Should the sudo command or elevated privileges be used with Git?
You should not be using the sudo command or elevated privileges, such as administrator permissions, with Git. If you have a very good reason you must use sudo, then ensure you are using it with every command (it’s probably just better to use su to get a shell as root at that point). If you generate SSH keys without sudo and then try to use a command like sudo git push, you won’t be using the same keys that you generated.
Check that you are connecting to the correct server
Typing is hard, we all know it. Pay attention to what you type; you won’t be able to connect to «githib.com» or «guthub.com». In some cases, a corporate network may cause issues resolving the DNS record as well.
To make sure you are connecting to the right domain, you can enter the following command:
$ ssh -vT git@github.com
> OpenSSH_8.1p1, LibreSSL 2.7.3
> debug1: Reading configuration data /Users/YOU/.ssh/config
> debug1: Reading configuration data /etc/ssh/ssh_config
> debug1: /etc/ssh/ssh_config line 47: Applying options for *
> debug1: Connecting to github.com port 22.The connection should be made on port 22, unless you’re overriding settings to use SSH over HTTPS.
Always use the «git» user
All connections, including those for remote URLs, must be made as the «git» user. If you try to connect with your GitHub username, it will fail:
$ ssh -T GITHUB-USERNAME@github.com
> Permission denied (publickey).If your connection failed and you’re using a remote URL with your GitHub username, you can change the remote URL to use the «git» user.
You should verify your connection by typing:
$ ssh -T git@github.com
> Hi USERNAME! You've successfully authenticated...Make sure you have a key that is being used
- Open TerminalTerminalGit Bash.
- Verify that you have a private key generated and loaded into SSH.
# start the ssh-agent in the background $ eval "$(ssh-agent -s)" > Agent pid 59566 $ ssh-add -l -E sha256 > 2048 SHA256:274ffWxgaxq/tSINAykStUL7XWyRNcRTlcST1Ei7gBQ /Users/USERNAME/.ssh/id_rsa (RSA)
If you have GitHub Desktop installed, you can use it to clone repositories and not deal with SSH keys.
-
If you are using Git Bash, turn on ssh-agent:
# start the ssh-agent in the background $ eval "$(ssh-agent -s)" > Agent pid 59566If you are using another terminal prompt, such as Git for Windows, turn on ssh-agent:
# start the ssh-agent in the background $ eval $(ssh-agent -s) > Agent pid 59566 -
Verify that you have a private key generated and loaded into SSH.
$ ssh-add -l -E sha256 > 2048 SHA256:274ffWxgaxq/tSINAykStUL7XWyRNcRTlcST1Ei7gBQ /Users/USERNAME/.ssh/id_rsa (RSA)
- Open TerminalTerminalGit Bash.
- Verify that you have a private key generated and loaded into SSH.
$ ssh-add -l -E sha256 > 2048 SHA256:274ffWxgaxq/tSINAykStUL7XWyRNcRTlcST1Ei7gBQ /Users/USERNAME/.ssh/id_rsa (RSA)
The ssh-add command should print out a long string of numbers and letters. If it does not print anything, you will need to generate a new SSH key and associate it with GitHub.
Tip: On most systems the default private keys (~/.ssh/id_rsa and ~/.ssh/identity) are automatically added to the SSH authentication agent. You shouldn’t need to run ssh-add path/to/key unless you override the file name when you generate a key.
Getting more details
You can also check that the key is being used by trying to connect to git@github.com:
$ ssh -vT git@github.com
> ...
> debug1: identity file /Users/YOU/.ssh/id_rsa type -1
> debug1: identity file /Users/YOU/.ssh/id_rsa-cert type -1
> debug1: identity file /Users/YOU/.ssh/id_dsa type -1
> debug1: identity file /Users/YOU/.ssh/id_dsa-cert type -1
> ...
> debug1: Authentications that can continue: publickey
> debug1: Next authentication method: publickey
> debug1: Trying private key: /Users/YOU/.ssh/id_rsa
> debug1: Trying private key: /Users/YOU/.ssh/id_dsa
> debug1: No more authentication methods to try.
> Permission denied (publickey).In that example, we did not have any keys for SSH to use. The «-1» at the end of the «identity file» lines means SSH couldn’t find a file to use. Later on, the «Trying private key» lines also indicate that no file was found. If a file existed, those lines would be «1» and «Offering public key», respectively:
$ ssh -vT git@github.com
> ...
