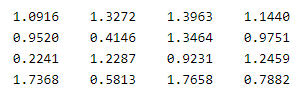5,059 views (last 30 days)
Hi, I’m very new to MATLAB and I am having some trouble. Lots of people have had the same problem but nobody seems to be able to explain or solve it in plain English. Could somebody please explain what this error is and how to fix it?
I have a simple function:
function [r]=Mec134function(w,theta_deg)
t2=10000;
theta_rad=(theta_deg./180).*pi;
t1=55090./(10*sin(theta_rad));
rx=(t1.*cos(theta_rad))-t2;
ry=w-(t1.*sin(theta_rad));
r=((rx).^2+(ry).^2).^0.5;
end
It seems to give this error for line 3 but I’m not sure why.
Thanks.
Accepted Answer
Your function defines 2 input arguments (w and theta_deg). When you run Mec134function, you must specify exactly two inputs, otherwise you will get the error «Not enough input arguments».
For example, if you run the Mec134function in the command window without specifying any arguments:
You get this error:
Not enough input arguments.
Error in Mec134function (line 3)
theta_rad=(theta_deg./180).*pi;
If you run the Mec134function and specify two input arguments, «w» and «theta_deg» (assuming «w» and «theta_deg» are defined), you do not get the error message:
>> Mec134function(w,theta_deg)
If you have the file «Mec134function.m» open in the Editor and you try to run the function by pressing the «Run» button or F5, MATLAB runs the Mec134function without any input arguments, and you get the error «Not enough input arguments». The «Run» button dropdown menu then opens prompting you to enter values for the missing input arguments.
Add the desired values and press enter. The values you enter are set as the default inputs when you click the «Run» button or F5 in the future.
To change the values, press the down arrow below the «Run» button and enter new values.
More Answers (18)
sorry the function is
function [r]=Mec134function(w,theta_deg)
t2=10000;
theta_rad=(theta_deg./180).*pi;
t1=55090./(10*sin(theta_rad));
rx=(t1.*cos(theta_rad))-t2;
ry=w-(t1.*sin(theta_rad));
r=((rx).^2+(ry).^2).^0.5;
end
if that’s clearer 
Thanks 
will have a look at the «getting started»
I have a simple function:
function [r]=Mec134function(w,theta_deg)
t2=10000;
theta_rad=(theta_deg./180).*pi;
t1=55090./(10*sin(theta_rad));
rx=(t1.*cos(theta_rad))-t2;
ry=w-(t1.*sin(theta_rad));
r=((rx).^2+(ry).^2).^0.5;
end
that seems to give this error for line 2 but I’m not sure why.
I too am very new to Matlab, and tried to run the code above in .m (JP Donlon on Nov. 7th). However, I keep getting an error stating «Not enough input arguments.» I’m not sure what this means, because I have attempted to run other code by professors which works on other computers. Is it something with my preference settings?
Also, when I run the Code Analyzer, there are no issues…not sure what is going on.
How to rectify this error
Error using DetectFace (line 68)
Not enough input arguments.
the code is given below
I=imread(‘lena.jpg’);
minFace = 20;
maxFace = 4000;
overlappingThreshold = 0.5;
numThreads = 24;
if nargin > 2 && ~isempty(options)
if isfield(options, ‘minFace’) && ~isempty(options.minFace)
minFace = options.minFace;
end
if isfield(options, ‘maxFace’) && ~isempty(options.maxFace)
maxFace = options.maxFace;
end
if isfield(options, ‘overlappingThreshold’) && ~isempty(options.overlappingThreshold)
overlappingThreshold = options.overlappingThreshold;
end
if isfield(options, ‘numThreads’) && ~isempty(options.numThreads)
numThreads = options.numThreads;
end
end
if ~ismatrix(I)
I = rgb2gray(I);
end
candi_rects = NPDScan(model, I, minFace, maxFace, numThreads);
if isempty(candi_rects)
rects = [];
return;
end
clc; clear; close all;
xo=0.4;
A=[];
b=[];
Aeq=[];
beq=[];
Q=100;
R=1;
N = 50;
U0= zeros(100,1);
x=xo; h = 0.1;
xo=[-0.5,0.5];
options = optimoptions(@fmincon,‘Algorithm’,‘sqp’);
U = fmincon(@cost1,U0,[],[],[],[],[],[],@confuneq,options);
for k =1:N
S1= F(x(k),U(k));
S2=F(x(k)+0.5*h*S1,U(k));
S3=F(x(k)+0.5*h*S2,U(k));
S4=F(x(k)+h*S3,U(k));
x(k+1) = x(k) + (1/6)* (S1+ 2*S2+ 2*S3 + S4)*h;
k = k + 1 ;
end
plot(U);
grid on
figure(); plot(x)
grid on
I new to matlab.Can anyone help me to fix the iisue here.
Its showing not enough input arguments.
Hello sir,I am newer to matlab. I am getting error in this code like «preprocessing requries more input arugument to run». can you please to run this program. my project topic is recognition and matching fake logos using filters.
