As far as HTTP status codes go, 402 is a bit of an odd one (even among 400 error codes). The HTTP 402 or “Payment Required” code isn’t a standard response, and most browsers don’t use it. Therefore, if you see a 402 status, it usually means there was a problem with a payment.
HTTP status 402 is a rare code classified as “experimental” or under development. It was created for future use with microtransactions in mind. However, some developers have already started using it to let users know when there’s a problem with a payment.
Check Out Our Video Guide to the HTTP 402 Status Code
In this article, we’re going to talk about what the 402 “Payment Required” error means and what causes it. Then we’ll go over how to fix this unorthodox HTTP status code. Let’s get to it!
What Does the 402 “Payment Required” Status Mean?
As the web continues to evolve, it’s not uncommon for browsers to add new HTTP error codes to deal with issues that arise. HTTP 402 is a code still being developed and reserved for future use.
The goal of the 402 status code is to help deal with payment issues that might arise in the future when users use microtransactions or digital cash payments through their browsers (if such an implementation arrives).
In 2022, HTTP error 402 is still not widely used, and there’s no convention for what messages might appear when this error pops up.
Some developers use code 402 for different types of errors. The Google Developers API, for example, utilizes the code to signal when a developer exceeds their request limit. Furthermore, platforms such as Stripe and Shopify use error code 402 to let users know when there’s a problem with their payments.
Overall, the meaning of the 402 status can vary depending on which website generates the issue. However, if we’re talking strictly about HTTP status codes, 402 is a type of error that doesn’t have widespread implementation.
As far as HTTP status codes go, 402 is a bit of an odd one (even among 400 error codes). 😅 This guide can help you sort through it 💪.Click to Tweet
What Causes the HTTP 402 Error?
As we mentioned before, HTTP code 402 is still experimental. That means it’s not widely used, and there’s no standard form of implementation for the code among browsers.
Many platforms use error code 402 in the spirit in which it was developed: to signal errors with payments. Two examples that we mentioned before are Shopify and Stripe, which return these error codes when there’s a problem with a payment, such as a card being declined.
By contrast, other platforms use code 402 for internal troubleshooting purposes. Alternatively, they might return the code through their API without showing the HTTP status message to users.
It’s important to understand that these error implementations don’t occur at the browser “level”. For example, when you try to visit a page that doesn’t exist, most browsers will unanimously return a 404 error.
If you run into an issue while making a payment online, that doesn’t mean you’ll see an HTTP 402 error. The message you get will depend on the platform or payment processor that you’re using. If that website doesn’t want to show or doesn’t support a 402 error code, you’ll see another kind of message or HTTP status.
How To Fix the HTTP 402 Error
Since there’s no standard implementation for the 402 error code, there’s also no universal way to solve it. In most cases, if you run into a 402 error code, it will be due to an online payment issue, such as your card being declined.
In that scenario, the online platform or payment processor you’re using will let you know how to proceed. However, you might also run into platforms that use 402 error codes for other types of issues, such as Google Developers.
If you see a 402 error and are unsure what’s causing it, your best bet is to check the documentation for the platform or software you’re using. Failing that, you’ll need to contact support directly to figure out why you’re seeing a 402 error.
If you’re running a WordPress website, your visitors shouldn’t run into 402 error codes since they’re not implemented by most ecommerce plugins (including WooCommerce). HTTP 402 statuses don’t appear out of anywhere, so you shouldn’t have to troubleshoot them on your WordPress site.
If you run into other client-side issues or HTTP error messages while using Kinsta, our support team can help you figure out what’s causing them. You can access our help directly through the MyKinsta dashboard.
You’ll also get access to Kinsta APM. Our Application Performance Monitoring tool can help track your website’s performance and troubleshoot errors!
HTTP status 402 is a rare code classified as “experimental” or under development… but with help from this guide, it doesn’t have to slow down your site ✅Click to Tweet
Summary
There are a lot of HTTP status codes and errors that you’ll run into while browsing online or working on your website. Most of these errors are relatively easy to fix if you understand each code’s meaning. Error 402 is a bit more confusing because it’s still an experimental code without widespread implementation.
If you run into an HTTP 402 error online, the platform or service decided to implement the code internally. Traditionally, 402 errors signal payment failures. However, other platforms might use 402 statuses for different types of technical issues.
Are you looking for an ecommerce hosting solution that can help you out with any technical issues? Check out our Kinsta managed WooCommerce hosting plans and take the stress out of running your online store!
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275 PoPs worldwide
Test it yourself with $20 off your first month of Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is a list of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response status codes. Status codes are issued by a server in response to a client’s request made to the server. It includes codes from IETF Request for Comments (RFCs), other specifications, and some additional codes used in some common applications of the HTTP. The first digit of the status code specifies one of five standard classes of responses. The optional message phrases shown are typical, but any human-readable alternative may be provided, or none at all.
Unless otherwise stated, the status code is part of the HTTP standard (RFC 9110).
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) maintains the official registry of HTTP status codes.[1]
All HTTP response status codes are separated into five classes or categories. The first digit of the status code defines the class of response, while the last two digits do not have any classifying or categorization role. There are five classes defined by the standard:
- 1xx informational response – the request was received, continuing process
- 2xx successful – the request was successfully received, understood, and accepted
- 3xx redirection – further action needs to be taken in order to complete the request
- 4xx client error – the request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled
- 5xx server error – the server failed to fulfil an apparently valid request
1xx informational response
An informational response indicates that the request was received and understood. It is issued on a provisional basis while request processing continues. It alerts the client to wait for a final response. The message consists only of the status line and optional header fields, and is terminated by an empty line. As the HTTP/1.0 standard did not define any 1xx status codes, servers must not[note 1] send a 1xx response to an HTTP/1.0 compliant client except under experimental conditions.
- 100 Continue
- The server has received the request headers and the client should proceed to send the request body (in the case of a request for which a body needs to be sent; for example, a POST request). Sending a large request body to a server after a request has been rejected for inappropriate headers would be inefficient. To have a server check the request’s headers, a client must send
Expect: 100-continueas a header in its initial request and receive a100 Continuestatus code in response before sending the body. If the client receives an error code such as 403 (Forbidden) or 405 (Method Not Allowed) then it should not send the request’s body. The response417 Expectation Failedindicates that the request should be repeated without theExpectheader as it indicates that the server does not support expectations (this is the case, for example, of HTTP/1.0 servers).[2] - 101 Switching Protocols
- The requester has asked the server to switch protocols and the server has agreed to do so.
- 102 Processing (WebDAV; RFC 2518)
- A WebDAV request may contain many sub-requests involving file operations, requiring a long time to complete the request. This code indicates that the server has received and is processing the request, but no response is available yet.[3] This prevents the client from timing out and assuming the request was lost.
- 103 Early Hints (RFC 8297)
- Used to return some response headers before final HTTP message.[4]
2xx success
This class of status codes indicates the action requested by the client was received, understood, and accepted.[1]
- 200 OK
- Standard response for successful HTTP requests. The actual response will depend on the request method used. In a GET request, the response will contain an entity corresponding to the requested resource. In a POST request, the response will contain an entity describing or containing the result of the action.
- 201 Created
- The request has been fulfilled, resulting in the creation of a new resource.[5]
- 202 Accepted
- The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. The request might or might not be eventually acted upon, and may be disallowed when processing occurs.
- 203 Non-Authoritative Information (since HTTP/1.1)
- The server is a transforming proxy (e.g. a Web accelerator) that received a 200 OK from its origin, but is returning a modified version of the origin’s response.[6][7]
- 204 No Content
- The server successfully processed the request, and is not returning any content.
