I’m working on a django project. One of the views calls Popen(). Most of the time everything works fine. But once in a while Popen() would fail with the following error messages:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:***views.py", line 116, in process_request
proc = Popen(['python', exec_path, input_excel, current_tab, project])
File "C:Python34libsubprocess.py", line 754, in __init__
_cleanup()
File "C:Python34libsubprocess.py", line 474, in _cleanup
res = inst._internal_poll(_deadstate=sys.maxsize)
File "C:Python34libsubprocess.py", line 1146, in _internal_poll
if _WaitForSingleObject(self._handle, 0) == _WAIT_OBJECT_0:
OSError: [WinError 6] The handle is invalid
Restarting the server usually solves the problem but it could show up again later. Attempts immediately after the failure usually fail too (implemented with loops). Manually reloading the page multiple times solve the problem sometimes.
I also tried both 64 bit and 32 bit python versions. The problem shows on both.
It seems that _cleanup() manages the _active list which is used to avoid zombie processes. Considering I’m on windows, I commented out the _cleanup() in Popen() which seems to be working fine so far. Clearly it’s not a proper fix. Any better idea?
Update:
Following eryksun’s advice I looked closer at the handles. It seems that the process handle is closed by django’s autoreload.py for some reason. See below for details.
---------------------------------------------------
try handle:
Handle(908)
File "manage.py", line 10, in <module>
execute_from_command_line(sys.argv)
File "C:Python34libsite-packagesdjangocoremanagement__init__.py", line 338, in execute_from_command_line
utility.execute()
File "C:Python34libsite-packagesdjangocoremanagement__init__.py", line 330, in execute
self.fetch_command(subcommand).run_from_argv(self.argv)
File "C:Python34libsite-packagesdjangocoremanagementbase.py", line 393, in run_from_argv
self.execute(*args, **cmd_options)
File "C:Python34libsite-packagesdjangocoremanagementcommandsrunserver.py", line 49, in execute
super(Command, self).execute(*args, **options)
File "C:Python34libsite-packagesdjangocoremanagementbase.py", line 444, in execute
output = self.handle(*args, **options)
File "C:Python34libsite-packagesdjangocoremanagementcommandsrunserver.py", line 88, in handle
self.run(**options)
File "C:Python34libsite-packagesdjangocoremanagementcommandsrunserver.py", line 97, in run
autoreload.main(self.inner_run, None, options)
File "C:Python34libsite-packagesdjangoutilsautoreload.py", line 325, in main
reloader(wrapped_main_func, args, kwargs)
File "C:Python34libsite-packagesdjangoutilsautoreload.py", line 291, in python_reloader
reloader_thread()
File "C:Python34libsite-packagesdjangoutilsautoreload.py", line 267, in reloader_thread
change = fn()
File "C:Python34libsite-packagesdjangoutilsautoreload.py", line 204, in code_changed
for filename in gen_filenames():
File "C:Python34libsite-packagesdjangoutilsautoreload.py", line 92, in gen_filenames
_cached_filenames = clean_files(_cached_filenames)
File "C:Python34libsite-packagesdjangoutilsautoreload.py", line 139, in clean_files
if os.path.exists(filename):
File "C:Python34libgenericpath.py", line 19, in exists
os.stat(path)
File "C:Python34libsubprocess.py", line 452, in Close
print(traceback.print_stack())
None
handle closed.
---------------------------------------------------
The above error information is generated by the modification below.
def Close(self, CloseHandle=_winapi.CloseHandle):
print ('---------------------------------------------------')
print ('try handle:')
print (self)
if not self.closed:
self.closed = True
CloseHandle(self)
print(traceback.print_stack())
print ('handle closed.')
print ('---------------------------------------------------')
Later the exceptions complain about Handle (908).
I can’t quite follow how os.stat(path) closed the handle and why the process isn’t taken off the _active list by subprocess.py.
I have a Win2012R2 FileServer, running smoothly, no problem.. until today
A user called and he coundn´t open an Excel file, through SMB share
I´ve tried, locally, directlry on file system and.. nothing.
can´t rename, move, delete.
Procces Explorer from sysinternals shows proc ID 4, SYSTEM, opening the Excel file and the «close handle» option says that there is no handle… weird..
IOOrbi Unlocker can´t unlock, not even in force mode, nor rename, nor move.. showing that there is no lock at the file
http://www.iobit.com/en/recommend/db.php?name=iobit_unlocker
It´s a production… i´m trying to avoid: stop the sharing of the folder and rebooting the file server.
The last used who used the file has rebooted and kept the PC powered off.. i would like to close the hadle, be able to rename or unlock the file without any radical procedure…
any ideias?
handle.exe -c 5D0 -p 4
Nthandle v4.1 — Handle viewer
5D0: File (R—) v1.xls
Close handle 5D0 in System (PID 4)? (y/n) y
Error closing handle:
The handle is invalid.
handle.exe -c 2260 -p 4
Nthandle v4.1 — Handle viewer
2260: File (—) v1.xls
Close handle 2260 in System (PID 4)? (y/n) y
Error closing handle:
The handle is invalid.
-
Edited by
Friday, September 29, 2017 2:34 PM
typo
Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Windows Server 2008 Enterprise without Hyper-V Windows Server 2008 Datacenter Windows Server 2008 Datacenter without Hyper-V Windows Server 2008 Standard Windows Server 2008 Standard without Hyper-V Windows Server 2008 Web Edition Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation More…Less
Symptoms
Assume that you set CScript.exe as the default script engine on a computer that is running an x64-based version of Windows Server 2008. Then, you run a command that runs a script and saves the output to a file. For example, you run the following command:
script_to_run.vbs > output_result.txtIn this situation, you receive the following error message:
The handle is invalid
Cause
This issue occurs because Windows in Windows 64-bit (WOW64) processes cannot duplicate non-pseudo handles from Process Environment Block (PEB32) processes.
Resolution
This hotfix is also available at Microsoft Update Catalog.
Hotfix information
A supported hotfix is available from Microsoft. However, this hotfix is intended to correct only the problem that is described in this article. Apply this hotfix only to systems that are experiencing the problem described in this article. This hotfix might receive additional testing. Therefore, if you are not severely affected by this problem, we recommend that you wait for the next software update that contains this hotfix.
If the hotfix is available for download, there is a «Hotfix download available» section at the top of this Knowledge Base article. If this section does not appear, contact Microsoft Customer Service and Support to obtain the hotfix.
Note If additional issues occur or if any troubleshooting is required, you might have to create a separate service request. The usual support costs will apply to additional support questions and issues that do not qualify for this specific hotfix. For a complete list of Microsoft Customer Service and Support telephone numbers or to create a separate service request, visit the following Microsoft website:
http://support.microsoft.com/contactus/?ws=supportNote The «Hotfix download available» form displays the languages for which the hotfix is available. If you do not see your language, it is because a hotfix is not available for that language.
Prerequisites
To apply this hotfix, you must be running Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 (SP2). For more information about how to obtain a Windows Vista service pack, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
935791 How to obtain the latest Windows Vista service pack
For more information about how to obtain a Windows Server 2008 service pack, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
968849 How to obtain the latest service pack for Windows Server 2008
Registry information
To apply this hotfix, you do not have to make any changes to the registry.
Restart requirement
You must restart the computer after you apply this hotfix.
Hotfix replacement information
This hotfix does not replace a previously released hotfix.
File information
The global version of this hotfix installs files that have the attributes that are listed in the following tables. The dates and the times for these files are listed in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The dates and the times for these files on your local computer are displayed in your local time together with your current daylight saving time (DST) bias. Additionally, the dates and the times may change when you perform certain operations on the files.
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 file information notes
Important Windows Vista hotfixes and Windows Server 2008 hotfixes are included in the same packages. However, only «Windows Vista» is listed on the Hotfix Request page. To request the hotfix package that applies to one or both operating systems, select the hotfix that is listed under «Windows Vista» on the page. Always refer to the «Applies To» section in articles to determine the actual operating system that each hotfix applies to.
-
The files that apply to a specific product, SR_Level (RTM, SPn), and service branch (LDR, GDR) can be identified by examining the file version numbers as shown in the following table.
Version
Product
SR_Level
Service branch
6.0.600
2.
22xxxWindows Vista and Windows Server 2008
SP2
LDR
-
Service Pack 1 is integrated into the release version of Windows Server 2008. Therefore, RTM milestone files apply only to Windows Vista. RTM milestone files have a 6.0.0000.xxxxxx version number.
-
The MANIFEST files (.manifest) and the MUM files (.mum) that are installed for each environment are listed separately in the «Additional file information for Windows Server 2008 and for Windows Vista» section. MUM files and MANIFEST files, and the associated security catalog (.cat) files, are extremely important to maintaining the state of the updated component. The security catalog files, for which the attributes are not listed, are signed with a Microsoft digital signature.
For all supported x64-based versions of Windows Server 2008 and of Windows Vista
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ntoskrnl.exe |
6.0.6002.22925 |
4,685,696 |
05-Sep-2012 |
11:52 |
x64 |
Status
Microsoft has confirmed that this is a problem in the Microsoft products that are listed in the «Applies to» section.
More Information
For more information about software update terminology, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
824684 Description of the standard terminology that is used to describe Microsoft software updates
Additional file information
Additional file information for Windows Server 2008
Additional files for all supported x64-based versions of Windows Server 2008
|
File name |
Amd64_94fcf318b75291065378d78441c6fe12_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.22925_none_411911e496ac5059.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
701 |
|
Date (UTC) |
05-Sep-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
12:09 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_99c5423e0d0a44a70adc461119144ce8_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.22925_none_012e0c262330c519.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
721 |
|
Date (UTC) |
05-Sep-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
12:09 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_microsoft-windows-os-kernel_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.22925_none_caae825382d00fce.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
17,282 |
|
Date (UTC) |
05-Sep-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
12:09 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_microsoft-windows-r..gistry-trustedtypes_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.22925_none_e27c1a45fd151a68.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
7,656 |
|
Date (UTC) |
04-Sep-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
17:19 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
Need more help?
HI,
first of all: I’m relatively new to LabWindows, working on it during some practical work as a Student
(yeah, and sorry for the bad english, I’m from Germany)
To the Problem:
The first important Information:
After having searched for a solution, I just don’t know, what to do,
My Project consists of ONE Main.uir-File with a Tab, a «Main.c» that basically handles the main .uir-Stuff and some Initiating-Stuff and in addition to that Several Sub-Sourc-Files, one for each Tab-Panel of the Main.uir-Tab.
To use the UI-Items on the Main-Tab with the Sub-Sources, I am initiating Tab-Handles at startup, that can be used by the SubSource-Files, like:
GetPanelHandleFromTabPage (PANEL, PANEL_TAB, 2, &BALU);
With this Handle, I can identify every UI-Items, when working with the SubSources
The second important information:
In some of the TabPages of the .uir there are several ControlArrays. To use them I create a ControlArrayHandle, like:
MWSAverageHandle = GetCtrlArrayFromResourceID (BALU, MWSAverageArray);
No, I am able to identify specific elements of the Arrays, like:
SetCtrlVal (BALU, GetCtrlArrayItem (MWSProgressHandle, ActiveBalun), ProgressString);
Now there is a Problem, I am not able to solve:
During runtime, everything works out fine, I can use every element of a ControlArray with this ControlArrayHandle («MWSProgressHandle»), everything works perfect, no errors at all. BUT, when closing the programm, I get the following error-message:
NON-FATAL RUN-TIME ERROR: «Baluns.c», line 313, col 16, thread id 0x00000AB8:
Library function error (return value == -4 [0xfffffffc]). Panel, menu bar, or control array handle is invalid
But this seems somehow ridiulous to me, because at runtime every single line works perfect, every Array-Item can be used without Problems…
Is there anything I am just not able to see???
Thanks a lot for your help.
Greeting from Lübeck, Germany!
Mathias
На чтение 7 мин. Просмотров 33.3k. Опубликовано 03.09.2019
Если вы получаете код ошибки ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE ‘ с описанием «Неверный дескриптор», выполните действия по устранению неполадок, перечисленные в этой статье, чтобы исправить это.
Содержание
- «Недопустимый дескриптор»
- Исправлено: дескриптор недействителен в Windows 10
- Ошибка «Неверный дескриптор» не позволяет пользователям войти в систему
- «Неверный дескриптор» ошибки принтера
- Исправлено: «Неверный дескриптор» в Windows XP, Vista, Windows 7 и 8.1
«Недопустимый дескриптор»
Эта ошибка затрагивает пользователей Windows 10, когда они пытаются войти на свои компьютеры. Сообщение об ошибке «Неверный дескриптор» не позволяет пользователям подключаться к своим учетным записям и фактически использовать свои ПК.
Есть две основные причины этой ошибки: последнее обновление Windows 10 не было установлено правильно или некоторые системные файлы были повреждены или повреждены. Вот как один пользователь описывает эту проблему:
Поэтому я только что установил обновление, и какое-то время оно работало просто замечательно.
Но теперь все шло как с ума, а BSOD […] я попытался перезагрузить компьютер, и он выдал «Неверный дескриптор». […]
Другая проблема – когда я нажимаю кнопку выключения после того, как дескриптор недействителен, он остается включенным и не выключается.
В Windows 10 эта ошибка также блокирует процесс печати, в результате чего пользователи не могут добавить принтер или использовать уже установленный.
Ошибка «Неверный дескриптор» также влияет на более старые версии Windows, не позволяя пользователям устанавливать какие-либо обновления или программное обеспечение на свои компьютеры.
В этой статье мы покажем вам, как исправить ошибку «Неверный дескриптор» в Windows 10, а также в более старых версиях Windows.
Исправлено: дескриптор недействителен в Windows 10
Ошибка «Неверный дескриптор» не позволяет пользователям войти в систему
Решение 1. Нажмите кнопку перезагрузки .
Если вы не можете получить доступ к своей учетной записи из-за ошибки «Неверный дескриптор», попробуйте перезагрузить компьютер несколько раз. Многие пользователи подтвердили, что это простое действие решает проблему.
Если вы не хотите выполнять полный сброс, вы можете удерживать нажатой клавишу Shift и нажимать экранную кнопку питания, выбрать вариант перезапуска, удерживая клавишу Shift, а затем выбрать «Перейти к Windows 10».
Это заставит Windows восстанавливать поврежденные или поврежденные файлы обновления.
Узнайте все, что нужно знать об управлении учетными записями пользователей, из нашего замечательного руководства!
Решение 2. Загрузитесь в безопасном режиме и удалите обновления безопасности
1. Удерживая клавишу Shift, нажмите кнопку питания на экране.
2. Выберите опцию перезапуска, удерживая клавишу Shift
3. Выберите Устранение неполадок> Дополнительные параметры> Параметры запуска> нажмите Перезагрузить

