- 27 Фев 2010
Всем привет! Вот трабла, Сканер HP 2400 комп- Wind XP SP3, 2 проблемы.
1. При сканировании документов через HP Director, через раз при сохранении в фаил отсканированных документов (pdf), вылазит ошибка, Internal drs error 2100:80:6
2. Думал отказаться просто от HP Director, потому что раньше Microsoft Office Document Scanning сканировал без проблем… но тут ещё снова трабла!((( На этом системнике, Document sanning не видит сканеров в своём списке!(((
Ребят, поделитесь пожалуста опытом как мне разрешить делему?
- 27 Фев 2010
Переустановить дрова, у тебя не виден не сканер, а Twane драйвер, поэтому и проблемы возникают, еще машинку на вирусы проверь.
- 27 Фев 2010
Драйвера переустанавливал и от сканера, и Офис Сканер ставился на чистую машинку, и постоянно работает антивир.
- 27 Фев 2010
А как он себя ведет если ты пытаешся отсканировать в фотожоп?
- 27 Фев 2010
там пользовательсая машина, у них нету фотошопа, вроде когда сам сканирую, норм, ничего не пишет, они раз начинают, и у них снова ошибка :S, сам сканер сканирует без проблем… проблема то встаёт при сохранении… начинает сохранять, можер на первом листе дать ошибку, может на втором листе, фз..
- 27 Фев 2010
Пусть пробуют спосканирить в FineReadr 7 или 8 там есть возможность сканировать использовав Twine драйвер или использовать драйвер самого FineReder и все сразу станет ясно, еще может скорячится система, т.к. Microsoft Office Document Scanning использует для сканирования свою карявочку (не помню как она называется) типа обработки изображений и факсов, доступна прямо из окна «Мой компутер»
- 27 Фев 2010
JohnK, а больше никаких способов нет? корпоративная политика не позволяет устанавливать стороннее ПО
- 27 Фев 2010
MaRio_ml сказал(а):
корпоративная политика не позволяет устанавливать стороннее ПО
А на попробовать не позволит, кроме того можно же качнуть FineReader 8 портативную версию, ее устанавливать не нужно.
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
I am having a strange issue in DNS of our child domains. we have 1 forest and 1 child domain 2008 R2 in our environment. DNS servers on forest are the primary active directory integrated and on Child domains are the secondary.
My issue is when i trying to lookup any FQDN record exists on child domain from secondary DNS, it gives the below Timeout message and than resolves and if i put dot at the last of FQDN name it resolves fine.
> filenet.xxx.xxx.xxx
Server: childdc1.domain.com
Address: 10.1.x.xDNS request timed out.
timeout was 2 seconds.
DNS request timed out.
timeout was 2 seconds.
Name: filenet.xxx.xxx.xxx
Address: 10.1.x.xand resolves fine when lookup with netbios name only. on the other hand same record resolves perfect from Primary DNS with FQDN and netbios both.
Regards, Sarfraz Aslam
-
Edited by
Wednesday, September 6, 2017 12:44 PM
-
Edited by
Answers
-
Hi Sarfraz Aslam,
>>So
what is the conclusion, is there any thing misconfigured on my DNS servers? As all my clients have 2 sec timeout issue.From the previous
results, we could see the other suffix:Without a trailing dot, you are asking your computer to try and guess the suffix added on to end of the name with childdomain.com,
com.pk and parentdomain.com. And this is the reason why error timeout was 2 second. It spends some time to query for the wrong suffix.In addition, if the information provided was helpful, please «mark it as answer» to help other community members find the helpful reply quickly.
Thanks for your understanding.
Best Regards,
Candy
Please remember to mark the replies as answers if they help.
If you have feedback for TechNet Subscriber Support, contact
tnmff@microsoft.com.-
Marked as answer by
Sarfraz Aslam
Thursday, September 7, 2017 9:39 AM
-
Marked as answer by
If a user’s browser window comes up blank with a message that the “server DNS address cannot be found,” this signals a DNS error that needs your instant attention. The inability to access the internet or particular sites can have an immediate negative business impact. DNS troubleshooting can be a headache for managed services providers (MSPs), but it’s crucial that they understand the ins and outs of what DNS is and have a solution in place as needed.
How do you troubleshoot DNS issues when you’re not sure what they are? This article outlines the basic DNS knowledge you need, how to diagnose DNS issues (including identifying what really aren’t DNS issues), and how to resolve basic DNS problems.
Why does a DNS error occur?
DNS errors occur essentially because you’re unable to connect to an IP address, signaling that you may have lost network or internet access. DNS stands for Domain Name System. It is the network of servers that tracks alphanumeric names for every internet-connected device, and every website in the world, and matches them with the correct numerical IP addresses.
In other words, the DNS translates your web domain name into an IP address and vice versa. Without DNS, if you entered “www.google.com” into your browser, the servers would have no idea what that means and would not know where to direct you.
DNS is a hierarchical tree data structure. At the top are root name servers. Network administrators can delegate and subdelegate several layers down. Every DNS zone has an authoritative server which answers queries only with original dynamic data; nonauthoritative servers may have only caches. If a DNS error occurs, you may have to investigate at a few different levels to understand precisely what is causing the problem and how you can quickly get users back online.
Basic troubleshooting for a DNS issue

- Check your cables and connections: If you have wired connections, make sure everything is plugged in properly. If you are on a wireless network, make sure your Wi-Fi is on and you are connected. Make sure your router is plugged in and functional.
- Reboot your router: Wait a minute before turning it back on again and wait until the indicator lights stop blinking before trying to connect.
- Run a malware scan: In some cases, a virus may be blocking internet access. In this case, you may have bigger issues to deal with before you address IP connectivity.
- Check the site: If you are having trouble accessing a particular website (your own or someone else’s), confirm that the problem is with DNS and not the site itself. One way to do this is with a website like DownForEveryoneOrJustMe. Similarly, you can issue the ping command for your web address with the command prompt. If it responds, it means the site is live and you just can’t access it, which suggests that the problem is indeed with your DNS. If the result of the ping is that “request could not find host,” it suggests the website is down, which is not necessarily a DNS problem.
What is the DNS problem?
If basic troubleshooting didn’t solve your problems, it may be time for more in-depth DNS troubleshooting. The following are some common DNS problems that could be causing the blockage:
- Check the TCP/IP settings: These settings define how your computer communicates with others. You may have recently changed these settings and tried to input them manually. Go to your computer’s networking or control panel and find “Manage network connections.” Under “Local Area Connections,” “Properties,” find and click on both IPv6 and IPv4 “Properties.” Make sure that each is set to “Obtain an IP address automatically” and “Obtain DNS servers address automatically.”
- Flush your DNS cache: The DNS cache is where your computer stores networking information on recent visits and attempts to connect to web domains. The cache can become corrupted with inaccurate information. To flush, or clear, this cache, enter ipconfig /flushdns into the command prompt. The next time you revisit a website, the DNS cache will have to renew the DNS information.
- Renew your domain name: Is your web address working but redirecting to a strange website? It’s likely you forgot to renew your domain name. It happens to the best of us—even Google briefly lost “google.com” in 2015 when it forgot to renew. Your best bet is to quickly contact the registrar, as many will wait 20 – 30 days after a domain expires before auctioning it off.
How do I fix a DNS server not responding?
If your Windows DNS server is still not responding, it may be necessary to dig more deeply to understand errors or misconfigurations that could be causing the issues. To do so you may need to utilize nslookup, a tool built into Windows (and commonly used for DNS probes by hackers). Nslookup is integral to various software solutions, including SolarWinds Remote Monitoring and Management, and you can use nslookup DNS troubleshooting commands to determine specific internal or external issues.
Nslookup was one of the original DNS diagnostics. It is available in both interactive and noninteractive modes. For our purposes, it is generally more useful in interactive mode. Most commonly, it can be used to confirm both your IP address and that of the DNS server you are on. To find the IP address of a host, enter the command prompt and type nslookup followed by your domain. This will likely return a local server. To find the authoritative server, set the query type to NS and enter the domain name.
These commands allow you to look up your DNS records. Here are the most common and important kinds of DNS records that could cause DNS issues:
- A record: A records are the very basic DNS data that matches a domain with an IP address. To check an A record, use the nslookup command followed by the domain. Then, you can confirm that the domain is going to the right IP address and vice versa. An AAAA record is the same as an A record but for IPv6.
- CNAME: CNAME stands for Canonical Name. This record is used to point one domain name at another domain name. (The latter domain name will presumably have an A record that points it toward an IP address.) CNAME records can sometimes cause trouble with emails. In any case, verify that the domains are pointing to the right places. For nslookup, the command is “set type=cname” followed by your domain.
- MX: The Mail Exchange (MX) Record directs email from your domain to a host server. If this is incorrect, it could explain why users are having trouble sending email to addresses at your domain. Be sure the MX maps to your domain (A or AAAA record) and not a CNAME record. The command is “set type=mx” followed by your domain.
What are some common causes of DNS issues?
When it comes to network performance, a few common issues may affect user connectivity and lead to DNS errors. For troubleshooting DNS issues, you may want to consider how the following factors could be impacting your clients:
1) Time to live (TTL)
Time to live is the expiration date attached to data in networking. When a caching (recurring) server queries the authoritative name server for any DNS records, the authoritative name server tells the caching server how long those records are good for—which is usually between a few minutes and one day. Until the TTL expires, the caching server will not query the authoritative name server for that same data again but will assume the records are still good.
