I upgraded new version over 0.14.2 I’ve compiled from source and I’am running with existing config and datadir but I get following:
$ bitcoin-cli getinfo
error code: -32601
error message:
Method not found
console shows:
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Bitcoin version v0.15.99.0-g09627b1dd41
2017-09-16 05:02:03 InitParameterInteraction: parameter interaction: -whitelistforcerelay=1 -> setting -whitelistrelay=1
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Assuming ancestors of block 0000000000000000003b9ce759c2a087d52abc4266f8f4ebd6d768b89defa50a have valid signatures.
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Setting nMinimumChainWork=000000000000000000000000000000000000000000723d3581fe1bd55373540a
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Using the 'sse4' SHA256 implementation
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Default data directory /home/lauri/.bitcoin
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Using data directory /media/lauri/Storage_2/blocks
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Using config file /media/lauri/Storage_2/blocks/bitcoin.conf
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Using at most 125 automatic connections (1024 file descriptors available)
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Using 16 MiB out of 32/2 requested for signature cache, able to store 524288 elements
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Using 16 MiB out of 32/2 requested for script execution cache, able to store 524288 elements
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Using 4 threads for script verification
2017-09-16 05:02:03 scheduler thread start
2017-09-16 05:02:03 HTTP: creating work queue of depth 16
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Config options rpcuser and rpcpassword will soon be deprecated. Locally-run instances may remove rpcuser to use cookie-based auth, or may be replaced with rpcauth. Please see share/rpcuser for rpcauth auth generation.
2017-09-16 05:02:03 HTTP: starting 4 worker threads
2017-09-16 05:02:03 init message: Verifying wallet(s)...
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Using BerkeleyDB version Berkeley DB 5.3.28: (September 9, 2013)
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Using wallet wallet.dat
2017-09-16 05:02:03 CDBEnv::Open: LogDir=/media/lauri/Storage_2/blocks/database ErrorFile=/media/lauri/Storage_2/blocks/db.log
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Cache configuration:
2017-09-16 05:02:03 * Using 2.0MiB for block index database
2017-09-16 05:02:03 * Using 8.0MiB for chain state database
2017-09-16 05:02:03 * Using 440.0MiB for in-memory UTXO set (plus up to 286.1MiB of unused mempool space)
2017-09-16 05:02:03 init message: Loading block index...
2017-09-16 05:02:03 Opening LevelDB in /media/lauri/Storage_2/blocks/blocks/index
2017-09-16 05:02:04 Opened LevelDB successfully
2017-09-16 05:02:04 Using obfuscation key for /media/lauri/Storage_2/blocks/blocks/index: 0000000000000000
2017-09-16 05:02:09 LoadBlockIndexDB: last block file = 1000
2017-09-16 05:02:09 LoadBlockIndexDB: last block file info: CBlockFileInfo(blocks=24, size=17425327, heights=485483...485506, time=2017-09-16...2017-09-16)
2017-09-16 05:02:09 Checking all blk files are present...
2017-09-16 05:02:10 LoadBlockIndexDB: transaction index disabled
2017-09-16 05:02:10 Opening LevelDB in /media/lauri/Storage_2/blocks/chainstate
2017-09-16 05:02:11 Opened LevelDB successfully
2017-09-16 05:02:11 Using obfuscation key for /media/lauri/Storage_2/blocks/chainstate: 8d8097229925b59c
2017-09-16 05:02:11 Loaded best chain: hashBestChain=000000000000000001115a1bd0b4909d2f5cf24f5b031a54b81a19d3c5d88333 height=485506 date=2017-09-16 04:44:56 progress=0.999987
2017-09-16 05:02:11 init message: Rewinding blocks...
2017-09-16 05:02:13 init message: Verifying blocks...
2017-09-16 05:02:13 Verifying last 6 blocks at level 3
2017-09-16 05:02:13 [0%]...[16%]...[33%]...[50%]...[66%]...[83%]...[99%]...[DONE].
2017-09-16 05:02:24 No coin database inconsistencies in last 7 blocks (7701 transactions)
2017-09-16 05:02:24 block index 20765ms
2017-09-16 05:02:24 init message: Loading wallet...
2017-09-16 05:02:24 nFileVersion = 159900
2017-09-16 05:02:24 Keys: 1002 plaintext, 0 encrypted, 1002 w/ metadata, 1002 total
2017-09-16 05:02:24 wallet 145ms
2017-09-16 05:02:24 setKeyPool.size() = 1000
2017-09-16 05:02:24 mapWallet.size() = 0
2017-09-16 05:02:24 mapAddressBook.size() = 1
2017-09-16 05:02:24 mapBlockIndex.size() = 485526
2017-09-16 05:02:24 nBestHeight = 485506
2017-09-16 05:02:24 torcontrol thread start
2017-09-16 05:02:24 AddLocal([2001:14ba:13ff:5000:225:22ff:fead:9768]:8333,1)
2017-09-16 05:02:24 Discover: IPv6 eth0: 2001:14ba:13ff:5000:225:22ff:fead:9768
2017-09-16 05:02:24 Bound to [::]:8333
2017-09-16 05:02:24 Bound to 0.0.0.0:8333
2017-09-16 05:02:24 init message: Loading P2P addresses...
2017-09-16 05:02:24 Leaving InitialBlockDownload (latching to false)
2017-09-16 05:02:24 Loaded 63857 addresses from peers.dat 268ms
2017-09-16 05:02:24 init message: Loading banlist...
2017-09-16 05:02:24 init message: Starting network threads...
2017-09-16 05:02:24 dnsseed thread start
2017-09-16 05:02:24 opencon thread start
2017-09-16 05:02:24 init message: Done loading
2017-09-16 05:02:24 net thread start
2017-09-16 05:02:24 msghand thread start
2017-09-16 05:02:24 addcon thread start
2017-09-16 05:02:25 receive version message: /Satoshi:0.14.0/: version 70015, blocks=485507, us=82.181.198.63:46502, peer=0
2017-09-16 05:02:26 connect() to 52.227.161.139:8333 failed after select(): Connection refused (111)
2017-09-16 05:02:29 Imported mempool transactions from disk: 2245 successes, 0 failed, 0 expired
2017-09-16 05:02:33 connect() to 196.213.185.226:8333 failed after select(): Connection refused (111)
2017-09-16 05:02:35 Loading addresses from DNS seeds (could take a while)
2017-09-16 05:02:38 234 addresses found from DNS seeds
2017-09-16 05:02:38 dnsseed thread exit
2017-09-16 05:02:39 receive version message: /Satoshi:0.14.0/: version 70015, blocks=485507, us=82.181.198.63:47170, peer=2
2017-09-16 05:02:40 UpdateTip: new best=000000000000000000843ba2466a4e786f54709431ec4f7de0f09cef1c4723d3 height=485507 version=0x20000000 log2_work=87.114157 tx=254843392 date='2017-09-16 05:01:07' progress=0.999999 cache=1.3MiB(9506txo) warning='6 of last 100 blocks have unexpected version'
2017-09-16 05:02:40 receive version message: /Satoshi:0.14.1/: version 70015, blocks=485507, us=[2001:14ba:13ff:5000:225:22ff:fead:9768]:35118, peer=3
2017-09-16 05:02:46 receive version message: /Satoshi:0.14.2/: version 70015, blocks=485507, us=82.181.198.63:56904, peer=4
2017-09-16 05:02:53 receive version message: /Satoshi:0.14.2/: version 70015, blocks=485507, us=82.181.198.63:54536, peer=5
2017-09-16 05:02:54 receive version message: /Satoshi:0.14.2/: version 70015, blocks=485507, us=82.181.198.63:34404, peer=6
2017-09-16 05:02:55 receive version message: /Satoshi:0.14.1/: version 70015, blocks=485507, us=82.181.198.63:45106, peer=7
2017-09-16 05:02:55 ProcessMessages(version, 111 bytes) FAILED peer=8
2017-09-16 05:03:05 receive version message: /Satoshi:0.11.2/: version 70002, blocks=462579, us=82.181.198.63:60964, peer=9
