У пользователя часто возникают различные неполадки при использовании интернета. Сегодня речь пойдет о распространенной error 411 или ошибка 411, которая вызывает массу вопросов у новичков.
Если не пытаться устранить этот изъян, то есть 90% того, что пользователь не сможет сделать удачный запрос к сервису через определенный URL.
Полное название этого кода 411 Length Required. Первая арабская цифра обозначает состояние результата запроса пользователя, то есть HTTP. Все коды, которые начинаются с числовой последовательности в виде 4xx, обозначают статус «Client Error», а по-русски «Ошибка клиента».
Это один из пяти классов состояния кода, который описан в документе RFC, и является стандартом.
Чтобы человеку не приходилось запоминать все термины числовых обозначений, после них идёт поясняющая фраза, отделенная пробелом. Она написана на английском языке и описывает суть отказа работы клиентского запроса в сервис.
В нашем случае словосочетание «Length Required» переводится, как «Требуемая длина». По названию понятно, что задача скрывается в сердце запроса, отправляемый в сервис.
Причины появления этой ошибки
Когда в браузере появляется надпись в виде кода 411, то это свидетельствует об ограничении объёма байтов. Также причиной могут послужить вирусы или повреждённый реестр.
Ошибки запроса
Единственная причина, по которой происходит неожиданный разрыв соединения — это ошибки синтаксической структуры на сервере. Обычно появляется на запросах вида POST, иногда PUT.
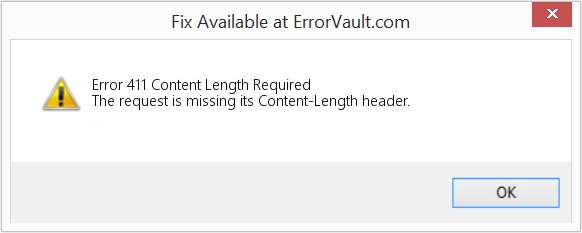
Когда после отправки команды в браузере вылазит данный код ошибки, то это показывает отсутствие определенного заголовка Content-Length. В переводе означает «Длина контента».
Для устранения этих неполадок требуется в заголовке запроса указать размер Content-Length. Без написания этой строки бесполезно делать повторный запрос на определенном URL — будет такая же реакция. По существу — это количество байтов, которые указаны в кодированном заголовке. 1 символ в данном случае принимается за 1 байт.
Пример возникновения ошибки 411
Допустим, в браузере на определенном URL происходит скачивание файлов контента. Если на сервере стоит ограничение на объем байтов, то проще проверить заголовок Content-Length и, если количество файлов превышает максимальный лимит, то скачивание будет провалено.
Если игнорировать эти действия, то бесполезная сильная нагрузка сети приведет к разрыву соединения и ошибке 411. При ее появлении не забудьте подкорректировать на сервере все заголовки, чтобы робот удачно проиндексировал веб-страницу.
Признаки появления ошибки 411
Для выявления этого недуга недостаточно просто зайти в свой ПК.
Основные признаки, которые говорят о появлении ошибки, можно увидеть в ниже представленном списке:
- периодически выскакивает ошибка 411, после чего окно сайта моментально закрывается или становится неактивное;
- вместо открытого URL выскакивает надпись «Content Length Required»;
- ПК неоднократно глючит при использовании на 3-4 секунды, иногда больше;
- Windows ведёт медленную работу независимо от нагрузки жёсткого диска. С задержкой реагирует на ввод данных с клавиатуры и нажатие мышки.
Но есть и исключения, поэтому если пользователь один раз заметит ошибку, то значит сайт работает должным образом. Необходимо убедится, что код 411 вылазит из-за проблем пользователя, а не из-за плохого сайта.
Основные причины появления ошибки 411
Если вы не являетесь создателем сайта, который по своей вине не доделал заголовок в запросе, и надоедливая табличка вылазит на каждой веб-странице, то в этом виноват ваш ПК.
Есть несколько причин, из-за которых высвечивается ответ кода 411:
- попадание вредителя, который смог поменять или захватить ваш браузер;
- испорченный реестр, из-за обновления ПО в системе;
- злокачественная программа, которая изменяет конфигурацию кеша, связанный с интернет-браузером.
Ухудшение работоспособности реестра Windows обусловлено установленным вредоносным программным обеспечением. В результате это приведет не только к плохой работе сайтов, но и к появлению более опасных ошибок.
Как устранить ошибку 411?
Для устранения Content Length Required будет представлен перечень вариантов решения. Список начнется от самого простого к более сложному, поэтому рекомендуется применять способы по порядку, чтобы не тратить много сил и времени.
На данный момент известно множество способов по устранению ошибки 411:
- восстановить реестр в прежнее состояние;
- скачать защитную программу на сканирование и удаление опасного ПО;
- с помощью чистки диска провести удаление ненужных временных папок и файлов;
- установить утилиту и обновить драйвера устройств;
- использовать услугу Восстановление системы, чтобы избавиться от последних действий Windows;
- в пункте Программы и компоненты найти Windows Operating System. Требуется удалить программу, а затем снова восстановить её;
- провести проверку файлов системы. В поисковике ПК нужно ввести фразу command, затем зажатием CNTR-Shift нажать Enter. В диалоговом окне нажать на Да и продолжить работу. Мигающим курсором вести словосочетание «sfc/scannow». После нажатия Enter начнется диагностика системы на выявление проблем;
- скачать необходимые обновления для вашего Windows;
- создать резервную копию документов и заново проделать установку Windows.
Не стоит проводить восстановительные процедуры в ручную, если вы слабо владеете компьютером. По ошибке можно скачать дополнительный вирус или забыть создать резервную копию файлов.
In an HTTP request, a server will send the desired resources to your browser, allowing you to see a certain website. If something goes wrong during this process, you may see an HTTP status code like the “411 Length Required” error.
Fortunately, you can easily fix the “411 Length Required” error. This HTTP status code happens when the server requires a content-length header, but it isn’t specified in a request. To resolve this issue, you can simply define a content length.
Check Out Our Video Guide to the “411 Length Required” Error
In this post, we’ll explain the “411 Length Required” status code and what causes it. Then, we’ll show you how to locate and fix this error. Let’s get started!
What Is the “411 Length Required” Error?
Whenever you click on a link or search for a URL, your browser will send a request to the website’s server. Then, the server will process the request and respond by sending the requested data.
