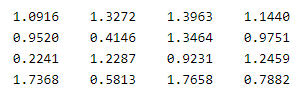|
79 / 34 / 6 Регистрация: 11.11.2010 Сообщений: 496 |
|
|
1 |
|
Возведение экспоненты в степень19.11.2011, 17:09. Показов 58383. Ответов 3
Пытаюсь вычислить выражение 100*j*sqrt(2)*exp^(-j*pi/4) Выдает ошибку: Error using exp В чем дело?
__________________
1 |
|
Programming Эксперт 94731 / 64177 / 26122 Регистрация: 12.04.2006 Сообщений: 116,782 |
19.11.2011, 17:09 |
|
3 |
|
2 / 2 / 1 Регистрация: 15.11.2011 Сообщений: 47 |
|
|
20.11.2011, 10:24 |
2 |
|
j так понимаю мнимая единица?
1 |
|
Sergik1 128 / 127 / 10 Регистрация: 09.11.2010 Сообщений: 200 |
||||||||
|
20.11.2011, 13:07 |
3 |
|||||||
|
Оператор exp уже подразумевает использование аргумента в скобках как показателя степени. Так что оператор ^ здесь лишний.
ответ:
3 |
|
79 / 34 / 6 Регистрация: 11.11.2010 Сообщений: 496 |
|
|
20.11.2011, 14:33 [ТС] |
4 |
|
j так понимаю мнимая единица? Да. Sergik1, спасибо.
1 |
Introduction to Matlab not enough input arguments
Matlab provides the different functions to the user, in which that user can perform the different operations as per their requirement. We write the script or function in Matlab that takes in no input argument, and we try to run that script or function. At that time, Matlab showed an error message that there was not enough input argument because the function required the input argument that we write the script or function, and inside that function, we passed two matrices together. So this is not a valid way to write the script or function; in this case, we need to write a separate function or script. In this topic, we are going to learn about Matlab, not enough input arguments.
Syntax
specified function name sample = add (argument name 1, argument name 2)
sample = argument name 1+ argument name 2;
end
Explanation
In the above syntax, we use different parameters as follows.
specified function name: It is used to specify the function name with argument.
add: add is a function, and it is used to make the addition of two arguments that we pass inside the function.
In the above syntax, we created a function with a name sample, and we made the addition of two matrices that are argument name 1 and argument name 2, as shown in the above syntax.
How to solve Matlab’s not enough input arguments problem?
Now let’s see how to solve the not enough input argument problem in Matlab as follows.
Basically, there are two ways to solve this problem as follows.
1 By using the Command Prompt:
This is a very simple method to solve the not enough input argument error. In this method, we simply create the input whatever we require on the command prompt, and after that, we need to execute that input by using the function or script that we already write.
2 By using Matlab Editor:
Under the Run button, there is a dark arrow. In the event that you click on that arrow button, you can determine the variable you might want to get from the MATLAB workspace by composing the manner in which you need to call the capacity precisely, as you have found in technique 1. But, first, be certain that the variable you are indicating inside the function must exist in the MATLAB workspace.
Examples of Matlab not enough input arguments
Now let’s see the different examples of not enough input arguments in Matlab to better understand this problem as follows.
First, see how not enough input argument error occurs by using the following example as follows.
function Z = add(X, Y)
Z = X + Y;
end
Explanation
In the above example, we created a simple function, in which we write the function definition for addition. Here we pass the two arguments X and Y as shown in the above function, but it shows the error message like not enough input argument error because here we try to make the addition of two matrices, and this is not possible by using the above syntax. The final output of this program we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now let’s see how we can avoid this error by using different methods as follows.
The simplest way is to pass the input argument in the command prompt, and after that, we need to run a function with new values. So let’s see the example of this type as follows.
Write the following code in the command prompt as follows.
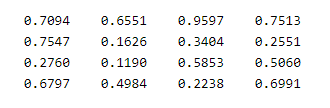
X = rand (4, 4)
Y = rand (4, 4)
Z = add (4, 4)
Explanation
In the above code, we use rand () to print the 4 by 4 arrays, and after that, we make the addition of X and Y arrays as shown in the above code. So in this way, we can avoid the not enough input argument error. The final output of this program we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now let’s see another way to avoid this error as follows.
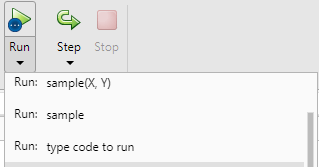
In the second method, we need to click on the Run button, open the dropdown menu, and write down the input argument name that we need to run but be assured that the argument name must be present in the function. Let’s see some screenshots of this method as follows.
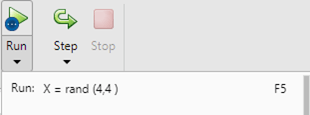
In the above screen, we show the dropdown menu and write here the input argument that we need to execute. In this example, we pass X = rand (4,4) as shown in the below screenshot as follows.
After execution, the final result is shown below screenshot as follows.
How to avoid Matlab’s not enough input arguments problem?
Now let’s see how we can avoid not enough input argument problems in Matlab as follows.
First thing when we open a Matlab file in the editor, and we try to run that file, or we can say that function by using the Run button. At that time, Matlab runs that function without any argument; then, we will get an error message, not enough input argument. At that the same time drop-down menu is open through the Run button and enters the values for the missing argument for the function. So add different values as per our requirement, hit the enter now entered values map with the function, and click on the Run button. So in this way, we can avoid the not enough input argument problem.
Another way to avoid not enough input argument problems is that, suppose we created one function that is fun () and inside that we pass two arguments that A and B. At the same time, if we need to provide some more input arguments at that time, we need to use an anonymous function.
Now we have one more way to avoid the not enough input argument problem. We use the command line option when we execute the function at that same time; we need to pass the input argument for that function. By using this method, we can easily avoid this problem.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you learn Matlab, not enough input argument. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of not enough input argument, and we also see different examples of not enough input argument. From this article, we learned how and when we use Matlab not enough input argument.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab not enough input arguments. Here we discuss the basic syntax and different examples of not enough input argument. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
- Matlab Mod
- Matlab Backslash
- Matlab limit
- Matlab Block Comment
You need to use function handles.
Change your call to
Netn(@function1, @dfunction1, 3)
Change you main function to (you need to use feval when evaluating the functions passed by function handles)
function [new, iter] = Netn(func1,dfunc1,x)
tol=0.0001;
old=x;
u=feval(func1,x);
v=feval(dfunc1,x);
new=old-u/v;
iter=1;
while (abs(new-old)>=tol)
old=new;
u=feval(func1,old);
v=feval(dfunc1,old);
new=old-u/v;
iter=iter+1;
end
end
Now you can also create other objective and derivative functions, with other names. And you pass those names as function handles in your call to Netn, without changing the code to Netn.