> debug1: identity file /Users/YOU/.ssh/id_rsa type 1
> ...
> debug1: Authentications that can continue: publickey
> debug1: Next authentication method: publickey
> debug1: Offering RSA public key: /Users/YOU/.ssh/id_rsaVerify the public key is attached to your account
You must provide your public key to GitHub to establish a secure connection.
-
Open Terminal.
-
Start SSH agent in the background.
$ eval "$(ssh-agent -s)" > Agent pid 59566 -
Find and take a note of your public key fingerprint.
$ ssh-add -l -E sha256 > 2048 SHA256:274ffWxgaxq/tSINAykStUL7XWyRNcRTlcST1Ei7gBQ /Users/USERNAME/.ssh/id_rsa (RSA) -
In the upper-right corner of any page, click your profile photo, then click Settings.
-
In the «Access» section of the sidebar, click SSH and GPG keys.
-
Compare the list of SSH keys with the output from the
ssh-addcommand.
-
Open the command line.
-
Start SSH agent in the background.
$ ssh-agent -s > Agent pid 59566 -
Find and take a note of your public key fingerprint.
$ ssh-add -l -E sha256 > 2048 SHA256:274ffWxgaxq/tSINAykStUL7XWyRNcRTlcST1Ei7gBQ /Users/USERNAME/.ssh/id_rsa (RSA) -
In the upper-right corner of any page, click your profile photo, then click Settings.
-
In the «Access» section of the sidebar, click SSH and GPG keys.
-
Compare the list of SSH keys with the output from the
ssh-addcommand.
-
Open Terminal.
-
Start SSH agent in the background.
$ eval "$(ssh-agent -s)" > Agent pid 59566 -
Find and take a note of your public key fingerprint. If you’re using OpenSSH 6.7 or older:
$ ssh-add -l > 2048 a0:dd:42:3c:5a:9d:e4:2a:21:52:4e:78:07:6e:c8:4d /Users/USERNAME/.ssh/id_rsa (RSA)If you’re using OpenSSH 6.8 or newer:
$ ssh-add -l -E md5 > 2048 MD5:a0:dd:42:3c:5a:9d:e4:2a:21:52:4e:78:07:6e:c8:4d /Users/USERNAME/.ssh/id_rsa (RSA) -
In the upper-right corner of any page, click your profile photo, then click Settings.
-
In the «Access» section of the sidebar, click SSH and GPG keys.
-
Compare the list of SSH keys with the output from the
ssh-addcommand.
If you don’t see your public key in GitHub, you’ll need to add your SSH key to GitHub to associate it with your computer.
Warning: If you see an SSH key you’re not familiar with on GitHub, delete it immediately and contact GitHub Support, for further help. An unidentified public key may indicate a possible security concern. For more information, see «Reviewing your SSH keys.»
Решение ошибки remote: Permission to user/repo denied to user/other-repo. fatal: unable to access user/repo: The requested URL returned error: 403
Дата: 27.03.2017
В данном уроке рассмотрим варианты решения данной оишбки:
remote: Permission to user/repo denied to user/other-repo.
fatal: unable to access user/repo: The requested URL returned error: 403
Возникает она чаще всего у новичков при попытке выполнить команду:
$ git push
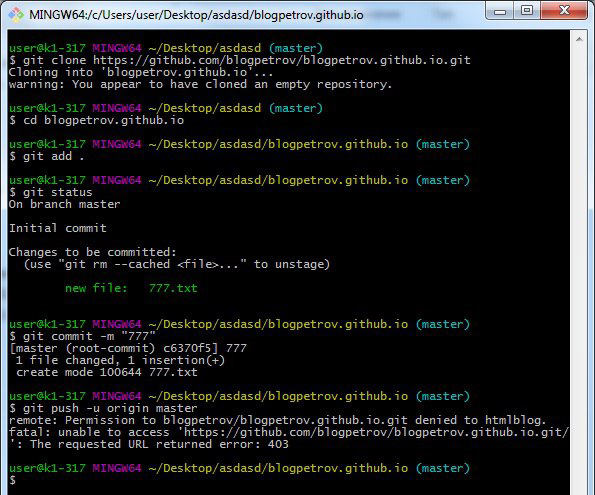
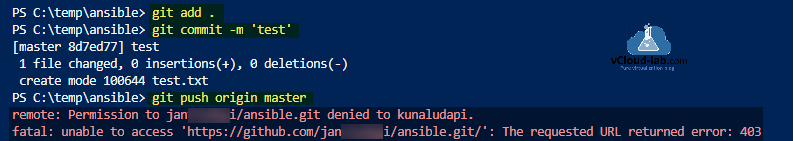
Пример ошибки на скриншоте ниже.