Although you might not see them, the server will also send a status code in the HTTP header. Your browser will only notify you of HTTP status codes if something went wrong during the request.
For example, a common HTTP status code is a 400 bad request. This is a generic client-side error that can happen when you incorrectly type a URL.
HTTP status codes are grouped into five different classes:
- 100s: Informational responses
- 200s: Successful responses
- 300s: Redirection codes
- 400s: Client-side error codes
- 500s: Server-side error codes
No idea what the “411 Length Required” error means, let alone how to fix it? 😅 Have no fear 👇Click to Tweet
Now that you know about HTTP status codes, let’s discuss the “411 Length Required” error. Since this is a less common error, you might become frustrated when it happens.
In a “411 Length Required” error, your request is rejected because it lacks a content-length header. If a server requires this information, you won’t be able to access the site without it.
What Causes the “411 Length Required” Error?
In an HTTP request and response, the client and server can place additional information in HTTP headers. Since the “411 Length Required” status code is a client-side error, this means that there was a problem with the request header.
You can use the request header to provide context about the request, allowing the server to tailor its response. The request header can include:
- Source IP address and port number
- Content-type
- Browser type (user-agent)
- Requested URL
HTTP headers can also define the size of the entity-body. By specifying the content-length value, you can let the server know the anticipated size of the request. This is identified in a decimal number of octets.
For example, you can view the content length of a web page by right-clicking on an element and selecting Inspect. Under Network, you should find information about the request header.
In general, most HTTP requests will have both a request body and content-length header. However, some clients choose not to define the content length. This can be useful when performing chunked transfer-encoding.
Sometimes, a server will indicate that it requires a content-length header. When you receive a “411 Length Required” HTTP status code, you’ll likely need to define this value to proceed with the request.
How To Locate the “411 Length Required” Error
Since the “411 Length Required” status code is a client-side error, you might not know if this is happening to your website. Fortunately, you can monitor your site’s HTTP requests so you can ensure all visitors can access your content.
With a Kinsta hosting account, you can check for failed HTTP requests directly from your MyKinsta dashboard. To do this, you can look through your website logs.
First, open MyKinsta and log in. Then, navigate to Sites and select the website you want to analyze. You’ll only be able to monitor HTTP requests on your live website, so be sure not to click on your local environment:
This will take you to the Info page, where you can see basic details about your website. On the left-hand side, click on the Logs tab:
The Log viewer will automatically be set to display your site’s error logs. Using the dropdown menu, select the access.log option:
In the access log, you can view all of the requests for your website. This will show the date, time, bytes sent, and user-agent. Here, you can also see the HTTP status codes for each request:
You’ll see a 200 code if everything processes correctly. To locate possible “411 Length Required” errors, you can use the search bar to find a 411 status code.
How To Fix the “411 Length Required” Error (4 Methods)
Although you can keep track of “411 Length Required” status codes using your website logs, keep in mind that this is a client-side issue.
That means, like all 400 HTTP status codes, the error is caused by incorrect settings on the user’s side. To fix the issue, you have to alter the HTTP request. Let’s look at four ways you may be able to do this.
1. Check the Requested URL
First, you can try some general methods to fix 400 HTTP status codes. Since the “411 Length Required” is a client-side issue, you can review the information in your request. This can ensure that the browser understands it.
When fixing any 400 status codes, it’s a good idea to review the requested URL. If you manually entered a URL to reach a website, the address may have a typo in it. To check to see if this is the problem, try re-typing the address.
If you’re sure the URL is correct but the error persists, you can enter it into a search engine along with a keyword. For instance, you can find Kinsta’s article on speeding up a WooCommerce store by searching ‘site:kinsta.com speed up WooCommerce’:
Since the “411 Length Required” error is a client-side issue, this is one basic step you can take. However, keep in mind that this may not resolve this specific status code. To do this, you’ll likely need to set a content-length header.
2. Set a Content-Length Header
If you receive a “411 Length Required” status code, the most direct way to solve this issue is by setting a content-length header. Since the server notes that content length is required to fulfill the request, it’s important to include it.
For example, if you’re sending a POST request to example.com, it may look something like this:
curl --verbose -X POST https://example.comIf you receive a “411 Length Required” status code, you’ll need to add a content-length header. This value is the number of bytes in the request. These bytes are represented by two hexadecimal digits, so you can divide the number of digits by two to determine the content length.
For example, ‘48656c6c6f21’ has 12 hexadecimal digits. To transition this value into bytes, you can divide it by two, which would make the content length 6 bytes.
Here’s what a 6 byte content length can look like in a request:
curl --verbose -X POST -H 'Content-Length: 6' https://example.comDefining the content length will likely remove the “411 Length Required” error message and send back a 200 HTTP status code. Essentially, this means that the request was processed correctly.
3. Clear Your Browser Cache
Often, determining a content-length header is all you need to do to resolve the “411 Length Required error. If you still receive this status code, however, there are some additional steps you can take.
When you first access a website, your browser stores certain data. Even after you set a content-length header, this could cause a “411 Length Required” error to appear. To remove the message, try clearing your browser cache.
If you’re using Google Chrome, click on the three-dot icon in the top right corner. Then, select More Tools > Clear Browsing Data…:
This will open a pop-up window that you can use to manage browsing history, cookies, and cached data. Make sure to select Cached images and files, along with any other information you want to clear. Finally, click on Clear data:
For Safari users, you can navigate to Safari in your toolbar. Here, select Clear history:
Then, you can choose whether to clear your entire browsing history, data from the last hour, or from the last few days. When finished, click on Clear History:
If you want to clear the cache on Mozilla Firefox, find the hamburger icon in the top-right corner. Next, select the History option:
On the next page, navigate to Clear recent history:
Be sure to select Cache and any other data you want to clear. After this, click on OK:
Now you can try your HTTP request again to see if this resolved the “411 Length Required” error!
4. Uninstall Recent Updates or Extensions
An additional way to fix the “411 Length Required” error is to disable browser extensions. Occasionally, certain extensions can interfere with your browser, making them unable to interpret requests. If you’ve installed an extension recently, you can consider removing them.
If you’re using Google Chrome, this process will be similar to clearing your browser cache. First, find the menu icon and select More Tools > Extensions:
From your list of extensions, find the one you want to remove. You can either remove them completely or simply turn them off using the slider:
Likewise, new software updates can cause HTTP error codes. To uninstall a recent Windows update, you can navigate to the Windows Update tab under Update & Security in your Settings app.
