I was learning Adam Drozdek’s book «Data Structures and Algorithms in C++», well, I typed the code in page 15 in my vim and compiled it in terminal of my Ubuntu 11.10.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
char *name;
int age;
Node(char *n = "", int a = 0){
name = new char[strlen(n) + 1];
strcpy(name, n);
age = a;
}
};
Node node1("Roger", 20), node2(node1);
cout << node1.name << ' ' << node1.age << ' ' << node2.name << ' ' << node2.age;
strcpy(node2.name, "Wendy");
node2.name = 30;
cout << node1.name << ' ' << node1.age << ' ' << node2.name << ' ' << node2.age;
But there’s some error:
oo@oo:~$ g++ unproper.cpp -o unproper
unproper.cpp:15:23: warning: deprecated conversion from string constant to ‘char*’ [-Wwrite-strings]
unproper.cpp:16:1: error: ‘cout’ does not name a type
unproper.cpp:17:7: error: expected constructor, destructor, or type conversion before ‘(’ token
unproper.cpp:18:1: error: ‘node2’ does not name a type
unproper.cpp:19:1: error: ‘cout’ does not name a type
I have searched this,this,this and this, but I can’t find the answer.
Any help would be appreciated:)
Error does not name a type in C++
The «error does not name a type» in C/C++ is defined as the when user declares outside of the function or does not include it properly in the main file this error will through.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Why this error occurs?
- How to resolve:
- Solution 1:
- Solution 2:
- Solution 3:
- Conclusion
Why this error occurs?
File: sample.h
#ifndef SAMPLE_H__<br />#define SAMPLE_H__
namespace Sampletest {
class CP_M_ReferenceCounted<br />{<br />};
}
#endif
<br />File : test.cpp
#include "sample.h"
typedef CP_M_ReferenceCounted FxRC;
<br />int main(int argc, char **argv)<br />{
<p>return 0;<br />}
If you run the above code you will get the error «…error: CP_M_ReferenceCounted does not name a type»
How to resolve :
To overcome this error follow this two methods of solutions
Solution 1:
To avoid this error, we have to add the «using namespace Sampletest» at the start of the program in C++.
To avoid this error, we have to add the «using namespace Sampletest» at the start of the program in C++.
<p>File : test.cpp</p>
<p><code>#include "sample.h"</p>
<p>//Add the following to your code</p>
<p>using namespace Sampletest</p>
<p>typedef CP_M_ReferenceCounted FxRC;</p>
<p><br />int main(int argc, char **argv)<br />{</p>
<p>return 0;<br />}</code></p>
Solution 2:
To avoid this kind of error we need to add the header «#include sample.h» at the starting of the program in C++.
Same Problem while declaring outside of the function
These kinds of errors are also acquired while printing outside of any function.
A statement which isn’t declaration in C++ need to be printed inside of the function
File test.cpp
<p>#include <iostream><br />#include <cstring><br />using namespace std;</p>
<p>struct Node{<br />char *name;<br />int age;<br />Node(char *nc = "", int ax = 0){<br />name = new char[strlen(nc) + 1];<br />strcpy(name, n);<br />age = ax;<br />}<br />};</p>
<p>Node node1("Roger", 20), node2(node1);<br />cout << node1.name << ' ' << node1.age << ' ' << node2.name << ' ' << node2.age;<br />strcpy(node2.name, "Wendy");<br />node2.name = 30;<br />cout << node1.name << ' ' << node1.age << ' ' << node2.name << ' ' << node2.age;</p>
<p> </p>
<p><b>Output :</b></p>
<p>error: ‘node2’ does not name a type</p>
<br/>
Solution 3:
To avoid these types of errors you need to add everything inside the function,
because a statement that isn’t a declaration in C++ needs to be inside the function
<p><code>int main() {<br />Node node1("Roger", 20), node2(node1);<br />cout << node1.name << ' ' << node1.age << ' ' << node2.name << ' ' << node2.age;<br />strcpy(node2.name, "Wendy");<br />node2.name = 30;<br />cout << node1.name << ' ' << node1.age << ' ' << node2.name << ' ' << node2.age;<br />}</code></p>
Conclusion:
In this article, we have seen why the undefined error occurs in C/C++ and discussed how to resolve these errors in various methods.
|
Dancing_god 15 / 2 / 1 Регистрация: 18.09.2015 Сообщений: 227 |
||||
|
1 |
||||
|
17.12.2020, 01:23. Показов 10745. Ответов 14 Метки c++ (Все метки)
Здравствуйте. Пишу программу на С++, реализующую структуру данных множество в виде класса.
