Improve Article
Save Article
Improve Article
Save Article
An unexpected, unwanted event that disturbed the normal flow of a program is called an Exception.
There are mainly two types of exception in Java:
1. Checked Exception
2. Unchecked Exception
ExceptionInInitializerError is the child class of the Error class and hence it is an unchecked exception. This exception is rise automatically by JVM when JVM attempts to load a new class as, during class loading, all static variables and static initializer block are being evaluated. This exception also acts as a signal that tells us that an unexpected exception has occurred in a static initializer block or in the assignment of value to the static variable.
There are basically two cases when ExceptionInInitializerError can occur in a Java Program:
1. ExceptionInInitializerError While Assigning Value To The Static Variable
In the below example we assign a static variable to 20/0 where 20/0 gives an undefined arithmetic behavior and hence there occurs an exception in the static variable assignment and ultimately we will get ExceptionInInitializerError.
Java
class GFG {
static int x = 20 / 0;
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("The value of x is " + x);
}
}
2. ExceptionInInitializerError While Assigning Null Value Inside A Static Block
In the below example we have declared a static block inside which we create a string s and assign a null value to it, and then we are printing the length of string, so we will get NullPointerException because we were trying to print the length of a string that has its value as null and as we see that this exception occurs inside the static block, so we will get ExceptionInInitializerError.
Java
class GFG {
static
{
String s = null;
System.out.println(s.length());
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("GeeksForGeeks Is Best");
}
}
How to Resolve Java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError ?
- We can resolve the java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError by ensuring that static initializer block of classes does not throw any Runtime Exception.
- We can resolve also resolve this exception by ensuring that the initializing static variable of classes also doesn’t throw any Runtime Exception.
Содержание
- How to Fix Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError in Java Program? Example
- Cause of «Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError»
- Things to remember:
- Install Spark Exception #900
- Comments
- How to Handle the Exception In Initializer Runtime Error in Java
- Introduction to Runtime Errors & Exceptions
- ExceptionInInitializerError Error: What, Why & How?
- How to handle the ExceptionInInitializerError Error
- java.lang.exceptionininitializererror – How to handle Exception Initializer Error
- How to deal with the ExceptionInInitializerError
- Final comments on the Error
- Когда Java выбрасывает ошибку ExceptionInInitializerError?
- 1. Обзор
- 2. Ошибка exceptioninitializererror
- 3. Блок Статического Инициализатора
- 4. Инициализация статической Переменной
- 5. Проверенные исключения
- 5.1. OpenJDK
- 6. Заключение
How to Fix Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError in Java Program? Example
JVM throws java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError , when there is an Exception inside static initializer block. If you know about static variables in Java, then you may know that they are initialized at the time of class loading. If there is an Exception during that initialization of static variables, you will see ExceptionInInitializerError in Java. This could be any exception e.g. java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBound or java.lang.NullPointerException . Java developers are often confused with this error because they think that they have not defined any static initializer block, then how come they are getting ExceptionInInitializerError; well, by default Java combines all static variable initialization inside a static initializer block and initialize them in the order they are declared in the source file.
I suppose a variable ABC is declared at line 1, used at line 2 but initialized at line 3, then code at line 2 will throw java.lang.NullPointerException , which will be wrapped by JVM in ExceptionInInitializerError , and if that code happens to be executed by the main thread then you will see «Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError» in your console or log file.
In a large application with huge log files sometimes this error got unnoticed, and programmers get alerted by the dreaded java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError. Unfortunately, this error comes when the client class tries to use the class, which was not loaded because of ExceptionInInitializerError . Since class loading was failed earlier, JVM is now throwing NoClassDefFoundError .
Sometimes this misleads Java developers, and they start looking at classpath, path and java.library.path for missing class and confused them with hell not finding any anomalies. If you are investigating the cause of NoClassDefFoundError, it’s always a better idea to check your application log files for ExceptionInInitializerError before looking at CLASSPATH .
In this article, we will see an example code, which generates exceptions during static initialization and results in «Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError» . In the later part, we will see how to fix this error.
