1. SSH connected to server as root, generated certificate signing request with openssl:
Code: Select all
openssl req -new -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout server.key -out server.csr
Common Name: *.domain.tld
The rest: Country/State/Org/ …
2. Processed Comodo EssentialSSL Wildcard (got from NameCheap) with the generated CSR > received certificate bundle by email including the 1 signed cert file and 3 cert authority files.
3. VestaCP admin > Web > SSL Support > Copy pasted signed certificate into «SSL Certificate» box, Copy pasted private key into «SSL Key» box > Save
That causes Error: certificate authority not found.
Help appreciated.
SOLUTION:
xD gotta copy paste the certificate authority info into the certificate authority box (the third box in the «SSL Support» section)
Comodo (or other SSL provider) will email you a bundle zip file containing 4 files, 1 of them (ex. STAR_domain_tld.crt) is the signed certificate to be copy pasta’d into the first box like I mentioned I did. And then the 3 remaining .crt files (ex. AddTrust…, COMODORSAAddTrustCA, COMODORSADomainValid…) should be copy pasta’d into that third box (create a new text file and copy paste the 3 certs into there first, then mass copy paste from the summed text).
Like:
Code: Select all
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
....
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
.....
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
......
-----END CERTIFICATE-----I have installed SSL on my VestaCP , but browser says my site is insecure, why this is happening on this my site?
Installing an SSL Certificate in Vesta CP is quite easy. However, missing certificates and improper installation may lead to errors on websites.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from our customers to set up VestaCP SSL as part of our Server Management Services
Today, we’ll see how our Support Engineers set up VestaCP SSL and fix related errors.
How we install an SSL Certificate in Vesta CP
Usually, site owners installing an SSL certificate on their website to increase their confidentiality. While installing an SSL Certificate, they promise their customers that they will never compromise their details with anyone.
So, this is an unavoidable factor for their business.
Now, Let’s see how our Support Engineers install an SSL Certificate in Vesta CP.
1. Before going to the SSL installation, we make sure that we have all the files that are provided by the SSL providers. It includes,
- SSLCertificateFile.
- SSLCertificateKeyFile.
- SSLCACertificateFile.
2. Then, we log into the Vesta CP control panel.
3. We go to WEB, click the domain we want to install an SSL certificate and click on the Edit button.
4. On the next page, we locate SSL Support tab and enable it.
5. Next, we paste the certificate, Private Key and CA Bundle files into the corresponding fields.
6. Finally, we click the Save button.
That’s it!
How we fixed errors while installing VestaCP SSL
From our experience in managing servers, we’ve seen customers facing problems with the VestaCP SSL setup. Now, Let’s take a closer look at how our Support Engineers fixed some common problems.
Improper installation SSL certificates
Installing an SSL for a domain is very easy. Also, when a control panel is installed on the server, it becomes very easy. Customers can often face problems when pasting certificates into the SSL field of VestaCPls. The ones might be confused about what they have to paste on.
So, definitely, the certificate will not be installed. It will throw an error using installation.
Therefore, our Support Engineers ensure that all the certificates provided by the SSL provider are correct. If not, we will do the installation once again on behalf of the customer.
Missing certificates
Recently, one of our customers contacted us with a problem while installing the SSL via VestaCP. When he tried to install an SSL Certificate, he continued to receive the following error message
Error: root or/and intermediate cerificate not found
Error: certificate authority not found
Normally, this happens when the customer leaves the field SSL Certificate Authority / Intermediate as empty. But, due to some reason, VestaCP does not allow to install the SSL without this field.
So, our Support Engineers installed the bundled keys,
For GoDaddy, it should look like gd_bundle.crt file which received with the certs.
[Having trouble while installing SSL on VestaCP? We’ll fix it for you.]
Conclusion
In short, installing VestaCP SSL needs much attention because missing certificates and improper installation will result in SSL failure. Today, we saw how our Support Engineers install SSL on Vestacp and fix related errors.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.
GET STARTED
var google_conversion_label = «owonCMyG5nEQ0aD71QM»;
I’m getting started with the facebook API.
I downloaded the example code from facebook, configured with my appID and secret keys.
<?php
require '../src/facebook.php';
// Create our Application instance (replace this with your appId and secret).
$facebook = new Facebook(array(
'appId' => '...',
'secret' => '....',
));
// Get User ID
$user = $facebook->getUser();
if ($user) {
try {
// Proceed knowing you have a logged in user who's authenticated.
$user_profile = $facebook->api('/me');
} catch (FacebookApiException $e) {
error_log($e);
$user = null;
}
}
// Login or logout url will be needed depending on current user state.
if ($user) {
$logoutUrl = $facebook->getLogoutUrl();
} else {
$loginUrl = $facebook->getLoginUrl();
}
// This call will always work since we are fetching public data.
$naitik = $facebook->api('/naitik');
?>
on localhost,the script work with no errors. But on host I getting the following error:
Invalid or no certificate authority found, using bundled information
the .crt file was uploaded with success
one may point out my error?
thanks in advance.
asked Sep 10, 2011 at 19:50
1
Set the option in CURL to point to your certificate file
This option will tell CURL that your fb_ca_chain_bundle.crt file is in the same folder as your script.
Facebook::$CURL_OPTS[CURLOPT_CAINFO] = getcwd().'/fb_ca_chain_bundle.crt';
In base_facebook.php line 844 curl_exec fails and the error is generated. Then the script sets:
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_CAINFO,
dirname(__FILE__) . '/fb_ca_chain_bundle.crt');
and tries again.
