
Read on to find out the most relevant cause and solve it at the earliest.
The unresolved compilation problems occur because of syntax mistakes and typos. Moreover, using unknown or undefined classes and modules throw the same error. Please go through the causes described below to better understand the issues:
– The Class or Module Is Not Imported
If you use a class or module without importing the same in your program, then you’ll get the said java lang error. It indicates that you are instantiating a class or using a module that is unknown to the stated program.
– Using Non-existent Classes
If you use a class that isn’t already defined, then the same exception will pop up on your screen.
– A Syntax Error Resulting in Exception in Thread “main” java.lang.error: Unresolved Compilation Problem:
Even a common syntax error such as a missing or an extra curly bracket “{“ or a semicolon “;” can output the said exception. It includes sending the wrong arguments while calling the functions.
The below example code highlights the above-stated syntax errors:
public class myClass{
public static void main(String[] args){
anotherClass obj2 = new anotherClass();
obj2.myFunc(“Three”)
}
public class anotherClass{
public String myFunc(int num){
System.out.println(“You have entered:” + num);
}
}
– A Typographical Error
Another common cause behind the java lang error can be a typographical error. It usually happens when you code in hurry without realizing that you’ve typed the variable or function name incorrectly.
For example, you will get the above error if you have accidentally called the println() function as pirntln().
How To Fix the Compilation Exception?
Here are the easy-to-implement working solutions to lower your frustration level and resolve the said exception.
– Import the Necessary Classes and Modules
Look for the classes and modules used in your program. Next, import the given classes and modules. The stated simple step will kick away the exception if it is related to the classes and modules.
– Remove or Replace the Undefined Classes
You must remove the code that instantiates the undefined classes. Also, if you intended to call another class, then replacing the class name with a valid class name will work too.
– How To Resolve Java Lang Error in Eclipse?
You can notice the warnings shown in the Eclipse to identify the mistakes and correct them. Consequently, you will resolve the resulting java lang error.
– Use an Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
Using an IDE is the best possible solution to make the java lang error go away. It is because you’ll be notified regarding the typos and syntax errors. Moreover, you’ll be informed about the unknown modules and classes. You can then easily make the corrections and import the required classes or modules.
The above solution will let you skip the double-checking step before executing the code.
FAQ
The following questions might be disturbing you. So, here are the simplest answers to clear your confusion.
– What Is Unresolved Compilation Problem Java?
The above problem tells that there is a compilation error in the code. Although it is a generic error, you can learn more about it through the error description.
– What Is Exception in Thread Main Java Lang Error?
The stated exception tells that an error has occurred in the thread that is running the Java application. You can say that the given exception points towards the location of the error.
Wrapping Up
Now, it’s clear to you that the compilation error pops up due to common coding mistakes. Also, you get the said exception when the compiler isn’t aware of the classes and modules that are being used in your program. Plus, here is the list of fixing procedures obtained from the above article to make the long talk short:
- You should import all the necessary classes and modules in your program
- You should use only valid classes and modules
- Using the IDE can help you in determining and correcting most of the coding mistakes that help in fixing the java lang error

- Author
- Recent Posts
Position Is Everything: Your Go-To Resource for Learn & Build: CSS,JavaScript,HTML,PHP,C++ and MYSQL.
Did you know that in Java’s standard library, there are a total of more than 500 different exceptions! There lots of ways for programmers to make mistakes — each of them unique and complex. Luckily we’ve taken the time to unwrap the meaning behind many of these errors, so you can spend less time debugging and more time coding. To begin with, let’s have a look at the syntax errors!
Syntax Errors
If you just started programming in Java, then syntax errors are the first problems you’ll meet! You can think of syntax as grammer in English. No joke, syntax errors might look minimal or simple to bust, but you need a lot of practice and consistency to learn to write error-free code. It doesn’t require a lot of math to fix these, syntax just defines the language rules. For further pertinent information, you may refer to java syntax articles.
Working with semicolons (;)
Think of semi-colons (;) in Java as you think of a full-stop (.) in English. A full stop tells readers the message a sentence is trying to convey is over. A semi-colon in code indicates the instruction for that line is over. Forgetting to add semi-colons (;) at the end of code is a common mistake beginners make. Let’s look at a basic example.