- 205 Reset Content
- The server successfully processed the request, asks that the requester reset its document view, and is not returning any content.
- 206 Partial Content
- The server is delivering only part of the resource (byte serving) due to a range header sent by the client. The range header is used by HTTP clients to enable resuming of interrupted downloads, or split a download into multiple simultaneous streams.
- 207 Multi-Status (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The message body that follows is by default an XML message and can contain a number of separate response codes, depending on how many sub-requests were made.[8]
- 208 Already Reported (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The members of a DAV binding have already been enumerated in a preceding part of the (multistatus) response, and are not being included again.
- 226 IM Used (RFC 3229)
- The server has fulfilled a request for the resource, and the response is a representation of the result of one or more instance-manipulations applied to the current instance.[9]
3xx redirection
This class of status code indicates the client must take additional action to complete the request. Many of these status codes are used in URL redirection.[1]
A user agent may carry out the additional action with no user interaction only if the method used in the second request is GET or HEAD. A user agent may automatically redirect a request. A user agent should detect and intervene to prevent cyclical redirects.[10]
- 300 Multiple Choices
- Indicates multiple options for the resource from which the client may choose (via agent-driven content negotiation). For example, this code could be used to present multiple video format options, to list files with different filename extensions, or to suggest word-sense disambiguation.
- 301 Moved Permanently
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI.
- 302 Found (Previously «Moved temporarily»)
- Tells the client to look at (browse to) another URL. The HTTP/1.0 specification (RFC 1945) required the client to perform a temporary redirect with the same method (the original describing phrase was «Moved Temporarily»),[11] but popular browsers implemented 302 redirects by changing the method to GET. Therefore, HTTP/1.1 added status codes 303 and 307 to distinguish between the two behaviours.[10]
- 303 See Other (since HTTP/1.1)
- The response to the request can be found under another URI using the GET method. When received in response to a POST (or PUT/DELETE), the client should presume that the server has received the data and should issue a new GET request to the given URI.
- 304 Not Modified
- Indicates that the resource has not been modified since the version specified by the request headers If-Modified-Since or If-None-Match. In such case, there is no need to retransmit the resource since the client still has a previously-downloaded copy.
- 305 Use Proxy (since HTTP/1.1)
- The requested resource is available only through a proxy, the address for which is provided in the response. For security reasons, many HTTP clients (such as Mozilla Firefox and Internet Explorer) do not obey this status code.
- 306 Switch Proxy
- No longer used. Originally meant «Subsequent requests should use the specified proxy.»
- 307 Temporary Redirect (since HTTP/1.1)
- In this case, the request should be repeated with another URI; however, future requests should still use the original URI. In contrast to how 302 was historically implemented, the request method is not allowed to be changed when reissuing the original request. For example, a POST request should be repeated using another POST request.
- 308 Permanent Redirect
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI. 308 parallel the behaviour of 301, but does not allow the HTTP method to change. So, for example, submitting a form to a permanently redirected resource may continue smoothly.
4xx client errors
This class of status code is intended for situations in which the error seems to have been caused by the client. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. These status codes are applicable to any request method. User agents should display any included entity to the user.
- 400 Bad Request
- The server cannot or will not process the request due to an apparent client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, size too large, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing).
- 401 Unauthorized
- Similar to 403 Forbidden, but specifically for use when authentication is required and has failed or has not yet been provided. The response must include a WWW-Authenticate header field containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. See Basic access authentication and Digest access authentication. 401 semantically means «unauthorised», the user does not have valid authentication credentials for the target resource.
- Some sites incorrectly issue HTTP 401 when an IP address is banned from the website (usually the website domain) and that specific address is refused permission to access a website.[citation needed]
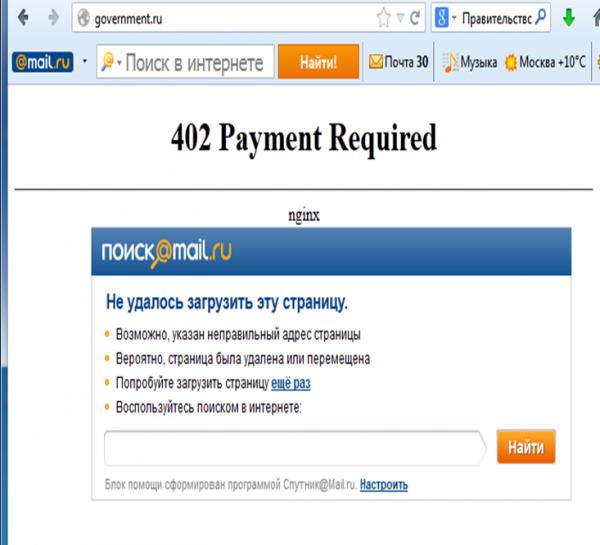
- 402 Payment Required
- Reserved for future use. The original intention was that this code might be used as part of some form of digital cash or micropayment scheme, as proposed, for example, by GNU Taler,[13] but that has not yet happened, and this code is not widely used. Google Developers API uses this status if a particular developer has exceeded the daily limit on requests.[14] Sipgate uses this code if an account does not have sufficient funds to start a call.[15] Shopify uses this code when the store has not paid their fees and is temporarily disabled.[16] Stripe uses this code for failed payments where parameters were correct, for example blocked fraudulent payments.[17]
- 403 Forbidden
- The request contained valid data and was understood by the server, but the server is refusing action. This may be due to the user not having the necessary permissions for a resource or needing an account of some sort, or attempting a prohibited action (e.g. creating a duplicate record where only one is allowed). This code is also typically used if the request provided authentication by answering the WWW-Authenticate header field challenge, but the server did not accept that authentication. The request should not be repeated.
- 404 Not Found
- The requested resource could not be found but may be available in the future. Subsequent requests by the client are permissible.
- 405 Method Not Allowed
- A request method is not supported for the requested resource; for example, a GET request on a form that requires data to be presented via POST, or a PUT request on a read-only resource.
- 406 Not Acceptable
- The requested resource is capable of generating only content not acceptable according to the Accept headers sent in the request. See Content negotiation.
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required
- The client must first authenticate itself with the proxy.
- 408 Request Timeout
- The server timed out waiting for the request. According to HTTP specifications: «The client did not produce a request within the time that the server was prepared to wait. The client MAY repeat the request without modifications at any later time.»
- 409 Conflict
- Indicates that the request could not be processed because of conflict in the current state of the resource, such as an edit conflict between multiple simultaneous updates.
- 410 Gone
- Indicates that the resource requested was previously in use but is no longer available and will not be available again. This should be used when a resource has been intentionally removed and the resource should be purged. Upon receiving a 410 status code, the client should not request the resource in the future. Clients such as search engines should remove the resource from their indices. Most use cases do not require clients and search engines to purge the resource, and a «404 Not Found» may be used instead.
- 411 Length Required
- The request did not specify the length of its content, which is required by the requested resource.
- 412 Precondition Failed
- The server does not meet one of the preconditions that the requester put on the request header fields.
- 413 Payload Too Large
- The request is larger than the server is willing or able to process. Previously called «Request Entity Too Large» in RFC 2616.[18]
- 414 URI Too Long
- The URI provided was too long for the server to process. Often the result of too much data being encoded as a query-string of a GET request, in which case it should be converted to a POST request. Called «Request-URI Too Long» previously in RFC 2616.[19]
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
- The request entity has a media type which the server or resource does not support. For example, the client uploads an image as image/svg+xml, but the server requires that images use a different format.
