From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
HTTP 403 is an HTTP status code meaning access to the requested resource is forbidden. The server understood the request, but will not fulfill it.
Specifications[edit]
HTTP 403 provides a distinct error case from HTTP 401; while HTTP 401 is returned when the client has not authenticated, and implies that a successful response may be returned following valid authentication, HTTP 403 is returned when the client is not permitted access to the resource despite providing authentication such as insufficient permissions of the authenticated account.[a]
Error 403: «The server understood the request, but is refusing to authorize it.» (RFC 7231)[1]
Error 401: «The request requires user authentication. The response MUST include a WWW-Authenticate header field (section 14.47) containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. The client MAY repeat the request with a suitable Authorization header field (section 14.8). If the request already included Authorization credentials, then the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials.» (RFC 2616)[2]
The Apache web server returns 403 Forbidden in response to requests for URL[3] paths that corresponded to file system directories when directory listings have been disabled in the server and there is no Directory Index directive to specify an existing file to be returned to the browser. Some administrators configure the Mod proxy extension to Apache to block such requests and this will also return 403 Forbidden. Microsoft IIS responds in the same way when directory list
ings are denied in that server. In WebDAV, the 403 Forbidden response will be returned by the server if the client issued a PROPFIND request but did not also issue the required Depth header or issued a Depth header of infinity.[3]
Substatus error codes for IIS[edit]
The following nonstandard codes are returned by Microsoft’s Internet Information Services, and are not officially recognized by IANA.
- 403.1 – Execute access forbidden
- 403.2 – Read access forbidden
- 403.3 – Write access forbidden
- 403.4 – SSL required
- 403.5 – SSL 128 required
- 403.6 – IP address rejected
- 403.7 – Client certificate required
- 403.8 – Site access denied
- 403.9 – Too many users
- 403.10 – Invalid configuration
- 403.11 – Password change
- 403.12 – Mapper denied access
- 403.13 – Client certificate revoked
- 403.14 – Directory listing denied
- 403.15 – Client Access Licenses exceeded
- 403.16 – Client certificate is untrusted or invalid
- 403.17 – Client certificate has expired or is not yet valid
- 403.18 – Cannot execute request from that application pool
- 403.19 – Cannot execute CGIs for the client in this application pool
- 403.20 – Passport logon failed
- 403.21 – Source access denied
- 403.22 – Infinite depth is denied
- 403.502 – Too many requests from the same client IP; Dynamic IP Restriction limit reached
- 403.503 – Rejected due to IP address restriction
See also[edit]
- List of HTTP status codes
- URL redirection
Notes[edit]
- ^ See #403 substatus error codes for IIS for possible reasons of why a webserver may refuse to fulfill a request.
References[edit]
- ^
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content. IETF. sec. 6.5.3. doi:10.17487/RFC7231. RFC 7231. - ^ Nielsen, Henrik; Mogul, Jeffrey; Masinter, Larry M.; Fielding, Roy T.; Gettys, Jim; Leach, Paul J.; Berners-Lee, Tim (June 1999). «RFC 2616 — Hypertext Transfer Protocol — HTTP/1.1». Tools.ietf.org. doi:10.17487/RFC2616. Retrieved 2018-04-09.
- ^ a b «HTTP Extensions for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV)». IETF. June 2007. Archived from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved January 12, 2016.
External links[edit]
- Apache Module mod_proxy – Forward
- Working with SELinux Contexts Labeling files
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content
Introduction
When a web server denies access to a particular webpage or web content, it displays the 403 Forbidden error. Different web servers report different variations of the 403 Forbidden error.
In this article, you will learn what a 403 error is and how to fix it.
The 403 Forbidden error happens when a web server denies access to a webpage to a user trying to access it trough a web browser. The name «403 error» derives from the HTTP status code that the web server uses to describe that type of error.
There are several variations of the error and several reasons why the web server has denied access. The following sections deal with the different ways the error is displayed and its causes.
Common 403 Error Messages
Like with other errors, webmasters can customize how the 403 error is displayed. Its contents also depend on the web server used. That is why there are many different 403 pages across different websites.
Some common 403 error messages are:
- 403 Forbidden
- HTTP 403
- Forbidden
- HTTP Error 403 – Forbidden
- HTTP Error 403.14 – Forbidden
- Error 403
- Forbidden: You don’t have permission to access [directory] on this server
- Error 403 – Forbidden
- 403 Forbidden Error
- 403 Error
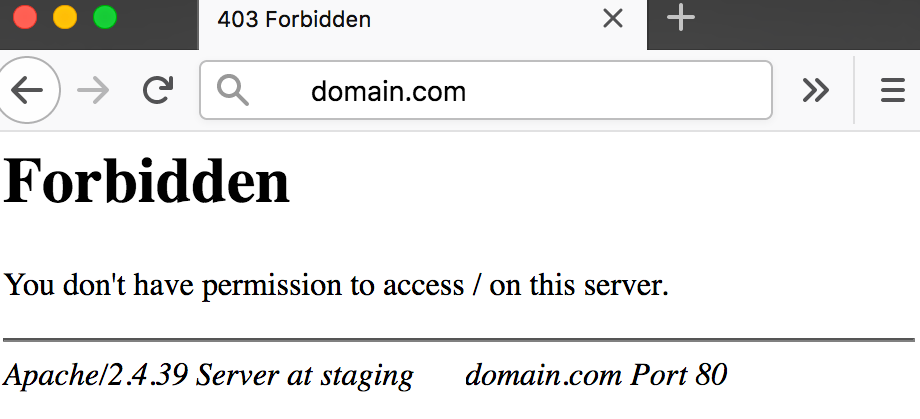
The image above shows an example of a 403 Forbidden error served by an Nginx web server.
What Causes the 403 Forbidden Error
The 403 Forbidden error usually occurs due to access misconfiguration. The misconfiguration involves improper read, write, or execute permission settings for a file or directory.
Possible causes for the 403 Forbidden error are:
- An empty website directory. If there is no index.php or index.html page, the 403 error displays.
- Missing index page. The 403 error may occur if the homepage name isn’t index.html or index.php.
- Permission/ownership errors. Incorrect permission settings or ownership cause the 403 error.
- Incorrect .htaccess file settings. The .htaccess file holds important website configuration settings, and it could be corrupted.
- Malware infection. If your files are infected with malware, it can keep corrupting the .htaccess file.
- Cached outdated webpage. The 403 error comes up if the page link has been updated, which is now different from the cached version.
- Faulty plugin. Improperly configured WordPress plugins or their incompatibility could trigger the 403 error.
The following section deals with different ways of fixing the 403 Forbidden error.
How to Fix the 403 Forbidden Error (Tips for Webmasters)
You can do several things to fix the 403 Forbidden error, depending on whether you are a website visitor or a webmaster.
The following fixes for the 403 Forbidden error are resources for site webmasters:
Check Website Directory
An empty website directory may cause the 403 error. Make sure that the content is in the correct directory on the server.
Depending on the server you are using, the correct directory for your content is:
- For Nginx: /var/www/vhosts/domain.com/httpdocs/
- For Apache: /home/username/public_html/
If there is no such directory, create one.
Add an Index Page
The website homepage by default is index.html or index.php. If there is no such page on your website, the visitors can encounter a 403 Error. Resolve this by uploading an index page to your httpdocs or public_html directory.
If you already have a homepage named other than index, you can rename it or set up a redirect in your .htaccess file to that homepage.
Warning: Be careful when editing the .htaccess file as it contains server configuration instructions and affects your web server’s behavior. The file is usually hidden as a precaution, but you can find it in your public_html directory by checking the Show Hidden Files option.
To redirect to your homepage, follow the steps below:
1. Log in to cPanel and navigate to your public_html directory.
Note: You can also download and edit the .htaccess file locally using an FTP client instead of cPanel.
2. Right-click the .htaccess file and choose Edit from the dropdown menu.
3. Redirect the index.php or index.html file to your existing homepage by inserting the following code snippet:
redirect /index.html /homepage.htmlReplace homepage.html with the actual name of your page.
Check File and Directory Permissions
Each file and directory on your website have permissions that control access to those files and directories. Incorrect file or directory permissions can cause the 403 Forbidden error. The permissions specify who has read or write access to the file or directory in question.
The permissions are represented with numeric values. The general practice is to use:
- 755 for directories
- 644 for static content
- 700 for dynamic content
Note: Linux file permissions can include numbers, letters, or words, as well as an entry stating to whom the file has been assigned — Owner, Group, or Both.
You can change file permissions recursively with the chmod command. If you prefer a GUI, use an FTP client to change file or directory permissions.
Create a New .htaccess File
A 403 error can be the result of improper .htaccess file configuration. The .htaccess file controls the high-level website configuration.
Follow the steps below to check if the .htaccess file is the cause of the 403 error:
1. Find the .htaccess file via your file management software (e.g., cPanel) or via an sFTP or FTP client.
2. Right-click the .htaccess file and select Download to create a local backup.
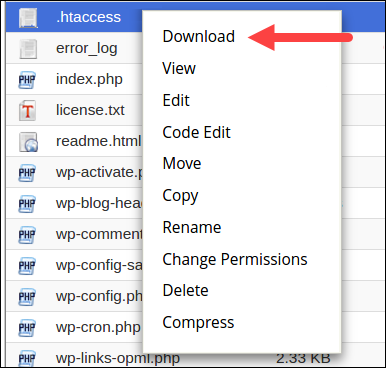
3. Next, click Delete to delete the file.
4. Visit your website. If the 403 error no longer appears, it means that the .htaccess file was corrupt.
5. Now you need to generate a new .htaccess file. Log in to your dashboard and click Settings > Permalinks.
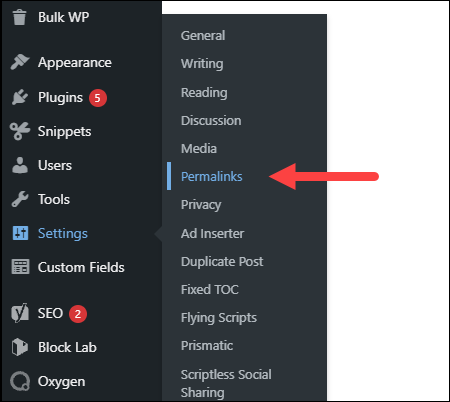
6. Don’t make any changes. Just click the Save Changes button to create a new .htaccess file.
Visit your website to check if the error is fixed.
Enable Directory Browsing
If the website shows a 403 error when you’re trying to browse a directory, you may need to enable directory browsing in your web server software. You can turn on directory browsing in the config file. If you don’t feel confident editing the config files yourself, seek help from a web master or your hosting provider.
The following examples show how to enable directory browsing in different web servers:
- IIS Express
1. Open the Web.config file of your project.
2. Add the following tags within <system.webServer>:
<directoryBrowse enabled="true" />
<modules runAllManagedModulesForAllRequests="true" />
- Nginx
Change the autoindex value to on in the config file:
The following is an example of the config file with the on value for autoindex.
server {
listen 80;
server_name phoenixnap.com www.phoenixnap.com;
access_log /var/...........................;
root /path/to/root;
location / { index index.php index.html index.htm; }
location /somedir { autoindex on; }
}
Apache
You have to specify the DirectoryIndex directive in the site’s .conf file (found in /etc/apache2/sites-available on Linux).
Turn on directory browsing in the Options directive. Following is an example of the .conf file with directory browsing turned on:
<Directory /usr/local/apache2/htdocs/listme>
Options +Indexes
</Directory>
Contact the Hosting Company
The reason for the 403 Forbidden error could be with the hosting company and not with you. If everything else fails to remove the error, get in touch with your hosting company and let them check what could be causing the issue.
Disable WordPress Plugins
Sometimes, a faulty or incompatible plugin is what causes a 403 forbidden error. You can try to fix the error by disabling all plugins to check if the error goes away.
Follow the steps below to disable all plugins:
1. Log into the WP Admin and navigate to Plugins > Installed Plugins.
2. Select all plugins, choose Deactivate from the drop-down menu and click Apply.
3. Try to access your website. If there is no 403 forbidden error, that means that the cause was one of the plugins.
4. Now enable one plugin at a time to determine which one is causing the 403 error. When you find the root of the problem, update or remove the plugin or install an alternative one to resolve the issue.
Check the A Record
One of the reasons for the 403 Forbidden error can be a domain name pointing to the wrong IP address, where you don’t have the permission to view the content. This happens when the A record of a migrated website still points to the old IP address.
Follow the steps below to check if the domain A record points to the right IP address:
1. Log in to cPanel.
2. In the Domains section, click DNS Zone Editor.

