Содержание
- Mysql connect error [localhost]: (1040) Too many connections (400)
- Причины ошибки
- Методы обнаружения проблемы
- Как исправить
- Подключение MySQL после ошибки 1040: слишком много соединений
- И снова ERROR 1040…
- Root-пользователь тоже не может подключиться! Почему?!
- Как гарантировать доступ к экземпляру
- Настройка Percona Server
- Настройка в MySQL Community
- Использование для мониторинга и проверок работоспособности
- Помогите! Мне нужно войти, но все порты заняты!
- Подключение MySQL после ошибки 1040: слишком много соединений
- И снова ERROR 1040…
- Root-пользователь тоже не может подключиться! Почему?!
- Как гарантировать доступ к экземпляру
- Настройка Percona Server
- Настройка в MySQL Community
- Использование для мониторинга и проверок работоспособности
- Помогите! Мне нужно войти, но все порты заняты!
- Preventing MySQL Error 1040: Too Many Connections
- Accurately Tune the max_connections Parameter
- Avoiding Common Scenarios Resulting in Overuse of Connections
- Safeguard Yourself From Being Locked Out
- Use a Proxy
- Limits Per User
Mysql connect error [localhost]: (1040) Too many connections (400)
Ошибка Mysql connect error [localhost]: (1040) Too many connections (400) возникает в случае превышения лимита одновременных соединений с базой данных MySQL.
Причины ошибки
Как сказано выше, причина проста — «Много одновременных соединений с БД». Стоит понимать, что имеется ввиду БД с которой работает Битрикс, но с этой БД может и работать другой сайт по удаленному подключению. Причины:
- Много пользователей на сайте;
- DDos атака на сайт;
- DDos атака на сайт, который использует данную БД через удаленное подключение;
- Ошибка в скрипте сайта (в следствии чего, сайт не может закрывать запросы, при этом образовывается много SLEEP запросов);
- Ошибка в скрипте сайта, который использует удаленное подключение (в следствии чего, сайт не может закрывать запросы, при этом образовывается много SLEEP запросов);
Методы обнаружения проблемы
Чтобы обнаружить, в чем именно проблема, нужноузнать количество соединений к MySql и проанализировать их (время, какой пользователь делает, с какого IP).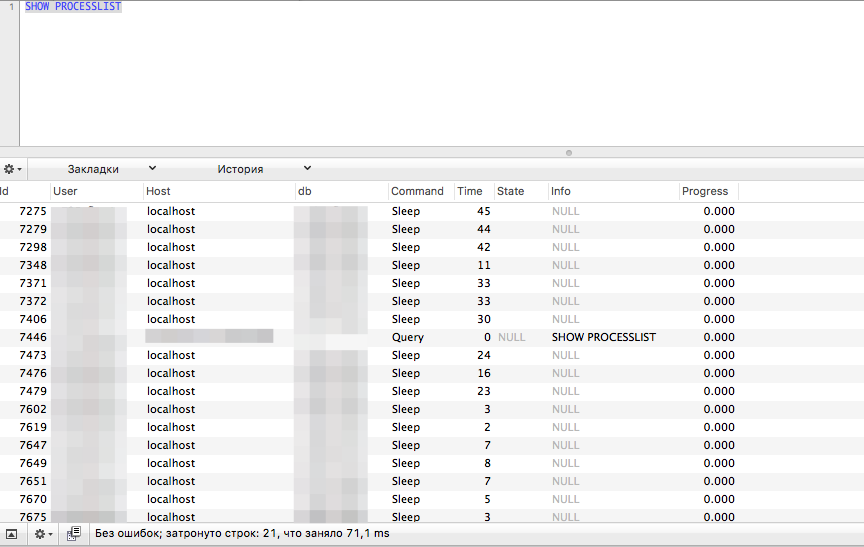
Пример анализа запросов к БД
Как исправить
Есть всего 3 варианта исправления: увеличить количество одновременных соединений (если проблема связанна с большим посещением сайта реальных пользователей ), отражение DDOS атаки, или оптимизацией кода сайта. Как вы понимаете, универсального рецепта нет и быть не может. Если вам не помогло увеличения лимита, и вы не знаете что делать в случае DDOS или как оптимизировать код сайта — обращайтесь к профессионалам.
Источник
Подключение MySQL после ошибки 1040: слишком много соединений
И снова ERROR 1040…
Техподдержка получает много жалоб на эту печально известную ошибку: ERROR 1040: Too many connections — слишком много соединений. Проблема очевидна: приложение или пользователи создают больше соединений, чем допускает сервер, то есть текущее число соединений превышает значение переменной max_connections .
Ситуация уже сама по себе проблема для конечных пользователей, но если еще при этом у вас нет доступа к серверу для диагностики и исправления причины, все становится совсем плохо. Обычно приходится завершать экземпляр и перезапускать его, чтобы восстановить.