The Second time all is well, there is no problem it just makes a mess of your log
DO NOT use
Facebook::$CURL_OPTS[CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER] = false;
Or a man-in-middle will be able to intercept your call!
answered Jul 18, 2012 at 18:50
MattMatt
2162 silver badges2 bronze badges
5
Disable the SSL security feature
Though I don’t recognize that exact error message, SSL problems when communicating with Facebook via the PHP SDK (and thus Curl) are common. Have you tried doing something like this?
Facebook::$CURL_OPTS[CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER] = false;
This will disable the SSL «Verify Peer» security feature so that it stops generating the error message.
answered Sep 10, 2011 at 20:03
4
I’ve checked the server config and everything seems fine. However I’ve seen a few other posts on the internet where users have fixed the issue by editing the following lines in
«base_facebook.php»
/**
* Default options for curl.
*/
public static $CURL_OPTS = array(
CURLOPT_CONNECTTIMEOUT => 10,
CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER => true,
CURLOPT_TIMEOUT => 60,
CURLOPT_USERAGENT => 'facebook-php-3.2',
CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER => false, (ADDED THIS LINE)
);
I’ve tested it and this now works, and it successfully posts to the Facebook page.
Cheers!
Mudassar Ali
answered Jul 18, 2014 at 7:10


При открытии сайтов в браузере иногда возникают ошибки – домен в адресной строке выделяется красным с зачеркиванием или ресурс вообще не открывается. Типовая причина скрывается в сбоях работы сертификата SSL. Исправить их может только администратор сайта, но перед обращением к нему стоит проверить собственный компьютер.
Что такое SSL
Текущие тенденции сайтостроения предполагают высокую безопасность соединения пользователя с веб-ресурсом. Это необходимо для защиты персональных данных, секретных номеров банковских карт и информации о проводимых сделках. Организуется безопасность подключением протокола шифрования Secure Sockets Layer (сокращенно SSL).
Особенности сертификата:
- Сертификат выпускается доверенным центром Certification Authority (CA).
- После выдачи он подключается к домену средствами провайдера хостинга.
- Срок его действия ограничен 1 годом, после чего требуется продление.
Работа сайта возможна и без SSL, но поисковые системы «не доверяют» таким ресурсам и помечают их в браузере как неблагонадежные. Поэтому лучше разобраться, как решить проблему с защитой и полноценно пользоваться протоколом HTTPS. Сертификат актуален на сайтах, где присутствует регистрация, предлагается покупка товаров или онлайн-оплата различных сервисов.
При появлении любых сомнений в исправности защиты регистрироваться на сайте или вводить ранее выданные логин и пароль не рекомендуется. Тем более не стоит осуществлять онлайн-оплату с банковских карт или электронных кошельков, ведь не исключено, что проблема возникла из-за взлома ресурса злоумышленниками.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Причины появления ошибок SSL
Существует всего две причины, почему браузер отображает ошибку сертификата SSL со стороны сервера. Первая заключается в окончании срока активации, вторая – это покупка сертификата у поставщика без достаточных полномочий для выдачи «полноценной защиты». Например, виной может быть выбор самоподписанного сертификата, лишь эмулирующего работу реального протокола.
Остальные проблемы обычно скрываются на локальном компьютере:
- Произошел сброс системного времени.
- Неправильно настроена антивирусная программа.
- Сбоит браузер или установленное расширение.
- Срабатывает вредоносный скрипт.
Чтобы выяснить настоящую причину, пользователю браузера рекомендуется проверить все перечисленные факторы. При том же заражении компьютерными вирусами возможно проявление сразу нескольких симптомов – от изменения текущего времени и блокировки антивирусом до подключения перенаправления страниц в браузере и других неприятностей.
Изредка встречаются ситуации, когда проблема возникла со стороны администратора, если он ошибся при подключении нового сертификата или забыл продлить его действие. Обычно такие неполадки устраняются быстро, потому что после активации сайт проверяется и, в случае неработоспособности сертификата, проводится повторное подключение вплоть до получения положительного результата.
Время и дата
Сертификат SSL имеет четко обозначенный срок действия с датой активации и деактивации. Такой подход отчасти дает дополнительную защиту, потому что в случае технического сбоя в системных часах компьютера сайты перестают открываться. Сброс времени обычно происходит «назад», на дату изготовления материнской платы, на что и реагирует система.
Варианты исправления ситуации:
- Вручную внести корректную дату и время, после чего обновить страницу в браузере.
- Воспользоваться функцией синхронизации через интернет, встроенной в Windows.
- Заменить батарейку на памяти BIOS. При первом запуске ПК нужно внести корректные данные.
Каждый раз после изменения времени рекомендуется ручное обновление страницы или перезапуск браузера. Такой шаг активирует повторное соединение с сервером и позволяет зайти на сайт «с нуля», но уже с правильным временем, соответствующим сроку действия сертификата SSL (после активации и до ее завершения).
