By default login failed error message is nothing but a client user connection has been refused by the server due to mismatch of login credentials. First task you might check is to see whether that user has relevant privileges on that SQL Server instance and relevant database too, thats good. Obviously if the necessary prvileges are not been set then you need to fix that issue by granting relevant privileges for that user login.
Althought if that user has relevant grants on database & server if the Server encounters any credential issues for that login then it will prevent in granting the authentication back to SQL Server, the client will get the following error message:
Msg 18456, Level 14, State 1, Server <ServerName>, Line 1
Login failed for user '<Name>'
Ok now what, by looking at the error message you feel like this is non-descriptive to understand the Level & state. By default the Operating System error will show ‘State’ as 1 regardless of nature of the issues in authenticating the login. So to investigate further you need to look at relevant SQL Server instance error log too for more information on Severity & state of this error. You might look into a corresponding entry in log as:
2007-05-17 00:12:00.34 Logon Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 8.
or
2007-05-17 00:12:00.34 Logon Login failed for user '<user name>'.
As defined above the Severity & State columns on the error are key to find the accurate reflection for the source of the problem. On the above error number 8 for state indicates authentication failure due to password mismatch. Books online refers: By default, user-defined messages of severity lower than 19 are not sent to the Microsoft Windows application log when they occur. User-defined messages of severity lower than 19 therefore do not trigger SQL Server Agent alerts.
Sung Lee, Program Manager in SQL Server Protocols (Dev.team) has outlined further information on Error state description:The common error states and their descriptions are provided in the following table:
ERROR STATE ERROR DESCRIPTION
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2 and 5 Invalid userid
6 Attempt to use a Windows login name with SQL Authentication
7 Login disabled and password mismatch
8 Password mismatch
9 Invalid password
11 and 12 Valid login but server access failure
13 SQL Server service paused
18 Change password required
Well I'm not finished yet, what would you do in case of error:
2007-05-17 00:12:00.34 Logon Login failed for user '<user name>'.
You can see there is no severity or state level defined from that SQL Server instance’s error log. So the next troubleshooting option is to look at the Event Viewer’s security log [edit because screen shot is missing but you get the
idea, look in the event log for interesting events].
===================================
Cannot connect to ACER-PC.
===================================
Login failed for user ‘sa’. (.Net SqlClient Data Provider)
——————————
For help, click: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink?ProdName=Microsoft+SQL+Server&EvtSrc=MSSQLServer&EvtID=18456&LinkId=20476
——————————
Server Name: ACER-PC
Error Number: 18456
Severity: 14
State: 1
Line Number: 65536
——————————
Program Location:
at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlInternalConnection.OnError(SqlException exception, Boolean breakConnection)
at System.Data.SqlClient.TdsParser.ThrowExceptionAndWarning(TdsParserStateObject stateObj)
at System.Data.SqlClient.TdsParser.Run(RunBehavior runBehavior, SqlCommand cmdHandler, SqlDataReader dataStream, BulkCopySimpleResultSet bulkCopyHandler, TdsParserStateObject stateObj)
at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlInternalConnectionTds.CompleteLogin(Boolean enlistOK)
at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlInternalConnectionTds.AttemptOneLogin(ServerInfo serverInfo, String newPassword, Boolean ignoreSniOpenTimeout, Int64 timerExpire, SqlConnection owningObject)
at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlInternalConnectionTds.LoginNoFailover(String host, String newPassword, Boolean redirectedUserInstance, SqlConnection owningObject, SqlConnectionString connectionOptions, Int64 timerStart)
at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlInternalConnectionTds.OpenLoginEnlist(SqlConnection owningObject, SqlConnectionString connectionOptions, String newPassword, Boolean redirectedUserInstance)
at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlInternalConnectionTds..ctor(DbConnectionPoolIdentity identity, SqlConnectionString connectionOptions, Object providerInfo, String newPassword, SqlConnection owningObject, Boolean redirectedUserInstance)
at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnectionFactory.CreateConnection(DbConnectionOptions options, Object poolGroupProviderInfo, DbConnectionPool pool, DbConnection owningConnection)
at System.Data.ProviderBase.DbConnectionFactory.CreateNonPooledConnection(DbConnection owningConnection, DbConnectionPoolGroup poolGroup)
at System.Data.ProviderBase.DbConnectionFactory.GetConnection(DbConnection owningConnection)
at System.Data.ProviderBase.DbConnectionClosed.OpenConnection(DbConnection outerConnection, DbConnectionFactory connectionFactory)
at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection.Open()
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.UI.ConnectionDlg.Connector.ConnectorThread()
-
Changed type
Monday, February 12, 2018 5:06 PM
question
I can’t seem to connect to our local instance of Microsoft SQL Server. I obtained the followinf infrotmation from the error log and I can’t find anything in regards to Severity 14 and state 1. If anyone has any information in regards to this it would be much appreciated. Thanks in advance!
===================================
Cannot connect to 10.1.0.191.
