Содержание
- Способ 1: Проверка доступности конечного адреса
- Способ 2: Очистка куки
- Способ 3: Добавление адреса в файл hosts
- Способ 4: Использование архивной версии сайта
- Кэш Google
- Сервис Wayback Machine
- Вопросы и ответы
Способ 1: Проверка доступности конечного адреса
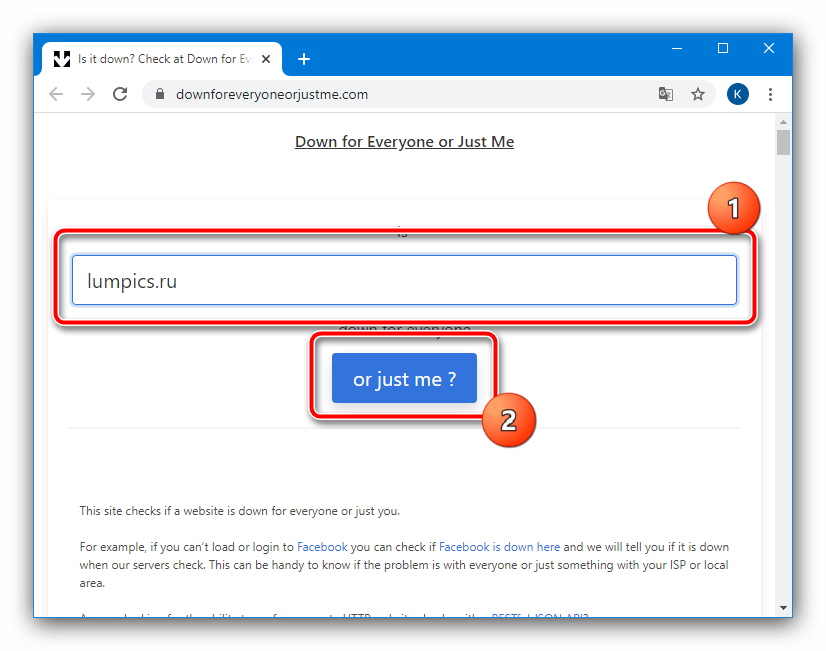
Наиболее часто сообщение об ошибке с кодом 521 появляется в ситуации, когда сервер, на котором находится нужный сайт, по каким-то причинам недоступен. Самый простой способ убедиться в этом – воспользоваться сервисом проверки, вроде Down For Everyone.
Официальный сайт сервиса
- С помощью любого браузера (желательно всё-таки Google Chrome) перейдите по ссылке выше. После загрузки введите в поле, отмеченное на скриншоте, адрес проблемного ресурса и нажмите «or just me?».
- Подождите, пока сервис проанализирует данные. Если вы получаете сообщение «It’s just you, *название сайта* is up» – ресурс доступен, и причина возникновения ошибки в чём-то другом.
- Если же сообщение гласит «It’s not just you…», явно проблема на стороне веб-ресурса. В этой ситуации остаётся только подождать, пока технические проблемы будут устранены, или же воспользоваться так называемым «зеркалом» (запасным адресом, который расположен на другом сервере), если таковое предусмотрено.
Способ 2: Очистка куки
Также сбой может быть характерным для следующей ситуации: хост-сервер обновил DNS, тогда как в имеющихся cookies записаны старые, уже недоступные значения. Решением будет удаление куки проблемного сайта – описание процедуры для всех популярных веб-обозревателей вы можете найти по ссылкам далее.
Подробнее: Как очистить cookies в Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Opera, Яндекс.Браузере, Internet Explorer
Способ 3: Добавление адреса в файл hosts
В некоторых случаях работает следующая процедура: точный адрес сайта добавляется в системный файл hosts, после чего можно получить доступ к нужному ресурсу.
- Самый быстрый способ открыть и отредактировать hosts в Windows – воспользоваться «Командной строкой», запущенной от имени администратора. Для этого следует найти оснастку в «Поиске» и задействовать соответствующий пункт запуска.
Подробнее: Как открыть «Командную строку» от имени администратора в Windows 7 и Windows 10
- После появления интерфейса введите в нём следующую команду, после чего нажмите Enter.
Notepad C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts - Появится окно «Блокнота», в котором уже будет открытый для редактирования файл. Поместите курсор в конец документа – это обязательно должна быть новая строка, поэтому при необходимости сделайте её нажатием на Enter, затем напишите адрес ресурса.
- Снова проверьте точность ввода, после чего сохраните изменения сочетанием Ctrl+S, закройте все запущенные окна и перезагрузите компьютер.
После полного запуска ОС попробуйте перейти на проблемный ресурс – не исключено, что теперь доступ появится.
Способ 4: Использование архивной версии сайта
Если сайт «лежит» уже давно, существует вероятность, что он удалён с сервера, и обычными методами получить к нему доступ не выйдет. В такой ситуации пригодятся возможности просмотра более недоступных страниц, которых существует две: кэш поисковика или специальный сервис.
Кэш Google
Самый крупный в мире поисковик уже достаточно давно предоставляет возможность кэширования страниц и их последующего просмотра.
- Откройте основной ресурс «корпорации добра», где введите в поисковую строку адрес искомого сайта и нажмите «Поиск в Google».
- Найдите среди выдачи нужный результат, затем кликните левой кнопкой мыши по стрелке рядом с названием ресурса, где выберите пункт «Сохранённая копия».
- Подождите, пока сайт откроется. Если информация закэшировалась корректно, вы получите пригодную для просмотра версию.
Сервис Wayback Machine
Несколько лет назад появилась инициатива, целью которой является создание архива интернет-страниц для будущих поколений. Результатом её деятельности стал сервис Wayback Machine: он тоже позволяет просматривать копии сайтов, в том числе и давно удалённых из основного пространства интернета.
Официальный сайт архива Wayback Machine
- Перейдите на страницу сервиса, затем воспользуйтесь строкой ввода, в которой укажите нужный адрес и нажмите «Browse History».
- Результаты поиска обычно выдаются в формате ленты времени – выберите на ней интересующий год и кликните по соответствующей полоске.
- Теперь появится календарь с месяцами года, выбранного на предыдущем шаге. Даты, отмеченные синим – активные ссылки c сохранёнными снимками сайта. Наведите на неё курсор, затем щёлкните по одному из временных отрезков.
- Копии вполне функциональны: нередко сохраняются даже прикреплённые файлы плюс возможен переход по ссылкам на другие части ресурса, но только в том случае, если их снимки тоже присутствуют в архиве.
Этот метод сложно назвать полноценным решением рассматриваемой проблемы, однако он пригодится в случаях, когда критически важно получить информацию с недоступной страницы.
Еще статьи по данной теме:
Помогла ли Вам статья?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is a list of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) response status codes. Status codes are issued by a server in response to a client’s request made to the server. It includes codes from IETF Request for Comments (RFCs), other specifications, and some additional codes used in some common applications of the HTTP. The first digit of the status code specifies one of five standard classes of responses. The optional message phrases shown are typical, but any human-readable alternative may be provided, or none at all.
Unless otherwise stated, the status code is part of the HTTP standard (RFC 9110).
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) maintains the official registry of HTTP status codes.[1]
All HTTP response status codes are separated into five classes or categories. The first digit of the status code defines the class of response, while the last two digits do not have any classifying or categorization role. There are five classes defined by the standard:
- 1xx informational response – the request was received, continuing process
- 2xx successful – the request was successfully received, understood, and accepted
- 3xx redirection – further action needs to be taken in order to complete the request
- 4xx client error – the request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled
- 5xx server error – the server failed to fulfil an apparently valid request
1xx informational response
An informational response indicates that the request was received and understood. It is issued on a provisional basis while request processing continues. It alerts the client to wait for a final response. The message consists only of the status line and optional header fields, and is terminated by an empty line. As the HTTP/1.0 standard did not define any 1xx status codes, servers must not[note 1] send a 1xx response to an HTTP/1.0 compliant client except under experimental conditions.
- 100 Continue
- The server has received the request headers and the client should proceed to send the request body (in the case of a request for which a body needs to be sent; for example, a POST request). Sending a large request body to a server after a request has been rejected for inappropriate headers would be inefficient. To have a server check the request’s headers, a client must send
Expect: 100-continueas a header in its initial request and receive a100 Continuestatus code in response before sending the body. If the client receives an error code such as 403 (Forbidden) or 405 (Method Not Allowed) then it should not send the request’s body. The response417 Expectation Failedindicates that the request should be repeated without theExpectheader as it indicates that the server does not support expectations (this is the case, for example, of HTTP/1.0 servers).[2] - 101 Switching Protocols
- The requester has asked the server to switch protocols and the server has agreed to do so.
- 102 Processing (WebDAV; RFC 2518)
- A WebDAV request may contain many sub-requests involving file operations, requiring a long time to complete the request. This code indicates that the server has received and is processing the request, but no response is available yet.[3] This prevents the client from timing out and assuming the request was lost.
- 103 Early Hints (RFC 8297)
- Used to return some response headers before final HTTP message.[4]
2xx success
This class of status codes indicates the action requested by the client was received, understood, and accepted.[1]
- 200 OK
- Standard response for successful HTTP requests. The actual response will depend on the request method used. In a GET request, the response will contain an entity corresponding to the requested resource. In a POST request, the response will contain an entity describing or containing the result of the action.
- 201 Created
- The request has been fulfilled, resulting in the creation of a new resource.[5]
- 202 Accepted
- The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing has not been completed. The request might or might not be eventually acted upon, and may be disallowed when processing occurs.
- 203 Non-Authoritative Information (since HTTP/1.1)
- The server is a transforming proxy (e.g. a Web accelerator) that received a 200 OK from its origin, but is returning a modified version of the origin’s response.[6][7]
- 204 No Content
- The server successfully processed the request, and is not returning any content.
- 205 Reset Content
- The server successfully processed the request, asks that the requester reset its document view, and is not returning any content.
- 206 Partial Content
- The server is delivering only part of the resource (byte serving) due to a range header sent by the client. The range header is used by HTTP clients to enable resuming of interrupted downloads, or split a download into multiple simultaneous streams.
- 207 Multi-Status (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The message body that follows is by default an XML message and can contain a number of separate response codes, depending on how many sub-requests were made.[8]
- 208 Already Reported (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The members of a DAV binding have already been enumerated in a preceding part of the (multistatus) response, and are not being included again.
- 226 IM Used (RFC 3229)
- The server has fulfilled a request for the resource, and the response is a representation of the result of one or more instance-manipulations applied to the current instance.[9]
3xx redirection
This class of status code indicates the client must take additional action to complete the request. Many of these status codes are used in URL redirection.[1]
A user agent may carry out the additional action with no user interaction only if the method used in the second request is GET or HEAD. A user agent may automatically redirect a request. A user agent should detect and intervene to prevent cyclical redirects.[10]
- 300 Multiple Choices
- Indicates multiple options for the resource from which the client may choose (via agent-driven content negotiation). For example, this code could be used to present multiple video format options, to list files with different filename extensions, or to suggest word-sense disambiguation.
- 301 Moved Permanently
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI.
- 302 Found (Previously «Moved temporarily»)
- Tells the client to look at (browse to) another URL. The HTTP/1.0 specification (RFC 1945) required the client to perform a temporary redirect with the same method (the original describing phrase was «Moved Temporarily»),[11] but popular browsers implemented 302 redirects by changing the method to GET. Therefore, HTTP/1.1 added status codes 303 and 307 to distinguish between the two behaviours.[10]
- 303 See Other (since HTTP/1.1)
- The response to the request can be found under another URI using the GET method. When received in response to a POST (or PUT/DELETE), the client should presume that the server has received the data and should issue a new GET request to the given URI.
- 304 Not Modified
- Indicates that the resource has not been modified since the version specified by the request headers If-Modified-Since or If-None-Match. In such case, there is no need to retransmit the resource since the client still has a previously-downloaded copy.
- 305 Use Proxy (since HTTP/1.1)
- The requested resource is available only through a proxy, the address for which is provided in the response. For security reasons, many HTTP clients (such as Mozilla Firefox and Internet Explorer) do not obey this status code.
- 306 Switch Proxy
- No longer used. Originally meant «Subsequent requests should use the specified proxy.»
- 307 Temporary Redirect (since HTTP/1.1)
- In this case, the request should be repeated with another URI; however, future requests should still use the original URI. In contrast to how 302 was historically implemented, the request method is not allowed to be changed when reissuing the original request. For example, a POST request should be repeated using another POST request.
