I ran into something odd early this week, I figured out part of it, but the other part is making no sense to me.
When I added this switch into Cisco prime logging I noticed one port had the following message.
Prime:
duplex mismatch discovered on GigabitEthernet1/0/39 (not full duplex), with SIP708105B36C4A eth0 (full duplex)
Switch log:
*Oct 27 12:32:46.541: %CDP-4-DUPLEX_MISMATCH: duplex mismatch discovered on GigabitEthernet1/0/39 (not full duplex), with SIP708105B36C4A eth0 (full duplex).
Here is the interesting part I don’t understand: After changing this phone from full/100 to auto the errors on the switch side stopped. The errors kept showing in prime though. We tried this with another similar phone and it was the same settings, and errors in that switch too. We changed it and the switch log cleared, but I don’t have the syslog on that switch dumping to prime yet.
What I don’t understand is how prime is getting reports of events from what appears to be syslog when the switch itself shows no further events.
Any ideas?
Thanks -C
We have warnings on some of our Cisco small business network switches; network performance/quality seems to be fine.
[21 Cisco PoE and non-PoE switches SG-200, SG-250HP and SG-500 currently on the network].
VoIP system configured throughout our network that has been up and running for the past 6 months without any problems.
The warning messages are recent, and came up on our SG-500 core switches [Flash memory logs]
Warning is declared as «%CDP-W-VOICE_VLAN_MISMATCH: Voice VLAN mismatch detected on interface X» — where X is the up-link port number connecting to core/edge switch.
Ports affected are all (only) up-links, core to core or core to edge.
* All switches have the latest firmware installed
* All configured with the same VLAN IDs (Default VLAN is 1 & Voice VLAN 30, configured trunk ports, separated tagged from untagged)
* Dynamic voice VLAN disabled on all switches
* Auto voice VLAN disabled on all switches
* CDP enabled on all switches
* Global settings for QoS trust mode is CoS/802.1p
Well without seeing the entire config I can’t be sure but I think it your problem lies with how you have wired/configured it…. Make sure and configure the stack before configuring the switchports. This is good practice and I outlined the steps below. My diag of you error message is stated below as well.
6d21h: %CDP-4-NATIVE_VLAN_MISMATCH: Native VLAN mismatch discovered on GigabitEthernet2/0/1 (1), with Switch GigabitEthernet1/0/1 (2).
4d23h: %CDP-4-NATIVE_VLAN_MISMATCH: Native VLAN mismatch discovered on GigabitEthernet2/0/1 (1), with Switch GigabitEthernet1/0/1 (2). (Switch-2)
On the back of the 3750 switches there are stacking ports and should have some cables that came with them. That is where you should be stacking the switch. So either you have the switch stacked with the right stacking cables and have switchport 1/0/1 and 2/0/1 plugged into each other or you did not use the stacking cables and are trying to stack the switches together using 1/0/1 and 2/0/1. If you did use the stacking cables then you need to unplug g 1/0/1 — g 2/0/1 between the switches and just use the stacking built into the switch. The stack as I hope you know is seen a 1 logical switch. So the ethernet connection would cause a spanning-tree loop / broadcast storm if spanning-tree is not configured correctly. I hope this makes sense. In short…
The error is because on switch 1 you have either not configured anything and the switch is defaulting to its native vlan 1. Also the other possibly is the command «switchport trunk native vlan 1» was issued on switch 1 instead of «switchport access vlan 2». Also, I have no idea why those switches are connected via ethernet g 1/0/1 and 2/0/1 if the switches are stacked. If this is how you were trying to stack them STOP and rip that off and look for the stacking cables that came with the switches. Not trying to talk down on you, so sorry if I come off a little harsh. Then again this is just a guess but I feel that this above is most likely the issue. If you have questions let me know.
First make sure you set the switch numbers in the stack
#show switch
#switch 2 renumber 1
The «switch 2 renumber 1» part is optional if it is not already the way you need it in the rack. Next set the priority of the switches in the stack, so the same router will boot as the master during the stackmaster election.
#switch 1 priority 15
#switch 2 priority 14
#wr
#reload
This will get the switches in the stack configured correctly (Well at lease the stack part of the config) If you have a question please let me know. Good Luck 
-Stealthkit
Edited November 30, 2012 by stealthkit
Overview:
Interface and cable issues can be due to collisions, errors, duplex mismatch or speed mismatch
Study Notes:
Collisions
- In full-duplex Ethernet, collision detection is disabled
- A collision is the mechanism used by Ethernet to control access and allocate shared bandwidth among stations that want to transmit at the same time on a shared medium.
- Because the medium is shared, a mechanism must exist where two stations can detect that they want to transmit at the same time. This mechanism is collision detection.
