-
Скачал библиотеку i2cdevlib для работы с датчиком MPU 6050(MPU 6000). Папки MPU6050 и I2Cdev скопировал в C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibraries
Папка со скетчами расположена по адресу C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduino
Использую Arduino IDE 1.0.3 for windows. Arduino IDE находится в папке C:ArduPilot-Arduino-1.0.3-windowsПробовал скомпилировать пример MPU6050_DMP6, получил кучу ошибок:
Building for ArduPilot Mega 2.x
Excluding arduino core from include paths
In file included from MPU6050_DMP6.ino:46:
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesI2Cdev/I2Cdev.h:77:29: error: Arduino.h: No such file or directory
In file included from C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesI2Cdev/I2Cdev.h:80,
from MPU6050_DMP6.ino:46:
C:ArduPilot-Arduino-1.0.3-windowslibrariesWire/Wire.h:26:20: error: Stream.h: No such file or directory
In file included from C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesI2Cdev/I2Cdev.h:80,
from MPU6050_DMP6.ino:46:
C:ArduPilot-Arduino-1.0.3-windowslibrariesWire/Wire.h:31: error: expected class-name before ‘{‘ token
C:ArduPilot-Arduino-1.0.3-windowslibrariesWire/Wire.h:60: error: ‘size_t’ does not name a type
C:ArduPilot-Arduino-1.0.3-windowslibrariesWire/Wire.h:61: error: ‘size_t’ does not name a type
C:ArduPilot-Arduino-1.0.3-windowslibrariesWire/Wire.h:69: error: ‘size_t’ does not name a type
C:ArduPilot-Arduino-1.0.3-windowslibrariesWire/Wire.h:70: error: ‘size_t’ does not name a type
C:ArduPilot-Arduino-1.0.3-windowslibrariesWire/Wire.h:71: error: ‘size_t’ does not name a type
C:ArduPilot-Arduino-1.0.3-windowslibrariesWire/Wire.h:72: error: ‘size_t’ does not name a type
C:ArduPilot-Arduino-1.0.3-windowslibrariesWire/Wire.h:73: error: ‘Print’ has not been declared
In file included from C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h:37,
from MPU6050_DMP6.ino:48:
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/helper_3dmath.h: In member function ‘float Quaternion::getMagnitude()’:
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/helper_3dmath.h:74: error: ‘sqrt’ was not declared in this scope
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/helper_3dmath.h: In member function ‘float VectorInt16::getMagnitude()’:
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/helper_3dmath.h:111: error: ‘sqrt’ was not declared in this scope
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/helper_3dmath.h: In member function ‘float VectorFloat::getMagnitude()’:
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/helper_3dmath.h:178: error: ‘sqrt’ was not declared in this scope
In file included from C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h:42,
from MPU6050_DMP6.ino:48:
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050.h: At global scope:
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050.h:876: error: ‘NULL’ was not declared in this scope
In file included from MPU6050_DMP6.ino:48:
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h: In member function ‘uint8_t MPU6050::dmpInitialize()’:
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h:329: error: ‘delay’ was not declared in this scope
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h: In member function ‘uint8_t MPU6050::dmpGetLinearAccelInWorld(VectorInt16*, VectorInt16*, Quaternion*)’:
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h:663: error: ‘memcpy’ was not declared in this scope
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h: In member function ‘uint8_t MPU6050::dmpGetEuler(float*, Quaternion*)’:
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h:684: error: ‘atan2’ was not declared in this scope
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h:685: error: ‘asin’ was not declared in this scope
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h: In member function ‘uint8_t MPU6050::dmpGetYawPitchRoll(float*, Quaternion*, VectorFloat*)’:
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h:691: error: ‘atan2’ was not declared in this scope
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h:693: error: ‘sqrt’ was not declared in this scope
C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibrariesMPU6050/MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h:693: error: ‘atan’ was not declared in this scope
MPU6050_DMP6.ino: In function ‘void setup()’:
MPU6050_DMP6:173: error: ‘Serial’ was not declared in this scope
MPU6050_DMP6:183: error: ‘F’ was not declared in this scope
MPU6050_DMP6:214: error: ‘RISING’ was not declared in this scope
MPU6050_DMP6:214: error: ‘attachInterrupt’ was not declared in this scope
MPU6050_DMP6:234: error: ‘OUTPUT’ was not declared in this scope
MPU6050_DMP6:234: error: ‘pinMode’ was not declared in this scope
MPU6050_DMP6.ino: In function ‘void loop()’:
MPU6050_DMP6:272: error: ‘Serial’ was not declared in this scope
MPU6050_DMP6:272: error: ‘F’ was not declared in this scope
MPU6050_DMP6:316: error: ‘Serial’ was not declared in this scope
MPU6050_DMP6:317: error: ‘M_PI’ was not declared in this scope
MPU6050_DMP6:370: error: ‘digitalWrite’ was not declared in this scopeПодскажите, что я неправильно делаю?