- 308 Permanent Redirect
- This and all future requests should be directed to the given URI. 308 parallel the behaviour of 301, but does not allow the HTTP method to change. So, for example, submitting a form to a permanently redirected resource may continue smoothly.
4xx client errors
This class of status code is intended for situations in which the error seems to have been caused by the client. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. These status codes are applicable to any request method. User agents should display any included entity to the user.
- 400 Bad Request
- The server cannot or will not process the request due to an apparent client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, size too large, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing).
- 401 Unauthorized
- Similar to 403 Forbidden, but specifically for use when authentication is required and has failed or has not yet been provided. The response must include a WWW-Authenticate header field containing a challenge applicable to the requested resource. See Basic access authentication and Digest access authentication. 401 semantically means «unauthorised», the user does not have valid authentication credentials for the target resource.
- Some sites incorrectly issue HTTP 401 when an IP address is banned from the website (usually the website domain) and that specific address is refused permission to access a website.[citation needed]
- 402 Payment Required
- Reserved for future use. The original intention was that this code might be used as part of some form of digital cash or micropayment scheme, as proposed, for example, by GNU Taler,[13] but that has not yet happened, and this code is not widely used. Google Developers API uses this status if a particular developer has exceeded the daily limit on requests.[14] Sipgate uses this code if an account does not have sufficient funds to start a call.[15] Shopify uses this code when the store has not paid their fees and is temporarily disabled.[16] Stripe uses this code for failed payments where parameters were correct, for example blocked fraudulent payments.[17]
- 403 Forbidden
- The request contained valid data and was understood by the server, but the server is refusing action. This may be due to the user not having the necessary permissions for a resource or needing an account of some sort, or attempting a prohibited action (e.g. creating a duplicate record where only one is allowed). This code is also typically used if the request provided authentication by answering the WWW-Authenticate header field challenge, but the server did not accept that authentication. The request should not be repeated.
- 404 Not Found
- The requested resource could not be found but may be available in the future. Subsequent requests by the client are permissible.
- 405 Method Not Allowed
- A request method is not supported for the requested resource; for example, a GET request on a form that requires data to be presented via POST, or a PUT request on a read-only resource.
- 406 Not Acceptable
- The requested resource is capable of generating only content not acceptable according to the Accept headers sent in the request. See Content negotiation.
- 407 Proxy Authentication Required
- The client must first authenticate itself with the proxy.
- 408 Request Timeout
- The server timed out waiting for the request. According to HTTP specifications: «The client did not produce a request within the time that the server was prepared to wait. The client MAY repeat the request without modifications at any later time.»
- 409 Conflict
- Indicates that the request could not be processed because of conflict in the current state of the resource, such as an edit conflict between multiple simultaneous updates.
- 410 Gone
- Indicates that the resource requested was previously in use but is no longer available and will not be available again. This should be used when a resource has been intentionally removed and the resource should be purged. Upon receiving a 410 status code, the client should not request the resource in the future. Clients such as search engines should remove the resource from their indices. Most use cases do not require clients and search engines to purge the resource, and a «404 Not Found» may be used instead.
- 411 Length Required
- The request did not specify the length of its content, which is required by the requested resource.
- 412 Precondition Failed
- The server does not meet one of the preconditions that the requester put on the request header fields.
- 413 Payload Too Large
- The request is larger than the server is willing or able to process. Previously called «Request Entity Too Large» in RFC 2616.[18]
- 414 URI Too Long
- The URI provided was too long for the server to process. Often the result of too much data being encoded as a query-string of a GET request, in which case it should be converted to a POST request. Called «Request-URI Too Long» previously in RFC 2616.[19]
- 415 Unsupported Media Type
- The request entity has a media type which the server or resource does not support. For example, the client uploads an image as image/svg+xml, but the server requires that images use a different format.
- 416 Range Not Satisfiable
- The client has asked for a portion of the file (byte serving), but the server cannot supply that portion. For example, if the client asked for a part of the file that lies beyond the end of the file. Called «Requested Range Not Satisfiable» previously RFC 2616.[20]
- 417 Expectation Failed
- The server cannot meet the requirements of the Expect request-header field.[21]
- 418 I’m a teapot (RFC 2324, RFC 7168)
- This code was defined in 1998 as one of the traditional IETF April Fools’ jokes, in RFC 2324, Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol, and is not expected to be implemented by actual HTTP servers. The RFC specifies this code should be returned by teapots requested to brew coffee.[22] This HTTP status is used as an Easter egg in some websites, such as Google.com’s «I’m a teapot» easter egg.[23][24][25] Sometimes, this status code is also used as a response to a blocked request, instead of the more appropriate 403 Forbidden.[26][27]
- 421 Misdirected Request
- The request was directed at a server that is not able to produce a response (for example because of connection reuse).
- 422 Unprocessable Entity
- The request was well-formed but was unable to be followed due to semantic errors.[8]
- 423 Locked (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The resource that is being accessed is locked.[8]
- 424 Failed Dependency (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The request failed because it depended on another request and that request failed (e.g., a PROPPATCH).[8]
- 425 Too Early (RFC 8470)
- Indicates that the server is unwilling to risk processing a request that might be replayed.
- 426 Upgrade Required
- The client should switch to a different protocol such as TLS/1.3, given in the Upgrade header field.
- 428 Precondition Required (RFC 6585)
- The origin server requires the request to be conditional. Intended to prevent the ‘lost update’ problem, where a client GETs a resource’s state, modifies it, and PUTs it back to the server, when meanwhile a third party has modified the state on the server, leading to a conflict.[28]
- 429 Too Many Requests (RFC 6585)
- The user has sent too many requests in a given amount of time. Intended for use with rate-limiting schemes.[28]
- 431 Request Header Fields Too Large (RFC 6585)
- The server is unwilling to process the request because either an individual header field, or all the header fields collectively, are too large.[28]
- 451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons (RFC 7725)
- A server operator has received a legal demand to deny access to a resource or to a set of resources that includes the requested resource.[29] The code 451 was chosen as a reference to the novel Fahrenheit 451 (see the Acknowledgements in the RFC).
5xx server errors
The server failed to fulfil a request.
Response status codes beginning with the digit «5» indicate cases in which the server is aware that it has encountered an error or is otherwise incapable of performing the request. Except when responding to a HEAD request, the server should include an entity containing an explanation of the error situation, and indicate whether it is a temporary or permanent condition. Likewise, user agents should display any included entity to the user. These response codes are applicable to any request method.
- 500 Internal Server Error
- A generic error message, given when an unexpected condition was encountered and no more specific message is suitable.
- 501 Not Implemented
- The server either does not recognize the request method, or it lacks the ability to fulfil the request. Usually this implies future availability (e.g., a new feature of a web-service API).
- 502 Bad Gateway
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and received an invalid response from the upstream server.
- 503 Service Unavailable
- The server cannot handle the request (because it is overloaded or down for maintenance). Generally, this is a temporary state.[30]
- 504 Gateway Timeout
- The server was acting as a gateway or proxy and did not receive a timely response from the upstream server.
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
- The server does not support the HTTP version used in the request.
- 506 Variant Also Negotiates (RFC 2295)
- Transparent content negotiation for the request results in a circular reference.[31]
- 507 Insufficient Storage (WebDAV; RFC 4918)
- The server is unable to store the representation needed to complete the request.[8]
- 508 Loop Detected (WebDAV; RFC 5842)
- The server detected an infinite loop while processing the request (sent instead of 208 Already Reported).
- 510 Not Extended (RFC 2774)
- Further extensions to the request are required for the server to fulfill it.[32]
- 511 Network Authentication Required (RFC 6585)
- The client needs to authenticate to gain network access. Intended for use by intercepting proxies used to control access to the network (e.g., «captive portals» used to require agreement to Terms of Service before granting full Internet access via a Wi-Fi hotspot).[28]
Unofficial codes
The following codes are not specified by any standard.
- 419 Page Expired (Laravel Framework)
- Used by the Laravel Framework when a CSRF Token is missing or expired.
- 420 Method Failure (Spring Framework)
- A deprecated response used by the Spring Framework when a method has failed.[33]
- 420 Enhance Your Calm (Twitter)
- Returned by version 1 of the Twitter Search and Trends API when the client is being rate limited; versions 1.1 and later use the 429 Too Many Requests response code instead.[34] The phrase «Enhance your calm» comes from the 1993 movie Demolition Man, and its association with this number is likely a reference to cannabis.[citation needed]
- 430 Request Header Fields Too Large (Shopify)
- Used by Shopify, instead of the 429 Too Many Requests response code, when too many URLs are requested within a certain time frame.[35]
- 450 Blocked by Windows Parental Controls (Microsoft)
- The Microsoft extension code indicated when Windows Parental Controls are turned on and are blocking access to the requested webpage.[36]
- 498 Invalid Token (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 498 indicates an expired or otherwise invalid token.[37]
- 499 Token Required (Esri)
- Returned by ArcGIS for Server. Code 499 indicates that a token is required but was not submitted.[37]
- 509 Bandwidth Limit Exceeded (Apache Web Server/cPanel)
- The server has exceeded the bandwidth specified by the server administrator; this is often used by shared hosting providers to limit the bandwidth of customers.[38]
- 529 Site is overloaded
- Used by Qualys in the SSLLabs server testing API to signal that the site can’t process the request.[39]
- 530 Site is frozen
- Used by the Pantheon Systems web platform to indicate a site that has been frozen due to inactivity.[40]
- 598 (Informal convention) Network read timeout error
- Used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network read timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.[41]
- 599 Network Connect Timeout Error
- An error used by some HTTP proxies to signal a network connect timeout behind the proxy to a client in front of the proxy.
Internet Information Services
Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS) web server expands the 4xx error space to signal errors with the client’s request.
- 440 Login Time-out
- The client’s session has expired and must log in again.[42]
- 449 Retry With
- The server cannot honour the request because the user has not provided the required information.[43]
- 451 Redirect
- Used in Exchange ActiveSync when either a more efficient server is available or the server cannot access the users’ mailbox.[44] The client is expected to re-run the HTTP AutoDiscover operation to find a more appropriate server.[45]
IIS sometimes uses additional decimal sub-codes for more specific information,[46] however these sub-codes only appear in the response payload and in documentation, not in the place of an actual HTTP status code.
nginx
The nginx web server software expands the 4xx error space to signal issues with the client’s request.[47][48]
- 444 No Response
- Used internally[49] to instruct the server to return no information to the client and close the connection immediately.
- 494 Request header too large
- Client sent too large request or too long header line.
- 495 SSL Certificate Error
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has provided an invalid client certificate.
- 496 SSL Certificate Required
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when a client certificate is required but not provided.
- 497 HTTP Request Sent to HTTPS Port
- An expansion of the 400 Bad Request response code, used when the client has made a HTTP request to a port listening for HTTPS requests.
- 499 Client Closed Request
- Used when the client has closed the request before the server could send a response.
Cloudflare
Cloudflare’s reverse proxy service expands the 5xx series of errors space to signal issues with the origin server.[50]
- 520 Web Server Returned an Unknown Error
- The origin server returned an empty, unknown, or unexpected response to Cloudflare.[51]
- 521 Web Server Is Down
- The origin server refused connections from Cloudflare. Security solutions at the origin may be blocking legitimate connections from certain Cloudflare IP addresses.
- 522 Connection Timed Out
- Cloudflare timed out contacting the origin server.
- 523 Origin Is Unreachable
- Cloudflare could not reach the origin server; for example, if the DNS records for the origin server are incorrect or missing.
- 524 A Timeout Occurred
- Cloudflare was able to complete a TCP connection to the origin server, but did not receive a timely HTTP response.
- 525 SSL Handshake Failed
- Cloudflare could not negotiate a SSL/TLS handshake with the origin server.
- 526 Invalid SSL Certificate
- Cloudflare could not validate the SSL certificate on the origin web server. Also used by Cloud Foundry’s gorouter.
- 527 Railgun Error
- Error 527 indicates an interrupted connection between Cloudflare and the origin server’s Railgun server.[52]
- 530
- Error 530 is returned along with a 1xxx error.[53]
AWS Elastic Load Balancer
Amazon’s Elastic Load Balancing adds a few custom return codes
- 460
- Client closed the connection with the load balancer before the idle timeout period elapsed. Typically when client timeout is sooner than the Elastic Load Balancer’s timeout.[54]
- 463
- The load balancer received an X-Forwarded-For request header with more than 30 IP addresses.[54]
- 561 Unauthorized
- An error around authentication returned by a server registered with a load balancer. You configured a listener rule to authenticate users, but the identity provider (IdP) returned an error code when authenticating the user.[55]
Caching warning codes (obsoleted)
The following caching related warning codes were specified under RFC 7234. Unlike the other status codes above, these were not sent as the response status in the HTTP protocol, but as part of the «Warning» HTTP header.[56][57]
Since this «Warning» header is often neither sent by servers nor acknowledged by clients, this header and its codes were obsoleted by the HTTP Working Group in 2022 with RFC 9111.[58]
- 110 Response is Stale
- The response provided by a cache is stale (the content’s age exceeds a maximum age set by a Cache-Control header or heuristically chosen lifetime).
