I added some extra repositories with the Software Sources program. But when I reload the package database, I get an error like the following:
W: GPG error: http://ppa.launchpad.net trusty InRelease: The following signatures couldn’t be verified because the public key is not available: NO_PUBKEY 8BAF9A6F
I know I can fix it using apt-key in a terminal, according to the official Ubuntu documentation. But I would have liked to do it graphically. Is there a way to do this without using a terminal?
Wilf
29.2k16 gold badges103 silver badges162 bronze badges
asked Nov 13, 2010 at 20:27
8
Execute the following commands in terminal
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys <PUBKEY>
where <PUBKEY> is your missing public key for repository, e.g. 8BAF9A6F.
Then update
sudo apt-get update
ALTERNATE METHOD:
sudo gpg --keyserver pgpkeys.mit.edu --recv-key <PUBKEY>
sudo gpg -a --export <PUBKEY> | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-get update
Note that when you import a key like this using apt-key you are telling the system that you trust the key you’re importing to sign software your system will be using. Do not do this unless you’re sure the key is really the key of the package distributor.
cjs
2851 silver badge11 bronze badges
answered Nov 28, 2010 at 18:49
karthick87karthick87
79.3k59 gold badges192 silver badges232 bronze badges
18
By far the simplest way to handle this now is with Y-PPA-Manager (which now integrates the launchpad-getkeys script with a graphical interface).
-
To install it, first add the webupd8 repository for this program:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/y-ppa-manager -
Update your software list and install Y-PPA-Manager:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install y-ppa-manager -
Run y-ppa-manager (i.e. type
y-ppa-managerthen press enter key). -
When the main y-ppa-manager window appears, click on «Advanced.»
-
From the list of advanced tasks, select «Try to import all missing GPG keys» and click OK.
You’re done! As the warning dialog says when you start the operation, it may take quite a while (about 2 minutes for me) depending on how many PPA’s you have and the speed of your connection.
answered Dec 4, 2013 at 15:52
monotaskermonotasker
3,6251 gold badge17 silver badges14 bronze badges
18
It happens when you don’t have a suitable public key for a repository.
To solve this problem use this command:
gpg --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 9BDB3D89CE49EC21
which retrieves the key from ubuntu key server. And then this:
gpg --export --armor 9BDB3D89CE49EC21 | sudo apt-key add -
which adds the key to apt trusted keys.
The solution can be found here & here & here.
Kevin Bowen
19.2k55 gold badges75 silver badges81 bronze badges
answered Mar 27, 2011 at 22:31
PedramPedram
5,5033 gold badges29 silver badges37 bronze badges
6
You need to get and import the key.
To get the key from a PPA, visit the PPA’s Launchpad page. On every PPA page at Launchpad you will find this link (2), after clicking on ‘Technical details about this PPA’ (1):
Follow it and click on the key ID link (3):
Save the page, this is your key file.
Now it’s time to import it:
Applications > Software Center,Edit > Software sources...,- Enter your password,
- Go to the
Authenticationtab and click onImport Key File..., finally - Select the saved key file and click on
OK.
xiota
4,6295 gold badges24 silver badges52 bronze badges
answered Nov 13, 2010 at 21:04
htorquehtorque
63.2k39 gold badges194 silver badges218 bronze badges
5
apt can only handle 40 keys in /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d . 41 keys and you will get the GPG error «no public key found» even if you go through all the steps to add the missing key(s).
Check to see if there are any unused keys in this file from ppa(s) you no longer use. If all are in use, consider removing some ppa(s) along with the corresponding keyfiles in /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d
Furthermore, using
sudo apt-key adv
Is considered a security risk and is not recommended as you are «undermining the whole security concept as this is not a secure way of recieving keys for various reasons (like: hkp is a plaintext protocol, short and even long keyids can be forged, …)«. http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=2195579
I believe the correct way to add missing keys (for example 1ABC2D34EF56GH78) is
gpg --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 1ABC2D34EF56GH78
gpg --export --armor 1ABC2D34EF56GH78 | sudo apt-key add -
answered Aug 7, 2014 at 22:33
mchidmchid
40.6k6 gold badges92 silver badges141 bronze badges
10
There is a tiny script packaged in the WebUpd8 PPA which I’ll link as a single .deb download so you don’t have to add the whole PPA — which automatically imports all missing GPG keys.