function img=preprocessing(I)
[x y o]=size(I);
if o==3
I=rgb2gray(I);
end
I=im2double(I);
med=medfilt2(I);
figure,imshow(med)
title(‘MEDIAN FILTERED IMAGE’)
[psnr_med,mse_med]=psnr(I,med)
out7= imfilter(I, fspecial(‘average’));
figure,imshow(out7)
title(‘MEAN FILTERED IMAGE’)
[psnr_avg,mse_avg]=psnr(I,out7)
gau=imfilter(I,fspecial(‘gaussian’));
figure,imshow(gau)
title(‘GAUSSIAN FILTER IMAGE’)
[psnr_gau,mse_avg]=psnr(I,gau)
psf=fspecial(‘gaussian’,7,10);
image1=imfilter(I,psf,‘conv’,‘circular’);
var1=(1/256)^2/12;
var2=var(I(:));
wei=deconvwnr(image1,psf,(var1/var2));
figure,imshow(wei);title(‘WEINER FILTERED IMAGE’);
[psnr_wei,mse_wei]=psnr(I,wei)
psnr_all=[psnr_med,psnr_avg,psnr_gau,psnr_wei];
psnr_max=max(psnr_all);
val=find(psnr_all==psnr_max);
if val==1
img=med;
disp(‘median have high psnr’);
elseif val==2
img=out7;
disp(‘mean have high psnr’);
elseif val==3
img=gau;
disp(‘gaussian have high psnr’);
else
img=wei;
disp(‘weiner have high psnr’);
end
I am getting error for below function as «Not enough input arguments. «
delayed_signal = mtapped_delay_fcn(input);
Hi I’m trying to run Dr. John Stockie’s matlab code but I am getting a «Not enough input argument» error. I’m not very well verse with Matlab, so I would appreciate any help…Thank you. I am pasting the code:
function C = ermak( x, y, z, H, Q, U, Wset, Wdep )
Umin = 0.0;
ay = 0.34; by = 0.82; az = 0.275; bz = 0.82;
sigmay = ay*abs(x).^by .* (x > 0);
sigmaz = az*abs(x).^bz .* (x > 0);
Kz = 0.5*az*bz*U*abs(x).^(bz-1) .* (x > 0);
if U < Umin,
C = 0 * z;
else
Wo = Wdep — 0.5*Wset;
C = Q ./ (2*pi*U*sigmay.*sigmaz) .* exp( -0.5*y.^2./sigmay.^2 ) .* …
exp( -0.5*Wset*(z-H)./Kz — Wset^2*sigmaz.^2/8./Kz.^2 ) .* …
( exp( -0.5*(z-H).^2./sigmaz.^2 ) + …
exp( -0.5*(z+H).^2./sigmaz.^2 ) — sqrt(2*pi)*Wo*sigmaz./Kz .* …
exp( Wo*(z+H)./Kz + 0.5*Wo^2*sigmaz.^2./Kz.^2 ) .* …
erfc( Wo*sigmaz/sqrt(2)./Kz + (z+H)./sqrt(2)./sigmaz ) );
ii = find(isnan(C) | isinf(C));
C(ii) = 0;
end
and the error message refers to «sigmay» in line 31
function test(num1, num2,small,s)
load (small, num1, num2)
s = sum(num1, num2)
end
this the code for this i’m getting these errors
Not enough input arguments.
Error in test (line 3)
load (small, num1, num2)
Hello. Am new in Matlab and I want to do my assignment with this function refraction_2layers and Matlab is saying error using refraction_2layers (line 18 and 25) Here is the whole program
function refraction_2layers(v1, v2, z, FIRST_ARRIVALS_ONLY);
if nargin < 4 FIRST_ARRIVALS_ONLY = 0; end
x = [0:5:300];
t1 = x./v1;
t2 = (2*z*sqrt(v2^2-v1^2)/(v1*v2))+x./v2;
xcrit = 2*z*v1/(sqrt(v2^2-v1^2));
if isreal(xcrit)
a = min(find(x>xcrit));
end
crossover = ((2*z*sqrt(v2^2-v1^2))/(v1*v2))/(1/v1-1/v2);
b = max(find(x<= crossover));
if FIRST_ARRIVALS_ONLY
plot(x(1:b),t1(1:b)*1000, ‘.—‘)
hold on
if isreal(t2)
plot(x(b:end), t2(b:end)*1000, ‘r.—‘)
end
else
plot(x,t1*1000, ‘.—‘)
hold on
if isreal(t2)
plot(x(a:end), t2(a:end)*1000, ‘r.—‘)
end
end
xlabel(‘GEOPHONE OFFSET (m)’)
ylabel(‘TIME (ms)’)
grid on
legend(‘DIRECT WAVE’, ‘HEAD WAVE’)
title([‘z1 = ‘, num2str(z), ‘ m; v1 = ‘, num2str(v1), ‘ m/s; v2 = ‘, num2str(v2), ‘ m/s’])
axis ([0 300 0 300])
hold off
I am really struggling to figure out this «not enough input arguments» error in my code. Any help would be greatly appreciated! This is for a batch distillation problem, and the error is referring to the temp function near the bottom. The code and error are below:
P = 912;
L0 = 100;
A = [6.90565 6.95464]; B=[1211.033 1344.8]; C=[220.79 219.482];
xtspan = linspace(0.40,0.80,100);
[xt, L] = ode45(@Moles, xtspan, L0);
L = L(end);
fprintf(‘The amount of liquid remaining in the still when liquid mole fraction of toluene reaches 0.80 is %f moles’, L);
function Kt = EquilibriumRatio(Psatt)
Kt = Psatt/P;
end
function Psatt = VaporPressuret(T,A,B,C)
Psatt = 10^(A(2)-B(2)/(T+C(2)));
end
function Psatb = VaporPressureb(T,A,B,C)
Psatb = 10^(A(1)-B(1)/(T+C(1)));
end
function dLdx = Moles(xt,L)
T0 = 95.585;
options = optimset(‘Display’,‘off’,‘TolX’,1e-6);
T = fzero(@temp, T0, options);
Psatt = VaporPressuret(T);
Kt = EquilibriumRatio(Psatt);
dLdx = L/(xt*(Kt-1));
end
function Tempfun = temp(T,xt,P,A,B,C)
Psatt = VaporPressuret(T,A,B,C);
Psatb = VaporPressureb(T,A,B,C);
Tempfun = Psatt*xt + Psatb*(1-xt) — P;
end
>> project2
Error using fzero (line 306)
FZERO cannot continue because user-supplied function_handle ==> temp failed with the error below.
Not enough input arguments.
Error in project2>Moles (line 30)
T = fzero(@temp, T0, options);
Error in odearguments (line 90)
f0 = feval(ode,t0,y0,args{:});
Error in ode45 (line 115)
odearguments(FcnHandlesUsed, solver_name, ode, tspan, y0, options, varargin);
Error in project2 (line 7)
[xt, L] = ode45(@Moles, xtspan, L0);
Hi,
I am getting error ‘Not enough input arguments.’ I am trying online trail oversion. When I click run icon, it does not allow me to enter the value for the input as there is no option for entering the values. Any advice here please?
Best
Sarah
hi
I am new to matlab. i am getting error message «extract_features» requires more input arguments to run.
anderror in command window :
>> Extract_Features
Not enough input arguments.
