The Tkinter library has many built-in functions and methods which can be used to implement the functional part of an application. We can use messagebox module in Tkinter to create various popup dialog boxes. The messagebox property has different types of built-in popup windows that the users can use in their applications.
If you need to display the error messagebox in your application, you can use showerror(«Title», «Error Message») method. This method can be invoked with the messagebox itself.
Example
# Import the required libraries
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import messagebox
# Create an instance of tkinter frame or window
win = Tk()
# Set the size of the tkinter window
win.geometry("700x350")
# Define a function to show the error message
def on_click():
messagebox.showerror('Python Error', 'Error: This is an Error Message!')
# Create a label widget
label = Label(win, text="Click the button to show the message ",
font=('Calibri 15 bold'))
label.pack(pady=20)
# Create a button to delete the button
b = Button(win, text="Click Me", command=on_click)
b.pack(pady=20)
win.mainloop()
Output
When you run the above code, it will show a button widget and a label in the window. Click the button to show the error message.
Python hosting: Host, run, and code Python in the cloud!
The Tkinter tkMessageBox has various methods to display a message box.
There is a slight difference between Tkinter for Python 2.7 and Python 3.
To find your Python version try one of these commands:
python --version
python3 --version
Related courses
- Python Desktop Apps with Tkinter
Tkinter Message box
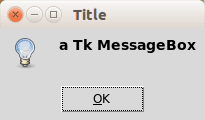
TkMessage boxTo show a minimalistic Tkinter message box, use the function showinfo() where the parameters are the window title and text.
The showinfo() function is in a different module depending on the Python version.
Python 3.x
from tkinter import messagebox
messagebox.showinfo("Title", "a Tk MessageBox")
Python 2.7
import Tkinter
import tkMessageBox
tkMessageBox.showinfo("Title", "a Tk MessageBox")
Tkinter showerror, showwarning and showinfo
Tk messagebox dialog
Tkinter includes several other message boxes:
- showerror()
- showwarning()
- showinfo()
Python 3.x
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
root = tkinter.Tk()
root.withdraw()
messagebox.showerror("Error", "Error message")
messagebox.showwarning("Warning","Warning message")
messagebox.showinfo("Information","Informative message")
Python 2.7
import Tkinter
import tkMessageBox
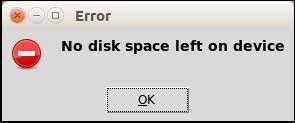
tkMessageBox.showerror("Error","No disk space left on device")
tkMessageBox.showwarning("Warning","Could not start service")
tkMessageBox.showinfo("Information","Created in Python.")
You may like: Tkinter Question Dialog or More Tkinter
If you are new to programming Tkinter, I highly recommend this course.
download tkinter examples
Содержание
- Tkinter messagebox
- Introduction to tkinter.messagebox module
- Tkinter messagebox examples
- Tkinter messagebox show error
- Окна подтверждения операции
- Настройка окон
- Python Tkinter – MessageBox Widget
- MessageBox Widget
- Диалоговые (всплывающие) окна / tkinter 9
- Окна уведомлений
- Как работают окна с уведомлениями
- Окна выбора ответа
- Как работают вопросительные окна
- Выбор файлов и папок
- Как работают окна выбора файлов и папок
- Python Tkinter messagebox + 19 Examples
- Python tkinter messagebox
- Python tkinter messagebox options
- Python tkinter messagebox size
- Python tkinter messagebox askquestion
- Python tkinter messagebox askyesno
- Python tkinter messagebox position
- Python tkinter messagebox documentation
- Python tkinter yes no dialog box
- Python Tkinter dialog window
- Python Tkinter dialog yes no
- Python Tkinter open path using the dialog window
- Python Tkinter dialog return value
- Python Tkinter dialog modal
- Python Tkinter dialog focus
- Python Tkinter popup message
- Python Tkinter popup input box
- Python Tkinter popup dialog
- Python Tkinter popup menu
- Python Tkinter close popup window
Tkinter messagebox
Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to show various message boxes using the tkinter.messagebox module.
Introduction to tkinter.messagebox module
When developing a Tkinter application, you often want to notify users about the events that occurred.
For example, when users click the save button, you want to notify them that the record has been saved successfully.
If an error occurred, for example, the database server is not reachable, you can notify users of the error.
When the update has been completed but the record already exists, you may want to show a warning.
To cover all of these scenarios, you can use various functions from the tkinter.messagebox module:
- showinfo() – notify that an operation completed successfully.
- showerror() – notify that an operation hasn’t completed due to an error.
- showwarrning() – notify that an operation completed but something didn’t behave as expected.
All of these functions accept two arguments:
- The title is displayed on the title bar of the dialog.
- The message is shown on the dialog.
To span the message multiple lines, you can add the new line character ‘n’ .
Tkinter messagebox examples
The following program consists of three buttons. When you click a button, the corresponding message box will display.
First, import the tkinter , tkinter.ttk , and tkinter.messagebox modules:
Second, create the root window and initialize its properties:
Third, create three buttons and assign a lambda expression to the command option of each button. Each lambda expression shows a corresponding message box.