Root-пользователь тоже не может подключиться! Почему?!
В правильно настроенной среде пользователь с привилегией SUPER сможет получить доступ к экземпляру и диагностировать причину ошибки 1040, из-за которой не хватает соединений. Это описано в руководстве:
mysqld разрешает max_connections + 1 клиентских соединений. Дополнительное соединение зарезервировано для аккаунтов с привилегиями SUPER . Когда эти привилегии предоставляются администраторам, а не обычным пользователям (которым они и не нужны), администратор, у которого есть еще и привилегия PROCESS , может подключиться к серверу и использовать SHOW PROCESSLIST , чтобы диагностировать проблемы, даже если подключено максимальное число клиентов без привилегий.
Но куча людей дают привилегии SUPER своим пользователям приложения или скрипта — из-за требований приложения (опасно!) или незнания последствий, а потом зарезервированное соединение занимает обычный пользователь, а административный пользователь (обычно root ) не может подключиться.
Как гарантировать доступ к экземпляру
Можно использовать хорошо известный хак с GDB, который советовал Ауримас лет 100 назад для ошибки 1040, но теперь есть решения получше. Правда сначала их надо включить.
С Percona Server 5.5.29 и выше и MySQL 8.0.14 и выше можно настроить еще один порт с дополнительным числом соединений. Приложение не будет использовать эти интерфейсы. Они только для администраторов баз данных и агентов мониторинга и проверки работоспособности (см. примечание ниже).
Настройка Percona Server
Начиная с Percona Server 5.5.29 можно просто добавить extra_port в my.cnf , и при следующем перезапуске порт будет доступен и будет ожидать данные по тому же bind_address , что и обычные соединения. Если не настроить переменную extra_port , дополнительного порта по умолчанию не будет.
Еще можно определить extra_max_connections , чтобы задать количество подключений, которое будет обрабатывать этот порт. Количество по умолчанию — 1.
Для примера я занял все подключения к порту обычных пользователей у экземпляра, где уже настроил extra_port и extra_max_connections в my.cnf :
Кстати, extra_port удален в Percona Server 8.0.14 и выше, поскольку в MySQL Community реализован admin_port с теми же функциями. Так что отредактируйте my.cnf при апгрейде до Percona Server 8.0.14 или выше, если вы уже определили extra_port.
Как я уже сказал, для этого нужен MySQL 8.0.14, где применен WorkLog 12138.
Чтобы включить админский интерфейс, нужно определить admin_addres, который должен быть единственным и уникальным (без подстановочных символов) IPv4, IPv6, IPv4-сопоставленным адресом или именем хоста, по которому админский интерфейс будет ожидать передачи данных. Если эта переменная не определена, интерфейс не включен.
Еще можно определить порт, но это не обязательно. По умолчанию это порт 33062 . Если этот порт свободен, это значение не нужно настраивать. Если настраиваете, то поместите обе переменные в раздел [mysqld] в my.cnf .
Наконец, можно настроить create_admin_listener_thread (отключено по умолчанию), который создает отдельный поток для обработки входящих соединений. Это может пригодиться в некоторых ситуациях.
Еще одно различие — в документации Oracle сказано, что:
Число административных соединений не ограничено.
(А у нас значение по умолчанию — 1). Не уверен, что это значит, но я бы был осторожен, чтобы случайно не установить 1 млн соединений. Они, конечно, не ограничены, но ресурсы-то все равно потребляют.
Использование для мониторинга и проверок работоспособности
Удобно, что не только люди могут использовать дополнительный интерфейс или порт в экстренной ситуации, когда мы достигли max_connections . К нему может подключиться система мониторинга и проверки работоспособности прокси/балансировщика нагрузки/обнаружения сервисов.
Скрипты мониторинга смогут извлекать данные для диаграмм, чтобы потом вы разобрались, откуда столько соединений. А скрипты проверки работоспособности будут докладывать об ухудшившемся состоянии сервера, и определенный код может указывать, что соединений много, но сервер справляется (то есть может разобраться сам и лучше чуть дольше подождать до отработки отказа).
Обязательно устанавливайте только по одному соединению за раз для мониторинга и проверки работоспособности, чтобы не забивать extra_max_connections в Percona Server и не создать миллион потоков в MySQL. То есть скрипты не должны подключаться снова, если предыдущий запрос или подключение к базе данных еще активны.
Для Percona Server 8.0.14 и выше процесс будет тем же, что и для MySQL Community.
Помогите! Мне нужно войти, но все порты заняты!
