ClassNotFoundException is a checked exception and occurs when the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) tries to load a particular class and the specified class cannot be found in the classpath.
In older days, there are no editors like Eclipse are available. Even in Notepad, people have done java coding and by using the “javac” command to compile the java files, and they will create a ‘.class’ file. Sometimes accidentally the generated class files might be lost or set in different locations and hence there are a lot of chances of “ClassNotFoundException” occurs. After the existence of editors like Eclipse, Netbeans, etc., IDE creates a “ClassPath” file kind of entries.
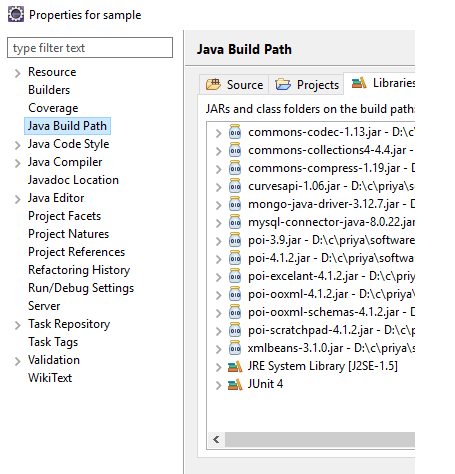
From the above image, we can see that many jar files are present. They are absolutely necessary if the java code wants to interact with MySQL, MongoDB, etc., kind of databases, and also few functionalities need these jar files to be present in the build path. If they are not added, first editors show the errors themselves and provide the option of corrections too.
Implementation: Sample program of connecting to MySQL database and get the contents
Example
Java
import java.sql.*;
public class MySQLConnectivityCheck {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(
"---------------------------------------------");
Connection con = null;
ResultSet res = null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
con = DriverManager.getConnection(
"root", "");
try {
}
catch (SQLException s) {
System.out.println(
"SQL statement is not executed!");
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
res = null;
con = null;
}
}
}
Output:
Case 1: In the above code, we are using com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver and in that case if we are not having mysql-connector-java-8.0.22.jar, then we will be getting ClassNotFoundException.
Case 2: So, keep the jar in the build path as shown below.
Note: Similarly for any database connectivity, we need to have the respective jars for connecting to that database. The list of database driver jars required by java to overcome ClassNotFoundException is given below in a tabular format
| Database | Command Line |
|---|---|
| MySQL | mysql-connector-java-8.0.22.jar |
| MongoDB | mongo-java-driver-3.12.7.jar |
| SQL Server | sqljdbc4.jar |
| MYSQL | sqljdbc.jar |
| Oracle | oracle.jdbc.driver.oracledriver |
Note:
- When we are developing Web based applications, the jars must be present in ‘WEB-INF/lib directory’.
- In Maven projects, jar dependency should be present in pom.xml
- Sample snippet of pom.xml for spring boot
Example 1 With Spring boot
XML
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
Example 2 Without spring boot
XML
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mongodb</groupId>
<artifactId>mongodb-driver</artifactId>
<version>3.6.3</version>
</dependency>
Example 3 Gradle based dependencies (MongoDB)
XML
dependencies {
compile 'org.mongodb:mongodb-driver:3.2.2'
}
Similarly, other DB drivers can be specified in this way. It depends upon the project nature, the dependencies has to be fixed. For ordinary class level projects, all the classes i.e parent class, child class, etc should be available in the classpath. If there are errors, then also .class file will not be created which leads to ClassNotFoundException, and hence in order to get the whole code working, one should correct the errors first by fixing the dependencies. IDE is much helpful to overcome such sort scenarios such as when the program throws ClassNotFoundException, it will provide suggestions to users about the necessity of inclusion of jar files(which contains necessary functionalities like connecting to database.
The java.lang.ClassNotFoundException is a checked exception in Java that occurs when the JVM tries to load a particular class but does not find it in the classpath.
Since the ClassNotFoundException is a checked exception, it must be explicitly handled in methods which can throw this exception — either by using a try-catch block or by throwing it using the throws clause.