===================================
Login failed for user ‘kbober’. (.Net SqlClient Data Provider)
——————————
For help, click: http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink?ProdName=Microsoft+SQL+Server&EvtSrc=MSSQLServer&EvtID=18456&LinkId=20476
——————————
Server Name: 10.1.0.191
Error Number: 18456
Severity: 14
State: 1
——————————
Program Location:
at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlInternalConnection.OnError(SqlException exception, Boolean breakConnection)
at System.Data.SqlClient.TdsParser.ThrowExceptionAndWarning(TdsParserStateObject stateObj)
at System.Data.SqlClient.TdsParser.Run(RunBehavior runBehavior, SqlCommand cmdHandler, SqlDataReader dataStream, BulkCopySimpleResultSet bulkCopyHandler, TdsParserStateObject stateObj)
at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlInternalConnectionTds.CompleteLogin(Boolean enlistOK)
at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlInternalConnectionTds.OpenLoginEnlist(SqlConnection owningObject, SqlConnectionString connectionOptions, String newPassword, Boolean redirectedUserInstance)
at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlInternalConnectionTds..ctor(DbConnectionPoolIdentity identity, SqlConnectionString connectionOptions, Object providerInfo, String newPassword, SqlConnection owningObject, Boolean redirectedUserInstance)
at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnectionFactory.CreateConnection(DbConnectionOptions options, Object poolGroupProviderInfo, DbConnectionPool pool, DbConnection owningConnection)
at System.Data.ProviderBase.DbConnectionFactory.CreateNonPooledConnection(DbConnection owningConnection, DbConnectionPoolGroup poolGroup)
at System.Data.ProviderBase.DbConnectionFactory.GetConnection(DbConnection owningConnection)
at System.Data.ProviderBase.DbConnectionClosed.OpenConnection(DbConnection outerConnection, DbConnectionFactory connectionFactory)
at System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection.Open()
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.UI.VSIntegration.ObjectExplorer.ObjectExplorer.ValidateConnection(UIConnectionInfo ci, IServerType server)
at Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.UI.ConnectionDlg.Connector.ConnectionThreadUser()
Updated in July 2020 with a few new states
I think we’ve all dealt with error 18456, whether it be an application unable to access SQL Server, credentials changing over time, or a user who can’t type a password correctly. The trick to troubleshooting this error number is that the error message returned to the client or application trying to connect is intentionally vague (the error message is similar for most errors, and the state is always 1). In a few cases, some additional information is included, but for the most part several of these conditions appear the same to the end user. In order to figure out what is really going wrong, you need to have alternative access to the SQL Server and inspect the log for the true state in the error message. I helped our support team just today solve a client’s 18456 issues – once we tracked down the error log and saw that it was state 16, it was easy to determine that their login had been set up with a default database that had been detached long ago.
In SQL Server 2012, there is a new feature called «contained databases» – I’ve blogged about it here and here. With this feature comes a new layer of security that may creep onto your radar if you use this functionality: contained user authentication failures. There are a variety of things that can go wrong here. If you connect with a contained user but forget to specify a database name, SQL Server will attempt to authorize you as a SQL login, and you will fail with state 5 (if there is no SQL login with that name) or state 8 (if there is also a SQL login with the same name and the password doesn’t match). There is also a new state 65 which occurs if you have specified the correct username and contained database, but entered an incorrect password. The way that the authentication process works is, if SQL Server doesn’t find your user in the contained database you specified, it tries again at the server level, then gives up (it won’t go check all the other contained databases in case you match there – I hope you agree that this is a good thing). If you don’t specify a database in your connection string, then it won’t succeed unless – by coincidence – you have a contained user with the same username and password as a server-level login who also has access to your contained database. This is confusing and I strongly recommend against it.
When I see folks struggling with this problem, I almost always see the answer point to this old (and now horribly formatted) MSDN blog post (see this other version from MSDN), which has a very brief partial list and a lot of unanswered questions. A newer list appears here, with some useful info, but it is still incomplete.
So here is what I consider a more complete listing of all the various states for login failures. I included an instance of 18470 under state 1 for completeness.
| State | Example / Description (note: the verbose message usually has [CLIENT: <IP>] suffix) |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Error: 18470, Severity: 14, State: 1. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: The account is disabled. |
| State 1 now occurs when a login is disabled – but actually, the error in the log is 18470, not 18456 – because the login is disabled, it doesn’t get that far. See state 7.Prior to SQL Server 2005, State 1 always appeared in the log for all login failures, making for fun troubleshooting. 🙂 | |
| 2 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 2. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Could not find a login matching the name provided. |
| The login (whether using SQL or Windows Authentication) does not exist. For Windows Auth, it likely means that the login hasn’t explicitly been given access to SQL Server – which may mean it is not a member of an appropriate domain group. It could also mean that you’ve created a server-level login, mapped a database user with a different name to that login, and are trying to connect using the user name, not the login name. This is the same as State 5, but State 2 indicates that the login attempt came from a remote machine. | |
| 5 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 5. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Could not find a login matching the name provided. |
| Like state 2, the login does not exist in SQL Server, but the login attempt came from the local machine. For both state 2 and 5, prior to SQL Server 2008, the reason was not included in the error log – just the login failed message. And starting in Denali, for both state 2 and 5, this error can happen if you specify the correct username and password for a contained database user, but the wrong (or no) database. Note that if you are trying to connect to a contained database using the connection dialog in SSMS, and you try to <Browse server…> for the database instead of typing the name explicitly, you will first receive a prompt «Browsing the available databases on the server requires connecting to the server. This may take a few moments. Would you like to continue?» If the SQL auth credentials do not also match a login at the server level, you will then receive an error message, because your contained user does not have access to master.sys.databases. The error message in the UI is, «Failed to connect to server <server>. (Microsoft.SqlServer.ConnectionInfo)Login failed for user ‘<x>’. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 18456).» The takeaway here: always specify the database name explicitly in the options tab of the connection dialog; do not use the browse feature. | |
| 6 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 6. Login failed for user ‘<xy>’. Reason: Attempting to use an NT account name with SQL Server Authentication. |
