validate( [options ] )Returns: Validator
Description: Validates the selected form.
-
validate( [options ] )
-
options
-
debug (default:
false)Enables debug mode. If true, the form is not submitted and certain errors are displayed on the console (will check if a
window.consoleproperty exists). Try to enable when a form is just submitted instead of validation stopping the submit.Example: Prevents the form from submitting and tries to help setting up the validation with warnings about missing methods and other debug messages.
-
submitHandler (default:
native form submit)Callback for handling the actual submit when the form is valid. Gets the form and the submit event as the only arguments. Replaces the default submit. The right place to submit a form via Ajax after it is validated.
Example: Submits the form via Ajax, using jQuery Form plugin, when valid.
1
2
3
4
5
submitHandler: function(form) {Example: Use submitHandler to process something and then using the default submit. Note that «form» refers to a DOM element, this way the validation isn’t triggered again.
1
2
3
4
5
6
submitHandler: function(form) {// do other things for a valid formThe callback gets passed two arguments:
-
form
The form currently being validated, as a DOMElement.
-
event
The submit event instance.
-
-
invalidHandler
Callback for custom code when an invalid form is submitted. Called with an event object as the first argument, and the validator as the second.
Example: Displays a message above the form, indicating how many fields are invalid when the user tries to submit an invalid form.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
invalidHandler: function(event, validator) {// 'this' refers to the formvar errors = validator.numberOfInvalids();var message = errors == 1? 'You missed 1 field. It has been highlighted': 'You missed ' + errors + ' fields. They have been highlighted';$("div.error span").html(message);The callback gets passed two arguments:
-
event
A custom event object, since this function is bound as an event handler.
-
validator
The validator instance for the current form.
-
-
ignore (default:
":hidden")Elements to ignore when validating, simply filtering them out. jQuery’s not-method is used, therefore everything that is accepted by not() can be passed as this option. Inputs of type submit and reset are always ignored, so are disabled elements.
Example: Ignores all elements with the class «ignore» when validating.
-
rules (default:
rules are read from markup (classes, attributes, data))Key/value pairs defining custom rules. Key is the name of an element (or a group of checkboxes/radio buttons), value is an object consisting of rule/parameter pairs or a plain String. Can be combined with class/attribute/data rules. Each rule can be specified as having a depends-property to apply the rule only in certain conditions. See the second example below for details.
Example: Specifies a name element as required and an email element as required (using the shortcut for a single rule) and a valid email address (using another object literal).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
// simple rule, converted to {required:true}Example: Specifies a contact element as required and as email address, the latter depending on a checkbox being checked for contact via email.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
depends: function(element) {return $("#contactform_email").is(":checked");Example: Configure a rule that requires a parameter, along with a
dependscallback.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
// at least 15€ when bonus material is included// min needs a parameter passed to itdepends: function(element) {return $("#bonus-material").is(":checked"); -
messages (default:
the default message for the method used)Key/value pairs defining custom messages. Key is the name of an element, value the message to display for that element. Instead of a plain message, another map with specific messages for each rule can be used. Overrides the title attribute of an element or the default message for the method (in that order). Each message can be a String or a Callback. The callback is called in the scope of the validator, with the rule’s parameters as the first argument and the element as the second, and must return a String to display as the message.
Example: Specifies a name element as required and an email element as required and a valid email address. A single message is specified for the name element, and two messages for email.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
name: "Please specify your name",required: "We need your email address to contact you",Example: Validates the name-field as required and having at least two characters. Provides a callback message using jQuery.validator.format to avoid having to specify the parameter in two places.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
required: "We need your email address to contact you",minlength: jQuery.validator.format("At least {0} characters required!") -
groups
Specify grouping of error messages. A group consists of an arbitrary group name as the key and a space separated list of element names as the value. Use errorPlacement to control where the group message is placed.
Example: Use a table layout for the form, placing error messags in the next cell after the input.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
errorPlacement: function(error, element) {if (element.attr("name") == "fname" || element.attr("name") == "lname" ) {error.insertAfter("#lastname");error.insertAfter(element); -
normalizer
Prepares/transforms the elements value for validation.
See normalizer docs for more details. -
onsubmit (default:
true)Validate the form on submit. Set to false to use only other events for validation.
Example: Disables onsubmit validation, allowing the user to submit whatever he wants, while still validating on keyup/blur/click events (if not specified otherwise).
-
onfocusout
Validate elements (except checkboxes/radio buttons) on blur. If nothing is entered, all rules are skipped, except when the field was already marked as invalid.
Set to a Function to decide for yourself when to run validation.
A boolean true is not a valid value.
Example: Disables focusout validation.
The callback gets passed two arguments:
-
element
The element currently being validated, as a DOMElement.
-
event
The event object for this focusout event.
-
-
onkeyup
Validate elements on keyup. As long as the field is not marked as invalid, nothing happens. Otherwise, all rules are checked on each key up event. Set to false to disable.
Set to a Function to decide for yourself when to run validation.
A boolean true is not a valid value.
Example: Disables onkeyup validation.
The callback gets passed two arguments:
-
element
The element currently being validated, as a DOMElement.
-
event
The event object for this keyup event.
-
-
onclick
Validate checkboxes, radio buttons, and select elements on click. Set to false to disable.
Set to a Function to decide for yourself when to run validation.
A boolean true is not a valid value.
Example: Disables onclick validation of checkboxes, radio buttons, and select elements.
The callback gets passed two arguments:
-
element
The element currently being validated, as a DOMElement.
-
event
The event object for this click event.
-
-
focusInvalid (default:
true)Focus the last active or first invalid element on submit via validator.focusInvalid(). The last active element is the one that had focus when the form was submitted, avoiding stealing its focus. If there was no element focused, the first one in the form gets it, unless this option is turned off.
Example: Disables focusing of invalid elements.
-
focusCleanup (default:
false)If enabled, removes the errorClass from the invalid elements and hides all error messages whenever the element is focused. Avoid combination with focusInvalid.
Example: Enables cleanup when focusing elements, removing the error class and hiding error messages when an element is focused.
-
errorClass (default:
"error")Use this class to create error labels, to look for existing error labels and to add it to invalid elements.
Example: Sets the error class to «invalid».
-
validClass (default:
"valid")This class is added to an element after it was validated and considered valid.
Example: Sets the valid class to «success».
-
errorElement (default:
"label")Use this element type to create error messages and to look for existing error messages. The default, «label», has the advantage of creating a meaningful link between error message and invalid field using the for attribute (which is always used, regardless of element type).
Example: Sets the error element to «em».
-
wrapper (default:
window)Wrap error labels with the specified element. Useful in combination with errorLabelContainer to create a list of error messages.
Example: Wrap each error element with a list item, useful when using an ordered or unordered list as the error container.
-
errorLabelContainer
Hide and show this container when validating.
Example: All error labels are displayed inside an unordered list with the ID «messageBox», as specified by the selector passed as errorContainer option. All error elements are wrapped inside a li element, to create a list of messages.
1
2
3
4
5
errorLabelContainer: "#messageBox",submitHandler: function() { alert("Submitted!") } -
errorContainer
Hide and show this container when validating.
Example: Uses an additonal container for error messages. The elements given as the errorContainer are all shown and hidden when errors occur. However, the error labels themselves are added to the element(s) given as errorLabelContainer, here an unordered list. Therefore the error labels are also wrapped into li elements (wrapper option).
1
2
3
4
5
6
errorContainer: "#messageBox1, #messageBox2",errorLabelContainer: "#messageBox1 ul",wrapper: "li", debug:true,submitHandler: function() { alert("Submitted!") } -
showErrors
A custom message display handler. Gets the map of errors as the first argument and an array of errors as the second, called in the context of the validator object. The arguments contain only those elements currently validated, which can be a single element when doing validation on focusout or keyup. You can trigger (in addition to your own messages) the default behaviour by calling this.defaultShowErrors().
