The java <class-name> command syntax
First of all, you need to understand the correct way to launch a program using the java (or javaw) command.
The normal syntax1 is this:
java [ <options> ] <class-name> [<arg> ...]
where <option> is a command line option (starting with a «-» character), <class-name> is a fully qualified Java class name, and <arg> is an arbitrary command line argument that gets passed to your application.
1 — There are some other syntaxes which are described near the end of this answer.
The fully qualified name (FQN) for the class is conventionally written as you would in Java source code; e.g.
packagename.packagename2.packagename3.ClassName
However some versions of the java command allow you to use slashes instead of periods; e.g.
packagename/packagename2/packagename3/ClassName
which (confusingly) looks like a file pathname, but isn’t one. Note that the term fully qualified name is standard Java terminology … not something I just made up to confuse you 
Here is an example of what a java command should look like:
java -Xmx100m com.acme.example.ListUsers fred joe bert
The above is going to cause the java command to do the following:
- Search for the compiled version of the
com.acme.example.ListUsersclass. - Load the class.
- Check that the class has a
mainmethod with signature, return type and modifiers given bypublic static void main(String[]). (Note, the method argument’s name is NOT part of the signature.) - Call that method passing it the command line arguments («fred», «joe», «bert») as a
String[].
Reasons why Java cannot find the class
When you get the message «Could not find or load main class …», that means that the first step has failed. The java command was not able to find the class. And indeed, the «…» in the message will be the fully qualified class name that java is looking for.
So why might it be unable to find the class?
Reason #1 — you made a mistake with the classname argument
The first likely cause is that you may have provided the wrong class name. (Or … the right class name, but in the wrong form.) Considering the example above, here are a variety of wrong ways to specify the class name:
-
Example #1 — a simple class name:
java ListUserWhen the class is declared in a package such as
com.acme.example, then you must use the full classname including the package name in thejavacommand; e.g.java com.acme.example.ListUser -
Example #2 — a filename or pathname rather than a class name:
java ListUser.class java com/acme/example/ListUser.class -
Example #3 — a class name with the casing incorrect:
java com.acme.example.listuser -
Example #4 — a typo
java com.acme.example.mistuser -
Example #5 — a source filename (except for Java 11 or later; see below)
java ListUser.java -
Example #6 — you forgot the class name entirely
java lots of arguments
Reason #2 — the application’s classpath is incorrectly specified
The second likely cause is that the class name is correct, but that the java command cannot find the class. To understand this, you need to understand the concept of the «classpath». This is explained well by the Oracle documentation:
- The
javacommand documentation - Setting the Classpath.
- The Java Tutorial — PATH and CLASSPATH
So … if you have specified the class name correctly, the next thing to check is that you have specified the classpath correctly:
- Read the three documents linked above. (Yes … READ them! It is important that a Java programmer understands at least the basics of how the Java classpath mechanisms works.)
- Look at command line and / or the CLASSPATH environment variable that is in effect when you run the
javacommand. Check that the directory names and JAR file names are correct. - If there are relative pathnames in the classpath, check that they resolve correctly … from the current directory that is in effect when you run the
javacommand. - Check that the class (mentioned in the error message) can be located on the effective classpath.
- Note that the classpath syntax is different for Windows versus Linux and Mac OS. (The classpath separator is
;on Windows and:on the others. If you use the wrong separator for your platform, you won’t get an explicit error message. Instead, you will get a nonexistent file or directory on the path that will be silently ignored.)
Reason #2a — the wrong directory is on the classpath
When you put a directory on the classpath, it notionally corresponds to the root of the qualified name space. Classes are located in the directory structure beneath that root, by mapping the fully qualified name to a pathname. So for example, if «/usr/local/acme/classes» is on the class path, then when the JVM looks for a class called com.acme.example.Foon, it will look for a «.class» file with this pathname:
/usr/local/acme/classes/com/acme/example/Foon.class
If you had put «/usr/local/acme/classes/com/acme/example» on the classpath, then the JVM wouldn’t be able to find the class.
Reason #2b — the subdirectory path doesn’t match the FQN
If your classes FQN is com.acme.example.Foon, then the JVM is going to look for «Foon.class» in the directory «com/acme/example»:
-
If your directory structure doesn’t match the package naming as per the pattern above, the JVM won’t find your class.
-
If you attempt rename a class by moving it, that will fail as well … but the exception stacktrace will be different. It is liable to say something like this:
Caused by: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: <path> (wrong name: <name>)because the FQN in the class file doesn’t match what the class loader is expecting to find.
To give a concrete example, supposing that:
- you want to run
com.acme.example.Foonclass, - the full file path is
/usr/local/acme/classes/com/acme/example/Foon.class, - your current working directory is
/usr/local/acme/classes/com/acme/example/,
then:
# wrong, FQN is needed
java Foon
# wrong, there is no `com/acme/example` folder in the current working directory
java com.acme.example.Foon
# wrong, similar to above
java -classpath . com.acme.example.Foon
# fine; relative classpath set
java -classpath ../../.. com.acme.example.Foon
# fine; absolute classpath set
java -classpath /usr/local/acme/classes com.acme.example.Foon
Notes:
- The
-classpathoption can be shortened to-cpin most Java releases. Check the respective manual entries forjava,javacand so on. - Think carefully when choosing between absolute and relative pathnames in classpaths. Remember that a relative pathname may «break» if the current directory changes.