2017-09-16 05:03:05 receive version message: /Satoshi:0.14.2/: version 70015, blocks=485507, us=82.181.198.63:54864, peer=10
2017-09-16 05:03:36 UpdateTip: new best=0000000000000000006c766a6292034ee1356820020c60c6a9905ecb95a6f0d1 height=485508 version=0x20000000 log2_work=87.114191 tx=254843776 date='2017-09-16 05:03:19' progress=1.000000 cache=1.4MiB(10707txo) warning='6 of last 100 blocks have unexpected version'
2017-09-16 05:09:02 receive version message: /Satoshi:0.14.1/: version 70015, blocks=485508, us=82.181.198.63:50784, peer=11
2017-09-16 05:10:00 connect() to 116.236.206.50:8333 failed after select(): Connection refused (111)
2017-09-16 05:10:54 connect() to 24.252.46.85:8333 failed after select(): Connection refused (111)
2017-09-16 05:11:39 connect() to 114.97.187.229:8333 failed after select(): Connection refused (111)
2017-09-16 05:17:23 UpdateTip: new best=00000000000000000073fa81dd67b7d49aca2aff49ae4495c82fa45f5f1ea539 height=485509 version=0x20000000 log2_work=87.114225 tx=254845521 date='2017-09-16 05:17:03' progress=1.000000 cache=2.3MiB(17257txo) warning='6 of last 100 blocks have unexpected version'
2017-09-16 05:17:27 connect() to 182.224.136.80:8333 failed after select(): Connection refused (111)
2017-09-16 05:24:08 connect() to 91.60.10.17:8333 failed after select(): Connection refused (111)
2017-09-16 05:24:33 UpdateTip: new best=000000000000000000cc9f2d9098b4bee4a5fd594933673735608ca460db0bfd height=485510 version=0x20000000 log2_work=87.114259 tx=254846326 date='2017-09-16 05:24:06' progress=1.000000 cache=2.7MiB(20077txo) warning='6 of last 100 blocks have unexpected version'
2017-09-16 05:24:38 UpdateTip: new best=000000000000000000de2f5da71ec30c8c3dd658c852add32526b928ad60b240 height=485511 version=0x20000000 log2_work=87.114294 tx=254846430 date='2017-09-16 05:24:34' progress=1.000000 cache=2.7MiB(20314txo) warning='6 of last 100 blocks have unexpected version'
2017-09-16 05:29:58 receive version message: /Satoshi:0.14.1/: version 70015, blocks=485511, us=[2001:14ba:13ff:5000:225:22ff:fead:9768]:53314, peer=12
2017-09-16 05:33:56 receive version message: /Satoshi:0.14.2/: version 70015, blocks=485511, us=82.181.198.63:54276, peer=13
2017-09-16 05:36:14 UpdateTip: new best=0000000000000000004c8e92769a19482f7275d5a4bbfac5fde4f3c8e6d15d3d height=485512 version=0x20000000 log2_work=87.114328 tx=254848419 date='2017-09-16 05:35:56' progress=1.000000 cache=3.3MiB(25440txo) warning='6 of last 100 blocks have unexpected version'
2017-09-16 05:37:35 UpdateTip: new best=00000000000000000009019976bef4f66b9835160e141b6c363032c49843e146 height=485513 version=0x20000000 log2_work=87.114362 tx=254848585 date='2017-09-16 05:37:09' progress=1.000000 cache=3.4MiB(25985txo) warning='6 of last 100 blocks have unexpected version'
2017-09-16 05:43:50 receive version message: /Satoshi:0.14.2/: version 70015, blocks=485513, us=82.181.198.63:32926, peer=14
2017-09-16 05:43:56 connect() to 87.189.193.43:8333 failed after select(): No route to host (113)
2017-09-16 05:49:54 receive version message: /Satoshi:0.14.2/UASF-Segwit:1.0(BIP148)/: version 70015, blocks=485513, us=82.181.198.63:37018, peer=15
2017-09-16 05:51:06 connect() to 94.242.243.185:8333 failed after select(): Connection refused (111)
Machine specs:
- OS: MX-linux (debian)
- CPU: i5-2500K
- RAM: 8GB
- Disk size: enough
- Disk Type (HD/SDD): datadir = HD
Everything worked fine with 0.14.2
You are getting an error message (Specification for Fault Code Interoperability, version 20010516) from the XMLRPC endpoint you’re communicating with.
It is a defined error code:
-32601 ---> server error. requested method not found
The RPC method you requested was not found by the server. Contact the support of the service you consume to get a list of all available methods. If that method should be available, contact the support and discuss the issue with them.
You asked in comment:
Is there any way [to] verify which methods are available?
That depends on the service. XMLRPC on sourceforge has a suggestion of defined methods you can call to list information about the functions available:
XML-RPC Introspection
system.listMethodssystem.methodSignaturesystem.methodHelp
You can try if it works with your service, too. AFAIK those are common, I wrapped up a quick example, you find the full code below. See the output below the code as well.
$path = 'http://xmlrpc-c.sourceforge.net/api/sample.php';
printf("n XMLRPC Service Discoverynn for: '%s'nn", $path);
$discovery = new Discovery($path);
$methods = $discovery->getMethods();
printf(" Method Summary:n ===============n", count($methods));
foreach ($methods as $i => $method)
{
printf(" %'.-2d %sn", $i + 1, $method->getName());
}
printf("n Method Details (%d):n ===================n", count($methods));
foreach ($methods as $i => $method)
{
printf(" %'.-2d %sn", $i + 1, $method->getName());
printf("n %sn", $method);
printf("n%snn", preg_replace('/^/um', ' ', wordwrap($method->getHelp(), 46)));
}
Output:
XMLRPC Service Discovery
for: 'http://xmlrpc-c.sourceforge.net/api/sample.php'
Method Summary:
===============
1. debug.authInfo
2. sample.add
3. sample.sumAndDifference
4. system.listMethods
5. system.methodHelp
6. system.methodSignature
Method Details (6):
===================
1. debug.authInfo
<struct> debug.authInfo
Report any HTTP authentication in use
2. sample.add
<int> sample.add (<int>, <int>)
Add two numbers
3. sample.sumAndDifference
<struct> sample.sumAndDifference (<int>, <int>)
Add and subtract two numbers
4. system.listMethods
<array> system.listMethods (<string>)
This method lists all the methods that the
XML-RPC server knows how to dispatch
5. system.methodHelp
<string> system.methodHelp (<string>)
Returns help text if defined for the method
passed, otherwise returns an empty string
6. system.methodSignature
<array> system.methodSignature (<string>)
Returns an array of known signatures (an array
of arrays) for the method name passed. If no
signatures are known, returns a none-array
(test for type != array to detect missing
signature)
You can find the sourcecode here: XMLRPC Discovery Service
On macOS Mojave I have a full bitcoin node synced using bitcoind.
I want to get the public address of the default account (i.e. the empty string "").
So I run bitcoin-cli getaddressesbyaccount "" but I get:
error code: -32601
error message:
Method not found
Version of bitcoind is: Bitcoin Core Daemon version v0.18.0.0-g2472733a24a9364e4c6233ccd04166a26a68cc65
Copyright (C) 2009-2019 The Bitcoin Core developers
And of bitcoin-cli is: Bitcoin Core RPC client version v0.18.0.0-g2472733a24a9364e4c6233ccd04166a26a68cc65
What’s wrong?
asked Jul 8, 2019 at 10:16
The account API has been deprecated for a while, and was completely removed in Bitcoin Core 0.18.0.
You should be using the new mutliwallet API, or handling account based labelling externally.
answered Jul 8, 2019 at 11:19
Raghav SoodRaghav Sood
16.7k3 gold badges21 silver badges42 bronze badges
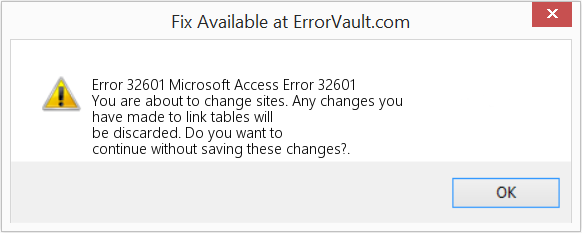
How to fix the Runtime Code 32601 Microsoft Access Error 32601
This article features error number Code 32601, commonly known as Microsoft Access Error 32601 described as You are about to change sites. Any changes you have made to link tables will be discarded. Do you want to continue without saving these changes?.