Download and install Launchpad-getkeys (ignore the ~natty in its version, it works with all Ubuntu versions from Karmic all the way to Oneiric). Once installed, open a terminal and type:
sudo launchpad-getkeys
If you’re behind a proxy, things are a bit more complicated so see this for more info
answered Jun 5, 2011 at 20:15
Alin AndreiAlin Andrei
7,3284 gold badges41 silver badges55 bronze badges
2
I faced the same issue while installing Heroku. The link below solved my problem —
http://naveenubuntu.blogspot.in/2011/08/fixing-gpg-keys-in-ubuntu.html
After fixing the NO_PUBKEY issue, the below issue remained
W: GPG error: xhttp://toolbelt.heroku.com ./ Release: The following signatures were invalid: BADSIG C927EBE00F1B0520 Heroku Release Engineering <release@heroku.com>
To fix it I executed the following commands in terminal:
sudo -i
apt-get clean
cd /var/lib/apt
mv lists lists.old
mkdir -p lists/partial
apt-get clean
apt-get update
Source — Link to solve it
answered Jan 30, 2013 at 17:12
dennyacdennyac
2175 silver badges7 bronze badges
1
Make sure you have apt-transport-https installed:
dpkg -s apt-transport-https > /dev/null || bash -c "sudo apt-get update;
sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https -y"
Add repository:
curl https://repo.skype.com/data/SKYPE-GPG-KEY | sudo apt-key add -
echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://repo.skype.com/deb stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/skype-stable.list
Install Skype for Linux:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install skypeforlinux -y
Source: https://community.skype.com/t5/Linux/Skype-for-Linux-Beta-signatures-couldn-t-be-verified-because-the/td-p/4645756
answered May 27, 2017 at 20:00
More generally, the following method should work for every repository. First of all search, with eventual help of a search engine, for a text on the program provider’s website looking like the following:
-----BEGIN PGP PUBLIC KEY BLOCK-----
Version: GnuPG v1.4.1 (GNU/Linux)
[...]
-----END PGP PUBLIC KEY BLOCK-----
Such a text is for example displayed on http://deb.opera.com. Copy the passage, paste it in an empty file that you create on your desktop. This results in the key file.
Then continue with the importation of the key:
- Applications > Sofware Center
- Edit > Sofware sources…, enter password
- Authentication tab, click on ‘Import Key File…’
- Select the saved key file and click on ‘Ok’.
You may now remove the previously created key file.
answered Nov 13, 2010 at 21:43
AgmenorAgmenor
15.5k18 gold badges65 silver badges103 bronze badges
0
This error can also occur when the apt list file by the PPA points to a local keyring, like
deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/SOMETHING.gpg] https://download.something.org/something something/
And while that file may exist on your system (possibly downloaded with a prior command), it may be unreadable due to missing permissions. I just fixed this kind of error by running
chmod 644 /usr/share/keyrings/*
after having fetched the keyring file. The underlying issue was the usage of sudo when I already was root user. Really weird as all of this is root anyway and there was no access permission failure message anywhere… but that fixed it
answered Jun 12, 2020 at 12:28
phil294phil294
5397 silver badges16 bronze badges
1
Good! I finaly found the way!
I’ve tested all method’s to fix GPG error NO_PUBKEY and nothing working for me.
I’ve deleted the entire contents of the folder /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d
cd /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d
sudo rm -R *
sudo apt-get update
And I use the Y-PPA-Manager method because I’m too lazy to create all pubkey’s manually (too many): http://www.unixmen.com/fix-w-gpg-error-no_pubkey-ubuntu/
run sudo apt-get update again and finaly all work great now! Tanks!
Based Source : post #17 on https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/apt/+bug/1263540
answered Apr 8, 2015 at 13:36
4
I had the same problem with DynDNS’s Updater client.
Turns out it was just expired keys.
Reinstalling the software (downloading a new .deb from the website, then using Software Centre to reinstall) fixed the problem.
Error message for reference:
W: GPG error: http://cdn.dyn.com stable/ Release: The following signatures were invalid: KEYEXPIRED 141943.......
kos
35k13 gold badges98 silver badges149 bronze badges
answered Jan 8, 2015 at 16:53
CrankyCranky
4245 silver badges11 bronze badges
2021 August. This is what worked for me.
cd /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d
sudo rm -R *
sudo apt-get update
The last line will raise errors of missing keys.
What you’d then have to do is manually install each of the keys listed in the errors
for example if the error is saying that your missing PUB_KEY is 9BDB3D89CE49EC21,
You can manually add the Key with the command sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys 9BDB3D89CE49EC21
Re-run sudo apt-get update
Repeat the process for the new key raised in the error
Say if the new key was 3BDB3D89CE49EC24,
Just Manually add the Key with the command sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys 3BDB3D89CE49EC24
Re-run sudo apt-get update and repeat the process until all the errors are gone.