- 416 Range Not Satisfiable
- The client has asked for a portion of the file (byte serving), but the server cannot supply that portion. For example, if the client asked for a part of the file that lies beyond the end of the file. Called «Requested Range Not Satisfiable» previously RFC 2616.[20]
- 417 Expectation Failed
- The server cannot meet the requirements of the Expect request-header field.[21]
- 418 I’m a teapot (RFC 2324, RFC 7168)
- This code was defined in 1998 as one of the traditional IETF April Fools’ jokes, in RFC 2324, Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol, and is not expected to be implemented by actual HTTP servers. The RFC specifies this code should be returned by teapots requested to brew coffee.[22] This HTTP status is used as an Easter egg in some websites, such as Google.com’s «I’m a teapot» easter egg.[23][24][25] Sometimes, this status code is also used as a response to a blocked request, instead of the more appropriate 403 Forbidden.[26][27]
- 421 Misdirected Request
- The request was directed at a server that is not able to produce a response (for example because of connection reuse).
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
- The request was well-formed but was unable to be followed due to semantic errors.[8]
- 423 Locked (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The resource that is being accessed is locked.[8]
- 424 Failed Dependency (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The request failed because it depended on another request and that request failed (e.g., a PROPPATCH).[8]
- 425 Too Early (RFC 8470)
- Indicates that the server is unwilling to risk processing a request that might be replayed.
- 426 Upgrade Required
- The client should switch to a different protocol such as TLS/1.3, given in the Upgrade header field.
- 428 Precondition Required (RFC 6585)
- The origin server requires the request to be conditional. Intended to prevent the ‘lost update’ problem, where a client GETs a resource’s state, modifies it, and PUTs it back to the server, when meanwhile a third party has modified the state on the server, leading to a conflict.[28]
- 429 Too Many Requests (RFC 6585)
- The user has sent too many requests in a given amount of time. Intended for use with rate-limiting schemes.[28]
- 431 Request Header Fields Too Large (RFC 6585)
- The server is unwilling to process the request because either an individual header field, or all the header fields collectively, are too large.[28]
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons (RFC 7725)
- A server operator has received a legal demand to deny access to a resource or to a set of resources that includes the requested resource.[29] The code 451 was chosen as a reference to the novel Fahrenheit 451 (see the Acknowledgements in the RFC).
5xx server errors
The server failed to fulfil a request.
Response status codes beginning with the digit «5» indicate cases in which the server is aware that it has encountered an error or is otherwise incapable of performing the request. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and indicate whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. Likewise, user agents should display any included entity to the user. These response codes are applicable to any request method.
- 500 Internal Server Error
- A generic error message, given when an unexpected condition was encountered and no more specific message is suitable.
- 501 Not Implemented
- The server either does not recognize the request method, or it lacks the ability to fulfil the request. Usually this implies future availability (e.g., a new feature of a web-service API).
- 502 Bad Gateway
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and received an invalid response from the upstream server.
- 503 Service Unavailable
- The server cannot handle the request (because it is overloaded or down for maintenance). Generally, this is a temporary state.[30]
- 504 Gateway Timeout
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and did not receive a timely response from the upstream server.
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
- The server does not support the HTTP version used in the request.
- 506 Variant Also Negotiates (RFC 2295)
- Transparent content negotiation for the request results in a circular reference.[31]
- 507 Insufficient Storage (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The server is unable to store the representation needed to complete the request.[8]
- 508 Loop Detected (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The server detected an infinite loop while processing the request (sent instead of 208 Already Reported).
- 510 Not Extended (RFC 2774)
- Further extensions to the request are required for the server to fulfill it.[32]
- 511 Network Authentication Required (RFC 6585)
- The client needs to authenticate to gain network access. Intended for use by intercepting proxies used to control access to the network (e.g., «captive portals» used to require agreement to Terms of Service before granting full Internet access via a Wi-Fi hotspot).[28]
Unofficial codes
The following codes are not specified by any standard.
- 419 Page Expired (Laravel Framework)
- Used by the Laravel Framework when a CSRF Token is missing or expired.
- 420 Method Failure (Spring Framework)
- A deprecated response used by the Spring Framework when a method has failed.[33]
- 420 Enhance Your Calm (Twitter)
- Returned by version 1 of the Twitter Search and Trends API when the client is being rate limited; versions 1.1 and later use the 429 Too Many Requests response code instead.[34] The phrase «Enhance your calm» comes from the 1993 movie Demolition Man, and its association with this number is likely a reference to cannabis.[citation needed]
- 430 Request Header Fields Too Large (Shopify)
- Used by Shopify, instead of the 429 Too Many Requests response code, when too many URLs are requested within a certain time frame.[35]
- 450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls (Microsoft)
- The Microsoft extension code indicated when Windows Parental Controls are turned on and are blocking access to the requested webpage.[36]
- 498 Invalid Token (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 498 indicates an expired or otherwise invalid token.[37]
- 499 Token Required (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 499 indicates that a token is required but was not submitted.[37]
- 509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded (Apache Web Server/cPanel)
- The server has exceeded the bandwidth specified by the server administrator; this is often used by shared hosting providers to limit the bandwidth of customers.[38]
- 529 Site is overloaded
- Used by Qualys in the SSLLabs server testing API to signal that the site can’t process the request.[39]
- 530 Site is frozen
- Used by the Pantheon Systems web platform to indicate a site that has been frozen due to inactivity.[40]
- 598 (Informal convention) Network read timeout error
- Used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network read timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.[41]
- 599 Network Connect Timeout Error
- An error used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network connect timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.
Internet Information Services
Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS) web server expands the 4xx error space to signal errors with the client’s request.
- 440 Login Time-out
- The client’s session has expired and must log in again.[42]
- 449 Retry With
- The server cannot honour the request because the user has not provided the required information.[43]
- 451 Redirect
- Used in Exchange ActiveSync when either a more efficient server is available or the server cannot access the users’ mailbox.[44] The client is expected to re-run the HTTP AutoDiscover operation to find a more appropriate server.[45]
IIS sometimes uses additional decimal sub-codes for more specific information,[46] however these sub-codes only appear in the response payload and in documentation, not in the place of an actual HTTP status code.
nginx
The nginx web server software expands the 4xx error space to signal issues with the client’s request.[47][48]
- 444 No Response
- Used internally[49] to instruct the server to return no information to the client and close the connection immediately.
- 494 Request header too large
- Client sent too large request or too long header line.
- 495 SSL Certificate Error
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has provided an invalid client certificate.
- 496 SSL Certificate Required
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when a client certificate is required but not provided.
- 497 HTTP Request Sent to HTTPS Port
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has made a HTTP request to a port listening for HTTPS requests.
- 499 Client Closed Request
- Used when the client has closed the request before the server could send a response.
Cloudflare
Cloudflare’s reverse proxy service expands the 5xx series of errors space to signal issues with the origin server.[50]
- 520 Web Server Returned an Unknown Error
- The origin server returned an empty, unknown, or unexpected response to Cloudflare.[51]
- 521 Web Server Is Down
- The origin server refused connections from Cloudflare. Security solutions at the origin may be blocking legitimate connections from certain Cloudflare IP addresses.
- 522 Connection Timed Out
- Cloudflare timed out contacting the origin server.
- 523 Origin Is Unreachable
- Cloudflare could not reach the origin server; for example, if the DNS records for the origin server are incorrect or missing.
- 524 A Timeout Occurred
- Cloudflare was able to complete a TCP connection to the origin server, but did not receive a timely HTTP response.
