I am asking it because I write very simply app but IT DON’T WORK.
I wrote this command in terminal in the /dir:
python3 -m http.server --cgi
My script is in dir/cgi-bin/hp.py and that code:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
print"Content-type: text/html"
print()
print"<h1>Hello world!</h1>"
This I saw in window of browser:
Error response
Error code: 403
Message: CGI script is not executable (‘/cgi-bin/hp.py’).
Error code explanation: HTTPStatus.FORBIDDEN — Request forbidden —
authorization will not help.»
How can I fix it?
bhansa
7,1263 gold badges29 silver badges54 bronze badges
asked Sep 15, 2017 at 13:42
4
Here are the following steps which I tried to reproduce the problem:
# app.py
print("Content-type: text/html")
print()
print("<h1>Hello world!</h1>")
- Created a file
app.pyincgi-bindirectory - Used command to run http.server with cgi
python -m http.server --bind localhost --cgi 8000
I tried accessing the path "http:localhost/cgi-bin/" got Error 403
Now the resolving part, which is opening the link in browser.
I ran the command:
python -mwebbrowser http://localhost:8000/cgi-bin/app.py
After the while it gave me the result, and I was able to access the link for the step 2 also.
I hope that helps you.
Result:
answered Sep 15, 2017 at 17:48
bhansabhansa
7,1263 gold badges29 silver badges54 bronze badges
1
IE 11 and Microsoft Edge both recommend logging in after receiving an HTTP 403: Forbidden.
The package hc says this about error 403:
Code explanation: Request forbidden — authorization will not help
Wikipedia also says:
Status codes 401 (Unauthorized) and 403 (Forbidden) have distinct meanings.
A 401 response indicates that access to the resource is restricted,
and the request did not provide any HTTP authentication. It is
possible that a new request for the same resource will succeed if
authentication is provided. The response must include an HTTP
WWW-Authenticate header to prompt the user-agent to provide
credentials. If credentials are not provided via HTTP Authorization,
then 401 should not be used.A 403 response generally indicates one of two conditions:
Authentication was provided, but the authenticated user is not
permitted to perform the requested operation.The operation is
forbidden to all users. For example, requests for a directory listing
return code 403 when directory listing has been disabled.
The error code given by IE and Edge would seem to imply there are cases in which logging in would help the problem. I filed a bug about this here, but I thought I’d give Microsoft some slack.
In which cases is logging in a solution to 403: Forbidden?
Hoping this is simple.
I have an old TS-439, running QTS 4.2.6 (2020/01/09). It’s been running my PLEX server for a number of years, but I finally moved that to a new NAS.
I cleaned the 439 off, and wanted to get the webserver running as a development environment (local LAN only).
I removed PLEX and a couple of other apps, enabled the Webserver in Control Panel, restored it to default configuration just to start fresh, but still, whenever I try visiting port :80 in a browser from my desktop, I get:
Code: Select all
Error response
Error code 403.
Message: Not Serving Client 192.168.1.48.
Error code explanation: 403 = Request forbidden -- authorization will not help.I’ve poured through all the settings I can find in the QTS, including the Allow/Deny list, user permissions, shared folders, nothing seems out of the ordinary. The «guest» user, which I assume the Webserver uses, does not appear anywhere, but I gather that’s typical.
Found a couple of posts about updating the apache.conf to use «Options FollowSymLinks», restarted/reloaded the apache service several times, nothing seems to help.
Anyone have any pointers, or is there a way to basically factory reset everything in QTS back to defaults (including conf files)?
Thanks!
-Carl
Receiving any error code while online can be a frustrating experience. While we’ve become accustomed to 404 Not Found pages, even to the extent that it’s become common to see cute placeholder pages to entertain us whenever we get lost, one of the more puzzling errors is the 403: Forbidden response.
What does it mean?
Simply put: the server has determined that you are not allowed access to the thing you’ve requested.
According to RFC 7231:
The 403 (Forbidden) status code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it…If authentication credentials were provided in the request, the server considers them insufficient to grant access.
The 403 response belongs to the 4xx range of HTTP responses: Client errors. This means either you, or your browser, did something wrong.
If you encounter this it usually means that you have already authenticated yourself with the server, i.e. you’ve logged in, but the resource you have requested expects someone with higher privileges.
Most commonly, you might be logged in as a standard user, but you are attempting to access an admin page.