You can see how this could affect DNS issues. If your DNS records change but your TTL is too high, there will be a delay as the caching server continues to send incorrect records to users until the TTL expires. On the other hand, if the TTL is too low it could overwhelm the authoritative name server with unnecessary queries.
If you are planning on updating DNS records, lower your TTL temporarily before you do so to ensure that users will receive updated data quickly. Servers sometimes don’t recognize a TTL of less than 30 seconds; five minutes (300s) is a typical short TTL.
In general, use short TTLs for records that are updated frequently, and longer TTLs for more steady records. Records that rarely change and should have longer TTLs of a day (86400s) include MX and TXT.
2) DNS latency
Latency refers to the time it takes queries to be transmitted and returned. When users complain of “the internet being slow today,” they are talking about high latency. DNS issues can be a big part of latency.
One major factor affecting your network speeds is simply the distance that data must travel, but you can potentially improve latency by checking on whether your DNS servers have a centralized or decentralized structure. Consider other providers if your DNS servers are all located significantly far from your users.
TTL also plays a role in latency. As mentioned before, keep TTLs high for consistent DNS records to reduce unnecessary queries.
3) DDOS attack
If you’ve thoroughly checked your network and don’t think the problems are on your end, it might be a problem with your ISP’s DNS servers. Give them a call and let them know. If they confirm a problem with their DNS servers, don’t be afraid to be persistent in following up until the problem is solved.
This might be the worst-case scenario, but if a sudden surge of traffic crashes your site, you may be the victim of a distributed denial of service attack. This is essentially a DNS issue in the sense that it overwhelms the servers. Contact your web host immediately and ask for a new IP. Clear your logs and make sure that your new records match the new IP.
DNS issues are just one type of problem that could interrupt your service. Need help with more than DNS troubleshooting? Explore our resources center for other troubleshooting information.
«An internal system error has occurred» when you try to install DirectX.
A week or so, I tried to install a game requiring the use of DirectX. Well when I go to install DirectX, it gives me an error that reads, ‘an internal system error has occurred. » «Please refer to DXError.log andDirectX.log in your Windows folder to determine the problem.«
I can’t find the files mentioned above on my computer, so therefore, I can’t see them.
Here’s my DXDIAG:
——————
Information System
——————
Time of this report: 07/02/2011, 17:24:20
Computer name: ZACH-PC
Operating system: Windows 7 Home Premium 64-bit (6.1, Build 7600) (7600.win7_gdr.100618 — 1621)
Language: English (regional setting: English)
Manufacturer: Acer
System model: Aspire 5532
BIOS: Version InsydeH2O V1.08
Processor: AMD Athlon (TM) Processor TF-20, ~1.6GHz
Memory: 3072 MB RAM
Available OS memory: 2812MB RAM
Page file: 1623MB used, 3998 MB of available space
Windows Dir: C:Windows
DirectX version: DirectX 11
DX setup parameters: not found
DPI setting: Using System DPI
System DPI setting: 96 DPI (100%)
DWM DPI Scaling: disabled
DxDiag Version: 6.01.7600.16385 64 bit Unicode
————
DxDiag Notes
————
Display 1 tab: No problems found.
Sound tab 1: No problems found.
2 Audio tab: No problems found.
3 Audio tab: No problems found.
Input tab: no problems found.
———————
DirectX Debug levels
———————
Direct3D: 0/4 (detail)
DirectDraw: 0/4 (detail)
DirectInput: 0/5 (retail)
DirectMusic: 0/5 (retail)
DirectPlay: 0/9 (detail)
DirectSound: 0/5 (retail)
DirectShow: 0/6 (detail)
—————
Display devices
—————
Card name: ATI Radeon HD 3200 graphics card
Manufacturer: ATI Technologies Inc.
Type of piece: ATI display adapter (0 x 9612)
DAC type: DAC (400 MHz) internal
The device key: EnumPCIVEN_1002 & DEV_9612 & SUBSYS_028D1025 & REV_00
Memory display: 1403 MB
Dedicated memory: 253 MB
Shared memory: 1150 MB
Current mode: 1366 x 768 (32 bit) (60 Hz)
Name of the monitor: generic PnP monitor
Monitor model: unknown
Monitor ID: AUO10EC
Native mode: 1366 x 768 (p) (60,114 Hz)
Output type: internal
Driver name: atiumd64.dll, atidxx64.dll, atiumdag, atidxx32, atiumdva, atiumd6a.cap, atitmm64.dll
The driver file version: 8.14.0010.0678 (English)
Driver version: 8.634.0.0
DDI version: 10
: Model WDDM 1.1 driver
Driver attributes: Final retail
Driver Date/size: 2009-07-29 06:43:14, 4059648 bytes
Would be WHQL logo: Yes
Date stamp WHQL:
The instrument identifier: {D7B71EE2-D552-11CF-3371-8722A1C2C535}
Vendor ID: 0 x 1002
Device ID: 0 x 9612
SubSys ID: 0x028D1025
Revision ID: 0x0000
Strong name of the driver: oem7.inf:ATI. Mfg.NTamd64.6.1:ati2mtag_RS780M:8.634.0.0:pciven_1002&dev_9612&subsys_028d1025
The driver rating: 00E60001
Video Accel: ModeMPEG2_A ModeMPEG2_C
Deinterlace caps: {335AA36E-7884-43A4-9C91-7F87FAF3E37E}: caps Frames(Prev/Fwd/Back) = (0,0,0) (In/Out) Format (YUY2, YUY2) = VideoProcess_YUV2RGB VideoProcess_StretchX VideoProcess_StretchY DeinterlaceTech_BOBVerticalStretch
{5A54A0C9-C7EC-4BD9-8EDE-F3C75DC4393B}: caps Frames(Prev/Fwd/Back) = (0,0,0) Format (In/Out) = (YUY2, YUY2) = VideoProcess_YUV2RGB VideoProcess_StretchX VideoProcess_StretchY
{335AA36E-7884-43A4-9C91-7F87FAF3E37E}: caps Frames(Prev/Fwd/Back) = (0,0,0) (In/Out) Format (UYVY, UYVY) = VideoProcess_YUV2RGB VideoProcess_StretchX VideoProcess_StretchY DeinterlaceTech_BOBVerticalStretch
{5A54A0C9-C7EC-4BD9-8EDE-F3C75DC4393B}: caps Frames(Prev/Fwd/Back) = (0,0,0) Format (In/Out) = (UYVY, UYVY) = VideoProcess_YUV2RGB VideoProcess_StretchX VideoProcess_StretchY
{5A54A0C9-C7EC-4BD9-8EDE-F3C75DC4393B}: Format (In/Out) (YV12, 0 x 32315659) = Frames(Prev/Fwd/Back) = (0,0,0) Caps
{335AA36E-7884-43A4-9C91-7F87FAF3E37E}: caps Frames(Prev/Fwd/Back) = (0,0,0) (In/Out) Format (NV12, 0x3231564e) = VideoProcess_YUV2RGB VideoProcess_StretchX VideoProcess_StretchY DeinterlaceTech_BOBVerticalStretch
{5A54A0C9-C7EC-4BD9-8EDE-F3C75DC4393B}: caps Frames(Prev/Fwd/Back) = (0,0,0) (In/Out) Format (NV12, 0x3231564e) = VideoProcess_YUV2RGB VideoProcess_StretchX VideoProcess_StretchY
{5A54A0C9-C7EC-4BD9-8EDE-F3C75DC4393B}: Format (In/Out) = (IMC1, UNKNOWN) Frames(Prev/Fwd/Back) = (0,0,0) Caps
{5A54A0C9-C7EC-4BD9-8EDE-F3C75DC4393B}: Format (In/Out) = (IMC2, UNKNOWN) Frames(Prev/Fwd/Back) = (0,0,0) Caps
{5A54A0C9-C7EC-4BD9-8EDE-F3C75DC4393B}: Format (In/Out) = (IMC3, UNKNOWN) Frames(Prev/Fwd/Back) = (0,0,0) Caps
{5A54A0C9-C7EC-4BD9-8EDE-F3C75DC4393B}: Format (In/Out) = (IMC4, UNKNOWN) Frames(Prev/Fwd/Back) = (0,0,0) Caps
{5A54A0C9-C7EC-4BD9-8EDE-F3C75DC4393B}: Format (In/Out) = (S340, UNKNOWN) Frames(Prev/Fwd/Back) = (0,0,0) Caps
{5A54A0C9-C7EC-4BD9-8EDE-F3C75DC4393B}: Format (In/Out) = (S342, UNKNOWN) Frames(Prev/Fwd/Back) = (0,0,0) Caps
D3d9 Overlay: Unsupported
DXVA-HD: not supported
DDraw status: enabled
D3D status: enabled
AGP status: enabled
————-
Sound Devices
————-
Description: Speakers (Realtek High Definition Audio)
Default audio playback: Yes
Default voice playback: Yes
Hardware ID: HDAUDIOFUNC_01 & VEN_10EC & DEV_0272 & SUBSYS_1025028D & REV_1000
Manufacturer ID: 1
Product ID: 100
Type: WDM
Driver name: RTKVHD64.sys
Driver version: 6.00.0001.5904 (English)
Driver attributes: Final retail
Would be WHQL logo: Yes
Date and size: 2009-07-28 08:00:14, 1966624 bytes
Other files:
Driver provider: Realtek Semiconductor Corp.
HW Accel level: basic
Cap flags: 0xF1F
Min/Max sample rate: 100, 200000
Mix beef static/Strm HW: 1, 0
Static/Strm HW 3D steers: 0, 0
HW memory: 0
Management of the voice: No.