Example: Update the number of invalid elements each time an error is displayed. Delegates to the default implementation for the actual error display.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
showErrors: function(errorMap, errorList) {$("#summary").html("Your form contains "+ this.numberOfInvalids()+ " errors, see details below.");this.defaultShowErrors();The callback gets passed two arguments:
-
errorMap
Key/value pairs, where the key refers to the name of an input field, values the message to be displayed for that input.
-
errorList
An array for all currently validated elements. Contains objects with the following two properties:
-
message
The message to be displayed for an input.
-
element
The DOMElement for this entry.
-
-
-
errorPlacement (default:
Places the error label after the invalid element)Customize placement of created error labels. First argument: The created error label as a jQuery object. Second argument: The invalid element as a jQuery object.
Example: Use a table layout for the form, placing error messages in the next cell after the input.
1
2
3
4
5
errorPlacement: function(error, element) {error.appendTo( element.parent("td").next("td") );The callback gets passed two arguments:
-
error
The error label to insert into the DOM.
-
element
The validated input, for relative positioning.
-
-
success
If specified, the error label is displayed to show a valid element. If a String is given, it is added as a class to the label. If a Function is given, it is called with the label (as a jQuery object) and the validated input (as a DOM element). The label can be used to add a text like «ok!».
Example: Add a class «valid» to valid elements, styled via CSS.
1
2
3
4
submitHandler: function() { alert("Submitted!") }Example: Add a class «valid» to valid elements, styled via CSS, and add the text «Ok!».
1
2
3
4
5
6
success: function(label) {label.addClass("valid").text("Ok!")submitHandler: function() { alert("Submitted!") }The callback gets passed two arguments:
-
label
The error label. Use to add a class or replace the text content.
-
element
The element currently being validated, as a DOMElement.
-
-
highlight (default:
Adds errorClass (see the option) to the element)How to highlight invalid fields. Override to decide which fields and how to highlight.
Example: Highlights an invalid element by fading it out and in again.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
highlight: function(element, errorClass) {$(element).fadeOut(function() {Example: Adds the error class to both the invalid element and its label
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
highlight: function(element, errorClass, validClass) {$(element).addClass(errorClass).removeClass(validClass);$(element.form).find("label[for=" + element.id + "]")unhighlight: function(element, errorClass, validClass) {$(element).removeClass(errorClass).addClass(validClass);$(element.form).find("label[for=" + element.id + "]").removeClass(errorClass);The callback gets passed three arguments:
-
element
The invalid DOM element, usually an
input. -
errorClass
Current value of the
errorClassoption. -
validClass
Current value of the
validClassoption.
-
-
unhighlight (default:
Removes the errorClass)Called to revert changes made by option highlight, same arguments as highlight.
-
ignoreTitle (default:
false)Set to skip reading messages from the title attribute, helps to avoid issues with Google Toolbar; default is false for compability, the message-from-title is likely to be completely removed in a future release.
Example: Configure the plugin to ignore title attributes on validated elements when looking for messages.
-
-
This method sets up event handlers for submit, focus, keyup, blur and click to trigger validation of the entire form or individual elements. Each one can be disabled, see the onxxx options (onsubmit, onfocusout, onkeyup, onclick). focusInvalid focuses elements when submitting an invalid form.
Use the debug option to ease setting up validation rules, it always prevents the default submit, even when script errors occur.
Use submitHandler to implement your own form submit, eg. via Ajax. Use invalidHandler to react when an invalid form is submitted.
Use rules and messages to specify which elements to validate, and how. See rules() for more details about specifying validation rules.
Use errorClass, errorElement, wrapper, errorLabelContainer, errorContainer, showErrors, success, errorPlacement, highlight, unhighlight, and ignoreTitle to control how invalid elements and error messages are displayed.
Из этой статьи вы узнаете, как реализовать простую валидацию формы с помощью jQuery-плагина.
Использование jQuery-плагина для проверки данных в форме удобно по нескольким причинам. Этот способ предоставляет дополнительные опции – например, возможность выводить сообщения об ошибках и добавлять обработку различных условий проверки. Применение готового плагина также позволяет добавлять валидацию в формы без внесения видимых изменений в макет страницы. Условия проверки можно с легкостью изменять, добавлять и удалять на любом этапе разработки.
- Приступаем к работе
- Валидация первой формы
- Опции validate() метода
- Добавление правил валидации для полей ввода
- Создание собственных сообщений об ошибках
- Кастомизация сообщений об ошибках
- Дополнительные опции настройки плагина
- Формы jQuery, доступные на CodeCanyon
- Конструктор пошаговых jQuery форм Timon Step Form
- Smart Forms
- Just Forms Advanced
- Forms Plus JS
- Sky Forms
- Заключение
В этом руководстве мы будем использовать плагин для валидации форм под названием jQuery Validation Plugin. Данный плагин имеет обширный набор функций, а также позволяет добавлять пользовательские условия проверки данных.
Перед использованием расширения на странице нам нужно будет добавить к нашему проекту необходимые файлы. Таких файлов два – первый включает в себя основную функциональность плагина для проверки базовых пользовательских данных. Второй файл содержит дополнительные методы валидации для проверки номеров банковских карт, телефонов и так далее.
Добавить файлы в проект можно с помощью менеджера пакетов – Bower или npm. Кроме того, можно получить прямую CDN-ссылку на эти файлы и вставить ее в тег script на странице. Поскольку это jQuery-плагин, вам также понадобится ссылка на соответствующую библиотеку:
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.4.0/jquery.min.js"></script> <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery-validate/1.19.0/jquery.validate.min.js"></script>
После того, как ссылки добавлены в код страницы, можно приступать к валидации любой формы с помощью метода validate.
Рассматриваемый нами плагин можно использовать без внесения каких-либо заметных изменений в разметку страницы. Единственная поправка, которую вам потребуется сделать – это добавить id или class к форме, к которой нужно подключить валидацию.
Ниже приведена разметка базовой формы, ввод данных в которой мы будем проверять с помощью jQuery-плагина.
<form id="basic-form" action="" method="post"> <p> <label for="name">Name <span>(required, at least 3 characters)</span></label> <input id="name" name="name" minlength="3" type="text" required> </p> <p> <label for="email">E-Mail <span>(required)</span></label> <input id="email" type="email" name="email" required> </p> <p> <input class="submit" type="submit" value="SUBMIT"> </p> </form>
Для проверки введенной информации не потребуется написание дополнительного кода на JavaScript. При этом плагин обеспечит вывод сообщений об ошибках под каждым текстовым полем. У нас также будет возможность оформить сообщения в любом желаемом стиле.
Для подключения валидации к этой форме надо всего лишь вставить приведенный ниже фрагмент, написанный на JavaScript, в код страницы:
$(document).ready(function() {
$("#basic-form").validate();
});
Подразумевается, что вы уже добавили к проекту необходимые файлы плагина. Вставка приведенного выше фрагмента кода обеспечит надлежащую проверку формы и вывод сообщений об ошибках. Вот рабочая демонстрация плагина:
Рассматриваемая нами библиотека обеспечивает максимально дружеское отношение к пользователю: сообщения об ошибках появляются только в том случае, когда это действительно необходимо. К примеру, если вы пройдетесь по полям для ввода имени и адреса электронной почты, не вводя никаких данных, сообщения об ошибке вы не получите. Однако если вы перейдете на поле для ввода email-адреса после введения всего одной буквы в поле имени, вы увидите сообщение о том, что имя должно состоять как минимум из трех символов.
Сообщения об ошибках передаются в DOM (объектную модель документа) с помощью элемента label. Поскольку этот элемент предусматривает класс error, к сообщениям можно легко применить собственные стили. То же самое справедливо в отношении invalid input, у которого тоже имеется класс error.