Источник
Tkinter messagebox show error
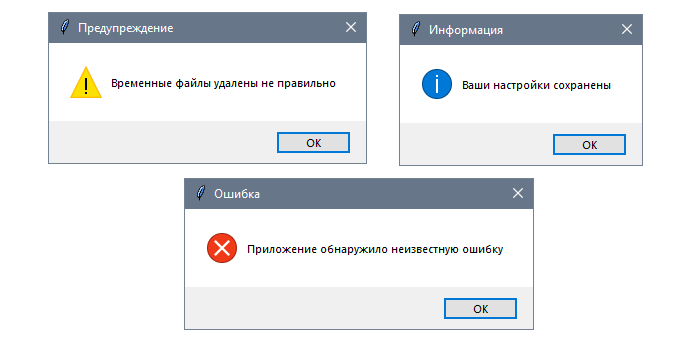
Tkinter имеет ряд встроенных окон для разных ситуаций, в частности, окна сообщений, функционал которых заключен в модуле tkinter.messagebox . Для отображения сообщений этот модуль предоставляет следующие функции:
showinfo() : предназначена для отображения некоторой информации
showerror() : предназначена для отображения ошибок
showwarrning() : предназначена для отображения предупреждений
Все эти функции принимают три параметра:
title : заголовок окна
message : отображаемое сообщение
options : настройки окна
В реальности различие между этими типами сообщений заключается лишь в изображении, которое отображается рядом с текстом сообщения:
Здесь по нажатию на каждую из трех кнопок отображается соответствующее сообщение:
Окна подтверждения операции
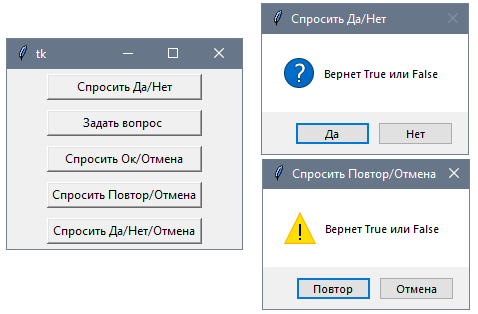
Модуль tkinter.messagebox также предоставляет ряд функций для подтверждения операции, где пользователю предлагается нажать на одну из двух кнопок:
Все эти функции принимают те же три параметра title, message и options. Отличие между ними только в том, что кнопки имеют разный текст. В случае нажатия на кнопку подтверждения, функция возвращает значение True , иначе возвращается False
В данном случае по нажатию на кнопку вызывается функция askyesno() , которая отображает диалоговое окно с двумя кнопками «Да» и «Нет». В зависимости от того, на какую кнопку нажмет пользователь, функция возвратит True или False. Получив результат функции, мы можем проверить его и выполнить те или иные действия.
Особняком стоит функция askquestion — она также отображает две кнопки для подтверждения или отмены действия (кнопки «Yes»(Да) и «No»(Нет)), но в зависимости от нажатой кнопки возвращает строку: «yes» или «no».
Также отдельно стоит функция askyesnocancel() — она отображает три кнопки: Yes (возвращает True), No (возвращает False) и Cancel (возвращает None):
В этом случае диалоговое окно предоставит выбор из трех альтернатив
Настройка окон
Дополнительно все вышерассмотренные функции принимают ряд параметров, которые могут применяться для настройки окон. Некоторые из них:
detail : дополнительный текст, который отображается под основным сообщением
icon : иконка, которая отображается рядом с сообщением. Должна представлять одно из втроенных изображений: info, error, question или warning
default : кнопка по умолчанию. Должна представлять одно из встроенных значений: abort, retry, ignore, ok, cancel, no, yes
При нажатии на кнопку отобразится следующее окно:
Источник
Python offers multiple options for developing GUI (Graphical User Interface). Out of all the GUI methods, tkinter is the most commonly used method. It is a standard Python interface to the Tk GUI toolkit shipped with Python. Python with tkinter is the fastest and easiest way to create the GUI applications. Creating a GUI using tkinter is an easy task.
Note: For more information, refer to Python GUI – tkinter
Python Tkinter – MessageBox Widget is used to display the message boxes in the python applications. This module is used to display a message using provides a number of functions.
Syntax:
Parameters:
There are various parameters :
- Function_Name: This parameter is used to represents an appropriate message box function.
- title: This parameter is a string which is shown as a title of a message box.
- message: This parameter is the string to be displayed as a message on the message box.
- options: There are two options that can be used are:
- default: This option is used to specify the default button like ABORT, RETRY, or IGNORE in the message box.
- parent: This option is used to specify the window on top of which the message box is to be displayed.
Function_Name:
There are functions or methods available in the messagebox widget.
- showinfo(): Show some relevant information to the user.
- showwarning(): Display the warning to the user.
- showerror(): Display the error message to the user.
- askquestion(): Ask question and user has to answered in yes or no.
- askokcancel(): Confirm the user’s action regarding some application activity.
- askyesno(): User can answer in yes or no for some action.
- askretrycancel(): Ask the user about doing a particular task again or not.
Источник
Диалоговые (всплывающие) окна / tkinter 9
Окна уведомлений
Распространенный сценарий применения диалоговых окон — уведомление пользователей о событиях, которые происходят в приложении: сделана новая запись или произошла ошибка при попытке открыть файл. Рассмотрим базовые функции Tkinter, предназначенные для отображения диалоговых окон.
В этой программе будет три кнопки, где каждая показывает определенное окно со своим статическим названием и сообщением. Сам по себе этот тип окон имеет лишь кнопку для подтверждения о прочтении и закрытия:
При запуске этого примера стоит обратить внимание на то, что каждое окно воспроизводит соответствующий платформе звук и показывает перевод метки в зависимости от языка системы:
Эти диалоговые окна открываются с помощью функций showinfo , showwarning и showerror из модуля tkinter.messagebox :
Как работают окна с уведомлениями
В первую очередь нужно импортировать модуль tkinter.messagebox , задав для него алиас mb . В Python2 этот модуль назывался tkMessageBox , поэтому такой синтаксис позволит изолировать проблемы совместимости.
Каждое окно обычно выбирается в зависимости от информации, которую нужно показать пользователю:
- showinfo — операция была завершена успешно,
- showwarning — операция была завершена, но что-то пошло не так, как планировалось,
- showerror — операция не была завершена из-за ошибки.
Все три функции получают две строки в качестве входящих аргументов: заголовок и сообщение.
Сообщение может быть выведено на нескольких строках с помощью символа новой строки n .
Окна выбора ответа
Другие типы диалоговых окон в Tkinter используются для запроса подтверждения от пользователя. Это нужно, например, при сохранении файла или перезаписывании существующего.
Эти окна отличаются от ранее рассмотренных тем, что значения, возвращаемые функцией, зависят от кнопки, по которой кликнул пользователь. Это позволяет взаимодействовать с программой: продолжать или же отменять действие.
В этой программе рассмотрим остальные диалоговые функции из модуля tkinter.messagebox . Каждая кнопка включает метки с описанием типа окна, которое откроется при нажатии:
У них есть кое-какие отличия, поэтому стоит попробовать каждое из окон, чтобы разобраться в них.
