Playing around with K8 and ingress in local minikube setup. Creating ingress from yaml file in networking.k8s.io/v1 api version fails. See below output.
Executing
> kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml
returns
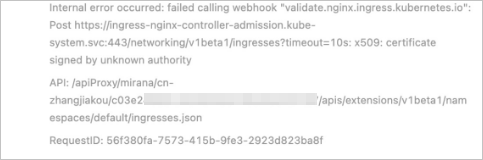
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating "ingress.yaml": Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "validate.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io": an error on the server ("") has prevented the request from succeeding
in local minikube environment with hyperkit as vm driver.
Here is the ingress.yaml file:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: mongodb-express-ingress
namespace: hello-world
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /$1
spec:
rules:
- host: mongodb-express.local
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: mongodb-express-service-internal
port:
number: 8081
Here is the mongodb-express deployment file:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mongodb-express
namespace: hello-world
labels:
app: mongodb-express
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mongodb-express
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mongodb-express
spec:
containers:
- name: mongodb-express
image: mongo-express
ports:
- containerPort: 8081
env:
- name: ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_ADMINUSERNAME
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mongodb-secret
key: mongodb-root-username
- name: ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_ADMINPASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mongodb-secret
key: mongodb-root-password
- name: ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_SERVER
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: mongodb-configmap
key: mongodb_url
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mongodb-express-service-external
namespace: hello-world
spec:
selector:
app: mongodb-express
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8081
targetPort: 8081
nodePort: 30000
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mongodb-express-service-internal
namespace: hello-world
spec:
selector:
app: mongodb-express
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8081
targetPort: 8081
Some more information:
> kubectl version
Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"19", GitVersion:"v1.19.7", GitCommit:"1dd5338295409edcfff11505e7bb246f0d325d15", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2021-01-13T13:23:52Z", GoVersion:"go1.15.5", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"darwin/amd64"}
Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"20", GitVersion:"v1.20.2", GitCommit:"faecb196815e248d3ecfb03c680a4507229c2a56", GitTreeState:"clean", BuildDate:"2021-01-13T13:20:00Z", GoVersion:"go1.15.5", Compiler:"gc", Platform:"linux/amd64"}
> minikube version
minikube version: v1.19.0
commit: 15cede53bdc5fe242228853e737333b09d4336b5
> kubectl get all -n hello-world
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/mongodb-68d675ddd7-p4fh7 1/1 Running 0 3h29m
pod/mongodb-express-6586846c4c-5nfg7 1/1 Running 6 3h29m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/mongodb-express-service-external LoadBalancer 10.106.185.132 <pending> 8081:30000/TCP 3h29m
service/mongodb-express-service-internal ClusterIP 10.103.122.120 <none> 8081/TCP 3h3m
service/mongodb-service ClusterIP 10.96.197.136 <none> 27017/TCP 3h29m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/mongodb 1/1 1 1 3h29m
deployment.apps/mongodb-express 1/1 1 1 3h29m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/mongodb-68d675ddd7 1 1 1 3h29m
replicaset.apps/mongodb-express-6586846c4c 1 1 1 3h29m
> minikube addons enable ingress
▪ Using image k8s.gcr.io/ingress-nginx/controller:v0.44.0
▪ Using image docker.io/jettech/kube-webhook-certgen:v1.5.1
▪ Using image docker.io/jettech/kube-webhook-certgen:v1.5.1
🔎 Verifying ingress addon...
🌟 The 'ingress' addon is enabled
> kubectl get all -n ingress-nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/ingress-nginx-admission-create-2bn8h 0/1 Completed 0 4h4m
pod/ingress-nginx-admission-patch-vsdqn 0/1 Completed 0 4h4m
pod/ingress-nginx-controller-5d88495688-n6f67 1/1 Running 0 4h4m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/ingress-nginx-controller NodePort 10.111.176.223 <none> 80:32740/TCP,443:30636/TCP 4h4m
service/ingress-nginx-controller-admission ClusterIP 10.97.107.77 <none> 443/TCP 4h4m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/ingress-nginx-controller 1/1 1 1 4h4m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/ingress-nginx-controller-5d88495688 1 1 1 4h4m
NAME COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE
job.batch/ingress-nginx-admission-create 1/1 7s 4h4m
job.batch/ingress-nginx-admission-patch 1/1 9s 4h4m
However, it works for the beta api version, i.e.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: mongodb-express-ingress-deprecated
namespace: hello-world
spec:
rules:
- host: mongodb-express.local
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: mongodb-express-service-internal
servicePort: 8081
Any help very much appreciated.
Содержание
- failed calling webhook «validate.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io» no route to host #8146
- Comments
- NGINX Ingress controller version (exec into the pod and run nginx-ingress-controller —version.):
- Kubernetes: nginx ingress controller — failed calling webhook
- Failed calling webhook «validate.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io» error while deploying ingress on RKE clusters with v1.21.1-rancher1-1 #33067
- Comments
- Failed calling webhook «validate.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io» error while deploying ingress on RKE clusters with v1.21.1-rancher1-1 #33067
- Comments
- Post https://ingress-nginx-controller-admission.ingress-nginx.svc:443/extensions/v1beta1/ingresses?timeout=30s: context deadline exceeded #5583
- Comments
- `[root@l000d01kms001 KubeHelm]# kubectl logs pod/ingress-nginx-admission-create-44q78 -n ingress-nginx ^C [root@l000d01kms001 KubeHelm]# kubectl logs pod/ingress-nginx-admission-patch-gqwbr -n ingress-nginx <«level»:»info»,»msg»:»patching webhook configurations ‘ingress-nginx-admission’ mutating=false, validating=true, failurePolicy=Fail»,»source»:»k8s/k8s.go:38″,»time»:»2020-05-20T20:29:52Z»> <«level»:»info»,»msg»:»Patched hook(s)»,»source»:»k8s/k8s.go:91″,»time»:»2020-05-20T20:29:52Z»> [root@l000d01kms001 KubeHelm]# kubectl logs pod/ingress-nginx-controller-f8d756996-rhmjl -n ingress-nginx
failed calling webhook «validate.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io» no route to host #8146
NGINX Ingress controller version (exec into the pod and run nginx-ingress-controller —version.):
Kubernetes version (use kubectl version ):
Environment:
- Cloud provider or hardware configuration: baremetal
- OS (e.g. from /etc/os-release): «AlmaLinux 8.5 (Arctic Sphynx)»
- Kernel (e.g. uname -a ): Linux node1 4.18.0-348.2.1.el8_5.x86_64
Basic structure #1 SMP Mon Nov 15 09:17:08 EST 2021 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
- Please mention how/where was the cluster created like kubeadm/kops/minikube/kind etc.
- kubectl version
- kubectl get nodes -o wide
node1 Ready control-plane,master 39h v1.22.5 AlmaLinux 8.5 (Arctic Sphynx) 4.18.0-348.2.1.el8_5.x86_64 containerd://1.5.8
node2 Ready control-plane,master 39h v1.22.5 AlmaLinux 8.5 (Arctic Sphynx) 4.18.0-348.2.1.el8_5.x86_64 containerd://1.5.8
node3 Ready control-plane,master 39h v1.22.5 AlmaLinux 8.5 (Arctic Sphynx) 4.18.0-348.2.1.el8_5.x86_64 containerd://1.5.8
- How was the ingress-nginx-controller installed:
- If helm was used then please show output of helm ls -A | grep -i ingress
ingress-nginx ingress-nginx 1 2022-01-14 18:17:03.9151248 +0100 CET deployed ingress-nginx-4.0.15 1.1.1
- If helm was used then please show output of helm -n get values
- Current State of the controller:
- kubectl describe ingressclasses
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
pod/ingress-nginx-controller-6sd6x 1/1 Running 0 114m node3
pod/ingress-nginx-controller-fxwxp 1/1 Running 0 114m node1
pod/ingress-nginx-controller-x8jbf 1/1 Running 0 114m node2
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
service/ingress-nginx-controller-admission ClusterIP 10.233.26.192 443/TCP 114m app.kubernetes.io/component=controller,app.kubernetes.io/instance=ingress-nginx,app.kubernetes.io/name=ingress-nginx
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE CONTAINERS IMAGES SELECTOR
daemonset.apps/ingress-nginx-controller 3 3 3 3 3 kubernetes.io/os=linux 114m controller k8s.gcr.io/ingress-nginx/controller:v1.1.1@sha256:0bc88eb15f9e7f84e8e56c14fa5735aaa488b840983f87bd79b1054190e660de app.kubernetes.io/component=controller,app.kubernetes.io/instance=ingress-nginx,app.kubernetes.io/name=ingress-nginx
- Others:
- Any other related information like ;
- copy/paste of the snippet (if applicable)
- kubectl describe . of any custom configmap(s) created and in use
- Any other related information that may help
- Any other related information like ;
What happened:
What you expected to happen:
How to reproduce it:
Anything else we need to know:
Whenever (almost) I create an ingress I get:
Error: Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook «validate.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io»: Post «https://ingress-nginx-controller-admission.ingress-nginx.svc:443/networking/v1/ingresses?timeout=10s»: dial tcp 10.233.26.192:443: connect: no route to host
when I exec into any pod and try to reach ingress-nginx-controller-admission.ingress-nginx.svc:443 i get:
wget: server returned error: HTTP/1.0 400 Bad Request
/ # wget -qO- 10.233.26.192:443
wget: can’t connect to remote host (10.233.26.192): No route to host
/ # wget -qO- 10.233.26.192:443
wget: can’t connect to remote host (10.233.26.192): No route to host
/ # wget -qO- 10.233.26.192:443
wget: server returned error: HTTP/1.0 400 Bad Request
It fails consistently 2 times out of 3 (and I have 3 pods) so I tried reaching each one by the node ip and it fails consistently when I try to reach one node from another node.