Related videos on Youtube
11 : 35
MATLAB: How to solve error (Undefined function for wrong input argument type)
04 : 03
MATLAB tutorial: Functions of multiple arguments
04 : 30
Variable Number of Input/Output Arguments in MATLAB | MATLAB Tutorial
02 : 16
Not Enough Input Arguments | MATLAB | Error Fixing
06 : 52
Error when submitting programming assignment in matlab Coursera | error in submitwithconfiguration
Comments
-
I’m new to Matlab and am working on implementing Newton’s method on a nonlinear system. I’m using a very simple example but when I call the function I create, I get the error: «Not enough input arguments.
Error in function1 (line 2)
f=x.^3-x.^2-1;»Here are my function definitions:
Newton’s method part:
function [new, iter] = Netn(function1,dfunction1,x)
tol=0.0001;
old=x;
u=function1(x);
v=dfunction1(x);
new=old-u/v;
iter=1;
while (abs(new-old)>=tol)
old=new;
u=function1(old);
v=dfunction1(old);
new=old-u/v;
iter=iter+1;
end
endSimple function definition
function f=function1(x)
f=x.^3-x.^2-1;
endSimple function derivative definition (for Newton’s)
function f=dfunction1(x)
f=3*x.^2-2*x;
endCan someone please help me with where I’m going wrong? Typing things like «Netn(function1, dfunction1, 3)» in the command window gets the error. I’d appreciate anything, thanks!
-
perfect, thanks so much!
Recents
Example
Often beginning MATLAB developers will use MATLAB’s editor to write and edit code, in particular custom functions with inputs and outputs. There is a Run button at the top that is available in recent versions of MATLAB:
Once the developer finishes with the code, they are often tempted to push the Run button. For some functions this will work fine, but for others they will receive a Not enough input arguments error and be puzzled about why the error occurs.
The reason why this error may not happen is because you wrote a MATLAB script or a function that takes in no input arguments. Using the Run button will run a test script or run a function assuming no input arguments. If your function requires input arguments, the Not enough input arguments error will occur as you have written a functions that expects inputs to go inside the function. Therefore, you cannot expect the function to run by simply pushing the Run button.
To demonstrate this issue, suppose we have a function mult that simply multiplies two matrices together:
function C = mult(A, B)
C = A * B;
end
In recent versions of MATLAB, if you wrote this function and pushed the Run button, it will give you the error we expect:
>> mult
Not enough input arguments.
Error in mult (line 2)
C = A * B;
There are two ways to resolve this issue:
Method #1 — Through the Command Prompt
Simply create the inputs you need in the Command Prompt, then run the function using those inputs you have created:
A = rand(5,5);
B = rand(5,5);
C = mult(A,B);
Method #2 — Interactively through the Editor
Underneath the Run button, there is a dark black arrow. If you click on that arrow, you can specify the variables you would like to get from the MATLAB workspace by typing the way you want to call the function exactly as how you have seen in method #1. Be sure that the variables you are specifying inside the function exist in the MATLAB workspace:
Hi, I’m very new to MATLAB and I am having some trouble. Lots of people have had the same problem but nobody seems to be able to explain or solve it in plain English. Could somebody please explain what this error is and how to fix it?
I have a simple function:
function [r]=Mec134function(w,theta_deg)
t2=10000;
theta_rad=(theta_deg./180).*pi;
t1=55090./(10*sin(theta_rad));
rx=(t1.*cos(theta_rad))-t2;
ry=w-(t1.*sin(theta_rad));
r=((rx).^2+(ry).^2).^0.5;
end
It seems to give this error for line 3 but I’m not sure why.
Thanks.
采纳的回答
Your function defines 2 input arguments (w and theta_deg). When you run Mec134function, you must specify exactly two inputs, otherwise you will get the error «Not enough input arguments».
For example, if you run the Mec134function in the command window without specifying any arguments:
You get this error:
Not enough input arguments.
Error in Mec134function (line 3)
theta_rad=(theta_deg./180).*pi;
If you run the Mec134function and specify two input arguments, «w» and «theta_deg» (assuming «w» and «theta_deg» are defined), you do not get the error message:
>> Mec134function(w,theta_deg)
If you have the file «Mec134function.m» open in the Editor and you try to run the function by pressing the «Run» button or F5, MATLAB runs the Mec134function without any input arguments, and you get the error «Not enough input arguments». The «Run» button dropdown menu then opens prompting you to enter values for the missing input arguments.
Add the desired values and press enter. The values you enter are set as the default inputs when you click the «Run» button or F5 in the future.
To change the values, press the down arrow below the «Run» button and enter new values.
更多回答(18 个)
sorry the function is
function [r]=Mec134function(w,theta_deg)
t2=10000;
theta_rad=(theta_deg./180).*pi;
t1=55090./(10*sin(theta_rad));
rx=(t1.*cos(theta_rad))-t2;
ry=w-(t1.*sin(theta_rad));
r=((rx).^2+(ry).^2).^0.5;
end
if that’s clearer 
Thanks 
will have a look at the «getting started»
I have a simple function:
function [r]=Mec134function(w,theta_deg)
t2=10000;
theta_rad=(theta_deg./180).*pi;
t1=55090./(10*sin(theta_rad));
rx=(t1.*cos(theta_rad))-t2;
ry=w-(t1.*sin(theta_rad));
r=((rx).^2+(ry).^2).^0.5;
end
that seems to give this error for line 2 but I’m not sure why.
I too am very new to Matlab, and tried to run the code above in .m (JP Donlon on Nov. 7th). However, I keep getting an error stating «Not enough input arguments.» I’m not sure what this means, because I have attempted to run other code by professors which works on other computers. Is it something with my preference settings?
Also, when I run the Code Analyzer, there are no issues…not sure what is going on.
How to rectify this error
Error using DetectFace (line 68)
Not enough input arguments.
the code is given below
I=imread(‘lena.jpg’);
minFace = 20;
maxFace = 4000;
overlappingThreshold = 0.5;
numThreads = 24;
if nargin > 2 && ~isempty(options)
if isfield(options, ‘minFace’) && ~isempty(options.minFace)
minFace = options.minFace;
end
if isfield(options, ‘maxFace’) && ~isempty(options.maxFace)
maxFace = options.maxFace;
end
if isfield(options, ‘overlappingThreshold’) && ~isempty(options.overlappingThreshold)
overlappingThreshold = options.overlappingThreshold;
end
if isfield(options, ‘numThreads’) && ~isempty(options.numThreads)
numThreads = options.numThreads;
end
end
if ~ismatrix(I)
I = rgb2gray(I);
end
candi_rects = NPDScan(model, I, minFace, maxFace, numThreads);
if isempty(candi_rects)
rects = [];
return;
end
clc; clear; close all;
xo=0.4;
A=[];
b=[];
Aeq=[];
beq=[];
Q=100;
R=1;
N = 50;
U0= zeros(100,1);
x=xo; h = 0.1;
xo=[-0.5,0.5];
options = optimoptions(@fmincon,‘Algorithm’,‘sqp’);
U = fmincon(@cost1,U0,[],[],[],[],[],[],@confuneq,options);
for k =1:N
S1= F(x(k),U(k));
S2=F(x(k)+0.5*h*S1,U(k));
S3=F(x(k)+0.5*h*S2,U(k));
S4=F(x(k)+h*S3,U(k));
x(k+1) = x(k) + (1/6)* (S1+ 2*S2+ 2*S3 + S4)*h;
k = k + 1 ;
end
plot(U);
grid on
figure(); plot(x)
grid on
I new to matlab.Can anyone help me to fix the iisue here.
