In my previous
Experts Exchange Articles, most have featured Basic and Intermediate VMware and Virtualisation Topics.
If you would like to read my Basic VMware articles, they are listed here for your convenience.
During this series of articles VMware released VMware vSphere 5.5 and VMware vSphere Hypervisor ESXi 5.5. These articles are also applicable to VMware vSphere Hypervisor ESXi 5.x and 5.5. For consistency, I have used VMware vSphere Hypervisor ESXi 5.1 through this series.
In this article we will show you
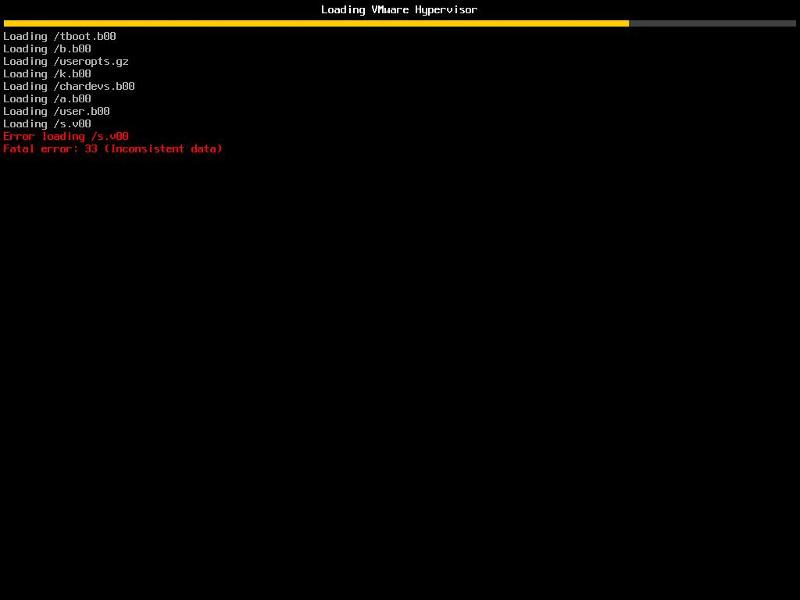
HOW TO: Fix the Error loading /s.v00 Fatal error: 33 (Inconsistent data) in the VMware vSphere Hypervisor. This method can be used with any version of the VMware vSphere Hypervisor from 4.0 to 5.5.
I feel this is a little more advanced, so I’ve not included it in the Basic VMware article series, as it does require some basic Linux skills and command usage.
Please note before you make any changes to a Production VMware vSphere Hypervisor Host server, which is hosting virtual machines, it is important to ensure you have valid backups of your virtual machines.
See my Experts Exchange article here —
Part 10: HOW TO: Backup (Export) and Restore (Import) virtual machines to VMware vSphere Hypervisor 5.1 for FREE if you want to use a quick and free method to backup important virtual machines.
If you perform a
Google Search for Fix the Error loading /s.v00 Fatal error: 33 (Inconsistent data) you are likely to stumble across the VMware Community forums, where VMware Administrators have reported this issue, or you will find the VMware Knowledgebase Article (2008817)
The issue is caused by either a corrupted file or faulty flash media if installed to USB flash drive or SD card, this fault can occur at random.
I’m writing this article,
HOW TO: Fix the Error loading /s.v00 Fatal error: 33 (Inconsistent data) in the VMware vSphere Hypervisor, because this has recently occurred to me three times, on different occasions, at different sites with servers from different manufacturers after changing Advanced Settings on the ESXi host. After a server restart the server fails to boot with
Error loading /s.v00 Fatal error: 33 (Inconsistent data).
The VMware knowledgebase would suggest reinstalling the ESXi OS. This however would result in a virgin installation and all the configuration would be lost, so reconfiguration would be required before the server could return to production.
This is how I fixed the issue.
Software Prerequisites
a copy of the file from a working installation of the VMware Hypervisor ESXi, e.g. /bootbank/s.v00
One of the following desktop hypervisors
1. Check the existing USB flash media or SD card for damage.
Remove the suspect USB flash drive or SD card from the physical server.
Download and install
Start the USB Imaging Tool application and create an image of the USB flash drive, this will create a backup copy of the flash drive, and whilst it reads the USB flash drive, it will detect and report any CRC checks if the flash drive has been damaged.
brand new good quality USB flash drive or SD card (e.g. HP, SanDisk, PNY, Lexar, Kingston).
2. Confirm the USB flash drive or SD card is Faulty using a virtual machine
To confirm if the VMware Hypervisor installation is faulty, I connect the backup USB flash drive I’ve created in Step 1, to a virtual machine, and try to start the Hypervisor. I’m using
in this guide, but any hypervisor can be used.
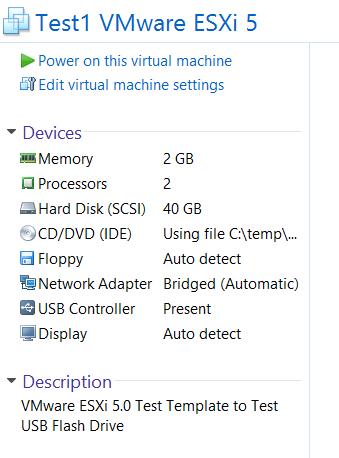
Create a small footprint VMware ESXi 5.0 Server virtual machine template, as long as the minimum requirements are met, you can BOOT the OS. e.g. 2 vCPUs, 2GB RAM, 40GB (thin hard disk) to test the USB flash drive.
Andy’s Handy Tip VMware Workstation cannot normally BOOT from a USB device, because the USB device needs to be available and connected to the VM before the VM is powered-on, and USB devices can only be connected to a VM, when the VM is powered on.
Catch22!! So I use the
Plop Boot Manager 5.0 LiveCD iso from
http://www.plop.at/en/bootmanager/plpbt.bin.htm. Connect the ISO to the CD ROM drive and BOOT the Virtual Machine as normal.
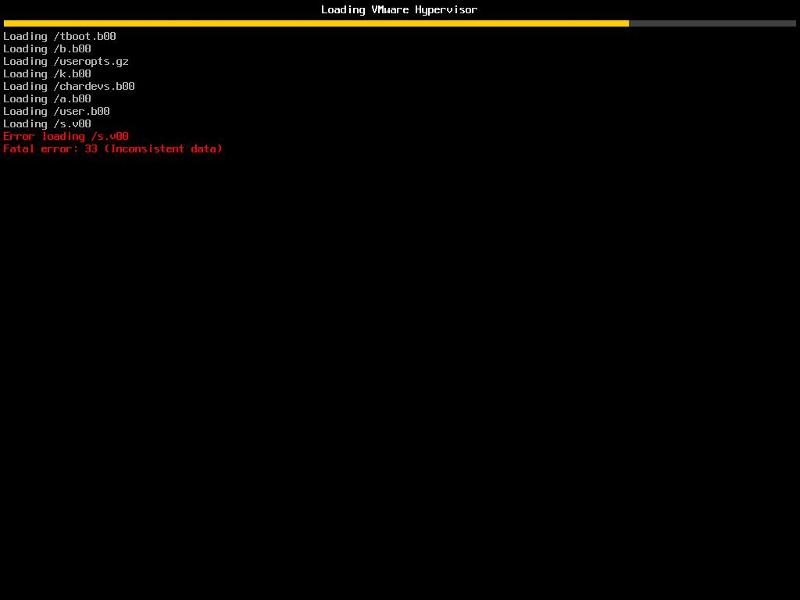
corrupted file.