Error in Extract_Features (line 2)
img1 = imread(filename);
code is written below:
function Extract_Features(filename,flag)
if ndims(img1) == 3; img1 = rgb2gray(img1); end
disp([‘Extracting features from ‘ filename ‘ …’]);
plot(fir(fir1,1),fir(fir1,2),‘r+’);
plot(fir(fir3,1),fir(fir3,2),‘bo’);
filename2=filename; filename2(end-1)=‘x’; filename2(end)=‘t’;
save(filename2,‘fir’,‘-ascii’);
Can someone help me please
envelope = sqrt(movmean(rec_EMG.^2), ‘window’);
I was trying to do get the RMS but it says:
Error using movmean Not enough input arguments.
I didn’t understand that, as I already use two arguments there.
Thanks fo ryour help
Can any one help me this please
function u = Anti_Tv(g,my,gamma)
gHS = uint8(imadjust (g));
gGC = uint8(255.*((double(g)./255).^(gamma)));
g = double(g(:));
n = length(g);
b = zeros(2*n,1);
d = b;
u = g;
eer = 1;k = 1;
tol = 1e-3;
Lambda = 0.05
[B, Bt, BtB] = DiffOper(sqrt(n));
Not enough input arguments
Dear Matlab experts, If anyone one of you would like to assist me running the below code i would be really greatfule to you.
The error i am getting.
qardlecm
Not enough input arguments.
Error in qardlecm (line 24)
nn = size(data,1);
The code i want to run
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
function[bigphia,bigpia,thett,distthett] = qardlecm(data,ppp,qqq,tau)
pd = makedist(‘normal’,‘mu’,0,‘sigma’,1);
hb(jj,1) = (4.5*normpdf(icdf(pd,tau(jj,1)))^4/(nn*(2*icdf(pd,tau(jj,1))^2+1)^2))^0.2;
hs(jj,1) = za^(2/3)*(1.5*normpdf(icdf(pd,tau(jj,1)))^2/(nn*(2*icdf(pd,tau(jj,1))^2+1)))^(1/3);
xx = data(:,2:size(data,2));
ee = xx(2:nn,:) — xx(1:(nn-1),:);
eei = zeros(nn-qqq,qqq*k0);
eei(:, ii+1+(jj-1)*qqq) = ee((qqq+1-ii):(nn-ii),jj);
yyi(:,ii) = yy((1+ppp-ii):(nn-ii),1);
X = [eei((size(eei,1)+1-size(yyi,1)):size(eei,1),:), xxi((size(xxi,1)+1-size(yyi,1)):size(xxi,1),:), yyi];
X = [eei, xxi, yyi((size(yyi,1)+1-size(xxi,1)):size(yyi,1),:)];
ONEX = [ones(size(X,1),1),X];
Y = yy((nn-size(X,1)+1):nn,1);
bt = zeros(size(ONEX,2),ss);
[bt1] = qregressMatlab(Y,ONEX,tau(jj,1));
fh(jj,1) = mean(normpdf(-uu(:,jj)/hb(jj,1)))/hb(jj,1);
barw = zeros(nn-1,qqq*k0);
barw(jj:(nn-1),(k0*(jj-1)+1):k0*jj) = ee(2:(nn-jj+1),:);
tw = [ones(nn-1,1), barw];
mm = (xx((qqq+1):nn,:)’*xx((qqq+1):nn,:) — xx((qqq+1):nn,:)’*tw(qqq:(nn-1),:)*inv(tw(qqq:(nn-1),:)’*tw(qqq:(nn-1),:))*tw(qqq:(nn-1),:)’*xx((qqq+1):nn,:))/(nn-qqq)^2;
bb(jj,1) = 1/((1-sum(bt(2+(qqq+1)*k0:1+(qqq+1)*k0+ppp,jj),1)’)*fh(jj,1));
qq(jj,ii) = (min(psu,[],1)’ — tau(jj,1)*tau(ii,1))*bb(jj,1)*bb(ii,1);
midbt(:,jj) = bt(2+qqq*k0:1+(qqq+1)*k0,jj)/(1-sum(bt(2+(qqq+1)*k0:1+(qqq+1)*k0+ppp,jj),1)’);
bigbt = reshape(midbt,[],1);
bigbtmm = kron(qq,inv(mm));
wwj = zeros(nn-ppp,qqq*k0);
yyj(:,jj) = yy((ppp+1-jj):(nn-jj),1);
wwj(:,jj+(ii-1)*qqq) = ee((ppp-jj+2):(nn-jj+1),ii);
kk = zeros(nn-ppp,ss*ppp);
ONEX = [ones(nn-ppp,1),xxj,wwj];
[bbt] = qregressMatlab(Y,ONEX,tau(ii,1));
kk(:,jj+(ii-1)*ppp) = kkk;
llla = (kka’*kka — kka’*tilw*inv(tilw’*tilw)*tilw’*kka)/(nn-ppp);
wwj = zeros(nn-qqq,qqq*k0);
yyj(:,jj) = yy((qqq+1-jj):(nn-jj),1);
wwj(:,jj+(ii-1)*qqq) = ee((qqq-jj+2):(nn-jj+1),ii);
kk = zeros(nn-qqq,ss*ppp);
ONEX = [ones(nn-qqq,1), xxj, wwj];
[bbt] = qregressMatlab(Y,ONEX,tau(jj,1));
kk(:,jj+(ii-1)*ppp) = kkk;
llla = (kka’*kka — kka’*tilw*inv(tilw’*tilw)*tilw’*kka)/(nn-qqq);
cc(jj,ii) = (min(psu,[],1)’ — tau(jj,1)*tau(ii,1))/(fh(ii,1)*fh(jj,1));
bigpia = zeros(ss*(ppp-1),ss*(ppp-1));
psu = inv(llla((jj-1)*(ppp-1)+1:jj*(ppp-1),(jj-1)*(ppp-1)+1:jj*(ppp-1)))*llla((jj-1)*(ppp-1)+1:jj*(ppp-1),(ii-1)*(ppp-1)+1:ii*(ppp-1))*inv(llla((ii-1)*(ppp-1)+1:ii*(ppp-1),(ii-1)*(ppp-1)+1:ii*(ppp-1)));
bigpia((jj-1)*(ppp-1)+1:jj*(ppp-1),(ii-1)*(ppp-1)+1:ii*(ppp-1)) = cc(jj,ii)*psu;
midphi(:,jj) = bt(2+(qqq+1)*k0:1+(qqq+1)*k0+ppp,jj);
bigphi = reshape(midphi,[],1);
bigphia = [bigphia1; bigphia2; bigphia3];
dg = [nn^(1/2),0,0; 0,nn^(1/2),0; 0,0,nn];
r2 = sum(tilwb,1)*(nn-2)^(-1);
r3 = sum(xx(3:nn,1),1)*(nn-2)^(-3/2);
rh9 = xx(3:nn,1)’*xx(3:nn,1);
QQQ = [r1, r2, r3 ; r4, r5, r6; r7, r8, r9];
psiu(rr,jj) = tau(jj,1)-1;
sigmma = psiu’*psiu*(1/(nn-2));
sigma1 = mean(psiu1.^(2));
sigma2 = mean(psiu2.^(2));
sigma3 = mean(psiu3.^(2));