Cause of «Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError»
Now if you look at full stack trace carefully, you don’t need to do anything because JVM prints name of the class, which caused ExceptionInInitializerError . It’s also a subclass of LinkageError , which means if this error has occurred then your class will not be loaded into JVM memory. Now let’s take a look at our example program, which upon execution, throwing the following error :
By looking at this stack trace, we know that the actual error is java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException , which came at line 12 of StaticInitiazerDemo class. It came because of call to get() method of ArrayList with index 0 and come because the size of ArrayList was also zero (Index: 0, Size: 0 part of stack-trace). Now by following this information, you know that our List is empty when we try to get the first CreditCard from this list.
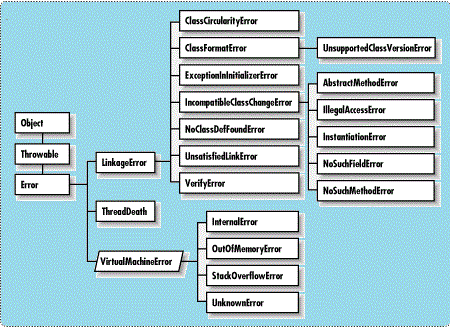
Here is a class hierarchy of all Error class in Java. You can see that ExceptionInInitializerError inherit from LinkageError. Its also worth knowing that like RuntimeException, Errors are also unchecked and compiler doesn’t check for mandatory error handling code.
Things to remember:
1) Remember «Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError» means Exception has occurred in the main thread, and it is java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError , which is a subclass of LinkageError and comes when JVM tries to load a class and it failed because of any RuntimeException in static initializer block e.g. IndexOutOfBoundsException or NullPointerException.
2) Remember that JVM combines all static variable initialization into one static initializer block in the order they appear in the source file. So, don’t think that absence of an explicit static initializer block will not cause this error. In fact, you must ensure the correct order of static variables i.e. if one variable initialization uses another variable then make sure that is initialized first.
3) Down the line, java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError can cause ClassNotFoundException or NoClassDefFoundError, if some other code tries to use the class, which caused ExceptionInInitializerError . Why? because loading of that class is failed and it’s not available inside JVM memory. So always check your log files for this before even if you are looking to solve any problem related to class not found.
4) Remember Static initializer block can throw RuntimeException but not checked Exception because later required mandatory catch block for handling.
Источник
Install Spark Exception #900
Problem encountered on https://dotnet.microsoft.com/learn/data/spark-tutorial/install-spark
Operating System: windows
I couldn’t setup Spark. I got an error after command
spark-submit —version
Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError
at org.apache.spark.unsafe.array.ByteArrayMethods.(ByteArrayMethods.java:54)
at org.apache.spark.internal.config.package$.(package.scala:1006)
at org.apache.spark.internal.config.package$.(package.scala)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmitArguments.$anonfun$loadEnvironmentArguments$3(SparkSubmitArguments.scala:157)