Данная ошибка возникает довольно часто при работе с Git в терминале Windows. Суть ошибка довольно таки простая, но почему-то в интернете постоянно создаются темы с вопросом на данную тему и нет внятного ответа на русском языке.
Ошибка говорит нам о том, что мы пытаемся отправить данные в чужой репозиторий. И о том, что текущий пользователь Git не имеет прав для отправки данных в указанный в команде репозиторий.
Существует два способа решить данную ошибку:
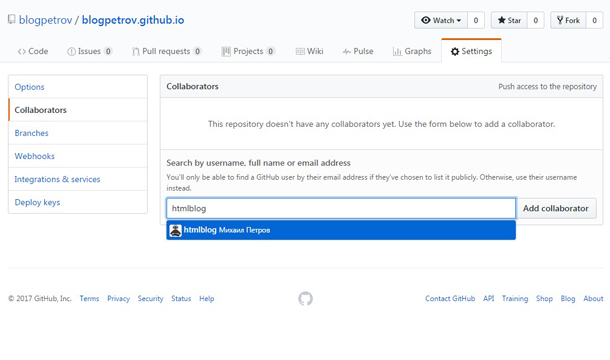
Вариант 1. Дать текущему пользователю права для работы с репозиторием
Данный способ подойдет, если вы являетесь владельцем обеих учетных записей указанных в ошибке. Необходимо зайти на GitHub под именем того пользователя, в чей репозиторий вы не можете отправить данные. В настройках репозитория указать необходимого соавтора. Ему на почту отправится приглашение, которое необходимо подтвердить, перейдя по ссылке в письме.
После этого вы сможете работать с репозиторием как со своим и ошибка больше не появится.
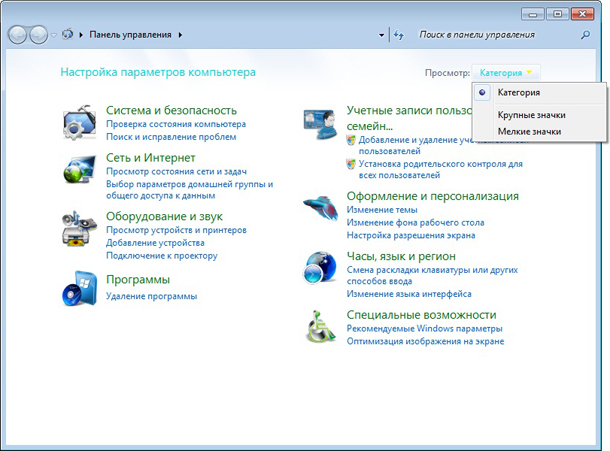
Вариант 2. Назначить в системе текущим пользователем Git ту учетную запись, в которую не можете отправить данные
Для этого необходимо перейти в Панель управления Windows. Выбрать отображение в виде категорий.
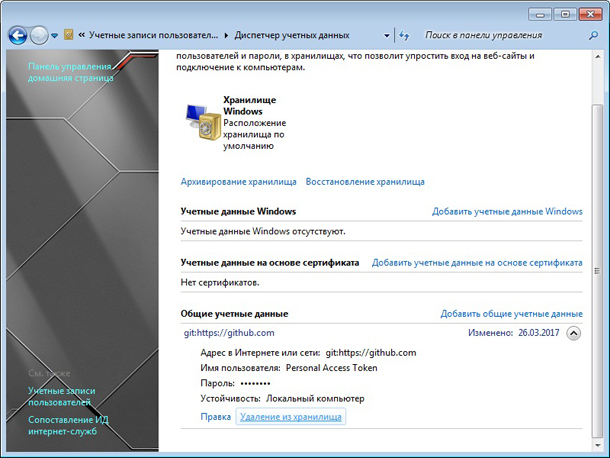
Перейти в раздел “Учетные записи пользователей и семейная безопасность”. Далее в раздел “Диспетчер учетных данных”. В самом низу будет блок “Общие учетные данные”. Нажмите в нем ссылку “Удаление из хранилища”.