distmt1 = nn*fh(1,1)^(-2)*sigmma(1,1)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt2 = nn*fh(1,1)^(-1)*fh(2,1)^(-1)*sigmma(1,2)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt3 = nn*fh(1,1)^(-1)*fh(3,1)^(-1)*sigmma(1,3)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt4 = nn*fh(2,1)^(-1)*fh(1,1)^(-1)*sigmma(2,1)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt5 = nn*fh(2,1)^(-2)*sigmma(2,2)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt6 = nn*fh(2,1)^(-1)*fh(3,1)^(-1)*sigmma(2,3)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt7 = nn*fh(3,1)^(-1)*fh(1,1)^(-1)*sigmma(3,1)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt8 = nn*fh(3,1)^(-1)*fh(2,1)^(-1)*sigmma(3,2)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distmt9 = nn*fh(3,1)^(-2)*sigmma(3,3)*inv(dg)*inv(QQQ)*inv(dg);
distcon1 = A11 + A12 + A13;
distcon2 = A21 + A22 + A23;
distcon3 = A31 + A32 + A33;
distcon4 = A41 + A42 + A43;
distcon5 = A51 + A52 + A53;
distcon6 = A61 + A62 + A63;
distcon7 = A71 + A72 + A73;
distcon8 = A81 + A82 + A83;
distcon9 = A91 + A92 + A93;
distthett = [distcon1, distcon2, distcon3 ; distcon4, distcon5, distcon6 ; distcon7, distcon8, distcon9];
thett1 = bt(2,1) + bt(3,1);
thett2 = bt(2,2) + bt(3,2);
thett3 = bt(2,3) + bt(3,3);
thett = [thett1 ; thett2 ; thett3];
I get Unrecognized function or variable ‘theta’.
how to fix it
%**************************************************************************
% polar_dB(theta,rho,rmin,rmax,rticks,line_style)
%**************************************************************************
% POLAR_DB is a MATLAB function that plots 2-D patterns in
% polar coordinates where:
% 0 <= THETA (in degrees) <= 360
% -infinity < RHO (in dB) < +infinity
%
% Input Parameters Description
% —————————-
% — theta (in degrees) must be a row vector from 0 to 360 degrees
% — rho (in dB) must be a row vector
% — rmin (in dB) sets the minimum limit of the plot (e.g., -60 dB)
% — rmax (in dB) sets the maximum limit of the plot (e.g., 0 dB)
% — rticks is the # of radial ticks (or circles) desired. (e.g., 4)
% — linestyle is solid (e.g., ‘-‘) or dashed (e.g., ‘—‘)
%
% Credits:
% S. Bellofiore
% S. Georgakopoulos
% A. C. Polycarpou
% C. Wangsvick
% C. Bishop
%
% Tabulate your data accordingly, and call polar_dB to provide the
% 2-D polar plot
%
% Note: This function is different from the polar.m (provided by
% MATLAB) because RHO is given in dB, and it can be negative
%——————————————————————————
function hpol =polar_dB(theta,rho,rmin,rmax,rticks,line_style)
% Convert degrees into radians
theta= theta* pi/180;
% Font size, font style and line width parameters
font_size = 16;
font_name = ‘Times’;
line_width = 1.5;
if nargin < 5
error(‘Requires 5 or 6 input arguments.’)
elseif nargin == 5
if isstr(rho)
line_style = rho;
rho = theta;
[mr,nr] = size(rho);
if mr == 1
theta = 1:nr;
else
th = (1:mr)’;
theta = th(:,ones(1,nr));
end
else
line_style = ‘auto’;
end
elseif nargin == 1
line_style = ‘auto’;
rho = theta;
[mr,nr] = size(rho);
if mr == 1
theta = 1:nr;
else
th = (1:mr)’;
theta = th(:,ones(1,nr));
end
end
if isstr(theta) || isstr(rho)
error(‘Input arguments must be numeric.’);
end
if any(size(theta) ~= size(rho))
error(‘THETA and RHO must be the same size.’);
end
% get hold state
cax = newplot;
next = lower(get(cax,‘NextPlot’));
hold_state = ishold;
% get x-axis text color so grid is in same color
tc = get(cax,‘xcolor’);
% Hold on to current Text defaults, reset them to the
% Axes’ font attributes so tick marks use them.
fAngle = get(cax, ‘DefaultTextFontAngle’);
fName = get(cax, ‘DefaultTextFontName’);
fSize = get(cax, ‘DefaultTextFontSize’);
fWeight = get(cax, ‘DefaultTextFontWeight’);
set(cax, ‘DefaultTextFontAngle’, get(cax, ‘FontAngle’), …
‘DefaultTextFontName’, font_name, …
‘DefaultTextFontSize’, font_size, …
‘DefaultTextFontWeight’, get(cax, ‘FontWeight’) )
% only do grids if hold is off
if ~hold_state
% make a radial grid
hold on;
% v returns the axis limits
% changed the following line to let the y limits become negative
hhh=plot([0 max(theta(:))],[min(rho(:)) max(rho(:))]);
v = [get(cax,‘xlim’) get(cax,‘ylim’)];
ticks = length(get(cax,‘ytick’));
delete(hhh);
% check radial limits (rticks)
if rticks > 5 % see if we can reduce the number
if rem(rticks,2) == 0
rticks = rticks/2;
elseif rem(rticks,3) == 0
rticks = rticks/3;
end
end
% define a circle
th = 0:pi/50:2*pi;
xunit = cos(th);
yunit = sin(th);
% now really force points on x/y axes to lie on them exactly
inds = 1:(length(th)-1)/4:length(th);
xunits(inds(2:2:4)) = zeros(2,1);
yunits(inds(1:2:5)) = zeros(3,1);
rinc = (rmax-rmin)/rticks;
% label r
% change the following line so that the unit circle is not multiplied
% by a negative number. Ditto for the text locations.