at scala.Option.orElse(Option.scala:447)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmitArguments.loadEnvironmentArguments(SparkSubmitArguments.scala:157)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmitArguments.(SparkSubmitArguments.scala:115)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit$$anon$2$$anon$3.(SparkSubmit.scala:990)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit$$anon$2.parseArguments(SparkSubmit.scala:990)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit.doSubmit(SparkSubmit.scala:85)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit$$anon$2.doSubmit(SparkSubmit.scala:1007)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit$.main(SparkSubmit.scala:1016)
at org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit.main(SparkSubmit.scala)
Caused by: java.lang.reflect.InaccessibleObjectException: Unable to make private java.nio.DirectByteBuffer(long,int) accessible: module java.base does not «opens java.nio» to unnamed module @5e5d171f
at java.base/java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject.checkCanSetAccessible(AccessibleObject.java:357)
at java.base/java.lang.reflect.AccessibleObject.checkCanSetAccessible(AccessibleObject.java:297)
at java.base/java.lang.reflect.Constructor.checkCanSetAccessible(Constructor.java:188)
at java.base/java.lang.reflect.Constructor.setAccessible(Constructor.java:181)
at org.apache.spark.unsafe.Platform.(Platform.java:56)
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
Источник
How to Handle the Exception In Initializer Runtime Error in Java
Table of Contents
Introduction to Runtime Errors & Exceptions
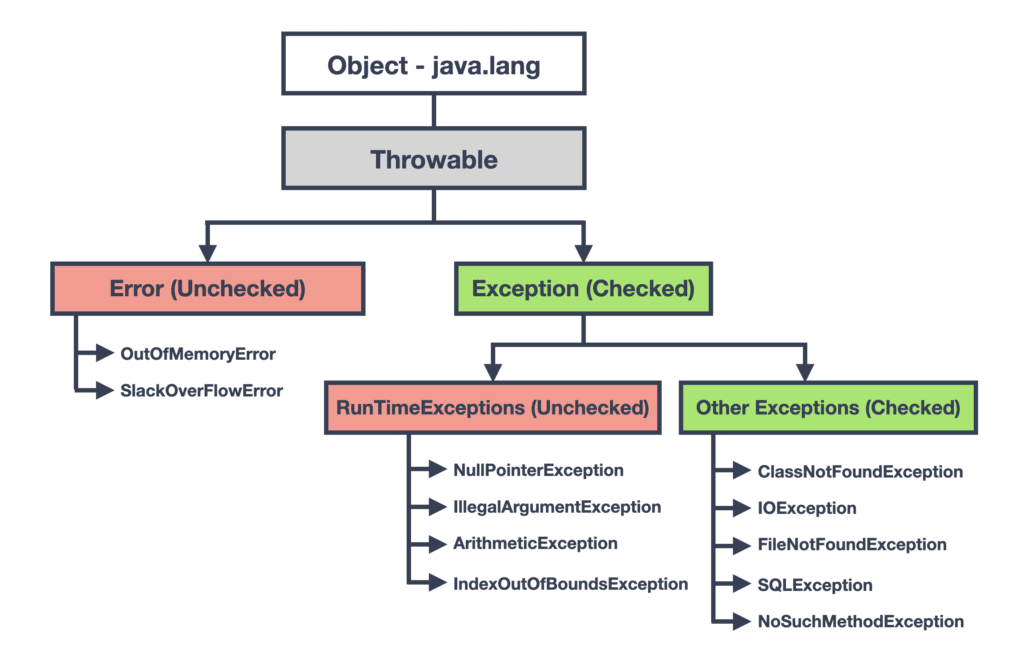
Unlike compile-time errors which are detected during compilation [1], runtime errors occur during program execution, i.e. runtime. Java’s runtime error hierarchy is somewhat complicated compared to other programming languages, but at the basic level there are two main categories: runtime errors and runtime exceptions, the latter of which being further divided into checked and unchecked exceptions (see Figure 1 below). Unchecked exceptions are also lumped into the somewhat confusingly named RuntimeException superclass, while all runtime errors are also considered to be unchecked. The term “unchecked” refers to errors and exceptions that Java doesn’t require to be caught or otherwise specified in the code [2]. Runtime Java errors and exceptions are otherwise jointly referred to as throwables, as per the name of the Throwable class—the parent class of all errors and exceptions in this language [3].
ExceptionInInitializerError Error: What, Why & How?
After successfully compiling a program, the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) performs dynamic loading, linking, and initializing of classes and interfaces, broadly known as the class loading process [5]. This process includes the evaluation of all static initializer blocks and variable assignments present in the compiled code. If, during this evaluation, any unexpected exception occurs, the JVM throws an ExceptionInInitializerError runtime error, points to the specific exception that caused the error, and subsequently exits the program.
The ExceptionInInitializerError error occurs every time there is an unchecked (and uncaught) exception taking place inside a static initializer or a static variable assignment. The JVM wraps this exception inside an instance of the java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError class (which itself is a subclass of the more generic java.lang.LinkageError class of errors [6]) and maintains a reference to it as the root cause.