Install the Java SDK to identify and fix exceptions
What Causes ClassNotFoundException in Java
Common causes of the java.lang.ClassNotFoundException are using the following methods to load a class:
Class.forName()ClassLoader.findSystemClass()ClassLoader.loadClass()
In all the above cases, the class attempted to be loaded is not found on the classpath, leading to the ClassNotFoundException in Java.
ClassNotFoundException in Java Example
A very common example of ClassNotFoundException is when a JDBC driver is attempted to be loaded using Class.forName() and the driver’s JAR file is not present in the classpath:
public class ClassNotFoundExceptionExample {
private static final String DRIVER_CLASS = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Loading MySQL JDBC driver");
Class.forName(DRIVER_CLASS);
}
}
Since the MySQL JDBC driver JAR file is not present in the classpath, running the above code leads to a java.lang.ClassNotFoundException:
Loading MySQL JDBC driver
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:602)
at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoaders.java:178)
at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:522)
at java.base/java.lang.Class.forName0(Native Method)
at java.base/java.lang.Class.forName(Class.java:340)
at ClassNotFoundExceptionExample.main(ClassNotFoundExceptionExample.java:6)To fix the Java exception, the mysql-connector JAR should be included in the application classpath.
How to Resolve ClassNotFoundException in Java
The following steps should be followed to resolve a ClassNotFoundException in Java:
- Find out which JAR file contains the problematic Java class. For example, in the case of com.mysql.jdbc.driver, the JAR file that contains it is mysql-connector-java.jar.
- Check whether this JAR is present in the application classpath. If not, the JAR should be added to the classpath in Java and the application should be recompiled.
- If that JAR is already present in the classpath, make sure the classpath is not overridden (e.g. by a start-up script). After finding out the exact Java classpath used by the application, the JAR file should be added to it.
To fix the Java exception, the mysql-connector JAR should be included in the application classpath.
Track, Analyze and Manage Java Errors With Rollbar

Managing errors and exceptions in your code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyze, and manage errors in real-time can help you to proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates Java error monitoring and triaging, making fixing errors easier than ever. Try it today.
Эта статья предназначена для начинающих Java, которые в настоящее время сталкиваются с проблемами java.lang.ClassNotFoundException. Он предоставит вам обзор этого распространенного исключения Java, пример Java-программы для поддержки вашего процесса обучения и стратегии решения.
Если вас интересуют более сложные проблемы, связанные с загрузчиком классов, я рекомендовал вам просмотреть мою серию статей на
java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError, так как эти исключения Java тесно связаны.
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: обзор
Согласно документации Oracle,
ClassNotFoundException генерируется после сбоя вызова загрузки класса с использованием его строкового имени, как показано ниже:
- Метод Class.forName
- Метод ClassLoader.findSystemClass
- Метод ClassLoader.loadClass
Другими словами, это означает, что один конкретный класс Java
не
был
найден или не
мог
быть загружен во время выполнения из загрузчика классов текущего контекста вашего приложения.
Эта проблема может быть особенно запутанной для начинающих Java. Вот почему я всегда рекомендую разработчикам Java изучать и совершенствовать свои знания о
загрузчиках классов Java . Если вы не вовлечены в динамическую загрузку классов и не используете Java Reflection API, есть вероятность, что ошибка ClassNotFoundException, которую вы получаете, связана не с кодом вашего приложения, а с API-интерфейсом, на который ссылаются. Другая распространенная проблема — неправильная упаковка кода вашего приложения. Мы вернемся к стратегии разрешения в конце статьи.
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: пример Java-программы
Теперь найдите ниже очень простую Java-программу, которая имитирует 2 наиболее распространенных сценария ClassNotFoundException с помощью Class.forName () и ClassLoader.loadClass (). Пожалуйста, просто скопируйте / вставьте и запустите программу с IDE по вашему выбору (
Eclipse IDE был использован для этого примера ).