Now that I managed to fix the issue (ie: open the port), I keep all of this here for the next person.
But I still want to ask, is it dangerous to keep port 8443 open to the public ? if I understand correctly ingress-nginx answers with 403 if we do not provide a token issued by the cluster. Am I right ? or should close the port and configure peer communication another way, or maybe only allow it from peers ?
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
Источник
Kubernetes: nginx ingress controller — failed calling webhook
3 min read | by Jordi Prats
On a kubernetes cluster you might find the following error:
This message is telling you that the nginx ingress controller is not responding: This can be due to the fact that it might have partially uninstalled it (for example, by removing the namespace) but some of the global objects still present (for example the ValidatingWebhookConfiguration object).
To remove the ValidatingWebhookConfiguration object for the nginx ingress controller is named ingress-nginx-admission, we can remove it with kubectl delete like this:
Once you have it removed, you will be able to create ingress objects as usual:
We should be considering this a workaround, we need to keep in mind that removing a namespace is not equivalent of uninstalling an application: Some applications might have created objects that are not namespaced:
Thus, be aware that by removing the nginx ingress controller namespace and the ingress-nginx-admission webhook you are not completely removed all the objects that were installed with the nginx ingress controller: You also want to check for the presence of some clusterroles and clusterrolebindings to also get rid of them:
Источник
Failed calling webhook «validate.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io» error while deploying ingress on RKE clusters with v1.21.1-rancher1-1 #33067
What kind of request is this (question/bug/enhancement/feature request): bug
Steps to reproduce (least amount of steps as possible):
- TL;DR — Deploy custom RKE1 cluster with k8s v1.21.1-rancher1-1 and try to create nginx-ingress based ingress — it will fail on:
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating «STDIN»: Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook «validate.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io»: Post «https://ingress-nginx-controller-admission.ingress-nginx.svc:443/networking/v1beta1/ingresses?timeout=10s»: dial tcp 10.43.163.232:443: connect: connection refused
Or try to deploy rancher on RKE1 cluster with v1.21.1-rancher1-1 :
- provision single VM with all the prerequisities for RKE1 clusters — I was trying ubuntu 18.04 in CI and sles15sp2 manually
- download latest (unstable) rke-1.3.0-rc3 with support for k8s v1.21.1-rancher1-1
- prepare cluster.yaml with following content (
borrowed from our CI):
- call rke-1.3.0-rc3 up —config cluster.yaml
- create needed resources and install cert-manager and rancher:
Result:
helm will fail on attemp to install rancher on following error:
Other details that may be helpful:
- Custom RKE1 clusters with k8s v1.21.1-rancher1-1 are also affected, simple reproducer:
Environment information
- Rancher version ( rancher/rancher / rancher/server image tag or shown bottom left in the UI): rancher/rancher:master-head b2f8824 (at the time of the attempt)
- Installation option (single install/HA): single or HA / any
Cluster information
- Cluster type (Hosted/Infrastructure Provider/Custom/Imported): local
- Machine type (cloud/VM/metal) and specifications (CPU/memory): any
- Kubernetes version (use kubectl version ): v1.21.1-rancher1-1
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
Источник
Failed calling webhook «validate.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io» error while deploying ingress on RKE clusters with v1.21.1-rancher1-1 #33067
What kind of request is this (question/bug/enhancement/feature request): bug
Steps to reproduce (least amount of steps as possible):
- TL;DR — Deploy custom RKE1 cluster with k8s v1.21.1-rancher1-1 and try to create nginx-ingress based ingress — it will fail on:
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating «STDIN»: Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook «validate.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io»: Post «https://ingress-nginx-controller-admission.ingress-nginx.svc:443/networking/v1beta1/ingresses?timeout=10s»: dial tcp 10.43.163.232:443: connect: connection refused
Or try to deploy rancher on RKE1 cluster with v1.21.1-rancher1-1 :
- provision single VM with all the prerequisities for RKE1 clusters — I was trying ubuntu 18.04 in CI and sles15sp2 manually
- download latest (unstable) rke-1.3.0-rc3 with support for k8s v1.21.1-rancher1-1
- prepare cluster.yaml with following content (
borrowed from our CI):
- call rke-1.3.0-rc3 up —config cluster.yaml
- create needed resources and install cert-manager and rancher:
Result:
helm will fail on attemp to install rancher on following error:
Other details that may be helpful:
- Custom RKE1 clusters with k8s v1.21.1-rancher1-1 are also affected, simple reproducer:
Environment information
- Rancher version ( rancher/rancher / rancher/server image tag or shown bottom left in the UI): rancher/rancher:master-head b2f8824 (at the time of the attempt)
- Installation option (single install/HA): single or HA / any
Cluster information
- Cluster type (Hosted/Infrastructure Provider/Custom/Imported): local
- Machine type (cloud/VM/metal) and specifications (CPU/memory): any
- Kubernetes version (use kubectl version ): v1.21.1-rancher1-1
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
Источник
Post https://ingress-nginx-controller-admission.ingress-nginx.svc:443/extensions/v1beta1/ingresses?timeout=30s: context deadline exceeded #5583
I’ve installed kubernetes cluster on three servers: l000d01kms001 (K8s master) and l000d01ksl001 & l000d01ksl001 — all basen Centos 7.5
docker-ce-cli-19.03.6-3.el7.x86_64
docker-ce-19.03.6-3.el7.x86_64
kubelet-1.17.3-0.x86_64
kubernetes-cni-0.7.5-0.x86_64
kubeadm-1.17.3-0.x86_64
kubectl-1.17.3-0.x86_64`
When trying to deploy endpoint.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: test-ingress
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:- path: /testpath
pathType: Prefix
backend:
serviceName: hellok8s-service
servicePort: 8080
- path: /testpath
I’m getting error as below:
[root@l000d01kms001 KubeHelm]# kubectl apply -f endpoint.yaml —validate=false
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating «endpoint.yaml»: Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook «validate.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io»: Post https://ingress-nginx-controller-admission.ingress-nginx.svc:443/extensions/v1beta1/ingresses?timeout=30s: context deadline exceeded
`[root@l000d01kms001 KubeHelm]# kubectl logs pod/ingress-nginx-admission-create-44q78 -n ingress-nginx
^C
[root@l000d01kms001 KubeHelm]# kubectl logs pod/ingress-nginx-admission-patch-gqwbr -n ingress-nginx
<«level»:»info»,»msg»:»patching webhook configurations ‘ingress-nginx-admission’ mutating=false, validating=true, failurePolicy=Fail»,»source»:»k8s/k8s.go:38″,»time»:»2020-05-20T20:29:52Z»>
<«level»:»info»,»msg»:»Patched hook(s)»,»source»:»k8s/k8s.go:91″,»time»:»2020-05-20T20:29:52Z»>
[root@l000d01kms001 KubeHelm]# kubectl logs pod/ingress-nginx-controller-f8d756996-rhmjl -n ingress-nginx
NGINX Ingress controller
Release: 0.32.0
Build: git-446845114
Repository: https://github.com/kubernetes/ingress-nginx
nginx version: nginx/1.17.10
I0520 20:29:56.807345 6 flags.go:204] Watching for Ingress class: nginx
W0520 20:29:56.807691 6 flags.go:249] SSL certificate chain completion is disabled (—enable-ssl-chain-completion=false)
W0520 20:29:56.807752 6 client_config.go:543] Neither —kubeconfig nor —master was specified. Using the inClusterConfig. This might not work.