3. Replacing the corrupted file using SLAX
Power down the existing virtual machine, created in Step 2, and connect the
Slax Linux pocket operating system Linux from
http://www.slax.org/ to the virtual machine.
We will use the Slax Linux pocket operating system to mount the VMware Hypervisor (ESXi) partitions to fix the corrupted file, by replacing with a known working version.
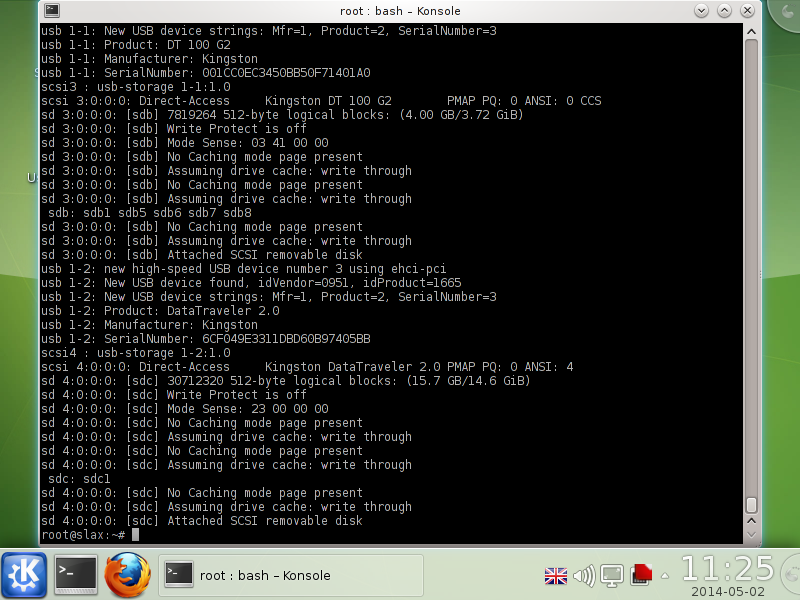
dmesg, you should be able to see the two connected USB flash drives. In this guide, device [sdb] is a Kingston DT 100 G2 4GB flash drive which contains the faulty OS, with the corrupted file, and device [sdc] Kingston DataTraveler 2.0 16GB flash drive contains the new file s.v00.
In the next few steps we will mount the USB flash drives partitions, and checksum the files, and finally copy and replace the corrupted file.
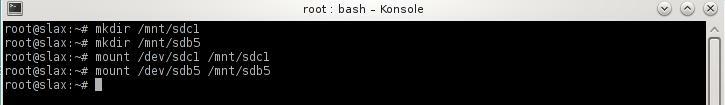
Type the following in the terminal window
mkdir /mnt/sdb5 — create a folder directory for the mounted partition for the ESXi.
mkdir /mnt/sdc1 — create a folder directory for the mounted partition.
mount /dev/sdb5 /mnt/sdb5 — mount the ESXi OS flash drive partition.
mount /dev/sdc1 /mnt/sdc1 — mount the flash drive partition.
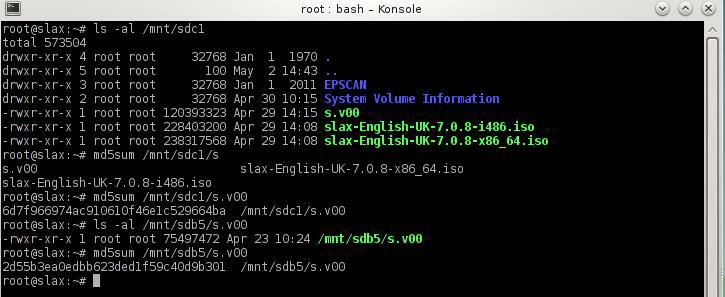
Type the following commands
ls -al /mnt/sdc1/s.v00 — check flash drive for file s.v00
md5sum /mnt/sdc1/s.v00 — checksum file ensure matches working copy from host.
ls -al /mnt/sdb5/s.v00 — check corrupted version
md5sum /mnt/sdb5/s.v00 — checksum corrupted file.
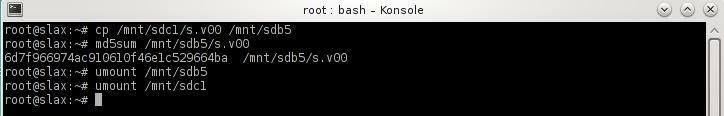
Type the following commands to copy the working copy of the file s.v00 to the ESXi OS faulty media.
cp /mnt/sdc1/s.v00 /mnt/sdb5
md5sum /mnt/sdb/s.v00
umount /mnt/sdb5
umount /mnt/sdc1
Exit terminal mode, disconnect the USB flash drives from the SLAX virtual machine.
Repeat Step 2 above.
You should find the server successfully boots, and the ESXi USB flash drive installation media, has been successfully repaired.
Congratulations, you have successfully Fixed the the Error loading /s.v00 Fatal error: 33 (Inconsistent data) in the VMware vSphere Hypervisor.
