In this tutorial, we’re going to provide information regarding the error message 500 Unable to service PORT commands, including ways to fix it.
What Does the Error Mean?
The error message 500 Unable to service PORT commands usually occurs if you attempt to access a folder or upload a file to your server using an Active FTP data transfer mode.
By default, FTP may run in two modes – Active and Passive. Active mode is not currently supported on our Shared hosting platform, as it is considered less secure and reliable. So, any attempt to access a directory or manipulate data in active FTP mode will be blocked by the FTP server’s firewall.
How Can I Resolve this Problem?
In order to resolve the situation and connect to your server properly, you would need to enable Passive data transfer mode in your FTP software application.
Below you’ll find illustrated instructions on how to enable Passive mode in some of the most used FTP software applications (such as FileZilla, Cyberduck, CoffeeCup and Dreamweaver).
Configuring Passive Mode in FileZilla
You can follow these simple instructions to enable Passive Mode in FileZilla:
-
- Launch FileZilla.
- Open the Edit menu and click Settings….
- In the left pane, select FTP.
- Switch the Transfer Mode from Active to Passive (recommended).
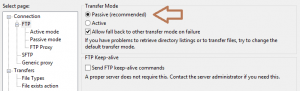
Once you have made the necessary corrections, press OK and retry the connection.
Configuring Passive Mode in Cyberduck
To make your Cyberduck FTP account run in Passive mode:
-
- Start Cyberduck.
- Open the File menu and select Open Connection.
- Next, click on the More Options button.
- Change the Connect Mode setting from Default to Passive (PASV).
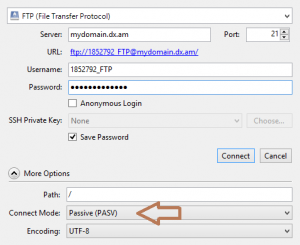
Press Connect and retry establishing an FTP connection.
Configuring Passive Mode in CoffeeCup
To enable Passive mode in CoffeeCup, perform the following actions:
-
- Launch CoffeeCup.
- Open the File menu and select Manage Servers.
- Next, click on the green plus icon.
- Mark the Passive Mode checkbox.
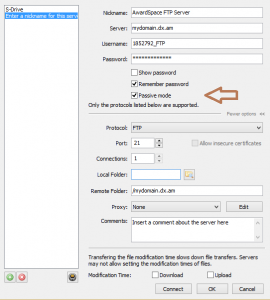
Press Connect, and then try to reconnect to your FTP server.
Configuring Passive Mode in Dreamweaver
You can configure Passive Mode in a Dreamweaver FTP client program in five easy steps:
-
- Start Dreamweaver.
- Open the Site menu and choose Manage Sites.
- Select the Servers tab and click on your existing AwardSpace FTP profile (account).
- Click More Options and select the checkbox Use Passive FTP.
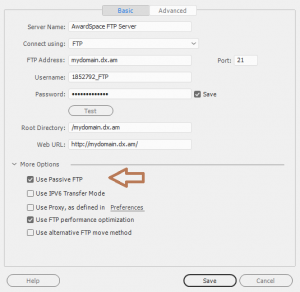
Click Save, and then re-attempt to establish a connection.
Am I Able to Use Passive Mode in Windows FTP (FTP.exe)?
Unfortunately, the Microsoft built-in FTP tool does not support passive FTP data transfers. As a result, you won’t be able to establish an FTP connection to our server or transfer files via FTP.exe.
Therefore, we highly recommend that you use an FTP client program for migrating your website data. Information on how to use and configure an FTP client program can be found on our FTP Connection Settings page.
Keep reading
- FTP Login Incorrect
- FTP Connection Settings
- “Response: 426 Transfer aborted. Operation not permitted.” error appears during file upload
Hello Forum!
Being very new into FileZilla I’m hoping that someone here might be able to assist me getting my setup work smoothly.
A short background overview of my setup:
A dedicated Windows 2012R2 server located in our DMZ zone, our IT department has demanded that it’s being configured to use FTPS (tcp-990), and they’ve configured the firewall configuration to support this.
Ok, so far so good…
On the server I’ve installed and configured FileZilla Server 0.9.60 beta, in the “FTP over TLS settings, I’ve selected “Enable FTP over TLS support (FTPS), & “Disallow plain unencrypted FTP”, I’ve generated a certificate, and selected “Allow explicit FTP over TLS” – entered port 990 in the “Listen for FTP over TLS connections” and finally selected “Force PORT P to encrypt file transfers when using FTP over TLS” and “Require TLS session resumption on data connection when using PORT P”
Ok then… — and now explaining my problem… :
When using the Filezilla FTP client on a computer, I try to connect to my server – in the server log I can see that the client connect (= the firewall rules are working as the should I guess) but… — I can see in the log the “connected on port 990, sending welcome message” -> 220 “Welcome to my FTP server” -> 500 syntax error, command unrecognized
When using the build in FTP client in Ghisler “Total commander” I can connect with the exact same username and password as I’m using in Filezilla FTP client, however I do at the beginning see a “The certificate was not signed by a trusted party, continue anyway?” – if I select “Yes” the client connects, and everything is working (I can upload, download, edit, delete files on the FTP server)
The error I see in the Filezilla FTP client are the following :
Status: Connecting to xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:990…
Status: Connection established, initializing TLS…
Error: GnuTLS error -15: An unexpected TLS packet was received.