После этого при попытке выполнить команду:
$ git push -u origin master
Терминал запросит у вас пароль от учетной записи на Github в чей репозиторий вы пытаетесь отправить данные.
После ввода пароля система установит данного пользователя как основного и будет использовать его в дальнейшем при работе с Git.
Надеюсь данный пост поможет вам решить ошибку, с которой я разбирался почти сутки.
git
github
Не забудьте сказать спасибо. Поставьте лайк!
Здравствуйте.
—
1) Вы пытаетесь загрузить с другого аккаунта, выйти из него я не знаю как, но зато, при установке git на ваш компьютер, создаётся файл .githistory, обычно пихается в пользовательскую папку, как и данные по composer. (for Windows) — для других систем не узнавал.
2) Если вы нашли .githistory — и используете другой аккаунт, удалите его. Возможно другие файлы со словом git так же стоит удалить.
3) Убедитесь, что вы после удаления истории сделали новую регистрацию:
$ git config --global user.name 'login'
$ git config --global user.email 'mail@yourmail.ru'
4) Когда создаёте репозиторий на GitHub , клонируйте его на свой компьютер.
Чтобы убедится, что вы открыли консоль [Git Bash] в нужном месте, просто сделайте команду$ git status
Если репозиторий и директория верны, он красным подсветит файлы, которые нужно добавить.
Если он пишет, что такой директории не существует, значит перейдите в вашу папку.$ cd your_folder — ещё раз проверьте статус.
Если git увидел ваш склонированный репозиторий, значит делайте запрос:$ git add .
или$ git add --all
Почему я не начал с $ git init ?
Если вы склонировали, то папка .git там уже есть.
Закидывайте к этой папке и файлу README.md ваши файлы, и делайте $ git add .
Только теперь можно делать коммиты$ git commit -m "your commit"
высветились все файлы? Тогда пропускаете $ git remote add origin.... — потому что ветка уже создана, при создании репозитория на сайте.
Теперь мы загружаем:$ git push -u origin master
Если не ошибаюсь, дописать записанное можно через команду:$ git pull
—-
Самое главное, это сменить пользователя на того, у которого есть права, иначе вам не поможет удаление программы и установка новой. Есть команда, которая чистит кеш истории$ git credential-cache exit
Но она почему-то в последнее время бесполезная и нерабочая, так что ищите способ очистить кеш.
Что касается ключей и ssh — их можно и не создавать, но как показывает практика, не только git , но и composer не дадут вам работать.
Успехов вам, надеюсь помог.
—
P.S. данный метод мне помог, если вы видите содержимое файла README.md смотрите в settings что у вас за ошибка, устраните её, и обновите браузер. Возможно, ещё придётся выбрать тему, или указать описание, так же смотрите, где у вас галочки стоят, они тоже могут вызвать головную боль.
Remote: Permission to UserName/repo.git denied to OtherUserName fatal: unable to access ‘https://github.com/UserName/repo.git/’: The requested URL returned error: 403
February 6, 2020 08:47PM
I was working on the one of the clients project hosted on github.com, I cloned the repo locally added few files to local repo and staged/committed project locally all was good.
git add .
git commit -m 'test'
But when tried to push the changes on remote repo on github.com. I was receiving below error.
git push origin master remote: Permission to UserName/repo.git denied to AnotherUserName. fatal: unable to access 'https://github.com/UserName/repo.git/': The requested URL returned error: 403
This error says that you are using wrong credential or wrong repo: the fact is when you are pushing its not asking for credentials, below are the possible reasons.
- Username needs to be the user, not the email
- Ensure you provide the proper password. If you have 2FA enabled on GitHub, you need to make sure you create an Access Token with proper access permissions and use the token as password instead.
- Repo format is: https://github.com/<user>/<repo>.git
- You have 2 different github (version control) accounts
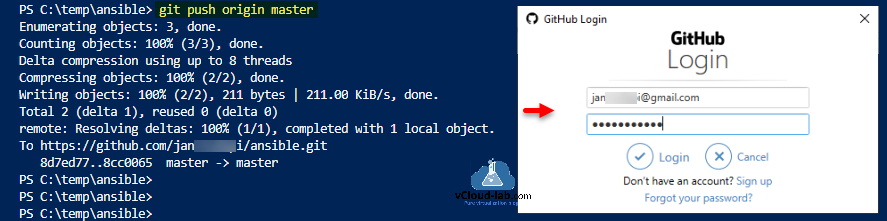
403 means GitHub is not granting you access so one or more of the 4 above cause are the problem. In my case this issue happened due to I have one personal github account and second received from client. Until now I was using my github account and in the past when I did push for the first time it asked my github credentials which got saved/ cached in windows credential manager, and today for the first time when I am using second account it is using username and password cached earlier for previous github account, causing access denied error.