3. In the list of DNS records, find the record with the A label in the Type column.
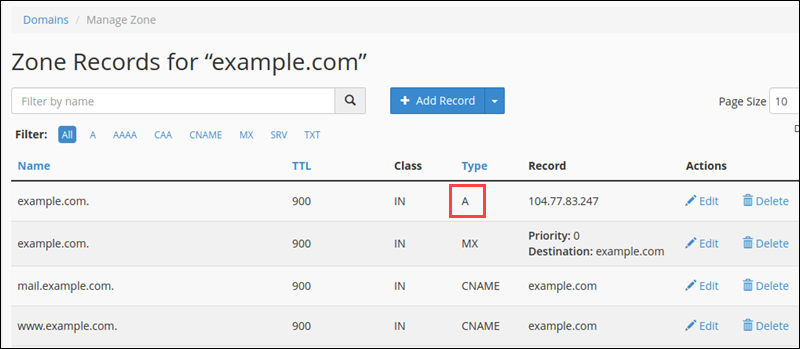
4. Check if the A record IP address in the Record column is correct. If it’s wrong, click Edit to change it.
5. Click Update to finish.
Revisit the website to see if the issue has been resolved.
Scan for Malware
Having malware on your web server can cause the 403 Forbidden error. The malware can keep injecting unwanted lines into the .htaccess file, and that way the error persists even if you generate a new .htaccess file.
Use a security plugin to scan your web server for malware and remove it if any is found. Most plugins also offer actions when detecting malware infected files, such as deleting the infected file or restoring it.
Some of the best security plugins for WordPress are Sucuri, Wordfence, Defender, etc.
How to Fix the 403 Forbidden Error (Tips for Site Visitors)
If you are a site visitor that has encountered the 403 error, below is a list of things you can try to fix the issue.
Check URL
A wrong URL is a common cause of the 403 Forbidden error. Make sure that you’re trying to access an actual webpage instead of a directory.
Many websites don’t allow visitors to browse through directories, so if you are trying to acces a directory, you will likely get a 403 Forbidden error.
Clear History/Cache
Your browser stores cached webpages to load them faster the next time you visit them. Sometimes the website link has been updated, making the actual link different from the cached version. Loading the cached version then results in a 403 error.
The stored cookies on your browser can also cause the 403 error. If the cookies are invalid or corrupted, they can cause improper server authentication. Clearing browser cache and cookies should resolve this issue.
Note: Clearing the browser cache and cookies means that the next time you load the webpage, your browser requests all the site files again, making it load slower. Clearing the cookies also signs you out from all logged-in websites.
Follow the steps below to clear the cache and cookies on Google Chrome:
- Click the three-dot button on the top right corner and select Settings.
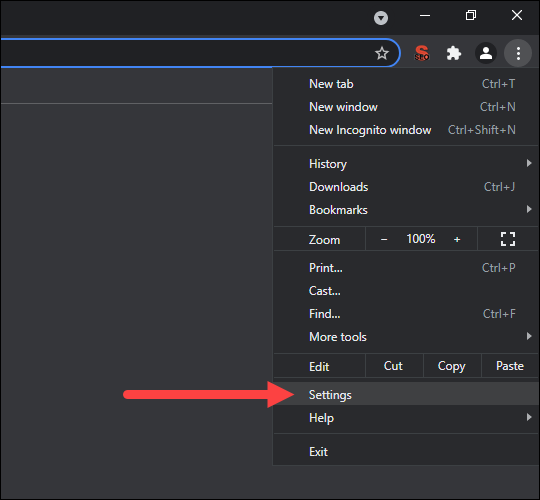
2. Find the Privacy and security section and click Clear browsing data.
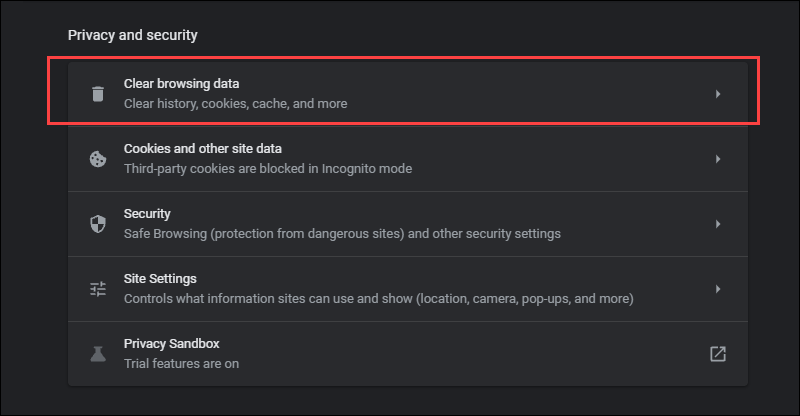
- In the drop-down menu, select the data deletion time frame.
- Check the Cookies and other site data and Cached images and files options and click Clear data.
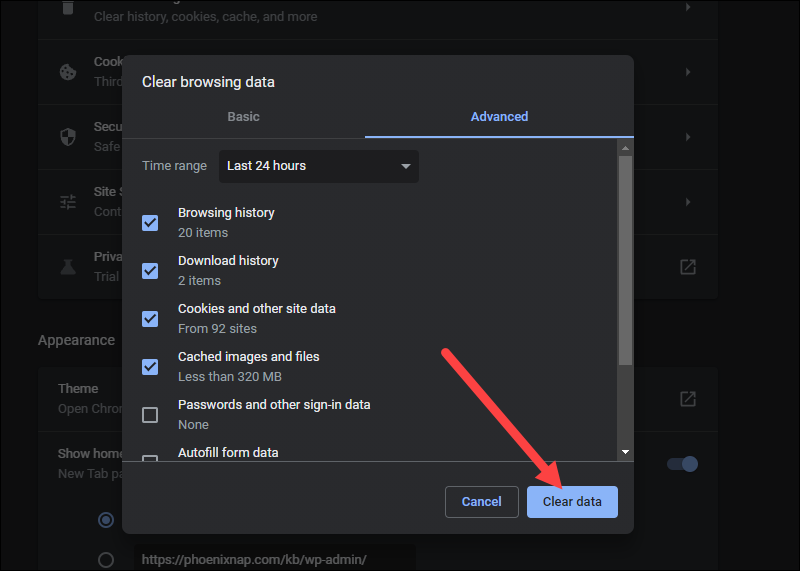
Try to reload the site to see if the problem persists.
Log in
A 403 Forbidden error code could sometimes appear because you need to log in to a website to access a page. If possible, log in with your credentials to gain access to the content.
Note: Although the 401 error is usually displayed when you need special permission to access content, sometimes the 403 Forbidden error is displayed instead.
Reload the Page
Sometimes, reloading the page is the trick to getting around the 403 Forbidden error. Each browser has its own reload button near the address bar. Press Ctrl+F5 on Windows and Linux or Cmd+Shift+R on Mac to reload the page if you prefer using the keyboard.
Try Later
If you aren’t the only one denied access to the website, then the problem is usually with the host. Revisit the site later and see if the issue has been resolved.
Contact Your ISP
If you cannot get around the 403 error on a website, but it works for other people, contact your internet service provider (ISP).
Your IP address could be added to a blocklist, and it is causing the 403 forbidden error. In that case, your ISP cannot help you, and the only way to access the website is to use a VPN.
Conclusion
High website availability provides the best user experience and shows reliability. That is why website owners try to keep their site available at all times and invest in website maintenance services.
Preventing or quickly resolving HTTP errors is crucial if you want to retain your visitors. After reading this guide, you should be able to promptly fix the 403 Forbidden error and keep your business running.
В этой статье мы расскажем о причинах, с которыми может быть связано возникновение ошибки 403. В качестве примера мы покажем вам, как исправить подобную ошибку на WordPress-сайте. Тем не менее, на других CMS или статических сайтах действия, которые необходимо предпринять, будут почти аналогичными:
Причины возникновения ошибки 403 могут отличаться в зависимости от различных обстоятельств. Иногда эта ошибка может быть результатом изменений или обновлений, которые ваш хостинг произвел в своей системе.
Рассмотрим эту тему подробнее. Затем мы перечислим различные причины возникновения этой ошибки и пути решения.
Что понадобится
- Доступ к панели управления хостингом.
- Что такое ошибка доступа 403?
- Почему возникает ошибка доступа 403
- Что делать если возникла ошибка доступа 403
- Шаг 1 — Проверка файла .htaccess
- Откройте «Диспетчер файлов» в панели управления хостингом
- Шаг 2 — Работа с правами доступа
- Шаг 3 — Отключение плагинов WordPress
- Заключение
Прежде чем мы продолжим и попытаемся исправить код ошибки 403, давайте сначала поймем, что это на самом деле такое. Ошибка доступа 403 — это код состояния HTTP.
Вот примеры сообщений об ошибке, с которыми можно столкнуться:
Forbidden: You don't have permission to access [directory] on this server HTTP Error 403 – Forbidden 403 forbidden request forbidden by administrative rules 403 Forbidden Access Denied You don't have permission to access
Давайте выясним, что вызывает эти ошибки.
Получение сообщения об ошибке 403 в процессе разработки может оказаться тревожным сигналом. Причина может заключаться в том, что вы пытаетесь получить доступ к тому, к чему у вас нет прав. Ошибка доступа 403 — это способ, с помощью которого сайт заявляет, что у вас недостаточно прав.
Эта ошибка обусловлена следующим:
- Неверные права доступа к файлам или папкам;
- Неправильные настройки в файле .htaccess.
Кратко рассмотрим, как можно это исправить.
Теперь, когда мы знаем факторы, провоцирующие возникновение ошибки, пришло время рассмотреть то, как от нее избавиться.
Действия, перечисленные ниже, будут касаться исправления ошибки 403 на WordPress-сайте. Но их также можно использовать и на других платформах. Рассмотрим весь процесс обнаружения ошибки 403 доступ запрещен, и ее исправления по этапам.
Возможно, вы не знакомы с файлом .htaccess. Это потому, что файл часто остается скрытым в директории проекта. Но если вы используете Hostinger File Manager, вы видите .htaccess по умолчанию:
Если вы используете CPanel, можно найти этот файл, используя «Диспетчер файлов». Давайте рассмотрим, как это делается:
В папке public_html найдите файл .htaccess. Если вы не видите его в этой папке, можно нажать на кнопку «Настройки» и включить параметр «Показать скрытые файлы»:
.htaccess — это файл конфигурации сервера, который предназначен для изменения настроек веб-сервера Apache.
Файл .htaccess присутствует на всех WordPress-сайтах. В тех редких случаях, когда сайт не его или он был удален непреднамеренно, нужно создать этот файл вручную.
После того как вы нашли файл .htaccess, чтобы исправить ошибку 403 forbidden, нужно:
- Скачать файл .htaccess на компьютер, чтобы создать резервную копию;
- После этого удалить файл.
- Теперь попробуйте получить доступ к сайту;
- Если он работает нормально, это просто указывает на то, что файл .htaccess был поврежден;
- Чтобы создать новый файл .htaccess, войдите в панель управления WordPress и выберите пункт Настройки> Постоянные ссылки;
- Без внесения изменений нажмите на кнопку «Сохранить», расположенную в нижней части страницы.
- Таким образом, для сайта будет создан новый файл .htaccess.
Если это не решит проблему, перейдите к следующему шагу.
Еще одна причина по которой возникает ошибка http 403 — это неверные права доступа к файлам или папкам. При создании файлов для них по умолчанию задаются определенные права доступа. Они указывают, как и кто может осуществлять их считывание, запись и выполнение. Но иногда нужно изменить права доступа по умолчанию.
Это можно сделать с помощью FTP-клиента или диспетчера файлов. FTP-клиент FileZilla предоставляет больше возможностей для изменения прав доступа к файлам и папкам. Поэтому мы рекомендуем использовать его, чтобы выполнить следующие действия:
- Зайдите на свой сайт через FTP;
- Перейдите в корневой каталог;
- Выберите основную папку, содержащую все файлы вашего сайта (обычно это public_html), кликните по ней правой кнопкой мыши и выберите пункт «Права доступа к файлам»:
- Установите флажок «Применить только к папкам», укажите права 755 в поле числового значения и нажмите кнопку «OK»;
- После того, как FileZilla изменит права доступа к папкам, повторите шаг 3, но на этот раз выберите параметр «Применить только для файлов» и введите 644:
- После этого попробуйте зайти на сайт и проверьте, не решена ли проблема.
Если ничего не изменилось, пришло время перейти к следующему шагу.
Высока вероятность того, что ошибка 403 была вызвана несовместимостью или некорректной работой плагина. На этом этапе мы отключим плагины, чтобы выяснить, не с ними ли связана ошибка 403. Лучше, конечно, отключить все плагины одновременно, а не каждый по отдельности. Так вы сможете обнаружить проблему и решить ее.
Вот, что нужно сделать:
- Перейдите на хостинг через FTP и найдите папку public_html (или папку, содержащую установочные файлы WordPress);
- Перейдите в папку wp-content;
- Перейдите в папку Plugins и переименуйте ее, например в «disabled-plugins«, чтобы ее было легче найти.
После отключения плагинов попробуйте снова зайти на сайт. Проблема исправлена? Если да, то причиной ошибки является некорректно работающий плагин. Попробуйте отключить плагины один за другим. Так вы сможете его обнаружить.
Затем можно попытаться обновить плагин. Если ни один из перечисленных способов не помог, то пришло время обратиться к своему хостинг-провайдеру.
Следуя приведенным выше рекомендациям, можно избавиться от ошибки 403 forbidden.
- Blog
- HTTP 403 FORBIDDEN

