Git Self-Signed Certificate Configuration
tl;dr
NEVER disable all SSL verification!
This creates a bad security culture. Don’t be that person.
The config keys you are after are:
http.sslverify— Always true. See above note.
These are for configuring host certificates you trust
http.sslCAPathhttp.sslCAInfo
These are for configuring YOUR certificate to respond to SSL challenges.
http.sslCerthttp.sslCertPasswordProtected
Selectively apply the above settings to specific hosts.
http.<url>.*
Global .gitconfig for Self-Signed Certificate Authorities
For my own and my colleagues’ sake here is how we managed to get self signed certificates to work without disabling sslVerify. Edit your .gitconfig to using git config --global -e add these:
# Specify the scheme and host as a 'context' that only these settings apply
# Must use Git v1.8.5+ for these contexts to work
[credential "https://your.domain.com"]
username = user.name
# Uncomment the credential helper that applies to your platform
# Windows
# helper = manager
# OSX
# helper = osxkeychain
# Linux (in-memory credential helper)
# helper = cache
# Linux (permanent storage credential helper)
# https://askubuntu.com/a/776335/491772
# Specify the scheme and host as a 'context' that only these settings apply
# Must use Git v1.8.5+ for these contexts to work
[http "https://your.domain.com"]
##################################
# Self Signed Server Certificate #
##################################
# MUST be PEM format
# Some situations require both the CAPath AND CAInfo
sslCAInfo = /path/to/selfCA/self-signed-certificate.crt
sslCAPath = /path/to/selfCA/
sslVerify = true
###########################################
# Private Key and Certificate information #
###########################################
# Must be PEM format and include BEGIN CERTIFICATE / END CERTIFICATE,
# not just the BEGIN PRIVATE KEY / END PRIVATE KEY for Git to recognise it.
sslCert = /path/to/privatekey/myprivatecert.pem
# Even if your PEM file is password protected, set this to false.
# Setting this to true always asks for a password even if you don't have one.
# When you do have a password, even with this set to false it will prompt anyhow.
sslCertPasswordProtected = 0
References:
- Git Credentials
- Git Credential Store
- Using Gnome Keyring as credential store
- Git Config http.<url>.* Supported from Git v1.8.5
Specify config when git clone-ing
If you need to apply it on a per repo basis, the documentation tells you to just run git config --local in your repo directory. Well that’s not useful when you haven’t got the repo cloned locally yet now is it?
You can do the global -> local hokey-pokey by setting your global config as above and then copy those settings to your local repo config once it clones…
OR what you can do is specify config commands at git clone that get applied to the target repo once it is cloned.
# Declare variables to make clone command less verbose
OUR_CA_PATH=/path/to/selfCA/
OUR_CA_FILE=$OUR_CA_PATH/self-signed-certificate.crt
MY_PEM_FILE=/path/to/privatekey/myprivatecert.pem
SELF_SIGN_CONFIG="-c http.sslCAPath=$OUR_CA_PATH -c http.sslCAInfo=$OUR_CA_FILE -c http.sslVerify=1 -c http.sslCert=$MY_PEM_FILE -c http.sslCertPasswordProtected=0"
# With this environment variable defined it makes subsequent clones easier if you need to pull down multiple repos.
git clone $SELF_SIGN_CONFIG https://mygit.server.com/projects/myproject.git myproject/
One Liner
EDIT: See VonC’s answer that points out a caveat about absolute and relative paths for specific git versions from 2.14.x/2.15 to this one liner
git clone -c http.sslCAPath="/path/to/selfCA" -c http.sslCAInfo="/path/to/selfCA/self-signed-certificate.crt" -c http.sslVerify=1 -c http.sslCert="/path/to/privatekey/myprivatecert.pem" -c http.sslCertPasswordProtected=0 https://mygit.server.com/projects/myproject.git myproject/
CentOS unable to load client key
If you are trying this on CentOS and your .pem file is giving you
unable to load client key: "-8178 (SEC_ERROR_BAD_KEY)"
Then you will want this StackOverflow answer about how curl uses NSS instead of Open SSL.