You can solve this problem by using few methods. But below simple method helps you to solve the issue.
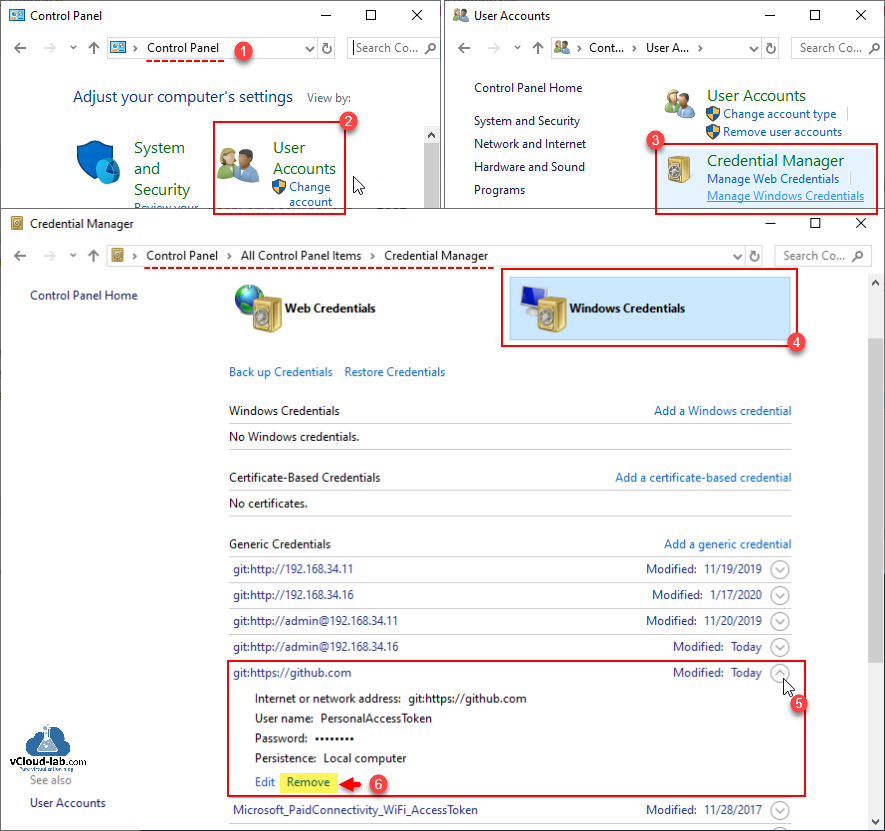
step 1: Go to Control Panel.
step 2: In the control panel find and go to user accounts
step 3: After that go to credential manager
step 4: Then Windows credentials
step 5: Go to Generic credentials, and search github.com, expand it
step 6: Finally delete the Github keys.
Once cached credentials are removed, try pushing project on remote by running command git push origin master, This will prompt for GitHub login prompt, once the authentication is successful with correct username and password, command will succeed and files/folders are pushed successfully on remote github repo.
If you don’t want to remove previous users credentials from windows credentials manager another way to resolve this issue is give previous user access over new github.com repo.
Useful Article
Solved Visual studio Code make sure you configure your user.name and user.email in git
Part 1 Git version control integration in Visual Studio Code
Part 2 Git master branch source control integration in Visual Studio Code
Part 3 Git clone version control integration in Visual Studio Code
Go Back
Содержание
- Решение ошибки remote: Permission to user/repo denied to user/other-repo. fatal: unable to access user/repo: The requested URL returned error: 403
- Существует два способа решить данную ошибку:
- Troubleshooting cloning errors
- In this article
- Help us make these docs great!
- GIT ERROR 403 как исправить?
