Содержание
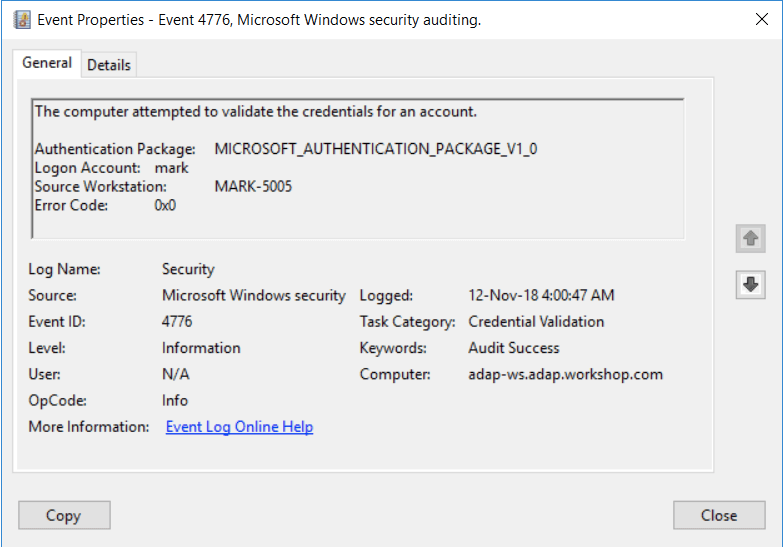
- 4776(S, F): The computer attempted to validate the credentials for an account.
- Security Monitoring Recommendations
- 4776(S, F): компьютер пытался проверить учетные данные для учетной записи.
- Рекомендации по контролю безопасности
4776(S, F): The computer attempted to validate the credentials for an account.
Event Description:
This event generates every time that a credential validation occurs using NTLM authentication.
This event occurs only on the computer that is authoritative for the provided credentials. For domain accounts, the domain controller is authoritative. For local accounts, the local computer is authoritative.
It shows successful and unsuccessful credential validation attempts.
It shows only the computer name (Source Workstation) from which the authentication attempt was performed (authentication source). For example, if you authenticate from CLIENT-1 to SERVER-1 using a domain account you’ll see CLIENT-1 in the Source Workstation field. Information about the destination computer (SERVER-1) isn’t presented in this event.
If a credential validation attempt fails, you’ll see a Failure event with Error Code parameter value not equal to “0x0”.
The main advantage of this event is that on domain controllers you can see all authentication attempts for domain accounts when NTLM authentication was used.
For monitoring local account logon attempts, it’s better to use event “4624: An account was successfully logged on” because it contains more details and is more informative.
This event also generates when a workstation unlock event occurs.
This event does not generate when a domain account logs on locally to a domain controller.
NoteВ В For recommendations, see Security Monitoring Recommendations for this event.
Event XML:
Required Server Roles: no specific requirements.
Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista.
Event Versions: 0.
Field Descriptions:
- Authentication Package [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of Authentication Package that was used for credential validation. It’s always “MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0” for 4776 event.
NoteВ В Authentication package is a DLL that encapsulates the authentication logic used to determine whether to permit a user to log on. Local Security Authority (LSA) authenticates a user logon by sending the request to an authentication package. The authentication package then examines the logon information and either authenticates or rejects the user logon attempt.
Logon Account [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the account that had its credentials validated by the Authentication Package. Can be user name, computer account name or well-known security principal account name. Examples:
User example: dadmin
Computer account example: WIN81$
Local System account example: Local
Local Service account example: Local Service
Source Workstation [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the computer from which the logon attempt originated.
Error Code [Type = HexInt32]: contains error code for Failure events. For Success events this parameter has “0x0” value. The table below contains most common error codes for this event:
| Error Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 0xC0000064 | The username you typed does not exist. Bad username. |
| 0xC000006A | Account logon with misspelled or bad password. |
| 0xC000006D | — Generic logon failure. Some of the potential causes for this: An invalid username and/or password was used LAN Manager Authentication Level mismatch between the source and target computers. |
| 0xC000006F | Account logon outside authorized hours. |
| 0xC0000070 | Account logon from unauthorized workstation. |
| 0xC0000071 | Account logon with expired password. |
| 0xC0000072 | Account logon to account disabled by administrator. |
| 0xC0000193 | Account logon with expired account. |
| 0xC0000224 | Account logon with «Change Password at Next Logon» flagged. |
| 0xC0000234 | Account logon with account locked. |
| 0xC0000371 | The local account store does not contain secret material for the specified account. |
| 0x0 | No errors. |
Security Monitoring Recommendations
For 4776(S, F): The computer attempted to validate the credentials for an account.
| Type of monitoring required | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| High-value accounts: You might have high-value domain or local accounts for which you need to monitor each action. Examples of high-value accounts are database administrators, built-in local administrator account, domain administrators, service accounts, domain controller accounts and so on. |
Monitor this event with the “Logon Account” that corresponds to the high-value account or accounts. |
| Anomalies or malicious actions: You might have specific requirements for detecting anomalies or monitoring potential malicious actions. For example, you might need to monitor for use of an account outside of working hours. | When you monitor for anomalies or malicious actions, use the “Logon Account” value (with other information) to monitor how or when a particular account is being used. To monitor activity of specific user accounts outside of working hours, monitor the appropriate Logon Account + Source Workstation pairs. |
| Non-active accounts: You might have non-active, disabled, or guest accounts, or other accounts that should never be used. | Monitor this event with the “Logon Account” that should never be used. |
| Account allow list: You might have a specific allow list of accounts that are the only ones allowed to perform actions corresponding to particular events. | If this event corresponds to a “allow list-only” action, review the “Logon Account” for accounts that are outside the allow list. |
| Restricted-use computers: You might have certain computers from which certain people (accounts) shouldn’t log on. | Monitor the target Source Workstation for credential validation requests from the “Logon Account” that you’re concerned about. |
| Account naming conventions: Your organization might have specific naming conventions for account names. | Monitor “Logon Account” for names that don’t comply with naming conventions. |
If NTLM authentication shouldn’t be used for a specific account, monitor for that account. Don’t forget that local logon will always use NTLM authentication if an account logs on to a device where its user account is stored.
You can use this event to collect all NTLM authentication attempts in the domain, if needed. Don’t forget that local logon will always use NTLM authentication if the account logs on to a device where its user account is stored.
If a local account should be used only locally (for example, network logon or terminal services logon isn’t allowed), you need to monitor for all events where Source Workstation and Computer (where the event was generated and where the credentials are stored) have different values.
Consider tracking the following errors for the reasons listed:
Источник
4776(S, F): компьютер пытался проверить учетные данные для учетной записи.
Описание события:
Это событие создает каждый раз, когда выполняется проверка учетных данных с помощью проверки подлинности NTLM.
Это событие происходит только на компьютере, который является полномочным для предоставленных учетных данных. Для учетных записей домена контроллер домена является полномочным. Для локальных учетных записей локальный компьютер является полномочным.
В нем показаны успешные и неудачные попытки проверки учетных данных.
Здесь отображается только имя компьютера (исходная рабочая станция), с которого была выполнена попытка проверки подлинности (источник проверки подлинности). Например, при проверке подлинности из CLIENT-1 в SERVER-1 с помощью учетной записи домена в поле Исходная рабочая станция появится клиент-1. Сведения о конечном компьютере (SERVER-1) не отображаются в этом событии.
Если попытка проверки учетных данных завершается сбоем, вы увидите событие Failure со значением параметра Кода ошибки , не равным «0x0«.
Основное преимущество этого события заключается в том, что на контроллерах домена можно увидеть все попытки проверки подлинности для учетных записей домена при использовании проверки подлинности NTLM.
Для мониторинга попыток входа в локальную учетную запись лучше использовать событие «4624: учетная запись успешно вошел в систему», так как она содержит больше сведений и более информативна.
Это событие также возникает при возникновении события разблокировки рабочей станции.
Это событие не возникает при локальном входе учетной записи домена в контроллер домена.
Примечание. Рекомендации приведены в разделе Рекомендации по мониторингу безопасности для этого события.
XML события:
Обязательные роли сервера: никаких конкретных требований.
Минимальная версия ОС: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista.
Версии события: 0.
Описания полей:
- Пакет проверки подлинности [Type = UnicodeString]: имя пакета проверки подлинности , который использовался для проверки учетных данных. Это всегда «MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0» для события 4776 .
Примечание Пакет проверки подлинности — это библиотека DLL, которая инкапсулирует логику проверки подлинности, используемую для определения разрешения пользователю на вход. Локальный центр безопасности (LSA) проверяет подлинность входа пользователя, отправляя запрос в пакет проверки подлинности. Затем пакет проверки подлинности проверяет сведения о входе и выполняет проверку подлинности или отклоняет попытку входа пользователя.