- 525 SSL Handshake Failed
- Cloudflare could not negotiate a SSL/TLS handshake with the origin server.
- 526 Invalid SSL Certificate
- Cloudflare could not validate the SSL certificate on the origin web server. Also used by Cloud Foundry’s gorouter.
- 527 Railgun Error
- Error 527 indicates an interrupted connection between Cloudflare and the origin server’s Railgun server.[52]
- 530
- Error 530 is returned along with a 1xxx error.[53]
AWS Elastic Load Balancer
Amazon’s Elastic Load Balancing adds a few custom return codes
- 460
- Client closed the connection with the load balancer before the idle timeout period elapsed. Typically when client timeout is sooner than the Elastic Load Balancer’s timeout.[54]
- 463
- The load balancer received an X-Forwarded-For request header with more than 30 IP addresses.[54]
- 561 Unauthorized
- An error around authentication returned by a server registered with a load balancer. You configured a listener rule to authenticate users, but the identity provider (IdP) returned an error code when authenticating the user.[55]
Caching warning codes (obsoleted)
The following caching related warning codes were specified under RFC 7234. Unlike the other status codes above, these were not sent as the response status in the HTTP protocol, but as part of the «Warning» HTTP header.[56][57]
Since this «Warning» header is often neither sent by servers nor acknowledged by clients, this header and its codes were obsoleted by the HTTP Working Group in 2022 with RFC 9111.[58]
- 110 Response is Stale
- The response provided by a cache is stale (the content’s age exceeds a maximum age set by a Cache-Control header or heuristically chosen lifetime).
- 111 Revalidation Failed
- The cache was unable to validate the response, due to an inability to reach the origin server.
- 112 Disconnected Operation
- The cache is intentionally disconnected from the rest of the network.
- 113 Heuristic Expiration
- The cache heuristically chose a freshness lifetime greater than 24 hours and the response’s age is greater than 24 hours.
- 199 Miscellaneous Warning
- Arbitrary, non-specific warning. The warning text may be logged or presented to the user.
- 214 Transformation Applied
- Added by a proxy if it applies any transformation to the representation, such as changing the content encoding, media type or the like.
- 299 Miscellaneous Persistent Warning
- Same as 199, but indicating a persistent warning.
See also
- Custom error pages
- List of FTP server return codes
- List of HTTP header fields
- List of SMTP server return codes
- Common Log Format
Explanatory notes
- ^ Emphasised words and phrases such as must and should represent interpretation guidelines as given by RFC 2119
References
- ^ a b c «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry». Iana.org. Archived from the original on December 11, 2011. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 10.1.1 «Expect»«.
- ^ Goland, Yaronn; Whitehead, Jim; Faizi, Asad; Carter, Steve R.; Jensen, Del (February 1999). HTTP Extensions for Distributed Authoring – WEBDAV. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2518. RFC 2518. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Oku, Kazuho (December 2017). An HTTP Status Code for Indicating Hints. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8297. RFC 8297. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ Stewart, Mark; djna. «Create request with POST, which response codes 200 or 201 and content». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.3.4».
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 7.7».
- ^ a b c d e Dusseault, Lisa, ed. (June 2007). HTTP Extensions for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV). IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC4918. RFC 4918. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Delta encoding in HTTP. IETF. January 2002. doi:10.17487/RFC3229. RFC 3229. Retrieved February 25, 2011.
- ^ a b «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.4 «Redirection 3xx»«.
- ^ Berners-Lee, Tim; Fielding, Roy T.; Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk (May 1996). Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.0. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC1945. RFC 1945. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «The GNU Taler tutorial for PHP Web shop developers 0.4.0». docs.taler.net. Archived from the original on November 8, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2017.
- ^ «Google API Standard Error Responses». 2016. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved June 21, 2017.
- ^ «Sipgate API Documentation». Archived from the original on July 10, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ «Shopify Documentation». Archived from the original on July 25, 2018. Retrieved July 25, 2018.
- ^ «Stripe API Reference – Errors». stripe.com. Retrieved October 28, 2019.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 413». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 414». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 416». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ TheDeadLike. «HTTP/1.1 Status Codes 400 and 417, cannot choose which». serverFault. Archived from the original on October 10, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Larry Masinter (April 1, 1998). Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol (HTCPCP/1.0). doi:10.17487/RFC2324. RFC 2324.
Any attempt to brew coffee with a teapot should result in the error code «418 I’m a teapot». The resulting entity body MAY be short and stout.
- ^ I’m a teapot
- ^ Barry Schwartz (August 26, 2014). «New Google Easter Egg For SEO Geeks: Server Status 418, I’m A Teapot». Search Engine Land. Archived from the original on November 15, 2015. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ^ «Google’s Teapot». Retrieved October 23, 2017.[dead link]
- ^ «Enable extra web security on a website». DreamHost. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ «I Went to a Russian Website and All I Got Was This Lousy Teapot». PCMag. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Nottingham, M.; Fielding, R. (April 2012). «RFC 6585 – Additional HTTP Status Codes». Request for Comments. Internet Engineering Task Force. Archived from the original on May 4, 2012. Retrieved May 1, 2012.
- ^ Bray, T. (February 2016). «An HTTP Status Code to Report Legal Obstacles». ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved March 7, 2015.
- ^ alex. «What is the correct HTTP status code to send when a site is down for maintenance?». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Holtman, Koen; Mutz, Andrew H. (March 1998). Transparent Content Negotiation in HTTP. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2295. RFC 2295. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk; Leach, Paul; Lawrence, Scott (February 2000). An HTTP Extension Framework. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2774. RFC 2774. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «Enum HttpStatus». Spring Framework. org.springframework.http. Archived from the original on October 25, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «Twitter Error Codes & Responses». Twitter. 2014. Archived from the original on September 27, 2017. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Status Codes and SEO: what you need to know». ContentKing. Retrieved August 9, 2019.
- ^ «Screenshot of error page». Archived from the original (bmp) on May 11, 2013. Retrieved October 11, 2009.
- ^ a b «Using token-based authentication». ArcGIS Server SOAP SDK. Archived from the original on September 26, 2014. Retrieved September 8, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Error Codes and Quick Fixes». Docs.cpanel.net. Archived from the original on November 23, 2015. Retrieved October 15, 2015.
- ^ «SSL Labs API v3 Documentation». github.com.
- ^ «Platform Considerations | Pantheon Docs». pantheon.io. Archived from the original on January 6, 2017. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ^ «HTTP status codes — ascii-code.com». www.ascii-code.com. Archived from the original on January 7, 2017. Retrieved December 23, 2016.
- ^
«Error message when you try to log on to Exchange 2007 by using Outlook Web Access: «440 Login Time-out»«. Microsoft. 2010. Retrieved November 13, 2013. - ^ «2.2.6 449 Retry With Status Code». Microsoft. 2009. Archived from the original on October 5, 2009. Retrieved October 26, 2009.
- ^ «MS-ASCMD, Section 3.1.5.2.2». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 26, 2015. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «Ms-oxdisco». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 31, 2014. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «The HTTP status codes in IIS 7.0». Microsoft. July 14, 2009. Archived from the original on April 9, 2009. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
- ^ «ngx_http_request.h». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on September 19, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «ngx_http_special_response.c». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «return» directive Archived March 1, 2018, at the Wayback Machine (http_rewrite module) documentation.
- ^ «Troubleshooting: Error Pages». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «Error 520: web server returns an unknown error». Cloudflare. Retrieved November 1, 2019.
