- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
Our customer has a small business server 2008. Now we have the problem that the document management system ELO-Office (mostly in the afternoon) brings the error-message Error 64 when accessing the syslog-File. The support from ELO says that this message
is equal to the Windows Error-Message ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED
64 (0x40) (The specified network name is
no longer available). Now we have checked many parameters (cable, Switch, Drivers, DNS) but nothing solves the problem. Say can you help how to anyalyze the message to get the reason for the the problem.thanking
you
in
anticipationArmin Braeu
Answers
-
Hi Armin, do you encounter any other error (especially network related) while using SBS 2008? Does the issue only occur on that specific application? Here is some information regarding the error:
«Explanation
The network resource that you specified was either temporarily taken offline or is no longer available. It is possible that: 1. The share at the server might have been temporarily deleted. 2. The server that shared the resource might have been turned off.
3. The permissions might have been changed.»http://www.microsoft.com/technet/support/ee/transform.aspx?ProdName=Windows+Operating+System&ProdVer=5.0&EvtID=64&EvtSrc=Kernel
Sean Zhu
TechNet Subscriber Support in forum
If you have any feedback on our support, please contact
tngfb@microsoft.com
Please remember to click “Mark as Answer” on the post that helps you, and to click “Unmark as Answer” if a marked post does not actually answer your question. This can be beneficial to other community members reading the thread.
-
Marked as answer by
Monday, June 6, 2011 3:09 AM
-
Marked as answer by
| Error Number: | Error 64 | |
| Error Name: | ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED | |
| Error Description: | The specified network name is no longer available. | |
| Hexadecimal: | 0x40 | |
| Developer: | Microsoft Corporation | |
| Software: | Windows Operating System | |
| Applies to: | Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10, 11 |
File corruption, missing, or deleted Windows 10 files can result in ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED executable errors, most commonly seen during the startup phase of 0x40. If your ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED file is suffering from one of those troubles, replacing it with a fresh file should resolve the issue. In some cases, the Windows registry is attempting to load a Windows 10 file that no longer exists, therefore we recommend running a registry scan to repair any invalid file path references.
Typical Windows 10 Errors
The most common Windows 10 errors that can appear on a Windows-based computer are:
- «Windows 10 Program Error.»
- «Win32 Software Error: Windows 10«
- «Windows 10 encountered a problem and will close.»
- «Sorry, we can’t find Windows 10.»
- «Windows 10 not found.»
- «Problem starting application: Windows 10.»
- «Windows 10 not executing.»
- «Windows 10 halted.»
- «Software Path Fault: Windows 10.»
0x40 Windows 10 issues occur with installation, while Windows 10-related software runs, during shutdown or startup, or less-likely during operating system updates. It’s important to note when Windows 10 issues happen, as it helps troubleshoot 0x40 problems (and report to Microsoft Corporation).
Source of Windows 10 Errors
These Windows 10 troubles are created by missing or corrupt Windows 10 files, invalid 0x40 registry entries, or malicious software.
More precisely, Windows 10 errors created from:
- Invalid (corrupt) Windows 10 registry entry.
- Virus or malware infection that has corrupted the Windows 10 file or related 0x40 program files.
- Windows 10 maliciously deleted (or mistakenly) by different rogue or valid program.
- Another program is in conflict with 0x40 and its shared referenced files.
- 0x40 (Windows 10) corrupted during download or install.
Product by Solvusoft
Download Now
WinThruster 2022 — Scan your PC for computer errors.
Compatible with Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, Vista, XP and 2000
Optional Offer for WinThruster by Solvusoft | EULA | Privacy Policy | Terms | Uninstall
Windows System Error Codes Knowledgebase
Article ID:
120921
Article Author:
Last Updated:
Popularity:
star rating here
Download Now (Error Fix)
Windows 7 Professional Windows 7 Enterprise Windows 7 Home Basic Windows 7 Home Premium Windows 7 Starter Windows 7 Ultimate Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium-Based Systems Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard More…Less
Symptoms
Assume that you start offline files synchronization on a computer that is running Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2. In this situation, the synchronization may not finish. Additionally, the following error message is logged in Sync Center:
The specified network name is no longer available.
Cause
This issue occurs because client-side caching (CSC) aborts the sync handle to make sure that other processes can access a file that is synchronizing. After the sync handle is aborted, CSC returns a STATUS_CONNECTION_DISCONNECTED status code, and then that results in an ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED error code. This causes the synchronization of all remaining offline files to be canceled.