Its showing not enough input arguments.
Hello sir,I am newer to matlab. I am getting error in this code like «preprocessing requries more input arugument to run». can you please to run this program. my project topic is recognition and matching fake logos using filters.
function img=preprocessing(I)
[x y o]=size(I);
if o==3
I=rgb2gray(I);
end
I=im2double(I);
med=medfilt2(I);
figure,imshow(med)
title(‘MEDIAN FILTERED IMAGE’)
[psnr_med,mse_med]=psnr(I,med)
out7= imfilter(I, fspecial(‘average’));
figure,imshow(out7)
title(‘MEAN FILTERED IMAGE’)
[psnr_avg,mse_avg]=psnr(I,out7)
gau=imfilter(I,fspecial(‘gaussian’));
figure,imshow(gau)
title(‘GAUSSIAN FILTER IMAGE’)
[psnr_gau,mse_avg]=psnr(I,gau)
psf=fspecial(‘gaussian’,7,10);
image1=imfilter(I,psf,‘conv’,‘circular’);
var1=(1/256)^2/12;
var2=var(I(:));
wei=deconvwnr(image1,psf,(var1/var2));
figure,imshow(wei);title(‘WEINER FILTERED IMAGE’);
[psnr_wei,mse_wei]=psnr(I,wei)
psnr_all=[psnr_med,psnr_avg,psnr_gau,psnr_wei];
psnr_max=max(psnr_all);
val=find(psnr_all==psnr_max);
if val==1
img=med;
disp(‘median have high psnr’);
elseif val==2
img=out7;
disp(‘mean have high psnr’);
elseif val==3
img=gau;
disp(‘gaussian have high psnr’);
else
img=wei;
disp(‘weiner have high psnr’);
end
I am getting error for below function as «Not enough input arguments. «
delayed_signal = mtapped_delay_fcn(input);
Hi I’m trying to run Dr. John Stockie’s matlab code but I am getting a «Not enough input argument» error. I’m not very well verse with Matlab, so I would appreciate any help…Thank you. I am pasting the code:
function C = ermak( x, y, z, H, Q, U, Wset, Wdep )
Umin = 0.0;
ay = 0.34; by = 0.82; az = 0.275; bz = 0.82;
sigmay = ay*abs(x).^by .* (x > 0);
sigmaz = az*abs(x).^bz .* (x > 0);
Kz = 0.5*az*bz*U*abs(x).^(bz-1) .* (x > 0);
if U < Umin,
C = 0 * z;
else
Wo = Wdep — 0.5*Wset;
C = Q ./ (2*pi*U*sigmay.*sigmaz) .* exp( -0.5*y.^2./sigmay.^2 ) .* …
exp( -0.5*Wset*(z-H)./Kz — Wset^2*sigmaz.^2/8./Kz.^2 ) .* …
( exp( -0.5*(z-H).^2./sigmaz.^2 ) + …
exp( -0.5*(z+H).^2./sigmaz.^2 ) — sqrt(2*pi)*Wo*sigmaz./Kz .* …
exp( Wo*(z+H)./Kz + 0.5*Wo^2*sigmaz.^2./Kz.^2 ) .* …
erfc( Wo*sigmaz/sqrt(2)./Kz + (z+H)./sqrt(2)./sigmaz ) );
ii = find(isnan(C) | isinf(C));
C(ii) = 0;
end
and the error message refers to «sigmay» in line 31
function test(num1, num2,small,s)
load (small, num1, num2)
s = sum(num1, num2)
end
this the code for this i’m getting these errors
Not enough input arguments.
Error in test (line 3)
load (small, num1, num2)
Hello. Am new in Matlab and I want to do my assignment with this function refraction_2layers and Matlab is saying error using refraction_2layers (line 18 and 25) Here is the whole program
function refraction_2layers(v1, v2, z, FIRST_ARRIVALS_ONLY);
if nargin < 4 FIRST_ARRIVALS_ONLY = 0; end
x = [0:5:300];
t1 = x./v1;
t2 = (2*z*sqrt(v2^2-v1^2)/(v1*v2))+x./v2;
xcrit = 2*z*v1/(sqrt(v2^2-v1^2));
if isreal(xcrit)
a = min(find(x>xcrit));
end
crossover = ((2*z*sqrt(v2^2-v1^2))/(v1*v2))/(1/v1-1/v2);
b = max(find(x<= crossover));
if FIRST_ARRIVALS_ONLY
plot(x(1:b),t1(1:b)*1000, ‘.—‘)
hold on
if isreal(t2)
plot(x(b:end), t2(b:end)*1000, ‘r.—‘)
end
else
plot(x,t1*1000, ‘.—‘)
hold on
if isreal(t2)
plot(x(a:end), t2(a:end)*1000, ‘r.—‘)
end
end
xlabel(‘GEOPHONE OFFSET (m)’)
ylabel(‘TIME (ms)’)
grid on
legend(‘DIRECT WAVE’, ‘HEAD WAVE’)
title([‘z1 = ‘, num2str(z), ‘ m; v1 = ‘, num2str(v1), ‘ m/s; v2 = ‘, num2str(v2), ‘ m/s’])
axis ([0 300 0 300])
hold off
I am really struggling to figure out this «not enough input arguments» error in my code. Any help would be greatly appreciated! This is for a batch distillation problem, and the error is referring to the temp function near the bottom. The code and error are below:
P = 912;
L0 = 100;
A = [6.90565 6.95464]; B=[1211.033 1344.8]; C=[220.79 219.482];
xtspan = linspace(0.40,0.80,100);
[xt, L] = ode45(@Moles, xtspan, L0);
L = L(end);
fprintf(‘The amount of liquid remaining in the still when liquid mole fraction of toluene reaches 0.80 is %f moles’, L);
function Kt = EquilibriumRatio(Psatt)
Kt = Psatt/P;
end
function Psatt = VaporPressuret(T,A,B,C)
Psatt = 10^(A(2)-B(2)/(T+C(2)));
end
function Psatb = VaporPressureb(T,A,B,C)
Psatb = 10^(A(1)-B(1)/(T+C(1)));
end
function dLdx = Moles(xt,L)
T0 = 95.585;
options = optimset(‘Display’,‘off’,‘TolX’,1e-6);
T = fzero(@temp, T0, options);
Psatt = VaporPressuret(T);
Kt = EquilibriumRatio(Psatt);
dLdx = L/(xt*(Kt-1));
end
function Tempfun = temp(T,xt,P,A,B,C)
Psatt = VaporPressuret(T,A,B,C);
Psatb = VaporPressureb(T,A,B,C);
Tempfun = Psatt*xt + Psatb*(1-xt) — P;
end
>> project2
Error using fzero (line 306)
FZERO cannot continue because user-supplied function_handle ==> temp failed with the error below.