Если это та самая причина, по которой вы читаете этот пост, используйте безумный хак с GDB (без обид, Ауримас, просто выглядит рисково :-D) или завершите экземпляр. К счастью, экземпляр почти всегда можно аккуратно завершить с помощью SIGTERM (-15) вместо SIGKILL (-9). Так сервер выполнит чистую остановку, и у потоков будет шанс нормально завершить работу. Просто следуйте инструкциям:
2) Отправьте SIGTERM в этот PID:
3) Следите в журнале ошибок, как выполняется завершение работы. Это будет выглядеть примерно так:
Это означает начало процесса завершения работы. Экземпляр будет завершен, когда вы увидите подобную строку:
Источник
Подключение MySQL после ошибки 1040: слишком много соединений
И снова ERROR 1040…
Техподдержка получает много жалоб на эту печально известную ошибку: ERROR 1040: Too many connections — слишком много соединений. Проблема очевидна: приложение или пользователи создают больше соединений, чем допускает сервер, то есть текущее число соединений превышает значение переменной max_connections .
Ситуация уже сама по себе проблема для конечных пользователей, но если еще при этом у вас нет доступа к серверу для диагностики и исправления причины, все становится совсем плохо. Обычно приходится завершать экземпляр и перезапускать его, чтобы восстановить.
Root-пользователь тоже не может подключиться! Почему?!
В правильно настроенной среде пользователь с привилегией SUPER сможет получить доступ к экземпляру и диагностировать причину ошибки 1040, из-за которой не хватает соединений. Это описано в руководстве:
mysqld разрешает max_connections + 1 клиентских соединений. Дополнительное соединение зарезервировано для аккаунтов с привилегиями SUPER . Когда эти привилегии предоставляются администраторам, а не обычным пользователям (которым они и не нужны), администратор, у которого есть еще и привилегия PROCESS , может подключиться к серверу и использовать SHOW PROCESSLIST , чтобы диагностировать проблемы, даже если подключено максимальное число клиентов без привилегий.
Но куча людей дают привилегии SUPER своим пользователям приложения или скрипта — из-за требований приложения (опасно!) или незнания последствий, а потом зарезервированное соединение занимает обычный пользователь, а административный пользователь (обычно root ) не может подключиться.
Как гарантировать доступ к экземпляру
Можно использовать хорошо известный хак с GDB, который советовал Ауримас лет 100 назад для ошибки 1040, но теперь есть решения получше. Правда сначала их надо включить.
С Percona Server 5.5.29 и выше и MySQL 8.0.14 и выше можно настроить еще один порт с дополнительным числом соединений. Приложение не будет использовать эти интерфейсы. Они только для администраторов баз данных и агентов мониторинга и проверки работоспособности (см. примечание ниже).
Настройка Percona Server
Начиная с Percona Server 5.5.29 можно просто добавить extra_port в my.cnf , и при следующем перезапуске порт будет доступен и будет ожидать данные по тому же bind_address , что и обычные соединения. Если не настроить переменную extra_port , дополнительного порта по умолчанию не будет.
Еще можно определить extra_max_connections , чтобы задать количество подключений, которое будет обрабатывать этот порт. Количество по умолчанию — 1.
Для примера я занял все подключения к порту обычных пользователей у экземпляра, где уже настроил extra_port и extra_max_connections в my.cnf :
Кстати, extra_port удален в Percona Server 8.0.14 и выше, поскольку в MySQL Community реализован admin_port с теми же функциями. Так что отредактируйте my.cnf при апгрейде до Percona Server 8.0.14 или выше, если вы уже определили extra_port.
Как я уже сказал, для этого нужен MySQL 8.0.14, где применен WorkLog 12138.
Чтобы включить админский интерфейс, нужно определить admin_addres, который должен быть единственным и уникальным (без подстановочных символов) IPv4, IPv6, IPv4-сопоставленным адресом или именем хоста, по которому админский интерфейс будет ожидать передачи данных. Если эта переменная не определена, интерфейс не включен.
Еще можно определить порт, но это не обязательно. По умолчанию это порт 33062 . Если этот порт свободен, это значение не нужно настраивать. Если настраиваете, то поместите обе переменные в раздел [mysqld] в my.cnf .
Наконец, можно настроить create_admin_listener_thread (отключено по умолчанию), который создает отдельный поток для обработки входящих соединений. Это может пригодиться в некоторых ситуациях.
Еще одно различие — в документации Oracle сказано, что:
Число административных соединений не ограничено.
(А у нас значение по умолчанию — 1). Не уверен, что это значит, но я бы был осторожен, чтобы случайно не установить 1 млн соединений. Они, конечно, не ограничены, но ресурсы-то все равно потребляют.
Использование для мониторинга и проверок работоспособности
Удобно, что не только люди могут использовать дополнительный интерфейс или порт в экстренной ситуации, когда мы достигли max_connections . К нему может подключиться система мониторинга и проверки работоспособности прокси/балансировщика нагрузки/обнаружения сервисов.