- 111 Revalidation Failed
- The cache was unable to validate the response, due to an inability to reach the origin server.
- 112 Disconnected Operation
- The cache is intentionally disconnected from the rest of the network.
- 113 Heuristic Expiration
- The cache heuristically chose a freshness lifetime greater than 24 hours and the response’s age is greater than 24 hours.
- 199 Miscellaneous Warning
- Arbitrary, non-specific warning. The warning text may be logged or presented to the user.
- 214 Transformation Applied
- Added by a proxy if it applies any transformation to the representation, such as changing the content encoding, media type or the like.
- 299 Miscellaneous Persistent Warning
- Same as 199, but indicating a persistent warning.
See also
- Custom error pages
- List of FTP server return codes
- List of HTTP header fields
- List of SMTP server return codes
- Common Log Format
Explanatory notes
- ^ Emphasised words and phrases such as must and should represent interpretation guidelines as given by RFC 2119
References
- ^ a b c «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry». Iana.org. Archived from the original on December 11, 2011. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 10.1.1 «Expect»«.
- ^ Goland, Yaronn; Whitehead, Jim; Faizi, Asad; Carter, Steve R.; Jensen, Del (February 1999). HTTP Extensions for Distributed Authoring – WEBDAV. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2518. RFC 2518. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Oku, Kazuho (December 2017). An HTTP Status Code for Indicating Hints. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8297. RFC 8297. Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ^ Stewart, Mark; djna. «Create request with POST, which response codes 200 or 201 and content». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.3.4».
- ^ «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 7.7».
- ^ a b c d e Dusseault, Lisa, ed. (June 2007). HTTP Extensions for Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV). IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC4918. RFC 4918. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Delta encoding in HTTP. IETF. January 2002. doi:10.17487/RFC3229. RFC 3229. Retrieved February 25, 2011.
- ^ a b «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15.4 «Redirection 3xx»«.
- ^ Berners-Lee, Tim; Fielding, Roy T.; Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk (May 1996). Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTP/1.0. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC1945. RFC 1945. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «The GNU Taler tutorial for PHP Web shop developers 0.4.0». docs.taler.net. Archived from the original on November 8, 2017. Retrieved October 29, 2017.
- ^ «Google API Standard Error Responses». 2016. Archived from the original on May 25, 2017. Retrieved June 21, 2017.
- ^ «Sipgate API Documentation». Archived from the original on July 10, 2018. Retrieved July 10, 2018.
- ^ «Shopify Documentation». Archived from the original on July 25, 2018. Retrieved July 25, 2018.
- ^ «Stripe API Reference – Errors». stripe.com. Retrieved October 28, 2019.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 413». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 414». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ «RFC2616 on status 416». Tools.ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 7, 2011. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ TheDeadLike. «HTTP/1.1 Status Codes 400 and 417, cannot choose which». serverFault. Archived from the original on October 10, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Larry Masinter (April 1, 1998). Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol (HTCPCP/1.0). doi:10.17487/RFC2324. RFC 2324.
Any attempt to brew coffee with a teapot should result in the error code «418 I’m a teapot». The resulting entity body MAY be short and stout.
- ^ I’m a teapot
- ^ Barry Schwartz (August 26, 2014). «New Google Easter Egg For SEO Geeks: Server Status 418, I’m A Teapot». Search Engine Land. Archived from the original on November 15, 2015. Retrieved November 4, 2015.
- ^ «Google’s Teapot». Retrieved October 23, 2017.[dead link]
- ^ «Enable extra web security on a website». DreamHost. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ «I Went to a Russian Website and All I Got Was This Lousy Teapot». PCMag. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ a b c d Nottingham, M.; Fielding, R. (April 2012). «RFC 6585 – Additional HTTP Status Codes». Request for Comments. Internet Engineering Task Force. Archived from the original on May 4, 2012. Retrieved May 1, 2012.
- ^ Bray, T. (February 2016). «An HTTP Status Code to Report Legal Obstacles». ietf.org. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved March 7, 2015.
- ^ alex. «What is the correct HTTP status code to send when a site is down for maintenance?». Stack Overflow. Archived from the original on October 11, 2016. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ Holtman, Koen; Mutz, Andrew H. (March 1998). Transparent Content Negotiation in HTTP. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2295. RFC 2295. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ Nielsen, Henrik Frystyk; Leach, Paul; Lawrence, Scott (February 2000). An HTTP Extension Framework. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC2774. RFC 2774. Retrieved October 24, 2009.
- ^ «Enum HttpStatus». Spring Framework. org.springframework.http. Archived from the original on October 25, 2015. Retrieved October 16, 2015.
- ^ «Twitter Error Codes & Responses». Twitter. 2014. Archived from the original on September 27, 2017. Retrieved January 20, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Status Codes and SEO: what you need to know». ContentKing. Retrieved August 9, 2019.
- ^ «Screenshot of error page». Archived from the original (bmp) on May 11, 2013. Retrieved October 11, 2009.
- ^ a b «Using token-based authentication». ArcGIS Server SOAP SDK. Archived from the original on September 26, 2014. Retrieved September 8, 2014.
- ^ «HTTP Error Codes and Quick Fixes». Docs.cpanel.net. Archived from the original on November 23, 2015. Retrieved October 15, 2015.
- ^ «SSL Labs API v3 Documentation». github.com.
- ^ «Platform Considerations | Pantheon Docs». pantheon.io. Archived from the original on January 6, 2017. Retrieved January 5, 2017.
- ^ «HTTP status codes — ascii-code.com». www.ascii-code.com. Archived from the original on January 7, 2017. Retrieved December 23, 2016.
- ^
«Error message when you try to log on to Exchange 2007 by using Outlook Web Access: «440 Login Time-out»«. Microsoft. 2010. Retrieved November 13, 2013. - ^ «2.2.6 449 Retry With Status Code». Microsoft. 2009. Archived from the original on October 5, 2009. Retrieved October 26, 2009.
- ^ «MS-ASCMD, Section 3.1.5.2.2». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on March 26, 2015. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «Ms-oxdisco». Msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on July 31, 2014. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ^ «The HTTP status codes in IIS 7.0». Microsoft. July 14, 2009. Archived from the original on April 9, 2009. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
- ^ «ngx_http_request.h». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on September 19, 2017. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «ngx_http_special_response.c». nginx 1.9.5 source code. nginx inc. Archived from the original on May 8, 2018. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «return» directive Archived March 1, 2018, at the Wayback Machine (http_rewrite module) documentation.
- ^ «Troubleshooting: Error Pages». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 9, 2016.
- ^ «Error 520: web server returns an unknown error». Cloudflare. Retrieved November 1, 2019.
- ^ «527 Error: Railgun Listener to origin error». Cloudflare. Archived from the original on October 13, 2016. Retrieved October 12, 2016.
- ^ «Error 530». Cloudflare. Retrieved November 1, 2019.
- ^ a b «Troubleshoot Your Application Load Balancers – Elastic Load Balancing». docs.aws.amazon.com. Retrieved August 27, 2019.
- ^ «Troubleshoot your Application Load Balancers — Elastic Load Balancing». docs.aws.amazon.com. Retrieved January 24, 2021.
- ^ «Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Caching». datatracker.ietf.org. Retrieved September 25, 2021.
- ^ «Warning — HTTP | MDN». developer.mozilla.org. Retrieved August 15, 2021.
Some text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.5 Generic (CC BY-SA 2.5) license.
- ^ «RFC 9111: HTTP Caching, Section 5.5 «Warning»«. June 2022.
External links
- «RFC 9110: HTTP Semantics and Content, Section 15 «Status Codes»«.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Status Code Registry
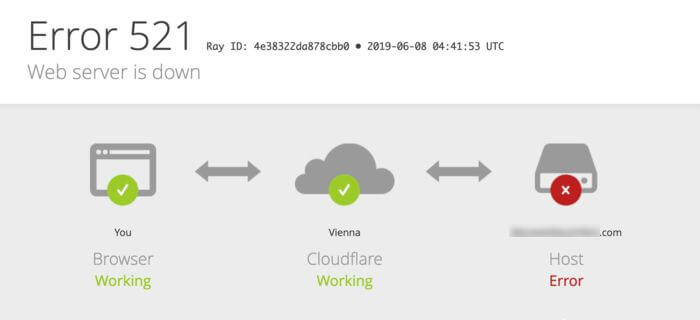
Ошибки 520, 521, 522, 524 связаны с проблемами в работе сервиса CloudFlare.
CloudFlare — сервис для перенаправления трафика на сайт с помощью облачного прокси-сервера, который обеспечивает дополнительную защиту от DDoS-атак и ускоряет загрузку вашего сайта.
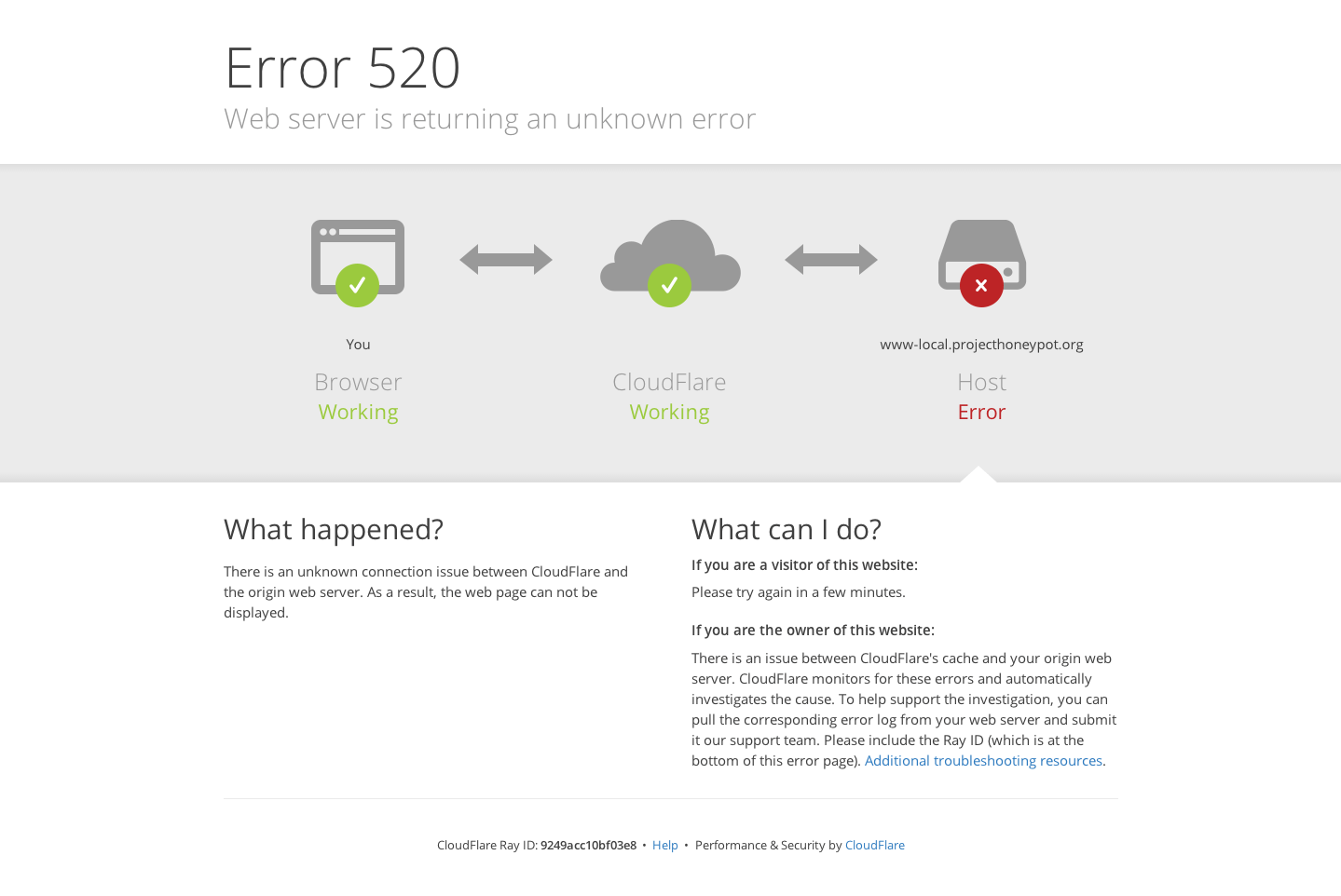
Ошибка 520 Unknown Error
Что означает ошибка 520? Система CloudFlare выдаёт 520 ошибку, если не может обработать ответ от веб-сервера, на котором расположен сайт:
Причины появления ошибки:
- сброс соединения (после успешного запроса сервер разорвал соединение);
- заголовок запроса превышает ограничение размера заголовка Cloudflare (более 8 КБ). Если у вас много файлов cookie или они очень большие, это может привести к увеличению размера заголовков. Так как у Cloudflare есть ограничение на размер заголовка в 8 КБ, он не может обработать длинный заголовок;
- пустой ответ от сервера. Это происходит, когда DNS домена указывают на неправильный сервер.