| This means you tried to specify SQL authentication but entered a Windows-style login in the form of DomainUsername. Make sure you choose Windows Authentication (and you shouldn’t have to enter your domain / username when using Win Auth unless you are using runas /netonly to launch Management Studio). In SQL Server 2012 at least, you will only get state 6 if the domainusername format matches an actual domain and username that SQL Server recognizes. If the domain is invalid or if the username isn’t an actual Windows account in that domain, it will revert to state 5 (for local attempts) or state 2 (for remote attempts), since the login doesn’t exist. | |
| 7 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 7. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: An error occurred while evaluating the password. |
| The login is disabled *and* the password is incorrect. This shows that password validation occurs first, since if the password is correct and the login is disabled, you get error 18470 (see state 1 above). It’s possible that your application is sending cached credentials and the password has been changed or reset in the meantime – you may try logging out and logging back in to refresh these credentials. | |
| 8 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 8. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Password did not match that for the login provided. |
|
Probably the simplest of all: the password is incorrect (cASe sEnsiTiVitY catches a lot of folks here). Note that it will say «the login provided» even if you attempted to connect as a contained database user but forgot to specify a database, specified the wrong database, or typed the password incorrectly – unless it finds a match, SQL Server doesn’t have any idea you were attempting to use a contained database user. An interesting case here is Docker containers – |
|
| 9 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 9. Login failed for user ‘<xy>’. |
| Like state 2, I have not seen this in the wild. It allegedly means that the password violated a password policy check, but I tried creating a login conforming to a weak password policy, strengthened the policy, and I could still log in fine. And obviously you can’t create a login with, or later set, a password that doesn’t meet the policy. Let me know if you’ve seen it. | |
| 10 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 10. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. |
| This is a rather complicated variation on state 9; as KB #925744 states, this means that password checking could not be performed because the login is disabled or locked on the domain controller (note that if SQL Server does not start, it could be because the account that is locked or disabled is the SQL Server service account). No reason or additional information is provided in the «verbose» message in the error log. | |
| 11 12 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 11. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Login-based server access validation failed with an infrastructure error. Check for previous errors. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 12. |
| States 11 and 12 mean that SQL Server was able to authenticate you, but weren’t able to validate with the underlying Windows permissions. It could be that the Windows login has no profile or that permissions could not be checked due to UAC. Try running SSMS as administrator and/or disabling UAC. Another reason could be that the domain controller could not be reached. You may need to resort to re-creating the login (see this post from Simon Sabin). Finally, PSS has recently released more information about states 11 and 12; see this post for potential scenarios and solutions, and also see states 146-149 below for changes in SQL Server 2016. | |
| 13 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 13. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: SQL Server service is paused. No new connections can be accepted at this time. |
| This state occurs when the SQL Server service has been paused (which you can do easily and even accidentally from the context menu in Object Explorer). | |
| 16 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 16. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. You may also see: A connection was successfully established with the server, but then an error occurred during the pre-login handshake. |
| State 16, which only occurs prior to SQL Server 2008, means that the default database was inaccessible. This could be because the database has been removed, renamed, or is offline (it may be set to AutoClose). This state does not indicate a reason in the error log. In 2008 and beyond, this is reported as state 40 (see below), with a reason. In SQL Server 2005, this state may also be reported if the user’s default database is online but the database they explicitly requested is not available for the reasons stated above (also see state 27). If you get the pre-login handshake message, it may be because you’ve disabled SSL on the server. | |
| 18 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 18. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. |
| Supposedly this indicates that the user needs to change their password. In SQL Server 2005, 2008 R2 and SQL Server 2012, I found this was raised as error 18488, not 18456; this is because for SQL logins the change password dialog just delays logging in, and is not actually a login failure. I suspect that, like state 16, this state will no longer appear in future versions of SQL Server. | |
| 23 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 23. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Access to server validation failed while revalidating the login on the connection. |
| There could be a few reasons for state 23. The most common one is that connections are being attempted while the service is being shut down. However if this error occurs and it is not surrounded in the log by messages about SQL Server shutting down, and there is no companion reason along with the message, I would look at KB #937745, which implies that this could be the result of an overloaded server that can’t service any additional logins because of connection pooling issues. Finally, if there *is* a companion reason, it may be the message indicated to the right, indicating that SQL Server was running as a valid domain account and, upon restarting, it can’t validate the account because the domain controller is offline or the account is locked or no longer valid. Try changing the service account to LocalSystem until you can sort out the domain issues. | |
| 27 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 27. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. |
| State 27, like state 16, only occurs prior to SQL Server 2008. It means that the database specified in the connection string has been removed, renamed, or is offline (possibly due to AutoClose) – though in every case I tried, it was reported as state 16. This state does not indicate a reason in the error log. In 2008 and onward this is reported as state 38 (see below), with a reason. | |
| 28 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 28. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. |
| I have not experienced this issue but I suspect it involves overloaded connection pooling and connection resets. I think you will only see state 28 prior to SQL Server 2008. | |
| 38 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 38. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Failed to open the database specified in the login properties. or Reason: Cannot open database «<database>» requested by the login. The login failed. |
|
The database specified in the connection string, or selected in the Options > Connection Properties tab of the SSMS connection dialog, is no longer valid or online (it might be set to AutoClose or the user may simply not have permission). I came across this once when I typed <default> here instead of picking that option from the list. This is reported as state 27 or state 16 prior to SQL Server 2008.
