Introduction to JavaFX Alert
In JavaFX, an Alert box is used to alert the user about further process. JavaFX Alert class is a subclass of Dialog class. Alert box in javafx alert the user about information, error messages, confirmation messages and warning messages to let know them the user about what exact dialog popup is about.
There are different ways to alert the user about what happening next. In that, there are 5 Alert types to alert the user.
Types of Alert Box in JavaFX
Below are the points which explain the types of alert box in javaFX:
- None Alert: The None alert types do not set to any default properties.
- Information Alert: The Information alert type informs the user about content information or suggests the user about what is going on in the next process.
- Error Alert: The Error alert type is showing the user about where things went wrong or what is the error with the functionality.
- Confirmation Alert: The Confirmation alert type is asking the user about permission to move further. We have two options available, Yes or If we click Yes means we have granted them permission to move next step of If we click No, then do not move to the next step.
- Warning Alert: The Warning alert type warns the user about some fact or action. The warning does not disturb the further process as like Error.
Methods and Constructors in Alert Box
Below we can see the methods and constructor of alert box:
Methods
- getAlertType(): Gives alert type.
- setAlertType(Alert.AlertType): Setting the alert type.
- getButtonTypes(): Get button type from the Observable list.
- setContentText(String s): Setting the content or text to alert the user about what is the dialog box.
- getContentText(): Gives the content text which we have set.
Constructors
- Alert(Alert.AlertType alertType): Create a new Alert object with an alert type parameter.
- Alert(Alert.AlertType alertType, String string, ButtonType… buttonType): Create new Alert object with alert type, String and Button type parameters.
How does Alert Box work in JavaFX?
Alert box in JavaFX mainly works on the value of alert type which is provided by Alert(AlertType.VALUE) constructor. Accessing JavaFX features user-defined class must extend Application
1.NONE Alert
Alert alertType=new Alert(AlertType.NONE);2. INFORMATION Alert
Alert alertType=new Alert(AlertType.INFORMATION);3. ERROR Alert
Alert alertType=new Alert(AlertType.ERROR);4. CONFIRMATION Alert
Alert alertType=new Alert(AlertType.INFORMATION);5. WARNING Alert
Alert alertType=new Alert(AlertType.WARNING);How to Create Alert Box in Java FX?
Steps to Create Alert Boxes:
Step 1: Create an Alert type
Alert alertType=new Alert(AlertType.TYPE);Step 2: Create a Pane or any other component.
TilePane tilePane=new TilePane ();Step 3: Creating a scene means screen to display output.
Scene screen = new Scene(tilePane, length, width);Step 4: Adding Scene reference screen to the Stage:
stage.setScene(screen);Step 5: showing stage reference with the show () method.
stage.show();Note: 2,3,4 and 5 steps are optional if we want any action classes with alert boxes then use 2,3,4 and 5 steps.
Examples of JavaFX Alert
Below are the examples of JavaFX Alert:
1. Information Alert
Code:
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.control.Alert;
import javafx.scene.control.Alert.AlertType;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class InformtionAlertType extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage outputStage) throws Exception {
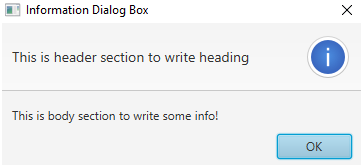
Alert alert = new Alert(AlertType.INFORMATION);// line 1
alert.setTitle("Information Dialog Box");// line 2
alert.setHeaderText("This is header section to write heading");// line 3
alert.setContentText("This is body section to write some info!");// line 4
alert.showAndWait(); // line 5
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args); // line 0
}
}Output:
Explanation to the above program: In the above code line 0 calls start method from internal JVM. Line 1 creates an information alert type. Line 2 sets the title to a dialog box. Line 3 sets the header text. Line 4 sets the body text of the dialog box. Line 5 shows the dialog box output. As you can see in the output information dialog box has a predefined image on the right end.