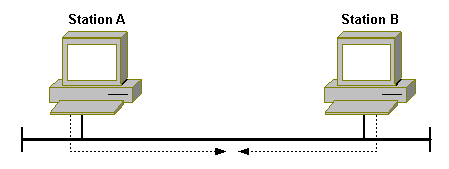
- Ethernet uses CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detect) as its collision detection method. Here is a simplified example of Ethernet operation:
- Station A wishes to send a frame. First, it checks if the medium is available (Carrier Sense). If it isn’t, it waits until the current sender on the medium has finished.
- Suppose Station A believes the medium is available and attempts to send a frame. Because the medium is shared (Multiple Access), other senders might also attempt to send at the same time. At this point, Station B tries to send a frame at the same time as Station A.
- Shortly after, Station A and Station B realize that there is another device attempting to send a frame (Collision Detect). Each station waits for a random amount of time before sending again. The time after the collision is divided into time slots; Station A and Station B each pick a random slot for attempting a retransmission.
- Should Station A and Station B attempt to retransmit in the same slot, they extend the number of slots. Each station then picks a new slot, thereby decreasing the probability of retransmitting in the same slot.
- Collisions are a way to distribute the traffic load over time by arbitrating access to the shared medium. Collisions are not bad; they are essential to correct Ethernet operation.
- The deferred counter counts the number of times the interface has tried to send a frame, but found the carrier busy at the first attempt (Carrier Sense). This does not constitute a problem, and is part of normal Ethernet operation.
- An increasing collision rate (number of packets output divided by the number of collisions) does not indicate a problem: it is merely an indication of a higher offered load to the network. An example of this could be because another station was added to the network.
- There is no set limit for «how many collisions are bad» or a maximum collision rate.
- The collisions counter does not provide a very useful statistic to analyze network performance or problems.
- The station that reports a late collision merely indicates the problem; it is generally not the cause of the problem. Possible causes are usually incorrect cabling or a non-compliant number of hubs in the network. Bad network interface cards (NICs) can also cause late collisions.
- Excessive collisions indicate a problem. Common causes are devices connected as full-duplex on a shared Ethernet, broken NICs, or simply too many stations on the shared medium. The excessive collisions can be resolved by hardcoding speed and duplex.
Use this command to view collisions:
show interfaces
- CRC — a high number of CRCs is usually the result of collisions or a station transmitting bad data.
- frame — shows the number of packets received incorrectly having a CRC error and a noninteger number of octets. On a LAN, this is usually the result of collisions or a malfunctioning Ethernet device.
- collisions — gives the number of messages retransmitted due to an Ethernet collision. This is usually the result of an overextended LAN (Ethernet or transceiver cable too long, more than two repeaters between stations, or too many cascaded multiport transceivers). A packet that collides is counted only once in output packets.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/interfaces-modules/port-adapters/12768-eth-collisions.html
Errors
Use this command to view errors:
show interfaces
- Ethernet is up, down or administratively down
- packets input gives the total number of error-free packets received by the system
- bytes input gives the total number of bytes, including data and MAC encapsulation, in the error-free packets received by the system
- input error includes runts, giants, no buffer, CRC, frame, overrun, and ignored counts. Other input-related errors can also cause the input error count to be increased, and some datagrams may have more than one error; therefore, this sum may not balance with the sum of enumerated input error counts.
- frame shows the number of packets received incorrectly having a CRC error and a noninteger number of octets. On a LAN, this is usually the result of collisions or a malfunctioning Ethernet device
- input packets with dribble condition detected gives the dribble bit error, which indicates that a frame is slightly too long. This frame error counter is incremented just for informational purposes; the router accepts the frame
- output errors gives the sum of all errors that prevented the final transmission of datagrams out of the interface being examined. Note that this may not balance with the sum of the enumerated output errors because some datagrams may have more than one error, and others may have errors that do not fall into any of the specifically tabulated categories
- restarts gives the number of times a Type 2 Ethernet controller was restarted because of errors.
https://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/internetworking/troubleshooting/guide/tr1904.html
Duplex and Speed
- duplex and speed should match on both ends or else you will have problems
- traffic can still pass with mismatched duplex and speed, but you will experience retransmissions and reduced throughput
- to verify duplex and speed run the command
show interface x/x
- If you want to hard code the speed and duplex on a switch that runs Cisco IOS Software (turn off auto-negotiation), issue the speed and duplex commands underneath the specific interface.
- Duplex is subservient to speed in the sense that if speed is set to auto, then the duplex cannot be manually set.
- You might see cyclic redundancy check (CRC) error messages when both the speed and duplex settings are hardcoded on the two devices. This might be because any one of the devices runs an earlier version of Cisco IOS.