Учетная запись входа [Type = UnicodeString]: имя учетной записи, учетные данные которой были проверены пакетом проверки подлинности. Может быть имя пользователя, имя учетной записи компьютера или хорошо известное имя учетной записи субъекта безопасности . Примеры:
Пример пользователя: dadmin
Пример учетной записи компьютера: WIN81$
Пример учетной записи локальной системы: Local
Пример учетной записи локальной службы: локальная служба
Исходная рабочая станция [Type = UnicodeString]: имя компьютера, с которого была предпринята попытка входа.
Код ошибки [Type = HexInt32]: содержит код ошибки для событий сбоя. Для событий успешного выполнения этот параметр имеет значение «0x0«. В таблице ниже приведены наиболее распространенные коды ошибок для этого события:
| Код ошибки | Описание |
|---|---|
| 0xC0000064 | Введенное имя пользователя не существует. Неправильное имя пользователя. |
| 0xC000006A | Вход в учетную запись с неправильным или неправильным паролем. |
| 0xC000006D | — сбой универсального входа. Некоторые из потенциальных причин этого: Использовалось недопустимое имя пользователя и (или) пароль. Несоответствие уровня проверки подлинности LAN Manager между исходным и целевым компьютерами. |
| 0xC000006F | Вход в учетную запись в нерабочее время. |
| 0xC0000070 | Вход учетной записи с несанкционированной рабочей станции. |
| 0xC0000071 | Вход в учетную запись с истекшим паролем. |
| 0xC0000072 | Вход в учетную запись отключен администратором. |
| 0xC0000193 | Вход в учетную запись с истекшим сроком действия. |
| 0xC0000224 | Вход в учетную запись с пометкой «Изменить пароль при следующем входе». |
| 0xC0000234 | Вход в учетную запись с заблокированной учетной записью. |
| 0xC0000371 | Локальное хранилище учетных записей не содержит секретных материалов для указанной учетной записи. |
| 0x0 | Нет ошибок. |
Таблица 1: Коды ошибок Winlogon.
Рекомендации по контролю безопасности
Для 4776(S, F): компьютер пытался проверить учетные данные для учетной записи.
| Тип требуемого мониторинга | Рекомендации |
|---|---|
| Учетные записи большой ценности: у вас может быть домен или локальные учетные записи большой ценности, для которых необходимо отслеживать каждое действие. Примеры учетных записей большой ценности: учетные записи администраторов баз данных, встроенная учетная запись локального администратора, учетные записи администраторов домена, учетные записи служб, учетные записи контроллеров домена и т. д. |
Отслеживайте это событие с помощью учетной записи входа , которая соответствует высокоценной учетной записи или учетным записям. |
| Аномалии и вредоносные действия: у вас могут быть особые требования касательно обнаружения аномалий или отслеживания потенциально вредоносных действий. Например, вам может потребоваться отслеживать использование учетной записи во внерабочее время. | При мониторинге аномалий или вредоносных действий используйте значение «Учетная запись входа» (с другими сведениями), чтобы отслеживать, как и когда используется определенная учетная запись. Чтобы отслеживать активность определенных учетных записей пользователей в нерабочее время, отслеживайте соответствующие пары учетных записей входа и исходная рабочая станция . |
| Неактивные учетные записи: у вас, возможно, есть неактивные, отключенные или гостевые учетные записи, а также другие учетные записи, которые не должны использоваться. | Отслеживайте это событие с помощью учетной записи входа , которую никогда не следует использовать. |
| Список разрешенных учетных записей: возможно, у вас есть список разрешенных учетных записей, которым разрешено выполнять действия, соответствующие определенным событиям. | Если это событие соответствует действию «разрешить только список», просмотрите «Учетную запись входа» для учетных записей, которые находятся за пределами списка разрешений. |
| Компьютеры с ограниченным использованием. Возможно, у вас есть определенные компьютеры, с которых определенные пользователи (учетные записи) не должны входить в систему. | Отслеживайте целевую исходную рабочую станцию для запросов на проверку учетных данных из учетной записи входа , о чем вас беспокоит. |
| Соглашения об именовании учетных записей: в вашей организации могут быть определенные соглашения об именовании учетных записей. | Отслеживайте «Учетная запись входа» для имен, которые не соответствуют соглашениям об именовании. |
Если проверка подлинности NTLM не должна использоваться для определенной учетной записи, отслеживайте ее. Не забывайте, что локальный вход всегда будет использовать проверку подлинности NTLM, если учетная запись входит в систему на устройстве, где хранится учетная запись пользователя.
Это событие можно использовать для сбора всех попыток проверки подлинности NTLM в домене, если это необходимо. Не забывайте, что локальный вход всегда будет использовать проверку подлинности NTLM, если учетная запись входит в систему на устройстве, где хранится учетная запись пользователя.
Если локальная учетная запись должна использоваться только локально (например, вход в сеть или вход в службы терминалов запрещен), необходимо отслеживать все события, на которых исходная рабочая станция и компьютер (где было создано событие и где хранятся учетные данные) имеют разные значения.
Рассмотрите возможность отслеживания следующих ошибок по перечисленным причинам:
Источник
| Operating Systems |
Windows 2008 R2 and 7
Windows 2012 R2 and 8.1 Windows 2016 and 10 Windows Server 2019 and 2022 |
|
Category • Subcategory |
Account Logon • Credential Validation |
| Type |
Success
Failure |
|
Corresponding events in Windows 2003 and before |
680 , 681
|
4776: The domain controller attempted to validate the credentials for an account
On this page
- Description of this event
- Field level details
- Examples
- Discuss this event
- Mini-seminars on this event
Despite what this event says, the computer is not necessarily a domain controller; member servers and workstations also log this event for logon attempts with local SAM accounts.
When a domain controller successfully authenticates a user via NTLM (instead of Kerberos), the DC logs this event. This specifies which user account who logged on (Account Name) as well as the client computer’s name from which the user initiated the logon in the Workstation field.
For Kerberos authentication see event 4768, 4769 and 4771.
This event is also logged on member servers and workstations when someone attempts to logon with a local account.
Authentication Package: Always «MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0»
Logon Account: name of the account
Source Workstation: computer name where logon attempt originated
Free Security Log Resources by Randy
- Free Security Log Quick Reference Chart
- Windows Event Collection: Supercharger Free Edtion
- Free Active Directory Change Auditing Solution
- Free Course: Security Log Secrets
Description Fields in
4776
Error Code:
| C0000064 | user name does not exist |
| C000006A | user name is correct but the password is wrong |
| C0000234 | user is currently locked out |
| C0000072 | account is currently disabled |
| C000006F | user tried to logon outside his day of week or time of day restrictions |
| C0000070 | workstation restriction |
| C0000193 | account expiration |
| C0000071 | expired password |
| C0000224 | user is required to change password at next logon |
| C0000225 | evidently a bug in Windows and not a risk |
Setup PowerShell Audit Log Forwarding in 4 Minutes
Your browser does not support video
Examples of 4776
The domain controller attempted to validate the credentials for an account.
Authentication Package: MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0
Logon Account: administrator
Source Workstation: WIN-R9H529RIO4Y
Error Code: 0xc0000064
Top 10 Windows Security Events to Monitor
Free Tool for Windows Event Collection
Mini-Seminars Covering Event ID 4776
- Security Log Exposed: What is the Difference Between “Account Logon” and “Logon/Logoff” Events?
- Insider Gone Bad: Tracking Their Steps and Building Your Case with the Security Log
- 27 Most Important Windows Security Events
- Daily Security Log Check for the SMB IT Admin
- How to do Logon Session Auditing with the Windows Security Log
- Anatomy of an Attack: How Password Spraying Exploits Weak Passwords So Effectively
- 4 Threat Detections using Active Directory Authentication Events from the Windows Security Log
- Understanding Active Directory Authentication Events in the Windows Security Log and Beyond
- Security Log Deep Dive: Mapping Active Directory Authentication and Account Management Events to MITRE ATT&CK TTPs
- Detecting and Preventing AD Authentication Risks: Golden Tickets, NTLM, Pass-the-Hash and Beyond
- Top 10 Windows Security Log Events to Monitor to Detect Lateral Movement
- Top 6 Security Events You Only Detect by Monitoring Workstation Security Logs
|
Upcoming Webinars |
Additional Resources |
Check out this guide to know about this credential validation event
by Vladimir Popescu
Being an artist his entire life while also playing handball at a professional level, Vladimir has also developed a passion for all things computer-related. With an innate fascination… read more
Published on December 16, 2022
Reviewed by
Alex Serban
After moving away from the corporate work-style, Alex has found rewards in a lifestyle of constant analysis, team coordination and pestering his colleagues. Holding an MCSA Windows Server… read more
- Every login attempt on a domain controller is recorded, and the DC logs the event ID 4776 for every successful or unsuccessful attempt.
- This guide will discuss this event ID and how to get rid of the error code if authentication fails.
XINSTALL BY CLICKING THE DOWNLOAD FILE
This software will repair common computer errors, protect you from file loss, malware, hardware failure and optimize your PC for maximum performance. Fix PC issues and remove viruses now in 3 easy steps:
- Download Restoro PC Repair Tool that comes with Patented Technologies (patent available here).