Собственно при компиляции gcc выдает: Код MySet does not name a type. Что означает, понятно. Но почему компилятор не видит прототип класса, объявленный в начале файла?
__________________
0 |
|
DrOffset 16495 / 8988 / 2205 Регистрация: 30.01.2014 Сообщений: 15,611 |
||||
|
17.12.2020, 01:33 |
2 |
|||
|
MySet C();
Добавлено через 2 минуты
0 |
|
15 / 2 / 1 Регистрация: 18.09.2015 Сообщений: 227 |
|
|
17.12.2020, 01:40 [ТС] |
3 |
|
Выше — это определенно ошибка, но может быть не единственная. Это попытка исправить ошибку в данной строке. И по незнанию, тоже ошибка. Код array.cpp:37:16: error: expected ‘;’ at end of member declaration
MySet& MySet operator = (const MySet&);
^~~~~
array.cpp:37:40: error: ‘MySet’ does not name a type
MySet& MySet operator = (const MySet&);
^~~~~
array.cpp:37:46: error: ISO C++ forbids declaration of ‘operator=’ with no type [-fpermissive]
MySet& MySet operator = (const MySet&);
^
array.cpp:37:16: error: field ‘MySet& MySet::MySet’ with same name as class [-fpermissive]
MySet& MySet operator = (const MySet&);
^~~~~
array.cpp:44:34: error: ‘MySet’ does not name a type
MySet& MySet::operator |= (const MySet& rightSet){
^~~~~
array.cpp:44:8: error: prototype for ‘MySet& MySet::operator|=(const int&)’ does not match any in class ‘MySet’
MySet& MySet::operator |= (const MySet& rightSet){
^~~~~
array.cpp:17:16: error: candidate is: MySet& MySet::operator|=(const MySet&)
MySet& operator |= (const MySet&);
^~~~~~~~
array.cpp:58:32: error: ‘MySet’ does not name a type
MySet MySet::operator | (const MySet& rightSet) const{
^~~~~
array.cpp:58:7: error: prototype for ‘MySet MySet::operator|(const int&) const’ does not match any in class ‘MySet’
MySet MySet::operator | (const MySet& rightSet) const{
^~~~~
array.cpp:19:15: error: candidate is: MySet MySet::operator|(const MySet&) const
MySet operator | (const MySet&) const;
array.cpp:64:34: error: ‘MySet’ does not name a type
MySet& MySet::operator &= (const MySet& rightSet){
^~~~~
array.cpp:64:8: error: prototype for ‘MySet& MySet::operator&=(const int&)’ does not match any in class ‘MySet’
MySet& MySet::operator &= (const MySet& rightSet){
^~~~~
array.cpp:21:16: error: candidate is: MySet& MySet::operator&=(const MySet&)
MySet& operator &= (const MySet&);
^~~~~~~~
array.cpp:79:32: error: ‘MySet’ does not name a type
MySet MySet::operator & (const MySet& rightSet) const{
^~~~~
array.cpp:79:7: error: prototype for ‘MySet MySet::operator&(const int&) const’ does not match any in class ‘MySet’
MySet MySet::operator & (const MySet& rightSet) const{
^~~~~
array.cpp:23:15: error: candidate is: MySet MySet::operator&(const MySet&) const
MySet operator & (const MySet&) const;
^~~~~~~~
array.cpp: In member function ‘MySet MySet::operator~() const’:
array.cpp:86:11: error: expected ‘;’ before ‘C’
MySet C();
^
array.cpp:96:13: error: ‘C’ was not declared in this scope
C.A[C.n++] = i;
^
array.cpp:99:12: error: ‘C’ was not declared in this scope
return C;
^
array.cpp: In constructor ‘MySet::MySet()’:
array.cpp:108:1: error: uninitialized reference member in ‘class MySet&’ [-fpermissive]
MySet::MySet(): n(0), S('A'+cnt++), A(new char[N+1]){
array.cpp:37:16: note: ‘MySet& MySet::MySet’ should be initialized
MySet& MySet operator = (const MySet&);
^~~~~
array.cpp: In constructor ‘MySet::MySet(char)’:
array.cpp:113:1: error: uninitialized reference member in ‘class MySet&’ [-fpermissive]
MySet::MySet(char): n(0), S('A'+cnt++), A(new char[N+1]){
^~~~~
array.cpp:37:16: note: ‘MySet& MySet::MySet’ should be initialized
MySet& MySet operator = (const MySet&);
^~~~~
array.cpp: At global scope:
array.cpp:125:20: error: ‘MySet’ does not name a type
MySet::MySet(const MySet& B): n(B.n), S('A'+cnt++), A(new char[N+1]){