- You can upgrade the Cisco IOS or set the speed and duplex to auto on both devices in order to resolve this.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/ethernet/10561-3.html
FYI, this is done in a non-production environment. I just booted a 2-member stack and got the following message on a ‘show switch’ command:
Switch#sh sw
Switch/Stack Mac Address : 00e1.6d09.ae00 — Local Mac Address
Mac persistency wait time: Indefinite
H/W Current
Switch# Role Mac Address Priority Version State
————————————————————
*1 Active 00e1.6d09.ae00 1 M0 Ready
2 Member 00e1.6d51.6780 1 0 V-Mismatch
In my case, in order to save some time, I copied the .bin file from flash: to flash-2: using the following command:
copy flash:cat3k_caa-universalk9.SPA.03.03.02.SE.150-1.EZ2.bin flash-2:
Then, you use the following command to install the correct version to the switch that has the version mismatch:
Switch#software auto-upgrade
% Auto upgrade has been initiated for the following incompatible switches: 2
INFO level system messages will be generated to provide status information during
the auto upgrade process
Switch#sh log
*Dec 1 10:29:47.546: %INSTALLER-6-AUTO_UPGRADE_SW_INITIATED: 1 installer: Auto upgrade initiated for switch 2
*Dec 1 10:29:47.547: %INSTALLER-6-AUTO_UPGRADE_SW: 1 installer: Searching stack for software to upgrade switch 2
*Dec 1 10:29:47.548: %INSTALLER-6-AUTO_UPGRADE_SW: 1 installer: Found donor switch 1 to auto upgrade switch 2
*Dec 1 10:29:47.548: %INSTALLER-6-AUTO_UPGRADE_SW: 1 installer: Upgrading switch 2 with software from switch 1
*Dec 1 10:31:03.973: %INSTALLER-6-AUTO_UPGRADE_SW: 1 installer: Finished installing software on switch 2
*Dec 1 10:31:03.973: %INSTALLER-6-AUTO_UPGRADE_SW: 1 installer: Reloading switch 2 to complete the auto upgrade
*Dec 1 10:31:04.005: %STACKMGR-1-RELOAD_REQUEST: 1 stack-mgr: Received reload request for switch 2, reason Auto upgrade
*Dec 1 10:31:04.468: %STACKMGR-1-STACK_LINK_CHANGE: 1 stack-mgr: Stack port 2 on switch 1 is down
*Dec 1 10:31:04.470: %STACKMGR-6-SWITCH_REMOVED: 1 stack-mgr: Switch 2 has been removed from the stack.
*Dec 1 10:31:04.474: Starting SWITCH-DELETE sequence, switch 2
*Dec 1 10:31:04.482: SWITCH-DELETE sequence complete, switch 2
*Dec 1 10:36:42.741: %STACKMGR-1-STACK_LINK_CHANGE: 1 stack-mgr: Stack port 2 on switch 1 is up
*Dec 1 10:36:57.017: %STACKMGR-6-SWITCH_ADDED: 1 stack-mgr: Switch 2 has been added to the stack.
*Dec 1 10:37:15.914: %STACKMGR-6-SWITCH_READY: 1 stack-mgr: Switch 2 is ready.
*Dec 1 10:37:15.918: Starting SWITCH-ADD sequence, switch 2
*Dec 1 10:37:16.044: %NGWC_USB_CONSOLE-6-CONFIG_ENABLE: Switch 2: Console media-type changed to default
*Dec 1 10:37:16.942: %NGWC_PLATFORM_FEP-6-FRU_PS_OIR: Switch 2: FRU power supply A inserted
*Dec 1 10:37:16.946: %NGWC_PLATFORM_FEP-6-FRU_PS_OIR: Switch 2: FRU power supply B inserted
*Dec 1 10:37:35.029: SWITCH-ADD sequence complete, switch 2
Switch#sh sw
Switch/Stack Mac Address : 00e1.6d09.ae00 — Local Mac Address
Mac persistency wait time: Indefinite
H/W Current
Switch# Role Mac Address Priority Version State
————————————————————
*1 Active 00e1.6d09.ae00 1 M0 Ready
2 Standby 00e1.6d51.6780 1 M0 HA sync in progress
Switch#sh sw
Switch/Stack Mac Address : 00e1.6d09.ae00 — Local Mac Address
Mac persistency wait time: Indefinite
H/W Current
Switch# Role Mac Address Priority Version State
————————————————————
*1 Active 00e1.6d09.ae00 1 M0 Ready
2 Standby 00e1.6d51.6780 1 M0 Ready
As you can see, switch 2 reloaded after the current version of software (in this case, 03.03.02) was installed and it only took about 6 minutes. The other option is to remove the switch from the stack, put a USB in it with the correct IOS version, copy the IOS version onto the switch and then do the ‘software install file flash:’ command and wait for it to reload. We’ve had 3850’s deployed for about 6 months now and are really liking them.