Note that this could also be a symptom of an orphaned login. After establishing mirroring, Availability Groups, log shipping, etc. you may have created a new login or associated a user with a login on the primary database. The database-level user information gets replayed on the secondary servers, but the login information does not. Everything will work fine – until you have a failover. In this situation, you will need to synchronize the login and user information (for one example, see this script from the late Robert Davis). |
|
| 40 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 40. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Failed to open the explicitly specified database. |
| Usually this means the login’s default database is offline (perhaps due to AutoClose) or no longer exists. Resolve by fixing the missing database, or changing the login’s default database using ALTER LOGIN (for older versions, use sp_defaultdb, which is now deprecated). This is reported as state 16 prior to SQL Server 2008. | |
| 46 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 46. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Failed to open the database configured in the login object while revalidating the login on the connection. |
| State 46 may occur when the login (or login mapping to the service account) does not have a valid database selected as their default database. (I am guessing here but I think this may occur when the login in question is attempting to perform log shipping. Again, just a guess based on the few conversations I discovered online.) It can also occur if the classifier function (Resource Governor) or a logon trigger refers to a database that is offline, no longer exists, or is set to AutoClose. | |
| 50 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 50. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Current collation did not match the database’s collation during connection reset. |
| As the message implies, this can occur if the default collation for the login is incompatible with the collation of their default database (or the database explicitly specified in the connection string). It can also happen if they are using a client tool like Management Studio which may, when they have been disconnected, try to connect to master upon reconnection instead of their default database. | |
| 51 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 51. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Failed to send an environment change notification to a log shipping partner node while revalidating the login. |
| Like states 11 & 12, this could have to do with UAC, or that the domain controller could not be reached, or that the domain account could not authenticate against the log shipping partner, or that the log shipping partner was down. Try changing the service account for SQL Server to a known domain or local account, rather than the built-in local service accounts, and validating that the partner instance is accessible, as well as the database that is being requested in the connection string and the default database of the login. Note that this could be trigged by the failover partner connection string attribute, and that the database may no longer exist or may be offline, single user, etc. | |
| 56 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 56. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Failed attempted retry of a process token validation. |
| State 56 is not very common – again, like states 11 & 12, this could have to do with UAC, or that the domain controller could not be reached. Try changing the service account for SQL Server to a known domain or local account, rather than the built-in local service accounts. | |
| 58 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 58. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: An attempt to login using SQL authentication failed. Server is configured for Windows authentication only. |
| State 58 occurs when SQL Server is set to use Windows Authentication only, and a client attempts to log in using SQL Authentication. It can also occur when SIDs do not match (in which case the error text might be slightly different). | |
| 62 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 62. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. |
| State 62 occurs when a Windows Authentication account tries to access a contained database, and the contained database exists, but the SIDs do not match. | |
| 65 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 65. Login failed for user ‘<x>’. Reason: Password did not match that for the user provided. [Database: ‘<x>’] |
| Contained user exists, the database is correct, but the password is invalid. This can also happen if you use a SQL login to connect to a contained database that has a contained user with the same name but a different password (one of several reasons this is not recommended). | |
| 102 103 … 110 111 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 102. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 103. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 104. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 105. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 106. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 107. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 108. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 109. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 110. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 111. |
| Documented by Microsoft as Azure Active Directory login failures. | |
| 122 123 124 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 122. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 123. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 124. |
| According to Microsoft, these indicate a blank or missing username and/or password. | |
| 126 | Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 126. |
| The docs say «Database requested by user does not exist.» But it’s not clear why you would get 126 instead of, say, 38 or 40. | |
| 132 133 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 132. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 133. |
| Documented by paschott and by Microsoft as Azure Active Directory login failures. | |
| 146 147 148 149 |
Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 146. Login failed for user ‘<Windows auth login>’. Reason: Token-based server access validation failed with an infrastructure error. Login lacks Connect SQL permission. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 147. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 148. Error: 18456, Severity: 14, State: 149. |
| These states replace states 11 and 12 above, but only in SQL Server 2016 or better. The goal was to make the actual underlying issue easier for the sysadmin to diagnose between SQL auth and Windows auth logins, and between connect and endpoint permissions (all without giving any further info to the user trying to log in). For more details, see the latter part of this post. |
I am sure I missed some, but I hope that is a helpful summary of most of the 18456 errors you are likely to come across. Please let me know if you spot any inaccuracies or if you know of any states (or reasons) that I missed.
If you are using contained databases, there will be a little extra complication in solving login failures, especially if you try to create contained users with the same name as server-level logins. This is a ball of wax you just probably don’t want to get into…
Thanks to Jonathan Kehayias (blog | twitter), Bob Ward (CSS blog | twitter), and Rick Byham for input and sanity checking.
0 / 0 / 1
Регистрация: 26.10.2017
Сообщений: 16
1
26.10.2017, 19:44. Показов 4029. Ответов 1
При добавлении записи в БД выскакивает ошибка:
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlException произошло
HResult=0x80131904
Сообщение = Must declare the scalar variable «@PhoneNumper».
Источник = .Net SqlClient Data Provider
Трассировка стека:
в System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection.OnError(SqlExc eption exception, Boolean breakConnection, Action`1 wrapCloseInAction)
в System.Data.SqlClient.SqlInternalConnection.OnErro r(SqlException exception, Boolean breakConnection, Action`1 wrapCloseInAction)
в System.Data.SqlClient.TdsParser.ThrowExceptionAndW arning(TdsParserStateObject stateObj, Boolean callerHasConnectionLock, Boolean asyncClose)
в System.Data.SqlClient.TdsParser.TryRun(RunBehavior runBehavior, SqlCommand cmdHandler, SqlDataReader dataStream, BulkCopySimpleResultSet bulkCopyHandler, TdsParserStateObject stateObj, Boolean& dataReady)
в System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand.FinishExecuteRead er(SqlDataReader ds, RunBehavior runBehavior, String resetOptionsString, Boolean isInternal, Boolean forDescribeParameterEncryption)
в System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand.CompleteAsyncExec uteReader(Boolean isInternal, Boolean forDescribeParameterEncryption)
в System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand.InternalEndExecut eNonQuery(IAsyncResult asyncResult, String endMethod, Boolean isInternal)
в System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand.EndExecuteNonQuer yInternal(IAsyncResult asyncResult)
в System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand.EndExecuteNonQuer yAsync(IAsyncResult asyncResult)
в System.Threading.Tasks.TaskFactory`1.FromAsyncCore Logic(IAsyncResult iar, Func`2 endFunction, Action`1 endAction, Task`1 promise, Boolean requiresSynchronization)
в System.Runtime.CompilerServices.TaskAwaiter.ThrowF orNonSuccess(Task task)
в System.Runtime.CompilerServices.TaskAwaiter.Handle NonSuccessAndDebuggerNotification(Task task)
в System.Runtime.CompilerServices.TaskAwaiter`1.GetR esult()
в BaseOne.StartScreen.<button1_Click>d__12.MoveNext( ) в C:UsersstavoDesktopBDBaseOneBaseOneForm1.cs :строка 138
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlException: «Must declare the scalar variable «@PhoneNumper».»