Настройки антивируса и брандмауэра
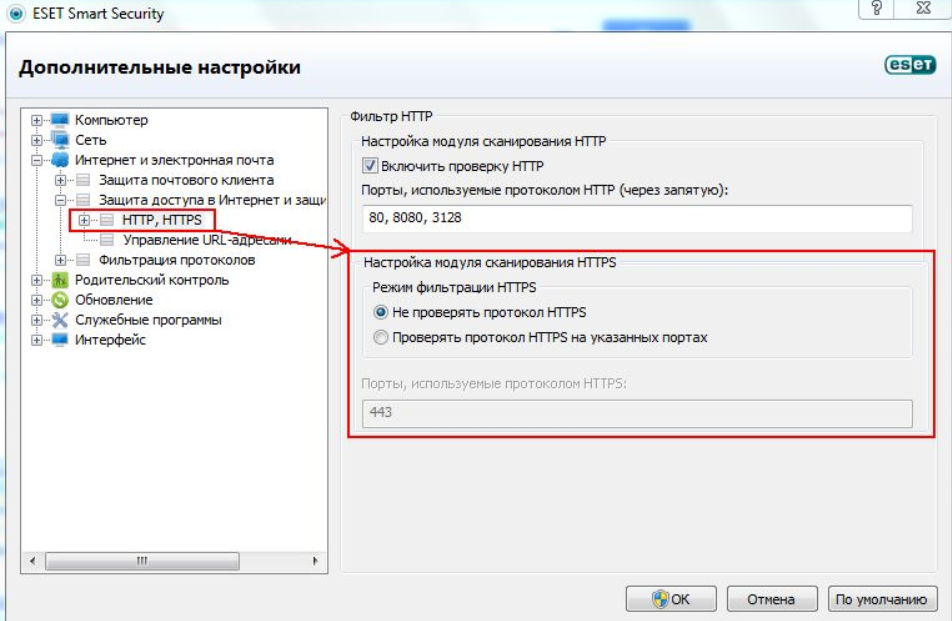
Программы для защиты компьютера от вирусов и хакерских атак иногда блокируют и «полезные» соединения, например, определенные домены или сразу весь протокол HTTPS, используемый при подключении сертификата SSL. Большинство антивирусов и брандмауэров проверяют его работу, и это становится причиной блокировки сайта как «злоумышленника, пытающего украсть данные».
Варианты исправления ситуации:
- Отключить режим «проверка протокола HTTPS». После этого зайти на сайт заново.
- Полностью выключить антивирусную программу. Перезагрузить ПК, открыть страницу.
- Сбросить настройки брандмауэра. Опять проводится перезапуск компьютера и веб-ресурса.
Функция временного отключения имеется в любой защитной программе, даже интегрированной в операционную систему Windows. Но это не гарантирует полную деактивацию приложения. В этом случае разобраться в ситуации поможет открытие сайта на другом компьютере или запуск безопасного режима (актуально для проводного подключения к интернету).
Браузер и операционная система
Наличие проблемы с браузером проще всего определить открытием сайта на другом устройстве или в другой программе. Иногда решение заключается в банальном обновлении версии приложения до актуальной. То же относится к операционной системе, если используется интегрированный браузер вроде Edge. Пакеты обновлений для того и выпускаются, чтобы устранять неполадки в ПО.
Варианты исправления ситуации:
- Полностью очистить историю браузера вместе с кэшем и другими данными.
- Временно отключить все ранее установленные и активные расширения.
- Переустановить программу после ее полной деинсталляции.
Остается еще один вариант – сбросить настройки браузера до состояния «по умолчанию». Способ аналогичен переустановке, но экономит время. Правда, он неэффективен, если проблема возникла из-за сбоя в одном из служебных файлов программы. Отдельное внимание стоит уделить расширению, выполняющему функции антивирусной защиты, ведь оно часто блокирует даже безопасное соединение.
Заражение компьютерными вирусами
Выдачей ошибки SSL браузер, вероятно, предупреждает о попытке его подмены, переадресации на сайт-клон или иной угрозе. В это случае рекомендуется провести полную проверку компьютера на наличие вирусов. Если присутствуют другие признаки заражения, стоит скачать парочку программ со свежими антивирусными базами (например, CureIt).
Варианты исправления ситуации:
- Временно отключить все программы из автозагрузки.
- Провести очистку диска от временных файлов.
- Перезагрузить компьютер после предыдущих шагов.
Выполняются перечисленные действия программами типа CCleaner. Они дают прямой доступ как к автозагрузке операционной системе, так и к списку расширений установленных браузеров. Также в таких программах обычно есть функция удаления ненужных системных файлов, в которых запросто может быть тело компьютерного вируса.
Если предложенные способы устранения ошибки SSL не помогли, остается ждать, пока проблему устранит администратор, или воспользоваться любым другим тематическим сайтом с аналогичным контентом.
Even if you do have an SSL certificate installed on your website, your users may run into the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error. Despite its intimidating name, the invalid certificate authority error isn’t something you should panic about.
Simply put, your browser doesn’t recognize the validity of your certificate. To keep you ‘safe’ it displays this error, so you’re aware that there’s something fishy going on. As the website owner, though, there are a lot of things you can do to fix the problem.
In this tutorial, we’ll talk about what the error message means, and how it looks in different browsers. Then we’ll teach you how to fix the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error by covering all of its likely causes.
Let’s get to work!
What Is NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID Error?
As the name of the error implies, this problem pops up when your browser can’t verify the validity of your website’s SSL certificate. If you haven’t set up a certificate or are using HTTP for your website, which isn’t recommended, you shouldn’t run into this error.
Generally speaking, there are three primary causes for the invalid certificate authority error. Let’s break down each one in turn:
- You’re using a self-signed SSL certificate. Using a self-signed certificate can save you money, but since browsers can’t verify its validity, your visitors may run into the error in question. Browser warnings can scare a lot of users away, so we recommend against this approach.
- Your certificate has expired. SSL certificates expire as a security precaution. How long your certificate lasts can vary, but at some point, you’ll need to renew it or automate the renewal process (some authorities and web hosts enable you to do this easily).
- The certificate comes from a non-trusted source. Just as with self-signed certificates, if browsers can’t verify the authority that generated your certificate, you’ll see an error.
Remember that every time a user visits a website with an SSL certificate, their browser needs to validate and decrypt it. If there are any errors during that process, they’ll see a warning.
In a lot of cases, browsers will actively prevent users from accessing the website in order to protect them. This often comes in the form of the “Your Connection is Not Private” error. As you might imagine, that’s a huge problem if it occurs on your own site.