About Runtime Code 32601
Runtime Code 32601 happens when Microsoft Access fails or crashes whilst it’s running, hence its name. It doesn’t necessarily mean that the code was corrupt in some way, but just that it did not work during its run-time. This kind of error will appear as an annoying notification on your screen unless handled and corrected. Here are symptoms, causes and ways to troubleshoot the problem.
Definitions (Beta)
Here we list some definitions for the words contained in your error, in an attempt to help you understand your problem. This is a work in progress, so sometimes we might define the word incorrectly, so feel free to skip this section!
- Access — DO NOT USE this tag for Microsoft Access, use [ms-access] instead
- Continue — A language construct typically used to bypass the rest of a loop and return to the beginning for the next iteration.
- Access — Microsoft Access, also known as Microsoft Office Access, is a database management system from Microsoft that commonly combines the relational Microsoft JetACE Database Engine with a graphical user interface and software-development tools
- Saving — To store data in a computer or on a storage device.
- Microsoft access — Microsoft Access, also known as Microsoft Office Access, is a database management system from Microsoft that commonly combines the relational Microsoft JetACE Database Engine with a graphical user interface and software-development tools
- Link — A hyperlink is a reference to a document or a section that can be followed for retrieval using a navigation system that allows selecting emphasized content within an originating document.
- Tables — DO NOT USE THIS TAG; it is ambiguous
Symptoms of Code 32601 — Microsoft Access Error 32601
Runtime errors happen without warning. The error message can come up the screen anytime Microsoft Access is run. In fact, the error message or some other dialogue box can come up again and again if not addressed early on.
There may be instances of files deletion or new files appearing. Though this symptom is largely due to virus infection, it can be attributed as a symptom for runtime error, as virus infection is one of the causes for runtime error. User may also experience a sudden drop in internet connection speed, yet again, this is not always the case.
(For illustrative purposes only)
Causes of Microsoft Access Error 32601 — Code 32601
During software design, programmers code anticipating the occurrence of errors. However, there are no perfect designs, as errors can be expected even with the best program design. Glitches can happen during runtime if a certain error is not experienced and addressed during design and testing.
Runtime errors are generally caused by incompatible programs running at the same time. It may also occur because of memory problem, a bad graphics driver or virus infection. Whatever the case may be, the problem must be resolved immediately to avoid further problems. Here are ways to remedy the error.
Repair Methods
Runtime errors may be annoying and persistent, but it is not totally hopeless, repairs are available. Here are ways to do it.
If a repair method works for you, please click the upvote button to the left of the answer, this will let other users know which repair method is currently working the best.
Please note: Neither ErrorVault.com nor it’s writers claim responsibility for the results of the actions taken from employing any of the repair methods listed on this page — you complete these steps at your own risk.
Method 1 — Close Conflicting Programs
When you get a runtime error, keep in mind that it is happening due to programs that are conflicting with each other. The first thing you can do to resolve the problem is to stop these conflicting programs.
- Open Task Manager by clicking Ctrl-Alt-Del at the same time. This will let you see the list of programs currently running.
- Go to the Processes tab and stop the programs one by one by highlighting each program and clicking the End Process buttom.
- You will need to observe if the error message will reoccur each time you stop a process.
- Once you get to identify which program is causing the error, you may go ahead with the next troubleshooting step, reinstalling the application.
Method 2 — Update / Reinstall Conflicting Programs
Using Control Panel
- For Windows 7, click the Start Button, then click Control panel, then Uninstall a program
- For Windows 8, click the Start Button, then scroll down and click More Settings, then click Control panel > Uninstall a program.
- For Windows 10, just type Control Panel on the search box and click the result, then click Uninstall a program
- Once inside Programs and Features, click the problem program and click Update or Uninstall.
- If you chose to update, then you will just need to follow the prompt to complete the process, however if you chose to Uninstall, you will follow the prompt to uninstall and then re-download or use the application’s installation disk to reinstall the program.
Using Other Methods
- For Windows 7, you may find the list of all installed programs when you click Start and scroll your mouse over the list that appear on the tab. You may see on that list utility for uninstalling the program. You may go ahead and uninstall using utilities available in this tab.
- For Windows 10, you may click Start, then Settings, then choose Apps.
- Scroll down to see the list of Apps and features installed in your computer.
- Click the Program which is causing the runtime error, then you may choose to uninstall or click Advanced options to reset the application.
Method 3 — Update your Virus protection program or download and install the latest Windows Update
Virus infection causing runtime error on your computer must immediately be prevented, quarantined or deleted. Make sure you update your virus program and run a thorough scan of the computer or, run Windows update so you can get the latest virus definition and fix.
Method 4 — Re-install Runtime Libraries
You might be getting the error because of an update, like the MS Visual C++ package which might not be installed properly or completely. What you can do then is to uninstall the current package and install a fresh copy.
- Uninstall the package by going to Programs and Features, find and highlight the Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable Package.
- Click Uninstall on top of the list, and when it is done, reboot your computer.
- Download the latest redistributable package from Microsoft then install it.
Method 5 — Run Disk Cleanup
You might also be experiencing runtime error because of a very low free space on your computer.
- You should consider backing up your files and freeing up space on your hard drive
- You can also clear your cache and reboot your computer
- You can also run Disk Cleanup, open your explorer window and right click your main directory (this is usually C: )
- Click Properties and then click Disk Cleanup
Method 6 — Reinstall Your Graphics Driver
If the error is related to a bad graphics driver, then you may do the following:
- Open your Device Manager, locate the graphics driver
- Right click the video card driver then click uninstall, then restart your computer
Method 7 — IE related Runtime Error
If the error you are getting is related to the Internet Explorer, you may do the following:
- Reset your browser.
- For Windows 7, you may click Start, go to Control Panel, then click Internet Options on the left side. Then you can click Advanced tab then click the Reset button.
- For Windows 8 and 10, you may click search and type Internet Options, then go to Advanced tab and click Reset.
- Disable script debugging and error notifications.
- On the same Internet Options window, you may go to Advanced tab and look for Disable script debugging
- Put a check mark on the radio button
- At the same time, uncheck the «Display a Notification about every Script Error» item and then click Apply and OK, then reboot your computer.
If these quick fixes do not work, you can always backup files and run repair reinstall on your computer. However, you can do that later when the solutions listed here did not do the job.
Other languages:
Wie beheben Fehler 32601 (Microsoft Access-Fehler 32601) — Sie sind dabei, die Site zu wechseln. Alle Änderungen, die Sie an Verknüpfungstabellen vorgenommen haben, werden verworfen. Möchten Sie fortfahren, ohne diese Änderungen zu speichern?.
Come fissare Errore 32601 (Errore di Microsoft Access 32601) — Stai per cambiare sito. Eventuali modifiche apportate alle tabelle di collegamento verranno eliminate. Vuoi continuare senza salvare queste modifiche?.
Hoe maak je Fout 32601 (Microsoft Access-fout 32601) — U staat op het punt van site te veranderen. Alle wijzigingen die u heeft aangebracht om tabellen te koppelen, worden genegeerd. Wilt u doorgaan zonder deze wijzigingen op te slaan?.
Comment réparer Erreur 32601 (Erreur Microsoft Access 32601) — Vous êtes sur le point de changer de site. Toutes les modifications que vous avez apportées aux tables de liaison seront supprimées. Voulez-vous continuer sans enregistrer ces modifications ?.
어떻게 고치는 지 오류 32601 (Microsoft 액세스 오류 32601) — 사이트를 변경하려고 합니다. 테이블 연결에 대한 변경 사항은 모두 삭제됩니다. 이 변경 사항을 저장하지 않고 계속하시겠습니까?
Como corrigir o Erro 32601 (Erro 32601 do Microsoft Access) — Você está prestes a mudar de site. Todas as alterações feitas para vincular as tabelas serão descartadas. Deseja continuar sem salvar essas alterações ?.
Hur man åtgärdar Fel 32601 (Microsoft Access-fel 32601) — Du håller på att byta webbplats. Alla ändringar du har gjort i länktabeller kommer att kasseras. Vill du fortsätta utan att spara dessa ändringar ?.