2. Error Alert
Code:
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.control.Alert;
import javafx.scene.control.Alert.AlertType;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class ErrorAlertType extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage outputStage) throws Exception {
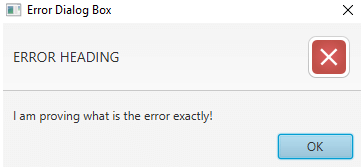
Alert alert = new Alert(AlertType.ERROR);// line 1
alert.setTitle("Error Dialog Box");// line 2
alert.setHeaderText("ERROR HEADING");// line 3
alert.setContentText("I am proving what is the error exactly!");// line 4
alert.showAndWait(); // line 5
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args); // line 0
}
}Output:
Explanation to the above program: In the above code line 0 calls start method from internal JVM. Line 1 creates an error alert type. Line 2 sets the title to the dialog box. Line 3 sets the header text. Line 4 sets the body text of the dialog box. Line 5 shows the dialog box output. As you can see in the output information dialog box has a predefined image on the right end.
3. Confirmation Alert
Code:
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.control.Alert;
import javafx.scene.control.Alert.AlertType;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class ConfirmationAlertType extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage outputStage) throws Exception {
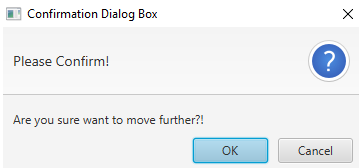
Alert alert = new Alert(AlertType.CONFIRMATION);// line 1
alert.setTitle("Confirmation Dialog Box");// line 2
alert.setHeaderText("Please Confirm!");// line 3
alert.setContentText("Are you sure want to move further?!");// line 4
alert.showAndWait(); // line 5
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args); // line 0
}
}Output:
Explanation to the above program: In the above code line 0 calls start method from internal JVM. Line 1 creates a confirmation alert type. Line 2 sets the title to the dialog box. Line 3 sets the header text. Line 4 sets the body text of the dialog box. Line 5 shows the dialog box output. As you can see in the output information dialog box has a predefined image on the right end.
4. Warning Alert
Code:
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.control.Alert;
import javafx.scene.control.Alert.AlertType;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class WarningAlertType extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage outputStage) throws Exception {
Alert alert = new Alert(AlertType.WARNING);// line 1
alert.setTitle("Warning Dialog Box");// line 2
alert.setHeaderText("Warning!");// line 3
alert.setContentText("Some packages may be installed additionally!");// line 4
alert.showAndWait(); // line 5
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args); // line 0
}
}Output:
Explanation to the above program: In the above code line 0 calls start method from internal JVM. Line 1 creates a warning alert type. Line 2 sets the title to the dialog box. Line 3 sets the header text. Line 4 sets the body text of the dialog box. Line 5 shows the dialog box output. As you can see in the output information dialog box has a predefined image on the right end.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to JavaFX Alert. Here we discuss Syntax, methods, and constructors, with how to create and different examples of JavaFX Alert. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –
- JavaFX Libraries
- JavaFX VBox
- JavaFX FileChooser
- JavaFX TextField

Today’s tutorial demonstrates creating a JavaFX message box in our Java application. The message box can be a confirmation, warning, information, or error alert.
Create JavaFX Message Box
To accomplish the following example code, we use Java version 18, JavaFX version 13 and Netbeans IDE version 13.