Как и в прошлом примере сначала нужно импортировать tkinter.messagebox с помощью синтаксиса import … as и вызывать каждую из функций вместе с title и message :
Как работают вопросительные окна
Чтобы избежать повторений при создании экземпляра кнопки и функции обратного вызова определим метод create_button , который будет переиспользоваться для каждой кнопки с диалогами. Команды всего лишь выводят результат функции dialog , переданной в качестве параметра, что позволит видеть значение, которое она возвращает в зависимости от нажатой пользователем кнопки.
Выбор файлов и папок
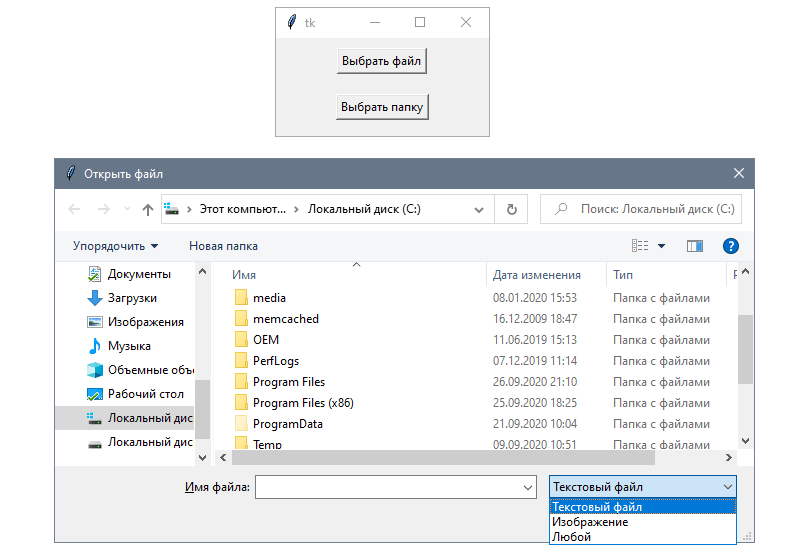
Диалоговые окна для выбора файлов позволяют выбирать один или несколько файлов из файловой системы. В Tkinter эти функции объявлены в модуле tkinter.filedialog , который также включает окна для выбора папок. Он также позволяет настраивать поведение нового окна: например, фильтрация по расширению или выбор папки по умолчанию.
В этом приложении будет две кнопки. Первая, «Выбрать файл», откроет диалоговое окно для выбора файла. По умолчанию в окне будут только файлы с расширением .txt :
Вторая — «Выбор папки». Она будет открывать похожее диалоговое окно для выбора папки.
Обе кнопки будут выводить полный путь к выбранным файлу или папке и не делать ничего, если пользователь выберет вариант Отмена .
Первая кнопка будет вызывать функцию askopenfilename , а вторая — askdirectory :
Поскольку пользователь может отменить выбор, также добавим условные инструкции, которые перед выводом в консоль будут проверять, не возвращает ли окно пустую строку. Такая валидация нужна для любого приложения, которое в дальнейшем будет работать с вернувшимся путем, считывая и копируя файлы или изменяя разрешения.
Как работают окна выбора файлов и папок
Создадим первое диалоговое окно с помощью функции askopenfilename , которая возвращает строку с полным путем к файлу. Она принимает следующие опциональные аргументы:
- title — название для диалогового окна.
- initialdir — начальная папка.
- filetypes — последовательность из двух строк. Первая — метка с типом файла в читаемом формате, а вторая — шаблон для поиска совпадения с названием файла.
- multiple — булево значение для определения того, может ли пользователь выбирать несколько файлов.
- defaultextension — расширение, добавляемое к файлу, если оно не было указано явно.
В этом примере задаем корневую папку в качестве начальной, а также название. В кортеже типов файлов есть следующие три варианта: текстовые файлы, сохраненные с расширением .txt, изображения с .jpg, .gif и .png, а также подстановочный знак («*») для всех файлов.
Стоит обратить внимание на то, что эти шаблоны не обязательно соответствуют формату данных в файле, поскольку есть возможность переименовать его с другим расширением:
Источник
Python Tkinter messagebox + 19 Examples
Keep reading to know more about the Python Tkinter messagebox, we will discuss the messagebox in Python Tkinter with examples.
- Python Tkinter messagebox
- Python Tkinter messagebox options
- Python tkinter messagebox size
- Python tkinter messagebox askquestion
- Python tkinter messagebox askyesno
- Python tkinter messagebox position
- Python tkinter messagebox documentation
- Python tkinter yes no dialog box
- Python tkinter yes no message box
- Python Tkinter dialog window
- Python Tkinter dialog yes no
- Python Tkinter open path using the dialog window
- Python Tkinter dialog return value
- Python Tkinter dialog modal
- Python Tkinter dialog focus
- Python Tkinter popup message
- python Tkinter popup input box
- python Tkinter popup dialog
- python Tkinter popup menu
- python Tkinter close popup window
If you are new to Python Tkinter or Python GUI programming, check out Python GUI Programming.
Table of Contents
Python tkinter messagebox
- Messagebox is used to display pop-up messages.
- To get started with message box import a library messagebox in Python.
- Messagebox provides mainly 6 types of message prompts like showinfo(), showerror(), showwarning(), askquestion(), askokcancel(), askyesno(), askretyrcancel().
| showinfo() | used when any confirmation/information needs to display. like login successful, message sent, etc. |
| showerror() | used to display error prompt with sound. The ideal time for its appearance is when the user makes any mistakes or skips the necessary step. |
| showwarning() | Shows warning prompt with exclamation sign. It warns the user about the upcoming errors. |
| askquestion() | It asks the user for Yes or No. also it returns ‘Yes‘ or ‘No‘ |
| askokcancel() | It prompts for ‘Ok’ or ‘Cancel‘, returns ‘True‘ or ‘False‘ |
| askyesno() | It prompts for ‘Yes’ or ‘No’. Returns True for ‘Yes’ and False for ‘No’ |
| askyesnocancel() | It prompts for ‘Yes’, ‘No’, or ‘Cancel’. Yes returns True, No returns False, and Cancel returns None |
| askretrycancel() | It prompts with Retry and Cancel options. Retry returns True and Cancel returns False. |
Python tkinter messagebox options
- Python Messagebox options are already mentioned in the above point
- So here we will look at it with an example, we will see examples for showinfo(), showwarning(), askquestion(), askokcancel(), askyesno(), askretrycancel().