Как исправить Ошибка 32601 (Ошибка Microsoft Access 32601) — Вы собираетесь сменить сайт. Любые изменения, внесенные вами для связывания таблиц, будут отменены. Вы хотите продолжить без сохранения этих изменений ?.
Jak naprawić Błąd 32601 (Błąd Microsoft Access 32601) — Zamierzasz zmienić witryny. Wszelkie zmiany wprowadzone w tabelach łączących zostaną odrzucone. Czy chcesz kontynuować bez zapisywania tych zmian?.
Cómo arreglar Error 32601 (Error de Microsoft Access 32601) — Estás a punto de cambiar de sitio. Se descartarán todos los cambios que haya realizado en las tablas de enlaces. ¿Quieres continuar sin guardar estos cambios ?.
About The Author: Phil Hart has been a Microsoft Community Contributor since 2010. With a current point score over 100,000, they’ve contributed more than 3000 answers in the Microsoft Support forums and have created almost 200 new help articles in the Technet Wiki.
Follow Us:
This repair tool can fix common computer problems such as blue screens, crashes and freezes, missing DLL files, as well as repair malware/virus damage and more by replacing damaged and missing system files.
STEP 1:
Click Here to Download and install the Windows repair tool.
STEP 2:
Click on Start Scan and let it analyze your device.
STEP 3:
Click on Repair All to fix all of the issues it detected.
DOWNLOAD NOW
Compatibility
Requirements
1 Ghz CPU, 512 MB RAM, 40 GB HDD
This download offers unlimited scans of your Windows PC for free. Full system repairs start at $19.95.
Article ID: ACX06723EN
Applies To: Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows XP, Windows 2000
Speed Up Tip #80
Turning off Unnecessary Windows Features:
Some of the bundled features that came with Windows are not really being used by most users. To free up some needed extra power to speed up your PC, disabling or uninstalling these features can be the best option to take. In the Control Panel, you can turn off services like Windows Meeting Space, DFS replication service, Media Features, Remote Differential Compression and a whole lot more.
Click Here for another way to speed up your Windows PC
Microsoft & Windows® logos are registered trademarks of Microsoft. Disclaimer: ErrorVault.com is not affiliated with Microsoft, nor does it claim such affiliation. This page may contain definitions from https://stackoverflow.com/tags under the CC-BY-SA license. The information on this page is provided for informational purposes only. © Copyright 2018
-
[Проблемы с выводами] Bibox Russia — открытие русскоговорящего комьюнити
Добрый день. Я являюсь официальным представителем комьюнити Bibox в России. https://www.bibox.com/
Присоединяйся к нашему сообществу телеграм и выигрывай токены BIX за общение: http://teleg.run/Bibox_rus
Все новости по Bibox на русском языке размещаются на следующих ресурсах:
Telegram channel: https://teleg.run/Bibox_rus_news
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/groups/bibox.russia/
Yandex: zen.yandex.ru/id/5dba0d95fe289100b23b8363
Vkontakte: https://vk.com/bibox_russia27 Nov 2019, 22:21
в Биржи криптовалют
-
-
Helber
-
7 Feb 2023, 14:30
-
-
Бельгийский депутат: «Эксперимент с получением зарплаты в BTC оказался успешным»
Член бельгийского парламента Кристоф де Бёкелаер, в течение года получавший зарплату в BTC, назвал свой эксперимент удачным, так как он повысил осведомленность местных законодателей о криптоактивах.
В конце января 2022 года Кристоф де Бёкелаер (Christophe De Beukelaer), представляющий партию «Гуманистический демократический центр» (CDH), стал первым европейским политиком, который согласился получать заработную плату в биткоинах. Он привел в пример американских мэров, работающих над тем, что10 Jan 2023, 08:28
в Новости криптовалют
-
-
News Bot
-
10 Jan 2023, 08:28
-
-
Банк Англии: криптовалюты следует регулировать до того, как возникнут систематические проблемы
Заместитель управляющего Банка Англии заявил, что криптоиндустрия очень быстро интегрируется в традиционные финансы, а потому должна тщательно регулироваться для защиты розничных инвесторов и финансовой системы в целом.
Джон Канлифф (Jon Cunliffe) назвал криптоиндустрию «казино» и заявил, что британский ЦБ активно рассматривает варианты регулирования отрасли. По словам чиновника, физические лица должны иметь возможность безопасно торговать цифровыми активами, как они делают это на традицио23 Dec 2022, 12:22
в Новости криптовалют
-
-
News Bot
-
23 Dec 2022, 12:22
-
-
PoS: проблемы и перспективы. Часть Вторая: Атаки
Одна из главных задач статьи – детализация первого
материала с помощью как конкретных примеров, так и теоретически синтезированных векторов атак.Еще одна задача: доказательство на основе простого неравенства Profit(Attack) >> Costs(Attack) того факта, что современное PoS-семейство построено на посыле работы в 1) доверенной среде, где 2) стоимость взлома всегда меньше полученной от взлома прибыли, тогда как Web 3.0 – сплошь среда не доверенная, а взлом может иметь деструктивные нача
18 Dec 2022, 07:10
в Новости криптовалют
-
-
News Bot
-
18 Dec 2022, 07:10
-
-
Проблемы с выводом эфира с кошелька ONTO
Не могу вывести 0.042 ETH с ONTO как на любой другой холодный кошелек, так и на биржу (пробовала разные способы как Basic, так и Custom).
Проблема выглядит так: выбираю тип basic или custom транзакции, потом ввожу пароль для подтверждения, далее следует загрузка цепочки, где есть слова по типу «Invalid JSON RPC response» и «обнаружена проблема при проверке сертификата»
В Лаборатории Касперского поменяла в Настройках сети на «не проверять защищенные соединения», громоздкая выкладка убр
22 Oct 2022, 17:43
в Общий
-
-
Helber
-
22 Oct 2022, 17:48
-
Я обнаружил, что исходная проблема:
Execution failed for task ‘:app:processDebugManifest’. [ +5 ms] >
Manifest merger failed : Attribute
meta-data#android.support.VERSION@value value=(25.4.0) from
[com.android.support:appcompat-v7:25.4.0] AndroidManifest.xml:28:13-35
[ +23 ms] is also present at [com.android.support:support-v4:26.1.0]
AndroidManifest.xml:28:13-35 value=(26.1.0). [ +8 ms] Suggestion: add
‘tools:replace = «android:value»‘ to element at
AndroidManifest.xml:26:9-28:38 to override.
Возможно, это связано с зависимостями старых пакетов firebase.
Мои первоначальные зависимости pubspec.yaml выглядели примерно так:
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
cupertino_icons: ^0.1.0
contact_picker: ^0.0.2
connectivity: ^0.3.0
image_picker: 0.1.1
google_sign_in: 0.3.1
firebase_analytics: 0.0.4
firebase_auth: 0.2.0
firebase_database: 0.0.1
firebase_storage: 0.0.5
firebase_messaging: 0.2.5
Если я обновлю pubspec.yaml, как показано ниже:
cupertino_icons: ^0.1.0
contact_picker: ^0.0.2
connectivity: ^0.3.0
image_picker: ^0.4.1
google_sign_in: ^3.0.3
firebase_analytics: ^0.3.3
firebase_auth: ^0.5.7
firebase_database: ^0.4.6
firebase_storage: ^0.3.3
firebase_messaging: ^0.2.5
В первую очередь нет Manifest merger failed, поэтому никаких изменений в файле build.gradle не требуется.
Я не уверен, как Manifest merger failed связан с другими пакетами firebase, однако после этого решения сборка работает нормально, и ошибок Manifest merger failed или Error -32601 received from application: Method not found нет.
| Номер ошибки: | Ошибка 32601 | |
| Название ошибки: | Microsoft Access Error 32601 | |
| Описание ошибки: | You are about to change sites. Any changes you have made to link tables will be discarded. Do you want to continue without saving these changes?. | |
| Разработчик: | Microsoft Corporation | |
| Программное обеспечение: | Microsoft Access | |
| Относится к: | Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10, 11 |
Объяснение «Microsoft Access Error 32601»
«Microsoft Access Error 32601» обычно является ошибкой (ошибкой), обнаруженных во время выполнения. Чтобы убедиться, что функциональность и операции работают в пригодном для использования состоянии, разработчики программного обеспечения, такие как Microsoft Corporation, выполняют отладку перед выпусками программного обеспечения. К сожалению, инженеры являются людьми и часто могут делать ошибки во время тестирования, отсутствует ошибка 32601.