- ^ «527 Error: Railgun Listener to origin error». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on October 13, 2016. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- ^ «Error 530». Cloudflare. Retrieved November 1, 2019.
- ^ a b «Troubleshoot Your Application Load Balancers – Elastic Load Balancing». docs.aws.amazon.com. Retrieved August 27, 2019.
- ^ «Troubleshoot your Application Load Balancers — Elastic Load Balancing». docs.aws.amazon.com. Retrieved January 24, 2021.
- ^ «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Caching». datatracker.ietf.org. Retrieved September 25, 2021.
- ^ «Warning — HTTP | MDN». developer.mozilla.org. Retrieved August 15, 2021.
Some text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.5 Generic (CC BY-SA 2.5) license.
- ^ «RFC 9111: HTTP Caching, Section 5.5 «Warning»«. June 2022.
External links
- «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15 «Status Codes»«.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry
Содержание
- Ошибка 402: коды ошибки сервера, причины и методы устранения
- Характеристика ошибки
- Признаки ошибки
- Причины ошибки
- Не спутайте!
- Этап 1: восстановление записей реестра
- Этап 2: сканирование системы на вирусы
- Этап 3: очистка компьютера от «мусора»
- Этап 4: обновление драйверов
- Этап 5: восстановление системы
- Этап 6: переустановка Windows Operating System
- Если ничего не помогает.
- Как исправить ошибку HTTP 402 (Payment Required)
- Типичные ошибки Payment Required
- Создатели Payment Required Трудности
- Ошибка 402: Описание ошибки, причины появления, решение
- Справочная информация
- Признаки 402-ой ошибки
- Откуда могла появится ошибка 402?
- Подвиды и классификация ошибки
- Как устранить ошибку 402: инструкции и методы
- Восстановление записей реестра
- Полное сканирование
- Долой временные файлы
- Неисправные драйверы
- Переустановка ОС
Ошибка 402: коды ошибки сервера, причины и методы устранения
Во время работы с компьютером на экране порой появляются те или иные сообщения об ошибках системы. Могут содержать в себе «тонну» нечитаемого для неопытного пользователя текста. Но он нам и не нужен. Распознать, что же хочет «сказать» вам компьютер окном предупреждения, можно по коду ошибки. Расшифровав его, вы получите необходимую информацию о найденной неполадке, сможете определиться с путем ее устранения. В статье мы предлагаем читателю разобрать ошибку 402. Рассмотрим ее признаки и причины, разберем, как устранить неисправность, для каких операционных систем она типична.
Характеристика ошибки
Что представляет собой ошибка 402? Разберем главные ее характеристики:
- Сообщение на экране: HTTP 402.
- Описание (нередко в предупредительном баннере выводится краткое объяснение проблемы): Payment is required. This error code is not yet operational.
Появление ошибки 402 характерно для работы с продуктами компании «Майкрософт». В частности, для операционной системы «Виндовс». Подобного рода ошибка при работе с компьютером появляется на следующих версиях ОС:
Признаки ошибки
Как распознать, что перед вами именно ошибка 402? Специалисты обозначают следующие ее характерные признаки:
- Отображается окно, сообщающее об ошибке с данным кодом, после чего открытая программа самопроизвольно закрывается.
- Интернет-браузер на вашем ПК при запуске разных сайтов выводит один и тот же баннер с кодом ошибки 402.
- Отображается также предупреждающий текст: Payment Required.
- ОС «Виндовс» медленно работает, «зависает». Отображение информации с клавиатуры, отклики на движения мышкой заторможены.
- Компьюттер «лагает», «зависает» на несколько секунд.
Иногда ПК может отображать сообщение об ошибке 402 даже в случае, когда корень проблемы не в ней. Например, часто выводится баннер с ошибкой вида HTTP 404 («Страница не может быть найдена») при отображении веб-страницы, которая открывается вместе с тем должным образом.
Причины ошибки
В чем причины этой ошибки? В основном это следующее:
- Вредоносная программа, вирус, перехвативший контроль над вашим браузером, повредивший его важные настройки.
- Повреждение реестра «Виндовс»- из-за изменения программного обеспечения (его установки или удаления), связанного с ОС.
- Злонамеренное инфицирование внешним вредоносным приложением файлов, связанных с браузером.
Итак, главная причина ошибки — вирусы, поселившиеся в вашем компьютере. Они могут повредить как используемый браузер, так и реестр «Виндовс».
Не спутайте!
Далее мы вам подробно расскажем, как исправить ошибку 402. Важно не спутать ее с иными проблемами, в корне отличающимися от данной:
- Ошибка подключения 402 в «Гольфстриме» (охранной системе). В чем здесь суть? Ошибка подключения с кодом 402 в «Гольфстриме» указывала на уязвимость системы. Хакеры могли получить личную информацию ее клиентов, что давало возможность удаленного управления сигнализацией многих объектов.
- Ошибка 091-402. Появляется не при работе браузера, а при неправильном функционировании МФУ «Ксерокс 3045».
- Ошибка 402 на Xiaomi. Возникает в случае, когда пользователь устанавливает на смартфон темы (вариации оформления рабочего стола, меню) из неофициальных источников.
А теперь перейдем к ошибке получения информации с сервиса 402. Проблема решается в несколько шагов.
Этап 1: восстановление записей реестра
Сразу предупредим читателя: самостоятельное редактирование реестра «Виндовс» с целью удаления ключей, содержащих в себе ошибку 402, не рекомендуется, если вы не имеете соответствующей подготовки. Дело в том, что непрофессионал может легко допустить ошибки при работе, которые будут чреваты общей неработоспособностью компьютера. Даже одна лишняя запятая воспрепятствует загрузке ОС!
Советуем даже опытному пользователю ПК обратиться к надежным инструментам очистки реестра. Например, к представленному «Майкрософт» WinThruster. Программа автоматически найдет поврежденные записи реестра, нерабочие ссылки, а также ссылки на поврежденные вирусом файлы. Проблему приложение исправляет самостоятельно. Что примечательно, WinThruster перед каждым сканированием реестра создает его резервную копию, которая в один клик мыши позволит отменить все изменения.
К ручной очистке реестра мы настоятельно советуем вам не прибегать! А вот автоматическая процедура (с помощью соответствующего ПО) отлично повышает производительность системы.
Этап 2: сканирование системы на вирусы
Как мы уже говорили, ошибка 402 чаще всего говорит о том, что ваш компьютер заражен вирусами. Соответственно, системе необходимо полное сканирование на наличие вредоносных файлов. Эту процедуру производит огромное количество утилит и приложений, платных и бесплатных.
Будьте внимательны: не все они могут не только обнаружить, но и удалить вирусы, поврежденные файлы. Проверенная программа в этом разнообразии — Emsisoft Anti-Malware. Разработчики данного антивируса гарантируют удаление своим продуктом вредоносного ПО.
Этап 3: очистка компьютера от «мусора»
Ежедневное использование ПК, постоянный интернет-серфинг ведут к тому, что система заполняется ненужными временными файлами и папками. Если от них не избавляться своевременно, то такой информационный мусор приведет как к снижению быстродействия системы, так и к возникновению ошибки 402. Причиной тут будет конфликт файлов либо перегрузка жестких дисков.
Отсюда выход из проблемы видится в очистке системы от временных папок с помощью специальных программ. Отметим, что встроенная утилита «Виндовс» «справляется» не со всем мусором. В частности, она не «видит» временные файлы «Хрома», приложений «Майкрософт Офис», Firefox и сотни других программ.