Resolution
Hotfix information
A supported hotfix is available from Microsoft. However, this hotfix is intended to correct only the problem that is described in this article. Apply this hotfix only to systems that are experiencing the problem described in this article. This hotfix might receive additional testing. Therefore, if you are not severely affected by this problem, we recommend that you wait for the next software update that contains this hotfix.
If the hotfix is available for download, there is a «Hotfix download available» section at the top of this Knowledge Base article. If this section does not appear, contact Microsoft Customer Service and Support to obtain the hotfix.
Note If additional issues occur or if any troubleshooting is required, you might have to create a separate service request. The usual support costs will apply to additional support questions and issues that do not qualify for this specific hotfix. For a complete list of Microsoft Customer Service and Support telephone numbers or to create a separate service request, visit the following Microsoft Web site:
http://support.microsoft.com/contactus/?ws=supportNote The «Hotfix download available» form displays the languages for which the hotfix is available. If you do not see your language, it is because a hotfix is not available for that language.
Prerequisites
To apply this hotfix, you must be running one of the following operating systems:
-
Windows 7 Service Pack 1 (SP1)
-
Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 (SP1)
For more information about how to obtain a Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2 service pack, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
976932 Information about Service Pack 1 for Windows 7 and for Windows Server 2008 R2
Registry information
To use the hotfix in this package, you do not have to make any changes to the registry.
Restart requirement
You must restart the computer after you apply this hotfix.
Hotfix replacement information
This hotfix does not replace a previously released hotfix.
File information
The global version of this hotfix installs files that have the attributes that are listed in the following tables. The dates and the times for these files are listed in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The dates and the times for these files on your local computer are displayed in your local time together with your current daylight saving time (DST) bias. Additionally, the dates and the times may change when you perform certain operations on the files.
Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 file information notes
Important Windows 7 hotfixes and Windows Server 2008 R2 hotfixes are included in the same packages. However, hotfixes on the Hotfix Request page are listed under both operating systems. To request the hotfix package that applies to one or both operating systems, select the hotfix that is listed under «Windows 7/Windows Server 2008 R2» on the page. Always refer to the «Applies To» section in articles to determine the actual operating system that each hotfix applies to.
-
The files that apply to a specific product, SR_Level (RTM, SPn), and service branch (LDR, GDR) can be identified by examining the file version numbers as shown in the following table.
Version
Product
SR_Level
Service branch
6.1.760
1.
17xxxWindows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2
SP1
GDR
6.1.760
1.
21xxxWindows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2
SP1
LDR
-
The MANIFEST files (.manifest) and the MUM files (.mum) that are installed for each environment are listed separately in the «Additional file information for Windows Server 2008 R2 and for Windows 7» section. MUM and MANIFEST files, and the associated security catalog (.cat) files, are extremely important to maintain the state of the updated components. The security catalog files, for which the attributes are not listed, are signed with a Microsoft digital signature.
For all supported x86-based versions of Windows 7
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Csc.sys |
6.1.7601.21772 |
388,096 |
16-Jul-2011 |
02:44 |
x86 |
|
Cscmig.dll |
6.1.7601.17514 |
109,568 |
20-Nov-2010 |
12:18 |
x86 |
|
Microsoft-windows-offlinefiles-core-ppdlic.xrm-ms |
Not applicable |
3,144 |
16-Jul-2011 |
05:08 |
Not applicable |
For all supported x64-based versions of Windows 7 and of Windows Server 2008 R2
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Csc.sys |
6.1.7601.21772 |
514,560 |
16-Jul-2011 |
02:37 |
x64 |
|
Cscmig.dll |
6.1.7601.17514 |
137,216 |
20-Nov-2010 |
13:25 |
x64 |
|
Microsoft-windows-offlinefiles-core-ppdlic.xrm-ms |
Not applicable |
3,144 |
16-Jul-2011 |
05:44 |
Not applicable |
Status
Microsoft has confirmed that this is a problem in the Microsoft products that are listed in the «Applies to» section.