- May 20, 2022
- by Admin
It is quite frustrating to be denied access to the information you need especially on your website. You may have been logging in with no problems, and then one day, you receive the ‘access denied’ notification.
The server informs you that you do not have permission to access your website! An HTTP 403 Forbidden code is sent and you have to figure out how to get around it. What is a 403 error response?
An HTTP 403 code means that the server understood the request but will not process it. If the server wants to make known why a request is forbidden, it can provide the reason in the payload. The server may consider the authentication codes supplied in the request inadequate.
The client should avoid the same request with the same codes. However, the client may create the same request using different or new credentials. A server may still send an HTTP 403 forbidden error code for reasons that have nothing to do with the credentials.
Code References
The code references look like this:
Rails HTTP Status Symbol: forbidden
Go HTTP Status Constant http.StatusForbidden
Symfony HTTP Status Constant Response::HTTP_FORBIDDEN
Python2 HTTP Status Constant httplib.FORBIDDEN
Python3+ HTTP Status Constant http.client.FORBIDDEN
Python3.5+ HTTP Status Constant http.HTTPStatus.FORBIDDEN
What is the 403 Forbidden Error?
HTTP status codes are used to provide information about requests made by a client. Apart from the 403 Forbidden error code, there are others such as 100, 200, 300, 400, and more.
A 403 Forbidden error response may look like this:
HTTP 1.1 403 Forbidden
Date: Fri, 30 Nov 2018 09: 19: 02 GMT
Web servers provide requested data in a variety of ways. The data or resources may be presented in URLs that refer to the source. Sometimes, the resources requested may be denied. A 403 Forbidden response is issued in such an instance.
If the access requires further authentication, a 402 response is generated.
So, what does 403 Forbidden mean? As mentioned in the intro, HTTP 403 forbidden error means the server acknowledges the request but refuses to process it. This status is much like the 401 code. The difference is that re-authentication will not produce positive results with the 403 code.
Access is completely banned. The reason provided is insufficient authentication codes. Naturally, this can be perturbing especially if you run the site and have no problem accessing it previously.
HTTP Status 403 forbidden Specification
HTTP 403 presents a unique error case in the sense that it is returned when the client is denied access to resources it requested. HTTP 401, on the other hand, is returned when the client fails to provide valid authentication. Once that is presented, the client will be allowed access.
The 403 code denies access and the reason given is that the credentials presented are not sufficient.
Substatus Error Codes of IIS
IIS describes nonstandard error codes that furnish the user with a particular reason for the 403 code response. A 403 code refuses re-authentication. The 401 code, on the other hand, insinuates that re-authentication may result in positive results if the credentials provided in the request are valid.
The response given must include a www-Authenticate header field that includes a challenge appropriate to the resource requested. The client may create the same request with a valid Authorization header field.
If the request contained Authorization codes, then the 401 code response may cite the codes as the reason for the response.
The client may request a URL path that corresponds to file system directories when directory listings have been disabled in the server. Also, there may be no directory index that determines a current file to be returned to the browser.
In either instance, the result will most likely be a 403 error code response from an Apache web server. Therefore, when you see a response such as 403 forbidden access is denied, or its variations, you have an inkling why,
Some administrations set up the Mod_proxy to Apache to reject such requests. This also results in a 403 code response. Microsoft IIS responds in a similar fashion when directory listings are rejected in that server.
Microsoft’s IIS returns the following nonstandard codes:
- 403.1 Execute access forbidden.
- 403.2 Read access forbidden.
- 403.3 Write access forbidden.
- 403.4 SSL required
- 403.5 SSL 128 required.
- 403.6 IP address rejected.
- 403.7 Client certificate required.
- 403.8 Site access denied.
- 403.9 Too many users.
- 403.10 Invalid configuration.
- 403.11 Password change.
- 403.12 Mapper denied access.
- 403.13 Client certificate revoked.
- 403.14 Directory listing denied.
- 403.15 Client Access Licenses exceeded.
- 403.16 Client certificate is untrusted or invalid.
- 403.17 Client certificate has expired or is not yet valid.
- 403.18 Cannot execute requests from that application pool.
- 403.19 Cannot execute CGIs for the client in this application pool.
- 403.20 Passport login failed.
- 403.21 Source access denied.
- 403.22 Infinite depth is denied.
- 403.502 Too many requests from the same client IP; Dynamic IP Restriction limit reached.
- 403.503 Rejected due to IP address restriction
- Icon Internet portal
- .htaccess
- List of HTTP status codes
- URL redirection
Why Am I Seeing a 403 Forbidden Error Message?
There are several reasons why you may be seeing a 403 Forbidden error message. The most obvious reason is that access to the page you requested has been denied. The server tells you that you do not have permission to access the page you asked for.
Three other common reasons for these particular error codes include the following:
A website Directory is Empty
In this case, check whether your site content is uploaded to the right directory. To access this information, type the following in your search bar:
Plesk server: /var/www/vhosts/example.com/httpdocs/
Once you connect to your FTP user, you can easily navigate browse to the httpdocs directory. Do not forget to include your actual domain name.
cPanel server: /home/example/public_html/
From your FTP user, you can connect to your public_html directory. Remember to erase the example and input the name of your cPanel account username.
Ownership or Permission Error
If the ownership or permissions on your site are incorrect, simply correct them.
Missing Index page
Your site’s home page is named index.html or index.php. If the page is missing, upload an index page to your httpdocs/public_html directory. If your home page goes by a different name, you can:
- Rename it
- Create a redirect on your index page to the real home page
- Create a different home page in your .htaccess file.
How to Fix a 403 Forbidden Error Message
When the response is you ‘are not allowed to use the server’, a user can be dismayed. Fortunately, it is possible to fix the problem.
First off, how does the 403 Forbidden error appear? Different servers present 403 Forbidden errors in different ways. Some servers customize the site’s HTTP 403 Forbidden error. However, these are few and far between.
Here are a few manifestations of the error message on a variety of servers:
- Forbidden
- HTTP 403
- HTTP 403.14-Forbidden
- HTTP Error 403-Forbidden
- 403 Forbidden
- Error 403
- Forbidden: You don’t have permission to access (directory) on this server
- Error 403-Forbidden
The error code appears inside the browser window and can be viewed in any browser on every operating system.
The Internet Explorer carries ‘The website declined to show this webpage’ option. This is a 403 Forbidden error message. When you open links in Microsoft Office programs, you may get ‘Unable to open URL. Cannot download the information you requested’.
Fixing the 403 Forbidden Error
Here are a few pointers on how to fix a 403 Forbidden error on your server.
Check for URL Errors: Ensure that you have identified a specific web page file name as well as the extension. A directory alone will not do. The number one reason for the 403 error code is directory browsing. Lots of websites are configured to prevent it.
Hence, the error code will pop up when attempting to present a folder instead of a particular page. If you operate the website that refuses to open, enable directory browsing in your web server. This will prevent HTTP status 403 forbidden error responses.
Clean up Your Browser’s cache: If you have cached a version of the page you are looking for, this could be the problem. A cache clean could be the perfect 403 error fix that your server needs.
Try Logging into the Website: If it is possible and appropriate, log into the website. The error code could simply mean that you need further access before you are allowed to view the page. Normally, a 401 error is generated by a website that demands special permission.
Clear Your Browser’s Cookies: This is especially necessary if you log into the website but your last attempt was unsuccessful. However, ensure the cookies are enabled on your browser. The 403 error message is also an alert that cookies may be involved in gaining proper access.
Contact the Website: The 403 Forbidden response may be a mistake. You and others may be seeing it but the site may be unaware that there is a problem. How do you find out if the error is seen by everyone, not just you?
Many websites run support-based accounts on social media platforms. This makes it easy to access them as users can simply click on the link provided. Several sites also provide contact details such as phone numbers and email addresses.
You may come across a thread on Twitter or Facebook discussing a site that has gone down. That is one way to know that a website is not accessible. If your website is popular, you will easily know if others cannot access it as users will be asking why.
Reach Out to Your Internet Provider: If others can easily access your website, the problem may be your internet provider. You may discover that your public IP address or ISP has been blacklisted for some reason. This may explain the 403 forbidden error response.
Revisit the Page Regularly: If you have ascertained that the page you are trying to access is the correct one, leave it for a while. Try to access it later and regularly until the issue is resolved. This is also an excellent option if you have established that the error is seen by everyone.
Other errors that look like the 403 Forbidden response include the following:
- 400 Bad Request
- 404 Not Found
- 408 Request Timeout
Slot Online
These are client-side errors that may be caused by client-related issues. There are code errors that are server-related as well. These include the following:
- 500 Inter Server Error
- 502 Service Unavailable
- 503 Bad gateway
- 504 Gateway Timeout
Ultimately, if you get a 403 Forbidden error response, there are some steps you can take to rectify it and access the information you need. In addition, it is possible to diagnose the problem and find solutions.
If the error code is visible to everyone, you may need to conduct some diagnostics to figure out what is wrong. If it is visible to you alone, then your service provider may provide a solution.
Http Error 533
Related Resources
Website virus scanner
Web Hosting
Free Website Hosting
Что это такое? Ошибка 403, возникшая на экране смартфона, ПК или планшета, говорит вам: «Сюда вход запрещен». Считается серверной ошибкой, однако это не технический сбой. Спровоцировать ее могут проделки провайдеров или мошенников.
Как устранить? Если ошибка 403 – дело рук хакеров, то придется пофиксить в настройках сайта. Если же сайт не открывается у пользователей всей страны (заблокировали по первым цифрам IP), то и здесь решить проблему можно. Для обхода запрета есть специальные сервисы.
В статье рассказывается:
- Что означает ошибка 403
- Причины появления ошибки 403
- Как решить проблему, если вы – пользователь
- Способ обхода ошибки 403
- Топ-7 прокси-серверов для обхода ошибки 403
- Как устранить ошибку 403 в Play Market
- Как исправить ошибку 403 в Крыму
- Как обойти ошибку 403 в Netflix
Многие пользователи впадают в недоумение, увидев сообщение «403 forbidden», и задаются вопросом, что это за ошибка. Если браузер отправил ее, это значит, что доступ к запрашиваемому ресурсу ограничен. Эта ошибка может быть отображена и по-другому:
-
403 Forbidden.
-
Access denied.
-
«В доступе отказано».
-
Forbidden.
-
You don’t have permission to access.
-
Запрещено 403.