I0520 20:29:56.807947 6 main.go:220] Creating API client for https://10.96.0.1:443
I0520 20:29:56.815151 6 main.go:264] Running in Kubernetes cluster version v1.17 (v1.17.3) — git (clean) commit 06ad960bfd03b39c8310aaf92d1e7c12ce618213 — platform linux/amd64
I0520 20:29:57.013592 6 main.go:105] SSL fake certificate created /etc/ingress-controller/ssl/default-fake-certificate.pem
I0520 20:29:57.018776 6 ssl.go:528] loading tls certificate from certificate path /usr/local/certificates/cert and key path /usr/local/certificates/key
I0520 20:29:57.043694 6 nginx.go:263] Starting NGINX Ingress controller
I0520 20:29:57.047238 6 event.go:278] Event(v1.ObjectReference): type: ‘Normal’ reason: ‘CREATE’ ConfigMap ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx-controller
I0520 20:29:58.244113 6 nginx.go:307] Starting NGINX process
I0520 20:29:58.244155 6 leaderelection.go:242] attempting to acquire leader lease ingress-nginx/ingress-controller-leader-nginx.
I0520 20:29:58.244567 6 nginx.go:327] Starting validation webhook on :8443 with keys /usr/local/certificates/cert /usr/local/certificates/key
I0520 20:29:58.244740 6 controller.go:139] Configuration changes detected, backend reload required.
I0520 20:29:58.248112 6 leaderelection.go:252] successfully acquired lease ingress-nginx/ingress-controller-leader-nginx
I0520 20:29:58.248192 6 status.go:86] new leader elected: ingress-nginx-controller-f8d756996-rhmjl
I0520 20:29:58.306048 6 controller.go:155] Backend successfully reloaded.
I0520 20:29:58.306087 6 controller.go:164] Initial sync, sleeping for 1 second.
[root@l000d01kms001 KubeHelm]#`
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
Источник
Problem scenario
When writing the configuration file of the ingress controller entry controller of kubernetes
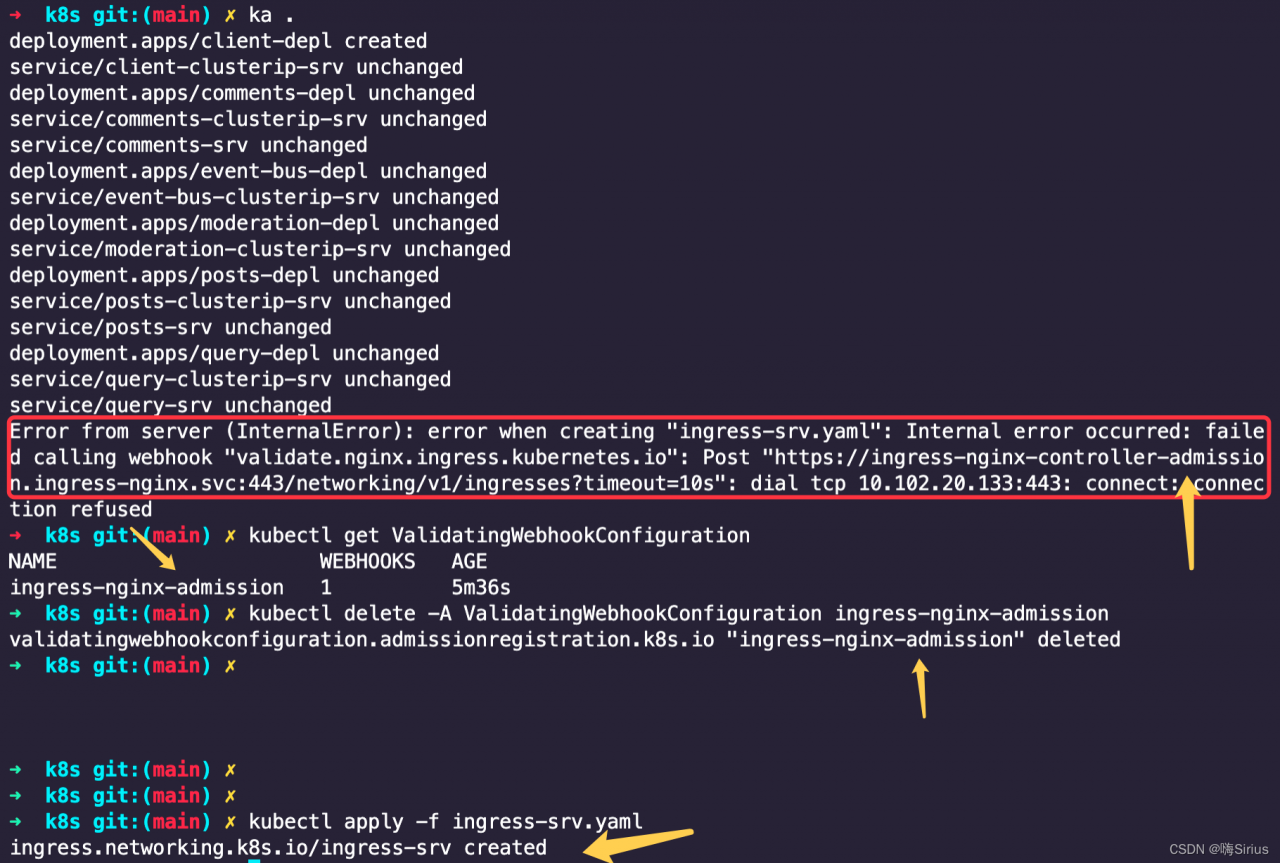
kubectl apply -f ingress-srv.yaml
Three Errors:
-
- Error 1:
no matches for kind “Ingress” in version “networking.k8s.io/v1beta1”
- Error 2: pathType is wrong after I modified APIVersion to v1.
Error 3: Error from server (InternalError): error when creating “ingress-srv.yaml”: Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook “validate.nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io”: Post “https://ingress-nginx-controller-admission.ingress-nginx.svc:443/networking/v1/ingresses?timeout=10s”: dial tcp 10.102.20.133:443: connect: connection refused
Solution 1:
no matches for kind “Ingress” in version “networking.k8s.io/v1beta1”
Modify
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
to
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
Solution 2:
pathType is wrong after I modified APIVersion to v1.
It is the version issue. here is the mofied codes below:
Original codes (report error):
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-srv
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/use-regex: "true"
spec:
rules:
- host: posts.com
http:
paths:
- path: /posts/create
backend:
serviceName: posts-clusterip-srv
servicePort: 4000
- path: /posts
backend:
serviceName: query-srv
servicePort: 4002
- path: /posts/?(.*)/comments
backend:
serviceName: comments-srv
servicePort: 4001
- path: /?(.*)
backend:
serviceName: client-srv
servicePort: 3000
Here is the modified code:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-srv
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/use-regex: "true"
spec:
rules:
- host: posts.com
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: "/posts/create"
backend:
service:
name: posts-clusterip-srv
port:
number: 4000
- pathType: Prefix
path: "/posts"
backend:
service:
name: query-srv
port:
number: 4002
- pathType: Prefix
path: "/posts/?(.*)/comments"
backend:
service:
name: comments-srv
port:
number: 4001
- pathType: Prefix
path: "/?(.*)"
backend:
service:
name: client-srv
port:
number: 3000
Solution 3:
1. First kubectl get ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
2. Then kubectl delete -A ValidatingWebhookConfiguration ingress-nginx-admission
3. Delete that admission, and then it’s normal
Read More:
This topic describes the procedure for diagnosing the NGINX Ingress controller and
how to troubleshoot errors. This topic also describes common diagnostic methods and
provides answers to some frequently asked questions about the NGINX Ingress controller.