^~~~~
array.cpp:125:1: error: prototype for ‘MySet::MySet(const int&)’ does not match any in class ‘MySet’
MySet::MySet(const MySet& B): n(B.n), S('A'+cnt++), A(new char[N+1]){
^~~~~
array.cpp:35:9: error: candidates are: MySet::MySet(const MySet&)
MySet(const MySet&);
^~~~~
array.cpp:108:1: error: MySet::MySet()
MySet::MySet(): n(0), S('A'+cnt++), A(new char[N+1]){
^~~~~
array.cpp:113:1: error: MySet::MySet(char)
MySet::MySet(char): n(0), S('A'+cnt++), A(new char[N+1]){
^~~~~
array.cpp:133:33: error: ‘MySet’ does not name a type
MySet& MySet::operator = (const MySet& B){
^~~~~
array.cpp:133:8: error: prototype for ‘MySet& MySet::operator=(const int&)’ does not match any in class ‘MySet’
MySet& MySet::operator = (const MySet& B){
array.cpp:7:7: error: candidates are: MySet& MySet::operator=(const MySet&)
class MySet{
^~~~~
array.cpp:37:22: error: int MySet::operator=(const int&)
MySet& MySet operator = (const MySet&);
компилирую только данный файл. В начале думал, что проблема с заголовочным файлом. Вынес прототип класса в исполняемый файл .cpp (в вышеприведенный).
0 |
|
hoggy 8719 / 4299 / 958 Регистрация: 15.11.2014 Сообщений: 9,744 |
||||
|
17.12.2020, 01:41 |
4 |
|||
|
Но почему компилятор не видит прототип класса, объявленный в начале файла? вот это что такое?
MySet& MySet operator = (const MySet&); а вот это что такое?
это — объявление прототипа функции, если ты вдруг не понял. одно неправильное объявление провоцирует другие ошибки: Код error: request for member ‘A’ in ‘C’, which is of non-class type ‘MySet()’
C.A[C.n++] = i;
^
и вот таких мелких косяков у тебя в коде: Код Error(s):
1151805807/source.cpp: In member function ‘MySet MySet::operator~() const’:
1151805807/source.cpp:80:15: error: request for member ‘A’ in ‘C’, which is of non-class type ‘MySet()’
C.A[C.n++] = i;
^
1151805807/source.cpp:80:19: error: request for member ‘n’ in ‘C’, which is of non-class type ‘MySet()’
C.A[C.n++] = i;
^
1151805807/source.cpp:83:12: error: invalid conversion from ‘MySet (*)()’ to ‘char’ [-fpermissive]
return C;
^
1151805807/source.cpp:19:9: note: initializing argument 1 of ‘MySet::MySet(char)’
MySet(char);
^~~~~
1151805807/source.cpp: In constructor ‘MySet::MySet()’:
1151805807/source.cpp:92:28: warning: conversion to ‘char’ from ‘int’ may alter its value [-Wconversion]
MySet::MySet(): n(0), S('A'+cnt++), A(new char[N+1]){
~~~^~~~~~
1151805807/source.cpp: In constructor ‘MySet::MySet(char)’:
1151805807/source.cpp:97:32: warning: conversion to ‘char’ from ‘int’ may alter its value [-Wconversion]
MySet::MySet(char): n(0), S('A'+cnt++), A(new char[N+1]){
~~~^~~~~~
1151805807/source.cpp:100:25: warning: conversion to ‘char’ from ‘int’ may alter its value [-Wconversion]
A[n++] = '0'+i;
~~~^~
1151805807/source.cpp: In copy constructor ‘MySet::MySet(const MySet&)’:
1151805807/source.cpp:108:44: warning: conversion to ‘char’ from ‘int’ may alter its value [-Wconversion]
MySet::MySet(const MySet& B): n(B.n), S('A'+cnt++), A(new char[N+1]){
~~~^~~~~~
1151805807/source.cpp:112:18: warning: suggest parentheses around assignment used as truth value [-Wparentheses]
while(*dst++ = *src++);
~~~~~~~^~~~~~~~
1151805807/source.cpp: In member function ‘MySet& MySet::operator=(const MySet&)’:
1151805807/source.cpp:120:22: warning: suggest parentheses around assignment used as truth value [-Wparentheses]
while(*dst++ = *src++);
~~~~~~~^~~~~~~~
1151805807/source.cpp:121:17: warning: conversion to ‘char’ from ‘int’ may alter its value [-Wconversion]
S = 'A' + cnt++;
~~~~^~~~~~~
1 |
|
16495 / 8988 / 2205 Регистрация: 30.01.2014 Сообщений: 15,611 |
|
|
17.12.2020, 01:44 |
5 |
|
Решение
array.cpp:37:16: error: expected ‘;’ at end of member declaration Прочитайте внимательно текст ошибки.