If you have a macOS operating system, this process is much more complicated. To roll back an update, you’ll need to have a Time Machine backup from before the update. Then, you can restore the data from the backup.
Keep in mind that this method should be a last resort after you’ve tried other solutions. Since you’re reverting to an older software version, you’ll likely lose important functionality and bug fixes.
This error may look intimidating, but rest assured- it couldn’t be easier to resolve it… with a little help from this guide 👀Click to Tweet
Summary
It can be frustrating when a server denies your HTTP request, displaying a “411 Length Required” error. Without specifying a content-length header, you may not be able to pull information from the server. However, there are a few ways you can resolve this issue.
To review, here’s how you can fix the “411 Length Required” error:
- Check the requested URL.
- Set a content-length header.
- Clear your browser cache.
- Uninstall recent updates or extensions.
To ensure every visitor can access your site, you might want to enable performance monitoring. With a Kinsta hosting plan, you get one of the best APM tools on the market. Using our APM dashboard, you can review external requests and immediately solve HTTP errors!
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275 PoPs worldwide
Test it yourself with $20 off your first month of Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
This article features error number Code 411, commonly known as Content Length Required described as The request is missing its Content-Length header.
About Status Codes
When you receive web error codes, you may either be having client or server issues. The problem could be related to browser or settings that are blocking your connection, or it can be any other issues related to the server you are trying to access.
To explain the problem further, here are some useful information about web error codes, their symptoms, causes and repair methods.
Definitions (Beta)
Here we list some definitions for the words contained in your error, in an attempt to help you understand your problem. This is a work in progress, so sometimes we might define the word incorrectly, so feel free to skip this section!
- Header — This tag is deprecated because it lacks discriminating power
- Request — A request is a message sent by a source to another object.
- Required — Required is an HTML attribute of an input element that forces that the input be supplied.
Symptoms of Code 411 — Content Length Required
Web error codes are also known as http status codes. There are five different classes of http status codes and they always start with the following digits, depending on what kind of error was encountered by the user. These are also the symptoms of the error that the user is experiencing. To explain further, here are the status codes.
4xx: Client Error
This error is sent back to the user when it is a client-side error. The user receives notifications of a bad request, content not found or unauthorized access to the content or something to that effect.
400 — Bad Request
401 — Unauthorized
402 — Payment Required
403 — Forbidden
404 — Not Found
405 — Method Not Allowed
406 — Not Accepted
407 — Proxy Authentication Required
408 — Request Timeout
409 — Conflict
410 — Gone
411 — Length Required
412 — Precondition Failed
413 — Request Entity Too Large
414 — Request-URI Too Long
415 — Unsupported Media Type
416 — Request Range Not Satisfied
417 — Expectation Failed
(For illustrative purposes only)
Causes of Content Length Required — Error 411
4XX codes are caused by the user or settings from the user’s side. The request was not understood by the server because of wrong address bar entry, incorrect syntax, unstable connection or erroneous OS.
Repair Methods
There are particular troubleshooting steps for particular Web Error codes. However, there are also generalized repair methods users can perform when faced with these kinds of errors.
If a repair method works for you, please click the upvote button to the left of the answer, this will let other users know which repair method is currently working the best.
Please note: Neither ErrorVault.com nor it’s writers claim responsibility for the results of the actions taken from employing any of the repair methods listed on this page — you complete these steps at your own risk.
Method 1 — Clear Browser Cache
When accessing a site, data gets stored in the browser cache. Sometimes, you have tried fixing a web error but the same message appears on your browser. In such cases, you need to clear your browser cache to get rid of the annoying message. Here are ways to do that in different kinds of browsers:
- On Google Chrome
- Open Chrome and click the three dots on the upper right portion of your browser
- Click More Tools and then Click Clear browsing data.
- You may choose to delete everything or just a certain browsing period.
- Check the boxes beside Cookies and other site data and Cached images and files.
- Finally, click Clear data.
- On Edge
- Click the … it is the rightmost button just beneath the close button.
- Scroll down and Click Settings.
- Look for Clear browsing data, and click Choose what to clear button.
- It will give you option to choose which type of data you want to clear, just put a check mark on the items you want to include, then click Clear.
- On Mozilla
- Go to History menu and select Clear Recent History.
- You may click the Alt button if the menu bar is hidden.
- You will see a dropdown menu where you can select the period or range you want to delete, click your selection.
- You can click on Details to choose what to clear, whether it be the entire cache or other items.
- Once selected, click Clear now and then reboot the browser to let changes take effect.
Method 2 — Check the Logs
- If you want to check log files, you may do so by first ensuring that you are logged into the web server computer as an Administrator.
- Click Start, then Settings, then click Control Panel.
- Open Administrator Tools and then double-click Internet Services Manager.
- Select the website from the list of different served sites.
- Right click the website and then point your mouse to Properties.
- Select Website tab and then click Properties. On it, you will see General Properties tab. On the bottom of the window, you may see the location of the log files generated.
- Open log files using WordPad, any text file viewer or Microsoft Word.
- Here, you should be able to analyze where you got the errors while accessing a server.
Method 3 — Check Requested URL
- There are also times when you manually enter the URL of a site you wish to explore. If you are getting errors after doing this, check the URL you just entered on the address bar if you are indeed accessing the correct address. If not, correct the items you typed incorrectly.
Method 4 — Uninstall Recent Updates
For Windows 7
- Search for Windows Updates on the search bar.
- Click enter when it comes up on the search results.
- Check recent updates and click Uninstall updates on recent dates when the error began happening.
For Windows 8 and Windows 10
- Press the window key and the letter X simultaneously to open Settings
- When you get to Windows settings, click Update & Security.
- Click view installed update history, then Uninstall updates.
Method 5 — Uninstall Extensions
- Sometimes, additional Extensions may give you Web Error Codes.
- Uninstall Extensions you recently installed by going to your browser settings and then clicking More Tools.
- You will see extensions than had been installed on your browser, choose the latest addition which you suspected caused the problem you are having.
Method 6 — Check for Server Configuration
- This troubleshooting is normally handled by the site admin. If that is you, then you need to have an understanding of Web server configurations.
- You may check which web server is running your site by using URL or domain checkers. You just need to enter the site address and analyze the results that you will get.
- You may also check for broken links by right clicking the webpage and clicking on Inspect. This should give you the code to the site on the right side. You may check each anchor text and see if the links connected to them are still live.