Sometimes, you may run into the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error due to local configuration settings. Throughout the next sections, we’ll show you the many faces this error can take and then we’ll talk about how to troubleshoot it.
When you see a NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error message pop up, you might be concerned 😬. Despite its intimidating name, this invalid certificate authority error isn’t cause for alarm. 😅 Learn how to fix it in a few simple steps. ⬇️Click to Tweet
What Are the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID Error Variations?
The way an error appears can vary a bit, depending on what browser you’re using. Your operating system and your certificate’s configuration can also play a role in the different error messages that appear.
With that in mind, let’s take a look at the most common variations of the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error, browser by browser.
- Your connection is not private
- Warning: Potential Security Risk Ahead
- Your connection isn’t private
- This Connection Is Not Private
Google Chrome
When you run into this error in Chrome, the browser will tell you right away that your connection isn’t private. Since the browser doesn’t recognize your certificate’s validity, it can’t encrypt your data.
That means if you proceed, you do so at your own risk. Here’s what the error message looks like:
Attackers might be trying to steal your information from domain.com (for example, passwords, messages, or credit cards).
Common variations of this error in Chrome include the following codes:
- NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID
- NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID (This occurs when the certificate does not match the domain)
- NET::ERR_CERT_WEAK_SIGNATURE_ALGORITHM
- NET::ERR_CERTIFICATE_TRANSPARENCY_REQUIRED
- NET::ERR_CERT_DATE_INVALID
- SSL CERTIFICATE ERROR
In every case, Chrome pinpoints the source of the error within the certificate. The browser lets you proceed to the website if you choose, but it warns you against doing so.
Mozilla Firefox
Firefox doesn’t waste any time in telling you that you may have run into a potential security risk. What’s more, this browser does a better job than Chrome when it comes to explaining the potential causes and telling you not to panic.
Here’s how the primary error message reads:
Firefox detected an issue and did not continue to domain.com. The website is either misconfigured or your computer clock is set to the wrong time.It’s likely the website’s certificate is expired, which prevents Firefox from connecting securely. If you visit this site, attackers could try to steal information like your passwords, emails, or credit card details.
That variation of the error doesn’t include a specific code, though. In most cases, the screen will include one of the following codes as well:
- SEC_ERROR_UNKNOWN_ISSUER
- SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_HANDSHAKE
- MOZILLA_PKIX_ERROR_KEY_PINNING_FAILURE
- SEC_ERROR_REUSED_ISSUER_AND_SERIAL
If you see an error code like one of the above, make sure to copy it down somewhere. That is the browser’s way of telling you where things went wrong. In our experience, a simple search for a specific error code is often enough to help you find a quick solution.
Microsoft Edge
The Microsoft Edge error message you see below should look familiar. It’s almost identical to the message Chrome displays, right down to the included code:
The error can also come in different flavors, including the following:
- DLG_FLAGS_SEC_CERTDATE_INVALID
- DLG_FLAGS_INVALID_CA
- DLG_FLAGS_SEC_CERT_CN_INVALID
- NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID
- ERROR CODE: O
Just as with Chrome, these error messages give you some insight into what’s at the root of your NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error.
Safari
If you’re a Safari user, you’ll run into a variation of the ‘this connection is not private’ error, which lets you know there’s a problem with the website’s certificate and encryption. Here’s what the message says:
This website may be impersonating “domain.com” to steal your personal or financial information. You should go back to the previous page.
That particular error is due to an expired certificate. As we mentioned before, expired certificates are one of the most common causes of the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error.
How to Fix the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID Error (9 Methods)
Now that you know what it looks like across most major browsers, it’s time to check out how to solve the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error. Earlier, we talked about its most common causes. However, we also mentioned that your local configuration can trigger it in some cases.
That means there are a lot of potential solutions to this issue. To keep things simple, we’ll start by tackling the three most common culprits, i.e. expired, self-signed, and ‘untrustworthy’ certificates. Then we’ll move on to more general solutions.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
1. Run an SSL Server Test
If you installed your SSL certificate shortly before the error began appearing, something may have gone wrong during the setup process. That can often happen if you installed the certificate manually, instead of through your web host.
The easiest way to check and see if your certificate is properly installed is by using an SSL check tool, such as the one offered by Qualys SSL Labs. This particular tool is free to use.
All you have to do is enter the domain where the error is popping up, and click on the Submit button:
Now, wait a couple of minutes while the results come up. Ideally, you should get an A+, with perfect scores for all your certificates:
If you don’t get a perfect score, scroll down to the list of certificates the tool shows you. There should be a section that tells you whether your certificate is trusted or not. If the tool gives you a negative result, then you’ll need to install a certificate from a trusted source instead.
2. Get a Certificate from a Valid Authority
There’s no excuse to use a self-signed certificate these days. If cost is the only factor, you can get a free certificate from Let’s Encrypt. Since it’s a valid authority, every browser will recognize your certificate’s validity:
If you’re a Kinsta user, we can help you set up your free Let’s Encrypt certificate in a matter of click through your MyKinsta dashboard:
For some websites, however, you’ll need more than a free certificate. Free certificates need to be renewed often, which can be a chore. Premium certificates offer more perks, such as insurance in the case of data breaches, encryption for multiple domains, and more.
For ecommerce sites, in particular, it can be worth it to pay for a premium SSL certificate. If you do buy a certificate, make sure it’s from a valid authority, in order to avoid running into the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error.
3. Renew Your SSL Certificate
SSL certificates need to be renewed every so often for security purposes. The renewal process verifies your domain’s ‘identity’, and without it, certificates would lose some of their validity. Free certificates from Let’s Encrypt renew every 90 days, whereas paid options have longer lifespans.