How do you fix it?
As a user without access to the server, you really only have a few options:
Authenticate yourself with a more appropriate account
Again, according to RFC 7231:
If authentication credentials were provided in the request, the server considers them insufficient to grant access. The client SHOULD NOT automatically repeat the request with the same credentials. The client MAY repeat the request with new or different credentials.
This is the only one that gives you any immediate power to rectify the issue.
If you have multiple accounts for a site and you are attempting to do something you can usually do, but this time are forbidden from doing, this is the option you should try. Log in with your other account.
You may find that this option also requires clearing your cache or cookies, just in case logging in as another user doesn’t sufficiently flush the previous authentication tokens. But this is usually unnecessary.
As a desperate move, you could also try disabling browser extensions that might be interfering with your use of the site. However, this is unlikely, since a 403 implies you are authenticated, but not authorized.
Notify the site owner that a 403 is being returned when you’d expect otherwise
If you fully expect that you should be able to access the resource in question, but you are still seeing this error, it is wise to let the team behind the site know — this could be an error on their part.
Once more from RFC 7231:
However, a request might be forbidden for reasons unrelated to the credentials.
A common cause for this happening unintentionally can be that a server uses allow- or deny-lists for particular IP addresses or geographical regions.
They might have a good reason for blocking your access outside of their strictly defined parameters, but it could also just be an oversight.
Give up.
Maybe you just aren’t supposed to be able to access that resource. It happens. It’s a big internet and it’s reasonable to expect that there are some areas off limits to you personally.
You could visit http.cat instead while ruminating on why your original request was forbidden.
As a reader of freeCodeCamp News, you are almost certainly not forbidden from following @JacksonBates on Twitter for more tech and programming related content.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Уведомления
- Начало
- » Web
- » CGIHTTPServer
#1 Янв. 19, 2009 10:18:45
CGIHTTPServer 
Можно пример с модулем CGIHTTPServer или SimpleHttpServer, который отобразит форму и примет POST — запрос от неё?
Хотел опробовать TinyMce потом, так-что нужно чтобы он и файлы отдавал c js и картинками.
Офлайн
- Пожаловаться
#2 Янв. 19, 2009 11:45:08
CGIHTTPServer 
эм
CGIHTTPServer — это как бы запулка CGI и есть.
#!/usr/bin/env pythonHOMEDIR = "webserv/"
PORT = 8000import CGIHTTPServer
import BaseHTTPServer
import os
os.chdir(HOMEDIR)class Handler(CGIHTTPServer.CGIHTTPRequestHandler):
cgi_directories = ["/cgi"]httpd = BaseHTTPServer.HTTPServer(("", PORT), Handler)
print "serving at port", PORT
httpd.serve_forever()
это запускалка
сам cgi
import cgitb; cgitb.enable()
import cgiprint "Content-Type: text/htmln"
form = cgi.FieldStorage()
print form
форму для поста сам нарисуй
Офлайн
- Пожаловаться
#3 Янв. 19, 2009 14:05:15
CGIHTTPServer 
1) Такое уже конечно пробовал. И получаю Форбидден.
Error code 403.
Message: CGI script is not a plain file (‘/cgi/’).
Error code explanation: 403 = Request forbidden – authorization will not help.
2) Имелась ввиду эмуляция силами модуля подобия cgi-ю, когда
пользователь всё время отправляет данные на одну страницу post-запросами,
а формы динамически появляются в зависимости от самого запроса! Вот. Так можно?
Офлайн
- Пожаловаться
#4 Янв. 20, 2009 18:17:05
CGIHTTPServer 
Ээй, тихо тут что-то? Может всё-таки кто поможет мне? Повторюсь — нужно встроить простейшие обработчики в код проги. А хотя-бы пример с приёмом post-запроса и обработкой в теле проги предоставить не займёт думаю времени?
Если я на неправильном пути — скажите, но имхо здесь 1 файл достаточен.
Или если не прав — скажите как форбидден исправить? (Работаю на ноуте с вистой, хочу сменить на родной шлак но это зависит от некоторых людей кроме меня.)
Офлайн
- Пожаловаться
#6 Янв. 20, 2009 19:40:59
CGIHTTPServer 
Спасибо, если честно смотрел только либу. Попробую вставить куски внутрь на выдачу.