Пользователи Microsoft Access могут столкнуться с сообщением об ошибке после выполнения программы, например «You are about to change sites. Any changes you have made to link tables will be discarded. Do you want to continue without saving these changes?.». Таким образом, конечные пользователи предупреждают поставщиков о наличии ошибок 32601 проблем, предоставляя информацию разработчику. Microsoft Corporation вернется к коду и исправит его, а затем сделает обновление доступным для загрузки. Эта ситуация происходит из-за обновления программного обеспечения Microsoft Access является одним из решений ошибок 32601 ошибок и других проблем.
Что вызывает ошибку 32601 во время выполнения?
Сбой во время выполнения Microsoft Access, как правило, когда вы столкнетесь с «Microsoft Access Error 32601» в качестве ошибки во время выполнения. Проанализируем некоторые из наиболее распространенных причин ошибок ошибки 32601 во время выполнения:
Ошибка 32601 Crash — это распространенная ошибка 32601 во время выполнения ошибки, которая приводит к полному завершению работы программы. Эти ошибки обычно возникают, когда входы Microsoft Access не могут быть правильно обработаны, или они смущены тем, что должно быть выведено.
Утечка памяти «Microsoft Access Error 32601» — Когда Microsoft Access обнаруживает утечку памяти, операционная система постепенно работает медленно, поскольку она истощает системные ресурсы. Это может быть вызвано неправильной конфигурацией программного обеспечения Microsoft Corporation или когда одна команда запускает цикл, который не может быть завершен.
Ошибка 32601 Logic Error — Логические ошибки проявляются, когда пользователь вводит правильные данные, но устройство дает неверный результат. Обычные причины этой проблемы связаны с ошибками в обработке данных.
Основные причины Microsoft Corporation ошибок, связанных с файлом Microsoft Access Error 32601, включают отсутствие или повреждение файла, или, в некоторых случаях, заражение связанного Microsoft Access вредоносным ПО в прошлом или настоящем. Как правило, любую проблему, связанную с файлом Microsoft Corporation, можно решить посредством замены файла на новую копию. Если ошибка Microsoft Access Error 32601 возникла в результате его удаления по причине заражения вредоносным ПО, мы рекомендуем запустить сканирование реестра, чтобы очистить все недействительные ссылки на пути к файлам, созданные вредоносной программой.
Классические проблемы Microsoft Access Error 32601
Частичный список ошибок Microsoft Access Error 32601 Microsoft Access:
- «Ошибка программного обеспечения Microsoft Access Error 32601. «
- «Ошибка программного обеспечения Win32: Microsoft Access Error 32601»
- «Извините за неудобства — Microsoft Access Error 32601 имеет проблему. «
- «К сожалению, мы не можем найти Microsoft Access Error 32601. «
- «Microsoft Access Error 32601 не найден.»
- «Ошибка запуска программы: Microsoft Access Error 32601.»
- «Не удается запустить Microsoft Access Error 32601. «
- «Отказ Microsoft Access Error 32601.»
- «Ошибка пути программного обеспечения: Microsoft Access Error 32601. «
Проблемы Microsoft Access Error 32601 с участием Microsoft Accesss возникают во время установки, при запуске или завершении работы программного обеспечения, связанного с Microsoft Access Error 32601, или во время процесса установки Windows. Документирование проблем Microsoft Access Error 32601 в Microsoft Access является ключевым для определения причины проблем с электронной Windows и сообщения о них в Microsoft Corporation.
Причины ошибок в файле Microsoft Access Error 32601
Проблемы Microsoft Access и Microsoft Access Error 32601 возникают из отсутствующих или поврежденных файлов, недействительных записей реестра Windows и вредоносных инфекций.
В частности, проблемы с Microsoft Access Error 32601, вызванные:
- Недопустимая (поврежденная) запись реестра Microsoft Access Error 32601.
- Вредоносные программы заразили Microsoft Access Error 32601, создавая повреждение.
- Microsoft Access Error 32601 ошибочно удален или злонамеренно программным обеспечением, не связанным с приложением Microsoft Access.
- Другое программное обеспечение, конфликтующее с Microsoft Access, Microsoft Access Error 32601 или общими ссылками.
- Microsoft Access/Microsoft Access Error 32601 поврежден от неполной загрузки или установки.
Продукт Solvusoft
Загрузка
WinThruster 2022 — Проверьте свой компьютер на наличие ошибок.
Совместима с Windows 2000, XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10 и 11
Установить необязательные продукты — WinThruster (Solvusoft) | Лицензия | Политика защиты личных сведений | Условия | Удаление
Привет, Хабр! Меня зовут Юра Кучанов @kuchanov, работаю Android разработчиком в Garage Eight и сегодня хочу рассказать о том, как мы делали Retrofit-подобную библиотеку для JSON-RPC протокола. Началось всё с того, что нам потребовалось для общения сервера и Android приложения использовать протокол JSON-RPC. Что значит “потребовалось”? Если кратко – бэкендеры предложили, а сильных аргументов против, в сущности, не нашлось =) Возможно, тут сработала, например, вот эта статья с хабра про выбор между REST и JSON-RPC. В итоге я пошёл искать библиотеки в сети и… И обнаружил, что готовые решения не подходят (так как там, конечно же, есть хотя бы один фатальный недостаток). В итоге сделал свою библиотеку в стиле Retrofit. Ниже расскажу, почему не подошли готовые решения, как реализовал своё через рефлексию и как копался в исходниках Retrofit и OkHttp для реализации нужного нам функционала.
Почему JSON-RPC и своя библиотека вместо стандартного REST API через Retrofit
Если вам удобнее видео формат, то вот тут есть запись с выступления на Mobius, а в тексте будет чуть больше подробностей, плюс ссылка на исходники.
Перед нами стояла задача – запустить с нуля новый продукт. То есть у нас своего рода стартап в рамках продуктовой компании. И свободы нам дали много – можно пробовать разное (в пределах разумного, конечно). На этапе выбора стэка технологий командой (я и Go-шник Илья) обсуждали несколько вариантов клиент-серверного общения и остановились на JSON-RPC протоколе. Он используется в основном продукте, также для бэкенда на Go в компании уже была своя проверенная библиотека и имелась в виду возможность в будущем перейти на реализацию от Google – gRPC. Однако, поспрашивав коллег по андроиду (тех, что основной продукт пилят) и изучив исходники оного, я выяснил, что клиент для JSON-RPC активно используется только на FrontEnd, а для андроида никаких решений в компании нет – там всё по привычному – REST API через Retrofit.
В итоге пошёл я в интернет смотреть, что же это за протокол такой. Выяснил следующее: JSON-RPC – это в первую очередь простой протокол. Он не указывает, какой тип транспорта вам использовать и не заставляет соблюдать множество сложных правил, число которых растёт год от года вместе с возможными интерпретациями этих правил. По ссылке вы можете найти исчерпывающее описание протокола. Оно крайне лаконичное, с последним обновлением в 2013 году. А вот ещё более упрощённая версия описания, нужная для понимания дальнейшего рассказа:
-
Клиент должен отправить на сервер JSON со следующими данными:
-
jsonrpc – версия протокола. Мы, конечно, используем вторую, самую свежую версию, засим отправляем всегда строчку «2.0» в качестве значения;
-
method – имя метода. Тут придётся решать одну из сложнейших вещей в нашей профессии – самим придумывать имена. Например: «user»;
-
params – параметры метода. Можно просто массив с ними, но мы будем слать JSON с полями – так нагляднее, ибо у параметров есть имена;
-
id – идентификатор запроса. Может быть строкой, целым числом, null-ом. Мы будем использовать целые числа. Значение должно задаваться на клиенте, сервер в ответе пришлёт такой же ID.
