Содержание
- Hls.Events.ERROR is called twice when throw fatal network error #1006
- Comments
- 7 Ways to fix hls.js Error in Chrome & Other Browsers
- What is hls.js error networkerror?
- Opera
- How can I fix hls.js network error in Chrome?
- 1. Turn off firewalls temporarily
- 2. Disable the Proxy Server
- 3. Reset the browser
- 4. Reinstall Chrome
- 5. Check your antivirus
- 6. Clear Chrome’s browser data
- 7. Get the video URL
- levelLoadError not fired after auto-recovery attempt failed #822
- Comments
- Hls js error networkerror fatal true manifestloadtimeout
- Solution choisie
- Ошибка загрузки манифеста, что делать?
- Ошибка загрузки mp4 манифеста что это значит?
- Как исправить ошибку загрузки манифеста
Hls.Events.ERROR is called twice when throw fatal network error #1006
Environment
- The stream has correct Access-Control-Allow-Origin headers (CORS)
- There are no network errors such as 404s in the browser console when trying to play the stream
- The issue observed is not already reported by searching on Github under https://github.com/dailymotion/hls.js/issues
- The issue occurs in the latest reference client on http://dailymotion.github.io/hls.js/demo and not just on my page
- Link to playable M3U8 file:
- Hls.js version:
- Browser name/version: Google Chrome 56.0.2924.87 (64-bit)
- OS name/version: OS X Yosemite 10.10.5
Steps to reproduce
1. git clone and build dist
2. open demo/index.html
3. Start to load video
4. Make offline
I’ve used «offline» mode on Chrome dev tool.
5. Show «fatal error :levelLoadError» twice on Console.
Expected behavior
Call Hls.Events.ERROR listner just one time.
Actual behavior
Call Hls.Events.ERROR listner twice.
Console output
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
Источник
7 Ways to fix hls.js Error in Chrome & Other Browsers
- The hls.js network error seems to appear for Google Chrome users but without other additional information.
- In this article, we will explore some of the steps you can make in order to fix it and regain the full functionality of Chrome.
- Your firewall or proxy server may be at fault, but an outdated browser or your antivirus can also cause the issue.
Usually, Chrome is a relatively stable and reliable browser to use in Windows 10 and it’s the first choice for millions of people all over the world. But sadly, issues can appear, one that users reported is hls.js error.
It seems as though the Google Chrome hls.js network error has given users a lot of headaches. This can cause Facebook videos not playing in various browsers among other issues.
In this article we will show you a few easy steps that you can make in order to solve it, so make sure to keep on reading.
What is hls.js error networkerror?
This error usually appears when trying to play an online video in your browser. There are multiple causes for this problem, but it’s possible that one of the necessary components isn’t working.
Alternatively, the problem can be related to your antivirus or firewall. Lastly, your browser configuration can cause this issue, but there are ways to fix that.
Keep reading to find out how to fix hls.js error network error – fatal true – manifestloaderror and other variations of this error.
Quick Tip:
This error is prevalent in Chrome, but not as much when using a different browser. So if you want a quick fix, try switching to an alternative. The recommended option is Opera because it’s very stable.
This browser is also much lighter on resources than Chrome, leading to lower error rates and faster loading pages. It supports most Chrome extensions and integrates social media apps, a VPN, and more.
Opera
Enjoy seamless browsing and say goodbye to Chrome’s errors by using this modern, reliable browser.
How can I fix hls.js network error in Chrome?
1. Turn off firewalls temporarily
- Go to the Search box in Windows 10.
- Type in the keyword firewall. Click Windows Defender Firewall.
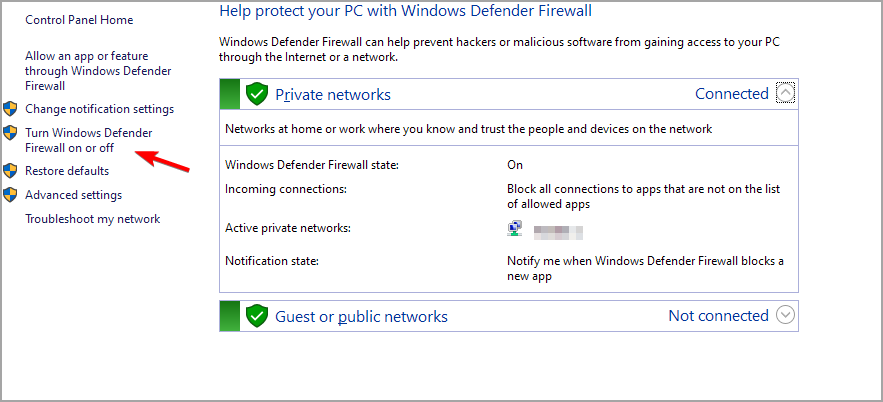
- Click Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or off.
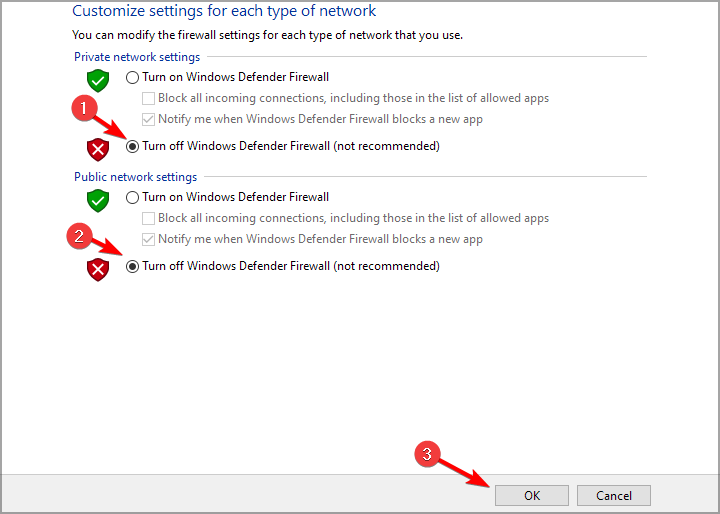
- Select the Turn off Windows Defender Firewall radio buttons, and click OK to confirm.
Your firewall can cause hls.js error: networkerror – fatal: true – manifestparsingerror, so make sure that it’s not interfering with your browser.
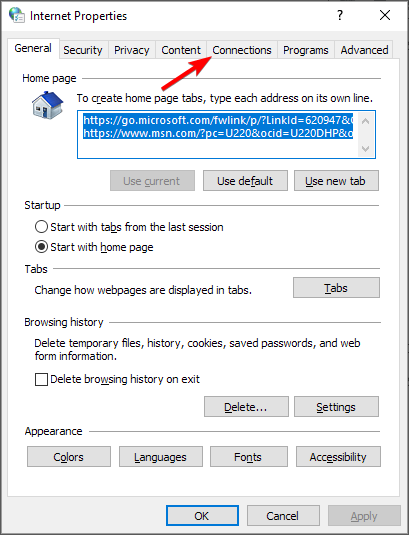
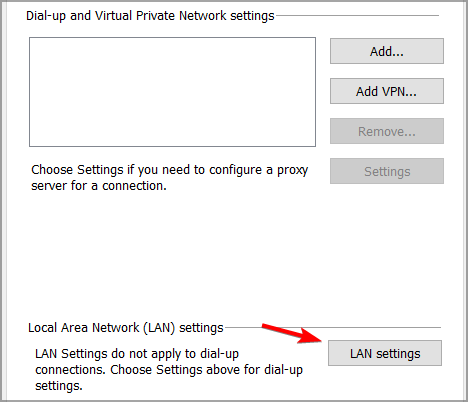
2. Disable the Proxy Server
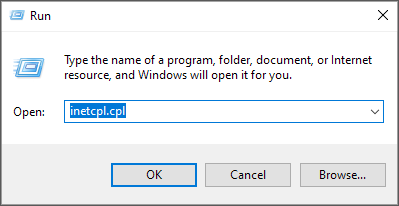
- Press Windows key + R . Type in inetcpl.cpl into Run and click OK.
- Next, make sure to select the Connections tab.
- Press the LAN settings button to open the Local Area Network (LAN) Settings window.
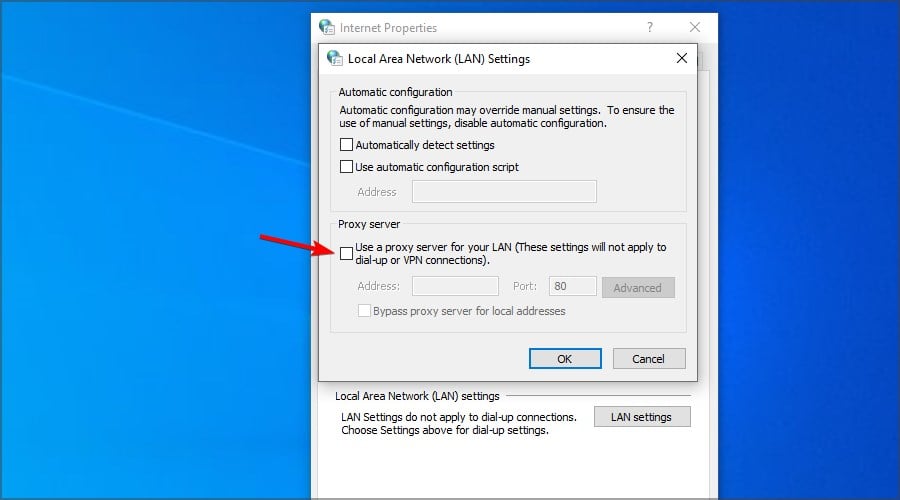
- Go to the Use a proxy server for your LAN checkbox and deselect it.
- Select the Automatically detect settings option.
- Click OK to exit the Local Area Network Settings window.
Expert tip:
SPONSORED
Some PC issues are hard to tackle, especially when it comes to corrupted repositories or missing Windows files. If you are having troubles fixing an error, your system may be partially broken.
We recommend installing Restoro, a tool that will scan your machine and identify what the fault is.
Click here to download and start repairing.
Your proxy can sometimes cause error code hls 4, a network error occurred: manifestloaderror, so it’s advised to disable it.
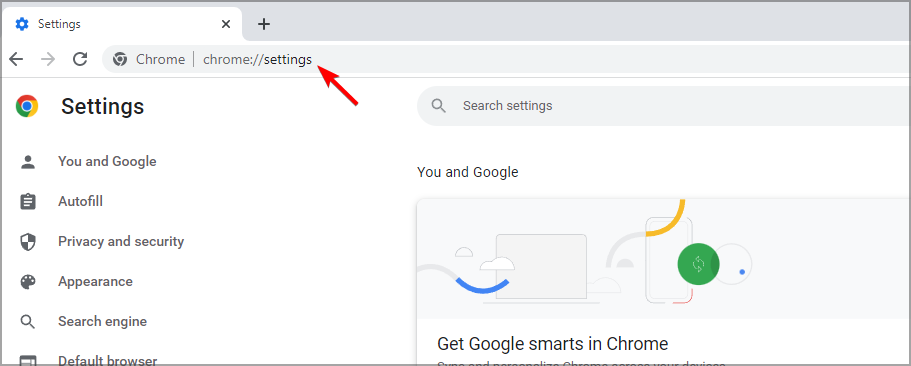
3. Reset the browser
- I n Chrome’s URL bar type chrome://settings/
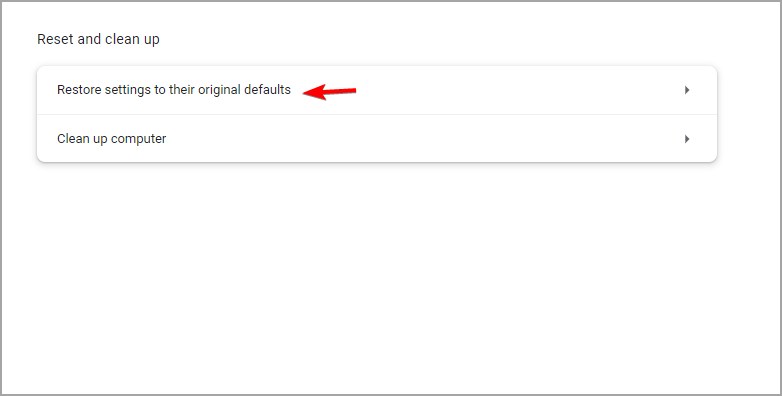
- Select Reset and clean up.
- Now pick Restore settings to their original defaults.
- Restart your device.
4. Reinstall Chrome
- Press the Windows key + R keyboard shortcut.
- Type appwiz.cpl and click the OK option.
- Select from the list Google Chrome.
- Next, click the Uninstall option for Google Chrome.
- Click Yes on confirmation prompts.
- Restart Windows when you’ve uninstalled Chrome.
- Go to the official page and download the Chrome browser on your device.
- Reinstall it and restart your device as well.
It’s possible that your browser installation is damaged, thus causing hls.js error mediaerror – fatal true – bufferstallederror. However, that can be fixed with a quick reinstall.
5. Check your antivirus
In case you are using a third-party antivirus, we would recommend that you disable it temporarily. Make sure that once you did this step, you restart your device and check to see if the error is still there.
If the issue doesn’t appear, make sure that you check antivirus settings and disable the one that is causing this issue.
6. Clear Chrome’s browser data
- Click the Menu button at the top right of the browser’s window. Select the More Tools and then select Clear browsing data.
- Select the All-time option on the drop-down menu.
- Next, select all three data options on the Basic tab for cookies, cache, and browsing history.
- Click the Clear data option.
Cache problems can cause hls.js error networkerror – fatal true – fragloaderror error, but that can be fixed by following the instructions from above.
Read more about this topic
7. Get the video URL
- Right-click the video that you want to play.
- Select Inspect.
- A new window will appear with the website code. Locate the URL of the video and copy it.
- Paste it into a different window and check if that solves the problem.