Хм, в висте конечно есть права доступа, но скрипты там разве имеют их? Я думал лишь о экзешнике питона!
Офлайн
- Пожаловаться
#7 Янв. 20, 2009 20:19:22
CGIHTTPServer 
Omro
тогда проверь путь к интерпретатору в заголовке cgi файла и команду python в консоли
кстати раз винда то наверно и путь к cgi не должен содержать /
добавь первой строкой что-то вроде
#!c:/Python/python.exe -u
Офлайн
- Пожаловаться
#8 Янв. 20, 2009 20:25:36
CGIHTTPServer 
С первым я решил не вписывать под виндой, надеясь на доброе здравие змея. Работает с обычными скриптами и джангой, а здесь задачка вроде простая и хочется найти простое решение чтобы вернуться к джанго.
Сейчас читаю ещё python cookbook и кажется нашёл что-то похожее. На пиратбэе выложили кучу книг, не зря одолжил, именно то вроде.
Офлайн
- Пожаловаться
#10 Июнь 29, 2011 00:02:53
CGIHTTPServer 
добрый вечер
тупой вопрос…
почему при попытке запуска скрипта через CGIHTTPServer скрипт не исполняется а тупо выдается все его содержимое ?
Python 3.2
OS Windows 7
запускаю сервер командой C:ServerPython32python.exe -m http.server
содержимое скрипта следующее:
print (“Content-Type: text/htmln”)
print (“test”)
запускаю через браузер
localhost:8000/cgi-bin/test.py
как заставить это дело работать?
Отредактировано (Июнь 29, 2011 01:53:41)
Офлайн
- Пожаловаться
- Начало
- » Web
-
» CGIHTTPServer
Все мы, путешествуя по просторам интернета, натыкаемся на различные ошибки при загрузке сайтов. Одна из них, кстати, достаточно часто встречается – я говорю об ошибке сервера 403 Forbidden Error. Сегодня я рассмотрю причины ее возникновения и способы устранения со стороны владельца сайта и его пользователя.
Что означает ошибка 403 и почему она появляется
Ошибка сервера 403 Forbidden означает ограничение или отсутствие доступа к материалу на странице, которую вы пытаетесь загрузить. Причин ее появления может быть несколько, и вот некоторые из них:
- Формат индексного файла неверен.
- Некорректно выставленные права на папку/файл.
- Файлы были загружены в неправильную папку.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Исправление ошибки сервера 403 Forbidden
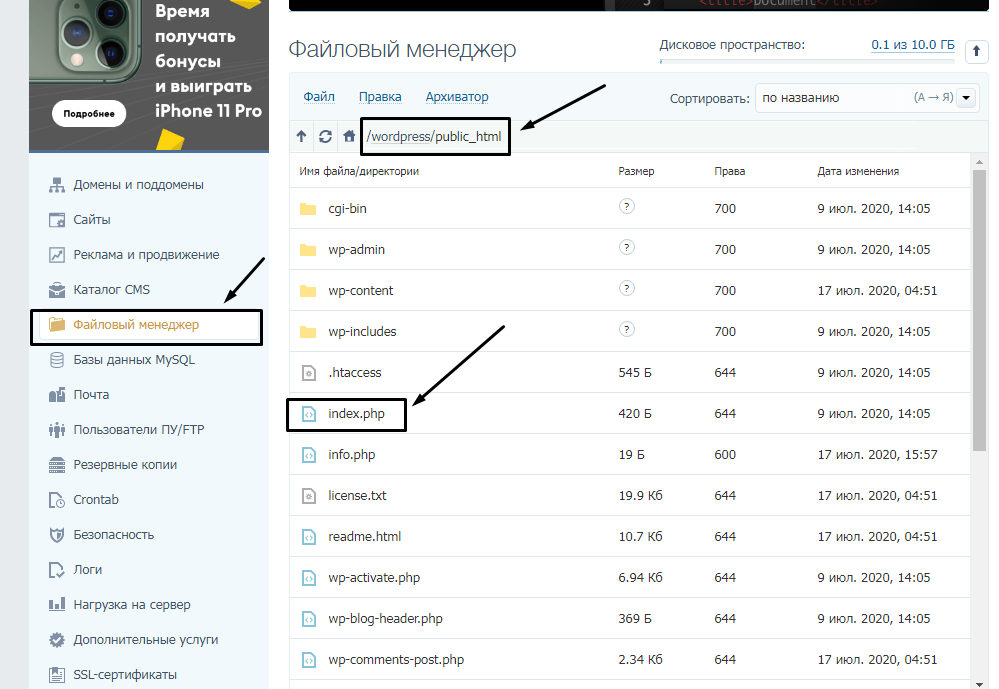
Чтобы исправить ошибку сервера 403 Forbidden, обязательно нужен доступ к панели управления вашего хостинга. Все описанные ниже шаги применимы к любой CMS, но примеры будут показаны на основе WordPress.