Reason #2c — dependencies missing from the classpath
The classpath needs to include all of the other (non-system) classes that your application depends on. (The system classes are located automatically, and you rarely need to concern yourself with this.) For the main class to load correctly, the JVM needs to find:
- the class itself.
- all classes and interfaces in the superclass hierarchy (e.g. see Java class is present in classpath but startup fails with Error: Could not find or load main class)
- all classes and interfaces that are referred to by means of variable or variable declarations, or method call or field access expressions.
(Note: the JLS and JVM specifications allow some scope for a JVM to load classes «lazily», and this can affect when a classloader exception is thrown.)
Reason #3 — the class has been declared in the wrong package
It occasionally happens that someone puts a source code file into the
the wrong folder in their source code tree, or they leave out the package declaration. If you do this in an IDE, the IDE’s compiler will tell you about this immediately. Similarly if you use a decent Java build tool, the tool will run javac in a way that will detect the problem. However, if you build your Java code by hand, you can do it in such a way that the compiler doesn’t notice the problem, and the resulting «.class» file is not in the place that you expect it to be.
Still can’t find the problem?
There lots of things to check, and it is easy to miss something. Try adding the -Xdiag option to the java command line (as the first thing after java). It will output various things about class loading, and this may offer you clues as to what the real problem is.
Also, consider possible problems caused by copying and pasting invisible or non-ASCII characters from websites, documents and so on. And consider «homoglyphs», where two letters or symbols look the same … but aren’t.
You may run into this problem if you have invalid or incorrect signatures in META-INF/*.SF. You can try opening up the .jar in your favorite ZIP editor, and removing files from META-INF until all you have is your MANIFEST.MF. However this is NOT RECOMMENDED in general. (The invalid signature may be the result of someone having injected malware into the original signed JAR file. If you erase the invalid signature, you are in infecting your application with the malware!) The recommended approach is to get hold of JAR files with valid signatures, or rebuild them from the (authentic) original source code.
Finally, you can apparently run into this problem if there is a syntax error in the MANIFEST.MF file (see https://stackoverflow.com/a/67145190/139985).
Alternative syntaxes for java
There are three alternative syntaxes for the launching Java programs using the java command.
-
The syntax used for launching an «executable» JAR file is as follows:
java [ <options> ] -jar <jar-file-name> [<arg> ...]e.g.
java -Xmx100m -jar /usr/local/acme-example/listuser.jar fredThe name of the entry-point class (i.e.
com.acme.example.ListUser) and the classpath are specified in the MANIFEST of the JAR file. -
The syntax for launching an application from a module (Java 9 and later) is as follows:
java [ <options> ] --module <module>[/<mainclass>] [<arg> ...]The name of the entrypoint class is either defined by the
<module>itself, or is given by the optional<mainclass>. -
From Java 11 onwards, you can use the
javacommand to compile and run a single source code file using the following syntax:java [ <options> ] <sourcefile> [<arg> ...]where
<sourcefile>is (typically) a file with the suffix «.java».
For more details, please refer to the official documentation for the java command for the Java release that you are using.
IDEs
A typical Java IDE has support for running Java applications in the IDE JVM itself or in a child JVM. These are generally immune from this particular exception, because the IDE uses its own mechanisms to construct the runtime classpath, identify the main class and create the java command line.
However it is still possible for this exception to occur, if you do things behind the back of the IDE. For example, if you have previously set up an Application Launcher for your Java app in Eclipse, and you then moved the JAR file containing the «main» class to a different place in the file system without telling Eclipse, Eclipse would unwittingly launch the JVM with an incorrect classpath.
In short, if you get this problem in an IDE, check for things like stale IDE state, broken project references or broken launcher configurations.
It is also possible for an IDE to simply get confused. IDE’s are hugely complicated pieces of software comprising many interacting parts. Many of these parts adopt various caching strategies in order to make the IDE as a whole responsive. These can sometimes go wrong, and one possible symptom is problems when launching applications. If you suspect this could be happening, it is worth trying other things like restarting your IDE, rebuilding the project and so on.
Other References
- From the Oracle Java Tutorials — Common Problems (and Their Solutions)
Java Could Not Find or Load Main Class
When starting your Java application, you may encounter this error:
Error: Could not find or load main class MyClass
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: MyClassCaused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: MyClassThis error is very common when creating new Java based projects. Whether you’re using Gradle or Maven, Spring Boot or Kafka, chances are you’ve encountered this error before.
Sometimes the error will occur unexpectedly. Sometimes the error is specific to your IDE.
Regardless, fixing the error is easy and it starts with understanding the cause:
What Causes the «Could Not Find or Load Main Class» Error?
This error is thrown whenever Java can’t find or load the main class of your application.
Let’s say you define a class like this:
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("My class is working!");
}
} public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("My class is working!"); }}When running this simple class, you could get the «could not find or load main class» error for several reasons…
1. IDE Configuration Issue
Most IDEs let you configure the starting point for your application. For example, in IntelliJ you can edit configuration to select a main class for running the project.