**************************
**********
**********
**********
**********
**********
Thank you for reading my article, please leave valuable feedback. If you liked my VMware article and would like to see more
Articles from me, please click the Yes button near the:
Was this article helpful? at the bottom of this article just below and to the right of this information. Thank You. Do not forget if you have a question about this article or another VMware, Virtualisation, Windows Server 2012 question, why not post a Question for me and the other Experts Exchange Experts in the VMware, Virtualisation, Windows 2008, Windows 2012 Zones. I look forward to hearing from you. — Andy :- twitter
@einsteinagogo
**************************
**********
**********
**********
**********
**********
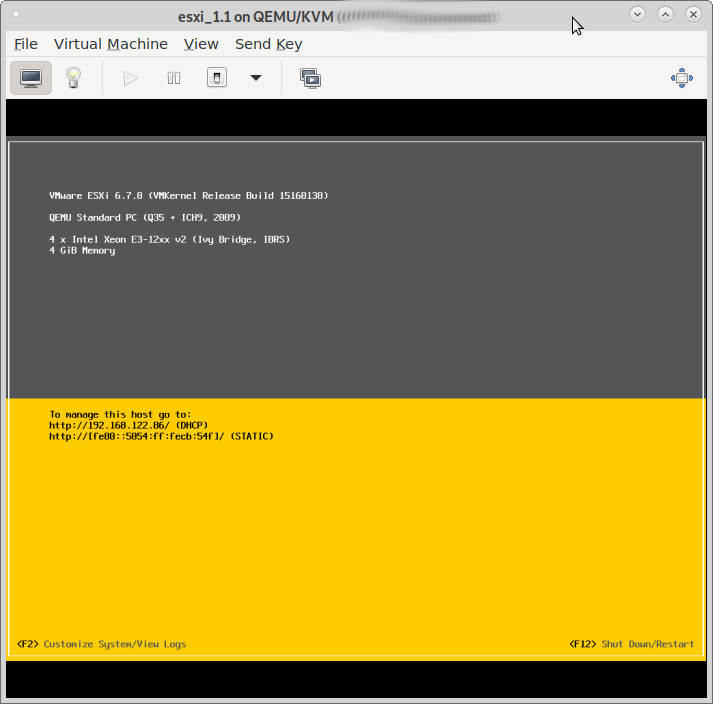
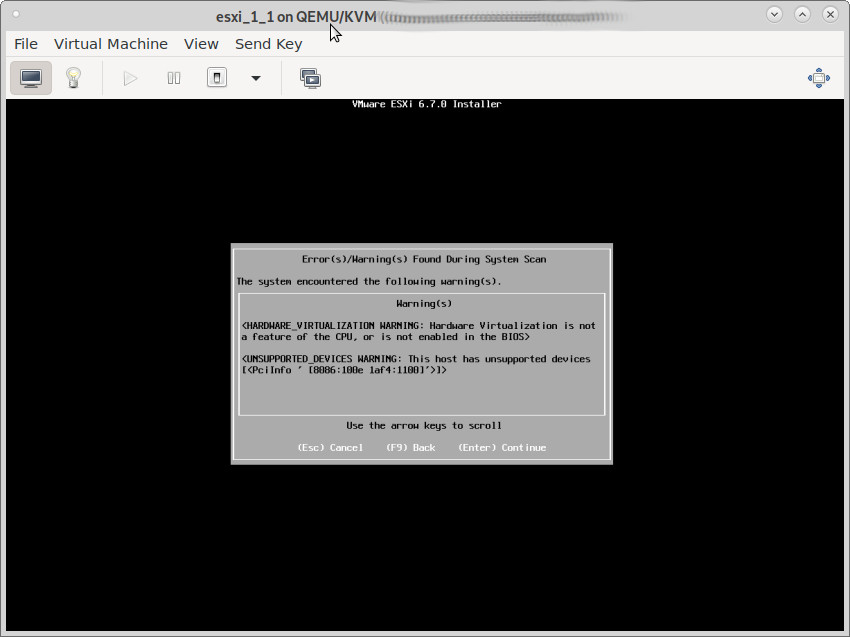
let’s say: in theory – it works
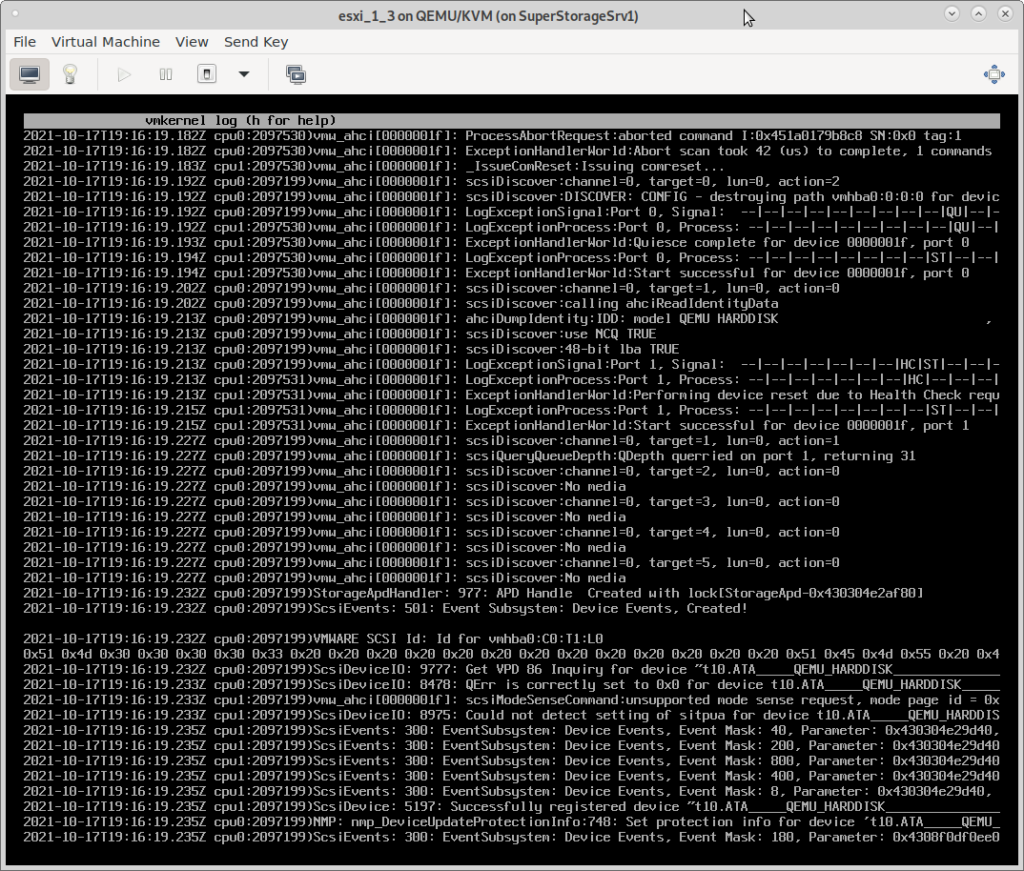
in reality – there are (currently) massive sata harddisk driver problems between esxi 6.7 and kvm-qemu’s virtual harddisk
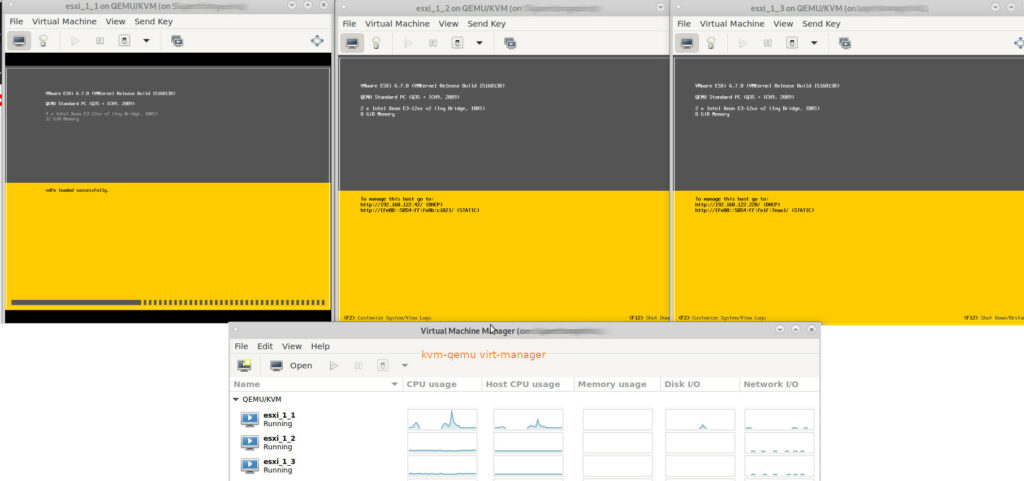
admin-user know: esxi is hardware picky (Dell bought VMWare in 2004 so, “officially” only Dell servers are 100% supported, but many servers of other vendors (SuperMicro, HP) work too) and yes with a little tinkering, it esxi 6.7 can “work” nested within kvm-qemu (right now (2021-10 latest Debian, latest kvm-qemu, (will retest that on older hp machine with CentOS7)) only with Xeon CPUs and massive harddisk (driver?) problems, but on the net, someone made it work with AMD too), nested esxi 7.0 is work in progress…
here is a config that worked: esxi-6.7-nested-within-kvm-qemu-tested-config-vmname.xml.txt
basic setup of kvm-qemu on Debian:
GNU Linux Debian 10 – how to install kvm virtualization (qemu) – basic virsh commands
esxi 6.7 setup:
vmware esxi within kvm-qemu – sb.v00 failed to decompress and admission check failed for memory resource – errors mean: need more RAM?