Спасибо. -
Папки с либами должны быть в Arduino IDE
-
Скопировал абсолютно все библиотеки(эти тоже MPU6050 и I2Cdev) из папки C:UsersAdmin(RCMS)DocumentsArduinolibraries в C:ArduPilot-Arduino-1.0.3-windowslibraries
Не помогло. Есть идеи?
-
Идей валом. Хотя и не телепат, но первая навскидку — раз не знаете, где библиотека должна лежать, то смело могли её и не правильно установить
-
Что вы имеете в виду под словом «установить»? Почти во всех мануалах (например http://arduino.ua/ru/guide/Libraries или http://www.freeduino.ru/arduino/libraries.html) установка описывается простым копированием файлов .cpp и .h (т.е папки в которой они находятся) в директорию, где хранятся библиотеки. Это либо пользовательские библиотеки C:Users<имя пользователя>DocumentsArduinolibraries, либо Ардуиновские (подкаталог libraries каталога Arduino IDE).
В моём случае они есть в обоих директориях и всё равно есть ошибки.
Кстати, данные библиотеки также появились в Скетч -> Импортировать библиотеку. Я импортировал MPU6050 и всё равно получил ошибки.Вот теперь пора включать телепатию.
-
Решение найдено! Всё дело в версии компилятора(в версии Arduino IDE). Скачал с офф сайта Arduino IDE версии 1.5.8, загрузил библиотеки, немного потанцевал с бубном и всё скомпилилось(правда на другом компе). Тему можно закрывать.
Я просто пытаюсь использовать функции sin, cos и sqrt, но продолжаю получать сообщения об ошибках «не объявлено в этой области». Я просмотрел все результаты поиска на предмет ошибки, и 1. кодировщики используют терминал для компиляции своего кода (а не CodeBlocks, которые я использую) 2. Я пробовал использовать вместо этого cmath , добавив using namespace std и используя абсолютные пути. Я расстраиваюсь.
#ifndef _MATH_H
#define _MATH_H
#include </usr/include/math.h>
#define PI 3.14159265
#define DEG_TO_RAD PI / 180.0f
struct Vector2
{
float x;
float y;
Vector2(float _x = 0.0f, float _y = 0.0f)
: x(_x), y(_y) {}
float MagnitudeSqr()
{
return x*x + y*y;
}
float Magnitude()
{
return (float)sqrt(x*x + y*y);
}
Vector2 Normalized()
{
float mag = Magnitude();
return Vector2(x/ mag, y /mag);
}
};
inline Vector2 operator +(const Vector2& lhs, const Vector2& rhs)
{
return Vector2(lhs.x + rhs.x, lhs.y + rhs.y);
}
inline Vector2 operator -(const Vector2& lhs, const Vector2& rhs)
{
return Vector2(lhs.x - rhs.x, lhs.y - rhs.y);
}
inline Vector2 RotateVector(Vector2& vec, float angle)
{
float radAngle = (float)(angle*DEG_TO_RAD);
return Vector2((float)(vec.x * cos(radAngle) - vec.y * sin(radAngle)), (float)(vec.x * sin(radAngle)) + vec.y * cos(radAngle));
}
#endif // _MATH_H
Без абсолютного пути
||=== Build: Debug in SDL (compiler: GNU GCC Compiler) ===|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|83|error: ‘::acos’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|102|error: ‘::asin’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|121|error: ‘::atan’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|140|error: ‘::atan2’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|161|error: ‘::ceil’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|180|error: ‘::cos’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|199|error: ‘::cosh’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|218|error: ‘::exp’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|237|error: ‘::fabs’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|256|error: ‘::floor’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|275|error: ‘::fmod’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|296|error: ‘::frexp’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|315|error: ‘::ldexp’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|334|error: ‘::log’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|353|error: ‘::log10’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|372|error: ‘::modf’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|384|error: ‘::pow’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|421|error: ‘::sin’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|440|error: ‘::sinh’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|459|error: ‘::sqrt’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|478|error: ‘::tan’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|497|error: ‘::tanh’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath||In function ‘constexpr int std::fpclassify(float)’:|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|545|error: ‘FP_NAN’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|545|error: ‘FP_INFINITE’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|545|error: ‘FP_NORMAL’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|546|error: ‘FP_SUBNORMAL’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|546|error: ‘FP_ZERO’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|546|note: suggested alternative: ‘FD_ZERO’|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath||In function ‘constexpr int std::fpclassify(double)’:|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|550|error: ‘FP_NAN’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|550|error: ‘FP_INFINITE’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|550|error: ‘FP_NORMAL’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|551|error: ‘FP_SUBNORMAL’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|551|error: ‘FP_ZERO’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|551|note: suggested alternative: ‘FD_ZERO’|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath||In function ‘constexpr int std::fpclassify(long double)’:|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|555|error: ‘FP_NAN’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|555|error: ‘FP_INFINITE’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|555|error: ‘FP_NORMAL’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|556|error: ‘FP_SUBNORMAL’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|556|error: ‘FP_ZERO’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|556|note: suggested alternative: ‘FD_ZERO’|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath||In function ‘constexpr typename __gnu_cxx::__enable_if<std::__is_integer<_Tp>::__value, int>::__type std::fpclassify(_Tp)’:|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|564|error: ‘FP_NORMAL’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|564|error: ‘FP_ZERO’ was not declared in this scope|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|564|note: suggested alternative: ‘FD_ZERO’|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|1080|error: ‘::double_t’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|1081|error: ‘::float_t’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|1084|error: ‘::acosh’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|1085|error: ‘::acoshf’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|1086|error: ‘::acoshl’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|1088|error: ‘::asinh’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|1089|error: ‘::asinhf’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|1090|error: ‘::asinhl’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|1092|error: ‘::atanh’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|1093|error: ‘::atanhf’ has not been declared|
/usr/include/c++/7/cmath|1094|error: ‘::atanhl’ has not been declared|
||More errors follow but not being shown.|
||Edit the max errors limit in compiler options...|
||=== Build failed: 50 error(s), 0 warning(s) (0 minute(s), 0 second(s)) ===|
С абсолютным:
||=== Build: Debug in SDL (compiler: GNU GCC Compiler) ===|
/home/zues/Projects/code/SDL/MathHelper.h||In member function ‘float Vector2::Magnitude()’:|
/home/zues/Projects/code/SDL/MathHelper.h|23|error: ‘sqrt’ was not declared in this scope|
/home/zues/Projects/code/SDL/MathHelper.h|23|note: suggested alternative: ‘short’|
/home/zues/Projects/code/SDL/MathHelper.h||In function ‘Vector2 RotateVector(Vector2&, float)’:|
/home/zues/Projects/code/SDL/MathHelper.h|48|error: ‘cos’ was not declared in this scope|
/home/zues/Projects/code/SDL/MathHelper.h|48|error: ‘sin’ was not declared in this scope|
||=== Build failed: 3 error(s), 0 warning(s) (0 minute(s), 0 second(s)) ===|
1 ответ
Лучший ответ
Ошибки, которые вы видите, скорее всего, связаны с использованием зарезервированного имени:
#define _MATH_H
Который также используется glibc.
Правило состоит в том, чтобы не начинать имена с _ (правила более сложные, но они охватывают многое и их легко запомнить).
Кроме того, обратите внимание, что вместо:
#include </usr/include/math.h>
Чтобы включить библиотеку C math.h, вам нужно только включить:
#include <math.h>
Если вы хотите убедиться, что функции находятся в глобальном пространстве имен, или:
#include <cmath>
Если вы хотите убедиться, что они находятся в пространстве имен std (рекомендуется).
5
Acorn
18 Авг 2020 в 02:56
Arduino programming is an open-source and simple stage that arranges the Arduino board into working with a particular goal in mind. An Arduino code is written in C++ yet with extra capacities and strategies. An Arduino is an equipment and programming stage broadly utilised in hardware.
In this article, we go through three quick fixes for the error ‘was not declared in this scope’.
Also read: How to solve the Tower of Hanoi problem using Python?
What does the error mean?