Table of contents
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Diagnostic procedure | Diagnostic procedure |
| Troubleshooting | Troubleshooting |
| Common diagnostic methods |
|
| FAQ |
|
Background information
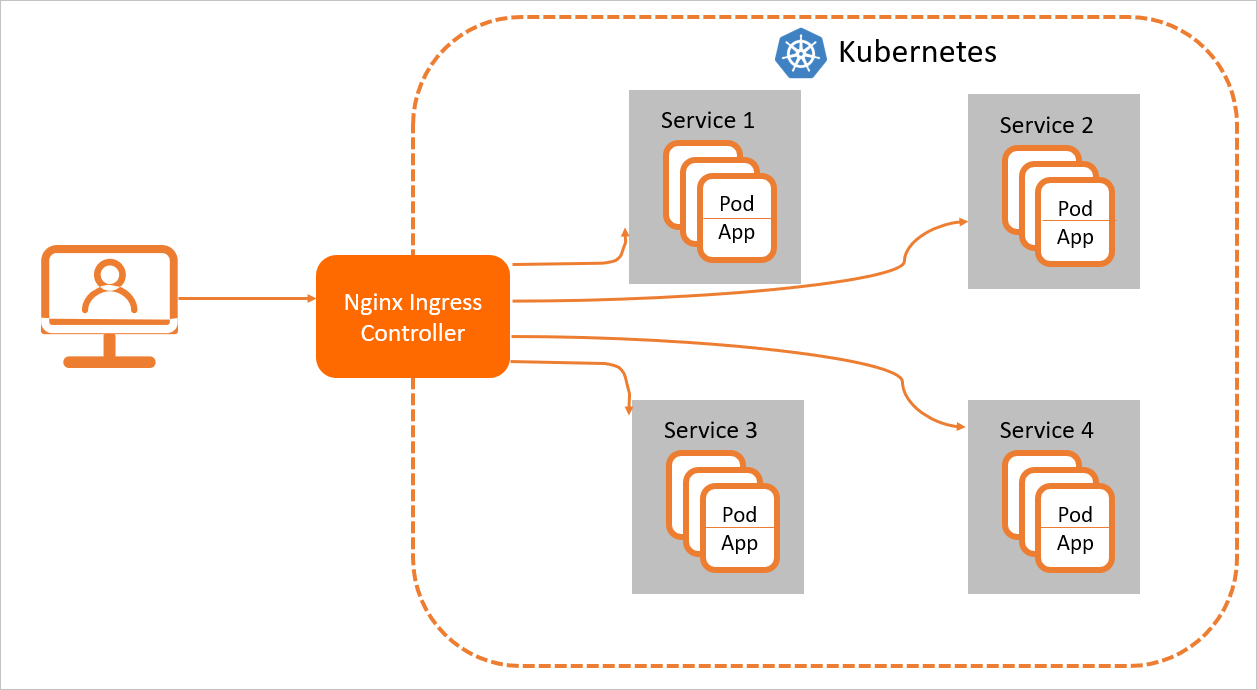
To ensure that the Ingress resource in a cluster works as expected, you must deploy
an Ingress controller in the cluster to parse the Ingress rules. After an Ingress
controller receives a request that matches an Ingress rule, the request is routed
to the corresponding Service. Then, the Service forwards the request to pods and the
pods process the request. In a Kubernetes cluster, Services, Ingresses, and Ingress
controllers work in the following process:
- A Service is an abstraction of an application that is deployed on a set of replicated
pods. - An Ingress contains reverse proxy rules. It controls to which Services HTTP or HTTPS
requests are routed. For example, an Ingress routes requests to different Services
based on the hosts and URL paths in the requests. - An Ingress controller is a reverse proxy program that parses Ingress rules. If changes
are made to the Ingress rules, the Ingress controller updates the Ingress rules accordingly.
After an Ingress controller receives a request, it redirects the request to a Service
based on the Ingress rules.
Ingress controllers acquire Ingress rule changes from the API server and dynamically
generate configuration files, such as nginx.conf. These configuration files are required by a load balancer, such as NGINX. Then,
the Ingress controllers reload the load balancer. For example, the Ingress controllers
run the nginx -s load command to reload NGINX.and then generate new Ingress rules.
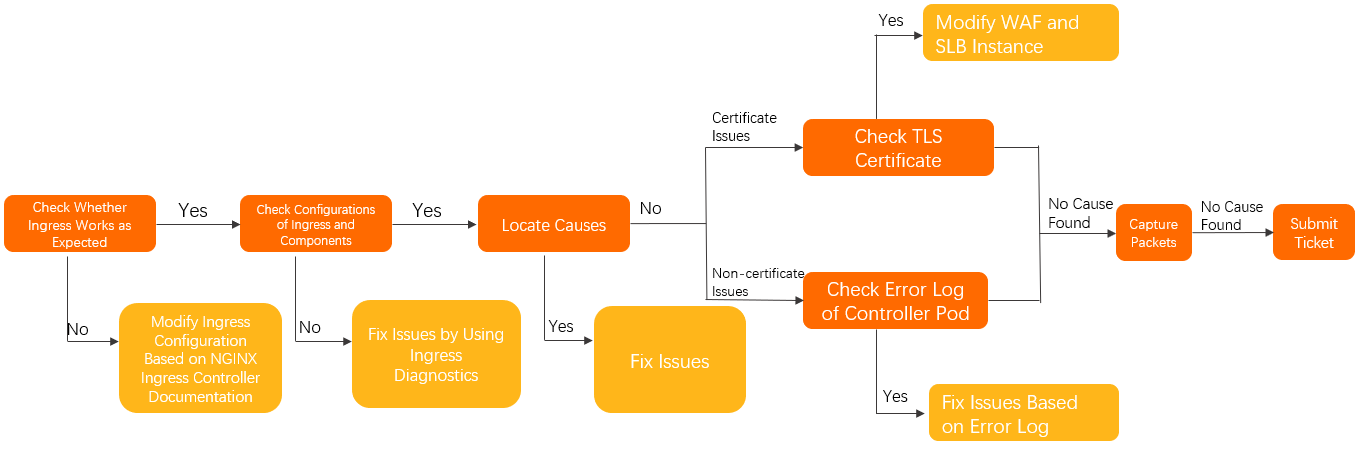
Diagnostic procedure
- You can perform the following steps to check whether an issue is caused by the Ingress.
Make sure that the configuration of the Ingress controller is valid.- Check whether you can access a specific pod from the controller pod. For more information,
see Manually access the Ingress and backend pod by using the Ingress controller pod. - Check whether the NGINX Ingress controller is properly configured. For more information,
see Documentation for the NGINX Ingress controller.
- Check whether you can access a specific pod from the controller pod. For more information,
- Use the Ingress diagnostics feature to check the configurations of the Ingress and
components. Then, modify the configurations based on the prompts. For more information,
see Use the Ingress diagnostics feature. - Locate the cause of the issue and refer to the relevant solution based on Troubleshooting.
- If the issue persists, perform the following steps:
- Issues that are related to TLS certificates:
- Check whether the domain name is added to Web Application Firewall (WAF) in CNAME
record mode or transparent proxy mode.- If the domain name is added to WAF, check whether the domain name has a TLS certificate.
- If the domain name is not added to WAF, proceed to the next step.
- Check whether a Layer 7 listener is added for the Server Load Balancer (SLB) instance.
- If a Layer 7 listener is added for the SLB instance, check whether a TLS certificate
is associated with the listener. - If no Layer 7 listener is added for the SLB instance, proceed to the next step.
- If a Layer 7 listener is added for the SLB instance, check whether a TLS certificate
- Check whether the domain name is added to Web Application Firewall (WAF) in CNAME
- If the issue is not related to TLS certificates, diagnose the error log of the controller
pod. For more information, see Diagnose the error log of the controller pod.
- Issues that are related to TLS certificates:
- If the issue persists, locate the cause of the issue by capturing packets in the controller
pod and the backend pod. For more information, see Capture packets. - If the issue persists, Submit a ticket for troubleshooting.
| Troubleshooting | Issue description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Issues related to connectivity | Pods in a cluster cannot access the Ingress. | Why do I fail to access the IP address of the LoadBalancer from within the Kubernetes cluster? |
| The Ingress controller cannot be accessed. | Why does the Ingress controller pod fail to access the Ingress controller? | |
| The test domain name cannot be resolved. | Why do I fail to access the Ingress by using the test domain name provided in the ACK console? | |
| TCP and UDP services cannot be accessed. | How do I add Services that use TCP or UDP? | |
| Issues related to HTTPS access | The certificate is not updated or the default certificate is returned. | Why is the default TLS certificate or previous TLS certificate used after I add a TLS certificate to the cluster or change the TLS certificate? |
The following error is returned: RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG/wrong version number.
|
Why is the following error returned for HTTPS requests: SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG? | |
| Errors occurred when you create an Ingress | The following error occurs when you create an Ingress: «failed calling webhook…». | Why does the following error occur when you create an Ingress: «failed calling webhook»? |
| An Ingress is created but the Ingress does not take effect. | Why do Ingress rules fail to take effect? | |
| Access fails to meet you expectations | Client IP addresses cannot be preserved. | Why does the Ingress controller pod fail to preserve client IP addresses? |
| IP whitelists do not take effect or do not function as expected. | ||
| gRPC Services that are exposed by an Ingress cannot be accessed. | Why do I fail to access gRPC Services that are exposed by an Ingress? | |
| Canary release rules do not take effect. | Why do canary release rules fail to take effect? | |
| Canary release rules are invalid or other traffic is distributed to backend pods that are associated with the canary Ingress. |
Why are requests not distributed based on the specified canary release rules or why do the canary release rules affect other Ingresses that are associated with the same Service? | |
The following error occurs: The plain HTTP request was sent to HTTPS port.
|
Why do I fail to access backend HTTPS services? | |
| A 502, 503, 413, or 499 status code is returned. | Common HTTP status codes | |
| Some pages cannot be displayed. | The rewrite-target annotation is configured but a 404 error occurs when you access the resource.
|
Why does the system fail to load some web page resources or return a blank white screen when requests are redirected to the root directory? |
One of the following errors occurs when you access the resource: net::ERR_FAILED or net::ERR_HTTP2_SERVER_REFUSED_STREAM.
|
The following error occurs: net::ERR_HTTP2_SERVER_REFUSED_STREAM. |
Commonly used diagnostic methods
Use the Ingress diagnostics feature
- Log on to the ACK console.