Скрипты мониторинга смогут извлекать данные для диаграмм, чтобы потом вы разобрались, откуда столько соединений. А скрипты проверки работоспособности будут докладывать об ухудшившемся состоянии сервера, и определенный код может указывать, что соединений много, но сервер справляется (то есть может разобраться сам и лучше чуть дольше подождать до отработки отказа).
Обязательно устанавливайте только по одному соединению за раз для мониторинга и проверки работоспособности, чтобы не забивать extra_max_connections в Percona Server и не создать миллион потоков в MySQL. То есть скрипты не должны подключаться снова, если предыдущий запрос или подключение к базе данных еще активны.
Вот тот же пример, но с MySQL.
Для Percona Server 8.0.14 и выше процесс будет тем же, что и для MySQL Community.
Помогите! Мне нужно войти, но все порты заняты!
Если это та самая причина, по которой вы читаете этот пост, используйте безумный хак с GDB (без обид, Ауримас, просто выглядит рисково :-D) или завершите экземпляр. К счастью, экземпляр почти всегда можно аккуратно завершить с помощью SIGTERM (-15) вместо SIGKILL (-9). Так сервер выполнит чистую остановку, и у потоков будет шанс нормально завершить работу. Просто следуйте инструкциям:
2) Отправьте SIGTERM в этот PID:
3) Следите в журнале ошибок, как выполняется завершение работы. Это будет выглядеть примерно так:
Это означает начало процесса завершения работы. Экземпляр будет завершен, когда вы увидите подобную строку:
Источник
Preventing MySQL Error 1040: Too Many Connections
One of the most common errors encountered in the MySQL world at large is the infamous Error 1040:
What this means in practical terms is that a MySQL instance has reached its maximum allowable limit for client connections. Until connections are closed, no new connection will be accepted by the server.
I’d like to discuss some practical advice for preventing this situation, or if you find yourself in it, how to recover.
Accurately Tune the max_connections Parameter
This setting defines the maximum number of connections that a MySQL instance will accept. Considerations on “why” you would want to even have a max number of connections are based on resources available to the server and application usage patterns. Allowing uncontrolled connections can crash a server, which may be considered “worse” than preventing further connections. Max_connections is a value designed to protect your server, not fix problems related to whatever is hijacking the connections.
Each connection to the server will consume both a fixed amount of overhead for things like the “thread” managing the connection and the memory used to manage it, as well as variable resources (for instance memory used to create an in-memory table. It is important to measure the application’s resource patterns and find the point at which exceeding that number of connections will become dangerous.
Percona Monitoring and Management (PMM) can help you find these values. Look at the memory usage patterns, threads running, and correlate these with the number of connections. PMM can also show you spikes in connection activity, letting you know how close to the threshold you’re coming. Tune accordingly, keeping in mind the resource constraints of the server.
Seen below is a server with a very steady connection pattern and there is a lot of room between Max Used and Max Connections.
Avoiding Common Scenarios Resulting in Overuse of Connections
Having worked in the Percona Managed Services team for years, I’ve had the first-hand opportunity to see where many businesses get into “trouble” from opening too many connections. Conventional wisdom says that it will usually be a bad code push where an application will behave badly by not closing its open connections or by opening too many quickly for frivolous reasons.
There are other scenarios that I’ve seen that will cause this too even if the application is performing “as expected”. Consider an application stack that utilizes a cache. Over time the application has scaled up and grown. Now consider the behavior under load if the cache is completely cleared. The workers in the application might try to repopulate the cache in mass generating a spike that will overwhelm a server.
It is important to consider the systems that use the MySQL server and prevent these sorts of edge case behaviors or it might lead to problems. If possible, it is a good idea to trap errors in the application and if you run into “Too many connections” have the application back off and slip for a bit before a retry to reduce the pressure on the connection pool.
Safeguard Yourself From Being Locked Out
MySQL actually gives you “breathing” room from being locked out. In versions 5.xx the SUPER user has a +1 always available connection and in versions 8.xx there is a +1 for users with CONNECTION_ADMIN privileges. However, many times a system has lax privilege assignments and maybe an application user is granted these permissions and consumes this extra emergency connection. It is a good idea to audit users and be sure that only true administrators have access to these privileges so that if a server does consume all its available connections, an administrator can step in and take action. There are other benefits to being strict on permissions. Remember that the minimum privilege policy is often a best practice for good reason! And not always just “security”.
MySQL 8.0.14+ also allows us to specify admin_address and admin_port to provide for a completely different endpoint, bypassing the primary endpoint and establishing a dedicated admin connection. If you’re running a lower version but are using Percona Server for MySQL, you’ll have the option of using extra_port and extra_max_connections to achieve another way of connecting.