this is for homeLab testing, not recommended for production use, because: vendor will not give support.
ok it is experimental, but those strange error messages above could mean two things:
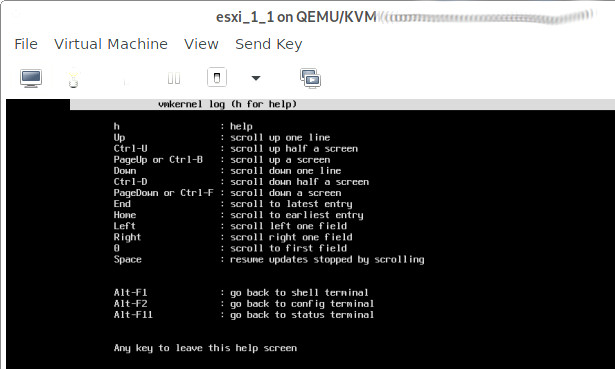
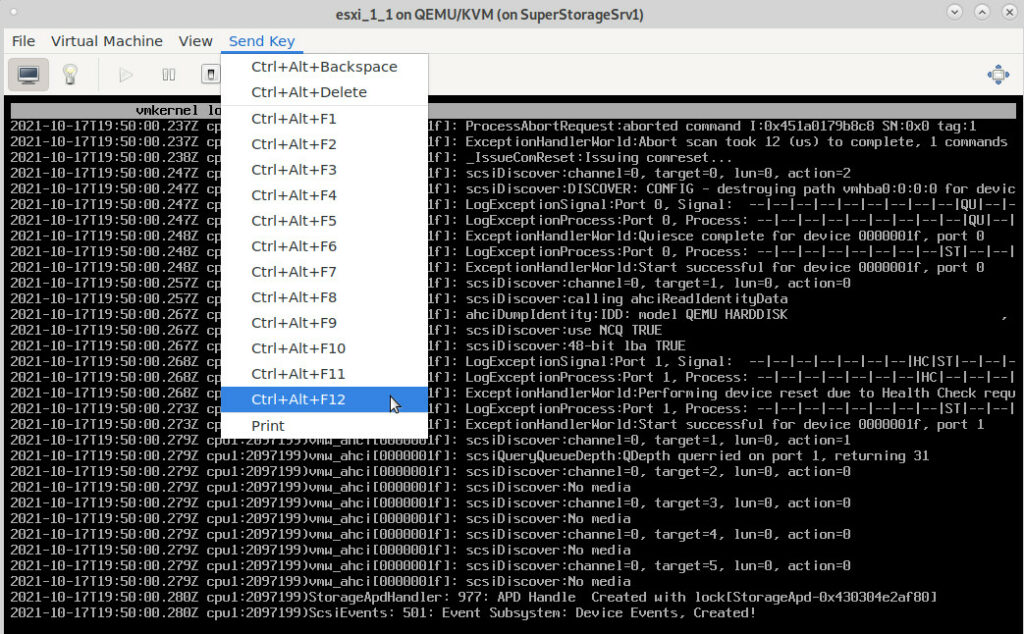
general help during setup: (what is missing here: Alt+F12 = the verbose debug log screen)
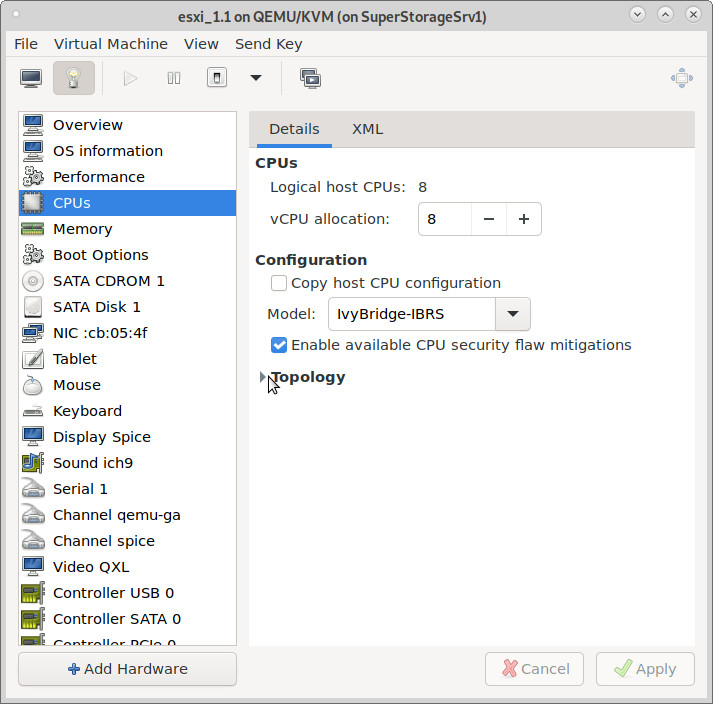
0. the right cpu for the job
SetupA) (works) SuperMicro + Xeon E3 (Ivy Bridge) + Debian 11 + esxi 6.7 (the software is the problem, not the hardware, aka storage controller (SATA) problems)
# with this hardware it runs just fine within esxi hostnamectl; # tested on host Operating System: Debian GNU/Linux 11 (bullseye) Kernel: Linux 5.10.0-8-amd64 Architecture: x86-64 head /proc/cpuinfo processor : 0 vendor_id : GenuineIntel cpu family : 6 model : 58 model name : Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E3-1270 V2 @ 3.50GHz stepping : 9 microcode : 0x21 cpu MHz : 1672.704 cache size : 8192 KB physical id : 0 dmidecode |less Manufacturer: Supermicro Product Name: X9SCI/X9SCA # run some checks # (not all are required to pass) # (those results are actual results for this setup) su - root get install cpu-checker kvm-ok INFO: /dev/kvm exists virt-host-validate QEMU: Checking for hardware virtualization : PASS QEMU: Checking if device /dev/kvm exists : PASS QEMU: Checking if device /dev/kvm is accessible : PASS QEMU: Checking if device /dev/vhost-net exists : PASS QEMU: Checking if device /dev/net/tun exists : PASS QEMU: Checking for cgroup 'cpu' controller support : PASS QEMU: Checking for cgroup 'cpuacct' controller support : PASS QEMU: Checking for cgroup 'cpuset' controller support : PASS QEMU: Checking for cgroup 'memory' controller support : PASS QEMU: Checking for