Вот код:
| C# | ||
|
__________________
Помощь в написании контрольных, курсовых и дипломных работ, диссертаций здесь
0
ИТ База знаний
Полезно
— Узнать IP — адрес компьютера в интернете
— Онлайн генератор устойчивых паролей
— Онлайн калькулятор подсетей
— Калькулятор инсталляции IP — АТС Asterisk
— Руководство администратора FreePBX на русском языке
— Руководство администратора Cisco UCM/CME на русском языке
— Руководство администратора по Linux/Unix
Навигация
Серверные решения
Телефония
FreePBX и Asterisk
Настройка программных телефонов
Корпоративные сети
Протоколы и стандарты
Популярное и похожее
Пошаговый ввод в домен Windows 10
Погружение в Iptables – теория и настройка
Как сбросить root пароль на MySQL?
Передача файлов по RDP – это просто
Решаем ошибку 18456 в SQL
2 минуты чтения
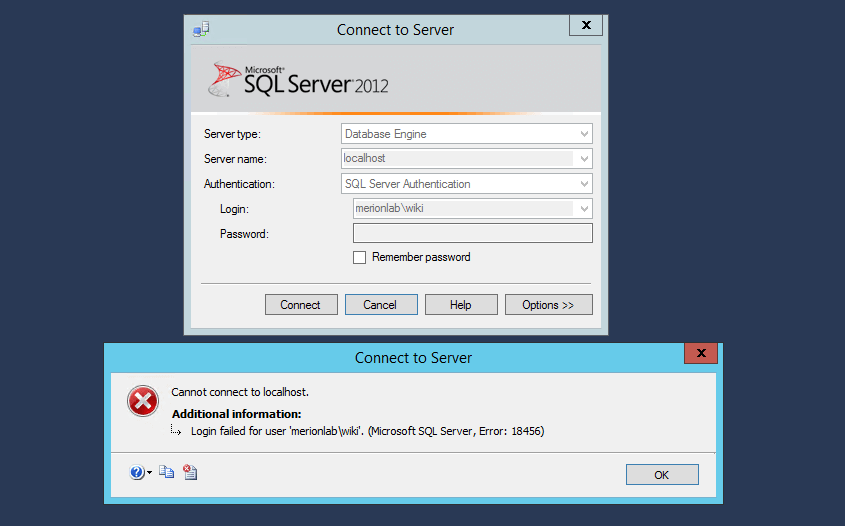
С нетерпением спешим поделиться с тобой способом решения ошибки 18456 — Login Failed for User (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 18456). Определим пользователя, который имеет права доступа к SQL и создадим новую учетную запись.
Если вы только столкнулись с проблемой, вам необходимо понять, какой пользователь имеет права на подключение к SQL. Как правило, это юзер, под которым был установлен SQL. Об этом и поговорим.
Получаем доступ
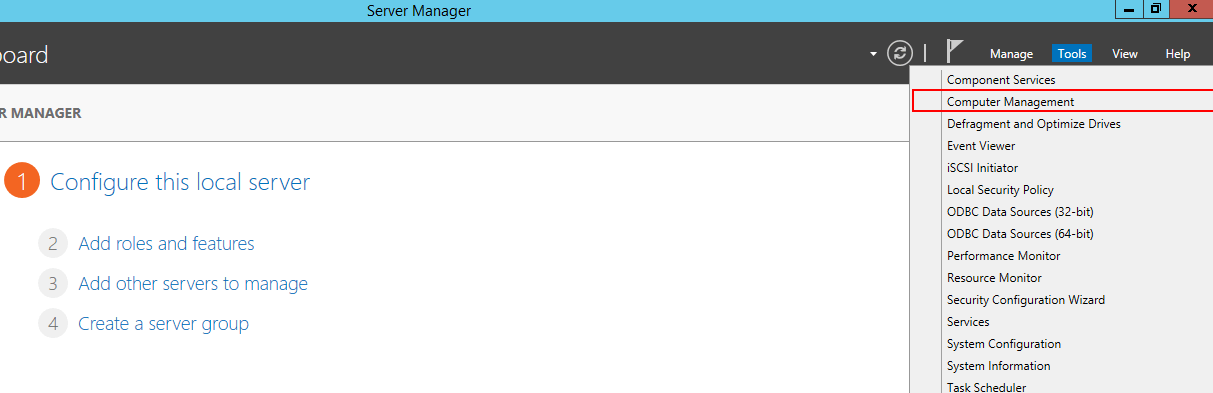
Запустите Server Manager в операционной системе. Переходим в раздел Tools → Computer Management:
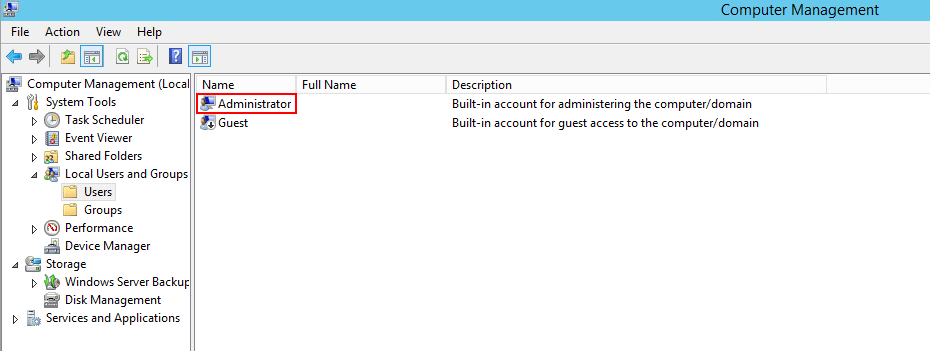
Раскрываем список Local Users and Groups, в разделе Computer Management → System Tools и нажимаем на Users.