Example Code:
//write your package name
package com.mycompany.javafx_messagebox;
//import required libraries
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.event.ActionEvent;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Alert;
import javafx.scene.control.Alert.AlertType;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.layout.TilePane;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
/**
* JavaFX App
*/
public class App extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
// create a tile pane
TilePane r = new TilePane();
//add padding
r.setPadding(new Insets(10, 10, 10, 10));
// an array of button names
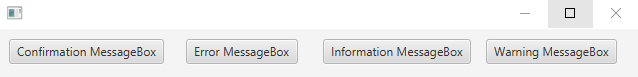
String[] buttonNames = {"Confirmation MessageBox",
"Error MessageBox",
"Information MessageBox",
"Warning MessageBox"};
//Show no alert at the startup of the program
Alert alert = new Alert(AlertType.NONE);
/*
a loop to create buttons, define actions when
they are pressed and add them to the tile pane
*/
for (String s : buttonNames) {
Button button = new Button(s);
button.setOnAction((ActionEvent event) -> {
if (null != button.getText()) {
switch (button.getText()) {
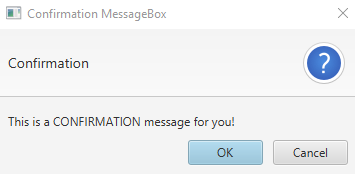
case "Confirmation MessageBox":
// set alert type, title, content text and then show it
alert.setAlertType(AlertType.CONFIRMATION);
alert.setTitle("Confirmation MessageBox");
alert.setContentText("This is a CONFIRMATION "+
"message for you!");
alert.show();
break;
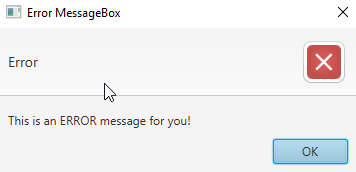
case "Error MessageBox":
// set alert type, title, content text and then show it
alert.setAlertType(AlertType.ERROR);
alert.setTitle("Error MessageBox");
alert.setContentText("This is an ERROR message for you!");
alert.show();
break;
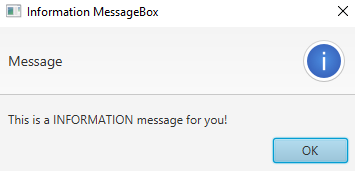
case "Information MessageBox":
// set alert type, title, content text and then show it
alert.setAlertType(AlertType.INFORMATION);
alert.setTitle("Information MessageBox");
alert.setContentText("This is a INFORMATION "+
"message for you!");
alert.show();
break;
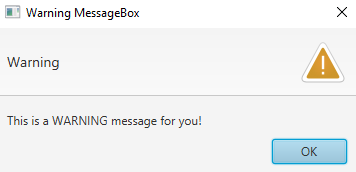
case "Warning MessageBox":
// set alert type, title, content text and then show it
alert.setAlertType(AlertType.WARNING);
alert.setTitle("Warning MessageBox");
alert.setContentText("This is a WARNING message for you!");
alert.show();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
});
//add button
r.getChildren().add(button);
}
// create a scene
Scene sc = new Scene(r, 640, 50);
// set the scene
stage.setScene(sc);
//show the stage
stage.show();
}//end start method
//main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}//end main
}//end App class
Output (main window):
Output (confirmation message box, displayed when we click on Confirmation MessageBox button):
Output (error message box, displayed when we click on Error MessageBox button):
Output (information message box, displayed when we click on Information MessageBox button):
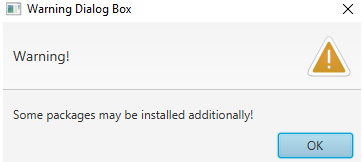
OUTPUT (warning message box, displayed when we click on the Warning MessageBox button):
For this tutorial, we don’t need to make any changes to the module-info.java and pom.xml files. Create a JavaFX project and practice the code given above.
We have a main class named App that extends the Application class (which is standard in Java). You can name the primary launch class (App).
Next, we override the start() method because the App is the child class of the Application class. Remember that the child class needs to implement all abstract functions/methods of the parent class.
After that, we have a start() method that takes one parameter of the Stage type. We are using the Stage type parameter because this is where all visual components JavaFX application will be displayed.
We do not need to create the Stage type object because the JavaFX runtime creates it. The following is the step-by-step explanation of what’s inside the start() method.
-
Create an object of JavaFX
TilePane, which is a layout component and lays out all its child components in the grid of same-sized cells. -
Add margins around the whole grid (
top/right/bottom/left). -
Create an array with the names of all buttons we need for this application.
-
Create an alert message box of type
NONEbecause we do not want to display any message box at the program’s startup. -
Next, we have a
forloop, which iterates over all the button names.- Inside the loop, we create a button of the current name.
- Set an action for that specific button based on the condition. We get the button text and display a message box based on the button name using the
switchstatement.
-
Add the button to the
TilePane. -
Create a scene using the
Sceneclass. -
Set the scene.
-
Finally, show the stage.