cgroup 'devices' controller support : PASS QEMU: Checking for cgroup 'blkio' controller support : PASS QEMU: Checking for device assignment IOMMU support : PASS QEMU: Checking if IOMMU is enabled by kernel : PASS QEMU: Checking for secure guest support : WARN (Unknown if this platform has Secure Guest support) LXC: Checking for Linux >= 2.6.26 : PASS LXC: Checking for namespace ipc : PASS LXC: Checking for namespace mnt : PASS LXC: Checking for namespace pid : PASS LXC: Checking for namespace uts : PASS LXC: Checking for namespace net : PASS LXC: Checking for namespace user : PASS LXC: Checking for cgroup 'cpu' controller support : PASS LXC: Checking for cgroup 'cpuacct' controller support : PASS LXC: Checking for cgroup 'cpuset' controller support : PASS LXC: Checking for cgroup 'memory' controller support : PASS LXC: Checking for cgroup 'devices' controller support : PASS LXC: Checking for cgroup 'freezer' controller support : FAIL (Enable 'freezer' in kernel Kconfig file or mount/enable cgroup controller in your system) LXC: Checking for cgroup 'blkio' controller support : PASS LXC: Checking if device /sys/fs/fuse/connections exists : PASS egrep -c '(vmx|svm|ept)' /proc/cpuinfo # should be more than 0 24 # want Y to be returned cat /sys/module/kvm/parameters/ignore_msrs N # want N to be returned cat /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/enable_apicv N # want Y to be returned cat /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/nested Y # want Y to be returned cat /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/ept Y # (creditz: https://fabianlee.org/2018/09/19/kvm-deploying-a-nested-version-of-vmware-esxi-6-7-inside-kvm/)
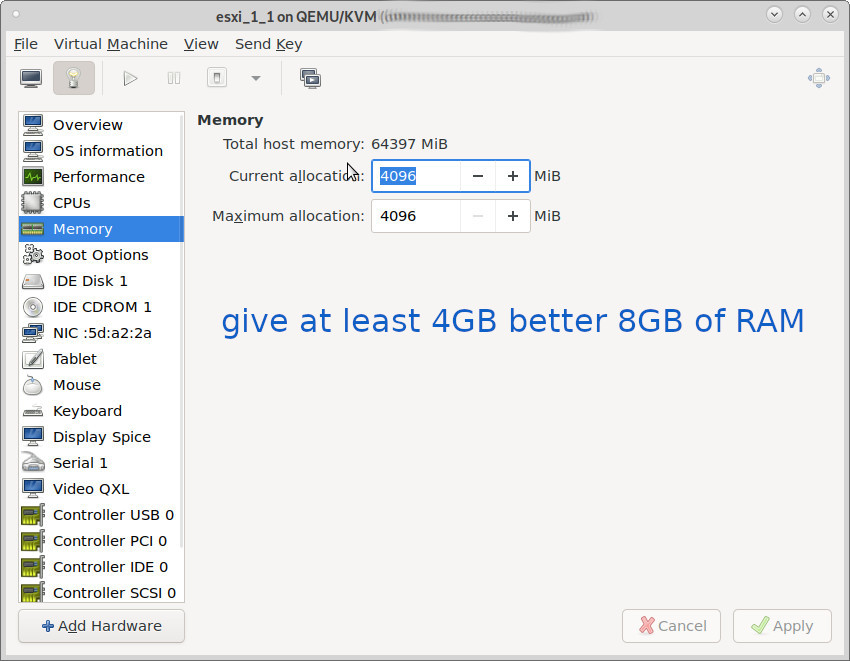
1. not enough RAM! X-D