Смотрим описание к пользователям. Находим описание юзера, которое начинается с Built-in account for administering the computer…. С большой вероятностью, это именно тот аккаунт, с которого мы получим доступ к SQL.
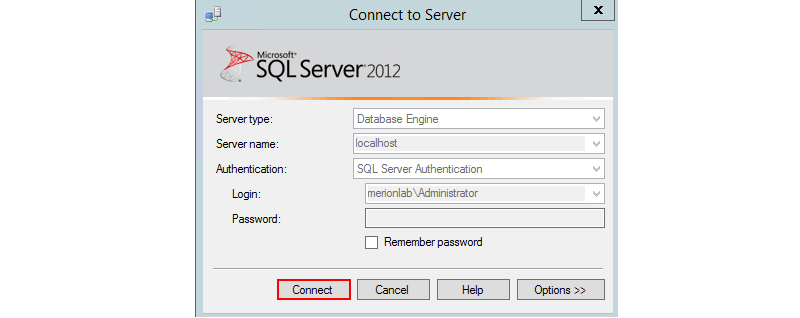
Выходим из под текущего юзера в операционной системе, заходим под пользователем Administrator. Пробуем подключиться – работает.
Даем права нужному пользователю
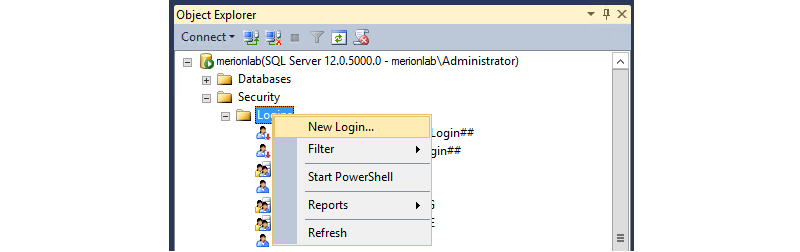
Подключившись к SQL Management Studio под пользователем Administrator, слева, в меню навигации, раскрываем список под именем сервера, переходим в раздел Security → Logins. Нажимаем на Logins правой кнопкой мыши и нажимаем New Login…:
Нажимаем на кнопку Search:
В появившемся окне укажите имя пользователя, которому необходимо предоставить права администратора SQL. Нажимаем OK:
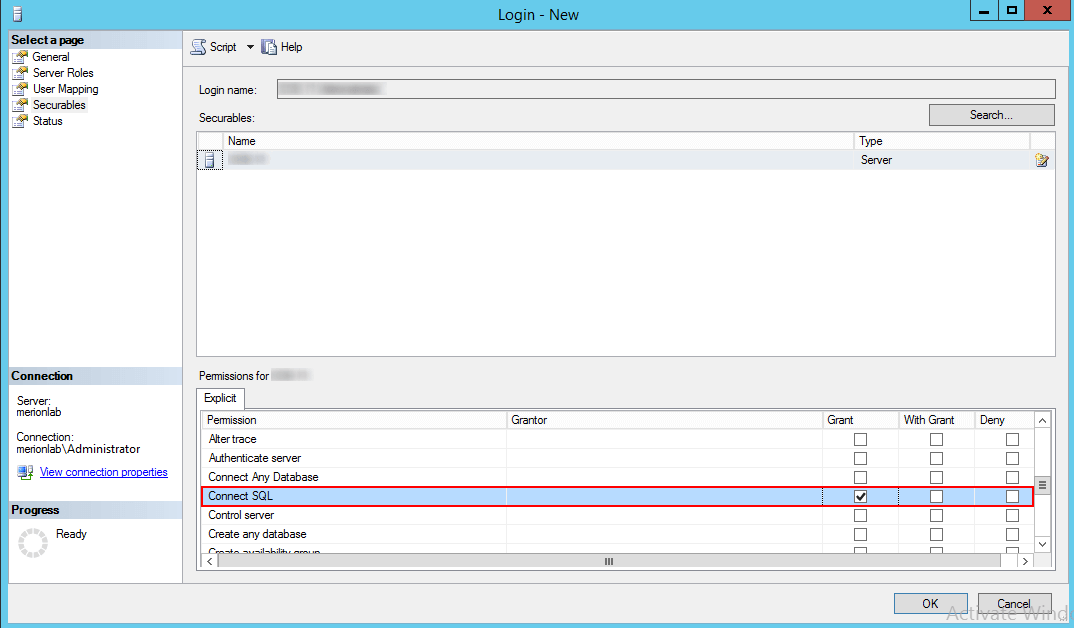
В разделе Server Roles выбираем sysadmin и жмем OK:
В разрешениях отмечаем Connect SQL и жмем OK.
Теперь, выходим из под пользователя Administrator в ОС и подключаемся под пользователем, с которым мы изначально пытались подключиться. Готово.
Полезна ли Вам эта статья?
Пожалуйста, расскажите почему?