4. Дождитесь перезагрузки Windows 10 и выберите Безопасный режим.
5. Перейдите в раздел «Обновления и безопасность»> «Центр обновления Windows»> «Дополнительные параметры»> «Просмотр истории обновлений»> «удалите последние обновления»> перезагрузите компьютер.
Многие пользователи сообщают, что кумулятивными являются накопительные обновления KB3135173 и KB3124262, и удаление этих двух обновлений устранило проблему.

Решение 3. Обновление Citrix VDA
Это решение работает только для пользователей, использующих Citric VDA. Некоторые обновления Windows несовместимы с Citrix VDA 7.6.300, что приводит к ошибке «Неверный дескриптор». Чтобы это исправить, скачайте накопительное обновление VDA 7.6.1000.
Если вы используете VDA v7.7, загрузите более новые версии VDA 7.8 или более поздней версии, в которых содержится исправление. Для получения дополнительной информации и пошагового руководства перейдите на страницу поддержки Citrix.
«Неверный дескриптор» ошибки принтера

Решение 1. Запустите полное сканирование системы .

Вредоносные программы могут вызвать различные проблемы на вашем компьютере, в том числе ошибки. Выполните полное сканирование системы, чтобы обнаружить любые вредоносные программы, работающие на вашем компьютере. Вы можете использовать встроенные в Windows антивирусные программы, Защитник Windows или сторонние антивирусные решения.
Решение 2. Обновите драйверы ПК .
Устаревшие драйверы также могут вызывать ошибку «Неверный дескриптор». В результате установите на компьютер последние обновления драйверов и посмотрите, решит ли это действие проблему.
Как обновить драйверы в Windows 10
Вы можете исправить наиболее распространенные проблемы с драйверами, установив последние обновления Windows. Просто введите «update» в поле поиска и нажмите «Проверить наличие обновлений», чтобы загрузить и установить последние обновления.
Если вы хотите установить определенные драйверы, запустите диспетчер устройств. Разверните доступные категории и выберите устройство, для которого вы хотите обновить драйвер.
Чтобы установить последние обновления драйверов для этого устройства, щелкните его правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Обновить драйвер».

Третий вариант – загрузить доступные обновления драйверов непосредственно с веб-сайта производителя.
Обновите свои драйверы как профессионал с нашим исчерпывающим руководством!
Мы также настоятельно рекомендуем Модуль обновления драйверов TweakBit (одобрен Microsoft и Norton) для автоматической загрузки всех устаревших драйверов на ваш компьютер.
Это отличный инструмент, который сканирует обновления, а антивирус – на наличие угроз. Этот инструмент обеспечит безопасность вашей системы, поскольку вы можете вручную загрузить и установить неправильную версию драйвера.
Решение 3. Обновите свою ОС .

Убедитесь, что на вашем компьютере установлены последние обновления ОС Windows. В качестве напоминания, Microsoft постоянно выпускает обновления для Windows, чтобы улучшить стабильность системы и устранить различные проблемы.
Перейдите в Центр обновления Windows, проверьте наличие обновлений и установите доступные обновления.
Решение 4. Восстановите реестр .
Самый простой способ восстановить реестр – использовать специальный инструмент, такой как CCleaner. Не забудьте сначала сделать резервную копию реестра, если что-то пойдет не так.
Если вы не установили очиститель реестра на свой компьютер, ознакомьтесь с нашей статьей о лучших очистителях реестра для использования на ПК с Windows 10.
Вы также можете использовать средство проверки системных файлов Microsoft для проверки повреждений системных файлов. Вот как запустить сканирование SFC:
1. Перейдите в Пуск>, введите cmd >, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши Командную строку> выберите Запуск от имени администратора.

