Ошибки¶
Приложения, работающие в Node.js, обычно сталкиваются с четырьмя категориями ошибок:
- Стандартные ошибки JavaScript, такие как {EvalError}, {SyntaxError}, {RangeError}, {ReferenceError}, {TypeError} и {URIError}.
- Системные ошибки, вызванные ограничениями базовой операционной системы, такими как попытка открыть несуществующий файл или попытка отправить данные через закрытый сокет.
- Пользовательские ошибки, вызванные кодом приложения.
AssertionErrors — это особый класс ошибок, который может быть вызван, когда Node.js обнаруживает исключительное логическое нарушение, которое никогда не должно происходить. Обычно они поднимаютсяassertмодуль.
Все ошибки JavaScript и системные ошибки, вызванные Node.js, наследуются от стандартного класса {Error} JavaScript или являются его экземплярами и гарантированно предоставляют по меньшей мере свойства, доступные в этом классе.
Распространение ошибок и перехват¶
Node.js поддерживает несколько механизмов распространения и обработки ошибок, возникающих во время работы приложения. То, как эти ошибки сообщаются и обрабатываются, полностью зависит от типа Error и стиль вызываемого API.
Все ошибки JavaScript обрабатываются как исключения, которые немедленно генерировать и выдавать ошибку с помощью стандартного JavaScript throw механизм. Они обрабатываются с помощью try…catch строить предоставляется языком JavaScript.
// Throws with a ReferenceError because z is not defined.
try {
const m = 1;
const n = m + z;
} catch (err) {
// Handle the error here.
}
Любое использование JavaScript throw механизм вызовет исключение, которое должен обрабатываться с использованием try…catch или процесс Node.js немедленно завершится.
За некоторыми исключениями, Синхронный API (любой метод блокировки, не принимающий callback функция, например fs.readFileSync), буду использовать throw сообщать об ошибках.
Ошибки, возникающие внутри Асинхронные API можно сообщить несколькими способами:
- Большинство асинхронных методов, которые принимают
callbackфункция приметErrorобъект, переданный в качестве первого аргумента этой функции. Если этот первый аргумент неnullи является экземпляромError, то произошла ошибка, которую необходимо обработать.
const fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('a file that does not exist', (err, data) => {
if (err) {
console.error(
'There was an error reading the file!',
err
);
return;
}
// Otherwise handle the data
});
- Когда асинхронный метод вызывается для объекта, который является
EventEmitter, ошибки могут быть перенаправлены на этот объект'error'событие.
const net = require('net');
const connection = net.connect('localhost');
// Adding an 'error' event handler to a stream:
connection.on('error', (err) => {
// If the connection is reset by the server, or if it can't
// connect at all, or on any sort of error encountered by
// the connection, the error will be sent here.
console.error(err);
});
connection.pipe(process.stdout);
- Некоторые обычно асинхронные методы в API Node.js могут по-прежнему использовать
throwмеханизм для создания исключений, которые должны обрабатываться с помощьюtry…catch. Исчерпывающего списка таких методов нет; обратитесь к документации по каждому методу, чтобы определить соответствующий требуемый механизм обработки ошибок.
Использование 'error' механизм событий наиболее распространен для потоковый а также на основе эмиттера событий API-интерфейсы, которые сами по себе представляют собой серию асинхронных операций с течением времени (в отличие от одной операции, которая может пройти или закончиться неудачей).
Для все EventEmitter объекты, если 'error' обработчик событий не предоставляется, будет выдана ошибка, в результате чего процесс Node.js сообщит о неперехваченном исключении и завершится сбоем, если только одно из следующих событий: domain модуль используется надлежащим образом или обработчик зарегистрирован для 'uncaughtException' событие.
const EventEmitter = require('events');
const ee = new EventEmitter();
setImmediate(() => {
// This will crash the process because no 'error' event
// handler has been added.
ee.emit('error', new Error('This will crash'));
});
Ошибки, сгенерированные таким образом не мочь быть перехваченным с помощью try…catch как они брошены после код вызова уже вышел.
Разработчики должны обращаться к документации по каждому методу, чтобы точно определить, как распространяются ошибки, вызванные этими методами.
Обратные вызовы при первой ошибке¶
Большинство асинхронных методов, предоставляемых основным API Node.js, следуют идиоматическому шаблону, называемому обратный вызов при первой ошибке. В этом шаблоне функция обратного вызова передается методу в качестве аргумента. Когда операция завершается или возникает ошибка, вызывается функция обратного вызова с Error объект (если есть) передается в качестве первого аргумента. Если ошибки не возникло, первый аргумент будет передан как null.
const fs = require('fs');
function errorFirstCallback(err, data) {
if (err) {
console.error('There was an error', err);
return;
}
console.log(data);
}
fs.readFile(
'/some/file/that/does-not-exist',
errorFirstCallback
);
fs.readFile(
'/some/file/that/does-exist',
errorFirstCallback
);
JavaScript try…catch механизм не мочь использоваться для перехвата ошибок, генерируемых асинхронными API. Распространенная ошибка новичков — пытаться использовать throw внутри обратного вызова с ошибкой:
// THIS WILL NOT WORK:
const fs = require('fs');
try {
fs.readFile(
'/some/file/that/does-not-exist',
(err, data) => {
// Mistaken assumption: throwing here...
if (err) {
throw err;
}
}
);
} catch (err) {
// This will not catch the throw!
console.error(err);
}
Это не сработает, потому что функция обратного вызова передана в fs.readFile() вызывается асинхронно. К моменту вызова обратного вызова окружающий код, включая try…catch блок, уже вышли. Выдача ошибки внутри обратного вызова может привести к сбою процесса Node.js в большинстве случаев. Если домены включены, или обработчик был зарегистрирован с process.on('uncaughtException'), такие ошибки можно перехватить.
Класс: Error¶
Общий объект JavaScript {Error}, не указывающий на конкретную причину возникновения ошибки. Error объекты фиксируют «трассировку стека», детализирующую точку в коде, в которой Error был создан, и может содержать текстовое описание ошибки.
Все ошибки, генерируемые Node.js, включая все системные ошибки и ошибки JavaScript, будут либо экземплярами, либо унаследованы от Error класс.
new Error(message)¶
message{нить}
Создает новый Error объект и устанавливает error.message в предоставленное текстовое сообщение. Если объект передается как message, текстовое сообщение создается при вызове message.toString(). В error.stack свойство будет представлять точку в коде, в которой new Error() назывался. Трассировки стека зависят от API трассировки стека V8. Трассировки стека распространяются только на (а) начало синхронное выполнение кода, или (b) количество кадров, заданное свойством Error.stackTraceLimit, в зависимости от того, что меньше.
Error.captureStackTrace(targetObject[, constructorOpt])¶
targetObject{Объект}constructorOpt{Функция}
Создает .stack собственность на targetObject, который при доступе возвращает строку, представляющую место в коде, в котором Error.captureStackTrace() назывался.
const myObject = {};
Error.captureStackTrace(myObject);
myObject.stack; // Similar to `new Error().stack`
Первая строка трассировки будет иметь префикс ${myObject.name}: ${myObject.message}.
Необязательный constructorOpt Аргумент принимает функцию. Если указано, все кадры выше constructorOpt, включая constructorOpt, будет исключен из сгенерированной трассировки стека.
В constructorOpt Аргумент полезен для сокрытия деталей реализации генерации ошибок от пользователя. Например:
function MyError() {
Error.captureStackTrace(this, MyError);
}
// Without passing MyError to captureStackTrace, the MyError
// frame would show up in the .stack property. By passing
// the constructor, we omit that frame, and retain all frames below it.
new MyError().stack;
Error.stackTraceLimit¶
- {количество}
В Error.stackTraceLimit указывает количество кадров стека, собранных трассировкой стека (независимо от того, сгенерированы ли они new Error().stack или Error.captureStackTrace(obj)).
Значение по умолчанию — 10 но может быть установлен на любой допустимый номер JavaScript. Изменения повлияют на любую записанную трассировку стека. после значение было изменено.
Если установлено нечисловое значение или задано отрицательное число, трассировки стека не будут захватывать какие-либо кадры.
error.code¶
- {нить}
В error.code Свойство — это строковая метка, определяющая тип ошибки. error.code это наиболее стабильный способ выявления ошибки. Он будет меняться только между основными версиями Node.js. Наоборот, error.message строки могут меняться между любыми версиями Node.js. Видеть Коды ошибок Node.js для получения подробной информации о конкретных кодах.
error.message¶
- {нить}
В error.message свойство — это строковое описание ошибки, установленное при вызове new Error(message). В message переданный конструктору, также появится в первой строке трассировки стека Error, однако изменение этого свойства после Error объект создан может нет изменить первую строку трассировки стека (например, когда error.stack читается до изменения этого свойства).
const err = new Error('The message');
console.error(err.message);
// Prints: The message
error.stack¶
- {нить}
В error.stack свойство — это строка, описывающая точку в коде, в которой Error был создан.
Error: Things keep happening!
at /home/gbusey/file.js:525:2
at Frobnicator.refrobulate (/home/gbusey/business-logic.js:424:21)
at Actor.<anonymous> (/home/gbusey/actors.js:400:8)
at increaseSynergy (/home/gbusey/actors.js:701:6)
Первая строка отформатирована как <error class name>: <error message>, за которым следует серия кадров стека (каждая строка начинается с «at»). Каждый фрейм описывает сайт вызова в коде, который приводит к сгенерированной ошибке. V8 пытается отобразить имя для каждой функции (по имени переменной, имени функции или имени метода объекта), но иногда не может найти подходящее имя. Если V8 не может определить имя функции, для этого фрейма будет отображаться только информация о местоположении. В противном случае определенное имя функции будет отображаться с информацией о местоположении, добавленной в круглые скобки.
Фреймы создаются только для функций JavaScript. Если, например, выполнение синхронно проходит через дополнительную функцию C ++, называемую cheetahify который сам вызывает функцию JavaScript, фрейм, представляющий cheetahify вызов не будет присутствовать в трассировке стека:
const cheetahify = require('./native-binding.node');
function makeFaster() {
// `cheetahify()` *synchronously* calls speedy.
cheetahify(function speedy() {
throw new Error('oh no!');
});
}
makeFaster();
// will throw:
// /home/gbusey/file.js:6
// throw new Error('oh no!');
// ^
// Error: oh no!
// at speedy (/home/gbusey/file.js:6:11)
// at makeFaster (/home/gbusey/file.js:5:3)
// at Object.<anonymous> (/home/gbusey/file.js:10:1)
// at Module._compile (module.js:456:26)
// at Object.Module._extensions..js (module.js:474:10)
// at Module.load (module.js:356:32)
// at Function.Module._load (module.js:312:12)
// at Function.Module.runMain (module.js:497:10)
// at startup (node.js:119:16)
// at node.js:906:3
Информация о местоположении будет одной из следующих:
native, если кадр представляет внутренний вызов V8 (как в[].forEach).plain-filename.js:line:column, если фрейм представляет собой внутренний вызов Node.js./absolute/path/to/file.js:line:column, если кадр представляет собой вызов в пользовательской программе или ее зависимостях.
Строка, представляющая трассировку стека, генерируется лениво, когда error.stack собственность доступ.
Количество кадров, захваченных трассировкой стека, ограничено меньшим из Error.stackTraceLimit или количество доступных кадров в текущем тике цикла событий.
Класс: AssertionError¶
- Расширяется: {errors.Error}
Указывает на неудачу утверждения. Подробнее см. Class: assert.AssertionError.
Класс: RangeError¶
- Расширяется: {errors.Error}
Указывает, что предоставленный аргумент находится за пределами набора или диапазона допустимых значений для функции; является ли это числовым диапазоном или вне набора опций для данного параметра функции.
require('net').connect(-1);
// Throws "RangeError: "port" option should be >= 0 and < 65536: -1"
Node.js сгенерирует и выбросит RangeError экземпляры немедленно как форма подтверждения аргумента.
Класс: ReferenceError¶
- Расширяется: {errors.Error}
Указывает, что предпринимается попытка получить доступ к переменной, которая не определена. Такие ошибки обычно указывают на опечатки в коде или на некорректную программу.
Хотя клиентский код может генерировать и распространять эти ошибки, на практике это будет делать только V8.
doesNotExist;
// Throws ReferenceError, doesNotExist is not a variable in this program.
Если приложение динамически не генерирует и не запускает код, ReferenceError экземпляры указывают на ошибку в коде или его зависимостях.
Класс: SyntaxError¶
- Расширяется: {errors.Error}
Указывает, что программа не является допустимым JavaScript. Эти ошибки могут возникать и распространяться только в результате оценки кода. Оценка кода может произойти в результате eval, Function, require, или vm. Эти ошибки почти всегда указывают на неработающую программу.
try {
require('vm').runInThisContext('binary ! isNotOk');
} catch (err) {
// 'err' will be a SyntaxError.
}
SyntaxError экземпляры невозможно восстановить в контексте, который их создал — они могут быть перехвачены только в других контекстах.
Класс: SystemError¶
- Расширяется: {errors.Error}
Node.js генерирует системные ошибки, когда в среде выполнения возникают исключения. Обычно это происходит, когда приложение нарушает ограничение операционной системы. Например, системная ошибка произойдет, если приложение попытается прочитать несуществующий файл.
address{строка} Если присутствует, адрес, к которому не удалось подключиться к сети.code{строка} Код ошибки строкиdest{строка} Если присутствует, путь к файлу при сообщении об ошибке файловой системыerrno{number} Номер ошибки, предоставленный системойinfo{Object} Если присутствует, дополнительные сведения о состоянии ошибкиmessage{string} Предоставляемое системой описание ошибки в удобной для чтения форме.path{строка} Если присутствует, путь к файлу при сообщении об ошибке файловой системыport{number} Если присутствует, порт сетевого подключения, который недоступенsyscall{строка} Имя системного вызова, вызвавшего ошибку
error.address¶
- {нить}
Если представить, error.address — это строка, описывающая адрес, к которому не удалось установить сетевое соединение.
error.code¶
- {нить}
В error.code свойство — это строка, представляющая код ошибки.
error.dest¶
- {нить}
Если представить, error.dest — это путь к файлу при сообщении об ошибке файловой системы.
error.errno¶
- {количество}
В error.errno свойство — отрицательное число, которое соответствует коду ошибки, определенному в libuv Error handling.
В Windows номер ошибки, предоставленный системой, будет нормализован libuv.
Чтобы получить строковое представление кода ошибки, используйте util.getSystemErrorName(error.errno).
error.info¶
- {Объект}
Если представить, error.info — объект с подробной информацией о состоянии ошибки.
error.message¶
- {нить}
error.message представляет собой удобочитаемое описание ошибки, предоставляемое системой.
error.path¶
- {нить}
Если представить, error.path — строка, содержащая соответствующий недопустимый путь.
error.port¶
- {количество}
Если представить, error.port порт сетевого подключения недоступен.
error.syscall¶
- {нить}
В error.syscall свойство — это строка, описывающая системный вызов это не удалось.
Общие системные ошибки¶
Это список системных ошибок, которые часто встречаются при написании программы на Node.js. Полный список см. В errno(3) справочная страница.
-
EACCES(В разрешении отказано): была сделана попытка получить доступ к файлу способом, запрещенным его разрешениями на доступ к файлу. -
EADDRINUSE(Адрес уже используется): попытка привязать сервер (net,http, илиhttps) на локальный адрес не удалось из-за того, что другой сервер в локальной системе уже занимает этот адрес. -
ECONNREFUSED(В соединении отказано): соединение не может быть установлено, потому что целевая машина активно отказалась от него. Обычно это происходит из-за попытки подключиться к неактивной службе на чужом хосте. -
ECONNRESET(Сброс соединения одноранговым узлом): соединение было принудительно закрыто одноранговым узлом. Обычно это происходит из-за потери соединения с удаленным сокетом из-за тайм-аута или перезагрузки. Обычно встречается черезhttpа такжеnetмодули. -
EEXIST(Файл существует): существующий файл был целью операции, которая требовала, чтобы цель не существовала. -
EISDIR(Является каталогом): операция ожидала файл, но указанный путь был каталогом. -
EMFILE(Слишком много открытых файлов в системе): максимальное количество файловые дескрипторы допустимый в системе, и запросы для другого дескриптора не могут быть выполнены, пока хотя бы один из них не будет закрыт. Это происходит при одновременном открытии множества файлов одновременно, особенно в системах (в частности, macOS), где существует низкий предел дескрипторов файлов для процессов. Чтобы исправить низкий предел, запуститеulimit -n 2048в той же оболочке, которая будет запускать процесс Node.js. -
ENOENT(Нет такого файла или каталога): обычно создаетсяfsоперации, чтобы указать, что компонент указанного пути не существует. По указанному пути не удалось найти ни один объект (файл или каталог). -
ENOTDIR(Не каталог): компонент с указанным путем существует, но не является каталогом, как ожидалось. Обычно выращиваетсяfs.readdir. -
ENOTEMPTY(Каталог не пустой): каталог с записями был целью операции, для которой требуется пустой каталог, обычноfs.unlink. -
ENOTFOUND(Ошибка поиска DNS): указывает на сбой DNS либоEAI_NODATAилиEAI_NONAME. Это не стандартная ошибка POSIX. -
EPERM(Операция запрещена): была сделана попытка выполнить операцию, требующую повышенных привилегий. -
EPIPE(Сломанный канал): запись в канал, сокет или FIFO, для которого нет процесса для чтения данных. Часто встречается наnetа такжеhttpУровни, указывающие на то, что удаленная сторона записываемого потока была закрыта. -
ETIMEDOUT(Превышено время ожидания операции): запрос на подключение или отправку завершился неудачно, поскольку подключенная сторона не ответила должным образом по прошествии определенного периода времени. Обычно встречаетсяhttpилиnet. Часто признак того, чтоsocket.end()не был должным образом назван.
Класс: TypeError¶
- Расширяет {errors.Error}
Указывает, что указанный аргумент не является допустимым типом. Например, передача функции параметру, который ожидает строку, будет TypeError.
require('url').parse(() => {});
// Throws TypeError, since it expected a string.
Node.js сгенерирует и выбросит TypeError экземпляры немедленно как форма подтверждения аргумента.
Исключения против ошибок¶
Исключение JavaScript — это значение, которое выбрасывается в результате недопустимой операции или как цель throw утверждение. Хотя не требуется, чтобы эти значения были экземплярами Error или классы, которые наследуются от Error, все исключения, создаваемые Node.js или средой выполнения JavaScript буду быть экземплярами Error.
Некоторые исключения безвозвратно на уровне JavaScript. Такие исключения будут всегда вызвать сбой процесса Node.js. Примеры включают assert() чеки или abort() вызывает в слое C ++.
Ошибки OpenSSL¶
Ошибки, возникающие в crypto или tls классные Error, и в дополнение к стандартному .code а также .message properties, могут иметь некоторые дополнительные свойства, специфичные для OpenSSL.
error.opensslErrorStack¶
Массив ошибок, который может дать контекст, откуда в библиотеке OpenSSL возникла ошибка.
error.function¶
Функция OpenSSL, в которой возникла ошибка.
error.library¶
Библиотека OpenSSL, в которой возникла ошибка.
error.reason¶
Строка в удобном для чтения виде, описывающая причину ошибки.
ABORT_ERR¶
Используется, когда операция была прервана (обычно с использованием AbortController).
API нет с использованием AbortSignals обычно не вызывают ошибки с этим кодом.
Этот код не использует обычный ERR_* соглашение об ошибках Node.js используется для обеспечения совместимости с веб-платформой. AbortError.
ERR_AMBIGUOUS_ARGUMENT¶
Аргумент функции используется таким образом, чтобы предположить, что сигнатура функции может быть неправильно понята. Это брошено assert модуль, когда message параметр в assert.throws(block, message) совпадает с сообщением об ошибке, выданным block потому что это использование предполагает, что пользователь верит message ожидаемое сообщение, а не сообщение AssertionError будет отображаться, если block не бросает.
ERR_ARG_NOT_ITERABLE¶
Итерируемый аргумент (т.е. значение, которое работает с for...of loops) требуется, но не предоставляется API Node.js.
ERR_ASSERTION¶
Особый тип ошибки, которая может быть вызвана всякий раз, когда Node.js обнаруживает исключительное логическое нарушение, которое никогда не должно происходить. Обычно они поднимаются assert модуль.
ERR_ASYNC_CALLBACK¶
Была сделана попытка зарегистрировать что-то, что не является функцией, как AsyncHooks Перезвоните.
ERR_ASYNC_TYPE¶
Недопустимый тип асинхронного ресурса. Пользователи также могут определять свои собственные типы при использовании общедоступного API для встраивания.
ERR_BROTLI_COMPRESSION_FAILED¶
Данные, переданные в поток Brotli, не были успешно сжаты.
ERR_BROTLI_INVALID_PARAM¶
Во время построения потока Brotli был передан недопустимый ключ параметра.
ERR_BUFFER_CONTEXT_NOT_AVAILABLE¶
Была сделана попытка создать Node.js Buffer из кода надстройки или встраивания, находясь в контексте механизма JS, который не связан с экземпляром Node.js. Данные, переданные в Buffer будет выпущен к тому времени, когда метод вернется.
При возникновении этой ошибки возможная альтернатива созданию Buffer пример — создать нормальный Uint8Array, который отличается только прототипом результирующего объекта. Uint8Arrays общеприняты во всех основных API Node.js, где Buffers есть; они доступны во всех контекстах.
ERR_BUFFER_OUT_OF_BOUNDS¶
Операция за пределами Buffer была предпринята попытка.
ERR_BUFFER_TOO_LARGE¶
Была сделана попытка создать Buffer больше максимально допустимого размера.
ERR_CANNOT_WATCH_SIGINT¶
Node.js не смог отследить SIGINT сигнал.
ERR_CHILD_CLOSED_BEFORE_REPLY¶
Дочерний процесс был закрыт до того, как родительский процесс получил ответ.
ERR_CHILD_PROCESS_IPC_REQUIRED¶
Используется, когда дочерний процесс разветвляется без указания канала IPC.
ERR_CHILD_PROCESS_STDIO_MAXBUFFER¶
Используется, когда основной процесс пытается прочитать данные из STDERR / STDOUT дочернего процесса, и длина данных больше, чем maxBuffer вариант.
ERR_CLOSED_MESSAGE_PORT¶
Была попытка использовать MessagePort экземпляр в закрытом состоянии, обычно после .close() был вызван.
ERR_CONSOLE_WRITABLE_STREAM¶
Console был создан без stdout поток, или Console имеет незаписываемый stdout или stderr транслировать.
ERR_CONSTRUCT_CALL_INVALID¶
Был вызван конструктор класса, который нельзя вызвать.
ERR_CONSTRUCT_CALL_REQUIRED¶
Конструктор класса был вызван без new.
ERR_CONTEXT_NOT_INITIALIZED¶
Контекст vm, переданный в API, еще не инициализирован. Это может произойти при возникновении (и обнаружении) ошибки во время создания контекста, например, при сбое выделения или при достижении максимального размера стека вызовов при создании контекста.
ERR_CRYPTO_CUSTOM_ENGINE_NOT_SUPPORTED¶
Был запрошен механизм сертификатов клиента, который не поддерживается используемой версией OpenSSL.
ERR_CRYPTO_ECDH_INVALID_FORMAT¶
Недопустимое значение для format аргумент был передан crypto.ECDH() класс getPublicKey() метод.
ERR_CRYPTO_ECDH_INVALID_PUBLIC_KEY¶
Недопустимое значение для key аргумент был передан crypto.ECDH() класс computeSecret() метод. Это означает, что открытый ключ лежит за пределами эллиптической кривой.
ERR_CRYPTO_ENGINE_UNKNOWN¶
Неверный идентификатор криптографической машины был передан в require('crypto').setEngine().
ERR_CRYPTO_FIPS_FORCED¶
В --force-fips был использован аргумент командной строки, но была попытка включить или отключить режим FIPS в crypto модуль.
ERR_CRYPTO_FIPS_UNAVAILABLE¶
Была сделана попытка включить или отключить режим FIPS, но режим FIPS был недоступен.
ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_FINALIZED¶
hash.digest() вызвали несколько раз. В hash.digest() метод должен вызываться не более одного раза для каждого экземпляра Hash объект.
ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_UPDATE_FAILED¶
hash.update() не удалось по какой-либо причине. Это должно происходить редко, если вообще когда-либо случаться.
ERR_CRYPTO_INCOMPATIBLE_KEY¶
Указанные криптографические ключи несовместимы с предпринятой операцией.
ERR_CRYPTO_INCOMPATIBLE_KEY_OPTIONS¶
Выбранная кодировка открытого или закрытого ключа несовместима с другими параметрами.
ERR_CRYPTO_INITIALIZATION_FAILED¶
Не удалось инициализировать криптоподсистему.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_AUTH_TAG¶
Предоставлен недопустимый тег аутентификации.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_COUNTER¶
Для шифра режима противодействия предоставлен неверный счетчик.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_CURVE¶
Была предоставлена неверная эллиптическая кривая.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_DIGEST¶
Недействительный алгоритм криптодайджеста было указано.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_IV¶
Предоставлен недопустимый вектор инициализации.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_JWK¶
Был предоставлен недопустимый веб-ключ JSON.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_KEY_OBJECT_TYPE¶
Данный тип объекта криптографического ключа недопустим для выполняемой операции.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_KEYLEN¶
Была предоставлена неверная длина ключа.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_KEYPAIR¶
Была предоставлена неверная пара ключей.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_KEYTYPE¶
Предоставлен недопустимый тип ключа.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_MESSAGELEN¶
Была предоставлена неверная длина сообщения.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_SCRYPT_PARAMS¶
Были предоставлены неверные параметры алгоритма шифрования.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_STATE¶
Крипто-метод был использован для объекта, находившегося в недопустимом состоянии. Например, позвонив cipher.getAuthTag() перед звонком cipher.final().
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_TAG_LENGTH¶
Предоставлена неверная длина тега аутентификации.
ERR_CRYPTO_JOB_INIT_FAILED¶
Не удалось инициализировать асинхронную криптооперацию.
ERR_CRYPTO_JWK_UNSUPPORTED_CURVE¶
Эллиптическая кривая Ключа не зарегистрирована для использования в Реестр эллиптических кривых веб-ключей JSON.
ERR_CRYPTO_JWK_UNSUPPORTED_KEY_TYPE¶
Тип асимметричного ключа ключа не зарегистрирован для использования в Реестр типов веб-ключей JSON.
ERR_CRYPTO_OPERATION_FAILED¶
Криптооперация завершилась неудачно по неустановленной причине.
ERR_CRYPTO_PBKDF2_ERROR¶
Алгоритм PBKDF2 завершился неудачно по неустановленным причинам. OpenSSL не предоставляет более подробной информации, и, следовательно, Node.js.
ERR_CRYPTO_SCRYPT_INVALID_PARAMETER¶
Один или больше crypto.scrypt() или crypto.scryptSync() параметры находятся за пределами допустимого диапазона.
ERR_CRYPTO_SCRYPT_NOT_SUPPORTED¶
Node.js был скомпилирован без scrypt служба поддержки. Невозможно с официальными двоичными файлами выпуска, но может произойти с пользовательскими сборками, включая сборки дистрибутива.
ERR_CRYPTO_SIGN_KEY_REQUIRED¶
Подпись key не был предоставлен sign.sign() метод.
ERR_CRYPTO_TIMING_SAFE_EQUAL_LENGTH¶
crypto.timingSafeEqual() был вызван с Buffer, TypedArray, или DataView аргументы разной длины.
ERR_CRYPTO_UNKNOWN_CIPHER¶
Указан неизвестный шифр.
ERR_CRYPTO_UNKNOWN_DH_GROUP¶
Было дано неизвестное название группы Диффи-Хеллмана. Видеть crypto.getDiffieHellman() для списка допустимых имен групп.
ERR_CRYPTO_UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION¶
Была сделана попытка вызвать неподдерживаемую криптографическую операцию.
ERR_DEBUGGER_ERROR¶
Произошла ошибка с отладчик.
ERR_DEBUGGER_STARTUP_ERROR¶
В отладчик истекло время ожидания освобождения необходимого хоста / порта.
ERR_DLOPEN_DISABLED¶
Загрузка собственных надстроек отключена с помощью --no-addons.
ERR_DLOPEN_FAILED¶
Звонок в process.dlopen() не смогли.
ERR_DIR_CLOSED¶
В fs.Dir ранее был закрыт.
ERR_DIR_CONCURRENT_OPERATION¶
Была предпринята попытка синхронного чтения или закрытия fs.Dir который имеет текущие асинхронные операции.
ERR_DNS_SET_SERVERS_FAILED¶
c-ares не удалось установить DNS-сервер.
ERR_DOMAIN_CALLBACK_NOT_AVAILABLE¶
В domain модуль нельзя было использовать, так как он не мог установить требуемые перехватчики обработки ошибок, потому что process.setUncaughtExceptionCaptureCallback() был вызван в более ранний момент времени.
ERR_DOMAIN_CANNOT_SET_UNCAUGHT_EXCEPTION_CAPTURE¶
process.setUncaughtExceptionCaptureCallback() нельзя было назвать, потому что domain модуль был загружен раньше.
Трассировка стека расширяется, чтобы включить момент времени, в который domain модуль был загружен.
ERR_ENCODING_INVALID_ENCODED_DATA¶
Данные предоставлены TextDecoder() API был недопустимым в соответствии с предоставленной кодировкой.
ERR_ENCODING_NOT_SUPPORTED¶
Кодировка предоставлена TextDecoder() API не был одним из WHATWG Поддерживаемые кодировки.
ERR_EVAL_ESM_CANNOT_PRINT¶
--print не может использоваться с входом ESM.
ERR_EVENT_RECURSION¶
Вызывается, когда делается попытка рекурсивно отправить событие на EventTarget.
ERR_EXECUTION_ENVIRONMENT_NOT_AVAILABLE¶
Контекст выполнения JS не связан со средой Node.js. Это может произойти, если Node.js используется в качестве встроенной библиотеки и некоторые хуки для движка JS не настроены должным образом.
ERR_FALSY_VALUE_REJECTION¶
А Promise это было выполнено обратным вызовом через util.callbackify() был отклонен с ложным значением.
ERR_FEATURE_UNAVAILABLE_ON_PLATFORM¶
Используется, когда используется функция, недоступная для текущей платформы, на которой работает Node.js.
ERR_FS_CP_DIR_TO_NON_DIR¶
Была сделана попытка скопировать каталог в не каталог (файл, символическую ссылку и т. Д.) С помощью fs.cp().
ERR_FS_CP_EEXIST¶
Была сделана попытка скопировать файл, который уже существовал с fs.cp(), с force а также errorOnExist установлен в true.
ERR_FS_CP_EINVAL¶
Когда используешь fs.cp(), src или dest указал на недопустимый путь.
ERR_FS_CP_FIFO_PIPE¶
Была сделана попытка скопировать именованный канал с fs.cp().
ERR_FS_CP_NON_DIR_TO_DIR¶
Была сделана попытка скопировать не каталог (файл, символическую ссылку и т. Д.) В каталог с помощью fs.cp().
ERR_FS_CP_SOCKET¶
Была сделана попытка скопировать в сокет с fs.cp().
ERR_FS_CP_SYMLINK_TO_SUBDIRECTORY¶
Когда используешь fs.cp(), символическая ссылка в dest указал на подкаталог src.
ERR_FS_CP_UNKNOWN¶
Была сделана попытка скопировать файл неизвестного типа с fs.cp().
ERR_FS_EISDIR¶
Путь — это каталог.
ERR_FS_FILE_TOO_LARGE¶
Была сделана попытка прочитать файл, размер которого превышает максимально допустимый размер для Buffer.
ERR_FS_INVALID_SYMLINK_TYPE¶
Недопустимый тип символической ссылки был передан в fs.symlink() или fs.symlinkSync() методы.
Была сделана попытка добавить дополнительные заголовки после того, как они уже были отправлены.
Указано недопустимое значение заголовка HTTP.
ERR_HTTP_INVALID_STATUS_CODE¶
Код состояния находился за пределами обычного диапазона кодов состояния (100–999).
ERR_HTTP_REQUEST_TIMEOUT¶
Клиент не отправил весь запрос в отведенное время.
ERR_HTTP_SOCKET_ENCODING¶
Изменение кодировки сокета запрещено RFC 7230, раздел 3.
ERR_HTTP_TRAILER_INVALID¶
В Trailer заголовок был установлен, хотя кодировка передачи не поддерживает это.
ERR_HTTP2_ALTSVC_INVALID_ORIGIN¶
Для фреймов HTTP / 2 ALTSVC требуется действительное происхождение.
ERR_HTTP2_ALTSVC_LENGTH¶
Кадры HTTP / 2 ALTSVC ограничены максимум 16 382 байтами полезной нагрузки.
Для запросов HTTP / 2 с использованием CONNECT метод, :authority псевдозаголовок обязателен.
ERR_HTTP2_CONNECT_PATH¶
Для запросов HTTP / 2 с использованием CONNECT метод, :path псевдозаголовок запрещен.
ERR_HTTP2_CONNECT_SCHEME¶
Для запросов HTTP / 2 с использованием CONNECT метод, :scheme псевдозаголовок запрещен.
ERR_HTTP2_ERROR¶
Произошла неспецифическая ошибка HTTP / 2.
ERR_HTTP2_GOAWAY_SESSION¶
Новые потоки HTTP / 2 нельзя открывать после Http2Session получил GOAWAY кадр от подключенного однорангового узла.
Было предоставлено несколько значений для поля заголовка HTTP / 2, которое должно было иметь только одно значение.
Дополнительные заголовки были указаны после того, как был инициирован ответ HTTP / 2.
Была сделана попытка отправить несколько заголовков ответа.
ERR_HTTP2_INFO_STATUS_NOT_ALLOWED¶
Информационные коды состояния HTTP (1xx) не может быть установлен в качестве кода состояния ответа в ответах HTTP / 2.
Заголовки соединения HTTP / 1 запрещено использовать в запросах и ответах HTTP / 2.
Указано недопустимое значение заголовка HTTP / 2.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_INFO_STATUS¶
Указан недопустимый информационный код состояния HTTP. Информационные коды состояния должны быть целыми числами между 100 а также 199 (включительно).
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_ORIGIN¶
HTTP / 2 ORIGIN кадры требуют действительного происхождения.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_PACKED_SETTINGS_LENGTH¶
Вход Buffer а также Uint8Array экземпляры переданы в http2.getUnpackedSettings() API должен иметь длину, кратную шести.