В предыдущем примере мы вызывали метод validate() без передачи ему каких-либо параметров. Однако у нас есть возможность передать этому методу объект, содержащий множество параметров. Значения этих параметров будут определять способы, с помощью которых плагин будет проводить валидацию данных, выводить ошибки и так далее.
Если вы хотите, чтобы плагин игнорировал какие-то элементы в ходе проверки, вы можете передать нужный класс или селектор в метод ignore(). С этого момента плагин будет игнорировать класс при проверке данных в форме.
Вы также можете передать определенные правила в метод validate() для установления правил, в соответствии с которыми должна проверяться введенная информация. Значением параметра rules должны быть пары «ключ-значение». Ключом в каждом случае является название проверяемого элемента, а значением – набор правил для проверки информации.
Также можно добавить проверку условий данных в различных полях – с использованием ключевого слова depends («зависит от») и возвращая, соответственно, результат true («истинно») или false («ложно»). Ниже приведен пример использования простого набора правил для определения корректности введенных данных:
$(document).ready(function() {
$("#basic-form").validate({
rules: {
name : {
required: true,
minlength: 3
},
age: {
required: true,
number: true,
min: 18
},
email: {
required: true,
email: true
},
weight: {
required: {
depends: function(elem) {
return $("#age").val() > 50
}
},
number: true,
min: 0
}
}
});
});
В приведенном выше фрагменте кода ключи name («имя»), age («возраст»), email и weight («вес») представляют собой названия элементов ввода input. Каждому ключу соответствует объект-значение, а пары ключей и значений определяют логику проверки информации, введенной в форму.
Такие опции валидации схожи с атрибутами, которые вы можете добавить в разметку формы. Например, установка параметра required на true сделает элемент обязательно необходимым для успешной отправки формы. Установление minlength на значение 3 обяжет пользователей вводить в поле как минимум три символа. Есть и другие встроенные методы валидации, с которыми можно ознакомиться на странице с технической документацией.
Важный момент, на который необходимо обратить внимание в приведенном выше коде – использование depends для того, чтобы сделать обязательным условием ввод веса, если возраст превышает 50 лет. Условие реализовано с помощью возвращения значения true функцией обратного вызова в том случае, если значение, введенное в поле age, превышает 50.
Рассматриваемый нами плагин позволяет создавать собственный набор сообщений об ошибках, соответствующих различным правилам проверки данных, введенных в форму. Создание сообщения об ошибке начинается с задания объекта-значения для ключа messages. Для каждого поля ввода определяется такая пара ключа и значения, и соответствующее сообщение об ошибке.
Ниже приведен пример кода, который обеспечивает вывод сообщений об ошибках при вводе неверных данных в любое из полей формы:
messages : {
name: {
minlength: "Name should be at least 3 characters"
},
age: {
required: "Please enter your age",
number: "Please enter your age as a numerical value",
min: "You must be at least 18 years old"
},
email: {
email: "The email should be in the format: abc@domain.tld"
},
weight: {
required: "People with age over 50 have to enter their weight",
number: "Please enter your weight as a numerical value"
}
}
Как и правила, messages опираются на названия полей ввода. Каждое из этих полей принимает объект, состоящий из ключа и значения. Ключом является правило валидации, а значением – сообщение об ошибке, которое выводится в случае нарушения правила.
Например, поле age с помощью свойства required вызовет сообщение об ошибке, если останется незаполненным. Кроме того, если введенная информация не является числовым значением, поле вызовет ошибку number.
Как вы сможете убедиться, плагин отображает сообщения об ошибках, используемые по умолчанию в том случае, если вы не предоставили ему свои собственные. Попробуйте ввести различные данные в приведенный ниже демонстрационный образец, и вы увидите как стандартные, так и кастомные уведомления об ошибках.
Иногда возникает необходимость добавления собственных классов к элементам ввода – для использования дополнительных правил или для лучшей интеграции с существующей темой оформления сайта.
Классы, связанные с корректными и неверными элементами ввода, можно менять с использованием ключей errorClass и validClass. Это поможет предотвратить нежелательные конфликты, которые могут возникать при повторном использовании одного и того же названия класса. По умолчанию класс ошибки errorприсваивается каждому недопустимому входному элементу и метке. Допустимый класс valid присваивается каждому корректному входному элементу.
При этом важно помнить, что присвоение errorClass уведомлениям fail-alert удаляет класс error из недопустимых элементов. Для присвоения нескольких классов одному и тому же элементу следует использовать errorClass: «error fail-alert». То же самое касается validClass.
Если пользователь вводит корректные данные, дополнительные метки к форме не добавляются. Таким образом, классы validClass остаются присвоенными корректным входным элементам.
Дополнительный JavaScript-код используется только для присвоения классов:
$(document).ready(function() {
$("#basic-form").validate({
errorClass: "error fail-alert",
validClass: "valid success-alert",
// ... More validation code from previous example
Далее приведен CSS -код, который мы будем использовать для оформления сообщений об ошибках:
label.error.fail-alert {
border: 2px solid red;
border-radius: 4px;
line-height: 1;
padding: 2px 0 6px 6px;
background: #ffe6eb;
}
input.valid.success-alert {
border: 2px solid #4CAF50;
color: green;
}
Помимо создания стиля для сообщений об ошибках, мы также добавим собственный стиль к допустимым входным элементам. Ниже приводится демонстрационный пример с готовым результатом.
Вы можете отключить валидацию при случайном переходе в поле с помощью клавиши или при клике мышью. Для этого надо установить параметры onfocusout, onkeyup, или onclick на false. Обратите внимание, что логическое true не является допустимым значением для этих событий. Другими словами, если вы хотите, чтобы плагин осуществлял валидацию при этих событиях – просто оставьте соответствующие ключи без изменений.
У вас также есть возможность изменить элемент, который используется для вывода ошибок. По умолчанию используется label, но при желании вы можете изменить его на em или любой другой элемент, используя параметр errorElemet. Выбранный элемент, в свою очередь, можно обернуть в другой HTML-элемент, применив параметр wrapper.
Рассмотренные варианты – наиболее типичные опции валидации данных. Кроме этих вариантов, вам могут пригодиться и некоторые другие – например, если вы захотите изменить местоположение уведомлений или сгруппировать их вместе.
Самостоятельная реализация валидации данных – очень полезный навык. Дополнительную функциональность помогут добавить готовые пакеты, созданные на основе jQuery и JavaScript.
Если вам нужна пошаговая форма, обратите внимание на пакет Timon Step Form. В состав этого набора входит множество готовых элементов форм, а также коллекция эффектов перехода. Это визуальный конструктор, для его использования не нужны навыки программирования. Имеется встроенная jQuery-валидация входных данных.
Smart Forms представляет собой полнофункциональный фреймворк для создания, как простых, так и сложных форм. В его состав входит поддержка Google reCAPTCHA, проверка номеров телефонов и многое другое. Валидация реализована на jQuery, что делает данный фреймворк отличным выбором.
Название данного пакета говорит само за себя – это инструмент для создания продвинутых форм. В поставку входит более 110 готовых форм, а сам фреймворк позволяет разработать уникальную форму самостоятельно.
Forms Plus – фреймворк для создания форм с валидацией и вычислениями. Включает в себя более 100 шаблонов для разработки форм. Поддерживает:
- ввод капчи;
- выбор даты, времени и цвета;
- группировку полей;
- скрытые поля;
- создание блоков для действий.
Мы заканчиваем обзор на фреймворке Sky Forms. Данный пакет включает в себя обширный набор стильных элементов, более 300 векторных иконок и множество цветовых схем, поддерживает любую кастомизацию. Предусматривает обработку шести состояний для элементов ввода, включая наведение курсора, фокус и так далее. Формы, созданные с помощью Sky Forms, корректно работают во всех наиболее популярных браузерах.