This snippet will produce the following error:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem:
Syntax error, insert ";" to complete BlockStatements
at topJavaErrors.JavaErrors.main(JavaErrors.java:3)You can resolve this error by adding a ; at the end of line 3.
String x = "A";Braces or parentheses [(), {}]
Initially, it can be hard keeping a track of the starting / closing parenthesis or braces. Luckily IDEs are here to help. IDE stands for integrated development environment, and it’s a place you can write and run code. Replit for example, is an IDE. Most IDEs have IntelliSense, which is auto-complete for programmers, and will add closing brackets and parentheses for you. Despite the assistance, mistakes happen. Here’s a quick example of how you can put an extra closing bracket or miss the ending brace to mess up your code.
If you try to execute this, you’ll get the following error.
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem:
Syntax error on token ")", delete this token
at topJavaErrors.SyntaxErrors.main(SyntaxErrors.java:11)You can resolve this exception by removing the extra ) on line 9.
Output
My full name is: Justin Delaware
Double Quotes or Quotation Marks (“ ”)
Another pit fall is forgetting quotation marks not escaping them propperly. The IntelliSense can rescue you if you forget the remaining double quotes. If you try including quotation marks inside strings, Java will get confused. Strings are indicated using quotation marks, so having quotation marks in a string will make Java think the string ended early. To fix this, add a backslash () before quotation marks in strings. The backslash tells Java that this string should not be included in the syntax.
Output
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problems:
Syntax error on token "Java", instanceof expected
The preview feature Instanceof Pattern is only available with source level 13 and above
is cannot be resolved to a type
Syntax error, insert ")" to complete MethodInvocation
Syntax error, insert ";" to complete Statement
The method favourtie(String) is undefined for the type SyntaxErrors
Syntax error on token "language", ( expected
at topJavaErrors.SyntaxErrors.main(SyntaxErrors.java:5)In order for you avoid such exceptions, you can add backslahes to the quotes in the string on line 4.
Output
What did Justin say?
Justin said, "Java is my favourite language"Here’s your required output, nicely put with double quotes! 
Other Miscellaneous Errors
Accessing the “Un-Initialized” Variables
If you’re learning Java and have experience with other programming languages (like C++) then you might have a habit of using un-initialized variables (esp integers). Un-initialized variables are declared variables without a value. Java regulates this and doesn’t allow using a variable that has not been initialized yet.
If you attempt to access an uninitialized variable then you’ll get the following exception.
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem:
The local variable contactNumber may not have been initialized
at topJavaErrors.UninitialziedVars.main(UninitialziedVars.java:5)You can initialize the variable “contactNumber” to resolve this exception.
int contactNumber = 9935856;Accessing the “Out of Scope” Variables
If you define a variable in a certain method you’re only allowed to access that in the defined scope of it. Like each state has their legitimate currency, and that cannot be used in another state. You cannot use GBP in place of USD in America. Similarly, a variable defined in one method has restricted scope to it. You cannot access a local variable defined in some function in the main method. For further detailed illustration let’s look at an example.
Output
As soon as you run this snippet, you’ll get the exception
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem:
country cannot be resolved to a variable
at topJavaErrors.OutOfScopeVars.main(OutOfScopeVars.java:9)You can not access the variable “country” outside the method getPersonalDetails since its scope is local.
Modifying the “CONSTANT” Values
Java and other programming languages don’t allow you to update or modify constant variables. You can use the keyword “final” before a variable to make it constant in Java. Apart from that, it’s a convention to write a constant in ALL CAPS for distinction purposes, As a constant resource is often used cross methods across a program.
Output
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem:
The final field ConstVals.SSN cannot be assigned
at topJavaErrors.ConstVals.main(ConstVals.java:5)Remove line 4 for the perfectly functional code.
Misinterpretted Use of Operators ( == vs .equals())
A lot of beginners start working with integers while learning the basics of a programming language. So it can be a challenge to remember that for string comparisons we use the “.equals()” method provided by Java and not == operator like in integers.
Output
It's not a Wednesday!
It's a Wednesday!The output is contradictory because “today” and “thirdWeekDay” are referred to 2 different objects in the memory. However, the method “.equals()” compares the content stored in both arrays and returns true if it’s equal, false otherwise.