- Click Start Scan to find Windows issues that could be causing PC problems.
- Click Repair All to fix issues affecting your computer’s security and performance
- Restoro has been downloaded by 0 readers this month.
Event ID 4776: the computer attempted to validate the credentials for an account gives you essential information which helps you identify the sources of the login attempts.
Here we will discuss what Event ID 4776 means and how to fix error code 0xc0000064. Let’s get started!
What does the Event ID 4776 computer attempted to validate credentials mean?
Event ID 4776 is a security-related event. It is generated every time a computer tries to validate credentials using NTLM authentication. It occurs only on the computer with authority for the provided credentials.
The event contains detailed information about the user account used for authentication, the destination and the source of the authentication request, along with the status of the attempt.
If Windows Event ID 4776 is successful, there is no need to worry. However, seeing multiple failed instances might indicate the relay, cracking attacks, and reverse brute force attacks. Therefore keeping an eye on this event ID is important.
What causes Event ID 4776 error code 0xc0000064?
A few reasons for the error to occur are mentioned below:
- User name doesn’t exist – This error comes up when the username you typed does not exist or is incorrect.
- Third-party programs cache – If any third-party programs cache the user’s wrong password, this error code may come up.
- Incorrect status by Net Logon service – When the Netlogon.dll manages the returned status incorrectly, the issue occurs.
- Kerberos fails while authenticating RDP – If you connect to the network using a Remote desk protocol, it uses Kerberos to authenticate. But, if it fails, then it has to use NTLM. Hence the error
What can I do to fix Event ID 4776 error code 0xc0000064?
1. Identifying the Logon account and the source workstation when blank or unknown
1.1 Enable Netlogon to find the source
- Press the Windows key, type CMD and click Run as administrator.
- Type the following command and press Enter:
nltest /dbflag:0x2080ffff - Close the CMD window.
- To access your Netlogon files, press Windows + R to open the Run window.
- Type the following command and press Enter:
%SYSTEMROOT%debugnetlogon.log - Now check the username and other details to identify the login attempt.
1.2 Use a Packet Analyzer
Tools like Wireshark can be used to keep an eye on your network on a microscopic level. It can capture the traffic simultaneously when someone tries to log in and helps you find the source. The tool can identify IP addresses so that you can easily locate the logons.
2. Identifying the Logon account and the source workstation if there is a remote client
2.1 Use firewall
You can use your firewall to protect your server or computer from unknown login attempts. Follow the whitelists approach (block all, allow some) instead of denylists (allow all, block some). This will ensure that only authorized attempts are initiated outside the network.
2.2 Use VPN
Using a reliable VPN can also help you safe-keep your network. It will let remote users connect to the local server and then authenticate normally.
A great VPN option that we recommend is Private Internet Access (PIA) because it is fast and highly customizable and has unbreakable security thanks to its numerous privacy features that will keep your activity always safe.

Private Internet Access
Keep your data protected and secure all the time with the most privacy-focused VPN service.
Well, that’s all from our side on how to fix the event id 4776 error code 0xc0000064, and we hope that our solutions helped you solve this issue.
If you still have any issues, feel free to drop a comment below. We’re eager to hear from you.
Still having issues? Fix them with this tool:
SPONSORED
If the advices above haven’t solved your issue, your PC may experience deeper Windows problems. We recommend downloading this PC Repair tool (rated Great on TrustPilot.com) to easily address them. After installation, simply click the Start Scan button and then press on Repair All.
Newsletter
Your Domain Controller’s Windows Event Viewer might be logging tons of security events with strange usernames, misspelled names, attempts with expired or lockout accounts, or strange logon attempts outside business hours— all labeled with the Event ID 4776.
The “Event ID 4776: The computer attempted to validate the credentials for an account” gives you valuable information to help identify the sources of these attempts. Knowing how to troubleshoot and monitor these events can be detrimental to identifying potential brute force dictionary attacks or mal-intentional account uses.
In this post, we’ll go through the technical explanation of what is the Windows Event ID 4776, the details on how to read it, how to troubleshoot or solve the events, and how to monitor and audit using specific software.
Introduction: What is Windows Event ID 4776
“Event ID 4776: The computer attempted to validate the credentials for an account”
You might have come across the log Event ID 4776 while looking at your event logs in a Domain Controller (DC). This event tells you that this specific DC (but also servers and workstations) was used as a logon server to validate credentials. The event ID 4776 is logged every time the DC tries to validate the credentials of an account using NTLM (NT LAN Manager).
Event ID 4776 is a credential validation event that can either represent success or failure. It is displayed in Windows 2008 R2 and 7, Windows 2012 R2 and 8.1, Windows 2016 and 10, and Windows Server 2019 and 2022.
Note: The Event ID 4776 is not only logged for domain controllers attempting to validate credentials but also for other member Windows servers or workstations used for logon attempts with a local SAM account. This is because the NTLM is the default authentication mechanism for local logon.
Let’s go over the details of the Windows Event ID 4776
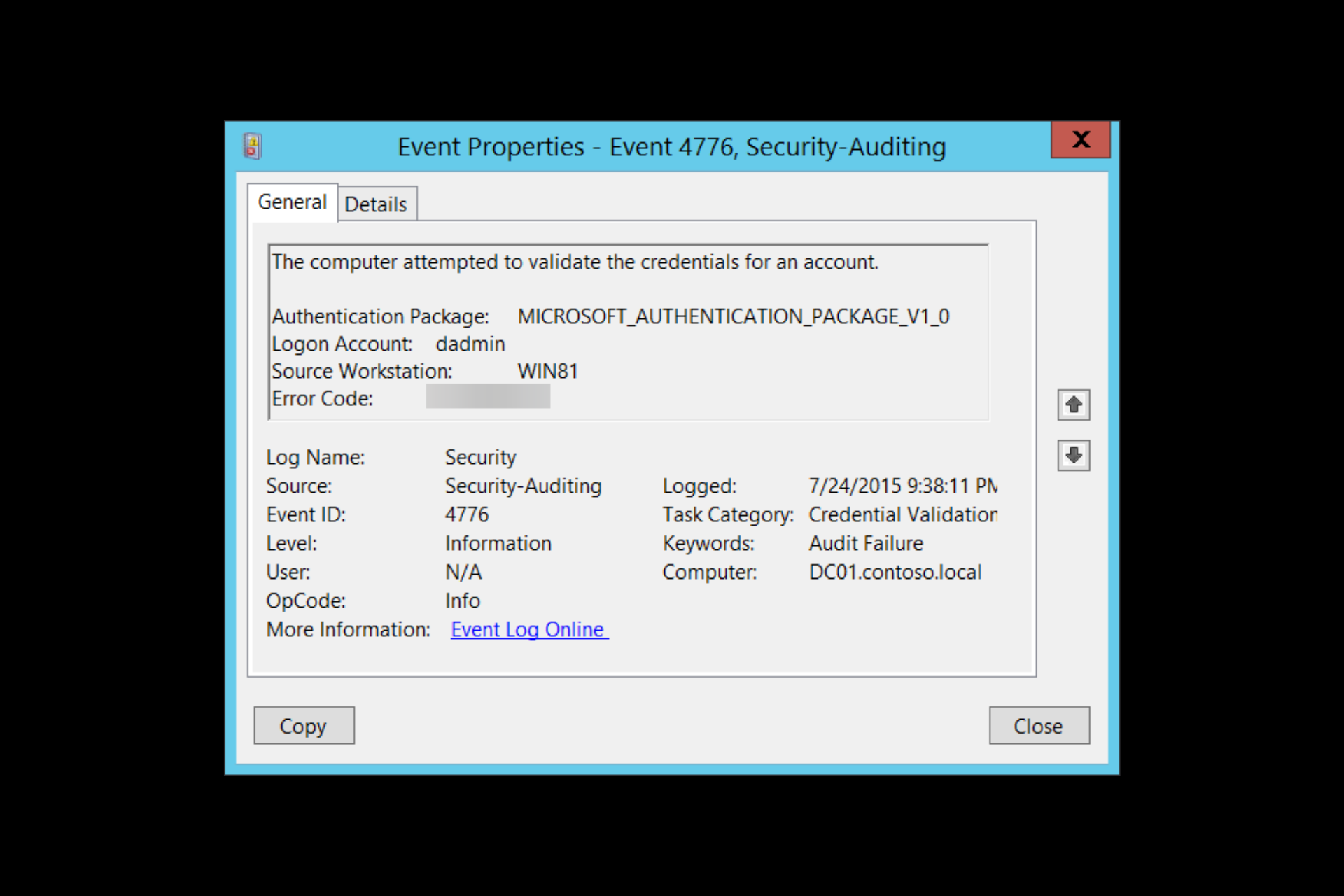
The domain controller attempted to validate the credentials for an account.Authentication Package: Always "MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0"Logon Account: name of the accountSource Workstation: computer name where logon attempt originatedError Code: 0x0
Every logon attempt on a domain controller is recorded on the DC. The DC logs the event ID 4776 when it validates the credentials and either succeeds or fails to authenticate a user via NTLM (not Kerberos). In addition, if there was a logon attempt via a local SAM account, where a server or a workstation validates credentials, then the event ID 4776 is logged on the local machine.