Check Out Our Video Guide to Choosing The Best SSL Certificate For Your Site
When the term is up, you’ll need to renew your certificate manually if your web host doesn’t handle that for you. In any case, Let’s Encrypt will contact you when your certificate is about to expire, so you can renew it ahead of time. Depending on which web host you use, however, you might not get access to renewal options through your control panel.
If you have access to your server, you can use the Certbot tool to install and renew SSL certificates through the command line.
Once you renew your SSL certificate, try loading your website again to see if the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error persists.
4. Try Reloading the Page (Or Using Incognito Mode)
If neither of the above fixes worked, it’s time to start troubleshooting directly from your computer.
In many cases, the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error disappears on its own when you try to reload the page. It only takes a second to do so, so it doesn’t hurt to try.
If the error persists across multiple reloads, we recommend that you try accessing the website using an ‘incognito mode’ if your browser offers that option:
If the website loads fine in incognito mode, that means the error is likely caused by your browser attempting to load an outdated cached version of the page. That gives you enough information to tackle the problem directly (as we’ll see in the next section).
5. Clear Your Browser’s Cache and Cookies
If switching your browser to incognito mode made the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error go away, then the issue is probably related to your browser’s cache.
Clearing your cache and cookies is easy, but the process varies depending on which browser you’re using. Below you can find instructions for clearing the cache in all the major browsers:
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Google Chrome
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Mozilla Firefox
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Safari
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Internet Explorer
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Microsoft Edge
- How to Clear Browser Cache for Opera
Another solution can be to try and force refresh your website specifically, so you don’t have to delete your entire cache. Force refreshing sometimes doesn’t work, however, so clearing your cache is our recommended solution.
6. Sync Your Computer’s Clock
One of the most common causes for the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID is because your computer has the wrong date or time set. To clarify, errors with your device’s clock can interfere with your browser’s ability to verify a website’s certificate.
The good news is that if this is the problem, it’s an easy fix. If you notice a discrepancy between your computer’s clock and the current time, you can adjust it in seconds. Exactly how you do this will depend on which Operating System (OS) you’re using.
Windows
Go to the system tray and right-click on your computer’s time, then select the option that says Adjust date/time:
A settings window will appear. Look for the option that reads Sync now under Synchronize your clock, and click on it: Syncing your computer clock.
If you have an internet connection, Windows will make sure the date and time are correct. To avoid this issue in the future, we recommend that you enable the Set time automatically option. This setting should ensure that your computer always has the correct time.
Mac
If you’re using macOS, the syncing process is also remarkably simple. All you have to do is follow these steps:
- Select the System Preferences option within the Apple menu.
- Click on the Date & Time icon.
- Turn on the Set date & time automatically option.
Before you close the settings screen, swing by the Time Zone tab and make sure you’re using the correct time zone. Once that’s done, you can check to see if the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error still persists.
7. Try Using a Different Network
In some cases, the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error pops up when you’re using a public network, such as the ones you can find in coffee shops or tourist spots. These networks often don’t route traffic securely, which can trigger the error.
If you’re using a public network for your computer, we recommend trying to access your website through your smartphone using its mobile data. Your goal here is to determine whether the original network was causing the problem.
If the error disappears when you’re using mobile data, then you know you need to switch networks. Another option to protect your privacy if you regularly use public internet access is to sign up for a Virtual Private Network (VPN).
A good VPN service will help protect your data even if you’re using an unsecured point of access. You will need to pay if you want to use a quality VPN service, but the expense is well worth it if you’re always on the move.
8. Disable Your VPN or Antivirus Software
If you’re already using a VPN and you run into the NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error, the service itself may be triggering it.
Another common culprit is antivirus software. After you’ve tried everything else, we recommend that you temporarily turn off your VPN and disable your antivirus software. Then try accessing your site again and use force refresh to make sure it’s not loading from your browser’s cache.
If the error is gone, try re-enabling both services, one at a time, and see if you get the invalid certificate notification once more. This will let you know which is at fault. You may then choose to try and update the software, contact its support team for help, or look for an alternative solution.
9. Wipe Your Computer’s SSL State
Your computer keeps cached copies of certificates from websites you visit on a temporary basis, so it doesn’t have to run through the entire verification process each time you access them.
You can think of your SSL state as a cache, only for certificates. Just as with your cache, you can wipe your computer’s SSL state when you run into invalid certificate authority errors.
In Windows, you can do this by accessing the Internet Options menu from your control panel, and moving to the Content tab:
Click on the button that says Clear SSL state, close the window, and try reloading your website.
If you’re using macOS, and have accepted an untrusted certificate in the past, you may need to delete the certificate exception created for it from your Mac Keychain.
To do this, click on the Finder icon, followed by Go > Utilities > Keychain Access:
Under the Category section, select Certificates. Any untrusted certificates should have a red ‘X’ under their names. To delete them, click on Edit at the top of the screen, followed by Delete.
The NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID might look scary 😱, but this guide will give you the tools you need to tackle it across browsers 💪Click to Tweet
Summary
The NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error can take a while to troubleshoot if you’re unable to determine what’s causing it. Plus, if your visitors are seeing it as well, that can harm both your traffic and your reputation.
The good news is that most fixes take little time to implement. You’ll want to start by making sure your SSL certificate is up to date and valid, then perform some basic troubleshooting tasks such as reloading the page and clearing your browser’s cache.
After that, you can move on to more involved fixes, like wiping your SSL state and running an SSL server test.
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275 PoPs worldwide
Test it yourself with $20 off your first month of Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
If you have a website and even if you have installed the SSL certificate, it is possible that your users will run into the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error.