Accessing a non-static resource from a static method
If you want to access a non-static variable from a static method [let’s say the main method] then you need to create an instance of that object first. But if you fail to do that, java will get angry.
Output
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem:
Cannot make a static reference to the non-static field postalCode
at topJavaErrors.NonStaticAccess.main(NonStaticAccess.java:17)You can fix it, just by replacing line 9.
// Accessing the non-static member variable
// by creating an instance of the object
System.out.println("What's the postal code of your area? " + address.postalCode);Conclusion
Programming errors are a part of the learning curve. Frequent errors might slow you down. But as a new programmer, it’s okay to learn things slowly. Now you’re familiar with some of the most common issues. Make sure you practise enough to get ahead of them. Happy coding and keep practising! 
Errors in Java occur when a programmer violates the rules of Java programming language.
It might be due to programmer’s typing mistakes while developing a program. It may produce incorrect output or may terminate the execution of the program abnormally.
For example, if you use the right parenthesis in a Java program where a right brace is needed, you have made a syntax error. You have violated the rules of Java language.
Therefore, it is important to detect and fix properly all errors occurring in a program so that the program will not terminate during execution.
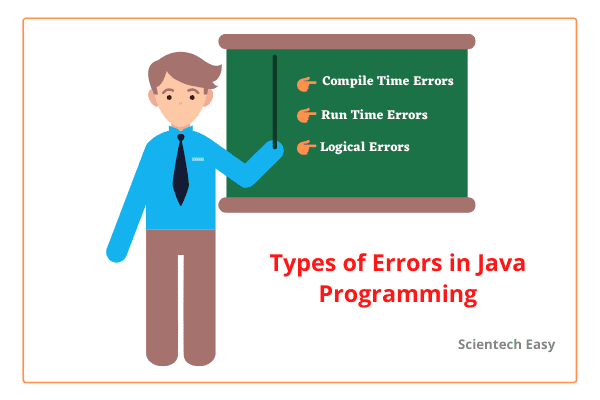
Types of Errors in Java Programming
When we write a program for the first time, it usually contains errors. These errors are mainly divided into three types:
1. Compile-time errors (Syntax errors)
2. Runtime errors
3. Logical errors
Compile-time errors occur when syntactical problems occur in a java program due to incorrect use of Java syntax.
These syntactical problems may be missing semicolons, missing brackets, misspelled keywords, use of undeclared variables, class not found, missing double-quote in Strings, and so on.
These problems occurring in a program are called syntax errors in Java.
Since all syntax errors are detected by Java compiler, therefore, these errors are also known as compile time errors in Java.
When Java compiler finds syntax errors in a program, it prevents the code from compile successfully and will not create a .class file until errors are not corrected. An error message will be displayed on the console screen.
These errors must be removed by debugging before successfully compile and run the program. Let’s take an example program where we will get a syntax error.
Program source code 1:
public class CompileTimeErrorEx
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("a") // Syntax error. Semicolon missing.
}
}
Compile time error in Java code:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem:
Syntax error, insert ";" to complete BlockStatements
When you will try to compile the above program, Java compiler will tell you where errors are in the program. Then you can go to the appropriate line, correct error, and recompile the program.
Let’s create a program where we will try to call the undeclared variable. In this case, we will get unresolved compilation problem.
Program source code 2:
public class MisspelledVar
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 20, y = 30;
// Declare variable sum.
int sum = x + y;
// Call variable Sum with Capital S.
System.out.println("Sum of two numbers: " + Sum); // Calling of undeclared variable.
}
}
Compile time error in Java code:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem:
Sum cannot be resolved to a variable
Program source code 3: Missing parenthesis in for statement.
public class MissingBracket
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int i;
int sum = 0;
// Missing bracket in for statement.
for (i = 1; i <= 5; i++ // insert " ) Statement" to complete For Statement.
{
sum = sum + i;
}
System.out.println("Sum of 1 to 5 n");
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
Compile time error in Java code:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem:
Syntax error, insert ") Statement" to complete ForStatement
Program source code 4: Missing double quote in String literal.
public class MissingDoubleQuote
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str = "Scientech; // Missing double quote in String literal.