Listen/Src/EAX (TM) 2.0: No, no
Listen/Src/I3DL2 (TM): No, no
Sensaura (TM) ZoomFX ™: No.
Description: Speakers (Avnex Virtual Audio Device)
Default audio playback: No.
Default voice playback: no
Hardware ID:
Manufacturer ID: 1
Product ID: 100
Type: WDM
Driver name: {0.0.0.00000000}. {1f21753a-ec03-4b7e-b4b5-fc9a36a3aafd}
Driver version:)
Driver attributes: Final retail
WHQL Logo would be: No.
Date and size:, 0 bytes
Other files:
Driver provider: AVNEX Ltd.
HW Accel level: basic
Cap flags: 0xF1F
Min/Max sample rate: 100, 200000
Mix beef static/Strm HW: 1, 0
Static/Strm HW 3D steers: 0, 0
HW memory: 0
Management of the voice: No.
Listen/Src/EAX (TM) 2.0: No, no
Listen/Src/I3DL2 (TM): No, no
Sensaura (TM) ZoomFX ™: No.
Description: Speakers (USB-2 Audio device)
Default audio playback: No.
Default voice playback: no
Hardware ID: USBVID_0D8C & PID_0008 & REV_0100 & MI_00
Manufacturer ID: 65535
Product ID: 65535
Type: WDM
Driver name: USBAUDIO.sys
Driver version: 6.01.7600.16385 (in English)
Driver attributes: Final retail
Would be WHQL logo: Yes
Date and size: 2009-07-13 19:06:32, 109568 bytes
Other files:
Driver provider: Microsoft
HW Accel level: basic
Cap flags: 0xF1F
Min/Max sample rate: 100, 200000
Mix beef static/Strm HW: 1, 0
Static/Strm HW 3D steers: 0, 0
HW memory: 0
Management of the voice: No.
Listen/Src/EAX (TM) 2.0: No, no
Listen/Src/I3DL2 (TM): No, no
Sensaura (TM) ZoomFX ™: No.
———————
Sound Capture devices
———————
Description: Microphone (2 — USB Audio Device)
Capture audio by default: Yes
Default voice Capture: Yes
Driver name: USBAUDIO.sys
Driver version: 6.01.7600.16385 (in English)
Driver attributes: Final retail
Date and size: 2009-07-13 19:06:32, 109568 bytes
Cap flags: 0x1
Format flags: 0xFFFFF
Description: Microphone (Avnex Virtual Audio Device)
Capture audio by default: No.
Default voice Capture: No.
Driver name: {0.0.1.00000000}. {748162c7-28eb-437c-928f-6328b0338d58}
Driver version:)
Driver attributes: Final retail
Date and size:, 0 bytes
Cap flags: 0x1
Format flags: 0xFFFFF
——————-
DirectInput devices
——————-
Device name: mouse
Joint: 1
Controller ID: n/a
Vendor/product ID: n/a
FF driver: n/a
Device name: keyboard
Joint: 1
Controller ID: n/a
Vendor/product ID: n/a
FF driver: n/a
Device name: Razer gaming device
Joint: 1
Controller ID: 0 x 0
Suppliers of products/ID: 0xBEEF, 0x0EED
FF driver: n/a
Device name: C-Media USB Audio Device
Joint: 1
Controller ID: 0 x 0
Suppliers of products/ID: 0x0D8C, 0 x 0008
FF driver: n/a
Poll w / Interrupt: No.
————
USB devices
————
+ USB root hub
| Suppliers of products/ID: 0 x 1002, 0 x 4397
| Matching Device ID: usbroot_hub
| Service: usbhub
| Driver: usbhub.sys, 13/07/2009 19:07:09, 343040 bytes
| Driver: usbd.sys, 13/07/2009 19:06:23, 7936 bytes
|
+ — + DeathAdder mouse
| | Suppliers of products/ID: 1532 0 x, 0 x 0007
| | Location: Port_ #0001.Hub_ #0001
| | Matching device ID: usbvid_1532 & pid_0007
| | Lower filters: DAdderFltr
| | Service: HidUsb
| | Driver: dadder.sys, 19/04/2010 17:04:44, 12032 bytes
| | Driver: hidusb.sys, 13/07/2009 19:06:22, 30 208 bytes
| | Driver: hidclass.sys, 13/07/2009 19:06:21, 76288 bytes
| | Driver: hidparse.sys, 13/07/2009 19:06:17, 32896 bytes
| |
| + — + HID-compliant mouse
| | | Suppliers of products/ID: 1532 0 x, 0 x 0007
| | | Matching Device ID: hid_device_system_mouse
| | | Service: me
| | | Driver: mouhid.sys, 2009-07-13 19:00:20, 31232 bytes
| | | Driver: mouclass.sys, 2009-07-13 20:48:27, 49216 bytes
—————-
Gameport devices
—————-
————
PS/2 devices
————
+ Launch Manager
| Matching Device ID: * pnp0303
| High filters: DKbFltr
| Service: i8042prt
| Driver: C:windowssystem32driversdkbfltr.sys, 2009-03-25 22:16:08, 25608 bytes
| Driver: i8042prt.sys, 13/07/2009 18:19:57, 105472 bytes
| Driver: kbdclass.sys, 2009-07-13 20:48:04, 50768 bytes
|
+ Keyboard HID device
| Matching Device ID: hid_device_system_keyboard
| Service: kbdhid
| Driver: kbdhid.sys, 2009-07-13 19:00:20, 33280 bytes
| Driver: kbdclass.sys, 2009-07-13 20:48:04, 50768 bytes
|
+ Server terminal keyboard driver
| Matching Device ID: rootrdp_kbd
| High filters: kbdclass
| Service: TermDD
| Driver: i8042prt.sys, 13/07/2009 18:19:57, 105472 bytes
| Driver: kbdclass.sys, 2009-07-13 20:48:04, 50768 bytes
|
+ Synaptics PS/2 Port TouchPad
| Matching Device ID: * syn1b1d
| High filters: SynTP
| Service: i8042prt
| Pilot: SynTP.sys, 18/06/2009 07:12:32, 272432 bytes
| Driver: C:windowssystem32syntpapi.dll, 2009-06-18 07:10:42, 203560 bytes
| Driver: C:windowssystem32syncom.dll, 2009-06-18 07:10:36, 395048 bytes
| Pilot: SynCtrl.dll, 18/06/2009 07:10:38, 260904 bytes
| Driver: SynTPRes.dll, 2009-06-18 07:10:46, 8054568 bytes
| Driver: SynTPCpl.dll, 2009-06-18 07:10:46, 1525032 bytes
| Driver: SynCntxt.rtf, 2009-06-18 07:02:14, 7118958 bytes
| Driver: SynZMetr.exe, 2009-06-18 07:10:34, 247080 bytes
| Driver: SynMood.exe, 2009-06-18 07:10:32, 238888 bytes
| Pilot: SynTPEnh.exe, 18/06/2009 07:10:32, 1808168 bytes
| Pilot: SynTPCOM.dll, 18/06/2009 07:10:44, 120104 bytes
| Pilot: Tutorial.exe, 18/06/2009 07:10:36, 337192 bytes
| Pilot: InstNT.exe, 18/06/2009 07:10:28, 149800 bytes
| Pilot: SynISDLL.dll, 18/06/2009 07:10:40, 197928 bytes
| Driver: SynUnst.ini, 2009-06-25 20:39:44, 620786 bytes
| Driver: SynChiralRotate.mpg, 2008-09-17 00:13:08, 382277 bytes
| Driver: SynFlick.mpg, 02/09/2008 22:27:28, 737975 bytes
| Driver: SynPinch.mpg, 02/09/2008 22:27:28, 286463 bytes
| Driver: SynMomentum.mpg, 02/09/2008 22:27:28, 246230 bytes
| Driver: SynLinearVHScroll.mpg, 02/09/2008 22:27:28, 929103 bytes
| Driver: SynChiralVHScroll.mpg, 02/09/2008 22:27:28, 1620778 bytes
| Driver: SynTwoFingerVHScroll.mpg, 2009-03-15 20:44, 746464 bytes
| Driver: SynPivotRotate_ChiralRotate.mpg, 04-09-2009 04:04:14, 1142810 bytes
| Driver: SynThreeFingerFlick.mpg, 2009-03-15 20:44, 633621 bytes
| Driver: SynThreeFingersDown.mpg, 2009-03-15 20:44, 215907 bytes
| Pilot: SynTPHelper.exe, 18/06/2009 07:10:32, 120616 bytes
| Driver: fx04.wav, 08/05/2007 20:48:26, 16898 bytes
| Driver: SynAcer.exe, 2009-06-18 07:10:48, 160552 bytes
| Driver: SynAcerCpl.cpl, 2009-06-18 06:38:40, 323072 bytes
| Driver: SynTwoFingerVScroll.mpg, 2009-03-15 20:44, 501787 bytes
| Driver: SynFlickLR.mpg, 02/09/2008 22:27:28, 495798 bytes
| Driver: C:windowssystem32syncom.dll, 2009-06-18 07:10:36, 169256 bytes
| Pilot: SynCtrl.dll, 18/06/2009 07:10:38, 206120 bytes
| Pilot: SynTPCOM.dll, 18/06/2009 07:10:44, 107816 bytes
| Driver: i8042prt.sys, 13/07/2009 18:19:57, 105472 bytes
| Driver: mouclass.sys, 2009-07-13 20:48:27, 49216 bytes
| Driver: SynTPCo4.dll, 2009-06-18 07:10:42, 147752 bytes
| Driver: WdfCoInstaller01009.dll, 2009-05-20 20:43:50, 1436920 bytes
|
+ HID-compliant mouse
| Matching Device ID: hid_device_system_mouse
| Service: me
| Driver: mouhid.sys, 2009-07-13 19:00:20, 31232 bytes
| Driver: mouclass.sys, 2009-07-13 20:48:27, 49216 bytes
|
+ Terminal Server mouse driver
| Matching Device ID: rootrdp_mou
| High filters: mouclass
| Service: TermDD
| Driver: termdd.sys, 13/07/2009 20:45:55, 62544 bytes
| Driver: sermouse.sys, 2009-07-13 19:00:20, 26624 bytes
| Driver: mouclass.sys, 2009-07-13 20:48:27, 49216 bytes
————————
Disk & CD-ROM/DVD-ROM readers
————————
Drive: C:
Free space: 31.2 GB
Total space: 140.2 GB
File system: NTFS
Model: WDC WD1600BEVT-22ZCT0 ATA Device
Drive: D:
Model: TSSTcorp CDDVDW TS-L633C ATA Device
Driver: c:windowssystem32driverscdrom.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 13/07/2009-18:19:54, 147456 bytes
—————
System devices
—————
Name: Bridge PCI to PCI standard PCI
Device ID: PCIVEN_1022 & DEV_9602 & SUBSYS_96021022 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 & 08
Driver: C:Windowssystem32DRIVERSpci.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 20:45:45, 183872 bytes
Name: OpenHCD Standard USB host controller
Device ID: PCIVEN_1002 & DEV_4398 & SUBSYS_028D1025 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 & 91
Pilot: C:Windowssystem32driversusbohci.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 19:06:30, 25600 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32driversusbport.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 19:06:31, 324608 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32driversusbhub.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 19:07:09, 343040 bytes
Name: The standard host PCI bridge CPU
Device ID: PCIVEN_1022 & DEV_9600 & SUBSYS_028D1025 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 & 00
Pilot: s/o
Name: OpenHCD Standard USB host controller
Device ID: PCIVEN_1002 & DEV_4397 & SUBSYS_028D1025 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 & 90
Pilot: C:Windowssystem32driversusbohci.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 19:06:30, 25600 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32driversusbport.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 19:06:31, 324608 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32driversusbhub.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 19:07:09, 343040 bytes
Name: AMD Setup various
Device ID: PCIVEN_1022 & DEV_1103 & SUBSYS_00000000 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 & C3
Pilot: s/o
Name: Standard enhanced PCI to USB Host Controller
Device ID: PCIVEN_1002 & DEV_4396 & SUBSYS_028D1025 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 & 92
Driver: C:Windowssystem32driversusbehci.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 19:06:30, 51200 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32driversusbport.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 19:06:31, 324608 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32driversusbhub.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 19:07:09, 343040 bytes