Проверка индексного файла
Сначала я проверю, правильно ли назван индексный файл. Все символы в его имени должны быть в нижнем регистре. Если хотя бы один символ набран заглавной буквой, возникнет ошибка 403 Forbidden. Но это больше относится к ОС Linux, которой небезразличен регистр.
Еще не стоит забывать, что индексный файл может быть нескольких форматов, в зависимости от конфигураций сайта: index.html, index.htm, или index.php. Кроме того, он должен храниться в папке public_html вашего сайта. Файл может затеряться в другой директории только в том случае, если вы переносили свой сайт.
Любое изменение в папке или файле фиксируется. Чтобы узнать, не стала ли ошибка итогом деятельности злоумышленников, просто проверьте графу «Дата изменения».
Настройка прав доступа
Ошибка 403 Forbidden появляется еще тогда, когда для папки, в которой расположен искомый файл, неправильно установлены права доступа. На все директории должны быть установлены права на владельца. Но есть другие две категории:
- группы пользователей, в числе которых есть и владелец;
- остальные, которые заходят на ваш сайт.
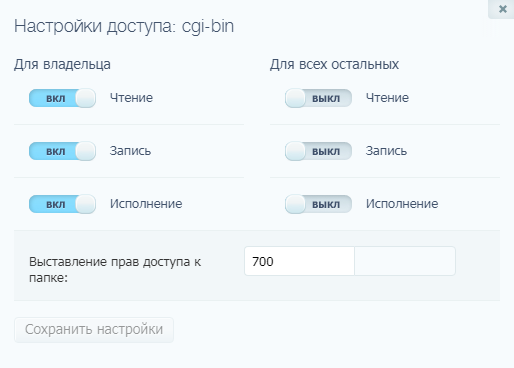
На директории можно устанавливать право на чтение, запись и исполнение.
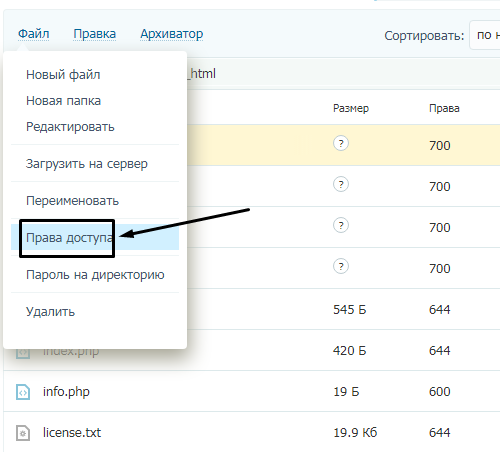
Так, по умолчанию на все папки должно быть право исполнения для владельца. Изменить их можно через панель управления TimeWeb. Для начала я зайду в раздел «Файловый менеджер», перейду к нужной папке и выделю ее. Далее жму на пункт меню «Файл», «Права доступа».
Откроется новое окно, где я могу отрегулировать права как для владельца, так и для всех остальных.
Отключение плагинов WordPress
Если даже после всех вышеперечисленных действий ошибка не исчезла, вполне допустимо, что влияние на работу сайта оказано со стороны некоторых плагинов WordPress. Быть может они повреждены или несовместимы с конфигурациями вашего сайта.