- некорректный ответ от сервера;
- система безопасности блокирует запросы. Укажите IP-адреса Cloudflare в белом списке, чтобы система не блокировала запросы.
Способы устранения ошибки:
- Отключить CloudFlare. Так вы сможете понять, где находится ошибка (на сервере или в CloudFlare).
- Удалить плагины. Для плагинов иногда требуется много файлов cookies. Если на сайте много плагинов, это может повлиять на размер заголовков. Они могут быть слишком большими по размеру, и Cloudflare не справится с ними. Чтобы исправить ошибку, отключите плагины один за другим. Если ошибка пропадёт, удалите некоторые из плагинов.
- Проверьте настройки DNS в CloudFlare. Убедитесь, что запись A указывает на правильный IP-адрес.
Подробные рекомендации по исправлению ошибки 520 даны в справке CloudFlare.
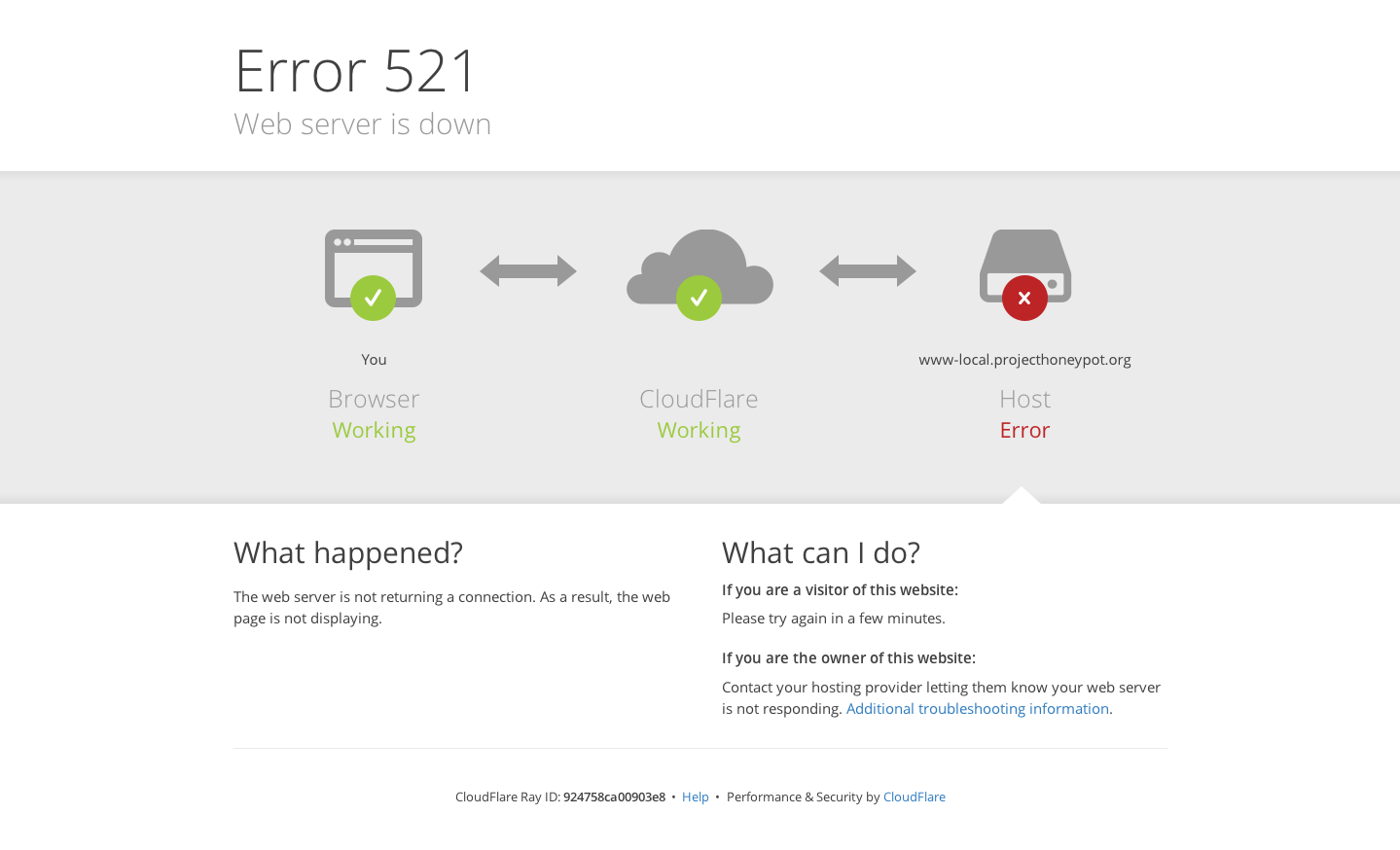
Ошибка 521 Web Server Is Down
Код ошибки 521 возникает, когда веб-сервер обрывает соединение с CloudFlare:
Это может произойти в двух случаях:
- сервер не отвечает или недоступен. Необходимо проверить работоспособность сервера;
- веб-сервер блокирует запросы CloudFlare. Поскольку CloudFlare работает как обратный прокси-сервер, все запросы к серверам поступают от IP-адресов CloudFlare. Иногда система безопасности хостинга принимает постоянные подключения с одних и тех же IP-адресов за DDoS-атаку. В результате на IP-адреса CloudFlare накладывается блокировка/ограничения по скорости.
Диапазон IP-адресов CloudFlare вы можете увидеть по ссылке.
Рекомендации по исправлению ошибки 521 даны в справке CloudFlare.
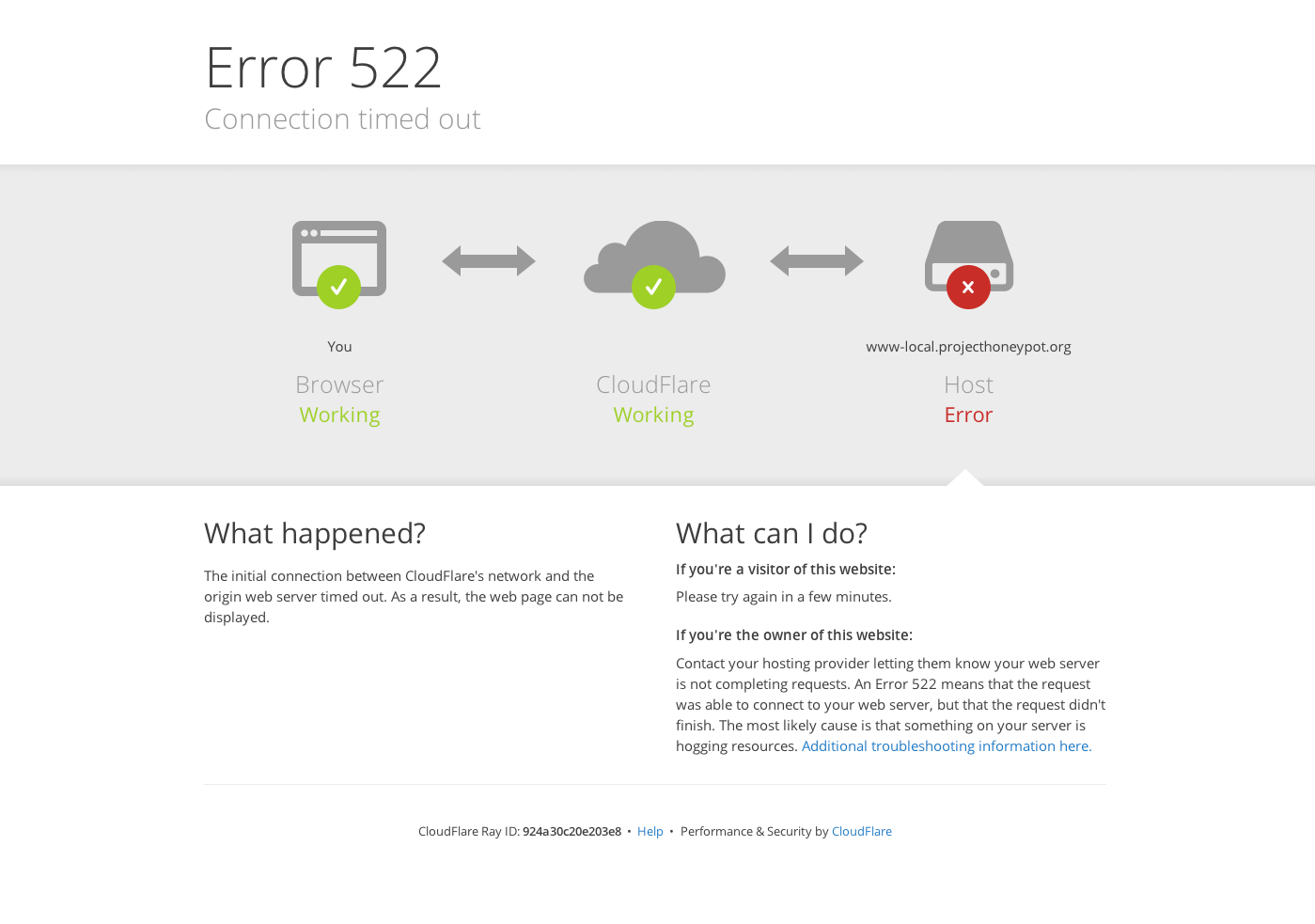
Ошибка 522 Connection timed out
Ошибка 522 возникает, если превышено время ожидания ответа от веб-сервера и пользователь не может попасть на страницу:
Основные причины:
- веб-сервер перегружен и не ответил на запрос,
- на веб-сервере стоит система защиты, которая блокирует запросы от CloudFlare,
- веб-сервер недоступен,
- некорректный IP-адрес, установленный в настройках DNS на CloudFlare (Запрос от CloudFlare был отправлен на другой IP),
- проблемы с маршрутизацией сети между CloudFlare и веб-сервером.
Что делать? Для решения проблемы удостоверьтесь, что ваш веб-сервер активен и принимает HTTP-запросы. Проверьте, корректны ли настройки DNS в Личном кабинете на CloudFlare.
Подробные рекомендации по исправлению ошибки 522 даны в справке CloudFlare.
Как исправить ошибку 522 в Google Chrome
Методы решения:
- Очистите кеш браузера. Браузер может быть переполнен данными о посещении сайтов. Освободите место в кэше браузера по инструкции.
- Удалите расширение браузера, которое нарушает соединение с сервером. Отключайте расширения по очереди, чтобы найти то, которое выдает ошибку.
- Проверьте подключение к интернету. Низкая скорость интернета или перебои при подключении может повлиять на время получения ответа сервера. Из-за этого и появляется ошибка 522.
Как проверить подключение к интернету
-
1.
Откройте командную строку. Для этого введите в поисковую строку «Командная строка» и выберите появившееся приложение:
-
2.
Введите в командной строке:
Готово, вы получите сообщение с количеством переданных и полученных пакетов. Если потерянных пакетов нет, значит, у вас хорошее соединение с интернетом и проблема в другом. Если потерянные пакеты есть, свяжитесь с интернет-провайдером, чтобы улучшить интернет-соединение.
4. Очистите кеш DNS. Проблемы с соединением могут возникнуть из-за несоответствия IP-адреса сервера сайта в кэше компьютера с реальным адресом. Такое происходит, когда владельцы сайтов по какой-либо причине меняют IP-адреса сервера. Чтобы устранить эту проблему, воспользуйтесь инструкцией.