Not enough input arguments.
Error in project2>Moles (line 30)
T = fzero(@temp, T0, options);
Error in odearguments (line 90)
f0 = feval(ode,t0,y0,args{:});
Error in ode45 (line 115)
odearguments(FcnHandlesUsed, solver_name, ode, tspan, y0, options, varargin);
Error in project2 (line 7)
[xt, L] = ode45(@Moles, xtspan, L0);
Hi,
I am getting error ‘Not enough input arguments.’ I am trying online trail oversion. When I click run icon, it does not allow me to enter the value for the input as there is no option for entering the values. Any advice here please?
Best
Sarah
hi
I am new to matlab. i am getting error message «extract_features» requires more input arguments to run.
anderror in command window :
>> Extract_Features
Not enough input arguments.
Error in Extract_Features (line 2)
img1 = imread(filename);
code is written below:
function Extract_Features(filename,flag)
if ndims(img1) == 3; img1 = rgb2gray(img1); end
disp([‘Extracting features from ‘ filename ‘ …’]);
plot(fir(fir1,1),fir(fir1,2),‘r+’);
plot(fir(fir3,1),fir(fir3,2),‘bo’);
filename2=filename; filename2(end-1)=‘x’; filename2(end)=‘t’;
save(filename2,‘fir’,‘-ascii’);
Can someone help me please
envelope = sqrt(movmean(rec_EMG.^2), ‘window’);
I was trying to do get the RMS but it says:
Error using movmean Not enough input arguments.
I didn’t understand that, as I already use two arguments there.
Thanks fo ryour help
Can any one help me this please
function u = Anti_Tv(g,my,gamma)
gHS = uint8(imadjust (g));
gGC = uint8(255.*((double(g)./255).^(gamma)));
g = double(g(:));
n = length(g);
b = zeros(2*n,1);
d = b;
u = g;
eer = 1;k = 1;
tol = 1e-3;
Lambda = 0.05
[B, Bt, BtB] = DiffOper(sqrt(n));
Not enough input arguments
Dear Matlab experts, If anyone one of you would like to assist me running the below code i would be really greatfule to you.
The error i am getting.
qardlecm
Not enough input arguments.
Error in qardlecm (line 24)
nn = size(data,1);
The code i want to run
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
function[bigphia,bigpia,thett,distthett] = qardlecm(data,ppp,qqq,tau)
pd = makedist(‘normal’,‘mu’,0,‘sigma’,1);
hb(jj,1) = (4.5*normpdf(icdf(pd,tau(jj,1)))^4/(nn*(2*icdf(pd,tau(jj,1))^2+1)^2))^0.2;
hs(jj,1) = za^(2/3)*(1.5*normpdf(icdf(pd,tau(jj,1)))^2/(nn*(2*icdf(pd,tau(jj,1))^2+1)))^(1/3);
xx = data(:,2:size(data,2));
ee = xx(2:nn,:) — xx(1:(nn-1),:);
eei = zeros(nn-qqq,qqq*k0);
eei(:, ii+1+(jj-1)*qqq) = ee((qqq+1-ii):(nn-ii),jj);
yyi(:,ii) = yy((1+ppp-ii):(nn-ii),1);
X = [eei((size(eei,1)+1-size(yyi,1)):size(eei,1),:), xxi((size(xxi,1)+1-size(yyi,1)):size(xxi,1),:), yyi];
X = [eei, xxi, yyi((size(yyi,1)+1-size(xxi,1)):size(yyi,1),:)];
ONEX = [ones(size(X,1),1),X];
Y = yy((nn-size(X,1)+1):nn,1);
bt = zeros(size(ONEX,2),ss);
[bt1] = qregressMatlab(Y,ONEX,tau(jj,1));
fh(jj,1) = mean(normpdf(-uu(:,jj)/hb(jj,1)))/hb(jj,1);
barw = zeros(nn-1,qqq*k0);
barw(jj:(nn-1),(k0*(jj-1)+1):k0*jj) = ee(2:(nn-jj+1),:);
tw = [ones(nn-1,1), barw];
mm = (xx((qqq+1):nn,:)’*xx((qqq+1):nn,:) — xx((qqq+1):nn,:)’*tw(qqq:(nn-1),:)*inv(tw(qqq:(nn-1),:)’*tw(qqq:(nn-1),:))*tw(qqq:(nn-1),:)’*xx((qqq+1):nn,:))/(nn-qqq)^2;
bb(jj,1) = 1/((1-sum(bt(2+(qqq+1)*k0:1+(qqq+1)*k0+ppp,jj),1)’)*fh(jj,1));
qq(jj,ii) = (min(psu,[],1)’ — tau(jj,1)*tau(ii,1))*bb(jj,1)*bb(ii,1);
midbt(:,jj) = bt(2+qqq*k0:1+(qqq+1)*k0,jj)/(1-sum(bt(2+(qqq+1)*k0:1+(qqq+1)*k0+ppp,jj),1)’);
bigbt = reshape(midbt,[],1);
bigbtmm = kron(qq,inv(mm));
wwj = zeros(nn-ppp,qqq*k0);
yyj(:,jj) = yy((ppp+1-jj):(nn-jj),1);
wwj(:,jj+(ii-1)*qqq) = ee((ppp-jj+2):(nn-jj+1),ii);
kk = zeros(nn-ppp,ss*ppp);
ONEX = [ones(nn-ppp,1),xxj,wwj];
[bbt] = qregressMatlab(Y,ONEX,tau(ii,1));
kk(:,jj+(ii-1)*ppp) = kkk;
llla = (kka’*kka — kka’*tilw*inv(tilw’*tilw)*tilw’*kka)/(nn-ppp);
wwj = zeros(nn-qqq,qqq*k0);
yyj(:,jj) = yy((qqq+1-jj):(nn-jj),1);
wwj(:,jj+(ii-1)*qqq) = ee((qqq-jj+2):(nn-jj+1),ii);
kk = zeros(nn-qqq,ss*ppp);
ONEX = [ones(nn-qqq,1), xxj, wwj];
[bbt] = qregressMatlab(Y,ONEX,tau(jj,1));
kk(:,jj+(ii-1)*ppp) = kkk;
llla = (kka’*kka — kka’*tilw*inv(tilw’*tilw)*tilw’*kka)/(nn-qqq);
cc(jj,ii) = (min(psu,[],1)’ — tau(jj,1)*tau(ii,1))/(fh(ii,1)*fh(jj,1));
bigpia = zeros(ss*(ppp-1),ss*(ppp-1));
psu = inv(llla((jj-1)*(ppp-1)+1:jj*(ppp-1),(jj-1)*(ppp-1)+1:jj*(ppp-1)))*llla((jj-1)*(ppp-1)+1:jj*(ppp-1),(ii-1)*(ppp-1)+1:ii*(ppp-1))*inv(llla((ii-1)*(ppp-1)+1:ii*(ppp-1),(ii-1)*(ppp-1)+1:ii*(ppp-1)));
bigpia((jj-1)*(ppp-1)+1:jj*(ppp-1),(ii-1)*(ppp-1)+1:ii*(ppp-1)) = cc(jj,ii)*psu;
midphi(:,jj) = bt(2+(qqq+1)*k0:1+(qqq+1)*k0+ppp,jj);
bigphi = reshape(midphi,[],1);
bigphia = [bigphia1; bigphia2; bigphia3];
dg = [nn^(1/2),0,0; 0,nn^(1/2),0; 0,0,nn];
r2 = sum(tilwb,1)*(nn-2)^(-1);
r3 = sum(xx(3:nn,1),1)*(nn-2)^(-3/2);
rh9 = xx(3:nn,1)’*xx(3:nn,1);
QQQ = [r1, r2, r3 ; r4, r5, r6; r7, r8, r9];
psiu(rr,jj) = tau(jj,1)-1;
sigmma = psiu’*psiu*(1/(nn-2));
sigma1 = mean(psiu1.^(2));