If you are able to log in as an admin account, you may be able to kill connections, use pt-kill to kill open connections, adjust timeouts, ban offending accounts, or raise the max_connections to free up the server.
If you are unable to log in, you may try to adjust the max_connection value on the fly as a last resort. Please see Too many connections? No problem!
Use a Proxy
Another way to alleviate connection issues (or move the issue to a different layer in the stack), is to adopt the user of a proxy server, such as ProxySQL to handle multiplexing. See Multiplexing (Mux) in ProxySQL: Use Case.
Limits Per User
Another variable that MySQL can use to determine if a connection should be allowed is max_user_connections. By setting this value, it puts a limit on the number of connections for any given user. If you have a smaller number of application users that can stand some limit on their connection usage, you can set this value appropriately to prevent total server connection maximum.
For instance, if we know we have 3 application users and we expect those 3 users to never individually exceed 300 connections, we could set max_user_connections to 300. Between the 3 application users, only a total of 900 connections would be allowed. If max_connections was set to 1000, we’d still have 100 open slots.
Another approach in this same vein that is even more granular is to limit connections PER USER account. To achieve this you can create an account like this:
Источник
Error Message:
ERROR 1040 (HY000): Too many connections
| MySQL Too many connections |
Reason for this error:
This error occurs when connection reaches the maximum limit as defined in the configuration file. The variables holding this value is max_connections
To check the current value of this variable, login as root user and run the following command:
show global variables like max_connections;
| MySQL max_connections variable |
Note: In above step, you can login using root, you may wonder, when it is showing Too many connection error, how can you login as root? The answer is, MySQL by default will consider maximum allowed connection as max_connection + 1 for SUPER user to fix this issue.
In our example — max_connection = 1, so MySQL will consider maximum allowed connection as 1 + 1 = 2.
Workaround 1:
Login to MySQL using root user and increase the max_connections variable to higher value.
SET GLOBAL max_connections = 100;
| SET GLOBAL max_connections |
Now login to MySQL, the too many connection error fixed. This method does not require server restart. After MySQL server restart, the max_connection variable value again roll back to previous value. In order to make the max_connection value persistent, modify the value in the configuration file.
Workaround 2:
Stop the MySQL server:
Service mysql stop
Edit the configuration file my.cnf.
vi /etc/my.cnf
Find the variable max_connections under mysqld section.
[mysql]
max_connections = 100
Set into higher value and save the file.
Start the server.
Service mysqld start
Note: use systemctl manager to stop and start the service if, service command not working.
I hope this post, will help you to fix the issue. If still you are unable to fix this issue, mention on the below comment section. I will get back to you fix this issue.
Update 1:
You can avoid this too many connection error by using this method. For example, 5 applications are connecting MySQL server. So, the calculations to set the max_connections value is as follows.
Total users = 5 applications = 5 Users
Concurrent connections = 200 (depends on your applications)
max_connections = 5 x 200 + 200 = 1200.
In case of all users are connecting, maximum it reaches 1000 users and still 200 connections are remaining. This example is only for our understanding. You should not implement this method on production system, we should have a detailed understanding of the application access to limit the max_connections value.
Update 2:
Before increasing the max_connections variable value, make sure that, the server has adequate memory for new requests and connections.
MySQL pre-allocate memory for each connections and de-allocate only when the connection get closed. And, when new connections are querying, system should have enough resources such memory, network and computation power to satisfy the user requests.
Also, you should consider increasing the open tables limit in MySQL server to accommodate the additional request. And finally. it is very important to close the connections which are completed transaction on the server.
One of the most common errors encountered in the MySQL world at large is the infamous Error 1040:
|
ERROR 1040 (00000): Too many connections |
What this means in practical terms is that a MySQL instance has reached its maximum allowable limit for client connections. Until connections are closed, no new connection will be accepted by the server.
I’d like to discuss some practical advice for preventing this situation, or if you find yourself in it, how to recover.
Accurately Tune the max_connections Parameter
This setting defines the maximum number of connections that a MySQL instance will accept. Considerations on “why” you would want to even have a max number of connections are based on resources available to the server and application usage patterns. Allowing uncontrolled connections can crash a server, which may be considered “worse” than preventing further connections. Max_connections is a value designed to protect your server, not fix problems related to whatever is hijacking the connections.
Each connection to the server will consume both a fixed amount of overhead for things like the “thread” managing the connection and the memory used to manage it, as well as variable resources (for instance memory used to create an in-memory table. It is important to measure the application’s resource patterns and find the point at which exceeding that number of connections will become dangerous.
Percona Monitoring and Management (PMM) can help you find these values. Look at the memory usage patterns, threads running, and correlate these with the number of connections. PMM can also show you spikes in connection activity, letting you know how close to the threshold you’re coming. Tune accordingly, keeping in mind the resource constraints of the server.