Когда в сообщении об ошибке будет указан код 403, то практически во всех случаях потребуется использование стороннего программного обеспечения либо выход в Интернет через удаленный сервер.
Такое сообщение не связано с техническими неполадками, оно дает понять, что доступ к ресурсу ограничен самим провайдером.
Ошибка 403 может появиться при попытке открыть любой сайт, страницу, файл, сценарий, к которым по тем или иным причинам решено ограничить доступ пользователя.
Причины появления ошибки 403
Существует целый ряд причин, по которым пользователь может увидеть ошибку запроса 403. Таковыми могут быть как случайные или ошибочные действия провайдера, так и намеренное ограничение доступа, обусловленное политическими мотивами, соображениями безопасности данных, неготовностью материалов к публикации. Подробнее о разных вариантах.
Доступ к ресурсу может быть ограничен для пользователя из какой-либо страны
Сразу, как только пользователь выходит в Интернет, он получает IP-адрес. По нему происходит обмен данными между его устройством и любым интернет-ресурсом. IP представляет собой набор цифр, разделенных точками на четыре части по два или три знака. Первые цифры в этом коде указывают на страну, из которой осуществляется доступ к серверу.

В частности, один из самых посещаемых в мире поисковик Google в ряде стран невозможно открыть из-за ограничения доступа, поэтому пользователи из этих стран видят ошибку 403 при попытке зайти на него. Характерным примером подобной ситуации являются непростые отношения России с целым рядом зарубежных государств, из-за чего вне закона оказалось множество популярных иностранных ресурсов. Заходя на них, пользователи из России видят ошибку http 403. Кроме того, на устаревшем оборудовании провайдера при присвоении пользователю IP-адреса может указываться недостоверный код страны.
Крайне низка вероятность того, что ошибка 403 связана с тем, что сервер запретил доступ именно конкретному пользователю. Это возможно при наличии выделенной линии, при которой IP-адрес не изменяется при каждом подключении. В большинстве же случаев он присваивается заново при каждом доступе в Интернет, поэтому блокировка одного адреса не будет действовать при новом подключении. Если ошибка 403 появилась на сайте Гугл или на другом свободном в России ресурсе, следует попробовать переподключиться и зайти под другими логином и паролем. Иногда проблема решается автоматически по прошествии непродолжительного времени – не более нескольких дней.
В работе сайта возникли сбои в связи с изменениями, внесёнными в код
Если у вас в Сети создан свой сайт, то и здесь можно столкнуться с ошибкой авторизации 403. Причины могут быть следующие:
-
Сайт был взломан, в результате действий злоумышленников файл с индексными данными оказался поврежден;
-
при переносе ресурса его данные были размещены в месте хранения с неправильным адресом;
-
в вашем IP содержатся данные, при наличии которых доступ к сайту ограничен.
Индексные файлы – это записи сайта, к которым сервер при поступлении запроса от пользователя обращается в первую очередь, на основании данных, содержащихся в нем, уже обрабатываются остальные его данные. Если сервер управляется операционной системой Linux, то нужно быть внимательным к регистру при указании имени файла.
Собрали все фишки маркетинга в одном месте, чтобы вы смогли показать, что ваш продукт – лучший.
Для ресурсов, которые написаны на языке HTML и являются статичными, индексный файл будет иметь название Index и расширение html. Динамические сайты имеют index files с расширением php. У ресурса Joomla, например, два таких – Index1 и Index2. Индексный файл можно использовать из готового дистрибутива, распаковав его на локальном компьютере.
Может выясниться, что дистрибутив сайта помещен не в папку верхнего уровня, а в одну из подчиненных директорий, например, со сценариями, после чего появляется ошибка страницы 403. Не нужно тратить время на перенос данных, проще переименовать папки.

Для удаленных действий на сервере можно пользоваться протоколом FTP. Однако эффективнее будет выполнить вход непосредственно на server, поскольку так можно будет увидеть следы несанкционированных действий и обнаружить признаки вирусной атаки. Все действия на сайте фиксируются сервером с указанием их даты и времени. Вирусный код можно легко идентифицировать по записям типа ?php eval или iframe.
Если все указанные действия не помогают, остается только связаться с провайдером через службу техподдержки.
Браузер пишет «Ошибка 403», когда пользователь пытается загрузить конкретную страницу
Такие проблемы возникают гораздо чаще. В частности, если сайт был перемещен с локального сервера веб-разработчика на хостинг, как это произошло с площадкой Virtue Mart. На ней систематически возникают проблемы при нажатии кнопки «Купить».

Однако вместо страницы с данными о заказе пользователь видит ошибку 403. Вряд ли он станет думать, что делать, он просто сделает покупку в другом магазине. Поэтому в сфере интернет-торговли такие неполадки – просто непозволительная роскошь.
Отказы доступа к отдельным страницам сайта вызываются неверными настройками, которые указаны в корне сайта. Для управления нужными для открытия ресурса правами используется программа CHMOD, отличающаяся удобным интерфейсом. К каждой директории и любому файлу на сайте есть три уровня доступа:
-
хозяин сайта или суперпользователь;
-
группа доверенных лиц (администраторы);
-
посетители сайта.
С помощью программы CHMOD можно задать для страниц и папок действия, которые допускается совершать с ними тем или иным пользователям:
-
читать – обозначается цифрой 7 или буквой «r»;
-
редактировать (изменять) – цифра 7 или буква «w»;
-
исполнять – цифра 7 или буква «х».
Если файлу назначили права доступа 777 (в буквенном коде: rwx–rwx–rwx), то это означает, что любой пользователь Сети может совершать с ним действия наравне с хозяином сайта – изменять, удалять, редактировать данные.
Как создать продающий прайс-лист, чтобы клиенты отдали предпочтение вам, а не конкурентам.
Чаще всего встречается режим доступа 755 (в буквенном обозначении: rwx–r-x–r-x). Это значит, что редактировать файл может только суперпользователь, а администраторы и посетители сайта – только читать и исполнять. Буква «w» для суперпользователя позволяет получить ему неограниченный доступ к сайту. Знак «r», если он отсутствует в наборе прав хозяина, лишит доступа к сайту даже его. Ну а без режима «x» ни один посетитель не сможет оформить заказ и увидит ошибку браузера 403, как в случае с вышеупомянутым Virtue Mart.
В программе CHMOD все папки и файлы представляются в виде таблицы. Для изменения режима доступа достаточно кликнуть по соответствующей ячейке рядом с названием. Не зная, какой режим выбрать, указывайте 755, он подходит для большинства случаев.
Провоцируем 403 сами
Мы выяснили, что означает ошибка 403. Теперь разберемся, как воспроизвести ее самостоятельно. Например, вы хотите ограничить доступ какому-то пользователю или их группе по тому или иному признаку. В этом поможет файл .htaccess. В стандартном дистрибутиве CMS Joomla он называется htaccess.txt. Присвойте ему новое имя, поставив в начале заголовка точку. Также можно использовать программу Notepad ++, в ней нужно прописать следующее:

Этой командой вы ограничите возможность доступа к файлу всем пользователям, IP которых будет отличаться от указанного. Как вы помните, интернет-протокол большинства пользователей динамический, поэтому ограничения нужно указывать в директиве Deny. Третью и четвертую группу цифр в IP-адресе заполните нулями. Можно заблокировать пользователей из определённой страны. Так, например, если указать 81.4.0.0/14, то доступ к ресурсу не смогут получить все пользователи, интернет-протокол которых начинается с 81.4; на блокировку указывает число 14 после косой черты.
Чтобы установить IP-адрес злоумышленника, нужно воспользоваться одним из следующих вариантов:
-
компоненты CMS (форум) указывают этот адрес, и администратор узнает о новом посте;
-
изучите log-файл, который хранится на хосте.
Log-файл достаточно объемный, однако, потратив время на его изучение, вы безошибочно вычислите злодея, соотнеся момент его появления на сайте со временем вредоносных изменений, а затем сможете легко его заблокировать.
Также можно ограничить доступ к критически важным директориям. В Joomla к таковым относится папка Libraries.
Сформируйте файл .htaccess и укажите в нем следующие параметры:
Order allow deny
Deny from all
Файл нужно разместить в папке, доступ к которой будет ограничен. После этого по запросу, в котором указано имя сайта и за ним – /Libraries, пользователю будет направлено сообщение «Ошибка 403 disallowed useragent».
Кейс: VT-metall
Узнай как мы снизили стоимость привлечения заявки в 13 раз для металлообрабатывающей компании в Москве
Узнать как
Хостинг недоступен
Нередко ошибка сервера 403 может возникать, если нет доступа к хостингу, который может оказаться заблокирован самим провайдером для конкретного пользователя. Это чаще всего связано с нарушением технических требований или условий hosting-договора. Как правило, перед блокировкой направляется электронное письмо с предупреждением и указанием ее причин, дается время на устранение недостатков. По истечении срока, если нарушения не устранены, происходит блокировка.

Таким образом, в первую очередь нужно проверить свою электронную почту и найти там письмо соответствующего содержания, а затем выполнить указанные в нем требования провайдера. Если такого послания не обнаружилось, то скорее всего причина проблемы кроется в другом.
Отключение плагинов WordPress
Если так и не удалось установить, почему появляется ошибка 403, то существует вероятность проблемы в плагинах WordPress. Они могут быть неработоспособны или несовместимы с теми настройками сайта, которые вы указали.
В этом случае сначала нужно попытаться отключить плагины. Для этого переходим в раздел «Wp-content» и находим в нем папку «Plugins». Переименуйте ее, после этого сайт не сможет обнаружить и подгрузить ранее указанный плагин. Теперь вновь откройте страницу. Если она загрузилась, то проблема крылась именно в plugins. Осталось лишь выяснить, какой именно из них вызвал неполадки. Для этого можно вернуть прежние имена папкам, а затем аналогичным способом отключать каждую отдельно. Когда проблемный плагин будет обнаружен, его нужно переустановить или заменить на другой.
Защита Hotlink
Хотлинкинг предполагает использование одним порталом ресурсов другого посредством ссылок. Выглядит этот так. Например, на сайте 1 размещены какие-то объемные видеоматериалы, которые понравились владельцу ресурса 2. Владелец веб 2 решил разместить их у себя, указав на них ссылки. Пользователь, заходя на сайт 2, видит эти материалы так же, как если бы они были размещены непосредственно на нем. Однако нагрузка на веб 1 и сервер, на котором он размещен, возрастает, сказываясь негативно на его пропускной способности.
Для предотвращения такого положения хозяин ресурса 1 может указать зону рефереров. В этом случае пользователь, пытающийся ретранслировать материалы с портала 1 на сторонние вебы, будет видеть сообщение «Ошибка 403 доступ запрещен» вплоть до того момента, как хозяин сайта 1 отменит ограничения. Исправить ее самостоятельно владелец ресурса 2 не сможет.