Программа Java позволяет вам выбирать между проблемным сценарием № 1 или проблемным сценарием № 2, как показано ниже. Просто измените на 1 или 2 в зависимости от сценария, который вы хотите изучить.
# Class.forName() private static final int PROBLEM_SCENARIO = 1; # ClassLoader.loadClass() private static final int PROBLEM_SCENARIO = 2;
# ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator
package org.ph.javaee.training5;
/**
* ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator
* @author Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau
*
*/
public class ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator {
private static final String CLASS_TO_LOAD = "org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA";
private static final int PROBLEM_SCENARIO = 1;
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("java.lang.ClassNotFoundException Simulator - Training 5");
System.out.println("Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau");
System.out.println("http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com");
switch(PROBLEM_SCENARIO) {
// Scenario #1 - Class.forName()
case 1:
System.out.println("n** Problem scenario #1: Class.forName() **n");
try {
Class<?> newClass = Class.forName(CLASS_TO_LOAD);
System.out.println("Class "+newClass+" found successfully!");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Class "+CLASS_TO_LOAD+" not found!");
} catch (Throwable any) {
System.out.println("Unexpected error! "+any);
}
break;
// Scenario #2 - ClassLoader.loadClass()
case 2:
System.out.println("n** Problem scenario #2: ClassLoader.loadClass() **n");
try {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
Class<?> callerClass = classLoader.loadClass(CLASS_TO_LOAD);
Object newClassAInstance = callerClass.newInstance();
System.out.println("SUCCESS!: "+newClassAInstance);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Class "+CLASS_TO_LOAD+" not found!");
} catch (Throwable any) {
System.out.println("Unexpected error! "+any);
}
break;
}
System.out.println("nSimulator done!");
}
}
# ClassA
package org.ph.javaee.training5;
/**
* ClassA
* @author Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau
*
*/
public class ClassA {
private final static Class<ClassA> CLAZZ = ClassA.class;
static {
System.out.println("Class loading of "+CLAZZ+" from ClassLoader '"+CLAZZ.getClassLoader()+"' in progress...");
}
public ClassA() {
System.out.println("Creating a new instance of "+ClassA.class.getName()+"...");
doSomething();
}
private void doSomething() {
// Nothing to do...
}
}
Если вы запустите программу как есть, вы увидите вывод, как показано ниже для каждого сценария:
Вывод сценария 1 (базовый уровень)
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException Simulator - Training 5 Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com ** Problem scenario #1: Class.forName() ** Class loading of class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA from ClassLoader 'sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@bfbdb0' in progress... Class class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA found successfully! Simulator done!
Вывод сценария 2 (базовый уровень)
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException Simulator - Training 5 Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com ** Problem scenario #2: ClassLoader.loadClass() ** Class loading of class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA from ClassLoader 'sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@2a340e' in progress... Creating a new instance of org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA... SUCCESS!: org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA@6eb38a Simulator done!
Для «базового» запуска Java-программа может успешно загрузить ClassA.
Теперь давайте добровольно изменим полное имя ClassA и повторно запустим программу для каждого сценария. Может быть получен следующий вывод:
#ClassA изменен на
ClassB
private static final String CLASS_TO_LOAD = "org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB";
# Вывод сценария 1 (проблема репликации)
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException Simulator - Training 5
Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau
http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com
** Problem scenario #1: Class.forName() **
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:366)
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:355)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:354)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:423)
at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:308)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:356)
at java.lang.Class.forName0(Native Method)
at java.lang.Class.forName(Class.java:186)
at org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator.main(ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator.java:29)
Class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB not found!
Simulator done!
Вывод сценария 2 (проблема репликации)
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException Simulator - Training 5
Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau
http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com
** Problem scenario #2: ClassLoader.loadClass() **
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:366)
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:355)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:354)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:423)
at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:308)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:356)
at org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator.main(ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator.java:51)
Class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB not found!
Simulator done!