В этой статье мы рассмотрели, как можно вывести валидацию форм на новый уровень, используя jQuery- плагин. Реализация проверки данных на основе JavaScript предоставляет разработчику дополнительный контроль над вводом, в отличие от базовой HTML-валидации. К примеру, вы сможете без труда добавить к форме сообщения об ошибках, которые будут выводиться, если пользователь введет недопустимые данные в соответствующие поля ввода.
В то же время вы сможете определить, какие действия пользователя и для каких входных элементов плагин должен игнорировать. Я настоятельно рекомендую изучить официальную документацию к плагину и некоторые примеры его использования.
Есть множество статей о том, как написать свои правила для плагина jQuery validate, но мало какие из них объясняют внутреннюю работу этого плагина, что мы и обсудим в этой статье.
Это первая часть серии статей «Понимание ненавязчивой валидации Asp.NET MVC»
1. Работа плагина jQuery validate изнутри
2. Понимание Html-кода, сгенерированного ненавязчивой валидацией в ASP.Net MVC
3. Внутренняя работа плагина unobtrusive jQuery validate в ASP.Net MVC.
Что мы узнаем из этой статьи:
1. Как валидировать форму.
2. Сообщения валидации и как они работают.
3. Добавление собственных правил валидации.
4. Что именно происходит, когда мы вызываем метод валидации.
Как валидировать форму
Есть 2 основных способа, чтобы валидировать форму.
1. Использовать имена классов как правила
Как это работает
Мы добавляем к полю, которое нужно провалидировать, html атрибут «class», и это подключит валидацию.
Итак, если нам нужно, чтобы текстовое поле было обязательным мы добавляем в элемент input значение атрибута class = «required»
Html
<form action="/" method="post">
<input id="Name" type="text" name="Name" value="" class ="required" />
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form>
JavaScript
$(document).ready(function() {
$('form').validate();
});
Так вы можете добавить к определенным классам несколько правил.
Плюсы и минусы такого подхода:
Работает только с правилами, которые не принимают аргументов.
Мы используем html атрибут «class» для того, для чего он не предназначен.
Но его легко установить.
Использование метода «addClassRules»
Использование функции «addClassRules» дает нам возможность использовать составное правило для одного класса.
JavaScript
$.validator.addClassRules({
name: {
required: true,
minlength: 2
},
zip: {
required: true,
digits: true,
minlength: 5,
maxlength: 5
}
});
Этот код добавляет 2 новых правила для класса «name» и «zip», и, если у нас есть элемент «input», у которого класс «zip», то к нему применяются правила: его значение является обязательным, пользователь может вводить только цифры и длина должна быть точно 5 символов.
Html
<input class="zip" type="text" name="zipCode" />
Информация: Чтобы использовать собственное сообщение для определенного правила requires в составном правиле, нам нужно придумать псевдоним для правила «required», создать новое правило с этим псевдонимом и установить для него сообщение по умолчанию.
JavaScript
$.validator.addMethod("newrequired", $.validator.methods.required, "new name is required");
Или мы можем использовать html атрибут «title», его значение будет сообщением об ошибке для составного правила.
Заметка: Валидация по имени класса работает только для правил валидации, не принимающих никаких аргументов.
2. Добавление правил как JSON объекта к методу validate()
По названию, вы должны были догадаться, что этот метод валидации принимает объект json, поэтому мы можем определить поля, которые нам нужно валидировать и правила валидации для них.
Html
<form>
<input id="something" type="text" name="userEmail" />
<input id="submit" type="submit" value="submit" />
</form>
JavaScript
$('form').validate({
rules: {
userEmail: {
email: true,
required: true
}
}
});
Заметка: Когда мы передаем объект «rules» функции «validate» ключом должно быть значение атрибута «name», а не значение «id». Как можно увидеть в примере: ключ -это «userEmail», значение атрибута «name», а у атрибута «id» другое значение.
Плюсы и минусы этого подхода:
Этот подход дает нам возможность использовать больше правил валидации, которые принимают аргументы, такие как minlength, remote, equalTo и т.д.
Отличный и настраиваемый вручную контроль над всем.
Но пользователь должен делать отдельную функцию «validate» с разными опциями для каждой формы.
Добавление или удаление динамических правил.
Добавление правил
Чтобы добавить правило мы должны использовать метод «rules» для элементов jQuery после того как форма провалидирована и передавать как первый параметр строку «add» и как второй параметр — объект правил, которые мы хотим добавить к этому элементу (также мы можем передавать объект «сообщение» для правил, которые мы добавили).
JavaScript
$('.input').rules('add', {
required: true,
messages: {
required: true
}
})
Удаление правил
Если мы хотим удалить правило или набор правил, мы передаем строку «remove», как первый параметр для метода «rules», а вторым параметром будет строка, которая содержит правила, которые мы хотим удалить, отделенные пробелом.
JavaScript
$('.input').rules('remove', 'min max');
Подход настройки вручную
JavaScript
var validator = $('form').data('validator');
validator.settings.rules.objectName = {
required: true
}
Этот подход очень полезен, если у вас есть созданные правила и объекты сообщений, вы можете расширить правила валидатора своими собственными:
JavaScript
$.extend(validator.settings, { rules: rules, messages: messages });
Сообщения валидации и как они работают
Есть три способа настроить сообщение валидации
1. Передать объект «messages» методу «validate». Объект «messages» состоит из пар ключзначение. Ключ — это значение атрибута «name» элемента. Значение — объект, содержащий каждое правило и его сообщение.
JavaScript
$('form').validate({
rules: {
userEmail: {
email: true,
required: true
}
},
messages: {
userEmail: {
email: "Please enter your email",
required: "*"
}
}
});
2. Определить значение атрибута «title» элемента
Html
<input id="Email" title="you have to enter a value" type="text" name="Email" />
3. Использовать сообщение по умолчанию. Когда определяется правило валидации, есть встроенные сообщения по умолчанию для встроенных правил.
Заметка: Эти три способа переопределяют друг друга, основываясь на приоритетности, самый приоритетный — переданный объект «messages», а наименее приоритетный — сообщение по умолчанию.
Добавление собственных правил валидации
Когда мы хотим добавить больше правил валидации, чем определены по умолчанию, мы используем метод
$.validator.addMethod
Этот метод принимает как параметры следующее:
- имя правила;
- функцию, которая осуществляет валидацию;
- сообщение по умолчанию.
Функция, которая производит валидацию, может быть с двумя или тремя параметрами
JavaScript
function validationMethod (value, element)
// OR
function validationMethod (value, element, params)
Давайте объясню эти параметры.
Значение: значение DOM элемента, который будет валидироваться
Элемент: сам элемент DOM
Параметры: то, что мы передаем как значение. Для этого примера правила валидации — это то, чему должен равняться params.
JavaScript
$('form').validate({
rules: {
firstname: {
compare: {
type: "notequal",
otherprop: "lastname"
}
}
}
});
в этом примере params будет равен {type:«notequal», otherprop: «lastname»}
Пример добавления собственного правила:
JavaScript
$.validator.addMethod("notnumbers", function(value, element) {
return !/[0-9]*/.test(value);
},
"Please don't insert numbers.")
Что именно происходит, когда мы вызываем метод «validate»
Когда мы вызваем метод validate на форме, за кулисами происходит много разных вещей:
Создается объект «validator» со всеми правилами и опциями, присоединенными к форме.
Метод «validate» присоединяет «validator» используя «$.data». Мы можем получить его выбрав форму и вызвав функцию jQuery «$.data» и передать ее «validator». Объект «vaidator» — это все метаданные для валидации, которые дают нам возможность доступа к опциям валидации в любое время жизненного цикла страницы.
Используя этот объект, мы можем изменить во время выполнения опции, которые мы передали методу валидации, такие как добавление или удаление правил, изменение поведения, если поле валидное или невалидное, или даже введение селектора игнорирования.