sigma2 = mean(psiu2.^(2));
sigma3 = mean(psiu3.^(2));
distmt1 = nn*fh(1,1)^(-2)*sigmma(1,1)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt2 = nn*fh(1,1)^(-1)*fh(2,1)^(-1)*sigmma(1,2)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt3 = nn*fh(1,1)^(-1)*fh(3,1)^(-1)*sigmma(1,3)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt4 = nn*fh(2,1)^(-1)*fh(1,1)^(-1)*sigmma(2,1)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt5 = nn*fh(2,1)^(-2)*sigmma(2,2)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt6 = nn*fh(2,1)^(-1)*fh(3,1)^(-1)*sigmma(2,3)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt7 = nn*fh(3,1)^(-1)*fh(1,1)^(-1)*sigmma(3,1)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt8 = nn*fh(3,1)^(-1)*fh(2,1)^(-1)*sigmma(3,2)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt9 = nn*fh(3,1)^(-2)*sigmma(3,3)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distcon1 = A11 + A12 + A13;
distcon2 = A21 + A22 + A23;
distcon3 = A31 + A32 + A33;
distcon4 = A41 + A42 + A43;
distcon5 = A51 + A52 + A53;
distcon6 = A61 + A62 + A63;
distcon7 = A71 + A72 + A73;
distcon8 = A81 + A82 + A83;
distcon9 = A91 + A92 + A93;
distthett = [distcon1, distcon2, distcon3 ; distcon4, distcon5, distcon6 ; distcon7, distcon8, distcon9];
thett1 = bt(2,1) + bt(3,1);
thett2 = bt(2,2) + bt(3,2);
thett3 = bt(2,3) + bt(3,3);
thett = [thett1 ; thett2 ; thett3];
I get Unrecognized function or variable ‘theta’.
how to fix it
%**************************************************************************
% polar_dB(theta,rho,rmin,rmax,rticks,line_style)
%**************************************************************************
% POLAR_DB is a MATLAB function that plots 2-D patterns in
% polar coordinates where:
% 0 <= THETA (in degrees) <= 360
% -infinity < RHO (in dB) < +infinity
%
% Input Parameters Description
% —————————-
% — theta (in degrees) must be a row vector from 0 to 360 degrees
% — rho (in dB) must be a row vector
% — rmin (in dB) sets the minimum limit of the plot (e.g., -60 dB)
% — rmax (in dB) sets the maximum limit of the plot (e.g., 0 dB)
% — rticks is the # of radial ticks (or circles) desired. (e.g., 4)
% — linestyle is solid (e.g., ‘-‘) or dashed (e.g., ‘—‘)
%
% Credits:
% S. Bellofiore
% S. Georgakopoulos
% A. C. Polycarpou
% C. Wangsvick
% C. Bishop
%
% Tabulate your data accordingly, and call polar_dB to provide the
% 2-D polar plot
%
% Note: This function is different from the polar.m (provided by
% MATLAB) because RHO is given in dB, and it can be negative
%——————————————————————————
function hpol =polar_dB(theta,rho,rmin,rmax,rticks,line_style)
% Convert degrees into radians
theta= theta* pi/180;
% Font size, font style and line width parameters
font_size = 16;
font_name = ‘Times’;
line_width = 1.5;
if nargin < 5
error(‘Requires 5 or 6 input arguments.’)
elseif nargin == 5
if isstr(rho)
line_style = rho;
rho = theta;
[mr,nr] = size(rho);
if mr == 1
theta = 1:nr;
else
th = (1:mr)’;
theta = th(:,ones(1,nr));
end
else
line_style = ‘auto’;
end
elseif nargin == 1
line_style = ‘auto’;
rho = theta;
[mr,nr] = size(rho);
if mr == 1
theta = 1:nr;
else
th = (1:mr)’;
theta = th(:,ones(1,nr));
end
end
if isstr(theta) || isstr(rho)
error(‘Input arguments must be numeric.’);
end
if any(size(theta) ~= size(rho))
error(‘THETA and RHO must be the same size.’);
end
% get hold state
cax = newplot;
next = lower(get(cax,‘NextPlot’));
hold_state = ishold;
% get x-axis text color so grid is in same color
tc = get(cax,‘xcolor’);
% Hold on to current Text defaults, reset them to the
% Axes’ font attributes so tick marks use them.
fAngle = get(cax, ‘DefaultTextFontAngle’);
fName = get(cax, ‘DefaultTextFontName’);
fSize = get(cax, ‘DefaultTextFontSize’);
fWeight = get(cax, ‘DefaultTextFontWeight’);
set(cax, ‘DefaultTextFontAngle’, get(cax, ‘FontAngle’), …
‘DefaultTextFontName’, font_name, …
‘DefaultTextFontSize’, font_size, …
‘DefaultTextFontWeight’, get(cax, ‘FontWeight’) )
% only do grids if hold is off
if ~hold_state
% make a radial grid
hold on;
% v returns the axis limits
% changed the following line to let the y limits become negative
hhh=plot([0 max(theta(:))],[min(rho(:)) max(rho(:))]);
v = [get(cax,‘xlim’) get(cax,‘ylim’)];
ticks = length(get(cax,‘ytick’));
delete(hhh);
% check radial limits (rticks)
if rticks > 5 % see if we can reduce the number
if rem(rticks,2) == 0
rticks = rticks/2;
elseif rem(rticks,3) == 0
rticks = rticks/3;
end
end
% define a circle
th = 0:pi/50:2*pi;
xunit = cos(th);
yunit = sin(th);
% now really force points on x/y axes to lie on them exactly
inds = 1:(length(th)-1)/4:length(th);
xunits(inds(2:2:4)) = zeros(2,1);
yunits(inds(1:2:5)) = zeros(3,1);
rinc = (rmax-rmin)/rticks;
% label r
% change the following line so that the unit circle is not multiplied
% by a negative number. Ditto for the text locations.