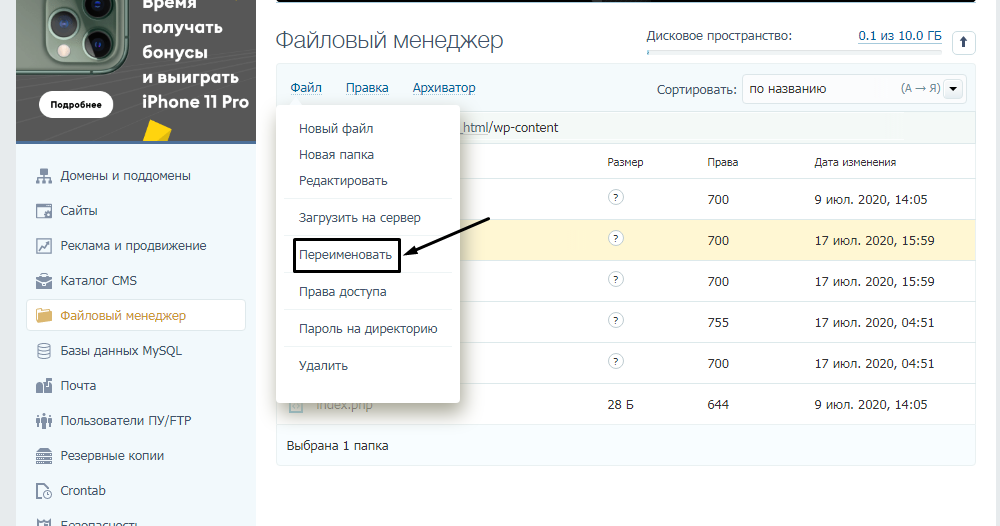
Для решения подобной проблемы необходимо просто отключить их. Но сначала надо найти папку с плагинами. Открываю папку своего сайта, перехожу в раздел «wp-content» и нахожу в нем директорию «plugins». Переименовываю папку – выделяю ее, жму на меню «Файл» и выбираю соответствующий пункт. Название можно дать вот такое: «plugins-disable». Данное действие отключит все установленные плагины.
Теперь нужно попробовать вновь загрузить страницу. Если проблема исчезла, значит, какой-то конкретный плагин отвечает за появление ошибки с кодом 403.
Но что делать, если у вас плагин не один, а какой из них влияет на работу сайта – неизвестно? Тогда можно вернуть все как было и провести подобные действия с папками для определенных плагинов. Таким образом, они будут отключаться по отдельности. И при этом каждый раз надо перезагружать страницу и смотреть, как работает сайт. Как только «виновник торжества» найден, следует переустановить его, удалить или найти альтернативу.
Читайте также
Как решить проблему, если вы – пользователь
Выше я рассмотрела способы устранения ошибки 403 Forbidden для владельцев сайта. Теперь же разберу методы исправления в случаях с пользователем.
- Сначала надо убедиться, что проблема заключается именно в вашем устройстве. Внимательно проверьте, правильно ли вы ввели URL сайта. Может, в нем есть лишние символы. Или, наоборот, какие-то символы отсутствуют.
- Попробуйте загрузить страницу с другого устройства. Если на нем все будет нормально, значит, проблема кроется именно в используемом вами девайсе. Если нет – надо перейти к последнему шагу.
- Еще хороший вариант – немного подождать и обновить страницу. Делается это либо кликом по иконке возле адресной строки браузера, либо нажатием на комбинацию Ctrl + F5. Можно и без Ctrl, на ваше усмотрение.
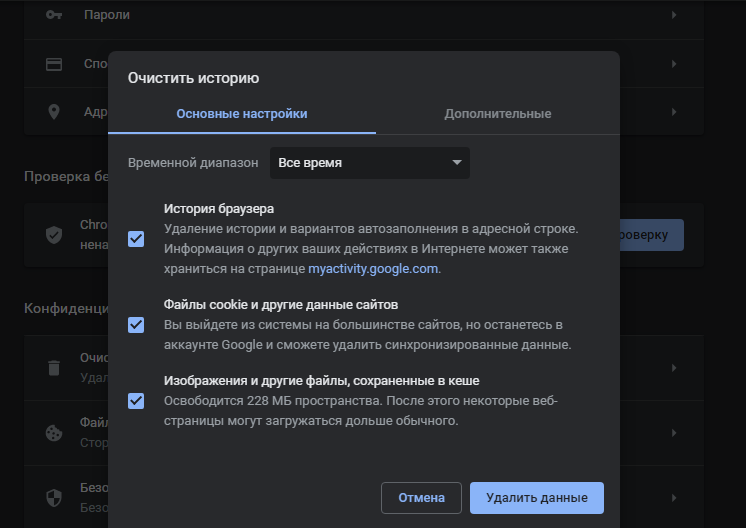
- Если ничего из вышеперечисленного не помогло, надо очистить кэш и cookies. Провести такую процедуру можно через настройки браузера. Для этого необходимо открыть историю просмотров, чтобы через нее перейти к инструменту очистки. Эту же утилиту часто можно найти в настройках, в разделе «Конфиденциальность и безопасность». В новом окне нужно отметить пункты с кэшем и cookies и нажать на кнопку для старта очистки.