Error: Could not connect to server
So… – I’m under the impression that the firewall properly is configured as it should be, and that the problem properly is located somewhere in my setup of the server client.
I’ve tried to follow all the “best practice” guides I could come across, however, no luck so far.
I would therefore be very thankful if anyone here have any suggestions!
Thanks in advance!
Kind regards
Lars
I am trying to create a script that uploads a .wav file after processing to a linux FTP server (utilizing vsftpd).
The script looks as follows:
@echo off
echo user anonymous> ftpcmd.dat
echo >> ftpcmd.dat
echo put C:UsersAnwenderDownloads%1 %1>> ftpcmd.dat
REM echo quit>> ftpcmd.dat
ftp -n -s:ftpcmd.dat 194.26.183.194
del ftpcmd.dat
My vsftpd.conf:
# Example config file /etc/vsftpd.conf
#
# The default compiled in settings are fairly paranoid. This sample file
# loosens things up a bit, to make the ftp daemon more usable.
# Please see vsftpd.conf.5 for all compiled in defaults.
#
# READ THIS: This example file is NOT an exhaustive list of vsftpd options.
# Please read the vsftpd.conf.5 manual page to get a full idea of vsftpd's
# capabilities.
#
#
# Run standalone? vsftpd can run either from an inetd or as a standalone
# daemon started from an initscript.
listen=NO
#
# This directive enables listening on IPv6 sockets. By default, listening
# on the IPv6 "any" address (::) will accept connections from both IPv6
# and IPv4 clients. It is not necessary to listen on *both* IPv4 and IPv6
# sockets. If you want that (perhaps because you want to listen on specific
# addresses) then you must run two copies of vsftpd with two configuration
# files.
listen_ipv6=YES
#
# Allow anonymous FTP? (Disabled by default).
anonymous_enable=YES
#
# Uncomment this to allow local users to log in.
local_enable=YES
#
# Uncomment this to enable any form of FTP write command.
write_enable=YES
#
# Default umask for local users is 077. You may wish to change this to 022,
# if your users expect that (022 is used by most other ftpd's)
#local_umask=022
#
# Uncomment this to allow the anonymous FTP user to upload files. This only
# has an effect if the above global write enable is activated. Also, you will
# obviously need to create a directory writable by the FTP user.
anon_upload_enable=YES
#
# Uncomment this if you want the anonymous FTP user to be able to create
# new directories.
#anon_mkdir_write_enable=YES
#
# Activate directory messages - messages given to remote users when they
# go into a certain directory.
dirmessage_enable=YES
#
# If enabled, vsftpd will display directory listings with the time
# in your local time zone. The default is to display GMT. The
# times returned by the MDTM FTP command are also affected by this
# option.
use_localtime=YES
#
# Activate logging of uploads/downloads.
xferlog_enable=YES
#
# Make sure PORT transfer connections originate from port 20 (ftp-data).
connect_from_port_20=YES
#
# If you want, you can arrange for uploaded anonymous files to be owned by
# a different user. Note! Using "root" for uploaded files is not
# recommended!
#chown_uploads=YES
#chown_username=whoever
#
# You may override where the log file goes if you like. The default is shown
# below.
#xferlog_file=/var/log/vsftpd.log
#
# If you want, you can have your log file in standard ftpd xferlog format.
# Note that the default log file location is /var/log/xferlog in this case.
#xferlog_std_format=YES
#
# You may change the default value for timing out an idle session.
#idle_session_timeout=600
#
# You may change the default value for timing out a data connection.
#data_connection_timeout=120
#
# It is recommended that you define on your system a unique user which the
# ftp server can use as a totally isolated and unprivileged user.
#nopriv_user=ftpsecure
#
# Enable this and the server will recognise asynchronous ABOR requests. Not
# recommended for security (the code is non-trivial). Not enabling it,
# however, may confuse older FTP clients.
#async_abor_enable=YES
#
# By default the server will pretend to allow ASCII mode but in fact ignore
# the request. Turn on the below options to have the server actually do ASCII
# mangling on files when in ASCII mode.
# Beware that on some FTP servers, ASCII support allows a denial of service
# attack (DoS) via the command "SIZE /big/file" in ASCII mode. vsftpd
# predicted this attack and has always been safe, reporting the size of the
# raw file.
# ASCII mangling is a horrible feature of the protocol.
#ascii_upload_enable=YES
#ascii_download_enable=YES
#
# You may fully customise the login banner string:
#ftpd_banner=Welcome to blah FTP service.