System.out.println(str);
}
}
Compile time error in Java code:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem:
String literal is not properly closed by a double-quote
We may also face another error related to the directory path. An error such as
javac : command not found
means that you have not set the path correctly.
Runtime Errors in Java
Runtime errors occur when a program is successfully compiled creating the .class file but does not run properly. It is detected at run time (i.e. during the execution of the program).
Java compiler has no technique to detect runtime errors during compilation because a compiler does not have all of the runtime information available to it. JVM is responsible to detect runtime errors while the program is running.
Such a program that contains runtime errors, may produce wrong results due to wrong logic or terminate the program. These runtime errors are usually known as exceptions.
For example, if a user inputs a value of string type in a program but the computer is expecting an integer value, a runtime error will be generated.
The most common runtime errors are as follows:
1. Dividing an integer by zero.
2. Accessing an element that is out of range of the array.
3. Trying to store a value into an array that is not compatible type.
4. Passing an argument that is not in a valid range or valid value for a method.
5. Striving to use a negative size for an array.
6. Attempting to convert an invalid string into a number.
7. and many more.
When such errors are encountered in a program, Java generates an error message and terminates the program abnormally. To handle these kinds of errors during the runtime, we use exception handling technique in java program.
Let’s take different kinds of example programs to understand better. In this program, we will divide an integer number by zero. Java compiler cannot detect it.
Program source code 5:
public class DivisionByZeroError
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a = 20, b = 5, c = 5;
int z = a/(b-c); // Division by zero.
System.out.println("Result: " +z);
}
}
Output:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at errorsProgram.DivisionByZeroError.main(DivisionByZeroError.java:8)
The above program is syntactically correct. There is no syntax error and therefore, does not cause any problem during compilation. While executing, runtime error occurred that is not detected by compiler.
The error is detected by JVM only in runtime. Default exception handler displays an error message and terminates the program abnormally without executing further statements in the program.
Let’s take an example program where we will try to retrieve a value from an array using an index that is out of range of the array.
Program source code 6:
public class AccessingValueOutOfRangeError
{
public static void main(String[ ] args)
{
int arr[ ] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // Here, array size is 5.
System.out.println("Value at 5th position: "+arr[5]);
}
}
Output:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 5
at errorsProgram.AccessingValueOutOfRangeError.main(AccessingValueOutOfRangeError.java:9)
Logical Errors in Java Program
Logical errors in Java are the most critical errors in a program and they are difficult to detect. These errors occur when the programmer uses incorrect logic or wrong formula in the coding.
The program will be compiled and executed successfully but does not return the expected output.
Logical errors are not detected either by Java compiler or JVM (Java runtime system). The programmer is entirely responsible for them. They can be detected by application testers when they compare the actual result with its expected result.
For example, a programmer wants to print even numbers from an array but he uses division (/) operator instead of modulus (%) operator to get the remainder of each number. Due to which he got the wrong results.
Let’s see the following source code related to this problem.
Program source code 7:
public class LogicalErrorEx
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a[]={1, 2 , 5, 6, 3, 10, 12, 13, 14};
System.out.println("Even Numbers:");
for(int i = 0; i <a.length; i++)
{
if(a[i] / 2 == 0) // Using wrong operator.
{
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
}
}
}
Output:
Even Numbers:
1
As you can see the program is successfully compiled and executed but the programmer got the wrong output due to logical errors in the program.
Seldom does a program run successfully at its first attempt. A software engineer in a company also commits several errors while designing the project or developing code.
These errors in a program are also called bugs and the process of fixing these bugs is called debugging.
All modern integrated development environments (IDEs) such as Eclipse, NetBeans, JBuilder, etc provide a tool known as debugger that helps to run the program step by step to detect bugs.
If you need professional help with Java homework assignments online, please address experts from AssignmentCore to get your Java projects done with no errors.
In this tutorial, we have familiarized different types of errors in java that may possibly occur in a program.
Thanks for reading!!!