- ‘403 Forbidden’ error message when you try to push to a GitHub repository
- Problem
- Cause
- Resolution
- Virtual Geek
- Tales from real IT system administrators world and non-production environment
- Remote: Permission to UserName/repo.git denied to OtherUserName fatal: unable to access ‘https://github.com/UserName/repo.git/’: The requested URL returned error: 403
Решение ошибки remote: Permission to user/repo denied to user/other-repo. fatal: unable to access user/repo: The requested URL returned error: 403
В данном уроке рассмотрим варианты решения данной оишбки:
remote: Permission to user/repo denied to user/other-repo. fatal: unable to access user/repo: The requested URL returned error: 403
Возникает она чаще всего у новичков при попытке выполнить команду:
Пример ошибки на скриншоте ниже.
Данная ошибка возникает довольно часто при работе с Git в терминале Windows. Суть ошибка довольно таки простая, но почему-то в интернете постоянно создаются темы с вопросом на данную тему и нет внятного ответа на русском языке.
Ошибка говорит нам о том, что мы пытаемся отправить данные в чужой репозиторий. И о том, что текущий пользователь Git не имеет прав для отправки данных в указанный в команде репозиторий.
Существует два способа решить данную ошибку:
Вариант 1. Дать текущему пользователю права для работы с репозиторием
Данный способ подойдет, если вы являетесь владельцем обеих учетных записей указанных в ошибке. Необходимо зайти на GitHub под именем того пользователя, в чей репозиторий вы не можете отправить данные. В настройках репозитория указать необходимого соавтора. Ему на почту отправится приглашение, которое необходимо подтвердить, перейдя по ссылке в письме.
После этого вы сможете работать с репозиторием как со своим и ошибка больше не появится.
Вариант 2. Назначить в системе текущим пользователем Git ту учетную запись, в которую не можете отправить данные
Для этого необходимо перейти в Панель управления Windows. Выбрать отображение в виде категорий.
Перейти в раздел “Учетные записи пользователей и семейная безопасность”. Далее в раздел “Диспетчер учетных данных”. В самом низу будет блок “Общие учетные данные”. Нажмите в нем ссылку “Удаление из хранилища”.
После этого при попытке выполнить команду:
$ git push -u origin master
Терминал запросит у вас пароль от учетной записи на Github в чей репозиторий вы пытаетесь отправить данные.
После ввода пароля система установит данного пользователя как основного и будет использовать его в дальнейшем при работе с Git.
Надеюсь данный пост поможет вам решить ошибку, с которой я разбирался почти сутки.
Источник
Troubleshooting cloning errors
In this article
If you’re having trouble cloning a repository, check these common errors.
HTTPS cloning errors
There are a few common errors when using HTTPS with Git. These errors usually indicate you have an old version of Git, or you don’t have access to the repository.
Here’s an example of an HTTPS error you might receive:
Check your Git version
There’s no minimum Git version necessary to interact with GitHub, but we’ve found version 1.7.10 to be a comfortable stable version that’s available on many platforms. You can always download the latest version on the Git website.
Ensure the remote is correct
The repository you’re trying to fetch must exist on GitHub.com, and the URL is case-sensitive.
You can find the URL of the local repository by opening the command line and typing git remote -v :
Alternatively, you can change the URL through our GitHub Desktop application.
Provide an access token
To access GitHub, you must authenticate with a personal access token instead of your password. For more information, see «Creating a personal access token.»
If you are accessing an organization that uses SAML SSO and you are using a personal access token (classic), you must also authorize your personal access token to access the organization before you authenticate. For more information, see «About authentication with SAML single sign-on» and «Authorizing a personal access token for use with SAML single sign-on.»
Check your permissions
When prompted for a username and password, make sure you use an account that has access to the repository.
Tip: If you don’t want to enter your credentials every time you interact with the remote repository, you can turn on credential caching. If you are already using credential caching, please make sure that your computer has the correct credentials cached. Incorrect or out of date credentials will cause authentication to fail.
Use SSH instead
If you’ve previously set up SSH keys, you can use the SSH clone URL instead of HTTPS. For more information, see «About remote repositories.»
Error: Repository not found
If you see this error when cloning a repository, it means that the repository does not exist or you do not have permission to access it. There are a few solutions to this error, depending on the cause.
Check your spelling
Typos happen, and repository names are case-sensitive. If you try to clone git@github.com:user/repo.git , but the repository is really named User/Repo you will receive this error.
To avoid this error, when cloning, always copy and paste the clone URL from the repository’s page. For more information, see «Cloning a repository.»
To update the remote on an existing repository, see «Managing remote repositories».
Checking your permissions
If you are trying to clone a private repository but do not have permission to view the repository, you will receive this error.