- In the left-side navigation pane of the ACK console, click Clusters.
- On the Clusters page, find the cluster on which you want to perform a check and choose in the Actions column.
- In the left-side navigation pane of the Container Intelligence Service page, choose
. - On the Diagnosis page, click Ingress Diagnosis.
- In the Ingress Diagnosis panel, enter the URL that cannot be accessed, such as https://www.example.com. Select I know and agree and then click Create diagnosis.
After the diagnostic is completed, you can view the diagnostic result and try to fix
the issue.
Diagnose the access log of the NGINX Ingress controller pod in Log Service
You can check the access log format of the NGINX Ingress controller in the nginx-configuration
ConfigMap in the kube-system namespace.
The following sample code shows the default format of the access log of the NGINX
Ingress controller:
$remote_addr - [$remote_addr] - $remote_user [$time_local]
"$request" $status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" $request_length
$request_time [$proxy_upstream_name] $upstream_addr $upstream_response_length
$upstream_response_time $upstream_status $req_id $host [$proxy_alternative_upstream_name]Notice After you modify the log format, you must modify the log collection rules of Log Service
accordingly. Otherwise, the access log of the NGINX Ingress controller cannot be collected
to Log Service. Proceed with caution when you modify the log format.
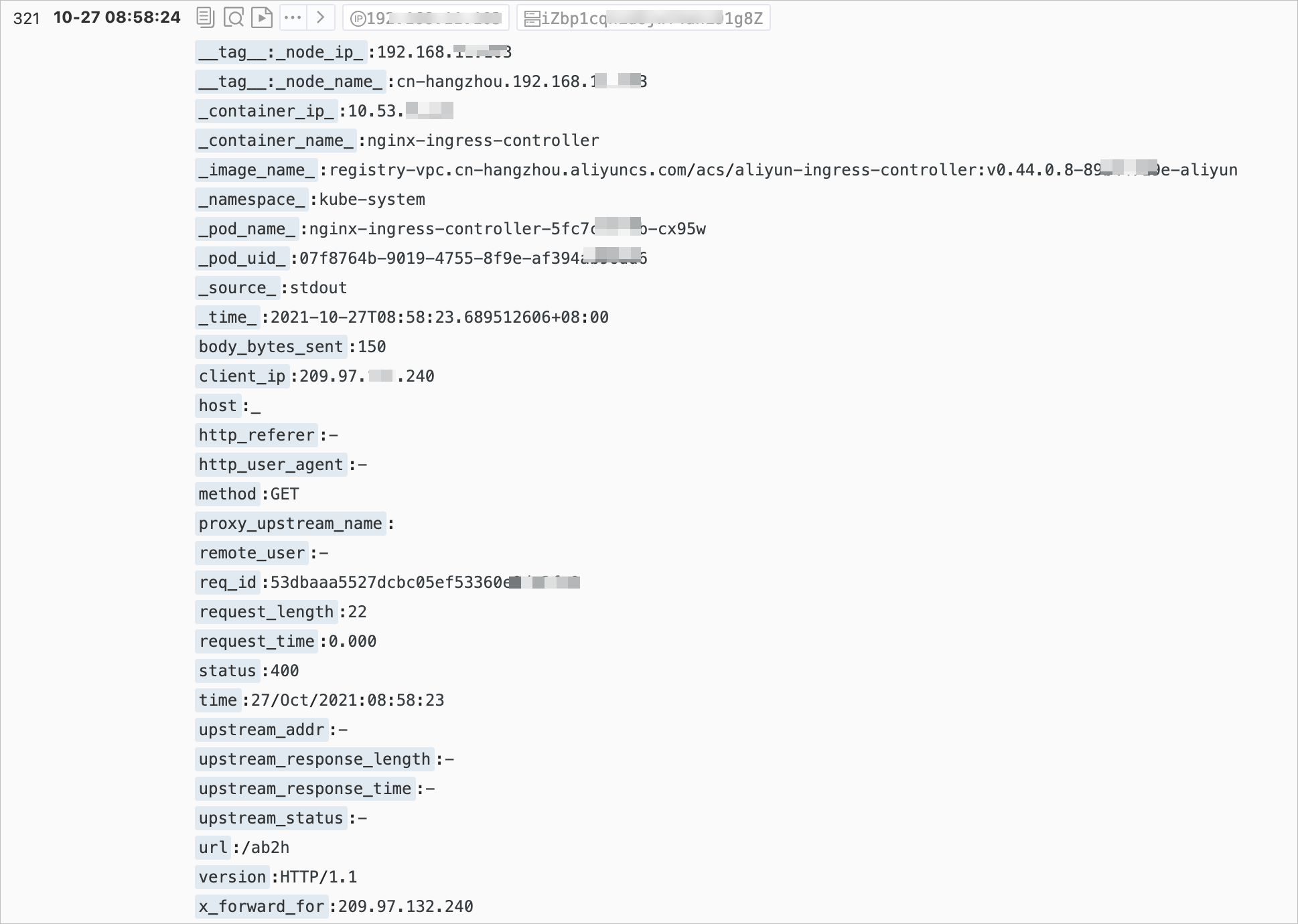
The following figure shows the page on which the access log of the NGINX Ingress controller
is displayed in the Log Service console. For more information, see Step 4: View log data.
The following table describes the log fields that are displayed in the Log Service console. Some log fields that are displayed in the console are different from the actual
log fields.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
remote_addr/client_ip |
The IP address of the client. |
request/(method+url+version) |
Details about the request. The request method, URL, and HTTP version are included. |
request_time |
The processing time of the request. The time starts when the first bytes of the client request are received and ends when the last bytes of the response are sent. The value of this field varies based on the network conditions of the client and therefore does not reflect the request processing capability. |
upstream_addr |
The IP address of the upstream server. If no upstream server receives the request, the returned value is empty. If the request is sent to multiple upstream servers due to server failures, multiple IP addresses that are separated by commas (,) are returned. |
upstream_status |
The HTTP status code in the response from the upstream server. If the HTTP status code indicates a successful request, the upstream server can be accessed. If a 502 status code is returned, no upstream server can be accessed. Multiple status codes are separated by commas (,). |
upstream_response_time |
The response time of the upstream server. Unit: seconds. |
proxy_upstream_name |
The name of the upstream server. The name is in the following format: <Namespace>-<Service name>-<Port number>.
|
proxy_alternative_upstream_name |
The name of the alternative upstream server. If the request is forwarded to an alternative upstream server, the name of the alternative upstream server is returned. For example, you implement a canary release. |
By default, you can run the following command to query the recent access log of the
NGINX Ingress controller:
kubectl logs <controller pod name> -n <namespace> | lessExpected output:
42.11.**.** - [42.11.**.**]--[25/Nov/2021:11:40:30 +0800]"GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 615 "_" "curl/7.64.1" 76 0.001 [default-nginx-svc-80] 172.16.254.208:80 615 0.000 200 46b79dkahflhakjhdhfkah**** 47.11.**.**[]
42.11.**.** - [42.11.**.**]--[25/Nov/2021:11:40:31 +0800]"GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 615 "_" "curl/7.64.1" 76 0.001 [default-nginx-svc-80] 172.16.254.208:80 615 0.000 200 fadgrerthflhakjhdhfkah**** 47.11.**.**[]
Diagnose the error log of the NGINX Ingress controller pod
You can diagnose the error log of the NGINX Ingress controller pod to narrow down
the scope of troubleshooting. The error log of the Ingress controller pod includes
the following types:
- The log that records errors of the Ingress controller. Typically, this type of error
log is generated due to invalid Ingress configurations. You can run the following
command to query this type of error log:kubectl logs <controller pod name> -n <namespace> | grep -E ^[WE]Note During the initialization of an Ingress controller, a few warning events may be generated.