Fixing this kind of error can be pretty simple, all you need to do is make sure that your antivirus is not blocking chrome and that the cache and history have been deleted.
In most cases uninstalling and reinstalling the browser is also a good idea, many users are stating that this has helped them solve the error.
This isn’t the only video issue, and many users reported that YouTube freezes on Chrome, but we covered that in a separate guide.
If you have additional recommendations or suggestions, please let us know in the comments section below.
Источник
levelLoadError not fired after auto-recovery attempt failed #822
Environment
- The stream has correct Access-Control-Allow-Origin headers (CORS)
- There are no network errors such as 404s in the browser console when trying to play the stream
- The issue observed is not already reported by searching on Github under https://github.com/dailymotion/hls.js/issues
- The issue occurs in the latest reference client on http://dailymotion.github.io/hls.js/demo and not just on my page
- Link to playable M3U8 file: live playlist
- Hls.js version: 0.6.8/0.6.9
- Browser name/version: Chrome Version 54.0.2840.98 (64-bit)
- OS name/version: Mac OSX 10.11.6
Steps to reproduce
The problem occurs if is provided a playlist.m3u8 that contains two levels that are not reachable and gives 404 on chunklist request.
Expected behavior
I expect that hls.js tries to recover itself for the first time I get the error (thing that actually does), but that it fires a LEVEL_LOAD_ERROR in case the auto recover fails.
Actual behavior
It doesn’t fire the LEVEL_LOAD_ERROR.
It fires another error that is too much general for my purposes:
ERROR: <«type»:»otherError»,»details»:»internalException»,»fatal»:false,»event»:»hlsError»,»err»:<>>
This looks strange to me since, according to [this lines of code] (https://github.com/dailymotion/hls.js/blob/v0.6.8/src/controller/level-controller.js#L250-L259) the behavior should be the one I expect to be.
Console output
I’m sorry there are no timestamps, but I think isn’t relevant for this kind of error.
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
Источник
Hls js error networkerror fatal true manifestloadtimeout
This problem is driving me crazy! It was working until few days ago.
I can’t watch any videos from this website/domain: http://redeglobo.globo.com/videos/ Things I’ve tried: — private browsing — safe mode — new profile/refresh — portable version — uninstall/reinstall — older versions — uninstalled kaspersky/windows defender is disabled — HOSTS file is clean(Windows 7 x64)
The thing is, the ads load but not the video content. If the ad is long, an error message appears while the audio is still playing in the background. Another computer in the same network plays them fine. All other browsers can play these videos, this problem only happens in Firefox. I’ve tested a virtual machine in this same computer and then it works. Is there anything else I can do to try to fix this?
[error][hlsjs: unrecoverable network fatal error.] Object < evt: «hlsError», data: <…>> player.min.js:1:1237298
[error][player_error] Object < description: «hls error: type: networkError, details: levelLoadError, response: <«code»:0,»text»:»»>«, level: «FATAL», origin: «hls», scope: «playback», raw: <…>, code: «hls:networkError_levelLoadError», UI: <…>> player.min.js:1:1237298
Modifié le 27 novembre 2018 à 15:26:21 HNP par anitoad
Solution choisie
Well, look at that. Actually the problem persists but now I know where it comes from. Videos started playing again when my PC clock changed automatically to 1 hour earlier. I tried to change time zone with an addon but the website gets the time from the system clock. I suspect it’s related to daylight savings. Thanks anyway, I now know it’s probably not a Firefox issue.
Источник
Ошибка загрузки манифеста, что делать?
При просмотре видео в сети, или при запуске (работе) какой-либо программы, пользователь может столкнуться с ошибкой и соответствующим сообщением «Ошибка загрузки манифеста» («файл манифеста отсутствует или недоступен для чтения», «unable to load manifest file» и др.). Обычно в данной проблеме нет прямой вины пользователя. Потому, в большинстве случаев, необходимо будет проявить немного терпения, дождавшись момента, когда администрация сайта исправит возникшую дисфункцию. В данном материале я расскажу, что делать, если вы столкнулись с «ошибкой манифеста», каковы причины данного явления, и как исправить ошибку загрузки манифеста на ваших ПК.
Ошибка загрузки mp4 манифеста что это значит?
Файл с названием «манифест» (англ. – «manifest») обычно являет собой текстовый файл с расширением .txt, в котором располагаются ряд настроек системы (или какой-либо программы). В частности, при воспроизведении видео в HTML5 (данный язык используется для представления содержимого веб-страниц), в файле manifest.txt может находиться список файлов, которые необходимо кешировать.
При повреждении (удалении) данного файла на каком-либо интернет-ресурсе (или в теле программы) система выдаст вам сообщение об ошибке загрузки манифеста.
В большинстве случаев при возникновении подобной проблемы на каком-либо интернет-ресурсе прямой вины пользователя в этом нет (проблема должна быть решена администрацией сайта). В остальных же случаях причиной ошибки может быть следующее:
- Расширение (дополнение) вашего браузера препятствуют корректной работе системы с файлом «manifest»;
- Пользователь случайно или намеренно удалил файл «manifest» в теле программы;
- Указанный файл был удалён вирусной программой на ПК;
- Некорректно работает сам пользовательский браузер.
Как исправить ошибку загрузки манифеста
После того, как мы выяснили, что означает «Ошибка загрузки манифеста», перейдём к вариантам того, как избавиться от ошибки загрузки манифеста на вашем компьютере. Рекомендую выполнить следующее:
- Подождите некоторое время. Если проблема возникла на каком-либо интернет-ресурсе, то, обычно, вашей вины в этом нет. Могу посоветовать проявить терпение и выдержку, на протяжении одной или двух суток (а то и ранее) ситуация нормализуется;
- Напишите письмо в техническую поддержку интернет-ресурса (возможно, они просто не в курсе возникшей проблемы);
- Проверьте, не является ли какое-либо из расширений (дополнений) для вашего браузера причиной ошибки загрузки манифеста. Для реализации этого рекомендую использовать режим «инкогнито» в Google Chrom. Если в этом режиме ошибка не возникает, тогда поочерёдно отключайте расширения для выявления непосредственного виновника проблемы. В других же браузерах отключите (или удалите) внешние расширения (дополнения) вашего веб-навигатора, чтобы выявить возможную причину дисфункции;
- Проверьте ваш компьютер на наличие вирусных программ (помогут Dr.Web CureIt!, AdwCleaner, Malwarebytes Anti-Malware и ряд других аналогов);
- Переустановите проблемную программу. Если ошибка возникла во время работы какой-то программы – попробуйте установить её свежую версию. Если это репак – попробуйте установить репак другого автора;
- Используйте другой браузер (если пользуетесь «Chrome» – тогда используйте «Firefox» и наоборот);
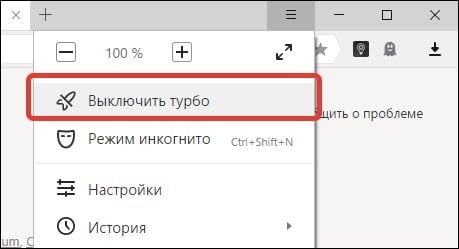
- Отключите режим «Turbo» в вашем браузере (актуально для браузеров «Opera», «Yandex» и др.);
- Запускайте ваш браузер от имени администратора (наведите курсор мышки на ярлык браузера, нажмите правую клавишу мыши, и в появившемся меню выберите «Запуск от имени администратора»);
- Попробуйте запустить ваш браузер в режиме совместимости с более ранней ОС. Для этого наведите курсор на иконку браузера, кликните правой клавишей мыши, в появившемся меню выберите «Свойства». В открывшемся окне перейдите на вкладку «Совместимость», поставьте галочку рядом с опцией «Запустить программу в режиме совместимости с» и выберите более раннюю ОС. Затем нажмите на «ОК», запустите браузер, и попробуйте открыть проблемную страницу;
- Откатите систему на более раннее состояние. Если ранее проблемная программа работала стабильно, то нажмите на кнопку «Пуск», в строке поиска введите rstrui, и нажмите ввод. Найдите стабильную точку восстановления, и откатите систему к указанному стабильному состоянию.
Источник
by Radu Tyrsina
Radu Tyrsina has been a Windows fan ever since he got his first PC, a Pentium III (a monster at that time). For most of the kids of… read more
Published on June 17, 2022
- The hls.js network error seems to appear for Google Chrome users but without other additional information.
- In this article, we will explore some of the steps you can make in order to fix it and regain the full functionality of Chrome.
- Your firewall or proxy server may be at fault, but an outdated browser or your antivirus can also cause the issue.
- Easy migration: use the Opera assistant to transfer exiting data, such as bookmarks, passwords, etc.
- Optimize resource usage: your RAM memory is used more efficiently than Chrome does
- Enhanced privacy: free and unlimited VPN integrated
- No ads: built-in Ad Blocker speeds up loading of pages and protects against data-mining
- Download Opera
Usually, Chrome is a relatively stable and reliable browser to use in Windows 10 and it’s the first choice for millions of people all over the world. But sadly, issues can appear, one that users reported is hls.js error.
It seems as though the Google Chrome hls.js network error has given users a lot of headaches. This can cause Facebook videos not playing in various browsers among other issues.
In this article we will show you a few easy steps that you can make in order to solve it, so make sure to keep on reading.
What is hls.js error networkerror?
This error usually appears when trying to play an online video in your browser. There are multiple causes for this problem, but it’s possible that one of the necessary components isn’t working.
Alternatively, the problem can be related to your antivirus or firewall. Lastly, your browser configuration can cause this issue, but there are ways to fix that.
Keep reading to find out how to fix hls.js error network error – fatal true – manifestloaderror and other variations of this error.
Quick Tip:
This error is prevalent in Chrome, but not as much when using a different browser. So if you want a quick fix, try switching to an alternative. The recommended option is Opera because it’s very stable.
This browser is also much lighter on resources than Chrome, leading to lower error rates and faster loading pages. It supports most Chrome extensions and integrates social media apps, a VPN, and more.

Opera
Enjoy seamless browsing and say goodbye to Chrome’s errors by using this modern, reliable browser.
How can I fix hls.js network error in Chrome?
1. Turn off firewalls temporarily
NOTE
In case you have installed on your device a third-party antivirus software that has a firewall incorporated, make sure to right-click the system tray icon. Next, you should select to disable the antivirus utility’s context menu to temporarily deactivate it.
- Go to the Search box in Windows 10.
- Type in the keyword firewall. Click Windows Defender Firewall.
- Click Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or off.
- Select the Turn off Windows Defender Firewall radio buttons, and click OK to confirm.
Your firewall can cause hls.js error: networkerror – fatal: true – manifestparsingerror, so make sure that it’s not interfering with your browser.
2. Disable the Proxy Server
- Press Windows key + R. Type in inetcpl.cpl into Run and click OK.
- Next, make sure to select the Connections tab.
- Press the LAN settings button to open the Local Area Network (LAN) Settings window.
- Go to the Use a proxy server for your LAN checkbox and deselect it.
- Select the Automatically detect settings option.
- Click OK to exit the Local Area Network Settings window.
Some PC issues are hard to tackle, especially when it comes to corrupted repositories or missing Windows files. If you are having troubles fixing an error, your system may be partially broken.
We recommend installing Restoro, a tool that will scan your machine and identify what the fault is.
Click here to download and start repairing.
Your proxy can sometimes cause error code hls 4, a network error occurred: manifestloaderror, so it’s advised to disable it.
3. Reset the browser
- In Chrome’s URL bar type
chrome://settings/ - Select Reset and clean up.
- Now pick Restore settings to their original defaults.
- Restart your device.
4. Reinstall Chrome
- Press the Windows key + R keyboard shortcut.
- Type appwiz.cpl and click the OK option.
- Select from the list Google Chrome.
- Next, click the Uninstall option for Google Chrome.
- Click Yes on confirmation prompts.
- Restart Windows when you’ve uninstalled Chrome.
- Go to the official page and download the Chrome browser on your device.
- Reinstall it and restart your device as well.
It’s possible that your browser installation is damaged, thus causing hls.js error mediaerror – fatal true – bufferstallederror. However, that can be fixed with a quick reinstall.
5. Check your antivirus
In case you are using a third-party antivirus, we would recommend that you disable it temporarily. Make sure that once you did this step, you restart your device and check to see if the error is still there.
If the issue doesn’t appear, make sure that you check antivirus settings and disable the one that is causing this issue.
6. Clear Chrome’s browser data
- Click the Menu button at the top right of the browser’s window. Select the More Tools and then select Clear browsing data.
- Select the All-time option on the drop-down menu.
- Next, select all three data options on the Basic tab for cookies, cache, and browsing history.
- Click the Clear data option.
Cache problems can cause hls.js error networkerror – fatal true – fragloaderror error, but that can be fixed by following the instructions from above.
- 9 Tested Ways to Fix Chrome if Full Screen Is Not Working
- Amazon Prime Video not Working in Chrome: 3 Ways to Fix it
- Chrome Toolbar Missing: 5 Tested Ways to Get It Back
- Can’t Uninstall Google Chrome? Here’s How to Fix That
- How to Stop Multiple Chrome Processes in Task Manager
7. Get the video URL
- Right-click the video that you want to play.
- Select Inspect.
- A new window will appear with the website code. Locate the URL of the video and copy it.
- Paste it into a different window and check if that solves the problem.
Fixing this kind of error can be pretty simple, all you need to do is make sure that your antivirus is not blocking chrome and that the cache and history have been deleted.
In most cases uninstalling and reinstalling the browser is also a good idea, many users are stating that this has helped them solve the error.
This isn’t the only video issue, and many users reported that YouTube freezes on Chrome, but we covered that in a separate guide.
If you have additional recommendations or suggestions, please let us know in the comments section below.