- Ошибка 403 Forbidden возникает и тогда, когда пользователь пытается открыть страницу, для доступа к которой сначала надо осуществить вход в систему. Если у вас есть профиль, просто войдите в него и попробуйте вновь загрузить нужную страницу.
- Если вы заходите со смартфона, попробуйте отключить функцию экономии трафика в браузере. Она находится в настройках, в мобильном Google Chrome под нее отведен отдельный раздел.
- Последний шаг – подождать. Когда ни один способ не помогает, значит, неполадки возникли именно на сайте. Возможно, его владелец уже ищет способы решения проблемы и приступает к их исполнению, но это может занять какое-то время. Пользователям остается только дождаться, когда все работы будут завершены.
Еще одна допустимая причина появления ошибки сервера 403 – доступ к сайту запрещен для определенного региона или страны, в которой вы находитесь. Бывает и такое, что сайт доступен для использования только в одной стране. Если вы используете VPN, попробуйте отключить его и перезагрузите страницу. Вдруг получится все исправить.
Если ничего из вышеперечисленного не сработало, рекомендуется обратиться к владельцу сайта. Есть вероятность, что никто не знает о возникшей проблеме, и только ваше сообщение может изменить ситуацию.
Jun 22, 2022 7:41:27 AM |
403 Forbidden Error: What It Is and How to Fix It
A detailed explanation of what a 403 Forbidden Error response is, including troubleshooting tips to help you resolve this error.
The 403 Forbidden Error is an HTTP response status code that indicates an identified client does not have proper authorization to access the requested content. As with most HTTP response codes, a 403 Forbidden Error can be challenging to diagnose and resolve properly.
With a pool of over 50 potential status codes representing the complex relationship between the client, a web application, a web server, and often multiple third-party web services, determining the cause of a particular status code can be a challenge under the best of circumstances.
This article will examine the 403 Forbidden Error in more detail. We’ll look at what causes this message, along with a handful of tips for diagnosing and debugging your own application. We’ll even examine a number of the most popular content management systems (CMSs) for potential problem areas that could cause your own website to be generating a 403 Forbidden Error. Let’s dive in!
Server- or Client-Side?
All HTTP response status codes in the 4xx category are considered client error responses. These messages contrast with errors in the 5xx category, such as the 502 Bad Gateway Error. 500 errors are considered server error responses.
That said, the appearance of a 4xx error doesn’t necessarily mean the issue has something to do with the client (the web browser or device used to access the application). Oftentimes, if you’re trying to diagnose an issue with your own application, you can ignore most client-side code and components. This includes HTML, cascading style sheets (CSS), client-side JavaScript, etc. This doesn’t apply just to websites, either. Behind the scenes, normal web applications power smartphone apps that use a modern-looking user interface.
Although the 403 Forbidden Error is considered a client error response, you shouldn’t rule out the server as the culprit. The server network object is producing the 403 Error and returning it as the HTTP response code to the client. On the other hand, this doesn’t rule out the client as the actual cause of a 403 Forbidden Error, either. The client might be trying to access an invalid URL, the browser could be failing to send the proper credentials to the site, and so forth. We’ll explore some of these scenarios (and potential solutions) below.
Start With a Thorough Application Backup
Before making changes to your application, make sure to back up your system. This might include a full backup of your application, database, and so forth.
If you have the capability, create a complete copy of the application onto a secondary staging server that isn’t «live» or available to the public. This will allow you to test all potential fixes without threatening the security of your live application.
Diagnosing a 403 Forbidden Error
As previously mentioned, many 403 Forbidden Errors involve the server denying authorization to a client (a web browser, in most cases) that has requested content.
This typically occurs in one of two scenarios:
- The client sent its authentication credentials to the server and the server authenticated that the client was valid. Yet, the server rejected the authorized client from accessing the requested content for some reason.