Seen below is a server with a very steady connection pattern and there is a lot of room between Max Used and Max Connections.
Avoiding Common Scenarios Resulting in Overuse of Connections
Having worked in the Percona Managed Services team for years, I’ve had the first-hand opportunity to see where many businesses get into “trouble” from opening too many connections. Conventional wisdom says that it will usually be a bad code push where an application will behave badly by not closing its open connections or by opening too many quickly for frivolous reasons.
There are other scenarios that I’ve seen that will cause this too even if the application is performing “as expected”. Consider an application stack that utilizes a cache. Over time the application has scaled up and grown. Now consider the behavior under load if the cache is completely cleared. The workers in the application might try to repopulate the cache in mass generating a spike that will overwhelm a server.
It is important to consider the systems that use the MySQL server and prevent these sorts of edge case behaviors or it might lead to problems. If possible, it is a good idea to trap errors in the application and if you run into “Too many connections” have the application back off and slip for a bit before a retry to reduce the pressure on the connection pool.
Safeguard Yourself From Being Locked Out
MySQL actually gives you “breathing” room from being locked out. In versions 5.xx the SUPER user has a +1 always available connection and in versions 8.xx there is a +1 for users with CONNECTION_ADMIN privileges. However, many times a system has lax privilege assignments and maybe an application user is granted these permissions and consumes this extra emergency connection. It is a good idea to audit users and be sure that only true administrators have access to these privileges so that if a server does consume all its available connections, an administrator can step in and take action. There are other benefits to being strict on permissions. Remember that the minimum privilege policy is often a best practice for good reason! And not always just “security”.
MySQL 8.0.14+ also allows us to specify admin_address and admin_port to provide for a completely different endpoint, bypassing the primary endpoint and establishing a dedicated admin connection. If you’re running a lower version but are using Percona Server for MySQL, you’ll have the option of using extra_port and extra_max_connections to achieve another way of connecting.
If you are able to log in as an admin account, you may be able to kill connections, use pt-kill to kill open connections, adjust timeouts, ban offending accounts, or raise the max_connections to free up the server.
If you are unable to log in, you may try to adjust the max_connection value on the fly as a last resort. Please see Too many connections? No problem!
Use a Proxy
Another way to alleviate connection issues (or move the issue to a different layer in the stack), is to adopt the user of a proxy server, such as ProxySQL to handle multiplexing. See Multiplexing (Mux) in ProxySQL: Use Case.
Limits Per User
Another variable that MySQL can use to determine if a connection should be allowed is max_user_connections. By setting this value, it puts a limit on the number of connections for any given user. If you have a smaller number of application users that can stand some limit on their connection usage, you can set this value appropriately to prevent total server connection maximum.
For instance, if we know we have 3 application users and we expect those 3 users to never individually exceed 300 connections, we could set max_user_connections to 300. Between the 3 application users, only a total of 900 connections would be allowed. If max_connections was set to 1000, we’d still have 100 open slots.
Another approach in this same vein that is even more granular is to limit connections PER USER account. To achieve this you can create an account like this:
|
CREATE USER ‘user’@‘localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘XXXXXXXX’ WITH MAX_USER_CONNECTIONS 10; |
It is a good idea to limit connections to tools/applications/monitoring that are newly being introduced in your environment and make sure they do not “accidentally” consume too many connections.
Close Unused Connections
MySQL provides the wait_timeout variable. If you observe connections climbing progressively over time and not in a spike (and your application can handle it), you may want to reduce this variable from its default of 28800 seconds to something more reasonable. This will essentially ask the server to close sleeping connections.
These are just a few considerations when dealing with “Too many connections”. I hope they help you. You may also consider further reading on the topic in this previous Percona blog post, MySQL Error: Too many connections.
In our role as Server administration specialists for server owners, database errors are something that that we resolve for them. A commonly reported one is the MySQL ‘Too many connections’ error.
Many server owners who have their sites running on MySQL database server, often come across this error in the websites or server:
ERROR 1040 (HY000): Too many connections
In the case of PHP based websites with MySQL database server in the backend, the error message can be something like:
PHP Warning: mysqli_connect(): (HY000/1040): Too many connections
MySQL ‘Too many connections’ – The causes and fix
When a MySQL server is initially installed, it will have 150 as the default value for maximum permitted number of simultaneous client connections. This value can be adjusted further in servers.
An additional admin connection is also possible to monitor these client connections. This extra connection is reserved for use by accounts that have CONNECTION_ADMIN or SUPER user privilege.
The number of connections is defined by ‘max_connections’ value. When the number of client connections exceed this value, MySQL shows ‘Too many connections’ error.
This can happen in multiple scenarios, and the fix for the error would vary with the actual cause. Here, we’ll see the various causes that trigger MySQL ‘Too many connections’ error.