for i=(rmin+rinc):rinc:rmax
is = i — rmin;
plot(xunit*is,yunit*is,‘-‘,‘color’,tc,‘linewidth’,0.5);
text(0,is+rinc/20,[‘ ‘ num2str(i)],‘verticalalignment’,‘bottom’ );
end
% plot spokes
th = (1:6)*2*pi/12;
cst = cos(th); snt = sin(th);
cs = [-cst; cst];
sn = [-snt; snt];
plot((rmax-rmin)*cs,(rmax-rmin)*sn,‘-‘,‘color’,tc,‘linewidth’,0.5);
% plot the ticks
george=(rmax-rmin)/30; % Length of the ticks
th2 = (0:36)*2*pi/72;
cst2 = cos(th2); snt2 = sin(th2);
cs2 = [(rmax-rmin-george)*cst2; (rmax-rmin)*cst2];
sn2 = [(rmax-rmin-george)*snt2; (rmax-rmin)*snt2];
plot(cs2,sn2,‘-‘,‘color’,tc,‘linewidth’,0.15); % 0.5
plot(-cs2,-sn2,‘-‘,‘color’,tc,‘linewidth’,0.15); % 0.5
% annotate spokes in degrees
% Changed the next line to make the spokes long enough
rt = 1.1*(rmax-rmin);
for i = 1:max(size(th))
text(rt*cst(i),rt*snt(i),int2str(abs(i*30-90)),‘horizontalalignment’,‘center’ );
if i == max(size(th))
loc = int2str(90);
elseif i*30+90<=180
loc = int2str(i*30+90);
else
loc = int2str(180-(i*30+90-180));
end
text(-rt*cst(i),-rt*snt(i),loc,‘horizontalalignment’,‘center’ );
end
% set viewto 2-D
view(0,90);
% set axis limits
% Changed the next line to scale things properly
axis((rmax-rmin)*[-1 1 -1.1 1.1]);
end
% Reset defaults.
set(cax, ‘DefaultTextFontAngle’, fAngle , …
‘DefaultTextFontName’, font_name, …
‘DefaultTextFontSize’, fSize, …
‘DefaultTextFontWeight’, fWeight );
% transform data to Cartesian coordinates.
% changed the next line so negative rho are not plotted on the other side
for i = 1:length(rho)
if (rho(i) > rmin)
if theta(i)*180/pi >=0 && theta(i)*180/pi <=90
xx(i) = (rho(i)-rmin)*cos(pi/2-theta(i));
yy(i) = (rho(i)-rmin)*sin(pi/2-theta(i));
elseif theta(i)*180/pi >=90
xx(i) = (rho(i)-rmin)*cos(-theta(i)+pi/2);
yy(i) = (rho(i)-rmin)*sin(-theta(i)+pi/2);
elseif theta(i)*180/pi < 0
xx(i) = (rho(i)-rmin)*cos(abs(theta(i))+pi/2);
yy(i) = (rho(i)-rmin)*sin(abs(theta(i))+pi/2);
end
else
xx(i) = 0;
yy(i) = 0;
end
end
% plot data on top of grid
if strcmp(line_style,‘auto’)
q = plot(xx,yy);
else
q = plot(xx,yy,line_style);
end
if nargout > 0
hpol = q;
end
if ~hold_state
axis(‘equal’);axis(‘off’);
end
% reset hold state
if ~hold_state, set(cax,‘NextPlot’,next); end
Dear Matlab expert, please help me. My Matlab is 2016a, I try to run a code but there is an error «Not enough input arguments.»
Error in astar (line 3)
ssNode = startNode;
function [ClosedList,cost,heuristic,func,iteration] = astar(source,target,weights,heuristics,startNode,goalNode)
[s,t,n,sNode,gNode] = refactor(source,target,weights,sNode,ggNode);
ClosedList = struct(‘Path’ ,sNode,‘Cost’,0,‘Heuristic’,heuristics(sNode),‘F’,heuristics(sNode));
OpenList = [OpenList ClosedList];
while(isGoalReached(OpenList,gNode)==0 && ~isempty(OpenList)) [minI,minP] = minPath(OpenList);
newPaths = getNewPaths(s,t,weights,heuristics,minP); OpenList = [OpenList newPaths];
[~,minP] = minPath(OpenList);
ClosedList = n(minP.Path);
heuristic = minP.Heuristic;
function [minIndex,ClosedList] = minPath(paths)
ClosedList = paths(minIndex);
if(paths(i).F < ClosedList.F)
ClosedList = paths(minIndex);
function isGoal = isGoalReached(paths,goalNode)
[~,minP] = minPath(paths);
if(minP.Path(length(minP.Path)) == goalNode)
function weight = getWeight(s,t,weights,nodeA,nodeB)
if(s(i)==nodeA && t(i)==nodeB)
function paths = getNewPaths(s,t,w,h,path)
uniqueNodes = getNodes(s,t);
currentNode = path.Path(length(path.Path)); childs = getChilds(s,t,currentNode);
if(isempty(find(path.Path==childs(i), 1)))
c = path.Cost + getWeight(s,t,w,currentNode,childs(i));
heur = h(uniqueNodes==childs(i));
p = struct(‘Path’,[path.Path childs(i)],‘Cost’,c,‘Heuristic’,heur,‘F’,f);
function childs = getChilds(source,target,node)
childs = sort(target(source==node));
function nodes = getNodes(s,t)
nodes = unique(horzcat(s,t));
function [s,t,n,sn,gn] = refactor(source,target,~,startNode,goalNode)
uNodes = unique(horzcat(source,target)); n = uNodes;
uNodes = unique(horzcat(source,target));
[~,sIndex] = ismember(source(i),uNodes);
[~,tIndex] = ismember(target(i),uNodes);
See Also
Categories
Community Treasure Hunt
Find the treasures in MATLAB Central and discover how the community can help you!