Name: Configuration of the HyperTransport (MC) and DRAM AMD tracking Mode
Device ID: PCIVEN_1022 & DEV_1102 & SUBSYS_00000000 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 C2
Pilot: s/o
Name: Controller Serial ATA Standard AHCI 1.0
Device ID: PCIVEN_1002 & DEV_4391 & SUBSYS_028D1025 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 & 88
Driver: C:Windowssystem32DRIVERSmsahci.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 20:48:27, 30272 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32DRIVERSpciidex.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 20:45:46, 48720 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32DRIVERSatapi.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 20:52:21, 24128 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32DRIVERSataport.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 20:52:21, 155728 bytes
Name: Atheros AR8132 PCI-E Fast Ethernet (NDIS 6.20) controller
Device ID: PCIVEN_1969 & DEV_1062 & SUBSYS_028D1025 & REV_C04 & 7A7D559 & 0 & 0028
Driver: C:Windowssystem32DRIVERSL1C62x64.sys, 1.00.0000.0010 (English), 27/07/2009 02:04:36, 58880 bytes
Name: AMD Configuration map address
Device ID: PCIVEN_1022 & DEV_1101 & SUBSYS_00000000 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 & C1
Pilot: s/o
Name: ATI i/o Communications Processor SMBus Controller
Device ID: PCIVEN_1002 & DEV_4385 & SUBSYS_028D1025 & REV_3C3 & 2411E6FE & 1 & A0
Pilot: s/o
Name: Atheros AR5B93 Wireless Network adapt
Device ID: PCIVEN_168C & DEV_002A & SUBSYS_E01F105B & REV_014 & 137E0A89 & 0 & 0020
Driver: C:Windowssystem32DRIVERSathrx.sys, 8.00.0000.0177 (English), 07-16-2009 06:33:44, 1488384 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32driversvwifibus.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 19:07:21, 24576 bytes
Name: AMD HyperTransport (MC) Configuration
Device ID: PCIVEN_1022 & DEV_1100 & SUBSYS_00000000 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 & C0
Pilot: s/o
Name: ATI i/o Communications Processor PCI Bus controller
Device ID: PCIVEN_1002 & DEV_4384 & SUBSYS_00000000 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 & A4
Driver: C:Windowssystem32DRIVERSpci.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 20:45:45, 183872 bytes
Name: Bridge PCI to PCI standard PCI
Device ID: PCIVEN_1022 & DEV_9605 & SUBSYS_028D1025 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 & 28
Driver: C:Windowssystem32DRIVERSpci.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 20:45:45, 183872 bytes
Name: Card ATI Radeon HD 3200 graphics
Device ID: PCIVEN_1002 & DEV_9612 & SUBSYS_028D1025 & REV_004 & F4E2B40 & 0 & 2808
Driver: C:Windowssystem32DRIVERSatikmdag.sys, 8.01.0001.0921 (English), 2009-07-29 17:11:24, 6038016 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32DRIVERSati2erec.dll, 1.00.0000.0019 (English), 29/07/2009 06:06:42, 53248 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atiumd64.dll, 8.14.0010.0678 (English), 29/07/2009 06:43:14, 4059648 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atiumd6a.dll, 8.14.0010.0228 (English), 29/07/2009 06:38:10, 2622976 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atitmm64.dll, 6.14.0011.0022 (English), 29/07/2009 07:02:32, 120320 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atiicdxx.dat, 2009-06-17 23:29:04, 197654 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32amdpcom64.dll, 8.14.0010.0023 (English), 29/07/2009 06:21:12, 52224 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atimpc64.dll, 8.14.0010.0023 (English), 29/07/2009 06:21:12, 52224 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atiadlxx.dll, 6.14.0010.1050 (English), 29/07/2009 06:20:42, 251904 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atiumd6a.cap, 2009-07-29 06:35:56, 219120 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atimuixx.dll, 6.14.0010.1001 (English), 29/07/2009 07:01:46, 12288 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atiesrxx.exe, 6.14.0011.1033 (English), 29/07/2009 07:03:42, 203264 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atieclxx.exe, 6.14.0011.1033 (English), 29/07/2009 07:04:14, 420352 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atipdl64.dll, 6.14.0010.2556 (English), 29/07/2009 07:02:14, 421376 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atiedu64.dll, 6.14.0010.2514 (English), 29/07/2009-07:01:42, 59392 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32ATIDEMGX.dll, 2.00.3497.39731 (English), 29/07/2009 07:04:22, 442368 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atio6axx.dll, 6.14.0010.8794 (English), 29/07/2009 07:00:22, 15072768 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atibtmon.exe, 2.00.0000.0000 (English), 11/05/2009 01:35:30, 118784 bytes
Driver: C:Windowssystem32atidxx64.dll, 8.15.0010.0212 (English), 29/07/2009-06:53:38, 2921984 bytes
Driver: C:WindowsSysWOW64atiumdag.dll, 8.14.0010.0678 (English), 29/07/2009 06:47:52, 3105280 bytes
Driver: C:WindowsSysWOW64atiumdva.dll, 8.14.0010.0228 (English), 29/07/2009 06:32:54, 2868736 bytes
Driver: C:WindowsSysWOW64amdpcom32.dll, 8.14.0010.0023 (English), 29/07/2009 06:21:06, 51712 bytes
Driver: C:WindowsSysWOW64atimpc32.dll, 8.14.0010.0023 (English), 29/07/2009 06:21:06, 51712 bytes
Driver: C:WindowsSysWOW64atiadlxy.dll, 6.14.0010.1050 (English), 29/07/2009-06:20:36, 184320 bytes
Driver: C:WindowsSysWOW64atiumdva.cap, 29/07/2009 06:32:32, 219120 bytes
Driver: C:WindowsSysWOW64atipdlxx.dll, 6.14.0010.2556 (English), 29/07/2009-07:02:06, 356352 bytes
Driver: C:WindowsSysWOW64ati2edxx.dll, 6.14.0010.2514 (English), 29/07/2009-07:01:36, 43520 bytes
Driver: C:WindowsSysWOW64atioglxx.dll, 6.14.0010.8794 (English), 29/07/2009 06:38:52, 11660800 bytes
Driver: C:WindowsSysWOW64atidxx32.dll, 8.15.0010.0212 (English), 29/07/2009 06:58:52, 2469888 bytes
Driver: C:Windowsatiogl.xml, 13/07/2009 12:26:06, 18335 bytes
Name: High Definition Audio Controller
Device ID: PCIVEN_1002 & DEV_4383 & SUBSYS_028D1025 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 & A2
Driver: C:Windowssystem32DRIVERShdaudbus.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 19:06:13, 122368 bytes
Name: Bridge PCI to PCI standard PCI
Device ID: PCIVEN_1022 & DEV_9604 & SUBSYS_028D1025 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 & 20
Driver: C:Windowssystem32DRIVERSpci.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 20:45:45, 183872 bytes
Name: PCI standard ISA bridge
Device ID: PCIVEN_1002 & DEV_439D & SUBSYS_028D1025 & REV_003 & 2411E6FE & 1 & A3
Driver: C:Windowssystem32DRIVERSmsisadrv.sys, 6.01.7600.16385 (in English), 2009-07-13 20:48:27, 15424 bytes
——————
DirectShow filters
——————
DirectShow filters:
WMAudio Decoder DMO, 0 x 00800800, 1, 1, WMADMOD. DLL, 6.01.7600.16385
WMAPro over S/PDIF DMO, 0 x 00600800, 1, 1, WMADMOD. DLL, 6.01.7600.16385
WMSpeech Decoder DMO, 0 x 00600800, 1, 1, WMSPDMOD. DLL, 6.01.7600.16385
MP3 DMO, 0 x 00600800, 1, 1, mp3dmod.dll, 6.01.7600.16385 decoder
Mpeg4s decoder DMO, 0 x 00800001, 1, 1, mp4sdecd.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
Decoder WMV DMO, 0 x 00600800, 1 screen, 1, wmvsdecd.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
Decoder DMO WMVideo, 0 x 00800001, 1, 1, wmvdecod.dll, 6.01.7600.16597
Mpeg43 decoder DMO, 0 x 00800001, 1, 1, mp43decd.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
MPEG4 Decoder DMO, 0 x 00800001, 1, 1, mpg4decd.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
DV Muxer, 0x00400000, 0, 0, qdv.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
Converter, 0 x 00400001, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490 color space
Reader, 0x00400000, 0, 0, qasf.dll, WM ASF 12.00.7600.16385
Filter, 0 x 00200000, 0, 1, wmpsrcwp.dll, 12.00.7600.16385 screenshot
AVI Splitter, 0 x 00600000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
VGA 16 color Ditherer, 0 x 00400000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
SBE2MediaTypeProfile, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0, SBE.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
Microsoft DTV — DVD video Decoder, 0x005fffff, 2, 4, msmpeg2vdec.dll, 6.01.7140.0000
AC3 parser Filter, 0 x 00600000, 1, 1, mpg2splt.ax, 6.06.7600.16648
StreamBufferSink, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0, sbe.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
Microsoft TV legends Decoder, 0 x 00200001, 1, 0, MSTVCapn.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
MJPEG Decompressor, 0 x 00600000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
CBVA DMO wrapper filter, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, cbva.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
MPEG-I Stream Splitter, 0 x 00600000, 1, 2, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
Parser, 0 x 00400000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490 SAMI (CC)
The IST Codec, 0 x 00600000, 1, 4, VBICodec.ax, 6.06.7600.16385
MPEG-2 Splitter, 0x005fffff, 1, 0, mpg2splt.ax, 6.06.7600.16648
Filter, 0 x 00200000, 2, 5, cca.dll, 6.06.7600.16385 analysis of closed captioning
SBE2FileScan, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0, SBE.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
Microsoft MPEG-2 video encoding, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, msmpeg2enc.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
Renderer, 0 x 00800001, 1, 0, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490 Script command internal
MPEG Audio Decoder, 0 x 03680001, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