for i=(rmin+rinc):rinc:rmax
is = i — rmin;
plot(xunit*is,yunit*is,‘-‘,‘color’,tc,‘linewidth’,0.5);
text(0,is+rinc/20,[‘ ‘ num2str(i)],‘verticalalignment’,‘bottom’ );
end
% plot spokes
th = (1:6)*2*pi/12;
cst = cos(th); snt = sin(th);
cs = [-cst; cst];
sn = [-snt; snt];
plot((rmax-rmin)*cs,(rmax-rmin)*sn,‘-‘,‘color’,tc,‘linewidth’,0.5);
% plot the ticks
george=(rmax-rmin)/30; % Length of the ticks
th2 = (0:36)*2*pi/72;
cst2 = cos(th2); snt2 = sin(th2);
cs2 = [(rmax-rmin-george)*cst2; (rmax-rmin)*cst2];
sn2 = [(rmax-rmin-george)*snt2; (rmax-rmin)*snt2];
plot(cs2,sn2,‘-‘,‘color’,tc,‘linewidth’,0.15); % 0.5
plot(-cs2,-sn2,‘-‘,‘color’,tc,‘linewidth’,0.15); % 0.5
% annotate spokes in degrees
% Changed the next line to make the spokes long enough
rt = 1.1*(rmax-rmin);
for i = 1:max(size(th))
text(rt*cst(i),rt*snt(i),int2str(abs(i*30-90)),‘horizontalalignment’,‘center’ );
if i == max(size(th))
loc = int2str(90);
elseif i*30+90<=180
loc = int2str(i*30+90);
else
loc = int2str(180-(i*30+90-180));
end
text(-rt*cst(i),-rt*snt(i),loc,‘horizontalalignment’,‘center’ );
end
% set viewto 2-D
view(0,90);
% set axis limits
% Changed the next line to scale things properly
axis((rmax-rmin)*[-1 1 -1.1 1.1]);
end
% Reset defaults.
set(cax, ‘DefaultTextFontAngle’, fAngle , …
‘DefaultTextFontName’, font_name, …
‘DefaultTextFontSize’, fSize, …
‘DefaultTextFontWeight’, fWeight );
% transform data to Cartesian coordinates.
% changed the next line so negative rho are not plotted on the other side
for i = 1:length(rho)
if (rho(i) > rmin)
if theta(i)*180/pi >=0 && theta(i)*180/pi <=90
xx(i) = (rho(i)-rmin)*cos(pi/2-theta(i));
yy(i) = (rho(i)-rmin)*sin(pi/2-theta(i));
elseif theta(i)*180/pi >=90
xx(i) = (rho(i)-rmin)*cos(-theta(i)+pi/2);
yy(i) = (rho(i)-rmin)*sin(-theta(i)+pi/2);
elseif theta(i)*180/pi < 0
xx(i) = (rho(i)-rmin)*cos(abs(theta(i))+pi/2);
yy(i) = (rho(i)-rmin)*sin(abs(theta(i))+pi/2);
end
else
xx(i) = 0;
yy(i) = 0;
end
end
% plot data on top of grid
if strcmp(line_style,‘auto’)
q = plot(xx,yy);
else
q = plot(xx,yy,line_style);
end
if nargout > 0
hpol = q;
end
if ~hold_state
axis(‘equal’);axis(‘off’);
end
% reset hold state
if ~hold_state, set(cax,‘NextPlot’,next); end
Dear Matlab expert, please help me. My Matlab is 2016a, I try to run a code but there is an error «Not enough input arguments.»
Error in astar (line 3)
ssNode = startNode;
function [ClosedList,cost,heuristic,func,iteration] = astar(source,target,weights,heuristics,startNode,goalNode)
[s,t,n,sNode,gNode] = refactor(source,target,weights,sNode,ggNode);
ClosedList = struct(‘Path’ ,sNode,‘Cost’,0,‘Heuristic’,heuristics(sNode),‘F’,heuristics(sNode));
OpenList = [OpenList ClosedList];
while(isGoalReached(OpenList,gNode)==0 && ~isempty(OpenList)) [minI,minP] = minPath(OpenList);
newPaths = getNewPaths(s,t,weights,heuristics,minP); OpenList = [OpenList newPaths];
[~,minP] = minPath(OpenList);
ClosedList = n(minP.Path);
heuristic = minP.Heuristic;
function [minIndex,ClosedList] = minPath(paths)
ClosedList = paths(minIndex);
if(paths(i).F < ClosedList.F)
ClosedList = paths(minIndex);
function isGoal = isGoalReached(paths,goalNode)
[~,minP] = minPath(paths);
if(minP.Path(length(minP.Path)) == goalNode)
function weight = getWeight(s,t,weights,nodeA,nodeB)
if(s(i)==nodeA && t(i)==nodeB)
function paths = getNewPaths(s,t,w,h,path)
uniqueNodes = getNodes(s,t);
currentNode = path.Path(length(path.Path)); childs = getChilds(s,t,currentNode);
if(isempty(find(path.Path==childs(i), 1)))
c = path.Cost + getWeight(s,t,w,currentNode,childs(i));
heur = h(uniqueNodes==childs(i));
p = struct(‘Path’,[path.Path childs(i)],‘Cost’,c,‘Heuristic’,heur,‘F’,f);
function childs = getChilds(source,target,node)
childs = sort(target(source==node));
function nodes = getNodes(s,t)
nodes = unique(horzcat(s,t));
function [s,t,n,sn,gn] = refactor(source,target,~,startNode,goalNode)
uNodes = unique(horzcat(source,target)); n = uNodes;
uNodes = unique(horzcat(source,target));
[~,sIndex] = ismember(source(i),uNodes);
[~,tIndex] = ismember(target(i),uNodes);
另请参阅
类别
Community Treasure Hunt
Find the treasures in MATLAB Central and discover how the community can help you!
Start Hunting!
发生错误
由于页面发生更改,无法完成操作。请重新加载页面以查看其更新后的状态。
Translated by 
Содержание
- Why is there error?
- Direct link to this question
- Direct link to this question
- Direct link to this comment
- Direct link to this comment
- Accepted Answer
- Direct link to this answer
- Direct link to this answer
- More Answers (0)
- See Also
- Categories
- Community Treasure Hunt
- How to Get Best Site Performance
- Americas
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Error using exp matlab
- Examples
- Numeric Representation of e
- Euler’s Identity
- Plot Exponential Function
- Input Arguments
- X — Input array scalar | vector | matrix | multidimensional array
- Output Arguments
- Y — Exponential values scalar | vector | matrix | multidimensional array
- Extended Capabilities
- Tall Arrays Calculate with arrays that have more rows than fit in memory.