Как решить проблему, если вы – пользователь
Часто с ошибкой скачивания 403 сталкиваются не только администраторы сайтов, но и рядовые пользователи. Что делать:
-
Прежде всего удостоверьтесь, что данные нужного ресурса в Интернете указаны в адресной строке без ошибок.
-
Если ошибка 403 проявляется на андроиде, попробуйте загрузить страницу с другого устройства. Возможно, причина проблемы непосредственно в вашем гаджете.
-
Могут быть временные неполадки у провайдера, поэтому, если сообщение об ошибке 403 направлено удаленным сервером, обновите страницу и проверьте, не исчезла ли она.
-
Выполните очистку кэша и cookies. Для этого нужно зайти в соответствующие настройки браузера, которые могут отличаться и находиться в разных разделах в каждом из них. В нужном меню отметьте файлы кэша и cookies, после чего нажмите «Очистить».
-
Пользователь может видеть сообщение «403 ошибка на сайте», если для доступа к нему нужно выполнить вход с логином и паролем. Зарегистрируйтесь или войдите под своей учетной записью, и проблема должна исчезнуть.
-
При выходе в Интернет с телефона ошибка 403 может появляться, если включён режим экономии трафика. Для ее отключения найдите соответствующий раздел в Google Chrome.
-
Если ничего не помогло, то остается только ждать. Вполне вероятно, что владелец сайта уже знает об ошибке и пытается ее устранить, но для этого требуется определенное время. Выждав пару дней, попробуйте зайти на ресурс снова.
Способ обхода ошибки 403
Ошибку приложения 403 можно преодолеть достаточно легко. Для этого лишь нужно воспользоваться прокси-сервером. В этом случае запрос пользователя будет оправляться не напрямую на целевой сервер, а сначала проходить через промежуточный компьютер, для которого ограничения не установлены. Тот от своего имени получит требуемые данные и передаст их исходному пользователю. Это очень эффективный способ обхода ограничений в Сети, а также надёжный инструмент для того, чтобы сохранить анонимность.
Прокси-серверы работают как в России, так и за границей. Как правило, подобная услуга предоставляется на возмездной основе.

Прокси может использоваться для расширения возможностей связи, на нем основан, в частности, GPRS, который изменяет IP сотового телефона несколько раз за один выход в Интернет. Связано это с тем, что голосовые сообщения обладают приоритетом при передаче по линиям сотовой связи, а остальные данные передаются по свободным каналам. Провайдеры при использовании несимметричного выхода в Интернет также используют прокси, когда запрос направляется по каналу GPRS, а ответный сигнал принимается по спутниковой связи.
Топ-7 прокси-серверов для обхода ошибки 403
Рассмотрим наиболее популярные прокси-серверы. Ниже представлены как резидентные и мобильные решения, так и серверные прокси с доступными тарифами.
AstroProxy
Предоставляет пользователю как серверные, так и резидентные и мобильные прокси. IP у всех изменяется.

Преимущества:
-
Наглядное управление через веб-интерфейс и сбор статистики.
-
Изменяемые IP, сводящие к минимуму возможность обнаружения подключения через удалённый сервер.
-
Огромный выбор прокси, привязанных более чем к 100 странам по всему миру.
-
Широкий ассортимент тарифных планов, включая безлимитные варианты.
-
Моментальный доступ ко всему перечню доступных прокси-серверов.
-
Возможность платежей как традиционными валютами – рублями, долларами, евро, так и многими видами криптовалюты.
-
Поддержка русского языка.
-
Тестовый период, в течение которого возможности сервиса можно опробовать бесплатно.
Недостатки:
-
Имеется перекос в сторону прокси, привязанных к определенным регионам.
-
Невысокий дисконт при использовании значительных объёмов переданных данных.
Особенности AstroProxy:
-
Пользователю предоставляется порт, с которым связаны однотипные прокси. Для каждого из них в полном объеме поддерживается HTTP(S) и SOCKS, которые можно использовать параллельно друг с другом. Данные с каждого порта могут быть моментально активированы через VPN.
-
Оплачивается трафик только в одном направлении – либо входящий, либо исходящий, в зависимости от того, на какой из них приходится наибольшая часть данных.
-
Если вы приводите новых пользователей, то вам предоставляется на счет до 10 % от каждого сделанного ими платежа, в то время как у большинства иных провайдеров бонус зачисляется только с первой такой суммы.
Oxylabs
На данном сервисе можно воспользоваться всеми тремя видами proxy – мобильными, динамическими и приватными. Доступны и shared, и частные прокси.

Преимущества:
-
Самое большое количество прокси в мире – более 100 млн.
-
Поддержка HTTP(S) и SOCKS5;
-
Высокая скорость передачи данных.
-
К пользователю прикрепляется персональный менеджер.
-
Изменение прокси как вручную, так и в автоматическом режиме.
-
Семь дней бесплатного использования для оценки возможностей, рефанд в течение трех дней.
Недостатки:
-
Дороговизна (от $ 100 для shared, от $ 300 для резидентных прокси и от $ 500 — для мобильных proxy);
-
Нет поддержки русского языка.
Особенности Oxylabs:
-
Целевая аудитория – крупные бизнес-компании. Сервис относит себя к премиальному сегменту, предоставляя пользователям широкий набор FPI инструментов из поисковых сайтов, (в частности – SERP Scraper), с онлайн-магазинов (E-Commerce Scraper API), обычных сайтов (Web Scraper API).
-
Официальный плагин для Chrome, который дает возможность использовать весь спектр прокси.
-
Имеются резидентные и мобильные proxy в широком перечне государств.
Storm Proxies
К услугам пользователей – резидентные прокси с изменяемым IP, а также серверные, как приватные, так и shared.

Преимущества:
-
Тарифы, предоставляющие неограниченный трафик.
-
Доступность тарифов (от $ 39/месяц за выделенные динамические прокси).
-
Не требуется логин и пароль.
-
Отдельные прокси для сбора данных с сайтов по продаже билетов и со сникер-ботами.
Недостатки:
-
Ограничение по частоте изменения IP (не чаще одного раза в три минуты в ручном режиме и не чаще одного раза в 15 минут в автоматическом).
-
Ограниченный перечень IP (чуть более 200 000).
-
Не поддерживается протокол SOCKS.
-
Доступ без логина и пароля снижает безопасность.
Особенности Storm Proxies:
-
Целевая аудитория – частные пользователи и низкобюджетные стартапы. Может использоваться как основа для запуска сникер- и тикет-ботов. Для трафик-ботов могут использоваться также изменяемые IP. Хорошо подходит для SEO-парсинга и операций с использованием скрейперов.
-
Удобство для начинающих пользователей прокси, выражающееся в простом интерфейсе и ограниченных возможностях настройки.
SOAX
Доступны мобильные proxy и резидентные прокси с изменяемым IP-адресом.

Преимущества:
-
Надежность соединения.
-
Доступна функция таргетинга не только по государству, но и по городам и ASN (более 100 стран).
-
Оперативная поддержка пользователей.
-
Пробный период с минимальной оплатой – за 1,99 долларов можно получить 100 МБ данных.
-
Широкие опции для изменения IP (sticky-сессия продолжительностью 90–600 секунд, длительность может быть увеличена).
-
Поддержка протоколов HTTP(S) и SOCKS5.
-
Доступная цена, не превышающая предложения конкурентов (99 долларов за мобильные и резидентные прокси).
Недостатки:
-
Количество портов для доступа HTTP(S) и SOCKS5 ограничено.
-
Частое падение скорости передачи данных.
Особенности SOAX:
-
Принцип работы: После входа в панель управления пользователю предоставляется перечень всех доступных прокси, нужные вносятся им в отдельный белый список. Также настраиваются частота и режим изменения IP, геолокация, после чего к порту привязывается перечень этих адресов.
-
Пользователю в его аккаунте предоставляется список всех действующих прокси и активных ASN.
Smartproxy
Наряду с резидентными прокси, Smartproxy предоставляет пользователю серверные варианты, которые могут быть как с изменяемым IP, так и предоставляться по выделенной линии.

Преимущества:
-
Быстрота передачи данных, минимальное время отклика на запрос пользователя на любом виде прокси.
-
Развернутая информация о пользовании сервисом прямо на сайте.
-
Пользователю предоставляется полный перечень имеющихся резидентных прокси.
-
Вспомогательное программное обеспечение, предоставляемое безвозмездно.
-
У резидентных прокси по выделенной линии IP-адрес меняется каждый месяц.
-
Возможность совершения платежей криптовалютой (используется биткойн).
Недостатки:
-
Протокол SOCKS5 не работает.
-
Нет мобильных и ISP прокси;
-
Все серверные proxy размещены на территории Соединенных Штатов Америки.
-
Для резидентных прокси не работает ASN-таргетинг.
-
Пользователи из России и Белоруссии могут совершать платежи только криптовалютой, для использования традиционных валют требуется наличие PayPal или банковской карты, которая зарегистрирована за пределами этих стран.
Особенности Smartproxy:
-
Имеется собственный безопасный браузер X-Browser, а также плагины для сторонних программ для серфинга в Сети. Предоставляется скрейпер как отдельное приложение (SERP), так и в виде плагина для браузера (Smart Scraper).
Bright Data (ex. Iluminati)
Пользователю предоставляются ISP-прокси, резидентные и мобильные, частные и shared серверные proxy.

Преимущества:
-
Огромный опыт в предоставлении прокси-услуг. Компания, созданная в Израиле, находится на рынке с 2014 года.
-
Наряду с прокси, пользователю предоставляется полноценный сервис по сбору сведений.
-
Имеются все популярные предложения proxy.
-
Искусственный интеллект подбирает прокси, который наиболее отвечает нуждам пользователя (технология Proxy Waterfall).
-
Бесперебойная работа сервиса и предоставляемого им proxy-канала.
-
Наличие русскоязычного интерфейса.
Недостатки:
-
Дороговизна (за резидентные или мобильные прокси придется выложить не менее $ 500);
-
Плохо подходит новичкам, так как предполагает наличие навыков программирования и сетевого администрирования.
Особенности Bright Data:
-
Является полноценным решением для профессионалов, которые, помимо прокси, предлагает также и эффективные решения для скрейпинга, парсинга, настройки изменения IP, возможность расширенного сбора данных. Также отличается безопасностью, которой способствует как собственная технология Data Unblocker, отслеживающая cookies и активность браузера, так и наличие плагина для популярных браузеров.
-
Предлагается не менее 72 млн прокси всех видов.
NetNut
Предоставляются как shred-прокси для серверов, так и ISP, и резидентные proxy с постоянным и с изменяемым IP-адресом.

