What does that pacman output have to do with anything? Post the complete output from the command that’s failing. Also first build with makepkg — if that gives an error post it here.
EDIT: I can replicate the problem. The error is during the build and it’s just bad code from the upstream source:
/tmp/php71/src/php-7.1.33/ext/intl/collator/collator_sort.c: In function ‘zif_collator_sort’:
/tmp/php71/src/php-7.1.33/ext/intl/collator/collator_sort.c:349:26: error: ‘TRUE’ undeclared (first use in this function)
349 | collator_sort_internal( TRUE, INTERNAL_FUNCTION_PARAM_PASSTHRU );
| ^~~~
/tmp/php71/src/php-7.1.33/ext/intl/collator/collator_sort.c:349:26: note: each undeclared identifier is reported only once for each function it appears in
/tmp/php71/src/php-7.1.33/ext/intl/collator/collator_sort.c: In function ‘zif_collator_asort’:
/tmp/php71/src/php-7.1.33/ext/intl/collator/collator_sort.c:543:26: error: ‘FALSE’ undeclared (first use in this function)
543 | collator_sort_internal( FALSE, INTERNAL_FUNCTION_PARAM_PASSTHRU );
| ^~~~~
make: *** [Makefile:1136: ext/intl/collator/collator_sort.lo] Error 1
make: *** Waiting for unfinished jobs....
==> ERROR: A failure occurred in build().
Aborting...I suspect simply replacing those with true and false might work, otherwise just define them as 1 and 0.
EDIT: now I see what ICU has to do with this — there are comments on the AUR page for php71 trying to blame this on an ICU change. But that’s nonsense. The upstream code assuming nonstandard macros will be defined when they didn’t define or check for themselves is the problem.
EDIT 2: This fix worked, in a sed line in the PKGBUILD, but the error popped up on other source files — it seems a pervasive issue in the code. So just add definitions of TRUE and FALSE to CFLAGS … or not — F*** Me that’s annoying, the makefile ignores CFLAGS settings. It looks like one might be able to set «EXTRA_CFLAGS» — I’m trying that now.
Last edited by Trilby (2021-02-09 23:40:53)
«UNIX is simple and coherent…» — Dennis Ritchie, «GNU’s Not UNIX» — Richard Stallman
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 |
#include <windows.h> #include <tchar.h> #define DIB_RGB(r, g, b) ((DWORD)((r & 0xFF) << 16) | ((g & 0xFF) << 8) | (b & 0xFF)) void fill_rect(__int32*, int, int, int, int, int, DWORD); // 24/32 бит BOOL SaveArrFile(const TCHAR* filename, const __int32* arr, int width, int height, int bpp = 24){ if((bpp < 24) || (bpp > 32)) // только 24/32 бит return FALSE; DWORD p_row = (DWORD)((width * bpp + 31) & ~31) / 8uL; DWORD size = (DWORD)(height * p_row); // формируем файловый заголовок BITMAPFILEHEADER hdr; ZeroMemory(&hdr, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER)); hdr.bfType = 0x4D42; hdr.bfOffBits = sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER) + sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER); hdr.bfSize = hdr.bfOffBits + size; // заголовок описателя растра BITMAPINFO dib; ZeroMemory(&dib, sizeof(BITMAPINFO)); dib.bmiHeader.biSize = sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER); dib.bmiHeader.biBitCount = bpp; dib.bmiHeader.biCompression = BI_RGB; dib.bmiHeader.biPlanes = 1u; dib.bmiHeader.biWidth = (long)width; dib.bmiHeader.biHeight = (long)-height; dib.bmiHeader.biSizeImage = size; dib.bmiHeader.biXPelsPerMeter = 11811L; dib.bmiHeader.biYPelsPerMeter = 11811L; dib.bmiHeader.biClrImportant = 0uL; dib.bmiHeader.biClrUsed = 0uL; // далее запись в файл HANDLE fp = CreateFile(filename, GENERIC_WRITE, FILE_SHARE_WRITE, NULL, CREATE_ALWAYS, FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL, NULL); if(fp == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) return FALSE; // записываем заголовки... DWORD dwr = 0uL; WriteFile(fp, (LPCVOID)&hdr, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER), &dwr, NULL); WriteFile(fp, (LPCVOID)&dib.bmiHeader, sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER), &dwr, NULL); // запись массива пикселей if(bpp == 32) // 32-бит WriteFile(fp, (LPCVOID)arr, size, &dwr, NULL); else if(bpp == 24) { // 24-бит с дополнением до 32-разрядной границы BYTE nil = 0u; int