This problem is also known as an invalid certificate authority error, this occurs when the browser used by the user visiting the website does not recognize the SSL certificate as a valid certificate.
In the following article, How to solve the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error, we will see what an SSL certificate is and what causes the error.
After seeing the reasons for the error, we will look at possible solutions to solve it.
What is an SSL certificate
The SSL certificate is part of a network protocol for securing communications between the client (i.e., the browser) and the server on which the Web site is hosted.
This certificate specifically ensures that website navigation is encrypted and that connections are established through a secure connection.
Therefore, whenever a user browses a website that has an SSL certificate, they are browsing a secure site that protects their personal information, data, and credit card information.
This makes it possible to ensure that any customer or user data is secure and cannot be intercepted by unauthorized persons or individuals.
If the browser fails to verify that the site’s SSL certificate is valid, it may display a warning with the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error. This notice is intended to inform you that the site does not use a secure or private connection.
How is the SSL certificate obtained?
Nowadays, the SSL certificate comes with hosting. Each provider provides its potential customers with a number of different packages for purchasing hosting or servers, all of which now generally come with an SSL Certificate included.
If you have recently adopted the secure protocol, going from http to https, you need to generate the SSL certificate.
All of our hosting plans include the SSL certificate which is activated automatically. If, however, you need to install the SSL certificate before automatic activation, you can follow our tutorial on how to install the SSL certificate for free and check its status.
Now that we have seen how to get an SSL certificate, let’s see what the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error looks like.
What is the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error?
As you may have already understood by now, the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error occurs when the browser cannot recognize the validity of your SSL certificate.
The reasons why this error occurs can be different, but in general we can point to three main issues.
The SSL certificate is self-signed.
If the certificate you are using is self-signed, browsers will not be able to check its validity. This means that they will treat it as non valid SSL certificate and will display an ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error warning the users trying to access your site.
Many users at the sight of this warning message choose to turn away from the site and seek the desired information or product elsewhere. This can, therefore, represent an economic loss.
The certificate has expired
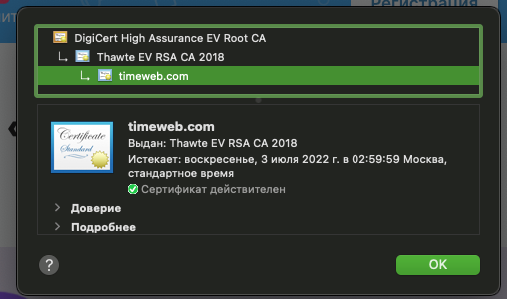
You can check the expiration of the certificate from the browser. You just click on the icon shaped like a padlock, an i, or a triangle in case an error appears on the site and then click on Certificate. You will then be able to see the expiration indicated in the “Valid from xx/xx/xxx to” section.

SSL certificates have a limited and variable duration, when they expire they must be renewed to prevent them from becoming invalid. As we will see later, there are also cases where renewal occurs automatically because it is completely managed by the provider.
The certificate is not trusted
The certificate you have chosen to purchase comes from an untrusted source, so the browser cannot verify the authenticity of who generated the certificate and the error will appear. SSL certificates must, in fact, be issued by an authorized body (Certification Authority).
What actually happens in these cases?
This is what happens when an issue of the kind we have just seen has occurred.
The user clicks on the desired search result (your website listed in the search engine SERP) and the loading of the site is interrupted by presenting an error page.
The web page will report the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error and ask the user if he/she intends to continue browsing the site even though it is not secure or if he/she wants to abandon it instead.
The user doesn’t even have time to see your Web site if they don’t first agree that they want to continue. This type of error makes it, in fact, unable to reach site and, in most cases, the user abandons the website and moves on to another one that is more secure and reliable.
This is because nowadays online security is prioritized, so when faced with an issue that manifests an error and informs us that we are entering an unsafe site, we prefer not to risk it and abandon it.
This is a huge problem because it will inevitably hurt you. From an economic point of view, if you have an online sales site for products or services, you will see your sales inevitably drop.
At the same time, however, with more and more users abandoning your website and the number of visits dropping, the search engine will tend to penalize you by negatively changing your position within the SERP.
That’s why, should your site experience a similar issue, it’s a good idea to take immediate action.
Variants of the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error
Depending on the browser we are using, the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error can occur in several variations.
Let’s see what kind of alerts the different browsers show us.
Google Chrome
Google Chrome is definitely the most widely used browser in the world. When encountering an ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error with this browser, the warning web page will inform the user that the connection is not private.
The site is not blocked altogether, but the user is left with the choice of whether to access it or not. Obviously by accessing the site the user takes the risk and responsibility of browsing an unprotected site.
We need to get into the mindset that entering an unsecured site puts us at risk, because any malicious parties may try to steal data, for example personal information or credit card details. But also passwords, pins or usernames to access personal profiles, banking and so on.
Google Chrome can detect several variants of the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error, here are te following:
- NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID.
- NET::ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID
- NET::ERR_CERT_WEAK_SIGNATURE_ALGORITHM
- NET::ERR_CERTIFICATE_TRANSPARENCY_REQUIRED
- ERR-CERTIFICATE TRANSPARENCY REQUIRED.
- NET::ERR_CERT_DATE_INVALID
- SSL CERTIFICATE ERROR.
All of these errors are at the root of issues encountered with the SSL certificate.
Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox goes into more detail and in addition to warning you of the security risks you may run into on the site, it offers an extended message explaining what may happen. Here is the message it presents:
In this case Firefox does not include a specific code, but may in some cases report one of the following statements:
- SEC_ERROR_UNKNOWN_ISSUER
- SSL_ERROR_RX_MALFORMED_HANDSHAKE
- MOZILLA_PKIX_ERROR_KEY_PINNING_FAILURE
- SEC_ERROR_REUSED_ISSUER_AND_SERIAL
Microsoft Edge
Here is the error code that Microsoft Edge will show you: ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID.