#
# You may specify a file of disallowed anonymous e-mail addresses. Apparently
# useful for combatting certain DoS attacks.
#deny_email_enable=YES
# (default follows)
#banned_email_file=/etc/vsftpd.banned_emails
#
# You may restrict local users to their home directories. See the FAQ for
# the possible risks in this before using chroot_local_user or
# chroot_list_enable below.
#chroot_local_user=YES
#
# You may specify an explicit list of local users to chroot() to their home
# directory. If chroot_local_user is YES, then this list becomes a list of
# users to NOT chroot().
# (Warning! chroot'ing can be very dangerous. If using chroot, make sure that
# the user does not have write access to the top level directory within the
# chroot)
#chroot_local_user=YES
#chroot_list_enable=YES
# (default follows)
#chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list
#
# You may activate the "-R" option to the builtin ls. This is disabled by
# default to avoid remote users being able to cause excessive I/O on large
# sites. However, some broken FTP clients such as "ncftp" and "mirror" assume
# the presence of the "-R" option, so there is a strong case for enabling it.
#ls_recurse_enable=YES
#
# Customization
#
# Some of vsftpd's settings don't fit the filesystem layout by
# default.
#
# This option should be the name of a directory which is empty. Also, the
# directory should not be writable by the ftp user. This directory is used
# as a secure chroot() jail at times vsftpd does not require filesystem
# access.
secure_chroot_dir=/var/run/vsftpd/empty
#
# This string is the name of the PAM service vsftpd will use.
pam_service_name=ftp
#
# This option specifies the location of the RSA certificate to use for SSL
# encrypted connections.
rsa_cert_file=/etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem
rsa_private_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key
ssl_enable=NO
pasv_enable=YES
port_enable=YES
#
# Uncomment this to indicate that vsftpd use a utf8 filesystem.
#utf8_filesystem=YES
pasv_enable=YES
port_enable=YES
Have both been tryed with param. «NO» combined and seperated
With this result:
Gewartet wird 0 Sekunden. Weiter mit beliebiger Taste...
Verbindung mit 194.26.183.194 wurde hergestellt.
220 (vsFTPd 3.0.3)
200 Always in UTF8 mode.
ftp> user anonymous
331 Please specify the password.
230 Login successful.
ftp> put C:UsersAnwenderDownloadsAnwender_DESKTOP-V30SJ8P_2021-09-07-15-07-12.wav Anwender_DESKTOP-V30SJ8P_2021-09-07-15-07-12.wav
500 Illegal PORT command.
425 Use PORT or PASV first.
ftp>
I have a hard time understanding what I am supposed to do and would be very thankful for any hints regarding further steps.
FTP server return codes always have three digits, and each digit has a special meaning.[1] The first digit denotes whether the response is good, bad or incomplete:
1xx
The requested action is being initiated; expect another reply before proceeding with a new command. (The user-process sending another command before the completion reply would be in violation of protocol; but server-FTP processes should queue any commands that arrive while a preceding command is in progress.) This type of reply can be used to indicate that the command was accepted and the user-process may now pay attention to the data connections, for implementations where simultaneous monitoring is difficult. The server-FTP process may send at most, one 1xx reply per command.
2xx
The requested action has been successfully completed. A new request may be initiated.
3xx
The command has been accepted, but the requested action is being held in abeyance, pending receipt of further information. The user should send another command specifying this information. This reply is used in command sequence groups.
4xx
The command was not accepted and the requested action did not take place, but the error condition is temporary and the action may be requested again. The user should return to the beginning of the command sequence, if any. It is difficult to assign a meaning to «transient», particularly when two distinct sites (Server- and User-processes) have to agree on the interpretation. Each reply in the 4xx category might have a slightly different time value, but the intent is that the user-process is encouraged to try again. A rule of thumb in determining if a reply fits into the 4xx or the 5xx (Permanent Negative) category is that replies are 4xx if the commands can be repeated without any change in command form or in properties of the User or Server (e.g., the command is spelled the same with the same arguments used; the user does not change his file access or user name; the server does not put up a new implementation.)
5xx
The command was not accepted and the requested action did not take place. The User-process is discouraged from repeating the exact request (in the same sequence). Even some «permanent» error conditions can be corrected, so the human user may want to direct his User-process to reinitiate the command sequence by direct action at some point in the future (e.g., after the spelling has been changed, or the user has altered his directory status.)