Syntax:
Code:
Here is the code to represent all kinds of message boxes.
Output:
Here are the options displayed when Click Me button is clicked.
Python tkinter messagebox size
- There is no way to change the size of the messagebox.
- Only more text can stretch the size of messagebox.
- In this example, I will change the text content to stretch the message box size.
Code:
Output:
Python tkinter messagebox askquestion
- askquestion prompt is used to ask questions from the user.
- The response can be collected in the ‘Yes‘ or ‘No‘ form.
- This function returns the ‘yes‘ or ‘no‘.
- These return types can be controlled using an if-else statement.
- We will see this in the below example.
Code:
In this Python code, we have implemented the askquestion messagebox. We stored the value of messagebox in a variable ‘res’. Then we have compared the variable with the return type i.e ‘yes’ or ‘no’.
Output:
In this output, there is a button which when clicked will prompt with the question. The user will reply in ‘yes’ or ‘no’. accordingly another messagebox will prompt.
Python tkinter messagebox askyesno
- askyesno is used to prompt users with ‘yes’ or ‘no’ options.
- the response can be collected in the ‘yes’ or ‘no’ format.
- askyesno function returns boolean values i.e. ‘True’ or ‘False’.
- To control the yes or no use if-else statement.
Code:
Output:
In this output, the user will see a window with the ‘Kill the Window’ button. Once the user will click on this button.
Python tkinter messagebox position
- In this section, we will talk about the messagebox position
- This can be achieved using a Toplevel widget.
- any other widget can be placed on a Toplevel widget.
- It is similar to python frames but is specially created for creating customized prompts.
- In the below example we have placed image, label & 2 buttons.
- It will look like a prompt but we can position things as per our requirement.
- for image we have couple of options listed below.
- ::tk::icons::error
- ::tk::icons::information
- ::tk::icons::warning
- ::tk::icons::question
Code:
Here is a code in Python to create messagebox with customized position of widgets in it. We have placed an icon or image of the question over here. But you can replace it with ‘error’, ‘warning’, ‘question’ or ‘information’
Output:
In this output, the main window has a button which when clicked will prompt a user whether he wants to quit this page or not. If a user says ‘Yes’ this page will disappear’. Since it is a question you can notice a small icon of a question mark on the left side of the prompt.
Python tkinter messagebox documentation
Information message box
To display information showinfo function is used.
Warning message box
To display warning or error message showwarning and showerror is used.
Question message box
To ask question there are multiple options:
- askquestion
- askokcancel
- askretrycancel
- askyesno
- askyesnocancel
Python tkinter yes no dialog box
Let us see, how to generate Yes or No Popups in Python Tkinter or Python tkinter yes no message box. Python Tkinter provides a messagebox module that allows generating Yes and No prompts.
- Yes or No Popups are used to ask for confirmation before performing a task. It is mainly used to make sure that the user has not accidentally triggered a task.
- Yes or No prompts can be seen while the user is about to exit the program or while he is about to initiate any sensitive task. for example, while transferring money you see a prompt “Do you want to Proceed”.
- There are two functions inside the messagbox module that are used to generate Yes or No Prompts:
- messagebox.askquestion()
- messagebox.askyesno()
- messagebox.askquestion() function is used to ask a question from the user and the user has to reply in yes or no. The function returns True when the user clicks on the Yes button and Flase when the user clicks on the No button.
- messagebox.askyesno() function also does the same thing that it asks the user to reply in yes or no. The function returns True for yes and False for no.
- We have a complete section on Python Tkinter messagebox with an example. In this, we have covered all the available options for message box.
Syntax:
- Here is the syntax of the messagebox in Python Tkinter. In the first line, we have imported the messagebox module from the Tkinter library.
- In the second line, the option is the function that will generate a prompt. There are seven options to generate the prompt but in this tutorial, we’ll discuss only two of them:
- messagebox.askquestion()
- messagebox.askyesno()
Example of Yes No popups in Python Tkinter
- This application shows two options to the user. One is to donate & another one is to Exit the application.
- If the user clicks on the transfer button, askquestion() function is triggered & it requests the user for confirmation.
- if the user clicks on the Exit button, askyesno() function is triggered and it asks the user if he is sure to exit the application.
Output of the above code
Here is the output of the above code, In this code user wants to exit the application. He sees Yes No popup after clicking on the exit button.
This is how to generate Yes No Popup in Python Tkinter or Python Tkinter yes no dialog box.
Python Tkinter dialog window
In this section, we will learn how to create a dialog window in Python Tkinter.
A dialog window is used to communicate between the user and the software program or we can also say that it is simply used to display the message and require acknowledgment from the user.
Code:
In the following code, we import the library Simpledialog which is used for creating a dialog window to get the value from the user.
- simpledialog.askinteger() is used to get an integer from the user.
- simpledialog.askstring() is used to get a string value from the user.
- simpledialog.askfloat() is used to get a float value from the user.
Output:
After running the above code we get the following output in which we see a dialog window in which users enter their names. After entering the name click on ok.
After clicking on ok next dialog window will open in which the user can enter their name. After entering their age click on OK.
After clicking on ok next dialog window will open where the user can enter their salary and finally click on ok.
After clicking on ok the overall data will show on the command prompt.
Python Tkinter dialog yes no
In this section, we will learn how to create a yes or no dialog box in Python Tkinter.
This is an alert dialog box in which users can choose they want to continue or quit. if the user wants to quit click on the Yes if they don’t want to quit click on No.
Output:
In the following code, we import tkinter.messagebox library for giving the alert message yes and no. We also create a window and giving the title “Python Guides” to the window on which a yes or no pop-up message will show.
askyesno()function to show a dialog that asks for user confirmation.