As with Chrome, even on Microsoft Edge we can run into some variants of this code, here are the most frequent ones:
- DLG_FLAGS_SEC_CERTDATE_INVALID
- DLG_FLAGS_INVALID_CA
- DLG_FLAGS_SEC_CERT_CN_INVALID
- ERR_CERT_COMMON_NAME_INVALID
- ERROR CODE: 0.
Opera
On Opera the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error is very similar to what appears on Google Chrome. The browser reports the error code and warns us that “the connection is not reserved.”
Other variations of the error on this browser include the following:
- NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID
- NET::ERR_CERT_INVALID
- NET::ERR_CERT_WEAK_SIGNATURE_ALGORITHM
- SSL certificate error.
Safari
On Safari the error occurs in the variant “This connection is not private.” Again, the browser alerts us by telling us that:
“This website may impersonate (domain of the website in question) to steal your personal or financial information. You should return to the previous page.”
If we view the details of the error, the browser can provide us with more detailed information about the problem, for example by warning us that the site’s certificate has expired or is invalid, as in this example below.
To get more details, again we can view the certificate directly from the browser. This way we can figure out what is causing the error. In this specific case that I show you below, the site uses a self-signed certificate.
How to solve ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error
Now that we know what an ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error is, what issues we can run into, and how the error is shown to us on different browsers, it’s time to find out how we can solve this problem.
As we will see, there are several possible solutions to solve the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error. Therefore, in the next paragraphs, let’s go over the details on how to deal with the different issues.
Check the validity of the SSL certificate
If the message appears after installing our SSL certificate, it is important to verify that the installation was done correctly.
During the installation process mistakes are bound to happen and you might not notice them right away. This happens especially when you choose to install the certificate manually.
There is a testing tool that will allow you to run a test and verify that the installation was done correctly. You can find several platforms that offer you this possibility online, for example Qualys SSL Labs offers a free verification tool.
The test you are going to run will allow you to see what problem has occurred. These tests will also allow you to see whether or not your SSL certificate is trusted.
In this example, the tool helps us identify the cause of the error, which is a self-signed certificate.
If the test shows that there are errors, then you can follow the suggestions shown to solve them. For example, if there are problems about the trustworthiness of the certificate, you will need to install one issued by a trusted entity.
Choose to purchase an authoritative certificate.
Today it is possible to obtain authoritative certificates without any problem so there is no point in using a self-signed certificate that will make visitors to your site come across the error ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID.
In case you do not want to incur a financial expense, you can get free certificates from Let’s Encrypt. This service provider is considered reliable by all browsers, so you will not encounter any problems with its certificates.
This solution is ideal in many cases, and to get your free certificate all you have to do is log on to the Let’s Encrypt Homepage.
On the other hand, it is not ideal when you want to create an ecommerce site that either deal with products or info-products or services. In this case it is, in fact, more suitable to use premium SSL certificates, which are always paid for.
This choice will allow you to provide your customers with more security when purchasing on your website. In this case, always remember to purchase SSL certificates from a valid authority recognized by browsers, so that you do not run into the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error.
Those who opt for the free version and get it directly from the Let’s Encrypt site, should remember that since it is a free product it has a quick expiration date and you will therefore need to remember to update it.
With all of our plans starting from shared hostong, WordPress hosting, semidedicated hosting up to dedicated services such as VPS cloud hosting and dedicated server, we provide a free SSL certificate (Let’s Encrypt).
If you use our services, SSL certificate installation and activation is done automatically. SSL certificate renewal is also automatic, so you won’t have to worry about renewing it when it expires.
Renew your SSL certificate.
We mentioned that another frequent issue is, to be faced with an expired certificate; for security reasons, every certificate must be renewed at a specific cadence.
This speed of expiration is additional protection for you and your users-for example, free certificates tend to expire every 90 days or so, while paid options far exceed this time frame.
Unless we have automated everything, we will have to remember to renew the various certificates otherwise users trying to access our site will run into the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error message.
The procedure for renewal varies depending on where you purchased the certificate and then by host. Many hosts do not allow you to access the renewal settings for the various SSL certificates, while others allow you to renew them even before they expire.
In our case, as we said before, the renewal of Let’s Encrypt SSL certificate is done automatically.
How does your host work? Inform yourself during the purchase on how you should deal with the various renewals, whether they will be done automatically or you will have to do them yourself.
If your site encounters the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error and the problem is the expired certificate, just renew it and make sure the warning no longer appears.
Loading errors
Often the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error appears due to an error in page loading that may also be related to a connection issue.
In these cases the problem is momentary, in fact, you will only have to reload the page to see that the warning is no longer there.
That is why before you panic at the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error, it is good to run some tests and really understand what the problem is.
Cache problems
To check whether the problem is related to your browser cache, simply access your site by taking advantage of incognito mode in Google Chrome or another browser.
If this way the warning is gone, then it means that the problem is caused by your browser cache loading an older and outdated version of your website.
To solve the problem in this case you just need to clear the browser cache. Let’s see how you can clear your cache based on the browser you are using.
How to clear cache from Google Chrome
After opening Google Chrome, you will find an icon with three dots (⁝) in the upper right corner. Click the icon and you will see that a drop-down will open. From the menu click the Other Tools item and you will see a sub-menu open where you have to click the Delete browsing data item.
After that, select the data you want to delete. For example, you can delete cached files and cookies, but keep history and passwords.

After you click Clear Data, your cache will be wiped clean and you can return to browsing safely.