Newsletter
Содержание
- «Ошибка загрузки манифеста» как исправить
- Что это такое
- Как исправить ошибку
- Переустановка с очисткой
- Чистая загрузка
- Изменение настроек браузера
- Заключение
- Ошибка загрузки манифеста, что делать?
- Ошибка загрузки mp4 манифеста что это значит?
- Как исправить ошибку загрузки манифеста
- Fail to play m3u8 URL with «manifestLoadError» error #4473
- Comments
- TadpoleInnovationInc commented Dec 27, 2021
- philcluff commented Dec 27, 2021
- TadpoleInnovationInc commented Dec 28, 2021
- philcluff commented Dec 28, 2021
- 7 Ways to fix hls.js Error in Chrome & Other Browsers
- What is hls.js error networkerror?
- Opera
- How can I fix hls.js network error in Chrome?
- 1. Turn off firewalls temporarily
- 2. Disable the Proxy Server
- 3. Reset the browser
- 4. Reinstall Chrome
- 5. Check your antivirus
- 6. Clear Chrome’s browser data
- 7. Get the video URL
«Ошибка загрузки манифеста» как исправить
Сегодня мы расскажем о сбое при просмотре страниц, запуске расширений или загрузке видео, фильмов «Что то пошло не так: Ошибка загрузки манифеста», она же «manifest_loading_error». Иногда указывается код расширения (MP4). Данный баг может проявляться на всех востребованных браузерах (Google Chrome, Яндекс, Opera, Mozilla FireFox). Мы расскажем как исправить этот сбой.
Сбой при запуске фильма «Ошибка загрузки манифеста»
Что это такое
Ошибка может возникать по самым разным причинам: основная — это проблемы на стороне сайта, крайне редко сбой проявляется при изменении вшитых настроек в браузере. Конкретно данная ошибка загрузки манифеста появилась недавно и, судя по всему, будет в скором времени устранена посредством нескольких апдейтов браузера. Ранее пользователи сталкивались с несколько другой проблемой — «Файл манифеста отсутствует или недоступен для чтения», которая возникает при попытке установить некоторые расширения в не ту папку.
Говоря простыми словами — сбой возникает из-за того, что для запуска страниц, видео или расширений, браузер подгружает свои настройки и библиотеки. Если такой путь нарушен, либо папка со вложенными файлами изменены — выскакивает подобная ошибка.
Ошибка манифеста при загрузке расширения
Как исправить ошибку
Мы выбрали все лучшие советы по решению бага, которые рекомендуются на различных тематических ресурсах. Выберите для себя наиболее подходящий, либо пробуйте их поочередно, начиная с самого простого. Сразу оговорюсь — решения применяются с оглядкой на то, что Adobe Flash Player и актуальная версия браузера уже имеются на компьютере. VPN, прокси и анонимайзеры — не активны.
Часто баг единичен — просто обновите страницу, стерев весь кэш, через команду CTRL+F5
Переустановка с очисткой
Самый простой вариант — попробуйте полную переустановку браузера, очистив все остаточные папки и сохранения. Сделаем все на примере популярного Google Chrome.
- Заходите в «Программы и компоненты» и удаляйте браузер.
- После следует прочистить реестр от остаточных записей. Для таких целей я применяю CCleaner. Примените через него опцию «Реестр» и там выполняйте исправление ошибок.
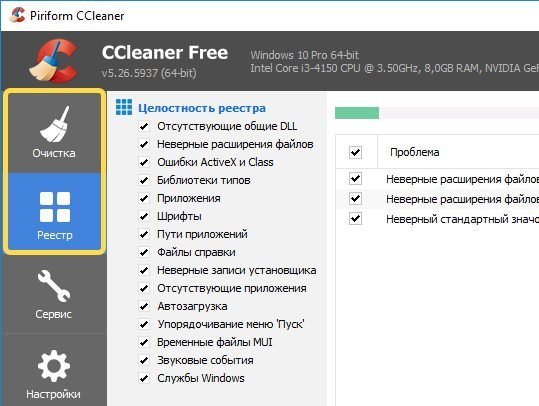
Еще пару слов о Хроме. Некоторым помогает инструмент очистки и исправления ошибок: Chrome Cleanup Tool. Там все просто: скачиваем — запускаем — очищаем.
Чистая загрузка
Если баг остается — идем дальше. Наиболее часто проблема возникает, когда помимо браузера в фоне работает множество программ. Например, многим помогает полное удаление всех компонентов iTunes, если таковые есть или были в Windows. В таком случае примените чистый запуск Windows. После пробуйте запустить видео на проблемной странице в браузере (Яндекс, Мозилла, Опера, Хром). Вот видео-инструкция по поводу чистой загрузки.
Изменение настроек браузера
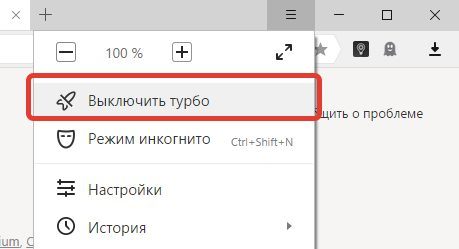
- Отключите все предустановленные расширения и включайте их по одному, проверяя ушла ошибка или нет.
- Для Яндекса. Проходим в настройки и отключаем (если активирован) «Режим Турбо».
Заключение
Многим данные советы помогают в решении проблемы «Ошибка загрузки манифеста», в том числе MP4. Не забывайте и другое — возможно проблема возникла на стороне самого сайта, поэтому следует немного подождать.
Источник
Ошибка загрузки манифеста, что делать?
При просмотре видео в сети, или при запуске (работе) какой-либо программы, пользователь может столкнуться с ошибкой и соответствующим сообщением «Ошибка загрузки манифеста» («файл манифеста отсутствует или недоступен для чтения», «unable to load manifest file» и др.). Обычно в данной проблеме нет прямой вины пользователя. Потому, в большинстве случаев, необходимо будет проявить немного терпения, дождавшись момента, когда администрация сайта исправит возникшую дисфункцию. В данном материале я расскажу, что делать, если вы столкнулись с «ошибкой манифеста», каковы причины данного явления, и как исправить ошибку загрузки манифеста на ваших ПК.
Ошибка загрузки mp4 манифеста что это значит?
Файл с названием «манифест» (англ. – «manifest») обычно являет собой текстовый файл с расширением .txt, в котором располагаются ряд настроек системы (или какой-либо программы). В частности, при воспроизведении видео в HTML5 (данный язык используется для представления содержимого веб-страниц), в файле manifest.txt может находиться список файлов, которые необходимо кешировать.
При повреждении (удалении) данного файла на каком-либо интернет-ресурсе (или в теле программы) система выдаст вам сообщение об ошибке загрузки манифеста.
В большинстве случаев при возникновении подобной проблемы на каком-либо интернет-ресурсе прямой вины пользователя в этом нет (проблема должна быть решена администрацией сайта). В остальных же случаях причиной ошибки может быть следующее:
- Расширение (дополнение) вашего браузера препятствуют корректной работе системы с файлом «manifest»;
- Пользователь случайно или намеренно удалил файл «manifest» в теле программы;
- Указанный файл был удалён вирусной программой на ПК;
- Некорректно работает сам пользовательский браузер.
Как исправить ошибку загрузки манифеста
После того, как мы выяснили, что означает «Ошибка загрузки манифеста», перейдём к вариантам того, как избавиться от ошибки загрузки манифеста на вашем компьютере. Рекомендую выполнить следующее:
- Подождите некоторое время. Если проблема возникла на каком-либо интернет-ресурсе, то, обычно, вашей вины в этом нет. Могу посоветовать проявить терпение и выдержку, на протяжении одной или двух суток (а то и ранее) ситуация нормализуется;
- Напишите письмо в техническую поддержку интернет-ресурса (возможно, они просто не в курсе возникшей проблемы);
- Проверьте, не является ли какое-либо из расширений (дополнений) для вашего браузера причиной ошибки загрузки манифеста. Для реализации этого рекомендую использовать режим «инкогнито» в Google Chrom. Если в этом режиме ошибка не возникает, тогда поочерёдно отключайте расширения для выявления непосредственного виновника проблемы. В других же браузерах отключите (или удалите) внешние расширения (дополнения) вашего веб-навигатора, чтобы выявить возможную причину дисфункции;
- Проверьте ваш компьютер на наличие вирусных программ (помогут Dr.Web CureIt!, AdwCleaner, Malwarebytes Anti-Malware и ряд других аналогов);
- Переустановите проблемную программу. Если ошибка возникла во время работы какой-то программы – попробуйте установить её свежую версию. Если это репак – попробуйте установить репак другого автора;
- Используйте другой браузер (если пользуетесь «Chrome» – тогда используйте «Firefox» и наоборот);
- Отключите режим «Turbo» в вашем браузере (актуально для браузеров «Opera», «Yandex» и др.);
- Запускайте ваш браузер от имени администратора (наведите курсор мышки на ярлык браузера, нажмите правую клавишу мыши, и в появившемся меню выберите «Запуск от имени администратора»);
- Попробуйте запустить ваш браузер в режиме совместимости с более ранней ОС. Для этого наведите курсор на иконку браузера, кликните правой клавишей мыши, в появившемся меню выберите «Свойства». В открывшемся окне перейдите на вкладку «Совместимость», поставьте галочку рядом с опцией «Запустить программу в режиме совместимости с» и выберите более раннюю ОС. Затем нажмите на «ОК», запустите браузер, и попробуйте открыть проблемную страницу;
- Откатите систему на более раннее состояние. Если ранее проблемная программа работала стабильно, то нажмите на кнопку «Пуск», в строке поиска введите rstrui, и нажмите ввод. Найдите стабильную точку восстановления, и откатите систему к указанному стабильному состоянию.
Источник
Fail to play m3u8 URL with «manifestLoadError» error #4473
What version of Hls.js are you using?
1.1.2
What browser (including version) are you using?
Google Chrome Version 96.0.4664.45 (Official Build) (64-bit)
What OS (including version) are you using?
Windows 10
But, the VLC player can play it successfully.
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
When i curl that URL I don’t get a HLS manifest in the response (in fact I get a 200 with an empty response) — this doesn’t play in either VLC or HLS.js for me.
I’m guessing this URL may have expired. Here’s some things to check if you can get a fresh URL:
Is there a HTTPS version of this URL? It looks like you’re trying to load a HTTP resource from a HTTPS URL, which won’t work.
Are there correct CORS headers on the response?
Yes, the URL I provided last time has expired. So, I provide it again. The below two links has the same symptoms can’t play via the hls demo «https://hls-js.netlify.com/demo» but work well with the VLC player.
I am not sure if there a HTTPS version of this URL since the URL is provided by the server-side. As for the question about «CORS headers», I am not sure how to check if it’s correct CORS headers. Could you please give more information? Thanks.
Hi @TadpoleInnovationInc thanks for the updated URLs.
For the first URL, «iQiyi», this is failing because the content is not available over HTTPS, and the HLS.js demo page only loads over HTTPS. When loaded on a page over HTTP, this stream works fine (try: http://philcluff.co.uk/players/hls-js.html for example)
For the second URL, «Sohu», this stream is indeed missing CORS headers as I commented above, there is no Access-Control-Allow-Origin header on the manifest responses.
Источник
7 Ways to fix hls.js Error in Chrome & Other Browsers
- The hls.js network error seems to appear for Google Chrome users but without other additional information.
- In this article, we will explore some of the steps you can make in order to fix it and regain the full functionality of Chrome.
- Your firewall or proxy server may be at fault, but an outdated browser or your antivirus can also cause the issue.
- Easy migration: use the Opera assistant to transfer exiting data, such as bookmarks, passwords, etc.
- Optimize resource usage: your RAM memory is used more efficiently than Chrome does
- Enhanced privacy: free and unlimited VPN integrated
- No ads: built-in Ad Blocker speeds up loading of pages and protects against data-mining
- Download Opera
Usually, Chrome is a relatively stable and reliable browser to use in Windows 10 and it’s the first choice for millions of people all over the world. But sadly, issues can appear, one that users reported is hls.js error.
It seems as though the Google Chrome hls.js network error has given users a lot of headaches. This can cause Facebook videos not playing in various browsers among other issues.
In this article we will show you a few easy steps that you can make in order to solve it, so make sure to keep on reading.
What is hls.js error networkerror?
This error usually appears when trying to play an online video in your browser. There are multiple causes for this problem, but it’s possible that one of the necessary components isn’t working.
Alternatively, the problem can be related to your antivirus or firewall. Lastly, your browser configuration can cause this issue, but there are ways to fix that.
Keep reading to find out how to fix hls.js error network error – fatal true – manifestloaderror and other variations of this error.
Quick Tip:
This error is prevalent in Chrome, but not as much when using a different browser. So if you want a quick fix, try switching to an alternative. The recommended option is Opera because it’s very stable.
This browser is also much lighter on resources than Chrome, leading to lower error rates and faster loading pages. It supports most Chrome extensions and integrates social media apps, a VPN, and more.
Opera
Enjoy seamless browsing and say goodbye to Chrome’s errors by using this modern, reliable browser.
How can I fix hls.js network error in Chrome?
1. Turn off firewalls temporarily
- Go to the Search box in Windows 10.
- Type in the keyword firewall. Click Windows Defender Firewall.
- Click Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or off.
- Select the Turn off Windows Defender Firewall radio buttons, and click OK to confirm.
Your firewall can cause hls.js error: networkerror – fatal: true – manifestparsingerror, so make sure that it’s not interfering with your browser.
2. Disable the Proxy Server
- Press Windows key + R . Type in inetcpl.cpl into Run and click OK.
- Next, make sure to select the Connections tab.
- Press the LAN settings button to open the Local Area Network (LAN) Settings window.
- Go to the Use a proxy server for your LAN checkbox and deselect it.
- Select the Automatically detect settings option.
- Click OK to exit the Local Area Network Settings window.