cb = sizeof(RGBQUAD); int align = ((cb - ((width*bpp + 7) / 8) % cb) % cb); for(int y = 0; y < height; y++) { for(int x = 0; x < width; x++) WriteFile(fp, (LPCVOID)&arr[y*width+x], sizeof(RGBTRIPLE), &dwr, NULL); for(int i = 0; i < align; i++) // до границы DWORD WriteFile(fp, (LPCVOID)&nil, sizeof(BYTE), &dwr, NULL); } } FlushFileBuffers(fp); CloseHandle(fp); return TRUE; } int main(void) { //массив пикселей __int32 arr[111*222] = {0}; int cw = 222; int ch = 111; // нарисуем что-нибудь DWORD rgb; int sx = ch / 5; int sy = cw / 10; for(int y = 0; y < 5; y++) { for(int x = 0; x < 10; x++) { rgb = DIB_RGB(rand()%2*0xFF, rand()%2*0xFF, rand()%2*0xFF); fill_rect(arr, cw, x*sx, y*sy, sx, sy, rgb); } } // сохраняем в файл if(SaveArrFile(_T("grid.bmp"), arr, cw, ch, 24)) _putts(_T("Good save file.")); else _putts(_T("Error save file !")); _gettchar(); return 0; } // вывод прямоугольника void fill_rect(__int32* arr, int width, int x, int y, int cx, int cy, DWORD color){ for(int r = y; r <= (y + cy); r++) { for(int c = x; c <= (x + cx); c++) arr[r*width + c] = color; } } |
Improve Article
Save Article
Improve Article
Save Article
Variables: A variable is the name given to a memory location. It is the basic unit of storage in a program.
- The value stored in a variable can be changed during program execution.
- A variable is only a name given to a memory location, all the operations done on the variable effects that memory location.
- All the variables must be declared before use.
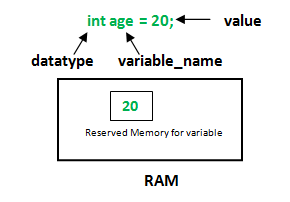
How to declare variables?
We can declare variables in common languages (like C, C++, Java etc) as follows:
where: datatype: Type of data that can be stored in this variable. variable_name: Name given to the variable. value: It is the initial value stored in the variable.
How to avoid errors while creating variables?
- The identifier is undeclared: In any programming language, all variables have to be declared before they are used. If you try to use the name of a such that hasn’t been declared yet, an “undeclared identifier” compile-error will occur.
Example:
#include <stdio.h>intmain(){printf("%d", x);return0;}Compile Errors:
prog.c: In function 'main': prog.c:5:18: error: 'x' undeclared (first use in this function) printf("%d", x); ^ prog.c:5:18: note: each undeclared identifier is reported only once for each function it appears in - No initial value is given to the variable: This error commonly occurs when the variable is declared, but not initialized. It means that the variable is created but no value is given to it. Hence it will take the default value then. But in C language, this might lead to error as this variable can have a garbage value (or 0) as its default value. In other languages, 0 will be its default value.
Example:
#include <stdio.h>intmain(){intx;printf("%d", x);return0;}Output:
0
- Using variable out of its Scope: Scope of a variable is the part of the program where the variable is accessible. Like C/C++, in Java, all identifiers are lexically (or statically) scoped, i.e.scope of a variable can be determined at compile time and independent of the function call stack.
Example:
#include <stdio.h>intmain(){{intx = 5;}printf("%d", x);return0;}Compile Errors:
prog.c: In function 'main': prog.c:5:18: error: 'x' undeclared (first use in this function) printf("%d", x); ^ prog.c:5:18: note: each undeclared identifier is reported only once for each function it appears inHow to Correct the above code: Declare the variable x before using it in the outer scope. Or you can use the already defined variable x in its own scope
Example:
#include <stdio.h>intmain(){{intx = 5;printf("%d", x);}return0;}Output:
5
- Creating a variable with an incorrect type of value: This arises due to the fact that values are implicitly or explicitly converted into another type. Sometimes this can lead to Warnings or errors.
Example:
#include <stdio.h>intmain(){char* x;inti = x;printf("%d", x);return0;}Warning:
prog.c: In function 'main': prog.c:7:13: warning: initialization makes integer from pointer without a cast [-Wint-conversion] int i = x; ^