For example, if you do not specify the kubeconfig file or IngressClass resource, warning
events are generated. These events do not affect the Ingress controller and can be
ignored. - The log that records errors of the NGINX application. Typically, this type of error
log is generated due to request processing failures. You can run the following command
to query this type of error log:kubectl logs <controller pod name> -n <namespace> | grep error
Manually access the Ingress and backend pod by using the Ingress controller pod
- Run the following command to log on to the Ingress controller pod:
kubectl exec <controller pod name> -n <namespace> -it -- bash - The Ingress controller pod is preinstalled with curl and OpenSSL, which allow you
to test network connectivity and verify certificates.- Run the following command to test the network connectivity between the Ingress and
the backend pod:# Replace your.domain.com with the actual domain name of the Ingress. curl -H "Host: your.domain.com" http://127.0.**.**/ # for http curl --resolve your.domain.com:443:127.0.0.1 https://127.0.0.1/ # for https - Run the following command to verify the certificate:
openssl s_client -servername your.domain.com -connect 127.0.0.1:443 - Test access to the backend pod.
Note An Ingress controller directly connects to the IP address of the backend pod instead
of using a ClusterIP Service.- Run the following kubectl command to query the IP address of the backend pod:
kubectl get pod -n <namespace> <pod name> -o wideExpected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES nginx-dp-7f5fcc7f-**** 1/1 Running 0 23h 10.71.0.146 cn-beijing.192.168.**.** <none> <none>The output shows that the IP address of the backend pod is 10.71.0.146.
- To test the network connectivity between the Ingress controller pod and the backend
pod, run the following command to connect to the IP address by using the Ingress controller
pod:curl http://<your pod ip>:<port>/path
- Run the following kubectl command to query the IP address of the backend pod:
- Run the following command to test the network connectivity between the Ingress and
Capture packets
If you cannot identify the issue, capture and diagnose packets.
- Check whether the issue is related to the Ingress controller pod or the application
pod. If this cannot be done, capture packets for both the Ingress controller pod and
the application pod. - Log on to the nodes on which the application pod and Ingress controller pod run.
- Run the following command on the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances to capture
all recent packets that are received by the Ingress:tcpdump -i any host <Application pod IP or Ingress controller pod IP> -C 20 -W 200 -w /tmp/ingress.pcap - If an error is identified in the log data, stop capturing packets.
- Diagnose the packets that are transferred during the time period in which the error
occurred.Note
- Packet capture does not affect your service and only causes a slight increase in the
CPU utilization and disk I/O. - The preceding command rotates the captured packets and can generate at most 200 .pcap files, each of which is 20 MB in size.
- Packet capture does not affect your service and only causes a slight increase in the
Why do I fail to access the IP address of the LoadBalancer from within the Kubernetes
cluster?
Symptom
In a Kubernetes cluster, only specific nodes can access the IP address of the LoadBalancer
if externalTrafficPolicy is set to Local for the LoadBalancer.
Causes
externalTrafficPolicy: Local is set for the LoadBalancer. In Local mode, the IP address of the LoadBalancer is
accessible only from pods that are provisioned on the local node (the node that runs
the LoadBalancer). The IP address of the LoadBalancer is inaccessible from pods on
other nodes in the cluster. The IP address of the LoadBalancer is external to the
Kubernetes cluster. If nodes or pods in the ACK cluster cannot access the IP address
without using a second hop, requests do not pass through the LoadBalancer. As a result,
the IP address of the LoadBalancer is considered an extended IP address of the Service
that uses the LoadBalancer. Requests are forwarded by kube-proxy based on iptables
or IP Virtual Server (IPVS).
In this scenario, if the requested pod is not provisioned on the local node, a connectivity
issue occurs. The IP address of the LoadBalancer is accessible only if the requested
pod is provisioned on the local node. For more information about external-lb, see
kube-proxy adds the IP address of external-lb to the node local iptables rules.
Solutions
- We recommend that you access the IP address of the LoadBalancer from within the Kubernetes
cluster by using the ClusterIP Service or the Ingress name.The Ingress name is
nginx-ingress-lbin the kube-system namespace. - Run the
kubectl edit svc nginx-ingress-lb -n kube-systemcommand to modify the Ingress. SetexternalTrafficPolicytoClusterfor the LoadBalancer. After you change the setting, client IP addresses cannot be
preserved. - If the network plug-in of the cluster is set to Terway and the exclusive or inclusive
ENI mode is selected, you can setexternalTrafficPolicytoClusterfor the LoadBalancer and add the ENI annotation. The annotation adds pods that are
signed elastic network interfaces (ENIs) as the backend servers of the LoadBalancer.
This way, client IP addresses can be preserved and the IP address of the LoadBalancer
can be accessed from within the cluster.Example:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: annotations: service.beta.kubernetes.io/backend-type: eni # Add pods that are signed ENIs as the backend servers of the LoadBalancer. labels: app: nginx-ingress-lb name: nginx-ingress-lb namespace: kube-system spec: externalTrafficPolicy: ClusterFor more information about the annotations of Services, see Use annotations to configure load balancing.
Why does the Ingress controller pod fail to access the Ingress controller?
Symptom
In a cluster for which Flannel is used, when the Ingress controller pod accesses the
Ingress controller through a domain name, an SLB IP address, or cluster IP address,
some or all of the requests sent from the Ingress controller pod are dropped.
Causes
By default, Flannel does not allow loopback requests.
Solutions
- We recommend that you create a new cluster that uses the Terway network plug-in and
migrate your workloads to the new cluster. - If you do not want to create a new cluster, you can enable
hairpinModein the configurations of Flannel. After you modify the configurations, recreate the
Flannel pod for the modification to take effect.- Run the following command to modify the configurations of Flannel:
kubectl edit cm kube-flannel-cfg -n kube-system - In the cni-config.json file that is returned, add
"hairpinMode": truein thedelegatefield.Example:
cni-conf.json: | { "name": "cb0", "cniVersion":"0.3.1", "type": "flannel", "delegate": { "isDefaultGateway": true, "hairpinMode": true } } - Run the following command to restart Flannel:
kubectl delete pod -n kube-system -l app=flannel - Delete and recreate the pod.
- Run the following command to modify the configurations of Flannel:
Why is the default TLS certificate or previous TLS certificate used after I add a
TLS certificate to the cluster or change the TLS certificate?
Symptom
You added a Secret to the cluster or modified a Secret in the cluster, and updated
the Secret name in the secretName field in the Ingress. When you access the cluster,
the default certificate (Kubernetes Ingress Controller Fake Certificate) or the previous
certificate is used.
Causes
- The certificate is not returned by the Ingress controller in the cluster.
- The certificate is invalid and the Ingress controller cannot load the certificate.
- The certificate is returned by the Ingress controller based on the Server Name Indication
(SNI) field. The SNI field may not be sent as a part of the TLS handshake.
Solutions
- Use one of the following methods to check whether the SNI field is sent as a part
of the TLS handshake:- Upgrade your browser to a version that supports SNI.
- When you run the
openssl s_clientcommand to check whether the certificate is in use, specify the-servernameparameter. - When you run
curlcommands, add hosts or use the--resolveparameter to map the domain name, other than using the host request header.
- Make sure that no TLS certificate is specified when you connect the website to WAF
in CNAME record mode or transparent proxy mode, or no TLS certificate is associated
with the Layer 7 listener of the SLB instance. The TLS certificate must be returned
by the Ingress controller in the cluster. - Navigate to the Container Intelligence Service console and diagnose the Ingress. In
the diagnostic report, check whether the configurations of the Ingress are valid and
whether the log data shows errors. For more information, see Use the Ingress diagnostics feature. - Run the following command to view the error log of the Ingress controller pod and
troubleshoot the issue based on the log data.kubectl logs <ingress pod name> -n <pod namespace> | grep -E ^[EW]
Why do I fail to access the Ingress by using the test domain name provided in the
ACK console?
Notice The test domain name is provided only for testing purposes. The availability of the
test domain name is not guaranteed. Do not use the test domain name in production
environments.
Symptom
You cannot access the Ingress by using the test domain name (*.cxxxxxxxxxxx.xxx.alicontainer.com)
provided in the ACK console.