Make sure that you have access to the repository in one of these ways:
- The owner of the repository
- A collaborator on the repository
- A member of a team that has access to the repository (if the repository belongs to an organization)
Check your SSH access
In rare circumstances, you may not have the proper SSH access to a repository.
You should ensure that the SSH key you are using is attached to your personal account on GitHub. You can check this by typing the following into the command line:
If the repository belongs to an organization and you’re using an SSH key generated by an OAuth App, OAuth App access may have been restricted by an organization owner. For more information, see «About OAuth App access restrictions.»
Check that the repository really exists
If all else fails, make sure that the repository really exists on GitHub.com! If you’re trying to push to a repository that doesn’t exist, you’ll get this error.
Error: Remote HEAD refers to nonexistent ref, unable to checkout
This error occurs if the default branch of a repository has been deleted on GitHub.com.
Detecting this error is simple; Git will warn you when you try to clone the repository:
To fix the error, you’ll need to be an administrator of the repository on GitHub.com. You’ll want to change the default branch of the repository.
After that, you can get a list of all the available branches from the command line:
Then, you can just switch to your new branch:
Help us make these docs great!
All GitHub docs are open source. See something that’s wrong or unclear? Submit a pull request.
Источник
GIT ERROR 403 как исправить?
вот такая ошибочка после PUSH , логин и пароль не запрашивает.
ранее пользовался гитом, но через другой акк гитхаба.
- Вопрос задан более трёх лет назад
- 51000 просмотров
Оценить 1 комментарий
Здравствуйте.
—
1) Вы пытаетесь загрузить с другого аккаунта, выйти из него я не знаю как, но зато, при установке git на ваш компьютер, создаётся файл .githistory , обычно пихается в пользовательскую папку, как и данные по composer. (for Windows) — для других систем не узнавал.
2) Если вы нашли .githistory — и используете другой аккаунт, удалите его. Возможно другие файлы со словом git так же стоит удалить.
3) Убедитесь, что вы после удаления истории сделали новую регистрацию:
4) Когда создаёте репозиторий на GitHub , клонируйте его на свой компьютер.
Чтобы убедится, что вы открыли консоль [Git Bash] в нужном месте, просто сделайте команду
$ git status
Если репозиторий и директория верны, он красным подсветит файлы, которые нужно добавить.
Если он пишет, что такой директории не существует, значит перейдите в вашу папку.
$ cd your_folder — ещё раз проверьте статус.
Если git увидел ваш склонированный репозиторий, значит делайте запрос:
$ git add .
или
$ git add —all
Почему я не начал с
$ git init ?
Если вы склонировали, то папка .git там уже есть.
Закидывайте к этой папке и файлу README.md ваши файлы, и делайте
$ git add .
Только теперь можно делать коммиты
$ git commit -m «your commit»
высветились все файлы? Тогда пропускаете
$ git remote add origin. — потому что ветка уже создана, при создании репозитория на сайте.
Теперь мы загружаем:
$ git push -u origin master
Если не ошибаюсь, дописать записанное можно через команду:
$ git pull
—-
Самое главное, это сменить пользователя на того, у которого есть права, иначе вам не поможет удаление программы и установка новой. Есть команда, которая чистит кеш истории
$ git credential-cache exit
Но она почему-то в последнее время бесполезная и нерабочая, так что ищите способ очистить кеш.
Что касается ключей и ssh — их можно и не создавать, но как показывает практика, не только git , но и composer не дадут вам работать.
Источник
‘403 Forbidden’ error message when you try to push to a GitHub repository
This article discusses a problem that may occur when you try to push to a remote GitHub repository using HTTPS from an A2 Hosting server.
Problem
When you try to push changes to a GitHub repository from an A2 Hosting server using an HTTPS URL, you receive the following error message:
Cause
There are a few possible causes for this problem:
- You typed an incorrect password. Make sure you are using the correct GitHub password for the account.
- The Git client on the A2 Hosting server requires a modified HTTPS URL to work correctly. If this is the cause, the password prompt does not even appear when you try to do a push operation.
Resolution
If you are sure you are using the correct GitHub password, there are two ways to resolve the “403 Forbidden” problem:
Method #1: Use SSH
Instead of using HTTPS URLs to push changes to GitHub, you can use SSH instead. For information about how to do this, please visit https://help.github.com/articles/changing-a-remote-s-url.