Expert tip:
SPONSORED
Some PC issues are hard to tackle, especially when it comes to corrupted repositories or missing Windows files. If you are having troubles fixing an error, your system may be partially broken.
We recommend installing Restoro, a tool that will scan your machine and identify what the fault is.
Click here to download and start repairing.
Your proxy can sometimes cause error code hls 4, a network error occurred: manifestloaderror, so it’s advised to disable it.
3. Reset the browser
- I n Chrome’s URL bar type chrome://settings/
- Select Reset and clean up.
- Now pick Restore settings to their original defaults.
- Restart your device.
4. Reinstall Chrome
- Press the Windows key + R keyboard shortcut.
- Type appwiz.cpl and click the OK option.
- Select from the list Google Chrome.
- Next, click the Uninstall option for Google Chrome.
- Click Yes on confirmation prompts.
- Restart Windows when you’ve uninstalled Chrome.
- Go to the official page and download the Chrome browser on your device.
- Reinstall it and restart your device as well.
It’s possible that your browser installation is damaged, thus causing hls.js error mediaerror – fatal true – bufferstallederror. However, that can be fixed with a quick reinstall.
5. Check your antivirus
In case you are using a third-party antivirus, we would recommend that you disable it temporarily. Make sure that once you did this step, you restart your device and check to see if the error is still there.
If the issue doesn’t appear, make sure that you check antivirus settings and disable the one that is causing this issue.
6. Clear Chrome’s browser data
- Click the Menu button at the top right of the browser’s window. Select the More Tools and then select Clear browsing data.
- Select the All-time option on the drop-down menu.
- Next, select all three data options on the Basic tab for cookies, cache, and browsing history.
- Click the Clear data option.
Cache problems can cause hls.js error networkerror – fatal true – fragloaderror error, but that can be fixed by following the instructions from above.
Read more about this topic
7. Get the video URL
- Right-click the video that you want to play.
- Select Inspect.
- A new window will appear with the website code. Locate the URL of the video and copy it.
- Paste it into a different window and check if that solves the problem.
Fixing this kind of error can be pretty simple, all you need to do is make sure that your antivirus is not blocking chrome and that the cache and history have been deleted.
In most cases uninstalling and reinstalling the browser is also a good idea, many users are stating that this has helped them solve the error.
This isn’t the only video issue, and many users reported that YouTube freezes on Chrome, but we covered that in a separate guide.
If you have additional recommendations or suggestions, please let us know in the comments section below.
Источник
HLS.js v1 API
See API Reference for a complete list of interfaces available in the hls.js package.
- Getting started
- First step: setup and support
- Second step: instantiate Hls object and bind it to
<video>element - Third step: load a manifest
- Fourth step: control through
<video>element - Fifth step: error handling
- Fatal Error Recovery
hls.startLoad()hls.recoverMediaError()- Error recovery sample code
hls.swapAudioCodec()
- Fatal Error Recovery
- Final step: destroying, switching between streams
- Fine Tuning
Hls.DefaultConfig get/setcapLevelToPlayerSizecapLevelOnFPSDropignoreDevicePixelRatiodebugautoStartLoadstartPositiondefaultAudioCodecinitialLiveManifestSizemaxBufferLengthbackBufferLengthmaxBufferSizemaxBufferHolemaxStarvationDelaymaxLoadingDelaylowBufferWatchdogPeriod(deprecated)highBufferWatchdogPeriodnudgeOffsetnudgeMaxRetrymaxFragLookUpTolerancemaxMaxBufferLengthliveSyncDurationCountliveMaxLatencyDurationCountliveSyncDurationliveMaxLatencyDurationmaxLiveSyncPlaybackRateliveDurationInfinityliveBackBufferLength(deprecated)enableWorkerenableSoftwareAESstartLevelfragLoadingTimeOut/manifestLoadingTimeOut/levelLoadingTimeOutfragLoadingMaxRetry/manifestLoadingMaxRetry/levelLoadingMaxRetryfragLoadingMaxRetryTimeout/manifestLoadingMaxRetryTimeout/levelLoadingMaxRetryTimeoutfragLoadingRetryDelay/manifestLoadingRetryDelay/levelLoadingRetryDelaystartFragPrefetchtestBandwidthprogressivelowLatencyModefpsDroppedMonitoringPeriodfpsDroppedMonitoringThresholdappendErrorMaxRetryloaderfLoaderpLoaderxhrSetupfetchSetupabrControllerbufferControllercapLevelControllerfpsControllertimelineControllerenableDateRangeMetadataCuesenableEmsgMetadataCuesenableID3MetadataCuesenableWebVTTenableIMSC1enableCEA708CaptionscaptionsTextTrack1LabelcaptionsTextTrack1LanguageCodecaptionsTextTrack2LabelcaptionsTextTrack2LanguageCodecaptionsTextTrack3LabelcaptionsTextTrack3LanguageCodecaptionsTextTrack4LabelcaptionsTextTrack4LanguageCoderenderTextTracksNativelystretchShortVideoTrackmaxAudioFramesDriftforceKeyFrameOnDiscontinuityabrEwmaFastLiveabrEwmaSlowLiveabrEwmaFastVoDabrEwmaSlowVoDabrEwmaDefaultEstimateabrBandWidthFactorabrBandWidthUpFactorabrMaxWithRealBitrateminAutoBitrateemeEnabledwidevineLicenseUrl(deprecated)licenseXhrSetuplicenseResponseCallbackdrmSystems- `drmSystems[KEY-SYSTEM].generateRequest
drmSystemOptionsrequestMediaKeySystemAccessFunccmcd
- Video Binding/Unbinding API
hls.attachMedia(videoElement)hls.detachMedia()hls.media
- Quality switch Control API
hls.levelshls.currentLevelhls.nextLevelhls.loadLevelhls.nextLoadLevelhls.firstLevelhls.startLevelhls.autoLevelEnabledhls.autoLevelCappinghls.maxHdcpLevelhls.capLevelToPlayerSizehls.bandwidthEstimatehls.removeLevel(levelIndex, urlId)
- Version Control
Hls.version
- Network Loading Control API
hls.startLoad(startPosition=-1)hls.stopLoad()
- Audio Tracks Control API
hls.audioTrackshls.audioTrack
- Subtitle Tracks Control API
hls.subtitleTrackshls.subtitleTrackhls.subtitleDisplay
- Live stream API
hls.liveSyncPositionhls.latencyhls.maxLatencyhls.targetLatencyhls.drifthls.playingDate
- Runtime Events
- Creating a Custom Loader
- Errors
- Network Errors
- Media Errors
- Mux Errors
- EME Key System Errors
- Other Errors
- Objects
- Level
- LevelDetails
- Fragment
Getting started
First step: setup and support
First include https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/hls.js@latest (or /hls.js for unminified) in your web page.
<script src="//cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/hls.js@latest"></script>
Invoke the following static method: Hls.isSupported() to check whether your browser is supporting MediaSource Extensions.
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/hls.js@latest"></script> <script> if (Hls.isSupported()) { console.log('hello hls.js!'); } </script>
Second step: instantiate Hls object and bind it to <video> element
Let’s
- create a
<video>element - create a new HLS object
- bind video element to this HLS object
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/hls.js@latest"></script> <video id="video"></video> <script> if (Hls.isSupported()) { var video = document.getElementById('video'); var hls = new Hls(); // bind them together hls.attachMedia(video); // MEDIA_ATTACHED event is fired by hls object once MediaSource is ready hls.on(Hls.Events.MEDIA_ATTACHED, function () { console.log('video and hls.js are now bound together !'); }); } </script>
Third step: load a manifest
You need to provide manifest URL as below:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/hls.js@latest"></script> <video id="video"></video> <script> if (Hls.isSupported()) { var video = document.getElementById('video'); var hls = new Hls(); hls.on(Hls.Events.MEDIA_ATTACHED, function () { console.log('video and hls.js are now bound together !'); }); hls.on(Hls.Events.MANIFEST_PARSED, function (event, data) { console.log( 'manifest loaded, found ' + data.levels.length + ' quality level' ); }); hls.loadSource('http://my.streamURL.com/playlist.m3u8'); // bind them together hls.attachMedia(video); } </script>
Fourth step: control through <video> element
Video is controlled through HTML <video> element.
HTMLVideoElement control and events could be used seamlessly.
Fifth step: error handling
All errors are signalled through a unique single event.
Each error is categorized by:
- its type:
Hls.ErrorTypes.NETWORK_ERRORfor network related errorsHls.ErrorTypes.MEDIA_ERRORfor media/video related errorsHls.ErrorTypes.OTHER_ERRORfor all other errors
- its details:
- refer to Errors details
- its fatality:
falseif error is not fatal, hls.js will try to recover ittrueif error is fatal, an action is required to (try to) recover it.
Full details are described below
See sample code below to listen to errors:
hls.on(Hls.Events.ERROR, function (event, data) { var errorType = data.type; var errorDetails = data.details; var errorFatal = data.fatal; switch (data.details) { case Hls.ErrorDetails.FRAG_LOAD_ERROR: // .... break; default: break; } });
Fatal Error Recovery
hls.js provides means to ‘try to’ recover fatal network and media errors, through these 2 methods:
hls.startLoad()
Should be invoked to recover network error.
hls.recoverMediaError()
Should be invoked to recover media error.
Error recovery sample code
hls.on(Hls.Events.ERROR, function (event, data) { if (data.fatal) { switch (data.type) { case Hls.ErrorTypes.NETWORK_ERROR: // try to recover network error console.log('fatal network error encountered, try to recover'); hls.startLoad(); break; case Hls.ErrorTypes.MEDIA_ERROR: console.log('fatal media error encountered, try to recover'); hls.recoverMediaError(); break; default: // cannot recover hls.destroy(); break; } } });
hls.swapAudioCodec()
If media error are still raised after calling hls.recoverMediaError(),
calling this method, could be useful to workaround audio codec mismatch.
the workflow should be:
on First Media Error : call hls.recoverMediaError()
if another Media Error is raised ‘quickly’ after this first Media Error : first call hls.swapAudioCodec(), then call hls.recoverMediaError().
Final step: destroying, switching between streams
hls.destroy() should be called to free used resources and destroy hls context.
Fine Tuning
Configuration parameters could be provided to hls.js upon instantiation of Hls object.
var config = { autoStartLoad: true, startPosition: -1, debug: false, capLevelOnFPSDrop: false, capLevelToPlayerSize: false, defaultAudioCodec: undefined, initialLiveManifestSize: 1, maxBufferLength: 30, maxMaxBufferLength: 600, backBufferLength: Infinity, maxBufferSize: 60 * 1000 * 1000, maxBufferHole: 0.5, highBufferWatchdogPeriod: 2, nudgeOffset: 0.1, nudgeMaxRetry: 3, maxFragLookUpTolerance: 0.25, liveSyncDurationCount: 3, liveMaxLatencyDurationCount: Infinity, liveDurationInfinity: false, enableWorker: true, enableSoftwareAES: true, manifestLoadingTimeOut: 10000, manifestLoadingMaxRetry: 1, manifestLoadingRetryDelay: 1000, manifestLoadingMaxRetryTimeout: 64000, startLevel: undefined, levelLoadingTimeOut: 10000, levelLoadingMaxRetry: 4, levelLoadingRetryDelay: 1000, levelLoadingMaxRetryTimeout: 64000, fragLoadingTimeOut: 20000, fragLoadingMaxRetry: 6, fragLoadingRetryDelay: 1000, fragLoadingMaxRetryTimeout: 64000, startFragPrefetch: false, testBandwidth: true, progressive: false, lowLatencyMode: true, fpsDroppedMonitoringPeriod: 5000, fpsDroppedMonitoringThreshold: 0.2, appendErrorMaxRetry: 3, loader: customLoader, fLoader: customFragmentLoader, pLoader: customPlaylistLoader, xhrSetup: XMLHttpRequestSetupCallback, fetchSetup: FetchSetupCallback, abrController: AbrController, bufferController: BufferController, capLevelController: CapLevelController, fpsController: FPSController, timelineController: TimelineController, enableDateRangeMetadataCues: true, enableEmsgMetadataCues: true, enableID3MetadataCues: true, enableWebVTT: true, enableIMSC1: true, enableCEA708Captions: true, stretchShortVideoTrack: false, maxAudioFramesDrift: 1, forceKeyFrameOnDiscontinuity: true, abrEwmaFastLive: 3.0, abrEwmaSlowLive: 9.0, abrEwmaFastVoD: 3.0, abrEwmaSlowVoD: 9.0, abrEwmaDefaultEstimate: 500000, abrBandWidthFactor: 0.95, abrBandWidthUpFactor: 0.7, abrMaxWithRealBitrate: false, maxStarvationDelay: 4, maxLoadingDelay: 4, minAutoBitrate: 0, emeEnabled: false, licenseXhrSetup: undefined, drmSystems: {}, drmSystemOptions: {}, requestMediaKeySystemAccessFunc: requestMediaKeySystemAccess, cmcd: undefined, }; var hls = new Hls(config);
Hls.DefaultConfig get/set
This getter/setter allows retrieval and override of the Hls default configuration.
This configuration will be applied by default to all instances.
capLevelToPlayerSize
(default: false)
- if set to true, the adaptive algorithm with limit levels usable in auto-quality by the HTML video element dimensions (width and height).
If dimensions between multiple levels are equal, the cap is chosen as the level with the greatest bandwidth. - if set to false, levels will not be limited. All available levels could be used in auto-quality mode taking only bandwidth into consideration.
capLevelOnFPSDrop
(default: false)
- when set to true, if the number of dropped frames over the period
config.fpsDroppedMonitoringPeriodexceeds the ratio set byconfig.fpsDroppedMonitoringThreshold,
then the quality level is dropped and capped at this lower level. - when set to false, levels will not be limited. All available levels could be used in auto-quality mode taking only bandwidth into consideration.
ignoreDevicePixelRatio
(default: false)
- when set to true, calculations related to player size will ignore browser
devicePixelRatio. - when set to false, calculations related to player size will respect browser
devicePixelRatio.
debug
(default: false)
Setting config.debug = true; will turn on debug logs on JS console.