-
-
Сервер обязательно ответит JSON-ом такого вида:
-
jsonrpc – версия протокола. Неудивительно, что приходить будет «2.0» в качестве значения;
-
id – идентификатор запроса. Значение должно быть точно такое же, какое было в запросе от клиента;
-
result – собственно результат вызова метода. Если запрос успешен, тут точно что-то будет. Что именно – зависит от метода. Например, такой JSON для метода user: { «id»:1, «name»: «Ivan» }. Или массив объектов. Или просто строка, число etc. А может — вообще придёт пустой объект в виде {};
-
error – исчерпывающая информация об ошибке. Если что-то пошло не так, то в ответе сервера будет это поле вместо поля result. Вот что будет и может быть внутри:
-
code – номер ошибки. Может быть только целым числом. Например: 42 – так мы поймём, например, что юзера с запрошенным ID не существует. Какой код за что отвечает, каждый решает сам, в протоколе это не прописано;
-
message – текст ошибки. Просто строка с описанием ошибки; Именно тут мы будем видеть всякие “Internal error” когда на бэке какой-то микросервис не задеплоится и всё сломается. Если же всё хорошо – тут будет человеко читаемый текст ошибки
-
data – опциональное поле с дополнительными данными. Сюда можете положить всё что угодно: более подробное описание ошибки, какое-то число или структуру для множества вложенных ошибок.
-
-
Собственно, вот и всё, что нам нужно знать для того, чтобы его использовать. Вот примеры запроса/ответа:
Успешный запрос:
--> {"jsonrpc": "2.0", "method": "subtract", "params": {"first": 42, "second": 23}, "id": 1}
<-- {"jsonrpc": "2.0", "result": 19, "id": 1}Неуспешный запрос к несуществующему методу:
--> {"jsonrpc": "2.0", "method": "foobar", "id": "2"}
<-- {"jsonrpc": "2.0", "error": {"code": -32601, "message": "Method not found"}, "id": "2"}Что насчёт готовых реализаций?
Они, конечно, есть. Самая популярная и известная – gRPC от Google (не совсем JSON-RPC, скорее просто RPC, но мы планируем его потом использовать. На бэке — уже используем). Там реализации на нескольких языках и для сервера, и для клиента + всякие оптимизации типа proto-файлов с описанием всех запросов и с ответами к ним, по которым будет генерироваться код сервера и клиента. Однако это стало одной из причин для поиска другого, более простого решения. Мы хотели как можно быстрее начать писать код и не завязываться в самом начале на решение с кодогенерацией и сервера, и клиента, чтобы не мешать друг другу. Нашим BackEnd-ерам было проще: в компании уже была своя реализация протокола для Go, её они и взяли (через несколько месяцев, правда, к нам пришёл Go-шник Слава и таки затащил gRPC на бэк. Видимо, в будущем буду писать статью про то, как со своего велосипеда для JSON-RPC на gRPC под Android переезжали. Пока что у нас на нём только микросервисы меж собой общаются. А клиенты c бэком — через JSON-RPC). А меня отправили спрашивать коллег из основного продукта, где реализация под андроид. А её не было. Оказалось, что протокол успели поддержать на FrontEnd, а на Android оно почти не использовалось и отдельного решения никто не делал.
Но это не беда – поищем в интернете. И найдём несколько реализаций. Вот, например, очень пригодившаяся мне статья – A simple Retrofit-style JSON-RPC client. Там почти всё что нужно уже сделано и описано, но самой библиотеки я не нашёл. Да и там не хватало пары вещей типа возможности выбора либы для JSON и использовалась RxJava, а мы решили на модных корутинах писать. Ещё есть jsonrpc4j (с Jackson внутри и заточенную на использование на сервере на Spring) и Simple JSON-RPC (тоже Jackson внутри). В общем, у каждой хотя бы один недостаток – использованы неподходящие библиотеки, например Jackson для парсинга JSON и RxJava, либо библиотека была в т. ч. и для серверной части, что нам просто не нужно. Изучая варианты, я пришёл к выводу, что могу и сам реализовать всё, что нам нужно, подглядывая в исходники других библиотек.
Так как в сети есть примеры того, что нужно и что явно работает, то решено было делать так:
-
Смотрим в Retrofit, как из метода интерфейса, окружённого аннотациями, получается сетевой запрос.
-
Смотрим в найденные ранее библиотеки для JSON-RPC в поисках вдохновения для парсинга JSON и как они делают то, что хотим мы.
-
В OkHttp подглядим реализацию Interceptor: они нам точно пригодятся.
Приступим с самого начала. А там – рефлексия. Что же, придётся разбираться.
Рефлексия в Retrofit
Вспоминаем, что такое рефлексия. Рефлексия (от позднелат. reflexio – обращение назад) – это механизм исследования данных о программе во время её выполнения. Рефлексия позволяет исследовать информацию о полях, методах и конструкторах классов. Если заглянуть в исходники Retrofit, то обнаружится, что именно с помощью рефлексии осуществляется вся магия (хотя я почему-то когда-то давно думал, что там кодогенерация). Вспомним, как выглядит использование Retorfit:
-
Создаём интерфейс, описывающий запросы в сеть. Например UserApi. Методы и аргументы методов помечаем аннотациями.
-
Создаём экземпляр класса, делающего запросы в сеть – OkHttpClient.
-
С его помощью делаем экземпляр класса, создающего реализации интерфейса из п.1.
Как же, собственно, создаётся экземпляр класса, реализующего наш интерфейс? Для этого используется класс java.lang.reflect.Proxy. Он позволяет динамически, в runtime, создавать экземпляры классов, реализующих один или несколько интерфейсов. Для создания экземпляра Proxy требуется передать ему реализацию интерфейса java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler, который предельно прост – всего один метод invoke. Именно в этом методе и происходит вся магия: он имеет всю информацию о вызываемом методе проксируемого интерфейса (имя, тип возвращаемого значения, аннотации etc) и все его аргументы, т. е. всё, что нужно, чтобы совершить те действия, которые нам требуются.
Таким образом, когда мы используем Retrofit, мы делегируем выполнение метода Proxy классу, а он направляет его InvocationHandler-у. Тот, наконец, передаёт вызов классу, который по значениям из аннотаций над методом, его аргументами, параметрами самого Retrofit и с помощью переданного ранее OkHttpClient сделает сетевой запрос.
Реализуем JSON-RPC
Вот мы и добрались до написания своего кода. Сделаем следующее:
-
Интерфейс JsonRpcClient с методом отправки запроса – принимаем JsonRpcRequest возвращаем JsonRpcResponse.
-
Реализуем интерфейс. Для реализации нам понадобятся:
-
адрес сервера;
-
OkHttpClient;
-
сериализатор параметров запроса;
-
десериализатор ответа сервера.
-
-
Реализуем InvocationHandler, а в нём:
-
сформируем JsonRpcRequest по информации, полученной с помощью рефлексии из вызываемого метода;
-
осуществим сетевой вызов с помощью JsonRpcClient;
-
десериализуем и вернём требуемые данные в случае успеха и прокинем ошибку в случае неудачи.
-
-
Соединяем всё вместе.
-
JsonRpcClient и описание JSON запроса и ответа
data class JsonRpcRequest(
val id: Long,
val method: String,
val params: Map<String, Any?> = emptyMap(),
val jsonrpc: String = "2.0"
)
data class JsonRpcError(
val message: String,
val code: Int,
val data: Any?
)
data class JsonRpcResponse(
val id: Long,
val result: Any?,
val error: JsonRpcError?
)
interface JsonRpcClient {
fun call(jsonRpcRequest: JsonRpcRequest): JsonRpcResponse
}-
JsonRpcClientImpl — делаем сетевой запрос, добавляем описания возможных ошибок и объявляем интерфейсы для сериализации/десериализации JSON
interface RequestConverter {
fun convert(request: JsonRpcRequest): String
}
interface ResponseParser {
fun parse(data: ByteArray): JsonRpcResponse
}
class NetworkRequestException(
override val message: String?,
override val cause: Throwable
) : RuntimeException(message, cause)
class TransportException(
val httpCode: Int,
val response: Response,
override val message: String?,
override val cause: Throwable? = null
) : RuntimeException(message, cause)
data class JsonRpcException(
override val message: String,
val code: Int,
val data: Any?