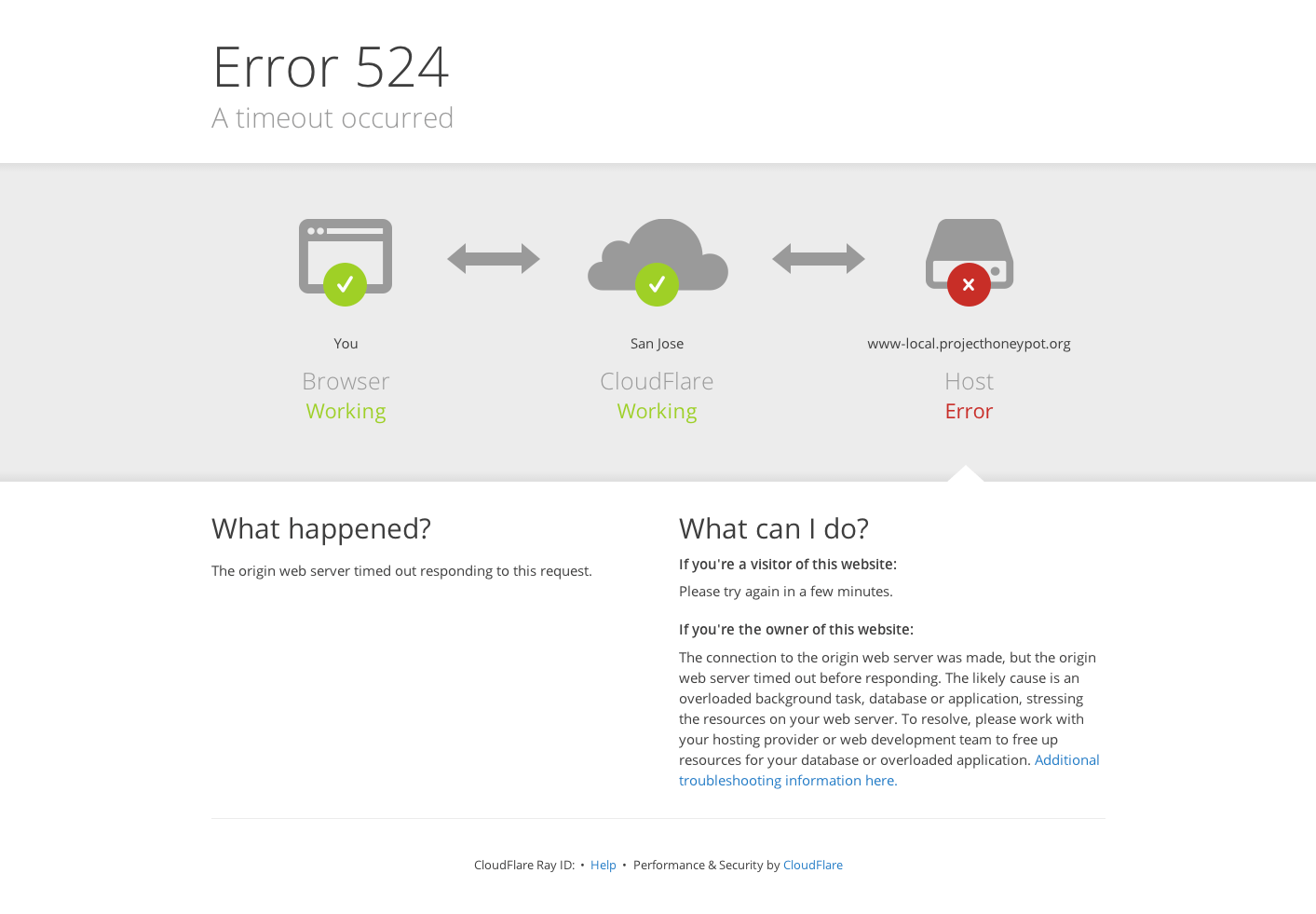
Ошибка 524 A timeout occurred
Ошибка 524 возникает, когда подключение с веб-сервером установлено, но он не ответил за установленное время ожидания соединения:
Время ожидания HTTP-ответа на CloudFlare — 100 секунд. Если веб-сервер не предоставил ответ, система выдаст 524 ошибку.
Основные причины:
- длительная работа PHP-процесса или запроса к базе данных;
- веб-сервер перегружен. Проверьте доступные ресурсы сервера, в том числе процессор и оперативную память.
Если вы регулярно выполняете тяжёлые запросы, которые могут занять больше 100 секунд, переместите эти процессы на субдомен, который не проксимируется в Cloudflare.
Рекомендации по исправлению ошибки 524 даны в справке CloudFlare.
Техническая поддержка
Специалисты REG.RU не оказывают техническую поддержку по сервису CloudFlare. Для устранения ошибки обратитесь в техническую поддержку CloudFlare. Если некорректная работа сайта связана с хостингом REG.RU, напишите заявку в службу технической поддержки.
Ошибки 520-524 требуют много знаний о сервере и его работе, поэтому самый верный способ решить проблему ― обратиться к хостинг-провайдеру, администратору сайта или к технической поддержке CloudFlare (если проблема на стороне их сервиса).
Устранение ошибки 521 при открытии сайтов
Способ 1: Проверка доступности конечного адреса
Наиболее часто сообщение об ошибке с кодом 521 появляется в ситуации, когда сервер, на котором находится нужный сайт, по каким-то причинам недоступен. Самый простой способ убедиться в этом – воспользоваться сервисом проверки, вроде Down For Everyone.
- С помощью любого браузера (желательно всё-таки Google Chrome) перейдите по ссылке выше. После загрузки введите в поле, отмеченное на скриншоте, адрес проблемного ресурса и нажмите «or just me?».
Способ 2: Очистка куки
Также сбой может быть характерным для следующей ситуации: хост-сервер обновил DNS, тогда как в имеющихся cookies записаны старые, уже недоступные значения. Решением будет удаление куки проблемного сайта – описание процедуры для всех популярных веб-обозревателей вы можете найти по ссылкам далее.
Способ 3: Добавление адреса в файл hosts
В некоторых случаях работает следующая процедура: точный адрес сайта добавляется в системный файл hosts, после чего можно получить доступ к нужному ресурсу.
- Самый быстрый способ открыть и отредактировать hosts в Windows – воспользоваться «Командной строкой», запущенной от имени администратора. Для этого следует найти оснастку в «Поиске» и задействовать соответствующий пункт запуска.
Подробнее: Как открыть «Командную строку» от имени администратора в Windows 7 и Windows 10
После появления интерфейса введите в нём следующую команду, после чего нажмите Enter.
Notepad C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts
Появится окно «Блокнота», в котором уже будет открытый для редактирования файл. Поместите курсор в конец документа – это обязательно должна быть новая строка, поэтому при необходимости сделайте её нажатием на Enter, затем напишите адрес ресурса.
После полного запуска ОС попробуйте перейти на проблемный ресурс – не исключено, что теперь доступ появится.
Способ 4: Использование архивной версии сайта
Если сайт «лежит» уже давно, существует вероятность, что он удалён с сервера, и обычными методами получить к нему доступ не выйдет. В такой ситуации пригодятся возможности просмотра более недоступных страниц, которых существует две: кэш поисковика или специальный сервис.
Кэш Google
Самый крупный в мире поисковик уже достаточно давно предоставляет возможность кэширования страниц и их последующего просмотра.
- Откройте основной ресурс «корпорации добра», где введите в поисковую строку адрес искомого сайта и нажмите «Поиск в Google».
- Найдите среди выдачи нужный результат, затем кликните левой кнопкой мыши по стрелке рядом с названием ресурса, где выберите пункт «Сохранённая копия».
Сервис Wayback Machine
Несколько лет назад появилась инициатива, целью которой является создание архива интернет-страниц для будущих поколений. Результатом её деятельности стал сервис Wayback Machine: он тоже позволяет просматривать копии сайтов, в том числе и давно удалённых из основного пространства интернета.
- Перейдите на страницу сервиса, затем воспользуйтесь строкой ввода, в которой укажите нужный адрес и нажмите «Browse History».
- Результаты поиска обычно выдаются в формате ленты времени – выберите на ней интересующий год и кликните по соответствующей полоске.
- Теперь появится календарь с месяцами года, выбранного на предыдущем шаге. Даты, отмеченные синим – активные ссылки c сохранёнными снимками сайта. Наведите на неё курсор, затем щёлкните по одному из временных отрезков.
- Копии вполне функциональны: нередко сохраняются даже прикреплённые файлы плюс возможен переход по ссылкам на другие части ресурса, но только в том случае, если их снимки тоже присутствуют в архиве.
Этот метод сложно назвать полноценным решением рассматриваемой проблемы, однако он пригодится в случаях, когда критически важно получить информацию с недоступной страницы.
Источник
Ошибки 520, 521, 522, 524 на сайте
Ошибки 520, 521, 522, 524 связаны с проблемами в работе сервиса CloudFlare.
CloudFlare — сервис для перенаправления трафика на сайт с помощью облачного прокси-сервера, который обеспечивает дополнительную защиту от DDoS-атак и ускоряет загрузку вашего сайта.
Ошибка 520 Unknown Error
Что означает ошибка 520? Система CloudFlare выдаёт 520 ошибку, если не может обработать ответ от веб-сервера, на котором расположен сайт:
Причины появления ошибки:
- сброс соединения (после успешного запроса сервер разорвал соединение);
- заголовок запроса превышает ограничение размера заголовка Cloudflare (более 8 КБ). Если у вас много файлов cookie или они очень большие, это может привести к увеличению размера заголовков. Так как у Cloudflare есть ограничение на размер заголовка в 8 КБ, он не может обработать длинный заголовок;
- пустой ответ от сервера. Это происходит, когда DNS домена указывают на неправильный сервер.
- некорректный ответ от сервера;
- система безопасности блокирует запросы. Укажите IP-адреса Cloudflare в белом списке, чтобы система не блокировала запросы.
Способы устранения ошибки:
- Отключить CloudFlare. Так вы сможете понять, где находится ошибка (на сервере или в CloudFlare).
- Удалить плагины. Для плагинов иногда требуется много файлов cookies. Если на сайте много плагинов, это может повлиять на размер заголовков. Они могут быть слишком большими по размеру, и Cloudflare не справится с ними. Чтобы исправить ошибку, отключите плагины один за другим. Если ошибка пропадёт, удалите некоторые из плагинов.
- Проверьте настройки DNS в CloudFlare. Убедитесь, что запись A указывает на правильный IP-адрес.
Подробные рекомендации по исправлению ошибки 520 даны в справке CloudFlare.
Ошибка 521 Web Server Is Down
Код ошибки 521 возникает, когда веб-сервер обрывает соединение с CloudFlare:
Это может произойти в двух случаях:
- сервер не отвечает или недоступен. Необходимо проверить работоспособность сервера;
- веб-сервер блокирует запросы CloudFlare. Поскольку CloudFlare работает как обратный прокси-сервер, все запросы к серверам поступают от IP-адресов CloudFlare. Иногда система безопасности хостинга принимает постоянные подключения с одних и тех же IP-адресов за DDoS-атаку. В результате на IP-адреса CloudFlare накладывается блокировка/ограничения по скорости.
Диапазон IP-адресов CloudFlare вы можете увидеть по ссылке.
Рекомендации по исправлению ошибки 521 даны в справке CloudFlare.
Ошибка 522 Connection timed out
Ошибка 522 возникает, если превышено время ожидания ответа от веб-сервера и пользователь не может попасть на страницу:
- веб-сервер перегружен и не ответил на запрос,
- на веб-сервере стоит система защиты, которая блокирует запросы от CloudFlare,
- веб-сервер недоступен,
- некорректный IP-адрес, установленный в настройках DNS на CloudFlare (Запрос от CloudFlare был отправлен на другой IP),
- проблемы с маршрутизацией сети между CloudFlare и веб-сервером.
Что делать? Для решения проблемы удостоверьтесь, что ваш веб-сервер активен и принимает HTTP-запросы. Проверьте, корректны ли настройки DNS в Личном кабинете на CloudFlare.
Подробные рекомендации по исправлению ошибки 522 даны в справке CloudFlare.
Как исправить ошибку 522 в Google Chrome
- Очистите кеш браузера. Браузер может быть переполнен данными о посещении сайтов. Освободите место в кэше браузера по инструкции.
- Удалите расширение браузера, которое нарушает соединение с сервером. Отключайте расширения по очереди, чтобы найти то, которое выдает ошибку.
- Проверьте подключение к интернету. Низкая скорость интернета или перебои при подключении может повлиять на время получения ответа сервера. Из-за этого и появляется ошибка 522.
Откройте командную строку. Для этого введите в поисковую строку «Командная строка» и выберите появившееся приложение:
Источник
Ошибки 520, 521, 522, 524
Ошибки 520, 521, 522, 524 могут появляться на сайте в том случае, если вы используете для своего сайта сервисы Cloudflare. Cloudflare — сервис, перенаправляющий трафик. Он позволяет увеличить скорость загрузки сайта и обеспечивает защиту от хакерских и DDoS-атак.