A logger object could also be provided for custom logging: config.debug = customLogger;.
autoStartLoad
(default: true)
- if set to true, start level playlist and first fragments will be loaded automatically, after triggering of
Hls.Events.MANIFEST_PARSEDevent - if set to false, an explicit API call (
hls.startLoad(startPosition=-1)) will be needed to start quality level/fragment loading.
startPosition
(default -1)
- if set to -1, playback will start from initialTime=0 for VoD and according to
liveSyncDuration/liveSyncDurationCountconfig params for Live - Otherwise, playback will start from predefined value. (unless stated otherwise in
autoStartLoad=falsemode : in that case startPosition can be overridden usinghls.startLoad(startPosition)).
defaultAudioCodec
(default: undefined)
If audio codec is not signaled in variant manifest, or if only a stream manifest is provided, hls.js tries to guess audio codec by parsing audio sampling rate in ADTS header.
If sampling rate is less or equal than 22050 Hz, then hls.js assumes it is HE-AAC, otherwise it assumes it is AAC-LC. This could result in bad guess, leading to audio decode error, ending up in media error.
It is possible to hint default audiocodec to hls.js by configuring this value as below:
mp4a.40.2(AAC-LC) ormp4a.40.5(HE-AAC) orundefined(guess based on sampling rate)
initialLiveManifestSize
(default 1)
number of segments needed to start a playback of Live stream. Buffering will begin after N chunks are available in the current playlist. If you want playback to begin liveSyncDurationCount chunks from the live edge at the beginning of a stream, set initialLiveManifestSize to liveSyncDurationCount or higher.
maxBufferLength
(default: 30 seconds)
Maximum buffer length in seconds. If buffer length is/become less than this value, a new fragment will be loaded.
This is the guaranteed buffer length hls.js will try to reach, regardless of maxBufferSize.
backBufferLength
(default: Infinity)
The maximum duration of buffered media to keep once it has been played, in seconds. Any video buffered past this duration will be evicted. Infinity means no restriction on back buffer length; 0 keeps the minimum amount. The minimum amount is equal to the target duration of a segment to ensure that current playback is not interrupted.
maxBufferSize
(default: 60 MB)
‘Minimum’ maximum buffer size in bytes. If buffer size upfront is bigger than this value, no fragment will be loaded.
maxBufferHole
(default: 0.5 seconds)
‘Maximum’ inter-fragment buffer hole tolerance that hls.js can cope with when searching for the next fragment to load.
When switching between quality level, fragments might not be perfectly aligned.
This could result in small overlapping or hole in media buffer. This tolerance factor helps cope with this.
maxStarvationDelay
(default 4s)
ABR algorithm will always try to choose a quality level that should avoid rebuffering.
In case no quality level with this criteria can be found (lets say for example that buffer length is 1s,
but fetching a fragment at lowest quality is predicted to take around 2s … ie we can forecast around 1s of rebuffering …)
then ABR algorithm will try to find a level that should guarantee less than maxStarvationDelay of buffering.
maxLoadingDelay
(default 4s)
max video loading delay used in automatic start level selection : in that mode ABR controller will ensure that video loading time
(ie the time to fetch the first fragment at lowest quality level + the time to fetch the fragment at the appropriate quality level is less than maxLoadingDelay )
lowBufferWatchdogPeriod (deprecated)
lowBufferWatchdogPeriod has been deprecated. Use highBufferWatchdogPeriod instead.
highBufferWatchdogPeriod
(default 3s)
if media element is expected to play and if currentTime has not moved for more than highBufferWatchdogPeriod and if there are more than maxBufferHole seconds buffered upfront, hls.js will jump buffer gaps, or try to nudge playhead to recover playback
nudgeOffset
(default 0.1s)
In case playback continues to stall after first playhead nudging, currentTime will be nudged evenmore following nudgeOffset to try to restore playback.
media.currentTime += (nb nudge retry -1)*nudgeOffset
nudgeMaxRetry
(default 3)
Max nb of nudge retries before hls.js raise a fatal BUFFER_STALLED_ERROR
maxFragLookUpTolerance
(default 0.25s)
This tolerance factor is used during fragment lookup.
Instead of checking whether buffered.end is located within [start, end] range, frag lookup will be done by checking within [start-maxFragLookUpTolerance, end-maxFragLookUpTolerance] range.
This tolerance factor is used to cope with situations like:
buffered.end = 9.991
frag[0] : [0,10]
frag[1] : [10,20]
buffered.end is within frag[0] range, but as we are close to frag[1], frag[1] should be choosen instead
If maxFragLookUpTolerance = 0.2, this lookup will be adjusted to
frag[0] : [-0.2,9.8]
frag[1] : [9.8,19.8]
This time, buffered.end is within frag[1] range, and frag[1] will be the next fragment to be loaded, as expected.
maxMaxBufferLength
(default 600s)
Maximum buffer length in seconds. Hls.js will never exceed this value, even if maxBufferSize is not reached yet.
hls.js tries to buffer up to a maximum number of bytes (60 MB by default) rather than to buffer up to a maximum nb of seconds.
this is to mimic the browser behaviour (the buffer eviction algorithm is starting after the browser detects that video buffer size reaches a limit in bytes)
maxBufferLength is the minimum guaranteed buffer length that hls.js will try to achieve, even if that value exceeds the amount of bytes 60 MB of memory.
maxMaxBufferLength acts as a capping value, as if bitrate is really low, you could need more than one hour of buffer to fill 60 MB.
liveSyncDurationCount
(default: 3)
edge of live delay, expressed in multiple of EXT-X-TARGETDURATION.
if set to 3, playback will start from fragment N-3, N being the last fragment of the live playlist.
decreasing this value is likely to cause playback stalls.
liveMaxLatencyDurationCount
(default: Infinity)
maximum delay allowed from edge of live, expressed in multiple of EXT-X-TARGETDURATION.
if set to 10, the player will seek back to liveSyncDurationCount whenever the next fragment to be loaded is older than N-10, N being the last fragment of the live playlist.
If set, this value must be stricly superior to liveSyncDurationCount
a value too close from liveSyncDurationCount is likely to cause playback stalls.
liveSyncDuration
(default: undefined)
Alternative parameter to liveSyncDurationCount, expressed in seconds vs number of segments.
If defined in the configuration object, liveSyncDuration will take precedence over the default liveSyncDurationCount.
You can’t define this parameter and either liveSyncDurationCount or liveMaxLatencyDurationCount in your configuration object at the same time.
A value too low (inferior to ~3 segment durations) is likely to cause playback stalls.
liveMaxLatencyDuration
(default: undefined)
Alternative parameter to liveMaxLatencyDurationCount, expressed in seconds vs number of segments.
If defined in the configuration object, liveMaxLatencyDuration will take precedence over the default liveMaxLatencyDurationCount.
If set, this value must be stricly superior to liveSyncDuration which must be defined as well.
You can’t define this parameter and either liveSyncDurationCount or liveMaxLatencyDurationCount in your configuration object at the same time.
A value too close from liveSyncDuration is likely to cause playback stalls.
maxLiveSyncPlaybackRate
(default: 1 min: 1 max: 2)
When set to a value greater than 1, the latency-controller will adjust video.playbackRate up to maxLiveSyncPlaybackRate to catch up to target latency in a live stream. hls.targetLatency is based on liveSyncDuration|Count or manifest PART-|HOLD-BACK.
Defaults to 1, which disables playback rate adjustment. Set maxLiveSyncPlaybackRate to a value greater than 1 to enable playback rate adjustment at the live edge.
liveDurationInfinity
(default: false)
Override current Media Source duration to Infinity for a live broadcast.
Useful, if you are building a player which relies on native UI capabilities in modern browsers.
If you want to have a native Live UI in environments like iOS Safari, Safari, Android Google Chrome, etc. set this value to true.
liveBackBufferLength (deprecated)
liveBackBufferLength has been deprecated. Use backBufferLength instead.
enableWorker
(default: true)
Enable WebWorker (if available on browser) for TS demuxing/MP4 remuxing, to improve performance and avoid lag/frame drops.
enableSoftwareAES
(default: true)
Enable to use JavaScript version AES decryption for fallback of WebCrypto API.
startLevel
(default: undefined)
When set, use this level as the default hls.startLevel. Keep in mind that the startLevel set with the API takes precedence over config.startLevel configuration parameter.
fragLoadingTimeOut / manifestLoadingTimeOut / levelLoadingTimeOut
(default: 20000ms for fragment / 10000ms for level and manifest)
URL Loader timeout.
A timeout callback will be triggered if loading duration exceeds this timeout.
no further action will be done : the load operation will not be cancelled/aborted.
It is up to the application to catch this event and treat it as needed.
fragLoadingMaxRetry / manifestLoadingMaxRetry / levelLoadingMaxRetry
(default: 6 / 1 / 4)
Max number of load retries.
fragLoadingMaxRetryTimeout / manifestLoadingMaxRetryTimeout / levelLoadingMaxRetryTimeout
(default: 64000 ms)
Maximum frag/manifest/key retry timeout (in milliseconds) in case I/O errors are met.
This value is used as capping value for exponential grow of loading retry delays, i.e. the retry delay can not be bigger than this value, but overall time will be based on the overall number of retries.
fragLoadingRetryDelay / manifestLoadingRetryDelay / levelLoadingRetryDelay
(default: 1000 ms)
Initial delay between XMLHttpRequest error and first load retry (in ms).
Any I/O error will trigger retries every 500ms,1s,2s,4s,8s, … capped to fragLoadingMaxRetryTimeout / manifestLoadingMaxRetryTimeout / levelLoadingMaxRetryTimeout value (exponential backoff).
Prefetch start fragment although media not attached.
startFragPrefetch
(default: false)
Start prefetching start fragment although media not attached yet.
testBandwidth
(default: true)
You must also set startLevel = -1 for this to have any impact. Otherwise, hls.js will load the first level in the manifest and start playback from there. If you do set startLevel = -1, a fragment of the lowest level will be downloaded to establish a bandwidth estimate before selecting the first auto-level.
Disable this test if you’d like to provide your own estimate or use the default abrEwmaDefaultEstimate.
progressive
(default: false)
Enable streaming segment data with fetch loader (experimental).
lowLatencyMode
(default: true)
Enable Low-Latency HLS part playlist and segment loading, and start live streams at playlist PART-HOLD-BACK rather than HOLD-BACK.
fpsDroppedMonitoringPeriod
(default: 5000)
The period used by the default fpsController to observe fpsDroppedMonitoringThreshold.
fpsDroppedMonitoringThreshold
(default: 0.2)
The ratio of frames dropped to frames elapsed within fpsDroppedMonitoringPeriod needed for the default fpsController to emit an FPS_DROP event.
appendErrorMaxRetry
(default: 3)
Max number of sourceBuffer.appendBuffer() retry upon error.
Such error could happen in loop with UHD streams, when internal buffer is full. (Quota Exceeding Error will be triggered). In that case we need to wait for the browser to evict some data before being able to append buffer correctly.
loader
(default: standard XMLHttpRequest-based URL loader)
Override standard URL loader by a custom one. Use composition and wrap internal implementation which could be exported by Hls.DefaultConfig.loader.
Could be useful for P2P or stubbing (testing).
Use this, if you want to overwrite both the fragment and the playlist loader.
Note: If fLoader or pLoader are used, they overwrite loader!
var customLoader = function () { /** * Calling load() will start retrieving content located at given URL (HTTP GET). * * @param {object} context - loader context * @param {string} context.url - target URL * @param {string} context.responseType - loader response type (arraybuffer or default response type for playlist) * @param {number} [context.rangeStart] - start byte range offset * @param {number} [context.rangeEnd] - end byte range offset * @param {Boolean} [context.progressData] - true if onProgress should report partial chunk of loaded content * @param {object} config - loader config params * @param {number} config.maxRetry - Max number of load retries * @param {number} config.timeout - Timeout after which `onTimeOut` callback will be triggered (if loading is still not finished after that delay) * @param {number} config.retryDelay - Delay between an I/O error and following connection retry (ms). This to avoid spamming the server * @param {number} config.maxRetryDelay - max connection retry delay (ms) * @param {object} callbacks - loader callbacks * @param {onSuccessCallback} callbacks.onSuccess - Callback triggered upon successful loading of URL. * @param {onProgressCallback} callbacks.onProgress - Callback triggered while loading is in progress. * @param {onErrorCallback} callbacks.onError - Callback triggered if any I/O error is met while loading fragment. * @param {onTimeoutCallback} callbacks.onTimeout - Callback triggered if loading is still not finished after a certain duration. @callback onSuccessCallback @param response {object} - response data @param response.url {string} - response URL (which might have been redirected) @param response.data {string/arraybuffer/sharedarraybuffer} - response data (reponse type should be as per context.responseType) @param stats {LoadStats} - loading stats @param stats.aborted {boolean} - must be set to true once the request has been aborted @param stats.loaded {number} - nb of loaded bytes @param stats.total {number} - total nb of bytes @param stats.retry {number} - number of retries performed @param stats.chunkCount {number} - number of chunk progress events @param stats.bwEstimate {number} - download bandwidth in bits/s @param stats.loading { start: 0, first: 0, end: 0 } @param stats.parsing { start: 0, end: 0 } @param stats.buffering { start: 0, first: 0, end: 0 } @param context {object} - loader context @param networkDetails {object} - loader network details (the xhr for default loaders) @callback onProgressCallback @param stats {LoadStats} - loading stats @param context {object} - loader context @param data {string/arraybuffer/sharedarraybuffer} - onProgress data (should be defined only if context.progressData === true) @param networkDetails {object} - loader network details (the xhr for default loaders) @callback onErrorCallback @param error {object} - error data @param error.code {number} - error status code @param error.text {string} - error description @param context {object} - loader context @param networkDetails {object} - loader network details (the xhr for default loaders) @callback onTimeoutCallback @param stats {LoadStats} - loading stats @param context {object} - loader context */ this.load = function (context, config, callbacks) {}; /** Abort any loading in progress. */ this.abort = function () {}; /** Destroy loading context. */ this.destroy = function () {}; };
fLoader
(default: undefined)
This enables the manipulation of the fragment loader.