Then go back to the package site you were trying to install and repeat the installation process.
For my case, the error was coming while I tried installing Sublime Text
Doing the above and returning to the Sublime installation guide here solved the issues.
Don’t forget to upvote if this works for you. And it must do
answered Aug 29, 2021 at 6:20
NMukamaNMukama
2961 silver badge13 bronze badges
Ubuntu and update errors are inseparable. Every now and then I encounter errors while updating the system after adding a new source. The other day I was trying to install Mate desktop environment when I got this GPG error while updating the system:
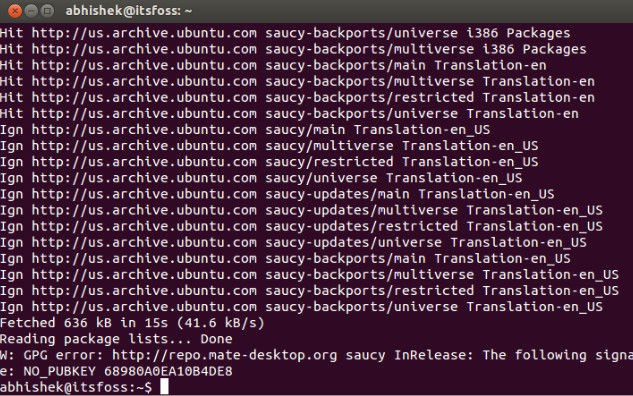
W: GPG error: http://repo.mate-desktop.org saucy InRelease: The following signatures couldn’t be verified because the public key is not available: NO_PUBKEY 68980A0EA10B4DE8
Here’s a screenshot of the error:
In this quick post I’ll show you how to fix this W: GPG error: The following signatures couldn’t be verified because the public key is not available: NO error. I’ll also explain why you see this error in the first place and how the solution I mention fixes the error.
Fix GPG error: The following signatures couldn’t be verified
The error tells you that your system cannot identify a certain GPG public key (PUBKEY). What you need to do is to fetch this public key in the system.
Get the key number from the error message displayed on your system. In the above message, the unidentified key is 68980A0EA10B4DE8. It will be something different for you.
Now add this public key to your Ubuntu system using the apt-key command:
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv-keys 68980A0EA10B4DE8If you see a warning message about apt-key command being deprecated, please ignore it.
The above command will add the key to the system. Just do an sudo apt-get update and you should not see this error anymore.
Now that you know how to fix this error, learn why this error occurs and how it was fixed.
Why do you see this error?
The APT package manager on Ubuntu and Debian-based distributions employs a trust/security mechanism with GPG. Like SSH, GPG also has public-private key pair. Public key is shared and private key is kept secret.
Every repository, be it from Ubuntu itself or a PPA or a third party repository, is signed with GPG keys by its developer. When you add a repository to your system, the public GPG key of its developer is added in trusted GPG keys on your system. This ensures that your Linux system trusts the packages coming from the repository.
You can see the GPG keys stored on your system using this command:
apt-key list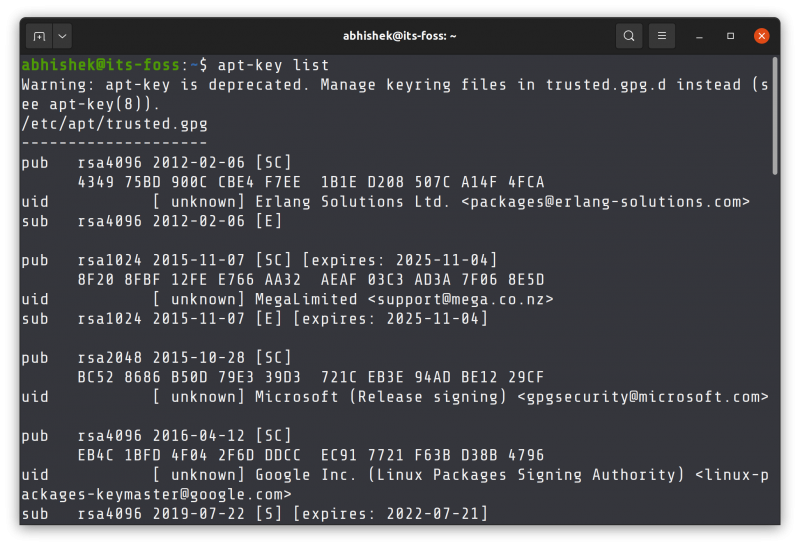
As you can see in the screenshot above, some GPG keys also have expiry dates. If the developer doesn’t renew his/her keys or if the developer changes the key, your system will complain about it.