Method 7 — Other techniques
- You may also check for any unwanted characters on the codes and script by Debug Application Codes and Scripts. If you don’t have any idea how to do it, you may check this resource to do that.
- You may also try to Refresh website. Sometimes, the error you are getting is an old error which has not gone away and a simple refresh by clicking F5 may do the job.
Other languages:
Wie beheben Fehler 411 (Inhalt Länge erforderlich) — Der Anforderung fehlt der Content-Length-Header.
Come fissare Errore 411 (Contenuto Lunghezza Richiesto) — Nella richiesta manca l’intestazione Content-Length.
Hoe maak je Fout 411 (Inhoud Lengte Vereist) — Het verzoek mist de kop Content-Length.
Comment réparer Erreur 411 (Contenu Longueur requis) — Il manque son en-tête Content-Length à la requête.
어떻게 고치는 지 오류 411 (콘텐츠 길이 필수) — 요청에 Content-Length 헤더가 없습니다.
Como corrigir o Erro 411 (Comprimento do conteúdo necessário) — A solicitação está sem seu cabeçalho Content-Length.
Hur man åtgärdar Fel 411 (Innehåll Längd Obligatoriskt) — Begäran saknar rubriken Content-Length.
Как исправить Ошибка 411 (Content Length Обязательно) — В запросе отсутствует заголовок Content-Length.
Jak naprawić Błąd 411 (Treść Długość Wymagana) — W żądaniu brakuje nagłówka Content-Length.
Cómo arreglar Error 411 (Longitud del contenido requerida) — A la solicitud le falta su encabezado Content-Length.
About The Author: Phil Hart has been a Microsoft Community Contributor since 2010. With a current point score over 100,000, they’ve contributed more than 3000 answers in the Microsoft Support forums and have created almost 200 new help articles in the Technet Wiki.
Follow Us:
Last Updated:
11/08/22 11:20 : A Android user voted that repair method 1 worked for them.
This repair tool can fix common computer problems such as blue screens, crashes and freezes, missing DLL files, as well as repair malware/virus damage and more by replacing damaged and missing system files.
STEP 1:
Click Here to Download and install the Windows repair tool.
STEP 2:
Click on Start Scan and let it analyze your device.
STEP 3:
Click on Repair All to fix all of the issues it detected.
DOWNLOAD NOW
Compatibility
Requirements
1 Ghz CPU, 512 MB RAM, 40 GB HDD
This download offers unlimited scans of your Windows PC for free. Full system repairs start at $19.95.
Article ID: ACX01609EN
Applies To: Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows XP, Windows 2000
Speed Up Tip #15
Tweak Windows with Free Programs:
You can boost the speed of your computer by fine-tuning its settings using free software. Tweaking Windows XP, Windows 7 and even Windows 10 can be done easily using power utilities that you can download for free online.
Click Here for another way to speed up your Windows PC
Errors in Alphabetical Order: A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Microsoft & Windows® logos are registered trademarks of Microsoft. Disclaimer: ErrorVault.com is not affiliated with Microsoft, nor does it claim such affiliation. This page may contain definitions from https://stackoverflow.com/tags under the CC-BY-SA license. The information on this page is provided for informational purposes only. © Copyright 2018
This is how I call a service with .NET:
var requestedURL = "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/token?code=" + code + "&client_id=" + client_id + "&client_secret=" + client_secret + "&redirect_uri=" + redirect_uri + "&grant_type=authorization_code";
HttpWebRequest authRequest = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(requestedURL);
authRequest.ContentType = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded";
authRequest.Method = "POST";
WebResponse authResponseTwitter = authRequest.GetResponse();
but when this method is invoked, I get:
Exception Details: System.Net.WebException: The remote server returned
an error: (411) Length Required.
what should I do?
huseyint
14.9k15 gold badges55 silver badges78 bronze badges
asked Aug 21, 2013 at 8:15
When you’re using HttpWebRequest and POST method, you have to set a content (or a body if you prefer) via the RequestStream. But, according to your code, using authRequest.Method = «GET» should be enough.
In case you’re wondering about POST format, here’s what you have to do :
ASCIIEncoding encoder = new ASCIIEncoding();
byte[] data = encoder.GetBytes(serializedObject); // a json object, or xml, whatever...
HttpWebRequest request = WebRequest.Create(url) as HttpWebRequest;
request.Method = "POST";
request.ContentType = "application/json";
request.ContentLength = data.Length;
request.Expect = "application/json";
request.GetRequestStream().Write(data, 0, data.Length);
HttpWebResponse response = request.GetResponse() as HttpWebResponse;
answered Aug 21, 2013 at 8:25
AtlasmaybeAtlasmaybe
1,44611 silver badges25 bronze badges
1
you need to add Content-Length: 0 in your request header.
a very descriptive example of how to test is given here
answered Aug 21, 2013 at 8:26
EhsanEhsan
31.2k6 gold badges55 silver badges63 bronze badges
2
When you make a POST HttpWebRequest, you must specify the length of the data you are sending, something like:
string data = "something you need to send"
byte[] postBytes = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(data);
request.ContentLength = postBytes.Length;
if you are not sending any data, just set it to 0, that means you just have to add to your code this line:
request.ContentLength = 0;
Usually, if you are not sending any data, chosing the GET method instead is wiser, as you can see in the HTTP RFC
answered Aug 21, 2013 at 8:25
SaveSave
11.1k1 gold badge17 silver badges23 bronze badges
1
var requestedURL = "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/token?code=" + code + "&client_id=" + client_id + "&client_secret=" + client_secret + "&redirect_uri=" + redirect_uri + "&grant_type=authorization_code";
HttpWebRequest authRequest = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(requestedURL);
authRequest.ContentType = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded";
authRequest.Method = "POST";
//Set content length to 0
authRequest.ContentLength = 0;
WebResponse authResponseTwitter = authRequest.GetResponse();
The ContentLength property contains the value to send as the Content-length HTTP header with the request.
Any value other than -1 in the ContentLength property indicates that the request uploads data and that only methods that upload data are allowed to be set in the Method property.