More Information
For more information about software update terminology, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
Additional file information
Additional file information for Windows 7 and for Windows Server 2008 R2
Additional files for all supported x86-based versions of Windows 7
|
File name |
X86_b3dac53017a20d2e92223972afeda6af_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.21772_none_2851700668a041e6.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
705 |
|
Date (UTC) |
18-Jul-2011 |
|
Time (UTC) |
18:18 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
X86_microsoft-windows-offlinefiles-core_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.21772_none_a0967167d379750a.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
11,640 |
|
Date (UTC) |
18-Jul-2011 |
|
Time (UTC) |
18:21 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
Additional files for all supported x64-based versions of Windows 7 and of Windows Server 2008 R2
|
File name |
Amd64_82f2cf875d3ad7cec7f117bdaeb0ddb5_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.21772_none_f6430121d0b3b26b.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
709 |
|
Date (UTC) |
18-Jul-2011 |
|
Time (UTC) |
18:18 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_microsoft-windows-offlinefiles-core_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.21772_none_fcb50ceb8bd6e640.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
11,644 |
|
Date (UTC) |
18-Jul-2011 |
|
Time (UTC) |
18:18 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
Need more help?
User-1809261048 posted
Greetings,
I’m not 100% sure this is performance related but the other subforums felt even less adequate. We have a site that is accessed both at an intranet and a remote level via a static IP. At certain intervals of days (sometimes it’s less than 5, sometimes it’s
up to three weeks) the site just crashes and until the app pool is restarted, IIS just can’t serve the page.
Trying to isolate issues, we separated the app pools, so we left one for the intranet access and another for the remote one, the intranet never crashed again (we are talking about 6+ months without a crash) whereas the remote one still faces the same issue
mentioned above.
IIS list this at the end of the line where things start going awry: 500 0 64 7 , the error 64 means ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED but for the life of me I couldn’t find what it really means and how to deal with it. Initially I thought this happened because of rapid
fail protection but the executable set to run when it triggers never does, so now I’m unsure about that. That executable restarts that one app pool, if I run it manually then everything goes back to normal.
So… in a nutshell, anyone has any idea of how to deal with this situation? Is it related to rapid fail protection or not? If it is, why isn’t the executable running? If it isn’t, is there any way to get a better description of the situation
/ error? Moreover, why would this happen only with the app pool that serves the site remotely when they are the same version of the site with the exact same files loaded for use?
Any kind of help will be greatly appreciated.
I’m writing a tcp server in Windows NT using completion ports to exploit asynchronous I/O.
I have a TcpSocket class, a TcpServer class and some (virtual functions) callbacks to call when an I/O operation is completed, e.g. onRead() for when a read is completed. I have also onOpen() for when the connection is established and onEof() for when the connection is closed, and so on.
I always have a pending read for the socket, so if the socket effectively gets data (the read will be completed with size > 0) it calls onRead(), instead if the client closes the socket from the client side (the read will be completed with size == 0) it calls onEof(), and the server is aware of when the client closes the socket with closesocket(server_socket); from its side.
All works gracefully, but I have noticed a thing:
when i call closesocket(client_socket); on the server’s side endpoint of the connection, instead of the client side, (either with setting linger {true, 0} or not), the pending read will be completed as erroneous,
that is, the read size will not only be == 0, but also GetLastError() returns an error: 64, or ‘ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED’. I have searched much about this on the web, but didn’t find nothing interesting.
Then I asked myself: but is this a real error? I mean, can this really be considered an error?
The problem is that on the server side, the onError() callback will be called when I closesocket(client_socket); instead of the onEof(). So I thought this:
What about if I, when this ‘ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED’ «error» is received, call onEof() instead of onError() ?
Would that introduce some bugs or undefined behavior?
Another important point that made me ask this question is this:
When I have received this read completion with ‘ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED’, I have checked the OVERLAPPED
structure, in particular the overlapped->Internal parameter which contain the NTSTATUS error code
of the underlying driver. If we see a list of NTSTATUS error codes [ http://www.tenox.tc/links/ntstatus.html ]
we can clearly see that the ‘ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED’ is generated by the NTSTATUS 0xC000013B, which is an error, but it is called ‘STATUS_LOCAL_DISCONNECT’. Well, it doesn’t look like a name for an error. It seems more like `ERROR_IO_PENDING’ which is an error, but also a status for a correct behavior.
So what about checking the OVERLAPPED structure’s Internal parameter, and when this is == to ‘STATUS_LOCAL_DISCONNECT’ a call to the onEof() callback is performed? Would mess things up?