Так на чем же остановиться? Отличный вариант — WinSweeper от той же «Майкрософт». Программа предназначена для комплексной очистки жесткого диска от временных файлов. Достаточно раз в день запускать приложение в режиме автоматического сканирования, чтобы освободить ПК от информационного мусора.
Этап 4: обновление драйверов
Появление ошибки 402 может быть связано с поврежденными или устаревшими драйверами устройств. Причин их внезапной неисправности очень много. Однако вы всегда можете обновить драйверы, чтобы избавиться от ошибки 402.
Чтобы максимально упростить и ускорить этот процесс, рекомендуем обратиться к специальной утилите для автоматического обновления драйверов. Среди надежных продуктов можно выделить DriverDoc от «Майкрософт».
Этап 5: восстановление системы
Нередко ошибка 402 может возникнуть в результате неверных настроек системы, которые задали либо вы сами, либо вредоносное ПО. Отсюда отличный вариант решения проблемы — отправить компьютер в прошлое — в то время, когда вредная перенастройка еще не была произведена.
Для этого пользователи обращаются к «Восстановлению системы» на «Виндовс». Процедура несложная, проходит в несколько шагов:
- Зайдите в меню «Пуск».
- В строке поиска введите «Восстановление системы».
- Компьютер найдет данный раздел.
- Перейдите в него. Возможно, система попросит вас ввести пароль администратора для внесения изменений.
- Теперь вам нужно следовать инструкциям “Мастера” для определения точки восстановления.
- Изменения вступят в силу после перезагрузки компьютера.
Этап 6: переустановка Windows Operating System
Программа может быть непосредственно связана с возникновением данной ошибки. Поэтому проблему решит ее удаление и последующая переустановка.
На ХР алгоритм действий такой:
- Зайдите в «Пуск».
- Переместитесь в «Панель управления».
- Выберите «Установку и удаление программ».
- В спектре установленных программ найдите Windows Operating System.
- Нажмите на надпись. Затем кликните на кнопку «Удалить», появившуюся справа от нее.
- Следуйте дальнейшим инструкциям системы для полного удаления программы.
- Заново загрузить ее можно на сайте «Майкрософт». Откройте установочный файл Windows Operating System, чтобы вернуть программу на компьютер.
Теперь инструкция для новых версий — 8 и 10:
- Перейдите в меню «Пуск».
- Остановитесь на разделе «Программы и компоненты».
- В «Имени» найдите Windows Operating System.
- Нажмите запись. В верхней части окна кликните на «Удалить».
- Следуйте инструкциям системы для полного удаления приложения.
- Заново загрузите программу на сайте «Майкрософт», запустите установочный файл, чтобы вернуть Windows Operating System на свой компьютер.
Если ничего не помогает.
Ни один из вышеперечисленных этапов не смог устранить ошибку 402? В таком случае советуем вам обратиться еще к трем возможным решениям проблемы:
- Проверка системных файлов с помощью встроенного инструмента «Виндовс» sfc /scannow.
- Установка всех доступных на данный момент обновлений операционной системы.
- Переустановка «Виндовс» на вашем компьютере. Перед процедурой не забудьте скопировать всю важную информацию на жестком диске.
Ошибка 402 чаще всего говорит о том, что вредоносные вирусы повредили ваш браузер или иные компоненты ОС «Виндовс». Мы представили несколько способов решения данной проблемы.
Источник
Как исправить ошибку HTTP 402 (Payment Required)
| Номер ошибки: | Ошибка HTTP 402 | |
| Название ошибки: | Payment Required | |
| Описание ошибки: | Payment is required. This error code is not yet operational. | |
| Разработчик: | Microsoft Corporation | |
| Программное обеспечение: | Windows Operating System | |
| Относится к: | Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10, 11 |
Основные причины Windows 10 ошибок, связанных с файлом Payment Required, включают отсутствие или повреждение файла, или, в некоторых случаях, заражение связанного Edge вредоносным ПО в прошлом или настоящем. Как правило, решить проблему позволяет получение новой копии файла Windows 10 , которая не содержит вирусов. Помимо прочего, в качестве общей меры по профилактике и очистке мы рекомендуем использовать очиститель реестра для очистки любых недопустимых записей файлов, расширений файлов Windows 10 или разделов реестра, что позволит предотвратить появление связанных с ними сообщений об ошибках.
Типичные ошибки Payment Required
Лучшие ошибки Payment Required с Edge в Windows:
- «Ошибка в файле Payment Required.»
- «Payment Required удален, отсутствует или перемещен. «
- «Отсутствует файл: Payment Required»
- «Не удалось загрузить Payment Required. «
- «Не удалось зарегистрироваться: Payment Required. «
- «Ошибка времени выполнения Payment Required. «
- «Ошибка загрузки: Payment Required. «
Эти сообщения об ошибках Windows 10 могут появляться во время установки программы, в то время как программа, связанная с Payment Required (например, Edge ) работает, во время запуска или завершения работы Windows, или даже во время установки операционной системы Windows. Документирование случаев ошибок Payment Required является ключевым для определения причины проблемы и сообщения о них Microsoft Corporation для исправлений.
Создатели Payment Required Трудности
Проблемы Edge и Payment Required возникают из отсутствующих или поврежденных файлов, недействительных записей реестра Windows и вредоносных инфекций.
В частности, проблемы Payment Required, созданные:
- Недопустимый Payment Required или поврежденный раздел реестра.
- Зазаражение вирусом повреждает файл Payment Required.
- Payment Required злонамеренно или ошибочно удален другим программным обеспечением (кроме Edge ).
- Другая программа, конфликтующая с Payment Required или другой общей ссылкой Edge .
- Некомплектная установка приложения, связанного с Payment Required, или поврежденная загрузка.
Совместима с Windows 2000, XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10 и 11
Источник
Ошибка 402: Описание ошибки, причины появления, решение
Т.к. система идентифицировала проблему, пользователю остается разобрать сущность проблемы и найти пути ее разрешения. Ошибка 402 становится довольно частым гостей ОС, поэтому ей стоит уделить внимание. Особенно, если с этой целью была открыта данная публикация.
Справочная информация
Чаще всего ошибка возникает на базе системных продуктов. Появляется она на относительно последних версиях Виндовс, начиная от ХР и заканчивая «десяткой». Уведомление, как правило, имеет краткое содержание HTTP 402. Payment is required.
Признаки 402-ой ошибки
Обнаружение именно этой ошибки обусловлено признаками, которые выделили специалисты. Данный перечень позволит не спутать эту ошибку с десятками других, которые время от времени появляются на устройстве. Речь идет о следующих признаках:
- При запуске любого сайта появляется баннер с указанным кодом.
- Сообщение об ошибке появляется в отдельном окне и после этого закрывается активная программа.
- Постоянные «лаги» устройства.
- Отображение текста Payment Required, носящий предупредительный характер.
Отметим, что в некоторых ситуациях ошибка 402 скрывается под видом ошибки 404, хотя несуществующая страница работает как подобает веб-ресурсу.
Откуда могла появится ошибка 402?
Выделяют 3 наиболее распространенные причины:
- Вирус повредил браузер и начал выдавать подобные уведомления.
- В результате изменения системного ПО мог повредиться реестр.
- Файлы, связанные с веб-обозревателем, были инфицированы приложением вредоносного содержания.
К слову, повреждение реестра также могло стать следствием деятельность вируса.
Подвиды и классификация ошибки
Помимо основной вариации 402-й, существует еще как минимум 3 типа указанной ошибки, которые свидетельствуют о других проблемах:
- Управление сигнализацией и получение данных в рамках охранной системы «Гольфстрим». Появляется уведомление об ошибке подключения.