Только допустимые псевдозаголовки HTTP / 2 (:status, :path, :authority, :scheme, а также :method) может быть использовано.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_SESSION¶
Действие было выполнено с Http2Session объект, который уже был уничтожен.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_SETTING_VALUE¶
Для параметра HTTP / 2 указано недопустимое значение.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_STREAM¶
Операция была выполнена над потоком, который уже был уничтожен.
ERR_HTTP2_MAX_PENDING_SETTINGS_ACK¶
Всякий раз, когда HTTP / 2 SETTINGS фрейм отправляется подключенному одноранговому узлу, одноранговый узел должен отправить подтверждение, что он получил и применил новый SETTINGS. По умолчанию максимальное количество неподтвержденных SETTINGS кадры могут быть отправлены в любой момент времени. Этот код ошибки используется при достижении этого предела.
ERR_HTTP2_NESTED_PUSH¶
Была сделана попытка инициировать новый push-поток из push-потока. Вложенные push-потоки не разрешены.
ERR_HTTP2_NO_MEM¶
Недостаточно памяти при использовании http2session.setLocalWindowSize(windowSize) API.
ERR_HTTP2_NO_SOCKET_MANIPULATION¶
Была предпринята попытка напрямую манипулировать (чтение, запись, пауза, возобновление и т. Д.) Сокетом, подключенным к Http2Session.
ERR_HTTP2_ORIGIN_LENGTH¶
HTTP / 2 ORIGIN кадры ограничены длиной 16382 байта.
ERR_HTTP2_OUT_OF_STREAMS¶
Количество потоков, созданных в одном сеансе HTTP / 2, достигло максимального предела.
ERR_HTTP2_PAYLOAD_FORBIDDEN¶
Полезная нагрузка сообщения была указана для кода ответа HTTP, для которого полезная нагрузка запрещена.
ERR_HTTP2_PING_CANCEL¶
Пинг HTTP / 2 был отменен.
ERR_HTTP2_PING_LENGTH¶
Полезные данные ping HTTP / 2 должны иметь длину ровно 8 байтов.
Псевдозаголовок HTTP / 2 использован ненадлежащим образом. Псевдо-заголовки — это имена ключей заголовков, которые начинаются с : приставка.
ERR_HTTP2_PUSH_DISABLED¶
Была сделана попытка создать push-поток, который был отключен клиентом.
ERR_HTTP2_SEND_FILE¶
Была сделана попытка использовать Http2Stream.prototype.responseWithFile() API для отправки каталога.
ERR_HTTP2_SEND_FILE_NOSEEK¶
Была сделана попытка использовать Http2Stream.prototype.responseWithFile() API для отправки чего-то другого, кроме обычного файла, но offset или length были предоставлены варианты.
ERR_HTTP2_SESSION_ERROR¶
В Http2Session закрывается с ненулевым кодом ошибки.
ERR_HTTP2_SETTINGS_CANCEL¶
В Http2Session настройки отменены.
ERR_HTTP2_SOCKET_BOUND¶
Была сделана попытка подключить Http2Session возражать против net.Socket или tls.TLSSocket который уже был привязан к другому Http2Session объект.
ERR_HTTP2_SOCKET_UNBOUND¶
Была сделана попытка использовать socket собственность Http2Session это уже было закрыто.
ERR_HTTP2_STATUS_101¶
Использование 101 Информационный код статуса запрещен в HTTP / 2.
ERR_HTTP2_STATUS_INVALID¶
Указан недопустимый код состояния HTTP. Коды состояния должны быть целыми числами между 100 а также 599 (включительно).
ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_CANCEL¶
An Http2Stream был уничтожен до того, как какие-либо данные были переданы подключенному узлу.
ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_ERROR¶
Ненулевой код ошибки был указан в RST_STREAM Рамка.
ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_SELF_DEPENDENCY¶
При установке приоритета для потока HTTP / 2 этот поток может быть помечен как зависимость для родительского потока. Этот код ошибки используется, когда делается попытка пометить поток и зависит от него самого.
ERR_HTTP2_TOO_MANY_INVALID_FRAMES¶
Предел приемлемых недопустимых кадров протокола HTTP / 2, отправленных партнером, как указано в maxSessionInvalidFrames вариант, был превышен.
ERR_HTTP2_TRAILERS_ALREADY_SENT¶
Конечные заголовки уже отправлены на Http2Stream.
ERR_HTTP2_TRAILERS_NOT_READY¶
В http2stream.sendTrailers() метод не может быть вызван до тех пор, пока 'wantTrailers' событие испускается на Http2Stream объект. В 'wantTrailers' событие будет сгенерировано только в том случае, если waitForTrailers опция установлена для Http2Stream.
ERR_HTTP2_UNSUPPORTED_PROTOCOL¶
http2.connect() был передан URL-адрес, использующий любой протокол, кроме http: или https:.
ERR_ILLEGAL_CONSTRUCTOR¶
Была предпринята попытка построить объект с использованием закрытого конструктора.
ERR_INCOMPATIBLE_OPTION_PAIR¶
Пара опций несовместима друг с другом и не может использоваться одновременно.
ERR_INPUT_TYPE_NOT_ALLOWED¶
Стабильность: 1 — экспериментальная
В --input-type Флаг использовался для попытки выполнить файл. Этот флаг можно использовать только при вводе через --eval, --print или STDIN.
ERR_INSPECTOR_ALREADY_ACTIVATED¶
При использовании inspector module была предпринята попытка активировать инспектор, когда он уже начал прослушивать порт. Использовать inspector.close() прежде чем активировать его на другом адресе.
ERR_INSPECTOR_ALREADY_CONNECTED¶
При использовании inspector модуль, была предпринята попытка подключения, когда инспектор уже был подключен.
ERR_INSPECTOR_CLOSED¶
При использовании inspector модуля, была предпринята попытка использовать инспектор после того, как сессия уже закрылась.
ERR_INSPECTOR_COMMAND¶
Произошла ошибка при подаче команды через inspector модуль.
ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_ACTIVE¶
В inspector не активен, когда inspector.waitForDebugger() называется.
ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_AVAILABLE¶
В inspector модуль недоступен для использования.
ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_CONNECTED¶
При использовании inspector модуль, была предпринята попытка использовать инспектор до его подключения.
ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_WORKER¶
В основном потоке был вызван API, который можно использовать только из рабочего потока.
ERR_INTERNAL_ASSERTION¶
Ошибка в Node.js или некорректное использование внутренних компонентов Node.js. Чтобы исправить ошибку, откройте проблему на https://github.com/nodejs/node/issues.
ERR_INVALID_ADDRESS_FAMILY¶
Указанное семейство адресов не распознается API Node.js.
ERR_INVALID_ARG_TYPE¶
В API Node.js был передан аргумент неправильного типа.
ERR_INVALID_ARG_VALUE¶
Для данного аргумента было передано недопустимое или неподдерживаемое значение.
ERR_INVALID_ASYNC_ID¶
Недействительный asyncId или triggerAsyncId был передан с использованием AsyncHooks. Идентификатор меньше -1 никогда не должен происходить.
ERR_INVALID_BUFFER_SIZE¶
Обмен был произведен на Buffer но его размер был несовместим с операцией.
ERR_INVALID_CALLBACK¶
Требовалась функция обратного вызова, но она не была предоставлена API Node.js.
ERR_INVALID_CHAR¶
В заголовках обнаружены недопустимые символы.
ERR_INVALID_CURSOR_POS¶
Курсор в данном потоке нельзя переместить в указанную строку без указанного столбца.
ERR_INVALID_FD¶
Дескриптор файла (‘fd’) недействителен (например, имеет отрицательное значение).
ERR_INVALID_FD_TYPE¶
Недопустимый тип дескриптора файла (‘fd’).
ERR_INVALID_FILE_URL_HOST¶
API-интерфейс Node.js, который потребляет file: URL-адреса (например, определенные функции в fs module) обнаружил URL-адрес файла с несовместимым хостом. Эта ситуация может возникнуть только в Unix-подобных системах, где только localhost или поддерживается пустой хост.
ERR_INVALID_FILE_URL_PATH¶
API-интерфейс Node.js, который потребляет file: URL-адреса (например, определенные функции в fs module) обнаружил URL-адрес файла с несовместимым путем. Точная семантика для определения возможности использования пути зависит от платформы.
ERR_INVALID_HANDLE_TYPE¶
Была сделана попытка отправить неподдерживаемый «дескриптор» по каналу связи IPC дочернему процессу. Видеть subprocess.send() а также process.send() для дополнительной информации.
ERR_INVALID_HTTP_TOKEN¶
Предоставлен недопустимый токен HTTP.
ERR_INVALID_IP_ADDRESS¶
IP-адрес недействителен.
ERR_INVALID_MODULE¶
Была сделана попытка загрузить несуществующий или недействительный модуль.
ERR_INVALID_MODULE_SPECIFIER¶
Строка импортированного модуля является недопустимым URL-адресом, именем пакета или указателем подпути пакета.
ERR_INVALID_PACKAGE_CONFIG¶
Недействительный package.json файл не прошел синтаксический анализ.
ERR_INVALID_PACKAGE_TARGET¶
В package.json "exports" Поле содержит недопустимое значение сопоставления цели для попытки разрешения модуля.
ERR_INVALID_PERFORMANCE_MARK¶
При использовании Performance Timing API (perf_hooks), отметка о производительности недействительна.
ERR_INVALID_PROTOCOL¶
Недействительный options.protocol был передан http.request().
ERR_INVALID_REPL_EVAL_CONFIG¶
Оба breakEvalOnSigint а также eval параметры были установлены в REPL config, который не поддерживается.
ERR_INVALID_REPL_INPUT¶
Вход не может использоваться в REPL. Условия, при которых используется эта ошибка, описаны в REPL документация.
ERR_INVALID_RETURN_PROPERTY¶
Выбрасывается в случае, если параметр функции не предоставляет допустимое значение для одного из свойств возвращаемого объекта при выполнении.
ERR_INVALID_RETURN_PROPERTY_VALUE¶
Выбрасывается в случае, если параметр функции не предоставляет тип ожидаемого значения для одного из свойств возвращаемого объекта при выполнении.
ERR_INVALID_RETURN_VALUE¶
Вызывается в случае, если опция функции не возвращает ожидаемый тип значения при выполнении, например, когда ожидается, что функция вернет обещание.
ERR_INVALID_STATE¶
Указывает, что операция не может быть завершена из-за недопустимого состояния. Например, объект может быть уже уничтожен или может выполнять другую операцию.
ERR_INVALID_SYNC_FORK_INPUT¶
А Buffer, TypedArray, DataView или string был предоставлен как вход stdio для асинхронной вилки. См. Документацию по child_process модуль для получения дополнительной информации.
ERR_INVALID_THIS¶
Функция API Node.js была вызвана с несовместимым this ценить.
const urlSearchParams = new URLSearchParams(
'foo=bar&baz=new'
);
const buf = Buffer.alloc(1);
urlSearchParams.has.call(buf, 'foo');
// Throws a TypeError with code 'ERR_INVALID_THIS'
ERR_INVALID_TRANSFER_OBJECT¶
Недопустимый объект передачи был передан в postMessage().
ERR_INVALID_TUPLE¶
Элемент в iterable предоставлен WHATWG URLSearchParams конструктор не представлял [name, value] кортеж — то есть, если элемент не повторяется или не состоит ровно из двух элементов.
ERR_INVALID_URI¶
Передан неверный URI.
ERR_INVALID_URL¶
Недействительный URL был передан в WHATWG URL конструктор или наследие url.parse() быть разобранным. Выброшенный объект ошибки обычно имеет дополнительное свойство 'input' который содержит URL-адрес, который не удалось проанализировать.
ERR_INVALID_URL_SCHEME¶
Была сделана попытка использовать URL несовместимой схемы (протокола) для определенной цели. Он используется только в WHATWG URL API поддержка в fs модуль (который принимает только URL-адреса с 'file' схема), но может использоваться и в других API Node.js в будущем.
ERR_IPC_CHANNEL_CLOSED¶
Была сделана попытка использовать канал связи IPC, который уже был закрыт.
ERR_IPC_DISCONNECTED¶
Была сделана попытка отключить уже отключенный канал связи IPC. См. Документацию по child_process модуль для получения дополнительной информации.
ERR_IPC_ONE_PIPE¶
Была предпринята попытка создать дочерний процесс Node.js, использующий более одного канала связи IPC. См. Документацию по child_process модуль для получения дополнительной информации.
ERR_IPC_SYNC_FORK¶
Была предпринята попытка открыть канал связи IPC с помощью синхронно разветвленного процесса Node.js. См. Документацию по child_process модуль для получения дополнительной информации.
ERR_MANIFEST_ASSERT_INTEGRITY¶
Была предпринята попытка загрузить ресурс, но ресурс не соответствовал целостности, определенной в манифесте политики. Документацию для политика манифесты для получения дополнительной информации.
ERR_MANIFEST_DEPENDENCY_MISSING¶
Была предпринята попытка загрузить ресурс, но ресурс не был указан как зависимость от расположения, в котором его пытались загрузить. Документацию для политика манифесты для получения дополнительной информации.
ERR_MANIFEST_INTEGRITY_MISMATCH¶
Была сделана попытка загрузить манифест политики, но в манифесте было несколько записей для ресурса, которые не совпадали друг с другом. Обновите записи манифеста, чтобы они соответствовали, чтобы устранить эту ошибку. Документацию для политика манифесты для получения дополнительной информации.
ERR_MANIFEST_INVALID_RESOURCE_FIELD¶
Ресурс манифеста политики имел недопустимое значение для одного из полей. Обновите запись манифеста, чтобы она соответствовала, чтобы устранить эту ошибку. Документацию для политика манифесты для получения дополнительной информации.
ERR_MANIFEST_INVALID_SPECIFIER¶
Ресурс манифеста политики имел недопустимое значение для одного из сопоставлений зависимостей. Обновите запись манифеста, чтобы она соответствовала разрешению этой ошибки. Документацию для политика манифесты для получения дополнительной информации.
ERR_MANIFEST_PARSE_POLICY¶
Была предпринята попытка загрузить манифест политики, но не удалось проанализировать манифест. Документацию для политика манифесты для получения дополнительной информации.
ERR_MANIFEST_TDZ¶
Была предпринята попытка чтения из манифеста политики, но инициализация манифеста еще не произошла. Вероятно, это ошибка в Node.js.
ERR_MANIFEST_UNKNOWN_ONERROR¶
Манифест политики был загружен, но для его поведения «onerror» было неизвестно значение. Документацию для политика манифесты для получения дополнительной информации.
ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATION_FAILED¶
Была предпринята попытка выделить память (обычно на уровне C ++), но она не удалась.
ERR_MESSAGE_TARGET_CONTEXT_UNAVAILABLE¶
Сообщение отправлено MessagePort не удалось десериализовать в целевой vm Context. Не все объекты Node.js могут быть успешно созданы в любом контексте в настоящее время, и попытки передать их с помощью postMessage() в этом случае может выйти из строя принимающая сторона.
ERR_METHOD_NOT_IMPLEMENTED¶
Метод требуется, но не реализован.
ERR_MISSING_ARGS¶
Не был передан обязательный аргумент API Node.js. Это используется только для строгого соответствия спецификации API (которая в некоторых случаях может принимать func(undefined) но нет func()). В большинстве собственных API-интерфейсов Node.js func(undefined) а также func() рассматриваются одинаково, а ERR_INVALID_ARG_TYPE вместо этого можно использовать код ошибки.
ERR_MISSING_OPTION¶
Для API-интерфейсов, которые принимают объекты параметров, некоторые параметры могут быть обязательными. Этот код выдается, если отсутствует необходимая опция.
ERR_MISSING_PASSPHRASE¶
Была сделана попытка прочитать зашифрованный ключ без указания ключевой фразы.
ERR_MISSING_PLATFORM_FOR_WORKER¶
Платформа V8, используемая этим экземпляром Node.js, не поддерживает создание рабочих. Это вызвано отсутствием поддержки Embedder для Workers. В частности, эта ошибка не возникает при использовании стандартных сборок Node.js.
ERR_MISSING_TRANSFERABLE_IN_TRANSFER_LIST¶
Объект, который должен быть явно указан в transferList аргумент находится в объекте, переданном в postMessage() звоните, но не указано в transferList для этого звонка. Обычно это MessagePort.
В версиях Node.js до v15.0.0 использованный здесь код ошибки был ERR_MISSING_MESSAGE_PORT_IN_TRANSFER_LIST. Однако набор переносимых типов объектов был расширен, чтобы охватить больше типов, чем MessagePort.
ERR_MODULE_NOT_FOUND¶
Стабильность: 1 — экспериментальная
An Модуль ES не может быть решен.
ERR_MULTIPLE_CALLBACK¶
Обратный звонок был вызван более одного раза.
Обратный вызов почти всегда предназначен для однократного вызова, поскольку запрос может быть выполнен или отклонен, но не оба одновременно. Последнее станет возможным, если вызвать обратный вызов более одного раза.
ERR_NAPI_CONS_FUNCTION¶
При использовании Node-API, переданный конструктор не является функцией.
ERR_NAPI_INVALID_DATAVIEW_ARGS¶
Во время звонка napi_create_dataview(), данный offset находился за пределами окна просмотра данных или offset + length был больше, чем длина заданного buffer.
ERR_NAPI_INVALID_TYPEDARRAY_ALIGNMENT¶
Во время звонка napi_create_typedarray()предоставленные offset не был кратен размеру элемента.
ERR_NAPI_INVALID_TYPEDARRAY_LENGTH¶
Во время звонка napi_create_typedarray(), (length * size_of_element) + byte_offset был больше, чем длина заданного buffer.
ERR_NAPI_TSFN_CALL_JS¶
Произошла ошибка при вызове части JavaScript поточно-ориентированной функции.
ERR_NAPI_TSFN_GET_UNDEFINED¶
Произошла ошибка при попытке получить код JavaScript. undefined ценить.
ERR_NAPI_TSFN_START_IDLE_LOOP¶
В основном потоке значения удаляются из очереди, связанной с поточно-ориентированной функцией, в цикле ожидания. Эта ошибка указывает на то, что произошла ошибка при попытке запустить цикл.
ERR_NAPI_TSFN_STOP_IDLE_LOOP¶
Если в очереди больше не осталось элементов, цикл простоя должен быть приостановлен. Эта ошибка указывает на то, что не удалось остановить цикл холостого хода.
ERR_NO_CRYPTO¶
Была предпринята попытка использовать функции шифрования, пока Node.js не был скомпилирован с поддержкой шифрования OpenSSL.
ERR_NO_ICU¶
Была предпринята попытка использовать функции, требующие ICU, но Node.js не был скомпилирован с поддержкой ICU.
ERR_NON_CONTEXT_AWARE_DISABLED¶
Родной аддон, не зависящий от контекста, был загружен в процессе, который их запрещает.
ERR_OUT_OF_RANGE¶
Заданное значение выходит за пределы допустимого диапазона.
ERR_PACKAGE_IMPORT_NOT_DEFINED¶
В package.json "imports" поле не определяет заданное отображение спецификатора внутреннего пакета.
ERR_PACKAGE_PATH_NOT_EXPORTED¶
В package.json "exports" не экспортирует запрошенный подпуть. Поскольку экспорт инкапсулирован, частные внутренние модули, которые не экспортируются, не могут быть импортированы через разрешение пакета, если не используется абсолютный URL-адрес.
ERR_PERFORMANCE_INVALID_TIMESTAMP¶
Для отметки производительности или показателя было предоставлено недопустимое значение метки времени.
ERR_PERFORMANCE_MEASURE_INVALID_OPTIONS¶
Предусмотрены недопустимые варианты измерения производительности.
ERR_PROTO_ACCESS¶
Доступ Object.prototype.__proto__ было запрещено использовать --disable-proto=throw. Object.getPrototypeOf а также Object.setPrototypeOf следует использовать для получения и установки прототипа объекта.
ERR_REQUIRE_ESM¶
Стабильность: 1 — экспериментальная
Была сделана попытка require() ан Модуль ES.
ERR_SCRIPT_EXECUTION_INTERRUPTED¶
Выполнение скрипта было прервано SIGINT (Например, Ctrl+C был нажат.)
ERR_SCRIPT_EXECUTION_TIMEOUT¶
Истекло время выполнения сценария, возможно, из-за ошибок в выполняемом сценарии.
ERR_SERVER_ALREADY_LISTEN¶
В server.listen() метод был вызван в то время как net.Server уже слушал. Это относится ко всем экземплярам net.Server, включая HTTP, HTTPS и HTTP / 2 Server экземпляры.
ERR_SERVER_NOT_RUNNING¶
В server.close() метод был вызван, когда net.Server не работал. Это относится ко всем экземплярам net.Server, включая HTTP, HTTPS и HTTP / 2 Server экземпляры.
ERR_SOCKET_ALREADY_BOUND¶
Была сделана попытка привязать уже связанный сокет.
ERR_SOCKET_BAD_BUFFER_SIZE¶
Был передан недопустимый (отрицательный) размер для recvBufferSize или sendBufferSize варианты в dgram.createSocket().
ERR_SOCKET_BAD_PORT¶
Функция API, ожидающая порта> = 0 и <65536, получила недопустимое значение.
ERR_SOCKET_BAD_TYPE¶
Функция API, ожидающая типа сокета (udp4 или udp6) получил недопустимое значение.
ERR_SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE¶
При использовании dgram.createSocket(), размер получения или отправки Buffer не может быть определено.
ERR_SOCKET_CLOSED¶
Была сделана попытка работать с уже закрытым сокетом.
ERR_SOCKET_DGRAM_IS_CONNECTED¶
А dgram.connect() вызов был сделан на уже подключенном сокете.
ERR_SOCKET_DGRAM_NOT_CONNECTED¶
А dgram.disconnect() или dgram.remoteAddress() звонок был сделан на отключенной розетке.
ERR_SOCKET_DGRAM_NOT_RUNNING¶
Был сделан вызов, но подсистема UDP не работала.
ERR_SRI_PARSE¶
Строка была предоставлена для проверки целостности подресурса, но не может быть проанализирована. Проверьте формат атрибутов целостности, посмотрев на Спецификация целостности подресурсов.
ERR_STREAM_ALREADY_FINISHED¶
Был вызван метод потока, который не может быть завершен, поскольку поток был завершен.
ERR_STREAM_CANNOT_PIPE¶
Была сделана попытка позвонить stream.pipe() на Writable транслировать.
ERR_STREAM_DESTROYED¶
Был вызван метод потока, который не может быть завершен, поскольку поток был уничтожен с использованием stream.destroy().
ERR_STREAM_NULL_VALUES¶
Была сделана попытка позвонить stream.write() с null кусок.
ERR_STREAM_PREMATURE_CLOSE¶
Ошибка, возвращенная stream.finished() а также stream.pipeline(), когда поток или конвейер завершаются некорректно, без явной ошибки.
ERR_STREAM_PUSH_AFTER_EOF¶
Была сделана попытка позвонить stream.push() после null(EOF) был отправлен в поток.
ERR_STREAM_UNSHIFT_AFTER_END_EVENT¶
Была сделана попытка позвонить stream.unshift() после 'end' событие было отправлено.
ERR_STREAM_WRAP¶
Предотвращает прерывание, если строковый декодер был установлен на Socket или если декодер находится в objectMode.
const Socket = require('net').Socket;
const instance = new Socket();
instance.setEncoding('utf8');
ERR_STREAM_WRITE_AFTER_END¶
Была сделана попытка позвонить stream.write() после stream.end() был вызван.
ERR_STRING_TOO_LONG¶
Была сделана попытка создать строку длиннее максимально допустимой.
ERR_SYNTHETIC¶
Искусственный объект ошибки, используемый для захвата стека вызовов для диагностических отчетов.
ERR_SYSTEM_ERROR¶
В процессе Node.js произошла неопределенная или неспецифическая системная ошибка. Объект ошибки будет иметь err.info свойство объекта с дополнительной информацией.
ERR_TLS_CERT_ALTNAME_INVALID¶
При использовании TLS имя хоста / IP-адрес однорангового узла не соответствует ни одному из subjectAltNames в его сертификате.
ERR_TLS_DH_PARAM_SIZE¶
При использовании TLS параметр, предлагаемый для алгоритма Диффи-Хеллмана (DH) протокол согласования ключей слишком мал. По умолчанию длина ключа должна быть больше или равна 1024 битам, чтобы избежать уязвимостей, хотя настоятельно рекомендуется использовать 2048 бит или больше для большей безопасности.
ERR_TLS_HANDSHAKE_TIMEOUT¶
Время ожидания подтверждения TLS / SSL истекло. В этом случае сервер также должен прервать соединение.
ERR_TLS_INVALID_CONTEXT¶
Контекст должен быть SecureContext.
ERR_TLS_INVALID_PROTOCOL_METHOD¶
Указанный secureProtocol метод недействителен. Он либо неизвестен, либо отключен, потому что небезопасен.
ERR_TLS_INVALID_PROTOCOL_VERSION¶
Допустимые версии протокола TLS: 'TLSv1', 'TLSv1.1', или 'TLSv1.2'.
ERR_TLS_INVALID_STATE¶
Сокет TLS должен быть подключен и надежно установлен. Перед продолжением убедитесь, что «безопасное» событие запущено.
ERR_TLS_PROTOCOL_VERSION_CONFLICT¶
Попытка установить протокол TLS minVersion или maxVersion конфликтует с попыткой установить secureProtocol явно. Используйте тот или иной механизм.
ERR_TLS_PSK_SET_IDENTIY_HINT_FAILED¶
Не удалось установить подсказку идентификатора PSK. Подсказка может быть слишком длинной.
ERR_TLS_RENEGOTIATION_DISABLED¶
Была сделана попытка повторно согласовать TLS на экземпляре сокета с отключенным TLS.
ERR_TLS_REQUIRED_SERVER_NAME¶
При использовании TLS server.addContext() был вызван без указания имени хоста в первом параметре.
ERR_TLS_SESSION_ATTACK¶
Обнаружено чрезмерное количество повторных согласований TLS, что является потенциальным вектором атак типа «отказ в обслуживании».
ERR_TLS_SNI_FROM_SERVER¶
Была предпринята попытка выдать указание имени сервера из сокета на стороне сервера TLS, который действителен только для клиента.
ERR_TRACE_EVENTS_CATEGORY_REQUIRED¶
В trace_events.createTracing() требуется по крайней мере одна категория событий трассировки.
ERR_TRACE_EVENTS_UNAVAILABLE¶
В trace_events модуль не может быть загружен, потому что Node.js был скомпилирован с --without-v8-platform флаг.
ERR_TRANSFORM_ALREADY_TRANSFORMING¶
А Transform поток завершился, пока он все еще преобразовывался.
ERR_TRANSFORM_WITH_LENGTH_0¶
А Transform поток закончился с данными, все еще находящимися в буфере записи.
ERR_TTY_INIT_FAILED¶
Инициализация TTY не удалась из-за системной ошибки.
ERR_UNAVAILABLE_DURING_EXIT¶
Функция была вызвана в process.on('exit') обработчик, который не должен вызываться внутри process.on('exit') обработчик.
ERR_UNCAUGHT_EXCEPTION_CAPTURE_ALREADY_SET¶
process.setUncaughtExceptionCaptureCallback() был вызван дважды, без предварительного сброса обратного вызова на null.
Эта ошибка предназначена для предотвращения случайной перезаписи обратного вызова, зарегистрированного из другого модуля.
ERR_UNESCAPED_CHARACTERS¶
Получена строка, содержащая неэкранированные символы.
ERR_UNHANDLED_ERROR¶
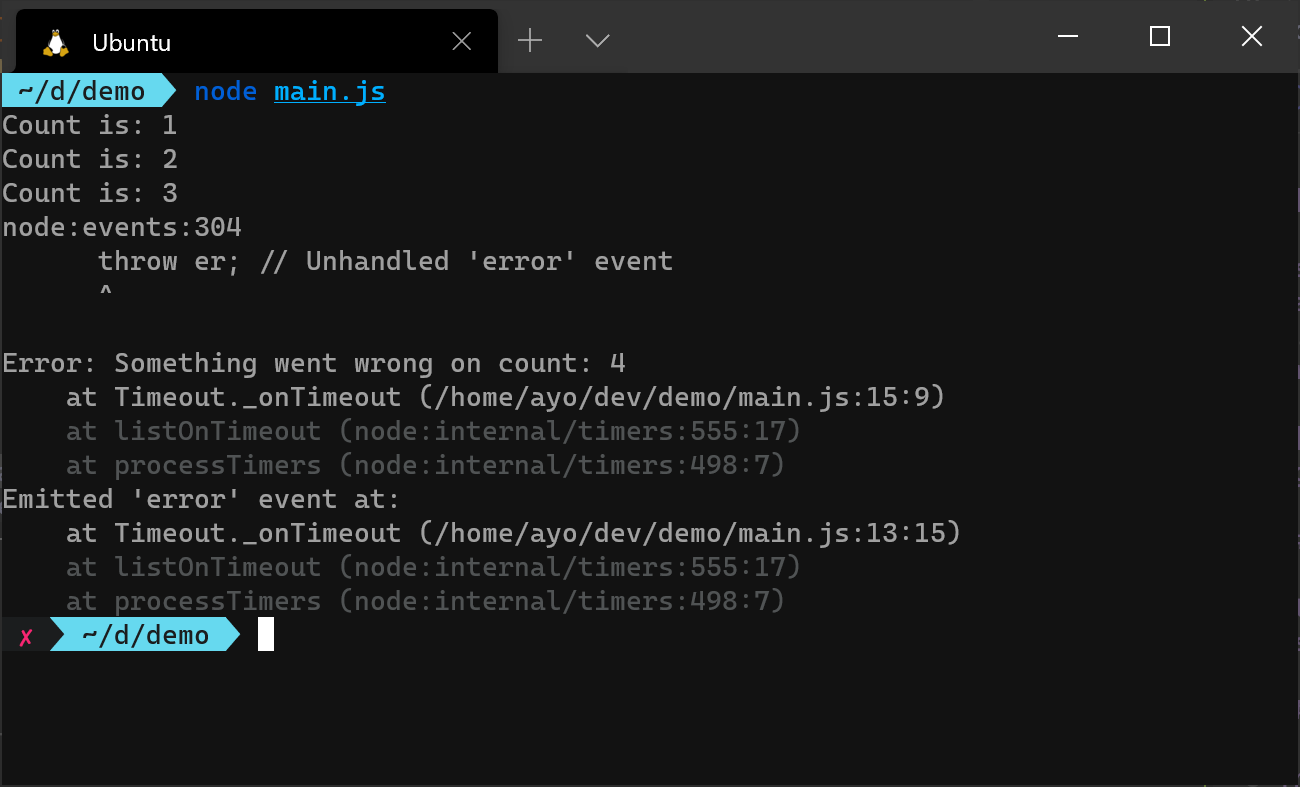
Произошла необработанная ошибка (например, когда 'error' событие испускается EventEmitter но 'error' обработчик не зарегистрирован).
ERR_UNKNOWN_BUILTIN_MODULE¶
Используется для определения определенного вида внутренней ошибки Node.js, которая обычно не должна запускаться кодом пользователя. Экземпляры этой ошибки указывают на внутреннюю ошибку в самом двоичном файле Node.js.
ERR_UNKNOWN_CREDENTIAL¶
Был передан несуществующий идентификатор группы или пользователя Unix.
ERR_UNKNOWN_ENCODING¶
В API передан неверный или неизвестный параметр кодировки.
ERR_UNKNOWN_FILE_EXTENSION¶
Стабильность: 1 — экспериментальная
Была сделана попытка загрузить модуль с неизвестным или неподдерживаемым расширением файла.
ERR_UNKNOWN_MODULE_FORMAT¶
Стабильность: 1 — экспериментальная
Была сделана попытка загрузить модуль с неизвестным или неподдерживаемым форматом.
ERR_UNKNOWN_SIGNAL¶
Неверный или неизвестный сигнал процесса был передан API, ожидающему действительного сигнала (например, subprocess.kill()).
ERR_UNSUPPORTED_DIR_IMPORT¶
import URL-адрес каталога не поддерживается. Вместо, Самостоятельная ссылка на пакет, используя его имя а также определить настраиваемый подпуть в "exports" поле package.json файл.
import './'; // unsupported
import './index.js'; // supported
import 'package-name'; // supported
ERR_UNSUPPORTED_ESM_URL_SCHEME¶
import со схемами URL, отличными от file а также data не поддерживается.
ERR_VALID_PERFORMANCE_ENTRY_TYPE¶
При использовании Performance Timing API (perf_hooks) допустимые типы записей производительности не найдены.
ERR_VM_DYNAMIC_IMPORT_CALLBACK_MISSING¶
Обратный вызов динамического импорта не указан.
ERR_VM_MODULE_ALREADY_LINKED¶
Модуль, который пытались связать, не подходит для связывания по одной из следующих причин:
- Он уже был связан (
linkingStatusявляется'linked') - Это связано (
linkingStatusявляется'linking') - Не удалось установить связь для этого модуля (
linkingStatusявляется'errored')
ERR_VM_MODULE_CACHED_DATA_REJECTED¶
В cachedData Параметр, переданный конструктору модуля, недопустим.
ERR_VM_MODULE_CANNOT_CREATE_CACHED_DATA¶
Кэшированные данные не могут быть созданы для модулей, которые уже были оценены.
ERR_VM_MODULE_DIFFERENT_CONTEXT¶
Модуль, возвращаемый функцией компоновщика, находится в другом контексте, чем родительский модуль. Связанные модули должны иметь общий контекст.
ERR_VM_MODULE_LINKING_ERRORED¶
Функция компоновщика вернула модуль, для которого не удалось выполнить связывание.
ERR_VM_MODULE_LINK_FAILURE¶
Модуль не удалось связать из-за сбоя.
ERR_VM_MODULE_NOT_MODULE¶
Выполненное значение обещания связывания не является vm.Module объект.
ERR_VM_MODULE_STATUS¶
Текущий статус модуля не позволяет выполнить эту операцию. Конкретный смысл ошибки зависит от конкретной функции.
ERR_WASI_ALREADY_STARTED¶
Экземпляр WASI уже запущен.
ERR_WASI_NOT_STARTED¶
Экземпляр WASI не запущен.
ERR_WORKER_INIT_FAILED¶
В Worker Ошибка инициализации.
ERR_WORKER_INVALID_EXEC_ARGV¶
В execArgv вариант передан в Worker конструктор содержит недопустимые флаги.