In addition, I have to say that from the server side, if I call DisconnectEx() before calling
closesocket(client_socket); I will not receive that error. But what about I don’t want to call DisconnectEx() ? E.g. when the server is shutting down and doesn’t want to wait all DisconnectEx() completions, but just want to close all client’s connected.
Categories: Troubleshooting, Error Codes, XenServer, Hyper-V, Physical Systems, Alike v3, Alike v4
Introduction
The following list of common error codes are separated into three categories: Windows systems, Alike Backup Delegate (ABD), and miscellaneous Alike errors. Get a description of each and when possible, a resolution.
Service/Windows Error Codes
Error 1219
(ERROR_SESSION_CREDENTIAL_CONFLICT)
This is a very common, and confusing, error but fortunately easy to fix. Windows throws an error 1219 when you try to login to a resource, such as a network share, with two different user accounts within the same session. The most common cause is when a Windows Explorer window is opened to a network share (e.g. the ADS folder), causing a conflict with Alike’s session.
Example
“Multiple connections to a server or shared resource by the same user, using more than one user name, are not allowed. Disconnect all previous connections to the server or shared resource and try again.”
Resolution
If this is the case, simply close the offending explorer window and try again. You can also check the output of the command, net use, and close any conflicting sessions.
Close the sessions with the following syntax: net use /DELETE \path.tosession
Error 86
(ERROR_INVALID_PASSWORD)
“The specified network password is not correct.”
Example
Failed to connect to DS share (\IP.TO.ADSQSDSdata) with error code: 86 (User Account)
Resolution
This is usually caused by incorrect credentials, or a missing profile entry in the Alike Credential Profile manager for Q-Hybrid jobs. If you have no credentials entered, adding a new, default entry could solve this issue.
Error 1326
(ERROR_LOGON_FAILURE)
Example
“The user name or password is incorrect.”
Resolution
This is usually caused by incorrect credentials for your VM in the Alike Credential Profile manager for Q-Hybrid jobs.
Error 1727
(RPC_S_CALL_FAILED_DNE)
“The remote procedure call failed and did not execute.”
Example
Failed to connect to DS share (\IP.TO.ADSQSDSdata) with error code: 1727 (User Account)
Resolution
This is often caused by improper permissions to access WMI/DCOM on the remote system, but can also be related to CIFS or NTFS permissions on the ADS itself.
Error 71
(ERROR_REQ_NOT_ACCEP)
“No more connections can be made to this remote computer at this time because there are already as many connections as the computer can accept.”
Example
The system hosting your ADS CIFS share has run out of available connections. This is often caused by an overwhelmed or under powered device sharing your ADS CIFS share. The most common cause is when the Alike ADS is being hosted on a workstation grade OS (Windows XP, Vista, 7, etc.), which impose connection limits.
Resolution
To resolve this issue you must either reduce the load of that share, or move the ADS to a more robust system.
Error 3
(ERROR_PATH_NOT_FOUND)
“The system cannot find the path specified.”
Example
Dedupe cache generation failed, backup performance may be degraded. Failed to open file on file \\datajobsxyz.HCA with error: The system cannot find the path specified. (code: 3)
Resolution
This most often occurs when your Alike Data Store (ADS) is local to your Alike server, and the IP address has changed since your installation of Alike. To resolve this, either change your Alike server’s IP address back to the original address used, perform a recovery installation of Alike on top of your existing copy, or contact support for assistance.
Another common cause is when you specify your ADS path using a DNS name, instead of an IP Address. Since not all devices can resolve name, or they do not always resolve to the same device, using an IP address for your ADS path will usually solve this issue.
Error 64
(ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED)
Symptoms:
- “ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED” appears and crashes the active program window.
- Your PC frequently crashes with Error 64 when running the same program.
- “The specified network name is no longer available” is displayed.
- Windows runs sluggishly and responds slowly to mouse or keyboard input.
- Your computer periodically “freezes” for a few seconds at a time.
These 64 error messages can appear during program installation, while a Microsoft Corporation-related software program (eg. Windows Operating System) is running, during Windows startup or shutdown, or even during the installation of the Windows operating system. Keeping track of when and where your ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED error occurs is a critical piece of information in troubleshooting the problem.
Example
Corrupt download or incomplete installation of Windows Operating System software. Corrupt Windows registry keys associated with Windows Operating System. Virus or malware infection that has corrupted Windows system files or Windows Operating System-related program files. Another program maliciously or mistakenly deleted Windows Operating System-related files. ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED.