1 |
|
15 / 2 / 1 Регистрация: 18.09.2015 Сообщений: 227 |
|
|
17.12.2020, 01:47 [ТС] |
6 |
|
это — объявление прототипа функции, если ты вдруг не понял. Я не спорю, что это ошибка. И сейчас, да, понимаю, что прототип функции. Исправление этой ошибки все же не решило главной проблемы.
0 |
|
16495 / 8988 / 2205 Регистрация: 30.01.2014 Сообщений: 15,611 |
|
|
17.12.2020, 01:48 |
7 |
|
Dancing_god, обычно в диагностике компилятора существует только одна ошибка, которую вы и должны устранять — она самая первая в списке. На остальное можно не обращать внимания до тех пор, пока вы не устраните первую. В данном случае у вас лишний
1 |
|
15 / 2 / 1 Регистрация: 18.09.2015 Сообщений: 227 |
|
|
17.12.2020, 01:51 [ТС] |
8 |
|
Прочитайте внимательно текст ошибки. Да, прочитал. Действительно глупая ошибка. Спасибо за помощь. Добавлено через 27 секунд
спровоцированы этой, первой. Именно так.
0 |
|
KZProg 0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 05.08.2021 Сообщений: 51 |
||||
|
07.09.2021, 18:02 |
9 |
|||
|
У меня ошибка: ‘S’ does not name a type. Вот текст программы — по вычислению площади замкнутой области методом трапеций:
. Помогите!
0 |
|
Вездепух 10435 / 5704 / 1553 Регистрация: 18.10.2014 Сообщений: 14,098 |
|
|
07.09.2021, 18:23 |
10 |
|
Вот текст программы — по вычислению площади замкнутой области методом трапеций: Это не «текст программы». Это огрызок текста программы, по котрому ничего сказать нельзя. В какой строке ошибка?
0 |
|
0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 05.08.2021 Сообщений: 51 |
|
|
07.09.2021, 18:47 |
11 |
|
Во второй.
0 |
|
Вездепух 10435 / 5704 / 1553 Регистрация: 18.10.2014 Сообщений: 14,098 |
|
|
07.09.2021, 20:21 |
12 |
|
Во второй. Вы что-то выдумываете. Приводите реальный текст программы.
0 |
|
2057 / 1615 / 532 Регистрация: 29.06.2020 Сообщений: 6,080 |
|
|
07.09.2021, 22:31 |
14 |
|
KZProg, и где f1, f2 и x1, x2.
0 |
|
Вездепух 10435 / 5704 / 1553 Регистрация: 18.10.2014 Сообщений: 14,098 |
|
|
07.09.2021, 22:34 |
15 |
|
В том-то как раз и дело, что текст приводится так, как есть в источнике. А, ну то есть вы совершенно не понимаете, что делаете. Если вы действительно читали источник, то вам должно быть понятно, что это никакая не «программа», а лишь фрагмент программы. Пытаться компилировать вот этот фрагмент как «программу» совершенно бесполезно. Ваш источник обладает относительно низким качеством изложения, но как должна выглядеть программа на языке С там более-менее объяснено. (Также, в вашем источнике идет речь о языке С. Почему вы постите это все в форум по языку С++?)