Что произошло? Итак, поскольку мы изменили полное имя класса на org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB, такой класс не был найден во время выполнения (не существует), что привело к сбою вызовов Class.forName () и ClassLoader.loadClass ().
Вы также можете повторить эту проблему, упаковав каждый класс этой программы в свой собственный JAR-файл, а затем пропустите jar-файл, содержащий ClassA.class, из основного пути к классу. Попробуйте это и посмотрите сами результаты… (подсказка: NoClassDefFoundError)
Теперь давайте перейдем к стратегии разрешения.
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: стратегии разрешения
Теперь, когда вы понимаете эту проблему, пришло время решить ее. Разрешение может быть довольно простым или очень сложным в зависимости от первопричины.

- Не спешите со сложными первопричинами слишком быстро, сначала исключите самые простые причины.
- Сначала просмотрите трассировку стека java.lang.ClassNotFoundException согласно приведенному выше и определите, какой класс Java не был загружен должным образом во время выполнения, например, код приложения, сторонний API, сам контейнер Java EE и т. Д.
- Определите вызывающего, например, Java-класс, который вы видите по трассировке стека непосредственно перед вызовами Class.forName () или ClassLoader.loadClass (). Это поможет вам понять, является ли код вашего приложения ошибочным по сравнению с API стороннего производителя.
- Определите, правильно ли упакован код вашего приложения, например, отсутствуют файлы JAR из вашего classpath
- Если отсутствующий класс Java отсутствует в коде вашего приложения, то определите, принадлежит ли он стороннему API, который вы используете в соответствии с вашим приложением Java. Как только вы определите его, вам нужно будет добавить отсутствующие JAR-файлы в ваш путь к классам во время выполнения или файл WAR / EAR веб-приложения.
- Если после нескольких попыток разрешения проблемы все еще не решены, это может означать более сложную проблему иерархии загрузчиков классов. В этом случае, пожалуйста, просмотрите мою серию статей NoClassDefFoundError для большего количества примеров и стратегий разрешения
Я надеюсь, что эта статья помогла вам понять и вернуться к этому распространенному исключению Java.
Пожалуйста, не стесняйтесь оставлять комментарии или вопросы, если вы все еще боретесь с проблемой java.lang.ClassNotFoundException.
This article is intended for Java beginners currently facing java.lang.ClassNotFoundException challenges. It will provide you with an overview of this common Java exception, a sample Java program to support your learning process and resolution strategies.
If you are interested on more advanced class loader related problems, I recommended that you review my article series on java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError since these Java exceptions are closely related.
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: Overview
As per the Oracle documentation, ClassNotFoundException is thrown following the failure of a class loading call, using its string name, as per below:
- The Class.forName method
- The ClassLoader.findSystemClass method
- The ClassLoader.loadClass method
In other words, it means that one particular Java class was
not
found or could
not
be loaded at “runtime” from your application current context class loader.
This problem can be particularly confusing for Java beginners. This is why I always recommend to Java developers to learn and refine their knowledge on Java class loaders. Unless you are involved in dynamic class loading and using the Java Reflection API, chances are that the ClassNotFoundException error you are getting is not from your application code but from a referencing API. Another common problem pattern is a wrong packaging of your application code. We will get back to the resolution strategies at the end of the article.
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: Sample Java program
Now find below a very simple Java program which simulates the 2 most common ClassNotFoundException scenarios via Class.forName() & ClassLoader.loadClass(). Please simply copy/paste and run the program with the IDE of your choice (Eclipse IDE was used for this example).
The Java program allows you to choose between problem scenario #1 or problem scenario #2 as per below. Simply change to 1 or 2 depending of the scenario you want to study.