If you’re running your application through an IDE, make sure that it is configured properly to look for the main class in the right place.
2. Wrong Class Name
Remember that class names must be unique in Java. Furthermore, they are case sensitive…
Let’s say you are running your program from the CLI using the java tool..
java myclassThis will result in the «Could not find or load main class» error because class names are case sensitive.
3. Wrong Extension
When running from the command line, many developers accidentally append an extension like:
java MyClass.javaor
java MyClass.classThe correct way is to run without any extension:
java MyClass4. Wrong Location
Let’s say your class is part of a package like this:
package com.myproject;
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("My class is working!");
}
}public class MyClass { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("My class is working!"); }}If you don’t run your class with the fully qualified name AND from the right directory, you will get the «Could not find or load main class» error…
5. Wrong Class Path
The class path is where the JVM looks for classes to load into your program. Sometimes developers provide a specified path like this:
java MyClass -cp /usr/local/pathWhile the optional -cp argument allows you to specify your own class path, you can easily get the «Could not find or load main class» error if this is incorrect…
How to fix the «Could Not Find or Load Main Class» Error
1. Make sure your IDE is configured properly
Make sure that your IDE has the correct configuration for finding the main class/entry point of your application.
2. Make sure your class name is correct
If you are running your program from the CLI, make sure that you are specifying the right class name without extensions…
java MyClass3. Make sure you are running your application from the right directory
Make sure you are running your application from the right folder. If your class is part of a package then you must run it from the parent directory….
java com.myproject.MyClass4. Make sure your class path is correct
Make sure your class path is correct. By default, the class path is the current working directory «.». If you override this with the -cp argument then make sure it’s accurate!
Understanding the Java Error «Could Not Find or Load Main Class»
While this error is self explanatory and easy to fix, it’s worth understanding how Class Loaders work behind the scenes. This gives you a better understanding of why the «Could Not Find or Load Main Class» error happens…
When are Classes Loaded in Java?
Classes are loaded dynamically. This means classes are loaded into memory only when they are needed.
Unlike C++, Java is a dynamically compiled language. This means the language is compiled to machine code while the program is running.
Of course, some classes must be loaded initially when your program starts. The JRE utilizes a native class loader to load the main entry point of your application. From here, class loaders are used to dynamically load (lazy load) classes as they are needed by the application.
The Class Loading Mechanism in Java
Java utilizes a delegation mechanism for loading classes at runtime. There are 3 built-in class loaders used by the JRE at runtime:
1. Bootstrap class loader: This loads the standard runtime classes found in rt.jar
2. Extensions: This loads any extension classes used by the JRE
3. System: This loads classes defined by the application and found on the class path
Each class loader first checks a cache to see if the requested class has already been loaded into memory. If nothing is found in the cache, it delegates the finding of the class to the parent class loader.
This process happens recursively…
If the system class loader can’t find the class, it delegates to the extension class loader.
If the extension class loader can’t find the class, it delegates to the bootstrap class loader.
If the bootstrap class loader can’t find the class, it tells the extension class loader to find it
If the extension class loader can’t find the class, it tells the system class loader to find it
If the system class loader can’t find it, it throws an ClassNotFound exception
This mechanism works to ensure uniqueness, visibility and delegation are applied to the class loading mechanism in Java.
Uniqueness explains the reason why no two classes can have the same name. By keeping class names unique, class loaders can easily find the single representation of a defined class.
Visibility explains the child-parent relationship between class loaders. While children can view parent classes, parents can’t view child classes. This ensures an isolation level needed to create the hierarchy between class loaders.
Delegation explains how the class loaders work together to recursively retrieve a unique class. By delegating to parent classes, class loaders ensure only one representation of a defined class exists.
Java Class Loading Order
1) Class loader searches cache for loaded classes
2) If cache has the class, it is returned. Otherwise, the class loader delegates to parent class to retrieve the class
3) Parent class loaders ultimately delegate to the bootstrap class loader. If the class isn’t found, the bootstrap loader returns responsibility to child loader.
4) Either the system loader finds and loads the class, or a ClassNotFound exception is thrown.
Custom Class Loaders
You can create your own class loaders by extending the ClassLoader class:
public class CustomClassLoader extends ClassLoader { ...Most developers don’t need to worry about creating custom class loaders. There are times where it makes sense however. Sometimes custom class loaders are used to implementing class versioning. Other custom class loaders allow you to create classes dynamically or switch implementations etc.
Conclusion
The «Could not find or load main class» error is common and easy to fix. Its cause usually has to do with specifying the wrong class name, extension, or class path.
This error can be easily fixed by checking IDE configurations, class path variables, class names, and making sure you’re running the application from the right directory.
The JRE utilizes a class loading mechanism to dynamically load classes into memory. This mechanism relies on a recursive process where class loaders delegate retrieval to parent loaders if they can’t find the class already loaded in memory.
You can create your own custom class loaders for dynamic class creation and versioning.
Your thoughts?
1. Overview
Occasionally when we run a Java program, we might see “Could not find or load main class.” It’s easy to guess the reason: The JVM failed to find the main class and gave this error. But why couldn’t it?