Output:
In the following output, we see the window on which a yes or no pop-up message will show.
After clicking on Ask yes/No the confirmation message will show “Are you sure that you want to quit?” with the yes and No buttons. On clicking on yes all the programs will quit otherwise they stay on the first window.
Python Tkinter open path using the dialog window
In this section, we will learn how to create an open path using the dialog box in Python Tkinter.
The open dialog allows the user to specify the drive, directory, and the name of the file to open.
Code:
In the following code, we import library filedialog as fd and also create window ws= Tk() with the title “Python Guides”.
- fd.askopenfilename() function return the file name we selected and also support other function that displayed by dialog.
- error_msg = It show the error msg when file is not supported.
- Button() can display the text or images.
Output:
In the following output we see a window inside the window we add a button with the name“File Open”.
After clicking the button a dialog box is open. Select the file name after selecting click on the open button.
After clicking on the open button the file path and location is shown on the command prompt as shown in this image.
Python Tkinter dialog return value
In this section, we will learn how to create a dialog return value in python Tkinter.
The return value is something when the user enters the number in a dialog. And the number entered by the user is displayed on the main window as a return value.
Code:
In the following code, we create a window ws = TK() inside the window we add a button with the text “Get Input”. We also create labels and entries for taking the input from the user.
- Label() function is used as a display box where the user can place text.
- Button() is used for submitting the text.
- customdialog() is used to get the pop-up message on the main window.
Output:
After running the above code we get the following output in this we create a window inside the window we add a button with the title “Get Input”.
After clicking on the “Get Input” button we get a dialog box. Inside the dialog box user can enter anything. After entering input click on the OK button.
After clicking on the ok button we get the return value on the main window.
Python Tkinter dialog modal
In this section, we will learn how to create a dialog modal in Python Tkinter.
The modal window creates a way that damages the main window but makes it visible with the modal window. We can use the modal window as the main window. This is design for computer applications.
Code:
In the following code, we import .ttk import Style library for giving the style to the window. Here we create a window inside the window we add some labels and buttons.
- Label()function is used as a display box where the user can place text.
- Button()function is used when the user is pressed a button by a mouse click some action is started.
- Pop.destroy() is used for destroying the window after use.
Output:
In the following output, we see a window inside the window a button is placed. By clicking on the “Click Here” button some action is started and move to the next command.
After click on the “Click Here” button, the confirmation window is open with the text “Would You Like to Proceed” if yes click on yes if no click on.
After click on the yes button, we see some text is showing o the main window.
Python Tkinter dialog focus
In this section, we will learn how to create a dialog focus in Python Tkinter.
Before moving forward we should have a piece of knowledge about focus. Focus is that to giving attention to a particular thing or we can say that a center point of all the activity.
Dialog focus is when the user enters some input into a dialog box and wants to move forward then they click on the button so there completely focus on the button.
Code:
In the following code, we create a window inside the window we create an entry widget and buttons. Button widget which complete has the focus.
- Entry()is used for giving input from the user.
- Button() function is used when the user is pressed a button by a mouse click some action is started.
Output:
Here is a dialog widget in which the user enters the input and future proceeding they click on the button. In this the button widget completely has focus.
So, in this tutorial, we discussed Python Tkinter Dialog Box Window and we have also covered different examples.
In this section, we will learn about how to create a Popup message in Python Tkinter.
Before moving forward we should have a piece of knowledge about Popup. Popup is defined as notification that occurs suddenly and catches the audience’s attention. Popup message occurs on the user window.
Code:
In the following code, we create a window inside the window we also create a button with the text “Click Me”. After clicking on them a Popup window will be open.
import tkinter.messagebox importing this library for showing the message on the Popup screen.
tkinter.messagebox.showinfo() is used for displaying the important information.
Output:
In the following output, we see a window inside the window a button is placed.
By clicking on this button a Popup window is generated which shows some message.
In this following section, we will learn how to create a Popup input box in Python Tkinter.
Inputbox is where the user can enter some value, text after entering there is a button to move forward to complete the task. The Popup input box is similar where the user can insert the text when the pop input box window will appear.
Code:
In the following code, we create a window inside the window we add a label and button. We also define a Popup input window as Popup_win inside this window we create an entry where we can insert some text.
Output:
In the following output, we see a label and button present on the window where the label is used to describe the task and the button is used for continuing the task.
On the clicking, the Press button a Popup input box is shown on the screen where we can insert some text in the input box on clicking on the place text button. After inserting click on the ok button.
In the following section, we will learn how to create a Popup dialog in Python Tkinter.
The Popup dialog box is similar to the popup message this is shown on top of the existing window.
Code:
In the following code, we see a window inside the window buttons are placed on clicking on any of these buttons a Popup dialog box appear on the screen.
Output:
After running the above code we get the following output in which we see four buttons Paced at “Top”, “Bottom”, “Left”, “Right” inside the window.
On clicking on the Top button a Popup dialog open with the message“Top button
In this section, we will learn how to create a Popup menu in Python Tkinter.
The Popup menu appears on the main window by right-clicking on the main window. A menu bar is Popup on the screen with limited choices.
Code:
In the following code, we create a window inside the window we add a label with the text “Right-click To Display a Menu”.As the label describes what to do as the menu bar is Popup on the screen.
- Menu() is used to display the menubar on the screen.
- pop_up.add_command()is used to add some command in the menubar.
Output:
In the following output, as we see there is a label and button place inside the window.
When we right-click anywhere on the window menubar is a popup on the window.
In this section, we will learn how we can create close the popup window in Python Tkinter.
In the close popup window, we want to close the window that is currently Popup on the screen.
Code:
In the following code, we import tkinter.messagebox library for showing the message on the popup window and want to close this window with a show warning message.
- tkinter.messagebox.askyesno() is used for taking the user response if they want to quit click on yes if no click on no.
- tkinter.messagebox.showwarning() is used for showing the warning for verifying the user response.
- tkinter.messagebox.showinfo() is used for showing the information that the POPup window is closed.
Output:
In the following output er see a window inside a window a button is placed on clicking on them we get askyesno message.
As shown in this picture we choose the option yes or no if we want to close the popup window then click on yes.