Windows System Error Codes such as “ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED” can be caused by a variety of factors, so it is important that you troubleshoot each of the possible causes to prevent it from recurring. The important thing to note is that this is a DNS related issue.
Resolution
- Check your ADS settings and change the DNS name/NETBIOS name to the IP address of the storage. Instead of having: \storage.mycompany.domain.tlddata, or \STORAGEdata, you should \192.168.1.100data or whatever your IP is.
- Repair Registry Entries Associated with Error 64
- Conduct a Full Malware Scan
- Clean Out Your System Junk (Temporary Files and Folders) With Disk Cleanup
- Update Your Device Drivers
- Utilize Windows System Restore to “Undo” Recent System Changes
- Uninstall and Reinstall the Windows Operating System Program Associated with ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED
- Run Windows System File Checker (“sfc /scannow”)
- Install All Available Windows Updates
- Perform a Clean Installation of Windows
Error 67
(ERROR_BAD_NET_NAME)
“The network name cannot be found.”
Example
The network name cannot be found. This error is returned if the network with the neighbor IP address is unreachable.
Resolution
The first step is to check your ADS settings and change the DNS name/NETBIOS name to the IP address of the storage. Instead of having: \storage.mycompany.domain.tlddata, or \STORAGEdata, you should \192.168.1.100data or whatever your IP is. The ResolveIpNetEntry2 function is used to resolve the physical address for a neighbor IP address entry on a local computer. Learn more here.
Error 87
(ERROR_INVALID_PARAMETER)
“The parameter is incorrect.”
Example
The WriteFile() or ReadFile() function call may fail with this error if you are operating on a named pipe and using overlapped I/O.
Resolution
Microsoft recommends the following for Alignment and File Access Requirements: “File access sizes, including the optional file offset in the OVERLAPPED structure, if specified, must be for a number of bytes that is an integer multiple of the volume sector size. For example, if the sector size is 512 bytes, an application can request reads and writes of 512, 1,024, 1,536, or 2,048 bytes, but not of 335, 981, or 7,171 bytes.
File access buffer addresses for read and write operations should be physical sector-aligned, which means aligned on addresses in memory that are integer multiples of the volume’s physical sector size. Depending on the disk, this requirement may not be enforced.”
Learn more here.
ABD Related Error Codes (linux errno.h codes)
Error 22
- Example: Seek failed on file /dev/nbd0 with error code : 22
This is most often caused by networking related issues between the source and destination ABDs. Often, this is due to aggressive idle settings in firewalls or network devices which forcibly close the network connection between the two devices. It can also be caused by network intermittencies or a generally unreliable connection between the two locations.
- Resolution: If this is the case, simply close the offending explorer window and try again. You can also check the output of the command, net use, and close any conflicting sessions.
Close the sessions with the following syntax: net use /DELETE \path.tosession
Error 137
- Example: “failure for device: X. Output: 137”
This is caused by the ABD running out of memory during the course of the job (usually a restore job).
- Resolution: It can be resolved by assigning additional memory to the ABD template for the pool in question (i.e. going from 128MB to 512MB ram), and re-running the job.
PLEASE NOTE: This problem typically affects only older versions of Alike (pre v3.0). However, this error can occur in newer versions. If a newer installation of Alike encounters this issue, please open a support ticket.
Error Message: ABD Failed to mount ADS. mount: Cannot allocate memory
This misleading error may mean that the ABD appliance cannot fully connect to your CIFS network share, usually due to a permissions problem.
- Resolution: Double-check the NTFS and CIFS Sharing permissions on the Alike Data Store (ADS) allows full access by the user account defined in the Alike Manager under Settings–>Storage.
Miscellaneous Errors
Error Message: “Failed to copy databases”
- Resolution: Change the “Archive internal databases every___hours” setting under Tools–>System Settings–>Show Advanced Settings.
The default is undefined. Change this setting to archive every 6 to 8 hours.
Final Notes
If you didn’t find what you’re looking for here, or need help troubleshooting, please open a support ticket. See the KB article, “How to Use Quadric Support,” for instructions and tips on making your support experience as efficient as possible.
Scott
|
Published: October 24, 2017
The following errors are probably some of the least common errors that BatchPatch users encounter, but they can also be the most difficult to understand and troubleshoot, so I want to take some time today to address them.