Now, it is the main method’s turn. We can launch the JavaFX application without having the main method, but it is useful when we are required to use parameters that are passed to the application using the command line.
- java.lang.Object
-
- java.lang.Enum<Alert.AlertType>
-
- javafx.scene.control.Alert.AlertType
-
- All Implemented Interfaces:
Serializable,Comparable<Alert.AlertType>
- Enclosing class:
- Alert
public static enum Alert.AlertType extends Enum<Alert.AlertType>An enumeration containing the available, pre-built alert types that
theAlertclass can use to pre-populate various properties.- Since:
- JavaFX 8u40
-
-
Enum Constant Summary
Enum Constants
Enum Constant Description CONFIRMATIONThe CONFIRMATION alert type configures the Alert dialog to appear in a
way that suggests the content of the dialog is seeking confirmation from
the user.ERRORThe ERROR alert type configures the Alert dialog to appear in a
way that suggests that something has gone wrong.INFORMATIONThe INFORMATION alert type configures the Alert dialog to appear in a
way that suggests the content of the dialog is informing the user of
a piece of information.NONEThe NONE alert type has the effect of not setting any default properties
in the Alert.WARNINGThe WARNING alert type configures the Alert dialog to appear in a
way that suggests the content of the dialog is warning the user about
some fact or action.
-
Method Summary
All Methods Static Methods Concrete Methods
Modifier and Type Method Description static Alert.AlertTypevalueOf(String name)Returns the enum constant of this type with the specified name.
static Alert.AlertType[]values()Returns an array containing the constants of this enum type, in
the order they are declared.-
Methods inherited from class java.lang.Enum
clone, compareTo, equals, finalize, getDeclaringClass, hashCode, name, ordinal, toString, valueOf
-
Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object
getClass, notify, notifyAll, wait, wait, wait
-
-
-
-
Enum Constant Detail
-
NONE
public static final Alert.AlertType NONE
The NONE alert type has the effect of not setting any default properties
in the Alert.
-
INFORMATION
public static final Alert.AlertType INFORMATION
The INFORMATION alert type configures the Alert dialog to appear in a
way that suggests the content of the dialog is informing the user of
a piece of information. This includes an ‘information’ image, an
appropriate title and header, and just an OK button for the user to
click on to dismiss the dialog.
-
WARNING
public static final Alert.AlertType WARNING
The WARNING alert type configures the Alert dialog to appear in a
way that suggests the content of the dialog is warning the user about
some fact or action. This includes a ‘warning’ image, an
appropriate title and header, and just an OK button for the user to
click on to dismiss the dialog.
-
CONFIRMATION
public static final Alert.AlertType CONFIRMATION
The CONFIRMATION alert type configures the Alert dialog to appear in a
way that suggests the content of the dialog is seeking confirmation from
the user. This includes a ‘confirmation’ image, an
appropriate title and header, and both OK and Cancel buttons for the
user to click on to dismiss the dialog.
-
ERROR
public static final Alert.AlertType ERROR
The ERROR alert type configures the Alert dialog to appear in a
way that suggests that something has gone wrong. This includes an
‘error’ image, an appropriate title and header, and just an OK button
for the user to click on to dismiss the dialog.
-
-
Method Detail
-
values
public static Alert.AlertType[] values()
Returns an array containing the constants of this enum type, in
the order they are declared. This method may be used to iterate
over the constants as follows:for (Alert.AlertType c : Alert.AlertType.values()) System.out.println(c);
- Returns:
- an array containing the constants of this enum type, in the order they are declared
-
valueOf
public static Alert.AlertType valueOf(String name)
Returns the enum constant of this type with the specified name.