2. Теперь введите команду sfc/scannow

3. Дождитесь завершения процесса сканирования и перезагрузите компьютер. Все поврежденные файлы будут заменены при перезагрузке.
Решение 5. Загрузите универсальный драйвер печати HP
Многие пользователи Windows 10 сообщили, что при загрузке универсального драйвера печати HP исправлена ошибка «Неверный дескриптор».
В качестве быстрого напоминания этот инструмент автоматически обнаруживает и настраивает поддерживаемые устройства HP и некоторые устройства не HP.
Вы можете загрузить универсальный драйвер печати HP с веб-сайта HP.
Решение 6. Удалите и переустановите Microsoft Print в PDF
Некоторые пользователи подтвердили, что удаление принтера и его повторная установка решают проблему, поэтому вы можете попробовать это.
- Перейдите в раздел Устройства и принтеры .
-
Найдите Microsoft Print to PDF , щелкните правой кнопкой мыши и выберите Удалить устройство .
-
Нажмите кнопку Добавить принтер .
- Нажмите Нужного принтера нет в списке .
- Выберите Добавить локальный принтер или сетевой принтер с ручными настройками и нажмите Далее .
-
Выберите в меню PORTPROMPT: (локальный порт) и нажмите Далее .
-
Выберите Microsoft и Microsoft Print to PDF .
-
Выберите Заменить текущий драйвер и нажмите Далее .
- Добавьте имя для принтера и подождите, пока Windows установит его.
Драйвер принтера поврежден? Вот пошаговое руководство по устранению проблемы!
Исправлено: «Неверный дескриптор» в Windows XP, Vista, Windows 7 и 8.1
Что касается более старых версий Windows, ошибка «Неверный дескриптор» возникает при печати, при попытке скопировать код или текст, при использовании Synergy для совместного использования мыши и клавиатуры между несколькими компьютерами и т. Д.
Вот как исправить ошибку «Неверный дескриптор» в старых версиях Windows:
Решение 1. Установите последние обновления или обновите до Windows 10 .
Microsoft регулярно выпускает обновления для всех поддерживаемых версий Windows. Перейдите в Пуск> введите «обновление»> нажмите «Проверить наличие обновлений»> установить доступные обновления.
Microsoft по-прежнему предлагает Windows 10 в качестве бесплатного обновления с помощью помощника по обновлению для пользователей Windows 7 и Windows 8.1.
Если ваш компьютер совместим с Creators Update, нажмите кнопку обновления, чтобы установить его.
Решение 2. Обновите приложение, подверженное этой ошибке
Установка последней версии приложения, затронутая ошибкой «Неверный дескриптор», может помочь вам решить проблему.
Для этого вы можете использовать кнопку обновления приложения или перейти на официальный веб-сайт приложения и установить последнюю версию оттуда.
Решение 3 – Загрузите универсальный драйвер печати HP
Если из-за ошибки «Неверный дескриптор» вы не можете использовать принтер, загрузите универсальный драйвер печати HP.Этот инструмент автоматически обнаруживает и настраивает поддерживаемые устройства HP и некоторые устройства не HP.
Вы можете загрузить универсальный драйвер печати HP для Windows 7 и новее с веб-сайта HP.
Мы надеемся, что эти решения помогли вам исправить ошибку «Дескриптор неверен».
Как всегда, если вы сталкивались с другими обходными путями, чтобы исправить эту ошибку, вы можете помочь сообществу WindowsReport, перечислив действия по устранению неполадок в комментариях ниже.
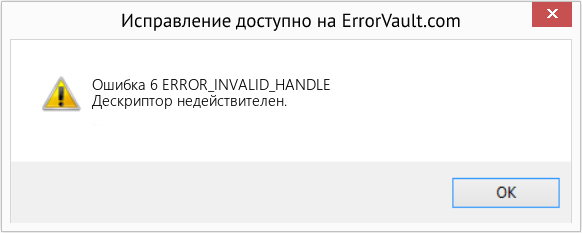
В этой статье представлена ошибка с номером Ошибка 6, широко известная как ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE, и ее описание Дескриптор недействителен.
О системной ошибке Windows
Системные ошибки Windows возникают в разное время во время нормального использования операционной системы. Пользователи должны получить код ошибки, который они могут использовать для анализа и расследования того, что произошло с компьютером. Однако эти коды не всегда предоставляют подробную информацию. А поскольку такие коды может выдавать и несистемное программное обеспечение, при анализе ошибок пользователю потребуется понимание контекста программы и времени выполнения. Вот несколько способов понять симптомы, причины и общие решения.
Определения (Бета)
Здесь мы приводим некоторые определения слов, содержащихся в вашей ошибке, в попытке помочь вам понять вашу проблему. Эта работа продолжается, поэтому иногда мы можем неправильно определить слово, так что не стесняйтесь пропустить этот раздел!
- Handle — Handle — это абстракция ресурса или ссылка на объект.
Симптомы Ошибка 6 — ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE
Во время обработки Windows отправляет коды системных ошибок, чтобы сообщить пользователю о проблеме, возникшей с компьютером. Они появляются в неожиданное время, поэтому их трудно обнаружить, если не проанализировать сообщение об ошибке. Коды системных ошибок Windows являются симптомами других проблем, происходящих с компьютером, поэтому пользователям необходимо обратить внимание на сообщение об ошибке, время и процессы, запущенные во время ее возникновения.
(Только для примера)
Причины ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE — Ошибка 6
Системные ошибки Windows могут быть вызваны программным или аппаратным сбоем. Иногда программное обеспечение не работает согласованно с аппаратным обеспечением из-за изменений или общих аппаратных сбоев. В некоторых случаях пользователи могли установить противоречивые драйверы или повредить ОС. Возможно, в каком-то компоненте произошел аномальный скачок напряжения, который может повредить детали и повлиять на его работу. Могли произойти различные факторы, которые привели к появлению ошибки System в определенные периоды использования компьютера. Проблемы с программным и аппаратным обеспечением, конечно, легко решаются, если пользователь может точно определить часть, которая вызывает сбой. Чтобы решить проблемы с ошибками такого рода, попробуйте следующие методы ремонта.
Методы ремонта
Если метод ремонта вам подошел, пожалуйста, нажмите кнопку upvote слева от ответа, это позволит другим пользователям узнать, какой метод ремонта на данный момент работает лучше всего.
Обратите внимание: ни ErrorVault.com, ни его авторы не несут ответственности за результаты действий, предпринятых при использовании любого из методов ремонта, перечисленных на этой странице — вы выполняете эти шаги на свой страх и риск.
Метод 1 — Восстановить поврежденные или отсутствующие системные файлы
Проверка системных файлов — этот инструмент работает почти так же, как программа проверки реестра, но помогает находить и восстанавливать поврежденные или отсутствующие системные файлы, поэтому его запуск занимает немного больше времени.
- Чтобы запустить команду, откройте командную строку с повышенными привилегиями, набрав ее в окне поиска, затем щелкните правой кнопкой мыши командную строку и выберите «Запуск от имени администратора».
- Введите в командной строке sfc / scannow и дождитесь успешного завершения процесса проверки.
Запустите Checkdisk — Chkdsk исправляет многие несоответствия с ОС. Системные ошибки также можно исправить с помощью этой утилиты. Чтобы запустить это,
- Откройте командную строку, введя ее в поле поиска, а затем, когда вы увидите результат в верхней части списка, щелкните его правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Запуск от имени администратора».
- Ваша система может сказать, что вы не можете запустить ее в данный момент, потому что вы все еще обрабатываете данные, и спросит вас, хотите ли вы запустить ее перед следующим запуском, просто нажмите y для подтверждения, а затем выйдите с экрана и перезагрузите компьютер.
- После перезагрузки компьютера вы увидите, что checkdisk работает вне Windows, просто дайте ему закончить, пока он не даст вам отчет о том, что было найдено, исправлено или отмечено.