# Class.forName() private static final int PROBLEM_SCENARIO = 1; # ClassLoader.loadClass() private static final int PROBLEM_SCENARIO = 2;
# ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator
package org.ph.javaee.training5;
/**
* ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator
* @author Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau
*
*/
public class ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator {
private static final String CLASS_TO_LOAD = "org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA";
private static final int PROBLEM_SCENARIO = 1;
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("java.lang.ClassNotFoundException Simulator - Training 5");
System.out.println("Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau");
System.out.println("http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com");
switch(PROBLEM_SCENARIO) {
// Scenario #1 - Class.forName()
case 1:
System.out.println("n** Problem scenario #1: Class.forName() **n");
try {
Class<?> newClass = Class.forName(CLASS_TO_LOAD);
System.out.println("Class "+newClass+" found successfully!");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Class "+CLASS_TO_LOAD+" not found!");
} catch (Throwable any) {
System.out.println("Unexpected error! "+any);
}
break;
// Scenario #2 - ClassLoader.loadClass()
case 2:
System.out.println("n** Problem scenario #2: ClassLoader.loadClass() **n");
try {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
Class<?> callerClass = classLoader.loadClass(CLASS_TO_LOAD);
Object newClassAInstance = callerClass.newInstance();
System.out.println("SUCCESS!: "+newClassAInstance);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Class "+CLASS_TO_LOAD+" not found!");
} catch (Throwable any) {
System.out.println("Unexpected error! "+any);
}
break;
}
System.out.println("nSimulator done!");
}
}
# ClassA
package org.ph.javaee.training5;
/**
* ClassA
* @author Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau
*
*/
public class ClassA {
private final static Class<ClassA> CLAZZ = ClassA.class;
static {
System.out.println("Class loading of "+CLAZZ+" from ClassLoader '"+CLAZZ.getClassLoader()+"' in progress...");
}
public ClassA() {
System.out.println("Creating a new instance of "+ClassA.class.getName()+"...");
doSomething();
}
private void doSomething() {
// Nothing to do...
}
}
f you run the program as is, you will see the output as per below for each scenario:
#Scenario 1 output (baseline)
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException Simulator - Training 5 Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com ** Problem scenario #1: Class.forName() ** Class loading of class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA from ClassLoader 'sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@bfbdb0' in progress... Class class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA found successfully! Simulator done!
#Scenario 2 output (baseline)
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException Simulator - Training 5 Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com ** Problem scenario #2: ClassLoader.loadClass() ** Class loading of class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA from ClassLoader 'sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@2a340e' in progress... Creating a new instance of org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA... SUCCESS!: org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA@6eb38a Simulator done!
For the “baseline” run, the Java program is able to load ClassA successfully.
Now let’s voluntary change the full name of ClassA and re-run the program for each scenario. The following output can be observed:
#ClassA changed to ClassB
private static final String CLASS_TO_LOAD = "org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB";
#Scenario 1 output (problem replication)
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException Simulator - Training 5
Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau
http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com
** Problem scenario #1: Class.forName() **
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:366)
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:355)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:354)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:423)
at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:308)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:356)
at java.lang.Class.forName0(Native Method)
at java.lang.Class.forName(Class.java:186)
at org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator.main(ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator.java:29)
Class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB not found!
Simulator done!
#Scenario 2 output (problem replication)
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException Simulator - Training 5
Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau
http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com
** Problem scenario #2: ClassLoader.loadClass() **
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:366)
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:355)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:354)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:423)
at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:308)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:356)
at org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator.main(ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator.java:51)
Class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB not found!
Simulator done!
What happened? Well since we changed the full class name to org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB, such class was not found at runtime (does not exist), causing both Class.forName() and ClassLoader.loadClass() calls to fail.
You can also replicate this problem by packaging each class of this program to its own JAR file and then omit the jar file containing ClassA.class from the main class path Please try this and see the results for yourself…(hint: NoClassDefFoundError)
Now let’s jump to the resolution strategies.
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: Resolution strategies
Now that you understand this problem, it is now time to resolve it. Resolution can be fairly simple or very complex depending of the root cause.
- Don’t jump on complex root causes too quickly, rule out the simplest causes first.