Start Hunting!
An Error Occurred
Unable to complete the action because of changes made to the page. Reload the page to see its updated state.
Introduction to Matlab not enough input arguments
Matlab provides the different functions to the user, in which that user can perform the different operations as per their requirement. We write the script or function in Matlab that takes in no input argument, and we try to run that script or function. At that time, Matlab showed an error message that there was not enough input argument because the function required the input argument that we write the script or function, and inside that function, we passed two matrices together. So this is not a valid way to write the script or function; in this case, we need to write a separate function or script. In this topic, we are going to learn about Matlab, not enough input arguments.
Syntax
specified function name sample = add (argument name 1, argument name 2)
sample = argument name 1+ argument name 2;
end
Explanation
In the above syntax, we use different parameters as follows.
specified function name: It is used to specify the function name with argument.
add: add is a function, and it is used to make the addition of two arguments that we pass inside the function.
In the above syntax, we created a function with a name sample, and we made the addition of two matrices that are argument name 1 and argument name 2, as shown in the above syntax.
How to solve Matlab’s not enough input arguments problem?
Now let’s see how to solve the not enough input argument problem in Matlab as follows.
Basically, there are two ways to solve this problem as follows.
1 By using the Command Prompt:
This is a very simple method to solve the not enough input argument error. In this method, we simply create the input whatever we require on the command prompt, and after that, we need to execute that input by using the function or script that we already write.
2 By using Matlab Editor:
Under the Run button, there is a dark arrow. In the event that you click on that arrow button, you can determine the variable you might want to get from the MATLAB workspace by composing the manner in which you need to call the capacity precisely, as you have found in technique 1. But, first, be certain that the variable you are indicating inside the function must exist in the MATLAB workspace.
Examples of Matlab not enough input arguments
Now let’s see the different examples of not enough input arguments in Matlab to better understand this problem as follows.
First, see how not enough input argument error occurs by using the following example as follows.
function Z = add(X, Y)
Z = X + Y;
end
Explanation
In the above example, we created a simple function, in which we write the function definition for addition. Here we pass the two arguments X and Y as shown in the above function, but it shows the error message like not enough input argument error because here we try to make the addition of two matrices, and this is not possible by using the above syntax. The final output of this program we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now let’s see how we can avoid this error by using different methods as follows.
The simplest way is to pass the input argument in the command prompt, and after that, we need to run a function with new values. So let’s see the example of this type as follows.
Write the following code in the command prompt as follows.
X = rand (4, 4)
Y = rand (4, 4)
Z = add (4, 4)
Explanation
In the above code, we use rand () to print the 4 by 4 arrays, and after that, we make the addition of X and Y arrays as shown in the above code. So in this way, we can avoid the not enough input argument error. The final output of this program we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Now let’s see another way to avoid this error as follows.
In the second method, we need to click on the Run button, open the dropdown menu, and write down the input argument name that we need to run but be assured that the argument name must be present in the function. Let’s see some screenshots of this method as follows.
In the above screen, we show the dropdown menu and write here the input argument that we need to execute. In this example, we pass X = rand (4,4) as shown in the below screenshot as follows.
After execution, the final result is shown below screenshot as follows.
How to avoid Matlab’s not enough input arguments problem?
Now let’s see how we can avoid not enough input argument problems in Matlab as follows.
First thing when we open a Matlab file in the editor, and we try to run that file, or we can say that function by using the Run button. At that time, Matlab runs that function without any argument; then, we will get an error message, not enough input argument. At that the same time drop-down menu is open through the Run button and enters the values for the missing argument for the function. So add different values as per our requirement, hit the enter now entered values map with the function, and click on the Run button. So in this way, we can avoid the not enough input argument problem.
Another way to avoid not enough input argument problems is that, suppose we created one function that is fun () and inside that we pass two arguments that A and B. At the same time, if we need to provide some more input arguments at that time, we need to use an anonymous function.
Now we have one more way to avoid the not enough input argument problem. We use the command line option when we execute the function at that same time; we need to pass the input argument for that function. By using this method, we can easily avoid this problem.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you learn Matlab, not enough input argument. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of not enough input argument, and we also see different examples of not enough input argument. From this article, we learned how and when we use Matlab not enough input argument.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Matlab not enough input arguments. Here we discuss the basic syntax and different examples of not enough input argument. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
- Matlab Mod
- Matlab Backslash
- Matlab limit
- Matlab Block Comment
Example
Often beginning MATLAB developers will use MATLAB’s editor to write and edit code, in particular custom functions with inputs and outputs. There is a Run button at the top that is available in recent versions of MATLAB:
Once the developer finishes with the code, they are often tempted to push the Run button. For some functions this will work fine, but for others they will receive a Not enough input arguments error and be puzzled about why the error occurs.
The reason why this error may not happen is because you wrote a MATLAB script or a function that takes in no input arguments. Using the Run button will run a test script or run a function assuming no input arguments. If your function requires input arguments, the Not enough input arguments error will occur as you have written a functions that expects inputs to go inside the function. Therefore, you cannot expect the function to run by simply pushing the Run button.
To demonstrate this issue, suppose we have a function mult that simply multiplies two matrices together:
function C = mult(A, B)
C = A * B;
end
In recent versions of MATLAB, if you wrote this function and pushed the Run button, it will give you the error we expect:
>> mult
Not enough input arguments.