Every programming language has a concept of Scope. Scope tells us where a specific variable, constant or function is accessible and usable. It refers to the area of code a statement, block, or name. The scope of an entity determines where that entity is usable in other parts of the program. The scope of a block determines where that block can be used in other blocks, and the scope of a name determines where that name can be used in other names.
There are two types of scope in programming languages: local and global. Local scope refers to the identifiers and symbols visible inside a block of code. Global scope, on the other hand, refers to the identifiers and symbols visible outside a block of code.
The error ‘was not declared in this scope’ generally occurs when a variable or function is not accessible to its call. A global variable in Arduino is the variable that is declared outside any function, including the setup() and loop() functions. Any variable declared inside a function or loop has restrictive access and is a local variable.
If any other function calls a local variable, it gives an error. To call any variable or function in any other function, including the setup() and loop() function, it should be declared as a global variable.
Also read: How to stop an Arduino program?
There are the quick fixes for the Arduino error: was not declared in the scope.
Declare the variable
Before assigning a value to the variable, make sure to define it. There are 16 data types commonly used in Arduino coding. Each data type expresses the nature of the value assigned to it. If the data type and value doesn’t match, an error arises. Also, if a variable is assigned any value without its declaration or data type, the error occurs.
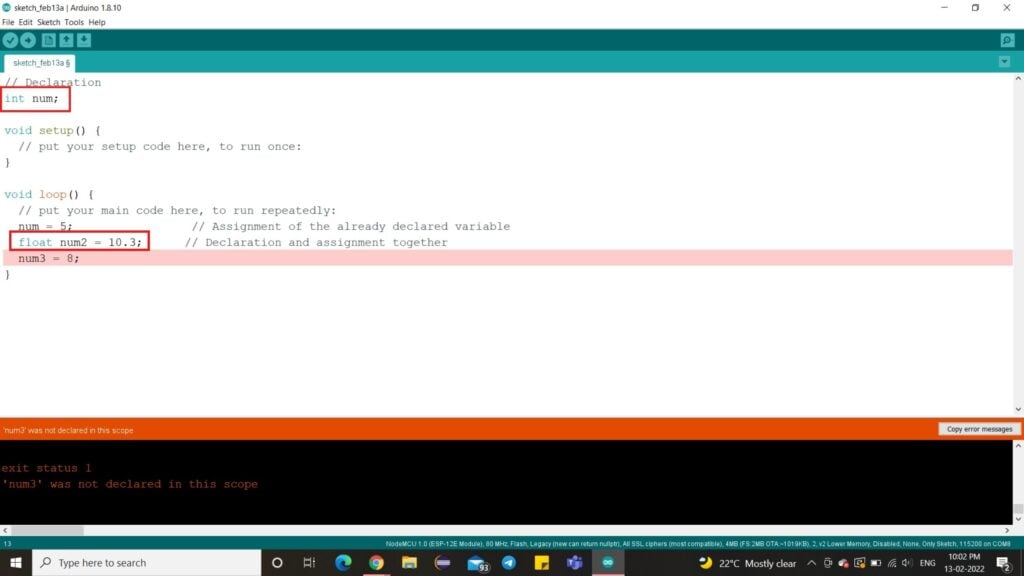
Always ensure to declare the variable before the assignment. There are two ways to do this.
There are three variables in the above example – num1, num2 and num3. The variable num1 has been declared separately and assigned to a data type corresponding value in the loop. The variable num2 has been declared and assigned in the same line of code. The variable num3, on the other hand, has directly been assigned a value without its declaration. This causes the error, as shown above.
Other details
There may be errors arising even after proper declaration and assignment of the variable. This may be due to incorrect or absence of the closing brackets, semicolons or improper declaration of functions. Ensure proper use of syntax when defining loops and functions. Every opening in curly brace must be accounted for and closed. Extra closing braces also cause errors. Alongside, semicolons hold their importance. A semicolon missed can cause the entire program to go haywire.
Library folder
Many times, variables call or use functions that require importing a few specific libraries.
In the example above, the variable num calls the square root function – sqrt() from the maths library of Arduino. If we call a function without including its library first, an error occurs. There are multiple inbuilt and standard libraries in Arduino, while a few special libraries must be included separately.
Also read: What is ‘does not name a type’ in Arduino: 2 Fixes.