) : RuntimeException(message)
class JsonRpcClientImpl(
private val baseUrl: String,
private val okHttpClient: OkHttpClient,
private val requestConverter: RequestConverter,
private val responseParser: ResponseParser
) : JsonRpcClient {
override fun call(jsonRpcRequest: JsonRpcRequest): JsonRpcResponse {
val requestBody = requestConverter.convert(jsonRpcRequest).toByteArray().toRequestBody()
val request = Request.Builder()
.post(requestBody)
.url(baseUrl)
.build()
val response = try {
okHttpClient.newCall(request).execute()
} catch (e: Exception) {
throw NetworkRequestException(
message = "Network error:
cause = e
)
}
return if (response.isSuccessful) {
response.body?.let { responseParser.parse(it.bytes()) }
?: throw IllegalStateException("Response body is null")
} else {
throw TransportException(
httpCode = response.code,
message = "HTTP ${response.code}. ${response.message}",
response = response,
)
}
}
}-
Реализуем InvocationHandler. Чтобы получать информацию из аннотаций, не забываем аннотацию объявить. А также добавим единый источник значений для параметра ID запроса:
annotation class JsonRpc(val value: String)
val requestId = AtomicLong(0)
private fun <T> createInvocationHandler(
service: Class<T>,
client: JsonRpcClient,
resultParser: ResultParser,
): InvocationHandler {
return object : InvocationHandler {
override fun invoke(proxy: Any, method: Method, args: Array<Any?>?): Any {
val methodAnnotation =
method.getAnnotation(JsonRpc::class.java)
?: throw IllegalStateException("Method should be annotated with JsonRpc annotation")
val id = requestId.incrementAndGet()
val methodName = methodAnnotation.value
val parameters = method.jsonRpcParameters(args, service)
val request = JsonRpcRequest(id, methodName, parameters)
val response = clinet.call(request)
val returnType: Type = if (method.genericReturnType is ParameterizedType) {
method.genericReturnType
} else {
method.returnType
}
if (response.result != null) {
return resultParser.parse<Any>(returnType, response.result)
} else {
checkNotNull(response.error)
throw JsonRpcException(
response.error.message,
response.error.code,
response.error.data
)
}
}
}
}
/**
* Формируем данные для наполнения JsonRpcRequest
*/
private fun Method.jsonRpcParameters(args: Array<Any?>?, service: Class<*>): Map<String, Any?> {
return parameterAnnotations
.map { annotation -> annotation?.firstOrNull { JsonRpc::class.java.isInstance(it) } }
.mapIndexed { index, annotation ->
when (annotation) {
is JsonRpc -> annotation.value
else -> throw IllegalStateException(
"Argument #" class="formula inline">index of name()" +
" must be annotated with @
)
}
}
.mapIndexed { i, name -> name to args?.get(i) }
.associate { it }
}-
Соединяем всё вместе, создавая прокси.
fun <T> createJsonRpcService(
service: Class<T>,
client: JsonRpcClient,
resultParser: ResultParser,
): T {
val classLoader = service.classLoader
val interfaces = arrayOf<Class<*>>(service)
val invocationHandler = createInvocationHandler(
service,
client,
resultParser,
)
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, invocationHandler) as T
}Теперь у нас всё готово, можем использовать.
-
Объявим интерфейс, пометим аннотациями:
interface UserApi {
@JsonRpc("getUser")
fun getUser(@JsonRpc("id") id: Int): User
}-
Создадим его экземпляр через Proxy, используя код, приведённый выше:
lateinit var userApi: UserApi
private fun initJsonRpcLibrary() {
val logger = HttpLoggingInterceptor.Logger { Log.d(TAG, it) }
val loggingInterceptor =
HttpLoggingInterceptor(logger).setLevel(HttpLoggingInterceptor.Level.BODY)
val okHttpClient = OkHttpClient.Builder()
.addInterceptor(loggingInterceptor)
.build()
val jsonRpcClient = JsonRpcClientImpl(
baseUrl = BASE_URL,
okHttpClient = okHttpClient,
requestConverter = MoshiRequestConverter(),
responseParser = MoshiResponseParser()
)
userApi = createJsonRpcService(
service = UserApi::class.java,
client = jsonRpcClient,
resultParser = MoshiResultParser()
)
}-
Запустим запрос через, например, корутины:
binding.getUserButton.setOnClickListener {
lifecycleScope.launch {
withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
try {
val user = userApi.getUser(42)
withContext(Dispatchers.Main) {
binding.requestResponseTextView.text = user.toString()
}
} catch (e: Exception) {
e.printStackTrace()
if (e is JsonRpcException) {
withContext(Dispatchers.Main) {
Toast.makeText(
this@MainActivity,
"JSON-RPC error with code " class="formula inline">{e.code} and message ${e.message}",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG
).show()
binding.requestResponseTextView.text = e.toString()
}
} else {
withContext(Dispatchers.Main) {
Toast.makeText(
this@MainActivity,
e.message ?: e.toString(),
Toast.LENGTH_LONG
).show()
}
}
}
}
}
}Т.к. в OkHttpClient мы добавили перехватчик для логгирования, то в логах при успешном запросе увидим что-то такое:
D/JSON-RPC: --> POST http://192.168.43.226:8080/
D/JSON-RPC: Content-Length: 61
D/JSON-RPC:
D/JSON-RPC: {"id":1,"method":"getUser","params":{"id":1},"jsonrpc":"2.0"}
D/JSON-RPC: --> END POST (61-byte body)
D/JSON-RPC: <-- 200 http://192.168.43.226:8080/ (69ms)
D/JSON-RPC: Content-Type: application/json-rpc
D/JSON-RPC: Content-Length: 62
D/JSON-RPC: Date: Tue, 03 May 2022 14:37:29 GMT
D/JSON-RPC: Keep-Alive: timeout=60
D/JSON-RPC: Connection: keep-alive
D/JSON-RPC:
D/JSON-RPC: {"jsonrpc":"2.0","id":1,"result":{"id":1,"name":"User name"}}
D/JSON-RPC: <-- END HTTP (62-byte body)А как же Interceptor-ы для запросов?
Кажется, что наше решение прекрасно работает. Однако это не вполне так. Что, если нам надо как-то по-особенному реагировать на определённые ошибки, которые нам пришлёт сервер (протух токен, например) и/или надо модифицировать каждый запрос (добавлять токен к запросу)?
Часть этих потребностей можно решить через перехватчики на уровне OkHttp. Для этого договоримся, например, что токен мы будем прикреплять в заголовке запроса. Однако если токен на сервере захотят получать в теле запроса и/или если нам надо поудобнее обрабатывать ошибки, то нам не обойтись без собственного перехватчика. Давайте посмотрим, как это реализовано в OkHttp.