Error 1611: 64. Failure Error 1620: 64. Failure Error 1611: 2250. Failure Error 1620: 2250. Failure
Generally speaking, all four of these errors typically have the same underlying cause, though their manifestation is slightly different. The 1611 and 1620 numbers simply indicate where in BatchPatch the errors occurred. However, the numbers that come after the 1611 and 1620 are the actual Windows system error codes being generated during the failure. In the case of this posting we are focusing specifically on Windows System Error Codes 64 and 2250.
The entire set of Windows system error codes and their meanings are available from Microsoft at this link: Windows System Error Codes
ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED
64 (0x40)
The specified network name is no longer available.
ERROR_NOT_CONNECTED
2250 (0x8CA)
This network connection does not exist.
In both cases BatchPatch is successfully establishing a connection with the target computer briefly, but then that connection is severed very soon after being established, which causes BatchPatch to display one of the above errors.
The primary question that needs to be answered when one of these errors is encountered is what could possibly be interrupting an existing connection between the BatchPatch computer and the target computer?
Likely Causes of Errors 64 and 2250
The most common/likely causes of an interruption to an existing connection are the following, in no particular order, but it’s certainly possible that something else is responsible for the issue. Below are only the things that we have ever seen cause this:
-
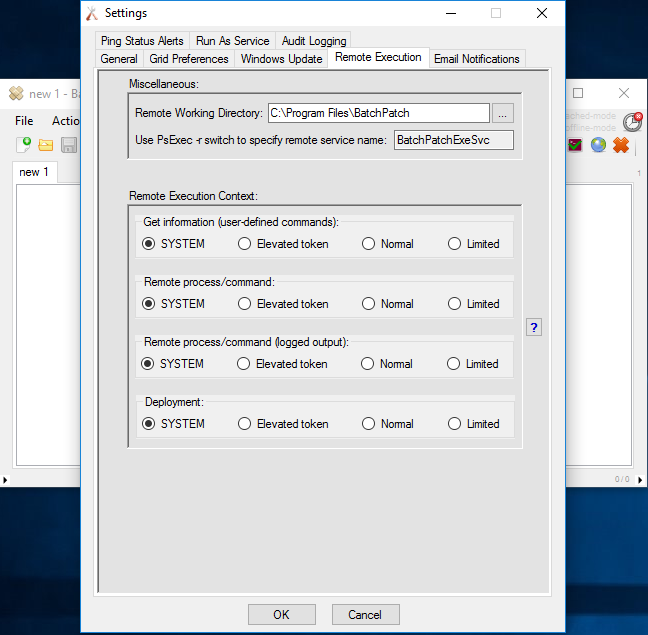
Host Instrusion Prevention/Protection Software (HIPS). This type of software may very well be the cause. It could be severing the network connection or perhaps more likely might be killing the remote psexesvc.exe process/service, which then causes the 64 or 2250 error to occur back at the BatchPatch console. Consider disabling any HIPS software to test. If disabling the software solves the problem, then consider re-enabling the software but whitelisting psexesvc.exe and psexec.exe. Alternatively, we have found that in these cases where HIPS or similar software is the culprit, using a custom remote service process name instead of psexesvc.exe is frequently sufficient to bypass detection. In BatchPatch under ‘Tools > Settings > Remote Execution > Use PsExec -r switch’ you can provide a custom name for the remote service. We recommend something like ‘BatchPatchExeSvc‘.
- Anti-virus software or any other similar security related or endpoint protection type software. These apps can all cause similar behavior, and they would be addressed in the same way as described above for HIPS.
- Firewall. A traditional firewall might be less likely to be the typical culprit for 64 and 2250, but it’s still possible that there is something going on with a firewall that could cause the issue. If all else fails, it would be worth re-examining your firewall configuration just to make sure. However, in most cases a security application (one that is *not* a traditional firewall application) installed on the target computer or on the BatchPatch computer, such as the type of software mentioned above, is more likely to be the culprit.
Additional considerations: It’s worth also trying FQDN or IP address instead of NetBIOS name. Additionally, consider trying integrated security instead of alternate credentials, or vice versa.
This entry was posted in Blog, General, Tutorials and tagged 1611, 1620, 2250, 64, ERROR_NETNAME_DELETED, ERROR_NOT_CONNECTED. Bookmark the permalink. Both comments and trackbacks are currently closed.