How to handle the ExceptionInInitializerError Error
To avoid this error, simply ensure that:
- static initializers of classes do not throw any unchecked exception, and that
- static class variable initializations do not throw any unchecked exceptions.
Источник
java.lang.exceptionininitializererror – How to handle Exception Initializer Error
In this tutorial we will discuss about Java’s ExceptionInInitializerError and how to deal with it. The ExceptionInInitializerError is a sub-class of the LinkageError class and denotes that an unexpected exception has occurred in a static initializer or the initializer for a static variable. As of Java release 1.4, this error conforms to the general purpose exception-chaining mechanism.
The ExceptionInInitializerError is thrown when the JVM attempts to load a new class. During the class loading procedure, all static variables and static initializers are being evaluated. A static initializer is a block enclosed within curly braces without having any name and return type, except having the keyword static .
A sample example of a static initializer is shown below:
The static initializer is evaluated only once during the class loading procedure. Thus, a thrown exception in the evaluation of a static variable or initializer is wrapped into an ExceptionInInitializerError , in order for the JVM to indicate that the class could not be initialized and loaded.
A sample example that throws the aforementioned error is the following:
If we execute the above code snippet, we will receive the following error:
We can use the following methods, in order to retrieve more information about the underlying exception:
- getException() : Returns the exception that occurred during a static initialization that caused this error to be created. However, after the exception has conformed to the general-purpose exception chaining, the preferred method to use is getCause .
- getCause() :Returns the exception that caused this error to be thrown.
How to deal with the ExceptionInInitializerError
The ExceptionInInitializerError is used as a wrapper to indicate that an exception arises in the static initializer block or the evaluation of a static variable’s value. Thus, we have to ensure that the original exception is fixed, in order for the JVM to be able to load our class successfully.
It is very important to mention that you can throw unchecked / runtime exceptions from the block of a static initializer. However, you cannot allow a checked exception to propagate out of a static block, because is not possible to handle these exceptions in your source.
Источник
Когда Java выбрасывает ошибку ExceptionInInitializerError?
Узнайте, что заставляет Java выдавать ExceptionInInitializerError, используя несколько практических примеров
Автор: Ali Dehghani
Дата записи
1. Обзор
В этом кратком руководстве мы увидим, что заставляет Java выбрасывать экземпляр ExceptionInInitializerError исключение.
Начнем с небольшой теории. Затем мы увидим несколько примеров этого исключения на практике.
2. Ошибка exceptioninitializererror
ExceptionInInitializerError указывает, что в статическом инициализаторе произошло непредвиденное исключение . В принципе, когда мы видим это исключение, мы должны знать, что Java не удалось вычислить статический блок инициализатора или создать экземпляр статической переменной.
Фактически, каждый раз, когда какое-либо исключение происходит внутри статического инициализатора, Java автоматически обертывает это исключение внутри экземпляра класса ExceptionInInitializerError . Таким образом, он также поддерживает ссылку на фактическое исключение в качестве основной причины.
Теперь, когда мы знаем причину этого исключения, давайте рассмотрим его на практике.
3. Блок Статического Инициализатора
Чтобы иметь неудачный инициализатор статического блока, мы намеренно разделим целое число на ноль:
Теперь, если мы инициализируем инициализацию класса с помощью чего-то вроде:
Тогда мы увидим следующее исключение:
Как упоминалось ранее, Java создает исключение ExceptionInInitializerError , сохраняя при этом ссылку на первопричину:
Также стоит упомянуть, что метод является методом инициализации класса в JVM.