Ошибка 520 (Web server is returning an unknown error)
Если Cloudflare не удается обработать ответ сервера, на котором размещен сайт, то он выдает эту ошибку.
Причины появления ошибки 520
- Разрыв соединения, когда запрос к серверу был успешным.
- Превышение размера заголовка запроса (больше 8 КБ).
- Ответ сервера не содержит информацию.
- Ответ сервера некорректен.
Способы устранения ошибки 520 Web server is returning an unknown error
Если любое из вышеперечисленных условий исходит от веб-сервера, на котором размещен сайт, нужно обратиться в техподдержку хостинг-провайдера.
Правила ограничения скорости Cloudflare или другие запросы фильтрации иногда могут вызывать проблемы в работе сайта. Важно проверить и протестировать ваш сайт после подключения сервисов Cloudflare. Если на сервере хостинга используются системы безопасности, блокирующие запросы к сайту, обязательно укажите IP-адреса Cloudflare в белом списке, чтобы исключить вероятность блокировки запросов.
Ошибка 521 (Web Server Is Down)
Браузер показывает ошибку 521, когда веб-сервер неожиданно обрывает соединение с Cloudflare.
Причины появления ошибки 521
- Невозможно получить ответ от сервера.
- Система безопасности веб-сервера внесла запросы Cloudflare в черный список. Это связано с тем, что система работает по принципу обратного прокси-сервера. Ваша система безопасности могла принять периодические подключения от статических IP-адресов за DDoS-атаку. Из-за этого адреса блокируются или ограничиваются по скорости.
Способы устранения ошибки 521 Web Server Is Down
Возможно, веб-сервер отключен или работает с перебоями. В таком случае:
- Убедитесь, что ваш веб-сервер работает нормально.
- Просмотрите журналы ошибок сервера, чтобы выявить причину ошибки.
Если веб-сервер или хостинг-провайдер блокируют запросы Cloudflare, внесите в белый список все диапазоны IP-адресов сервиса в брандмауэре сервера или другом программном обеспечении безопасности.
Ошибка 522 (Connection timed out)
Появляется в случае, когда превышено время ожидания ответа от веб-сервера.
Причины появления ошибки 522
- Веб-сервер не может ответить на запрос из-за высокой загруженности.
- Система защиты веб-сервера блокирует запросы Cloudflare.
- Нет доступа к веб-серверу.
- IP-адреса Cloudflare не блокируются в брандмауэре.
- Ваш хостинг-провайдер не ограничивает скорость и не блокирует запросы от Cloudflare.
- Веб-сервер не перегружен.
Неисправную маршрутизацию в сети между Cloudflare и исходным веб-сервером устранить сложнее. Прежде чем перейти к этому пункту, исключите предыдущие. Если вы считаете, что причиной могут быть проблемы с сетью, отправьте заявку в службу поддержки Cloudflare.
Ошибка 524 (A timeout occurred)
Браузер покажет эту страницу, когда подключение к веб-серверу будет установлено, но его ответ превысит лимит ожидания. Cloudflare ожидает HTTP-ответ в течение 100 секунд.
Причины появления ошибки 524
- Проблемы в работе PHP-скриптов или сбой базы данных.
- Высокая загруженность веб-сервера.
Способы устранения ошибки 524 A timeout occurred
Проверьте доступные ресурсы веб-сервера, включая процессор, оперативную память и общий уровень трафика. Высокий уровень использования памяти память или высокая загрузка процессора могут сигнализировать о проблеме с ресурсами.
Если вы регулярно отправляете HTTP-запросы, выполнение которых занимает более 100 секунд (например, экспорт больших данных), рассмотрите возможность перемещения этих длительных процессов в поддомен, который не проксируется Cloudflare.
 Туториал: как исправить ошибки сервера
Туториал: как исправить ошибки сервера
Источник
На сайте ошибки 520, 521, 522, 524
520, 521, 522, 524 — это нестандартные типы ошибок, которые можно встретить при использовании сервиса CloudFlare. CloudFlare — сервис, с помощью которого можно перенаправить трафик на сайт, ускорить загрузку его страниц и настроить дополнительную защиту от DDoS-атак. Cloudflare работает как обратный прокси-сервер для сайта.
Unknown Error — ошибка 520
Если CloudFlare не может обработать ответ от веб-сервера, на котором расположен сайт, вы увидите ошибку 520:
Возможные причины ошибки:
- сервер дает некорректный ответ;
- приходит пустой ответ от сервера;
- сервер разорвал соединение после успешного запроса;
- заголовок запроса превышает ограничение размера (более 8 КБ).
Исправить ошибку 520 можно с помощью инструкций в справке CloudFlare.
Web Server Is Down — ошибка 521
Если между веб-сервером и CloudFlare оборвалось соединение, вы увидите ошибку 521:
Основные причины ошибки:
- сервер недоступен или не отвечает — проверьте работоспособность сервера;
- веб-сервер блокирует все запросы. Поскольку CloudFlare работает по принципу обратного прокси-сервера, все запросы приходят от IP-адресов системы. Система безопасности принимает регулярные подключения с одинаковых адресов IP за DDoS-атаку. Из-за этого накладываются ограничения по скорости.
На официальном сайте можно увидеть диапазон IP-адресов CloudFlare. Ошибку 521 можно исправить с помощью инструкций в справке CloudFlare.
Connection timed out — ошибка 522
Если время ожидания ответа от веб-сервера превышено, вы увидите ошибку 522:
Ошибка может возникнуть, если:
- веб-сервер недоступен;
- веб-сервер перегружен и не отвечает;
- запросы от CloudFlare блокирует система защиты веб-сервера;
- некорректные настройки маршрутизации между веб-сервером и CloudFlare;
- в настройках DNS на CloudFlare установлен некорректный IP-адрес.
Перед решением проблемы убедитесь, что ваш веб-сервер принимает HTTP-запросы. Также проверьте, что DNS в Личном кабинете на CloudFlare настроены корректно. Ошибку 522 можно исправить с помощью инструкций в справке CloudFlare.
A timeout occurred — Ошибка 524
В случае когда подключение с веб-сервером установлено, но он не успел ответить за установленное время ожидания, может возникнуть ошибка 524. Время ожидания HTTP-ответа на CloudFlare — 100 секунд.
Основные причины ошибки:
- перегружен веб-сервер (проверьте процессор, оперативную память и другие ресурсы сервера);
- задержка запроса к базам данных или PHP-процесса.
Ошибку 522 можно исправить с помощью инструкций в справке CloudFlare.
Обратите внимание!
Специалисты 2domains не оказывают техническую поддержку по сервису CloudFlare. По вопросам возникновения ошибок обращайтесь в техническую поддержку CloudFlare. Если некорректная работа сайта связана с хостингом 2domains, оставьте заявку в клиентскую службу.
Источник
Ошибки 520, 521, 522, 524 могут появляться на сайте в том случае, если вы используете для своего сайта сервисы Cloudflare. Cloudflare — сервис, перенаправляющий трафик. Он позволяет увеличить скорость загрузки сайта и обеспечивает защиту от хакерских и DDoS-атак.
Ошибка 520 (Web server is returning an unknown error)
Если Cloudflare не удается обработать ответ сервера, на котором размещен сайт, то он выдает эту ошибку.
Причины появления ошибки 520
- Разрыв соединения, когда запрос к серверу был успешным.
- Превышение размера заголовка запроса (больше 8 КБ).
- Ответ сервера не содержит информацию.
- Ответ сервера некорректен.
Способы устранения ошибки 520 Web server is returning an unknown error
Если любое из вышеперечисленных условий исходит от веб-сервера, на котором размещен сайт, нужно обратиться в техподдержку хостинг-провайдера.
Правила ограничения скорости Cloudflare или другие запросы фильтрации иногда могут вызывать проблемы в работе сайта. Важно проверить и протестировать ваш сайт после подключения сервисов Cloudflare. Если на сервере хостинга используются системы безопасности, блокирующие запросы к сайту, обязательно укажите IP-адреса Cloudflare в белом списке, чтобы исключить вероятность блокировки запросов.
Список диапазонов IP-адресов Cloudflare
Ошибка 521 (Web Server Is Down)
Браузер показывает ошибку 521, когда веб-сервер неожиданно обрывает соединение с Cloudflare.
Причины появления ошибки 521
- Невозможно получить ответ от сервера.
- Система безопасности веб-сервера внесла запросы Cloudflare в черный список. Это связано с тем, что система работает по принципу обратного прокси-сервера. Ваша система безопасности могла принять периодические подключения от статических IP-адресов за DDoS-атаку. Из-за этого адреса блокируются или ограничиваются по скорости.
Способы устранения ошибки 521 Web Server Is Down
Возможно, веб-сервер отключен или работает с перебоями. В таком случае:
- Убедитесь, что ваш веб-сервер работает нормально.
- Просмотрите журналы ошибок сервера, чтобы выявить причину ошибки.
Если веб-сервер или хостинг-провайдер блокируют запросы Cloudflare, внесите в белый список все диапазоны IP-адресов сервиса в брандмауэре сервера или другом программном обеспечении безопасности.
Ошибка 522 (Connection timed out)
Появляется в случае, когда превышено время ожидания ответа от веб-сервера.
Причины появления ошибки 522
- Веб-сервер не может ответить на запрос из-за высокой загруженности.
- Система защиты веб-сервера блокирует запросы Cloudflare.
- Нет доступа к веб-серверу.
-
Некорректно указаны настройки DNS на Cloudflare: запросы отправляются по другому адресу.
-
Неверная настройка маршрутизации между Cloudflare и веб-сервером.
Способы устранения ошибки 522 Connection timed out
Убедитесь, что:
- IP-адреса Cloudflare не блокируются в брандмауэре.
- Ваш хостинг-провайдер не ограничивает скорость и не блокирует запросы от Cloudflare.
- Веб-сервер не перегружен.
Неисправную маршрутизацию в сети между Cloudflare и исходным веб-сервером устранить сложнее. Прежде чем перейти к этому пункту, исключите предыдущие. Если вы считаете, что причиной могут быть проблемы с сетью, отправьте заявку в службу поддержки Cloudflare.
Ошибка 524 (A timeout occurred)
Браузер покажет эту страницу, когда подключение к веб-серверу будет установлено, но его ответ превысит лимит ожидания. Cloudflare ожидает HTTP-ответ в течение 100 секунд.
Причины появления ошибки 524
- Проблемы в работе PHP-скриптов или сбой базы данных.
- Высокая загруженность веб-сервера.
Способы устранения ошибки 524 A timeout occurred
Проверьте доступные ресурсы веб-сервера, включая процессор, оперативную память и общий уровень трафика. Высокий уровень использования памяти память или высокая загрузка процессора могут сигнализировать о проблеме с ресурсами.
Если вы регулярно отправляете HTTP-запросы, выполнение которых занимает более 100 секунд (например, экспорт больших данных), рассмотрите возможность перемещения этих длительных процессов в поддомен, который не проксируется Cloudflare.
Служба поддержки RU-CENTER не оказывает техническую поддержку по сервису Cloudflare. Для устранения ошибок, пожалуйста, обратитесь в техническую поддержку Cloudflare. Если неполадки в работе сайта связаны с хостингом RU-CENTER, пожалуйста, отправьте заявку в нашу службу технической поддержки.
 Туториал: как исправить ошибки сервера
Туториал: как исправить ошибки сервера
Error 521 is a Cloudflare-specific error message (like error 520) that appears when your WordPress site’s server refuses a connection with Cloudflare.
In this post, you’ll learn:
- More about what the Error 521 message is
- What causes the Error 521 message
- How to fix Error 521 for Cloudflare and WordPress
What is Error 521 Web Server is Down?
As you learned above, the Error 521 message is an error message that’s specific to Cloudflare.
Essentially, it means that your web browser was able to successfully connect to Cloudflare, but Cloudflare was not able to connect to the origin web server – AKA your WordPress site’s server.
Specifically, Cloudflare tried to connect to your WordPress site’s server but received a connection refused error in response.
Because Cloudflare cannot connect to your site, it’s unable to display your site to visitors and shows the Error 521 message instead:
What Causes the Error 521 Message?
Typically, the Error 521 message is caused by one of two situations:
First, your WordPress site’s server may be down. Even if everything else is configured properly, if your WordPress site’s server is offline, Cloudflare simply won’t be able to connect.