- Закройте окно и дайте компьютеру нормально перезагрузиться.
Метод 2 — Обновите или переустановите драйвер
Изменения, внесенные в ваш компьютер, могут испортить ваш драйвер. В этом случае вы можете переустановить драйвер или обновить его. Для этого вы можете сделать следующее.
- Если вы получили код ошибки диспетчера устройств, обратите внимание на описание, чтобы вы могли точно определить драйвер или компонент, вызывающий ошибку.
- Запустите диспетчер устройств, выполнив поиск Диспетчер устройств или запустив «devmgmt.msc»
- Найдите драйвер в списке и щелкните его правой кнопкой мыши.
- Нажмите Удалить , если вы хотите переустановить драйвер, или Обновить программное обеспечение драйвера , если пытаетесь его обновить.
- Появится окно подтверждения. Убедитесь, что флажок Удалить программное обеспечение драйвера снят.
- Нажмите «ОК» и перезагрузите компьютер.
Вы можете сделать это поочередно:
- Вы можете вручную загрузить драйвер от производителя.
- Запустите его, чтобы заменить текущий драйвер, который вы используете.
- После этого перезагрузите компьютер.
Метод 3 — Откатите свой драйвер
Вы также можете вернуться к исходному драйверу, установленному на вашем компьютере. Для этого:
- В диспетчере устройств найдите проблемный драйвер.
- Щелкните устройство правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Свойства».
- Когда вы увидите окно «Свойства», щелкните вкладку «Драйвер».
- Вы увидите кнопку «Откатить драйвер», нажмите ее.
- Подтвердите откат, нажав «Да», когда появится вопрос «Вы уверены, что хотите вернуться к ранее установленному программному обеспечению драйвера?»
- После этого перезагрузите компьютер.
Метод 4 — Использовать восстановление системы
Для окна 7
- Нажмите «Пуск»> «Все программы»> «Стандартные»> «Системные инструменты».
- Нажмите «Восстановление системы», а затем нажмите «Далее».
- Выбирайте точку восстановления, когда знаете, что с вашим компьютером все в порядке.
- Продолжайте нажимать «Далее», а затем — «Готово».
- Это займет время, так что наберитесь терпения и дождитесь полной остановки операции.
Для Windows 8, 8.1 или 10
- Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши кнопку «Пуск», затем выберите «Система».
- В окне «Система» нажмите «Система и безопасность».
- Нажмите «Система» и слева нажмите «Защита системы».
- Нажмите «Восстановление системы», следуйте инструкциям, чтобы выбрать точку восстановления, а затем нажимайте «Далее», пока не увидите кнопку «Готово».
- Дождитесь завершения процесса восстановления.
Метод 5 — Восстановите переустановку с помощью компакт-диска с ОС или флэш-накопителя
- Лучший способ восстановить системное программное обеспечение — это переустановить его. Процесс восстановления и переустановки помогает сохранить файлы при восстановлении операционной системы. Тем не менее, вам нужно убедиться, что вы создали резервную копию своего файла, если вам действительно нужно переустановить компьютер. Вам нужно будет вставить установочный носитель и перезагрузить компьютер.
- Войдите в BIOS, процесс отличается от модели компьютера к модели, это может быть кнопка F1, F2 или Del.
- Оказавшись там, перейдите в раздел загрузки, установите загрузку с установочного диска и сохраните настройки.
- Для более ранней версии Windows вам может потребоваться нажать на клавиатуру, пока вы ждете, пока компьютер не получит доступ к установочному диску.
- Сначала выберите утилиту восстановления, а не чистую установку ОС. Это может сэкономить вам много хлопот. Однако, если проблема не исчезнет после перезагрузки компьютера, просто сделайте резервную копию файлов и выполните чистую переустановку.
Другие языки:
How to fix Error 6 (ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE) — The handle is invalid.
Wie beheben Fehler 6 (ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE) — Der Verweis ist ungültig.
Come fissare Errore 6 (ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE) — L’handle non è valido.
Hoe maak je Fout 6 (ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE) — Het handvat is ongeldig.
Comment réparer Erreur 6 (ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE) — Le descripteur n’est pas valide.
어떻게 고치는 지 오류 6 (ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE) — 핸들이 잘못되었습니다.
Como corrigir o Erro 6 (ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE) — O identificador é inválido.
Hur man åtgärdar Fel 6 (ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE) — Handtaget är ogiltigt.
Jak naprawić Błąd 6 (ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE) — Uchwyt jest nieprawidłowy.
Cómo arreglar Error 6 (ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE) — El mango no es válido.
Об авторе: Фил Харт является участником сообщества Microsoft с 2010 года. С текущим количеством баллов более 100 000 он внес более 3000 ответов на форумах Microsoft Support и создал почти 200 новых справочных статей в Technet Wiki.
Следуйте за нами:
Последнее обновление:
21/12/21 05:00 : Пользователь iPhone проголосовал за то, что метод восстановления 1 работает для него.
Этот инструмент восстановления может устранить такие распространенные проблемы компьютера, как синие экраны, сбои и замораживание, отсутствующие DLL-файлы, а также устранить повреждения от вредоносных программ/вирусов и многое другое путем замены поврежденных и отсутствующих системных файлов.
ШАГ 1:
Нажмите здесь, чтобы скачать и установите средство восстановления Windows.
ШАГ 2:
Нажмите на Start Scan и позвольте ему проанализировать ваше устройство.
ШАГ 3:
Нажмите на Repair All, чтобы устранить все обнаруженные проблемы.
СКАЧАТЬ СЕЙЧАС
Совместимость
Требования
1 Ghz CPU, 512 MB RAM, 40 GB HDD
Эта загрузка предлагает неограниченное бесплатное сканирование ПК с Windows. Полное восстановление системы начинается от $19,95.
ID статьи: ACX013928RU
Применяется к: Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows XP, Windows 2000
Ошибки в алфавитном порядке: A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Логотипы Microsoft и Windows® являются зарегистрированными торговыми марками Microsoft. Отказ от ответственности: ErrorVault.com не связан с Microsoft и не заявляет о такой связи. Эта страница может содержать определения из https://stackoverflow.com/tags по лицензии CC-BY-SA. Информация на этой странице представлена исключительно в информационных целях. © Copyright 2018
Created on 2019-06-23 18:42 by efiop, last changed 2022-04-11 14:59 by admin. This issue is now closed.
subprocess keeps the list of active processes in its `_active` list. Whenever you try to Popen a new process, it is immediately (like right in the first line of Popen.__init__ [1]) trying to go clean up the old ones. If one of the processes in that list is gone, then ``` (_WaitForSingleObject(self._handle, 0) ``` [2] will get `OSError: [WinError 6] The handle is invalid` and will prevent you from creating any new processes with Popen after that, because the line where that handle is removes from _active list is not reached. On *nix [3] _internal_poll will actually try-except waitpid and will catch OSError without re-raising it, so if the process is gone, it will simply report it as dead and successfully remove it from _active list. It seems like we should do the same thing on Windows and if we catch `The handle is invalid` error, just report that process as dead and remove it from _active list. [1] https://github.com/python/cpython/blob/v3.8.0b1/Lib/subprocess.py#L715 [2] https://github.com/python/cpython/blob/v3.8.0b1/Lib/subprocess.py#L1310 [3] https://github.com/python/cpython/blob/v3.8.0b1/Lib/subprocess.py#L1710