DV Splitter, 0 x 00600000, 1, 2, qdv.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
Video Mixing Renderer 9 0 x 00200000, 1, 0, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
Microsoft MPEG — 2 encode, 0 x 00200000, 2, 1, msmpeg2enc.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
ACM Wrapper, 0 x 00600000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
Video Renderer, 0 x 00800001, 1, 0, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
Video stream MPEG — 2 Analyzer, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0, sbe.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
Line 21 decoder, 0 00600000, 1, 1, x
Port video Manager, 0 x 00600000, 2, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
Video Renderer, 0x00400000, 1, 0, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
Decoder, 0 x 00200000 VPS, 0, 0, WSTPager.ax, 6.06.7600.16385
Writer, 0x00400000, 0, 0, qasf.dll, WM ASF 12.00.7600.16385
Allocator, 0 x 00600000, 1, 1, vbisurf.ax, 6.01.7600.16385 Surface of VBI
File writer, 00200000 x 0, 1, 0, qcap.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
iTV Sink, 0 x 00600000, 1, 0, itvdata.dll, 6.06.7600.16385 data
iTV to Capture data filter 0 x 00600000, 1, 1, itvdata.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
DVD Navigator, 0 x 00200000, 0, 3, qdvd.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
Microsoft TV subtitles Decoder, 0 x 00200001, 1, 0, MSTVCapn.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
Mixer2, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, overlay
RDP DShow Redirection Filter, 0xffffffff, 1, 0, DShowRdpFilter.dll,
Microsoft MPEG-2 Audio Encoder, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, msmpeg2enc.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
Pager, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, WSTPager.ax, 6.06.7600.16385 WST
MPEG2 demux, 0 x 00600000, 1, 1, mpg2splt.ax, 6.06.7600.16648
Decoder, 0 x 00800000, 1, 1, qdv.dll, 6.06.7600.16385 DV video
SampleGrabber, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, qedit.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
Renderer, 00200000 x 0, 1, 0, qedit.dll, 6.06.7600.16385 null
Tables, 0x005fffff, 1, 0, mpeg2data.ax, 6.06.7600.16385 and MPEG — 2 Sections
Microsoft AC3 Encoder, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, msac3enc.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
StreamBufferSource, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0, sbe.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
Smart Tee, 0 x 00200000, 1, 2, qcap.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
Overlay mixer, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0,
AVI Decompressor, 0 x 00600000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
NetBridge, 00200000 x 0, 2, 0, netbridge.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
Source, 0 x 00400000, 0, 2, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490 AVI/WAV file
Parser, 0 x 00400000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490 wave
Parser, 0 x 00400000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490 noon
Multi-fichier Parser, 0 x 00400000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
File stream renderer, 0x00400000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
Microsoft DTV — DVD Audio Decoder, 0x005fffff, 1, 1, msmpeg2adec.dll, 6.01.7140.0000
StreamBufferSink2, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0, sbe.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
AVI Mux, 00200000 x 0, 1, 0, qcap.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
Line 21 decoder 2, 0 x 00600002, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
File Source (Async.), 0 x 00400000, 0, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
File Source (URL), 0 x 00400000, 0, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
Media Center Extender encryption Filter, 0 x 00200000, 2, 2, Mcx2Filter.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
Dest, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0, WavDest.dll AudioRecorder WAV,.
Wave WavDest.dll AudioRecorder form, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0,.,
SoundRecorder Null Renderer, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0, WavDest.dll,
Infinite pin Tee Filter, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, qcap.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
Renderer, 00200000 x 0, 1, 0, evr.dll, 6.01.7600.16385 improved video
BDA MPEG2 Transport Information Filter, 0 x 00200000, 2, 0, psisrndr.ax, 6.06.7600.16385
Decoder, 0 x 40000001, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490 MPEG video
WDM Streaming Tee/Splitter devices:
Converter, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, ksproxy.ax, 6.01.7600.16385 tee/sink — to the-wells
Video compressors:
WMVideo8 encoder DMO, 0 x 00600800, 1, 1, wmvxencd.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
WMVideo9 encoder DMO, 0 x 00600800, 1, 1, wmvencod.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
Encoder 9 MSScreen DMO, 0 x 00600800, 1, 1, wmvsencd.dll, 6.01.7600.16385
Encode, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0, qdv.dll, 6.06.7600.16385 DV video
MJPEG Compressor, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
Audio compressors:
WM Encoder DMO speech, 0 00600800, 1, 1, x WMSPDMOE. DLL, 6.01.7600.16385
WMAudio encoder DMO, 0 x 00600800, 1, 1, WMADMOE. DLL, 6.01.7600.16385
IMA ADPCM, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
PCM, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
Microsoft ADPCM, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
GSM 6.10, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
CCITT A — Law, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
CCITT u — Law, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
MPEG Layer-3, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
Audio Capture sources:
Microphone (2 — USB Audio Device, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0, qcap.dll, 6.06.7600.16385)
Microphone (Avnex Virtual Audio, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0, qcap.dll, 6.06.7600.16385)
PBDA CP filters:
PBDA DTFilter, 0 x 00600000, 1, 1, CPFilters.dll, 6.06.7600.16648
ETFilter, 0 x 00200000 PBDA, 0, 0, CPFilters.dll, 6.06.7600.16648
PTFilter, 0 x 00200000 PBDA, 0, 0, CPFilters.dll, 6.06.7600.16648
Midi converters:
Default MidiOut Device, 0 x 00800000, 1, 0, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
Synth, 00200000 x 0, 1, 0, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490 Microsoft GS Wavetable
WDM Streaming Capture devices:
0 x 00000000, 0, 0,
0 x 00000000, 0, 0,
AVnex Virtual Audio Device, 0 x 00200000, 2, 2, ksproxy.ax, 6.01.7600.16385
Device, 0 x 00200000, 2, 2, ksproxy.ax, 6.01.7600.16385 Audio USB
WDM Streaming making devices:
Realtek HD Audio output, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, ksproxy.ax, 6.01.7600.16385
AVnex Virtual Audio Device, 0 x 00200000, 2, 2, ksproxy.ax, 6.01.7600.16385
Device, 0 x 00200000, 2, 2, ksproxy.ax, 6.01.7600.16385 Audio USB
BDA network providers:
Provider, 0 x 00200000, 0, 1, MSDvbNP.ax, 6.06.7600.16385 Microsoft ATSC network
DVBC Microsoft Network Provider, 0 x 00200000, 0, 1, MSDvbNP.ax, 6.06.7600.16385
Provider, 0 x 00200000, 0, 1, MSDvbNP.ax, network 6.06.7600.16385 Microsoft DVBS
Provider, 0 x 00200000, 0, 1, MSDvbNP.ax, 6.06.7600.16385 network Microsoft t
Microsoft Network Provider, 0 x 00200000, 0, 1, MSNP.ax, 6.06.7600.16648
Multiple instances Codecs VBI Capable:
The IST Codec, 0 x 00600000, 1, 4, VBICodec.ax, 6.06.7600.16385
BDA Transport Information converters:
BDA MPEG2 Transport Information Filter 0 x 00600000, 2, 0, psisrndr.ax, 6.06.7600.16385
Tables, 0 x 00600000, 1, 0, mpeg2data.ax, 6.06.7600.16385 and MPEG — 2 Sections
CP/CA BDA filters:
Decrypt/Tag,0x00600000,1,1,EncDec.dll,6.06.7600.16385
Encrypt/Tag,0x00200000,0,0,EncDec.dll,6.06.7600.16385
PTFilter, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0, EncDec.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
XDS Codec, 0 x 00200000, 0, 0, EncDec.dll, 6.06.7600.16385
WDM Streaming transformations of the Communication:
Converter, 0 x 00200000, 1, 1, ksproxy.ax, 6.01.7600.16385 tee/sink — to the-wells
Audio converters:
Speakers (Realtek High Definiti, 00200000 x 0, 1, 0, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490)
DirectSound Device, 0 x 00800000, 1, 0, quartz.dll, default 6.06.7600.16490
Default WaveOut Device, 0 x 00200000, 1, 0, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
DirectSound: Speakers (2 — USB Audio Device), 0 x 00200000, 1, 0, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
DirectSound: Speakers (Avnex Virtual Audio Device), 0 x 00200000, 1, 0, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
DirectSound: Speakers (Realtek High definition Audio), 0 x 00200000, 1, 0, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
Speakers (2 — USB Audio Device), 0 x 00200000, 1, 0, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490
Speakers (Virtual Audio D, 0 x 00200000 Avnex, 1, 0, quartz.dll, 6.06.7600.16490)
—————
EVR power information
—————
Current value: {651288E5-A7ED-4076-A96B-6CC62D848FE1} (balanced)
Quality indicators: 2576
Activated:
Limitation of the force
That allow half deinterlace
Allow the scaling
Decode power usage: 100
Balanced flags: 1424
Activated:
Limitation of the force
Allow batch processing
Force half deinterlace
Force the scaling
Decode power usage: 50
PowerFlags: 1424
Activated:
Limitation of the force
Allow batch processing
Force half deinterlace
Force the scaling
Decode power usage: 0
Any help is appreciated. Thank you in advance.