JavaScript
//getting the validator
var validator = $("selector").data("validator")
Заметка: Когда вы вызываете метод «validate» на форме, которая уже провалидирована, он вернет только объект «validator», используется также $.data, и все предыдущие опции, переданные методом «validate», будут стерты.
JavaScript
var validator = $(".selector").validate(/* rules will be omitted */)
Присоединение событий формы
Что произойдет, когда мы нажмем submit(отправить форму), и в форме будет введено неверное значение для поля, к которому мы присоединили валидацию. Если одно из полей невалидное, то плагин валидации будет присматриваться к нему более пристально, чтобы проверять, валидное оно или нет, по событиям на этом поле.
Сообытия формы, на которые подписывается плагин — это «click», «focusin», «focusout», «keyup», «submit».
Заметка: Вы можете отключить валидацию по определенным событиям, передав их как ключи в методе validate, и false в качестве значений.
JavaScript
$(".selector").validate({
onfocusout: false,
onkeyup: false,
onclick: false,
onsubmit: false
});
Перевод статьи Nadeem Khedr «How the jQuery validate plugin works internally». nadeemkhedr.wordpress.com/2012/08/12/how-the-jquery-validate-plugin-works-internally/#goCallValidate
update 01.06.13: добавлены ссылки на другие посты серии
Today I came with another jQuery article guys! Have you seen validations when you are trying to sign up or login to a site? Without submitting your data? This is the simplest way to do it. As you have seen in web sites, there are two types of validations basically. They are front end and back end. Front end means your input details are validated real time while you are typing and without a submission. As an example, think you have entered an email with an invalid format. When you are trying input next data, error message is shown for the previous invalid input on the frond end user interface. Back end means, your inputs are validated after a submission through a button click. It is not much user friendly because if a user has entered wrong inputs for several times, he or she will have to submit again and again and get the corrected data, to get registered in a site.
This jQuery plugin does the job for you. Real time front end validation is done through this plugin. Let’s see how to get the benefit of this plugin. Here I will use Codeigniter framework for PHP and Bootstrap framework for styling. This is a short demo of the application what will we build today. Watch it!
First create a project folder and put the codeigniter files into it.
If you are not familiar with Codeigniter, this will be difficult. Refer my Codeigniter articles here to learn the framework.
As usual, a database is required for this. So, create a database called validation. You can give any name you want. So basic configurations are like this.
Project folder => jQueryForm
Base URL => $config[‘base_url’] = ‘http://localhost/jQueryForm/
Database name => validation
Database table name => users
Autoload libraries => database
Autoload helpers => form , url
Default Controller => Register
Import the SQL file called validation.sql in my GitHub folder to get create the database.
We have to create the view file first. For that go into the applications/views folder and create a view called signup.php.
In this view we are going to link validation plugin through a JS file. Visit the below site to get the source file.
https://github.com/jquery-validation/jquery-validation/releases/tag/1.17.0
Or otherwise you can include the CDN
https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery-validate/1.17.0/jquery.validate.js
Include this JS file just before the ending body tag of the view as I have done below. Configuration is explained after this code.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>jQuery Validation</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<!-- Bootstrap CSS styles -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-BVYiiSIFeK1dGmJRAkycuHAHRg32OmUcww7on3RYdg4Va+PmSTsz/K68vbdEjh4u" crossorigin="anonymous">
<!-- Roboto Google font -->
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Roboto" rel="stylesheet">
<!-- Google jQuery CDN -->
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.2.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<!-- Custom CSS -->
<style type="text/css">
body {
font-family: 'Roboto', sans-serif;
}
label {
font-size: 16px;
}
.error {
color: #a94442;
border-color: #a94442;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.panel {
border: 1px solid;
border-color: black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="col-lg-12">
<div class="col-lg-4"></div>
<div class="col-lg-4">
<h2 style="margin-top: 30px;text-align: center;">jQuery Form Validation</h2>
<br>
<div class="panel panel-default">
<div class="panel-heading">
<br>
<h3 class="panel-title text-center">Fill the form to sign up</h3>
<br>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<!-- success message to be displayed after adding a user to the database successfully -->
<?php if($this->session->flashdata('success')): ?>
<div class="alert alert-success alert-dismissible" role="alert">
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close">
<span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
<?php echo $this->session->flashdata('success');?>
</div>
<?php endif; ?>
<!-- Form -->
<?php echo form_open('Register/signUp', array('id' => 'signup-form','method' => 'POST'));?>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Username</label>
<br>
<input type="text" id="username" name="username" class="form-control">
<br>
<!-- validation message for username checking with database -->
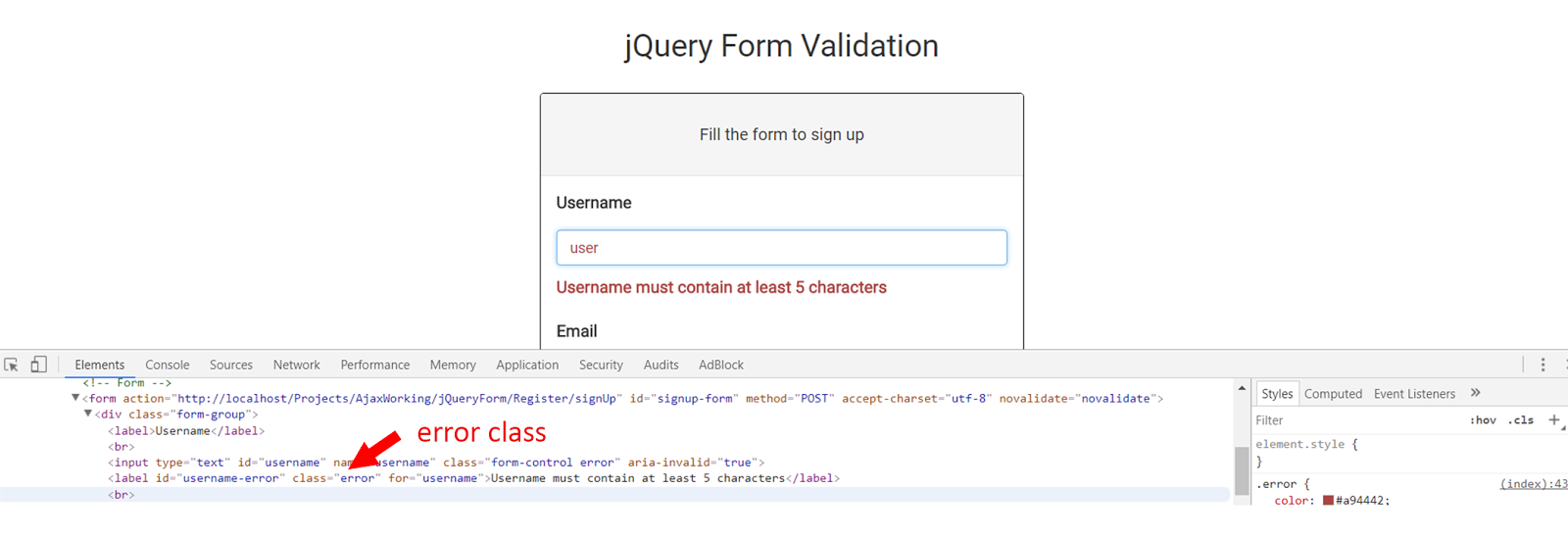
<?php echo validation_errors('<div style="color: #a94442;font-weight: bold;font-size: 16px;"><p>','</p></div>'); ?>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Email</label>
<br>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" class="form-control" placeholder="">
<br>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Password</label>
<br>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password" class="form-control" placeholder="">
<br>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>Confirm Password</label>
<br>
<input type="password" id="cpassword" name="cpassword" class="form-control" placeholder="">
<br>
</div>
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" value="Sign Up">
<br>
<?php echo form_close();?>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-4"></div>
</div>
<!-- validation plugin configuration -->
<script type="text/javascript">
// wait untill the page is loaded completely
$(document).ready(function(){
// include the validation for the form function comes with this plugin
$('#signup-form').validate({
// set validation rules for input fields
rules: {
username: {
required : true,
minlength: 5
},
email: {
required : true,
email: true
},
password: {
required : true,
minlength: 5
},
cpassword: {
required : true,
equalTo: "#password"
}
},
// set validation messages for the rules are set previously
messages: {
username: {
required : "Username is required",
minlength: "Username must contain at least 5 characters"
},
email: {
required : "Email is required",
email: "Enter a valid email. Ex: example@gmail.com"
},
password: {
required : "Password is required",
minlength: "Password must contain at least 5 characters"
},
cpassword: {
required : "Confirm Password is required",
equalTo: "Confirm Password must be matched with Password"
}
}
});
});
</script>
<!-- Bootstrap JS file -->
<script src="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/js/bootstrap.min.js" integrity="sha384-Tc5IQib027qvyjSMfHjOMaLkfuWVxZxUPnCJA7l2mCWNIpG9mGCD8wGNIcPD7Txa" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<!-- Validation JS file -->
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery-validate/1.17.0/jquery.validate.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Validation Plugin Configuration
You can see a new script tag at the end of the file. I’m going to explain it.