ERR_WORKER_NOT_RUNNING¶
Операция завершилась неудачно, потому что Worker экземпляр в настоящее время не запущен.
ERR_WORKER_OUT_OF_MEMORY¶
В Worker Экземпляр остановлен, поскольку достиг предела памяти.
ERR_WORKER_PATH¶
Путь для основного скрипта рабочего не является ни абсолютным, ни относительным путем, начинающимся с ./ или ../.
ERR_WORKER_UNSERIALIZABLE_ERROR¶
Все попытки сериализации неперехваченного исключения из рабочего потока завершились неудачно.
ERR_WORKER_UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION¶
Запрошенная функциональность не поддерживается в рабочих потоках.
ERR_ZLIB_INITIALIZATION_FAILED¶
Создание zlib сбой объекта из-за неправильной конфигурации.
Получено слишком много данных заголовка HTTP. Для защиты от злонамеренных или неправильно настроенных клиентов, если получено более 8 КБ данных HTTP-заголовка, анализ HTTP будет прерван без создания объекта запроса или ответа, и Error с этим кодом будет выпущен.
HPE_UNEXPECTED_CONTENT_LENGTH¶
Сервер отправляет как Content-Length заголовок и Transfer-Encoding: chunked.
Transfer-Encoding: chunked позволяет серверу поддерживать постоянное соединение HTTP для динамически генерируемого контента. В этом случае Content-Length Заголовок HTTP использовать нельзя.
Использовать Content-Length или Transfer-Encoding: chunked.
MODULE_NOT_FOUND¶
Не удалось разрешить файл модуля при попытке require() или import операция.
Устаревшие коды ошибок Node.js¶
Стабильность: 0 — Не рекомендуется. Эти коды ошибок либо несовместимы, либо были удалены.
ERR_CANNOT_TRANSFER_OBJECT¶
Значение, переданное в postMessage() содержит объект, который не поддерживается для передачи.
ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_DIGEST_NO_UTF16¶
Кодировка UTF-16 использовалась с hash.digest(). В то время как hash.digest() метод позволяет encoding аргумент, который должен быть передан, в результате чего метод возвращает строку, а не Buffer, кодировка UTF-16 (например, ucs или utf16le) не поддерживается.
ERR_HTTP2_FRAME_ERROR¶
Используется при сбое отправки отдельного кадра в сеансе HTTP / 2.
Используется, когда ожидается объект заголовков HTTP / 2.
Используется, когда в сообщении HTTP / 2 отсутствует требуемый заголовок.
Информационные заголовки HTTP / 2 должны отправляться только прежний позвонить в Http2Stream.prototype.respond() метод.
ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_CLOSED¶
Используется, когда действие было выполнено над уже закрытым потоком HTTP / 2.
ERR_HTTP_INVALID_CHAR¶
Используется, когда в сообщении статуса ответа HTTP (фраза причины) обнаружен недопустимый символ.
ERR_INDEX_OUT_OF_RANGE¶
Данный индекс был вне допустимого диапазона (например, отрицательные смещения).
ERR_INVALID_OPT_VALUE¶
В объект опций было передано недопустимое или неожиданное значение.
ERR_INVALID_OPT_VALUE_ENCODING¶
Передана неверная или неизвестная кодировка файла.
ERR_MISSING_MESSAGE_PORT_IN_TRANSFER_LIST¶
Этот код ошибки был заменен на ERR_MISSING_TRANSFERABLE_IN_TRANSFER_LIST в Node.js v15.0.0, потому что он больше не точен, поскольку теперь существуют и другие типы переносимых объектов.
ERR_NAPI_CONS_PROTOTYPE_OBJECT¶
Используется Node-API когда Constructor.prototype не объект.
ERR_NO_LONGER_SUPPORTED¶
API Node.js был вызван неподдерживаемым способом, например Buffer.write(string, encoding, offset[, length]).
ERR_OPERATION_FAILED¶
Не удалось выполнить операцию. Обычно это используется, чтобы сигнализировать об общем сбое асинхронной операции.
ERR_OUTOFMEMORY¶
Обычно используется для определения того, что операция вызвала нехватку памяти.
ERR_PARSE_HISTORY_DATA¶
В repl модулю не удалось проанализировать данные из файла истории REPL.
ERR_SOCKET_CANNOT_SEND¶
Данные не могут быть отправлены через сокет.
ERR_STDERR_CLOSE¶
Была сделана попытка закрыть process.stderr транслировать. По замыслу Node.js не позволяет stdout или stderr потоки должны быть закрыты кодом пользователя.
ERR_STDOUT_CLOSE¶
Была сделана попытка закрыть process.stdout транслировать. По замыслу Node.js не позволяет stdout или stderr потоки должны быть закрыты кодом пользователя.
ERR_STREAM_READ_NOT_IMPLEMENTED¶
Используется, когда делается попытка использовать читаемый поток, который не реализован readable._read().
ERR_TLS_RENEGOTIATION_FAILED¶
Используется, когда запрос на повторное согласование TLS завершился ошибкой неспецифическим образом.
ERR_TRANSFERRING_EXTERNALIZED_SHAREDARRAYBUFFER¶
А SharedArrayBuffer чья память не управляется механизмом JavaScript или Node.js. во время сериализации. Такой SharedArrayBuffer не может быть сериализован.
Это может произойти только тогда, когда нативные аддоны создают SharedArrayBuffers в «внешнем» режиме или поместите существующий SharedArrayBuffer во внешний режим.
ERR_UNKNOWN_STDIN_TYPE¶
Была предпринята попытка запустить процесс Node.js с неизвестным stdin тип файла. Эта ошибка обычно указывает на ошибку в самом Node.js, хотя пользовательский код может вызвать ее.
ERR_UNKNOWN_STREAM_TYPE¶
Была предпринята попытка запустить процесс Node.js с неизвестным stdout или stderr тип файла. Эта ошибка обычно указывает на ошибку в самом Node.js, хотя пользовательский код может вызвать ее.
ERR_V8BREAKITERATOR¶
V8 BreakIterator API использовался, но не установлен полный набор данных ICU.
ERR_VALUE_OUT_OF_RANGE¶
Используется, когда заданное значение выходит за пределы допустимого диапазона.
ERR_VM_MODULE_NOT_LINKED¶
Перед созданием экземпляра модуль должен быть успешно связан.
ERR_WORKER_UNSUPPORTED_EXTENSION¶
Имя пути, используемое для основного сценария рабочего, имеет неизвестное расширение файла.
ERR_ZLIB_BINDING_CLOSED¶
Используется, когда делается попытка использовать zlib объект после того, как он уже был закрыт.
ERR_CPU_USAGE¶
Родной звонок от process.cpuUsage не может быть обработано.
Ошибки есть в каждом коде. Мы перевели гайд разработчика Айо Исайя, в котором он рассказывает о системе ошибок и о том, как их устранять.
Раз вы читаете эту статью, вы, конечно, знакомы с концепцией ошибок в программировании. Это ошибки в коде, они же баги, которые приводят к сбою или неожиданному поведению программы. В отличие от некоторых языков, таких как Go и Rust, где вы вынуждены взаимодействовать с потенциальными ошибками на каждом этапе пути, в JavaScript и Node.js можно обойтись без согласованной стратегии обработки ошибок.
Однако именно такая стратегия делает жизнь проще. Цель статьи — познакомить вас с этими шаблонами для создания, доставки и обработки потенциальных ошибок. Шаблоны помогут обнаружить и обработать потенциальные ошибки в коде до развёртывания.
Что такое ошибки в Node.js
Ошибка в Node.js — это любой экземпляр объекта Error. Общие примеры включают встроенные классы ошибок: ReferenceError, RangeError, TypeError, URIError, EvalError и SyntaxError. Пользовательские ошибки также можно создать путём расширения базового объекта Error, встроенного класса ошибки или другой настраиваемой ошибки. При создании ошибок таким путём нужно передать строку сообщения, описывающую ошибку. К сообщению можно получить доступ через свойство message объекта. Объект Error также содержит свойства name и stack, которые указывают имя ошибки и точку в коде, в которой объект создаётся.
const userError = new TypeError("Something happened!");
console.log(userError.name); // TypeError
console.log(userError.message); // Something happened!
console.log(userError.stack);
/*TypeError: Something happened!
at Object.<anonymous> (/home/ayo/dev/demo/main.js:2:19)
<truncated for brevity>
at node:internal/main/run_main_module:17:47 */Функции объекта Error можно передать или вернуть из функции. Если бросить его с помощью throw, объект Error станет исключением. Когда вы передаёте ошибку из функции, она переходит вверх по стеку, пока исключение не будет поймано. В противном случае uncaught exception может обвалить всю работу.
Как обработать ошибку
Оптимальный способ обработки ошибок функции JavaScript зависит от того, выполняет ли эта функция синхронную или асинхронную операцию. Рассмотрим четыре общих шаблона, позволяющих обрабатывать ошибки функций в Node.js.
Исключения
Чаще всего ошибки функций обрабатывают путём генерации. В этом случае ошибка становится исключением, после чего её можно поймать где-нибудь в стеке с помощью блока try / catch. Если у ошибки есть разрешение всплывать в стеке, не будучи перехваченной, она преобразуется в формат uncaughtException, что приводит к преждевременному завершению работы приложения. Например, встроенный метод JSON.parse () выдаёт ошибку, если строковый аргумент не является допустимым объектом JSON.
function parseJSON(data) {
return JSON.parse(data);
}
try {
const result = parseJSON('A string');
} catch (err) {
console.log(err.message); // Unexpected token A in JSON at position 0
}Для использования этого шаблона в функциях нужно добавить ключевое слово throw перед экземпляром ошибки. Этот шаблон сообщения об ошибках и обработки идиоматичен для функций, выполняющих синхронные операции.
function square(num) {
if (typeof num !== 'number') {
throw new TypeError(`Expected number but got: ${typeof num}`);
}
return num * num;
}
try {
square('8');
} catch (err) {
console.log(err.message); // Expected number but got: string
}Колбэк с первым аргументом-ошибкой
Из-за своей асинхронной природы Node.js интенсивно использует функции колбэка для обработки большей части ошибок. Колбэк (обратный вызов) передаётся в качестве аргумента другой функции и выполняется, когда последняя завершает свою работу.
Node.js использует колбэк с первым аргументом-ошибкой в большинстве асинхронных методов, чтобы гарантировать проверку ошибок до результатов операции. Колбэк обычно является последним аргументом функции, инициирующей асинхронную операцию, и вызывается один раз при возникновении ошибки или получении результата:
function (err, result) {}Первый аргумент зарезервирован для объекта ошибки. Если ошибка возникает в ходе асинхронной операции, она доступна через аргумент err при неопределённом результате. Однако, если ошибки не возникает, err будет иметь значение null или undefined, а result будет содержать ожидаемый результат операции. Этот шаблон работает, если прочитать содержимое файла с помощью встроенного метода fs.readFile ():
const fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('/path/to/file.txt', (err, result) => {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
return;
}
// Log the file contents if no error
console.log(result);
});Метод readFile () использует колбэк в качестве своего последнего аргумента, который, в свою очередь, соответствует подписи функции «первая ошибка». В этом сценарии result включает в себя содержимое файла, который читается, если ошибки не возникает. В противном случае он определяется как undefined, а аргумент err заполняется объектом ошибки, содержащим информацию о проблеме: файл не найден или недостаточно полномочий.
Как правило, методы, использующие колбэк для обработки ошибок, не могут определить, насколько важна выявленная ошибка. Они возвращают ошибку пользователю для обработки. Важно контролировать поток содержимого колбэка, проверять функцию на наличие ошибки, прежде чем пытаться получить доступ к результату операции.
Чтобы использовать шаблон колбэка с первым аргументом-ошибкой в собственных асинхронных функциях, нужно принять функцию в качестве последнего аргумента и вызвать её:
function square(num, callback) {
if (typeof callback !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError(`Callback must be a function. Got: ${typeof callback}`);
}
// simulate async operation
setTimeout(() => {
if (typeof num !== 'number') {
// if an error occurs, it is passed as the first argument to the callback
callback(new TypeError(`Expected number but got: ${typeof num}`));
return;
}
const result = num * num;
// callback is invoked after the operation completes with the result
callback(null, result);
}, 100);
}Любой вызывающий функцию square должен пройти через колбэк, чтобы получить доступ к нужному результату или ошибке.
Не нужно непосредственно обрабатывать ошибку в функции колбэка. Её можно распространить вверх по стеку, передав на другой колбэк. Но сначала убедитесь, что вы не генерируете исключение внутри функции. Асинхронное исключение невозможно отследить, потому что окружающий блок try / catch завершается до выполнения колбэка. Следовательно, исключение будет распространяться на вершину стека, что приведёт к завершению работы приложения. Исключение — когда обработчик зарегистрирован для process.on ('uncaughtException').
try {
square('8', (err, result) => {
if (err) {
throw err; // not recommended
}
console.log(result);
});
} catch (err) {
// This won't work
console.error("Caught error: ", err);
}Отклонение обещаний
Обещания в JavaScript — это актуальный способ выполнения асинхронных операций в Node.js. Они предпочтительнее колбэков из-за лучшего потока, который соответствует современным способам анализа программ, особенно с шаблоном async / await. Любой API-интерфейс Node.js, использующий колбэки с ошибкой для асинхронной обработки ошибок, может быть преобразован в обещания с помощью встроенного метода util.promisify (). Например, заставить метод fs.readFile () использовать обещания можно так:
const fs = require('fs');
const util = require('util');
const readFile = util.promisify(fs.readFile);Переменная readFile — это версия fs.readFile () с обещаниями, в которой отклонения обещаний используются для сообщения об ошибках. Эти ошибки можно отследить, связав метод catch:
readFile('/path/to/file.txt')
.then((result) => console.log(result))
.catch((err) => console.error(err));Также можно использовать обещанные API в функциях async. Так выглядит основной способ использования обещаний в современном JavaScript: в нём код читается как синхронный, и для обработки ошибок применяют знакомый механизм try / catch. Перед асинхронным запуском важно использовать await, чтобы обещание было выполнено или отклонено до того, как функция возобновит выполнение. При отклонении обещания выражение await выбрасывает отклонённое значение, которое впоследствии попадает в окружающий блок catch.
(async function callReadFile() {
try {
const result = await readFile('/path/to/file.txt');
console.log(result);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
})();Обещанияможно использовать в асинхронных функциях, возвращая обещание из функции и помещая код функции в обратный вызов обещания. Если есть ошибка, её стоит отклонить (reject) с помощью объекта Error. В противном случае можно разрешить (resolve) обещание с результатом, чтобы оно было доступно в цепочке метода .then или напрямую как значение функции async при использовании async / await.
function square(num) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (typeof num !== 'number') {
reject(new TypeError(`Expected number but got: ${typeof num}`));
}
const result = num * num;
resolve(result);
}, 100);
});
}
square('8')
.then((result) => console.log(result))
.catch((err) => console.error(err));Источники событий
Другой шаблон, подходящий для работы с длительными асинхронными операциями, которые могут приводить к множественным ошибкам или результатам, — это возврат EventEmitter из функции и выдача события как для успешного, так и для неудачного случая:
const { EventEmitter } = require('events');
function emitCount() {
const emitter = new EventEmitter();
let count = 0;
// Async operation
const interval = setInterval(() => {
count++;
if (count % 4 == 0) {
emitter.emit(
'error',
new Error(`Something went wrong on count: ${count}`)
);
return;
}
emitter.emit('success', count);
if (count === 10) {
clearInterval(interval);
emitter.emit('end');
}
}, 1000);
return emitter;
}Функция emitCount () возвращает новый эмиттер событий, который сообщает об успешном исходе в асинхронной операции. Она увеличивает значение переменной count и каждую секунду генерирует событие успеха и событие ошибки, если значение count делится на 4. Когда count достигает 10, генерируется событие завершения. Этот шаблон позволяет передавать результаты по мере их поступления вместо ожидания завершения всей операции.
Вот как можно отслеживать и реагировать на каждое из событий, генерируемых функцией emitCount ():
const counter = emitCount();
counter.on('success', (count) => {
console.log(`Count is: ${count}`);
});
counter.on('error', (err) => {
console.error(err.message);
});
counter.on('end', () => {
console.info('Counter has ended');
});Функция колбэка для каждого прослушивателя событий выполняется независимо, как только событие генерируется. Событие ошибки (error) — это особый случай для Node.js, потому что при отсутствии прослушивателя процесс Node.js выходит из строя. Вы можете закомментировать прослушиватель событий ошибки выше и запустить программу, чтобы увидеть, что произойдёт.
Расширение объекта ошибки
Необходимо создавать собственные пользовательские классы ошибок, чтобы лучше отражать разные типы ошибок: класс ValidationError для ошибок, возникающих при проверке пользовательского ввода, класс DatabaseError для операций с базами данных, TimeoutError для операций, для которых истекло назначенное им время ожидания.
Пользовательские классы ошибок, расширяющие объект Error, сохранят основные свойства ошибки: сообщение (message), имя (name) и стек (stack). Но у них есть собственные свойства. ValidationError можно улучшить, добавив значимые свойства — часть ввода, вызвавшую ошибку.
Вот как можно расширить встроенный объект Error в Node.js:
class ApplicationError extends Error {
constructor(message) {
super(message);
// name is set to the name of the class
this.name = this.constructor.name;
}
}
class ValidationError extends ApplicationError {
constructor(message, cause) {
super(message);
this.cause = cause
}
}Класс ApplicationError — общая ошибка, а класс ValidationError представляет любую ошибку, возникающую при проверке ввода данных пользователем. Он наследуется от класса ApplicationError и дополняет его свойством cause для указания ввода, вызвавшего ошибку. Пользовательские классы ошибки можно использовать, как и обычные:
function validateInput(input) {
if (!input) {
throw new ValidationError('Only truthy inputs allowed', input);
}
return input;
}
try {
validateInput(userJson);
} catch (err) {
if (err instanceof ValidationError) {
console.error(`Validation error: ${err.message}, caused by: ${err.cause}`);
return;
}
console.error(`Other error: ${err.message}`);
}Ключевое слово instanceof следует использовать для проверки конкретного типа ошибки. Не используйте имя ошибки для проверки типа, как в err.name === 'ValidationError': это не сработает, если ошибка получена из подкласса ValidationError.
Типы ошибок
Типы ошибок можно разделить на две основные категории: ошибки программиста и операционные проблемы. К первому типу можно отнести неудачные или неправильные аргументы функции, в то время как временные сбои при работе с внешними API однозначно относятся ко второй категории.
Операционные ошибки
Операционные ошибки — это предсказуемые ошибки, которые возникают в процессе выполнения приложения. Это не обязательно баги, чаще это даже внешние обстоятельства, способные нарушить ход выполнения программы. В таких случаях можно полностью понять влияние ошибки на процессы:
-
Запрос API не выполняется по какой-либо причине (например, сервер не работает или превышен лимит скорости).
-
Соединение с базой данных потеряно, например, из-за неисправного сетевого соединения.
-
ОС не может выполнить запрос на открытие файла или запись в него.
-
Пользователь отправляет на сервер недопустимые данные: неверный номер телефона или адрес электронной почты.
Ошибки программиста
Ошибки программиста — это ошибки в логике или синтаксисе программы, которые можно исправить только путём изменения исходного кода. Ошибки этого типа невозможно обработать, потому что это недочёты в программе:
-
Синтаксические ошибки: незакрытая фигурная скобка.
-
Ошибки типа при попытке сделать что-то неправильное: выполнение операций с операндами несовпадающих типов.
-
Неверные параметры при вызове функции.
-
Ссылки на ошибки при неправильном написании имени переменной, функции или свойства.
-
Попытка получить доступ к местоположению за концом массива.
-
Неспособность обработать операционную ошибку.
Обработка операционных ошибок
Операционные ошибки в большинстве случаев предсказуемы. Их обработка — это рассмотрение вероятности неудачного завершения операции, возможных причин и последствий. Рассмотрим несколько стратегий обработки операционных ошибок в Node.js.
Сообщить об ошибке в стек
Во многих случаях лучше остановить выполнение программы, очистить все незавершённые процессы и сообщить об ошибке в стек. Зачастую это единственный способ исправить ошибку, когда функция, в которой она возникла, находится дальше по стеку.
Повторить операцию
Сетевые запросы к внешним службам иногда могут завершаться ошибкой, даже если запрос полностью верен. Это случается из-за сбоя и неполадках сети или перегрузке сервера. Можно повторить запрос несколько раз, пока он не будет успешно завершён или пока не будет достигнуто максимальное количество повторных попыток. Первое, что нужно сделать, — это определить, уместно ли повторить запрос. Если исходный код состояния HTTP ответа — 500, 503 или 429, повторте запрос через некоторое время.
Проверьте, присутствует ли в ответе HTTP-заголовок Retry-After. Он указывает на точное время ожидания перед выполнением последующего запроса. Если его нет, необходимо отложить последующий запрос и постепенно увеличивать временной промежуток для каждой повторной попытки. Этот метод известен как стратегия экспоненциального отката. Нужно ещё определить максимальное время задержки и число запросов до отказа от дальнейших попыток.
Отправить ошибку клиенту
По умолчанию пользователи вводят данные неправильно. Поэтому первое, что нужно сделать перед запуском каких-либо процессов, — проверить введённые данные и незамедлительно сообщить пользователю о любых ошибках. При обработке ошибок клиента обязательно включите всю информацию, необходимую для создания сообщения об ошибке и имеющую смысл для пользователя.
Прервать программу.
В случае неисправимых системных ошибок разумный выход — зарегистрировать ошибку и немедленно завершить работу программы. Если исключение невозможно исправить на уровне JavaScript, то, возможно, не получится корректно завершить работу сервера. Тогда нужен системный администратор, способный всё исправить.
Предотвращение ошибок программиста
Ошибки программиста сами по себе не могут быть обработаны, потому что их причина в коде или в логике. Однако ошибаться можно реже.
Принять TypeScript
TypeScript — это строго типизированное надмножество JavaScript. Основная цель его проектирования — статическая идентификация потенциально ошибочных конструкций без штрафных санкций во время выполнения. Принимая TypeScript в проекте (с максимально возможными параметрами компилятора), можно устранить целый класс ошибок программиста в ходе компиляции.
Когда проект на TypeScript, такие ошибки, как undefined is not a function, синтаксические или ссылочные ошибки, исчезают из кодовой базы. Перенос на TypeScript можно выполнять постепенно. Для быстрой миграции есть инструмент ts-migrate.
Определить поведение для неверных параметров
Многие ошибки возникают из-за передачи неверных параметров. Это может быть связано не только с очевидными ошибками, такими как передача строки вместо числа, но и с небольшими погрешностями, когда аргумент функции имеет правильный тип, но выходит за пределы диапазона, который функция способна обработать. Когда функция вызывается таким образом, она может выдать неверное значение, например NaN. Когда сбой обнаруживается, сперва трудно определить его причину.
При работе с неверными параметрами и определяйте их поведение, либо выдавая ошибку, либо возвращая специальное значение, такое как null, undefined или -1, когда проблема может быть решена локально. Первый вариант— это подход, используемый JSON.parse (), который выдаёт исключение SyntaxError, если строка для синтаксического анализа недействительна. Второй вариант — метод string.indexOf () .
Автоматизированное тестирование
Автоматизированные наборы тестов повышает вероятность исправления ошибок. Тесты помогают выяснить, как функция работает с нетипичными значениями. Для модульного тестирования подходят среды, такие как Jest или Mocha.
Неперехваченные исключения и необработанные отклонения обещаний
Неперехваченные исключения и необработанные отклонения обещаний вызываются ошибками программиста. Событие uncaughtException генерируется, когда исключение не перехватывается до того как достигнет цикла обработки событий. При обнаружении неперехваченного исключения приложение немедленно выходит из строя. Для переопределения такого поведения всегда можно добавить обработчик события:
// unsafe
process.on('uncaughtException', (err) => {
console.error(err);
});Но неперехваченное исключение указывает на то, что приложение находится в неопределённом состоянии. Поэтому попытка возобновить работу в обычном режиме без восстановления после ошибки небезопасна и может привести к утечке памяти и зависанию сокетов. Лучше использовать обработчик uncaught Exception для очистки всех выделенных ресурсов, закрытия соединений и ведения лога ошибок для оценки перед завершением процесса.
// better
process.on('uncaughtException', (err) => {
Honeybadger.notify(error); // log the error in a permanent storage
// attempt a gracefully shutdown
server.close(() => {
process.exit(1); // then exit
});
// If a graceful shutdown is not achieved after 1 second,
// shut down the process completely
setTimeout(() => {
process.abort(); // exit immediately and generate a core dump file
}, 1000).unref()
});Событие unhandledRejection генерируется, когда отклонённое обещание не обрабатывается блоком catch. В отличие от uncaughtException, эти события не вызывают немедленного сбоя приложения. Однако необработанные отклонения обещаний сейчас признаны устаревшими и могут немедленно завершить процесс в следующих релизах Node.js. Отслеживать необработанные отклонения обещаний можно с помощью прослушивателя событий unhandledRejection:
process.on('unhandledRejection', (reason, promise) => {
Honeybadger.notify({
message: 'Unhandled promise rejection',
params: {
promise,
reason,
},
});
server.close(() => {
process.exit(1);
});
setTimeout(() => {
process.abort();
}, 1000).unref()
});Серверы необходимо запускать с помощью диспетчера процессов, который автоматически перезапустит их в случае сбоя. Распространённый вариант — PM2, но для Linux существуют также systemd и upstart, а пользователи Docker могут использовать собственную политику перезапуска. По завершении всех процессов стабильное обслуживание будет восстановлено почти мгновенно, а у вас будт информация о неперехваченном исключении. Можно запутсить несколько процессов и применить балансировщик нагрузки для распределения входящих запросов. Это поможет предотвратить простои.
Централизованная отчётность об ошибках
Ни одна стратегия обработки ошибок не будет полной без надёжной стратегии ведения журнала ошибок. Когда происходит сбой, важно узаписать как можно больше информации о проблеме. Централизация логов позволяет оценить, что происходит в коде.
Honeybadger предоставляет всё необходимое для отслеживания ошибок. Интегрируется так:
Установите пакет
Используйте npm для установки пакета:
$ npm install @honeybadger-io/js --save
Импортируйте библиотеку
Импортируйте библиотеку и настройте её с помощью ключа API, чтобы получать сообщения об ошибках:
const Honeybadger = require('@honeybadger-io/js');
Honeybadger.configure({
apiKey: '[ YOUR API KEY HERE ]'
});
Сообщите об ошибках
Метоодом notify ():
try {
// ...error producing code
} catch(error) {
Honeybadger.notify(error);
}Просмотрите полную документацию или ознакомьтесь с образцом Node.js / Express на GitHub.
Без обработки ошибок не бывает надёжного софта.
Спасибо за внимание и удачного кода!