1. High traffic to sites
Many a times, the web traffic can go high due to peak sales or promotions. If there number of connections allowed for your MySQL server is not enough, users will get “Too many connections” error in websites.
In such scenarios, we first examine the MySQL processes in the server and analyze the web server traffic to figure out which site is causing the issue.
If the traffic is valid, we tweak the maximum number of connections to the database that are allowed, and increase it to a value that is high enough to meet the website requirements.
For resource-intensive websites, sometimes increasing the connection limit alone would not be sufficient. We do an in-depth analysis and tweak various service parameters to handle this high traffic.
2. Web server attacks
Often, it has been seen that a sudden increase in website traffic and intermittent ‘Too many connections’ errors denote a flooding attack to the web server.
If the connection limit is increased without noticing or preventing the attack, it will eventually crash your server, as a flooding attack is aimed at exhausting server resources with too many requests.
Bobcares’ engineers detect such attack attempts proactively, and immediately pinpoint the source of the attack and block those IP addresses, before it crashes the server.
We examine the access logs, network connections to the server, malicious scripts and processes, etc. in the server, to figure out the depth and extent of the attack.
3. Poorly coded applications
Many websites have custom code and applications running on them. Many often, this code may contain bugs or can lead to infinite loops of MySQL queries, leading to too many connections.
Too many persistent connections to MySQL server or the application not closing connections properly, can also lead to MySQL ‘Too many connections’ error.
If the timeout for idle connections is too high, it can cause too many sleeping connections, and thereby use up the allowable limit of MySQL connections in the server.
By examining the MySQL processes and queries that are running, we figure out the code that is causing issue, and optimise it further to fix ‘Too many connections’ error.
MySQL ‘Too many connections’ fix – What to keep in mind!
One common question that comes into the mind of server owners, is what exactly should be the value of max_connections parameter for MySQL. The fact is that, there is no such specific value.
The number of allowable connections depends on the amount of RAM available and memory usage for each connection. Increasing the value too much can use up the RAM and cause server to crash.
At Bobcares, we examine the available memory in the server and other parameters that require the RAM, before going ahead and increasing the connection limit.
Other parameters such as the timeout settings, cache and open tables can also influence the memory utilised for MySQL and the connections possible.
By doing an iterative tweaking and examining the MySQL server performance and memory usage after each iteration, we configure the MySQL server to serve connections with maximum efficiency.
Conclusion
MySQL ‘Too many connections’ is a commonly seen, but confusing database server error. The major hurdle involved in fixing it, is finding the actual root cause of the error. From attacks to database server settings, we’ve seen the various causes for the error and how to fix it permanently.
FIX SERVER ERRORS
Worried over server errors? Consult our 24/7 server experts to ensure seamless server functioning.
FIX YOUR SERVER ERRORS
How to interpret “MySQL error 1040 – Too many connections ! ” ?
When a client tries to log into MySQL it may sometimes be rejected and receive an error message saying that there are “too many connections“. This means that the maximum number of clients that may be connected to the server has been reached. Either the client will have to wait for another client to log off, or the administrator will have to increase the maximum number of connections allowed.
Information about connections to a server can be found using the SHOW STATUS statement:
SHOW STATUS LIKE 'max_used_connections';
Prerequisite – Few points to remember before working or troubleshooting MySQL ” Too many connections ! ” error
- MySQL does not have it’s own thread handling mechanism / implementation and it completely relies on the thread handling implementation of the underlying operating system.
- MySQL system variable max_connections control the maximum number of clients the server permits to connect simultaneously, You may have to increase max_connections if more clients attempt to connect simultaneously then the server is configured to handle (Explained more in detail – “Too many connections”).
- How MySQL connection handling (both connects and disconnects) works ?
- MySQL Clients connects to MySQL Server via a simple and regular TCP-IP connect message though port 3306 on the Server instance
- The incoming connection requests are queued and then processed by the receiver thread one by one, All that receiver thread does is create user thread. It’s actually user thread which handles the client-server protocol for connection management, Which involves allocate and initialize the corresponding THD for user authentication based on credentials stored on THD’s security policies / directories and finally if successfully authorized in the connection phase, the user thread will enter command phase
- The receiver thread will either create a new OS thread or reuse and existing “free” OS thread if available in the thread cache. So we strongly recommend increasing thread cache in cases where number of connections fluctuates between ver few connections and having many connections. But there are three things which a thread might need to wait for: A mutex, a database lock, or IO.
- THD basically is a large data structure used for several purposes like connection management, authorization and even unto to query execution, So how much THD consumes memory is directly proportionate to the query execution complexities and connection traffic.
MySQL error – Too many connections, How to fix ?