After clicking on yes we see this popup window come on the screen by click on the ok button they close the popup window.
You may like the following Python tutorials:
In this tutorial, we have learned about Python tkinter messagebox. We have also covered these topics.
- Python tkinter messagebox
- python tkinter messagebox options
- python tkinter messagebox size
- python tkinter messagebox askquestion
- python tkinter messagebox askyesno
- python tkinter messagebox position
- python tkinter messagebox documentation
- Python tkinter yes no message box
- Python tkinter yes no dialog box
- Python Tkinter dialog window
- Python Tkinter dialog yes no
- Python Tkinter open path using the dialog window
- Python Tkinter dialog return value
- Python Tkinter dialog modal
- Python Tkinter dialog focus
- Python Tkinter popup message
- python Tkinter popup input box
- python Tkinter popup dialog
- python Tkinter popup menu
- python Tkinter close popup window
Python is one of the most popular languages in the United States of America. I have been working with Python for a long time and I have expertise in working with various libraries on Tkinter, Pandas, NumPy, Turtle, Django, Matplotlib, Tensorflow, Scipy, Scikit-Learn, etc… I have experience in working with various clients in countries like United States, Canada, United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, etc. Check out my profile.
Источник
Последнее обновление: 24.09.2022
Окна сообщений
Tkinter имеет ряд встроенных окон для разных ситуаций, в частности, окна сообщений, функционал которых заключен в модуле tkinter.messagebox.
Для отображения сообщений этот модуль предоставляет следующие функции:
-
showinfo(): предназначена для отображения некоторой информации
-
showerror(): предназначена для отображения ошибок
-
showwarrning(): предназначена для отображения предупреждений
Все эти функции принимают три параметра:
showinfo(title, message, **options) showerror(title, message, **options) showwarrning(title, message, **options)
-
title: заголовок окна
-
message: отображаемое сообщение
-
options: настройки окна
В реальности различие между этими типами сообщений заключается лишь в изображении, которое отображается рядом с текстом сообщения:
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter.messagebox import showerror, showwarning, showinfo
root = Tk()
root.title("METANIT.COM")
root.geometry("250x200")
def open_info():
showinfo(title="Информация", message="Информационное сообщение")
def open_warning():
showwarning(title="Предупреждение", message="Сообщение о предупреждении")
def open_error():
showerror(title="Ошибка", message="Сообщение об ошибке")
info_button = ttk.Button(text="Информация", command=open_info)
info_button.pack(anchor="center", expand=1)
warning_button = ttk.Button(text="Предупреждение", command=open_warning)
warning_button.pack(anchor="center", expand=1)
error_button = ttk.Button(text="Ошибка", command=open_error)
error_button.pack(anchor="center", expand=1)
root.mainloop()
Здесь по нажатию на каждую из трех кнопок отображается соответствующее сообщение:
Окна подтверждения операции
Модуль tkinter.messagebox также предоставляет ряд функций для подтверждения операции, где пользователю предлагается
нажать на одну из двух кнопок:
-
askyesno()
-
askokcancel()
-
askretrycancel()
Все эти функции принимают те же три параметра title, message и options. Отличие между ними только в том, что кнопки имеют разный текст. В случае нажатия на кнопку подтверждения, функция возвращает значение True, иначе возвращается False
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter.messagebox import showinfo, askyesno
root = Tk()
root.title("METANIT.COM")
root.geometry("250x200")
def click():
result = askyesno(title="Подтвержение операции", message="Подтвердить операцию?")
if result: showinfo("Результат", "Операция подтверждена")
else: showinfo("Результат", "Операция отменена")
ttk.Button(text="Click", command=click).pack(anchor="center", expand=1)
root.mainloop()
В данном случае по нажатию на кнопку вызывается функция askyesno(), которая отображает диалоговое окно с двумя кнопками «Да» и «Нет».
В зависимости от того, на какую кнопку нажмет пользователь, функция возвратит True или False. Получив результат функции, мы можем проверить его и выполнить те или иные действия.
Особняком стоит функция askquestion — она также отображает две кнопки для подтверждения или отмены действия (кнопки «Yes»(Да) и «No»(Нет)),
но в зависимости от нажатой кнопки возвращает строку: «yes» или «no».
Также отдельно стоит функция askyesnocancel() — она отображает три кнопки: Yes (возвращает True), No (возвращает False) и Cancel
(возвращает None):
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter.messagebox import showinfo, askyesnocancel
root = Tk()
root.title("METANIT.COM")
root.geometry("250x200")
def click():
result = askyesnocancel(title="Подтвержение операции", message="Подтвердить операцию?")
if result==None: showinfo("Результат", "Операция приостановлена")
elif result: showinfo("Результат", "Операция подтверждена")
else : showinfo("Результат", "Операция отменена")
ttk.Button(text="Click", command=click).pack(anchor="center", expand=1)
root.mainloop()
В этом случае диалоговое окно предоставит выбор из трех альтернатив
Настройка окон
Дополнительно все вышерассмотренные функции принимают ряд параметров, которые могут применяться для настройки окон. Некоторые из них:
-
detail: дополнительный текст, который отображается под основным сообщением -
icon: иконка, которая отображается рядом с сообщением. Должна представлять одно из втроенных изображений: info, error, question или warning -
default: кнопка по умолчанию. Должна представлять одно из встроенных значений: abort, retry, ignore, ok, cancel, no, yes
from tkinter import *
from tkinter import ttk
from tkinter.messagebox import OK, INFO, showinfo
root = Tk()
root.title("METANIT.COM")
root.geometry("250x200")
def click():
showinfo(title="METANIT.COM", message="Добро пожаловать на сайт METANIT.COM",
detail="Hello World!", icon=INFO, default=OK)
ttk.Button(text="Click", command=click).pack(anchor="center", expand=1)
root.mainloop()
При нажатии на кнопку отобразится следующее окно:
Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to show various message boxes using the tkinter.messagebox module.
Introduction to tkinter.messagebox module
When developing a Tkinter application, you often want to notify users about the events that occurred.
For example, when users click the save button, you want to notify them that the record has been saved successfully.