Содержание
- Node.js v19.4.0 documentation
- Errors #
- Error propagation and interception #
- Error-first callbacks #
- Class: Error #
- new Error(message[, options]) #
- Error.captureStackTrace(targetObject[, constructorOpt]) #
- Error.stackTraceLimit #
- error.cause #
- error.code #
- error.message #
- error.stack #
- Class: AssertionError #
- Class: RangeError #
- Class: ReferenceError #
- Class: SyntaxError #
- Class: SystemError #
- error.address #
- error.code #
- error.dest #
- error.errno #
- error.info #
- error.message #
- error.path #
- error.port #
- error.syscall #
- Common system errors #
- Class: TypeError #
- Exceptions vs. errors #
- OpenSSL errors #
- error.opensslErrorStack #
- error.function #
- error.library #
- error.reason #
- Node.js error codes #
- ABORT_ERR #
- ERR_AMBIGUOUS_ARGUMENT #
- ERR_ARG_NOT_ITERABLE #
- ERR_ASSERTION #
- ERR_ASSERT_SNAPSHOT_NOT_SUPPORTED #
- ERR_ASYNC_CALLBACK #
- ERR_ASYNC_TYPE #
- ERR_BROTLI_COMPRESSION_FAILED #
- ERR_BROTLI_INVALID_PARAM #
- ERR_BUFFER_CONTEXT_NOT_AVAILABLE #
- ERR_BUFFER_OUT_OF_BOUNDS #
- ERR_BUFFER_TOO_LARGE #
- ERR_CANNOT_WATCH_SIGINT #
- ERR_CHILD_CLOSED_BEFORE_REPLY #
- ERR_CHILD_PROCESS_IPC_REQUIRED #
- ERR_CHILD_PROCESS_STDIO_MAXBUFFER #
- ERR_CLOSED_MESSAGE_PORT #
- ERR_CONSOLE_WRITABLE_STREAM #
- ERR_CONSTRUCT_CALL_INVALID #
- ERR_CONSTRUCT_CALL_REQUIRED #
- ERR_CONTEXT_NOT_INITIALIZED #
- ERR_CRYPTO_CUSTOM_ENGINE_NOT_SUPPORTED #
- ERR_CRYPTO_ECDH_INVALID_FORMAT #
- ERR_CRYPTO_ECDH_INVALID_PUBLIC_KEY #
- ERR_CRYPTO_ENGINE_UNKNOWN #
- ERR_CRYPTO_FIPS_FORCED #
- ERR_CRYPTO_FIPS_UNAVAILABLE #
- ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_FINALIZED #
- ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_UPDATE_FAILED #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INCOMPATIBLE_KEY #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INCOMPATIBLE_KEY_OPTIONS #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INITIALIZATION_FAILED #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_AUTH_TAG #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_COUNTER #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_CURVE #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_DIGEST #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_IV #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_JWK #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_KEY_OBJECT_TYPE #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_KEYLEN #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_KEYPAIR #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_KEYTYPE #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_MESSAGELEN #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_SCRYPT_PARAMS #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_STATE #
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_TAG_LENGTH #
- ERR_CRYPTO_JOB_INIT_FAILED #
- ERR_CRYPTO_JWK_UNSUPPORTED_CURVE #
- ERR_CRYPTO_JWK_UNSUPPORTED_KEY_TYPE #
- ERR_CRYPTO_OPERATION_FAILED #
- ERR_CRYPTO_PBKDF2_ERROR #
- ERR_CRYPTO_SCRYPT_INVALID_PARAMETER #
- ERR_CRYPTO_SCRYPT_NOT_SUPPORTED #
- ERR_CRYPTO_SIGN_KEY_REQUIRED #
- ERR_CRYPTO_TIMING_SAFE_EQUAL_LENGTH #
- ERR_CRYPTO_UNKNOWN_CIPHER #
- ERR_CRYPTO_UNKNOWN_DH_GROUP #
- ERR_CRYPTO_UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION #
- ERR_DEBUGGER_ERROR #
- ERR_DEBUGGER_STARTUP_ERROR #
- ERR_DLOPEN_DISABLED #
- ERR_DLOPEN_FAILED #
- ERR_DIR_CLOSED #
- ERR_DIR_CONCURRENT_OPERATION #
- ERR_DNS_SET_SERVERS_FAILED #
- ERR_DOMAIN_CALLBACK_NOT_AVAILABLE #
- ERR_DOMAIN_CANNOT_SET_UNCAUGHT_EXCEPTION_CAPTURE #
- ERR_DUPLICATE_STARTUP_SNAPSHOT_MAIN_FUNCTION #
- ERR_ENCODING_INVALID_ENCODED_DATA #
- ERR_ENCODING_NOT_SUPPORTED #
- ERR_EVAL_ESM_CANNOT_PRINT #
- ERR_EVENT_RECURSION #
- ERR_EXECUTION_ENVIRONMENT_NOT_AVAILABLE #
- ERR_FALSY_VALUE_REJECTION #
- ERR_FEATURE_UNAVAILABLE_ON_PLATFORM #
- ERR_FS_CP_DIR_TO_NON_DIR #
- ERR_FS_CP_EEXIST #
- ERR_FS_CP_EINVAL #
- ERR_HTTP_CONTENT_LENGTH_MISMATCH #
- ERR_FS_CP_FIFO_PIPE #
- ERR_FS_CP_NON_DIR_TO_DIR #
- ERR_FS_CP_SOCKET #
- ERR_FS_CP_SYMLINK_TO_SUBDIRECTORY #
- ERR_FS_CP_UNKNOWN #
- ERR_FS_EISDIR #
- ERR_FS_FILE_TOO_LARGE #
- ERR_FS_INVALID_SYMLINK_TYPE #
- ERR_HTTP_HEADERS_SENT #
- ERR_HTTP_INVALID_HEADER_VALUE #
- ERR_HTTP_INVALID_STATUS_CODE #
- ERR_HTTP_REQUEST_TIMEOUT #
- ERR_HTTP_SOCKET_ENCODING #
- ERR_HTTP_TRAILER_INVALID #
- ERR_HTTP2_ALTSVC_INVALID_ORIGIN #
- ERR_HTTP2_ALTSVC_LENGTH #
- ERR_HTTP2_CONNECT_AUTHORITY #
- ERR_HTTP2_CONNECT_PATH #
- ERR_HTTP2_CONNECT_SCHEME #
- ERR_HTTP2_ERROR #
- ERR_HTTP2_GOAWAY_SESSION #
- ERR_HTTP2_HEADER_SINGLE_VALUE #
- ERR_HTTP2_HEADERS_AFTER_RESPOND #
- ERR_HTTP2_HEADERS_SENT #
- ERR_HTTP2_INFO_STATUS_NOT_ALLOWED #
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_CONNECTION_HEADERS #
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_HEADER_VALUE #
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_INFO_STATUS #
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_ORIGIN #
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_PACKED_SETTINGS_LENGTH #
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_PSEUDOHEADER #
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_SESSION #
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_SETTING_VALUE #
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_STREAM #
- ERR_HTTP2_MAX_PENDING_SETTINGS_ACK #
- ERR_HTTP2_NESTED_PUSH #
- ERR_HTTP2_NO_MEM #
- ERR_HTTP2_NO_SOCKET_MANIPULATION #
- ERR_HTTP2_ORIGIN_LENGTH #
- ERR_HTTP2_OUT_OF_STREAMS #
- ERR_HTTP2_PAYLOAD_FORBIDDEN #
- ERR_HTTP2_PING_CANCEL #
- ERR_HTTP2_PING_LENGTH #
- ERR_HTTP2_PSEUDOHEADER_NOT_ALLOWED #
- ERR_HTTP2_PUSH_DISABLED #
- ERR_HTTP2_SEND_FILE #
- ERR_HTTP2_SEND_FILE_NOSEEK #
- ERR_HTTP2_SESSION_ERROR #
- ERR_HTTP2_SETTINGS_CANCEL #
- ERR_HTTP2_SOCKET_BOUND #
- ERR_HTTP2_SOCKET_UNBOUND #
- ERR_HTTP2_STATUS_101 #
- ERR_HTTP2_STATUS_INVALID #
- ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_CANCEL #
- ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_ERROR #
- ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_SELF_DEPENDENCY #
- ERR_HTTP2_TOO_MANY_INVALID_FRAMES #
- ERR_HTTP2_TRAILERS_ALREADY_SENT #
- ERR_HTTP2_TRAILERS_NOT_READY #
- ERR_HTTP2_UNSUPPORTED_PROTOCOL #
- ERR_ILLEGAL_CONSTRUCTOR #
- ERR_IMPORT_ASSERTION_TYPE_FAILED #
- ERR_IMPORT_ASSERTION_TYPE_MISSING #
- ERR_IMPORT_ASSERTION_TYPE_UNSUPPORTED #
- ERR_INCOMPATIBLE_OPTION_PAIR #
- ERR_INPUT_TYPE_NOT_ALLOWED #
- ERR_INSPECTOR_ALREADY_ACTIVATED #
- ERR_INSPECTOR_ALREADY_CONNECTED #
- ERR_INSPECTOR_CLOSED #
- ERR_INSPECTOR_COMMAND #
- ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_ACTIVE #
- ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_AVAILABLE #
- ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_CONNECTED #
- ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_WORKER #
- ERR_INTERNAL_ASSERTION #
- ERR_INVALID_ADDRESS_FAMILY #
- ERR_INVALID_ARG_TYPE #
- ERR_INVALID_ARG_VALUE #
- ERR_INVALID_ASYNC_ID #
- ERR_INVALID_BUFFER_SIZE #
- ERR_INVALID_CHAR #
- ERR_INVALID_CURSOR_POS #
- ERR_INVALID_FD #
- ERR_INVALID_FD_TYPE #
- ERR_INVALID_FILE_URL_HOST #
- ERR_INVALID_FILE_URL_PATH #
- ERR_INVALID_HANDLE_TYPE #
- ERR_INVALID_HTTP_TOKEN #
- ERR_INVALID_IP_ADDRESS #
- ERR_INVALID_MIME_SYNTAX #
- ERR_INVALID_MODULE #
- ERR_INVALID_MODULE_SPECIFIER #
- ERR_INVALID_OBJECT_DEFINE_PROPERTY #
- ERR_INVALID_PACKAGE_CONFIG #
- ERR_INVALID_PACKAGE_TARGET #
- ERR_INVALID_PERFORMANCE_MARK #
- ERR_INVALID_PROTOCOL #
- ERR_INVALID_REPL_EVAL_CONFIG #
- ERR_INVALID_REPL_INPUT #
- ERR_INVALID_RETURN_PROPERTY #
- ERR_INVALID_RETURN_PROPERTY_VALUE #
- ERR_INVALID_RETURN_VALUE #
- ERR_INVALID_STATE #
- ERR_INVALID_SYNC_FORK_INPUT #
- ERR_INVALID_THIS #
- ERR_INVALID_TRANSFER_OBJECT #
- ERR_INVALID_TUPLE #
- ERR_INVALID_URI #
- ERR_INVALID_URL #
- ERR_INVALID_URL_SCHEME #
- ERR_IPC_CHANNEL_CLOSED #
- ERR_IPC_DISCONNECTED #
- ERR_IPC_ONE_PIPE #
- ERR_IPC_SYNC_FORK #
- ERR_LOADER_CHAIN_INCOMPLETE #
- ERR_MANIFEST_ASSERT_INTEGRITY #
- ERR_MANIFEST_DEPENDENCY_MISSING #
- ERR_MANIFEST_INTEGRITY_MISMATCH #
- ERR_MANIFEST_INVALID_RESOURCE_FIELD #
- ERR_MANIFEST_INVALID_SPECIFIER #
- ERR_MANIFEST_PARSE_POLICY #
- ERR_MANIFEST_TDZ #
- ERR_MANIFEST_UNKNOWN_ONERROR #
- ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATION_FAILED #
- ERR_MESSAGE_TARGET_CONTEXT_UNAVAILABLE #
- ERR_METHOD_NOT_IMPLEMENTED #
- ERR_MISSING_ARGS #
- ERR_MISSING_OPTION #
- ERR_MISSING_PASSPHRASE #
- ERR_MISSING_PLATFORM_FOR_WORKER #
- ERR_MISSING_TRANSFERABLE_IN_TRANSFER_LIST #
- ERR_MODULE_NOT_FOUND #
- ERR_MULTIPLE_CALLBACK #
- ERR_NAPI_CONS_FUNCTION #
- ERR_NAPI_INVALID_DATAVIEW_ARGS #
- ERR_NAPI_INVALID_TYPEDARRAY_ALIGNMENT #
- ERR_NAPI_INVALID_TYPEDARRAY_LENGTH #
- ERR_NAPI_TSFN_CALL_JS #
- ERR_NAPI_TSFN_GET_UNDEFINED #
- ERR_NAPI_TSFN_START_IDLE_LOOP #
- ERR_NAPI_TSFN_STOP_IDLE_LOOP #
- ERR_NOT_BUILDING_SNAPSHOT #
- ERR_NO_CRYPTO #
- ERR_NO_ICU #
- ERR_NON_CONTEXT_AWARE_DISABLED #
- ERR_OUT_OF_RANGE #
- ERR_PACKAGE_IMPORT_NOT_DEFINED #
- ERR_PACKAGE_PATH_NOT_EXPORTED #
- ERR_PARSE_ARGS_INVALID_OPTION_VALUE #
- ERR_PARSE_ARGS_UNEXPECTED_POSITIONAL #
- ERR_PARSE_ARGS_UNKNOWN_OPTION #
- ERR_PERFORMANCE_INVALID_TIMESTAMP #
- ERR_PERFORMANCE_MEASURE_INVALID_OPTIONS #
- ERR_PROTO_ACCESS #
- ERR_REQUIRE_ESM #
- ERR_SCRIPT_EXECUTION_INTERRUPTED #
- ERR_SCRIPT_EXECUTION_TIMEOUT #
- ERR_SERVER_ALREADY_LISTEN #
- ERR_SERVER_NOT_RUNNING #
- ERR_SOCKET_ALREADY_BOUND #
- ERR_SOCKET_BAD_BUFFER_SIZE #
- ERR_SOCKET_BAD_PORT #
- ERR_SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE #
- ERR_SOCKET_CLOSED #
- ERR_SOCKET_CLOSED_BEFORE_CONNECTION #
- ERR_SOCKET_DGRAM_IS_CONNECTED #
- ERR_SOCKET_DGRAM_NOT_CONNECTED #
- ERR_SOCKET_DGRAM_NOT_RUNNING #
- ERR_SRI_PARSE #
- ERR_STREAM_ALREADY_FINISHED #
- ERR_STREAM_CANNOT_PIPE #
- ERR_STREAM_DESTROYED #
- ERR_STREAM_NULL_VALUES #
- ERR_STREAM_PREMATURE_CLOSE #
- ERR_STREAM_PUSH_AFTER_EOF #
- ERR_STREAM_UNSHIFT_AFTER_END_EVENT #
- ERR_STREAM_WRAP #
- ERR_STREAM_WRITE_AFTER_END #
- ERR_STRING_TOO_LONG #
- ERR_SYNTHETIC #
- ERR_SYSTEM_ERROR #
- ERR_TAP_LEXER_ERROR #
- ERR_TAP_PARSER_ERROR #
- ERR_TAP_VALIDATION_ERROR #
- ERR_TEST_FAILURE #
- ERR_TLS_CERT_ALTNAME_FORMAT #
- ERR_TLS_CERT_ALTNAME_INVALID #
- ERR_TLS_DH_PARAM_SIZE #
- ERR_TLS_HANDSHAKE_TIMEOUT #
- ERR_TLS_INVALID_CONTEXT #
- ERR_TLS_INVALID_PROTOCOL_METHOD #
- ERR_TLS_INVALID_PROTOCOL_VERSION #
- ERR_TLS_INVALID_STATE #
- ERR_TLS_PROTOCOL_VERSION_CONFLICT #
- ERR_TLS_PSK_SET_IDENTIY_HINT_FAILED #
- ERR_TLS_RENEGOTIATION_DISABLED #
- ERR_TLS_REQUIRED_SERVER_NAME #
- ERR_TLS_SESSION_ATTACK #
- ERR_TLS_SNI_FROM_SERVER #
- ERR_TRACE_EVENTS_CATEGORY_REQUIRED #
- ERR_TRACE_EVENTS_UNAVAILABLE #
- ERR_TRANSFORM_ALREADY_TRANSFORMING #
- ERR_TRANSFORM_WITH_LENGTH_0 #
- ERR_TTY_INIT_FAILED #
- ERR_UNAVAILABLE_DURING_EXIT #
- ERR_UNCAUGHT_EXCEPTION_CAPTURE_ALREADY_SET #
- ERR_UNESCAPED_CHARACTERS #
- ERR_UNHANDLED_ERROR #
- ERR_UNKNOWN_BUILTIN_MODULE #
- ERR_UNKNOWN_CREDENTIAL #
- ERR_UNKNOWN_ENCODING #
- ERR_UNKNOWN_FILE_EXTENSION #
- ERR_UNKNOWN_MODULE_FORMAT #
- ERR_UNKNOWN_SIGNAL #
- ERR_UNSUPPORTED_DIR_IMPORT #
- ERR_UNSUPPORTED_ESM_URL_SCHEME #
- ERR_USE_AFTER_CLOSE #
- ERR_VALID_PERFORMANCE_ENTRY_TYPE #
- ERR_VM_DYNAMIC_IMPORT_CALLBACK_MISSING #
- ERR_VM_MODULE_ALREADY_LINKED #
- ERR_VM_MODULE_CACHED_DATA_REJECTED #
- ERR_VM_MODULE_CANNOT_CREATE_CACHED_DATA #
- ERR_VM_MODULE_DIFFERENT_CONTEXT #
- ERR_VM_MODULE_LINK_FAILURE #
- ERR_VM_MODULE_NOT_MODULE #
- ERR_VM_MODULE_STATUS #
- ERR_WASI_ALREADY_STARTED #
- ERR_WASI_NOT_STARTED #
- ERR_WEBASSEMBLY_RESPONSE #
- ERR_WORKER_INIT_FAILED #
- ERR_WORKER_INVALID_EXEC_ARGV #
- ERR_WORKER_NOT_RUNNING #
- ERR_WORKER_OUT_OF_MEMORY #
- ERR_WORKER_PATH #
- ERR_WORKER_UNSERIALIZABLE_ERROR #
- ERR_WORKER_UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION #
- ERR_ZLIB_INITIALIZATION_FAILED #
- HPE_HEADER_OVERFLOW #
- HPE_UNEXPECTED_CONTENT_LENGTH #
- MODULE_NOT_FOUND #
- Legacy Node.js error codes #
- ERR_CANNOT_TRANSFER_OBJECT #
- ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_DIGEST_NO_UTF16 #
- ERR_HTTP2_FRAME_ERROR #
- ERR_HTTP2_HEADERS_OBJECT #
- ERR_HTTP2_HEADER_REQUIRED #
- ERR_HTTP2_INFO_HEADERS_AFTER_RESPOND #
- ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_CLOSED #
- ERR_HTTP_INVALID_CHAR #
- ERR_INDEX_OUT_OF_RANGE #
- ERR_INVALID_OPT_VALUE #
- ERR_INVALID_OPT_VALUE_ENCODING #
- ERR_MISSING_MESSAGE_PORT_IN_TRANSFER_LIST #
- ERR_NAPI_CONS_PROTOTYPE_OBJECT #
- ERR_NETWORK_IMPORT_BAD_RESPONSE #
- ERR_NETWORK_IMPORT_DISALLOWED #
- ERR_NO_LONGER_SUPPORTED #
- ERR_OPERATION_FAILED #
- ERR_OUTOFMEMORY #
- ERR_PARSE_HISTORY_DATA #
- ERR_SOCKET_CANNOT_SEND #
- ERR_STDERR_CLOSE #
- ERR_STDOUT_CLOSE #
- ERR_STREAM_READ_NOT_IMPLEMENTED #
- ERR_TLS_RENEGOTIATION_FAILED #
- ERR_TRANSFERRING_EXTERNALIZED_SHAREDARRAYBUFFER #
- ERR_UNKNOWN_STDIN_TYPE #
- ERR_UNKNOWN_STREAM_TYPE #
- ERR_V8BREAKITERATOR #
- ERR_VALUE_OUT_OF_RANGE #
- ERR_VM_MODULE_NOT_LINKED #
- ERR_VM_MODULE_LINKING_ERRORED #
- ERR_WORKER_UNSUPPORTED_EXTENSION #
- ERR_ZLIB_BINDING_CLOSED #
Node.js v19.4.0 documentation
Errors #
Applications running in Node.js will generally experience four categories of errors:
- Standard JavaScript errors such as , , , , , and .
- System errors triggered by underlying operating system constraints such as attempting to open a file that does not exist or attempting to send data over a closed socket.
- User-specified errors triggered by application code.
- AssertionError s are a special class of error that can be triggered when Node.js detects an exceptional logic violation that should never occur. These are raised typically by the node:assert module.
All JavaScript and system errors raised by Node.js inherit from, or are instances of, the standard JavaScript class and are guaranteed to provide at least the properties available on that class.
Error propagation and interception #
Node.js supports several mechanisms for propagating and handling errors that occur while an application is running. How these errors are reported and handled depends entirely on the type of Error and the style of the API that is called.
All JavaScript errors are handled as exceptions that immediately generate and throw an error using the standard JavaScript throw mechanism. These are handled using the try…catch construct provided by the JavaScript language.
Any use of the JavaScript throw mechanism will raise an exception that must be handled using try…catch or the Node.js process will exit immediately.
With few exceptions, Synchronous APIs (any blocking method that does not accept a callback function, such as fs.readFileSync ), will use throw to report errors.
Errors that occur within Asynchronous APIs may be reported in multiple ways:
Most asynchronous methods that accept a callback function will accept an Error object passed as the first argument to that function. If that first argument is not null and is an instance of Error , then an error occurred that should be handled.
When an asynchronous method is called on an object that is an EventEmitter , errors can be routed to that object’s ‘error’ event.
A handful of typically asynchronous methods in the Node.js API may still use the throw mechanism to raise exceptions that must be handled using try…catch . There is no comprehensive list of such methods; please refer to the documentation of each method to determine the appropriate error handling mechanism required.
The use of the ‘error’ event mechanism is most common for stream-based and event emitter-based APIs, which themselves represent a series of asynchronous operations over time (as opposed to a single operation that may pass or fail).
For all EventEmitter objects, if an ‘error’ event handler is not provided, the error will be thrown, causing the Node.js process to report an uncaught exception and crash unless either: The domain module is used appropriately or a handler has been registered for the ‘uncaughtException’ event.
Errors generated in this way cannot be intercepted using try…catch as they are thrown after the calling code has already exited.
Developers must refer to the documentation for each method to determine exactly how errors raised by those methods are propagated.
Error-first callbacks #
Most asynchronous methods exposed by the Node.js core API follow an idiomatic pattern referred to as an error-first callback. With this pattern, a callback function is passed to the method as an argument. When the operation either completes or an error is raised, the callback function is called with the Error object (if any) passed as the first argument. If no error was raised, the first argument will be passed as null .
The JavaScript try…catch mechanism cannot be used to intercept errors generated by asynchronous APIs. A common mistake for beginners is to try to use throw inside an error-first callback:
This will not work because the callback function passed to fs.readFile() is called asynchronously. By the time the callback has been called, the surrounding code, including the try…catch block, will have already exited. Throwing an error inside the callback can crash the Node.js process in most cases. If domains are enabled, or a handler has been registered with process.on(‘uncaughtException’) , such errors can be intercepted.
Class: Error #
A generic JavaScript object that does not denote any specific circumstance of why the error occurred. Error objects capture a «stack trace» detailing the point in the code at which the Error was instantiated, and may provide a text description of the error.
All errors generated by Node.js, including all system and JavaScript errors, will either be instances of, or inherit from, the Error class.
new Error(message[, options]) #
Creates a new Error object and sets the error.message property to the provided text message. If an object is passed as message , the text message is generated by calling String(message) . If the cause option is provided, it is assigned to the error.cause property. The error.stack property will represent the point in the code at which new Error() was called. Stack traces are dependent on V8’s stack trace API. Stack traces extend only to either (a) the beginning of synchronous code execution, or (b) the number of frames given by the property Error.stackTraceLimit , whichever is smaller.
Error.captureStackTrace(targetObject[, constructorOpt]) #
Creates a .stack property on targetObject , which when accessed returns a string representing the location in the code at which Error.captureStackTrace() was called.
The first line of the trace will be prefixed with $: $ .
The optional constructorOpt argument accepts a function. If given, all frames above constructorOpt , including constructorOpt , will be omitted from the generated stack trace.
The constructorOpt argument is useful for hiding implementation details of error generation from the user. For instance:
Error.stackTraceLimit #
The Error.stackTraceLimit property specifies the number of stack frames collected by a stack trace (whether generated by new Error().stack or Error.captureStackTrace(obj) ).
The default value is 10 but may be set to any valid JavaScript number. Changes will affect any stack trace captured after the value has been changed.
If set to a non-number value, or set to a negative number, stack traces will not capture any frames.
error.cause #
If present, the error.cause property is the underlying cause of the Error . It is used when catching an error and throwing a new one with a different message or code in order to still have access to the original error.
The error.cause property is typically set by calling new Error(message, < cause >) . It is not set by the constructor if the cause option is not provided.
This property allows errors to be chained. When serializing Error objects, util.inspect() recursively serializes error.cause if it is set.
error.code #
The error.code property is a string label that identifies the kind of error. error.code is the most stable way to identify an error. It will only change between major versions of Node.js. In contrast, error.message strings may change between any versions of Node.js. See Node.js error codes for details about specific codes.
error.message #
The error.message property is the string description of the error as set by calling new Error(message) . The message passed to the constructor will also appear in the first line of the stack trace of the Error , however changing this property after the Error object is created may not change the first line of the stack trace (for example, when error.stack is read before this property is changed).
error.stack #
The error.stack property is a string describing the point in the code at which the Error was instantiated.
The first line is formatted as : , and is followed by a series of stack frames (each line beginning with «at «). Each frame describes a call site within the code that lead to the error being generated. V8 attempts to display a name for each function (by variable name, function name, or object method name), but occasionally it will not be able to find a suitable name. If V8 cannot determine a name for the function, only location information will be displayed for that frame. Otherwise, the determined function name will be displayed with location information appended in parentheses.
Frames are only generated for JavaScript functions. If, for example, execution synchronously passes through a C++ addon function called cheetahify which itself calls a JavaScript function, the frame representing the cheetahify call will not be present in the stack traces:
The location information will be one of:
- native , if the frame represents a call internal to V8 (as in [].forEach ).
- plain-filename.js:line:column , if the frame represents a call internal to Node.js.
- /absolute/path/to/file.js:line:column , if the frame represents a call in a user program (using CommonJS module system), or its dependencies.
- :///url/to/module/file.mjs:line:column , if the frame represents a call in a user program (using ES module system), or its dependencies.
The string representing the stack trace is lazily generated when the error.stack property is accessed.
The number of frames captured by the stack trace is bounded by the smaller of Error.stackTraceLimit or the number of available frames on the current event loop tick.
Class: AssertionError #
Indicates the failure of an assertion. For details, see Class: assert.AssertionError .
Class: RangeError #
Indicates that a provided argument was not within the set or range of acceptable values for a function; whether that is a numeric range, or outside the set of options for a given function parameter.
Node.js will generate and throw RangeError instances immediately as a form of argument validation.
Class: ReferenceError #
Indicates that an attempt is being made to access a variable that is not defined. Such errors commonly indicate typos in code, or an otherwise broken program.
While client code may generate and propagate these errors, in practice, only V8 will do so.
Unless an application is dynamically generating and running code, ReferenceError instances indicate a bug in the code or its dependencies.
Class: SyntaxError #
Indicates that a program is not valid JavaScript. These errors may only be generated and propagated as a result of code evaluation. Code evaluation may happen as a result of eval , Function , require , or vm. These errors are almost always indicative of a broken program.
SyntaxError instances are unrecoverable in the context that created them – they may only be caught by other contexts.
Class: SystemError #
Node.js generates system errors when exceptions occur within its runtime environment. These usually occur when an application violates an operating system constraint. For example, a system error will occur if an application attempts to read a file that does not exist.
- address If present, the address to which a network connection failed
- code The string error code
- dest If present, the file path destination when reporting a file system error
- errno The system-provided error number
- info If present, extra details about the error condition
- message A system-provided human-readable description of the error
- path If present, the file path when reporting a file system error
- port If present, the network connection port that is not available
- syscall The name of the system call that triggered the error
error.address #
If present, error.address is a string describing the address to which a network connection failed.
error.code #
The error.code property is a string representing the error code.
error.dest #
If present, error.dest is the file path destination when reporting a file system error.
error.errno #
The error.errno property is a negative number which corresponds to the error code defined in libuv Error handling .
On Windows the error number provided by the system will be normalized by libuv.
To get the string representation of the error code, use util.getSystemErrorName(error.errno) .
error.info #
If present, error.info is an object with details about the error condition.
error.message #
error.message is a system-provided human-readable description of the error.
error.path #
If present, error.path is a string containing a relevant invalid pathname.
error.port #
If present, error.port is the network connection port that is not available.
error.syscall #
The error.syscall property is a string describing the syscall that failed.
Common system errors #
This is a list of system errors commonly-encountered when writing a Node.js program. For a comprehensive list, see the errno (3) man page.
EACCES (Permission denied): An attempt was made to access a file in a way forbidden by its file access permissions.
EADDRINUSE (Address already in use): An attempt to bind a server ( net , http , or https ) to a local address failed due to another server on the local system already occupying that address.
ECONNREFUSED (Connection refused): No connection could be made because the target machine actively refused it. This usually results from trying to connect to a service that is inactive on the foreign host.
ECONNRESET (Connection reset by peer): A connection was forcibly closed by a peer. This normally results from a loss of the connection on the remote socket due to a timeout or reboot. Commonly encountered via the http and net modules.
EEXIST (File exists): An existing file was the target of an operation that required that the target not exist.
EISDIR (Is a directory): An operation expected a file, but the given pathname was a directory.
EMFILE (Too many open files in system): Maximum number of file descriptors allowable on the system has been reached, and requests for another descriptor cannot be fulfilled until at least one has been closed. This is encountered when opening many files at once in parallel, especially on systems (in particular, macOS) where there is a low file descriptor limit for processes. To remedy a low limit, run ulimit -n 2048 in the same shell that will run the Node.js process.
ENOENT (No such file or directory): Commonly raised by fs operations to indicate that a component of the specified pathname does not exist. No entity (file or directory) could be found by the given path.
ENOTDIR (Not a directory): A component of the given pathname existed, but was not a directory as expected. Commonly raised by fs.readdir .
ENOTEMPTY (Directory not empty): A directory with entries was the target of an operation that requires an empty directory, usually fs.unlink .
ENOTFOUND (DNS lookup failed): Indicates a DNS failure of either EAI_NODATA or EAI_NONAME . This is not a standard POSIX error.
EPERM (Operation not permitted): An attempt was made to perform an operation that requires elevated privileges.
EPIPE (Broken pipe): A write on a pipe, socket, or FIFO for which there is no process to read the data. Commonly encountered at the net and http layers, indicative that the remote side of the stream being written to has been closed.
ETIMEDOUT (Operation timed out): A connect or send request failed because the connected party did not properly respond after a period of time. Usually encountered by http or net . Often a sign that a socket.end() was not properly called.
Class: TypeError #
Indicates that a provided argument is not an allowable type. For example, passing a function to a parameter which expects a string would be a TypeError .
Node.js will generate and throw TypeError instances immediately as a form of argument validation.
Exceptions vs. errors #
A JavaScript exception is a value that is thrown as a result of an invalid operation or as the target of a throw statement. While it is not required that these values are instances of Error or classes which inherit from Error , all exceptions thrown by Node.js or the JavaScript runtime will be instances of Error .
Some exceptions are unrecoverable at the JavaScript layer. Such exceptions will always cause the Node.js process to crash. Examples include assert() checks or abort() calls in the C++ layer.
OpenSSL errors #
Errors originating in crypto or tls are of class Error , and in addition to the standard .code and .message properties, may have some additional OpenSSL-specific properties.
error.opensslErrorStack #
An array of errors that can give context to where in the OpenSSL library an error originates from.
error.function #
The OpenSSL function the error originates in.
error.library #
The OpenSSL library the error originates in.
error.reason #
A human-readable string describing the reason for the error.
Node.js error codes #
ABORT_ERR #
Used when an operation has been aborted (typically using an AbortController ).
APIs not using AbortSignal s typically do not raise an error with this code.
This code does not use the regular ERR_* convention Node.js errors use in order to be compatible with the web platform’s AbortError .
ERR_AMBIGUOUS_ARGUMENT #
A function argument is being used in a way that suggests that the function signature may be misunderstood. This is thrown by the node:assert module when the message parameter in assert.throws(block, message) matches the error message thrown by block because that usage suggests that the user believes message is the expected message rather than the message the AssertionError will display if block does not throw.
ERR_ARG_NOT_ITERABLE #
An iterable argument (i.e. a value that works with for. of loops) was required, but not provided to a Node.js API.
ERR_ASSERTION #
A special type of error that can be triggered whenever Node.js detects an exceptional logic violation that should never occur. These are raised typically by the node:assert module.
ERR_ASSERT_SNAPSHOT_NOT_SUPPORTED #
An attempt was made to use assert.snapshot() in an environment that does not support snapshots, such as the REPL, or when using node —eval .
ERR_ASYNC_CALLBACK #
An attempt was made to register something that is not a function as an AsyncHooks callback.
ERR_ASYNC_TYPE #
The type of an asynchronous resource was invalid. Users are also able to define their own types if using the public embedder API.
ERR_BROTLI_COMPRESSION_FAILED #
Data passed to a Brotli stream was not successfully compressed.
ERR_BROTLI_INVALID_PARAM #
An invalid parameter key was passed during construction of a Brotli stream.
ERR_BUFFER_CONTEXT_NOT_AVAILABLE #
An attempt was made to create a Node.js Buffer instance from addon or embedder code, while in a JS engine Context that is not associated with a Node.js instance. The data passed to the Buffer method will have been released by the time the method returns.
When encountering this error, a possible alternative to creating a Buffer instance is to create a normal Uint8Array , which only differs in the prototype of the resulting object. Uint8Array s are generally accepted in all Node.js core APIs where Buffer s are; they are available in all Contexts.
ERR_BUFFER_OUT_OF_BOUNDS #
An operation outside the bounds of a Buffer was attempted.
ERR_BUFFER_TOO_LARGE #
An attempt has been made to create a Buffer larger than the maximum allowed size.
ERR_CANNOT_WATCH_SIGINT #
Node.js was unable to watch for the SIGINT signal.
ERR_CHILD_CLOSED_BEFORE_REPLY #
A child process was closed before the parent received a reply.
ERR_CHILD_PROCESS_IPC_REQUIRED #
Used when a child process is being forked without specifying an IPC channel.
ERR_CHILD_PROCESS_STDIO_MAXBUFFER #
Used when the main process is trying to read data from the child process’s STDERR/STDOUT, and the data’s length is longer than the maxBuffer option.
ERR_CLOSED_MESSAGE_PORT #
There was an attempt to use a MessagePort instance in a closed state, usually after .close() has been called.
ERR_CONSOLE_WRITABLE_STREAM #
Console was instantiated without stdout stream, or Console has a non-writable stdout or stderr stream.
ERR_CONSTRUCT_CALL_INVALID #
A class constructor was called that is not callable.
ERR_CONSTRUCT_CALL_REQUIRED #
A constructor for a class was called without new .
ERR_CONTEXT_NOT_INITIALIZED #
The vm context passed into the API is not yet initialized. This could happen when an error occurs (and is caught) during the creation of the context, for example, when the allocation fails or the maximum call stack size is reached when the context is created.
ERR_CRYPTO_CUSTOM_ENGINE_NOT_SUPPORTED #
A client certificate engine was requested that is not supported by the version of OpenSSL being used.
ERR_CRYPTO_ECDH_INVALID_FORMAT #
An invalid value for the format argument was passed to the crypto.ECDH() class getPublicKey() method.
ERR_CRYPTO_ECDH_INVALID_PUBLIC_KEY #
An invalid value for the key argument has been passed to the crypto.ECDH() class computeSecret() method. It means that the public key lies outside of the elliptic curve.
ERR_CRYPTO_ENGINE_UNKNOWN #
An invalid crypto engine identifier was passed to require(‘node:crypto’).setEngine() .
ERR_CRYPTO_FIPS_FORCED #
The —force-fips command-line argument was used but there was an attempt to enable or disable FIPS mode in the node:crypto module.
ERR_CRYPTO_FIPS_UNAVAILABLE #
An attempt was made to enable or disable FIPS mode, but FIPS mode was not available.
ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_FINALIZED #
hash.digest() was called multiple times. The hash.digest() method must be called no more than one time per instance of a Hash object.
ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_UPDATE_FAILED #
hash.update() failed for any reason. This should rarely, if ever, happen.
ERR_CRYPTO_INCOMPATIBLE_KEY #
The given crypto keys are incompatible with the attempted operation.
ERR_CRYPTO_INCOMPATIBLE_KEY_OPTIONS #
The selected public or private key encoding is incompatible with other options.
ERR_CRYPTO_INITIALIZATION_FAILED #
Initialization of the crypto subsystem failed.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_AUTH_TAG #
An invalid authentication tag was provided.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_COUNTER #
An invalid counter was provided for a counter-mode cipher.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_CURVE #
An invalid elliptic-curve was provided.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_DIGEST #
An invalid crypto digest algorithm was specified.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_IV #
An invalid initialization vector was provided.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_JWK #
An invalid JSON Web Key was provided.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_KEY_OBJECT_TYPE #
The given crypto key object’s type is invalid for the attempted operation.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_KEYLEN #
An invalid key length was provided.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_KEYPAIR #
An invalid key pair was provided.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_KEYTYPE #
An invalid key type was provided.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_MESSAGELEN #
An invalid message length was provided.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_SCRYPT_PARAMS #
Invalid scrypt algorithm parameters were provided.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_STATE #
A crypto method was used on an object that was in an invalid state. For instance, calling cipher.getAuthTag() before calling cipher.final() .
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_TAG_LENGTH #
An invalid authentication tag length was provided.
ERR_CRYPTO_JOB_INIT_FAILED #
Initialization of an asynchronous crypto operation failed.
ERR_CRYPTO_JWK_UNSUPPORTED_CURVE #
Key’s Elliptic Curve is not registered for use in the JSON Web Key Elliptic Curve Registry.
ERR_CRYPTO_JWK_UNSUPPORTED_KEY_TYPE #
Key’s Asymmetric Key Type is not registered for use in the JSON Web Key Types Registry.
ERR_CRYPTO_OPERATION_FAILED #
A crypto operation failed for an otherwise unspecified reason.
ERR_CRYPTO_PBKDF2_ERROR #
The PBKDF2 algorithm failed for unspecified reasons. OpenSSL does not provide more details and therefore neither does Node.js.
ERR_CRYPTO_SCRYPT_INVALID_PARAMETER #
One or more crypto.scrypt() or crypto.scryptSync() parameters are outside their legal range.
ERR_CRYPTO_SCRYPT_NOT_SUPPORTED #
Node.js was compiled without scrypt support. Not possible with the official release binaries but can happen with custom builds, including distro builds.
ERR_CRYPTO_SIGN_KEY_REQUIRED #
A signing key was not provided to the sign.sign() method.
ERR_CRYPTO_TIMING_SAFE_EQUAL_LENGTH #
crypto.timingSafeEqual() was called with Buffer , TypedArray , or DataView arguments of different lengths.
ERR_CRYPTO_UNKNOWN_CIPHER #
An unknown cipher was specified.
ERR_CRYPTO_UNKNOWN_DH_GROUP #
An unknown Diffie-Hellman group name was given. See crypto.getDiffieHellman() for a list of valid group names.
ERR_CRYPTO_UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION #
An attempt to invoke an unsupported crypto operation was made.
ERR_DEBUGGER_ERROR #
An error occurred with the debugger.
ERR_DEBUGGER_STARTUP_ERROR #
The debugger timed out waiting for the required host/port to be free.
ERR_DLOPEN_DISABLED #
Loading native addons has been disabled using —no-addons .
ERR_DLOPEN_FAILED #
A call to process.dlopen() failed.
ERR_DIR_CLOSED #
The fs.Dir was previously closed.
ERR_DIR_CONCURRENT_OPERATION #
A synchronous read or close call was attempted on an fs.Dir which has ongoing asynchronous operations.
ERR_DNS_SET_SERVERS_FAILED #
c-ares failed to set the DNS server.
ERR_DOMAIN_CALLBACK_NOT_AVAILABLE #
The node:domain module was not usable since it could not establish the required error handling hooks, because process.setUncaughtExceptionCaptureCallback() had been called at an earlier point in time.
ERR_DOMAIN_CANNOT_SET_UNCAUGHT_EXCEPTION_CAPTURE #
process.setUncaughtExceptionCaptureCallback() could not be called because the node:domain module has been loaded at an earlier point in time.
The stack trace is extended to include the point in time at which the node:domain module had been loaded.
ERR_DUPLICATE_STARTUP_SNAPSHOT_MAIN_FUNCTION #
v8.startupSnapshot.setDeserializeMainFunction() could not be called because it had already been called before.
ERR_ENCODING_INVALID_ENCODED_DATA #
Data provided to TextDecoder() API was invalid according to the encoding provided.
ERR_ENCODING_NOT_SUPPORTED #
Encoding provided to TextDecoder() API was not one of the WHATWG Supported Encodings.
ERR_EVAL_ESM_CANNOT_PRINT #
—print cannot be used with ESM input.
ERR_EVENT_RECURSION #
Thrown when an attempt is made to recursively dispatch an event on EventTarget .
ERR_EXECUTION_ENVIRONMENT_NOT_AVAILABLE #
The JS execution context is not associated with a Node.js environment. This may occur when Node.js is used as an embedded library and some hooks for the JS engine are not set up properly.
ERR_FALSY_VALUE_REJECTION #
A Promise that was callbackified via util.callbackify() was rejected with a falsy value.