How to clear cache from Mozilla Firefox
For Mozilla Firefox, you need to open your browser and click on the menu in the upper right corner. Here select the history item and then Clear Recent History.

After a few minutes your browser will be back to browsing properly.
How to clear cache from Internet Explorer
In order to clear the cache from Internet Explorer you will have to click on the top right gear icon (tools menu).
In the menu that opens select the Security item, a submenu will open and you will have to click on Delete Browsing History.

How to clear cache from Safari
On Safari, by opening the browser, you will be able to click on the top menu the History item.
At this point in the new window you will have to click on Clear History.
After that you just choose the period, choosing all history will erase all of Safari’s history both recent and past.
However, if you want to clear only the cache and cookies then you can opt for another option, here’s what you need to do: enable the Development menu by going to preferences and clicking Advanced.
After that you can click on the Empty Cache item from the Development menu.

If, on the other hand, you want to delete all cookies from a single site, you can go to Settings -> Privacy and click on Manage Website Data.

After that you can delete the cookies you see listed.

How to clear the cache from Opera
Open Opera, click the icon in the upper left-hand corner and a menu will open. Among the various items you will have to select History and then Delete Browsing Data.
Opera will ask you to select the data you want to delete, then you should check only the Cached images and files box and click Delete data.

How to clear cache from Microsoft Edge
For Microsoft Edge you will need to click on the 3 dots icon in the upper right corner. Click on the Settings heading and search for “clear browsing data” in the search bar. Then click on Choose what to delete.
To only clear the cache you will need to check the box next to Cached images and files, as seen below.

Missing synchronization of the PC Clock.
Another problem that can cause the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error is that the PC clock is not synchronized, so your PC is marking the wrong date and time or only one of the two.
It may sound silly, but actually if your PC clock is not set correctly it can interfere with your browser and thus generate various errors.
Fortunately, everything can be solved in a few minutes; in fact, you only need to set the correct time and date on your PC to fix the error.
Then make sure you enter the correct date and time and reload the web page. If the error depended on the clock settings, you will see that the alert will no longer appear.
Let’s see how to set the clock according to your operating system.
Windows
On Windows you can change the settings by clicking on the clock that appears in the taskbar. Right-click on the time and then click on Adjust Date/Time.

After opening the settings you can set the date and time to update automatically. You just need to enable the Set time automatically option as you see shown below.
MAC
If you have a macOS operating system, let’s see what is the procedure by which you can change your date and time and resolve issues related to the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error.
Firstly, you will need to open System Preferences from the Apple menu.

After that click on Date and Time.
You will then need to check the option set date and time automatically.
Make sure the time zone is also correct. If the problem was the time or date was not synchronized, the error will be fixed.
Change the network
If you are using a public network, then it is possible that the error message will appear because of this. Public networks are those that we find in common areas that are open to the public such as parks, cafes, bars or hotels.
These networks have very high traffic and are not always secure, which is why you may encounter the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error. To check if this is really the problem you just need to access the website using another network.
You can, for example, take advantage of your mobile network, so you have two options either try to access the website using your smartphone or you can share the mobile connection with your computer via tethering.
If this way the error does not occur, then you only need to use a different network than the one you were using.
If you often work in public places and take advantage of public wi-fi networks, one way to protect yourself is to rely on the virtual private network known by the acronym VPN.
This network allows every user to browse in total security, of course it is not a public network but a private network and is chargeable.
Online you can also come across free VPNs but they do not perform well, so if you want to explore this option, it is best to purchase a good service. VPN allows you to protect all your data even if you have taken advantage of an unsecured access point.
Disable the VPN or antivirus.
If you are already using a VPN it is possible that the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error code is due to it, so the option is to try temporarily disabling it.
Antivirus may also be the cause of the appearance of the error because it recognizes the site as invalid. In the case of both VPN and antivirus, it is good to do a test run.
The test is to disable the service and see if the website is working properly, if yes then the problem is one of the two services. Try reactivating one at a time, if you use both, to see which one is generated by which one.
Once the service causing the error is identified, the solution is to contact the support team and request assistance or try clearing the cache and reloading the page.
Remove SSL status from PC.
Your PC tends to keep a cached copy of the various SSL certificates of the websites you have visited for a short time, this is to achieve better browsing results and not have to re-run the whole identification procedure each time.
You can try clearing the computer’s SSL status to try to resolve the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error. To do so you will need to change some settings. This procedure can also help you resolve other errors such as err_ssl_version_or_cipher_mismatch error. Let’s see how to do it in the next paragraphs.
Windows
On Windows open the Control Panel and click on Internet Options. Then enter the contents tab and click on Clear SSL State.

Now all you have to do is verify that the problem has disappeared, then go back to the site and reload the page.
MAC
If you’re using macOS you’ll have to go and delete the certificate directly in the Mac’s keychain. So click on the Finder icon and select GO, then select Utilities and from the submenu select Keychain Access.
Now that you are inside the keychain, you have the ability to take action and delete what you are interested in, this solution proves useful when in the past we have agreed to access a website that had an invalid certificate.
So our operating system has registered this option in this section and allows us to change the settings by deleting that certificate.
Now we must therefore select category and finally certificates. All certificates that show a red X are unreliable so you can delete them by selecting Edit at the top of the screen and finally Delete them.
Conclusion
In this article, How to solve the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error, we have taken you through the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error that is particularly common and easy to run into.
We have seen what the error looks like on different browsers and what are its possible variants.
We’ve explained what an SSL certificate is, how to purchase it, and which ones are most suitable based on the site. And finally we saw what are the reasons that cause the ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID error and how you can solve them, one by one.
Were you able to resolve the error? What was the cause in your case? Let me know in the comments below.