Источник ошибки net sqlclient data provider
Вопрос
Объект: Виртуальный сервер Windows Server 2008 R2 SE на нем SQL Server 2008 R2 64x
Позавчера встало обновление KB2979597, но со второго раза. Безумно долгая перезагрузка, но терпеливо ждал до 5-ти утра. В итоге получил проблему со входом Management Console
Error: 18401
Login failed for user ‘ ‘. Reason: Server is in script upgrade mode. Only administrator can connect at this time.
Проделал это: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/2163980 (Исправил: поскольку дело было бессонной ночью, описанное здесь проделал не до конца. Возможно дело в этом).
не помню перезагружался или нет, службу SQL сервер отрестартил. Консоль запустилась, клиентские подключения тоже заработали. Далее система осталась без изменений.
На настоящий момент клиентские подключения работают, к консоли подключиться можно, но при попытке раскрыть перечень баз получаем:
Не удалось получить данные по этому запросу. (Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Enumerator.Process(Object connectionInfo, Request request)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.UI.VSIntegration.ObjectExplorer.NavigableItemBuilder.NavigableItemBuilderDataReader.RunQuery()
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.UI.VSIntegration.ObjectExplorer.NavigableItemBuilder.NavigableItemBuilderDataReader.Process()
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.UI.VSIntegration.ObjectExplorer.NavigableItemBuilder.NavigableItemBuilderDataReader.get_PropertyNames()
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.UI.VSIntegration.ObjectExplorer.NavigableItemBuilder.BuildDynamicItemWithQuery(IList`1 nodes, INodeInformation source, INavigableItem sourceItem, String urnQuery, Boolean registerBuilder, Boolean registerBuiltItems)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.UI.VSIntegration.ObjectExplorer.NavigableItemBuilder.BuildDynamicItem(IList`1 nodes, INodeInformation source, INavigableItem sourceItem, IFilterProvider filter)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.UI.VSIntegration.ObjectExplorer.NavigableItemBuilder.Build(IList`1 nodes, INodeInformation source, INavigableItem sourceItem, IFilterProvider filter)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.UI.VSIntegration.ObjectExplorer.NavigableItem.RequestChildren(IGetChildrenRequest request)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.UI.VSIntegration.ObjectExplorer.ExplorerHierarchyNode.BuildChildren(WaitHandle quitEvent)
При выполнении инструкции или пакета Transact-SQL возникло исключение. (Microsoft.SqlServer.ConnectionInfo)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Common.ServerConnection.ExecuteReader(String sqlCommand, SqlCommand& command)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.ExecuteSql.GetDataReader(String query, SqlCommand& command)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.DataProvider.SetConnectionAndQuery(ExecuteSql execSql, String query)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.ExecuteSql.GetDataProvider(StringCollection query, Object con, StatementBuilder sb, RetriveMode rm)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.ExecuteSql.ExecuteWithResults(StringCollection query, Object con, StatementBuilder sb)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.SqlObjectBase.FillData(ResultType resultType, StringCollection sql, Object connectionInfo, StatementBuilder sb)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.SqlObjectBase.FillDataWithUseFailure(SqlEnumResult sqlresult, ResultType resultType)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.SqlObjectBase.BuildResult(EnumResult result)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.SqlObjectBase.GetData(EnumResult erParent)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Environment.GetData()
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Environment.GetData(Request req, Object ci)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Enumerator.GetData(Object connectionInfo, Request request)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc.Enumerator.Process(Object connectionInfo, Request request)
Недопустимое имя объекта «msdb.dbo.syspolicy_configuration». (.Net SqlClient Data Provider)
——————————
Имя сервера: SDB
Номер ошибки: 208
Серьезность: 16
Состояние: 1
Номер строки: 3
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Common.ConnectionManager.ExecuteTSql(ExecuteTSqlAction action, Object execObject, DataSet fillDataSet, Boolean catchException)
в Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Common.ServerConnection.ExecuteReader(String sqlCommand, SqlCommand& command)
Не открываются не только базы. Гугление пока ни к чему не привело. Поиск по «microsoft sql server ошибка 208» тоже дает несхожие с моей ситуацией результаты.
Источник ошибки net sqlclient data provider
Александр Жевелев
Автор
Сообщений: 2672
Откуда: Новосибирск
с приложением одновременно работают 10-50 пользователей, иногда (и даже не каждый день) от одного или нескольких пользователей прилетает такая ошибка:
Собственно, вопрос в заглавии поста.
PaulWist
1. Причин разрыва соединения может быть масса (для начала посмотри в логах сервера на предмет таймаута, deadlock-a итп).
2. Писать аналог фоксовской SQLIDLDISCONNECT(), те проверять если соединение «умерло», то заново коннектиться (если хранишь логин-пароль, «в тихую», если делаешь правильно и не хранишь логин-пароль, то дать соединиться юзеру интерактивно) и выполнять последоватеность команд заново.
Igor Korolyov
blogs.msdn.com
От те цельная куча возможных причин.
Александр Жевелев
Автор
Сообщений: 2672
Откуда: Новосибирск
Влад Колосов
Сообщений: 22664
Откуда: Ростов-на-Дону
KILL сессиям делают админы или робот, тогда такие сообщения приходят.
Еще слишком умный роутер может сессии прибивать, если нет трафика
Исправлено: Влад Колосов, 12.11.15 14:28
Аспид
Сообщений: 3371
Откуда: Москва
Помнится отлаживал обрыв связи, так шнурок от компа, прямо под руку положил, и рвал.
Добивался, что бы само при восстановлении восстанавливалось )))
зы. И может лучше коннект, на кажный чих, и дисконнект? Должно исчезнуть?