- First review the java.lang.ClassNotFoundException stack trace as per the above and determine which Java class was not loaded properly at runtime e.g. application code, third party API, Java EE container itself etc.
- Identify the caller e.g. Java class you see from the stack trace just before the Class.forName() or ClassLoader.loadClass() calls. This will help you understand if your application code is at fault vs. a third party API.
- Determine if your application code is not packaged properly e.g. missing JAR file(s) from your classpath
- If the missing Java class is not from your application code, then identify if it belongs to a third party API you are using as per of your Java application. Once you identify it, you will need to add the missing JAR file(s) to your runtime classpath or web application WAR/EAR file.
- If still struggling after multiple resolution attempts, this could means a more complex class loader hierarchy problem. In this case, please review my NoClassDefFoundError article series for more examples and resolution strategies
I hope this article has helped you to understand and revisit this common Java exception.
Please feel free to post any comment or question if you are still struggling with your java.lang.ClassNotFoundException problem.
In this article we’ll see what is java.lang.ClassNotFoundException and how to resolve ClassNotFoundException in Java.
ClassNotFoundException in Java
ClassNotFoundException is a child class of Exception class. Being a descendant of Exception class also makes it a
checked exception
that means it needs to be either caught in a method (with in a try-catch block), or the method needs to specify that exception in a throws clause declaration.
When is ClassNotFoundException thrown
ClassNotFoundException is thrown when a Java application tries to load in a class through its string name but definition for the class with the specified name
could not be found.
Methods that can be used for loading a class through its String name are as following-
- The Class.forName method in class Class.
- The findSystemClass method in class ClassLoader.
- The loadClass method in class ClassLoader.
ClassNotFoundException is thrown at runtime since classloader tries to load the class at runtime using the String name.
Java ClassNotFoundException example
As the name of the exception itself suggests this exception is thrown when the class that has to be loaded is not found. One scenario where you may find this
exception is if you try to load JDBC drivers using Class.forName() but the required jar is not in the classpath.
I have also encountered ClassNotFoundException when upgrading to new version of jar in my system and using some new classes available in that jar but not
upgrading the jar in the Test server or production. With that you get the scenario which is often quoted by the developers “In my system it is working fine”!!!
For example following program tries to load Oracle driver but the required ojdbcxx.jar is not present in the classpath.
public class JDBCCon {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
try {
// Loading driver
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
// Creating connection
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe",
"root", "admin");
// creating Statement
Statement stmt = connection.createStatement();
// Executing Query
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("Select * from Employee");
// Processing Resultset
while(rs.next()){
System.out.println("id : " + rs.getInt("id") + " Name : "
+ rs.getString("name") + " Age : " + rs.getInt("age"));
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(connection != null){
//closing connection
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
Output
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.BuiltinClassLoader.loadClass(BuiltinClassLoader.java:583) at java.base/jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoaders.java:178) at java.base/java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:521) at java.base/java.lang.Class.forName0(Native Method) at java.base/java.lang.Class.forName(Class.java:332) at org.netjs.prgrm.JDBCCon.main(JDBCCon.java:16)
As evident from the exception stack trace OracleDriver is not found so the ClassNotFoundException is thrown.
Resolving ClassNotFoundException in Java
As seen in the above example it is easy to see from the error log or exception stacktrace which class is causing the exception. Then you need to check whether
the required jar (where the class resides) is present in the classpath or not.
If jar is there then ensure that you have the correct version and the class you are trying to load is part of that jar version.
If you are packaging your application and putting that jar or war in a server or another system to run make sure that all the classes are packaged properly and
there are no omissions.
If class is there in the classpath then do ensure that there is no classpath change as part of some startup script.
That’s all for this topic java.lang.ClassNotFoundException — Resolving ClassNotFoundException in Java. If you have any doubt or any suggestions to make please drop a comment. Thanks!