See issue 36067 for a related discussion. The _active list and _cleanup function are not required in Windows. When a process exits, it gets rundown to free its handle table and virtual memory. Only the kernel object remains, which is kept alive by pointer and handle references to it that can query information such as the exit status code. As soon as the last reference is closed, the Process object is automatically reaped. It doesn't have to be waited on.
Hi Eryk! Thanks for a swift reply! So the current plan for fixing it is: 1) disable _cleanup, _active, and remove _internal_poll() for windows 2) ignore EBADF(OSError: [WinError 6] The handle is invalid) in terminate() and probably some other methods Please let me know if I'm missing something. Also, is anyone working on this, or should I prepare a PR? Thanks, Ruslan

> 1) disable _cleanup, _active, and remove _internal_poll() for windows _active only gets appended to in __del__. We can skip the entire body of __del__. Also, calling _cleanup can be skipped in __init__. _internal_poll is required for poll(). 2) ignore EBADF(OSError: [WinError 6] The handle is invalid) in terminate() and probably some other methods ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE should not be ignored. terminate() is doing the right thing by not masking ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE. The only concern is the case where our handle has been closed elsewhere (not by subprocess) and the handle value was subsequently reused as a handle for another process to which we have terminate access. This is a bad handle at a logical, application level, but it's valid and accessible for TerminateProcess. It was suggested to initially get the pid and process startup time in order to validate the call, but Alexey Izbyshev is right that it's not worth complicating the code in subprocess to address an uncommon bug in particular application or library code.

> 2) ignore EBADF(OSError: [WinError 6] The handle is invalid) in terminate() and probably some other methods That sounds like a bad idea. We should avoid using a handle if it can become invalid out of our control. A handle might be recycled, no?
Thanks for pointing that out! I've submitted a tiny patch to skip ``_collect()`` and ``__del__``. Please find it in the Github PR attached. Looking forward to your feedback!

> See issue 36067 for a related discussion. The _active list and _cleanup function are not required in Windows. When a process exits, it gets rundown to free its handle table and virtual memory. Only the kernel object remains, which is kept alive by pointer and handle references to it that can query information such as the exit status code. As soon as the last reference is closed, the Process object is automatically reaped. It doesn't have to be waited on. Linux (for example) has the same design: the kernel doesn't keep a "full process" alive, but a lightweight structure just for its parent process which gets the exit status. That's the concept of "zombie process". One issue on Linux is that the zombie process keeps the pid used until the parent reads the child exit status, and Linux pids are limited to 32768 by default. Now I'm not sure that I understand what it means on Windows. The subprocess module uses a magic Handle object which calls CloseHandle(handle) in its __del__() method. I dislike relying on destructors. If an object is kept alive by a reference cycle, it's never released: CloseHandle() isn't called. So code spawning process should wait until subprocesses complete to ensure that CloseHandle() is called, no? Except that Popen._internal_poll() doesn't clear the handle even after the process completes. If Popen.__del__() doesn't add active processes to the _active list, it should at least explicitly call CloseHandle(), no?

The handle can deliberately live beyond the process, but it does not have to. If it is closed early then the kernel object will be freed when no handles remain, which will be at process exit. So it's a classic __exit__/__del__ case, where both are needed if you want deterministic resource disposal. But it is in no way tied to the life of the child process, so waiting first is optional.

> One issue on Linux is that the zombie process keeps the pid used until > the parent reads the child exit status, and Linux pids are limited to > 32768 by default. Windows allocates Process and Thread IDs out of a kernel handle table, which can grow to about 2**24 entries (more than 16 million). So the practical resource limit for inactive Process and Thread objects is available memory, not running out of PID/TID values. > Linux (for example) has the same design: the kernel doesn't keep a > "full process" alive, but a lightweight structure just for its parent > process which gets the exit status. That's the concept of "zombie > process". In Unix, the zombie remains visible in the task list (marked as <defunct> in Linux), but in Windows an exited process is removed from the Process Manager's active list, so it's no longer visible to users. Also, a Process object is reaped as soon as the last reference to it is closed, since clearly no one needs it anymore. > The subprocess module uses a magic Handle object which calls > CloseHandle(handle) in its __del__() method. I dislike relying on > destructors. If an object is kept alive by a reference cycle, it's > never released: CloseHandle() isn't called. We could call self._handle.Close() in _wait(), right after calling GetExitCodeProcess(self._handle). With this change, __exit__ will ensure that _handle gets closed in a deterministic context. Code that needs the handle indefinitely can call _handle.Detach() before exiting the with-statement context, but that should rarely be necessary. I don't understand emitting a resource warning in Popen.__del__ if a process hasn't been waited on until completion beforehand (i.e. self.returncode is None). If a script wants to be strict about this, it can use a with statement, which is documented to wait on the process. I do understand emitting a resource warning in Popen.__del__ if self._internal_poll() is None. In this case, in Unix only now, the process gets added to the _active list to try to avoid leaking a zombie. The list gets polled in subprocess._cleanup, which is called in Popen.__init__. Shouldn't _cleanup also be set as an atexit function? There should be a way to indicate a Popen instance is intended to continue running detached from our process, so scripts don't have to ignore an irrelevant resource warning.