- C/C++ Code Generation Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
- GPU Code Generation Generate CUDA® code for NVIDIA® GPUs using GPU Coder™.
- Thread-Based Environment Run code in the background using MATLAB® backgroundPool or accelerate code with Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool .
- GPU Arrays Accelerate code by running on a graphics processing unit (GPU) using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
- Distributed Arrays Partition large arrays across the combined memory of your cluster using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
- Error using exp matlab
- Examples
- Numeric Representation of e
- Euler’s Identity
- Plot Exponential Function
- Input Arguments
- X — Input array scalar | vector | matrix | multidimensional array
- Output Arguments
- Y — Exponential values scalar | vector | matrix | multidimensional array
- Extended Capabilities
- Tall Arrays Calculate with arrays that have more rows than fit in memory.
- C/C++ Code Generation Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
- GPU Code Generation Generate CUDA® code for NVIDIA® GPUs using GPU Coder™.
- Thread-Based Environment Run code in the background using MATLAB® backgroundPool or accelerate code with Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool .
- GPU Arrays Accelerate code by running on a graphics processing unit (GPU) using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
- Distributed Arrays Partition large arrays across the combined memory of your cluster using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
- Error using inline/subsref (line 13) Not enough inputs to inline function.
- Direct link to this question
- Direct link to this question
- Accepted Answer
- Direct link to this answer
- Direct link to this answer
- Direct link to this comment
- Direct link to this comment
- More Answers (0)
- See Also
- Categories
- Community Treasure Hunt
- How to Get Best Site Performance
- Americas
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Документация
- Синтаксис
- Описание
- Примеры
- Числовое Представление e
- Идентичность Эйлера
- Графическое изображение показательной функции
- Входные параметры
- X — Входной массив скаляр | вектор | матрица | многомерный массив
- Выходные аргументы
- Y — Экспоненциальные значения скаляр | вектор | матрица | многомерный массив
- Расширенные возможности
- «Высокие» массивы Осуществление вычислений с массивами, которые содержат больше строк, чем помещается в памяти.
- Генерация кода C/C++ Генерация кода C и C++ с помощью MATLAB® Coder™.
- Генерация кода графического процессора Сгенерируйте код CUDA® для NVIDIA® графические процессоры с помощью GPU Coder™.
- Основанная на потоке среда Запустите код в фоновом режиме с помощью MATLAB® backgroundPool или ускорьте код с Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool .
- Массивы графического процессора Ускорьте код путем работы графического процессора (GPU) с помощью Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
- Распределенные массивы Большие массивы раздела через объединенную память о вашем кластере с помощью Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
- Смотрите также
- Открытый пример
- Документация MATLAB
- Поддержка
Why is there error?
Direct link to this question
Direct link to this question
1 Comment
Accepted Answer
Direct link to this answer
Direct link to this answer
0 Comments
More Answers (0)
See Also
Categories
Find the treasures in MATLAB Central and discover how the community can help you!
An Error Occurred
Unable to complete the action because of changes made to the page. Reload the page to see its updated state.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list:
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- Deutsch
- English
- Français
- United Kingdom (English)
Asia Pacific
- Australia (English)
- India (English)
- New Zealand (English)
- 中国
- 简体中文 Chinese
- English
- 日本 Japanese (日本語)
- 한국 Korean (한국어)
Accelerating the pace of engineering and science
MathWorks is the leading developer of mathematical computing software for engineers and scientists.
Источник
Error using exp matlab
Y = exp( X ) returns the exponential e x for each element in array X . For complex elements z = x + iy , it returns the complex exponential
e z = e x ( cos y + i sin y ) .
Use expm to compute a matrix exponential.
Examples
Numeric Representation of e
Calculate the exponential of 1, which is Euler’s number, e .
Euler’s Identity
Euler’s identity is the equality e i π + 1 = 0 .
Compute the value of e i π .
Plot Exponential Function
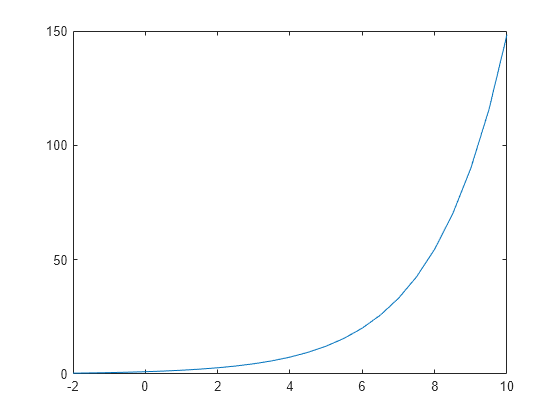
Plot y = e x / 2 for x values in the range [ — 2 , 1 0 ] .
Input Arguments
X — Input array
scalar | vector | matrix | multidimensional array
Input array, specified as a scalar, vector, matrix, or multidimensional array.
Data Types: single | double
Complex Number Support: Yes
Output Arguments
Y — Exponential values
scalar | vector | matrix | multidimensional array
Exponential values, returned as a scalar, vector, matrix, or multidimensional array.
For real values of X in the interval (- Inf , Inf ), Y is in the interval ( 0 , Inf ). For complex values of X , Y is complex. The data type of Y is the same as that of X .
Extended Capabilities
Tall Arrays
Calculate with arrays that have more rows than fit in memory.
This function fully supports tall arrays. For more information, see Tall Arrays.
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
GPU Code Generation
Generate CUDA® code for NVIDIA® GPUs using GPU Coder™.
Thread-Based Environment
Run code in the background using MATLAB® backgroundPool or accelerate code with Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool .
This function fully supports thread-based environments. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions in Thread-Based Environment.
GPU Arrays
Accelerate code by running on a graphics processing unit (GPU) using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
This function fully supports GPU arrays. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox) .
Distributed Arrays
Partition large arrays across the combined memory of your cluster using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
This function fully supports distributed arrays. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions with Distributed Arrays (Parallel Computing Toolbox) .
Источник
Error using exp matlab
Y = exp( X ) returns the exponential e x for each element in array X . For complex elements z = x + iy , it returns the complex exponential
e z = e x ( cos y + i sin y ) .
Use expm to compute a matrix exponential.
Examples
Numeric Representation of e
Calculate the exponential of 1, which is Euler’s number, e .
Euler’s Identity
Euler’s identity is the equality e i π + 1 = 0 .
Compute the value of e i π .
Plot Exponential Function
Plot y = e x / 2 for x values in the range [ — 2 , 1 0 ] .
Input Arguments
X — Input array
scalar | vector | matrix | multidimensional array
Input array, specified as a scalar, vector, matrix, or multidimensional array.
Data Types: single | double
Complex Number Support: Yes
Output Arguments
Y — Exponential values
scalar | vector | matrix | multidimensional array
Exponential values, returned as a scalar, vector, matrix, or multidimensional array.