Second, your web server might be running fine but blocking Cloudflare’s requests for some reason. Because of how Cloudflare works, some server-side security solutions might inadvertently block Cloudflare’s IP addresses.
Because Cloudflare is a reverse proxy, all of the traffic coming to your origin server will appear as if it’s coming from a small range of Cloudflare IPs (rather than each individual visitor’s unique IP address). As such, some security solutions will view high traffic from a limited number of IP addresses as an attack and block them.
When that happens, Cloudflare won’t be able to connect and will display the Error 521 message instead.
How to Fix Error 521 for Cloudflare and WordPress
Now that you know what’s happening, let’s dig into how to fix Error 521 in WordPress.
Step 1: Test if the Origin Server is Online
Before going any further, you’ll want to make sure that your WordPress site’s server is online and functioning normally. If it’s not, there’s no sense digging into further troubleshooting steps.
To test this, you can run a cURL command. If you’re on Mac or Linux, you can run this right from Terminal.
Windows doesn’t have cURL installed by default and, while you can install it, a simpler way is to use KeyCDN’s online HTTP Header Check tool.
All you do is plug in http://1.2.3.4, where 1.2.3.4 is the actual IP address of your server.
If you host at Kinsta, you can find your server IP address in the Sites tab:
Or, you can also take it from the A record for your domain in the DNS area of the Cloudflare web dashboard.
If your server is up, you should see an HTTP 200 response. Or, if you host at Kinsta, you’ll see 404 Not Found, which also means the web server is up (there’s just no page associated with that IP):
If there’s a problem, you’ll see something like Host Not Found or Failed to connect:
If there’s a problem with your server and you’re not sure what’s going on, reach out to your host’s support (you can access Kinsta support from anywhere in your dashboard via the Intercom widget).
Step 2: Whitelist all Cloudflare IP ranges in your server’s firewall
If your WordPress site’s server is functioning normally but you still see the Error 521 message when you try to access your site, the next step is to whitelist all of Cloudflare’s IP ranges to make sure that your server isn’t blocking them.
Here’s a full list of Cloudflare’s IP ranges.
You’ll want to make sure you aren’t blocking these IP addresses in .htaccess, iptables, or your firewall. And you’ll also want to make sure that your hosting provider isn’t rate limiting or blocking IP requests from Cloudflare’s IP addresses.
If you’re not sure how to do this, reach out to your host’s support. At Kinsta, these IP ranges should already be whitelisted.
Step 3: Consider more specific issues
Finally, here are some more specific technical steps you can take, depending on your server’s configuration.
1) If you just started using Cloudflare’s HTTPS, your origin server might not be configured to allow Cloudflare’s IP addresses to access port 443. If you can’t configure your firewall to allow this, try using Flexible SSL instead of Full SSL at Cloudflare.
2) Make sure you’re using the most recent versions of Bad Behavior or mod_security, if applicable.
3) If you’re using the mod_antiloris or mod_reqtimeout Apache modules, disable and unload those modules.
Conclusion
If you host at Kinsta and are still experiencing the 521 Error after implementing these tweaks, our support will be able to help – just reach out through the Intercom chat widget in your Kinsta dashboard.
Suggested reading: How to Set up Cloudflare APO for WordPress and How to Fix the “SSL Handshake Failed” Error (5 Methods).
Get all your applications, databases and WordPress sites online and under one roof. Our feature-packed, high-performance cloud platform includes:
- Easy setup and management in the MyKinsta dashboard
- 24/7 expert support
- The best Google Cloud Platform hardware and network, powered by Kubernetes for maximum scalability
- An enterprise-level Cloudflare integration for speed and security
- Global audience reach with up to 35 data centers and 275 PoPs worldwide
Test it yourself with $20 off your first month of Application Hosting or Database Hosting. Explore our plans or talk to sales to find your best fit.
- Unknown Error — ошибка 520
- Web Server Is Down — ошибка 521
- Connection timed out — ошибка 522
- A timeout occurred — Ошибка 524
520, 521, 522, 524 — это нестандартные типы ошибок, которые можно встретить при использовании сервиса CloudFlare. CloudFlare — сервис, с помощью которого можно перенаправить трафик на сайт, ускорить загрузку его страниц и настроить дополнительную защиту от DDoS-атак. Cloudflare работает как обратный прокси-сервер для сайта.
Unknown Error — ошибка 520
Если CloudFlare не может обработать ответ от веб-сервера, на котором расположен сайт, вы увидите ошибку 520:
Возможные причины ошибки:
- сервер дает некорректный ответ;
- приходит пустой ответ от сервера;
- сервер разорвал соединение после успешного запроса;
- заголовок запроса превышает ограничение размера (более 8 КБ).
Исправить ошибку 520 можно с помощью инструкций в справке CloudFlare.
Web Server Is Down — ошибка 521
Если между веб-сервером и CloudFlare оборвалось соединение, вы увидите ошибку 521:
Основные причины ошибки:
- сервер недоступен или не отвечает — проверьте работоспособность сервера;
- веб-сервер блокирует все запросы. Поскольку CloudFlare работает по принципу обратного прокси-сервера, все запросы приходят от IP-адресов системы. Система безопасности принимает регулярные подключения с одинаковых адресов IP за DDoS-атаку. Из-за этого накладываются ограничения по скорости.
На официальном сайте можно увидеть диапазон IP-адресов CloudFlare. Ошибку 521 можно исправить с помощью инструкций в справке CloudFlare.
Connection timed out — ошибка 522
Если время ожидания ответа от веб-сервера превышено, вы увидите ошибку 522:
Ошибка может возникнуть, если:
- веб-сервер недоступен;
- веб-сервер перегружен и не отвечает;
- запросы от CloudFlare блокирует система защиты веб-сервера;
- некорректные настройки маршрутизации между веб-сервером и CloudFlare;
- в настройках DNS на CloudFlare установлен некорректный IP-адрес.
Перед решением проблемы убедитесь, что ваш веб-сервер принимает HTTP-запросы. Также проверьте, что DNS в Личном кабинете на CloudFlare настроены корректно. Ошибку 522 можно исправить с помощью инструкций в справке CloudFlare.
A timeout occurred — Ошибка 524
В случае когда подключение с веб-сервером установлено, но он не успел ответить за установленное время ожидания, может возникнуть ошибка 524. Время ожидания HTTP-ответа на CloudFlare — 100 секунд.
Основные причины ошибки:
- перегружен веб-сервер (проверьте процессор, оперативную память и другие ресурсы сервера);
- задержка запроса к базам данных или PHP-процесса.
Ошибку 522 можно исправить с помощью инструкций в справке CloudFlare.
Обратите внимание!
Специалисты 2domains не оказывают техническую поддержку по сервису CloudFlare. По вопросам возникновения ошибок обращайтесь в техническую поддержку CloudFlare. Если некорректная работа сайта связана с хостингом 2domains, оставьте заявку в клиентскую службу.
Cloudflare will return an error 521 message when your website refuses a connection with Cloudflare.
This is frequently caused by firewall or security software. The error looks something like this 👇🏻
Similar to Cloudflare error 520, there are a couple of different ways to fix this error.
Let’s look a little close at why an error 521 occurs, and how to fix it.
What is Error 521 Web Server is Down?
Cloudflare error 521 occurs when Cloudflare cannot make a TCP connection to your origin server. Cloudflare attempted to connect to your origin server on port 80 or 443, but received a connection refused error. Error 521 is commonly caused by security or firewall software and happens if the origin server has directly denied Cloudflare’s proxy request.
What Causes the Error 521 Message?
There are two main reasons why Cloudflare will throw an error 521.
#1 Your server is down
Cloudflare tried to connect with your site’s server (i.e. the place where your website is hosted) but failed because the origin web server was offline.
If your server is up, the other possible reason is that—
#2 Your firewall or other security software could be interfering with Cloudflare requests
This is common because many server security solutions flag and block Cloudflare IP addresses.
Cloudflare works via a reverse proxy. That means that instead of having all your visitors’ IP addresses go straight to your origin web server, it will seem they are from Cloudflare IPs.
Many (poorly built) server security solutions will flag this disproportionate traffic and IP addresses as an attack.
Now that we understand a bit more about what error 521 is, here’s how to fix it.
How to Fix Error 521 on Cloudflare
- Check Your Origin Server
- Test Your Origin Web Server
- Whitelist All Cloudflare Ip Ranges in Your Server’s Firewall
- Check for More Specific Technical Issues
1. Check Your Origin Server
Cloudflare will not connect with your origin server if it’s offline or misconfigured. Your first call should be checking it before you go on to the next possible solutions.
Be sure to see that your web server is running properly independent of Cloudflare.
The easiest way to do this is to contact your hosting provider and ask them if their servers are online.
If you’d rather test them yourself, go to step 2 below.
2. Test Your Origin Web Server
To test if your origin server is working correctly, you need to run a cURL command. Mac and Linux users can directly do this from their terminal, while Windows users need to install the cURL to achieve the same.
Check the DNS section of the Cloudflare dashboard for the IP address of your server. You will find it in the A record for your domain.
Plugin http://x.x.x.x into the tool, where x.x.x.x is the actual IP address of your origin server.
An HTTP 200 response means your server is working correctly.
If there is a problem, you will get a Failed to Connect or Host Not Found Error.
This means there’s an issue with your server.
Contact your host’s support and ask them to help you get your server back up.
3. Whitelist All Cloudflare Ip Ranges in Your Server’s Firewall
If you’ve confirmed your site’s server is online but you’re still getting a Cloudflare error 521, the next step is to whitelist all of Cloudflare’s IP ranges.
This is an easy way to ensure that your server is not blocking them. You can check the list of Cloudflare IPs here.
Then using this list—
- Ensure that you are not bocking the Cloudflare IPs in iptables, .htaccess, or in your firewall.
- Check that your hosting service provider is not rate-limiting (you might have to ask them). Similarly, check to see if they are not blocking IP requests from Cloudflare IPs. If your hosting service does this, ask that they whitelist all IP addresses from https://www.cloudflare.com/ips.
- A faulty firewall can also create a false 521 error instead of an error 524. The Error messages might be from a faulty firewall’s configuration that makes it drop packets instead of having a connection refused. If you’re on WordPress, try deactivating any security-related plugins to see if that resolves the issue.
4. Check for More Specific Technical Issues
If after trying the above, the error message persists, then you should consider any of the following technical solutions. Note that, your server’s configuration would determine the solution that would suit you.
- If you are new to Cloudflare’s HTTP, your origin web server might still have wrong configurations. Ensure that the server allows Cloudflare IP addresses access port 443. If you can’t re-configure your server/firewall to listen to port 443, try using flexible SSL instead of the Full SSL at Cloudflare.
- Ensure that your mod_security and Bad Behavior versions are up to date where applicable. Your mod_security particularly, check to see if its rules are not blocking Cloudflare requests.
- Custom Apache modules like mod_reqtimeout and mod-antiloris block IPs when they connect more than 22 times. Because your connections now come from Cloudflare, you will always exceed the limit hence the error. Disable and unload these modules, and the error should disappear.
- If you see the error message: “railgun.wan_error: connection failed”, your Railgun configuration is probably faulty. Please disable it and revisit your website.
- If the error happens when you use Workers to load Javascript on your website, note that Workers subrequest can override your DNS origin web server address. It does this by making subrequest to an external website. Check the script to see if you’re testing the right origin web server.
Conclusion
Error 521 occurs when Cloudflare has its connection refused by the origin web server (i.e. where you host your website).
If none of the solutions above fixed your issue, I’d recommend contacting Cloudflare support and asking for their help. I hope you get this issue fixed soon 🙂️
If you’re looking for (free) tips to optimize your site speed with Cloudflare and rank higher on Google,
you can follow me on Twitter 👉🏻 @bitofseo.
Please DM me if you have any questions about this Cloudflare article (or have some feedback to make it better 😄️).