Method #2: Modify the HTTPS URL
Some A2 Hosting managed servers have an old version of the Git client installed. To push changes to GitHub using this older client version, you must include your GitHub username in the HTTPS URL.
To do this, follow these steps:
- Log in to your A2 Hosting account using SSH.
- At the command prompt, change to the directory where the Git repository is located.
- Type the following command:
You should see output that resembles the following:
You need to add your GitHub username to the github.com portion of the URL. To do this, type the following command, replacing the values in red with your own account information:
To verify the new remote URL setting, type the following command:
Now when you try to push changes to the GitHub repository, you are prompted for a password, and the push operation should succeed.
Источник
Virtual Geek
Tales from real IT system administrators world and non-production environment
Remote: Permission to UserName/repo.git denied to OtherUserName fatal: unable to access ‘https://github.com/UserName/repo.git/’: The requested URL returned error: 403
I was working on the one of the clients project hosted on github.com, I cloned the repo locally added few files to local repo and staged/committed project locally all was good.
But when tried to push the changes on remote repo on github.com. I was receiving below error.
This error says that you are using wrong credential or wrong repo: the fact is when you are pushing its not asking for credentials, below are the possible reasons.
- Username needs to be the user, not the email
- Ensure you provide the proper password. If you have 2FA enabled on GitHub, you need to make sure you create an Access Token with proper access permissions and use the token as password instead.
- Repo format is: https://github.com/ / .git
- You have 2 different github (version control) accounts
403 means GitHub is not granting you access so one or more of the 4 above cause are the problem. In my case this issue happened due to I have one personal github account and second received from client. Until now I was using my github account and in the past when I did push for the first time it asked my github credentials which got saved/ cached in windows credential manager, and today for the first time when I am using second account it is using username and password cached earlier for previous github account, causing access denied error.
You can solve this problem by using few methods. But below simple method helps you to solve the issue.
step 1: Go to Control Panel.
step 2: In the control panel find and go to user accounts
step 3: After that go to credential manager
step 4: Then Windows credentials
step 5: Go to Generic credentials, and search github.com, expand it
step 6: Finally delete the Github keys.
Once cached credentials are removed, try pushing project on remote by running command git push origin master, This will prompt for GitHub login prompt, once the authentication is successful with correct username and password, command will succeed and files/folders are pushed successfully on remote github repo.
Источник
Error Description:
- We can clone a copy of this repo over HTTPS authenticated.
- We have made some commits and want to come back to the GitHub server. Using Cygwin on Windows 7 x64.
C:cygwinhomeXPheriorCodelunch_call>git push
Password:
error: The requested URL returned error: 403 while accessing https://MichaelDrog
[email protected]/derekerdmann/lunch_call.git/info/refs
fatal: HTTP request failed
Solution 1:
Github give the idea it supports ssh way to read & write the repo, whereas https way also displayed ‘Read & Write’.
- Now you need to change your repo config on your PC to ssh way:
1. Edit .git/config file under your repo directory
2. Find url=entry under section [remote "origin"]
3. Change it from url=https://[email protected]/derekerdmann/lunch_call.git to url=ssh://[email protected]/derekerdmann/lunch_call.git. ie, change all the texts before @ symbol to ssh://git
4. Save config file and quit. You can use git push origin master to sync your repo on GitHub
Solution 2:
- To login using
https protocol,you should first set your authentication credential to the git Remote URI:
- Now you’ll be asked for a password when try to
git push. - In fact, this is on the http authentication format. Now you have to set a password :
- You should be aware that your github password will be stored in plaintext in your .git directory, which is undesirable.
Solution 3:
- On behalf of editing
.git/configfile manually, you can usegit remote set-urlcommand. - In your case it should be:
Solution 4:
- Edit
.git/configfile under your repo directory - Find
url=entry under section[remote "origin"] - Change it from
url=https://github.com/rootux/ms-Dropdown.gittohttps://[email protected]/rootux/ms-Dropdown.git - Where
USERNAMEis your github user name
Solution 5:
- When permission denied 403 error while using ssh(according to Xiao) or http urls you can also try these commands
git config --global --unset-all credential.helper
git config --unset-all credential.helper
With administrator rights
git config --system --unset-all credential.helper
UP NEXT IN GIT
- Git Tutorial
- Git Interview Questions and Answers
- Git HR Interview Questions and Answers
- Git Sample Resume
- Git Interview Dress Code
- Git Job Apply Letters
- Git Forums