I asked a friend to real for my friends to come take a look at what was going on & he was able to remedy.
My DirectX running smoothly now.
Thank you all for all the help, if.
Какая безответственность! Просто вопиющая! Его спрашиваешь – он молчит. Снова спрашиваешь – он опять молчит. Вот такой нам достался DNS-сервер: не лает, не кусает, в интернет не пускает. И ни за что не отвечает.
Почему этот важный узел объявил нам бойкот? Как заставить его снова отвечать на наши запросы? Давайте разбираться.
Содержание
- Причины молчания DNS-сервера
- Самое простое решение
- Локализуем источник сбоя
- Обвиняется браузер
- Вероятный виновник – роутер
- Внимание на настройки DNS
- Демилитаризованная зона
- Ограничения провайдеров
- Сбой на компьютере. Что делать?
- Проверьте работу службы «DNS-клиент»
- Пропишите адреса ДНС в настройках подключения вручную
- Проверьте настройки брандмауэра или файервола
- Просканируйте систему антивирусом
- Сделайте восстановление системы
- Проверьте системные файлы на целостность
- Восстановите доступ к сети с помощью Complete Internet Repair
Причины молчания DNS-сервера
Сервер Domain Name System – это сетевое устройство (хост) или программа, чья задача – преобразовывать имена веб-ресурсов, которые мы открываем в браузере, в их IP-адреса, чтобы обеспечить соединение этих ресурсов и наших компьютеров.
Сайтов в интернете миллиарды, а серверов DNS – миллионы. И если один-единственный из этого легиона – тот, что первый принимает наши запросы, не ответит, то вместо интернета мы получим следующее:
И так до бесконечности.
Ниже – причины, по которым ошибка «DNS-сервер не отвечает» возникает чаще всего:
- В сетевых настройках ПК или роутера указаны IP недоступных или несуществующих ДНС.
- Адрес DNS указан верно, но сервер временно отключен, заблокирован настройками или запрещен интернет-провайдером.
- На компьютере не запущена или некорректно работает служба DNS-клиент.
- Связь с сервером заблокирована брандмауэром Windows или сторонними средствами контроля интернет-трафика.
- Компьютер заражен вредоносным ПО.
- Повреждены системные файлы и сетевые структуры Windows (иногда как следствие работы вирусов).
- Если проблема раз за разом возникает в одном конкретном браузере, ее источником может быть сбойное расширение или плагин либо данные в кэше.
А теперь поехали разбираться.
Самое простое решение
Самое легкое и быстрое решение большинства проблем с интернетом обеспечивает уже знакомое нам Средство диагностики сетей Windows. Многие ошибки утилита исправляет сама, а если ей это не удается, она сообщает причину сбоя, чтобы пользователь попытался устранить его другим способом.
Для запуска средства диагностики нажмите правой клавишей мыши на значок сети в области уведомлений панели задач Windows, затем кликните в меню соответствующий пункт.
Если утилита предложит выбрать сетевой адаптер для диагностики, а вы не знаете, какой, то отметьте вариант «Все» и нажмите «Далее».
Через 10-30 секунд откроется уведомление об устранении ошибки или ее причине, как в примере на скриншоте ниже:
Если проблема осталась нерешенной, двигаемся дальше. Сначала…
Локализуем источник сбоя
Он, как мы выяснили, может «гнездиться» в трех локациях: на компьютере, роутере или в браузере.
Чтобы найти точное место «засады», сделайте следующее:
- Попытайтесь открыть сайт, к которому нет доступа, в другом браузере. Если он загрузится нормально, значит, виновник ошибки – браузер и его надстройки (расширения, плагины и т. д.).
- Проверьте, есть ли интернет на других устройствах домашней сети, подключенных к этому же роутеру. Если его нет нигде, то причина сбоя в настройках роутера или у провайдера.
- Если ошибка ДНС возникает во всех браузерах только на одном компьютере, значит, ее виновник находится там же.
Что делать дальше, зависит от того, где локализуется причина.
Обвиняется браузер
Веб-браузер, который используется как основной, не просто приложение. Это уникальная сложная система, построенная из расширений, плагинов, скинов и скриптов в «обрамлении» индивидуальных настроек. Чем больше в ней элементов, тем выше вероятность поломки.
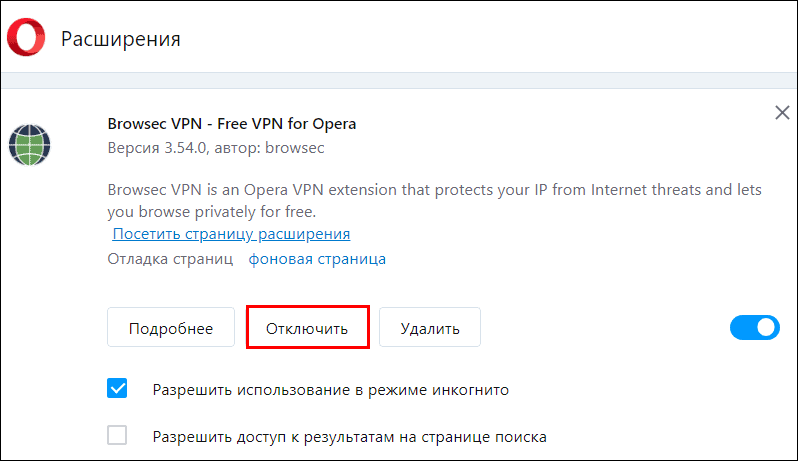
Ошибки, связанные с DNS, чаще всего происходят по вине расширений для фильтрации контента (родительский контроль), блокировки рекламы, защиты от вредоносного ПО и перенаправления трафика по альтернативному маршруту (VPN, прокси, ускорители загрузки страниц). Исключения – тоже не редкость: виновником большой головной боли может оказаться что-то мелкое и, казалось бы, безобидное, поэтому проверять необходимо все.
Неполадка может произойти как из-за сбоя в одном расширении, например, в VPN с собственным сервером DNS, который забанил «Роскомпозор», так и из-за конфликта при совместной работе нескольких: антивируса + родительского контроля, VPN + блокировщика рекламы и т. д.
Найти источник проблемы можно поочередным отключением надстроек, начиная с самых подозрительных.
Также не забудьте очистить кэш DNS браузера, поскольку ошибка, закравшаяся в эту область, может проявляться раз за разом, даже если связь уже восстановилась.
Для этого вставьте в адресную строку браузера следующую команду:
- В Google Chrome: chrome://net-internals/#dns
- В Опере: opera://net-internals/#dns
- В Яндекс.Браузере: browser://net-internals/#dns
затем нажмите кнопку перехода и на открывшейся станице щелкните «Clear host cache».
Если команда не сработала, очистите кэш-память браузера традиционным способом. В большинстве обозревателей эта функция находится в меню «История» -> «Очистить (удалить) историю». В Firefox – в меню «Журнал» -> «Удалить историю».