Note: This will overwrite the default loader, as well as your own loader function (see above).
var customFragmentLoader = function () { // See `loader` for details. };
pLoader
(default: undefined)
This enables the manipulation of the playlist loader.
Note: This will overwrite the default loader, as well as your own loader function (see above).
var customPlaylistLoader = function () { // See `loader` for details. };
if you want to just make slight adjustments to existing loader implementation, you can also eventually override it, see an example below :
// special playlist post processing function function process(playlist) { return playlist; } class pLoader extends Hls.DefaultConfig.loader { constructor(config) { super(config); var load = this.load.bind(this); this.load = function (context, config, callbacks) { if (context.type == 'manifest') { var onSuccess = callbacks.onSuccess; callbacks.onSuccess = function (response, stats, context) { response.data = process(response.data); onSuccess(response, stats, context); }; } load(context, config, callbacks); }; } } var hls = new Hls({ pLoader: pLoader, });
xhrSetup
(default: undefined)
XMLHttpRequest customization callback for default XHR based loader.
Parameter should be a function with two arguments (xhr: XMLHttpRequest, url: string).
If xhrSetup is specified, default loader will invoke it before calling xhr.send().
This allows user to easily modify/setup XHR. See example below.
var config = { xhrSetup: function (xhr, url) { xhr.withCredentials = true; // do send cookies }, };
fetchSetup
(default: undefined)
Fetch customization callback for Fetch based loader.
Parameter should be a function with two arguments (context and Request Init Params).
If fetchSetup is specified and Fetch loader is used, fetchSetup will be triggered to instantiate Request Object.
This allows user to easily tweak Fetch loader. See example below.
var config = { fetchSetup: function (context, initParams) { // Always send cookies, even for cross-origin calls. initParams.credentials = 'include'; return new Request(context.url, initParams); }, };
abrController
(default: internal ABR controller)
Customized Adaptive Bitrate Streaming Controller.
Parameter should be a class providing a getter/setter and a destroy() method:
- get/set
nextAutoLevel: return next auto-quality level/force next auto-quality level that should be returned (currently used for emergency switch down) destroy(): should clean-up all used resources
For hls.bandwidthEstimate() to return an estimate from your custom controller, it will also need to satisfy abrController.bwEstimator.getEstimate().
bufferController
(default: internal buffer controller)
Customized buffer controller.
A class in charge of managing SourceBuffers.
capLevelController
(default: internal cap level controller)
Customized level capping controller.
A class in charge of setting hls.autoLevelCapping to limit ABR level selection based on player size.
Enable the default cap level controller by setting capLevelToPlayerSize to true.
fpsController
(default: internal fps controller)
Customized fps controller.
A class in charge of monitoring frame rate, that emits FPS_DROP events when frames dropped exceeds configured threshold.
Enable the default fps controller by setting capLevelOnFPSDrop to true.
timelineController
(default: internal track timeline controller)
Customized text track synchronization controller.
Parameter should be a class with a destroy() method:
destroy(): should clean-up all used resources
enableDateRangeMetadataCues
(default: true)
whether or not to add, update, and remove cues from the metadata TextTrack for EXT-X-DATERANGE playlist tags
parameter should be a boolean
enableEmsgMetadataCues
(default: true)
whether or not to add, update, and remove cues from the metadata TextTrack for ID3 Timed Metadata found in CMAF Event Message (emsg) boxes
parameter should be a boolean
enableID3MetadataCues
(default: true)
whether or not to add, update, and remove cues from the metadata TextTrack for ID3 Timed Metadata found in audio and MPEG-TS containers
parameter should be a boolean
enableWebVTT
(default: true)
whether or not to enable WebVTT captions on HLS
parameter should be a boolean
enableIMSC1
(default: true)
whether or not to enable IMSC1 captions on HLS
parameter should be a boolean
enableCEA708Captions
(default: true)
whether or not to enable CEA-708 captions
parameter should be a boolean
captionsTextTrack1Label
(default: English)
Label for the text track generated for CEA-708 captions track 1. This is how it will appear in the browser’s native menu for subtitles and captions.
parameter should be a string
captionsTextTrack1LanguageCode
(default: en)
RFC 3066 language code for the text track generated for CEA-708 captions track 1.
parameter should be a string
captionsTextTrack2Label
(default: Spanish)
Label for the text track generated for CEA-708 captions track 2. This is how it will appear in the browser’s native menu for subtitles and captions.
parameter should be a string
captionsTextTrack2LanguageCode
(default: es)
RFC 3066 language code for the text track generated for CEA-708 captions track 2.
parameter should be a string
captionsTextTrack3Label
(default: Unknown CC)
Label for the text track generated for CEA-708 captions track 3. This is how it will appear in the browser’s native menu for subtitles and captions.
parameter should be a string
captionsTextTrack3LanguageCode
(default: «)
RFC 3066 language code for the text track generated for CEA-708 captions track 3.
parameter should be a string
captionsTextTrack4Label
(default: Unknown CC)
Label for the text track generated for CEA-708 captions track 4. This is how it will appear in the browser’s native menu for subtitles and captions.
parameter should be a string
captionsTextTrack4LanguageCode
(default: «)
RFC 3066 language code for the text track generated for CEA-708 captions track 4.
parameter should be a string
renderTextTracksNatively
(default: true)
Whether or not render captions natively using the HTMLMediaElement’s TextTracks. Disable native captions rendering
when you want to handle rending of track and track cues using Hls.Events.NON_NATIVE_TEXT_TRACKS_FOUND and Hls.Events.CUES_PARSED events.
parameter should be a boolean
stretchShortVideoTrack
(default: false)
If a segment’s video track is shorter than its audio track by > maxBufferHole, extend the final video frame’s duration to match the audio track’s duration.
This helps playback continue in certain cases that might otherwise get stuck.
parameter should be a boolean
maxAudioFramesDrift
(default: 1)
Browsers are really strict about audio frames timings.
They usually play audio frames one after the other, regardless of the timestamps advertised in the fmp4.
If audio timestamps are not consistent (consecutive audio frames too close or too far from each other), audio will easily drift.
hls.js is restamping audio frames so that the distance between consecutive audio frame remains constant.
if the distance is larger than the max allowed drift, hls.js will either
- drop the next audio frame if distance is too small (if next audio frame timestamp is smaller than expected time stamp — max allowed drift)
- insert silent frames if distance is too big (next audio frame timestamp is bigger than expected timestamp + max allowed drift)
parameter should be an integer representing the max number of audio frames allowed to drift.
keep in mind that one audio frame is 1024 audio samples (if using AAC), at 44.1 kHz, it gives 1024/44100 = 23ms
forceKeyFrameOnDiscontinuity
(default: true)
Whether or not to force having a key frame in the first AVC sample after a discontinuity.
If set to true, after a discontinuity, the AVC samples without any key frame will be dropped until finding one that contains a key frame.
If set to false, all AVC samples will be kept, which can help avoid holes in the stream.
Setting this parameter to false can also generate decoding weirdness when switching level or seeking.
parameter should be a boolean
abrEwmaFastLive
(default: 3.0)
Fast bitrate Exponential moving average half-life, used to compute average bitrate for Live streams.
Half of the estimate is based on the last abrEwmaFastLive seconds of sample history.
Each of the sample is weighted by the fragment loading duration.
parameter should be a float greater than 0
abrEwmaSlowLive
(default: 9.0)
Slow bitrate Exponential moving average half-life, used to compute average bitrate for Live streams.
Half of the estimate is based on the last abrEwmaSlowLive seconds of sample history.
Each of the sample is weighted by the fragment loading duration.
parameter should be a float greater than abrEwmaFastLive
abrEwmaFastVoD
(default: 3.0)
Fast bitrate Exponential moving average half-life, used to compute average bitrate for VoD streams.
Half of the estimate is based on the last abrEwmaFastVoD seconds of sample history.
Each of the sample is weighted by the fragment loading duration.
parameter should be a float greater than 0
abrEwmaSlowVoD
(default: 9.0)
Slow bitrate Exponential moving average half-life, used to compute average bitrate for VoD streams.
Half of the estimate is based on the last abrEwmaSlowVoD seconds of sample history.
Each of the sample is weighted by the fragment loading duration.
parameter should be a float greater than abrEwmaFastVoD
abrEwmaDefaultEstimate
(default: 500000)
Default bandwidth estimate in bits/s prior to collecting fragment bandwidth samples.
parameter should be a float
abrBandWidthFactor
(default: 0.95)
Scale factor to be applied against measured bandwidth average, to determine whether we can stay on current or lower quality level.
If abrBandWidthFactor * bandwidth average > level.bitrate then ABR can switch to that level providing that it is equal or less than current level.
abrBandWidthUpFactor
(default: 0.7)
Scale factor to be applied against measured bandwidth average, to determine whether we can switch up to a higher quality level.
If abrBandWidthUpFactor * bandwidth average > level.bitrate then ABR can switch up to that quality level.
abrMaxWithRealBitrate
(default: false)
max bitrate used in ABR by avg measured bitrate
i.e. if bitrate signaled in variant manifest for a given level is 2Mb/s but average bitrate measured on this level is 2.5Mb/s,
then if config value is set to true, ABR will use 2.5 Mb/s for this quality level.
minAutoBitrate
(default: 0)
Return the capping/min bandwidth value that could be used by automatic level selection algorithm.
Useful when browser or tab of the browser is not in the focus and bandwidth drops
emeEnabled
(default: false)
Set to true to enable DRM key system access and license retrieval.
widevineLicenseUrl (deprecated)
(default: undefined)
widevineLicenseUrl has been deprecated. Use drmSystems['com.widevine.alpha'].licenseUrl instead.
licenseXhrSetup
(default: undefined, type (xhr: XMLHttpRequest, url: string, keyContext: MediaKeySessionContext, licenseChallenge: Uint8Array) => void | Uint8Array | Promise<Uint8Array | void>)
A pre-processor function for modifying license requests. The license request URL, request headers, and payload can all be modified prior to sending the license request, based on operating conditions, the current key-session, and key-system.
var config = { licenseXhrSetup: function (xhr, url, keyContext, licenseChallenge) { let payload = licenseChallenge; // Send cookies with request xhr.withCredentials = true; // Call open to change the method (default is POST), modify the url, or set request headers xhr.open('POST', url, true); // call xhr.setRequestHeader after xhr.open otherwise licenseXhrSetup will throw and be called a second time after HLS.js call xhr.open if (keyContext.keySystem === 'com.apple.fps') { xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json'); payload = JSON.stringify({ keyData: base64Encode(keyContext.decryptdata?.keyId), licenseChallenge: base64Encode(licenseChallenge), }); } else { xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/octet-stream'); } // Return the desired payload or a Promise<Uint8Array>. // Not returning a value, or returning `undefined` or` Promise<void>` will result in the `licenseChallenge` being used. return fetchDRMToken(this.authData).then((result) => { xhr.setRequestHeader('token', token); return payload; }); }, };
licenseResponseCallback
(default: undefined, type (xhr: XMLHttpRequest, url: string, keyContext: MediaKeySessionContext) => data: ArrayBuffer)
A post-processor function for modifying the license response before passing it to the key-session (MediaKeySession.update).
var config = { licenseResponseCallback: function (xhr, url, keyContext) { const keySystem = keyContext.keySystem; const response = xhr.response; if (keyContext.keySystem === 'com.apple.fps') { try { const responseObject = JSON.parse( new TextDecoder().decode(response).trim(); ); const keyResponse = responseObject['fairplay-streaming-response']['streaming-keys'][0]; return base64Decode(keyResponse.ckc); } catch (error) { console.error(error); } } return response; }
drmSystems
(default: {})
Define license settings for given key-systems according to your own DRM provider. Ex:
drmSystems: { 'com.apple.fps': { licenseUrl: 'https://your-fps-license-server/path', serverCertificateUrl: 'https://your-fps-license-server/certificate/path', }, 'com.widevine.alpha': { licenseUrl: 'https://your-widevine-license-server/path' } }
Supported key-systems include ‘com.apple.fps’, ‘com.microsoft.playready’, ‘com.widevine.alpha’, and ‘org.w3.clearkey’. Mapping to other values in key-system access requests can be done by customizing requestMediaKeySystemAccessFunc.
When loading content with DRM Keys, the player will only request access
to key-systems for the Session Keys or Playlist Keys for which there are
also key-systems defined in drmSystems.