-
03-08-2009
#1
Registered User
Not declared in this scope
Hey if anyone could help me out here I would really appreciate it. I’m not sure what do to to get rid of the below errors/warnings.
prime.cpp: In function ‘int main()’:
prime.cpp:12: error: ‘isPrime’ was not declared in this scope
prime.cpp: In function ‘int isPrime(int)’:
prime.cpp:39: warning: converting to ‘int’ from ‘double’Code:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <math.h> #define TRUE 1; #define FALSE 0; int main() { int number; if (isPrime(number)) cout << "n" << number << "is a prime numbern"; else cout << "n" << number << "is not a prime numbern"; return 0; } void getNumber(int &number) { cout << "Please enter a positive number "; cin >> number; if (!cin.good()) { printf("Invalid number enteredn"); exit(1); } } int isPrime(int number) { int count, s; /* Every even number is not prime */ if (number % 2 == 0) return TRUE; /* check every odd number up to the square root of the number */ s = sqrt(number); for (count=3; count<=s; count+=2); { if (number % count == 0) return TRUE; } return FALSE; }
-
03-08-2009
#2
Registered User
The compiler doesn’t know that «isPrime» is defined later in the file. You need to declare it before using it. Add the following before main:
int isPrime(int);
The compiler will then know that «isPrime» is a function taking/returning int, when it sees it.
gg
-
03-08-2009
#3
Registered User
I tried that but it came up with an «unexpected initialiser before int» error.
-
03-08-2009
#4
Registered User
Sorry I know what it was I was doing wrong.
Can anyone help me with why it is always printing out:
Please enter a positive number 4
-4195180is a prime number
Updated code:
Code:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <math.h> int isPrime(int); void getNumber(int); #define TRUE 1; #define FALSE 0; int main() { int number; getNumber(number); if (isPrime(number)) cout << "n" << number << "is a prime numbern"; else cout << "n" << number << "is not a prime numbern"; return 0; } void getNumber(int number) { cout << "Please enter a positive number "; cin >> number; if (!cin.good()) { printf("Invalid number enteredn"); exit(1); } } int isPrime(int number) { int count, s; /* Every even number is not prime */ if (number % 2 == 0) return TRUE; /* check every odd number up to the square root of the number */ s = sqrt(number); for (count=3; count<=s; count+=2); { if (number % count == 0) return TRUE; } return FALSE; }Last edited by Taka; 03-08-2009 at 09:12 PM.
-
03-08-2009
#5
C++ Witch
You should use pass by reference instead of pass by value, otherwise the number variable in the main function is never modified by getNumber().
By the way, C++ has a bool type with true and false constants, so it does not make sense to use an int with TRUE and FALSE macros.
Originally Posted by Bjarne Stroustrup (2000-10-14)
I get maybe two dozen requests for help with some sort of programming or design problem every day. Most have more sense than to send me hundreds of lines of code. If they do, I ask them to find the smallest example that exhibits the problem and send me that. Mostly, they then find the error themselves. «Finding the smallest program that demonstrates the error» is a powerful debugging tool.
Look up a C++ Reference and learn How To Ask Questions The Smart Way
-
03-08-2009
#6
Registered User
I’m sorry but I don’t know what you mean at all.
-
03-08-2009
#7
and the Hat of Guessing
You had it right the first time — compare the original getNumber with your new one.
Not only should «#define TRUE 1» never appear in C++, given that «true» already exists, it should most definitely not appear with a semicolon at the end. Since isPrime asks a true-false question, you should use a true-false datatype, specifically «bool».
-
03-08-2009
#8
Registered User
When I left it as
Code:
void getNumber(int &number)
I got a compile error:
prime.cpp: In function ‘int isPrime(int)’:
prime.cpp:44: warning: converting to ‘int’ from ‘double’
Undefined first referenced
symbol in file
getNumber(int) /var/tmp//cc1BaH0f.o
ld: fatal: Symbol referencing errors. No output written to a.out
collect2: ld returned 1 exit status
-
03-08-2009
#9
and the Hat of Guessing
Did you remember to change the prototype too? Otherwise post code.