Error in mult (line 2)
C = A * B;
There are two ways to resolve this issue:
Method #1 — Through the Command Prompt
Simply create the inputs you need in the Command Prompt, then run the function using those inputs you have created:
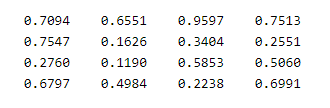
A = rand(5,5);
B = rand(5,5);
C = mult(A,B);
Method #2 — Interactively through the Editor
Underneath the Run button, there is a dark black arrow. If you click on that arrow, you can specify the variables you would like to get from the MATLAB workspace by typing the way you want to call the function exactly as how you have seen in method #1. Be sure that the variables you are specifying inside the function exist in the MATLAB workspace:
error
Выдать ошибку и отобразить сообщение
Синтаксис
Описание
пример
error( выдает ошибку и отображает сообщение об ошибке.msg)
error( отображает сообщение об ошибке, которое содержит символы преобразования форматирования, такие как используемые с MATLAB®msg,A1,...,An)
sprintf функция. Каждый символ преобразования в msg преобразован в одно из значений A1,...,An.
error( включает ошибочный идентификатор на исключении. Идентификатор позволяет вам отличить ошибки и управлять тем, что происходит, когда MATLAB сталкивается с ошибками. Можно включать любой из входных параметров в предыдущих синтаксисах.errID,___)
пример
error( выдает ошибку поля в скалярной структуре.errorStruct)
пример
error( обеспечивает предложенное исправление для исключения. Можно включать любой из входных параметров в предыдущих синтаксисах. correction,___)
Примеры
свернуть все
Бросок ошибки
msg = 'Error occurred.';
error(msg)
Бросок ошибки с форматированным сообщением
Выдайте отформатированное сообщение об ошибке с разрывом строки. Необходимо задать больше чем один входной параметр с error если вы хотите, чтобы MATLAB преобразовал специальные символы (такие как n) в сообщении об ошибке. Включайте информацию о классе переменной n в сообщении об ошибке.
n = 7; if ~ischar(n) error('Error. nInput must be a char, not a %s.',class(n)) end
Error.
Input must be a char, not a double.
Если вы только используете один входной параметр с error, затем MATLAB не преобразует n к разрыву строки.
if ~ischar(n) error('Error. nInput must be a char.') end
Error. nInput must be a char.
Выдайте ошибку с идентификатором.
if ~ischar(n) error('MyComponent:incorrectType',... 'Error. nInput must be a char, not a %s.',class(n)) end
Error.
Input must be a char, not a double.
Используйте MException.last просмотреть последнее неперехваченное исключение.
exception = MException.last
exception =
MException with properties:
identifier: 'MyComponent:incorrectType'
message: 'Error.
Input must be a char, not a double.'
cause: {0x1 cell}
stack: [0x1 struct]
Бросок структуры ошибки
Создайте структуру с полями идентификатора и сообщением. Чтобы сохранить пример простым, не используйте поле стека.
errorStruct.message = 'Data file not found.'; errorStruct.identifier = 'MyFunction:fileNotFound';
errorStruct =
message: 'Data file not found.'
identifier: 'MyFunction:fileNotFound'
Выдайте ошибку.
Выдайте ошибку с предложенным исправлением
Создайте функциональный hello это требует одного входного параметра. Добавьте предложенный входной параметр "world" к сообщению об ошибке.
function hello(audience) if nargin < 1 aac = matlab.lang.correction.AppendArgumentsCorrection('"world"'); error(aac, 'MATLAB:notEnoughInputs', 'Not enough input arguments.') end fprintf("Hello, %s!n", audience) end
Вызовите функцию без аргумента.
Error using hello (line 4)
Not enough input arguments.
Did you mean:
>> hello("world")
Входные параметры
свернуть все
msg — Информация об ошибке
вектор символов | строковый скаляр
Информация об ошибке в виде вектора символов или строкового скаляра. Это индикаторы сообщения как сообщение об ошибке. Чтобы отформатировать сообщение, используйте escape-последовательности, такие как t или n. Также можно использовать любые спецификаторы формата, поддержанные sprintf функция, такая как %s или %d. Задайте значения для спецификаторов преобразования через A1,...,An входные параметры. Для получения дополнительной информации см. Форматирующий текст.
Примечание
Необходимо задать больше чем один входной параметр с error если вы хотите, чтобы MATLAB преобразовал специальные символы (такие как tNS, и %d) в сообщении об ошибке.
Пример: 'File not found.'
errID — Идентификатор для ошибки
вектор символов | строковый скаляр
Идентификатор для ошибки в виде вектора символов или строкового скаляра. Используйте ошибочный идентификатор, чтобы помочь идентифицировать источник ошибки или управлять выбранным подмножеством ошибок в вашей программе.
Ошибочный идентификатор включает одно или несколько полей компонента и мнемоническое поле. Поля должны быть разделены двоеточием. Например, ошибочный идентификатор с полем component компонента и мнемоническое поле mnemonic задан как 'component:mnemonic'. И мнемонические поля компонента должны каждый начаться с буквы. Оставшиеся символы могут быть буквенно-цифровым индикатором (A–Z, a–z, 0–9) и символы нижнего подчеркивания. Никакие пробельные символы не могут появиться нигде в errID. Для получения дополнительной информации смотрите MException.
Пример: 'MATLAB:singularMatrix'
Пример: 'MATLAB:narginchk:notEnoughInputs'
A1,...,An Значения
вектор символов | строковый скаляр | числовой скаляр
Значения, которые заменяют спецификаторы преобразования в msgВ виде вектора символов, строкового скаляра или числового скаляра.
errorStruct — Информация о сообщении об ошибке
скалярная структура
Информация о сообщении об ошибке в виде скалярной структуры. Структура должна содержать по крайней мере одно из этих полей.
message |
Сообщение об ошибке. Для получения дополнительной информации смотрите |
identifier |
Ошибочный идентификатор. Для получения дополнительной информации смотрите |
stack |
Поле стека для ошибки. Когда |
correction — Предложенное исправление для этого исключения
matlab.lang.correction.AppendArgumentsCorrection возразите | matlab.lang.correction.ConvertToFunctionNotationCorrection возразите | matlab.lang.correction.ReplaceIdentifierCorrection объект
Советы
-
Когда вы выдаете ошибку, MATLAB получает информацию об этом и хранит ее в структуре данных, которая является объектом
MExceptionкласс. Можно получить доступ к информации в объекте исключения при помощиtry/catch. Или, если ваша программа завершает работу из-за исключения и возвращает управление в Командную строку, можно использоватьMException.last. -
MATLAB не прекращает осуществление программы, если ошибка происходит в
tryблок. В этом случае MATLAB передает управление кcatchблок. -
Если все входные параметры к
errorпусты, MATLAB не выдает ошибку.
Расширенные возможности
Генерация кода C/C++
Генерация кода C и C++ с помощью MATLAB® Coder™.