`drmSystems[KEY-SYSTEM].generateRequest
(default: undefined, type (initDataType: string, initData: ArrayBuffer | null, keyContext: MediaKeySessionContext) => { initDataType: string; initData: ArrayBuffer | null } | undefined)
Used to map initData or generate initData for playlist keys before
MediaKeySession generateRequest is called.
drmSystemOptions
(default: {})
Define optional MediaKeySystemConfiguration arguments to be passed to requestMediaKeySystemAccess. Ex:
{ audioRobustness: 'SW_SECURE_CRYPTO', videoRobustness: 'SW_SECURE_CRYPTO', audioEncryptionScheme: null, videoEncryptionScheme: null, persistentState: 'not-allowed'; distinctiveIdentifier: 'not-allowed'; sessionTypes: ['temporary']; sessionType: 'temporary'; }
With the default argument, '' will be specified for each option (i.e. no specific robustness required).
requestMediaKeySystemAccessFunc
(default: A function that returns the result of window.navigator.requestMediaKeySystemAccess.bind(window.navigator) or null)
Allows for the customization of window.navigator.requestMediaKeySystemAccess. This can be used to map key-system access request to from a supported value to a custom one:
var hls new Hls({ requestMediaKeySystemAccessFunc: (keySystem, supportedConfigurations) => { if (keySystem === 'com.microsoft.playready') { keySystem = 'com.microsoft.playready.recommendation'; } return navigator.requestMediaKeySystemAccess(keySystem, supportedConfigurations); } });
cmcd
When the cmcd object is defined, Common Media Client Data (CMCD)
data will be passed on all media requests (manifests, playlists, a/v segments, timed text). It’s configuration values are:
sessionId: The CMCD session id. One will be automatically generated if none is provided.contentId: The CMCD content id.useHeaders: Send CMCD data in request headers instead of as query args. Defaults tofalse.
Video Binding/Unbinding API
hls.attachMedia(videoElement)
Calling this method will:
- bind videoElement and hls instance,
- create MediaSource and set it as video source
- once MediaSource object is successfully created, MEDIA_ATTACHED event will be fired.
hls.detachMedia()
Calling this method will:
- unbind VideoElement from hls instance,
- signal the end of the stream on MediaSource
- reset video source (
video.src = '')
hls.media
- get: Return the bound videoElement from the hls instance
Quality switch Control API
By default, hls.js handles quality switch automatically, using heuristics based on fragment loading bitrate and quality level bandwidth exposed in the variant manifest.
It is also possible to manually control quality switch using below API.
hls.levels
- get: Return array of available quality levels.
hls.currentLevel
- get: Return current playback quality level.
- set: Trigger an immediate quality level switch to new quality level. This will abort the current fragment request if any, flush the whole buffer, and fetch fragment matching with current position and requested quality level.
Set to -1 for automatic level selection.
hls.nextLevel
- get: Return next playback quality level (playback quality level for next buffered fragment). Return
-1if next fragment not buffered yet. - set: Trigger a quality level switch for next fragment. This could eventually flush already buffered next fragment.
Set to -1 for automatic level selection.
hls.loadLevel
- get: return last loaded fragment quality level.
- set: set quality level for next loaded fragment.
Set to -1 for automatic level selection.
hls.nextLoadLevel
- get: Return quality level that will be used to load next fragment.
- set: Force quality level for next loaded fragment. Quality level will be forced only for that fragment.
After a fragment at this quality level has been loaded,hls.loadLevelwill prevail.
hls.firstLevel
- get: First level index (index of first level appearing in Manifest. it is usually defined as start level hint for player).
hls.startLevel
- get/set: Start level index (level of first fragment that will be played back).
- if not overridden by user: first level appearing in manifest will be used as start level.
- if -1: automatic start level selection, playback will start from level matching download bandwidth (determined from download of first segment).
Default value is hls.firstLevel.
hls.autoLevelEnabled
- get: Tell whether auto level selection is enabled or not.
hls.autoLevelCapping
- get/set: Capping/max level value that could be used by ABR Controller.
Default value is -1 (no level capping).
hls.maxHdcpLevel
- get/set: The maximum HDCP-LEVEL allowed to be selected by auto level selection. Must be a valid HDCP-LEVEL value (‘NONE’, ‘TYPE-0’, ‘TYPE-1’, ‘TYPE-2’), or null (default).
hls.maxHdcpLevelis automatically set to the next lowest value when aKEY_SYSTEM_STATUS_OUTPUT_RESTRICTEDerror occurs. To prevent manual selection of levels with specific HDCP-LEVEL attribute values, usehls.removeLevel()onMANIFEST_LOADEDor on error.
Default value is null (no level capping based on HDCP-LEVEL)
hls.capLevelToPlayerSize
- get: Enables or disables level capping. If disabled after previously enabled,
nextLevelSwitchwill be immediately called. - set: Whether level capping is enabled.
Default value is set via capLevelToPlayerSize in config.
hls.bandwidthEstimate
get: Returns the current bandwidth estimate in bits/s, if available. Otherwise, NaN is returned.
hls.removeLevel(levelIndex, urlId)
Remove a loaded level from the list of levels, or a url from a level’s list of redundant urls.
This can be used to remove a rendition or playlist url that errors frequently from the list of levels that a user
or hls.js can choose from.
Modifying the levels this way will result in a Hls.Events.LEVELS_UPDATED event being triggered.
Version Control
Hls.version
Static getter: return hls.js dist version number.
Network Loading Control API
By default, hls.js will automatically start loading quality level playlists, and fragments after Hls.Events.MANIFEST_PARSED event has been triggered (and video element has been attached).
However if config.autoStartLoad is set to false, the following method needs to be called to manually start playlist and fragments loading:
hls.startLoad(startPosition=-1)
Start/restart playlist/fragment loading. this is only effective if MANIFEST_PARSED event has been triggered and video element has been attached to hls object.
startPosition is the initial position in the playlist.
If startPosition is not set to -1, it allows to override default startPosition to the one you want (it will bypass hls.config.liveSync* config params for Live for example, so that user can start playback from whatever position)
hls.stopLoad()
stop playlist/fragment loading. could be resumed later on by calling hls.startLoad()
Audio Tracks Control API
hls.audioTracks
get : array of audio tracks exposed in manifest
hls.audioTrack
get/set : audio track id (returned by)
Subtitle Tracks Control API
hls.subtitleTracks
get : array of subtitle tracks exposed in manifest
hls.subtitleTrack
get/set : subtitle track id (returned by). Returns -1 if no track is visible. Set to -1 to disable all subtitle tracks.
hls.subtitleDisplay
(default: true)
get/set : if set to true the active subtitle track mode will be set to showing and the browser will display the active subtitles. If set to false, the mode will be set to hidden.
Live stream API
hls.liveSyncPosition
get : position of live sync point (ie edge of live position minus safety delay defined by hls.config.liveSyncDuration).
If playback stalls outside the sliding window, or latency exceeds liveMaxLatencyDuration hls.js will seek ahead to
liveSyncPosition to get back in sync with the stream stream.
hls.latency
get : estimated position (in seconds) of live edge (ie edge of live playlist plus time sync playlist advanced)
returns 0 before first playlist is loaded
hls.maxLatency
get : maximum distance from the edge before the player seeks forward to hls.liveSyncPosition
configured using liveMaxLatencyDurationCount (multiple of target duration) or liveMaxLatencyDuration
returns 0 before first playlist is loaded
hls.targetLatency
get : target distance from the edge as calculated by the latency controller
hls.drift
get : the rate at which the edge of the current live playlist is advancing or 1 if there is none
hls.playingDate
get: the datetime value relative to media.currentTime for the active level Program Date Time if present
Runtime Events
hls.js fires a bunch of events, that could be registered and unregistered as below:
function onLevelLoaded(event, data) { var level_duration = data.details.totalduration; } // subscribe event hls.on(Hls.Events.LEVEL_LOADED, onLevelLoaded); // unsubscribe event hls.off(Hls.Events.LEVEL_LOADED, onLevelLoaded); // subscribe for a single event call only hls.once(Hls.Events.LEVEL_LOADED, onLevelLoaded);
Full list of Events is available below:
Hls.Events.MEDIA_ATTACHING— fired before MediaSource is attaching to media element- data: { media }
Hls.Events.MEDIA_ATTACHED— fired when MediaSource has been successfully attached to media element- data: { media }
Hls.Events.MEDIA_DETACHING— fired before detaching MediaSource from media element- data: { }
Hls.Events.MEDIA_DETACHED— fired when MediaSource has been detached from media element- data: { }
Hls.Events.BUFFER_RESET— fired when we buffer is going to be reset- data: { }
Hls.Events.BUFFER_CODECS— fired when we know about the codecs that we need buffers for to push into- data: { audio? :
[Track], video? :[Track]}
- data: { audio? :
Hls.Events.BUFFER_CREATED— fired when sourcebuffers have been created- data: { tracks : { audio? :
[Track], video? :[Track], audiovideo?:[Track]} }
interface Track { id: ‘audio’ | ‘main’, buffer?: SourceBuffer, container: string, codec?: string, initSegment?: Uint8Array, levelCodec?: string, metadata?: any }
- data: { tracks : { audio? :
Hls.Events.BUFFER_APPENDING— fired when we append a segment to the buffer- data: { parent, type, frag, part, chunkMeta, data }
Hls.Events.BUFFER_APPENDED— fired when we are done with appending a media segment to the buffer- data: { parent : playlist type triggered
BUFFER_APPENDING, type, frag, part, chunkMeta, timeRanges : { video?: TimeRange, audio?: TimeRange, audiovideo?: TimeRange } }
- data: { parent : playlist type triggered
Hls.Events.BUFFER_EOS— fired when the stream is finished and we want to notify the media buffer that there will be no more data- data: { type: SourceBufferName }
Hls.Events.BUFFER_FLUSHING— fired when the media buffer should be flushed- data: { startOffset, endOffset, type: SourceBufferName }
Hls.Events.BUFFER_FLUSHED— fired when the media buffer has been flushed- data: { type: SourceBufferName }
Hls.Events.BACK_BUFFER_REACHED— fired when the back buffer is reached as defined by the backBufferLength config option- data: { bufferEnd: number }
Hls.Events.MANIFEST_LOADING— fired to signal that a manifest loading starts- data: { url : manifestURL }
Hls.Events.MANIFEST_LOADED— fired after manifest has been loaded- data: { levels : [available quality levels], audioTracks : [available audio tracks], captions? [available closed-captions media], subtitles?: [available subtitle tracks], url : manifestURL, stats : [LoaderStats], sessionData: [parsed #EXT-X-SESSION-DATA], networkDetails: [Loader specific object for debugging (XMLHttpRequest or fetch Response)]}
Hls.Events.MANIFEST_PARSED— fired after manifest has been parsed- data: { levels : [ available quality levels ], firstLevel : index of first quality level appearing in Manifest, audioTracks, subtitleTracks, stats, audio: boolean, video: boolean, altAudio: boolean }
Hls.Events.LEVEL_SWITCHING— fired when a level switch is requested- data: {
leveland Level object properties (please see below for more information) }
- data: {
Hls.Events.LEVEL_SWITCHED— fired when a level switch is effective- data: { level : id of new level }
Hls.Events.LEVEL_LOADING— fired when a level playlist is requested (unless it is the only media playlist loaded viahls.loadSource())- data: { url : level URL, level : id of level being loaded, deliveryDirectives: LL-HLS delivery directives or
nullwhen blocking reload is not supported }
- data: { url : level URL, level : id of level being loaded, deliveryDirectives: LL-HLS delivery directives or
Hls.Events.LEVEL_LOADED— fired when a level playlist loading finishes- data: { details : LevelDetails, level : id of loaded level, stats : [LoadStats] }
Hls.Events.LEVEL_UPDATED— fired when a level’s details have been updated based on previous details, after it has been loaded- data: { details : LevelDetails, level : id of updated level }
Hls.Events.LEVEL_PTS_UPDATED— fired when a level’s PTS information has been updated after parsing a fragment- data: { details : LevelDetails, level : id of updated level, drift: PTS drift observed when parsing last fragment, type, start, end }
Hls.Events.LEVELS_UPDATED— fired when a level is removed after callingremoveLevel()- data: { levels : [ available quality levels ] }
Hls.Events.AUDIO_TRACKS_UPDATED— fired to notify that audio track lists has been updated- data: { audioTracks : audioTracks }
Hls.Events.AUDIO_TRACK_SWITCHING— fired when an audio track switching is requested- data: { id : audio track id, type : playlist type (‘AUDIO’ | ‘main’), url : audio track URL }
Hls.Events.AUDIO_TRACK_SWITCHED— fired when an audio track switch actually occurs- data: { id : audio track id }
Hls.Events.AUDIO_TRACK_LOADING— fired when an audio track loading starts- data: { url : audio track URL, id : audio track id }
Hls.Events.AUDIO_TRACK_LOADED— fired when an audio track loading finishes- data: { details : LevelDetails, id : audio track id, stats : [LoadStats] }
Hls.Events.SUBTITLE_TRACKS_UPDATED— fired to notify that subtitle track lists has been updated- data: { subtitleTracks : subtitleTracks }
Hls.Events.SUBTITLE_TRACK_SWITCH— fired when a subtitle track switch occurs- data: { id : subtitle track id, type? : playlist type (‘SUBTITLES’ | ‘CLOSED-CAPTIONS’), url? : subtitle track URL }
Hls.Events.SUBTITLE_TRACK_LOADING— fired when a subtitle track loading starts- data: { url : audio track URL, id : audio track id }
Hls.Events.SUBTITLE_TRACK_LOADED— fired when a subtitle track loading finishes- data: { details : LevelDetails, id : subtitle track id, stats : [LoadStats] }
Hls.Events.SUBTITLE_FRAG_PROCESSED— fired when a subtitle fragment has been processed- data: { success : boolean, frag : [the processed fragment object], error?: [error parsing subtitles if any] }
Hls.Events.INIT_PTS_FOUND— fired when the first timestamp is found- data: { d : demuxer id, initPTS: initPTS, timescale: timescale, frag : fragment object }
Hls.Events.FRAG_LOADING— fired when a fragment loading starts- data: { frag : fragment object, targetBufferTime: number | null [The unbuffered time that we expect to buffer with this fragment] }
Hls.Events.FRAG_LOAD_PROGRESS— [deprecated]Hls.Events.FRAG_LOAD_EMERGENCY_ABORTED— Identifier for fragment load aborting for emergency switch down- data: { frag : fragment object }
Hls.Events.FRAG_LOADED— fired when a fragment loading is completed- data: { frag : fragment object, payload : fragment payload, stats : [LoadStats]}
Hls.Events.FRAG_DECRYPTED— fired when a fragment decryption is completed- data: { id : demuxer id, frag : fragment object, payload : fragment payload, stats : { tstart, tdecrypt}}
Hls.Events.FRAG_PARSING_INIT_SEGMENT— fired when Init Segment has been extracted from fragment- data: { id: demuxer id, frag : fragment object, moov : moov MP4 box, codecs : codecs found while parsing fragment }
Hls.Events.FRAG_PARSING_USERDATA— fired when parsing sei text is completed- data: { id : demuxer id, frag: fragment object, samples : [ sei samples pes ], details: LevelDetails }
Hls.Events.FRAG_PARSING_METADATA— fired when parsing ID3 is completed- data: { id: demuxer id, frag : fragment object, samples : [ ID3 pes — pts and dts timestamp are relative, values are in seconds], details: LevelDetails }
Hls.Events.FRAG_PARSING_DATA— [deprecated]Hls.Events.FRAG_PARSED— fired when fragment parsing is completed- data: { frag : fragment object, partIndex }
Hls.Events.FRAG_BUFFERED— fired when fragment remuxed MP4 boxes have all been appended into SourceBuffer- data: { id: demuxer id, frag : fragment object, stats : [LoadStats] }
Hls.Events.FRAG_CHANGED— fired when fragment matching with current video position is changing- data: { id : demuxer id, frag : fragment object }
Hls.Events.FPS_DROP— triggered when FPS drop in last monitoring period is higher than given threshold- data: { curentDropped : nb of dropped frames in last monitoring period, currentDecoded : nb of decoded frames in last monitoring period, totalDroppedFrames : total dropped frames on this video element }
Hls.Events.FPS_DROP_LEVEL_CAPPING— triggered when FPS drop triggers auto level capping- data: { level: suggested new auto level capping by fps controller, droppedLevel : level has too many dropped frames and will be restricted }
Hls.Events.ERROR— Identifier for an error event- data: { type : error type, details : error details, fatal : is error fatal or not, other error specific data }
Hls.Events.DESTROYING— fired when hls.js instance starts destroying. Different fromMEDIA_DETACHEDas one could want to detach and reattach a video to the instance of hls.js to handle mid-rolls for example- data: { }
Hls.Events.KEY_LOADING— fired when a decryption key loading starts- data: { frag : fragment object }
Hls.Events.KEY_LOADED— fired when a decryption key loading is completed- data: { frag : fragment object }
Hls.Events.STREAM_STATE_TRANSITION— [deprecated]Hls.Events.NON_NATIVE_TEXT_TRACKS_FOUND— WhenrenderTextTracksNativelyisfalse, this event will fire when a new captions or subtitle track is found, in the place of adding a TextTrack to the video element.- data: { tracks: Array<{ label, kind, default, subtitleTrack }> }
Hls.Events.CUES_PARSED— WhenrenderTextTracksNativelyisfalse, this event will fire when new captions or subtitle cues are parsed.- data: { type, cues, track } }
Creating a Custom Loader
You can use the internal loader definition for your own implementation via the static getter Hls.DefaultConfig.loader.