Causes
The test domain name is not resolved to the IP address of the Service that is associated
with the Ingress. Possible causes:
- The Service is not nginx-ingress-lb in the kube-system namespace.
- The external IP address of the Service is changed after the Ingress is created.
Solutions
- Associate the desired IP address with the nginx-ingress-lb Service in the kube-system
namespace. - On the cluster details page of the Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) console, click the Basic Information tab and then click Rebind Domain Name.
Why do I fail to access gRPC Services that are exposed by an Ingress?
Symptom
You cannot access gRPC Services that are exposed by an Ingress.
Causes
- You do not set annotations in the Ingress to specify the backend protocol.
- gRPC Services can be accessed only by using Transport Layer Security (TLS).
Solutions
- Set the following annotation in the Ingress:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol:"GRPC". - Make sure that clients use HTTPS ports to send requests and the traffic is encrypted
by using TLS.
Why do I fail to access backend HTTPS services?
Symptom
- You fail to access backend HTTPS services through the Ingress.
- A 400 error code may be returned and the following error message may be prompted:
The plain HTTP request was sent to HTTPS port.
Causes
The Ingress controller sends HTTP requests to the backend pods. This is the default
setting.
Solutions
Set the following annotation in the Ingress: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol:"HTTPS".
Why does the Ingress controller pod fail to preserve client IP addresses?
Symptom
The Ingress controller pod cannot preserve client IP addresses. Only the node IP,
the CIDR blocks 100.XX.XX.XX, or other IP addresses are preserved.
Causes
externalTrafficPolicyis set toClusterfor the Service that is associated with the Ingress.- A Layer 7 proxy is used by the SLB instance.
- Your website is connected to WAF in CNAME record mode or transparent proxy mode.
Solutions
- If
externalTrafficPolicyis set toClusterfor the Service and a Layer 4 SLB instance is used, perform the following steps:Set
externalTrafficPolicytoLocal. However, you may fail to access the Ingress by using the IP address of the SLB instance
from within the cluster. For more information, see Why do I fail to access the IP address of the LoadBalancer from within the Kubernetes cluster?. - Perform the following steps if a Layer 7 proxy is used, for example, a Layer 7 SLB
instance is used or your website is connected to WAF in CNAME record mode or transparent
proxy mode:- Make sure that the X-Forwarded-For header is enabled for the Layer 7 proxy.
- Add
enable-real-ip: "true"to the ConfigMap of the Ingress controller. By default, the ConfigMap is named nginx-configuration
and belongs to the kube-system namespace. - Analyze the log data to check whether client IP addresses can be preserved.
- If a client request traverses multiple hops before it reaches the Ingress controller
pod, for example, the request must pass through a reverse proxy before it reaches
the Ingress controller pod, you can check the value ofremote_addrafter you setenable-real-ipto true. If the value is a client IP address, this indicates that the X-Forwarded-For
header is enabled to pass client IP addresses to the Ingress controller pod. If the
X-Forwarded-For header is disabled, enable the X-Forwarded-For header or use other
methods to add client IP addresses to requests before the requests reach the Ingress
controller pod.
Why do canary release rules fail to take effect?
Symptom
You set canary release rules in a cluster but the rules do not take effect.
Causes
Possible causes:
- When you add
canary-*annotations, you do not setnginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary: "true". - The version of the NGINX Ingress controller is earlier than 0.47.0. When you add
canary-*annotations, you do not specify the domain name of your application in the host field.
Solutions
- Set
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary: "true"or specify the domain name of your application in the host field. - If the issue persists, see Why are requests not distributed based on the specified canary release rules or why do the canary release rules affect other Ingresses that are associated with the same Service?.
Why are requests not distributed based on the specified canary release rules or why
do the canary release rules affect other Ingresses that are associated with the same
Service?
Symptom
Requests are not distributed based on the canary release rules that you set, or the
canary release rules affect other Ingresses that are associated with the same Service.
Causes
Canary release rules in an NGINX Ingress controller take effect on all Ingresses that
are associated with the Service for which the canary release rules are created.
For more information about this issue, see An Ingress with canary annotations affects other Ingresses that are associated with the same Service.
Solutions
Canary Ingresses include Ingresses that are assigned the service-match or canary-* annotations. Before you create a canary Ingress, create two same Services that are
used for canary releases, and then map the Services to the backend pods that you want
to access.
Why does the following error occur when you create an Ingress: «failed calling webhook»?
Symptom
The following error occurs when you create an Ingress: «Internal error occurred: failed
calling webhook…».
Causes
When you create an Ingress resource, a Service is used to check whether the Ingress
is valid. By default, the Service named ingress-nginx-controller-admission is used.
If Webhook link errors occur, for example, the Service or the Ingress controller is
deleted, the Ingress cannot be created.
Solutions
- Check whether the resource exists and works as expected based on the following Webhook
link: ValidatingWebhookConfiguration > Service > Pod. - Make sure that the admission feature is enabled for the Ingress controller pod and
the pod can be accessed from outside the cluster. - If the Ingress controller is deleted or you do not want to use the Webhook feature,
you can delete the ValidatingWebhookConfiguration resource.
Why is the following error returned for HTTPS requests: SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG?
Symptom
One of the following errors is returned for HTTPS requests: SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG or routines:CONNECT_CR_SRVR_HELLO:wrong version number.
Causes
HTTPS requests are distributed to a non-HTTPS port, such as an HTTP port.
Common causes:
- Port 443 of the SLB instance is mapped to port 80 of the Ingress controller pod.
- Port 443 of the Service that is associated with the Ingress controller pod is mapped
to port 80 of the Ingress controller pod.
Solutions
Modify the configurations of the SLB instance or Service to ensure that HTTPS requests
can be distributed to the proper port.
Common HTTP status codes
Symptom
HTTP status codes other than 2xx and 3xx are returned, such as 502, 503, 413, and
499.
Causes and solutions
View the log and check whether the error is returned by the Ingress controller. For
more information, see Diagnose the access log of the NGINX Ingress controller pod in Log Service. If the error is returned by the Ingress controller, use the following solutions:
- 413 error
- Cause: The request size exceeds the upper limit.
- Solution: Increase the value of proxy-body-size in the ConfigMap of the Ingress controller.
The default value of proxy-body-size is 1 MB for the NGINX Ingress controller of open
source Kubernetes and the default value of proxy-body-size is 20 MB for the NGINX
Ingress controller of ACK.
- 499 error
- Cause: The client terminates the connection in advance. The error may not be caused
by the Ingress controller or backend services. - Solution:
- If the 499 error does not occur frequently and your workloads are not affected, you
can ignore the error. - If the 499 error occurs frequently, you must check whether the amount of time that
the backend pods cost to process requests exceeds the request timeout period that
is set on the client.
- If the 499 error does not occur frequently and your workloads are not affected, you
- Cause: The client terminates the connection in advance. The error may not be caused
- 502 error
- Cause: The Ingress controller cannot connect to backend pods.
- Solution:
- The issue occurs occasionally:
- Check whether the backend pods work as expected. If the backend pods are overloaded,
add more backend pods. - By default, the Ingress controller sends HTTP 1.1 requests to backend services and
HTTP keep-alive is enabled. Make sure that the keep-alive timeout period configured
for the backend pods is greater than that configured for the Ingress controller. By
default, the timeout period is set to 60 seconds.
- Check whether the backend pods work as expected. If the backend pods are overloaded,
- The issue occurs every time:
- Check whether the Service port is valid and whether the Service can be accessed from
the Ingress controller pod. - In the Container Intelligence Service console, choose . On the Diagnosis page, click Network diagnosis to check the network connectivity.
- Check whether the Service port is valid and whether the Service can be accessed from
- If the issue persists, capture and analyze packets, and then Submit a ticket.
- The issue occurs occasionally:
- 503 error
- Symptom: The Ingress controller cannot discover the backend pods, or the Ingress controller
fails to access all backend pods. - Solution:
- The issue occurs occasionally:
- Refer to the solution for resolving the 502 error.
- Check the status of the backend pods and configure health checks.
- The issue occurs every time:
Check whether the Service configuration is valid and whether the endpoint exists.
- If you cannot locate the cause by using the preceding methods, Submit a ticket.
- The issue occurs occasionally:
- Symptom: The Ingress controller cannot discover the backend pods, or the Ingress controller
The following error occurs: net::ERR_HTTP2_SERVER_REFUSED_STREAM.
Symptom
When you access the website, some resources cannot be loaded and one of the following
errors is prompted in the console: net::ERR_HTTP2_SERVER_REFUSED_STREAM or net::ERR_FAILED.