In this tutorial, we’ll discuss the probable reasons for failure to find the main class. We’ll also see how to fix them.
2. Sample Program
We’ll start with a HelloWorld program:
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world..!!!");
}
}Now let’s compile it:
$ javac HelloWorld.javaHere, the compiler will generate a .class file for our program. This .class file will be generated in the same directory. The .class file will have the same name as the class name given in the Java program. This .class file is executable.
In the following sections, we’ll run this .class file and try to understand the probable reasons for error “Could not find or load main class.”
3. Wrong Class Name
To run a .class file generated by Java compiler, we can use this command:
java <.class filename>Now let’s run our program:
$ java helloworld
Error: Could not find or load main class helloworldAnd it failed with the error “Could not find or load main class helloworld.”
As discussed earlier, the compiler will generate the .class file with the exact same name given to the Java class in the program. So in our case, the main class will have the name HelloWorld, not helloworld.
Let’s give it one more try with correct casing:
$ java HelloWorld
Hello world..!!!This time it ran successfully.
3.1. File Extension
To compile a Java program, we must provide the file name with its extension (.java):
$ javac HelloWorld.javaBut to run a .class file, we need to provide the class name, not the file name. So there is no need to provide the .class extension:
$ java HelloWorld.class
Error: Could not find or load main class HelloWorld.classAgain, let’s run our program using the correct class name:
$ java HelloWorld
Hello world..!!!4. Java Package Names
In Java, we keep similar classes together in what we call a package.
Let’s move HelloWorld class into the com.baeldung package:
package com.baeldung;
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world..!!!");
}
}Now let’s compile and run the updated HelloWorld program like before:
$ java HelloWorld
Error: Could not find or load main class HelloWorldBut again, we get the error “Could not find or load main class HelloWorld.”
Let’s try to understand what we missed here.
To run a Java class that is in a package, we must provide its fully qualified name. So in our case, HelloWorld‘s fully qualified name is com.baeldung.HelloWorld.
Now, when we created com.baeldung package, we actually created this folder structure:
com/baeldung/HelloWorld.javaFirst, let’s try to run our program from the com/baeldung directory:
$ java com.baeldung.HelloWorld
Error: Could not find or load main class com.baeldung.HelloWorldStill, we are not able to run our program.
Here, when we specified the fully qualified class name com.baeldung.HelloWorld, Java tried to find the HelloWorld.class file in com/baeldung, under the directory from where we were running the program.
As we were already inside com/baeldung, Java failed to find and run the HelloWorld program.
Now let’s move back to the parent folder and run it:
$ java com.baeldung.HelloWorld
Hello world..!!!And we are again able to say “Hello” to the world.
5. Invalid Classpath
Before going ahead, let’s first understand what the classpath is. It’s the set of classes available to our currently running JVM.
We use the classpath variable to tell the JVM where to find the .class files on the file system.
While running a program, we can provide the classpath using -classpath option:
java -classpath /my_programs/compiled_classes HelloWorldHere, Java will look for the HelloWorld.class file in /my_programs/compiled_classes folder, a folder whose name we just made up. By default, the classpath variable is set to “.”, meaning the current directory.
In the above section, we changed our directory to run our program. But what if we want to run it from some other folder? That’s when the classpath variable helps us.
To run our program from the directory com/baeldung, we can simply state that our classpath is two directories up — one for each package part:
$ java -claspath ../../ com.baeldung.HelloWorld
Hello world..!!!Here, “..” represents the parent directory. In our case “../../” represents the top of our package hierarchy.
6. Conclusion
In this article, we learned the probable reasons for the error “Could not find or load main class.”
Then, of course, we also learned how to solve this error.
In some situations, while executing a Java program from the command prompt, we may face the error “Could not find or load main class”. This occurs mainly when the JVM fails to find the main class or .class file. Whenever we compile a Java code, the compiler will automatically create a .class file with the same name as the class name. This will be present in the same directory where we have the .java file.

Let us see a simple Java code and try to compile and execute it from the command prompt.
public class HelloJava {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Java programming language");
}
}
First, we need to compile the code using the javac command.
D:Sample>javac HelloJava.java
This will produce the right result as below since we have compiled it correctly.
D:Sample>java HelloJava Java programming language
Now let us see the different reasons or causes to generate the error “Could not load or find the main class in Java“.
Whenever we compile the java code, the compiler creates a .class file in the same name as the class name. After compilation, if we try to run the code by providing an incorrect file name in the java command, it will result in an error “Could not load or find the main class in Java“.
D:Sample>java hellojava Error: Could not find or load main class hellojava Caused by: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: HelloJava (wrong name: hellojava)
Since the class names “HelloJava” and “hellojava” are different, it could not find the right file to execute. The Java file names are case-sensitive during execution.
Could not find or load main class in Java: Incorrect file extension
During compilation, we provide the file extension as.java. In this case, it compiles and successfully generates the .class file. But for executing a java code, we do not need to provide the .class extension. In case we provide the .class as file extension, it will generate the below error “Could not find or load main class in Java”.
D:Sample>java HelloJava.class Error: Could not find or load main class HelloJava.class Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: HelloJava.class
If we try to execute without the file extension, it will execute successfully.