And that’s exactly what happened in the error in my case. Probably the developer changed the GPG key and signed the repository with the new key. Since this new public key was not added in the trusted GPG key of the system, Ubuntu doesn’t download the packages from this particular repository and informs you that it could not verify the mentioned key.
So far, so good? Now, to solve the problem, what you did was to add the new, unverified key to your system’s trusted GPG key. With that, your system starts trusting the repositories signed by that GPG key and you don’t see the error anymore.
But that leaves you wondering with another question:
Should you blindly add the new GPG key?
Nope. You can always double check if the changed GPG key is actually coming from the developer or not.
How do you do that? From the developer’s repository page. I mean, usually developers have a page with this installation instructions on their project page. They mention the GPG key there. If the key was changed, the installation page should mention it. Otherwise, you may contact the developer.
If you used a PPA, you can go to the PPA page on Launchpad, click on the maintainer’s profile and you can see the public GPG key on this profile. You can match it with the changed key.
Of course, in all this, you are trusting the developer to provide you the correct repository and package. Well, you trusted the developer in the first place so unless you have good reasons against it, you may trust the developer again.
I hope you not only fixed the “The following signatures couldn’t be verified” error, you also know why it happened and how it was fixed.
Questions? Suggestions? The comment section is all yours.
I’m working on an embedded system on Debian 8 (to be upgraded).
When I do apt update, I’m getting the following:
...
...
Hit http://deb.debian.org stable/contrib arm64 Packages
Hit http://deb.debian.org stable/non-free arm64 Packages
Fetched 116 kB in 19s (6011 B/s)
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
109 packages can be upgraded. Run 'apt list --upgradable' to see them.
W: GPG error: http://deb.debian.org stable InRelease: The following signatures couldn't be verified because the public key is not available: NO_PUBKEY 648ACFD622F3D138 NO_PUBKEY 0E98404D386FA1D9 NO_PUBKEY 605C66F00D6C9793
I tried:
apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://p80.pool.sks-keyservers.net:80 --recv-keys
but got:
Executing: gpg --ignore-time-conflict --no-options --no-default-keyring --homedir /tmp/tmp.mXChDvLgjA --no-auto-check-trustdb --trust-model always --keyring /etc/apt/trusted.gpg --primary-keyring /etc/apt/trusted.gpg --keyring /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/debian-archive-jessie-automatic.gpg --keyring /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/debian-archive-jessie-security-automatic.gpg --keyring /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/debian-archive-jessie-stable.gpg --keyring /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/debian-archive-squeeze-automatic.gpg --keyring /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/debian-archive-squeeze-stable.gpg --keyring /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/debian-archive-wheezy-automatic.gpg --keyring /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/debian-archive-wheezy-stable.gpg --keyserver hkp://p80.pool.sks-keyserver.net:80 --recv-keys 605C66F00D6C9793
gpg: requesting key 0D6C9793 from hkp server p80.pool.sks-keyserver.net
?: p80.pool.sks-keyserver.net: Host not found
gpgkeys: HTTP fetch error 7: couldn't connect: No such file or directory
gpg: no valid OpenPGP data found.
gpg: Total number processed: 0
I also tried:
# gpg --keyserver pgp.mit.edu --recv-keys 648ACFD622F3D138 0E98404D386FA1D9 605C66F00D6C9793
which returned:
gpg: requesting key 22F3D138 from hkp server pgp.mit.edu
gpg: requesting key 386FA1D9 from hkp server pgp.mit.edu
gpg: requesting key 0D6C9793 from hkp server pgp.mit.edu
gpg: /root/.gnupg/trustdb.gpg: trustdb created
gpg: key 3CBBABEE: public key "Debian Archive Automatic Signing Key (10/buster) <ftpmaster@debian.org>" imported
gpg: key 8DD47936: public key "Debian Archive Automatic Signing Key (11/bullseye) <ftpmaster@debian.org>" imported
gpg: key 0D6C9793: public key "Debian Stable Release Key (11/bullseye) <debian-release@lists.debian.org>" imported
gpg: no ultimately trusted keys found
gpg: Total number processed: 3
gpg: imported: 3 (RSA: 3)
and running # apt update after wards still gives me the NO_PUBKEY error. How do I get this fixed properly?
My sources are the following:
cat /etc/apt/sources.list.d/multistrap-debian.list
deb [arch=arm64] http://deb.debian.org/debian stable main contrib non-free
deb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian stable main contrib non-free