even when the checkbox “copy host cpu configuration” is set, this checkbox will automatically be disabled and “Enable available CPU security flaw mitigations” will automatically be enabled when vm is started. no worries.
SetupB) (would be super fast, but no functional (yet)) Asus + Ryzen 5 + NVMe
dmidecode | less Manufacturer: ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. Product Name: Pro WS 565-ACE Version: Rev X.0x # would be cool if it worked with that NVMe enabled hardware head /proc/cpuinfo processor : 0 vendor_id : AuthenticAMD cpu family : 23 model : 113 model name : AMD Ryzen 5 3600 6-Core Processor (which translates for kmv-qemu to EPYC-IBPB) stepping : 0 microcode : 0x8701021 cpu MHz : 2566.794 cache size : 512 KB physical id : 0
For x86 guests there are 2 additional CPU flags associated with Spectre/Meltdown mitigation: spec-ctrl, and ibpb:
- spec-ctrl: exposes Indirect Branch Restricted Speculation (IBRS)
- ibpb: exposes Indirect Branch Prediction Barriers
src: https://www.qemu.org/2018/02/14/qemu-2-11-1-and-spectre-update/
# os used
hostnamectl
Operating System: Debian GNU/Linux 10 (buster)
Kernel: Linux 4.19.0-17-amd64
Architecture: x86-64
but then…. esxi 6.7 on kvm-qemu (Debian 10) OS: “Generic default” Copy CPU: “EPYC-IBPB” and 8GB of RAM
testing:
# if server is intel cat /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/nested 1 # if server is amd cat /sys/module/kvm_amd/parameters/nested 1
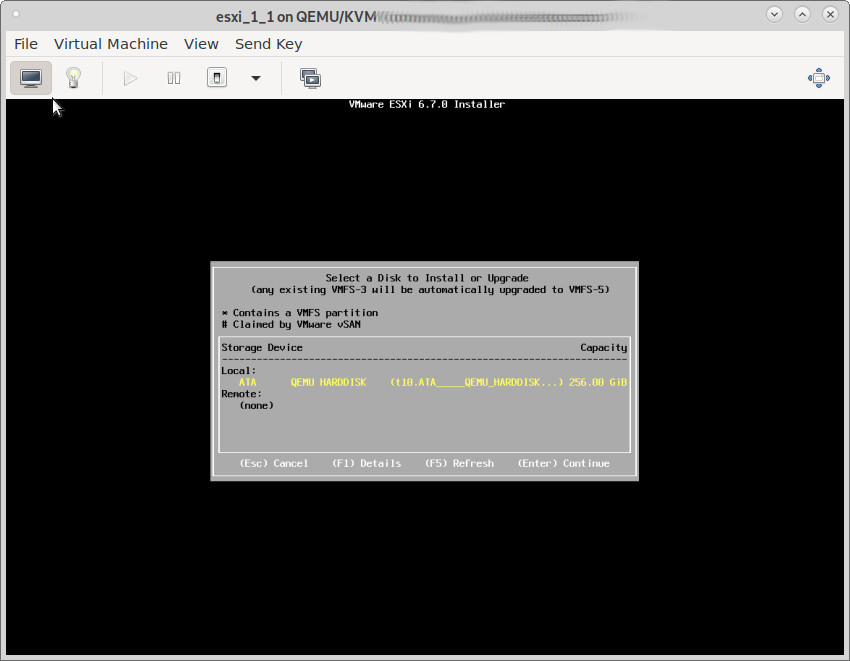
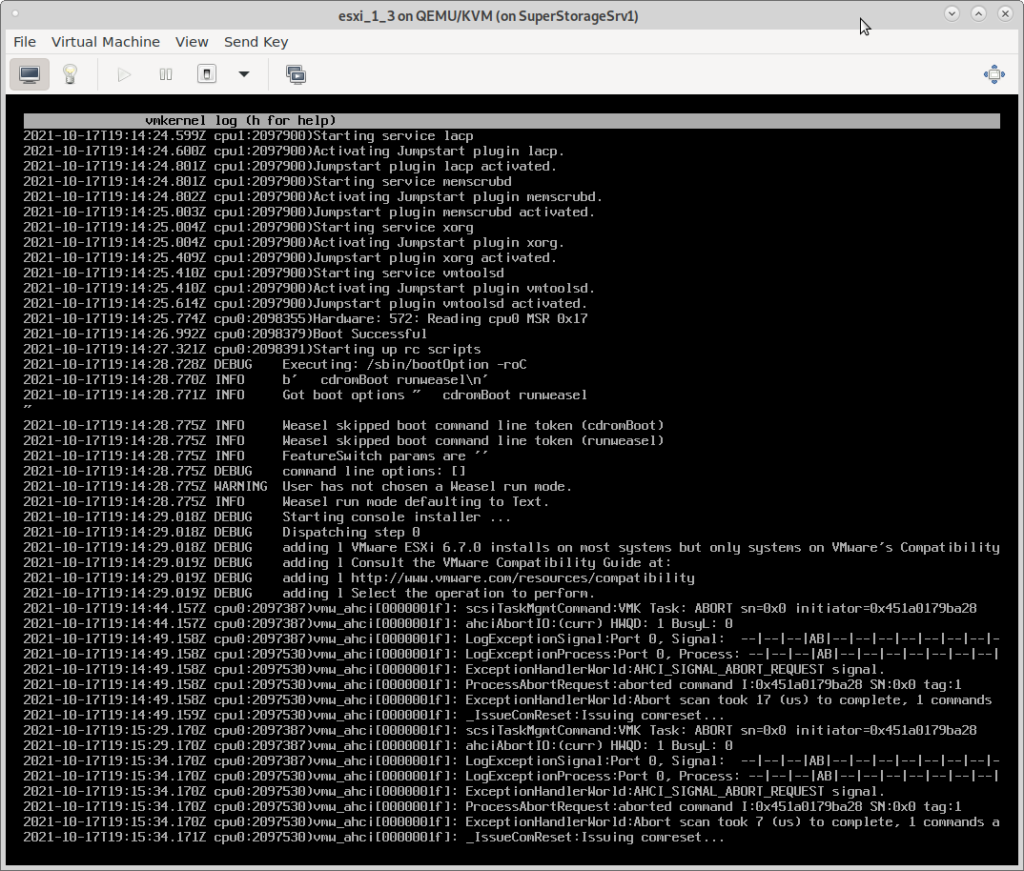
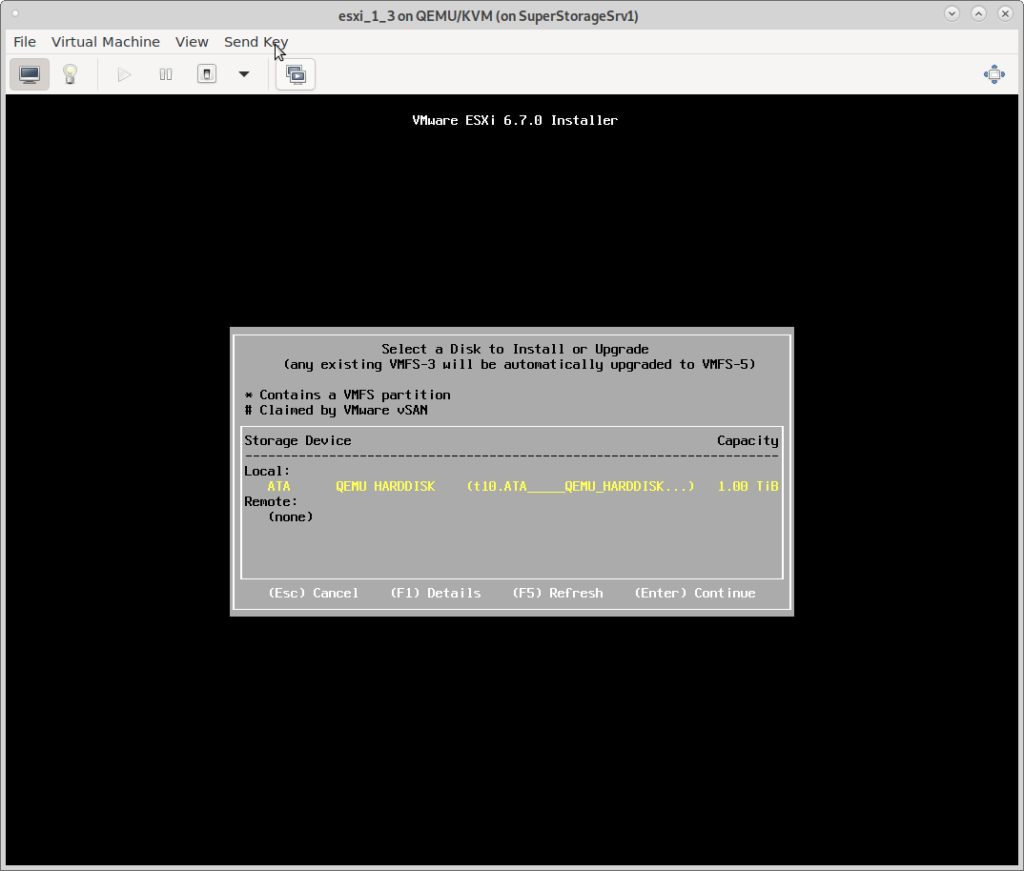
2. the picky harddisk controller problem
no harddisk found:
try this: stay at this screen for at least 10min… (Alt+F12 = watch the verbose debug output change as it detects)
1. actually starts detecting hardware BEFORE pressing enter
2. needs more time to detect hardware
wait for it…
dada!