6xx
The RFC 2228 introduced the concept of protected replies to increase security over the FTP communications. The 6xx replies are Base64 encoded protected messages that serves as responses to secure commands. When properly decoded, these replies fall into the above categories.
Below is a list of all known return codes that may be issued by an FTP server.
100 Series
110
MARK yyyy = mmmm where yyyy is User-process data stream marker, and mmmm server’s equivalent marker (note the spaces between markers and «=»).
120
125
150
200 Series
202
211
212
213
214
215
220
221
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
234
235
250
257
300 Series
331
332
334
335
350
400 Series
421
425
426
430
434
450
451
452
500 Series
501
502
503
504
530
532
534
550
551
552
553
600 Series
631
632
633
10000 Series
10054
10060
10061
10065
10066
10068
Опубликовал(а):
в: 08.11.2010

При FTP операциях некоторые клиенты не только пишут коды сообщений, но и расшифровавают их. Но не всегда. Например, при установке соединения, мы получили от FTP клиента код ошибки 434, и что это значит?
Попробуем разобраться разбив код ошибки на цифры (каждая позиция отвечает за свой набор значений):
Первая позиция
- 1 это — команда принята к выполнению но все еще не завершена
- 2 это — команда завершена успешно
- 3 это — команда принята, но ожидается дополнительная команда
- 4 это — в данный момент команда не может быть выполнена
- 5 это — невозможно выполнить команду в принципе
Вторая позиция
- 0 это — синтаксическая ошибка в команде
- 1 это — информационное сообщение
- 2 это — означает что сообщение относится к управляющему соединению либо соединению данных
- 3 это — сообщение о аутентификации пользователя и его правах
- 4 — не определено
- 5 — состояние файловой системы
Третья позиция
- Третья цифра окончательно специфицирует ошибку.
| Код | Описание |
| 100 | Запрошенное действие инициировано, дождитесь следующего ответа прежде, чем выполнять новую команду. |
| 110 | Комментарий |
| 120 | Функция будет реализована через nnn минут |
| 125 | Канал открыт, обмен данными начат |
| 150 | Статус файла правилен, подготавливается открытие канала |
| 200 | Команда корректна |
| 202 | Команда не поддерживается |
| 211 | Системный статус или отклик на справочный запрос |
| 212 | Состояние каталога |
| 213 | Состояние файла |
| 214 | Справочное поясняющее сообщение |
| 215 | Выводится вместе с информацией о системе по команде SYST |
| 220 | Слишком много подключений к FTP-серверу (можете попробовать позднее). В некоторых версиях указывает на успешное завершение промежуточной процедуры |
| 221 | Благополучное завершение по команде quit |
| 225 | Канал сформирован, но информационный обмен отсутствует |
| 226 | Закрытие канала, обмен завершен успешно |
| 227 | Переход в пассивный режим (h1,h2,h3,h4,p1,p2). |
| 228 | переход в длинный пассивный режим (длинный адрес, порт). |
| 229 | Переход в расширенный пассивный режим (|||port|). |
| 230 | Пользователь идентифицирован, продолжайте |
| 231 | Пользовательский сеанс окончен; Обслуживание прекращено. |
| 232 | Команда о завершении сеанса принята, она будет завершена по завершении передачи файла. |
| 250 | Запрос прошёл успешно |
| 257 | «ПУТЬ» создан. |
| 331 | Имя пользователя корректно, нужен пароль |
| 332 | Для входа в систему необходима аутентификация |
| 350 | Запрошенное действие над файлом требует большей информации |
| 404 | Данный удалённый сервер не найден |
| 421 | Процедура не возможна, канал закрывается |
| 425 | Открытие информационного канала не возможно |
| 426 | Канал закрыт, обмен прерван |
| 434 | Запрашиваемый хост недоступен |
| 450 | Запрошенная функция не реализована, файл не доступен, например, занят |
| 451 | Локальная ошибка, операция прервана |
| 452 | Ошибка при записи файла (недостаточно места) |
| 500 | Синтаксическая ошибка, команда не может быть интерпретирована (возможно она слишком длинна) |
| 501 | Синтаксическая ошибка (неверный параметр или аргумент) |
| 502 | Команда не используется (нелегальный тип MODE) |
| 503 | Неудачная последовательность команд |
| 504 | Команда не применима для такого параметра |
| 530 | Вход не выполнен! Требуется авторизация (not logged in) |
| 532 | Необходима аутентификация для запоминания файла |
| 550 | Запрошенная функция не реализована, файл не доступен, например, не найден |
| 551 | Запрошенная операция прервана. Неизвестный тип страницы. |
| 552 | Запрошенная операция прервана. Выделено недостаточно памяти |
| 553 | Запрошенная операция не принята. Недопустимое имя файла. |
Вот и все, надеюсь этот материал поможет Вам лучше понимать FTP :))