After the ContentLength property is set to a value, that number of bytes must be written to the request stream that is returned by calling the GetRequestStream method or both the BeginGetRequestStream and the EndGetRequestStream methods.
for more details click here
answered Aug 21, 2015 at 9:49
Musakkhir SayyedMusakkhir Sayyed
6,92213 gold badges39 silver badges64 bronze badges
Change the way you requested the method from POST to GET ..
answered Nov 24, 2018 at 10:30
Hey i’m using Volley and was getting Server error 411, I added to the getHeaders method the following line :
params.put("Content-Length","0");
And it solved my issue
answered Mar 4, 2015 at 8:05
shimi_tapshimi_tap
7,7525 gold badges22 silver badges23 bronze badges
Google search
2nd result
System.Net.WebException: The remote server returned an error: (411) Length Required.This is a pretty common issue that comes up when trying to make call a
REST based API method through POST. Luckily, there is a simple fix for
this one.This is the code I was using to call the Windows Azure Management API.
This particular API call requires the request method to be set as
POST, however there is no information that needs to be sent to the
server.
var request = (HttpWebRequest) HttpWebRequest.Create(requestUri);
request.Headers.Add("x-ms-version", "2012-08-01"); request.Method =
"POST"; request.ContentType = "application/xml";
To fix this error, add an explicit content length to your request
before making the API call.request.ContentLength = 0;
answered Aug 21, 2013 at 8:28
iabbottiabbott
8731 gold badge8 silver badges22 bronze badges
I had the same error when I imported web requests from fiddler captured sessions to Visual Studio webtests. Some POST requests did not have a StringHttpBody tag. I added an empty one to them and the error was gone. Add this after the Headers tag:
<StringHttpBody ContentType="" InsertByteOrderMark="False">
</StringHttpBody>
answered Apr 17, 2018 at 12:48
We had a very surprising cause to this error: we passed a header in which there was a newline character (in our case an Authorization bearer token header).
Our suspicion is that the newline confused the headers’ parser, and made it think there were no additional headers, which caused it to drop important headers like content-length.
answered Dec 6, 2021 at 17:17
Tama YoshiTama Yoshi
3032 silver badges15 bronze badges
| Номер ошибки: | Ошибка HTTP 411 | |
| Название ошибки: | Content Length Required | |
| Описание ошибки: | The request is missing its Content-Length header. | |
| Разработчик: | Microsoft Corporation | |
| Программное обеспечение: | Windows Operating System | |
| Относится к: | Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10, 11 |
Как правило, такие Windows 10 ошибки возникают из-за повреждённых или отсутствующих файлов Content Length Required, а иногда — в результате заражения вредоносным ПО в настоящем или прошлом, что оказало влияние на Edge. Обычно, установка новой версии файла Windows 10 позволяет устранить проблему, из-за которой возникает ошибка. Мы также рекомендуем выполнить сканирование реестра, чтобы очистить все недействительные ссылки на Content Length Required, которые могут являться причиной ошибки.
Распространенные сообщения об ошибках в Content Length Required
Типичные ошибки с Content Length Required возникают в Edge для Windows включают в себя:
- «Ошибка: Content Length Required. «
- «Content Length Required удален, отсутствует или перемещен. «
- «Не удалось найти Content Length Required. «
- «Не удалось загрузить модуль Content Length Required. «
- «Ошибка регистрации: Content Length Required. «
- «Ошибка выполнения: Content Length Required.»
- «Ошибка загрузки: Content Length Required. «
Проблемы Content Length Required, связанные с Edges, возникают во время установки, при запуске или завершении работы программного обеспечения, связанного с Content Length Required, или во время процесса установки Windows. Запись ошибок Content Length Required внутри Edge имеет решающее значение для обнаружения неисправностей электронной Edge и ретрансляции обратно в Microsoft Corporation для параметров ремонта.
Истоки проблем Content Length Required
Проблемы Content Length Required могут быть отнесены к поврежденным или отсутствующим файлам, содержащим ошибки записям реестра, связанным с Content Length Required, или к вирусам / вредоносному ПО.
В частности, проблемы Content Length Required, созданные:
- Недопустимая (поврежденная) запись реестра Content Length Required.
- Файл Content Length Required поврежден от заражения вредоносными программами.
- Content Length Required злонамеренно или ошибочно удален другим программным обеспечением (кроме Edge).
- Другая программа находится в конфликте с Edge и его общими файлами ссылок.
- Неполный или поврежденный Content Length Required из ошибочной загрузки или установки.
Продукт Solvusoft
Загрузка
WinThruster 2022 — Проверьте свой компьютер на наличие ошибок.
Совместима с Windows 2000, XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10 и 11
Установить необязательные продукты — WinThruster (Solvusoft) | Лицензия | Политика защиты личных сведений | Условия | Удаление
Коды состояний браузера в базе знаний
Идентификатор статьи:
120629
Автор статьи:
Последнее обновление:
Популярность:
star rating here
Загрузка (Исправление ошибки)
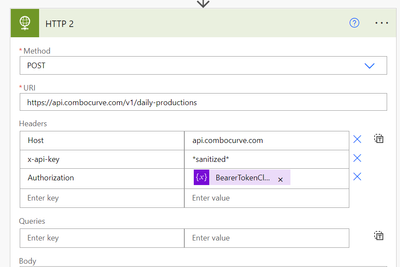
I’m trying to set up a flow that fetches a Bearer token using some Python code executed by Power Automate Desktop, then passes that bearer token to a HTTP POST action:
When I paste the Bearer token into the Authorization header as plain text it works fine, but if I try to use dynamic content, either as a parameter from a previous step or as an expression defining that value as a string, the error is the same 411:
OUTPUTS:
{
"statusCode": 411,
"headers": {
"Referrer-Policy": "no-referrer",
"Date": "Wed, 18 May 2022 20:00:19 GMT",
"Content-Length": "286",
"Content-Type": "text/html; charset=UTF-8"
},
"body": "n<html><head>n<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8">n<title>411 Length Required</title>n</head>n<body text=#000000 bgcolor=#ffffff>n<h1>Error: Length Required</h1>n<h2>POST requests require a <code>Content-length</code> header.</h2>n<h2></h2>n</body></html>n"
}into the Authorization header as plain text it works fine, but if I try to use dynamic content, either as a parameter from a previous step or as an expression defining a string equal to the parameter the error is the same.
Oddly, I’ve just discovered that if I put a carriage return at the end of the plain text authorization it stops working and returns the same error as the variable authorization. I’d appreciate any ideas or assistance.
Содержание
Составили подробный классификатор кодов состояния HTTP. Добавляйте в закладки, чтобы был под рукой, когда понадобится.