The event (as described in the details above) specifies:
- The authentication package specifies the package, which is always “MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0”.
- The Logon Account is the account name of the user or computer that attempted to log on. A logon account can also be a well-known security principle.
- The Source Workstation is the client’s computer name (source workstation) used to initiate the logon.
- Error Code The Error Code describes whether the authentication succeeded or failed (and the reasons). If you succeed, you’ll see an 0x0 error code, but if it fails, you’d see something other than 0x0—more on error codes in the next section.
Details on Windows Event ID 4776 Error Code
- Error Code equals (0x0) If this field is 0x0, the credentials were successfully validated as “Authentication Success – Event ID 4776 (S)”. No errors.
- Error Code not equal to (0x0) If the field is not equal to 0x0, it means that the credentials were not successfully validated (failed) “Authentication Failure – Event ID 4776 (F)”. Below is a table with more descriptions of the error code- not equal to 0x0.
| Error Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 0xC0000064 | Incorrect username. The username does not exist. |
| 0xC000006A | The username is correct, but not the password. |
| 0xC000006D | A generic logon failure. NTLM authentication-level mismatch. |
| 0xC000006F | Unauthorized account logon. Outside an authorized day or hour. |
| 0xC0000070 | Unauthorized account logon from a restricted workstation. |
| 0xC0000071 | The user tried to log on with an expired password. |
| 0xC0000072 | Unauthorized account logon due to a disabled account. |
| 0xC0000193 | Unauthorized account logon due to an expired account. |
| 0xC0000224 | A flag that the user needs to change the password at the next logon. |
| 0xC0000225 | Known to be a Windows bug. Not a risk. |
| 0xC0000234 | Attempted logon with a locked account. |
| 0xC0000371 | The local account storage does not contain information about the specific account. |
Troubleshooting the Windows Event ID 4776
If the Windows Event ID 4776 (S) is successful, you don’t have a problem. However, the problem starts when you get a few to hundreds or thousands of Windows Event ID 4776 (F) failed attempts. Although this would start to look like a problem, let us not draw quick conclusions just yet.
Although the evidence might indicate that your workstation is being a target of a brute force dictionary or rainbow attack, it could also indicate a relatively inoffensive system (such as a printer) is trying to authenticate with expired credentials.
How to solve the Windows Event ID 4776 failed attempts
- Start by identifying the logon account and the source workstation As you learned from the previous section, Event ID 4776 shows you the account name and the source workstation. Remember authentication happens via NTLM, which can help you identify the user or workstation quickly. But still, the source workstation could be attempting to log from outside, carrying a blank name, and also, the account could be random (made up). So, you’ll have to dig deeper.
- If this source workstation is blank or unknown To find out the source of an unknown workstation, you’ll need to involve other tools.
- Packet Sniffer Use third-party tools such as Wireshark deployed on the DC to capture the traffic at the same time as these events. You’ll need to use capture and display filters on Wireshark to be able to find exactly the source of these events. And also be able to correlate the exact time in Windows Event Viewer with Wireshark when this event happens. In addition, with Wireshark, you can quickly identify IP addresses to start drawing a better picture of where these logons are coming from.
- Network debugger Another handy third-party tool is a network debugger. Enable the NetLogon debugging utility on your DC. This tool will generate a log file with all these authentication requests. You can review this log file and find out where they originate.
- DCDiag The DCDiag is a Domain Controller Health Check tool that helps you with troubleshooting. Aside from running different health checks on the DC, the DCdiag also logs additional details like errors, warnings, or informational messages. Use the DCDiag with the verbose output (/v) to expand the output size.
- If a remote client is trying to authenticate using RDP (port 3389) You or the sys admin might have the port 3389 (RDP) open for users that connect remotely to machines inside the domain. When using the RDP, bear in mind that RDP prefers Kerberos to authenticate, but if it fails, it will fall back to using NTLM instead. Thus, this could be a reason you received the Event ID 4776 with an unknown source workstation. Below are a few solutions you can try:
- Use your firewall One of the most simple solutions is to use the firewall. Instead of using the denylists (allow all block some), use the zero-trust (or whitelists) approach (block all allow some) to only allow authorized attempts originating outside the network.
- Use a VPN A more advanced and efficient solution is to set up a VPN that allows remote users to connect to the local server and then authenticate normally.
Why should you monitor the Windows Event ID 4776
Always monitor the Windows Event ID 4776 to discover and list all the NTLM authentication attempts in your domain. Look for the events ID 4776 that were initiated by the accounts that are unauthorized or shouldn’t be using NTLM in the first place. Always remember that NTLM should only be used for local logon attempts (this is why you shouldn’t use RDP, but a VPN instead).
The reasons to monitor Event ID 4776:
- Identify relay and cracking attacks The NTLM authentication mechanism is vulnerable to relay attacks (fraudulent interception of information). First and most importantly, NTLM does not support modern cryptographic algorithms like SHA-256 or AES-256. This lack of encryption also makes it vulnerable to offline cracking attacks.
- Find reverse brute force, brute force, or enumeration attacks Monitor the Windows Event ID 4776 and keep track of multiple logon attempts within a short period, and with particular qualities like using multiple incorrect usernames. This type of behavior is strongly related to reverse brute force and enumeration attacks. In a similar case, you can keep track of this event and look for multiple logon attempts with incorrect (or misspelled password) within short periods. This behavior is related to brute-force attacks.
- Find potential malicious intent Keeping track of the Windows Event ID 4776 can help you find logon attempts outside authorized business hours or from unauthorized workstations. If these logon attempts are coming from a high-value account, then it might relate to malicious intent. In addition, logon attempts from locked expired, or disabled accounts could indicate mal-intentional use of resources.
Although it could be optimal to use more secure protocols such as the Kerberos (v5) and avoid these NTLM vulnerabilities, disabling NTLM authentication requests will ultimately hurt productivity and usability. There are still many NTLM authentication requests that need to be verified.
Kerberos is now the preferred authentication method used in Active Directory environments. As a good practice, before using more secure protocols like Kerberos and forcing Windows to limit NTLM traffic, it is first recommended to audit all security logs and events related to NTLM authentication. For these audits, there are a variety of tools you could use.
How to Monitor the Windows Event ID 4776
The Windows Event ID 4776 is a type of event log that should be monitored on an ongoing daily basis. You could use different practices and tools. We recommend knowing first how to properly use the Windows Event Viewer (along with its built-in capabilities) and then expanding to more robust audit tools like the ADAudit Plus.
1. Windows Event Viewer
Windows Event Viewer (From Windows Vista 7, Server 2008, and newer versions) allows you to introduce automation by associating a task to a specific event or log. When an event such as the Event ID 4776 is generated, you can associate it with a specific automated task. For instance, you can link it to an email, “Send me an email when Windows Event ID 4776 is generated”.
Windows Event Viewer does have some limitations, especially when it comes to its alerting and reporting engine. For instance, the email won’t give you granular information, such as the type of errors (i.e., attempts from unauthorized workstations, locked accounts, misspelled usernames, or outside business hours). In addition, Event Viewer also does not provide granular filtering capabilities to help you find what you are looking for.
2. ManageEngine ADAudit Plus
ManageEngine ADAudit Plus is an UBA-driven audit solution for full visibility into Active Directory environments. It provides real-time monitoring, behavior analytics, and reporting. This solution is perfect for monitoring the Windows Event ID 4776, as well as other events like ID 4724, 4726, 4769, 4768, 4740, and more.
Key Features
- Apply granular filters to look for specific threats.
- Get notified via email and SMS.
- Detect abnormal behaviors with UEBA (User and Entity Behavior Analytics).
- Out-of-the-box compliance reports for SOX, HIPAA, PCI, FISMA, GLBA, and the GDPR.
ADAudit Plus is a tool designed to monitor logons, analyze lockouts, and spot changes made to users, groups, OUs, or any Active Directory object. In addition, with the ADAudit Plus, you can also monitor local logons (NTLM), including changes made to users, groups, and security policies on Windows Servers. You can also monitor and audit various aspects within Windows workstations, including active time, changes to local users, security policies, USB activity, and more.
Download a 30-day ADAudit Plus trial, and start monitoring the Windows Event ID 4776, today.
Summary
The Windows Event ID 4776 (Audit Failure) – “The domain controller attempted to validate the credentials for an account” is an important event log that alerts you when a failed authentication event happens through the NTLM. This event log gives you valuable information, such as the workstation name, account, and the system or server used to pass the login request.
A way to solve this type of vulnerability is to audit NTLM authentication on this domain, monitor it, and, if possible, restrict it.