Преимущества:
-
Колоссальное количество доступных ISP-прокси – свыше 1 млн.
-
Предоставляется семь дней бесплатного использования для ознакомления с возможностями сервиса.
-
Не ограничивается число запросов, которые могут быть направлены в один момент времени.
-
Резидентные прокси имеют широкий выбор по их географическому размещению.
-
Бесперебойное соединение и передача данных по резидентным каналам.
Недостатки:
-
Русскоязычный интерфейс выполнен машинным способом, что значительно искажает значение многих опций для не владеющего английским языком;
-
Дороговизна с учетом отсутствия поддержки в рамках пакетов некоторых опций, которые в тех же тарифах на других сервисах дополнительно предоставляются пользователю (не менее $ 20 за 20 ГБ трафика, при этом нет поддержки белого списка, Skype и некоторых других возможностей).
-
Небольшой выбор ISP-прокси, привязанных к странам Азии и Африки.
-
Геолокация поддерживается только для прокси, IP которых приписаны к Соединённым Штатам Америки.
-
Неудобные интерфейс, который новичка собьет с толку, и справочник по часто возникающим проблемам.
Особенности NetNut:
-
Входит в число лидеров по выбору ISP-прокси, привязанных в основном к Европе и Соединенным Штатам Америки.
-
Имеется API приложение, которое обрабатывает запросы, заменяя proxy, что позволяет повысить продуктивность скрейпинга информации (данная возможность входит в цену наиболее дорогостоящих пакетов).
Скачайте полезный документ по теме:
Чек-лист: Как добиваться своих целей в переговорах с клиентами
Как устранить ошибку 403 в Play Market
Очень часто с ошибкой 403 сталкиваются пользователи Play Market при попытке установки приложения на гаджет. Как правило, проблема устраняется очисткой временных файлов и cookies в меню опций. Также код 403 указывается в ошибке Плей Маркета для пользователей в тех странах, в которых Google заблокирован. В этом случае придется воспользоваться VPN.
Столкнувшись с ошибкой Плей Маркета 403, попробуйте сперва протестировать стабильность соединения или канала Wi-Fi. Затем выключите и снова включите гаджет, проверьте, что свободный объем памяти достаточен для скачивания и установки данных.

Ошибку 403 в Плей Маркете исправить не так сложно. Для этого нужно войти в меню настроек и выполнить следующую последовательность действий:
-
откройте меню «Приложения» (может также называться «Приложения и уведомления»), найдите пункт «Сведения о приложении»;
-
кликните по заголовку «Play Маркет», если Android ниже 7 версии, также зайдите в хранилище;
-
кликните по опции «Стереть данные», на запрос системы о подтверждении действия ответьте утвердительно;
-
Повторно войдите в Play Market, попытайтесь скачать ранее недоступные данные вновь. Ошибка 403 может появиться и в этот раз, что значит недоступность сервера. В этом случае те же действия нужно вновь выполнить из меню настроек в приложении «Сервисы Google Play».
Как исправить ошибку 403 в Крыму
Спор из-за территориальной принадлежности Крыма повлек отказ многих западных компаний работать на данной территории, включая Google, отключившей для жителей полуострова Play Market, и Apple, заблокировавшей сервис AppStore.
Выручит в этой неприятной ситуации изменение IP-адреса, который эти сервисы будут видеть при обращении к ним пользователя. Для этого используйте VPN. Возможно, для полноценной работы потребуется скачать и установить на свой гаджет файл apk.

Для теста опробуем браузер Opera VPN:
-
Включите Opera VPN на вашем устройстве и кликните по надписи «Начать работу»
-
Увидев на дисплее вопрос о разрешении на подключение, отвечаем утвердительно.
-
После нажатия кнопки «Подключиться» весь исходящий трафик будет обрабатываться серверами Opera, которые размещены в Германии, Канаде, Нидерландах, Сингапуре и США. Приложение автоматически подключается к тому из них, который размещен ближе всего к устройству пользователя. Можно выбрать любой другой, но чем дальше находится сервер, тем сильнее падает скорость передачи данных.
-
В верхней части телефона должна появиться иконка ключа, что означает активность VPN. Попытайтесь зайти на сайт, который ранее выдавал ошибку 403. Если удалось выполнить вход, то виртуалка работает нормально.
Как обойти ошибку 403 в Netflix
Сервис Netflix официально приостановил работу на территории РФ, но пока не сообщал о полной блокировке. В результате пользователи при попытке войти на сервис видят сообщение nw 6 403. Netflix выдает такую ошибку, поскольку при обращении к сервису в запросе отображается российский IP-адрес. Рассмотрим, как ее исправить.
-
Устранение ошибки «Нетфликс» nw 6 403 на персональных компьютерах и смартфонах
Неплохим способом решения проблемы будет использование VPN-сервисов. Они позволяют скрыть местонахождение пользователя, предоставляя Netflix данные прокси сервера, через который подключается пользователь. Во многих случаях есть возможность выбрать конкретную локацию IP. Дело в том, что содержание контента, который предоставляется данной стриминговой платформой, даже без учета ограничений различно в зависимости от нахождения устройства, направившего запрос. Поэтому выбор VPN по локации позволит получить полный доступ к содержимому Netflix.

Нужно помнить о ряде факторов, с которыми будет сопряжено устранение на «Нетфликс» ошибки 403 с помощью VPN. Прежде всего это ограниченная скорость данных, которые будут передаваться пользователю, что повлечёт нестабильное воспроизведение видео. Также платформа запрещает использовать средства обхода региональных ограничений, за нарушение этого правила пользователя могут заблокировать. И, наконец, Netflix способен отслеживать подключение пользователя через VPN, после чего сразу происходит обрыв соединения. Таким образом, подобный способ обхода ошибки с кодом nw 6 403 не может гарантировать безотказную работу.
Если вы согласны мириться с этими неудобствами, то вопрос только в выборе подходящего VPN-сервиса. Платные платформы предлагают более широкие возможности и широкий перечень серверов и их типов. Стоит обратить внимание на такие из них, как ExpressVPN, Zenmate, Surfshark и CyberGhost. Зарегистрировавшись на сайте соответствующей площадки, нужно скачать приложение и установить его на телефон или ПК, после чего выполнить подключение к Интернету через VPN.
Проблемы могут возникнуть также с оплатой подписки в Netflix. Для этого в идеале нужен человек, который находится вне территории России и имеет карту зарубежного банка. В противном случае попробуйте воспользоваться VPN, который работает бесплатно. Эффективность невысока, но за неимением лучшего можно использовать и им. Попробуйте сервисы Proton VPN, плагин Windscribe, Browsec и Lantern.
-
Устранение ошибки 403 на телевизоре
В данном случае ситуация сложнее, чем в случае с ПК или смартфоном. На телевизор не получится установить какое-то стороннее программное обеспечение. Поэтому если ошибка nw 6 403 Netflix появилась на телевизоре, нужно изменить настройки роутера.
Они различны для разных производителей. В Сети можно найти для каждого роутера алгоритм действий, который позволит обойти ошибку eos in ff 403. Также для большинства моделей имеется возможность настроить VPN, в этом вам поможет Интернет.