If an error occurred, for example, the database server is not reachable, you can notify users of the error.
When the update has been completed but the record already exists, you may want to show a warning.
To cover all of these scenarios, you can use various functions from the tkinter.messagebox module:
showinfo()– notify that an operation completed successfully.showerror()– notify that an operation hasn’t completed due to an error.showwarrning()– notify that an operation completed but something didn’t behave as expected.
All of these functions accept two arguments:
Code language: Python (python)
showinfo(title, message) showerror(title, message) showwarrning(title, message)
- The
titleis displayed on the title bar of the dialog. - The
messageis shown on the dialog.
To span the message multiple lines, you can add the new line character 'n'.
Tkinter messagebox examples
The following program consists of three buttons. When you click a button, the corresponding message box will display.
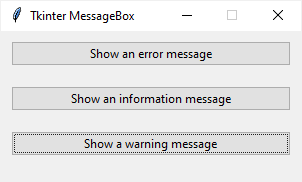
Code language: Python (python)
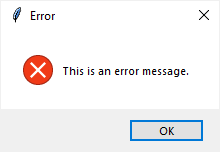
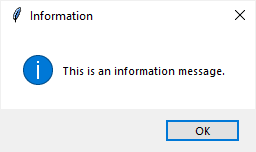
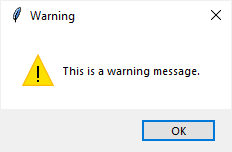
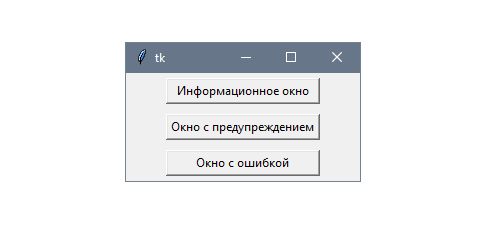
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk from tkinter.messagebox import showerror, showwarning, showinfo # create the root window root = tk.Tk() root.title('Tkinter MessageBox') root.resizable(False, False) root.geometry('300x150') # options = {'fill': 'both', 'padx': 10, 'pady': 10, 'ipadx': 5} ttk.Button( root, text='Show an error message', command=lambda: showerror( title='Error', message='This is an error message.') ).pack(**options) ttk.Button( root, text='Show an information message', command=lambda: showinfo( title='Information', message='This is an information message.') ).pack(**options) ttk.Button( root, text='Show an warning message', command=lambda: showwarning( title='Warning', message='This is a warning message.') ).pack(**options) # run the app root.mainloop()
How it works.
First, import the tkinter, tkinter.ttk, and tkinter.messagebox modules:
Code language: Python (python)
import tkinter as tk from tkinter import ttk from tkinter.messagebox import showerror, showwarning, showinfo
Second, create the root window and initialize its properties:
Code language: Python (python)
# create the root window root = tk.Tk() root.title('Tkinter MessageBox') root.resizable(False, False) root.geometry('300x150')
Third, create three buttons and assign a lambda expression to the command option of each button. Each lambda expression shows a corresponding message box.
Code language: Python (python)
ttk.Button( root, text='Show an error message', command=lambda: showerror( title='Error', message='This is an error message.') ).pack(**options) ttk.Button( root, text='Show an information message', command=lambda: showinfo( title='Information', message='This is an information message.') ).pack(**options) ttk.Button( root, text='Show an warning message', command=lambda: showwarning( title='Warning', message='This is a warning message.') ).pack(**options)
Finally, display the root window.
Code language: Python (python)
root.mainloop()
Summary
- Use
showinfo(),showerror(),showwarrning()functions from thetkinter.messageboxmodule to show an information, error, and warning message.
Did you find this tutorial helpful ?
What is Tkinter Messagebox?
Tkinter Messagebox is a module in python which provides a different set of dialogues that are used to display message boxes, showing errors or warnings, widgets to select files or change colors which is a pop-up box with a relevant message being displayed along with a title based on the requirement in python applications with an icon and interrupts the user flow to take input from the user is called Tkinter Messagebox and has different functions that are used to display the relevant messages based on the application requirements like info message, warning message, error message, or taking input from the user.
Syntax:
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
messagebox.functionname(title, message [,options])Explanation: In the above syntax, we have imported the Tkinter library, and from that, we imported the messagebox module using which we can call different functions and display the relevant messages along with title based on the application requirement.
Attributes of Tkinter Messagebox
In the previous section, we have discussed the syntax of the Tkinter messagebox. Now we will discuss in detail the parameters or attributes being used in the syntax. There are four attributes in the syntax: function name, title, message, and options.
- Function name: The function name represents the proper name for the message box function.
- Title: Title is a message which will be displayed in the dialogue box of the message in the title bar.
- Message: Messages is a text used to display a message to the appropriate function name.
- Options: Options are like a choice by which we can customize the message box, which is standard. Some of the options are default and parent. The default option is used to mention default operations or message boxes buttons such as ABORT, IGNORE or RETRY in the message box. Parent option is used to mention a parental window on top of which message box will be displayed.
Methods of Tkinter Messagebox
Let’s have a look at different functions available with Tkinter messagebox such as showinfo(), showwarning(), showerror(), askquestion(), askokcancel(), askyesno(), and, askretrycancel(). The above functions used to show appropriate message boxes, and all the functions have the same kind of syntax but with different functionalities. All the functions which we are going to discuss are with python3 and above.
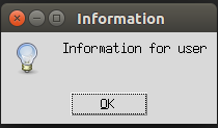
1. showinfo()
We use this messagebox function when we want to show some related or relevant information to the user. Let us try to create an information message box with an example below.
Code:
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
top = tkinter.Tk()
top.geometry("150x150")
messagebox.showinfo("Information","Information for user")
top.mainloop()Explanation: In the above example, we created a Tkinter object top using tkinter.Tk() and used messagebox with showinfo() function to display the information message.