> In Unix, the zombie remains visible in the task list (marked as <defunct> in Linux), but in Windows an exited process is removed from the Process Manager's active list, so it's no longer visible to users. Also, a Process object is reaped as soon as the last reference to it is closed, since clearly no one needs it anymore. > (...) > We could call self._handle.Close() in _wait(), right after calling GetExitCodeProcess(self._handle). With this change, __exit__ will ensure that _handle gets closed in a deterministic context. I created bpo-37410 and PR 14391 to close the handle when the process completes. IMHO this change is easy and safe, it can be backported to Python 3.7 and 3.8. > Code that needs the handle indefinitely can call _handle.Detach() before exiting the with-statement context, but that should rarely be necessary. > (...) > There should be a way to indicate a Popen instance is intended to continue running detached from our process, so scripts don't have to ignore an irrelevant resource warning. My point is that if you want to "detach" a process, it must be *explicit*. In my experience, processes are "leaked" implicitly: by mistake. In multiprocessing, it can be subtle, you don't manipulate subprocess.Popen directly. Users must not access private attributes (Popen._handle). After I added the ResourceWarning, I created bpo-27068 "Add a detach() method to subprocess.Popen". But I only created to reply to a request of Martin Panter, I didn't use this feature myself. At some point, I decided to just close the issue. Maybe it's time to reopen it. > I don't understand emitting a resource warning in Popen.__del__ if a process hasn't been waited on until completion beforehand (i.e. self.returncode is None). If a script wants to be strict about this, it can use a with statement, which is documented to wait on the process. The purpose is to help developers to find bugs in their bugs. Many are now aware that programs continue to run in the background and that leaking zombie processes is an issue on Unix. The process is not polled to be able to emit the warning in more cases, again, to ease debug. The warning is ignored by default.

> The process is not polled to be able to emit the warning in more
> cases, again, to ease debug.
It emits an incorrect warning if the process has already exited: "subprocess %s is still running". This can be rectified. Here's my current understanding:
def __del__(self, _maxsize=sys.maxsize, _warn=warnings.warn):
if not self._child_created or self.returncode is not None:
return
# In Unix, not reading the subprocess exit status creates a zombie
# process, which is only destroyed at the parent Python process exit.
# In Windows, no one else should have a reference to our _handle, so
# it should get finalized and thus closed, but we use the same warning
# in order to consistently educate developers.
if self._internal_poll(_deadstate=_maxsize) is not None:
_warn("subprocess %s was implicitly finalized" % self.pid,
ResourceWarning, source=self)
else:
_warn("subprocess %s is still running" % self.pid,
ResourceWarning, source=self)
# Keep this instance alive until we can wait on it, if needed.
if _active is not None:
_active.append(self)

Sorry, I'm lost :-( More and more different issues are discussed here. Would it be possible please to stick this issue to _active list and _cleanup() on Windows? From what I read, remove/disable _active and _cleanup() makes sense on Windows. I already created bpo-37410 to call CloseHandle() earlier. Eryk: Please open a separated issue if you want to change the ResourceWarning message.

Here is a concrete example of ResourceWarning when debugging/stressing multiprocessing code, I interrupt (CTRL+c) test_resource_tracker while it's running:
vstinner@apu$ ./python -m test test_multiprocessing_spawn --fail-env-changed -v -m test_resource_tracker
== CPython 3.9.0a0 (heads/master:689830ee62, Jun 26 2019, 23:07:31) [GCC 9.1.1 20190503 (Red Hat 9.1.1-1)]
== Linux-5.1.11-300.fc30.x86_64-x86_64-with-glibc2.29 little-endian
== cwd: /home/vstinner/prog/python/master/build/test_python_18573
== CPU count: 8
== encodings: locale=UTF-8, FS=utf-8
Run tests sequentially
0:00:00 load avg: 0.32 [1/1] test_multiprocessing_spawn
test_resource_tracker (test.test_multiprocessing_spawn.TestResourceTracker) ...
^C
/home/vstinner/prog/python/master/Lib/subprocess.py:917: ResourceWarning: subprocess 18576 is still running
_warn("subprocess %s is still running" % self.pid,
ResourceWarning: Enable tracemalloc to get the object allocation traceback
/home/vstinner/prog/python/master/Lib/test/libregrtest/runtest.py:283: ResourceWarning: unclosed file <_io.BufferedReader name=6>
return INTERRUPTED
ResourceWarning: Enable tracemalloc to get the object allocation traceback
== Tests result: INTERRUPTED ==
Test suite interrupted by signal SIGINT.
1 test omitted:
test_multiprocessing_spawn
Total duration: 304 ms
Tests result: INTERRUPTED

New changeset 042821ae3cf537e01963c9ec85d1a454d921e826 by Victor Stinner (Ruslan Kuprieiev) in branch 'master': bpo-37380: subprocess: don't use _active on win (GH-14360) https://github.com/python/cpython/commit/042821ae3cf537e01963c9ec85d1a454d921e826

I merged PR 14360 into master. Are Python 2.7, 3.7 and 3.8 impacted by the bug as well? Should we backport the change, or would it be too dangerous?
The `_active` code is pretty old and has not changed since 2.7, so it makes sense to backport it for now(also, should be very trivial to do that). To me, it doesn't seem dangerous to backport that, but I would love to hear what Eryk and others think :)

> To me, it doesn't seem dangerous to backport that, but I would love to hear what Eryk and others think :) In my experience, any change is dangerous :-) The initial bug doesn't contain any reproducer. I'm talking about: > If one of the processes in that list is gone, then (...) "The handle is invalid" (...) will prevent you from creating any new processes with Popen after that It's the first time that I see such bug report. It seems like subprocess works for most people :-) Can you elobrate how to reproduce this issue to justify a backport?

>> If one of the processes in that list is gone, then (...) "The handle
>> is invalid" (...) will prevent you from creating any new processes
>> with Popen after that
>
> It's the first time that I see such bug report.
IIRC it's the second time I've seen that issue reported. It should be rare. It should only occur if some other code in our process or another process closes our _handle value. It's not our bug. Here's an example in 3.7:
>>> p = subprocess.Popen('python -c "input()"', stdin=subprocess.PIPE)
>>> del p
>>> subprocess._active
[<subprocess.Popen object at 0x0000015E5C94E160>]
>>> subprocess._active[0]._handle.Close()
The process is active, but something closed our handle. The next time Popen.__init__ calls _cleanup, _internal_poll raises OSError due to the invalid handle:
>>> subprocess.call('python -V')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "C:Program FilesPython37libsubprocess.py", line 323, in call
with Popen(*popenargs, **kwargs) as p:
File "C:Program FilesPython37libsubprocess.py", line 664, in __init__
_cleanup()
File "C:Program FilesPython37libsubprocess.py", line 228, in _cleanup
res = inst._internal_poll(_deadstate=sys.maxsize)
File "C:Program FilesPython37libsubprocess.py", line 1216, in _internal_poll
if _WaitForSingleObject(self._handle, 0) == _WAIT_OBJECT_0:
OSError: [WinError 6] The handle is invalid
I wouldn't want _internal_poll to silence this error, but maybe it could be translated into a warning. That said, since there's no need to wait on a process in Windows, there's no need for __del__ to insert a running process in a list of active process, in which case there's nothing for _cleanup to do. Given we're in __del__, our private _handle is about to be closed, at least it will be in CPython. Other implementations should wait() or use a with statement, in order to explicitly close the process handle. The latter isn't implemented currently, but you opened issue 37410 to address this.