Статья опубликована: 08.09.2022
Облако тегов
Понравилась статья? Поделитесь:
Did you just try to access your WordPress site only to be hit by some message telling you something is “Forbidden” or that you don’t have permission to access something on your site? If so, you’ve likely run into the 403 Forbidden error on WordPress.
Seeing an error on your WordPress site can be frustrating and deflating, which is why we’ve created this detailed guide to help you fix the 403 Forbidden Error on WordPress and get your site functioning again as quickly as possible.
Let’s get started without any further introduction because we’re sure you just want to fix your site!
Prefer the video version?
What is the 403 Forbidden Error?
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) defines the error 403 Forbidden as:
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. A server that wishes to make public why the request has been forbidden can describe that reason in the response payload (if any).
| Error Code | 403 |
| Error Type | Authentication error |
| Error Variations | Forbidden – You don’t have permission to access / on this server
403 – Forbidden: Access is denied Error 403 – Forbidden 403 – Forbidden Error – You are not allowed to access this address 403 Forbidden – nginx HTTP Error 403 – Forbidden – You do not have permission to access the document or program you requested 403 Forbidden – Access to this resource on the server is denied 403. That’s an error. Your client does not have permission to get URL / from this server You are not authorized to view this page It appears you don’t have permission to access this page |
| Error Causes | Corrupt .htaccess file
Incorrect file permissions Plugin issues |
Like many other common WordPress errors, the 403 Forbidden error is an HTTP status code that a web server uses to communicate with your web browser.
Quick background on HTTP status codes – whenever you connect to a website with your browser, the web server responds with something called an HTTP header. Usually, this all happens behind the scenes because everything is working normally (that’s a 200 status code, in case you were wondering).
However, if something goes wrong, the server will respond back with a different numbered HTTP status code. While these numbers are frustrating to encounter, they’re actually quite important because they help you diagnose exactly what’s going wrong on your site.
The 403 Forbidden error means that your web server understands the request that the client (i.e. your browser) is making, but the server will not fulfill it.
In more human-friendly terms, it basically means that your server knows exactly what you want to do, it just won’t let you do it because you don’t have the proper permissions for some reason. It’s kind of like you’re trying to get into a private event, but your name got accidentally removed from the guestlist for some reason.
Other HTTP status codes mean different things. We’ve written guides on fixing issues with 404 not found errors, 500 internal server errors, 502 bad gateway errors, and 504 gateway timeout errors.
What Causes the 403 Forbidden Error on WordPress?
The two most likely causes of the 403 Forbidden Error on WordPress are:
- Corrupt
.htaccessfile - Incorrect file permissions
It’s also possible that you’re seeing the error because of an issue with a plugin that you’re using at your site. In this article, we’ll show you how to troubleshoot all of these potential issues.
403 Forbidden Error Variations
Like many other HTTP status codes, there are a lot of different variations for how this error code presents itself.
Here are some common variations that you might come across:
- “Forbidden – You don’t have permission to access / on this server”
- “403 – Forbidden: Access is denied”
- “Error 403 – Forbidden”
- “403 – Forbidden Error – You are not allowed to access this address”
- “403 Forbidden – nginx”
- “HTTP Error 403 – Forbidden – You do not have permission to access the document or program you requested”
- “403 Forbidden – Access to this resource on the server is denied”
- “403. That’s an error. Your client does not have permission to get URL / from this server”
- “You are not authorized to view this page”
- “It appears you don’t have permission to access this page.”
If you’re on an Nginx server, it will look like this below. Basically, if you see any mention of “forbidden” or “not allowed to access”, you’re probably dealing with a 403 Forbidden error.
How to Fix 403 Forbidden Error on WordPress
To help you fix the 403 Forbidden Error on your WordPress site, we’ll cover five separate troubleshooting steps in detail:
- File permissions
- .htaccess file
- Plugin issues
- CDN issues
- Hotlink protection
1. Modify Your File Permissions
Each folder and file on your WordPress site’s server has its own unique file permissions that control who can:
- Read – see the data in the file/view the contents of a folder.
- Write – modify the file/add or delete files inside a folder
- Execute – run the file and/or execute it as a script/access a folder and perform functions and commands.
These permissions are indicated by a 3-digit number, with each digit indicating the level of permission for each of the 3 categories above.
Normally, these permissions just “work” for your WordPress site. However, if something gets messed up with the file permissions at your WordPress site, it can cause the 403 Forbidden error.
To view and modify your site’s file permissions, you’ll need to connect via FTP/SFTP. Here’s how to use SFTP if you’re hosting at Kinsta.
For the screenshots in the tutorial below, we’ll be using the free FileZilla FTP program. The basic principles will apply to any FTP program, though – you’ll just need to apply them to a different interface.
Once you’re connected to your server, you can view a file or folder’s permissions by right-clicking on it:
Of course, manually checking the permissions for each file or folder isn’t really an option. Instead, you can automatically apply file permissions to all the files or folders inside of a folder.
According to the WordPress Codex, the ideal file permissions for WordPress are:
- Files – 644 or 640
- Directories – 755 or 750
One exception is that your wp-config.php file should be 440 or 400.
To set these permissions, right-click on the folder that contains your WordPress site (the folder name is public at Kinsta). Then, choose File Attributes:
Enter 755 or 750 in the Numeric value box. Then, choose Recurse into subdirectories and Apply to directories only:
Once you’ve applied the correct permissions for directories, you’ll repeat the process for files. Only this time:
- Enter 644 or 640 in the Numeric value box
- Choose Recurse into subdirectories
- Choose Apply to files only
To finish the process, you just need to manually adjust the permissions for your wp-config.php file to make them 440 or 400:
If file permissions issues were causing the 403 Forbidden Error, your site should now start working again.
2. Delete and Restore the .htaccess File
Kinsta uses the NGINX web server, so this potential issue doesn’t apply if you’re hosting your site at Kinsta because Kinsta sites do not have a .htaccess file.
However, if you’re hosting elsewhere and your host uses the Apache web server, one common cause of the 403 Forbidden error is a problem in your site’s .htaccess file.
The .htaccess file is a basic configuration file used by the Apache web server. You can use it to set up redirects, restrict access to all or some of your site, etc.
Because it’s so powerful, even if a little mistake can cause a big issue, like the 403 Forbidden error.
Rather than trying to troubleshoot the .htaccess file itself, a simpler solution is to just force WordPress to generate a new, clean .htaccess file.
To do that:
- Connect to your server via FTP
- Find the
.htaccessfile in your root folder - Download a copy of the file to your computer (it’s always a good idea to have a backup just in case)
- Delete the
.htaccessfile from your server after you have a safe backup copy on your local computer
Now, you should be able to access your WordPress site if your .htaccess file was the issue.
To force WordPress to generate a new, clean .htaccess file:
- Go to Settings → Permalinks in your WordPress dashboard
- Click Save Changes at the bottom of the page (you do not need to make any changes – just click the button)
And that’s it – WordPress will now generate a new .htaccess file for you.
3. Deactivate and then Reactivate Your Plugins
If neither your site’s file permissions nor .htaccess file are the problems, the next place to look is your plugins. It could be a bug in a plugin or a compatibility issue between different plugins.
No matter what the issue is, the easiest way to find the problematic plugin is with a little trial and error. Specifically, you’ll need to deactivate all of your plugins and then reactivate them one by one until you find the culprit.
If you can still access your WordPress dashboard, you can perform this process from the normal Plugins area.
If you cannot access your WordPress dashboard, you’ll instead need to connect to your WordPress site’s server via FTP/SFTP (here’s how to connect via SFTP at Kinsta).
Once you’re connected to your server via FTP:
- Browse to the wp-content folder
- Find the plugins folder inside of the wp-content folder
- Right-click on the plugins folder and choose Rename
- Change the name of the folder. You can name it anything different, but we recommend something like plugins-disabled to make it easy to remember.
By renaming the folder, you’ve effectively disabled all the plugins at your site.
Now, try accessing your site again. If your site is working, you know that one of your plugins is causing the 403 Forbidden error.
To find the culprit, reactivate your plugins one-by-one until you find which plugin is causing the issue.
After changing the file name of the plugins folder, you should see a number of errors that say plugin file does not exist when you go to the Plugins area on your site:
To fix this issue and regain the ability to manage your plugins, use your FTP program to change the name of the folder back to plugins. So, if you renamed it to plugins-disabled, just change it back to plugins.
Once you do that, you’ll see the full list of all your plugins again. Only now, they’ll all be deactivated:
Use the Activate button to reactivate them one-by-one.
Once you find the plugin that’s causing the issue, you can either reach out to the plugin’s developer for help or choose an alternate plugin that accomplishes the same thing (we’ve collected the best WordPress plugins here).
4. Deactivate CDN Temporarily
If you’re getting 403 forbidden errors on your assets (images, JavaScript, CSS), it could be a problem with your content delivery network (CDN). In this case, we recommend temporarily disabling your CDN and then checking your site to see if it works. If you’re a Kinsta client, click into your site and then on the “Kinsta CDN” tab. Once there, toggle the “Kinsta CDN” button off.
5. Check to See If Hotlink Protection Is Misconfigured
Hotlinking is when someone adds an image to their site, but the hosted link is still pointed to someone else’s site. To prevent this, some will set up what is called “hotlink protection” with their WordPress host or CDN provider.
When hotlink protection is enabled, it will typically return a 403 forbidden error. This is normal. However, if you’re seeing a 403 forbidden error on something you shouldn’t be, check to make sure hotlink protection is configured properly.
Still Having Issues? Reach Out to Your Hosting Provider
If none of the above solutions worked for you, then we recommend reaching out to your hosting provider. They can most likely help you pinpoint the issue and get you back up and running. If you’re a Kinsta client, open up a support ticket with our team. We are available 24/7.
Summary
The 403 Forbidden error means that your server is working, but you no longer have permission to view all or some of your site for some reason.
The two most likely causes of this error are issues with your WordPress site’s file permissions or .htaccess file. Beyond that, some plugin issues might also cause the 403 Forbidden error. Or it could be that something is misconfigured with hotlink protection or your CDN.
By following the troubleshooting steps in this guide, you should be able to get your site back to working in no time.
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275 PoPs worldwide
Test it yourself with $20 off your first month of Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
A clear explanation from Daniel Irvine [original link]:
There’s a problem with 401 Unauthorized, the HTTP status code for authentication errors. And that’s just it: it’s for authentication, not authorization.
Receiving a 401 response is the server telling you, “you aren’t
authenticated–either not authenticated at all or authenticated
incorrectly–but please reauthenticate and try again.” To help you out,
it will always include a WWW-Authenticate header that describes how
to authenticate.This is a response generally returned by your web server, not your web
application.It’s also something very temporary; the server is asking you to try
again.So, for authorization I use the 403 Forbidden response. It’s
permanent, it’s tied to my application logic, and it’s a more concrete
response than a 401.Receiving a 403 response is the server telling you, “I’m sorry. I know
who you are–I believe who you say you are–but you just don’t have
permission to access this resource. Maybe if you ask the system
administrator nicely, you’ll get permission. But please don’t bother
me again until your predicament changes.”In summary, a 401 Unauthorized response should be used for missing
or bad authentication, and a 403 Forbidden response should be used
afterwards, when the user is authenticated but isn’t authorized to
perform the requested operation on the given resource.
Another nice pictorial format of how http status codes should be used.
Nick T
25.2k11 gold badges79 silver badges120 bronze badges
answered Aug 4, 2011 at 6:24
23
Edit: RFC2616 is obsolete, see RFC9110.
401 Unauthorized:
If the request already included Authorization credentials, then the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials.
403 Forbidden:
The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfill it.
From your use case, it appears that the user is not authenticated. I would return 401.
emery
8,03510 gold badges42 silver badges49 bronze badges
answered Jul 21, 2010 at 7:28
OdedOded
485k98 gold badges877 silver badges1003 bronze badges
11
Something the other answers are missing is that it must be understood that Authentication and Authorization in the context of RFC 2616 refers ONLY to the HTTP Authentication protocol of RFC 2617. Authentication by schemes outside of RFC2617 is not supported in HTTP status codes and are not considered when deciding whether to use 401 or 403.
Brief and Terse
Unauthorized indicates that the client is not RFC2617 authenticated and the server is initiating the authentication process. Forbidden indicates either that the client is RFC2617 authenticated and does not have authorization or that the server does not support RFC2617 for the requested resource.
Meaning if you have your own roll-your-own login process and never use HTTP Authentication, 403 is always the proper response and 401 should never be used.
Detailed and In-Depth
From RFC2616
10.4.2 401 Unauthorized
The request requires user authentication. The response MUST include a WWW-Authenticate header field (section 14.47) containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. The client MAY repeat the request with a suitable Authorization header field (section 14.8).
and
10.4.4 403 Forbidden
The server understood the request but is refusing to fulfil it. Authorization will not help and the request SHOULD NOT be repeated.
The first thing to keep in mind is that «Authentication» and «Authorization» in the context of this document refer specifically to the HTTP Authentication protocols from RFC 2617. They do not refer to any roll-your-own authentication protocols you may have created using login pages, etc. I will use «login» to refer to authentication and authorization by methods other than RFC2617
So the real difference is not what the problem is or even if there is a solution. The difference is what the server expects the client to do next.
401 indicates that the resource can not be provided, but the server is REQUESTING that the client log in through HTTP Authentication and has sent reply headers to initiate the process. Possibly there are authorizations that will permit access to the resource, possibly there are not, but let’s give it a try and see what happens.
403 indicates that the resource can not be provided and there is, for the current user, no way to solve this through RFC2617 and no point in trying. This may be because it is known that no level of authentication is sufficient (for instance because of an IP blacklist), but it may be because the user is already authenticated and does not have authority. The RFC2617 model is one-user, one-credentials so the case where the user may have a second set of credentials that could be authorized may be ignored. It neither suggests nor implies that some sort of login page or other non-RFC2617 authentication protocol may or may not help — that is outside the RFC2616 standards and definition.
Edit: RFC2616 is obsolete, see RFC7231 and RFC7235.
answered Feb 5, 2013 at 17:14
ldrutldrut
3,7771 gold badge17 silver badges4 bronze badges
7
+-----------------------
| RESOURCE EXISTS ? (if private it is often checked AFTER auth check)
+-----------------------
| |
NO | v YES
v +-----------------------
404 | IS LOGGED-IN ? (authenticated, aka user session)
or +-----------------------
401 | |
403 NO | | YES
3xx v v
401 +-----------------------
(404 no reveal) | CAN ACCESS RESOURCE ? (permission, authorized, ...)
or +-----------------------
redirect | |
to login NO | | YES
| |
v v
403 OK 200, redirect, ...
(or 404: no reveal)
(or 404: resource does not exist if private)