D:Sample>java HelloJava Java programming language
Package names
When we have multiple classes that we want to group together, we can group them under a single package. When we place a Java file inside a package, we need to specify the fully qualified name. This means we need to execute the file as packagename.filename.
Now, let us see how to execute the java code when we place the HelloJava.java file inside the package “javaDemo“. In the below example, we are already within the directory “javaDemo“. Hence the compiler tries to find the class file javaDemo.HelloJava and fails to find it. This will result in an error “Could not find or load main class in Java”.
D:SamplejavaDemo>java javaDemo.HelloJava Error: Could not find or load main class javaDemo.HelloJava Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: javaDemo.HelloJava
Suppose we move one directory up. Now, it runs successfully. Whenever we execute a java file with a fully qualified name, we need to move one directory up.
D:Sample> java javaDemo.HelloJava Java programming language
Could not find or load main class in Java: Invalid classpath
A classpath is a path that instructs the JVM where the .class files are present. We can also execute a Java file by specifying the classpath using –cp or -classpath option in the java command.
We can specify the classpath after the -cp command as below. Here HelloJava is present inside the directory javaDemo.
C:Usersnandieclipse-workspaceFirstJavaProjectsrc>java -cp ./javaDemo;. HelloJava Java programming language
If we try to specify the classpath when we are already within the target directory, we will get the below error “Could not find or load main class in Java”. This is because it searching for the package javaDemo which is not present since we are already within the same directory.
C:Usersnandieclipse-workspaceFirstJavaProjectsrcjavaDemo>java -cp ./javaDemo;. HelloJava Error: Could not find or load main class HelloJava Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: HelloJava
Reference
- Could Not Find Error Due to Passing the Wrong Name in Java
- Could Not Find Error Due to Wrong Package Name in Java
- Could Not Find Error Due to Wrong CLASSPATH in Java
This tutorial introduces the could not find or load main class errors in Java.
Suppose we have written a code and compiled it. Till now, everything is working fine, but when we finally ran it, an error showed up.
could not find or load main class
This tutorial will discuss why this error occurs and how to resolve it. Let us first recap how we run a java program using the command prompt.
First, we compile the code using the javac command like below:
After executing the above command, A file with the .class extension gets created into the current folder.
The .class file will have the same class as the .java program. We then run the .class file using the following command to execute the Java code:
We may get the could not find or load main class error. This error is a runtime error and occurs when the Java Virtual machine cannot locate the main class (class containing the main method) we are trying to run.
This error most commonly occurs when running our Java programs using the command prompt. Before discussing the causes of this error, let us first understand CLASSPATH.
CLASSPATH in Java
This is the executable.class and other resource files.
The JVM uses it to locate the files. The default CLASSPATH is the current directory unless we explicitly set the CLASSPATH in the system variables.
To run a program, we need to pass the class name. We take the following example to illustrate the point:
public class DelftStack{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello from DelftStack");
}
}
Let’s first compile it using the javac command:
C:UsersUserDocumentsDelftStackjava>javac DelftStack.java
C:UsersUSerDocumentsDelftStackjava>
After the above command execution, a DelftStack.class file gets created in our current directory. Let’s run that file by using the java command.
C:UsersUserDocumentsDelftStackjava>java DelftStack.class
Error: Could not find or load main class DelftStack.class
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: DelftStack.class
Here, we are getting an error because we are trying to run the .class file. Instead, we just need to pass the class name.
Look below:
C:UsersUserDocumentsDelftStackjava>java DelftStack
Hello from DelftStack
Could Not Find Error Due to Passing the Wrong Name in Java
The could not find or load the main class can also occur when we pass the wrong class name. By continuing the previous example, if we try to run the program with the wrong name as follows:
C:UsersUserDocumentsDelftStackjava>java DelftStac
Error: Could not find or load main class DelftStac
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: DelftStac
We get the error above because we have misspelled the class name. Here, the JVM is trying to run a class named DelftStac, which doesn’t exist.
We can resolve this issue by correctly spelling out the class name as follows:
C:UsersUserDocumentsDelftStackjava>java DelftStack
Hello from DelftStack
We should also note here that the class name is case-sensitive. If we run the class Delftstack, we will get an error.
Look below:
C:UsersUserDocumentsDelftStackjava>java Delftstack
Error: Could not find or load main class Delftstack
Caused by: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: Delftstack (wrong name: Delftstack)
We should use the correct spelling and the correct cases to run a file successfully.
Could Not Find Error Due to Wrong Package Name in Java
Let’s move our DelftStack class into the com.DelftStack package. A package is used to keep similar classes together.
Look at the following code:
package com.DelftStack;
public class DelftStack{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello from DelftStack");
}
}
To compile a package in Java, we use the following command:
javac -d . <.java file name>
The -d flag switch is used to tell where to keep the generated class file. The . means the current directory.
We compile the above code as follows:
C:UsersUserDocumentsDelftStackjava>javac -d . DelftStack.java
After executing the above command, the following folder structure gets created in our current directory.
comDelftStackDelftStack.class
As we can see, our class file is two folders deep from our current directory. So if we try to run our class file like we were doing in previous cases, we get an error.