- The requested content is strictly forbidden for all clients, regardless of authorization. This occurs when attempting to access an invalid or forbidden URL that the web server software has restricted. For example, Apache servers return a 403 Forbidden Error when a client tries to access a URL corresponding to a file system directory.
Troubleshooting on the Client-Side
Since the 403 Forbidden Error is a client error response code, start troubleshooting any potential client-side issues first.
Here are some troubleshooting tips you can try on the browser or device that is giving you problems.
Check the Requested URL
The most common cause of a 403 Forbidden Error is simply inputting an incorrect URL. As discussed before, many tightly secured web servers disallow access to improper URLs. This could be anything from accessing a file directory to accessing a private page meant for other users. Thus, it’s a good idea to double-check the exact URL that is returning the 403 error.
Clear Relevant Cookies
As you may already be aware, HTTP copies store tiny pieces of data on your local device. The website then uses these cookies to to «remember» information abbot a particular browser and/or device.
As you may already be aware, HTTP cookies store tiny pieces of data on your local device. The website then uses these cookies to «remember» information about a particular browser and/or device. Most modern web apps take advantage of these cookies to store user authentication status.
Invalid or corrupted Cookies can cause improper authentication for the server, leading to the 403 Error. This is due to the fact that the client is no longer authenticated to perform this particular request.
In most cases, you should only worry about cookies relevant to the website or application causing issues. The application stores cookies based on where the domain is located. This means you can only remove cookies that match the website domain (e.g. airbrake.io) to keep most other cookies intact. However, if you aren’t experienced with manually removing certain cookies, remove all cookies at once. Not only is this easier, but it’s also a safer option.
Below, we’ve provided a list on how to clear cookies depending on the browser you’re using:
- Google Chrome
- Internet Explorer
- Microsoft Edge
- Mozilla Firefox
- Safari
Clear the Cache
Just like cookies, it’s also possible that the local browser cache could be causing the 403 Forbidden Error to appear.
A cache stores local copies of web content on your device for later use. A browser’s cache can include almost any type of data but typically stores compressed snapshots of webpages, images, and other binary data your browser often accesses. With a local copy of these resources on your device, your browser doesn’t need to spend time or bandwidth downloading this identical data every time you return to the same page. For example, when you open Facebook, there’s a good chance that the content you’re seeing has come from the cache on your device.
Since your browser’s cache stores local copies of web content and resources, it’s possible that a change to the live version of your application is conflicting with the cached version already on your device, which can sometimes produce a 403 Forbidden Error as a result. Try clearing your browser’s cache to see if that fixes the issue.
As with cookies, clearing the cache is browser-dependant, so here are a few links to that relevant documentation for the most popular browsers:
- Google Chrome
- Internet Explorer
- Microsoft Edge
- Mozilla Firefox
- Safari
Log Out and Log In
If the application you’re using has some form of user authentication, the last client-side step to try is to log out and then log back in. If you’ve recently cleared the browser cookies, this should usually log you out, so the next time you try to load the page, just log back in at this point.
In some situations, the application may be running into a problem with your previous session, which is just a string that the server sends to the client to identify that client during future requests. As with other data, your device should have stored the session token (or session string) locally on your device within the cookies. The client then transfers this data to the server during every request. If the server fails to recognize the session token or the server sees this particular token as invalid, this may result in a 403 Error.
But, with most web applications, you can recreate the local session token by logging out and logging back in.
Debugging Common Platforms
If you’re running common software packages on the server that is responding with the 403 Forbidden Error, you may want to start by looking into the stability and functionality of those platforms first. The most common content management systems (CMS) — like WordPress, Joomla!, and Drupal — are all typically well-tested out of the box, but once you start making modifications to the underlying extensions or PHP code (the language in which nearly all modern content management systems are written in), it’s all too easy to cause an unforeseen issue that results in a 403 Error.
Here are a few tips to help you troubleshoot some of these popular software platforms:
Rollback Recent Upgrades
If you recently updated the CMS itself just before the 403 Forbidden Error appeared, you may want to consider rolling back to the previous version you had installed when things were working fine. Similarly, any extensions or modules that you may have recently upgraded can also cause server-side issues, so reverting to previous versions of those may also help.
For assistance with this task, simply Google «downgrade [PLATFORM_NAME]» and follow along. In some cases, however, certain CMSs don’t provide a version downgrade capability, which indicates that they consider the base application, along with each new version released, to be extremely stable and bug-free. This is typically the case for the more popular platforms.