And you’ll like want to rebuild curl from source:
git clone http://github.com/curl/curl.git curl/
cd curl/
# Need these for ./buildconf
yum install autoconf automake libtool m4 nroff perl -y
#Need these for ./configure
yum install openssl-devel openldap-devel libssh2-devel -y
./buildconf
su # Switch to super user to install into /usr/bin/curl
./configure --with-openssl --with-ldap --with-libssh2 --prefix=/usr/
make
make install
restart computer since libcurl is still in memory as a shared library
Python, pip and conda
Related: How to add a custom CA Root certificate to the CA Store used by pip in Windows?
Disable SSL verification in git repositories with self-signed certificates
Raw
git_ssl_self_signed.md
Sometimes, we have to access git repositories over SSL and the server only provides a self-signed certificate 🙈. Although there are ways to increase the trust level for the self-signed certificate (https://confluence.atlassian.com/fishkb/unable-to-clone-git-repository-due-to-self-signed-certificate-376838977.html, https://confluence.atlassian.com/bitbucketserverkb/resolving-ssl-self-signed-certificate-errors-806029899.html), my recommendation is to just ignore SSL verification alltogether.
Prepend GIT_SSL_NO_VERIFY=true before every git command run to skip SSL verification. This is particularly useful if you haven’t checked out the repository yet.
Run git config http.sslVerify false to disable SSL verification if you’re working with a checked out repository already.
Copy link
luancardosolc
commented
Jul 7, 2021
luancardosolc
commented
Jul 7, 2021
Thank you so much!! it helped a lot!!
Copy link
scriptonian
commented
Jul 15, 2021
scriptonian
commented
Jul 15, 2021
thanks this helped!
Copy link
TediCreations
commented
May 8, 2022
TediCreations
commented
May 8, 2022
While this will work… it is considered a bad practice from security’s point of view.
A better approach is to download the self signed certificate into the list of approved certificates in your system.
Sign up for free
to join this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in to comment
- 28-Jul-2015

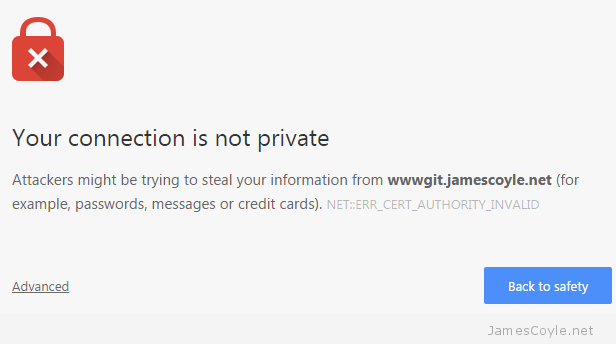
If you host something like this yourself, you’ll probably have entered the world called self signed certificates. These are SSL certificates that have not been signed by a known and trusted certificate authority. There is no security concern using a self signed certificate, the level of security will be similar to a paid for certificate, the problem is that your commuter won’t know that it can trust the certificate. You may have seen this error in a Web Browser, such as Chrome:
With Git, however, you’ll get an error from the git command line tool similar to the below:
$ git clone https://wwwgit.jamescoyle.net/test/test-project.git Cloning into 'test-project'... fatal: unable to access 'https://[email protected]/test/test-project.git/': SSL certificate problem: unable to get local issuer certificate
The preferred method of dealing with this error is to add the Certificate Authority’s signing certificate as a trusted Certificate Authority on your computer.The way to do this differs depending on your OS and is out of scope for this post.
There are two Git specific methods of forcing Git to accept the self signed certificates, which don’t require you to import the CA certificate to your computers Trusted CA store:
Turn off Git SSL Verification
You can stop the Git client from verifying your servers certificate and to trust all SSL certificates you use with the Git client. This has it’s own security risks as you would not be warned if there was a valid problem with the server you are trying to connect to.
That said, it’s the quickest and easiest fix for a non trusted server certificate. Simply run the below git command on your Git client.
git config --global http.sslVerify false
Tell Git Where Your Certificate Authority Certificates Are
Another option is to point your Git client towards a folder that contains the Certificate Authority certificate that was used to sign your Git server’s SSL certificate. You may not have one of these if you’re using Self Signed certificates.
Save the CA certificate to a folder on your Git client and run the following git command to tell your Git client to use it when connecting t the server:
git config --system http.sslCAPath /git/certificates