To audit and monitor this event successfully, learn how to use the Windows Event Viewer properly and then expand to more robust audit tools like the ADAudit Plus.
Windows Event ID 4776 FAQs
What does Event ID 4776 indicate?
Event ID 4776 indicates an attempted logon to a computer or network resource using a specific user account. This event is generated on the computer where the logon attempt was made.
What information is included in an Event ID 4776 log?
An Event ID 4776 log includes information such as the source network address, the logon type, the authentication package used, and the status of the logon attempt.
How can Event ID 4776 be used for security purposes?
Event ID 4776 can be used for security purposes by monitoring for unusual or unauthorized logon attempts. This can help detect potential security incidents or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Can Event ID 4776 be used to track logon activity on a network?
Yes, Event ID 4776 can be used to track logon activity on a network by collecting and analyzing the event logs from all relevant computers.
How can I view Event ID 4776 logs in Windows?
To view Event ID 4776 logs in Windows, you can use the Event Viewer tool and filter the security log for Event ID 4776.
Can Event ID 4776 be disabled?
No, Event ID 4776 cannot be disabled. It is an important security event that is generated by the operating system and is critical for monitoring and auditing logon activity on a computer or network.
| title | description | ms.pagetype | ms.prod | ms.mktglfcycl | ms.sitesec | ms.localizationpriority | author | ms.date | ms.reviewer | manager | ms.author | ms.technology | ms.collection | ms.topic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
4776(S, F) The computer attempted to validate the credentials for an account. (Windows 10) |
Describes security event 4776(S, F) The computer attempted to validate the credentials for an account. |
security |
windows-client |
deploy |
library |
none |
vinaypamnani-msft |
09/13/2021 |
aaroncz |
vinpa |
itpro-security |
highpri |
reference |
4776(S, F): The computer attempted to validate the credentials for an account.
Subcategory: Audit Credential Validation
Event Description:
This event generates every time that a credential validation occurs using NTLM authentication.
This event occurs only on the computer that is authoritative for the provided credentials. For domain accounts, the domain controller is authoritative. For local accounts, the local computer is authoritative.
It shows successful and unsuccessful credential validation attempts.
It shows only the computer name (Source Workstation) from which the authentication attempt was performed (authentication source). For example, if you authenticate from CLIENT-1 to SERVER-1 using a domain account you’ll see CLIENT-1 in the Source Workstation field. Information about the destination computer (SERVER-1) isn’t presented in this event.
If a credential validation attempt fails, you’ll see a Failure event with Error Code parameter value not equal to “0x0”.
The main advantage of this event is that on domain controllers you can see all authentication attempts for domain accounts when NTLM authentication was used.
For monitoring local account logon attempts, it’s better to use event “4624: An account was successfully logged on” because it contains more details and is more informative.
This event also generates when a workstation unlock event occurs.
This event does not generate when a domain account logs on locally to a domain controller.
Note For recommendations, see Security Monitoring Recommendations for this event.
Event XML:
- <Event xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event">
- <System>
<Provider Name="Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing" Guid="{54849625-5478-4994-A5BA-3E3B0328C30D}" />
<EventID>4776</EventID>
<Version>0</Version>
<Level>0</Level>
<Task>14336</Task>
<Opcode>0</Opcode>
<Keywords>0x8010000000000000</Keywords>
<TimeCreated SystemTime="2015-07-25T04:38:11.003163100Z" />
<EventRecordID>165437</EventRecordID>
<Correlation />
<Execution ProcessID="500" ThreadID="532" />
<Channel>Security</Channel>
<Computer>DC01.contoso.local</Computer>
<Security />
</System>
- <EventData>
<Data Name="PackageName">MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0</Data>
<Data Name="TargetUserName">dadmin</Data>
<Data Name="Workstation">WIN81</Data>
<Data Name="Status">0xc0000234</Data>
</EventData>
</Event>
Required Server Roles: no specific requirements.
Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista.
Event Versions: 0.
Field Descriptions:
- Authentication Package [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of Authentication Package that was used for credential validation. It’s always “MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0” for 4776 event.
Note Authentication package is a DLL that encapsulates the authentication logic used to determine whether to permit a user to log on. Local Security Authority (LSA) authenticates a user logon by sending the request to an authentication package. The authentication package then examines the logon information and either authenticates or rejects the user logon attempt.
-
Logon Account [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the account that had its credentials validated by the Authentication Package. Can be user name, computer account name or well-known security principal account name. Examples:
-
User example: dadmin
-
Computer account example: WIN81$
-
Local System account example: Local
-
Local Service account example: Local Service
-
-
Source Workstation [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the computer from which the logon attempt originated.
-
Error Code [Type = HexInt32]: contains error code for Failure events. For Success events this parameter has “0x0” value. The table below contains most common error codes for this event:
| Error Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 0xC0000064 | The username you typed does not exist. Bad username. |
| 0xC000006A | Account logon with misspelled or bad password. |
| 0xC000006D | — Generic logon failure. Some of the potential causes for this: An invalid username and/or password was used LAN Manager Authentication Level mismatch between the source and target computers. |
| 0xC000006F | Account logon outside authorized hours. |
| 0xC0000070 | Account logon from unauthorized workstation. |
| 0xC0000071 | Account logon with expired password. |
| 0xC0000072 | Account logon to account disabled by administrator. |
| 0xC0000193 | Account logon with expired account. |
| 0xC0000224 | Account logon with «Change Password at Next Logon» flagged. |
| 0xC0000234 | Account logon with account locked. |
| 0xC0000371 | The local account store does not contain secret material for the specified account. |
| 0x0 | No errors. |
Table 1. Winlogon Error Codes.
Security Monitoring Recommendations
For 4776(S, F): The computer attempted to validate the credentials for an account.
| Type of monitoring required | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| High-value accounts: You might have high-value domain or local accounts for which you need to monitor each action. Examples of high-value accounts are database administrators, built-in local administrator account, domain administrators, service accounts, domain controller accounts and so on. |
Monitor this event with the “Logon Account” that corresponds to the high-value account or accounts. |
| Anomalies or malicious actions: You might have specific requirements for detecting anomalies or monitoring potential malicious actions. For example, you might need to monitor for use of an account outside of working hours. | When you monitor for anomalies or malicious actions, use the “Logon Account” value (with other information) to monitor how or when a particular account is being used. To monitor activity of specific user accounts outside of working hours, monitor the appropriate Logon Account + Source Workstation pairs. |
| Non-active accounts: You might have non-active, disabled, or guest accounts, or other accounts that should never be used. | Monitor this event with the “Logon Account” that should never be used. |
| Account allow list: You might have a specific allow list of accounts that are the only ones allowed to perform actions corresponding to particular events. | If this event corresponds to a “allow list-only” action, review the “Logon Account” for accounts that are outside the allow list. |
| Restricted-use computers: You might have certain computers from which certain people (accounts) shouldn’t log on. | Monitor the target Source Workstation for credential validation requests from the “Logon Account” that you’re concerned about. |
| Account naming conventions: Your organization might have specific naming conventions for account names. | Monitor “Logon Account” for names that don’t comply with naming conventions. |
-
If NTLM authentication shouldn’t be used for a specific account, monitor for that account. Don’t forget that local logon will always use NTLM authentication if an account logs on to a device where its user account is stored.
-
You can use this event to collect all NTLM authentication attempts in the domain, if needed. Don’t forget that local logon will always use NTLM authentication if the account logs on to a device where its user account is stored.
-
If a local account should be used only locally (for example, network logon or terminal services logon isn’t allowed), you need to monitor for all events where Source Workstation and Computer (where the event was generated and where the credentials are stored) have different values.
-
Consider tracking the following errors for the reasons listed:
| Error to track | What the error might indicate |
|---|---|
| User logon with misspelled or bad user account | For example, N events in the last N minutes can be an indicator of an account enumeration attack, especially relevant for highly critical accounts. |
| User logon with misspelled or bad password | For example, N events in the last N minutes can be an indicator of a brute-force password attack, especially relevant for highly critical accounts. |
| User logon outside authorized hours | Can indicate a compromised account; especially relevant for highly critical accounts. |
| User logon from unauthorized workstation | Can indicate a compromised account; especially relevant for highly critical accounts. |
| User logon to account disabled by administrator | For example, N events in last N minutes can be an indicator of an account compromise attempt, especially relevant for highly critical accounts. |
| User logon with expired account | Can indicate an account compromise attempt; especially relevant for highly critical accounts. |
| User logon with account locked | Can indicate a brute-force password attack; especially relevant for highly critical accounts. |
User501181060 posted
Hi Guys,
We have been getting 4776 Events (status with 0xc0000064)on our IIS server stating that the account does not exists for multiple users.
But AD accounts is actually exists and not issues with AD accounts as well.
In Same server I can see Successful logon events for same users, don’t understand why its happening
Please help me on this…
Successful logon event 4624 for same user account on same server
An account was successfully logged on.