C:UsersUserDocumentsDelftStackjava>java DelftStack
Error: Could not find or load main class DelftStack
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: DelftStack
The reason for this error is that no DelftStack class exists in our current folder. To run the class present in a package, we need to pass its fully qualified name (com.DelftStack.DelftStack in this case).
C:UsersUserDocumentsDelftStackjava>java com.DelftStack.DelftStack
Hello from DelftStack
This tells Java to look for the class inside the comDelftStack folder.
Could Not Find Error Due to Wrong CLASSPATH in Java
The CLASSPATH tells the JVM where the .class files are present.
Suppose we are currently in a different folder, and we want to run a Java program whose class file exists in a different folder. In this case, we can pass the location of the class file using the -classpath option.
For example:
java -classpath XYZ/ABC <class name>
The above command tells Java to look for the .class file inside the ZYX/ABC folder.
In the previous case, we created a package.
Suppose we want to run the file inside the com/DelftStack folder. Using the following command, we can do so:
>java -classpath ../../ com.DelftStack.DelftStack
Hello from DelftStack
The ../ means the parent directory. So ../../ means to lookup two directory levels.
Let us take another example, suppose we are at the desktop (folder) location, and we want to run a class file somewhere else on the computer. We can do so by below.
>java -cp C:UsersUserDocumentsDelftStackjava com.DelftStack.DelftStack
Hello from DelftStack
The -cp flag is the shorthand for -classpath. Here, we passed the full location of the folder where the .class file is present.
Error: Could not find or load main class HelloWorld comes when you are trying to run your Java program using java command with the main class as HelloWorld but Java is not able to find the class. In order to solve this error, you must know how Java find and loads the classes, that’s a little bit complex topic for beginners, but we will touch the same base here. For the curious reader, I would suggest reading my post How Classpath works in Java, a must read for a beginner. For now, you just remember that there is an environment variable called CLASSPATH which includes directories where Java looks for all class files and if it doesn’t find your main class there then it throws «Error: Could not find or load main class XXX», where XXX is the name of your main class.
Since many Java programmer is now started programming using Eclipse they face this issue when they first try to run their Java program from command line. In Eclipse, it’s easy to compile and run the program because Eclipse takes care of all Classpath setup, but when you run your Java program from command line, CLASSPATH environment variable comes in picture.
Personally, I don’t like this environment variable and doesn’t define in my environment variable, because its confusing and source of so many classpath related issue. Instead, I use -cp or -classpath option with java command to run my program. This way you always know which JARs are included in your classpath.
For beginners, another important thing to understand is the difference between PATH and CLASSPATH, you must know that PATH is used locate system executable, commands or .exe, .dll files (in Windows) and .so files (in Linux). It is also used to locate native libraries used by your Java program. While, CLASSPATH is used to locate the class file or JAR files. It’s Java class loader who looked into CLASSPATH for loading classes.
Coming back to the problem in hand, if you are a beginner in Java, who are able to run the program from Eclipse but getting «Error: Could not find or load main class HelloWorld» when trying to run the same program from the command line then follow the steps given here to solve it.
Solving Error: Could not find or load main class HelloWorld
Unfortunately beginner’s book like Head First Java, which many developers used to learn Java, doesn’t teach you how to deal with this kind of errors. You need to build this skill by doing active development. In order to understand the problem little better, let’s reproduce it. This is one of the most important troubleshooting skill which will help you a long way in your career. Half of the problem is solved when you are able to reproduce it.
For our purpose we will use following HelloWorld program for our testing, interestingly I have named it HelloHP and it resides in a package called «dto». I have purposefully chosen a class with a package instead of HelloWorld in the default package because many programmers get «Could not find or load main class» error when they try to run a class which is inside a package.
package dto; /** * Simple Java program to demonstrate following error * Error :Could not find or load main class * * @author Javin Paul */ public class HelloHP { public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println("My first program in Java, HelloWorld !!"); } }
When you run this from Eclipse, by Right click on the source file and Choosing «Run as Java Program», it will run fine and print following line:
My first program in Java, HelloWorld !!
Everything as expected, Now we will try to run same Java program from command line. Since I am using Maven with Eclipse, its build process creates class files in project_directorytargetclasses directory. If you are not using Maven with Eclipse, then you can see the class file created by Eclipse’s Java compiler in project_directorybin. It doesn’t matter how those class files are created, but, what is important is the location of the class file.
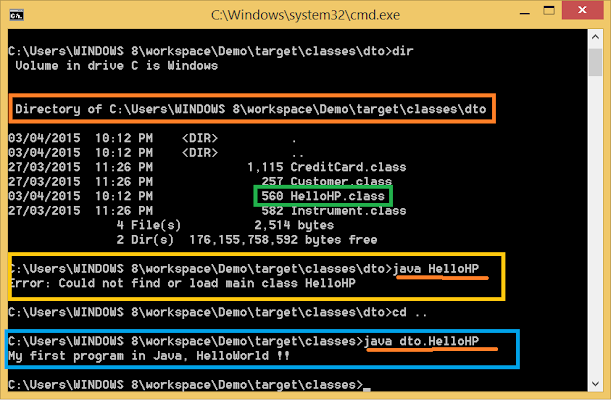
If your class is inside a non-default package e.g. «dto» in our case then compiler the will put the HelloHP.class file, which contains Java bytecode in a directory named «dto». In our case the full name of class dto.HelloHP and it is present in C:UsersWINDOWS 8workspaceDemotargetclassesdto. So in the first try, I go there and execute java command to launch my program, as seen below:
C:UsersWINDOWS 8workspaceDemotargetclassesdto>java HelloHP Error: Could not find or load main class HelloHP
Do you see the error? It’s coming because the full name of the class should be dto.HelloHP and not HelloHP. So let’s correct this error and try to run the same command from the same location but this time with fully qualified name:
C:UsersWINDOWS 8workspaceDemotargetclassesdto>java dto.HelloHP Error: Could not find or load main class dto.HelloHP
Still same error, right. Why? because I don’t have any CLASSPATH environment variable, neither I am using -classpath or -cp option to suggest the path, So by default Java is only searching in the current directory. It is looking for dto/HelloHP.class but since we are already inside dto, it is not able to find the class. So, what should we do now? let’s go to the parent directory «C:UsersWINDOWS 8workspaceDemotargetclasses» and execute the same command, this time, it should work:
C:UsersWINDOWS 8workspaceDemotargetclassesdto>cd .. C:UsersWINDOWS 8workspaceDemotargetclasses>java dto.HelloHP My first program in Java, HelloWorld !!
Bingo!!, our program ran successfully because, without any hint about where to find class files, Java is by default looking into the current directory, denoted by . (dot) and able to locate ./dto/HelloHP.class.
Now, what if you want to run this program from any other directory? Well, for that purpose whether we need to define CLASSPATH or just use -classpath or -cp option. I like the second option because it’s easier to control and change. Also, remember, it overrides any CLASSPATH environment variable. If you like to set CLASSPATH environment variable in Windows, see that tutorial.
Now let’s run the program target directory first without using -classpath option:
C:UsersWINDOWS 8workspaceDemotargetclasses>cd .. C:UsersWINDOWS 8workspaceDemotarget>java dto.HelloHP Error: Could not find or load main class dto.HelloHP
You can see we are again started getting the same error, Why? because Java is still looking into the current directory and there is no .targetdtoHelloHP.class there, as it’s one level down e.g. .targetclassesdtoHelloHP.class
Now let’s run the same command using -classpath option from target directory itself:
C:UsersWINDOWS 8workspaceDemotarget>java -cp ./classes;. dto.HelloHP My first program in Java, HelloWorld !!
Bingo!!, our program ran successfully again because now Java is also looking at ./classes directory and there it is able to find dtoHelloHP.class file.
There are many ways Error: Could not find or load main class HelloWorld manifests itself, but if you know the basics of Java Classpath, you can easily sort out the problem. Most of the time you just need to either correct your CLASSPATH environment variable or run your program with java -cp or -classpath option. By the way, there are more to it e.g. Main class defined in the manifest.mf file and that’s why I suggest reading about How Classpath works in Java (see the link in the first paragraph).
Summary
If you are getting «Error: Could not find or load main class XXX», where XXX is the name of your main class while running Java program then do this to solve that error:
1) If you are running Java program right from the directory where .class file is and you have CLASSPATH environment variable defined then make sure it include current directory. (dot). You can include it as set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;. in Windows and export CLASSPATH = ${CLASSPATH}:. (see the separator, in Windows it’s;(semicolon) while in Linux it is (colon), also note we have included current directory in existing classpath. If you still face the issue of setting classpath, see this step by step guide to set the classpath. Same thing applies if you are running your program using -cp or -classpath option.
2) If you are running Java program from the directory, your .class file is and you don’t have any CLASSPATH or -cp option then check whether your class is the in the package or not. If it’s the in the package then go outside of the package directory and run java command with fully qualified name e.g. if your program is com.abc package then runs following command from the parent directory of «com»
java com.abc.HelloWorld
without any classpath hints, Java will look into the current directory and search for comabcHelloWorld.class in Windows, so if com directory exists in your current directory, your program will run otherwise you will get «Error: Could not find or load main class dto.HelloHP».
3) You can run your Java program from anywhere with the help of proper CLASSPATH or java -cp option as shown below:
java -cp C:test;. com.abc.HelloWorld
If you still facing any issue just check whether you have accidentally using CLASSPATH environment variable, you can check this in Windows by running echo %CLASSPATH% command and in Linux by running echo $CLASSPATH. If CLASSPATH is nonempty then it will print its value otherwise just echo the same command.
4) If you are running in Java version 1.6 or 1.5, then instead of receiving «Error: Could not find or load main class», you will get Exception in thread «main» java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: HelloWorld. It’s only from JDK 1.7 onward we are started receiving this new error. The solution is exactly same, every bit of discussion applies to that case as well. So if you are not able to solve that problem by following steps here, do let me know and I will try to work with you to troubleshoot the problem.
Here is the screenshot of how I tried to reproduce and solve the error as discussed in the previous paragraph:
That’s all about how to solve «Error: Could not find or load main class HelloWorld» in Java. Classpath is little confusing topic to master, but you will understand it once you started writing and running some Java program. If you are still not able to fix your problem then post a comment there with what you have tried and we will try to troubleshoot together.
My goal is not just to give you solution but also make you able to explain why the solution is working and CLASSPATH basics are very important for a Java developer. I have seen many programmers getting frustrated, losing interest in Java due to various PATH and CLASSPATH issues e.g. NoClassDefFoundError and ClassNotFoundException and this is my humble effort to bring them back and empower with practical knowledge. Hope you understand.
Further Reading
Building debugging and troubleshooting skill is not easy and it takes lots of practice and experience to understand, reproduce and solve the error. If you are new Java developer then you first pick a book to learn Java from start to end, but if you are intermediate Java developer then you should look at the following resources to develop your debugging skill.
I have already shared the common problem java beginners face i.e illegal start of expression error. You can not find these kind of errors in java books. The only way to
familiarize yourself about the most common errors by using active java
development. Today we will look into another common problem for java beginners,i.e how to fix «error: could not find or load main class» error in java. As the name suggest,this error occurs when java is not able to find the class you are trying to execute. To better understand the error you should be familiar with CLASSPATH. If you are not familiar with CLASSPATH then please check this out what is CLASSPATH and how it differs from PATH.
Read Also: Difference between PATH and CLASSPATH
«Could not find or load main class : XXX» where the class name is XXX occurs if the CLASSPATH environment variable where java looks for all class files, does not found the class.
[Fixed] Error : Could not find or load main class
1. Calling .class file from java command
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println(" You have just run HelloWorld !"); } }
Suppose I have a simple HelloWorld java program. If I will compile it using command
javac HelloWorld.java
then HelloWorld.class file is created.
You will get the Error : Could not find or load main class if you try to run .class file using java command as shown below:
java HelloWorld.class
instead you should try
java HelloWorld
Yayy!! your problem is resolved.
You have just run HelloWorld !
2. If your casing incorrect
After compiling the code , you run the following command
java helloworld
then also «Could not find or load main class helloworld» error appears. Make sure casing is correct. In our program it should be HelloWorld ( where ‘H’ of hello and ‘W’ of world is in uppercase).
java HelloWorld
Yayy ! It will work fine and print
You have just run HelloWorld !
3. Class in a package
In the below example I have a HelloWorld class inside the com.javahungry package.
package com.javahungry; /** * Java program to demonstrate * Error :Could not find or load main class * * @author Subham Mittal */ public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String args[]) { System.out.println(" You have just run HelloWorld !"); } }
If you try to call
java HelloWorld
It will result in Error : Could not find or load main class HelloWorld. The error occurs because it must be called with its fully qualified name. To
be clear, the name of this class is not HelloWorld, It’s
com.javahungry.HelloWorld . Attempting to execute HelloWorld does not work,
because no class having that name exists. Not on the current classpath
anyway.
java com.javahungry.HelloWorld
Above command will also result in Error : Could not find or load main class HelloWorld because CLASSPATH environment variable is not set. I do not use -classpath or -cp command to suggest the path. By default java is searching the class file in the default directory.
java -cp . com.javahungry.HelloWorld
If your classpath is correct then above command will run the HelloWorld program. Otherwise, It will also result in Error : Could not find or load main class HelloWorld because -cp . command make sure the JVM looks for the class file in the current directory.
Follow below steps if error persist.
You must ensure that the location of the .class file is added in the
CLASSPATH. Suppose if «/Users/SubhamMittal/Desktop/» is on the classpath
and JVM looks for the class called «com.javahungry.HelloWorld», it will
look for the .class file in the following path:
«/Users/SubhamMittal/Desktop/com/javahungry/HelloWorld»
java -cp /Users/SubhamMittal/Desktop/ com.javahungry.HelloWorld
Yayy ! It will print
You have just run HelloWorld !
The above example is performed on Mac OS.
4. Class in a Package for Windows OS
Suppose My java class i.e HelloWorld (given above) after compilation is in the below path
D:projectcomjavahungry
The full name of the HelloWorld class is
com.javahungry.HelloWorld
so use cd .. back command to reach to the main directory
D:project
Then issue the java command
java com.javahungry.HelloWorld
Yayy ! The program ran successfully without setting any classpath. It is because java is looking for the current directory denoted by .(dot) and able to locate the .comjavahungryHelloWorld.class .
It will print
You have just run HelloWorld !
5. Setting CLASSPATH to current directory
if .class file in the current folder then set . to your CLASSPATH (note in Windows the CLASSPATH separator is semi colon ; while in Linux the separator is colon :).
You can set the CLASSPATH in Windows :
set CLASSPATH = %CLASSPATH%;.
(note . added at last for current directory)
You can set the CLASSPATH in Linux :
export CLASSPATH = ${CLASSPATH}:.
(note . added at last for current directory)
If you are using java 1.5 or 1.6 , instead of getting error : could not find or load main class you will get Exception in thread «main» java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError : HelloWorld. Since jdk 1.7 we started receiving this new error. The good news, Solution is exactly same.
If you are not able to solve the problem by using above steps then please mention in the comments.