Next ⇒ Exception handling Interview Programs for Practice
⇐ Prev Next ⇒
Содержание
- Unresolved Compilation Problem
- Java exception in thread main java lang error unresolved compilation problems
- exception in thread main java.lang.error unresolved compilation problems eclipse
- Javatpoint Services
- Training For College Campus
- Java exception in thread main java lang error unresolved compilation problems
- Breadcrumbs
Unresolved Compilation Problem

Hi!
My network flow problem doesn’t seem to work because of an unresolved compilation problem.
this is the code:




Hello Neyla, welcome to the Ranch!
You forgot to tell us what the compilation error you’re seeing is?
Tim Driven Development | Test until the fear goes away

I copied your code right in to Intellij and it compiles fine and even runs (waits for input).
What error are you getting?

Exception in thread «main» java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem:
that’s the error i get in eclipse..





Swastik Dey wrote: Does the class belong to any package named aww? If so it should be under the package called aww, and we don’t see any package statement in your code.
That’s really strange. I copied and pasted the code right into Intelli and it had no issues and even ran.
Try the community (free) edition of Intellij as a test.
I don’t think it’s your code.
And, I did zero configuration chores.









Just took one of my other code (managed by eclipse), and removed the package statement, but still kept it in the package. Eclipse will complain about something like «declared package AAA does not match BBB blah blah blah».
Additionally, ran that broken code (even though it has an error). eclipse will complain, and popup to confirm.. and forced eclipse to run anyway. The resultant error message at console was «unresolved compilation problem: at xxx.yyy.main(zzz.java)». just like as mentioned by the OP.
So, it is two problems. One, eclipse is configured to expect the class in the package, but with the code, the class is not in the package. And two, the error message is ignored; the application is forced to run, forcing eclipse to print out a nonsensical message, because that information is lost at run time.
Now, is the missing package the underlying cause? or did the OP simply didn’t cut and paste it? . This is not clear. There is no visibility into that. The OP need to tell us what the compilation errors are, and not just tell us the errors when forcing the application to run.
Источник
Java exception in thread main java lang error unresolved compilation problems
if (args.length == 0) <
for(int i = 0;i
| Re: Exception in thread «main» java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem: [message #1835638 is a reply to message #1835626] | Wed, 09 December 2020 09:45   |
|
|
||
| The error is shown because the source is lacking a final «>», as the error message says.
You then tried to run the code anyway, and then you correctly got the exception. You should have seen error markers in Eclipse, and you should have gotten a warning dialog when trying to run this via Eclipse that told you that there were still compilation problems. Источник exception in thread main java.lang.error unresolved compilation problems eclipsepublic class DrawingApp < ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(«spring.xml»); public class Triangle < > even though i am using eclipse there is no compilation error but when i run the program it gives an error plz tell me. |
 1 1  |
| me too facing the below Error while executing the below program, please help
Exception in thread «main» java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem: public class Method < public int multiply (int a,int b, int c)< int result=a*b*c; public static void main (String [] args)< Method obj = new Method (); int x=obj.multiply(10, 20, 30); > |
 0 0  |
By: [email protected] On: Sat Dec 03 21:04:29 IST 2016  0 0  0 0  0 0 |
 |
| Are You Satisfied : 0Yes 0No |
Javatpoint Services
JavaTpoint offers too many high quality services. Mail us on [email protected], to get more information about given services.
- Website Designing
- Website Development
- Java Development
- PHP Development
- WordPress
- Graphic Designing
- Logo
- Digital Marketing
- On Page and Off Page SEO
- PPC
- Content Development
- Corporate Training
- Classroom and Online Training
- Data Entry
Training For College Campus
JavaTpoint offers college campus training on Core Java, Advance Java, .Net, Android, Hadoop, PHP, Web Technology and Python. Please mail your requirement at [email protected]
Duration: 1 week to 2 week
Источник
Java exception in thread main java lang error unresolved compilation problems
Community
Participate
Eclipse IDE
Home » Newcomers » Newcomers » Exception in thread «main» java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem
|
|||||||
|
|||||||
|
While working with the programming languages like executing a software program, there are many instances that we run into issues due to the run time errors or compilation errors. All these errors occur when the application is running. You might come across an instance where the application acts differently in a negative way to the requirements, then it means that a runtime error took place.