Указания и ограничения по применению:
Не оказывает влияния в автономном коде, даже когда обнаружение ошибки времени выполнения включено. Смотрите Генерируют Автономный Код C/C++, Который Обнаруживает и Ошибки времени выполнения Отчетов (MATLAB Coder).
Основанная на потоке среда
Запустите код в фоновом режиме с помощью MATLAB® backgroundPool или ускорьте код с Parallel Computing Toolbox™ ThreadPool.
Эта функция полностью поддерживает основанные на потоке среды. Для получения дополнительной информации смотрите функции MATLAB Запуска в Основанной на потоке Среде.
Массивы графического процессора
Ускорьте код путем работы графического процессора (GPU) с помощью Parallel Computing Toolbox™.
Указания и ограничения по применению:
-
Эта функция принимает массивы графического процессора, но не работает на графическом процессоре.
Для получения дополнительной информации смотрите функции MATLAB Запуска на графическом процессоре (Parallel Computing Toolbox).
Представлено до R2006a
SNOP.
Re: Матлаб, решение системы линейных диффуров
10.05.2016, 19:03
26/04/16
11
У меня все работает.
global T E U11 U22 U21 U12 G T0 X0 A
T = 1
E = 2
U11 = 3
U22 = 4
U12 = 5
U21 = 6
G = 7
T0 = [0 1]
X0=[1;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0];
A = [0*1i, 0, T, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, —2*G*1i, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
T, -T, -E-G*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U21-U11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U22-U12, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
-T, T, 0, E-G*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U11-U21, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U21-U22, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, —2*G*1i, -T, T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, T, -T, -E-G*1i, 0, 0, 0, U22-U12, 0, 0, 0, 0, U21-U11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, -T, T, 0, E-G*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U12-U22, 0, 0, 0, 0, U21-U11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, —2*G*1i, T, T, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, E+U11-U21-G*1i, 0, T, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U12-U22, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, 0, U22-U12-3*G*1i-E, T, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U21-U22, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, T, —2*G*1i, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, U21-E-U11-G*1i, T, T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U12-U22, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, T, 0, 0, T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, T, 0, —2*G*1i, T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, T, T U21-U11-E-G*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, U22-U12, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, E+U12-U22-3*G*1i, T, T, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, U11-U21, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, 2*(E+U11-U21-G*1i), 0, T, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, 0, —4*G*1i, T, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, T, E+U12-U22-3*G*1i, 0, 0, 0, -T, U11-U21, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, —2*G*1i, T, T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, T E+U11-U21-G*1i, 0, T, 0, U12-U22, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, T, 0, -E+U22-U12-3*G*1i, 0, 0, 0, U21-U11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, T, T, —2*G*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, E+U11+U12-U21-U22-3*G*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, T
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, E+U11+U12-U21-U22-3*G*1i, 0, 0, -T, T, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T+U21+U12-E-U11-U22-3*G*1i, 0, 0, 0, T, -T
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U11+U22-U12-U21-E-3*G*1i, T, -T, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, T, —2*G*1i, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, 0, -T, 0, —4*G*1i, 0, 0
0*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, —4*G*1i];
function dX=func1(t, X)
global T E U11 U22 U21 U12 G T0 X0 A
dX=A*X;
end
ode45(@func1, T0, X0)
Да, заработало, возможно end не хватало. А не подскажете, как теперь построить только X(1)? Писать отдельную m-функцию или можно сразу после ode писать?
— 10.05.2016, 19:15 —
Решил разделить на две части:
Функцию:
function dX=func2(t, X)
global T E U11 U22 U21 U12 G T0 X0 A
dX=A*X;
end
И Решение как-то так:
T=1; E=0.21; U11=0;U21=0;U12=0;U22=0; G=0.001; T0=[0,1];
X0=[1;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0;0];
A = [0*1i, 0, T, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, —2*G*1i, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
T, -T, -E-G*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U21-U11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U22-U12, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
-T, T, 0, E-G*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U11-U21, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U21-U22, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, —2*G*1i, -T, T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, T, -T, -E-G*1i, 0, 0, 0, U22-U12, 0, 0, 0, 0, U21-U11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, -T, T, 0, E-G*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U12-U22, 0, 0, 0, 0, U21-U11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, —2*G*1i, T, T, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, E+U11-U21-G*1i, 0, T, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U12-U22, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, 0, U22-U12-3*G*1i-E, T, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U21-U22, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, T, —2*G*1i, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, U21-E-U11-G*1i, T, T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U12-U22, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, T, 0, 0, T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, T, 0, —2*G*1i, T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, T, T U21-U11-E-G*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, U22-U12, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, E+U12-U22-3*G*1i, T, T, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, U11-U21, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, 2*(E+U11-U21-G*1i), 0, T, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, 0, —4*G*1i, T, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, T, E+U12-U22-3*G*1i, 0, 0, 0, -T, U11-U21, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, —2*G*1i, T, T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, T E+U11-U21-G*1i, 0, T, 0, U12-U22, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, T, 0, -E+U22-U12-3*G*1i, 0, 0, 0, U21-U11, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, T, T, —2*G*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, E+U11+U12-U21-U22-3*G*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, T
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, E+U11+U12-U21-U22-3*G*1i, 0, 0, -T, T, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T+U21+U12-E-U11-U22-3*G*1i, 0, 0, 0, T, -T
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, U11+U22-U12-U21-E-3*G*1i, T, -T, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, T, —2*G*1i, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, 0, -T, 0, —4*G*1i, 0, 0
0*1i, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, -T, 0, T, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, T, 0, -T, 0, 0, 0, 0, —4*G*1i];
ode45(@func2, T0, X0);
plot(T,X(:,1),‘x’);
grid on
xlabel(‘t’);
В результате получаю:
Error using odeplot (line 63)
Error updating the ODEPLOT window. Solution data may have been corrupted. Argument Y cannot be complex.
Error in ode45 (line 435)
stop = feval(outputFcn,tout_new,yout_new(outputs,:),»,outputArgs{:});
Error in reshenie (line 36)
ode45(@func2, T0, X0);
Что за хрень?
— 10.05.2016, 19:20 —
Можно ли сделать так, чтобы строилась только действительная часть, то есть чтобы он считал все полностью, но строил только действительную часть?