> subprocess._active[0]._handle.Close() Why would you do that? You should not access the private _active list, nor access the private _handle attribute. I understand that it's a way to trigger such bug, but is it possible to trigger this bug without accessing any private attribute? > I wouldn't want _internal_poll to silence this error, but maybe it could be translated into a warning I disagree with that. It's very bad is suddenly the handle becomes invalid for no obvious reason. It's better to get an hard error (exception) in such case.

>> subprocess._active[0]._handle.Close() > > Why would you do that? You should not access the private _active list, > nor access the private _handle attribute. I understand that it's a way > to trigger such bug, but is it possible to trigger this bug without > accessing any private attribute? The example is just emulating a problem from someone else's code that's closing our handle. Typically this situation occurs because the code is holding onto a handle value for a kernel object (File, Section, Job, Process, Thread, Event, etc) that got closed. The handle value eventually gets reused, such as for our _handle. >> I wouldn't want _internal_poll to silence this error, but maybe it >> could be translated into a warning > > I disagree with that. It's very bad is suddenly the handle becomes > invalid for no obvious reason. It's better to get an hard error > (exception) in such case. I agree, but the exception breaks Popen.__init__. It would have to be ignored or translated to a warning somewhere if we continues to poll a list of active processes every time __init__() is called. But since the latter is unnecessary in Windows, I suggested to just skip it.

> The example is just emulating a problem from someone else's code that's closing our handle. Typically this situation occurs because the code is holding onto a handle value for a kernel object (File, Section, Job, Process, Thread, Event, etc) that got closed. Without accessing private attributes, I don't see how someone can discover the private handle. So for me, it's more a serious bug in an application, no? Blindly closing random handles doesn't sound like a good idea to me. > The handle value eventually gets reused, such as for our _handle. That's a side effect on the blindly closing random handles.

> Without accessing private attributes, I don't see how someone can > discover the private handle. So for me, it's more a serious bug in an > application, no? Blindly closing random handles doesn't sound like a > good idea to me. Say a library calls CreateEventW and gets handle 32. It passes this handle to some other library, which uses the event and closes the handle when it no longer needs it. But due to a miscommunication in the documentation, the first library thinks the handle remains open. Now handle 32 is free for reuse, but the library doesn't know this. subprocess.Popen subsequently calls CreateProcessW and gets handle 32. Later on, the library closes handle 32, making it invalid, at least until it gets assigned to some other kernel object.

> Say a library calls CreateEventW and gets handle 32. It passes this handle to some other library, which uses the event and closes the handle when it no longer needs it. But due to a miscommunication in the documentation, the first library thinks the handle remains open. Now handle 32 is free for reuse, but the library doesn't know this. subprocess.Popen subsequently calls CreateProcessW and gets handle 32. Later on, the library closes handle 32, making it invalid, at least until it gets assigned to some other kernel object. So yeah, it's a severe bug in an application. An application should not close the wrong handle by mistake :-) Thanks for the explanation. So it would be "nice" to backport the change to reduce the impact of such application bug, but it's not really a bug in Python itself. Python cannot fully protect developers for such class of bugs. On Unix, there is a similar bug with applications trying to close a file descriptor which is already closed. It can lead to very severe bugs (crashes): https://bugs.python.org/issue18748
I believe this to be a bug in the standard library instead of solely being the result of an application error. When a Popen instance is finalized by the garbage collector, the internal handle is also finalized and closed despite the instance being put on the active list. This results in _cleanup throwing because the handle can no longer be used. I've attached a small reproduction.
I see there is a merged patch for this (https://github.com/python/cpython/pull/14360); is it possible to get it tagged for backport to 3.7? I haven't seen the 3.7.5 tag drop yet so wanted to recommend it's included, it's giving us fits. On our Windows 10 dev boxes and Win 2016 servers, emanuel's repro fails 3.5.4, 3.6.8, 3.7.4, and 3.8.0b4, but not apparently 2.7 (I think we tested 2.7.12). Per vstinner's request, I agree and would like to see it get a 3.7 and 3.8 backport. Many thanks!

I triggered automatic backports to see how they go. Doesn't necessarily mean we'll merge them without looking more closely, but may as well check out what our automated tools suggest.

> When a Popen instance is finalized by the garbage collector, the internal handle is also finalized and closed despite the instance being put on the active list. This results in _cleanup throwing because the handle can no longer be used. Right, that's a more practical case where this bug still occurs on Python 3.8 and older. I would suggest to fix applications which should get a ResourceWarning warning in this case. Chip Lynch wrote me an email saying that his team is impacted by the bug on Windows with Python 3.7. I tried to write a simpler patch ignoring ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE, but then I read again this issue discussion: Eryk Sun and me agree that ignorning ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE is a bad idea, it can be worse: silence a real bug. So I now agree to backport the fix from master to 3.7 and 3.8 branches. I prefer to leave 2.7 unchanged even if it's affected. I don't want to take the risk of introducing another regression in 2.7. Moreover, subprocess.Popen has a __del__() method. Python 2.7 handles reference cycles differently than Python 3: it doesn't implement finalizers (PEP 442). While Python 2.7 might be affected, it should be affected differently.

New changeset 1e2707d7e82aedf73c59772bc7aa228286323c3c by Victor Stinner (Miss Islington (bot)) in branch '3.7': bpo-37380: subprocess: don't use _active on win (GH-14360) (GH-15706) https://github.com/python/cpython/commit/1e2707d7e82aedf73c59772bc7aa228286323c3c

New changeset 4d1abedce9422473af2ac78047e55cde73208208 by Victor Stinner (Miss Islington (bot)) in branch '3.8': bpo-37380: subprocess: don't use _active on win (GH-14360) (GH-15707) https://github.com/python/cpython/commit/4d1abedce9422473af2ac78047e55cde73208208

Thanks Ruslan Kuprieiev for the bug report and the fix. Thanks Eryk Sun (as usual!) for the great analysis of this issue. Ok, the bug should now be fixed in 3.7, 3.8 and master branches. I chose to not fix Python 2.7: see my previous comment. See bpo-37410 for the follow-up: "[Windows] subprocess: close the handle when the process completes".

Steve Dower: "I triggered automatic backports to see how they go. Doesn't necessarily mean we'll merge them without looking more closely, but may as well check out what our automated tools suggest." Thanks, I merged the backports.

> When a Popen instance is finalized by the garbage collector, the > internal handle is also finalized and closed despite the instance > being put on the active list. This results in _cleanup throwing > because the handle can no longer be used. Thanks. I hadn't considered that. It can lead to unusual behavior like this when __del__ keeps an object alive. The object can't assume that referenced objects haven't already been finalized. All of the subsequently required instance methods should take this into account. For example, Popen._internal_poll could set the return code to -1 if self._handle.closed is true. That's at a higher level, and much more reasonable, than trying to handle ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE, which could mask bugs.
Hello, Is there a means to work around that bug for Python 3.6 ? It seems that the fix was only backported to 3.7, and we were not planning on dropping Python 3.6 support quite yet in our project.