As it is one of the most common type of error that occurs during a software executive, let us get a deep idea on how to fix common types of runtime errors in Java and also the steps to be taken to resolve them on a timely basis.
Contents
- 1 Fix the 5 Most Common Types of Runtime Errors in Java
- 1.1 What is a Runtime Error in Java?
- 1.2 Differences Between Compile Time Error and Runtime Error in Java
- 1.3 Why Runtime Error Occurs in Java ?
- 1.4 1. Accessing Out of Range Value in an Array
- 1.5 2. Division by Zero Error
- 1.6 3. Less Space or Insufficient Space Memory Error
- 1.7 4. Conversion of an Invalid string into a Number
- 1.8 5. Attempting to Store an Incompatible Value to a Collection
- 1.9 How to solve Runtime Rrror in Java Programming?
Fix the 5 Most Common Types of Runtime Errors in Java
What is a Runtime Error in Java?
A runtime error in Java is referred to as an application error that comes up during the execution process of the program. This runtime error usually takes place when the syntax is corrected as expected while the issue lies during the program execution. All these errors can be detected by JVM – Java Virtual Machine and cannot be identified during the compilation time. Java is one of the most sought-after programming languages for the hiring managers across the world. So become an expert in Java through our Java Training and grab the best job opportunity.
Now, In this post, Let us discuss the top runtime errors in Java.
- Division by zero errors
- IO errors
- Out of range errors
- Undefined object errors
Differences Between Compile Time Error and Runtime Error in Java
Compile time errors are those errors in which the syntax would be incorrect in the application code. An example would be like missing semicolons, parenthesis, incorrect keywords, usage of undeclared variables, etc.
The Java compiler is capable of detecting the syntax errors during the compile time and the error message will be appearing on the screen. The compiler is also capable of preventing the code from the execution unless and until the error is resolved. Therefore it is important that these errors are addressed by making the necessary changes before the program is successfully executed.
The runtime errors occur during the program execution after the compilation has completed. Any program that is throwing a runtime error means that there are no issues with Syntax in the program.
Why Runtime Error Occurs in Java ?
Below listed are the most common types of runtime errors that occur in Java.
- Accessing an element that is out of range in an array
- Dividing a number with 0
- Less space or insufficient space memory
- Conversion of an invalid string into a number
- Attempting to store an incompatible value to a collection
When you come across such an address, you need to know that the Java compiler will be generating an error message and the program gets terminated abnormally. Runtime errors do not require to be caught explicitly. It is useful if you catch the runtime errors and resolve them to complete the program execution.
Let us review a few of the most common runtime errors in Java programming with examples to gain a deeper understanding.
1. Accessing Out of Range Value in an Array
|
public class ValueOutOfRangeErrorExample { public static void main(String[] args) { int k[] = new int[8]; System.out.println(«8th element in array: « + k[8]); } } |
In the above example, the array is initialized with 8 elements. with the above code, An element at position number 8 is trying to get access and does not exist at all, leading to the Exception java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:
Error :
|
Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 8 out of bounds for length 8 at ValueOutOfRangeErrorExample.main(ValueOutOfRangeErrorExample.java:4) |
2. Division by Zero Error
Below is an example of java.lang.ArithmeticException which occurs when the user is trying to code in such a way that they perform the division by zero.
|
public class ArithmeticExceptionExample { public static void main(String[] args) { int num1 = 10, num2 = 0; System.out.println(«Result: «+ num1/num2); } } |
In the above code, the integer num1 is getting to be divided by num2 which has a value of zero, which is leading to the exception called java.lang.ArithmeticException
Below is the Error Thrown :
|
Exception in thread «main» java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at ArithmeticExceptionExample.main(ArithmeticExceptionExample.java:4) |
3. Less Space or Insufficient Space Memory Error
Below is an example of java.lang.OutOfMemoryError, which occurs when the user is trying to initialize an Integer array with a very large size, and due to the Java heap being insufficient to allocate this memory space, it throws an Error java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
|
public class OutOfMemory { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer[] myArray = new Integer[1000*1000*1000]; } } |
Error :
|
Exception in thread «main» java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space at OutOfMemory.main(OutOfMemory.java:5) |
4. Conversion of an Invalid string into a Number
Below is an example of java.lang.NumberFormatException, occurs when the user is trying to convert an alphanumeric string to an integer which leads to java.lang.NumberFormatException
|
public class NumberFormatException { public static void main(String[] args) { int a; a= Integer.parseInt(«12Mehtab»); System.out.println(a); } } |
Error :
|
Exception in thread «main» java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: «12Mehtab» at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:580) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:615) at NumberFormatException.main(NumberFormatException.java:6) |
5. Attempting to Store an Incompatible Value to a Collection
Below is an example where user has created the ArrayList of String but trying to store the integer value which leads to Exception java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem
|
import java.util.ArrayList; public class IncompatibleType { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> student = new ArrayList<>(); student.add(1); } } |
Error :
|
Exception in thread «main» java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem: The method add(int, String) in the type ArrayList<String> is not applicable for the arguments (int) at IncompatibleType.main(IncompatibleType.java:7) |
How to solve Runtime Rrror in Java Programming?