Что такое код ответа HTTP
Когда посетитель переходит по ссылке на сайт или вбивает её в поисковую строку вручную, отправляется запрос на сервер. Сервер обрабатывает этот запрос и выдаёт ответ — трехзначный цифровой код HTTP от 100 до 510. По коду ответа можно понять реакцию сервера на запрос.
Первая цифра в ответе обозначает класс состояния, другие две — причину, по которой мог появиться такой ответ.
Как проверить код состояния страницы
Проверить коды ответа сервера можно вручную с помощью браузера и в панелях веб‑мастеров: Яндекс.Вебмастер и Google Search Console.
В браузере
Для примера возьмём Google Chrome.
-
Откройте панель разработчика в браузере клавишей F12, комбинацией клавиш Ctrl + Shift + I или в меню браузера → «Дополнительные инструменты» → «Инструменты разработчика». Подробнее об этом рассказывали в статье «Как открыть исходный код страницы».
-
Переключитесь на вкладку «Сеть» в Инструментах разработчика и обновите страницу:
В Яндекс.Вебмастере
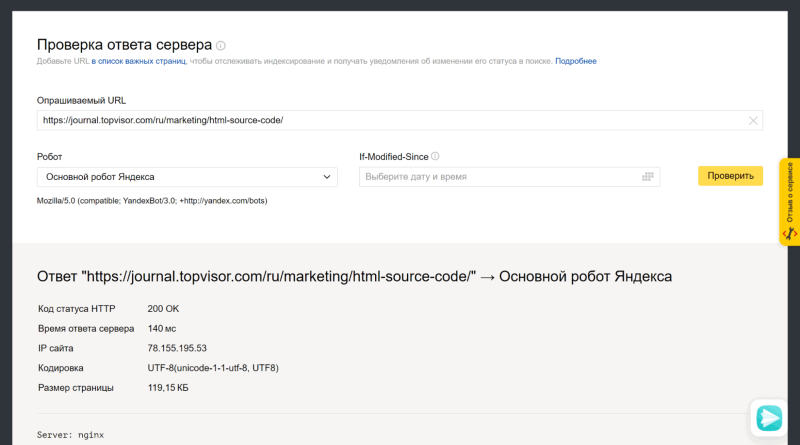
Откройте инструмент «Проверка ответа сервера» в Вебмастере. Введите URL в специальное поле и нажмите кнопку «Проверить»:
Как добавить сайт в Яндекс.Вебмастер и другие сервисы Яндекса
В Google Search Console
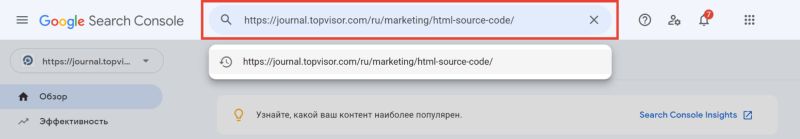
Чтобы посмотреть код ответа сервера в GSC, перейдите в инструмент проверки URL — он находится в самом верху панели:
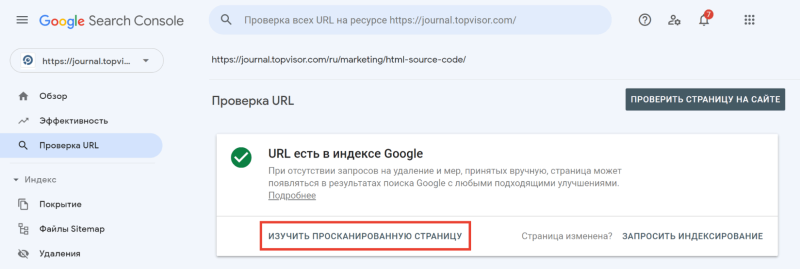
Введите ссылку на страницу, которую хотите проверить, и нажмите Enter. В результатах проверки нажмите на «Изучить просканированную страницу» в блоке «URL есть в индексе Google».
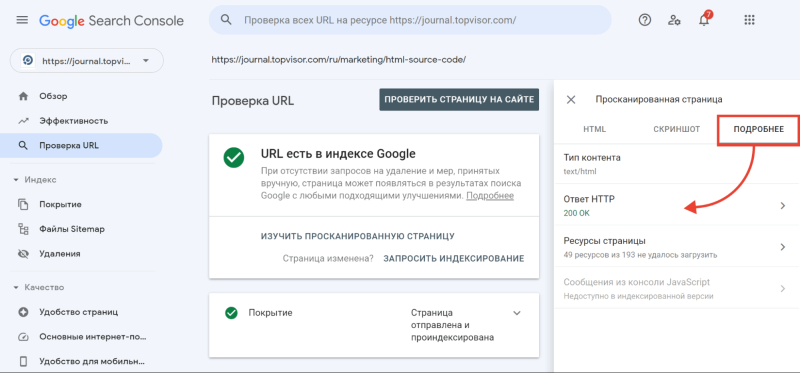
А затем в открывшемся окне перейдите на вкладку «Подробнее»:
Теперь расскажем подробнее про все классы кодов состояния HTTP.
1* класс кодов (информационные сообщения)
Это системный класс кодов, который только информирует о процессе передачи запроса. Такие ответы не являются ошибкой, хотя и могут отображаться в браузере как Error Code.
100 Continue
Этот ответ сообщает, что полученные сведения о запросе устраивают сервер и клиент может продолжать отправлять данные. Такой ответ может требоваться клиенту, если на сервер отправляется большой объём данных.
101 Switching Protocols
Сервер одобрил переключение типа протокола, которое запросил пользователь, и в настоящий момент выполняет действие.
102 Processing
Запрос принят — он находится в обработке, и на это понадобится чуть больше времени.
103 Checkpoint
Контрольная точка — используется в запросах для возобновления после прерывания запросов POST или PUT.
POST отправляет данные на сервер, PUT создает новый ресурс или заменяет существующий данными, представленными в теле запроса.
Разница между ними в том, что PUT работает без изменений: повторное его применение даёт такой же результат, что и в первый раз, а вот повторный вызов одного и того же метода POST часто меняет данные.
Пример — оформленный несколько раз интернет‑заказ. Такое часто происходит как раз по причине неоднократного использования запроса PUT.
105 Name Not Resolved
Не удается преобразовать DNS‑адрес сервера — это означает ошибку в службе DNS. Эта служба преобразует IP‑адреса в знакомые нам доменные имена.
2* класс кодов (успешно обработанные запросы)
Эти коды информируют об успешности принятия и обработки запроса. Также сервер может передать заголовки или тело сообщений.