Related Topics
- java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError — Resolving UnsupportedClassVersionError in Java
- Difference Between throw And throws in Java
- Multi-Catch Statement in Java Exception Handling
- Try-With-Resources in Java With Examples
- Java Exception Handling Interview Questions And Answers
You may also like-
- intern() Method in Java String
- Private Methods in Java Interface
- Java Program to Convert a File to Byte Array
- Batch Processing in Java JDBC — Insert, Update Queries as a Batch
- ConcurrentSkipListMap in Java
- Spring MVC Example With @PathVariable — Creating Dynamic URL
- Spring Web Reactive — Spring WebFlux Example Using Annotation-Based Programming
- Python Installation on Windows
This article is intended for Java beginners currently facing java.lang.ClassNotFoundException challenges. It will provide you with an overview of this common Java exception, a sample Java program to support your learning process and resolution strategies.
If you are interested on more advanced class loader related problems, I recommended that you review my article series on java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError since these Java exceptions are closely related.
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: Overview
As per the Oracle documentation, ClassNotFoundException is thrown following the failure of a class loading call, using its string name, as per below:
- The Class.forName method
- The ClassLoader.findSystemClass method
- The ClassLoader.loadClass method
In other words, it means that one particular Java class was not found or could not be loaded at “runtime” from your application current context class loader.
This problem can be particularly confusing for Java beginners. This is why I always recommend to Java developers to learn and refine their knowledge on Java class loaders. Unless you are involved in dynamic class loading and using the Java Reflection API, chances are that the ClassNotFoundException error you are getting is not from your application code but from a referencing API. Another common problem pattern is a wrong packaging of your application code. We will get back to the resolution strategies at the end of the article.
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException : Sample Java program
Now find below a very simple Java program which simulates the 2 most common ClassNotFoundException scenarios via Class.forName() & ClassLoader.loadClass(). Please simply copy/paste and run the program with the IDE of your choice (Eclipse IDE was used for this example).
The Java program allows you to choose between problem scenario #1 or problem scenario #2 as per below. Simply change to 1 or 2 depending of the scenario you want to study.
# Class.forName()
private static final int PROBLEM_SCENARIO = 1;
# ClassLoader.loadClass()
private static final int PROBLEM_SCENARIO = 2;
# ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator
package org.ph.javaee.training5;
/**
* ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator
* @author Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau
*
*/
public class ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator {
private static final String CLASS_TO_LOAD = "org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA";
private static final int PROBLEM_SCENARIO = 1;
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("java.lang.ClassNotFoundException Simulator - Training 5");
System.out.println("Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau");
System.out.println("http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com");
switch(PROBLEM_SCENARIO) {
// Scenario #1 - Class.forName()
case 1:
System.out.println("n** Problem scenario #1: Class.forName() **n");
try {
Class<?> newClass = Class.forName(CLASS_TO_LOAD);
System.out.println("Class "+newClass+" found successfully!");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Class "+CLASS_TO_LOAD+" not found!");
} catch (Throwable any) {
System.out.println("Unexpected error! "+any);
}
break;
// Scenario #2 - ClassLoader.loadClass()
case 2:
System.out.println("n** Problem scenario #2: ClassLoader.loadClass() **n");
try {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
Class<?> callerClass = classLoader.loadClass(CLASS_TO_LOAD);
Object newClassAInstance = callerClass.newInstance();
System.out.println("SUCCESS!: "+newClassAInstance);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Class "+CLASS_TO_LOAD+" not found!");
} catch (Throwable any) {
System.out.println("Unexpected error! "+any);
}
break;
}
System.out.println("nSimulator done!");
}
}
# ClassA
package org.ph.javaee.training5;
/**
* ClassA
* @author Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau
*
*/
public class ClassA {
private final static Class<ClassA> CLAZZ = ClassA.class;
static {
System.out.println("Class loading of "+CLAZZ+" from ClassLoader '"+CLAZZ.getClassLoader()+"' in progress...");
}
public ClassA() {
System.out.println("Creating a new instance of "+ClassA.class.getName()+"...");
doSomething();
}
private void doSomething() {
// Nothing to do...