ERR_FEATURE_UNAVAILABLE_ON_PLATFORM #
Used when a feature that is not available to the current platform which is running Node.js is used.
ERR_FS_CP_DIR_TO_NON_DIR #
An attempt was made to copy a directory to a non-directory (file, symlink, etc.) using fs.cp() .
ERR_FS_CP_EEXIST #
An attempt was made to copy over a file that already existed with fs.cp() , with the force and errorOnExist set to true .
ERR_FS_CP_EINVAL #
When using fs.cp() , src or dest pointed to an invalid path.
ERR_HTTP_CONTENT_LENGTH_MISMATCH #
Response body size doesn’t match with the specified content-length header value.
ERR_FS_CP_FIFO_PIPE #
An attempt was made to copy a named pipe with fs.cp() .
ERR_FS_CP_NON_DIR_TO_DIR #
An attempt was made to copy a non-directory (file, symlink, etc.) to a directory using fs.cp() .
ERR_FS_CP_SOCKET #
An attempt was made to copy to a socket with fs.cp() .
ERR_FS_CP_SYMLINK_TO_SUBDIRECTORY #
When using fs.cp() , a symlink in dest pointed to a subdirectory of src .
ERR_FS_CP_UNKNOWN #
An attempt was made to copy to an unknown file type with fs.cp() .
ERR_FS_EISDIR #
Path is a directory.
ERR_FS_FILE_TOO_LARGE #
An attempt has been made to read a file whose size is larger than the maximum allowed size for a Buffer .
ERR_FS_INVALID_SYMLINK_TYPE #
An invalid symlink type was passed to the fs.symlink() or fs.symlinkSync() methods.
An attempt was made to add more headers after the headers had already been sent.
An invalid HTTP header value was specified.
ERR_HTTP_INVALID_STATUS_CODE #
Status code was outside the regular status code range (100-999).
ERR_HTTP_REQUEST_TIMEOUT #
The client has not sent the entire request within the allowed time.
ERR_HTTP_SOCKET_ENCODING #
Changing the socket encoding is not allowed per RFC 7230 Section 3.
ERR_HTTP_TRAILER_INVALID #
The Trailer header was set even though the transfer encoding does not support that.
ERR_HTTP2_ALTSVC_INVALID_ORIGIN #
HTTP/2 ALTSVC frames require a valid origin.
ERR_HTTP2_ALTSVC_LENGTH #
HTTP/2 ALTSVC frames are limited to a maximum of 16,382 payload bytes.
For HTTP/2 requests using the CONNECT method, the :authority pseudo-header is required.
ERR_HTTP2_CONNECT_PATH #
For HTTP/2 requests using the CONNECT method, the :path pseudo-header is forbidden.
ERR_HTTP2_CONNECT_SCHEME #
For HTTP/2 requests using the CONNECT method, the :scheme pseudo-header is forbidden.
ERR_HTTP2_ERROR #
A non-specific HTTP/2 error has occurred.
ERR_HTTP2_GOAWAY_SESSION #
New HTTP/2 Streams may not be opened after the Http2Session has received a GOAWAY frame from the connected peer.
Multiple values were provided for an HTTP/2 header field that was required to have only a single value.
An additional headers was specified after an HTTP/2 response was initiated.
An attempt was made to send multiple response headers.
ERR_HTTP2_INFO_STATUS_NOT_ALLOWED #
Informational HTTP status codes ( 1xx ) may not be set as the response status code on HTTP/2 responses.
HTTP/1 connection specific headers are forbidden to be used in HTTP/2 requests and responses.
An invalid HTTP/2 header value was specified.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_INFO_STATUS #
An invalid HTTP informational status code has been specified. Informational status codes must be an integer between 100 and 199 (inclusive).
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_ORIGIN #
HTTP/2 ORIGIN frames require a valid origin.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_PACKED_SETTINGS_LENGTH #
Input Buffer and Uint8Array instances passed to the http2.getUnpackedSettings() API must have a length that is a multiple of six.
Only valid HTTP/2 pseudoheaders ( :status , :path , :authority , :scheme , and :method ) may be used.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_SESSION #
An action was performed on an Http2Session object that had already been destroyed.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_SETTING_VALUE #
An invalid value has been specified for an HTTP/2 setting.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_STREAM #
An operation was performed on a stream that had already been destroyed.
ERR_HTTP2_MAX_PENDING_SETTINGS_ACK #
Whenever an HTTP/2 SETTINGS frame is sent to a connected peer, the peer is required to send an acknowledgment that it has received and applied the new SETTINGS . By default, a maximum number of unacknowledged SETTINGS frames may be sent at any given time. This error code is used when that limit has been reached.
ERR_HTTP2_NESTED_PUSH #
An attempt was made to initiate a new push stream from within a push stream. Nested push streams are not permitted.
ERR_HTTP2_NO_MEM #
Out of memory when using the http2session.setLocalWindowSize(windowSize) API.
ERR_HTTP2_NO_SOCKET_MANIPULATION #
An attempt was made to directly manipulate (read, write, pause, resume, etc.) a socket attached to an Http2Session .
ERR_HTTP2_ORIGIN_LENGTH #
HTTP/2 ORIGIN frames are limited to a length of 16382 bytes.
ERR_HTTP2_OUT_OF_STREAMS #
The number of streams created on a single HTTP/2 session reached the maximum limit.
ERR_HTTP2_PAYLOAD_FORBIDDEN #
A message payload was specified for an HTTP response code for which a payload is forbidden.
ERR_HTTP2_PING_CANCEL #
An HTTP/2 ping was canceled.
ERR_HTTP2_PING_LENGTH #
HTTP/2 ping payloads must be exactly 8 bytes in length.
An HTTP/2 pseudo-header has been used inappropriately. Pseudo-headers are header key names that begin with the : prefix.
ERR_HTTP2_PUSH_DISABLED #
An attempt was made to create a push stream, which had been disabled by the client.
ERR_HTTP2_SEND_FILE #
An attempt was made to use the Http2Stream.prototype.responseWithFile() API to send a directory.
ERR_HTTP2_SEND_FILE_NOSEEK #
An attempt was made to use the Http2Stream.prototype.responseWithFile() API to send something other than a regular file, but offset or length options were provided.
ERR_HTTP2_SESSION_ERROR #
The Http2Session closed with a non-zero error code.
ERR_HTTP2_SETTINGS_CANCEL #
The Http2Session settings canceled.
ERR_HTTP2_SOCKET_BOUND #
An attempt was made to connect a Http2Session object to a net.Socket or tls.TLSSocket that had already been bound to another Http2Session object.
ERR_HTTP2_SOCKET_UNBOUND #
An attempt was made to use the socket property of an Http2Session that has already been closed.
ERR_HTTP2_STATUS_101 #
Use of the 101 Informational status code is forbidden in HTTP/2.
ERR_HTTP2_STATUS_INVALID #
An invalid HTTP status code has been specified. Status codes must be an integer between 100 and 599 (inclusive).
ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_CANCEL #
An Http2Stream was destroyed before any data was transmitted to the connected peer.
ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_ERROR #
A non-zero error code was been specified in an RST_STREAM frame.
ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_SELF_DEPENDENCY #
When setting the priority for an HTTP/2 stream, the stream may be marked as a dependency for a parent stream. This error code is used when an attempt is made to mark a stream and dependent of itself.
ERR_HTTP2_TOO_MANY_INVALID_FRAMES #
The limit of acceptable invalid HTTP/2 protocol frames sent by the peer, as specified through the maxSessionInvalidFrames option, has been exceeded.
ERR_HTTP2_TRAILERS_ALREADY_SENT #
Trailing headers have already been sent on the Http2Stream .
ERR_HTTP2_TRAILERS_NOT_READY #
The http2stream.sendTrailers() method cannot be called until after the ‘wantTrailers’ event is emitted on an Http2Stream object. The ‘wantTrailers’ event will only be emitted if the waitForTrailers option is set for the Http2Stream .
ERR_HTTP2_UNSUPPORTED_PROTOCOL #
http2.connect() was passed a URL that uses any protocol other than http: or https: .
ERR_ILLEGAL_CONSTRUCTOR #
An attempt was made to construct an object using a non-public constructor.
ERR_IMPORT_ASSERTION_TYPE_FAILED #
An import assertion has failed, preventing the specified module to be imported.
ERR_IMPORT_ASSERTION_TYPE_MISSING #
An import assertion is missing, preventing the specified module to be imported.
ERR_IMPORT_ASSERTION_TYPE_UNSUPPORTED #
An import assertion is not supported by this version of Node.js.
ERR_INCOMPATIBLE_OPTION_PAIR #
An option pair is incompatible with each other and cannot be used at the same time.
ERR_INPUT_TYPE_NOT_ALLOWED #
The —input-type flag was used to attempt to execute a file. This flag can only be used with input via —eval , —print , or STDIN .
ERR_INSPECTOR_ALREADY_ACTIVATED #
While using the node:inspector module, an attempt was made to activate the inspector when it already started to listen on a port. Use inspector.close() before activating it on a different address.
ERR_INSPECTOR_ALREADY_CONNECTED #
While using the node:inspector module, an attempt was made to connect when the inspector was already connected.
ERR_INSPECTOR_CLOSED #
While using the node:inspector module, an attempt was made to use the inspector after the session had already closed.
ERR_INSPECTOR_COMMAND #
An error occurred while issuing a command via the node:inspector module.
ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_ACTIVE #
The inspector is not active when inspector.waitForDebugger() is called.
ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_AVAILABLE #
The node:inspector module is not available for use.
ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_CONNECTED #
While using the node:inspector module, an attempt was made to use the inspector before it was connected.
ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_WORKER #
An API was called on the main thread that can only be used from the worker thread.
ERR_INTERNAL_ASSERTION #
There was a bug in Node.js or incorrect usage of Node.js internals. To fix the error, open an issue at https://github.com/nodejs/node/issues.
ERR_INVALID_ADDRESS_FAMILY #
The provided address family is not understood by the Node.js API.
ERR_INVALID_ARG_TYPE #
An argument of the wrong type was passed to a Node.js API.
ERR_INVALID_ARG_VALUE #
An invalid or unsupported value was passed for a given argument.
ERR_INVALID_ASYNC_ID #
An invalid asyncId or triggerAsyncId was passed using AsyncHooks . An id less than -1 should never happen.
ERR_INVALID_BUFFER_SIZE #
A swap was performed on a Buffer but its size was not compatible with the operation.
ERR_INVALID_CHAR #
Invalid characters were detected in headers.
ERR_INVALID_CURSOR_POS #
A cursor on a given stream cannot be moved to a specified row without a specified column.
ERR_INVALID_FD #
A file descriptor (‘fd’) was not valid (e.g. it was a negative value).
ERR_INVALID_FD_TYPE #
A file descriptor (‘fd’) type was not valid.
ERR_INVALID_FILE_URL_HOST #
A Node.js API that consumes file: URLs (such as certain functions in the fs module) encountered a file URL with an incompatible host. This situation can only occur on Unix-like systems where only localhost or an empty host is supported.
ERR_INVALID_FILE_URL_PATH #
A Node.js API that consumes file: URLs (such as certain functions in the fs module) encountered a file URL with an incompatible path. The exact semantics for determining whether a path can be used is platform-dependent.
ERR_INVALID_HANDLE_TYPE #
An attempt was made to send an unsupported «handle» over an IPC communication channel to a child process. See subprocess.send() and process.send() for more information.
ERR_INVALID_HTTP_TOKEN #
An invalid HTTP token was supplied.
ERR_INVALID_IP_ADDRESS #
An IP address is not valid.
ERR_INVALID_MIME_SYNTAX #
The syntax of a MIME is not valid.
ERR_INVALID_MODULE #
An attempt was made to load a module that does not exist or was otherwise not valid.
ERR_INVALID_MODULE_SPECIFIER #
The imported module string is an invalid URL, package name, or package subpath specifier.
ERR_INVALID_OBJECT_DEFINE_PROPERTY #
An error occurred while setting an invalid attribute on the property of an object.
ERR_INVALID_PACKAGE_CONFIG #
An invalid package.json file failed parsing.
ERR_INVALID_PACKAGE_TARGET #
The package.json «exports» field contains an invalid target mapping value for the attempted module resolution.
ERR_INVALID_PERFORMANCE_MARK #
While using the Performance Timing API ( perf_hooks ), a performance mark is invalid.
ERR_INVALID_PROTOCOL #
An invalid options.protocol was passed to http.request() .
ERR_INVALID_REPL_EVAL_CONFIG #
Both breakEvalOnSigint and eval options were set in the REPL config, which is not supported.
ERR_INVALID_REPL_INPUT #
The input may not be used in the REPL . The conditions under which this error is used are described in the REPL documentation.
ERR_INVALID_RETURN_PROPERTY #
Thrown in case a function option does not provide a valid value for one of its returned object properties on execution.
ERR_INVALID_RETURN_PROPERTY_VALUE #
Thrown in case a function option does not provide an expected value type for one of its returned object properties on execution.
ERR_INVALID_RETURN_VALUE #
Thrown in case a function option does not return an expected value type on execution, such as when a function is expected to return a promise.
ERR_INVALID_STATE #
Indicates that an operation cannot be completed due to an invalid state. For instance, an object may have already been destroyed, or may be performing another operation.
ERR_INVALID_SYNC_FORK_INPUT #
A Buffer , TypedArray , DataView , or string was provided as stdio input to an asynchronous fork. See the documentation for the child_process module for more information.
ERR_INVALID_THIS #
A Node.js API function was called with an incompatible this value.
ERR_INVALID_TRANSFER_OBJECT #
An invalid transfer object was passed to postMessage() .
ERR_INVALID_TUPLE #
An element in the iterable provided to the WHATWG URLSearchParams constructor did not represent a [name, value] tuple – that is, if an element is not iterable, or does not consist of exactly two elements.
ERR_INVALID_URI #
An invalid URI was passed.
ERR_INVALID_URL #
An invalid URL was passed to the WHATWG URL constructor or the legacy url.parse() to be parsed. The thrown error object typically has an additional property ‘input’ that contains the URL that failed to parse.
ERR_INVALID_URL_SCHEME #
An attempt was made to use a URL of an incompatible scheme (protocol) for a specific purpose. It is only used in the WHATWG URL API support in the fs module (which only accepts URLs with ‘file’ scheme), but may be used in other Node.js APIs as well in the future.
ERR_IPC_CHANNEL_CLOSED #
An attempt was made to use an IPC communication channel that was already closed.
ERR_IPC_DISCONNECTED #
An attempt was made to disconnect an IPC communication channel that was already disconnected. See the documentation for the child_process module for more information.
ERR_IPC_ONE_PIPE #
An attempt was made to create a child Node.js process using more than one IPC communication channel. See the documentation for the child_process module for more information.
ERR_IPC_SYNC_FORK #
An attempt was made to open an IPC communication channel with a synchronously forked Node.js process. See the documentation for the child_process module for more information.
ERR_LOADER_CHAIN_INCOMPLETE #
An ESM loader hook returned without calling next() and without explicitly signaling a short circuit.
ERR_MANIFEST_ASSERT_INTEGRITY #
An attempt was made to load a resource, but the resource did not match the integrity defined by the policy manifest. See the documentation for policy manifests for more information.
ERR_MANIFEST_DEPENDENCY_MISSING #
An attempt was made to load a resource, but the resource was not listed as a dependency from the location that attempted to load it. See the documentation for policy manifests for more information.
ERR_MANIFEST_INTEGRITY_MISMATCH #
An attempt was made to load a policy manifest, but the manifest had multiple entries for a resource which did not match each other. Update the manifest entries to match in order to resolve this error. See the documentation for policy manifests for more information.
ERR_MANIFEST_INVALID_RESOURCE_FIELD #
A policy manifest resource had an invalid value for one of its fields. Update the manifest entry to match in order to resolve this error. See the documentation for policy manifests for more information.
ERR_MANIFEST_INVALID_SPECIFIER #
A policy manifest resource had an invalid value for one of its dependency mappings. Update the manifest entry to match to resolve this error. See the documentation for policy manifests for more information.
ERR_MANIFEST_PARSE_POLICY #
An attempt was made to load a policy manifest, but the manifest was unable to be parsed. See the documentation for policy manifests for more information.
ERR_MANIFEST_TDZ #
An attempt was made to read from a policy manifest, but the manifest initialization has not yet taken place. This is likely a bug in Node.js.
ERR_MANIFEST_UNKNOWN_ONERROR #
A policy manifest was loaded, but had an unknown value for its «onerror» behavior. See the documentation for policy manifests for more information.
ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATION_FAILED #
An attempt was made to allocate memory (usually in the C++ layer) but it failed.
ERR_MESSAGE_TARGET_CONTEXT_UNAVAILABLE #
A message posted to a MessagePort could not be deserialized in the target vm Context . Not all Node.js objects can be successfully instantiated in any context at this time, and attempting to transfer them using postMessage() can fail on the receiving side in that case.
ERR_METHOD_NOT_IMPLEMENTED #
A method is required but not implemented.
ERR_MISSING_ARGS #
A required argument of a Node.js API was not passed. This is only used for strict compliance with the API specification (which in some cases may accept func(undefined) but not func() ). In most native Node.js APIs, func(undefined) and func() are treated identically, and the ERR_INVALID_ARG_TYPE error code may be used instead.
ERR_MISSING_OPTION #
For APIs that accept options objects, some options might be mandatory. This code is thrown if a required option is missing.
ERR_MISSING_PASSPHRASE #
An attempt was made to read an encrypted key without specifying a passphrase.
ERR_MISSING_PLATFORM_FOR_WORKER #
The V8 platform used by this instance of Node.js does not support creating Workers. This is caused by lack of embedder support for Workers. In particular, this error will not occur with standard builds of Node.js.
ERR_MISSING_TRANSFERABLE_IN_TRANSFER_LIST #
An object that needs to be explicitly listed in the transferList argument is in the object passed to a postMessage() call, but is not provided in the transferList for that call. Usually, this is a MessagePort .
In Node.js versions prior to v15.0.0, the error code being used here was ERR_MISSING_MESSAGE_PORT_IN_TRANSFER_LIST . However, the set of transferable object types has been expanded to cover more types than MessagePort .
ERR_MODULE_NOT_FOUND #
A module file could not be resolved by the ECMAScript modules loader while attempting an import operation or when loading the program entry point.
ERR_MULTIPLE_CALLBACK #
A callback was called more than once.
A callback is almost always meant to only be called once as the query can either be fulfilled or rejected but not both at the same time. The latter would be possible by calling a callback more than once.
ERR_NAPI_CONS_FUNCTION #
While using Node-API , a constructor passed was not a function.
ERR_NAPI_INVALID_DATAVIEW_ARGS #
While calling napi_create_dataview() , a given offset was outside the bounds of the dataview or offset + length was larger than a length of given buffer .
ERR_NAPI_INVALID_TYPEDARRAY_ALIGNMENT #
While calling napi_create_typedarray() , the provided offset was not a multiple of the element size.
ERR_NAPI_INVALID_TYPEDARRAY_LENGTH #
While calling napi_create_typedarray() , (length * size_of_element) + byte_offset was larger than the length of given buffer .
ERR_NAPI_TSFN_CALL_JS #
An error occurred while invoking the JavaScript portion of the thread-safe function.
ERR_NAPI_TSFN_GET_UNDEFINED #
An error occurred while attempting to retrieve the JavaScript undefined value.
ERR_NAPI_TSFN_START_IDLE_LOOP #
On the main thread, values are removed from the queue associated with the thread-safe function in an idle loop. This error indicates that an error has occurred when attempting to start the loop.
ERR_NAPI_TSFN_STOP_IDLE_LOOP #
Once no more items are left in the queue, the idle loop must be suspended. This error indicates that the idle loop has failed to stop.
ERR_NOT_BUILDING_SNAPSHOT #
An attempt was made to use operations that can only be used when building V8 startup snapshot even though Node.js isn’t building one.
ERR_NO_CRYPTO #
An attempt was made to use crypto features while Node.js was not compiled with OpenSSL crypto support.
ERR_NO_ICU #
An attempt was made to use features that require ICU, but Node.js was not compiled with ICU support.
ERR_NON_CONTEXT_AWARE_DISABLED #
A non-context-aware native addon was loaded in a process that disallows them.
ERR_OUT_OF_RANGE #
A given value is out of the accepted range.
ERR_PACKAGE_IMPORT_NOT_DEFINED #
The package.json «imports» field does not define the given internal package specifier mapping.
ERR_PACKAGE_PATH_NOT_EXPORTED #
The package.json «exports» field does not export the requested subpath. Because exports are encapsulated, private internal modules that are not exported cannot be imported through the package resolution, unless using an absolute URL.
ERR_PARSE_ARGS_INVALID_OPTION_VALUE #
When strict set to true , thrown by util.parseArgs() if a value is provided for an option of type , or if a value is provided for an option of type .
ERR_PARSE_ARGS_UNEXPECTED_POSITIONAL #
Thrown by util.parseArgs() , when a positional argument is provided and allowPositionals is set to false .
ERR_PARSE_ARGS_UNKNOWN_OPTION #
When strict set to true , thrown by util.parseArgs() if an argument is not configured in options .
ERR_PERFORMANCE_INVALID_TIMESTAMP #
An invalid timestamp value was provided for a performance mark or measure.
ERR_PERFORMANCE_MEASURE_INVALID_OPTIONS #
Invalid options were provided for a performance measure.
ERR_PROTO_ACCESS #
Accessing Object.prototype.__proto__ has been forbidden using —disable-proto=throw . Object.getPrototypeOf and Object.setPrototypeOf should be used to get and set the prototype of an object.
ERR_REQUIRE_ESM #
An attempt was made to require() an ES Module.
ERR_SCRIPT_EXECUTION_INTERRUPTED #
Script execution was interrupted by SIGINT (For example, Ctrl + C was pressed.)
ERR_SCRIPT_EXECUTION_TIMEOUT #
Script execution timed out, possibly due to bugs in the script being executed.
ERR_SERVER_ALREADY_LISTEN #
The server.listen() method was called while a net.Server was already listening. This applies to all instances of net.Server , including HTTP, HTTPS, and HTTP/2 Server instances.
ERR_SERVER_NOT_RUNNING #
The server.close() method was called when a net.Server was not running. This applies to all instances of net.Server , including HTTP, HTTPS, and HTTP/2 Server instances.
ERR_SOCKET_ALREADY_BOUND #
An attempt was made to bind a socket that has already been bound.
ERR_SOCKET_BAD_BUFFER_SIZE #
An invalid (negative) size was passed for either the recvBufferSize or sendBufferSize options in dgram.createSocket() .
ERR_SOCKET_BAD_PORT #
An API function expecting a port >= 0 and ERR_SOCKET_BAD_TYPE #
An API function expecting a socket type ( udp4 or udp6 ) received an invalid value.
ERR_SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE #
While using dgram.createSocket() , the size of the receive or send Buffer could not be determined.
ERR_SOCKET_CLOSED #
An attempt was made to operate on an already closed socket.
ERR_SOCKET_CLOSED_BEFORE_CONNECTION #
When calling net.Socket.write() on a connecting socket and the socket was closed before the connection was established.
ERR_SOCKET_DGRAM_IS_CONNECTED #
A dgram.connect() call was made on an already connected socket.
ERR_SOCKET_DGRAM_NOT_CONNECTED #
A dgram.disconnect() or dgram.remoteAddress() call was made on a disconnected socket.
ERR_SOCKET_DGRAM_NOT_RUNNING #
A call was made and the UDP subsystem was not running.
ERR_SRI_PARSE #
A string was provided for a Subresource Integrity check, but was unable to be parsed. Check the format of integrity attributes by looking at the Subresource Integrity specification.
ERR_STREAM_ALREADY_FINISHED #
A stream method was called that cannot complete because the stream was finished.
ERR_STREAM_CANNOT_PIPE #
An attempt was made to call stream.pipe() on a Writable stream.
ERR_STREAM_DESTROYED #
A stream method was called that cannot complete because the stream was destroyed using stream.destroy() .
ERR_STREAM_NULL_VALUES #
An attempt was made to call stream.write() with a null chunk.
ERR_STREAM_PREMATURE_CLOSE #
An error returned by stream.finished() and stream.pipeline() , when a stream or a pipeline ends non gracefully with no explicit error.
ERR_STREAM_PUSH_AFTER_EOF #
An attempt was made to call stream.push() after a null (EOF) had been pushed to the stream.
ERR_STREAM_UNSHIFT_AFTER_END_EVENT #
An attempt was made to call stream.unshift() after the ‘end’ event was emitted.
ERR_STREAM_WRAP #
Prevents an abort if a string decoder was set on the Socket or if the decoder is in objectMode .
ERR_STREAM_WRITE_AFTER_END #
An attempt was made to call stream.write() after stream.end() has been called.
ERR_STRING_TOO_LONG #
An attempt has been made to create a string longer than the maximum allowed length.
ERR_SYNTHETIC #
An artificial error object used to capture the call stack for diagnostic reports.
ERR_SYSTEM_ERROR #
An unspecified or non-specific system error has occurred within the Node.js process. The error object will have an err.info object property with additional details.
ERR_TAP_LEXER_ERROR #
An error representing a failing lexer state.
ERR_TAP_PARSER_ERROR #
An error representing a failing parser state. Additional information about the token causing the error is available via the cause property.
ERR_TAP_VALIDATION_ERROR #
This error represents a failed TAP validation.
ERR_TEST_FAILURE #
This error represents a failed test. Additional information about the failure is available via the cause property. The failureType property specifies what the test was doing when the failure occurred.
ERR_TLS_CERT_ALTNAME_FORMAT #
This error is thrown by checkServerIdentity if a user-supplied subjectaltname property violates encoding rules. Certificate objects produced by Node.js itself always comply with encoding rules and will never cause this error.
ERR_TLS_CERT_ALTNAME_INVALID #
While using TLS, the host name/IP of the peer did not match any of the subjectAltNames in its certificate.
ERR_TLS_DH_PARAM_SIZE #
While using TLS, the parameter offered for the Diffie-Hellman ( DH ) key-agreement protocol is too small. By default, the key length must be greater than or equal to 1024 bits to avoid vulnerabilities, even though it is strongly recommended to use 2048 bits or larger for stronger security.
ERR_TLS_HANDSHAKE_TIMEOUT #
A TLS/SSL handshake timed out. In this case, the server must also abort the connection.
ERR_TLS_INVALID_CONTEXT #
The context must be a SecureContext .
ERR_TLS_INVALID_PROTOCOL_METHOD #
The specified secureProtocol method is invalid. It is either unknown, or disabled because it is insecure.
ERR_TLS_INVALID_PROTOCOL_VERSION #
Valid TLS protocol versions are ‘TLSv1’ , ‘TLSv1.1’ , or ‘TLSv1.2’ .
ERR_TLS_INVALID_STATE #
The TLS socket must be connected and securely established. Ensure the ‘secure’ event is emitted before continuing.
ERR_TLS_PROTOCOL_VERSION_CONFLICT #
Attempting to set a TLS protocol minVersion or maxVersion conflicts with an attempt to set the secureProtocol explicitly. Use one mechanism or the other.
ERR_TLS_PSK_SET_IDENTIY_HINT_FAILED #
Failed to set PSK identity hint. Hint may be too long.
ERR_TLS_RENEGOTIATION_DISABLED #
An attempt was made to renegotiate TLS on a socket instance with TLS disabled.
ERR_TLS_REQUIRED_SERVER_NAME #
While using TLS, the server.addContext() method was called without providing a host name in the first parameter.
ERR_TLS_SESSION_ATTACK #
An excessive amount of TLS renegotiations is detected, which is a potential vector for denial-of-service attacks.
ERR_TLS_SNI_FROM_SERVER #
An attempt was made to issue Server Name Indication from a TLS server-side socket, which is only valid from a client.
ERR_TRACE_EVENTS_CATEGORY_REQUIRED #
The trace_events.createTracing() method requires at least one trace event category.
ERR_TRACE_EVENTS_UNAVAILABLE #
The node:trace_events module could not be loaded because Node.js was compiled with the —without-v8-platform flag.
ERR_TRANSFORM_ALREADY_TRANSFORMING #
A Transform stream finished while it was still transforming.
ERR_TRANSFORM_WITH_LENGTH_0 #
A Transform stream finished with data still in the write buffer.
ERR_TTY_INIT_FAILED #
The initialization of a TTY failed due to a system error.
ERR_UNAVAILABLE_DURING_EXIT #
Function was called within a process.on(‘exit’) handler that shouldn’t be called within process.on(‘exit’) handler.
ERR_UNCAUGHT_EXCEPTION_CAPTURE_ALREADY_SET #
process.setUncaughtExceptionCaptureCallback() was called twice, without first resetting the callback to null .
This error is designed to prevent accidentally overwriting a callback registered from another module.
ERR_UNESCAPED_CHARACTERS #
A string that contained unescaped characters was received.
ERR_UNHANDLED_ERROR #
An unhandled error occurred (for instance, when an ‘error’ event is emitted by an EventEmitter but an ‘error’ handler is not registered).
ERR_UNKNOWN_BUILTIN_MODULE #
Used to identify a specific kind of internal Node.js error that should not typically be triggered by user code. Instances of this error point to an internal bug within the Node.js binary itself.
ERR_UNKNOWN_CREDENTIAL #
A Unix group or user identifier that does not exist was passed.
ERR_UNKNOWN_ENCODING #
An invalid or unknown encoding option was passed to an API.
ERR_UNKNOWN_FILE_EXTENSION #
An attempt was made to load a module with an unknown or unsupported file extension.
ERR_UNKNOWN_MODULE_FORMAT #
An attempt was made to load a module with an unknown or unsupported format.
ERR_UNKNOWN_SIGNAL #
An invalid or unknown process signal was passed to an API expecting a valid signal (such as subprocess.kill() ).
ERR_UNSUPPORTED_DIR_IMPORT #
import a directory URL is unsupported. Instead, self-reference a package using its name and define a custom subpath in the «exports» field of the package.json file.
ERR_UNSUPPORTED_ESM_URL_SCHEME #
import with URL schemes other than file and data is unsupported.
ERR_USE_AFTER_CLOSE #
An attempt was made to use something that was already closed.
ERR_VALID_PERFORMANCE_ENTRY_TYPE #
While using the Performance Timing API ( perf_hooks ), no valid performance entry types are found.
ERR_VM_DYNAMIC_IMPORT_CALLBACK_MISSING #
A dynamic import callback was not specified.
ERR_VM_MODULE_ALREADY_LINKED #
The module attempted to be linked is not eligible for linking, because of one of the following reasons:
- It has already been linked ( linkingStatus is ‘linked’ )
- It is being linked ( linkingStatus is ‘linking’ )
- Linking has failed for this module ( linkingStatus is ‘errored’ )
ERR_VM_MODULE_CACHED_DATA_REJECTED #
The cachedData option passed to a module constructor is invalid.
ERR_VM_MODULE_CANNOT_CREATE_CACHED_DATA #
Cached data cannot be created for modules which have already been evaluated.
ERR_VM_MODULE_DIFFERENT_CONTEXT #
The module being returned from the linker function is from a different context than the parent module. Linked modules must share the same context.
ERR_VM_MODULE_LINK_FAILURE #
The module was unable to be linked due to a failure.
ERR_VM_MODULE_NOT_MODULE #
The fulfilled value of a linking promise is not a vm.Module object.
ERR_VM_MODULE_STATUS #
The current module’s status does not allow for this operation. The specific meaning of the error depends on the specific function.
ERR_WASI_ALREADY_STARTED #
The WASI instance has already started.
ERR_WASI_NOT_STARTED #
The WASI instance has not been started.
ERR_WEBASSEMBLY_RESPONSE #
The Response that has been passed to WebAssembly.compileStreaming or to WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming is not a valid WebAssembly response.
ERR_WORKER_INIT_FAILED #
The Worker initialization failed.
ERR_WORKER_INVALID_EXEC_ARGV #
The execArgv option passed to the Worker constructor contains invalid flags.
ERR_WORKER_NOT_RUNNING #
An operation failed because the Worker instance is not currently running.
ERR_WORKER_OUT_OF_MEMORY #
The Worker instance terminated because it reached its memory limit.
ERR_WORKER_PATH #
The path for the main script of a worker is neither an absolute path nor a relative path starting with ./ or ../ .
ERR_WORKER_UNSERIALIZABLE_ERROR #
All attempts at serializing an uncaught exception from a worker thread failed.
ERR_WORKER_UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION #
The requested functionality is not supported in worker threads.
ERR_ZLIB_INITIALIZATION_FAILED #
Creation of a zlib object failed due to incorrect configuration.
History
Max header size in http_parser was set to 8 KiB.
Too much HTTP header data was received. In order to protect against malicious or malconfigured clients, if more than 8 KiB of HTTP header data is received then HTTP parsing will abort without a request or response object being created, and an Error with this code will be emitted.
HPE_UNEXPECTED_CONTENT_LENGTH #
Server is sending both a Content-Length header and Transfer-Encoding: chunked .
Transfer-Encoding: chunked allows the server to maintain an HTTP persistent connection for dynamically generated content. In this case, the Content-Length HTTP header cannot be used.
Use Content-Length or Transfer-Encoding: chunked .
MODULE_NOT_FOUND #
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v11.4.0, v10.15.0 |
Added requireStack property.
A module file could not be resolved by the CommonJS modules loader while attempting a require() operation or when loading the program entry point.
Legacy Node.js error codes #
ERR_CANNOT_TRANSFER_OBJECT #
The value passed to postMessage() contained an object that is not supported for transferring.
ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_DIGEST_NO_UTF16 #
The UTF-16 encoding was used with hash.digest() . While the hash.digest() method does allow an encoding argument to be passed in, causing the method to return a string rather than a Buffer , the UTF-16 encoding (e.g. ucs or utf16le ) is not supported.
ERR_HTTP2_FRAME_ERROR #
Used when a failure occurs sending an individual frame on the HTTP/2 session.
Used when an HTTP/2 Headers Object is expected.
Used when a required header is missing in an HTTP/2 message.
HTTP/2 informational headers must only be sent prior to calling the Http2Stream.prototype.respond() method.
ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_CLOSED #
Used when an action has been performed on an HTTP/2 Stream that has already been closed.
ERR_HTTP_INVALID_CHAR #
Used when an invalid character is found in an HTTP response status message (reason phrase).
ERR_INDEX_OUT_OF_RANGE #
A given index was out of the accepted range (e.g. negative offsets).
ERR_INVALID_OPT_VALUE #
An invalid or unexpected value was passed in an options object.