- Подвид 091-402. Главное отличие – возникает не в браузере, а при работе с ксероксом (вернее, неправильной работе).
- Появление ошибки на смартфонах компании Касается тех случаев, когда установленная тема была загружена из неофициального источника.
Разобравшись во всех тонкостях проблемы, переходим к вариантам ее решения.
Как устранить ошибку 402: инструкции и методы
Восстановление записей реестра
Редактирование реестра чревато последствиями, поэтому важна каждая деталь и каждый знак. Лучше довериться утилите WinThruster от Майкрософт, чем в ручном режиме вносить изменения. Программа находит поврежденные файлы и ликвидирует их. Большой плюс приложения – создание резервной копии реестра для возможности отмены изменений.
Полное сканирование
Для осуществления этой процедуры разработчики представили уйму утилит, но многие из них не годятся для глубокого анализа системы. Рекомендуем обратиться к программе Emsisoft Anti-Malware, который не оставит и мокрого следа от вредоносного программного обеспечения.
Долой временные файлы
Работа на компьютере сулит накопление огромного количества мусора в устройстве. Для максимально эффективной очисти жесткого диска следует пользоваться утилитой WinSweeper. Применяя программу ежедневно в автоматическом режиме, в ПК не будут собираться нагружающие временные файлы.
Неисправные драйверы
Для надлежащего функционирования «дров» их постоянно нужно обновлять. Не стоит слишком углубляться в причины их выхода из строя — достаточно активировать программу DriverDoc и запустит масштабный процесс обновки.
Переустановка ОС
Радикальный шаг следует осуществлять вместе с профессионалом. Впрочем, до этих мер доходит не так часто и проблема скрывается в вирусах, драйверах или загруженности устройства лишними файлами.
Источник
Привет, читатель блога ZametkiNaPolyah.ru! Продолжим знакомиться с протоколом HTTP в рубрике Серверы и протоколы и ее разделе HTTP протокол. Эта запись целиком и полностью посвящена ошибка клиента при взаимодействие по HTTP протоколу. Мы с тобой рассмотрим коды ошибок клиента HTTP. Вообще, коды ошибок клиента в HTTP протоколе могут быть расширены любым сервером, мы рассмотрим только коды ошибок клиента, которые указаны в стандарте HTTP 1.1. Сперва, как и обычно при рассмотрение кодов HTTP протокола, мы дадим общее описания кодам ошибок клиента, а затем рассмотрим по отдельности каждый из 18 HTTP кодов ошибок клиента.
HTTP коды ошибок клиента
Общая информация о HTTP кодах ошибок клиента
Содержание статьи:
- Общая информация о HTTP кодах ошибок клиента
- HTTP код ошибки 400, код ошибки 401, код ошибки клиента 402, код ошибки 403, HTTP код ошибки клиента 404, ошибка клиента 405
- HTTP код ошибки 406, код ошибки 407, HTTP код ошибки клиента 408, код ответа сервера 409, код ошибки 410, код ошибки клиента 411, HTTP код 412
- HTTP код ошибки клиента 413, код ошибки клиента 414, ошибка клиента 415, ошибка 416, HTTP код 417
HTTP коды ошибок клиента говорят пользователю о том, что ему не удалось получить запрашиваемый ресурс, указанный в URI (запись про URI в HTTP), по вине самого пользователя или клиента, например, пользователь ошибся при вводе URL в браузере, в этом случае сервер даст ответ с кодом состояния 404. Все коды ошибок HTTP клиента начинаются с четверки. HTTP сервер всегда в случае ошибки клиента отправляет вместе с кодом состояния пояснения того, почему произошла ошибка, за исключение тех случаев, когда используется HTTP метод HEAD.
Давайте для удобства рассмотрения сведем в одну таблицу все коды ошибок HTTP клиента в одну таблицу. И не будем забывать, что в основе протокола HTTP лежит модель взаимодействия клиент-сервер, которая делит обязанности приложений на клиентские и серверные, рассматриваемый протокол довольно строго придерживается данной модели, и у нас есть специальные коды ошибок, которые происходят по вине серверных приложений и есть коды ошибок, которые происходят по вине человека или клиентского приложения, которым человек пользуется.
| Код ошибки HTTP клиента | Описание кода ошибки HTTP клиента |
| 400 Bad Request | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 400: плохой запрос Такой код состояния ошибки клиента вы можете увидеть тогда, когда сервер не понял ваш запрос из-за синтаксической ошибке в HTTP запросе. |
| 401 Unauthorized | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 401: не авторизован Такой код состояния ошибки клиента вы можете увидеть в том случае, если для доступа к ресурсу требуется аутентификация по соображениям безопасности HTTP сервера. |
| 402 Payment Required | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 402: требуется оплата Этот код состояния ошибки клиента на данный момент пока не используется, он предназначен для платных сервисов, а не для хостингов и интернет-провайдеров. |
| 403 Forbidden | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 403: запрещено Такой код состояния ошибки клиента вы увидите в том случае, когда сервер вас прекрасно понял, но отказывается вам предоставлять доступ к ресурсу из-за того, что у вас недостаточно прав доступа. |
| 404 Not Found | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 404: не найдено Самый популярный код состояния ошибки клиента. Вы его можете увидеть в том случае, когда ошиблись, вводя URL в браузере. |
| 405 Method Not Allowed | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 405: метод не дозволен Данный код состояния ошибки клиента можно увидеть в том случае, когда вы используете метод запроса, запрещенный в настройках HTTP сервера. |
| 406 Not Acceptable | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 406: не приемлем Этот код состояния вы увидите в том случае, когда HTTP сообщение вашего клиента содержит неправильные параметры для указанного в нем URI. |
| 407 Proxy Authentication Required | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 407: требуется установления подлинности через прокси-сервер Если вы видите этот код состояния ошибки клиента, то вам нужно пройти аутентификацию на прокси-сервере. |
| 408 Request Timeout | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 408: истекло время ожидания запроса Этот код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента вы увидите тогда, когда сервер устал ждать от вас сообщение. |
| 409 Conflict | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 409: конфликт Такой код состояния ошибки клиента будет появляться очень редко, когда будет происходить конфликт действий между двумя пользователями. |
| 410 Gone | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 410: удален А этот код состояния ошибки клиента будет показан сервером в том случае, когда ресурс был доступен по указанному URI, но теперь его там нет. |
| 411 Length Required | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 411: требуется длина Этот код состояния ошибки клиента появляется в том случае, когда серверу нужно обязательно указывать поле заголовка Content-Lenght |
| 412 Precondition Failed | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 412: предусловие неверно Сервер вернет HTTP ответ с таким кодом состояния в том случае, когда он не смог выполнить ни одно из условий из запроса клиента. |
| 413 Request Entity Too Large | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 413: объект запроса слишком велик
А такой код ошибки клиента можно увидеть в том случае, когда тело (HTTP объекты и тело сообщения) запроса слишком большое и сервер его получить не смог.
|
| 414 Request-url Too Long | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 414: URI запроса слишком длинный Такой код ошибки клиента сервер выдаст в том случае, если URI запроса слишком длинный. |
| 415 Unsupported Media Type | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 415: неподдерживаемый медиа тип Сервер может выдать такой код состояния ошибки клиента в том случае, если не захочет работать с указанным типом данных (типы данных в HTTP) тем методом, который указан в запросе клиента |
| 416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 416: запрашиваемый диапазон не достижим Данный код и ошибки клиента говорит нам о том, что диапазон фрагмента (единицы измерения в HTTP) в поле заголовка Range указан неверно. |
| 417 Expectation Failed | Код состояния ошибки HTTP клиента 417: ожидаемое неприемлимо Код состояния ошибки клиента 417 появится в том случае, если сервер не сможет удовлетворить значению, указанному в поле заголовка Expect. |
Далее мы рассмотрим более подробно коды ошибок HTTP клиента.