Если вы когда-то использовали перехватчики в OkHttp, то такой код будет вам знаком:
object : Interceptor {
override fun intercept(chain: Interceptor.Chain): Response {
val request = chain
.request()
.newBuilder()
.header(
"Authorization",
"tokenValue"
)
.build()
return chain.proceed(request)
}
}Вот как оно работает:
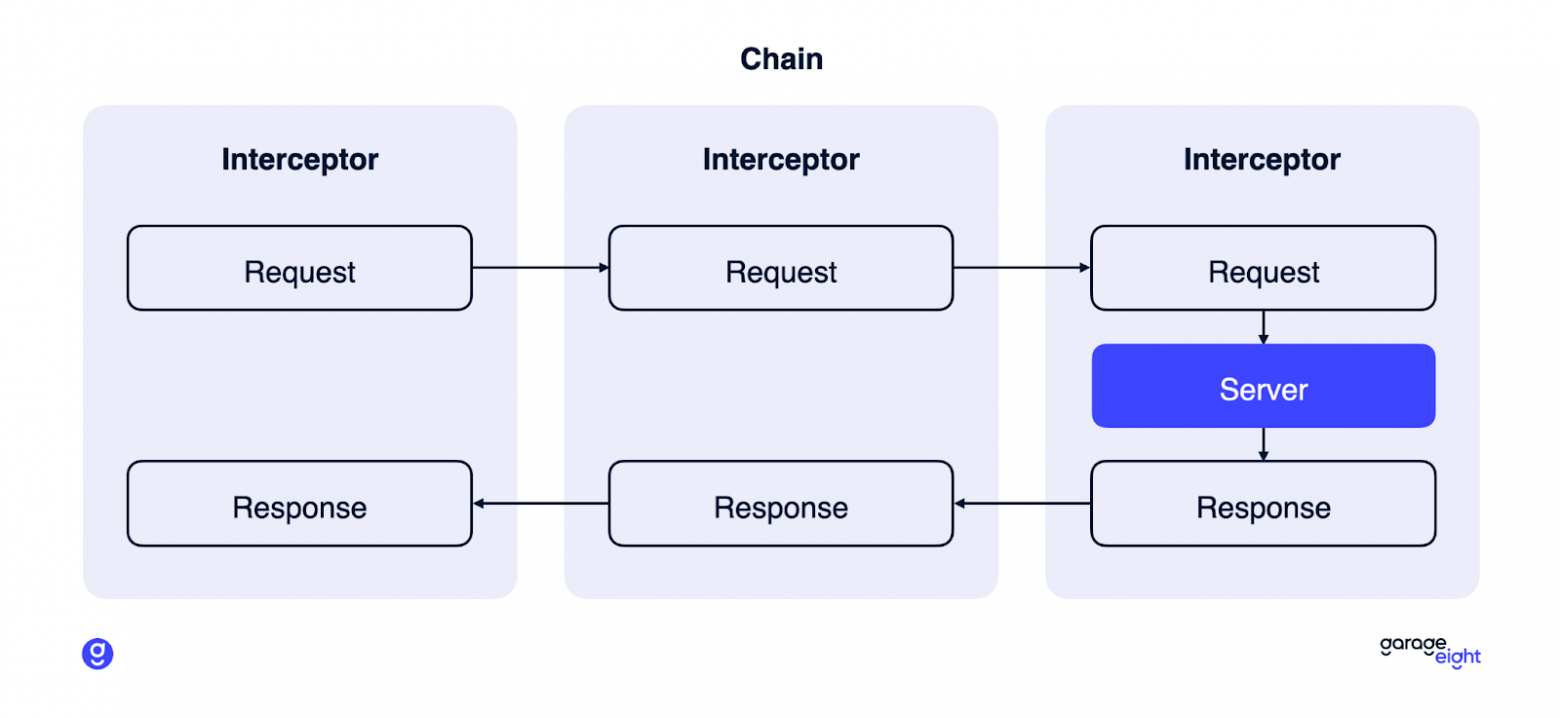
-
Добавляются 2 интерфейса: Chain и Interceptor.
-
Chain имеет метод proceed, принимающий запрос к серверу и возвращающий ответ сервера.
-
Interceptor имеет метод intercept, принимающий Chain и возвращающий ответ сервера.
-
-
Chain имеет реализацию RealInterceptorChain, принимающую в себя список Interceptor-ов и имеющую счётчик, по которому определяется, какой из цепочки Interceptor-ов следует вызывать.
-
С помощью счётчика происходит рекурсивный вызов Interceptor-ов.
-
В конец списка всех Interceptor-ов добавляется Interceptor, который непосредственно делает запрос на сервер, получая ответ оного.
-
В InvocationHandler вместо прямого вызова сервера создаётся RealInterceptorChain, в который передаются наши пользовательские Interceptor-ы в нужном нам порядке и вызывается метод intercept первого Interceptor-а в цепочке.
В итоге Interceptor-ы вызывают друг друга рекурсивно, пока не дойдут до последнего Interceptor-а, который вызовет сервера, после чего ответ сервера будет по цепочке возвращён к самому первому Interceptor-у. Таким образом, мы можем как модифицировать запрос, который по цепочке передаётся от одного Interceptor-а к другому, так и как-то отреагировать на ответ сервера.
Будем считать, что абстракция нам понятна, и попробуем прописать детали реализации.
Реализуем свои Interceptor-ы
-
Объявим интерфейс для цепочки:
interface Chain {
fun proceed(request: JsonRpcRequest): JsonRpcResponse
fun request(): JsonRpcRequest
}-
Объявим интерфейс для перехватчика:
interface JsonRpcInterceptor {
fun intercept(chain: Chain): JsonRpcResponse
}-
Реализуем Chain.
data class RealInterceptorChain(
private val client: JsonRpcClient,
val interceptors: List<JsonRpcInterceptor>,
private val request: JsonRpcRequest,
private val index: Int = 0
) : JsonRpcInterceptor.Chain {
override fun proceed(request: JsonRpcRequest): JsonRpcResponse {
// Call the next interceptor in the chain. Last one in chain is ServerCallInterceptor.
val nextChain = copy(index = index + 1, request = request)
val nextInterceptor = interceptors[index]
return nextInterceptor.intercept(nextChain)
}
override fun request(): JsonRpcRequest = request
}-
Реализуем перехватчик, который будет делать запрос на сервер.
class ServerCallInterceptor(private val client: JsonRpcClient) : JsonRpcInterceptor {
override fun intercept(chain: JsonRpcInterceptor.Chain): JsonRpcResponse {
return client.call(chain.request())
}
}Теперь в нашем InvocationHandler используем RealInterceptorChain, добавив возможность передавать Interceptor-ы при создании прокси-класса:
fun <T> createJsonRpcService(
...
interceptors: List<JsonRpcInterceptor> = listOf()
) : T {
...
val invocationHandler = createInvocationHandler(
...
interceptors
)
...
}
private fun <T> createInvocationHandler(
...
interceptors: List<JsonRpcInterceptor> = listOf()
): InvocationHandler {
return object : InvocationHandler {
override fun invoke(proxy: Any, method: Method, args: Array<Any?>?): Any {
...
//val response = clinet.call(request)
//добавляем перехватчик, который сделает запрос на сервер и получит от него ответ
val serverCallInterceptor = ServerCallInterceptor(client)
val finalInterceptors = interceptors.plus(serverCallInterceptor)
val chain = RealInterceptorChain(client, finalInterceptors, request)
//вместо прямого вызова через JsonRpcClient, вызываем intercept метод первого перехватчика в цепочке
val response = chain.interceptors.first().intercept(chain)
...
}
}
}Собственно, всё. Теперь у нас есть весь нужный нам функционал, и мы можем модифицировать запросы как на транспортном уровне, так и на уровне нашей библиотеки. Вот пример перехвата ошибки протухшего токена, отправки запроса на получение нового и повтора оригинального запроса с уже новым токеном:
fun createAccessTokenExpiredJsonRpcInterceptor(): JsonRpcInterceptor {
return object : JsonRpcInterceptor {
override fun intercept(chain: JsonRpcInterceptor.Chain): JsonRpcResponse {
val initialRequest = chain.request()
val initialResponse = chain.proceed(initialRequest)
return if (initialResponse.error != null && initialResponse.error?.code == 42) {
try {
val tokenResponse = // Отправляем запрос на получение нового токена
// Сохраняем, например, токен в префах
// и крепим его к каждому запросу в заголовке с помощью Interceptor из OkHttp
//повторяем изначальный запрос
chain.proceed(initialRequest)
} catch (e: Exception) {
throw e
}
} else {
initialResponse
}
}
}
}Каков итог и что можно улучшить?
Нас на данный момент устраивает то, что получилось. Но, конечно, можно и улучшить некоторые детали. Например, можно реализовать аналог CallAdapterFactory из Retrofit – они позволят в качестве типа возвращаемого значения методов наших интерфейсов использовать источники данных RxJava. Можно добавить больше реализаций интерфейсов парсинга JSON через другие библиотеки (Gson, Jackson etc). Ну и написать максимально подробную документацию, покрыть всё тестами и залить библиотеку в один из публичных репозиториев. Но это дело будущего. А исходники можно посмотреть на GitHub
Вот так, столкнувшись с интересной задачей, можно, основываясь на проектах с открытым исходным кодом, её успешно решить. Не бойтесь писать свой велосипед, если уже имеющиеся решения обладают хотя бы одним фатальным недостатком!