ERR_INVALID_OPT_VALUE_ENCODING #
An invalid or unknown file encoding was passed.
ERR_MISSING_MESSAGE_PORT_IN_TRANSFER_LIST #
This error code was replaced by ERR_MISSING_TRANSFERABLE_IN_TRANSFER_LIST in Node.js v15.0.0, because it is no longer accurate as other types of transferable objects also exist now.
ERR_NAPI_CONS_PROTOTYPE_OBJECT #
Used by the Node-API when Constructor.prototype is not an object.
ERR_NETWORK_IMPORT_BAD_RESPONSE #
Response was received but was invalid when importing a module over the network.
ERR_NETWORK_IMPORT_DISALLOWED #
A network module attempted to load another module that it is not allowed to load. Likely this restriction is for security reasons.
ERR_NO_LONGER_SUPPORTED #
A Node.js API was called in an unsupported manner, such as Buffer.write(string, encoding, offset[, length]) .
ERR_OPERATION_FAILED #
An operation failed. This is typically used to signal the general failure of an asynchronous operation.
ERR_OUTOFMEMORY #
Used generically to identify that an operation caused an out of memory condition.
ERR_PARSE_HISTORY_DATA #
The node:repl module was unable to parse data from the REPL history file.
ERR_SOCKET_CANNOT_SEND #
Data could not be sent on a socket.
ERR_STDERR_CLOSE #
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v12.0.0 |
Rather than emitting an error, process.stderr.end() now only closes the stream side but not the underlying resource, making this error obsolete.
Removed in: v10.12.0
An attempt was made to close the process.stderr stream. By design, Node.js does not allow stdout or stderr streams to be closed by user code.
ERR_STDOUT_CLOSE #
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v10.12.0 |
Rather than emitting an error, process.stderr.end() now only closes the stream side but not the underlying resource, making this error obsolete.
Removed in: v10.12.0
An attempt was made to close the process.stdout stream. By design, Node.js does not allow stdout or stderr streams to be closed by user code.
ERR_STREAM_READ_NOT_IMPLEMENTED #
Used when an attempt is made to use a readable stream that has not implemented readable._read() .
ERR_TLS_RENEGOTIATION_FAILED #
Used when a TLS renegotiation request has failed in a non-specific way.
ERR_TRANSFERRING_EXTERNALIZED_SHAREDARRAYBUFFER #
A SharedArrayBuffer whose memory is not managed by the JavaScript engine or by Node.js was encountered during serialization. Such a SharedArrayBuffer cannot be serialized.
This can only happen when native addons create SharedArrayBuffer s in «externalized» mode, or put existing SharedArrayBuffer into externalized mode.
ERR_UNKNOWN_STDIN_TYPE #
An attempt was made to launch a Node.js process with an unknown stdin file type. This error is usually an indication of a bug within Node.js itself, although it is possible for user code to trigger it.
ERR_UNKNOWN_STREAM_TYPE #
An attempt was made to launch a Node.js process with an unknown stdout or stderr file type. This error is usually an indication of a bug within Node.js itself, although it is possible for user code to trigger it.
ERR_V8BREAKITERATOR #
The V8 BreakIterator API was used but the full ICU data set is not installed.
ERR_VALUE_OUT_OF_RANGE #
Used when a given value is out of the accepted range.
ERR_VM_MODULE_NOT_LINKED #
The module must be successfully linked before instantiation.
ERR_VM_MODULE_LINKING_ERRORED #
The linker function returned a module for which linking has failed.
ERR_WORKER_UNSUPPORTED_EXTENSION #
The pathname used for the main script of a worker has an unknown file extension.
ERR_ZLIB_BINDING_CLOSED #
Used when an attempt is made to use a zlib object after it has already been closed.
Источник
Adblock
detector
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| v10.12.0 |
Nov 24, 2017 6:00:32 PM |
The Node.js Error Class Hierarchy
A brief overview of the Node.js error class hierarchy, including a quick look at all the top-level error classes in the standard library.
The Node.js error class hierarchy consists of about half a dozen unique classes, most of which inherit from the baseline Error class. A Node.js application will typically experience errors that fall into one of four categories:
- Standard JavaScript errors like
RangeError,ReferenceError, andTypeError. - System-level errors from the underlying operating system. These might occur due to invalid IO calls or insufficient memory issues.
- User errors generated by application code. These are the typical type of errors you’ll likely think of when evaluating errors in most programming languages.
- Assertion Errors, which are a special error type triggered whenever Node.js detects a logic violation.
One important distinction between Node.js and standard JavaScript is that all exceptions thrown by Node.js are instances of the Error class. This allows Node.js to associate the stack trace and other valuable metadata with every error that occurs within a Node.js application.
Here is the full Node.js error class hierarchy:
- Class: Error
- Class: AssertionError
- Class: RangeError
- Class: ReferenceError
- Class: SyntaxError
- Class: TypeError
- Class: System Error
Node.js Error Codes
Beyond the Error class and its children, starting with version 8+ Node.js now associates an error code property with each error that is thrown. These codes are simply string constants, but their existence allows code to check for a specific error type without having to worry about the messiness associated with checking the actual error message property string.
For example, in the past performing logic based on a specific caught error type involved something like this:
try {
// Node.js code generating an Error.
} catch (error) {
if (error.message === 'Uh oh, an error has occurred') {
// Perform some logic.
}
}
Comparing strings is a rather messy affair, particularly when internationalization gets involved with various locales. Thus, Node.js error codes were introduced and allow the error.code property to be checked against a standard string constant associated with the type of error you’re checking for. Thus, the code above using error codes looks something like this:
try {
// Node.js code generating an Error.
} catch (error) {
if (error.message === 'ERR_HTTP_INVALID_STATUS_CODE') {
// Perform some logic.
}
}
The full list of Node.js error codes can be found below:
- Node.js Error Codes
- ERR_ARG_NOT_ITERABLE
- ERR_ASSERTION
- ERR_ASYNC_CALLBACK
- ERR_ASYNC_TYPE
- ERR_BUFFER_OUT_OF_BOUNDS
- ERR_BUFFER_TOO_LARGE
- ERR_CHILD_CLOSED_BEFORE_REPLY
- ERR_CONSOLE_WRITABLE_STREAM
- ERR_CPU_USAGE
- ERR_CRYPTO_ECDH_INVALID_FORMAT
- ERR_CRYPTO_ENGINE_UNKNOWN
- ERR_CRYPTO_FIPS_FORCED
- ERR_CRYPTO_FIPS_UNAVAILABLE
- ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_DIGEST_NO_UTF16
- ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_FINALIZED
- ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_UPDATE_FAILED
- ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_DIGEST
- ERR_CRYPTO_SIGN_KEY_REQUIRED
- ERR_CRYPTO_TIMING_SAFE_EQUAL_LENGTH
- ERR_DNS_SET_SERVERS_FAILED
- ERR_ENCODING_INVALID_ENCODED_DATA
- ERR_ENCODING_NOT_SUPPORTED
- ERR_FALSY_VALUE_REJECTION
- ERR_HTTP_HEADERS_SENT
- ERR_HTTP_INVALID_CHAR
- ERR_HTTP_INVALID_STATUS_CODE
- ERR_HTTP_TRAILER_INVALID
- ERR_HTTP2_CONNECT_AUTHORITY
- ERR_HTTP2_CONNECT_PATH
- ERR_HTTP2_CONNECT_SCHEME
- ERR_HTTP2_FRAME_ERROR
- ERR_HTTP2_HEADER_REQUIRED
- ERR_HTTP2_HEADER_SINGLE_VALUE
- ERR_HTTP2_HEADERS_AFTER_RESPOND
- ERR_HTTP2_HEADERS_OBJECT
- ERR_HTTP2_HEADERS_SENT
- ERR_HTTP2_INFO_HEADERS_AFTER_RESPOND
- ERR_HTTP2_INFO_STATUS_NOT_ALLOWED
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_CONNECTION_HEADERS
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_HEADER_VALUE
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_INFO_STATUS
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_PACKED_SETTINGS_LENGTH
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_PSEUDOHEADER
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_SESSION
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_SETTING_VALUE
- ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_STREAM
- ERR_HTTP2_MAX_PENDING_SETTINGS_ACK
- ERR_HTTP2_NO_SOCKET_MANIPULATION
- ERR_HTTP2_OUT_OF_STREAMS
- ERR_HTTP2_PAYLOAD_FORBIDDEN
- ERR_HTTP2_PSEUDOHEADER_NOT_ALLOWED
- ERR_HTTP2_PUSH_DISABLED
- ERR_HTTP2_SEND_FILE
- ERR_HTTP2_SOCKET_BOUND
- ERR_HTTP2_STATUS_101
- ERR_HTTP2_STATUS_INVALID
- ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_CLOSED
- ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_ERROR
- ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_SELF_DEPENDENCY
- ERR_HTTP2_UNSUPPORTED_PROTOCOL
- ERR_INDEX_OUT_OF_RANGE
- ERR_INSPECTOR_ALREADY_CONNECTED
- ERR_INSPECTOR_CLOSED
- ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_AVAILABLE
- ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_CONNECTED
- ERR_INVALID_ARG_TYPE
- ERR_INVALID_ARG_VALUE
- ERR_INVALID_ARRAY_LENGTH
- ERR_INVALID_ASYNC_ID
- ERR_INVALID_BUFFER_SIZE
- ERR_INVALID_CALLBACK
- ERR_INVALID_CHAR
- ERR_INVALID_CURSOR_POS
- ERR_INVALID_DOMAIN_NAME
- ERR_INVALID_FD
- ERR_INVALID_FD_TYPE
- ERR_INVALID_FILE_URL_HOST
- ERR_INVALID_FILE_URL_PATH
- ERR_INVALID_HANDLE_TYPE
- ERR_INVALID_HTTP_TOKEN
- ERR_INVALID_IP_ADDRESS
- ERR_INVALID_OPT_VALUE
- ERR_INVALID_OPT_VALUE_ENCODING
- ERR_INVALID_PERFORMANCE_MARK
- ERR_INVALID_PROTOCOL
- ERR_INVALID_REPL_EVAL_CONFIG
- ERR_INVALID_SYNC_FORK_INPUT
- ERR_INVALID_THIS
- ERR_INVALID_TUPLE
- ERR_INVALID_URI
- ERR_INVALID_URL
- ERR_INVALID_URL_SCHEME
- ERR_IPC_CHANNEL_CLOSED
- ERR_IPC_DISCONNECTED
- ERR_IPC_ONE_PIPE
- ERR_IPC_SYNC_FORK
- ERR_METHOD_NOT_IMPLEMENTED
- ERR_MISSING_ARGS
- ERR_MISSING_DYNAMIC_INSTANTIATE_HOOK
- ERR_MISSING_MODULE
- ERR_MODULE_RESOLUTION_LEGACY
- ERR_MULTIPLE_CALLBACK
- ERR_NAPI_CONS_FUNCTION
- ERR_NAPI_CONS_PROTOTYPE_OBJECT
- ERR_NO_CRYPTO
- ERR_NO_ICU
- ERR_NO_LONGER_SUPPORTED
- ERR_OUTOFMEMORY
- ERR_OUT_OF_RANGE
- ERR_PARSE_HISTORY_DATA
- ERR_REQUIRE_ESM
- ERR_SERVER_ALREADY_LISTEN
- ERR_SOCKET_ALREADY_BOUND
- ERR_SOCKET_BAD_BUFFER_SIZE
- ERR_SOCKET_BAD_PORT
- ERR_SOCKET_BAD_TYPE
- ERR_SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE
- ERR_SOCKET_CANNOT_SEND
- ERR_SOCKET_CLOSED
- ERR_SOCKET_DGRAM_NOT_RUNNING
- ERR_STDERR_CLOSE
- ERR_STDOUT_CLOSE
- ERR_STREAM_CANNOT_PIPE
- ERR_STREAM_NULL_VALUES
- ERR_STREAM_PUSH_AFTER_EOF
- ERR_STREAM_READ_NOT_IMPLEMENTED
- ERR_STREAM_UNSHIFT_AFTER_END_EVENT
- ERR_STREAM_WRAP
- ERR_STREAM_WRITE_AFTER_END
- ERR_TLS_CERT_ALTNAME_INVALID
- ERR_TLS_DH_PARAM_SIZE
- ERR_TLS_HANDSHAKE_TIMEOUT
- ERR_TLS_RENEGOTIATION_FAILED
- ERR_TLS_REQUIRED_SERVER_NAME
- ERR_TLS_SESSION_ATTACK
- ERR_TRANSFORM_ALREADY_TRANSFORMING
- ERR_TRANSFORM_WITH_LENGTH_0
- ERR_UNESCAPED_CHARACTERS
- ERR_UNHANDLED_ERROR
- ERR_UNKNOWN_ENCODING
- ERR_UNKNOWN_FILE_EXTENSION
- ERR_UNKNOWN_MODULE_FORMAT
- ERR_UNKNOWN_SIGNAL
- ERR_UNKNOWN_STDIN_TYPE
- ERR_UNKNOWN_STREAM_TYPE
- ERR_V8BREAKITERATOR
- ERR_VALID_PERFORMANCE_ENTRY_TYPE
- ERR_VALUE_OUT_OF_RANGE
- ERR_ZLIB_BINDING_CLOSED
- ERR_ZLIB_INITIALIZATION_FAILED
As we publish future error-specific articles in this series we’ll update the full list above with relevant tutorial and article links for each error class and error code, so this post can act as a go-to resource for Node.js error handling tips.
Major Error Classes Overview
Let’s briefly look at each top-level error class type found in Node.js. These top-level errors will server as a basis for exploring specific errors and error codes in future articles.
Error
The Error class is a generic JavaScript Error object that doesn’t include any information about why this error occurred. However, since these are Node.js-generated Errors, each Error instance includes a stack trace, error code (if applicable), and any other relevant metadata. This metadata is provided via a handful of core Error class properties:
error.code— A string constant indicating the specific error type.error.message— A string that describes the error.error.stack— A string that describes where in the code theErroroccurred.
As we saw above, since all errors in Node.js inherit from the Error class, all errors will include these baseline properties.
AssertionError
Indicates an assertion failure using the assert module.
RangeError
Indicates that an argument was not within a valid set or range of values. Node.js generates and throws RangeErrors immediately when invalid arguments are detected.
ReferenceError
Indicates that an undefined variable was accessed.
SyntaxError
Indicates that a portion of the code is not valid JavaScript. Typically, SyntaxErrors will only occur as a result of code evaluation techniques, such as using the Function() or eval() functions.
TypeError
Indicates that an argument was passed to a function that expected an argument of a different type. Similar to the RangeError, Node.js will generate and throw TypeErrors immediately when an invalid argument type is detected.
System Error
As discussed in the introduction, one of the four common categories in which Node.js can experience errors is when something at the system level goes wrong. In such cases, a System Error is generated. These may occur due to improper IO operations, invalid permissions, and so forth.
In addition to the error.code property found in the inherited Error class, System Errors also include a few extra properties that are relevant to system-level problems:
error.errno— A number or string value indicating the error number associated with the particular system-levelerror.code.error.syscall— A string that describes thesyscallthat failed.error.address— An optional string that describes the remote address for which the connection-related error occurred.error.port— An optional number that describes the remote port for which the connection-related error occurred.
There are far too many possible System Error codes that can occur, but feel free to look at the man page documentation for more information.
That’s just a small taste of overall Node.js error class hierarchy. Stay tuned for more in-depth articles examining each of these error in greater detail, and be sure to check out Airbrake’s robust error monitoring software, which provides real-time error monitoring and automatic exception reporting for all your development projects. Airbrake’s state of the art web dashboard ensures you receive round-the-clock status updates on your application’s health and error rates. No matter what you’re working on, Airbrake easily integrates with all the most popular languages and frameworks. Plus, Airbrake makes it easy to customize exception parameters, while giving you complete control of the active error filter system, so you only gather the errors that matter most.
Check out Airbrake’s error monitoring software today and sign up for a 14-day free trial. See for yourself why so many of the world’s best engineering teams use Airbrake to revolutionize their exception handling practices!
Node.js inherits the JavaScript and system errors from the JavaScript <Error> class and it guarantees to provide the properties which are available on that class. The JavaScript exceptions that immediately throws errors using the throw mechanism that are handled by try…catch construct that is provided by the JavaScript.
Node.js handles errors that occur during the application running, supports multiple error mechanisms i.e. how all these errors are reported and handled depends on Error type and API style. Application code can trigger user-specified errors also. All those errors that are generated by the Node.js are either the instances or inherited from the Error class. In Node.js, it experiences many types of errors while running applications that are given below:
Class: AssertionError: AssertionErrors are Extended by the <errors.Error> Class. When it detects that an exceptional logic violation has occurred that should never occur, then these errors are triggered and the assert module raises all these errors. All those errors that are thrown by the assert module are instances of AssertionError class.
Example 1: Filename: index.js
const assert = require('assert');
console.log("Throws Assertion Error...");
assert.strictEqual(
{'Alfa':'hi', 'beta':'hello'},
{'Alfa':'hi', 'beta':'hello'}
);
Run index.js file using the following command:
node index.js
Output:
Throws Assertion Error
>> Throws Assertion Error…
>> assert.js:101
throw new AssertionError(obj);
AssertionError [ERR_ASSERTION]: Values have same structure but are not reference-equal:
{ Alfa: ‘hi’, beta: ‘hello’} at Object.<anonymous> (C:UsersAjay KumarDesktoptest2.js:12:8)……. operator: ?[32m’strictEqual’?[39m}
Class: RangeError: It shows that the provided argument was not within the acceptable range of values. It could be a numeric range, or outside the set of options.
Example 2: Filename: index.js
const http = require('http');
var server = http.createServer()
.listen(46456656, (err, res)=>{
});
Output:
Throws Range Error
>> internal/validators.js:192
throw new ERR_SOCKET_BAD_PORT(name, port);
RangeError [ERR_SOCKET_BAD_PORT]: options.port should be >= 0 and < 65536. Received 46456656……. code: ?[32m’ERR_SOCKET_BAD_PORT’?[39m}
Class: ReferenceError: It specifies that the variable anyone is trying to access is not defined. Such types of errors specify typos in code or a broken program. The instances of ReferenceError specify a bug in the code until an application is dynamically running code.
Example 3: Filename: index.js
try {
const alfa = 10;
const beta = alfa + gamma;
} catch (err) {
console.log(err.message);
console.log(err);
}
Output:
Throws Reference Error
>> gamma is not defined
>> ReferenceError: gamma is not defined
at Object.<anonymous> (C:UsersAjay KumarDesktoptest2.js:128:23)……at internal/main/run_main_module.js:17:47
Class: SyntaxError: It specifies that the program is not a valid JavaScript and it may be generated as a result of code evaluation. These errors mostly happen as a result of eval, Function, require, or vm.
Example 4: Filename: index.js
try {
require('vm').runInThisContext('alfa @ beta');
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
Output:
Throws Syntax Error
>> alfa @ beta
>> SyntaxError: Invalid or unexpected token
at new Script (vm.js:99:7)……at internal/main/run_main_module.js:17:47
Class: SystemError: System errors that are generated by Node.js occur due to exceptions within its runtime environment. when an application violates an operating system constraint then these errors could be expected.
Example 5: Filename: index.js
const fs = require('fs');
function errorCallback(err, data) {
if (err) {
console.error('There was an error', err);
return;
}
return(data);
}
fs.readFile('/some/non-existing/file', errorCallback);
Output:
Throws Error
>> There was an error [Error: ENOENT: no such file or directory, open ‘C:somenon-existingfile’] {
errno: -4058,
code: ‘ENOENT’,
syscall: ‘open’,
path: ‘C:\some\non-existing\file’}
Class: TypeError: It specifies that the argument provided is not an allowable type. For example, calling a function that actually doesn’t exist would be a TypeError. As if the form is of argument validation, it throws TypeError instances immediately.
Example 6: Filename: index.js
try {
if(1) {
if(2) {
console.loo('alfa')
}
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
Run index.js file using the following command:
node index.js
Output:
Throws Type Error
>> TypeError: console.loo is not a function
at Object.<anonymous> (C:UsersAjay KumarDesktoptest2.js:104:15)……at internal/main/run_main_module.js:17:47
Reference: https://nodejs.org/api/errors.html#errors_class_assertionerror
- 21 min read
- JavaScript,
Node.js,
Apps
error class pattern and how to use it for a better, more efficient way of handling errors across your applications.Error handling is one of those parts of software development that don’t quite get the amount of attention it really deserves. However, building robust applications requires dealing with errors properly.
You can get by in NodeJS without properly handling errors but due to the asynchronous nature of NodeJS, improper handling or errors can cause you pain soon enough — especially when debugging applications.
Before we proceed, I would like to point out the type of errors we’ll be discussing how to utilize error classes.
Operational Errors
These are errors discovered during the run time of a program. Operational errors are not bugs and can occur from time to time mostly because of one or a combination of several external factors like a database server timing out or a user deciding to make an attempt on SQL injection by entering SQL queries in an input field.
Below are more examples of operational errors:
- Failed to connect to a database server;
- Invalid inputs by the user (server responds with a
400response code); - Request timeout;
- Resource not found (server responds with a 404 response code);
- Server returns with a
500response.
It’s also worthy of note to briefly discuss the counterpart of Operational Errors.
Programmer Errors
These are bugs in the program which can be resolved by changing the code. These types of errors can not be handled because they occur as a result of the code being broken. Example of these errors are:
- Trying to read a property on an object that is not defined.
const user = {
firstName: 'Kelvin',
lastName: 'Omereshone',
}
console.log(user.fullName) // throws 'undefined' because the property fullName is not defined- Invoking or calling an asynchronous function without a callback.
- Passing a string where a number was expected.
This article is about Operational Error handling in NodeJS. Error handling in NodeJS is significantly different from error handling in other languages. This is due to the asynchronous nature of JavaScript and the openness of JavaScript with errors. Let me explain:
In JavaScript, instances of the error class is not the only thing you can throw. You can literally throw any data type this openness is not allowed by other languages.
For example, a JavaScript developer may decide to throw in a number instead of an error object instance, like so:
// bad
throw 'Whoops :)';
// good
throw new Error('Whoops :)')
You might not see the problem in throwing other data types, but doing so will result in a harder time debugging because you won’t get a stack trace and other properties that the Error object exposes which are needed for debugging.
Let’s look at some incorrect patterns in error handling, before taking a look at the Error class pattern and how it is a much better way for error handling in NodeJS.
More after jump! Continue reading below ↓
Bad Error Handling Pattern #1: Wrong Use Of Callbacks
Real-world scenario: Your code depends on an external API requiring a callback to get the result you expect it to return.
Let’s take the below code snippet:
'use strict';
const fs = require('fs');
const write = function () {
fs.mkdir('./writeFolder');
fs.writeFile('./writeFolder/foobar.txt', 'Hello World');
}
write();
Until NodeJS 8 and above, the above code was legitimate, and developers would simply fire and forget commands. This means developers weren’t required to provide a callback to such function calls, and therefore could leave out error handling. What happens when the writeFolder hasn’t been created? The call to writeFile won’t be made and we wouldn’t know anything about it. This might also result in race condition because the first command might not have finished when the second command started again, you wouldn’t know.
Let’s start solving this problem by solving the race condition. We would do so by giving a callback to the first command mkdir to ensure the directory indeed exists before writing to it with the second command. So our code would look like the one below:
'use strict';
const fs = require('fs');
const write = function () {
fs.mkdir('./writeFolder', () => {
fs.writeFile('./writeFolder/foobar.txt', 'Hello World!');
});
}
write();
Though we solved the race condition, we are not done quite yet. Our code is still problematic because even though we used a callback for the first command, we have no way of knowing if the folder writeFolder was created or not. If the folder wasn’t created, then the second call will fail again but still, we ignored the error yet again. We solve this by…
Error Handling With Callbacks
In order to handle error properly with callbacks, you must make sure you always use the error-first approach. What this means is that you should first check if there is an error returned from the function before going ahead to use whatever data(if any) was returned. Let’s see the wrong way of doing this:
'use strict';
// Wrong
const fs = require('fs');
const write = function (callback) {
fs.mkdir('./writeFolder', (err, data) => {
if (data) fs.writeFile('./writeFolder/foobar.txt', 'Hello World!');
else callback(err)
});
}
write(console.log);
The above pattern is wrong because sometimes the API you are calling might not return any value or might return a falsy value as a valid return value. This would make you end up in an error case even though you might apparently have a successful call of the function or API.
The above pattern is also bad because it’s usage would eat up your error(your errors won’t be called even though it might have happened). You will also have no idea of what is happening in your code as a result of this kind of error handling pattern. So the right way for the above code would be:
'use strict';
// Right
const fs = require('fs');
const write = function (callback) {
fs.mkdir('./writeFolder', (err, data) => {
if (err) return callback(err)
fs.writeFile('./writeFolder/foobar.txt', 'Hello World!');
});
}
write(console.log);
Wrong Error Handling Pattern #2: Wrong Use Of Promises
Real-world scenario: So you discovered Promises and you think they are way better than callbacks because of callback hell and you decided on promisifying some external API your code base depended upon. Or you are consuming a promise from an external API or a browser API like the fetch() function.
These days we don’t really use callbacks in our NodeJS codebases, we use promises. So let’s reimplement our example code with a promise:
'use strict';
const fs = require('fs').promises;
const write = function () {
return fs.mkdir('./writeFolder').then(() => {
fs.writeFile('./writeFolder/foobar.txt', 'Hello world!')
}).catch((err) => {
// catch all potential errors
console.error(err)
})
}
Let’s put the above code under a microscope — we can see that we are branching off the fs.mkdir promise into another promise chain(the call to fs.writeFile) without even handling that promise call. You might think a better way to do it would be:
'use strict';
const fs = require('fs').promises;
const write = function () {
return fs.mkdir('./writeFolder').then(() => {
fs.writeFile('./writeFolder/foobar.txt', 'Hello world!').then(() => {
// do something
}).catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
})
}).catch((err) => {
// catch all potential errors
console.error(err)
})
}
But the above would not scale. This is because if we have more promise chain to call, we would end up with something similar to the callback hell which promises were made to solve. This means our code will keep indenting to the right. We would have a promise hell on our hands.
Promisifying A Callback-Based API
Most times you would want to promisify a callback-based API on your own in order to better handle errors on that API. However, this is not really easy to do. Let’s take an example below to explain why.
function doesWillNotAlwaysSettle(arg) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
doATask(foo, (err) => {
if (err) {
return reject(err);
}
if (arg === true) {
resolve('I am Done')
}
});
});
}
From the above, if arg is not true and we don’t have an error from the call to the doATask function then this promise will just hang out which is a memory leak in your application.
Swallowed Sync Errors In Promises
Using the Promise constructor has several difficulties one of these difficulties is; as soon as it is either resolved or rejected it cannot get another state. This is because a promise can only get a single state — either it is pending or it is resolved/rejected. This means we can have dead zones in our promises. Let’s see this in code:
function deadZonePromise(arg) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
doATask(foo, (err) => {
resolve('I’m all Done');
throw new Error('I am never reached') // Dead Zone
});
});
}
From the above we see as soon as the promise is resolved, the next line is a dead zone and will never be reached. This means any following synchronous error handling perform in your promises will just be swallowed and will never be thrown.
Real-World Examples
The examples above help explain poor error handling patterns, let’s take a look at the sort of problems you might see in real-life.
Real World Example #1 — Transforming Error To String
Scenario: You decided the error returned from an API is not really good enough for you so you decided to add your own message to it.
'use strict';
function readTemplate() {
return new Promise(() => {
databaseGet('query', function(err, data) {
if (err) {
reject('Template not found. Error: ', + err);
} else {
resolve(data);
}
});
});
}
readTemplate();
Let’s look at what is wrong with the above code. From the above we see the developer is trying to improve the error thrown by the databaseGet API by concatenating the returned error with the string “Template not found”. This approach has a lot of downsides because when the concatenation was done, the developer implicitly runs toString on the error object returned. This way he loses any extra information returned by the error(say goodbye to stack trace). So what the developer has right now is just a string that is not useful when debugging.
A better way is to keep the error as it is or wrap it in another error that you’ve created and attached the thrown error from the databaseGet call as a property to it.
Real-World Example #2: Completely Ignoring The Error
Scenario: Perhaps when a user is signing up in your application, if an error occur you want to just catch the error and show a custom message but you completely ignored the error that was caught without even logging it for debugging purposes.
router.get('/:id', function (req, res, next) {
database.getData(req.params.userId)
.then(function (data) {
if (data.length) {
res.status(200).json(data);
} else {
res.status(404).end();
}
})
.catch(() => {
log.error('db.rest/get: could not get data: ', req.params.userId);
res.status(500).json({error: 'Internal server error'});
})
});
From the above, we can see that the error is completely ignored and the code is sending 500 to the user if the call to the database failed. But in reality, the cause for the database failure might be malformed data sent by the user which is an error with the status code of 400.
In the above case, we would be ending up in a debugging horror because you as the developer wouldn’t know what went wrong. The user won’t be able to give a decent report because 500 internal server error is always thrown. You would end up wasting hours in finding the problem which will tantamount to wastage of your employer’s time and money.
Real-World Example #3: Not Accepting The Error Thrown From An API
Scenario: An error was thrown from an API you were using but you don’t accept that error instead you marshall and transform the error in ways that make it useless for debugging purposes.
Take the following code example below:
async function doThings(input) {
try {
validate(input);
try {
await db.create(input);
} catch (error) {
error.message = `Inner error: ${error.message}`
if (error instanceof Klass) {
error.isKlass = true;
}
throw error
}
} catch (error) {
error.message = `Could not do things: ${error.message}`;
await rollback(input);
throw error;
}
}
A lot is going on in the above code that would lead to debugging horror. Let’s take a look:
- Wrapping
try/catchblocks: You can see from the above that we are wrappingtry/catchblock which is a very bad idea. We normally try to reduce the use oftry/catchblocks to minify the surface where we would have to handle our error (think of it as DRY error handling); - We are also manipulating the error message in the attempt to improve which is also not a good idea;
- We are checking if the error is an instance of type
Klassand in this case, we are setting a boolean property of the errorisKlassto truev(but if that check passes then the error is of the typeKlass); - We are also rolling back the database too early because, from the code structure, there is a high tendency that we might not have even hit the database when the error was thrown.
Below is a better way to write the above code:
async function doThings(input) {
validate(input);
try {
await db.create(input);
} catch (error) {
try {
await rollback();
} catch (error) {
logger.log('Rollback failed', error, 'input:', input);
}
throw error;
}
}
Let’s analyze what we are doing right in the above snippet:
- We are using one
try/catchblock and only in the catch block are we using anothertry/catchblock which is to serve as a guard in case something goes on with that rollback function and we are logging that; - Finally, we are throwing our original received error meaning we don’t lose the message included in that error.
Testing
We mostly want to test our code(either manually or automatically). But most times we are only testing for the positive things. For a robust test, you must also test for errors and edge cases. This negligence is responsible for bugs finding their way into production which would cost more extra debugging time.
Tip: Always make sure to test not only the positive things(getting a status code of 200 from an endpoint) but also all the error cases and all the edge cases as well.
Real-World Example #4: Unhandled Rejections
If you’ve used promises before, you have probably run into unhandled rejections.
Here is a quick primer on unhandled rejections. Unhandled rejections are promise rejections that weren’t handled. This means that the promise was rejected but your code will continue running.
Let’s look at a common real-world example that leads to unhandled rejections..
'use strict';
async function foobar() {
throw new Error('foobar');
}
async function baz() {
throw new Error('baz')
}
(async function doThings() {
const a = foobar();
const b = baz();
try {
await a;
await b;
} catch (error) {
// ignore all errors!
}
})();
The above code at first look might seem not error-prone. But on a closer look, we begin to see a defect. Let me explain: What happens when a is rejected? That means await b is never reached and that means its an unhandled rejection. A possible solution is to use Promise.all on both promises. So the code would read like so:
'use strict';
async function foobar() {
throw new Error('foobar');
}
async function baz() {
throw new Error('baz')
}
(async function doThings() {
const a = foobar();
const b = baz();
try {
await Promise.all([a, b]);
} catch (error) {
// ignore all errors!
}
})();
Here is another real-world scenario that would lead to an unhandled promise rejection error:
'use strict';
async function foobar() {
throw new Error('foobar');
}
async function doThings() {
try {
return foobar()
} catch {
// ignoring errors again !
}
}
doThings();
If you run the above code snippet, you will get an unhandled promise rejection, and here is why: Although it’s not obvious, we are returning a promise (foobar) before we are handling it with the try/catch. What we should do is await the promise we are handling with the try/catch so the code would read:
'use strict';
async function foobar() {
throw new Error('foobar');
}
async function doThings() {
try {
return await foobar()
} catch {
// ignoring errors again !
}
}
doThings();
Wrapping Up On The Negative Things
Now that you have seen wrong error handling patterns, and possible fixes, let’s now dive into Error class pattern and how it solves the problem of wrong error handling in NodeJS.
In this pattern, we would start our application with an ApplicationError class this way we know all errors in our applications that we explicitly throw are going to inherit from it. So we would start off with the following error classes:
ApplicationError
This is the ancestor of all other error classes i.e all other error classes inherits from it.DatabaseError
Any error relating to Database operations will inherit from this class.UserFacingError
Any error produced as a result of a user interacting with the application would be inherited from this class.
Here is how our error class file would look like:
'use strict';
// Here is the base error classes to extend from
class ApplicationError extends Error {
get name() {
return this.constructor.name;
}
}
class DatabaseError extends ApplicationError { }
class UserFacingError extends ApplicationError { }
module.exports = {
ApplicationError,
DatabaseError,
UserFacingError
}
This approach enables us to distinguish the errors thrown by our application. So now if we want to handle a bad request error (invalid user input) or a not found error (resource not found) we can inherit from the base class which is UserFacingError (as in the code below).
const { UserFacingError } = require('./baseErrors')
class BadRequestError extends UserFacingError {
constructor(message, options = {}) {
super(message);
// You can attach relevant information to the error instance
// (e.g.. the username)
for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(options)) {
this[key] = value;
}
}
get statusCode() {
return 400;
}
}
class NotFoundError extends UserFacingError {
constructor(message, options = {}) {
super(message);
// You can attach relevant information to the error instance
// (e.g.. the username)
for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(options)) {
this[key] = value;
}
}
get statusCode() {
return 404
}
}
module.exports = {
BadRequestError,
NotFoundError
}
One of the benefits of the error class approach is that if we throw one of these errors, for example, a NotFoundError, every developer reading this codebase would be able to understand what is going on at this point in time(if they read the code).