Subject:
Security ID:
NULL SID
Account Name: —
Account Domain: —
Logon ID:
0x0
Logon Type:
3
New Logon:
Security ID:
xxxxxxxxxxx
Account Name: xxxxxxxxxxx
Account Domain: xxxxxxxxxxx
Logon ID:
0x2d7af6a6e
Logon GUID:
{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000}
Process Information:
Process ID:
0x0
Process Name: —
Network Information:
Workstation Name: xxxxxxxxxxxx
Source Network Address: xx.xx.xx.xx
Source Port:
58480
Detailed Authentication Information:
Logon Process: NtLmSsp
Authentication Package: NTLM
Transited Services: —
Package Name (NTLM only): NTLM V2
Key Length:
0
This event is generated when a logon session is created. It is generated on the computer that was accessed.
The subject fields indicate the account on the local system which requested the logon. This is most commonly a service such as the Server service, or a local process such as Winlogon.exe or Services.exe.
The logon type field indicates the kind of logon that occurred. The most common types are 2 (interactive) and 3 (network).
The New Logon fields indicate the account for whom the new logon was created, i.e. the account that was logged on.
The network fields indicate where a remote logon request originated. Workstation name is not always available and may be left blank in some cases.
The authentication information fields provide detailed information about this specific logon request.
— Logon GUID is a unique identifier that can be used to correlate this event with a KDC event.
— Transited services indicate which intermediate services have participated in this logon request.
— Package name indicates which sub-protocol was used among the NTLM protocols.
— Key length indicates the length of the generated session key. This will be 0 if no session key was requested.
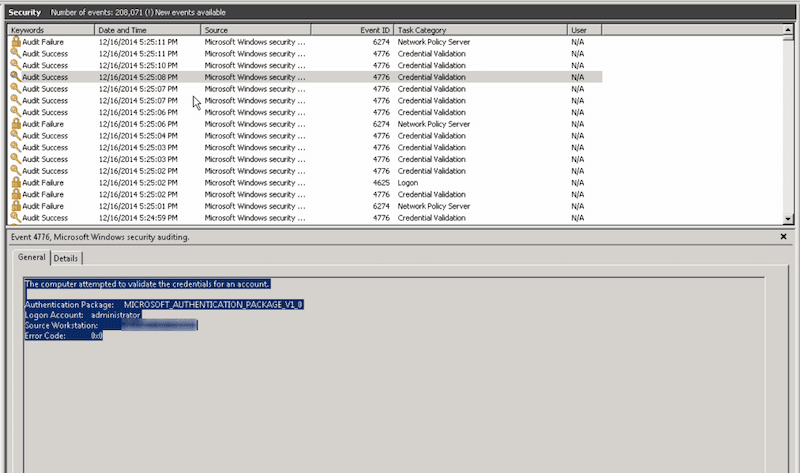
4776 Event screenshot
I’m seeing something very troubling on one of my servers. The security log is flooded with event id 4776 followed five seconds later by event id 4625. Then eighty-three seconds pass and it repeats. More troubling is the account names associated. «Dayle», «Dayton», «Dawna» etc. These aren’t in the form of our account names and appear to be going in alphabetical order.
This seems to be some form of hack attack, or malware but I don’t know how to track it down and put a stop to it.
The server is a hybrid Exchange server paired with our hosted Exchange and Office 365. It also has WSUS and SCCM on it.
Can anyone help me out?
Log Name: Security
Source: Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing
Date: 5/3/2016 12:34:36 PM
Event ID: 4776
Task Category: Credential Validation
Level: Information
Keywords: Audit Failure
User: N/A
Computer: EXCHANGE.doman.local
Description:
The computer attempted to validate the credentials for an account.
Authentication Package: MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0
Logon Account: dayle
Source Workstation: EXCHANGE
Error Code: 0xC0000064
Event Xml:
<Event xmlns=»http://schemas.micr Opens a new windowosoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event Opens a new window«>
<System>
<Provider Name=»Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing» Guid=»{54849625-5478-4994-A5BA-3E3B0328C30D}» />
<EventID>4776</EventID>
<Version>0</Version>
<Level>0</Level>
<Task>14336</Task>
<Opcode>0</Opcode>
<Keywords>0x8010000000000000</Keywords>
<TimeCreated SystemTime=»2016-05-03T16:34:36.148982700Z» />
<EventRecordID>13917444</EventRecordID>
<Correlation />
<Execution ProcessID=»696″ ThreadID=»748″ />
<Channel>Security</Channel>
<Computer>EXCHANGE.domain.local</Computer>
<Security />
</System>
<EventData>
<Data Name=»PackageName»>MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0</Data>
<Data Name=»TargetUserName»>dayle</Data>
<Data Name=»Workstation»>EXCHANGE</Data>
<Data Name=»Status»>0xc0000064</Data>
</EventData>
</Event>
Log Name: Security
Source: Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing
Date: 5/3/2016 12:34:41 PM
Event ID: 4625
Task Category: Logon
Level: Information
Keywords: Audit Failure
User: N/A
Computer: EXCHANGE.domain.local
Description:
An account failed to log on.
Subject:
Security ID: SYSTEM
Account Name: EXCHANGE
Account Domain: DOMAIN
Logon ID: 0x3E7
Logon Type: 8
Account For Which Logon Failed:
Security ID: NULL SID
Account Name: dayle
Account Domain:
Failure Information:
Failure Reason: Unknown user name or bad password.
Status: 0xC000006D
Sub Status: 0xC0000064
Process Information:
Caller Process ID: 0x6d2c
Caller Process Name: C:Program FilesMicrosoftExchange ServerV15BinMSExchangeFrontendTransport.exe
Network Information:
Workstation Name: EXCHANGE
Source Network Address: —
Source Port: —
Detailed Authentication Information:
Logon Process: Advapi
Authentication Package: MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0
Transited Services: —
Package Name (NTLM only): —
Key Length: 0
This event is generated when a logon request fails. It is generated on the computer where access was attempted.
The Subject fields indicate the account on the local system which requested the logon. This is most commonly a service such as the Server service, or a local process such as Winlogon.exe or Services.exe.
The Logon Type field indicates the kind of logon that was requested. The most common types are 2 (interactive) and 3 (network).
The Process Information fields indicate which account and process on the system requested the logon.
The Network Information fields indicate where a remote logon request originated. Workstation name is not always available and may be left blank in some cases.
The authentication information fields provide detailed information about this specific logon request.
— Transited services indicate which intermediate services have participated in this logon request.
— Package name indicates which sub-protocol was used among the NTLM protocols.
— Key length indicates the length of the generated session key. This will be 0 if no session key was requested.
Event Xml:
<Event xmlns=»http://schemas.micr Opens a new windowosoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event Opens a new window«>
<System>
<Provider Name=»Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing» Guid=»{54849625-5478-4994-A5BA-3E3B0328C30D}» />
<EventID>4625</EventID>
<Version>0</Version>
<Level>0</Level>
<Task>12544</Task>
<Opcode>0</Opcode>
<Keywords>0x8010000000000000</Keywords>
<TimeCreated SystemTime=»2016-05-03T16:34:41.180349400Z» />
<EventRecordID>13917445</EventRecordID>
<Correlation />
<Execution ProcessID=»696″ ThreadID=»748″ />
<Channel>Security</Channel>
<Computer>EXCHANGE.domain.local</Computer>
<Security />
</System>
<EventData>
<Data Name=»SubjectUserSid»>S-1-5-18</Data>
<Data Name=»SubjectUserName»>EXCHANGE</Data>
<Data Name=»SubjectDomainName»>DOMAIN</Data>
<Data Name=»SubjectLogonId»>0x3e7</Data>
<Data Name=»TargetUserSid»>S-1-0-0</Data>
<Data Name=»TargetUserName»>dayle</Data>
<Data Name=»TargetDomainName»>
</Data>
<Data Name=»Status»>0xc000006d</Data>
<Data Name=»FailureReason»>%%2313</Data>
<Data Name=»SubStatus»>0xc0000064</Data>
<Data Name=»LogonType»>8</Data>
<Data Name=»LogonProcessName»>Advapi </Data>
<Data Name=»AuthenticationPackageName»>MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0</Data>
<Data Name=»WorkstationName»>EXCHANGE</Data>
<Data Name=»TransmittedServices»>-</Data>
<Data Name=»LmPackageName»>-</Data>
<Data Name=»KeyLength»>0</Data>
<Data Name=»ProcessId»>0x6d2c</Data>
<Data Name=»ProcessName»>C:Program FilesMicrosoftExchange ServerV15BinMSExchangeFrontendTransport.exe</Data>
<Data Name=»IpAddress»>-</Data>
<Data Name=»IpPort»>-</Data>
</EventData>
</Event>
Содержание
- Компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные учетной записи
- Компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные учетной записи
- Вопрос
- 4776 (S, F): компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные для учетной записи.