The runtime errors can be solved by using the try catch blocks in Java. Below are the steps to be followed:
- You will need to Surround the statements that are capable of throwing an exception or a runtime error in the try catch blocks.
- The next step is to catch the error.
- Based on the requirements of the court or an application, it is important to take the necessary action.
Like we discussed earlier about the ArithmeticException example, it can be corrected by making the below changes.
|
public class ArithmeticExceptionExample { public static void main(String[] args) { try { int num1 = 10, num2 = 0; System.out.println(«Result: « + num1/num2); } catch (ArithmeticException ae) { System.out.println(«Arithmetic Exception — cannot divide by 0»); } System.out.println(«Let’s continue the execution…»); } } |
As the code is surrounded in the try catch blocks, the program will continue to execute after the exception is encountered.
Result :
|
Arithmetic Exception — cannot divide by 0 Let’s continue the execution... |
In this way, it is important for you to identify the Runtime errors and also clear them without any hesitation. You can make use of the try catch blocks and many other resolutions which were helped in successful program execution. Also you will be able to track, manage and analyze the errors in real time. So this was all from this tutorial about fixing the 5 most common types of Runtime Errors in Java But still, if you have any queries, feel free to ask in the comment section. And don’t forget to stay tuned with the Tutorials field to learn this type of awesome tutorial. HAPPY CODING.
People Are Also Reading…
- How to Play Mp3 File in Java Tutorial | Simple Steps
- Menu Driven Program in Java Using Switch Case
- Calculator Program in Java Swing/JFrame with Source Code
- Registration Form in Java With Database Connectivity
- How to Create Login Form in Java Swing
- Text to Speech in Java
- How to Create Splash Screen in Java
- Java Button Click Event
- 11 Best WebSites to Learn Java Online for Free
|
Fawx 0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 22.10.2016 Сообщений: 6 |
||||
|
1 |
||||
|
02.07.2017, 12:42. Показов 5312. Ответов 4 Метки нет (Все метки)
Помогите, что я сделал не так?
Exception in thread «main» java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem: at pp.abcd.main(abcd.java:23) В чем дело?
__________________
0 |
|
88 / 86 / 55 Регистрация: 14.11.2015 Сообщений: 1,099 |
|
|
02.07.2017, 13:50 |
2 |
|
Как файл с исходным кодом называется? Добавлено через 1 минуту
0 |
|
0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 22.10.2016 Сообщений: 6 |
|
|
02.07.2017, 13:58 [ТС] |
3 |
|
pp
0 |
|
88 / 86 / 55 Регистрация: 14.11.2015 Сообщений: 1,099 |
|
|
02.07.2017, 14:00 |
4 |
|
pp Если файл называется pp, то переименуйте в abcd(класс, с входной точкой в приложение).
0 |
|
0 / 0 / 0 Регистрация: 22.10.2016 Сообщений: 6 |
|
|
02.07.2017, 16:26 [ТС] |
5 |
|
Если файл называется pp, то переименуйте в abcd(класс, с входной точкой в приложение). Я понял наверное, у меня Эклипс Kepler, это наверное старый до 7 Джавы. Добавлено через 10 минут
0 |





 Thomas Wolf
Thomas Wolf 
 Heits Mkivi
Heits Mkivi 