200 ОК
Все хорошо — HTTP‑запрос успешно обработан (не ошибка).
201 Created
Создано — транзакция успешна, сформирован новый ресурс или документ.
202 Accepted
Принято — запрос принят, но ещё не обработан.
203 Non‑Authoritative Information
Информация не авторитетна — запрос успешно обработан, но передаваемая информация была взята не из первичного источника (данные могут быть устаревшими).
204 No Content
Нет содержимого — запрос успешно обработан, однако в ответе только заголовки без контента сообщения. Не нужно обновлять содержимое документа, но можно применить к нему полученные метаданные.
205 Reset Content
Сбросить содержимое. Запрос успешно обработан — но нужно сбросить введенные данные. Страницу можно не обновлять.
206 Partial Content
Частичное содержимое. Сервер успешно обработал часть GET‑запроса, а другую часть вернул.
GET — метод для чтения данных с сайта. Он говорит серверу, что клиент хочет прочитать какой‑то документ.
Представим интернет‑магазин и страницы каталога. Фильтры, которые выбирает пользователь, передаются благодаря методу GET. GET‑запрос работает с получением данных, а POST‑запрос нужен для отправки данных.
При работе с подобными ответами следует уделить внимание кэшированию.
207 Multi‑Status
Успешно выполнено несколько операций — сервер передал результаты выполнения нескольких независимых операций. Они появятся в виде XML‑документа с объектом multistatus.
226 IM Used
Успешно обработан IM‑заголовок (специальный заголовок, который отправляется клиентом и используется для передачи состояния HTTP).
3* класс кодов (перенаправление на другой адрес)
Эти коды информируют, что для достижения успешной операции нужно будет сделать другой запрос, возможно, по другому URL.
300 Multiple Choices
Множественный выбор — сервер выдает список нескольких возможных вариантов перенаправления (максимум — 5). Можно выбрать один из них.
301 Moved Permanently
Окончательно перемещено — страница перемещена на другой URL, который указан в поле Location.
302 Found/Moved
Временно перемещено — страница временно перенесена на другой URL, который указан в поле Location.
303 See Other
Ищите другую страницу — страница не найдена по данному URL, поэтому смотрите страницу по другому URL, используя метод GET.
304 Not Modified
Модификаций не было — с момента последнего визита клиента изменений не было.
305 Use Proxy
Используйте прокси — запрос к нужному ресурсу можно сделать только через прокси‑сервер, URL которого указан в поле Location заголовка.
306 Unused
Зарезервировано. Код в настоящий момент не используется.
307 Temporary Redirect
Временное перенаправление — запрашиваемый ресурс временно доступен по другому URL.
Этот код имеет ту же семантику, что код ответа 302 Found, за исключением того, что агент пользователя не должен изменять используемый метод HTTP: если в первом запросе использовался POST, то во втором запросе также должен использоваться POST.
308 Resume Incomplete
Перемещено полностью (навсегда) — запрашиваемая страница была перенесена на новый URL, указанный в поле Location заголовка. Метод запроса (GET/POST) менять не разрешается.
4* класс кодов (ошибки на стороне клиента)
Эти коды указывают на ошибки со стороны клиентов.
400 Bad Request
Неверный запрос — запрос клиента не может быть обработан, так как есть синтаксическая ошибка (возможно, опечатка).
401 Unauthorized
Не пройдена авторизация — запрос ещё в обработке, но доступа нет, так как пользователь не авторизован.
Для доступа к запрашиваемому ресурсу клиент должен представиться, послав запрос, включив при этом в заголовок сообщения поле Authorization.
402 Payment Required
Требуется оплата — зарезервировано для использования в будущем. Код предусмотрен для платных пользовательских сервисов, а не для хостинговых компаний.
403 Forbidden
Запрещено — запрос принят, но не будет обработан, так как у клиента недостаточно прав. Может возникнуть, когда пользователь хочет открыть системные файлы (robots, htaccess) или не прошёл авторизацию.
404 Not Found
Не найдено — запрашиваемая страница не обнаружена. Сервер принял запрос, но не нашёл ресурса по указанному URL (возможно, была ошибка в URL или страница была перемещена).
405 Method Not Allowed
Метод не разрешён — запрос был сделан методом, который не поддерживается данным ресурсом. Сервер должен предложить доступные методы решения в заголовке Allow.
406 Not Acceptable
Некорректный запрос — неподдерживаемый поисковиком формат запроса (поисковый робот не поддерживает кодировку или язык).
407 Proxy Authentication Required
Нужно пройти аутентификацию прокси — ответ аналогичен коду 401, только нужно аутентифицировать прокси‑сервер.
408 Request Timeout
Тайм‑аут запроса — запрос клиента занял слишком много времени. На каждом сайте существует свое время тайм‑аута — проверьте интернет‑соединение и просто обновите страницу.
409 Conflict
Конфликт (что‑то пошло не так) — запрос не может быть выполнен из‑за конфликтного обращения к ресурсу (несовместимость двух запросов).
410 Gone
Недоступно — ресурс раньше был размещён по указанному URL, но сейчас удалён и недоступен (серверу неизвестно месторасположение).
411 Length Required
Добавьте длины — сервер отклоняет отправляемый запрос, так как длина заголовка не определена, и он не находит значение Content‑Length.
Нужно исправить заголовки на сервере, и в следующий раз робот сможет проиндексировать страницу.
412 Precondition Failed
Предварительное условие не выполнено — стоит проверить правильность HTTP‑заголовков данного запроса.
413 Request Entity Too Large
Превышен размер запроса — перелимит максимального размера запроса, принимаемого сервером. Браузеры поддерживают запросы от 2 до 8 килобайт.
414 Request‑URI Too Long
Превышена длина запроса — сервер не может обработать запрос из‑за длинного URL. Такая ошибка может возникнуть, например, когда клиент пытается передать чересчур длинные параметры через метод GET, а не POST.
415 Unsupported Media Type
Формат не поддерживается — сервер не может принять запрос, так как данные подгружаются в некорректном формате, и сервер разрывает соединение.
416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable
Диапазон не поддерживается — ошибка возникает в случаях, когда в самом HTTP‑заголовке прописывается некорректный байтовый диапазон.
Корректного диапазона в необходимом документе может просто не быть, или есть опечатка в синтаксисе.