-
03-08-2009
#10
Registered User
Code:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <math.h> int isPrime(int); void getNumber(int); #define TRUE 1; #define FALSE 0; int main() { int number; getNumber(number); if (isPrime(number)) cout << "n" << number << "is a prime numbern"; else cout << "n" << number << "is not a prime numbern"; return 0; } void getNumber(int &number) { cout << "Please enter a positive number "; cin >> number; if (!cin.good()) { printf("Invalid number enteredn"); exit(1); } } int isPrime(int number) { int count, s; /* Every even number is not prime */ if (number % 2 == 0) return TRUE; /* check every odd number up to the square root of the number */ s = sqrt(number); for (count=3; count<=s; count+=2); { if (number % count == 0) return TRUE; } return FALSE; }
-
03-08-2009
#11
C++ Witch
Basically, this:
Code:
void getNumber(int);
should be either:
Code:
void getNumber(int& number);
or:
Then you make the change in the function definition (implementation) as well.Now this:
should be:
Code:
bool isPrime(int number);
then you get rid of these lines:
Code:
#define TRUE 1; #define FALSE 0;
Note that if you really did need them, those semi-colons should be removed, as mentioned by tabstop.
So, no more TRUE or FALSE. What to do? Just use true or false.
Originally Posted by Bjarne Stroustrup (2000-10-14)
I get maybe two dozen requests for help with some sort of programming or design problem every day. Most have more sense than to send me hundreds of lines of code. If they do, I ask them to find the smallest example that exhibits the problem and send me that. Mostly, they then find the error themselves. «Finding the smallest program that demonstrates the error» is a powerful debugging tool.
Look up a C++ Reference and learn How To Ask Questions The Smart Way
-
03-08-2009
#12
Registered User
So it should be like this?
Code:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #include <math.h> int isPrime(int); void getNumber(int& number); #define TRUE 1 #define FALSE 0 int main() { int number; getNumber(number); if (isPrime(number)) cout << "n" << number << "is a prime numbern"; else cout << "n" << number << "is not a prime numbern"; return 0; } void getNumber(int& number) { cout << "Please enter a positive number "; cin >> number; if (!cin.good()) { printf("Invalid number enteredn"); exit(1); } } int isPrime(int number) { int count, s; /* Every even number is not prime */ if (number % 2 == 0) return TRUE; /* check every odd number up to the square root of the number */ s = sqrt(number); for (count=3; count<=s; count+=2); { if (number % count == 0) return TRUE; } return FALSE; }
-
03-08-2009
#13
C++ Witch
Originally Posted by Taka
So it should be like this?
You’re not paying attention, are you? The code that you corrected should be removed. I was merely pointing out how it would be corrected if it were not to be removed.
There is another thing that I did not spot earlier: you have a using directive (using namespace std; ) before a header inclusion. That is bad practice, although it might not matter especially since the header is a standard header. Move the using directive to after the header inclusion.
Originally Posted by Bjarne Stroustrup (2000-10-14)
I get maybe two dozen requests for help with some sort of programming or design problem every day. Most have more sense than to send me hundreds of lines of code. If they do, I ask them to find the smallest example that exhibits the problem and send me that. Mostly, they then find the error themselves. «Finding the smallest program that demonstrates the error» is a powerful debugging tool.
Look up a C++ Reference and learn How To Ask Questions The Smart Way
-
03-08-2009
#14
Registered User
I’m sorry I’m trying to understand what you are saying but I am only learning C++ and I’m not really getting what you are trying to tell me.
I’ve been told I need to leave the True/False statements in there thats why I didn’t take them out.
-
03-09-2009
#15
Registered User
Code:
#include <iostream> #include <cmath> using namespace std; bool isPrime(int); int getNumber(); int main() { int number = getNumber(); if (isPrime(number)) cout << "n" << number << "is a prime numbern"; else cout << "n" << number << "is not a prime numbern"; return 0; } int getNumber() { int number; cout << "Please enter a positive number "; cin >> number; if (!cin.good()) { printf("Invalid number enteredn"); exit(1); } return number; } bool isPrime(int number) { int count, s; bool isprime = true; /* Every even number is not prime */ // if (number % 2 == 0) return TRUE; /* check every odd number up to the square root of the number */ s = sqrt(number); for (count=3; count<=s; count+=2); { if (number % count == 0) isprime = false; } return false; }Include «cmath» , not «math.h».
In main(), affect ‘number’ by returning the number. This is the most logical.
In the function ‘isPrime’ you don’t have to verify for both ‘true’ and ‘false’, just make it true unless otherwise found.
Try not to use ‘return’ in loops or functions, but affect a local variable which you return always in the end (although here it doesn’t really matter).