Вероятный виновник – роутер
Внимание на настройки DNS
Получение адреса DNS для подключения к интернету обычно происходит автоматически. Но любой пользователь, у которого есть доступ к админ-панели роутера, имеет возможность назначить его вручную.
Побаловаться с адресами ДНС могут и программы, в том числе вредоносные. Некоторые компьютерные вирусы умеют взламывать аутентификацию, особенно на тех устройствах, где логин и пароль для входа остались с завода, вроде «admin/admin».
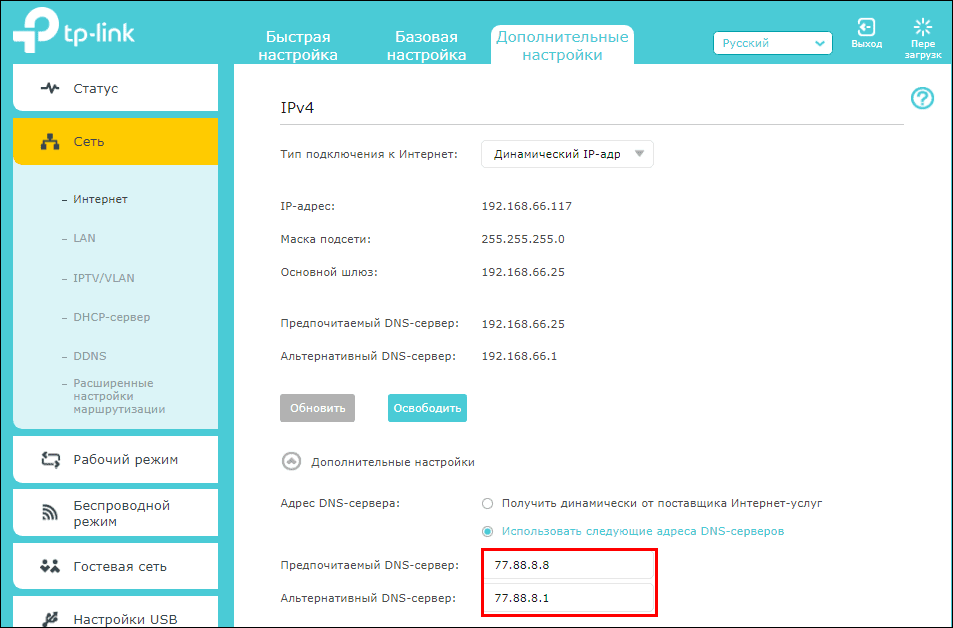
Чтобы проверить, не ваш ли это случай, войдите в панель управления роутером, откройте параметры интернета и посмотрите, какие IP назначены DNS-серверам. Если они не принадлежат провайдеру или надежному сервису, вроде Google (8.8.8.8 предпочитаемый и 8.8.4.4 альтернативный) или Яндекс (на скриншоте), переключите настройку на «Получать (адреса DNS) от поставщика интернет-услуг».
Впрочем, виновником ошибки «ДНС-сервер не отвечает» может оказаться даже надежный сервис, такой как DNS.Яндекс. В режимах «Безопасный» и «Семейный» у него предусмотрена фильтрация контента. Если сбой происходит только на сайтах определенной тематики (для взрослых), то, вероятно, вы используете один из таких режимов.
Демилитаризованная зона
Некоторые роутеры и модемы USB поддерживают «демилитаризованные зоны» (DMZ) – дополнительные настройки безопасности, которые позволяют отделить сегмент сети с ресурсами общего доступа от приватных.
Описаны случаи, когда включение этой функции приводило к нарушению связи с ДНС-сервером. Поэтому попробуйте для проверки ее не использовать.
Ограничения провайдеров
Слишком категоричными в выборе DNS бывают и некоторые интернет-провайдеры – они разрешают подключаться только к собственным серверам, а все прочие блокируют. Возможно, это повышает уровень защиты от фишинга и скама, но вместе с тем их абоненты теряют возможность использовать родительский контроль, VPN и другие сервисы, которые пропускают трафик через свои DNS.
А если у такого провайдера случится сбой в работе серверов, например, из-за хакерской атаки, то изменение ДНС в настройках ничем не поможет оставшимся без интернета пользователям.
Как это предотвратить или исправить, если проблема уже возникла? Выбор небольшой: подождать, когда «они там все починят» или подключиться к сети другого провайдера. К счастью, в большинстве городов РФ есть из кого выбирать. Например, повсеместно распространенные МТС и Ростелеком такими глупостями не страдают.
Сбой на компьютере. Что делать?
Приведенные ниже инструкции можно выполнять в любом прядке. Если одна из них помогла исправить ошибку, то остальные можно не делать, если не считаете это целесообразным.
А мы начнем с самого простого.
Проверьте работу службы «DNS-клиент»
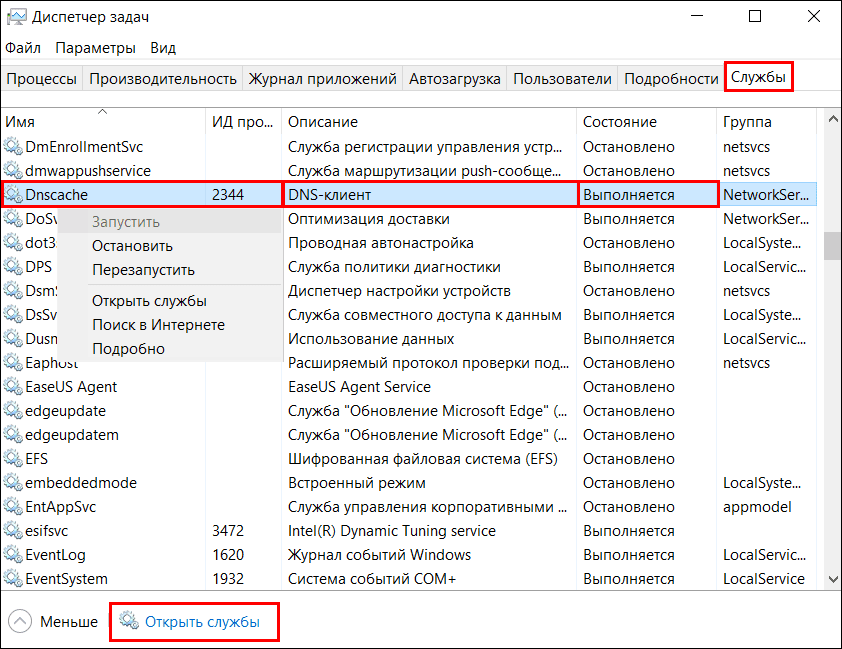
- Запустите «Диспетчер задач» и откройте вкладку (на Windows 7 и 10) или раздел (на Windows 11) «Службы». Кликните по заголовку столбца «Описание», чтобы записи в нем расположились по алфавиту (для удобства поиска).
- Найдите службу с описанием «DNS-клиент» и посмотрите, что указано возле нее в колонке «Состояние».
- Если эта служба остановлена, щелкните по строке с ее именем правой клавишей мыши, чтобы открыть контекстное меню, и нажмите «Запустить».
Чтобы «DNS-клиент» всегда запускался автоматически, кликните внизу окна «Открыть службы».
Затем:
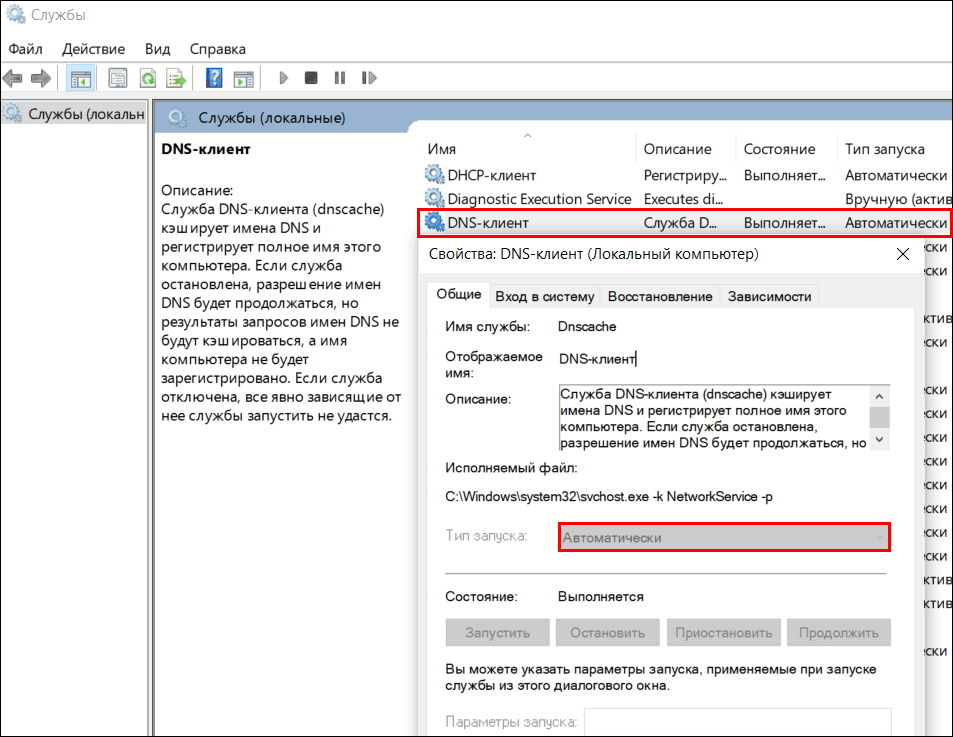
- Найдите в списке эту службу и двойным кликом по строке откройте ее свойства.