Recently one of customers ( among the top 5 largest e-commerce companies in the world ) called us to check how graceful their connection handling works during peak hours of business, They had issues in the past with ” ERROR 1040: Too many connections “ and that clearly explains the maximum number of clients that may be connected to the server has been reached so either the client will have to wait for another client to log off, or the administrator will have to increase the maximum number of connections allowed. so wanted us to do a detailed health-check on MySQL connection management and address “Too many connections” error proactively, We have explained below on how we could successfully reproduce this issue and recommended the fix:
Goal: Manage 50,000 connections on MySQL 8.0 (Ubuntu)
The default setting for system variable max_connections is “151”and we are benchmarking 50K connections so the first step before benchmarking is to increase max_connections to 50000. we increased max_connections to 50000 dynamically and what happened after that was not expected, We have copied the results below:
root@MDB1:~# mysql -uroot -pMDB@PassWd2020 -se "select @@max_connections" @@max_connections 697
We got only 697 connections, Let’s interpret MySQL error log before proceeding to next steps.. We have copied the same below:
2020-01-30T19:52:35.136192Z0 [Warning] Changed limits: max_open_files: 5129 (requested 10000) 2020-01-30T19:54:13.241937Z0 [Warning] Changed limits: max_connections: 4152 (requested 10000) 2020-01-30T19:57:47.51617Z0 [Warning] Changed limits: table_open_cache: 533 (requested 15000)
This is due to open files limitations for MySQL so let’s increase now the number of allowed open files for MySQL, The following steps we did to fix this resource limit issue:
- Option 1 – Locate the systemd configuration folder for MySQL and create file /etc/systemd/system/mysqld.service.d/override.conf (file can be called anything ending with .conf).
- Add LimitNOFILE=55000 in the file override.conf
- Add TasksMax=55000 in the file override.conf
- Add LimitNPROC=55000 in the file override.conf
- Option 2 – We can also create/modify the override file by using native systemctl command like: systemctl edit mysql
root@MDB1:~# cat /etc/systemd/system/mysql.service.d/override.conf [Service] LimitNOFILE=55000 TasksMax=55000 LimitNPROC=55000
** MySQL uses some files for additional work and we need to set LimitNOFILE, TasksMax and LimitMPROC higher to get 50000 connections, lets set it to 55000 and reload the systemd daemon and restart the MySQL service.
Reload the systmed daemon and restart the MySQL service:
root@MDB1:~# systemctl daemon-reload root@MDB1:~# systemctl restart mysql
Now let’s check max_connections to confirm the change applied:
root@MDB1:~# mysql -uroot -pMDB@PassWd2020 -se "select @@max_connections" mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure. @@max_connections 50000
Conclusion
We have no fixed value recommendations for system variable max_connections, It completely depends on your application load and how your application does connection handling. We advice our customers to avoid too many connections opened concurrently because each thread connected needs memory and there is also resource intensive context switching causing overall performance degradation, Thanks for reading and comments are welcome !
References
- https://mysqlserverteam.com/mysql-connection-handling-and-scaling/
- http://mysql-nordic.blogspot.com/2019/04/mysql-error-too-many-connections.html
- https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/using-systemd.html
Book your appointment for 30 minutes ( absolutely free ) MinervaDB consulting
If you have encountered the error “Too many connections” while trying to connect to a MySQL Server, that means it reached the maximum number of connections, or all available permitted are in use by other clients and your connection attempts will get rejected.
That number of connections is defined via the max_connections system variable. To open for more connections, you can set a higher value for max_connections.
To see the current value of max_connections, run this command:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE "max_connections";
By default, it’s set to 151. But MySQL actually allows up to max_connections + 1, which is 151 + 1 for the default setting. The extra connection can be used by the user with SUPER privilege only.
To increase the max_connections value, let’s say 500, run this command:
SET GLOBAL max_connections = 500;
The command takes effect right after you execute it, but it only applies to the current session. If you want it to be permanent until you re-adjust it the next time, you have to edit the configuration file my.cnf (normally it’s stored in /etc/my.cnf).
Under the [mysqld] section add the following line:
Then restart the MySQL server to take effect.
One thing to keep in mind that there is no hard limit to setting up maximum max_connections value, but increasing it will require more RAM to run. The number of maximum connections permitted has to be calculated based on how much RAM you have and how much is used per connection. In many cases, if you run out of usable disc space on your server partition or drive, MySQL might also return this error.
The maximum number can be estimated by the formula:
max.connection=(available RAM-global buffers)/thread buffers
So increase it with caution.
Need a good GUI Tool for MySQL? TablePlus is a modern, native tool with an elegant UI that allows you to simultaneously manage multiple databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Microsoft SQL Server and more.
Download TablePlus for Mac. It’s free anyway!
Not on Mac? Download TablePlus for Windows.
On Linux? Download TablePlus for Linux
Need a quick edit on the go? Download TablePlus for iOS.