1 |
|
IT_Exp Эксперт 87844 / 49110 / 22898 Регистрация: 17.06.2006 Сообщений: 92,604 |
07.09.2021, 22:34 |
|
Помогаю со студенческими работами здесь
interface uses [Ошибка] : Record, object or class type required Unit_Kartka.pas(134): Record, object or class type required
interface uses Ошибка type qualifier ‘std’ must be a struct or class name Ошибка: record, object or class type required interface uses Ошибка: Record object or class type required interface uses Искать еще темы с ответами Или воспользуйтесь поиском по форуму: 15 |
- Forum
- Beginners
- does not name a type error
does not name a type error
Hi, Code::Blocks keeps giving me this error message whenever I try to compile:
‘LinkListIterator’ does not name a type
I’ve checked for spelling errors in my preprocessor identifiers and header files, and made sure to include the appropriate header files in the implementation files. But Im stumped and have no idea how to fix this. Any assistance will be appreciated. Thanks.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Your headers are mutually inclusive. Only one of them can point to the other. To fix the inevitable compiler error: http://www.google.com/search?q=forward+declaration
For example:
|
|
Last edited on
Thank you helios and Alvaro (cpp-home.com). Forward declaration solved the problem. I was trying to use NodeType and LinkListIterator before providing their definitions.
|
|
|
|
Last edited on
Topic archived. No new replies allowed.
The Arduino software is an open-source and easy to use platform which configures the Arduino board into functioning in a certain way. An Arduino code is written in C++ but with additional functions and methods. An Arduino is a hardware and software platform widely used in electronics.
In this article, we will see a few quick fixes for the error ‘does not name a type‘ or the ‘no such file or directory‘ error.
Also read: How to stop an Arduino program?
What does the error mean?
In almost every coding language known to man, every variable has a specific data type. In general, there are multiple data types like int indicating integer, float for decimal values, char and String for alphabets and sentences, boolean for true or false and many more. In Arduino, there are 16 data types commonly used.
- void: Used in function declarations, and indicates that the function will not return anything.
- boolean: It is a true or false value.
- char: Stores a character value in one byte of the memory.
- Unsigned char: Unsigned data type which encodes numbers between 0 and 255 and occupies one byte of the memory.
- byte: It is an 8-bit unsigned number holding a value between 0 and 255.
- int: It is a primary data type which stores a 16-bit integer value. It can store negative values.
- Unsigned int: Unsigned integer that stores only positive integer values in the 2 byte memory.
- long: It is a 32-bit memory for storing numbers, both positive and negative.
- Unsigned long: Unsigned long variables store only positive numbers in the 32-bit memory storage.
- short: It is a 16-bit data type storing positive and negative numbers.
- float: It is a decimal value having a 32-bit memory.
- double: It is a double floating number having either 32 or 64 bit memory depending on the board.
- word: Based on the type of board, it stores either 16-bit or 32-bit unsigned number.
- array: It is a collection of variables which is accessible using index numbers.
- String-char array: Converts the string into an array of characters.
- String-object: Class which can be used to manipulate, concatenate and perform other operations on strings and arrays.
The error ‘does not name a type‘ or the ‘no such file or directory‘ are errors that occur during the compilation process. They generally indicate missing data types or wrongly used data types. It may also indicate missing directories or libraries.
Also read: Arduino UNO vs Arduino Mega.
Here are two ways to fix the error.
Check data type
Every user-defined function and variable initialised or declared in the code should have a corresponding data type. The data type of the variable or function should also coincide with the value being stored or returned.