Igor Korolyov
Не факт что лучше — всё ж это затратная процедура. При этом я имею в виду именно «физический» коннект (то что висит в адонетовском пуле даже если прога не пользует в данный момент ни каких Connection). Я надеюсь что автор таки следует «рекомендациям лучших собаководов» и работа с БД организована сравнительно короткими сеансами (подход UnitOfWork) вида
Просто инфраструктура пула не может сама прочухать что подлежащая коннекция протухла и надо бы её выкинуть и сделать новую.
А ежели автор таки пользует подход «при старте проги сделал одну DBConnection, запихал ея в static поле и таперича всегда и везде её пользую», то он таки неправ
Александр Жевелев
Автор
Сообщений: 2672
Откуда: Новосибирск
MSDN
Соединения и платформа Entity Framework
Entity Framework открывает соединения только по требованию, например чтобы выполнить запрос или вызвать метод SaveChanges, и закрывает соединение после завершения операции.
Вызов любого из следующих методов открывает соединение:
-SaveChanges или Refresh в ObjectContext.
-FirstOrDefault или First в ObjectQuery.
-Load в EntityCollection.
-Load в EntityReference.
-Любой метод LINQ или метод построителя запросов ObjectQuery, такой как Where, OrderBy или Select.
2. Похоже найдена и устранена причина ошибки в моем случае — Сервер, на котором крутится SQL server установлен на виртуальной машине, так вот скорость виртуальной сетевой карты виртуальной машины не соответствовала скорости реальной сетевой карты (была в 10 раз выше). После устранении несоответствия ошибок не возникает вообше!
Всем спасибо за внимание и советы!
Ошибка отсутствие установленного MS SQL server Native Client
При разнесении по разным серверам (хостам) Сервер 1С и MS SQL в попытке создать новую базу средствами утилиты администрирования Сервера 1С, нас встречает ошибка: «Ошибка создания информационной базы, Ошибка операции администрирования, Ошибка при получении значения из базы данных: Возможной причиной является отсутствие установленного MS SQL server Native Client. »
Конечно, данная тема также подымается и на курсе: Администратор 1С!
Конечно, получить ошибку «повезло не всем», а только тем, кто работает с 1С версии 8.3.8 и выше.
Благо решить проблему довольно просто, собственно дав Серверу 1С то, что он просит!
Где искать MS SQL server Native Client ?
Скорее всего файл установщик MS SQL server Native Client (он же sqlncli.msi) уже у Вас на диске!
Если Вы не удалили каталог «установщик», когда скачивали и затем ставили свой MS SQL server 2017 (Выпуск Evaluation).
Тогда искать долго не надо!
Идем «по умолчанию путь» на диск С: там ищем каталог «SQL server 2017 Media»
И уже в этом каталоге воспользовавшись обычным поиском sqlncli.msi, успешно находим наш MS SQL server Native Client!
Остается лишь его скопировать и установить там, где работает «Сервер 1С».
Установка очень простая, всего пару кликов по кнопке «Далее»
Ставим «Пакет SDK для SQL Server Native Client»
Также MS SQL server Native Client можно скачать и на официальном сайте Microsoft, например в пакете дополнительных компонентов для Microsoft® SQL Server® 2016:
Если Вы хотите больше узнать о технической стороне 1С, тогда регистрируйтесь на первый бесплатный модуль курса: Администратор 1С >>>
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlException: сбой входа для пользователя
При работе с моим проектом в режиме отладки у меня нет проблем. Однако при запуске его в IIS я получаю эту ошибку:
System.Data.SqlClient.SqlException: сбой входа для пользователя ‘домен имя-ПК $’.
Трассировка стека
Решение номер один, которое я могу найти в Google, — это изменить расширенные настройки идентификации пула приложений, которые не работали.
Я использую IIS 7.5 и подключаюсь к SQLServer 2012, моя строка подключения указана ниже.
Строка подключения
8 ответов
Предполагая, что вы собираетесь использовать проверку подлинности Windows для олицетворения учетной записи службы, необходимо настроить проверку подлинности Windows как в IIS, так и в ASP.NET.
В IIS убедитесь, что модуль проверки подлинности Windows добавлен и включен. Также убедитесь, что пул приложений работает под учетной записью домена, а не локальной учетной записью.
В ASP.NET убедитесь, что для атрибута режима аутентификации установлено значение «Windows»
Просто установите Integrated Security=False , и он будет работать в соответствии с комментарий разница между True и False :
True игнорирует User ID и —- +: = 5 =: + —-, если он предоставлен и использует те из запущенного процесса, Password он будет использовать их, если это предусмотрено, поэтому MS предпочитает это. Они эквивалентны тем, что используют один и тот же механизм безопасности для аутентификации, но это так.
Вы также можете получить эту ошибку, если ваш SQL Server не был настроен на использование проверки подлинности в смешанном режиме — он фактически не говорит вам, что это не включено!
У меня был похожий опыт, и мне потребовалось время, чтобы решить проблему. Хотя в моем случае это были ASP.Net MVC Core и Core рамки. Настройка Trusted_Connection=False; решила мою проблему.
Внутри appsettings.json файл
Я только что натолкнулся на эту ошибку, и ее устранение заняло несколько дней. Мы были зациклены на сообщении об ошибке «красная сельдь», упомянутом в первоначальном вопросе, плюс журнал ошибок Windows Event Viewer показал что-то похожее:
Ничего из этого не было правдой, у пользователя были все необходимые разрешения в SQL Server.
В нашем случае решением было переключить идентификатор пула приложений в IIS на NetworkService .
Здесь Numpty использовал аутентификацию SQL
вместо Windows (правильно)
при добавлении имени входа на SQL Server, что также выдает эту ошибку, если вы используете аутентификацию Windows.
Я столкнулся с такой же ситуацией. Создайте строку подключения следующим образом.
добавить постоянную информацию о безопасности = True; в строке подключения.