The string must match exactly an identifier used to declare an
enum constant in this type. (Extraneous whitespace characters are
not permitted.)- Parameters:
name— the name of the enum constant to be returned.- Returns:
- the enum constant with the specified name
- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException— if this enum type has no constant with the specified nameNullPointerException— if the argument is null
-
-
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.layout.*;
import javafx.event.ActionEvent;
import javafx.event.EventHandler;
import javafx.scene.control.*;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.control.Alert.AlertType;
public class Alert_2 extends Application {
public void start(Stage s)
{
s.setTitle("creating alerts");
Button b = new Button("Confirmation alert");
Button b1 = new Button("error alert");
Button b2 = new Button("Information alert");
Button b3 = new Button("Warning alert");
Button b4 = new Button("none alert");
TilePane r = new TilePane();
Alert a = new Alert(AlertType.NONE);
EventHandler<ActionEvent> event = new
EventHandler<ActionEvent>() {
public void handle(ActionEvent e)
{
a.setAlertType(AlertType.CONFIRMATION);
a.setContentText("ConfirmationDialog");
a.show();
}
};
EventHandler<ActionEvent> event1 = new
EventHandler<ActionEvent>() {
public void handle(ActionEvent e)
{
a.setAlertType(AlertType.ERROR);
a.setContentText("error Dialog");
a.show();
}
};
EventHandler<ActionEvent> event2 = new
EventHandler<ActionEvent>() {
public void handle(ActionEvent e)
{
a.setAlertType(AlertType.INFORMATION);
a.setContentText("Information Dialog");
a.show();
}
};
EventHandler<ActionEvent> event3 = new
EventHandler<ActionEvent>() {
public void handle(ActionEvent e)
{
a.setAlertType(AlertType.WARNING);
a.setContentText("Warning Dialog");
a.show();
}
};
EventHandler<ActionEvent> event4 = new
EventHandler<ActionEvent>() {
public void handle(ActionEvent e)
{
Alert a1 = new Alert(AlertType.NONE,
"default Dialog",ButtonType.APPLY);
a1.show();
}
};
b.setOnAction(event);
b1.setOnAction(event1);
b2.setOnAction(event2);
b3.setOnAction(event3);
b4.setOnAction(event4);
r.getChildren().add(b);
r.getChildren().add(b1);
r.getChildren().add(b2);
r.getChildren().add(b3);
r.getChildren().add(b4);
Scene sc = new Scene(r, 200, 200);
s.setScene(sc);
s.show();
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
launch(args);
}
}
JavaFX Alert Dialogs Tutorial
In this blog tutorial, you will learn to use the JavaFX alert dialogs. Alert is a subclass of the Dialog class. JavaFX alert dialog is used to show some information to the user.
Types of Alert dialogs in JavaFX
-
Confirmation – This type of alert is used to confirm from the user in a way that suggests the content of the dialog is seeking confirmation from the user. This includes confirmation of both the Ok and Cancel buttons.
-
Warning – This type of alert is used to show a warning alert to inform the user about some fact of action.
-
None – This is a type of alert that has the effect of not setting any default properties in the Alert.
-
Information – This type of alert is used to show a piece of information.
-
Error – This type of alert is used to show a piece of information that has gone wrong.
Source code to show alert dialog in JavaFX
Confirmation Alert
Alert alert = new Alert(Alert.AlertType.CONFIRMATION);
alert.setTitle("Confirmation alert Dialog");
alert.setContentText("Please confirm");
alert.setHeaderText("Confirmation");
alert.showAndWait();
Output
Warning Alert
Alert alert = new Alert(Alert.AlertType.WARNING);
alert.setTitle("Warning Dialog");
alert.setContentText("This is a warning alert!");
alert.setHeaderText("Warning alert");
alert.showAndWait();
Output
None Alert type
Alert alert = new Alert(Alert.AlertType.NONE);
alert.setTitle("None Alert type");
alert.setContentText("This is a none type alert!");
alert.setHeaderText(null);
alert.getDialogPane().getButtonTypes().add(ButtonType.CLOSE);
alert.showAndWait();
Output
Information Alert
Alert alert = new Alert(Alert.AlertType.INFORMATION);
alert.setTitle("Information Dialog");
alert.setContentText("This is an information alert!");
alert.setHeaderText("Information alert");
alert.showAndWait();
Output
Error Alert
Alert alert = new Alert(Alert.AlertType.ERROR);
alert.setTitle("Error Dialog");
alert.setContentText("This is an error alert!");
alert.setHeaderText("Error alert");
alert.showAndWait();
Output
YouTube Video
JavaFX Tutorial: Java Alert Box