hewego… X-D
thin-provision (bit slower but way smaller (dynamic growing) harddisk)
cat /scripts/kvm-qemu/harddisk_new_thin.sh #!/bin/bash PATH_VM="/where/vms/are/stored/$1.qcow2" if test -f "$PATH_VM"; then echo "... $PATH_VM hd file already exists, cancel process (otherwise will be overwritten)" else echo "... creating new thin provisioned virtual qcow2 harddisk with /path/name $PATH_VM and size $2GB ===" qemu-img
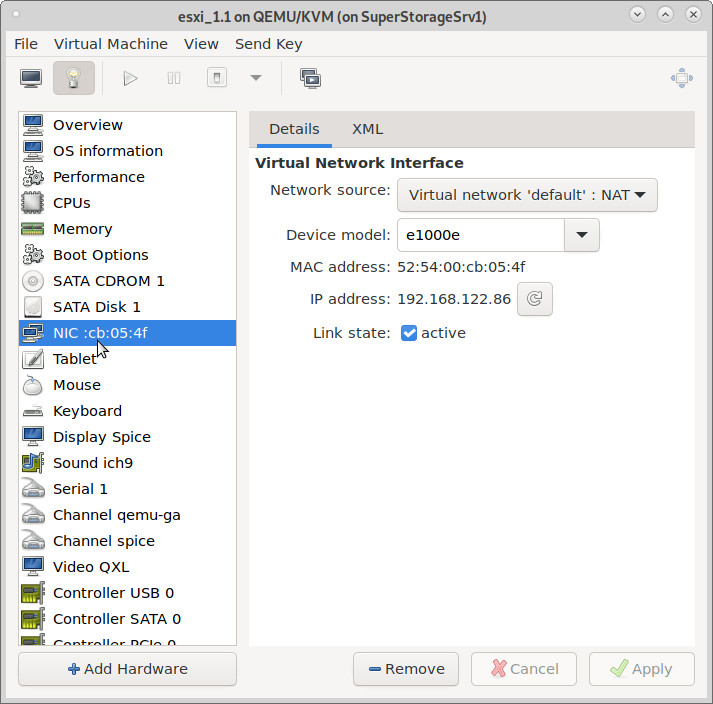
3. virtual network adapter e1000e works for exsi 6.7
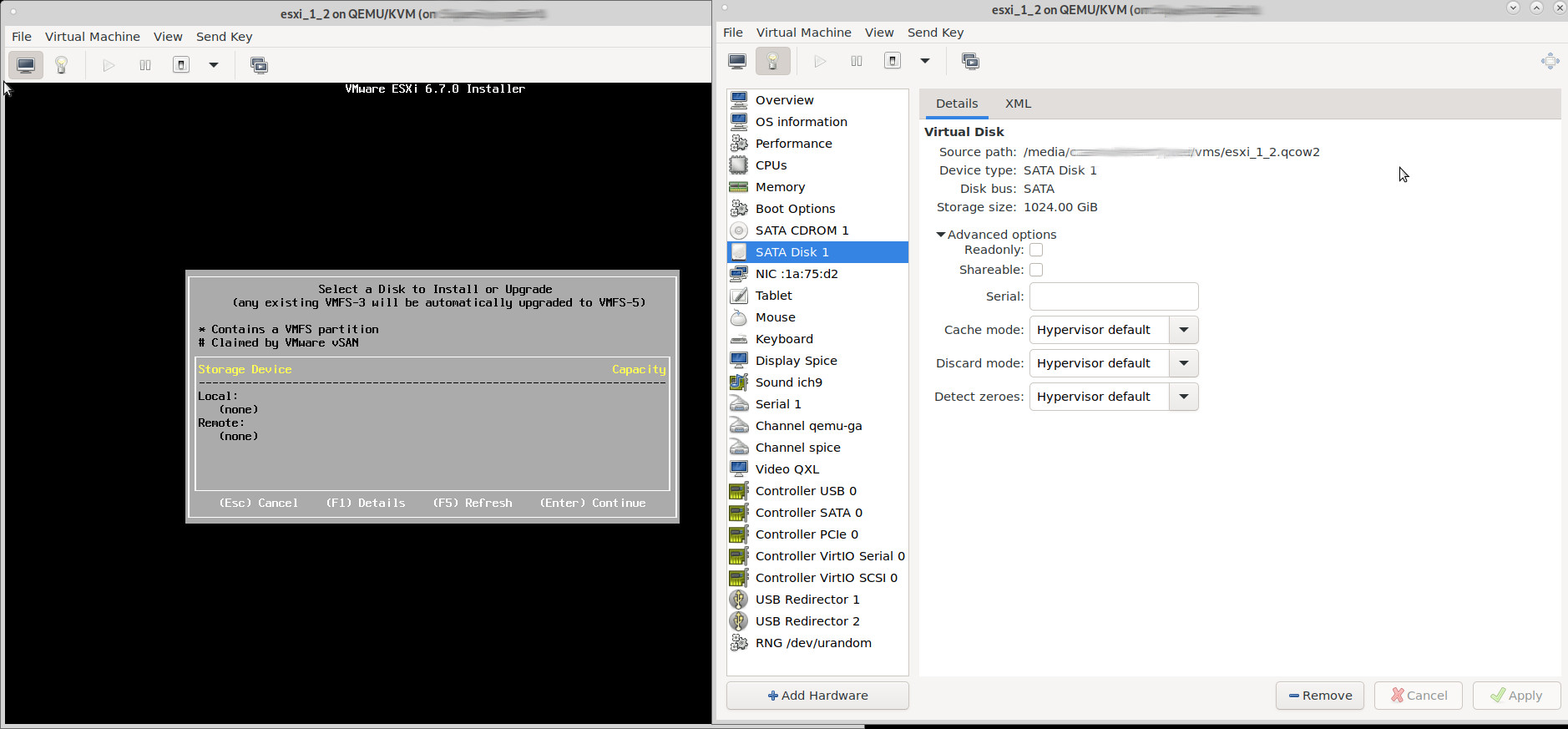
4. a working vmname.xml config example:
sometimes it is easier to copy and paste a working config via xml editor which can be done inside virt-manager (click on xml) or directly from bash-terminal:
here is a config that worked: esxi-6.7-nested-within-kvm-qemu-tested-config-vmname.xml.txt
virsh edit vmname
the end result should be…
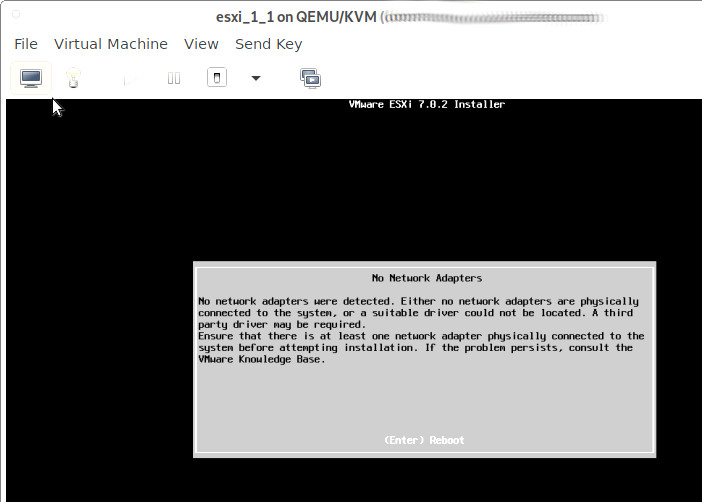
esxi 7.0: problems with virtual e1000
the newer version of esxi does not recognize the e1000 anymore 🙁
enable libvirt kvm qemu logging:
# to get a more verbose output combine setting this vim /etc/libvirt/libvirtd.conf # find and unquote those lines log_filters="1:qemu 1:libvirt 4:object 4:json 4:event 1:util" log_outputs="3:syslog:libvirtd" # no service needs to be restarted (?) "it just works" :) # fire up this one-liner (which works if tail does not have to process too much log files X-D) # without color but: you can scroll it :) find /var/log/* -type f ( -name "*" ) ! -path '*.gz*' -exec tail -n0 -f "$file" {} + # with color but no scroll :( (ccze is not available on all distros, but it is on CentOS7, Debian 9 to 11) find /var/log/* -type f ( -name "*" ) ! -path '*.gz*' -exec tail -n0 -f "$file" {} + | ccze
linux monitor all logs in real time 😀 – follow all – show changes to log files under /var/log
# sample output ==> /var/log/debug <== Oct 17 18:13:26 SuperStorageSrv1 libvirtd[572]: unsupported configuration: IDE controllers are unsupported for this QEMU binary or machine type ==> /var/log/syslog <== Oct 17 18:13:26 SuperStorageSrv1 libvirtd[572]: unsupported configuration: IDE controllers are unsupported for this QEMU binary or machine type
can it work on AMD CPUs: Ryzen?