First we have to load the jQuery function to wait until the page loading. Then we include the validation function comes with plugin. For this, an ID or a CLASS selector is needed for the signup form. Here I use an ID called signup-form. Next step is including validation rules for the inputs. They are defined in this plugin. Those rules can be set any order. For one input, several rules can be included.
Rules
Format:
input field name {
rule 1 : value 1,
rule 2 : value 2
}
required : true — Without this field, form can not be submitted
minlength : 5 — Requires at least 5 characters
email: true — Checks the email is with the standard email format
equalTo : «#password»
— Checks this input is same as another input
Ex: Confirm password and Password
Messages
Now we have to set validation messages that are displayed when a user input a wrong/invalid value for each input field.
Format:
input field name {
rule 1 : message 1,
rule 2 : message 2
}
These messages can be set as you want. But remember to set a proper and matching message for each input. Otherwise the user will get an wrong idea about the error of the entered input!
CSS for validation messages
When a user entered a wrong input, a label tag is automatically generated after the input field with a class called error. You can check it in the browser console->elements. That’s why I included a styling for a class named error, in the custom styles.
Styles for error class
.error {
color: #a94442;
border-color: #a94442;
margin-top: 10px;
}
I think now you have got the idea of including validation plugin. Next part is making the controller and the model to get a user registered.
Controller
<?php if ( ! defined('BASEPATH')) exit('No direct script access allowed');
class Register extends CI_Controller {
public function __construct()
{
parent::__construct();
$this->load->model('Register_model');
}
public function index()
{
$this->load->view('signup');
}
public function signUp()
{
// username availability is checcked after submission
$this->form_validation->set_rules('username', 'Username', 'trim|is_unique[users.username]');
if ($this->form_validation->run() == TRUE) {
$data = array(
//assign user data into array elements
'username' => $this->input->post('username'),
'email' =>$this->input->post('email'),
'password' =>sha1($this->input->post('password'))
);
$this->Register_model->insertUser($data);
//set message to be shown when registration is completed
$this->session->set_flashdata('success','User is registered!');
redirect('Register/Signup');
} else {
//return to the signup page again with validation errors
$this->load->view('signup');
}
}
}
Model
<?php if ( ! defined('BASEPATH')) exit('No direct script access allowed');
class Register_model extends CI_Model {
public function insertUser($data)
{
// insert data to the database
$this->db->insert('users', $data);
}
}
All the explanations are included in the files as comments. Read them for your understanding. After this step, you have completed this application! Now it’s the time to check. Hit the URL in browser and check whether the validations you have set are working or not. That’s all. Now I’m concluding this article..
Wait for the next article guys!
Good Bye!
jQuery Validate plugin for forms authentication provides a powerful feature that allows client-side form validation easier, while providing plenty of customization options to meet application needs. The plug-in bundled with a useful set of validation methods, including URL and email authentication, while providing a user-defined method for the preparation of the API. All binding method using English as the default error message, and has been translated into 37 other languages.
The plug-in is written and maintained by the Jorn Zaefferer, he is a member of the jQuery team is lead developer of jQuery UI team is QUnit maintenance personnel. The plug-in 2006 jQuery early when it is already beginning to emerge, and has been updated since. The current version is 1.14.0.
Access jQuery Validate the official website to download the latest version of jQuery Validate plugin.
Version 1.14.0 Download this tutorial: http://static.w3big.com/download/jquery-validation-1.14.0.zip
Import js library (using this tutorial CDN)
<script src="http://static.w3big.com/assets/jquery-validation-1.14.0/lib/jquery.js"></script> <script src="http://static.w3big.com/assets/jquery-validation-1.14.0/dist/jquery.validate.min.js"></script>
The default validation rules
| No. | rule | description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | required: true | You must enter the field. |
| 2 | remote: «check.php» | Using ajax method call check.php validate the input value. |
| 3 | email: true | You must enter the correct e-mail format. |
| 4 | url: true | You must enter the correct URL format. |
| 5 | date: true | You must enter the correct date format. Ie6 date validation error caution. |
| 6 | dateISO: true | You must enter the correct date format (ISO), for example: 2009-06-23,1998 / 01/22. Verifies only format that does not validate. |
| 7 | number: true | You must enter a valid number (negative numbers, decimals). |
| 8 | digits: true | You must enter an integer. |
| 9 | creditcard: | You must enter a valid credit card number. |
| 10 | equalTo: «# field» | Input values must #field same. |
| 11 | accept: | The input string has a legitimate extension (suffix upload files). |
| 12 | maxlength: 5 | Maximum length of the input string 5 (Kanji count as one character). |
| 13 | minlength: 10 | The minimum length of the input string is 10 (characters count as one character). |
| 14 | rangelength: [5,10] | Length of the input string must be between 5 and 10. (a kanji character count). |
| 15 | range: [5,10] | Enter the value must be between 5 and 10. |
| 16 | max: 5 | Enter a value not greater than 5. |
| 17 | min: 10 | Enter a value not less than 10. |
Default Tips
messages: {
required: "This field is required.",
remote: "Please fix this field.",
email: "Please enter a valid email address.",
url: "Please enter a valid URL.",
date: "Please enter a valid date.",
dateISO: "Please enter a valid date ( ISO ).",
number: "Please enter a valid number.",
digits: "Please enter only digits.",
creditcard: "Please enter a valid credit card number.",
equalTo: "Please enter the same value again.",
maxlength: $.validator.format( "Please enter no more than {0} characters." ),
minlength: $.validator.format( "Please enter at least {0} characters." ),
rangelength: $.validator.format( "Please enter a value between {0} and {1} characters long." ),
range: $.validator.format( "Please enter a value between {0} and {1}." ),
max: $.validator.format( "Please enter a value less than or equal to {0}." ),
min: $.validator.format( "Please enter a value greater than or equal to {0}." )
}
jQuery Validate provides tips Chinese information packet, located in the download package dist / localization / messages_zh.js, reads as follows:
(function( factory ) {
if ( typeof define === "function" && define.amd ) {
define( ["jquery", "../jquery.validate"], factory );
} else {
factory( jQuery );
}
}(function( $ ) {
/*
* Translated default messages for the jQuery validation plugin.