417 Expectation Failed
Ожидания не оправдались — прокси некорректно идентифицировал содержимое поля «Expect: 100‑Continue».
418 I’m a teapot
Первоапрельская шутка разработчиков в 1998 году. В расшифровке звучит как «я не приготовлю вам кофе, потому что я чайник». Не используется в работе.
422 Unprocessable Entity
Объект не обработан — сервер принял запрос, но в нём есть логическая ошибка. Стоит посмотреть в сторону семантики сайта.
423 Locked
Закрыто — ресурс заблокирован для выбранного HTTP‑метода. Можно перезагрузить роутер и компьютер. А также использовать только статистический IP.
424 Failed Dependency
Неуспешная зависимость — сервер не может обработать запрос, так как один из зависимых ресурсов заблокирован.
Выполнение запроса напрямую зависит от успешности выполнения другой операции, и если она не будет успешно завершена, то вся обработка запроса будет прервана.
425 Unordered Collection
Неверный порядок в коллекции — ошибка возникает, если клиент указал номер элемента в неупорядоченном списке или запросил несколько элементов в порядке, отличном от серверного.
426 Upgrade Required
Нужно обновление — в заголовке ответа нужно корректно сформировать поля Upgrade и Connection.
Этот ответ возникает, когда серверу требуется обновление до SSL‑протокола, но клиент не имеет его поддержки.
428 Precondition Required
Нужно предварительное условие — сервер просит внести в запрос информацию о предварительных условиях обработки данных, чтобы выдавать корректную информацию по итогу.
429 Too Many Requests
Слишком много запросов — отправлено слишком много запросов за короткое время. Это может указывать, например, на попытку DDoS‑атаки, для защиты от которой запросы блокируются.
431 Request Header Fields Too Large
Превышена длина заголовков — сервер может и не отвечать этим кодом, вместо этого он может просто сбросить соединение.
Исправляется это с помощью сокращения заголовков и повторной отправки запроса.
434 Requested Host Unavailable
Адрес запрашиваемой страницы недоступен.
444 No Response
Нет ответа — код отображается в лог‑файлах, чтобы подтвердить, что сервер никак не отреагировал на запрос пользователя и прервал соединение. Возвращается только сервером nginx.
Nginx — программное обеспечение с открытым исходным кодом. Его используют для создания веб‑серверов, а также в качестве почтового или обратного прокси‑сервера. Nginx решает проблему падения производительности из‑за роста трафика.
449 Retry With
Повторите попытку — ошибка говорит о необходимости скорректировать запрос и повторить его снова. Причиной становятся неверно указанные параметры (возможно, недостаточно данных).
450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls
Заблокировано родительским контролем — говорит о том, что с компьютера попытались зайти на заблокированный ресурс. Избежать этой ошибки можно изменением параметров системы родительского контроля.
451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
Недоступно по юридическим причинам — доступ к ресурсу закрыт, например, по требованию органов государственной власти или по требованию правообладателя в случае нарушения авторских прав.
456 Unrecoverable Error
Неустранимая ошибка — при обработке запроса возникла ошибка, которая вызывает некорректируемые сбои в таблицах баз данных.
499 Client Closed Request
Запрос закрыт клиентом — нестандартный код, используемый nginx в ситуациях, когда клиент закрыл соединение, пока nginx обрабатывал запрос.
5* класс кодов (ошибки на стороне сервера)
Эти коды указывают на ошибки со стороны серверов.
При использовании всех методов, кроме HEAD, сервер должен вернуть в теле сообщения гипертекстовое пояснение для пользователя. И его можно использовать в работе.
500 Internal Server Error
Внутренняя ошибка сервера — сервер столкнулся с неким условием, из‑за которого не может выполнить запрос.
Проверяйте, корректно ли указаны директивы в системных файлах (особенно htaccess) и нет ли ошибки прав доступа к файлам. Обратите внимание на ошибки внутри скриптов и их медленную работу.
501 Not Implemented
Не выполнено — код отдается, когда сам сервер не может идентифицировать метод запроса.
Сами вы эту ошибку не исправите. Устранить её может только сервер.
502 Bad Gateway
Ошибка шлюза — появляется, когда сервер, выступая в роли шлюза или прокси‑сервера, получил ответное сообщение от вышестоящего сервера о несоответствии протоколов.
Актуально исключительно для прокси и шлюзовых конфигураций.
503 Service Unavailable
Временно не доступен — сервер временно не имеет возможности обрабатывать запросы по техническим причинам (обслуживание, перегрузка и прочее).
В поле Retry‑After заголовка сервер укажет время, через которое можно повторить запрос.
504 Gateway Timeout
Тайм‑аут шлюза — сервер, выступая в роли шлюза или прокси‑сервера, не получил ответа от вышестоящего сервера в нужное время.
Исправить эту ошибку самостоятельно не получится. Здесь дело в прокси, часто — в веб‑сервере.
Первым делом просто обновите веб‑страницу. Если это не помогло, нужно почистить DNS‑кэш. Для этого нажмите горячие клавиши Windows+R и введите команду cmd (Control+пробел). В открывшемся окне укажите команду ipconfig / flushdns и подтвердите её нажатием Enter.
505 HTTP Version Not Supported
Сервер не поддерживает версию протокола — отсутствует поддержка текущей версии HTTP‑протокола. Нужно обеспечить клиента и сервер одинаковой версией.
506 Variant Also Negotiates
Неуспешные переговоры — с такой ошибкой сталкиваются, если сервер изначально настроен неправильно. По причине ошибочной конфигурации выбранный вариант указывает сам на себя, из‑за чего процесс и прерывается.
507 Insufficient Storage
Не хватает места для хранения — серверу недостаточно места в хранилище. Нужно либо расчистить место, либо увеличить доступное пространство.
508 Loop Detected
Обнаружен цикл — ошибка означает провал запроса и выполняемой операции в целом.
509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded
Превышена пропускная способность — используется при чрезмерном потреблении трафика. Владельцу площадки следует обратиться к своему хостинг‑провайдеру.
510 Not Extended
Не продлён — ошибка говорит, что на сервере отсутствует нужное для клиента расширение. Чтобы исправить проблему, надо убрать часть неподдерживаемого расширения из запроса или добавить поддержку на сервер.
511 Network Authentication Required
Требуется аутентификация — ошибка генерируется сервером‑посредником, к примеру, сервером интернет‑провайдера, если нужно ввести пароль для получения доступа к сети через платную точку доступа.