Sadly, 3.6 no longer get bug fixes, only security fixes: https://devguide.python.org/#status-of-python-branches
Yes, I understand that. I was wondering if there was a workaround that we could use to not drop 3.6 support right away! On Fri, May 29, 2020, 19:29 STINNER Victor <report@bugs.python.org> wrote: > > STINNER Victor <vstinner@python.org> added the comment: > > Sadly, 3.6 no longer get bug fixes, only security fixes: > https://devguide.python.org/#status-of-python-branches > > ---------- > > _______________________________________ > Python tracker <report@bugs.python.org> > <https://bugs.python.org/issue37380> > _______________________________________ >

> import subprocess > subprocess._cleanup = lambda: None
+ msg370334
+ msg370328
+ msg370326
+ sylvain.corlay
messages:
+ msg370325
+ msg351261
+ msg351240
resolution: fixed
messages:
+ msg351238
stage: backport needed -> resolved
+ msg351237
+ msg351236
+ msg351235
versions:
+ Python 3.8, Python 3.9
+ msg351209
+ pull_request15361
+ pull_request15360
+ Chip Lynch
messages:
+ msg351205
+ invalid_handle.py
nosy:
+ emanuel
messages:
+ msg348231
+ msg347024
+ msg347019
+ msg347016
+ msg347006
+ msg346994
+ msg346985
+ msg346973
+ msg346889
+ msg346828
+ msg346827
+ msg346695
+ msg346638
+ msg346635
+ msg346606
+ msg346581
+ msg346578
+ msg346568
+ msg346470
+ pull_request14176
+ vstinner
messages:
+ msg346461
+ msg346343
+ msg346338
+ patch
stage: patch review
pull_requests:
+ pull_request14147
+ eryksun
messages:
+ msg346333
+ gregory.p.smith
Whenever you open your Windows 10 Computer and try to log into it, you might get an error message, “The Handle Is Invalid Windows.” This could be even frustrating when the computer you’re working on is brand new with Genuine windows. The Error message “The Handle Is Invalid Windows” generally occurs for Windows 10 users. Contrary to that, some users have claimed to get the error message While Using Windows Server 2008 as well. In this article, we will be doing an in-depth break down of this error message and know what exactly triggers this error. Many approaches to eradicate this error message will be discussed in this article.
What is The Handle Is Invalid Windows Error Problem?
If we do a background analysis of the error message “The Handle Is Invalid Windows,” we may get confused because the error could occur while doing anything. You may be printing a document, Logging into your Windows XP, working on a windows server, Windows 7 or Windows 10. Your whole work is interrupted, and you have no choice but to close the operation.
Causes of The Handle Is Invalid Windows Error Issue –
This Particular Error Message doesn’t get triggered by doing one task. Several causes could induce this error message. It’s a tragic error which not only hampers printing work but also doesn’t let installation go through. Few common reasons that could affect this error are listed below.
- An unfinished Update for your windows
- A virus attack on your computer
- Corrupted Citrix VDA
- Registry problem with your Windows 10
- Malware swarmed your computer
- Windows processes cannot duplicate non-pseudo handles from Process Environment Block (PEB32) processes.
- Incorrect credentials while trying to log in
- You don’t remember the right password
- Someone else locked your computer without telling you
Types of The Handle Is Invalid Windows Error Issue:
Now you might be struggling with “The Handle is Invalid Windows” because you’re not able to print in windows 10 while someone else is getting the error while trying to log into his windows computer. My point is, The error message could vary from person to person and so the circumstances where they see this error message. Here are some common types of problems associated with this error message.
- Microsoft Windows network the handle is invalid windows 10
- The handle is invalid windows 10 network share
- The handle is invalid windows XP
- The handle is invalid windows 7 shared folder
- The handle is invalid server 2016
- The handle is invalid windows 7 sharing
How to Fix & Solve The Handle Is Invalid Windows Error Issue
1. Update your Citrix VDA –
java.io.ioexception The Handle is Invalid Windows is a technical glitch which could occur while you’re working with Citrix VDA. The following Solution is only for those who face “The Handle Is Invalid Windows 7” while working on Citrix. Few of the Windows Updates are Incompatible with the software Critix. Especially the Citrix users who are currently on the VDA 7.6.300 version face this error.
What you could do to fix this Microsoft windows network The Handle Is Invalid Windows error message is to update your Citrix VDA to VDA 7.6.1000. If you’re using a higher variant of Critics such as the VDA V7.7, update it to a higher version v7.8. The Newer and Higher Version of Citrix already contains the Fix.
2. Restart the Computer –
Another Approach to tackle the error “The Handle Is Invalid Windows 10” is to restart the computer. Although this step might seem a little novice. It has reportedly worked for a lot of people having trouble with their computer. Now there are two ways to restart the computer. One of them is Hard Restart, and the other one is a cold restart.
(A). Hot Restart:
- To hot restart, your computer locate the start button on your screen
- Press the start key and click on shit down this computer
- If the computer is locked, you’ll quickly see the shutdown key below the password box.
- Shut down your computer and restart it
(B). Cold Restart:
- To Cold restart, your computer Press the power key for five seconds
- The system will go blank automatically without any message
- Turn on your computer
Repeat restarting your computer, and most probably your Windows The Handle Is Invalid printing error will mitigate.
3. Run a Full Scan of your Computer –
If the error message “Windows The Handle is Invalid server 2012” arises due to a virus attack malware intrusion of your windows computer, you can scan it. To examine the entire computer, you can use the free utility tool provided by Windows known as the Windows Defender. Here’s how you can do it following the most straightforward steps.
- Open the Windows Defender through the Search box
- Locate the Full Scan option
- This step usually takes 10-15 minutes
- It might take longer depending on the content on your computer
- Terminate all the bugs and viruses
- Restart your computer
4. Update Drivers of Computer –
Another possible reason behind “Windows The Handle is Invalid shared folder” error message is unfinished updates on the drivers, or not up to date versions of them. Update the drivers via device manager o your windows.
- Press Windows key and letter R at the same time
- Type Devmgmt.msc in the run box
- Press enter
- Expand the relevant Catagory
- Double click to open the General view
- Go to the Driver tab
- Update the drivers
- Click okÂ
- Done!
5. Boot in Safe Mode & Uninstall the Updates –
One more way to resolve the “The Handle is invalid Windows 7 network” error message is by booting your windows computer in a safe mode and uninstall the latest update you installed on the computer. The reason behind that is sometimes the update for windows triggers a patch for bugs and remove some of the critical files the patch consider as a virus. What uninstalling update does is it takes back your computer to a previous state and fixes the error.
- Search for System Configuration in the Search box
- A single click on System configuration
- Go to the Boot section
- Choose Safe mode from Boot option
- Click OK
- Restart your computer
- Search Updates in the search box
- Go to the History of Updates
- Uninstall the Latest update
6. Contact Local IT Technician –
Finally, If all of these steps proved to be of no use, The only choice we have is contacting local IT services. You can book a home visit or take your computer to the store and get your system repaired for minimum cost. So that you will get rid out of this, The Handle Is Invalid Windows XP Error.
*Note: If your computer is under warranty limit, Claim the free support instead of paying for it.
Conclusion:
In this walkthrough of the error, The Handle Is Invalid Windows. I gave you the five best solutions to fix this error. Hope you liked this article, to read more of such error topics, visit article gallery of techinpost.
Comment down below if you’ve trouble following these The Handle Is Invalid Windows steps. Have a nice day!