- Рекомендации по контролю безопасности
- Компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные учетной записи
- Question
- Компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные учетной записи
- Спрашивающий
- Общие обсуждения
Компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные учетной записи
Сообщения: 14
Благодарности:
Включил аудит входа в систему и аудит событий входа в систему.
Теперь видна такая последовательность:
Фиксируются несколько событий Аудита Отказа Event 4776 Credential validation, например:
Имя журнала: Security
Источник: Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing
Дата: 20.04.2020 14:04:47
Код события: 4776
Категория задачи:Credential Validation
Уровень: Сведения
Ключевые слова:Аудит отказа
Пользователь: Н/Д
Компьютер: Bigbro
Описание:
Компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные учетной записи.
Пакет проверки подлинности: MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0
Учетная запись входа: ЮЛИАН
Исходная рабочая станция:
Код ошибки: 0xC0000064
Xml события:
4776
0
0
14336
0
0x8010000000000000
1411013
Security
Bigbro
MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0
ЮЛИАН
0xc0000064
в каждом из событий разные имена пользователей, похоже на часто используемые, но явно не мои, например
Demo
ЮЛИАН
administrator
bar
Office1
Гость
GLAVBUH
БАЗА2
далее идет Аудит отказа, событие Logon 4625, с соответсвующим именем пользователя
Имя журнала: Security
Источник: Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing
Дата: 20.04.2020 14:14:07
Код события: 4625
Категория задачи:Logon
Уровень: Сведения
Ключевые слова:Аудит отказа
Пользователь: Н/Д
Компьютер: Bigbro
Описание:
Учетной записи не удалось выполнить вход в систему.
Учетная запись, которой не удалось выполнить вход:
ИД безопасности: NULL SID
Имя учетной записи: БАЗА2
Домен учетной записи:
Сведения об ошибке:
Причина ошибки: Неизвестное имя пользователя или неверный пароль.
Состояние: 0xC000006D
Подсостояние: 0xC0000064
Данное событие возникает при неудачной попытке входа. Оно регистрируется на компьютере, попытка доступа к которому была выполнена.
Поля «Субъект» указывают на учетную запись локальной системы, запросившую вход. Обычно это служба, например, служба «Сервер», или локальный процесс, такой как Winlogon.exe или Services.exe.
В поле «Тип входа» указан тип выполненного входа. Наиболее распространенными являются типы 2 (интерактивный) и 3 (сетевой).
В полях «Сведения о процессе» указано, какая учетная запись и процесс в системе выполнили запрос на вход.
Поля «Сведения о сети» указывают на источник запроса на удаленный вход. Имя рабочей станции доступно не всегда, и в некоторых случаях это поле может оставаться незаполненным.
Поля сведений о проверке подлинности содержат подробные данные о конкретном запросе на вход.
— В поле «Промежуточные службы» указано, какие промежуточные службы участвовали в данном запросе на вход.
— Поле «Имя пакета» указывает на подпротокол, использованный с протоколами NTLM.
— Поле «Длина ключа» содержит длину созданного сеансового ключа. Это поле может иметь значение «0», если сеансовый ключ не запрашивался.
Xml события:
В тот момент когда идет попытка под Гостем, фикируется аудит успеха (вход), а потом аудит успеха (выход) который как раз я описал в первом сообщении.
Как можно попытаться найти источник этой гадости?
UPD!!
Проблема найдена. На роутере был проброшен 3389 в сторону компа. Соответсвенно видим обычный брутфорс RDP.
Видимо просто под гостем у них авторизация срабатывала, поэтому фиксировался аудит выхода который по дефолту пишется в журнал. Но под гостем RDP нельзя, так что перебор шел дальше..
Источник
Компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные учетной записи
Вопрос
Добрый день. Сегодня на контроллере домена в журнале аудита стали фиксироваться следующие события:
Имя журнала: Security
Источник: Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing
Дата: 10.04.2018 22:24:36
Код события: 4776
Категория задачи:Проверка учетных данных
Уровень: Сведения
Ключевые слова:Аудит отказа
Пользователь: Н/Д
Компьютер: DC.Z.RU
Описание:
Компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные учетной записи.
Пакет проверки подлинности: MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0
Учетная запись входа: JACK
Исходная рабочая станция:
Код ошибки: 0xC0000064
Xml события:
4776
0
0
14336
0
0x8010000000000000
479489427
Security
DC.DOMAIN.METIZ.RU
MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0
JACK
0xc0000064
Имя журнала: Security
Источник: Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing
Дата: 10.04.2018 22:38:19
Код события: 4776
Категория задачи:Проверка учетных данных
Уровень: Сведения
Ключевые слова:Аудит отказа
Пользователь: Н/Д
Компьютер: DC.Z.RU
Описание:
Компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные учетной записи.
Пакет проверки подлинности: MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0
Учетная запись входа: ZAKAZ
Исходная рабочая станция:
Код ошибки: 0xC0000064
Xml события:
4776
0
0
14336
0
0x8010000000000000
479490763
Security
DC.DOMAIN.METIZ.RU
MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0
ZAKAZ
0xc0000064
И так постоянно идет перебор разных несуществующих учеток. Что идет перебор не из вне уверен на 100%. Как определить компьютер, с которого происходит подбор?
Заметил. Подбор имен идет строго по алфавиту.
Источник
4776 (S, F): компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные для учетной записи.
Описание события:
Это событие создает каждый раз, когда проверка учетных данных происходит с помощью проверки подлинности NTLM.
Это событие происходит только на компьютере, который является авторитетным для предоставленных учетных данных. Для учетных записей домена контроллер домена является авторитетным. Для локальных учетных записей локальный компьютер является авторитетным.
В нем показаны успешные и неудачные попытки проверки учетных данных.
В нем показано только имя компьютера (Source Workstation), с которого была выполнена попытка проверки подлинности (источник проверки подлинности). Например, при проверке подлинности от CLIENT-1 до SERVER-1 с помощью учетной записи домена вы увидите CLIENT-1 в поле Source Workstation. Сведения о компьютере назначения (SERVER-1) не представлены в этом событии.
В случае сбоя попытки проверки учетных данных вы увидите событие с ошибкой со значением параметра Код ошибки, не равное «0x0».
Основное преимущество этого события заключается в том, что на контроллерах домена можно увидеть все попытки проверки подлинности для учетных записей домена при проверке подлинности NTLM.
Для мониторинга попыток логоса локальной учетной записи лучше использовать событие»4624:учетная запись была успешно зарегистрирована», так как она содержит дополнительные сведения и более информативна.
Это событие также создается, когда происходит событие разблокировки рабочей станции.
Это событие не создается при локальном входе учетной записи домена в контроллер домена.
Примечание. Рекомендации приведены в разделе Рекомендации по мониторингу безопасности для этого события.
XML события:
Необходимые роли сервера: никаких особых требований.
Минимальная версия ОС: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista.
Версии события: 0.
Описания полей:
**** Примечание Пакет проверки подлинности — это DLL, инкапсулирует логику проверки подлинности, используемую для определения того, следует ли разрешить пользователю войти в систему. Local Security Authority (LSA) сдает проверку подлинности логотипа пользователя, отправляя запрос в пакет проверки подлинности. Затем пакет проверки подлинности проверяет сведения о логотипе и проверяет или отклоняет попытку логоса пользователя.
Учетная запись Logon [Type = UnicodeString]: имя учетной записи, которая была проверена пакетом проверки подлинности. Может быть имя пользователя, имя учетной записи компьютера или хорошо известное имя основной учетной записи безопасности. Примеры:
Пример пользователя: dadmin
Пример учетной записи компьютера: WIN81$
Пример учетной записи локальной системы: Локальный
Пример учетной записи локальной службы: локализованная служба
Source Workstation [Type = UnicodeString]: имя компьютера, с которого возникла попытка логотипа.
Код ошибки [Type = HexInt32]: содержит код ошибки для событий сбоя. Для событий success этот параметримеет значение 0x0«. В таблице ниже приведены наиболее распространенные коды ошибок для этого события:
| Код ошибки | Описание |
|---|---|
| 0xC0000064 | Имя пользователя, впечатанный вами, не существует. Плохое имя пользователя. |
| 0xC000006A | Логотип учетной записи с ошибкой или плохим паролем. |
| 0xC000006D | — Сбой общего логотипа. Некоторые из возможных причин для этого: Было использовано имя пользователя и/или пароль, недействительный Несоответствие уровня проверки подлинности lan Manager между исходным и целевым компьютерами. |
| 0xC000006F | Логотип учетной записи за пределами разрешенных часов. |
| 0xC0000070 | Логотип учетной записи с несанкционированной рабочей станции. |
| 0xC0000071 | Логотип учетной записи с истекшим паролем. |
| 0xC0000072 | Логотип учетной записи для учетной записи отключен администратором. |
| 0xC0000193 | Логотип учетной записи с просроченной учетной записью. |
| 0xC0000224 | Логотип учетной записи с флагом «Изменение пароля в следующем логотипе». |
| 0xC0000234 | Логотип учетной записи с заблокированной учетной записью. |
| 0xC0000371 | Локальный магазин учетных записей не содержит секретных материалов для указанной учетной записи. |
| 0x0 | Никаких ошибок. |
Таблица 1: Коды ошибок Winlogon.