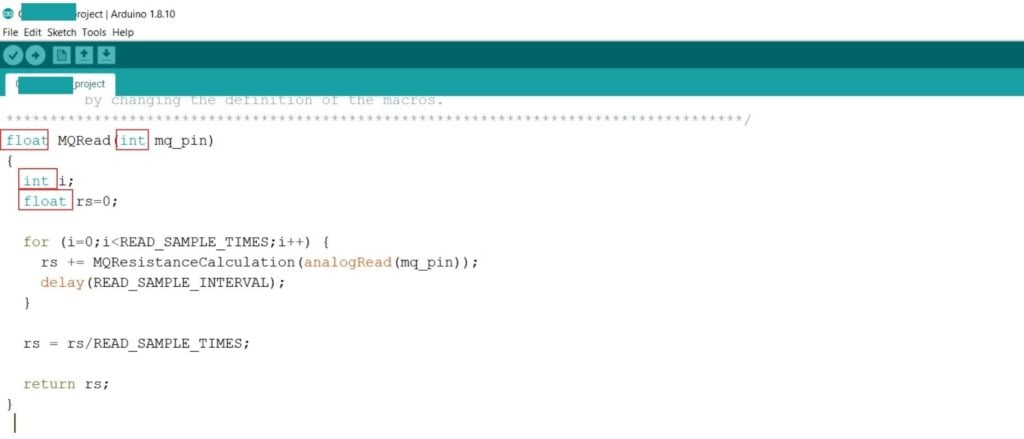
Consider a small example sample code below.
Here the function MQRead is of the type float. The variables i and mq_pin are integer type, while rs is float type. In the for loop, i is given the value 0, an integer value. The analogRead function always reads an integer value, which is being assigned to the mq_pin variable. Since the value or type for rs, the float type suffices for any value assigned to it as a result of the calculation. The user-defined function MQRead is of type float, which means that the return type for it is float, which is achieved by returning the value of rs for the function.
The error occurs if any of these data types don’t stand to the data being stored in the variables. Always check and recheck the data type for every variable, function and return type.
Library folder
In many cases, you may use libraries that are not standard or included in Arduino. But Arduino is flexible with the import of new libraries, making it easy to use all functions from any library. Follow the path below to check the currently available libraries in your Arduino software.
My Documents -> Arduino -> Libraries
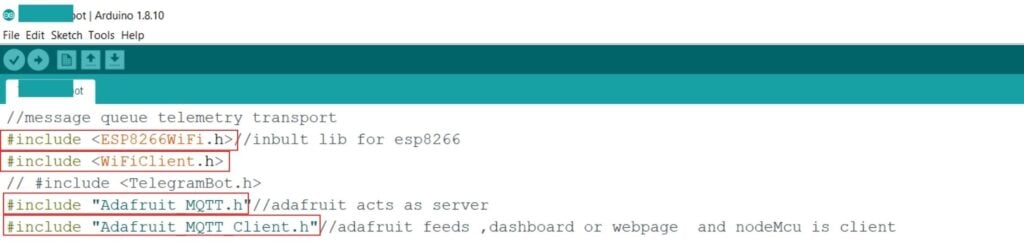
Consider the snippet of code below. There are four library folders that are included for the code to work. But these aren’t a part of the standard library of Arduino.
There are two ways to import a library to the Arduino.
Method 1
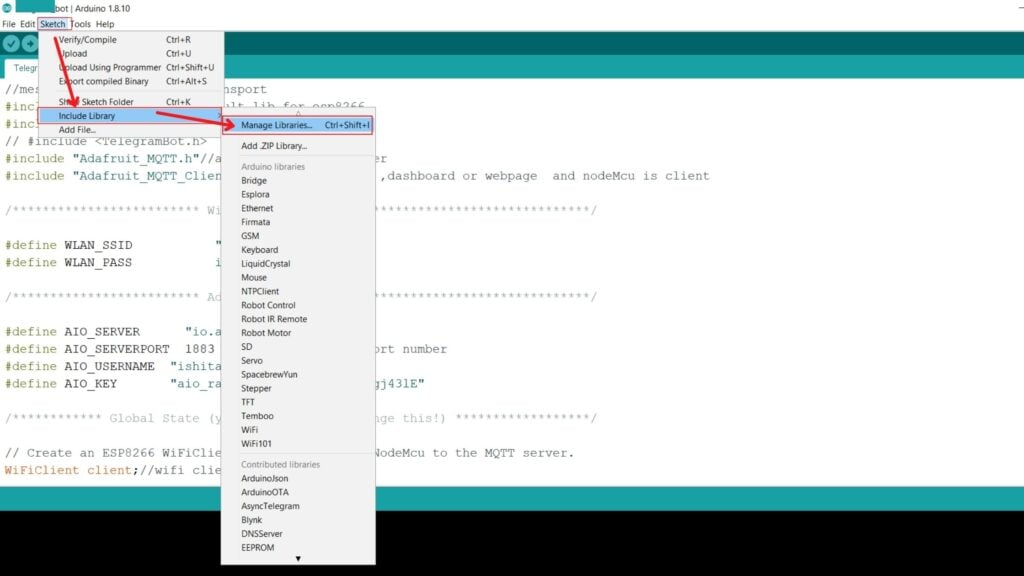
Step 1: Click on Sketch on the top left panel of the window. Go to the include Library option and select Manage Libraries.