(or 3xx: redirection)
Checks are usually done in this order:
- 404 if resource is public and does not exist or 3xx redirection
- OTHERWISE:
- 401 if not logged-in or session expired
- 403 if user does not have permission to access resource (file, json, …)
- 404 if resource does not exist or not willing to reveal anything, or 3xx redirection
UNAUTHORIZED: Status code (401) indicating that the request requires authentication, usually this means user needs to be logged-in (session). User/agent unknown by the server. Can repeat with other credentials. NOTE: This is confusing as this should have been named ‘unauthenticated’ instead of ‘unauthorized’. This can also happen after login if session expired.
Special case: Can be used instead of 404 to avoid revealing presence or non-presence of resource (credits @gingerCodeNinja)
FORBIDDEN: Status code (403) indicating the server understood the request but refused to fulfill it. User/agent known by the server but has insufficient credentials. Repeating request will not work, unless credentials changed, which is very unlikely in a short time span.
Special case: Can be used instead of 404 to avoid revealing presence or non-presence of resource (credits @gingerCodeNinja) in the case that revealing the presence of the resource exposes sensitive data or gives an attacker useful information.
NOT FOUND: Status code (404) indicating that the requested resource is not available. User/agent known but server will not reveal anything about the resource, does as if it does not exist. Repeating will not work. This is a special use of 404 (github does it for example).
As mentioned by @ChrisH there are a few options for redirection 3xx (301, 302, 303, 307 or not redirecting at all and using a 401):
- Difference between HTTP redirect codes
- How long do browsers cache HTTP 301s?
- What is correct HTTP status code when redirecting to a login page?
- What’s the difference between a 302 and a 307 redirect?
answered Feb 23, 2015 at 11:00
9
According to RFC 2616 (HTTP/1.1) 403 is sent when:
The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfill it. Authorization will not help and the request SHOULD NOT be repeated. If the request method was not HEAD and the server wishes to make public why the request has not been fulfilled, it SHOULD describe the reason for the refusal in the entity. If the server does not wish to make this information available to the client, the status code 404 (Not Found) can be used instead
In other words, if the client CAN get access to the resource by authenticating, 401 should be sent.
answered Jul 21, 2010 at 7:26
CumbayahCumbayah
4,3771 gold badge24 silver badges32 bronze badges
6
Assuming HTTP authentication (WWW-Authenticate and Authorization headers) is in use, if authenticating as another user would grant access to the requested resource, then 401 Unauthorized should be returned.
403 Forbidden is used when access to the resource is forbidden to everyone or restricted to a given network or allowed only over SSL, whatever as long as it is no related to HTTP authentication.
If HTTP authentication is not in use and the service has a cookie-based authentication scheme as is the norm nowadays, then a 403 or a 404 should be returned.
Regarding 401, this is from RFC 7235 (Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Authentication):
3.1. 401 Unauthorized
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for the target resource. The origin server MUST send a WWW-Authenticate header field (Section 4.4) containing at least one challenge applicable to the target resource. If the request included authentication credentials, then the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with a new or replaced Authorization header field (Section 4.1). If the 401 response contains the same challenge as the prior response, and the user agent has already attempted authentication at least once, then the user agent SHOULD present the enclosed representation to the user, since it usually contains relevant diagnostic information.
The semantics of 403 (and 404) have changed over time. This is from 1999 (RFC 2616):
10.4.4 403 Forbidden
The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfill it. Authorization will not help and the request SHOULD NOT be repeated. If the request method was not HEAD and the server wishes to make public why the request has not been fulfilled, it SHOULD describe the reason for the refusal in the entity. If the server does not wish to make this information available to the client, the status code 404 (Not Found) can be used instead.
In 2014 RFC 7231 (Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content) changed the meaning of 403:
6.5.3. 403 Forbidden
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. A server that wishes to make public why the request has been forbidden can describe that reason in the response payload (if any).
If authentication credentials were provided in the request, the server considers them insufficient to grant access. The client SHOULD NOT automatically repeat the request with the same credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with new or different credentials. However, a request might be forbidden for reasons unrelated to the credentials.
An origin server that wishes to «hide» the current existence of a forbidden target resource MAY instead respond with a status code of 404 (Not Found).
Thus, a 403 (or a 404) might now mean about anything. Providing new credentials might help… or it might not.
I believe the reason why this has changed is RFC 2616 assumed HTTP authentication would be used when in practice today’s Web apps build custom authentication schemes using for example forms and cookies.
answered Feb 27, 2013 at 9:44
6
- 401 Unauthorized: I don’t know who you are. This an authentication error.
- 403 Forbidden: I know who you are, but you don’t have permission to access this resource. This is an authorization error.
Premraj
72.1k25 gold badges236 silver badges175 bronze badges
answered Aug 6, 2019 at 12:37
4
This is an older question, but one option that was never really brought up was to return a 404. From a security perspective, the highest voted answer suffers from a potential information leakage vulnerability. Say, for instance, that the secure web page in question is a system admin page, or perhaps more commonly, is a record in a system that the user doesn’t have access to. Ideally you wouldn’t want a malicious user to even know that there’s a page / record there, let alone that they don’t have access. When I’m building something like this, I’ll try to record unauthenticate / unauthorized requests in an internal log, but return a 404.
OWASP has some more information about how an attacker could use this type of information as part of an attack.
answered Dec 25, 2014 at 9:09
4
This question was asked some time ago, but people’s thinking moves on.
Section 6.5.3 in this draft (authored by Fielding and Reschke) gives status code 403 a slightly different meaning to the one documented in RFC 2616.
It reflects what happens in authentication & authorization schemes employed by a number of popular web-servers and frameworks.
I’ve emphasized the bit I think is most salient.
6.5.3. 403 Forbidden
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. A server that wishes to make public why the request has been forbidden can describe that reason in the response payload (if any).
If authentication credentials were provided in the request, the server considers them insufficient to grant access. The client SHOULD NOT repeat the request with the same credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with new or different credentials. However, a request might be forbidden for reasons unrelated to the credentials.
An origin server that wishes to «hide» the current existence of a forbidden target resource MAY instead respond with a status code of 404 (Not Found).
Whatever convention you use, the important thing is to provide uniformity across your site / API.
answered May 22, 2014 at 10:54
Dave WattsDave Watts
8407 silver badges11 bronze badges
1
These are the meanings:
401: User not (correctly) authenticated, the resource/page require authentication
403: User’s role or permissions does not allow to access requested resource, for instance user is not an administrator and requested page is for administrators.
Note: Technically, 403 is a superset of 401, since is legal to give 403 for unauthenticated user too. Anyway is more meaningful to differentiate.
answered Nov 19, 2019 at 10:17
Luca C.Luca C.
11.1k1 gold badge86 silver badges77 bronze badges
3
!!! DEPR: The answer reflects what used to be common practice, up until 2014 !!!
TL;DR
- 401: A refusal that has to do with authentication
- 403: A refusal that has NOTHING to do with authentication
Practical Examples
If apache requires authentication (via .htaccess), and you hit Cancel, it will respond with a 401 Authorization Required
If nginx finds a file, but has no access rights (user/group) to read/access it, it will respond with 403 Forbidden
RFC (2616 Section 10)
401 Unauthorized (10.4.2)
Meaning 1: Need to authenticate
The request requires user authentication. …
Meaning 2: Authentication insufficient
… If the request already included Authorization credentials, then the 401 response indicates that authorization has been refused for those credentials. …
403 Forbidden (10.4.4)
Meaning: Unrelated to authentication
… Authorization will not help …
More details:
The server understood the request, but is refusing to fulfill it.
It SHOULD describe the reason for the refusal in the entity
The status code 404 (Not Found) can be used instead
(If the server wants to keep this information from client)
answered Feb 25, 2015 at 9:03
LeviteLevite
16.9k8 gold badges50 silver badges50 bronze badges
2
they are not logged in or do not belong to the proper user group
You have stated two different cases; each case should have a different response:
- If they are not logged in at all you should return 401 Unauthorized
- If they are logged in but don’t belong to the proper user group, you should return 403 Forbidden
Note on the RFC based on comments received to this answer:
If the user is not logged in they are un-authenticated, the HTTP equivalent of which is 401 and is misleadingly called Unauthorized in the RFC. As section 10.4.2 states for 401 Unauthorized:
«The request requires user authentication.»
If you’re unauthenticated, 401 is the correct response. However if you’re unauthorized, in the semantically correct sense, 403 is the correct response.
answered Oct 1, 2012 at 14:34
Zaid MasudZaid Masud
13.1k9 gold badges66 silver badges88 bronze badges
4
I have created a simple note for you which will make it clear.
answered Nov 11, 2021 at 12:19
PrathamPratham
4673 silver badges7 bronze badges
In English:
401
You are potentially allowed access but for some reason on this request you were
denied. Such as a bad password? Try again, with the correct request
you will get a success response instead.
403
You are not, ever, allowed. Your name is not on the list, you won’t
ever get in, go away, don’t send a re-try request, it will be refused,
always. Go away.
answered Apr 8, 2020 at 14:23
JamesJames
4,6155 gold badges36 silver badges48 bronze badges
2
401: You need HTTP basic auth to see this.
If the user just needs to log in using you site’s standard HTML login form, 401 would not be appropriate because it is specific to HTTP basic auth.
403: This resource exists but you are not authorized to see it, and HTTP basic auth won’t help.
I don’t recommend using 403 to deny access to things like /includes, because as far as the web is concerned, those resources don’t exist at all and should therefore 404.
In other words, 403 means «this resource requires some form of auth other than HTTP basic auth (such as using the web site’s standard HTML login form)».
https://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec10.html#sec10.4.2
answered Sep 23, 2017 at 12:33
Vlad KorneaVlad Kornea
4,2493 gold badges38 silver badges40 bronze badges
401: Who are you again?? (programmer walks into a bar with no ID or invalid ID)
403: Oh great, you again. I’ve got my eye on you. Go on, get outta here. (programmer walks into a bar they are 86’d from)
answered Aug 11, 2022 at 23:10
emeryemery
8,03510 gold badges42 silver badges49 bronze badges
0
I think it is important to consider that, to a browser, 401 initiates an authentication dialog for the user to enter new credentials, while 403 does not. Browsers think that, if a 401 is returned, then the user should re-authenticate. So 401 stands for invalid authentication while 403 stands for a lack of permission.
Here are some cases under that logic where an error would be returned from authentication or authorization, with important phrases bolded.
- A resource requires authentication but no credentials were specified.
401: The client should specify credentials.
- The specified credentials are in an invalid format.
400: That’s neither 401 nor 403, as syntax errors should always return 400.
- The specified credentials reference a user which does not exist.
401: The client should specify valid credentials.
- The specified credentials are invalid but specify a valid user (or don’t specify a user if a specified user is not required).
401: Again, the client should specify valid credentials.
- The specified credentials have expired.
401: This is practically the same as having invalid credentials in general, so the client should specify valid credentials.
- The specified credentials are completely valid but do not suffice the particular resource, though it is possible that credentials with more permission could.
403: Specifying valid credentials would not grant access to the resource, as the current credentials are already valid but only do not have permission.
- The particular resource is inaccessible regardless of credentials.
403: This is regardless of credentials, so specifying valid credentials cannot help.
- The specified credentials are completely valid but the particular client is blocked from using them.
403: If the client is blocked, specifying new credentials will not do anything.
answered Jun 2, 2018 at 23:34
401 response means one of the following:
- An access token is missing.
- An access token is either expired, revoked, malformed, or invalid.
403 response on the other hand means that the access token is indeed valid, but that the user does not have appropriate privileges to perform the requested action.
answered Feb 17, 2022 at 11:16
Ran TurnerRan Turner
12.7k4 gold badges38 silver badges48 bronze badges
0
Given the latest RFC’s on the matter (7231 and 7235) the use-case seems quite clear (italics added):
- 401 is for unauthenticated («lacks valid authentication»); i.e. ‘I don’t know who you are, or I don’t trust you are who you say you are.’
401 Unauthorized
The 401 (Unauthorized) status code indicates that the request has not
been applied because it lacks valid authentication credentials for
the target resource. The server generating a 401 response MUST send
a WWW-Authenticate header field (Section 4.1) containing at least one
challenge applicable to the target resource.
If the request included authentication credentials, then the 401
response indicates that authorization has been refused for those
credentials. The user agent MAY repeat the request with a new or
replaced Authorization header field (Section 4.2). If the 401
response contains the same challenge as the prior response, and the
user agent has already attempted authentication at least once, then
the user agent SHOULD present the enclosed representation to the
user, since it usually contains relevant diagnostic information.
- 403 is for unauthorized («refuses to authorize»); i.e. ‘I know who you are, but you don’t have permission to access this resource.’
403 Forbidden
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood
the request but refuses to authorize it. A server that wishes to
make public why the request has been forbidden can describe that
reason in the response payload (if any).
If authentication credentials were provided in the request, the
server considers them insufficient to grant access. The client
SHOULD NOT automatically repeat the request with the same
credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with new or different
credentials. However, a request might be forbidden for reasons
unrelated to the credentials.
An origin server that wishes to «hide» the current existence of a
forbidden target resource MAY instead respond with a status code of
404 (Not Found).
answered Jun 5, 2018 at 15:26
cjbarthcjbarth
4,0526 gold badges41 silver badges60 bronze badges
3
I have a slightly different take on it from the accepted answer.
It seems more semantic and logical to return a 403 when authentication fails and a 401 when authorisation fails.
Here is my reasoning for this:
When you are requesting to be authenticated, You are authorised to make that request. You need to otherwise no one would even be able to be authenticated in the first place.
If your authentication fails you are forbidden, that makes semantic sense.
On the other hand the forbidden can also apply for Authorisation, but
Say you are authenticated and you are not authorised to access a particular endpoint. It seems more semantic to return a 401 Unauthorised.
Spring Boot’s security returns 403 for a failed authentication attempt
answered Apr 6, 2022 at 22:44
theMyththeMyth
2544 silver badges14 bronze badges
In the case of 401 vs 403, this has been answered many times. This is essentially a ‘HTTP request environment’ debate, not an ‘application’ debate.
There seems to be a question on the roll-your-own-login issue (application).
In this case, simply not being logged in is not sufficient to send a 401 or a 403, unless you use HTTP Auth vs a login page (not tied to setting HTTP Auth). It sounds like you may be looking for a «201 Created», with a roll-your-own-login screen present (instead of the requested resource) for the application-level access to a file. This says:
«I heard you, it’s here, but try this instead (you are not allowed to see it)»
answered Dec 12, 2014 at 19:01
3