You would be able to pass in multiple properties specific to each error class as well during the instantiation of that error.
Another key benefit is that you can have properties that are always part of an error class, for example, if you receive a UserFacing error, you would know that a statusCode is always part of this error class now you can just directly use it in the code later on.
Tips On Utilizing Error Classes
- Make your own module(possibly a private one) for each error class that way you can simply import that in your application and use it everywhere.
- Throw only errors that you care about(errors that are instances of your error classes). This way you know your error classes are your only Source of Truth and it contains all information necessary to debug your application.
- Having an abstract error module is quite useful because now we know all necessary information concerning errors our applications can throw are in one place.
- Handle errors in layers. If you handle errors everywhere, you have an inconsistent approach to error handling which is hard to keep track of. By layers I mean like database, express/fastify/HTTP layers, and so on.
Let’s see how error classes looks in code. Here is an example in express:
const { DatabaseError } = require('./error')
const { NotFoundError } = require('./userFacingErrors')
const { UserFacingError } = require('./error')
// Express
app.get('/:id', async function (req, res, next) {
let data
try {
data = await database.getData(req.params.userId)
} catch (err) {
return next(err);
}
if (!data.length) {
return next(new NotFoundError('Dataset not found'));
}
res.status(200).json(data)
})
app.use(function (err, req, res, next) {
if (err instanceof UserFacingError) {
res.sendStatus(err.statusCode);
// or
res.status(err.statusCode).send(err.errorCode)
} else {
res.sendStatus(500)
}
// do your logic
logger.error(err, 'Parameters: ', req.params, 'User data: ', req.user)
});
From the above, we are leveraging that Express exposes a global error handler which allows you handle all your errors in one place. You can see the call to next() in the places we are handling errors. This call would pass the errors to the handler which is defined in the app.use section. Because express does not support async/await we are using try/catch blocks.
So from the above code, to handle our errors we just need to check if the error that was thrown is a UserFacingError instance and automatically we know that there would be a statusCode in the error object and we send that to the user (you might want to have a specific error code as well which you can pass to the client) and that is pretty much it.
You would also notice that in this pattern (error class pattern) every other error that you did not explicitly throw is a 500 error because it is something unexpected that means you did not explicitly throw that error in your application. This way, we are able to distinguish the types of error going on in our applications.
Conclusion
Proper error handling in your application can make you sleep better at night and save debug time. Here are some takeaway key points to take from this article:
- Use error classes specifically set up for your application;
- Implement abstract error handlers;
- Always use async/await;
- Make errors expressive;
- User promisify if necessary;
- Return proper error statuses and codes;
- Make use of promise hooks.
(ra, yk, il)
Applications running in Node.js will generally experience four categories of errors:
- Standard JavaScript errors such as <EvalError>, <SyntaxError>, <RangeError>, <ReferenceError>, <TypeError>, and <URIError>.
- System errors triggered by underlying operating system constraints such as attempting to open a file that does not exist or attempting to send data over a closed socket.
- User-specified errors triggered by application code.
-
AssertionErrors are a special class of error that can be triggered when Node.js detects an exceptional logic violation that should never occur. These are raised typically by theassertmodule.
All JavaScript and System errors raised by Node.js inherit from, or are instances of, the standard JavaScript <Error> class and are guaranteed to provide at least the properties available on that class.
Error Propagation and Interception
Node.js supports several mechanisms for propagating and handling errors that occur while an application is running. How these errors are reported and handled depends entirely on the type of Error and the style of the API that is called.
All JavaScript errors are handled as exceptions that immediately generate and throw an error using the standard JavaScript throw mechanism. These are handled using the try…catch construct provided by the JavaScript language.
// Throws with a ReferenceError because z is not defined.
try {
const m = 1;
const n = m + z;
} catch (err) {
// Handle the error here.
}
Any use of the JavaScript throw mechanism will raise an exception that must be handled using try…catch or the Node.js process will exit immediately.
With few exceptions, Synchronous APIs (any blocking method that does not accept a callback function, such as fs.readFileSync), will use throw to report errors.
Errors that occur within Asynchronous APIs may be reported in multiple ways:
- Most asynchronous methods that accept a
callbackfunction will accept anErrorobject passed as the first argument to that function. If that first argument is notnulland is an instance ofError, then an error occurred that should be handled.
const fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('a file that does not exist', (err, data) => {
if (err) {
console.error('There was an error reading the file!', err);
return;
}
// Otherwise handle the data
});
-
When an asynchronous method is called on an object that is an
EventEmitter, errors can be routed to that object’s'error'event.const net = require('net'); const connection = net.connect('localhost'); // Adding an 'error' event handler to a stream: connection.on('error', (err) => { // If the connection is reset by the server, or if it can't // connect at all, or on any sort of error encountered by // the connection, the error will be sent here. console.error(err); }); connection.pipe(process.stdout); -
A handful of typically asynchronous methods in the Node.js API may still use the
throwmechanism to raise exceptions that must be handled usingtry…catch. There is no comprehensive list of such methods; please refer to the documentation of each method to determine the appropriate error handling mechanism required.
The use of the 'error' event mechanism is most common for stream-based and event emitter-based APIs, which themselves represent a series of asynchronous operations over time (as opposed to a single operation that may pass or fail).
For all EventEmitter objects, if an 'error' event handler is not provided, the error will be thrown, causing the Node.js process to report an uncaught exception and crash unless either: The domain module is used appropriately or a handler has been registered for the 'uncaughtException' event.
const EventEmitter = require('events');
const ee = new EventEmitter();
setImmediate(() => {
// This will crash the process because no 'error' event
// handler has been added.
ee.emit('error', new Error('This will crash'));
});
Errors generated in this way cannot be intercepted using try…catch as they are thrown after the calling code has already exited.
Developers must refer to the documentation for each method to determine exactly how errors raised by those methods are propagated.
Error-first callbacks
Most asynchronous methods exposed by the Node.js core API follow an idiomatic pattern referred to as an error-first callback. With this pattern, a callback function is passed to the method as an argument. When the operation either completes or an error is raised, the callback function is called with the Error object (if any) passed as the first argument. If no error was raised, the first argument will be passed as null.
const fs = require('fs');
function errorFirstCallback(err, data) {
if (err) {
console.error('There was an error', err);
return;
}
console.log(data);
}
fs.readFile('/some/file/that/does-not-exist', errorFirstCallback);
fs.readFile('/some/file/that/does-exist', errorFirstCallback);
The JavaScript try…catch mechanism cannot be used to intercept errors generated by asynchronous APIs. A common mistake for beginners is to try to use throw inside an error-first callback:
// THIS WILL NOT WORK:
const fs = require('fs');
try {
fs.readFile('/some/file/that/does-not-exist', (err, data) => {
// Mistaken assumption: throwing here...
if (err) {
throw err;
}
});
} catch (err) {
// This will not catch the throw!
console.error(err);
}
This will not work because the callback function passed to fs.readFile() is called asynchronously. By the time the callback has been called, the surrounding code, including the try…catch block, will have already exited. Throwing an error inside the callback can crash the Node.js process in most cases. If domains are enabled, or a handler has been registered with process.on('uncaughtException'), such errors can be intercepted.
Class: Error
A generic JavaScript Error object that does not denote any specific circumstance of why the error occurred. Error objects capture a «stack trace» detailing the point in the code at which the Error was instantiated, and may provide a text description of the error.
All errors generated by Node.js, including all System and JavaScript errors, will either be instances of, or inherit from, the Error class.
new Error(message)
-
message<string>
Creates a new Error object and sets the error.message property to the provided text message. If an object is passed as message, the text message is generated by calling message.toString(). The error.stack property will represent the point in the code at which new Error() was called. Stack traces are dependent on V8’s stack trace API. Stack traces extend only to either (a) the beginning of synchronous code execution, or (b) the number of frames given by the property Error.stackTraceLimit, whichever is smaller.
Error.captureStackTrace(targetObject[, constructorOpt])
-
targetObject<Object> -
constructorOpt<Function>
Creates a .stack property on targetObject, which when accessed returns a string representing the location in the code at which Error.captureStackTrace() was called.
const myObject = {};
Error.captureStackTrace(myObject);
myObject.stack; // Similar to `new Error().stack`
The first line of the trace will be prefixed with ${myObject.name}: ${myObject.message}.
The optional constructorOpt argument accepts a function. If given, all frames above constructorOpt, including constructorOpt, will be omitted from the generated stack trace.
The constructorOpt argument is useful for hiding implementation details of error generation from an end user. For instance:
function MyError() {
Error.captureStackTrace(this, MyError);
}
// Without passing MyError to captureStackTrace, the MyError
// frame would show up in the .stack property. By passing
// the constructor, we omit that frame, and retain all frames below it.
new MyError().stack;
Error.stackTraceLimit
- <number>
The Error.stackTraceLimit property specifies the number of stack frames collected by a stack trace (whether generated by new Error().stack or Error.captureStackTrace(obj)).
The default value is 10 but may be set to any valid JavaScript number. Changes will affect any stack trace captured after the value has been changed.
If set to a non-number value, or set to a negative number, stack traces will not capture any frames.
error.code
- <string>
The error.code property is a string label that identifies the kind of error. error.code is the most stable way to identify an error. It will only change between major versions of Node.js. In contrast, error.message strings may change between any versions of Node.js. See Node.js Error Codes for details about specific codes.
error.message
- <string>
The error.message property is the string description of the error as set by calling new Error(message). The message passed to the constructor will also appear in the first line of the stack trace of the Error, however changing this property after the Error object is created may not change the first line of the stack trace (for example, when error.stack is read before this property is changed).
const err = new Error('The message');
console.error(err.message);
// Prints: The message
error.stack
- <string>
The error.stack property is a string describing the point in the code at which the Error was instantiated.
Error: Things keep happening! at /home/gbusey/file.js:525:2 at Frobnicator.refrobulate (/home/gbusey/business-logic.js:424:21) at Actor.<anonymous> (/home/gbusey/actors.js:400:8) at increaseSynergy (/home/gbusey/actors.js:701:6)
The first line is formatted as <error class name>: <error message>, and is followed by a series of stack frames (each line beginning with «at «). Each frame describes a call site within the code that lead to the error being generated. V8 attempts to display a name for each function (by variable name, function name, or object method name), but occasionally it will not be able to find a suitable name. If V8 cannot determine a name for the function, only location information will be displayed for that frame. Otherwise, the determined function name will be displayed with location information appended in parentheses.
Frames are only generated for JavaScript functions. If, for example, execution synchronously passes through a C++ addon function called cheetahify which itself calls a JavaScript function, the frame representing the cheetahify call will not be present in the stack traces:
const cheetahify = require('./native-binding.node');
function makeFaster() {
// `cheetahify()` *synchronously* calls speedy.
cheetahify(function speedy() {
throw new Error('oh no!');
});
}
makeFaster();
// will throw:
// /home/gbusey/file.js:6
// throw new Error('oh no!');
// ^
// Error: oh no!
// at speedy (/home/gbusey/file.js:6:11)
// at makeFaster (/home/gbusey/file.js:5:3)
// at Object.<anonymous> (/home/gbusey/file.js:10:1)
// at Module._compile (module.js:456:26)
// at Object.Module._extensions..js (module.js:474:10)
// at Module.load (module.js:356:32)
// at Function.Module._load (module.js:312:12)
// at Function.Module.runMain (module.js:497:10)
// at startup (node.js:119:16)
// at node.js:906:3
The location information will be one of:
-
native, if the frame represents a call internal to V8 (as in[].forEach). -
plain-filename.js:line:column, if the frame represents a call internal to Node.js. -
/absolute/path/to/file.js:line:column, if the frame represents a call in a user program, or its dependencies.
The string representing the stack trace is lazily generated when the error.stack property is accessed.
The number of frames captured by the stack trace is bounded by the smaller of Error.stackTraceLimit or the number of available frames on the current event loop tick.
Class: AssertionError
A subclass of Error that indicates the failure of an assertion. For details, see Class: assert.AssertionError.
Class: RangeError
A subclass of Error that indicates that a provided argument was not within the set or range of acceptable values for a function; whether that is a numeric range, or outside the set of options for a given function parameter.
require('net').connect(-1);
// Throws "RangeError: "port" option should be >= 0 and < 65536: -1"
Node.js will generate and throw RangeError instances immediately as a form of argument validation.
Class: ReferenceError
A subclass of Error that indicates that an attempt is being made to access a variable that is not defined. Such errors commonly indicate typos in code, or an otherwise broken program.
While client code may generate and propagate these errors, in practice, only V8 will do so.
doesNotExist; // Throws ReferenceError, doesNotExist is not a variable in this program.
Unless an application is dynamically generating and running code, ReferenceError instances should always be considered a bug in the code or its dependencies.
Class: SyntaxError
A subclass of Error that indicates that a program is not valid JavaScript. These errors may only be generated and propagated as a result of code evaluation. Code evaluation may happen as a result of eval, Function, require, or vm. These errors are almost always indicative of a broken program.
try {
require('vm').runInThisContext('binary ! isNotOk');
} catch (err) {
// 'err' will be a SyntaxError.
}
SyntaxError instances are unrecoverable in the context that created them – they may only be caught by other contexts.
Class: SystemError
Node.js generates system errors when exceptions occur within its runtime environment. These usually occur when an application violates an operating system constraint. For example, a system error will occur if an application attempts to read a file that does not exist.
-
address<string> If present, the address to which a network connection failed -
code<string> The string error code -
dest<string> If present, the file path destination when reporting a file system error -
errno<number> | <string> The system-provided error number -
info<Object> If present, extra details about the error condition -
message<string> A system-provided human-readable description of the error -
path<string> If present, the file path when reporting a file system error -
port<number> If present, the network connection port that is not available -
syscall<string> The name of the system call that triggered the error
error.address
- <string>
If present, error.address is a string describing the address to which a network connection failed.
error.code
- <string>
The error.code property is a string representing the error code.
error.dest
- <string>
If present, error.dest is the file path destination when reporting a file system error.
error.errno
- <string> | <number>
The error.errno property is a number or a string. If it is a number, it is a negative value which corresponds to the error code defined in libuv Error handling. See the libuv errno.h header file (deps/uv/include/uv/errno.h in the Node.js source tree) for details. In case of a string, it is the same as error.code.
error.info
- <Object>
If present, error.info is an object with details about the error condition.
error.message
- <string>
error.message is a system-provided human-readable description of the error.
error.path
- <string>
If present, error.path is a string containing a relevant invalid pathname.
error.port
- <number>
If present, error.port is the network connection port that is not available.
error.syscall
- <string>
The error.syscall property is a string describing the syscall that failed.
Common System Errors
This is a list of system errors commonly-encountered when writing a Node.js program. For a comprehensive list, see the errno(3) man page.
-
EACCES(Permission denied): An attempt was made to access a file in a way forbidden by its file access permissions. -
EADDRINUSE(Address already in use): An attempt to bind a server (net,http, orhttps) to a local address failed due to another server on the local system already occupying that address. -
ECONNREFUSED(Connection refused): No connection could be made because the target machine actively refused it. This usually results from trying to connect to a service that is inactive on the foreign host. -
ECONNRESET(Connection reset by peer): A connection was forcibly closed by a peer. This normally results from a loss of the connection on the remote socket due to a timeout or reboot. Commonly encountered via thehttpandnetmodules. -
EEXIST(File exists): An existing file was the target of an operation that required that the target not exist. -
EISDIR(Is a directory): An operation expected a file, but the given pathname was a directory. -
EMFILE(Too many open files in system): Maximum number of file descriptors allowable on the system has been reached, and requests for another descriptor cannot be fulfilled until at least one has been closed. This is encountered when opening many files at once in parallel, especially on systems (in particular, macOS) where there is a low file descriptor limit for processes. To remedy a low limit, runulimit -n 2048in the same shell that will run the Node.js process. -
ENOENT(No such file or directory): Commonly raised byfsoperations to indicate that a component of the specified pathname does not exist — no entity (file or directory) could be found by the given path. -
ENOTDIR(Not a directory): A component of the given pathname existed, but was not a directory as expected. Commonly raised byfs.readdir. -
ENOTEMPTY(Directory not empty): A directory with entries was the target of an operation that requires an empty directory — usuallyfs.unlink. -
ENOTFOUND(DNS lookup failed): Indicates a DNS failure of eitherEAI_NODATAorEAI_NONAME. This is not a standard POSIX error. -
EPERM(Operation not permitted): An attempt was made to perform an operation that requires elevated privileges. -
EPIPE(Broken pipe): A write on a pipe, socket, or FIFO for which there is no process to read the data. Commonly encountered at thenetandhttplayers, indicative that the remote side of the stream being written to has been closed. -
ETIMEDOUT(Operation timed out): A connect or send request failed because the connected party did not properly respond after a period of time. Usually encountered byhttpornet— often a sign that asocket.end()was not properly called.
Class: TypeError
A subclass of Error that indicates that a provided argument is not an allowable type. For example, passing a function to a parameter which expects a string would be considered a TypeError.
require('url').parse(() => { });
// Throws TypeError, since it expected a string.
Node.js will generate and throw TypeError instances immediately as a form of argument validation.
Exceptions vs. Errors
A JavaScript exception is a value that is thrown as a result of an invalid operation or as the target of a throw statement. While it is not required that these values are instances of Error or classes which inherit from Error, all exceptions thrown by Node.js or the JavaScript runtime will be instances of Error.
Some exceptions are unrecoverable at the JavaScript layer. Such exceptions will always cause the Node.js process to crash. Examples include assert() checks or abort() calls in the C++ layer.
OpenSSL Errors
Errors originating in crypto or tls are of class Error, and in addition to the standard .code and .message properties, may have some additional OpenSSL-specific properties.
error.opensslErrorStack
An array of errors that can give context to where in the OpenSSL library an error originates from.
error.function
The OpenSSL function the error originates in.
error.library
The OpenSSL library the error originates in.
error.reason
A human-readable string describing the reason for the error.
Node.js Error Codes
ERR_AMBIGUOUS_ARGUMENT
A function argument is being used in a way that suggests that the function signature may be misunderstood. This is thrown by the assert module when the message parameter in assert.throws(block, message) matches the error message thrown by block because that usage suggests that the user believes message is the expected message rather than the message the AssertionError will display if block does not throw.
ERR_ARG_NOT_ITERABLE
An iterable argument (i.e. a value that works with for...of loops) was required, but not provided to a Node.js API.
ERR_ASSERTION
A special type of error that can be triggered whenever Node.js detects an exceptional logic violation that should never occur. These are raised typically by the assert module.
ERR_ASYNC_CALLBACK
An attempt was made to register something that is not a function as an AsyncHooks callback.
ERR_ASYNC_TYPE
The type of an asynchronous resource was invalid. Users are also able to define their own types if using the public embedder API.
ERR_BROTLI_COMPRESSION_FAILED
Data passed to a Brotli stream was not successfully compressed.
ERR_BROTLI_INVALID_PARAM
An invalid parameter key was passed during construction of a Brotli stream.
ERR_BUFFER_CONTEXT_NOT_AVAILABLE
An attempt was made to create a Node.js Buffer instance from addon or embedder code, while in a JS engine Context that is not associated with a Node.js instance. The data passed to the Buffer method will have been released by the time the method returns.
When encountering this error, a possible alternative to creating a Buffer instance is to create a normal Uint8Array, which only differs in the prototype of the resulting object. Uint8Arrays are generally accepted in all Node.js core APIs where Buffers are; they are available in all Contexts.
ERR_BUFFER_OUT_OF_BOUNDS
An operation outside the bounds of a Buffer was attempted.
ERR_BUFFER_TOO_LARGE
An attempt has been made to create a Buffer larger than the maximum allowed size.
ERR_CANNOT_WATCH_SIGINT
Node.js was unable to watch for the SIGINT signal.
ERR_CHILD_CLOSED_BEFORE_REPLY
A child process was closed before the parent received a reply.
ERR_CHILD_PROCESS_IPC_REQUIRED
Used when a child process is being forked without specifying an IPC channel.
ERR_CHILD_PROCESS_STDIO_MAXBUFFER
Used when the main process is trying to read data from the child process’s STDERR/STDOUT, and the data’s length is longer than the maxBuffer option.
ERR_CONSOLE_WRITABLE_STREAM
Console was instantiated without stdout stream, or Console has a non-writable stdout or stderr stream.
ERR_CONSTRUCT_CALL_REQUIRED
A constructor for a class was called without new.
ERR_CONSTRUCT_CALL_INVALID
A class constructor was called that is not callable.
ERR_CPU_USAGE
The native call from process.cpuUsage could not be processed.
ERR_CRYPTO_CUSTOM_ENGINE_NOT_SUPPORTED
A client certificate engine was requested that is not supported by the version of OpenSSL being used.
ERR_CRYPTO_ECDH_INVALID_FORMAT
An invalid value for the format argument was passed to the crypto.ECDH() class getPublicKey() method.
ERR_CRYPTO_ECDH_INVALID_PUBLIC_KEY
An invalid value for the key argument has been passed to the crypto.ECDH() class computeSecret() method. It means that the public key lies outside of the elliptic curve.
ERR_CRYPTO_ENGINE_UNKNOWN
An invalid crypto engine identifier was passed to require('crypto').setEngine().
ERR_CRYPTO_FIPS_FORCED
The --force-fips command-line argument was used but there was an attempt to enable or disable FIPS mode in the crypto module.
ERR_CRYPTO_FIPS_UNAVAILABLE
An attempt was made to enable or disable FIPS mode, but FIPS mode was not available.
ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_DIGEST_NO_UTF16
The UTF-16 encoding was used with hash.digest(). While the hash.digest() method does allow an encoding argument to be passed in, causing the method to return a string rather than a Buffer, the UTF-16 encoding (e.g. ucs or utf16le) is not supported.
ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_FINALIZED
hash.digest() was called multiple times. The hash.digest() method must be called no more than one time per instance of a Hash object.
ERR_CRYPTO_HASH_UPDATE_FAILED
hash.update() failed for any reason. This should rarely, if ever, happen.
ERR_CRYPTO_INCOMPATIBLE_KEY_OPTIONS
The selected public or private key encoding is incompatible with other options.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_DIGEST
An invalid crypto digest algorithm was specified.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_KEY_OBJECT_TYPE
The given crypto key object’s type is invalid for the attempted operation.
ERR_CRYPTO_INVALID_STATE
A crypto method was used on an object that was in an invalid state. For instance, calling cipher.getAuthTag() before calling cipher.final().
ERR_CRYPTO_PBKDF2_ERROR
The PBKDF2 algorithm failed for unspecified reasons. OpenSSL does not provide more details and therefore neither does Node.js.
ERR_CRYPTO_SCRYPT_INVALID_PARAMETER
One or more crypto.scrypt() or crypto.scryptSync() parameters are outside their legal range.
ERR_CRYPTO_SCRYPT_NOT_SUPPORTED
Node.js was compiled without scrypt support. Not possible with the official release binaries but can happen with custom builds, including distro builds.
ERR_CRYPTO_SIGN_KEY_REQUIRED
A signing key was not provided to the sign.sign() method.
ERR_CRYPTO_TIMING_SAFE_EQUAL_LENGTH
crypto.timingSafeEqual() was called with Buffer, TypedArray, or DataView arguments of different lengths.
ERR_DNS_SET_SERVERS_FAILED
c-ares failed to set the DNS server.
ERR_DOMAIN_CALLBACK_NOT_AVAILABLE
The domain module was not usable since it could not establish the required error handling hooks, because process.setUncaughtExceptionCaptureCallback() had been called at an earlier point in time.
ERR_DOMAIN_CANNOT_SET_UNCAUGHT_EXCEPTION_CAPTURE
process.setUncaughtExceptionCaptureCallback() could not be called because the domain module has been loaded at an earlier point in time.
The stack trace is extended to include the point in time at which the domain module had been loaded.
ERR_ENCODING_INVALID_ENCODED_DATA
Data provided to TextDecoder() API was invalid according to the encoding provided.
ERR_ENCODING_NOT_SUPPORTED
Encoding provided to TextDecoder() API was not one of the WHATWG Supported Encodings.
ERR_FALSY_VALUE_REJECTION
A Promise that was callbackified via util.callbackify() was rejected with a falsy value.
ERR_FS_FILE_TOO_LARGE
An attempt has been made to read a file whose size is larger than the maximum allowed size for a Buffer.
ERR_FS_INVALID_SYMLINK_TYPE
An invalid symlink type was passed to the fs.symlink() or fs.symlinkSync() methods.
An attempt was made to add more headers after the headers had already been sent.
An invalid HTTP header value was specified.
ERR_HTTP_INVALID_STATUS_CODE
Status code was outside the regular status code range (100-999).
ERR_HTTP_TRAILER_INVALID
The Trailer header was set even though the transfer encoding does not support that.
ERR_HTTP2_ALTSVC_INVALID_ORIGIN
HTTP/2 ALTSVC frames require a valid origin.
ERR_HTTP2_ALTSVC_LENGTH
HTTP/2 ALTSVC frames are limited to a maximum of 16,382 payload bytes.
For HTTP/2 requests using the CONNECT method, the :authority pseudo-header is required.
ERR_HTTP2_CONNECT_PATH
For HTTP/2 requests using the CONNECT method, the :path pseudo-header is forbidden.
ERR_HTTP2_CONNECT_SCHEME
For HTTP/2 requests using the CONNECT method, the :scheme pseudo-header is forbidden.
ERR_HTTP2_ERROR
A non-specific HTTP/2 error has occurred.
ERR_HTTP2_GOAWAY_SESSION
New HTTP/2 Streams may not be opened after the Http2Session has received a GOAWAY frame from the connected peer.
An additional headers was specified after an HTTP/2 response was initiated.
An attempt was made to send multiple response headers.
Multiple values were provided for an HTTP/2 header field that was required to have only a single value.
ERR_HTTP2_INFO_STATUS_NOT_ALLOWED
Informational HTTP status codes (1xx) may not be set as the response status code on HTTP/2 responses.
HTTP/1 connection specific headers are forbidden to be used in HTTP/2 requests and responses.
An invalid HTTP/2 header value was specified.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_INFO_STATUS
An invalid HTTP informational status code has been specified. Informational status codes must be an integer between 100 and 199 (inclusive).
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_ORIGIN
HTTP/2 ORIGIN frames require a valid origin.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_PACKED_SETTINGS_LENGTH
Input Buffer and Uint8Array instances passed to the http2.getUnpackedSettings() API must have a length that is a multiple of six.
Only valid HTTP/2 pseudoheaders (:status, :path, :authority, :scheme, and :method) may be used.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_SESSION
An action was performed on an Http2Session object that had already been destroyed.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_SETTING_VALUE
An invalid value has been specified for an HTTP/2 setting.
ERR_HTTP2_INVALID_STREAM
An operation was performed on a stream that had already been destroyed.
ERR_HTTP2_MAX_PENDING_SETTINGS_ACK
Whenever an HTTP/2 SETTINGS frame is sent to a connected peer, the peer is required to send an acknowledgment that it has received and applied the new SETTINGS. By default, a maximum number of unacknowledged SETTINGS frames may be sent at any given time. This error code is used when that limit has been reached.
ERR_HTTP2_NESTED_PUSH
An attempt was made to initiate a new push stream from within a push stream. Nested push streams are not permitted.
ERR_HTTP2_NO_SOCKET_MANIPULATION
An attempt was made to directly manipulate (read, write, pause, resume, etc.) a socket attached to an Http2Session.
ERR_HTTP2_ORIGIN_LENGTH
HTTP/2 ORIGIN frames are limited to a length of 16382 bytes.
ERR_HTTP2_OUT_OF_STREAMS
The number of streams created on a single HTTP/2 session reached the maximum limit.
ERR_HTTP2_PAYLOAD_FORBIDDEN
A message payload was specified for an HTTP response code for which a payload is forbidden.
ERR_HTTP2_PING_CANCEL
An HTTP/2 ping was canceled.
ERR_HTTP2_PING_LENGTH
HTTP/2 ping payloads must be exactly 8 bytes in length.
An HTTP/2 pseudo-header has been used inappropriately. Pseudo-headers are header key names that begin with the : prefix.
ERR_HTTP2_PUSH_DISABLED
An attempt was made to create a push stream, which had been disabled by the client.
ERR_HTTP2_SEND_FILE
An attempt was made to use the Http2Stream.prototype.responseWithFile() API to send a directory.
ERR_HTTP2_SEND_FILE_NOSEEK
An attempt was made to use the Http2Stream.prototype.responseWithFile() API to send something other than a regular file, but offset or length options were provided.
ERR_HTTP2_SESSION_ERROR
The Http2Session closed with a non-zero error code.
ERR_HTTP2_SETTINGS_CANCEL
The Http2Session settings canceled.
ERR_HTTP2_SOCKET_BOUND
An attempt was made to connect a Http2Session object to a net.Socket or tls.TLSSocket that had already been bound to another Http2Session object.
ERR_HTTP2_SOCKET_UNBOUND
An attempt was made to use the socket property of an Http2Session that has already been closed.
ERR_HTTP2_STATUS_101
Use of the 101 Informational status code is forbidden in HTTP/2.
ERR_HTTP2_STATUS_INVALID
An invalid HTTP status code has been specified. Status codes must be an integer between 100 and 599 (inclusive).
ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_CANCEL
An Http2Stream was destroyed before any data was transmitted to the connected peer.
ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_ERROR
A non-zero error code was been specified in an RST_STREAM frame.
ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_SELF_DEPENDENCY
When setting the priority for an HTTP/2 stream, the stream may be marked as a dependency for a parent stream. This error code is used when an attempt is made to mark a stream and dependent of itself.
ERR_HTTP2_TRAILERS_ALREADY_SENT
Trailing headers have already been sent on the Http2Stream.
ERR_HTTP2_TRAILERS_NOT_READY
The http2stream.sendTrailers() method cannot be called until after the 'wantTrailers' event is emitted on an Http2Stream object. The 'wantTrailers' event will only be emitted if the waitForTrailers option is set for the Http2Stream.
ERR_HTTP2_UNSUPPORTED_PROTOCOL
http2.connect() was passed a URL that uses any protocol other than http: or https:.
ERR_INTERNAL_ASSERTION
There was a bug in Node.js or incorrect usage of Node.js internals. To fix the error, open an issue at https://github.com/nodejs/node/issues.
ERR_INCOMPATIBLE_OPTION_PAIR
An option pair is incompatible with each other and can not be used at the same time.
ERR_INPUT_TYPE_NOT_ALLOWED
The --input-type flag was used to attempt to execute a file. This flag can only be used with input via --eval, --print or STDIN.
ERR_INSPECTOR_ALREADY_CONNECTED
While using the inspector module, an attempt was made to connect when the inspector was already connected.
ERR_INSPECTOR_CLOSED
While using the inspector module, an attempt was made to use the inspector after the session had already closed.
ERR_INSPECTOR_COMMAND
An error occurred while issuing a command via the inspector module.
ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_ACTIVE
The inspector is not active when inspector.waitForDebugger() is called.
ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_AVAILABLE
The inspector module is not available for use.
ERR_INSPECTOR_NOT_CONNECTED
While using the inspector module, an attempt was made to use the inspector before it was connected.
ERR_INVALID_ADDRESS_FAMILY
The provided address family is not understood by the Node.js API.
ERR_INVALID_ARG_TYPE
An argument of the wrong type was passed to a Node.js API.
ERR_INVALID_ARG_VALUE
An invalid or unsupported value was passed for a given argument.
ERR_INVALID_ASYNC_ID
An invalid asyncId or triggerAsyncId was passed using AsyncHooks. An id less than -1 should never happen.
ERR_INVALID_BUFFER_SIZE
A swap was performed on a Buffer but its size was not compatible with the operation.
ERR_INVALID_CALLBACK
A callback function was required but was not been provided to a Node.js API.
ERR_INVALID_CHAR
Invalid characters were detected in headers.
ERR_INVALID_CURSOR_POS
A cursor on a given stream cannot be moved to a specified row without a specified column.
ERR_INVALID_FD
A file descriptor (‘fd’) was not valid (e.g. it was a negative value).
ERR_INVALID_FD_TYPE
A file descriptor (‘fd’) type was not valid.
ERR_INVALID_FILE_URL_HOST
A Node.js API that consumes file: URLs (such as certain functions in the fs module) encountered a file URL with an incompatible host. This situation can only occur on Unix-like systems where only localhost or an empty host is supported.
ERR_INVALID_FILE_URL_PATH
A Node.js API that consumes file: URLs (such as certain functions in the fs module) encountered a file URL with an incompatible path. The exact semantics for determining whether a path can be used is platform-dependent.
ERR_INVALID_HANDLE_TYPE
An attempt was made to send an unsupported «handle» over an IPC communication channel to a child process. See subprocess.send() and process.send() for more information.
ERR_INVALID_HTTP_TOKEN
An invalid HTTP token was supplied.
ERR_INVALID_IP_ADDRESS
An IP address is not valid.
ERR_INVALID_OPT_VALUE
An invalid or unexpected value was passed in an options object.
ERR_INVALID_OPT_VALUE_ENCODING
An invalid or unknown file encoding was passed.
ERR_INVALID_PACKAGE_CONFIG
An invalid package.json file was found which failed parsing.
ERR_INVALID_PERFORMANCE_MARK
While using the Performance Timing API (perf_hooks), a performance mark is invalid.
ERR_INVALID_PROTOCOL
An invalid options.protocol was passed to http.request().
ERR_INVALID_REPL_EVAL_CONFIG
Both breakEvalOnSigint and eval options were set in the REPL config, which is not supported.
ERR_INVALID_REPL_INPUT
The input may not be used in the REPL. All prohibited inputs are documented in the REPL‘s documentation.
ERR_INVALID_RETURN_PROPERTY
Thrown in case a function option does not provide a valid value for one of its returned object properties on execution.
ERR_INVALID_RETURN_PROPERTY_VALUE
Thrown in case a function option does not provide an expected value type for one of its returned object properties on execution.
ERR_INVALID_RETURN_VALUE
Thrown in case a function option does not return an expected value type on execution, such as when a function is expected to return a promise.
ERR_INVALID_SYNC_FORK_INPUT
A Buffer, TypedArray, DataView or string was provided as stdio input to an asynchronous fork. See the documentation for the child_process module for more information.