Рекомендации по контролю безопасности
Для 4776 (S, F): компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные для учетной записи.
| Тип требуемого мониторинга | Рекомендации |
|---|---|
| Учетные записи большой ценности: у вас может быть домен или локальные учетные записи большой ценности, для которых необходимо отслеживать каждое действие. Примеры учетных записей большой ценности: учетные записи администраторов баз данных, встроенная учетная запись локального администратора, учетные записи администраторов домена, учетные записи служб, учетные записи контроллеров домена и т. д. |
Отслеживайте это событие с помощью учетной записи Logon, соответствующей учетной записи или учетной записи с высокой стоимостью. |
| Аномалии и вредоносные действия: у вас могут быть особые требования касательно обнаружения аномалий или отслеживания потенциально вредоносных действий. Например, вам может потребоваться отслеживать использование учетной записи во внерабочее время. | При отслеживании аномалий или вредоносных действий используйте значение «Logon Account» (с другими сведениями), чтобы отслеживать, как или когда используется определенная учетная запись. Чтобы отслеживать активность определенных учетных записей пользователей вне рабочих часов, отслеживайте соответствующие пары учетных записей Logon + Source Workstation. |
| Неактивные учетные записи: у вас, возможно, есть неактивные, отключенные или гостевые учетные записи, а также другие учетные записи, которые не должны использоваться. | Отслеживайте это событие с помощью «Учетной записи Logon», которую нельзя использовать. |
| Список разрешенных учетных записей: возможно, у вас есть список разрешенных учетных записей, которым разрешено выполнять действия, соответствующие определенным событиям. | Если это событие соответствует действию «разрешить только список», просмотрите «Учетная запись Logon» для учетных записей, не вполне допустимых. |
| Компьютеры с ограниченным использованием. Возможно, у вас есть определенные компьютеры, с которых определенные люди (учетные записи) не должны входить в систему. | Отслеживайте целевые исходные рабочие станции для запросов проверки учетных данных из «Учетной записи Logon», которую вы беспокоите. |
| Соглашения об именовании учетных записей: в вашей организации могут быть определенные соглашения об именовании учетных записей. | Отслеживайте «Учетную запись логона» для имен, не соответствующих конвенциям имен. |
Если проверку подлинности NTLM не следует использовать для определенной учетной записи, отслеживайте эту учетную запись. Не забывайте, что локальный логотип всегда будет использовать проверку подлинности NTLM, если учетная запись входит в устройство, на котором хранится учетная запись пользователя.
Это событие можно использовать для сбора всех попыток проверки подлинности NTLM в домене, если это необходимо. Не забывайте, что локальный логотип всегда будет использовать проверку подлинности NTLM, если учетная запись входит в устройство, на котором хранится учетная запись пользователя.
Если локальная учетная запись должна использоваться только локально (например, не разрешен логотип сетевых или терминальных **** служб), необходимо отслеживать все события, в которых исходные рабочие станции и компьютеры (где событие было сгенерировано и где хранятся учетные данные) имеют разные значения.
Рассмотрите возможность отслеживания следующих ошибок по указанным ниже причинам:
Источник
Компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные учетной записи
Question
В последние дни наблюдаю возросшую блокировку учетных записей в результате применения политики учетных записей в AD. Но с одним пользователем имею проблему. Учетная запись блокируется несколько раз за день. Провели антивирусную проверку, очистили кэш паролей, удалили все лишние программы. Но найти причину блокировки так и не смог. Использование утилиты Netwrix Account Lockout Examiner также не дало ответ на причины блокировки.
До достижения предела числа сбойных попыток входа в журнале событий периодически регистрируется событие:
Источник: Microsoft Windows security auditing.
Категория: Проверка учетных данных
Компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные учетной записи.
Пакет проверки подлинности: MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0
Учетная запись входа: baranova
Исходная рабочая станция: PC-BARANOVA3
Код ошибки: 0xC000006A
Далее учетная запись блокируется. Регистрируется сообщение в журнале событий:
Источник: Microsoft Windows security auditing.
Категория: Управление учетными записями
ID: 4740
Заблокирована учетная запись пользователя.
Субъект:
Идентификатор безопасности: СИСТЕМА
Имя учетной записи: SRV-AD1$
Домен учетной записи: SFH
Идентификатор входа: 0x3E7
Заблокированная учетная запись:
Идентификатор безопасности: SFHBaranova
Имя учетной записи: Baranova
Дополнительные сведения:
Имя вызывающего компьютера: PC-BARANOVA3
В дальнейшем до разблокировки учетной записи периодически регистрируется ошибка:
Источник: Microsoft Windows security auditing.
Категория: Проверка учетных данных
ID: 4776
Компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные учетной записи.
Пакет проверки подлинности: MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0
Учетная запись входа: baranova
Исходная рабочая станция: PC-BARANOVA3
Код ошибки: 0xC0000234
На рабочей станции (Windows 7 Pro SP1) в журнале регистрируется ошибка:
Источник: Microsoft Windows security auditing.
Категория: Вход в систему
ID: 4625
Учетной записи не удалось выполнить вход в систему.
Субъект:
ИД безопасности: СИСТЕМА
Имя учетной записи: PC-BARANOVA3$
Домен учетной записи: SFH
Код входа: 0x3e7
Учетная запись, которой не удалось выполнить вход:
ИД безопасности: NULL SID
Имя учетной записи: Baranova
Домен учетной записи: SFH
Сведения об ошибке:
Причина ошибки: Неизвестное имя пользователя или неверный пароль.
Состояние: 0xc000006d
Подсостояние: 0xc000006a
Сведения о процессе:
Идентификатор процесса вызывающей стороны: 0x298
Имя процесса вызывающей стороны: C:WindowsSystem32winlogon.exe
Сведения о сети:
Имя рабочей станции: PC-BARANOVA3
Сетевой адрес источника: 127.0.0.1
Порт источника: 0
Данное событие возникает при неудачной попытке входа. Оно регистрируется на компьютере, попытка доступа к которому была выполнена.
Поля «Субъект» указывают на учетную запись локальной системы, запросившую вход. Обычно это служба, например, служба «Сервер», или локальный процесс, такой как Winlogon.exe или Services.exe.
В поле «Тип входа» указан тип выполненного входа. Наиболее распространенными являются типы 2 (интерактивный) и 3 (сетевой).
В полях «Сведения о процессе» указано, какая учетная запись и процесс в системе выполнили запрос на вход.
Поля «Сведения о сети» указывают на источник запроса на удаленный вход. Имя рабочей станции доступно не всегда, и в некоторых случаях это поле может оставаться незаполненным.
Поля сведений о проверке подлинности содержат подробные данные о конкретном запросе на вход.
— В поле «Промежуточные службы» указано, какие промежуточные службы участвовали в данном запросе на вход.
— Поле «Имя пакета» указывает на подпротокол, использованный с протоколами NTLM.
— Поле «Длина ключа» содержит длину созданного ключа сеанса. Это поле может иметь значение «0», если ключ сеанса не запрашивался.
Может быть кто-нибудь кто-нибудь подскажет, как найти источник проблемы.
Источник
Компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные учетной записи
Этот форум закрыт. Спасибо за участие!
Спрашивающий
Общие обсуждения
Всем доброго времени суток. Есть ряд рабочих станций Windows7 в домене. На каждй из них заведён локальный администратор. Доступ к стандартному общему ресурсу через администратора домена работает. Но если пытаюсь зайти через лок. администратора: имя_компьютераАдминистратор, не пускает, причём пароль вводится 100% правильно (проверял локально). Тип аутентификации вроде как и там и там NTLM. Учётную запись гостя включать не собираюсь. Вот кусок лога после неудачной попытки входа:
4776:
Компьютер попытался проверить учетные данные учетной записи.
Пакет проверки подлинности: MICROSOFT_AUTHENTICATION_PACKAGE_V1_0
Учетная запись входа: Администратор
Исходная рабочая станция: MYCOMP
Код ошибки: 0xc000006a
4625:
Учетной записи не удалось выполнить вход в систему.
Субъект:
ИД безопасности: NULL SID
Тип входа: 3
Учетная запись, которой не удалось выполнить вход:
ИД безопасности: NULL SID
Имя учетной записи: Администратор
Домен учетной записи: PROBLEM_COMP
Сведения об ошибке:
Причина ошибки: Неизвестное имя пользователя или неверный пароль.
Сведения о процессе:
Идентификатор процесса вызывающей стороны: 0x0
Сведения о сети:
Имя рабочей станции: MYCOMP
Сетевой адрес источника: 1.1.1.140
Порт источника: 61509
Сведения о проверке подлинности:
Источник