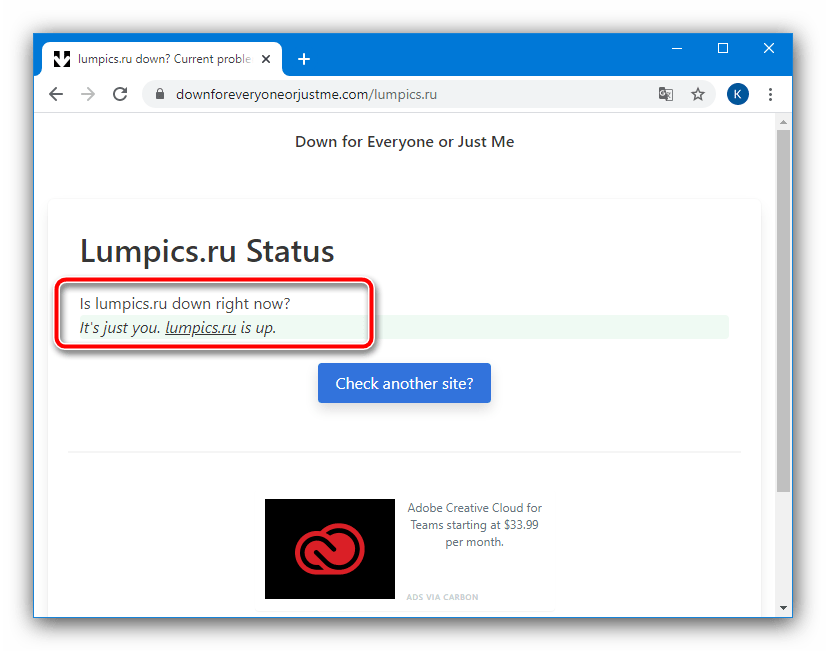
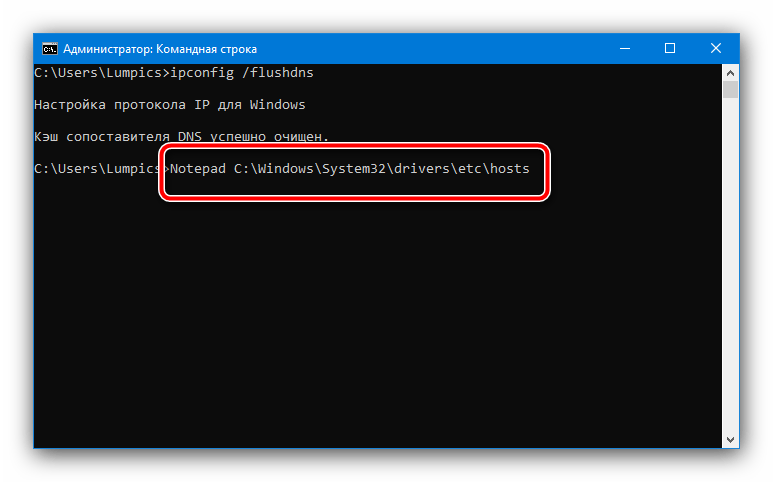
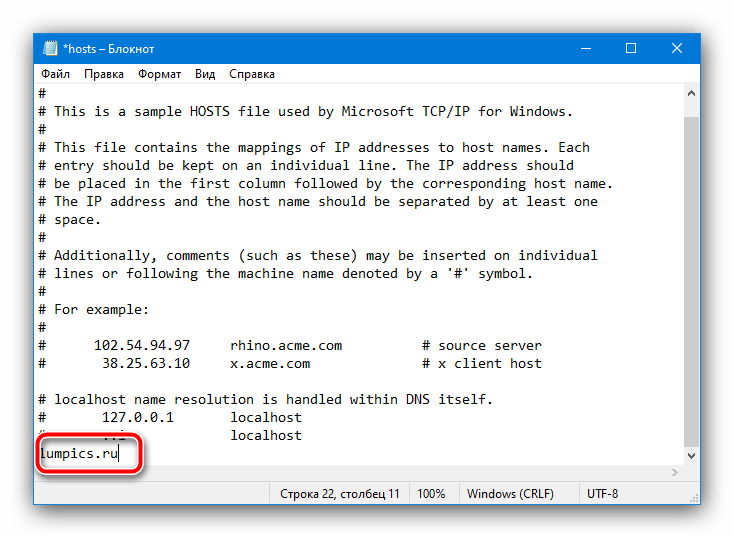
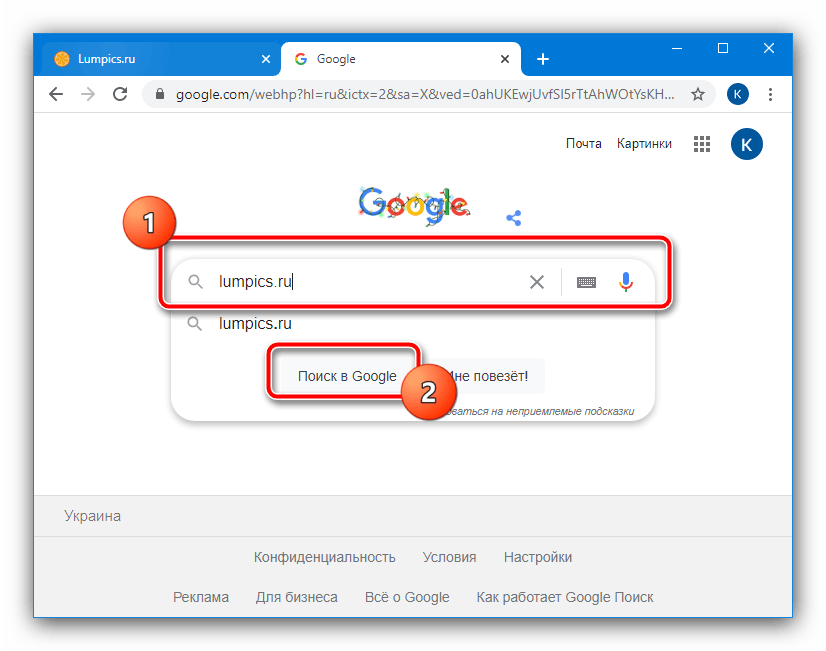
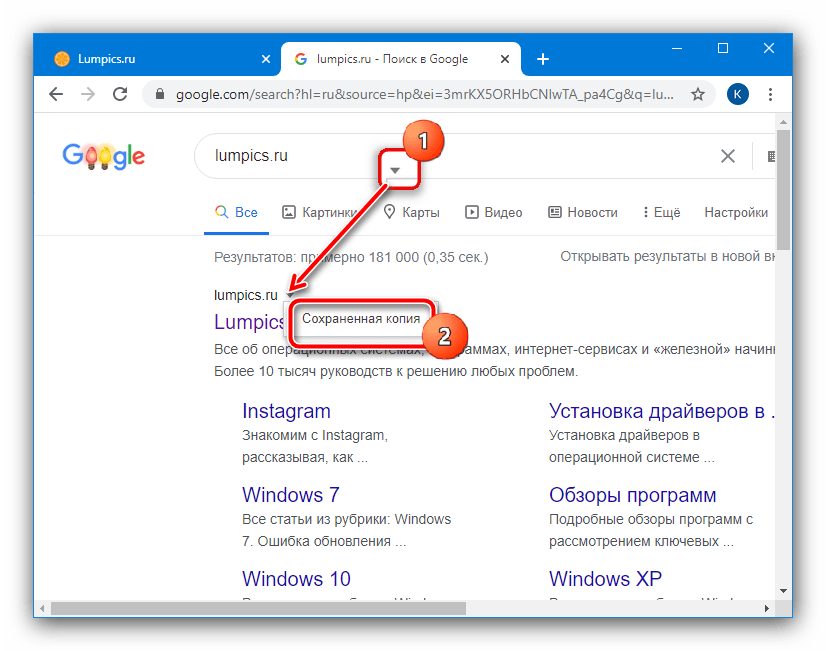

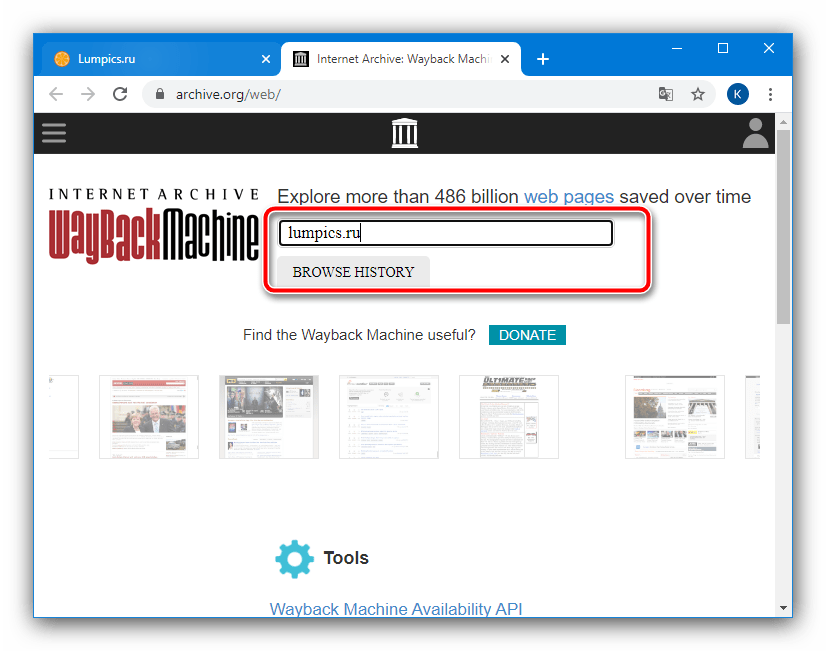
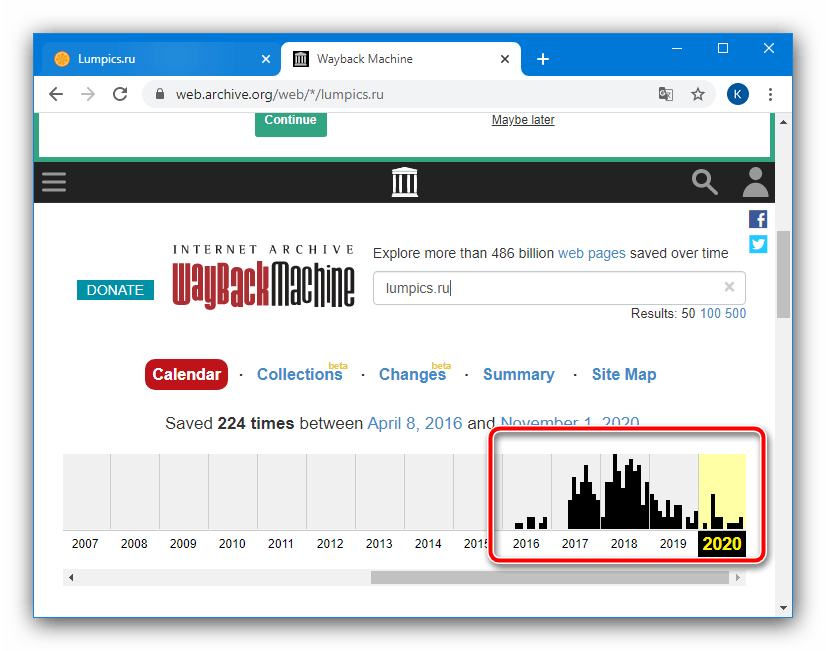
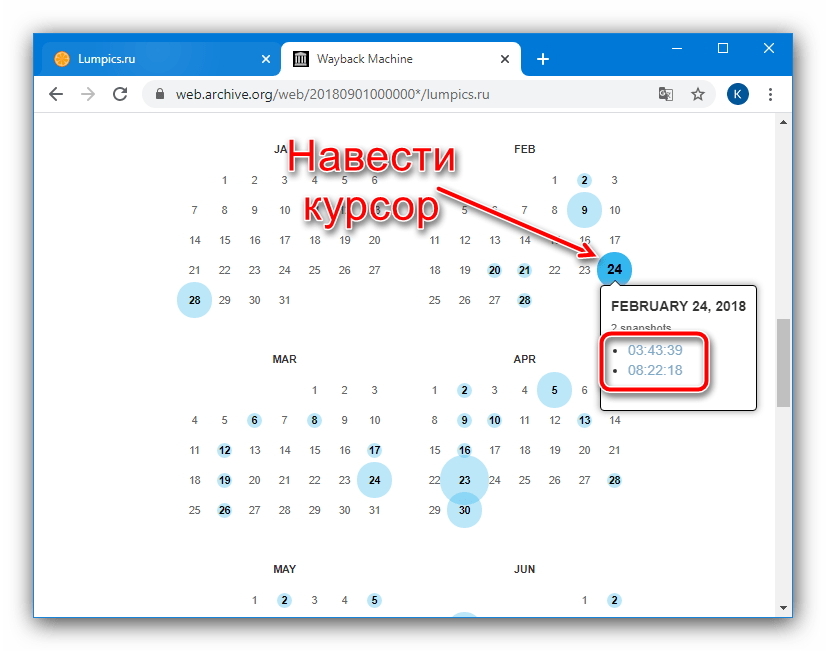

 Туториал: как исправить ошибки сервера
Туториал: как исправить ошибки сервера