* Locale: ZH (Chinese, 中文 (Zhongwén), 汉语, 漢語)
*/
$.extend($.validator.messages, {
required: "这是必填字段",
remote: "请修正此字段",
email: "请输入有效的电子邮件地址",
url: "请输入有效的网址",
date: "请输入有效的日期",
dateISO: "请输入有效的日期 (YYYY-MM-DD)",
number: "请输入有效的数字",
digits: "只能输入数字",
creditcard: "请输入有效的信用卡号码",
equalTo: "你的输入不相同",
extension: "请输入有效的后缀",
maxlength: $.validator.format("最多可以输入 {0} 个字符"),
minlength: $.validator.format("最少要输入 {0} 个字符"),
rangelength: $.validator.format("请输入长度在 {0} 到 {1} 之间的字符串"),
range: $.validator.format("请输入范围在 {0} 到 {1} 之间的数值"),
max: $.validator.format("请输入不大于 {0} 的数值"),
min: $.validator.format("请输入不小于 {0} 的数值")
});
}));
You can localize the information file dist / localization / messages_zh.js introduced to the page:
<script src="http://static.w3big.com/assets/jquery-validation-1.14.0/dist/localization/messages_zh.js"></script>
Use
1, the validation rules written control
<script src="http://static.w3big.com/assets/jquery-validation-1.14.0/lib/jquery.js"></script>
<script src="http://static.w3big.com/assets/jquery-validation-1.14.0/dist/jquery.validate.min.js"></script>
<script src="http://static.w3big.com/assets/jquery-validation-1.14.0/dist/localization/messages_zh.js"></script>
<script>
$.validator.setDefaults({
submitHandler: function() {
alert("提交事件!");
}
});
$().ready(function() {
$("#commentForm").validate();
});
</script>
<form class="cmxform" id="commentForm" method="get" action="">
<fieldset>
<legend>输入您的名字,邮箱,URL,备注。</legend>
<p>
<label for="cname">Name (必需, 最小两个字母)</label>
<input id="cname" name="name" minlength="2" type="text" required>
</p>
<p>
<label for="cemail">E-Mail (必需)</label>
<input id="cemail" type="email" name="email" required>
</p>
<p>
<label for="curl">URL (可选)</label>
<input id="curl" type="url" name="url">
</p>
<p>
<label for="ccomment">备注 (必需)</label>
<textarea id="ccomment" name="comment" required></textarea>
</p>
<p>
<input class="submit" type="submit" value="Submit">
</p>
</fieldset>
</form>
try it»
2, the validation rules written js code
$().ready(function() {
// 在键盘按下并释放及提交后验证提交表单
$("#signupForm").validate({
rules: {
firstname: "required",
lastname: "required",
username: {
required: true,
minlength: 2
},
password: {
required: true,
minlength: 5
},
confirm_password: {
required: true,
minlength: 5,
equalTo: "#password"
},
email: {
required: true,
email: true
},
topic: {
required: "#newsletter:checked",
minlength: 2
},
agree: "required"
},
messages: {
firstname: "请输入您的名字",
lastname: "请输入您的姓氏",
username: {
required: "请输入用户名",
minlength: "用户名必需由两个字母组成"
},
password: {
required: "请输入密码",
minlength: "密码长度不能小于 5 个字母"
},
confirm_password: {
required: "请输入密码",
minlength: "密码长度不能小于 5 个字母",
equalTo: "两次密码输入不一致"
},
email: "请输入一个正确的邮箱",
agree: "请接受我们的声明",
topic: "请选择两个主题"
}
});
messages at a control if there is no message, will use the default information
<form class="cmxform" id="signupForm" method="get" action="">
<fieldset>
<legend>验证完整的表单</legend>
<p>
<label for="firstname">名字</label>
<input id="firstname" name="firstname" type="text">
</p>
<p>
<label for="lastname">姓氏</label>
<input id="lastname" name="lastname" type="text">
</p>
<p>
<label for="username">用户名</label>
<input id="username" name="username" type="text">
</p>
<p>
<label for="password">密码</label>
<input id="password" name="password" type="password">
</p>
<p>
<label for="confirm_password">验证密码</label>
<input id="confirm_password" name="confirm_password" type="password">
</p>
<p>
<label for="email">Email</label>
<input id="email" name="email" type="email">
</p>
<p>
<label for="agree">请同意我们的声明</label>
<input type="checkbox" class="checkbox" id="agree" name="agree">
</p>
<p>
<label for="newsletter">我乐意接收新信息</label>
<input type="checkbox" class="checkbox" id="newsletter" name="newsletter">
</p>
<fieldset id="newsletter_topics">
<legend>主题 (至少选择两个) - 注意:如果没有勾选“我乐意接收新信息”以下选项会隐藏,但我们这里作为演示让它可见</legend>
<label for="topic_marketflash">
<input type="checkbox" id="topic_marketflash" value="marketflash" name="topic">Marketflash
</label>
<label for="topic_fuzz">
<input type="checkbox" id="topic_fuzz" value="fuzz" name="topic">Latest fuzz
</label>
<label for="topic_digester">
<input type="checkbox" id="topic_digester" value="digester" name="topic">Mailing list digester
</label>
<label for="topic" class="error">Please select at least two topics you'd like to receive.</label>
</fieldset>
<p>
<input class="submit" type="submit" value="提交">
</p>
</fieldset>
</form>
try it»
required: true value is a must.
required: «#aa: checked» is an expression of true, you need to verify.
required: function () {} return true, expressed the need for verification.
Two commonly used in the back, in the form need to fill or not fill elements.
Common methods and attention to issues
1, otherwise replace the default SUBMIT
$().ready(function() {
$("#signupForm").validate({
submitHandler:function(form){
alert("提交事件!");
form.submit();
}
});
});
Way to use ajax
$(".selector").validate({
submitHandler: function(form)
{
$(form).ajaxSubmit();
}
})
You can set default values validate worded as follows:
$.validator.setDefaults({
submitHandler: function(form) { alert("提交事件!");form.submit(); }
});
If you want to submit the form, you need to use form.submit (), instead of $ (form) .submit ().
2, debug, verification is not only submit the form
If this parameter is true, then the form is not submitted, only checks carried out, it is very convenient when debugging.
$().ready(function() {
$("#signupForm").validate({
debug:true
});
});
If a page has multiple forms want to set to debug, use:
$.validator.setDefaults({
debug: true
})
3, ignore: ignore certain elements are not verified
ignore: ".ignore"
4. Change the location of the error message displayed
errorPlacement:Callback
Indicate the location of misplaced, the default is: error.appendTo (element.parent ()); that is the wrong message behind authentication element.
errorPlacement: function(error, element) {
error.appendTo(element.parent());
}
Examples
<p>将错误信息放在 label 元素后并使用 span 元素包裹它</p>
<form method="get" class="cmxform" id="form1" action="">
<fieldset>
<legend>Login Form</legend>
<p>
<label for="user">Username</label>
<input id="user" name="user" required minlength="3">
</p>
<p>
<label for="password">Password</label>
<input id="password" type="password" maxlength="12" name="password" required minlength="5">
</p>
<p>
<input class="submit" type="submit" value="Login">
</p>
</fieldset>
</form>
try it»
The role of the code is: Under normal circumstances the error message is displayed in the <td class = «status»> </ td> if the radio is displayed in the <td> </ td>, if the checkbox is displayed in the content of Behind.
| 参数 | 类型 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| errorClass | String | 指定错误提示的 css 类名,可以自定义错误提示的样式。 | «error» |
| errorElement | String | 用什么标签标记错误,默认是 label,可以改成 em。 | «label» |
| errorContainer | Selector | 显示或者隐藏验证信息,可以自动实现有错误信息出现时把容器属性变为显示,无错误时隐藏,用处不大。 errorContainer: «#messageBox1, #messageBox2» |
|
| errorLabelContainer | Selector | 把错误信息统一放在一个容器里面。 | |
| wrapper | String | 用什么标签再把上边的 errorELement 包起来。 |
Usually these three attributes simultaneously, to achieve display all error functions in a container, and no information is automatically hidden.