Output:
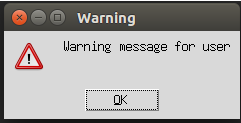
2. showwarning()
We use this messagebox function when we want to display a warning message to the user. Let us create a warning message to the user by using an example as below:
Code:
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
top = tkinter.Tk()
top.geometry("150x150")
messagebox.showwarning("Warning","Warning message for user")
top.mainloop()Explanation: In the above example, we created a Tkinter object top using tkinter.Tk() and used a messagebox with a showwarning() function to display the user’s warning message.
Output:
3. showerror()
We use this messagebox function when we want to display an error message to the user. Let us create an error message to the user by using an example as below:
Code:
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
top = tkinter.Tk()
top.geometry("150x150")
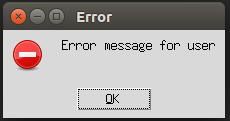
messagebox.showerror("Error","Error message for user")
top.mainloop()Explanation: In the above example, we created a Tkinter object top using tkinter.Tk() and used a messagebox with showerror() function to display the user’s warning message.
Output:
4. askquestion()
We use this messagebox function when we want to ask the user some questions, which can be answered by using yes or no. Let us create a program to ask the user a question whether the user wants to confirm it or not by using an example as below:
Code:
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
top = tkinter.Tk()
top.geometry("150x150")
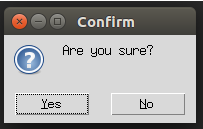
messagebox.askquestion("Confirm","Are you sure?")
top.mainloop()Explanation: In the above example, we created a Tkinter object top using tkinter.Tk() and used messagebox with askquestion() function to ask the user a question Confirm with a message Are you sure?
Output:
5. askokcancel()
We use this messagebox function when we want to confirm the user’s responses regarding the application behavior or activity. Let us create a program to confirm users response regarding an application by using an example as below:
Code:
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
top = tkinter.Tk()
top.geometry("150x150")
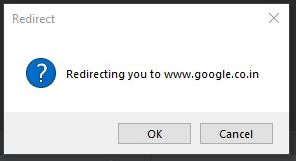
messagebox.askokcancel("Redirect","Redirecting you to www.google.co.in")
top.mainloop()Explanation: In the above example, we created a Tkinter object top using Tkinter.Tk() and used a messagebox with the askokcancel() function to get the user’s response regarding the application activity.
Output:
6. askyesno()
We use this messagebox function when we want to ask the user regarding some question that can be answered by using yes or no. Let us create a program to ask user regarding some question, and the user will answer by saying yes or no by using an example as below:
Code:
import tkinter
from tkinter import messagebox
top = tkinter.Tk()
top.geometry("150x150")
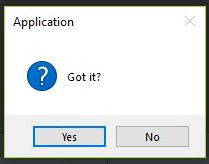
messagebox.askyesno("Application","Got it?")
top.mainloop()Explanation: In the above example, we created a Tkinter object top using tkinter.Tk() and used messagebox with askyesno() function to ask the user regarding some question with a message Got it?
Output:
Examples to Implement Tkinter Messagebox
Let us create an application using labels, grid, and Entry class to take input from it and apply the action after a button click as the below example.
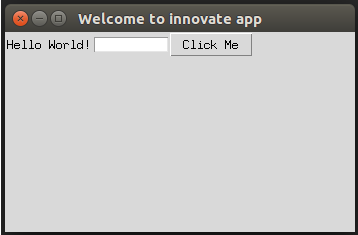
Code:
import tkinter
from tkinter import *
top = tkinter.Tk()
top.title("Welcome to innovate app")
top.geometry("350x200")
labl = Label(top, text=”Hello World!”)
labl.grid(column=0, row=0)
txt = Entry(top, width=10)
txt.grid(column=1, row=0)
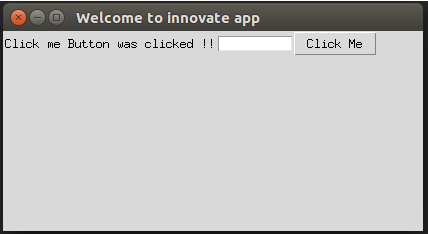
def click():
labl.configure(text="Click me Button was clicked ! !")
btn = Button(top, text ="Click Me", command=click)
btn.grid(column=2, row=0)
top.mainloop()Explanation: In the above example, we have created a Tkinter object top using tkinter.Tk() and the function click() where we are configuring the label with the text “Click me Button was clicked!!” and we have created a title to the Tkinter object, created a grid to display the output as below:
Output:
Conclusion
Finally, it’s an overview of the Tkinter messagebox module in python. So far, we have discussed what messagebox, its syntax, its attributes, and functions supported in the module, describing functions in detail, and finally explaining with an example using showinfo() function using the pack() method. I hope after reading this article, you will have a good understanding of the Tkinter messagebox module, its functions, and how to use them based on the application requirement.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Tkinter Messagebox. Here we discuss Syntax, the attributes, different methods and examples to implement with appropriate syntax and sample code. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –
- Tkinter Scrollbar
- Python Tkinter Label
- Tkinter Listbox
- Tkinter Menubutton
Introduction
In this blog, I am going to create an error message in a Python GUI application. When a user clicks an error item from the message menu, it will display the error message in the application screen.
Software requirement
Python 3.5 and IDLE (Python 3.5)
Programming code
- import tkinter as tk
- from tkinter import ttk
- from tkinter import Menu
- from tkinter import messagebox as mbox
- err = tk.Tk()
- err.title(«Python GUI App»)
- ttk.Label(err, text=«Error Messsage BoxApp»).grid(column=0,row=0,padx=20,pady=30)
- menuBar=Menu(err)
- err.config(menu=menuBar)
- def _msgBox():
- mbox.showerror(‘Python Error Message’,‘Error: You are Clicked ErrorMessage’)
- infoMenu=Menu(menuBar, tearoff=0)
- infoMenu.add_command(label=«Error», command=_msgBox)
- menuBar.add_cascade(label=«Message», menu=infoMenu)
- err.mainloop()
About the code
- First, I am importing the tkinter modules.
- Next, I assign a class and variables and give the application title.
- Next, I create a menu bar and add an item in the menu bar.
- Next, I create an error message function and add the error message in the displaying command menu.
- Finally, I have started the Windows event loop by calling the mainloop method, then execute the code.
Output