ERR_INVALID_THIS
A Node.js API function was called with an incompatible this value.
const urlSearchParams = new URLSearchParams('foo=bar&baz=new');
const buf = Buffer.alloc(1);
urlSearchParams.has.call(buf, 'foo');
// Throws a TypeError with code 'ERR_INVALID_THIS'
ERR_INVALID_TRANSFER_OBJECT
An invalid transfer object was passed to postMessage().
ERR_INVALID_TUPLE
An element in the iterable provided to the WHATWG URLSearchParams constructor did not represent a [name, value] tuple – that is, if an element is not iterable, or does not consist of exactly two elements.
ERR_INVALID_URI
An invalid URI was passed.
ERR_INVALID_URL
An invalid URL was passed to the WHATWG URL constructor to be parsed. The thrown error object typically has an additional property 'input' that contains the URL that failed to parse.
ERR_INVALID_URL_SCHEME
An attempt was made to use a URL of an incompatible scheme (protocol) for a specific purpose. It is only used in the WHATWG URL API support in the fs module (which only accepts URLs with 'file' scheme), but may be used in other Node.js APIs as well in the future.
ERR_IPC_CHANNEL_CLOSED
An attempt was made to use an IPC communication channel that was already closed.
ERR_IPC_DISCONNECTED
An attempt was made to disconnect an IPC communication channel that was already disconnected. See the documentation for the child_process module for more information.
ERR_IPC_ONE_PIPE
An attempt was made to create a child Node.js process using more than one IPC communication channel. See the documentation for the child_process module for more information.
ERR_IPC_SYNC_FORK
An attempt was made to open an IPC communication channel with a synchronously forked Node.js process. See the documentation for the child_process module for more information.
ERR_MANIFEST_ASSERT_INTEGRITY
An attempt was made to load a resource, but the resource did not match the integrity defined by the policy manifest. See the documentation for policy manifests for more information.
ERR_MANIFEST_DEPENDENCY_MISSING
An attempt was made to load a resource, but the resource was not listed as a dependency from the location that attempted to load it. See the documentation for policy manifests for more information.
ERR_MANIFEST_INTEGRITY_MISMATCH
An attempt was made to load a policy manifest, but the manifest had multiple entries for a resource which did not match each other. Update the manifest entries to match in order to resolve this error. See the documentation for policy manifests for more information.
ERR_MANIFEST_INVALID_RESOURCE_FIELD
A policy manifest resource had an invalid value for one of its fields. Update the manifest entry to match in order to resolve this error. See the documentation for policy manifests for more information.
ERR_MANIFEST_PARSE_POLICY
An attempt was made to load a policy manifest, but the manifest was unable to be parsed. See the documentation for policy manifests for more information.
ERR_MANIFEST_TDZ
An attempt was made to read from a policy manifest, but the manifest initialization has not yet taken place. This is likely a bug in Node.js.
ERR_MANIFEST_UNKNOWN_ONERROR
A policy manifest was loaded, but had an unknown value for its «onerror» behavior. See the documentation for policy manifests for more information.
ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATION_FAILED
An attempt was made to allocate memory (usually in the C++ layer) but it failed.
ERR_METHOD_NOT_IMPLEMENTED
A method is required but not implemented.
ERR_MISSING_ARGS
A required argument of a Node.js API was not passed. This is only used for strict compliance with the API specification (which in some cases may accept func(undefined) but not func()). In most native Node.js APIs, func(undefined) and func() are treated identically, and the ERR_INVALID_ARG_TYPE error code may be used instead.
ERR_MISSING_DYNAMIC_INSTANTIATE_HOOK
An ES Module loader hook specified format: 'dynamic' but did not provide a dynamicInstantiate hook.
ERR_MISSING_MESSAGE_PORT_IN_TRANSFER_LIST
A MessagePort was found in the object passed to a postMessage() call, but not provided in the transferList for that call.
ERR_MISSING_PASSPHRASE
An attempt was made to read an encrypted key without specifying a passphrase.
ERR_MISSING_PLATFORM_FOR_WORKER
The V8 platform used by this instance of Node.js does not support creating Workers. This is caused by lack of embedder support for Workers. In particular, this error will not occur with standard builds of Node.js.
ERR_MODULE_NOT_FOUND
An ES Module could not be resolved.
ERR_MULTIPLE_CALLBACK
A callback was called more than once.
A callback is almost always meant to only be called once as the query can either be fulfilled or rejected but not both at the same time. The latter would be possible by calling a callback more than once.
ERR_NAPI_CONS_FUNCTION
While using N-API, a constructor passed was not a function.
ERR_NAPI_INVALID_DATAVIEW_ARGS
While calling napi_create_dataview(), a given offset was outside the bounds of the dataview or offset + length was larger than a length of given buffer.
ERR_NAPI_INVALID_TYPEDARRAY_ALIGNMENT
While calling napi_create_typedarray(), the provided offset was not a multiple of the element size.
ERR_NAPI_INVALID_TYPEDARRAY_LENGTH
While calling napi_create_typedarray(), (length * size_of_element) + byte_offset was larger than the length of given buffer.
ERR_NAPI_TSFN_CALL_JS
An error occurred while invoking the JavaScript portion of the thread-safe function.
ERR_NAPI_TSFN_GET_UNDEFINED
An error occurred while attempting to retrieve the JavaScript undefined value.
ERR_NAPI_TSFN_START_IDLE_LOOP
On the main thread, values are removed from the queue associated with the thread-safe function in an idle loop. This error indicates that an error has occurred when attempting to start the loop.
ERR_NAPI_TSFN_STOP_IDLE_LOOP
Once no more items are left in the queue, the idle loop must be suspended. This error indicates that the idle loop has failed to stop.
ERR_NO_CRYPTO
An attempt was made to use crypto features while Node.js was not compiled with OpenSSL crypto support.
ERR_NO_ICU
An attempt was made to use features that require ICU, but Node.js was not compiled with ICU support.
ERR_OUT_OF_RANGE
A given value is out of the accepted range.
ERR_REQUIRE_ESM
An attempt was made to require() an ES Module.
ERR_SCRIPT_EXECUTION_INTERRUPTED
Script execution was interrupted by SIGINT (For example, when Ctrl+C was pressed).
ERR_SCRIPT_EXECUTION_TIMEOUT
Script execution timed out, possibly due to bugs in the script being executed.
ERR_SERVER_ALREADY_LISTEN
The server.listen() method was called while a net.Server was already listening. This applies to all instances of net.Server, including HTTP, HTTPS, and HTTP/2 Server instances.
ERR_SERVER_NOT_RUNNING
The server.close() method was called when a net.Server was not running. This applies to all instances of net.Server, including HTTP, HTTPS, and HTTP/2 Server instances.
ERR_SOCKET_ALREADY_BOUND
An attempt was made to bind a socket that has already been bound.
ERR_SOCKET_BAD_BUFFER_SIZE
An invalid (negative) size was passed for either the recvBufferSize or sendBufferSize options in dgram.createSocket().
ERR_SOCKET_BAD_PORT
An API function expecting a port >= 0 and < 65536 received an invalid value.
ERR_SOCKET_BAD_TYPE
An API function expecting a socket type (udp4 or udp6) received an invalid value.
ERR_SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE
While using dgram.createSocket(), the size of the receive or send Buffer could not be determined.
ERR_SOCKET_CANNOT_SEND
Data could be sent on a socket.
ERR_SOCKET_CLOSED
An attempt was made to operate on an already closed socket.
ERR_SOCKET_DGRAM_IS_CONNECTED
A dgram.connect() call was made on an already connected socket.
ERR_SOCKET_DGRAM_NOT_CONNECTED
A dgram.disconnect() or dgram.remoteAddress() call was made on a disconnected socket.
ERR_SOCKET_DGRAM_NOT_RUNNING
A call was made and the UDP subsystem was not running.
ERR_SRI_PARSE
A string was provided for a Subresource Integrity check, but was unable to be parsed. Check the format of integrity attributes by looking at the Subresource Integrity specification.
ERR_STREAM_CANNOT_PIPE
An attempt was made to call stream.pipe() on a Writable stream.
ERR_STREAM_DESTROYED
A stream method was called that cannot complete because the stream was destroyed using stream.destroy().
ERR_STREAM_NULL_VALUES
An attempt was made to call stream.write() with a null chunk.
ERR_STREAM_PREMATURE_CLOSE
An error returned by stream.finished() and stream.pipeline(), when a stream or a pipeline ends non gracefully with no explicit error.
ERR_STREAM_PUSH_AFTER_EOF
An attempt was made to call stream.push() after a null(EOF) had been pushed to the stream.
ERR_STREAM_UNSHIFT_AFTER_END_EVENT
An attempt was made to call stream.unshift() after the 'end' event was emitted.
ERR_STREAM_WRAP
Prevents an abort if a string decoder was set on the Socket or if the decoder is in objectMode.
const Socket = require('net').Socket;
const instance = new Socket();
instance.setEncoding('utf8');
ERR_STREAM_WRITE_AFTER_END
An attempt was made to call stream.write() after stream.end() has been called.
ERR_STRING_TOO_LONG
An attempt has been made to create a string longer than the maximum allowed length.
ERR_SYNTHETIC
An artificial error object used to capture the call stack for diagnostic reports.
ERR_SYSTEM_ERROR
An unspecified or non-specific system error has occurred within the Node.js process. The error object will have an err.info object property with additional details.
ERR_TLS_CERT_ALTNAME_INVALID
While using TLS, the hostname/IP of the peer did not match any of the subjectAltNames in its certificate.
ERR_TLS_DH_PARAM_SIZE
While using TLS, the parameter offered for the Diffie-Hellman (DH) key-agreement protocol is too small. By default, the key length must be greater than or equal to 1024 bits to avoid vulnerabilities, even though it is strongly recommended to use 2048 bits or larger for stronger security.
ERR_TLS_HANDSHAKE_TIMEOUT
A TLS/SSL handshake timed out. In this case, the server must also abort the connection.
ERR_TLS_INVALID_PROTOCOL_METHOD
The specified secureProtocol method is invalid. It is either unknown, or disabled because it is insecure.
ERR_TLS_INVALID_PROTOCOL_VERSION
Valid TLS protocol versions are 'TLSv1', 'TLSv1.1', or 'TLSv1.2'.
ERR_TLS_PROTOCOL_VERSION_CONFLICT
Attempting to set a TLS protocol minVersion or maxVersion conflicts with an attempt to set the secureProtocol explicitly. Use one mechanism or the other.
ERR_TLS_RENEGOTIATION_DISABLED
An attempt was made to renegotiate TLS on a socket instance with TLS disabled.
ERR_TLS_REQUIRED_SERVER_NAME
While using TLS, the server.addContext() method was called without providing a hostname in the first parameter.
ERR_TLS_SESSION_ATTACK
An excessive amount of TLS renegotiations is detected, which is a potential vector for denial-of-service attacks.
ERR_TLS_SNI_FROM_SERVER
An attempt was made to issue Server Name Indication from a TLS server-side socket, which is only valid from a client.
ERR_TRACE_EVENTS_CATEGORY_REQUIRED
The trace_events.createTracing() method requires at least one trace event category.
ERR_TRACE_EVENTS_UNAVAILABLE
The trace_events module could not be loaded because Node.js was compiled with the --without-v8-platform flag.
ERR_TRANSFERRING_EXTERNALIZED_SHAREDARRAYBUFFER
A SharedArrayBuffer whose memory is not managed by the JavaScript engine or by Node.js was encountered during serialization. Such a SharedArrayBuffer cannot be serialized.
This can only happen when native addons create SharedArrayBuffers in «externalized» mode, or put existing SharedArrayBuffer into externalized mode.
ERR_TRANSFORM_ALREADY_TRANSFORMING
A Transform stream finished while it was still transforming.
ERR_TRANSFORM_WITH_LENGTH_0
A Transform stream finished with data still in the write buffer.
ERR_TTY_INIT_FAILED
The initialization of a TTY failed due to a system error.
ERR_UNCAUGHT_EXCEPTION_CAPTURE_ALREADY_SET
process.setUncaughtExceptionCaptureCallback() was called twice, without first resetting the callback to null.
This error is designed to prevent accidentally overwriting a callback registered from another module.
ERR_UNESCAPED_CHARACTERS
A string that contained unescaped characters was received.
ERR_UNHANDLED_ERROR
An unhandled error occurred (for instance, when an 'error' event is emitted by an EventEmitter but an 'error' handler is not registered).
ERR_UNKNOWN_BUILTIN_MODULE
Used to identify a specific kind of internal Node.js error that should not typically be triggered by user code. Instances of this error point to an internal bug within the Node.js binary itself.
ERR_UNKNOWN_CREDENTIAL
A Unix group or user identifier that does not exist was passed.
ERR_UNKNOWN_ENCODING
An invalid or unknown encoding option was passed to an API.
ERR_UNKNOWN_FILE_EXTENSION
An attempt was made to load a module with an unknown or unsupported file extension.
ERR_UNKNOWN_MODULE_FORMAT
An attempt was made to load a module with an unknown or unsupported format.
ERR_UNKNOWN_SIGNAL
An invalid or unknown process signal was passed to an API expecting a valid signal (such as subprocess.kill()).
ERR_V8BREAKITERATOR
The V8 BreakIterator API was used but the full ICU data set is not installed.
ERR_VALID_PERFORMANCE_ENTRY_TYPE
While using the Performance Timing API (perf_hooks), no valid performance entry types were found.
ERR_VM_DYNAMIC_IMPORT_CALLBACK_MISSING
A dynamic import callback was not specified.
ERR_VM_MODULE_ALREADY_LINKED
The module attempted to be linked is not eligible for linking, because of one of the following reasons:
- It has already been linked (
linkingStatusis'linked') - It is being linked (
linkingStatusis'linking') - Linking has failed for this module (
linkingStatusis'errored')
ERR_VM_MODULE_DIFFERENT_CONTEXT
The module being returned from the linker function is from a different context than the parent module. Linked modules must share the same context.
ERR_VM_MODULE_LINKING_ERRORED
The linker function returned a module for which linking has failed.
ERR_VM_MODULE_NOT_LINKED
The module must be successfully linked before instantiation.
ERR_VM_MODULE_NOT_MODULE
The fulfilled value of a linking promise is not a vm.SourceTextModule object.
ERR_VM_MODULE_STATUS
The current module’s status does not allow for this operation. The specific meaning of the error depends on the specific function.
ERR_WORKER_INVALID_EXEC_ARGV
The execArgv option passed to the Worker constructor contains invalid flags.
ERR_WORKER_PATH
The path for the main script of a worker is neither an absolute path nor a relative path starting with ./ or ../.
ERR_WORKER_UNSERIALIZABLE_ERROR
All attempts at serializing an uncaught exception from a worker thread failed.
ERR_WORKER_UNSUPPORTED_EXTENSION
The pathname used for the main script of a worker has an unknown file extension.
ERR_WORKER_UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION
The requested functionality is not supported in worker threads.
ERR_ZLIB_INITIALIZATION_FAILED
Creation of a zlib object failed due to incorrect configuration.
Too much HTTP header data was received. In order to protect against malicious or malconfigured clients, if more than 8KB of HTTP header data is received then HTTP parsing will abort without a request or response object being created, and an Error with this code will be emitted.
MODULE_NOT_FOUND
A module file could not be resolved while attempting a require() or import operation.
Legacy Node.js Error Codes
Stability: 0 — Deprecated. These error codes are either inconsistent, or have been removed.
ERR_CANNOT_TRANSFER_OBJECT
The value passed to postMessage() contained an object that is not supported for transferring.
ERR_CLOSED_MESSAGE_PORT
Added in: v10.5.0Removed in: v11.12.0
There was an attempt to use a MessagePort instance in a closed state, usually after .close() has been called.
ERR_HTTP2_FRAME_ERROR
Added in: v9.0.0Removed in: v10.0.0
Used when a failure occurs sending an individual frame on the HTTP/2 session.
Added in: v9.0.0Removed in: v10.0.0
Used when an HTTP/2 Headers Object is expected.
Added in: v9.0.0Removed in: v10.0.0
Used when a required header is missing in an HTTP/2 message.
Added in: v9.0.0Removed in: v10.0.0
HTTP/2 informational headers must only be sent prior to calling the Http2Stream.prototype.respond() method.
ERR_HTTP2_STREAM_CLOSED
Added in: v9.0.0Removed in: v10.0.0
Used when an action has been performed on an HTTP/2 Stream that has already been closed.
ERR_HTTP_INVALID_CHAR
Added in: v9.0.0Removed in: v10.0.0
Used when an invalid character is found in an HTTP response status message (reason phrase).
ERR_INDEX_OUT_OF_RANGE
Added in: v10.0.0Removed in: v11.0.0
A given index was out of the accepted range (e.g. negative offsets).
ERR_NAPI_CONS_PROTOTYPE_OBJECT
Added in: v9.0.0Removed in: v10.0.0
Used by the N-API when Constructor.prototype is not an object.
ERR_NO_LONGER_SUPPORTED
A Node.js API was called in an unsupported manner, such as Buffer.write(string, encoding, offset[, length]).
ERR_OUTOFMEMORY
Added in: v9.0.0Removed in: v10.0.0
Used generically to identify that an operation caused an out of memory condition.
ERR_PARSE_HISTORY_DATA
Added in: v9.0.0Removed in: v10.0.0
The repl module was unable to parse data from the REPL history file.
ERR_STDERR_CLOSE
An attempt was made to close the process.stderr stream. By design, Node.js does not allow stdout or stderr streams to be closed by user code.
ERR_STDOUT_CLOSE
An attempt was made to close the process.stdout stream. By design, Node.js does not allow stdout or stderr streams to be closed by user code.
ERR_STREAM_READ_NOT_IMPLEMENTED
Added in: v9.0.0Removed in: v10.0.0
Used when an attempt is made to use a readable stream that has not implemented readable._read().
ERR_TLS_RENEGOTIATION_FAILED
Added in: v9.0.0Removed in: v10.0.0
Used when a TLS renegotiation request has failed in a non-specific way.
ERR_UNKNOWN_BUILTIN_MODULE
Added in: v8.0.0Removed in: v9.0.0
The 'ERR_UNKNOWN_BUILTIN_MODULE' error code is used to identify a specific kind of internal Node.js error that should not typically be triggered by user code. Instances of this error point to an internal bug within the Node.js binary itself.
ERR_UNKNOWN_STDIN_TYPE
Added in: v8.0.0Removed in: v11.7.0
An attempt was made to launch a Node.js process with an unknown stdin file type. This error is usually an indication of a bug within Node.js itself, although it is possible for user code to trigger it.
ERR_UNKNOWN_STREAM_TYPE
Added in: v8.0.0Removed in: v11.7.0
An attempt was made to launch a Node.js process with an unknown stdout or stderr file type. This error is usually an indication of a bug within Node.js itself, although it is possible for user code to trigger it.
ERR_VALUE_OUT_OF_RANGE
Added in: v9.0.0Removed in: v10.0.0
Used when a given value is out of the accepted range.
ERR_ZLIB_BINDING_CLOSED
Added in: v9.0.0Removed in: v10.0.0
Used when an attempt is made to use a zlib object after it has already been closed.
Other error codes
These errors have never been released, but had been present on master between releases.
ERR_ENTRY_TYPE_MISMATCH
The --entry-type=commonjs flag was used to attempt to execute an .mjs file or a .js file where the nearest parent package.json contains "type": "module"; or the --entry-type=module flag was used to attempt to execute a .cjs file or a .js file where the nearest parent package.json either lacks a "type" field or contains "type": "commonjs".
ERR_FS_WATCHER_ALREADY_STARTED
An attempt was made to start a watcher returned by fs.watch() that has already been started.
ERR_FS_WATCHER_NOT_STARTED
An attempt was made to initiate operations on a watcher returned by fs.watch() that has not yet been started.
ERR_HTTP2_ALREADY_SHUTDOWN
Occurs with multiple attempts to shutdown an HTTP/2 session.
ERR_HTTP2_ERROR
A non-specific HTTP/2 error has occurred.
ERR_INVALID_REPL_HISTORY
Used in the repl in case the old history file is used and an error occurred while trying to read and parse it.
ERR_INVALID_REPL_TYPE
The --entry-type=... flag is not compatible with the Node.js REPL.
ERR_MISSING_DYNAMIC_INSTANTIATE_HOOK
Used when an ES Module loader hook specifies format: 'dynamic' but does not provide a dynamicInstantiate hook.
ERR_STREAM_HAS_STRINGDECODER
Used to prevent an abort if a string decoder was set on the Socket.
const Socket = require('net').Socket;
const instance = new Socket();
instance.setEncoding('utf8');
ERR_STRING_TOO_LARGE
An attempt has been made to create a string larger than the maximum allowed size.
ERR_TTY_WRITABLE_NOT_READABLE
This Error is thrown when a read is attempted on a TTY WriteStream, such as process.stdout.on('data').
© Joyent, Inc. and other Node contributors
Licensed under the MIT License.
Node.js is a trademark of Joyent, Inc. and is used with its permission.
We are not endorsed by or affiliated with Joyent.
https://nodejs.org/dist/latest-v12.x/docs/api/errors.html
Handling errors plays a major role in your application. In error situations, you want to know the details of the issue and how to solve it. When developing your app, you can create your own errors.
Errors in Node.js are extensible classes. This tutorial walks you through the creation of your own error class.
Node.js Series Overview
- Node.js
- Strings
- Streams
- Date & Time
- Arrays
- Promises
- JSON
- Iterators
- Classes
- Numbers
- Objects
- File System
- Map
- Process
- Symbols
- Platform/OS
- HTTPS
- Hashing
-
Increase the Memory Limit for Your Process
-
Why You Should Add “node” in Your Travis Config
-
Create a PDF from HTML with Puppeteer and Handlebars
-
Create Your Own Custom Error
-
Retrieve a Request’s IP Address in Node.js
-
Detect the Node.js Version in a Running Process or App
-
How to Base64 Encode/Decode a Value in Node.js
-
Check if a Value Is Null or Undefined in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Fix “Uncaught SyntaxError: Cannot use import statement outside a module”
-
Fix „Socket Hang Up“ Errors
-
Nested Destructuring in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Increase the Memory Limit for Your Process -
Why You Should Add “node” in Your Travis Config -
Create a PDF from HTML with Puppeteer and Handlebars
- Create Your Own Custom Error
-
Retrieve a Request’s IP Address in Node.js
-
Detect the Node.js Version in a Running Process or App
-
How to Base64 Encode/Decode a Value in Node.js
-
Check if a Value Is Null or Undefined in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Fix “Uncaught SyntaxError: Cannot use import statement outside a module”
-
Fix „Socket Hang Up“ Errors
-
Nested Destructuring in JavaScript or Node.js
-
String Replace All Appearances
-
Remove All Whitespace From a String in JavaScript
-
Generate a Random ID or String in Node.js or JavaScript
-
Remove Extra Spaces From a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Remove Numbers From a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get the Part Before a Character in a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get the Part After a Character in a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Check if a Value is a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Check If a String Includes All Strings in JavaScript/Node.js/TypeScript
-
Check if a Value is a String in JavaScript and Node.js
-
Limit and Truncate a String to a Given Length in JavaScript and Node.js
-
Split a String into a List of Characters in JavaScript and Node.js
-
How to Generage a UUID in Node.js
-
Reverse a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Split a String into a List of Lines in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Split a String into a List of Words in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Detect if a String is in camelCase Format in Javascript or Node.js
-
Check If a String Is in Lowercase in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Check If a String is in Uppercase in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get the Part After First Occurrence in a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get the Part Before First Occurrence in a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get the Part Before Last Occurrence in a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get the Part After Last Occurrence in a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Count Words in a File
-
How to Shuffle the Characters of a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Append Characters or Words to a String in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Check if a String is Empty in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Ensure a String Ends with a Given Character in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Left-Trim Characters Off a String in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Right-Trim Characters Off a String in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Lowercase the First Character of a String in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Uppercase the First Character of a String in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Prepend Characters or Words to a String in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
String Replace All Appearances
-
Remove All Whitespace From a String in JavaScript
-
Generate a Random ID or String in Node.js or JavaScript
-
Remove Extra Spaces From a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Remove Numbers From a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get the Part Before a Character in a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get the Part After a Character in a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Check if a Value is a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Check If a String Includes All Strings in JavaScript/Node.js/TypeScript
-
Check if a Value is a String in JavaScript and Node.js
-
Limit and Truncate a String to a Given Length in JavaScript and Node.js
-
Split a String into a List of Characters in JavaScript and Node.js
-
How to Generage a UUID in Node.js
-
Reverse a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Split a String into a List of Lines in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Split a String into a List of Words in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Detect if a String is in camelCase Format in Javascript or Node.js
-
Check If a String Is in Lowercase in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Check If a String is in Uppercase in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get the Part After First Occurrence in a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get the Part Before First Occurrence in a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get the Part Before Last Occurrence in a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get the Part After Last Occurrence in a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Count Words in a File
-
How to Shuffle the Characters of a String in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Append Characters or Words to a String in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Check if a String is Empty in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Ensure a String Ends with a Given Character in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Left-Trim Characters Off a String in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Right-Trim Characters Off a String in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Lowercase the First Character of a String in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Uppercase the First Character of a String in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Prepend Characters or Words to a String in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Filter Data in Streams
-
Get Number of Seconds Since Epoch in JavaScript
-
Get Tomorrow’s Date in JavaScript
-
Increase a Date in JavaScript by One Week
-
Add Seconds to a Date in Node.js and JavaScript
-
Add Month(s) to a Date in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Add Week(s) to a Date in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get the Current Year in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Get a UNIX Timestamp in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Convert a UNIX Timestamp to a Date in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Add Days to a Date in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get Yesterday’s Date in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Add Minutes to a Date in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Add Hours to a Date in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Check If a Date Is Today in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Check If a Date is Tomorrow in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Check If a Date is Yesterday in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Format a Date YYYY-MM-DD in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get Number of Seconds Since Epoch in JavaScript
-
Get Tomorrow’s Date in JavaScript
-
Increase a Date in JavaScript by One Week
-
Add Seconds to a Date in Node.js and JavaScript
-
Add Month(s) to a Date in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Add Week(s) to a Date in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get the Current Year in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Get a UNIX Timestamp in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Convert a UNIX Timestamp to a Date in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Add Days to a Date in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get Yesterday’s Date in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Add Minutes to a Date in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Add Hours to a Date in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Check If a Date Is Today in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Check If a Date is Tomorrow in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Check If a Date is Yesterday in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Format a Date YYYY-MM-DD in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Run an Asynchronous Function in Array.map()
-
How to Reset and Empty an Array
-
Clone/Copy an Array in JavaScript and Node.js
-
Get an Array With Unique Values (Delete Duplicates)
-
Sort an Array of Integers in JavaScript and Node.js
-
Sort a Boolean Array in JavaScript, TypeScript, or Node.js
-
Check If an Array Contains a Given Value in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Add an Item to the Beginning of an Array in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Append an Item at the End of an Array in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Exit and Stop a for Loop in JavaScript and Node.js
-
Split an Array Into Smaller Array Chunks in JavaScript and Node.js
-
How to Get an Index in a for…of Loop in JavaScript and Node.js
-
How to Exit, Stop, or Break an Array#forEach Loop in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Retrieve a Random Item From an Array in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Reverse an Array in JavaScript and Node.js
-
Sort an Array of Strings in JavaScript, TypeScript or Node.js
-
Sort an Array of Objects in JavaScript, TypeScript or Node.js
-
Check If a Value Is an Array in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Join an Array of Strings to a Single String Value
(Coming soon)
-
How to Run an Asynchronous Function in Array.map() -
How to Reset and Empty an Array
-
for…of vs. for…in Loops
-
Clone/Copy an Array in JavaScript and Node.js
-
Get an Array With Unique Values (Delete Duplicates)
-
Sort an Array of Integers in JavaScript and Node.js
-
Sort a Boolean Array in JavaScript, TypeScript, or Node.js
-
Check If an Array Contains a Given Value in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Add an Item to the Beginning of an Array in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Append an Item at the End of an Array in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Exit and Stop a for Loop in JavaScript and Node.js
-
Split an Array Into Smaller Array Chunks in JavaScript and Node.js
-
How to Get an Index in a for…of Loop in JavaScript and Node.js
-
How to Exit, Stop, or Break an Array#forEach Loop in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Retrieve a Random Item From an Array in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Reverse an Array in JavaScript and Node.js
-
Sort an Array of Strings in JavaScript, TypeScript or Node.js
-
Sort an Array of Objects in JavaScript, TypeScript or Node.js
-
Check If a Value Is an Array in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Join an Array of Strings to a Single String Value
(Coming soon)
-
Callback and Promise Support in your Node.js Modules
-
Run Async Functions/Promises in Sequence
-
Run Async Functions/Promises in Parallel
-
Run Async Functions in Batches
-
How to Fix “Promise resolver undefined is not a function” in Node.js or JavaScript
-
Detect if Value Is a Promise in Node.js and JavaScript
-
Overview of Promise-Based APIs in Node.js
-
Callback and Promise Support in your Node.js Modules -
Run Async Functions/Promises in Sequence
-
Run Async Functions/Promises in Parallel
-
Run Async Functions in Batches
-
How to Fix “Promise resolver undefined is not a function” in Node.js or JavaScript
-
Detect if Value Is a Promise in Node.js and JavaScript
-
Overview of Promise-Based APIs in Node.js
-
Human-Readable JSON.stringify() With Spaces and Line Breaks
-
Write a JSON Object to a File
-
Create a Custom “toJSON” Function in Node.js and JavaScript
-
Human-Readable JSON.stringify() With Spaces and Line Breaks
-
Write a JSON Object to a File
-
Create a Custom “toJSON” Function in Node.js and JavaScript
-
Securely Parse JSON
-
Check If a Value Is Iterable in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Check If a Value Is Iterable in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Extend Multiple Classes (Multi Inheritance)
-
Retrieve the Class Name at Runtime in JavaScript and Node.js
-
Extend Multiple Classes (Multi Inheritance)
-
Retrieve the Class Name at Runtime in JavaScript and Node.js
-
Generate a Random Number in Range With JavaScript/Node.js
-
Ensure a Positive Number in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Check if a Number Is Infinity
-
Check If a Number has Decimal Places in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Use Numeric Separators for Better Readability
-
Generate a Random Number in Range With JavaScript/Node.js
-
Ensure a Positive Number in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Check if a Number Is Infinity
-
Check If a Number has Decimal Places in JavaScript or Node.js
(Coming soon)
-
Use Numeric Separators for Better Readability
-
How to Check if an Object is Empty in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to CamelCase Keys of an Object in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Snake_Case Keys of an Object in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Destructure a Dynamic Key in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Get All Keys (Including Symbols) from an Object in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Delete a Key From an Object in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Iterate Through an Object’s Keys and Values in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Convert URLSearchParams to Object
-
Check If a Value Is an Object in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Conditionally Add Properties to an Object in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Merge Objects
-
How to Check if an Object is Empty in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to CamelCase Keys of an Object in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Snake_Case Keys of an Object in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Destructure a Dynamic Key in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Get All Keys (Including Symbols) from an Object in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Delete a Key From an Object in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Iterate Through an Object’s Keys and Values in JavaScript or Node.js
-
How to Convert URLSearchParams to Object
-
Check If a Value Is an Object in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Conditionally Add Properties to an Object in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Get a File’s Created Date
-
Get a File’s Last Modified or Updated Date of a File
-
How to Create an Empty File
-
Check If a Path or File Exists
-
Check If a Path Is a Directory
-
Check If a Path Is a File
-
Retrieve the Path to the User’s Home Directory
-
Read File Content as String
-
Check If a Directory Is Empty
-
How to Create a Directory (and Parents If Needed)
-
Get a File Name (With or Without Extension)
-
Get a File’s Created Date
-
Get a File’s Last Modified or Updated Date of a File
-
How to Create an Empty File
-
Check If a Path or File Exists
-
How to Rename a File
-
Check If a Path Is a Directory
-
Check If a Path Is a File
-
Retrieve the Path to the User’s Home Directory
-
How to Touch a File
-
Read File Content as String
-
Check If a Directory Is Empty
-
How to Create a Directory (and Parents If Needed)
-
Get a File‘s Extension
-
Get the Size of a File
-
Get a File Name (With or Without Extension)
-
Read a JSON File
-
Create From Object
-
Transform to an Object
-
Determine the Node.js Version Running Your Script
-
Determine the Node.js Version Running Your Script
-
Check if a Value is a Symbol in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Check if a Value is a Symbol in JavaScript or Node.js
-
Detect if Running on Linux
-
Detect if Running on macOS
-
Detect if Running on Windows
-
Check if Running on 64bit or 32bit Platform
-
Constant for Platform-Specific Newline
-
Detect if Running on Linux
-
Detect if Running on macOS
-
Detect if Running on Windows
-
Check if Running on 64bit or 32bit Platform
-
Constant for Platform-Specific Newline
-
How to Download a File
-
Retrieve the List of Supported Hash Algorithms
-
Calculate an MD5 Hash
-
Retrieve the List of Supported Hash Algorithms
-
Calculate a SHA256 Hash
Create an Error Class
Node.js comes with an Error class. This error class gives you the core functionality of errors, like capturing a stack trace and assigning context data.
You can extend Node’s error class to create your own errors. Here’s an example of a NotEnoughCoffee error:
not-enough-coffee-error.js
class NotEnoughCoffee extends Error {
constructor (message) {
super(message)
// assign the error class name in your custom error (as a shortcut)
this.name = this.constructor.name
// capturing the stack trace keeps the reference to your error class
Error.captureStackTrace(this, this.constructor);
// you may also assign additional properties to your error
this.isSleepy = true
}
}
module.exports = NotEnoughCoffee
The custom error extends the default Node.js error class. Setting the this.name property to the constructor’s name will reference NotEnoughCoffee in stack traces instead of the generic Error name.
Go ahead and add other class properties when needed. You can even add methods that are more helpful. Here’s an example:
class CoffeeNotFound extends Error {
constructor (message) {
super(message)
Error.captureStackTrace(this, this.constructor);
this.name = this.constructor.name
this.status = 404
}
statusCode() {
return this.status
}
}
module.exports = CoffeeNotFound
This CoffeeNotFound error could be an HTTP error. You may intercept the response and map the error’s status to the HTTP response status.
Throwing Errors
Import the custom error in your app and use it when necessary. Here’s a simple example that just throws the NotEnoughCoffee error:
'use strict'
const NotEnoughCoffee = require('./error')
throw new NotEnoughCoffee('Well, you may need another coffee :)')
The related error output on your terminal looks like this:
Custom errors are a good way to help your coworkers and other developers to know what’s wrong with the app configuration.
Enjoy coding & make it rock!