HTTP код ошибки 400, код ошибки 401, код ошибки клиента 402, код ошибки 403, HTTP код ошибки клиента 404, ошибка клиента 405
HTTP код ошибки клиента 400: Bad Request или неверный запрос. Сервер вернет ответ с кодом ошибки 400 в том случае, когда обнаружит, что HTTP запрос клиента содержит синтаксическую ошибку.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 401: Unauthorized или не авторизован. Код ошибки клиента 401 сервер отправляет в том случае, когда для доступа к ресурсу требуется авторизация, при этом ответ HTTP сервера должен (читай про требования HTTP протокола) включать поле заголовка WWW-Authenticate и перечень условий для аутентификации клиента, после чего клиент может повторить запрос к серверу с полем Authorization, в котором будут указаны все необходимые данные для авторизации.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 402: Payment Required или требуется оплата. Данный код ошибки клиента зарезервирован для будущего использования и предназначен для оповещения клиента о том, что для доступа к ресурсу ему необходимо произвести оплату. Обратите внимание: данный код ошибки клиент не используется ни хостингами, ни интернет-магазина, ни даже интернет-провайдерами.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 403: Forbidden или запрещено. HTTP код ошибки клиента 403 отправляется сервером в том случае, когда он отказывается выполнить ваш запрос, причин на то могут быть разными. При этом сервер не должен сообщать является ли эта мера временной или постоянной. Одной из причин появления HTTP кода 403 может быть то, что у пользователя недостаточно прав доступа к ресурсу.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 404: Not Found или не найдено. HTTP код ошибки клиента 404 – самый популярный код ошибки клиента, код ошибки 404 видел, наверное, каждый. Ведь для того, чтобы увидеть код ошибки 404 достаточно ввести неверный URL.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 405: Method Not Allowed или метод не дозволен. Код ошибки 405 сервер отправляет клиенту в том случае, когда для ресурса, указанного в URI, нельзя применить метод, указанный в запросе клиента. Код ошибки 405 появляется в основном из-за конфигураций безопасности сервера, когда администратор преднамеренно запрещает выполнение тех или иных методов HTTP запросов на сервере. При этом ответ сервера с кодом ошибки 405 должен содержать поле заголовка Allow, в котором будут указаны доступные метода для ресурса.
HTTP код ошибки 406, код ошибки 407, HTTP код ошибки клиента 408, код ответа сервера 409, код ошибки 410, код ошибки клиента 411, HTTP код 412
HTTP код ошибки клиента 406: Not Acceptable или не приемлем. Код ошибки 406 говорит клиенту о том, что введенный URI не приемлем с теми характеристиками, которые были указаны в HTTP заголовке (читай про параметры HTTP протокола). Если метод запроса был отличным от метода HEAD, то серверу нужно включить в тело сообщения список доступных характеристик для данного URI. Формат HTTP объекта определяется медиа типом в поле заголовка Content-Length и в зависимости от клиента и его возможностей подходящий вариант запроса может быть выбран автоматически, этот код применяется при обсуждении содержимого в HTTP.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 407: Proxy Authentication Required или требуется установление подлинности через прокси-сервер. HTTP код ошибки клиента 407 появится в том случае, когда клиенту для доступа к указанному ресурсу необходимо авторизоваться на прокси-сервере. Когда возникает код ошибки 407 прокси-сервер должен возвратить поле заголовка Proxy-Authenticate содержащее вызов (challenge), применяемый прокси-сервером для запрошенного ресурса. Код ошибки 407 аналогичен по своему действию с кодом 401.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 408: Request Timeout или истекло время ожидания запроса. Код ошибки 408 возникает в том случае, когда клиент не произвел запрос в течение того времени, которое сервер готов ждать, но клиент может повторить запрос.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 409: Conflict или конфликт. Код ошибки клиента 409 возникает в том случае, когда происходит конфликт между несколькими клиентами при доступе к одному ресурсу. Код ошибки 409 показывается клиенту только в том случае, когда тот может устранить конфликт и повторить свой запрос. HTTP ответ сервера должен предоставить максимум информации для пользователя, чтобы он устранил конфликт, и код 409 больше не появлялся. Чаще всего ошибка 409 появляется при использование метода PUT.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 410: Gone или удален. HTTP код ошибки клиента 410 будет отправлен сервером в том случае, когда ресурс удален и сервер не знает, где искать копию ресурса или его новую версию. В том случае, когда у сервера есть информация о том, что ресурс может быть восстановлен, ему не следует показывать ошибку 410, а лучше показать код ошибки 404.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 411: Length Required или требуется длина. Код ошибки 411 будет показан клиенту в том случае, когда серверу для корректной обработки запроса требуется длина содержимого. Клиент может повторить запрос, если добавит допустимое поле заголовка Content-Length, содержащее длину тела сообщения (message-body) в сообщении запроса.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 412: Precondition Failed или предусловие неверно. Код ошибки 412 будет выслан клиенту сервером в том случае, когда сервер не может выполнить условия, указанные в заголовке HTTP запроса.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 413, код ошибки клиента 414, ошибка клиента 415, ошибка 416, HTTP код 417
HTTP код ошибки клиента 413: Request Entity Too Large или объект запроса слишком большой. Код ошибки 413 появляется в том случае, когда объект, передаваемый в запросе клиента слишком большой и сервер его не может обработать. Сервер может закрыть соединение (здесь написано про HTTP соединения), чтобы не дать клиенту возможность продолжить запрос. Если такая ситуация временная, то сервер в своем сообщении вместе кодом ошибки 413 передает поле заголовка Retry-After, в котором указывает время, через которое запрос может быть повторен.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 414: Request-URI Too Long или запроса слишком длинный. Сервер отправляет сообщение с кодом ошибки 414 в том случае, когда URI, указанный в запросе слишком длинный. Ошибка 414 обычно возникает тогда, когда клиент пытается передать кучу параметров методом GET, а следовало бы использовать метод POST.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 415: Unsupported Media Type или неподдерживаемый медиа тип. Код ошибки 415 сервер отправляет в том случае, когда он отказывается обслуживать запрос из-за некорректного типа данных для ресурса, который указан в URI: когда метод выбранный в запросе не соответствует типу данных ресурса.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 416: Requested Range Not Satisfiable или запрашиваемый диапазон не достижим. Сервер отправит сообщение с кодом ошибки 416 в том случае, когда в поле заголовка запроса Range был указан неверный диапазон фрагмента.
HTTP код ошибки клиента 417: Expectation Failed или ожидаемое неприемлемо. Код ошибки 417 появляется в том случае, когда сервер не может удовлетворить значению Expect, которое указано в заголовке HTTP запроса.
Мы рассмотрели коды ошибок HTTP клиента, давайте перейдем к последнему классу кодов состояния — HTTP коды ошибок серевра. Позволю себе напомнить, что в HTTP еще есть информационные коды состояния, успешные коды состояния и коды перенаправления. А если тебе нужна информацию обо всех кодах состояния, обратись к справочнику HTTP кодов состояния, в котором есть полное описание всех кодов.
Не забывайте делиться своим мнением в комментариях и оставлять отзывы, это поможет сделать нашу работу лучше, с уважением ZametkiNaPolyah.ru!