- Выберите из выпадающего списка «Тип запуска» вариант «Автоматически» и сохраните настройку.
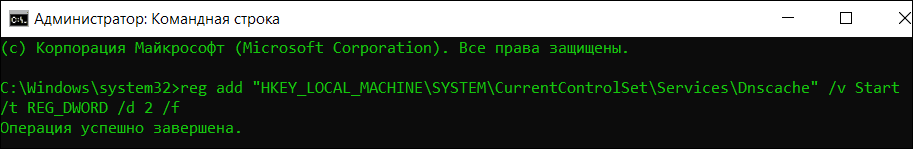
Если поле изменения типа запуска службы «DNS-клиент» неактивно, откройте командную строку с правами администратора и выполните следующую инструкцию:
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesDnscache" /v Start /t REG_DWORD /d 2 /f
Эта команда назначит службе Dnscache автоматический запуск (2) по умолчанию. Изменения будут внесены прямо в системный реестр.
Пропишите адреса ДНС в настройках подключения вручную
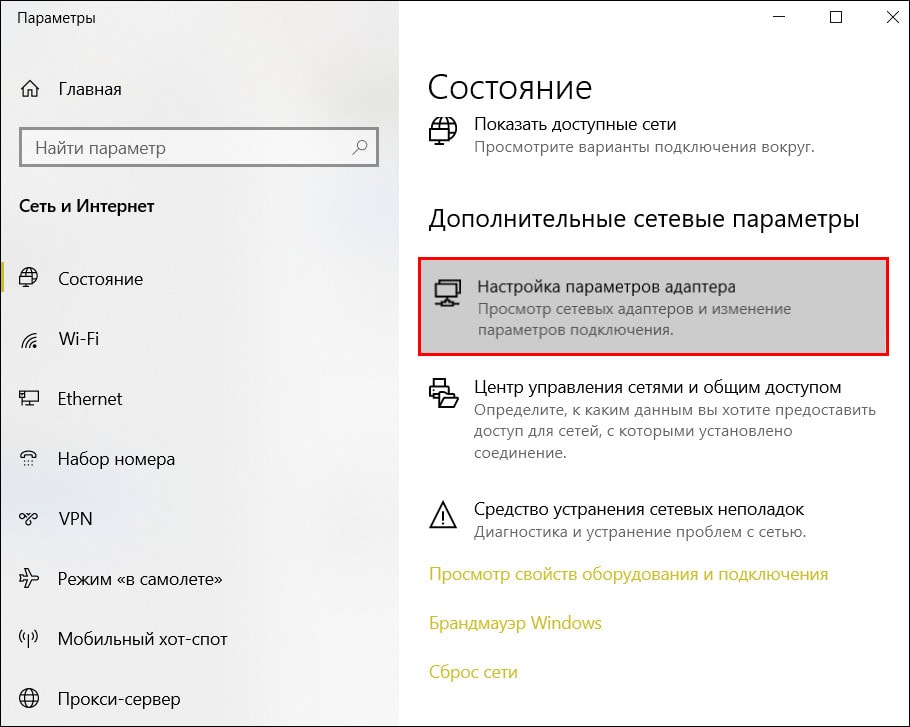
Откройте настройки текущего подключения на компьютере:
- Щелкните правой кнопкой по иконке сети в области уведомлений и выберите «Открыть параметры сети и Интернет» либо «Центр управления сетями и общим доступом».
- Перейдите в раздел «Настройка (изменение) параметров адаптера».
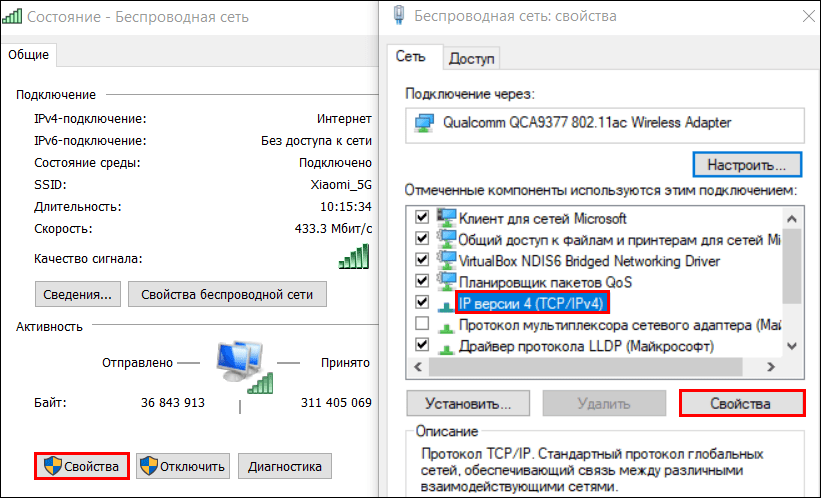
- Кликните два раза по значку текущего подключения и в окошке «Состояние», которое откроется после этого, нажмите «Свойства».
- В следующем окне выделите в списке компонентов, которые используются этим подключением, пункт «IP версии 4 TCP/IPv4» и снова нажмите кнопку «Свойства».
- Обратите внимание на настройку получения адреса ДНС. Если выбран вариант «Автоматически», переключитесь на «Использовать следующие адреса…» и введите айпи DNS-серверов вашего провайдера или доверенного альтернативного сервиса (если провайдер их не блокирует). Для примера на этом скриншоте введены адреса Яндекса:
- Сохраните новые параметры и отключитесь, затем снова подключитесь к сети.
Если доступ в интернет не восстановился, запустите «Диагностику сетевых неполадок» или выполните в командной строке инструкцию:
ipconfig /flushdns
Это удалит сбойные данные из кэша DNS.
Проверьте настройки брандмауэра или файервола
Чтобы исключить возможное влияние на связь с DNS-сервером брандмауэра Windows или файервола сторонней антивирусной программы, выключите его на время проверки. Если проблема разрешится, сбросьте настройки брандмауэра/файервола на умолчания или удалите правило, которое могло стать причиной сбоя.
Как открыть и сбросить брандмауэр Windows 10, мы рассказывали в статье «Почему не работает интернет».
О правилах блокировки сетевых ресурсов с помощью брандмауэра подробно написано в статье по ссылке.
Просканируйте систему антивирусом
Вредоносные программы нередко вмешиваются в работу сети на зараженных компьютерах. Есть даже категория зловредов, которая только и делает, что подменяет адреса в настройках DNS для перенаправления пользователей на фишинговые ресурсы. А если в этом процессе что-то идет не так, то вместо открытия поддельных сайтов возникает ошибка «DNS не отвечает» или «Сервер не найден».
Когда зараза укоренилась в системе, бесполезно менять настройки – скорее всего, она будет сбивать их снова и снова. Поэтому в первую очередь избавьтесь от нее при помощи любой антивирусной утилиты со свежими базами, а потом исправляйте результаты ее трудов.
После сканирования загляните в файл hosts, который находится в папке %Windir%System32driversetc. Ведь его тоже можно использовать для блокировки подключения к определенным ресурсам, в том числе хостам DNS.
Что это за файл, какую роль он играет в системе и как с ним работать, читайте в статье по ссылке.
Добавлять данные в hosts могут как пользователи с административными правами, так и программы. В числе последних не только вредоносные, но и нормальные, например, блокировщики рекламы.
Записи вредоносных программ необходимо удалять. Если в файле hosts много разных данных, и вы не знаете, какие из них блокируют доступ в интернет, можете удалить все. Блокировщик рекламы через некоторое время создаст их снова.
Сделайте восстановление системы
Ошибка подключения к DNS-серверу, возникшая после заражения или системного сбоя, может иметь скрытые причины, которые не распознает даже «Диагностика сетей». Справиться со многими из них помогает Восстановление системы Windows на контрольную точку, созданную до появления ошибки.
Если вы прибегли к этому инструменту после удаления вредоносного ПО, то последнее придется повторить, так как точное время заражения вам вряд ли известно. А процедура восстановления может вернуть удаленный вирус к жизни.
Проверьте системные файлы на целостность
Последствия некоторых сбоев успешно устраняет еще один встроенный инструмент Windows – средство проверки и восстановления целостности поврежденных системных файлов, связанных, в том числе, с работой сети. Это консольная утилита SFC, которой управляют при помощи командной строки.
Откройте консоль от имени администратора и выполните инструкцию:
SFC /SCANNOW
Параметр scannow означает «проверить все защищенные системные файлы и по возможности восстановить проблемные».
Если после того, как утилита SFC исправила поврежденные файлы, сделать восстановление системы на контрольную точку, то операцию проверки придется повторить. Так как некоторые или все исправленные файлы вернутся к предыдущим версиям.
Восстановите доступ к сети с помощью Complete Internet Repair
Исправили сетевые настройки, удалили вирусы, восстановили файлы, а сервер ДНС все равно не отвечает? Призовите на помощь бесплатную утилиту Complete Internet Repair.
Она успешно восстанавливает связь после атаки вредоносного и рекламного ПО, установки и удаления VPN, антивирусов, файерволов и других сетевых программ, а также системных сбоев.
В ее власти:
- Исправление ошибок реестра.
- Проверка и восстановление связи с DNS.
- Очистка кэша протоколов, каталогов и прочих сетевых структур.
- Сброс конфигурации брандмауэра.
- Удаление записей из hosts и многое другое.
Complete Internet Repair исправляет практически все разновидности сетевых неполадок на компьютерах с Windows, кроме аппаратных и связанных с драйверами.
А о том, как еще можно бороться с проблемами доступа в интернет, читайте в статье по ссылке.