Example:
let myHls = new Hls({ pLoader: function (config) { let loader = new Hls.DefaultConfig.loader(config); Object.defineProperties(this, { stats: { get: () => loader.stats, }, context: { get: () => loader.context, }, }); this.abort = () => loader.abort(); this.destroy = () => loader.destroy(); this.load = (context, config, callbacks) => { let { type, url } = context; if (type === 'manifest') { console.log(`Manifest ${url} will be loaded.`); } loader.load(context, config, callbacks); }; }, });
Alternatively, environments that support ES6 classes can extends the loader directly:
import Hls from 'hls.js'; let myHls = new Hls({ pLoader: class CustomLoader extends Hls.DefaultConfig.loader { load(context, config, callbacks) { let { type, url } = context; // Custom behavior super.load(context, config, callbacks); } }, });
Errors
Full list of errors is described below:
Network Errors
Hls.ErrorDetails.MANIFEST_LOAD_ERROR— raised when manifest loading fails because of a network error- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.MANIFEST_LOAD_ERROR, fatal :true, url : manifest URL, response : { code: error code, text: error text }, loader : URL loader }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.MANIFEST_LOAD_TIMEOUT— raised when manifest loading fails because of a timeout- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.MANIFEST_LOAD_TIMEOUT, fatal :true, url : manifest URL, loader : URL loader }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.MANIFEST_PARSING_ERROR— raised when manifest parsing failed to find proper content- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.MANIFEST_PARSING_ERROR, fatal :true, url : manifest URL, reason : parsing error reason }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.LEVEL_EMPTY_ERROR— raised when loaded level contains no fragments- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.LEVEL_EMPTY_ERROR, url: playlist URL, reason: error reason, level: index of the bad level }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.LEVEL_LOAD_ERROR— raised when level loading fails because of a network error- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.LEVEL_LOAD_ERROR, fatal :true, url : level URL, response : { code: error code, text: error text }, loader : URL loader }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.LEVEL_LOAD_TIMEOUT— raised when level loading fails because of a timeout- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.LEVEL_LOAD_TIMEOUT, fatal :false, url : level URL, loader : URL loader }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.LEVEL_PARSING_ERROR— raised when level parsing failed or found invalid content- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.LEVEL_PARSING_ERROR, fatal :false, url : level URL, error: Error }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.AUDIO_TRACK_LOAD_ERROR— raised when audio playlist loading fails because of a network error- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.AUDIO_TRACK_LOAD_ERROR, fatal :false, url : audio URL, response : { code: error code, text: error text }, loader : URL loader }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.AUDIO_TRACK_LOAD_TIMEOUT— raised when audio playlist loading fails because of a timeout- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.AUDIO_TRACK_LOAD_TIMEOUT, fatal :false, url : audio URL, loader : URL loader }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.SUBTITLE_LOAD_ERROR— raised when subtitle playlist loading fails because of a network error- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.SUBTITLE_LOAD_ERROR, fatal :false, url, response : { code: error code, text: error text }, loader : URL loader }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.SUBTITLE_TRACK_LOAD_TIMEOUT— raised when subtitle playlist loading fails because of a timeout- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.SUBTITLE_TRACK_LOAD_TIMEOUT, fatal :false, url, loader : URL loader }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.FRAG_LOAD_ERROR— raised when fragment loading fails because of a network error- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.FRAG_LOAD_ERROR, fatal :trueorfalse, frag : fragment object, response : { code: error code, text: error text } }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.FRAG_LOAD_TIMEOUT— raised when fragment loading fails because of a timeout- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.FRAG_LOAD_TIMEOUT, fatal :trueorfalse, frag : fragment object }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_LOAD_ERROR— raised when decrypt key loading fails because of a network error- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_LOAD_ERROR, fatal :false, frag : fragment object, response : { code: error code, text: error text } }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_LOAD_TIMEOUT— raised when decrypt key loading fails because of a timeout- data: { type :
NETWORK_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_LOAD_TIMEOUT, fatal :true, frag : fragment object }
- data: { type :
Media Errors
Hls.ErrorDetails.MANIFEST_INCOMPATIBLE_CODECS_ERROR— raised when manifest only contains quality level with codecs incompatible with MediaSource Engine.- data: { type :
MEDIA_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.MANIFEST_INCOMPATIBLE_CODECS_ERROR, fatal :true, url : manifest URL }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.FRAG_DECRYPT_ERROR— raised when fragment decryption fails- data: { type :
MEDIA_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.FRAG_DECRYPT_ERROR, fatal :true, reason : failure reason }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.FRAG_PARSING_ERROR— raised when fragment parsing fails- data: { type :
MEDIA_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.FRAG_PARSING_ERROR, fatal :trueorfalse, reason : failure reason }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_ADD_CODEC_ERROR— raised when MediaSource fails to add new sourceBuffer- data: { type :
MEDIA_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_ADD_CODEC_ERROR, fatal :false, error : error raised by MediaSource, mimeType: mimeType on which the failure happened }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_INCOMPATIBLE_CODECS_ERROR— raised when no MediaSource(s) could be created based on track codec(s)- data: { type :
MEDIA_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_INCOMPATIBLE_CODECS_ERROR, fatal :true, reason : failure reason }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_APPEND_ERROR— raised when exception is raised while calling buffer append- data: { type :
MEDIA_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_APPEND_ERROR, fatal :trueorfalse, parent : parent stream controller }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_APPENDING_ERROR— raised when exception is raised during buffer appending- data: { type :
MEDIA_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_APPENDING_ERROR, fatal :false}
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_STALLED_ERROR— raised when playback is stuck because buffer is running out of data- data: { type :
MEDIA_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_STALLED_ERROR, fatal :trueorfalse, buffer : buffer length (optional) }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_FULL_ERROR— raised when no data can be appended anymore in media buffer because it is full. this error is recovered by reducing the max buffer length.- data: { type :
MEDIA_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_FULL_ERROR, fatal :false}
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_SEEK_OVER_HOLE— raised after hls.js seeks over a buffer hole to unstuck the playback,- data: { type :
MEDIA_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_SEEK_OVER_HOLE, fatal :false, hole : hole duration }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_NUDGE_ON_STALL— raised when playback is stuck although currentTime is in a buffered area- data: { type :
MEDIA_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.BUFFER_NUDGE_ON_STALL, fatal :true|false} - Not fatal for the first few nudges, but if we reach
config.nudgeMaxRetryattempts and the player is still stalled, thenBUFFER_NUDGE_ON_STALLis fatal
- data: { type :
Mux Errors
Hls.ErrorDetails.REMUX_ALLOC_ERROR— raised when memory allocation fails during remuxing- data: { type :
MUX_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.REMUX_ALLOC_ERROR, fatal :false, bytes : mdat size, reason : failure reason }
- data: { type :
EME Key System Errors
Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_NO_KEYS— EME catch-all error- data: { type :
KEY_SYSTEM_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_NO_KEYS, fatal :true, error: Error }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_NO_ACCESS— EME MediaKeyFuncrequestMediaKeySystemAccess(keySystem, supportedConfigurations)failed to access key-system- data: { type :
KEY_SYSTEM_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_NO_ACCESS, fatal :true, error: Error }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_NO_SESSION— MediaKeySessiongenerateRequest(initDataType, initData)failed- data: { type :
KEY_SYSTEM_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_NO_SESSION, fatal :false, error: Error }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_NO_CONFIGURED_LICENSE— Player configuration is missingdrmSystemskey-system license options- data: { type :
KEY_SYSTEM_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_NO_CONFIGURED_LICENSE, fatal :false}
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_LICENSE_REQUEST_FAILED— Key-system license request failed (fails on first status 4xx, or after 3 tries (EMEController MAX_LICENSE_REQUEST_FAILURES))- data: { type :
KEY_SYSTEM_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_LICENSE_REQUEST_FAILED, fatal :true, networkDetails: XMLHttpRequest }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_SERVER_CERTIFICATE_REQUEST_FAILED— Key-system certificate request failed- data: { type :
KEY_SYSTEM_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_SERVER_CERTIFICATE_REQUEST_FAILED, fatal :true, networkDetails: XMLHttpRequest }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_SERVER_CERTIFICATE_UPDATE_FAILED—MediaKeys.setServerCertificate(certificateData)failed- data: { type :
KEY_SYSTEM_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_SERVER_CERTIFICATE_UPDATE_FAILED, fatal :true, error: Error }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_SESSION_UPDATE_FAILED— MediaKeySessionupdate(licenseResponse|acknowledged)failed- data: { type :
KEY_SYSTEM_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_SESSION_UPDATE_FAILED, fatal :true, error: Error }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_STATUS_OUTPUT_RESTRICTED— HDCP level output restricted for key-session- data: { type :
KEY_SYSTEM_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_STATUS_OUTPUT_RESTRICTED, fatal :false}
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR— key-session status changed to «internal-error»- data: { type :
KEY_SYSTEM_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.KEY_SYSTEM_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR, fatal :true}
- data: { type :
Other Errors
Hls.ErrorDetails.LEVEL_SWITCH_ERROR— raised when level switching fails- data: { type :
OTHER_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.LEVEL_SWITCH_ERROR, fatal :false, level : failed level index, reason : failure reason }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.INTERNAL_EXCEPTION— raised when an exception occurs in an internal hls.js event handler- data: { type :
OTHER_ERROR, details :Hls.ErrorDetails.INTERNAL_EXCEPTION, fatal :trueorfalse, event : event object or string, err : { message : error message } }
- data: { type :
Hls.ErrorDetails.UNKNOWN— Uncategorized error
Objects
Level
A Level object represents a given quality level.
It contains quality level related info, retrieved from manifest, such as:
- level bitrate
- used codecs
- video width/height
- level name
- level URL
See sample Level object below:
{ url: [ 'http://levelURL.com', 'http://levelURLfailover.com' ], bitrate: 246440, name: "240", codecs: "mp4a.40.5,avc1.42000d", width: 320, height: 136, }
urlis an array that might contains several items if failover/redundant streams are found in the manifest.
LevelDetails
A LevelDetails object contains level details retrieved after level playlist parsing, they are specified below:
- protocol version
- playlist type
- start sequence number
- end sequence number
- level total duration
- level fragment target duration
- array of fragments info
- is this level a live playlist or not?
See sample object below, available after corresponding LEVEL_LOADED event has been fired:
{ version: 3, type: 'VOD', // null if EXT-X-PLAYLIST-TYPE not present startSN: 0, endSN: 50, totalduration: 510, targetduration: 10, fragments: Array(51), live: false }
Fragment
The Fragment object contains fragment related info, such as:
- fragment URL
- fragment duration
- fragment sequence number
- fragment start offset
- level identifier
See sample object below:
{ duration: 10, level: 3, sn: 35, start: 30, url: 'http://fragURL.com' }