Causes
The number of concurrent HTTP/2 streams to the resource has reached the upper limit.
Solutions
- We recommend that you change
http2-max-concurrent-streamsin the ConfigMap to a greater value. The default value is 128. For more information,
see http2-max-concurrent-streams. - Disable HTTP/2 by setting
use-http2tofalsein the ConfigMap. For more information, see use-http2.
Why does the following error occur: The param of ServerGroupName is illegal?
Causes
ServerGroupName is generated in the following format: namespace+svcName+port. The server group name must be 2 to 128 characters in length and can contain letters,
digits, periods (.), underscores (_), and hyphens (-). The name must start with a
letter.
Solutions
Modify the server group name based on the required format.
Why does the «certificate signed by unknown authority» error occur when I create an
Ingress?
Causes
If multiple Ingresses are deployed in the cluster and the Ingresses use the same resources,
such as Secrets, Services, or webhook configurations, the preceding error occurs because
different SSL certificates are used to communicate with backend servers when webhooks
are triggered.
Solutions
Redeploy two Ingresses and make sure that the Ingresses use different resources. For
more information about the resources used by Ingresses, see What are the system updates after I update the NGINX Ingress controller on the Add-ons page of the ACK console?.
Why does the Ingress controller pod restart after it fails the health check?
Symptom
The Ingress controller pod restarts after it fails the health check.
Causes
- The Ingress controller pod or the node where the pod is deployed is overloaded. As
a result, the pod failed to pass the health check. - Kernel parameters such as
tcp_tw_reuseortcp_tw_timestampsmay be configured for the cluster node where the Ingress controller pod is deployed.
This may cause health check failures.
Solutions
- Add more Ingress controller pods and check whether the issue persists. For more information,
see Deploy an Ingress access layer with high reliability. - Disable
tcp_tw_reuseor set the value of the parameter to 2, disabletcp_tw_timestamps, and then check whether the issue persists.
How do I add Services that use TCP or UDP?
- Add specific entries to the tcp-services and udp-services ConfigMaps. By default,
the ConfigMaps belong to the kube-system namespace.The following code block shows an example on how to map port 8080 of example-go in
the default namespace to port 9000:apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: tcp-services namespace: ingress-nginx data: 9000: "default/example-go:8080" # Map port 8080 to port 9000. - Add port 9000 to the Deployment of the Ingress. By default, the Deployment is named
nginx-ingress-controller and belongs to the kube-system namespace. - Add the port 9000 to the Service that is associated with the Ingress.
Example:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: ingress-nginx namespace: ingress-nginx labels: app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginx spec: type: LoadBalancer ports: - name: http port: 80 targetPort: 80 protocol: TCP - name: https port: 443 targetPort: 443 protocol: TCP - name: proxied-tcp-9000 port: 9000 targetPort: 9000 protocol: TCP selector: app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx app.kubernetes.io/part-of: ingress-nginxFor more information about how to add Services that use TCP or UDP, see Expose Services that use TCP or UDP.
Why do Ingress rules fail to take effect?
Symptom
After you add or modify Ingress rules, the rules do not take effect.
Causes
- The configuration of the Ingress contains errors. As a result, the Ingress failed
to load the Ingress rules. - The configurations of Ingress resources contain errors.
- The Ingress controller does not have the required permissions. As a result, the Ingress
controller cannot monitor the changes made to Ingress resources. - The previous Ingress uses a domain name specified in the
server-aliasfield. The domain name is in conflict with that of the new Ingress. As a result,
the Ingress rules are ignored.
Solutions
- Navigate to the Container Intelligence Service console, diagnose the Ingress, and
resolve the issue based on the prompts. For more information, see Use the Ingress diagnostics feature. - Check whether the configuration of the previous Ingress contains errors or whether
configuration conflicts exist:- If
rewrite-targetis not used and the paths are specified in regular expressions, make sure that the
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/use-regex: "trueannotation is added. - Check whether PathType is set to an expected value. By default,
ImplementationSpecifichas the same effect asPrefix.
- If
- Make sure that the ClusterRole, ClusterRoleBinding, Role, RoleBinding, and ServiceAccount
that are associated with the Ingress controller exist. The default names are ingress-nginx. - Connect to the Ingress controller pod and view the rules that are added in the nginx.conf file.
- Run the following command to view the pod log and locate the causes:
kubectl logs <ingress pod name> -n <pod namespace> | grep -E ^[EW]
Why does the system fail to load some web page resources or return a blank white screen
when requests are redirected to the root directory?
Symptom
After you set the rewrite-target annotation in the Ingress to rewrite requests, some web page resources cannot be
loaded or a blank white screen is displayed when you access the backend service.
Causes
- You do not set
rewrite-targetin regular expressions. - The path of the requested resource is set to the root directory.
Solutions
- Check whether
rewrite-targetis set in regular expressions and whether capture groups are used. For more information,
see Rewrite. - Check whether requests are redirected to the expected path.
How do I fix the issue that Log Service cannot parse logs as expected after ingress-nginx-controller
is upgraded?
Symptom
The ingress-nginx-controller component has two commonly used versions: ingress-nginx-controller
0.20 and 0.30. After you upgrade ingress-nginx-controller from 0.20 to 0.30 on the
Add-ons page in the console, the Ingress dashboard may not show the actual statistics of
requests to the backend servers when you perform canary releases or blue-green releases
with an Ingress.
Causes
The default log format of ingress-nginx-controller 0.20 is different from that of
ingress-nginx-controller 0.30. Therefore, the Ingress dashboard may not show the actual
statistics of requests to the backend servers when you perform canary releases or
blue-green releases with an Ingress.
Solutions
To fix the issue, perform the following steps to update the nginx-configuration ConfigMap and the configuration of k8s-nginx-ingress.
- Update the
nginx-configurationConfigMap.- If you have not modified the
nginx-configurationConfigMap, copy the following content to a file namednginx-configuration.yamland run thekubectl apply -f nginx-configuration.yamlcommand to deploy the file.apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap data: allow-backend-server-header: "true" enable-underscores-in-headers: "true" generate-request-id: "true" ignore-invalid-headers: "true" log-format-upstream: $remote_addr - [$remote_addr] - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" $status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" $request_length $request_time [$proxy_upstream_name] $upstream_addr $upstream_response_length $upstream_response_time $upstream_status $req_id $host [$proxy_alternative_upstream_name] max-worker-connections: "65536" proxy-body-size: 20m proxy-connect-timeout: "10" reuse-port: "true" server-tokens: "false" ssl-redirect: "false" upstream-keepalive-timeout: "900" worker-cpu-affinity: auto metadata: labels: app: ingress-nginx name: nginx-configuration namespace: kube-system - If you have modified the
nginx-configurationConfigMap, run the following command to update the configuration. This ensures that
your previous modifications are not overwritten.kubectl edit configmap nginx-configuration -n kube-system
Append
[$proxy_alternative_upstream_name]to thelog-format-upstreamfield, save the changes, and then exit. - If you have not modified the
- Update the configuration of
k8s-nginx-ingress.Copy the following content to a file named
k8s-nginx-ingress.yamland run thekubectl apply -f k8s-nginx-ingress.yamlcommand to start the deployment.apiVersion: log.alibabacloud.com/v1alpha1 kind: AliyunLogConfig metadata: namespace: kube-system # your config name, must be unique in you k8s cluster name: k8s-nginx-ingress spec: # logstore name to upload log logstore: nginx-ingress # product code, only for k8s nginx ingress productCode: k8s-nginx-ingress # logtail config detail logtailConfig: inputType: plugin # logtail config name, should be same with [metadata.name] configName: k8s-nginx-ingress inputDetail: plugin: inputs: - type: service_docker_stdout detail: IncludeLabel: io.kubernetes.container.name: nginx-ingress-controller Stderr: false Stdout: true processors: - type: processor_regex detail: KeepSource: false Keys: - client_ip - x_forward_for - remote_user - time - method - url - version - status - body_bytes_sent - http_referer - http_user_agent - request_length - request_time - proxy_upstream_name - upstream_addr - upstream_response_length - upstream_response_time - upstream_status - req_id - host - proxy_alternative_upstream_name NoKeyError: true NoMatchError: true Regex: ^(S+)s-s[([^]]+)]s-s(S+)s[(S+)sS+s"(w+)s(S+)s([^"]+)"s(d+)s(d+)s"([^"]*)"s"([^"]*)"s(S+)s(S+)+s[([^]]*)]s(S+)s(S+)s(S+)s(S+)s(S+)s*(S*)s*[*([^]]*)]*.* SourceKey: content