errorContainer: "div.error",
errorLabelContainer: $("#signupForm div.error"),
wrapper: "li"
5, change the style of the error message displayed
Setting error of style, you can increase the icon is displayed, the system has established a validation.css, designed to maintain the style of the verification document.
input.error {border: 1px solid red;}
label.error {
background: url ( "./ demo / images / unchecked.gif") no-repeat 0px 0px;
padding-left: 16px;
padding-bottom: 2px;
font-weight: bold;
color: # EA5200;
}
label.checked {
background: url ( "./ demo / images / checked.gif") no-repeat 0px 0px;
}
6, each field is verified by performing a function
success: String, Callback
To verify that the elements by the operation after the verification, if followed by a string that will be treated as a css class, but also with a function.
success: function (label) {
// Set & nbsp; as text for IE
label.html ( "& nbsp;"). addClass ( "checked");
//label.addClass("valid").text("Ok! ")
}
Add «valid» to verify the elements defined in CSS style <style> label.valid {} </ style>.
success: "valid"
7, modify the trigger validation
Although the following is a boolean, but recommended unless you want to false, otherwise Freeze added.
| 触发方式 | 类型 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| onsubmit | Boolean | 提交时验证。设置为 false 就用其他方法去验证。 | true |
| onfocusout | Boolean | 失去焦点时验证(不包括复选框/单选按钮)。 | true |
| onkeyup | Boolean | 在 keyup 时验证。 | true |
| onclick | Boolean | 在点击复选框和单选按钮时验证。 | true |
| focusInvalid | Boolean | 提交表单后,未通过验证的表单(第一个或提交之前获得焦点的未通过验证的表单)会获得焦点。 | true |
| focusCleanup | Boolean | 如果是 true 那么当未通过验证的元素获得焦点时,移除错误提示。避免和 focusInvalid 一起用。 | false |
// Reset the form $ (). Ready (function () {
var validator = $ ( "# signupForm"). validate ({
submitHandler: function (form) {
alert ( "submitted");
form.submit ();
}
});
$ ( "# Reset"). Click (function () {
validator.resetForm ();
});
});
8, asynchronous verification
remote: URL
Way to authenticate using ajax, submitted to the current default value to a remote address verification, if required to submit other values, you can use the data option.
remote: "check-email.php"
remote: {
url: "check-email.php", // Spooler type: "post", // data transmission mode dataType: "json", // receive data format data: {username // data to be passed: function ( ) {
return $ ( "# username") val ().;
}
}
}
Remote address only output «true» or «false», can not have other output.
9, adding custom validation
addMethod: name, method, message
Custom authentication methods
// Characters two bytes jQuery.validator.addMethod ( "byteRangeLength", function (value, element, param) {
var length = value.length;
for (var i = 0; i <value.length; i ++) {
if (value.charCodeAt (i)> 127) {
length ++;
}
}
return this.optional (element) || (length> = param [0] && length <= param [1]);
}, $ .validator.format ( "Make sure that the value entered in {0} - {1} between bytes (one byte characters count 2)"));
// Postal code verification jQuery.validator.addMethod ( "isZipCode", function (value, element) {
var tel = / ^ [0-9] {6} $ /;
return this.optional (element) || (tel.test (value));
} "Please fill in the correct your zip code");
Note: To add additional-methods.js file or add jquery.validate.js file.Recommendations generally written in additional-methods.js file.
Note: messages_cn.js file, add: isZipCode: «can include text, letters, numbers, and underscores.»Before calling To add additional-methods.js file references.
10, radio and checkbox, select the verification
The radio must select a required representation.
<Input type = "radio" id = "gender_male" value = "m" name = "gender" required /> <Input type = "radio" id = "gender_female" value = "f" name = "gender" />
checkbox must select the required representation.
<Input type = "checkbox" class = "checkbox" id = "agree" name = "agree" required />
represents the minimum number of minlength checkbox must be checked, maxlength represents the maximum number of selected, rangelength: [2,3] represents the number of the selected range.
<Input type = "checkbox" class = "checkbox" id = "spam_email" value = "email" name = "spam []" required minlength = "2" /> <Input type = "checkbox" class = "checkbox" id = "spam_phone" value = "phone" name = "spam []" /> <Input type = "checkbox" class = "checkbox" id = "spam_mail" value = "mail" name = "spam []" />
select the required showing the selected value can not be empty.
<Select id = "jungle" name = "jungle" title = "Please select something!" Required>
<Option value = ""> </ option>
<Option value = "1"> Buga </ option>
<Option value = "2"> Baga </ option>
<Option value = "3"> Oi </ option>
</ Select>
select the selected representation minlength minimum number of (multiple choice of select), maxlength represents the maximum number of selected, rangelength: [2,3] represents the number of the selected interval.
<Select id = "fruit" name = "fruit" title = "Please select at least two fruits" class = "{required: true, minlength: 2}" multiple = "multiple">
<Option value = "b"> Banana </ option>
<Option value = "a"> Apple </ option>
<Option value = "p"> Peach </ option>
<Option value = "t"> Turtle </ option>
</ Select>
jQuery.validate Chinese API
| 名称 | 返回类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| validate(options) | Validator | 验证所选的 FORM。 |
| valid() | Boolean | 检查是否验证通过。 |
| rules() | Options | 返回元素的验证规则。 |
| rules(«add»,rules) | Options | 增加验证规则。 |
| rules(«remove»,rules) | Options | 删除验证规则。 |
| removeAttrs(attributes) | Options | 删除特殊属性并且返回它们。 |
| 自定义选择器 | ||
| :blank | Validator | 没有值的筛选器。 |
| :filled | Array <Element> | 有值的筛选器。 |
| :unchecked | Array <Element> | 没选择的元素的筛选器。 |
| 实用工具 | ||
| jQuery.format(template,argument,argumentN…) | String | 用参数代替模板中的 {n}。 |
Validator
validate method returns a Validator object. Validator object has many methods can be used to trigger the calibration procedure or change the contents of the form, several commonly used methods are listed below.
| 名称 | 返回类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| form() | Boolean | 验证 form 返回成功还是失败。 |
| element(element) | Boolean | 验证单个元素是成功还是失败。 |
| resetForm() | undefined | 把前面验证的 FORM 恢复到验证前原来的状态。 |
| showErrors(errors) | undefined | 显示特定的错误信息。 |
| Validator 函数 | ||
| setDefaults(defaults) | undefined | 改变默认的设置。 |
| addMethod(name,method,message) | undefined | 添加一个新的验证方法。必须包括一个独一无二的名字,一个 JAVASCRIPT 的方法和一个默认的信息。 |
| addClassRules(name,rules) | undefined | 增加组合验证类型,在一个类里面用多种验证方法时比较有用。 |
| addClassRules(rules) | undefined | 增加组合验证类型,在一个类里面用多种验证方法时比较有用。这个是同时加多个验证方法。 |
Built-in authentication
| 名称 | 返回类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| required() | Boolean | 必填验证元素。 |
| required(dependency-expression) | Boolean | 必填元素依赖于表达式的结果。 |
| required(dependency-callback) | Boolean | 必填元素依赖于回调函数的结果。 |
| remote(url) | Boolean | 请求远程校验。url 通常是一个远程调用方法。 |
| minlength(length) | Boolean | 设置最小长度。 |
| maxlength(length) | Boolean | 设置最大长度。 |
| rangelength(range) | Boolean | 设置一个长度范围 [min,max]。 |
| min(value) | Boolean | 设置最小值。 |
| max(value) | Boolean | 设置最大值。 |
| email() | Boolean | 验证电子邮箱格式。 |
| range(range) | Boolean | 设置值的范围。 |
| url() | Boolean | 验证 URL 格式。 |
| date() | Boolean | 验证日期格式(类似 30/30/2008 的格式,不验证日期准确性只验证格式)。 |
| dateISO() | