирается. Может быть я что-то упустил и неявно исправил, но вроде код тот-же… Миниатюры
0 |
|
retmas Жарю без масла 867 / 749 / 225 Регистрация: 13.01.2012 Сообщений: 1,702 |
||||||||
|
16.01.2017, 12:42 |
5 |
|||||||
|
— а разве обязательно c конст, допускают и без. не в этом дело. это разные операторы.
то при вызове Ship& operator=(Ship&) будет попытка присвоить неконстантной ссылке константный объект.
1 |
|
86 / 45 / 11 Регистрация: 20.12.2010 Сообщений: 216 Записей в блоге: 1 |
|
|
16.01.2017, 13:47 |
6 |
|
nofx, студия много чего собирает, хотя как по мне лучше бы выдало еррор ( даже не варнинг )
0 |
- Forum
- General C++ Programming
- binding reference of type ‘unsigned long
binding reference of type ‘unsigned long’ to value of type ‘const unsigned long’ drops ‘const’ qualifier
I defined two functions for my Solver class as follows:
solver.h
|
|
solver.cpp
|
|
I am getting these errors:
|
|
^
I am trying to define the variable histObs inside the class which can be used in different methods of the class and keep track of all the changes made in the obs_vector. I don’t know how it should be implemented in a right and efficient way?!! How can I fix these errors and correctly set up histObs variable?
Last edited on
Solver::ObsProb() is a const function, but Solver::store() changes the value of its first parameter. If you need to call store() from there then ObsProb() should be non-const.
@helios but I can not change the definition of ObsProb() because it should be used with other classes that I didn’t write in the DSPOMDP class. Is there anyway I can fix my problem?
Also, store and get_max should be static functions (not const members) since they don’t need access to the object (they could be separate functions). Just remove the const in both the declarations and definitions and put static before their declarations.
Last edited on
@dutch So following your suggestion, I should do
|
|
in the header and define them like this:
|
|
Is it a correct way?
Yeah, that’s right.
BTW, it may not be useful to pack the 3-bit values into an unsigned long. which can therefore only hold up to 21 of them. Maybe a vector (or possibly array) of chars would be better. Although this takes 2.5 times as much space per state, it allows you to store more than 21 states. It depends on how many states you might need to store and how much overall space they will take up.
Are you using this code? https://github.com/AdaCompNUS/despot
@dutch that is the right code and basically it shouldn’t go beyond 5,6 states. I am not comfortable coding in c++ but I was forced because I wanted to use this code. Well another errors now I am running to are
|
|
I think I should change how I defined Mask and BitsPerValue in my class too, right?
Last edited on
Yeah, BitsPerValue and Mask also need to be static, so just add «static» before their declarations.
Some of those errors still seem to be related to the «const» problem, so make sure you do what helios said, too.
@dutch thanks for answering my questions. Your suggestion partially reduced the errors. As I already asked @helios, I wrote down the ObsProb function because POMDP solver use it with this given structure. Don’t you think changing its type would cause a conflict and leads to more errors?
|
|
Last edited on
I wrote down the ObsProb function because POMDP solver use it with this given structure.
Then you have to figure out how to implement ObsProb() in such a way that it doesn’t involve changing the state of the object.
Either way you’re getting errors. You seem to be in a catch-22. Generally this indicates a design issue. I don’t really have the time to look into how you should fix it. I would need to see your full code and also read up on the other code you are using.
It’s possible you could make histObs static, too. It depends on how exactly you are using this class.
Last edited on
@dutch exactly I fix some problem another one pops up. Well, if someone professional could take a look at my whole code everything could be easily solved.
Topic archived. No new replies allowed.
We use the const reference in C++ when we want to refer to a const type. It prevents changing the bounded object and also refers to a constant value (like 6, 27, 2.4 ..etc). In my previous article, I have explained the reference in detail if you had not read it, please check this link, “Introduction of the reference“.
Note: Here I am saying const reference but basically it is a reference to const because the reference is not an object, so we cannot make a reference itself const.
const int data = 10; // Valid, rData bound to data it will but //cannot be used to change data const int &rData = data; //Invalid, because reference //could not be const. int & const rData = data;
Let’s compile the below example code to understand the above-described concept.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int data = 10;
//Invalid, because reference
//could not be const.
int & const rData = data;
return 0;
}
Output: ‘const’ qualifiers cannot be applied to ‘int&’
In C++ you can write reference to const in two ways. For example, if I need to create a reference to const integer then I can write the expression in two ways. Most programmers like the first expression.
1. const int& rData = data; 2. int const &rData = data;
Note: Reference to const means that reference itself could not modify the referred object.
When we assign a CV (const and volatile) qualified object to an ordinary reference, we will get the error. This type of initialization is illegal and breaks the promise which has been done by the const object.
You can also see these articles:
- Const Qualifier in C.
- Volatile qualifier in C
- Application of volatile and const keywords in C
See the below code, where I am assigning the const object to the ordinary reference and printing their value.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
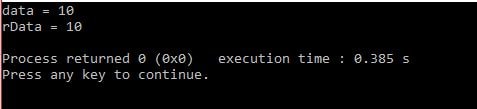
const int data = 10;
int &rData = data; // rData bound to data
cout <<"data = " << data << endl;
cout << "rData = " << rData << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
error: binding ‘const int’ to the reference of type ‘int&’ discards qualifiers.
A CV-qualified reference can refer to an ordinary object (not qualified by CV). It means a reference to const can refer to a non-const object. It is not an illegal statement and also does not break the rule because the reference to const only promises that it will not change the value of the referring object.
In the below example code, rData merely promises that the program won’t use rData to the value data.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int data = 10;
int const &rData = data; // rData bound to data
cout <<"data = " << data << endl;
cout << "rData = " << rData << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
If you will try to change the value of data, you will get the compile error.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int data = 10;
int const &rData = data; // rData bound to data
cout <<"data = " << data << endl;
cout << "rData = " << rData << endl;
rData = 12; //change the value
cout <<"data = " << data << endl;
cout << "rData = " << rData << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
error: assignment of read-only reference ‘rData’
You know that an ordinary reference must match the type of object to which it refers. But a reference to const initializes from any expression that can be converted to the type of the reference.
See below initialization, where a reference to const integer pointing to a float variable.
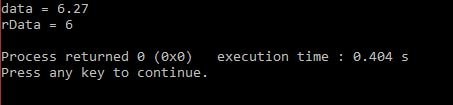
float data = 6.27; int const &rData = data; // rData bound to data
The initialization is valid because the compiler automatically creates a temporary integer object. It is an unnamed object which binds to the reference to const integer. So after creating the temporary object, the above initialization is looked like the below expression.
float data = 6.27; //float variable const int temp = data; // create a temporary const int from the float const int &rData = temp; // bind rData to that temporary
Let’s see some example code and their compilation result,
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float data = 6.27; //float variable
int const &rData = data; // rData bound to data
cout <<"data = " << data << endl;
cout << "rData = " << rData << endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
When binding character array to rData,
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char data[] = "Aticleworld"; //char array
int const &rData = data; // rData bound to data
cout <<"data = " << data << endl;
cout << "rData = " << rData << endl;
return 0;
}
Output: error: invalid conversion from ‘char*’ to ‘int’.
A reference with const is useful when you need to pass an object in the function without making a copy of the object with the guaranty that function will not change anything to passed object. It will save your stack memory and good thing is that you can also pass a non-const object to the function.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//function to print integer value
void printData(const int &data)
{
cout << "data = " << data << endl;
}
int main()
{
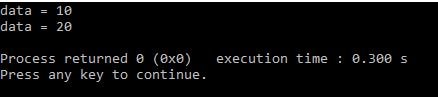
int a = 10; //non-const int
const int b =20; //const int
//print a
printData(a);
//print b
printData(b);
return 0;
}
Output:
If you want to learn C++11 from scratch then you can follow this course trial is free.
Your free trial is waiting.
typedef with reference to const
We can use the typedef with reference and create a new reference type.
typedef int & refToInt;
In the above expression, the newly created type refToInt is a reference to int. When we will create an identifier using the refToInt then the type of the identifier would be a reference to int.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int& refToInt;
int main()
{
int data = 24;
refToInt rData = data;
cout << rData << endl;
return 0;
}
Output: 24
You can also see the below article:
- 7 Application of typedef.
- typedef vs #define
But here you need to remember one thing if you will use newly reference type ( created by the typedef) with CV qualifier, the effect of the CV qualifier will not reflect on the reference identifier. See the below code,
In which I have used const with newly type but you can see the effect of const is not reflect on the rData and it is not initialized by a non-const object. In other words, you can say that the type of rData is “lvalue reference to int”, not “lvalue reference to const int”.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int& refToInt;
int main()
{
const int data = 24;
const refToInt rData = data;
cout << rData << endl;
return 0;
}
Output: error: binding ‘const int’ to reference of type ‘refToInt {aka int&}’ discards qualifiers|
If I will remove the const with data, you can see code will compile properly and you will get the proper result.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int& refToInt;
int main()
{
int data = 24;
const refToInt rData = data;
cout << rData << endl;
return 0;
}
Output: 24
Instead of using CV qualifier separately with new reference type (created by typedef) (because ill-formed), you can use the CV qualifier with typedef at the time of creating a new reference type.
typedef const int& refToInt;
See the example code,
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef const int& refToInt;
int main()
{
const int data = 24;
const refToInt rData = data;
cout << rData << endl;
return 0;
}
Recommended Post
- C++ MCQ for you.
- Amazing list of Gifts for Programmers, You must.
- Best electronic kits for programmers.
- C++ Interview Questions with Answers.
- constructors in c++.
- All about the new operator.
- Best mouse for the programmer.
- Introduction of reference in C++.
- C++ Interview Questions with Answers.
- 100 C interview Questions.
- C# Interview Questions with Answers.
- typedef vs #define in C.
- Macro in C, with example code.
- enum in C, you should know.
- Some online tools which help you in programming.
Recommended Answers
double Max(vector<geom_Point3> &Points, int n);
min_x = Min(Vertices_, 0);
Dave: Those are two different functions. Post the prototype for the Min() function, it apparently is different than for the Max() function which you posted.
>>but then isn’t it passing the entire array (which is very big in this …
Jump to Post
The problem is something else. Possibly something that has not been declared. Try this — it compiles ok for me with VC++ 2008 Express
struct geom_Point3 { int x,y; }; double Min(vector<geom_Point3> &Points, int n) { return 0.0; } int main() { vector<geom_Point3> Vertices_; double min_x = …
Jump to Post
All 6 Replies
daviddoria
334
Posting Virtuoso
Featured Poster
14 Years Ago
well i fixed it by taking the & out of the Max() declaration….
but then isn’t it passing the entire array (which is very big in this case) instead of just its address?
Ancient Dragon
5,243
Achieved Level 70
Team Colleague
Featured Poster
14 Years Ago
double Max(vector<geom_Point3> &Points, int n);
min_x = Min(Vertices_, 0);
Dave: Those are two different functions. Post the prototype for the Min() function, it apparently is different than for the Max() function which you posted.
>>but then isn’t it passing the entire array (which is very big in this case) instead of just its address?
Yes its passing the entire array, which can be very time consuming for the program when the vector has a large amount of items.
daviddoria
334
Posting Virtuoso
Featured Poster
14 Years Ago
Oh sorry, typo in the post. They should all be Min.
So why can’t I put the & there?
Ancient Dragon
5,243
Achieved Level 70
Team Colleague
Featured Poster
14 Years Ago
The problem is something else. Possibly something that has not been declared. Try this — it compiles ok for me with VC++ 2008 Express
struct geom_Point3
{
int x,y;
};
double Min(vector<geom_Point3> &Points, int n)
{
return 0.0;
}
int main()
{
vector<geom_Point3> Vertices_;
double min_x = Min(Vertices_, 0);
}
daviddoria
334
Posting Virtuoso
Featured Poster
14 Years Ago
Man, right again — I wish it would give more informative errors sometimes…
14 Years Ago
> I have a function double Min(vector<geom_Point3> &Points, int n); > Then in another class, I have a private member:
> vector<geom_Point3> Vertices_; > and in a class function, I call: min_x = Min(Vertices_, 0); > however, I get error: qualifiers dropped in binding reference... > What does that mean??
> i fixed it by taking the & out of the Max() declaration…
> but then isn’t it passing the entire array…
> So why can’t I put the & there?
the qualifiers the compiler is mentioning are cv-qualifiers (const/volatile)
the class member function where you call min_x = Min(Vertices_, 0); is a const member function.
modify the function signature to make it const-correct double Min( const vector<geom_Point3>& Points, int n ) ; and you should be ok.
Reply to this topic
Be a part of the DaniWeb community
We’re a friendly, industry-focused community of developers, IT pros, digital marketers,
and technology enthusiasts meeting, networking, learning, and sharing knowledge.
when running a program in which, among other functions, I minimise a deterministic finite automaton (DFA, for more information, https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aut%C3%B3mata_finito_determinista ), use the set and map containers of the C++ stl, but it gives me mistakes that I do not understand in that function (dfaminimum), the errors are the following:
I appreciate your help.
estadoDFA.cpp:34:12: error: binding ‘const std::map<char, int>’ to reference of type ‘std::map<char, int>&’ discards qualifiers
return trans_;
referring to the following line of the stateDFA file:
map<char,int>& estado:: get_transiciones(void) const{
return trans_; //LINEA 34
}
In that function I have made countless patches, putting what returns is always const, putting the const goes after get_transiciones(void)But it gives me a lot more mistakes.
the second mistake:
map unknown state: get_transitions(void) const{
return trans_;
!
PD: I have looked at similar questions with the same error, testing the solutions proposed, but it does not compile me.
DFA.cpp:414:74: error: ‘class std::map’ has no member named ‘second’
if(partvieja[k].find(*it).get_transiciones().second) == partvieja[k].end(){
I don’t understand this mistake either.
Here I leave the function code with error:
Dfaminimum in DFA.cpp
void dfa::dfaminimo(){ //cjtos.push_back(cjto); //un vector al que le inserto cosas parametro map<char,int>::iterator it1;//vector<set<int> > cjtos; set<estado> particion1; //el estado de muerte set<estado> particion2; //el resto de estados vector<set<estado> > conjuntos; //no hace falta llamar a la funcion operator <, lo llama insertar en su implementacion interna //particion2=cjtos; for(int i=0;i<estados_.size();i++){ if(estados_[i].get_aceptacion()!=true){ particion2.insert(estados_[i]); } else{ particion1.insert(estados_[i]); } } conjuntos.push_back(particion1); conjuntos.push_back(particion2); vector<set<estado> > temporal; do{ temporal = conjuntos; conjuntos = crear_nueva_particion(temporal); }while(conjuntos.size()!=temporal.size()); construir_dfa(conjuntos); }Here are the functions that are called:
vector<set<estado> > dfa::crear_nueva_particion(vector<set<estado> > temporal){
vector<set<estado> > conjunto;for(int i=0; i<temporal.size();i++){ //conjunto = conjunto | descomp(temporal[i],temporal); set<estado> newpart = descomp(temporal[i],temporal); //set<estado>::iterator it1; conjunto.push_back(newpart); } //unione.push_back(operando2); return conjunto; //return unione; }Here the function breaks down, where the sets are split
set<estado> dfa::descomp(set<estado> conj, vector<set<estado> > partvieja){set<estado> T = conj; map<char, int>::iterator it1; set<char> simbolos;//simbolos del alfabeto que el DFA reconoce for(it1=estados_[0].get_transiciones().begin();it1!=estados_[0].get_transiciones().end();it1++){ simbolos.insert((*it1).first); } set<char>::iterator it2; for(it2=simbolos.begin(); it2!=simbolos.end();it2++){ set<estado> P; set<estado>::iterator iterador; for(iterador= T.begin(); iterador!=T.end();iterador++){ set<estado> Tprima = part(conj,(*it2),partvieja); //P = P | Tprima; set<estado>::iterator it1; for(it1= Tprima.begin(); it1!=Tprima.end();it1++){ P.insert((*it1)); } } T = P; } return T; }Thank you.
I don’t know why I have this kind of error. I don’t use any of const value. append() gives the same error. Does it have anything to do with the fact that append() require const T &value? I’m pretty sure that something like that worked good for me in the past. What can be wrong here?
full error msg:
C:QtQt5.10.15.10.1mingw53_32includeQtCoreqlist.h:-1: In instantiation of ‘void QList<T>::node_construct(QList<T>::Node*, const T&) [with T = DobotMove]’:
C:QtQt5.10.15.10.1mingw53_32includeQtCoreqlist.h:584: required from ‘void QList<T>::append(const T&) [with T = DobotMove]’
C:QtQt5.10.15.10.1mingw53_32includeQtCoreqlist.h:386: required from ‘QList<T>& QList<T>::operator<<(const T&) [with T = DobotMove]’
C:DobotChessdobotdobot_queue.cpp:191: required from here
C:QtQt5.10.15.10.1mingw53_32includeQtCoreqlist.h:441: błąd: binding ‘const DobotMove’ to reference of type ‘DobotMove&’ discards qualifiers
else reinterpret_cast<T>(n) = t;
^
C:DobotChessdobotdobot_queue.cpp:1: In file included from dobotdobot_queue.cpp:1:0:
C:DobotChessdobotdobot_queue.h:12: note: initializing argument 1 of ‘DobotMove& DobotMove::operator=(DobotMove&)’
struct DobotMove
^
QList<DobotMove> _queuedCmdIDList;
struct DobotMove
{
uint64_t ID;
DOBOT_MOVE_TYPE type;
Point3D xyz;
DobotMove() :ID(0), type(DM_NONE), xyz(0,0,0) {}
DobotMove(uint64_t id, DOBOT_MOVE_TYPE MT, Point3D p): ID(id), type(MT), xyz(p) {}
};
void DobotQueue::addArmMoveToQueue(DOBOT_MOVE_TYPE Type, Point3D point)
{
_un64CoreQueuedCmdID += 1;
DobotMove cmdToQueue(_un64CoreQueuedCmdID, Type, point);
_queuedCmdIDList << cmdToQueue; //HERE
}
Also it would be better to have list of pointers to structs, or just list of structs?