theoretically yes
AMD‘s naming (other than intel i3, i5, i7, i9…) is a bit confusing, but basically there is currently the Ryzen 5, 7 and 9
a nice benchmark online comparison site: https://cpu.userbenchmark.com/
currently leading the charts: Core i9-11900K, +5% faster than AMD Ryzen 9 5900X (src)
Zen core architecture (2017–present)
Zen-based CPUs and some APUs use the “Ryzen”-brand: List of AMD Ryzen microprocessors, while some APUs use the brand “Athlon”: List of AMD accelerated processing unit microprocessors.
Zen series CPUs and APUs (released 2017)
- Summit Ridge Ryzen 1000 series (desktop)
- Whitehaven Ryzen Threadripper 1000 series (desktop)
- Raven Ridge Ryzen 2000 APU series with RX Vega (desktop & laptop)
- Naples Epyc (server)
Zen+ series CPUs and APUs (released 2018)
- Pinnacle Ridge Ryzen 2000 series (desktop)
- Colfax Ryzen Threadripper 2000 series (desktop)
- Picasso Ryzen 3000 APU series with RX Vega (desktop & laptop)
Zen 2 series CPUs and APUs (released 2019)
- Matisse Ryzen 3000 series (desktop)
- Castle Peak Ryzen Threadripper 3000 series (desktop)
- Renoir Ryzen 4000 APU series with RX Vega (desktop & laptop)
- Lucienne Ryzen 5000 APU series (laptop)
- Rome Epyc (server)
Zen 3 series CPUs and APUs (released 2020)
- Vermeer Ryzen 5000 series (desktop)
- Cezanne Ryzen 5000 series (laptop)
- Milan Epyc (server)
src: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_AMD_processors#K8_core_architecture_(2003%E2%80%932014)
Links:
https://fabianlee.org/2018/09/19/kvm-deploying-a-nested-version-of-vmware-esxi-6-7-inside-kvm/
https://www.cloudgardens.eu/blog/vmware-esxi-running-under-qemu-kvm/
https://www.libvirt.org/docs/libvirt-appdev-guide-python/en-US/html/libvirt_application_development_guide_using_python-Debug.html
https://www.berrange.com/posts/2018/06/29/cpu-model-configuration-for-qemu-kvm-on-x86-hosts/
- share
- share
- share
- share
- share
- tweet
- share
liked this article?
- only together we can create a truly free world
- plz support dwaves to keep it up & running!
- (yes the info on the internet is (mostly) free but beer is still not free (still have to work on that))
- really really hate advertisement
- contribute: whenever a solution was found, blog about it for others to find!
- talk about, recommend & link to this blog and articles
- thanks to all who contribute!
Buenas, como sabéis después de unas buenas y calmadas vacaciones vienen unos Lunes o Martes llenos de «tomatadas». En vacaciones, en muchas empresas se aprovecha para hacer mantenimientos preventivos de las cadenas de producción, Robots de soldadura, prensas etc etc y es muy típico que haya cortes de luz sin avisar por parte de mantenimiento. Estos cortes de luz sin avisar, provocan unos apagados inesperados de todo que se quede encendido con el riesgo de que no arranquen con normalidad, todo esto se puede solucionar con una buena SAI y una buena configuración para un apagado ordenado, pero en algunos casos esto falla por diferentes razones.
También aprovecho para recomendar y que os descarguéis el libro de VMwareporvExperts un gran libro escrito por 14 Bloggers y vExperts de habla Hispana
Uno de esos días era hoy, donde debido a un corte de luz, los 2 ESXi donde estaban todas las VMs, no iniciaban, en los 2 se podía ver el error «Error loading /sb.v00 Fatal error 33 (Inconsistent data)», no era exactamente el mismo error en los 2 ESXi, pero era parecido. Este error se debe a que algún fichero esta corrupto en el USB o SD Card donde esta instalado el Hypervisor, y con tan mala suerte que pasó en los 2 ESXi, por lo que se convirtió en un autentico brownie, de nada sirvieron los reinicios de rigor.
Si haces una búsqueda rápida por Google, uno de los primeros foros-web-blog que te encuentras con este error es el de experts-exchange, una Web que es canela en rama.
En este LINK, explican varias maneras de solucionar este problema, pero en mi caso la avería era gorda y el tiempo de experimentos corto.
Una cosa que se me ocurrió deprisa y corriendo era hacer un Recovery mode del ESXi, a ver si sonaba la flauta. Si no hubiese funcionado, hubiese intentado solucionarlo como lo hablaban en experts-exchange, aunque VMware recomienda la reinstalación.
NOTA: si la instalación del ESXi se ha hecho desde cero y no le has hecho ninguna actualización de parches o update, no te funcionará ya que no tendrás ningún punto para volver atrás.
En mi caso cuando se hizo la instalación por primera vez se utilizó la ESXi 5.5 Update 3a, mas tarde se actualizó a la ESXi 5.5 Update 3b + parches express, por lo que pude hacer el Rollback a la ESXi 5.5 Update 3a, en uno de los ESXi me funcionó, pero en el otro no, por lo que no es una solución 100% fiable. Tuve Suerte? quizás si, encima todas las VMs estaban en el ESXi que volvió a la vida (me imagino que en el corte de luz el HA los paso a este host). Y repito, esta no es la solución buena y correcta, pero si te funciona, te puede sacar de un apuro.
A través de la ILO (si es HP y la tienes configurada) cuando inicia, pulsas SHIFT+R, te aparecerán las 2 ultimas instalaciones-actualizaciones que se hayan hecho, la actual y la anterior, escribimos «Y» para confirmar el Rollback o «N» para cancelar.
Si funciona, iniciará con normalidad y con la release anterior.
Lo siguiente que hice, fue reinstalar de nuevo el ESXi que fallaba, configurarlo, pasar las VMs del otro ESXI y actualizar el ESXi «bueno».
Saludos y espero que os sirva.