}
}
If you run the program as is, you will see the output as per below for each scenario:
#Scenario 1 output (baseline)
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
Simulator – Training 5
Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau
http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com
** Problem scenario #1: Class.forName() **
Class loading of class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA from ClassLoader ‘sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@bfbdb0’ in progress…
Class class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA found successfully!
Simulator done!
#Scenario 2 output (baseline)
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
Simulator – Training 5
Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau
http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com
** Problem scenario #2: ClassLoader.loadClass() **
Class loading of class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA from ClassLoader ‘sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@2a340e’ in progress…
Creating a new instance of org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA…
SUCCESS!: org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassA@6eb38a
Simulator done!
For the “baseline” run, the Java program is able to load
ClassA
successfully.
Now let’s voluntary change the full name of
ClassA
and re-run the program for each scenario. The following output can be observed:
#ClassA changed to ClassB
private static final String CLASS_TO_LOAD = "org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB";
#Scenario 1 output (problem replication)
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
Simulator – Training 5
Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau
http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com
** Problem scenario #1: Class.forName() **
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
: org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(
URLClassLoader.java:366
)
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(
URLClassLoader.java:355
)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
Native Method
)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(
URLClassLoader.java:354
)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(
ClassLoader.java:423
)
at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(
Launcher.java:308
)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(
ClassLoader.java:356
)
at java.lang.Class.forName0(
Native Method
)
at java.lang.Class.forName(
Class.java:186
)
at org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator.main(
ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator.java:29
)
Class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB not found!
Simulator done!
#Scenario 2 output (problem replication)
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
Simulator – Training 5
Author: Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau
http://javaeesupportpatterns.blogspot.com
** Problem scenario #2: ClassLoader.loadClass() **
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
: org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(
URLClassLoader.java:366
)
at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(
URLClassLoader.java:355
)
at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(
Native Method
)
at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(
URLClassLoader.java:354
)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(
ClassLoader.java:423
)
at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(
Launcher.java:308
)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(
ClassLoader.java:356
)
at org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator.main(
ClassNotFoundExceptionSimulator.java:51
)
Class org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB not found!
Simulator done!
What happened? Well since we changed the full class name to org.ph.javaee.training5.ClassB, such class was not found at runtime (does not exist), causing both Class.forName() and ClassLoader.loadClass() calls to fail.
You can also replicate this problem by packaging each class of this program to its own JAR file and then omit the jar file containing ClassA.class from the main class path Please try this and see the results for yourself…(hint: NoClassDefFoundError)
Now let’s jump to the resolution strategies.
java.lang.ClassNotFoundException
: Resolution strategies
Now that you understand this problem, it is now time to resolve it. Resolution can be fairly simple or very complex depending of the root cause.
- Don’t jump on complex root causes too quickly, rule out the simplest causes first.
- First review the java.lang.ClassNotFoundException stack trace as per the above and determine which Java class was not loaded properly at runtime e.g. application code, third party API, Java EE container itself etc.
- Identify the caller e.g. Java class you see from the stack trace just before the Class.forName() or ClassLoader.loadClass() calls. This will help you understand if your application code is at fault vs. a third party API.
- Determine if your application code is not packaged properly e.g. missing JAR file(s) from your classpath
- If the missing Java class is not from your application code, then identify if it belongs to a third party API you are using as per of your Java application. Once you identify it, you will need to add the missing JAR file(s) to your runtime classpath or web application WAR/EAR file.
- If still struggling after multiple resolution attempts, this could means a more complex class loader hierarchy problem. In this case, please review my NoClassDefFoundError article series for more examples and resolution strategies
I hope this article has helped you to understand and revisit this common Java exception.
Please feel free to post any comment or question if you are still struggling with your java.lang.ClassNotFoundException problem.
Reference: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: How to resolve from our JCG partner Pierre-Hugues Charbonneau at the Java EE Support Patterns & Java Tutorial blog.