For real values of X in the interval (- Inf , Inf ), Y is in the interval ( 0 , Inf ). For complex values of X , Y is complex. The data type of Y is the same as that of X .
Extended Capabilities
Tall Arrays
Calculate with arrays that have more rows than fit in memory.
This function fully supports tall arrays. For more information, see Tall Arrays.
C/C++ Code Generation
Generate C and C++ code using MATLAB® Coder™.
GPU Code Generation
Generate CUDA® code for NVIDIA® GPUs using GPU Coder™.
Thread-Based Environment
Run code in the background using MATLAB® backgroundPool or accelerate code with Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool .
This function fully supports thread-based environments. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions in Thread-Based Environment.
GPU Arrays
Accelerate code by running on a graphics processing unit (GPU) using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
This function fully supports GPU arrays. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions on a GPU (Parallel Computing Toolbox) .
Distributed Arrays
Partition large arrays across the combined memory of your cluster using Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
This function fully supports distributed arrays. For more information, see Run MATLAB Functions with Distributed Arrays (Parallel Computing Toolbox) .
Источник
Error using inline/subsref (line 13) Not enough inputs to inline function.
Direct link to this question
Direct link to this question
0 Comments
Accepted Answer
Direct link to this answer
Direct link to this answer
1 Comment
More Answers (0)
See Also
Categories
Find the treasures in MATLAB Central and discover how the community can help you!
An Error Occurred
Unable to complete the action because of changes made to the page. Reload the page to see its updated state.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
You can also select a web site from the following list:
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
Americas
Europe
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Switzerland
- Deutsch
- English
- Français
- United Kingdom (English)
Asia Pacific
- Australia (English)
- India (English)
- New Zealand (English)
- 中国
- 简体中文 Chinese
- English
- 日本 Japanese (日本語)
- 한국 Korean (한국어)
Accelerating the pace of engineering and science
MathWorks is the leading developer of mathematical computing software for engineers and scientists.
Источник
Документация
Синтаксис
Описание
Y = exp( X ) возвращает экспоненциальный e x для каждого элемента в массиве X . Для комплексных элементов z = x + iy , это возвращает комплексную экпоненту
e z = e x ( cos y + i sin y ) .
Используйте expm вычислить матричный экспоненциал.
Примеры
Числовое Представление e
Вычислите экспоненциал 1, который является номером Эйлера, e .
Идентичность Эйлера
Идентичность Эйлера является равенством e i π + 1 = 0 .
Вычислите значение e i π .
Графическое изображение показательной функции
График y = e x / 2 для x значения в области значений [ — 2 , 1 0 ] .
Входные параметры
X — Входной массив
скаляр | вектор | матрица | многомерный массив
Входной массив, заданный как скалярный, векторный, матричный или многомерный массив.
Типы данных: single | double
Поддержка комплексного числа: Да
Выходные аргументы
Y — Экспоненциальные значения
скаляр | вектор | матрица | многомерный массив
Экспоненциальные значения, возвращенные как скаляр, вектор, матрица или многомерный массив.
Для вещественных значений X в интервале (- Inf Inf Y находится в интервале ( 0 Inf ). Для комплексных чисел X Y является комплексным. Тип данных Y совпадает с тем из X .
Расширенные возможности
«Высокие» массивы
Осуществление вычислений с массивами, которые содержат больше строк, чем помещается в памяти.
Генерация кода C/C++
Генерация кода C и C++ с помощью MATLAB® Coder™.
Генерация кода графического процессора
Сгенерируйте код CUDA® для NVIDIA® графические процессоры с помощью GPU Coder™.
Основанная на потоке среда
Запустите код в фоновом режиме с помощью MATLAB® backgroundPool или ускорьте код с Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool .
Эта функция полностью поддерживает основанные на потоке среды. Для получения дополнительной информации смотрите функции MATLAB Запуска в Основанной на потоке Среде.
Массивы графического процессора
Ускорьте код путем работы графического процессора (GPU) с помощью Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
Эта функция полностью поддерживает массивы графического процессора. Для получения дополнительной информации смотрите функции MATLAB Запуска на графическом процессоре (Parallel Computing Toolbox) .
Распределенные массивы
Большие массивы раздела через объединенную память о вашем кластере с помощью Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
Эта функция полностью поддерживает распределенные массивы. Для получения дополнительной информации смотрите функции MATLAB Запуска с Распределенными Массивами (Parallel Computing Toolbox) .
Смотрите также
Открытый пример
У вас есть модифицированная версия этого примера. Вы хотите открыть этот пример со своими редактированиями?
Документация MATLAB
Поддержка
© 1994-2021 The MathWorks, Inc.
1. Если смысл перевода понятен, то лучше оставьте как есть и не придирайтесь к словам, синонимам и тому подобному. О вкусах не спорим.
2. Не дополняйте перевод комментариями “от себя”. В исправлении не должно появляться дополнительных смыслов и комментариев, отсутствующих в оригинале. Такие правки не получится интегрировать в алгоритме автоматического перевода.
3. Сохраняйте структуру оригинального текста — например, не разбивайте одно предложение на два.
4. Не имеет смысла однотипное исправление перевода какого-то термина во всех предложениях. Исправляйте только в одном месте. Когда Вашу правку одобрят, это исправление будет алгоритмически распространено и на другие части документации.
5. По иным вопросам, например если надо исправить заблокированное для перевода слово, обратитесь к редакторам через форму технической поддержки.
Источник
It is a function (not an script) and it needs some input arguments to run (in this case A and x), so you cannot hit the run button and expect it to run.
The first way:
Instead you can use the command windows in MATLAB and enter the command:
A = rand(3,3); % define A here
x = ones(3,1); % define x here
test(A,x) % then run the function with its arguments
remember that A and x should be defined properly.
The second way is:
Also you can hit the little triangle besides the green run button (see the figure below), and it will show you another option, type command to run. And
there you can directly enter the same command test(A,x). After that, each time you just hit enter for this function and it runs this command instead of only the test command without any argument.
The third way:
function y = test(A, x)
%// TESTING CODE:
if nargin==0
A = default_value_for_A;
x = default_value_for_x;
end
... %// rest of the function code
This way allows you to click the play button and have your function run with no explicit input arguments. However, be advised that such a method should only be used:
- When debugging, so as not to allow users to call the function with no arguments if this is not its intended use case.
- If your function is not supposed to behave differently for a different number of inputs. See also function overloading in MATLAB based on number of input arguments.
MATLAB not enough input arguments
the reason why you get this error is because you run your code from this function script.
but you must run your code from your main script (the file that you invoke or use this function in it).
Related posts on MATLAB :
- How do you find the max of a row in MATLAB?
- How do you declare a string array in MATLAB?
- What is random function in Matlab?
- How do you write decimals in MATLAB?
- How do I completely Uninstall MATLAB?
- Does not equal MATLAB if statement?
- What is random integer in MATLAB?
- What are special characters in MATLAB?
- Is integer function in MATLAB?