4. Инициализация статической Переменной
То же самое происходит, если Java не инициализирует статическую переменную:
Опять же, если мы запустим процесс инициализации класса:
Затем происходит то же самое исключение:
Аналогично статическим блокам инициализатора, первопричина исключения также сохраняется:
5. Проверенные исключения
В рамках спецификации языка Java (JLS-11.2.3) мы не можем выбрасывать проверенные исключения внутри блока статического инициализатора или инициализатора статической переменной. Например, если мы попытаемся сделать это:
Компилятор потерпит неудачу со следующей ошибкой компиляции:
В качестве соглашения мы должны обернуть возможные проверенные исключения внутри экземпляра Исключение ininitializererror когда наша статическая логика инициализации выдает проверенное исключение:
Как показано выше, метод getDeclaredConstructor() вызывает проверенное исключение. Поэтому мы поймали проверенное исключение и завернули его, как предполагает конвенция.
Поскольку мы уже возвращаем экземпляр Исключение ininitializererror исключение явно, Java не будет заключать это исключение в еще одно Исключение ininitializererror пример.
Однако, если мы создадим любое другое непроверенное исключение, Java выдаст другое ExceptionInInitializerError :
Здесь мы заключаем проверенное исключение в непроверенное. Поскольку это непроверенное исключение не является экземпляром ExceptionInInitializerError, Java снова обернет его, что приведет к этой неожиданной трассировке стека:
Как показано выше, если мы будем следовать соглашению, то трассировка стека будет намного чище, чем это.
5.1. OpenJDK
В последнее время это соглашение даже используется в самом исходном коде OpenJDK. Например, вот как AtomicReference использует этот подход:
6. Заключение
В этом уроке мы увидели, что заставляет Java выбрасывать экземпляр ExceptionInInitializerError exception.
Как обычно, все примеры доступны на GitHub .
Источник
- Brief Introduction to
ExceptionInInitializerErrorin Java - Handle the
ExceptionInInitializerErrorin Java - Conclusion
In this article, we will learn about the ExceptionInInitializerError in Java.
Brief Introduction to ExceptionInInitializerError in Java
ExceptionInInitializerError is an unchecked exception in Java, and it’s the child of the Error class. It falls in the category of Runtime Exceptions.
In Java, whenever the JVM (Java Virtual Machine) fails to evaluate a static initializer block or instantiate or assign a value to a static variable, an exception ExceptionInInitializerError occurs. This indicates that something has gone wrong in the static initializer.
Whenever this exception occurs inside the static initializer, Java maintains the reference to the actual exception as the root cause by wrapping the exception inside the object of the ExceptionInInitializerError class.
Examples of ExceptionInInitializerError in Java
Based on the above discussion, ExceptionInInitializerError occurs in major cases. Let’s see some examples to understand it better.
Example 1: Scenario where we are assigning values to the static variable.
public class Test {
static int x = 100/0;
public static void main(String []args)
{
System.out.println("Value of x is "+x);
}
}
Output:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError
Caused by: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at Test.<clinit>(Test.java:4)
In the above code, we assigned a 100/0 value to a static variable x, which gives an undefined arithmetic behavior, so an exception occurs while assigning values to the static variable, which finally gives us the ExceptionInInitializerError.
We can also observe in the output that the actual exception ArithmeticException is wrapped inside an instance of the ExceptionInInitializerError class.
Example 2: Scenario where inside the static blocks, null values are assigned.
public class Test {
static
{
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.length());
}
public static void main(String []args)
{ }
}
Output:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError
Caused by: java.lang.NullPointerException: Cannot invoke "String.length()" because "str" is null
at Test.<clinit>(Test.java:7)
In the above code, we have created a static block inside which we have a string str with the null value. So, when we try to get its length using the length() method, we get NullPointerException as we print the length of a string with null as its value.
But, as this exception occurs inside a static block, it will be wrapped inside the ExceptionInInitializerError class, and we get ExceptionInInitializerError in the output.
Handle the ExceptionInInitializerError in Java
ExceptionInInitializerError in Java can be avoided by ensuring the following points:
- Make sure that initializing static variables in a program doesn’t throw any Runtime Exception.
- Make sure that the static initializer blocks in a program don’t throw any Runtime Exception.
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about ExceptionInInitializerError in Java, indicating that some exceptions occurred while initializing a static variable or evaluating a static block. This error works as a runtime wrapper for the underlying exception and stops the JVM until the programmer resolves the underlying exception.