Keyboard Shortcut: Ctrl+Shift+I.
Step 2: Search or select from the options available and click on Install.
Note that a few Libraries may not be available if your software isn’t updated with the latest version.
All the libraries you are planning to use may not be easily found under the Manage Libraries section. In such cases, we use Method 2 for importing the libraries.
Method 2
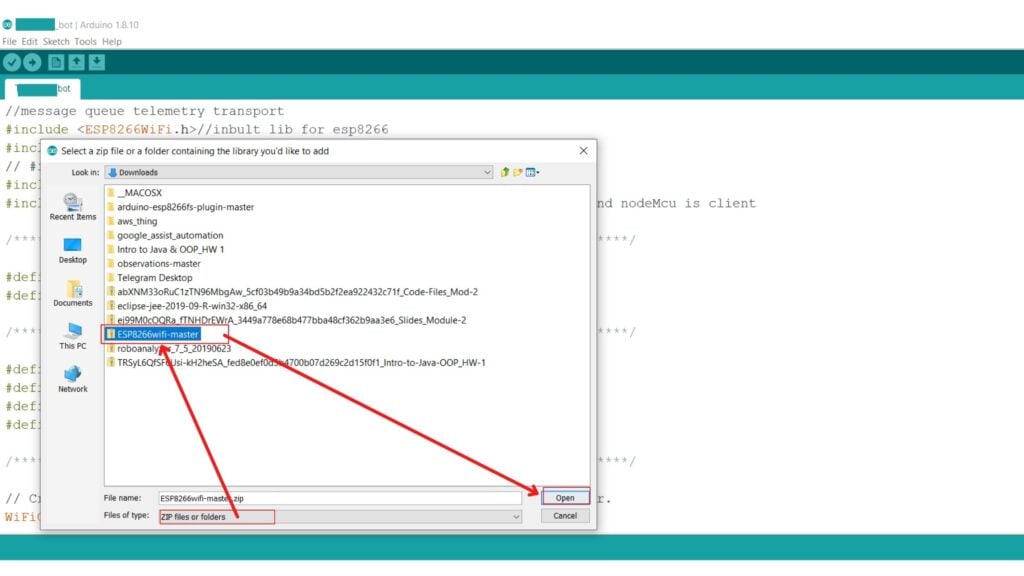
Step 1: Download a zip file for the library from GitHub or any other reliable source present online.
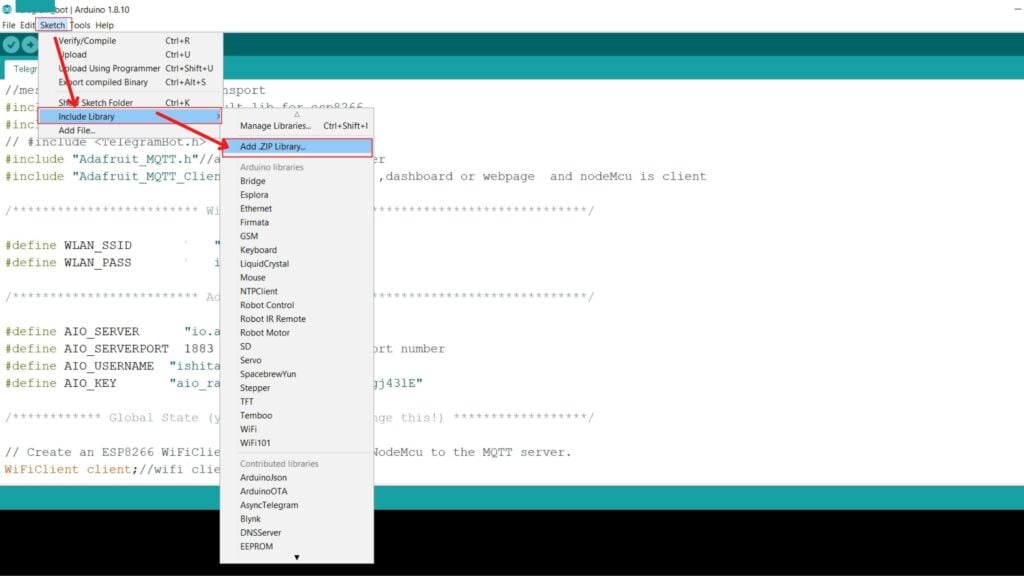
Step 2: Click on Sketch on the top left panel of the window. Go to the include Library option and select Add ZIP Library.
Step 3: Set the file type to be ZIP files and folders.
Step 4: Go to the download location of the zip file and select it. Click on Open.
The library is successfully added to the Arduino software now.
Also read: NodeMCU vs Arduino vs Raspberry Pi.
При попытке написать этот код я получаю сообщение об ошибке "cin doesnt name a type",
Я не знаю, в чем конкретно проблема, и я попытался написать «используя пространство имен std;», но он выдал ту же ошибку.
Вот код
#include<iostream>
namespace myStuff {
int value = 0;
}
using namespace myStuff;
int main {
std::cout << "enter integer " << ;
std::cin >> value;
std::cout << "nyouhaveenterd a value" << value ;
return 0;
}
Вот ошибка компиляции:
: extended initializer lists only available with `-std=c++0x` or `-std=gnu++0x` [enabled by default]|
: expected primary-expression before ‘;’ token|
expected `}` before `;` token|
`cin` does not name a type|
: `cout` does not name a type|
: expected unqualified-id before `return`|
: expected declaration before `}` token|
||=== Build finished: 6 errors, 1 warnings ===|
1
Решение
int main{
должно быть
int main(){
а также
std::cout << "enter integer " << ;
должно быть
std::cout << "enter integer ";
7
Другие решения
На этой линии:
std::cout << "enter integer " << ;
Там нет соответствующего операнда, чтобы сделать утверждение синтаксически допустимым. Это, вероятно, источник ваших ошибок.
1
Это предыдущая строка.
cout<<"enter integer" **<<** ;
что в прошлом << ожидает аргумент, который никогда не приводится
0
|
test local function definitions are illegal C++ |
|
|
Error C2660 : function does not take 3 arguments |
|
|
Error LNK2019 unresolved external symbol |
|
|
E0042 operand types are incompatible ( char and const char * ) |
|
|
E0025 quoted string should contain at least one character |
|
|
error: ‘cout’ in namespace ‘std’ does not name a type |
|
|
undefined reference to `std::cout’ |
Если начинается на C, то это ошибка компиллятора.
Если на L, то линкера.
test local function definitions are illegal C++
Появляется если Вы случайно определили функцию не перед main а внутри main.
Error C2660 : function does not take 3 arguments
Компилятор ждёт, что у функции будет другое количество аргументов.
Появляется, например, если Вы не подключили нужную функцию, но существует
функция перегрузка с другим количеством аргументов. Копилятор не находит
нужную функцию, находит ту у которой такое же название, пытается использовать,
но количество аргументов неправильно.
Error LNK2019 unresolved external symbol
Линкер видит, что вызывается функция, которая нигде не задана.
E0042 operand types are incompatible ( char and const char * )
Появляется обычно при сравнении char с символом в двойных кавычках.
Нужно заменить двойные кавычки одинарными
char s = line[0];
if (s == 'T') {
std::cout << "TopBicycle.ru" << std::endl;
}
E0025 quoted string should contain at least one character
Обычно появляется когда вы пытаетесь создать пустую строку но делаете это с одинарными кавычками.
Нужно заменить одинарные кавычки двойными.
empty_line = "";
‘cout’ in namespace ‘std’ does not name a type
error: ‘cout’ in namespace ‘std’ does not name a type
Скорее всего вы пытаетесь сделать вывод без функции
std::cout << «Hello»;
С++ на это ругается, поэтому нужно завернуть вывод в функцию
void log() {
std::cout << «Hello»;
}
undefined reference to `std::cout’
undefined reference to `std::cout’
Означает, что скорее всего вам нужен g++ а не gcc



 Сообщение было отмечено Dancing_god как решение
Сообщение было отмечено Dancing_god как решение