Uninstall New Extensions, Modules, or Plugins
Depending on the particular CMS your application is using, the exact name of these components will be different, but they serve the same purpose across every system: improving the capabilities and features of the platform beyond what it’s normally capable of out of the box. Be warned: such extensions can, more or less, take full control of the system and make virtually any changes, whether it be to the PHP code, HTML, CSS, JavaScript, or database. As such, try uninstalling any recently added extensions. Again, Google the extension name for the official documentation and assistance with this process.
Check for Unexpected Database Changes
Uninstalling a CMS extension does not guarantee that changes will fully revert. This is particularly true for WordPress extensions. These extensions have carte blanche status within an application, which allows them full access rights to the database. With this access, an extension can modify database records that don’t «belong» to the extension itself. That means it can change records created and managed by other extensions of the CMS itself.
In those scenarios, the extension may not know how to revert alterations to database records, so it will ignore such things during uninstallation. Diagnosing such problems can be tricky. Your best course of action, assuming you’re reasonably convinced an extension is the likely culprit for the 403 Forbidden Error, is to open the database and manually look through tables and records that were likely modified by the extension.
Confirm Proper File Permissions
If the application worked fine before and suddenly this error occurs, permissions are not a very likely culprit. However, if modifications were recently made (such as upgrades or installations), it’s possible that file permissions were changed or are otherwise incorrect, which could cause an issue to propagate its way throughout the application and eventually lead to a 403 Forbidden Error. The majority of servers use Unix-based operating systems.
In this Wikipedia article, File-System Permissions, you’ll learn more about how to set up proper permissions for application files and directories to keep your application secure without hindering your applications’ access.
Above all, Google is your friend. Search for specific terms related to your issue, such as the name of your application’s CMS, along with the 403 Forbidden Error. Chances are you’ll find someone (or, perhaps, many someones) who have experienced this issue and have found a solution.
Troubleshooting on the Server-Side
If you’re confident that your CMS isn’t the problem, a 403 Error could be a result of a server-side issue.
Troubleshoot the server with these tips.
Check Your Web Server Configuration
Most modern web servers provide one or more configuration files to adjust server behavior. These configurations are based on a wide range of circumstances. For example, the server may be configured to reject requests to certain directories or URLs, which could result in a 403 Error.
Configuration options for each different type of web server can vary dramatically. Here is a list of a few popular ones to give you some resources to look through:
- Apache
- Nginx
- IIS
- Node.js
- Apache Tomcat
Look Through the Logs
Nearly every web application will keep some form of server-side logs. Application logs contain the history of what the application did, such as which pages were requested, which servers it connected to, which database results it provided, and so forth. Server logs are related to the actual hardware that is running the application. They will often provide details about the health and status of all connected services, or even just the server itself. Google «logs [PLATFORM_NAME]» if you’re using a CMS, or «logs [PROGRAMMING_LANGUAGE]» and «logs [OPERATING_SYSTEM]» if you’re running a custom application, for more information on finding the logs in question.
Check the Database for User Authentication
As you know now, a 403 Error may indicate that the client properly authenticated at some point, but doesn’t have access to the requested resource. It’s worth checking the server to see why it denied the requested resource. Perhaps there’s an issue with the database and can’t authenticate the client.
Verify Server Connectivity
While it may sound simple, it’s entirely possible that a Forbidden Error simply indicates that a server somewhere in the chain is down or unreachable for whatever reason. Most modern applications don’t reside on a single server. Instead, applications may be spread over multiple servers or rely on third-party services to function. If any one of these servers are down for maintenance or otherwise inaccessible, this could result in an error that appears to be from your own application.
Debug Your Application Code or Scripts
If all else fails, manually debug your application by parsing through application and server logs. Ideally, make a copy of the entire application to a local development machine and perform a step-by-step debug process. This will allow you to recreate the exact scenario in which the 403 Forbidden Error occurred and view the application code at the moment something goes wrong.
But, for a faster way to debug, install Airbrake Error & Performance Monitoring. If there’s broken code that’s throwing a 403 Error, Airbrake will find it, and quickly. Create a free Airbrake dev account, today, and for the first 30-days, you’ll have access to unlimited error and performance events.
Note: We published this post in October 2017 and recently updated it in February 2022.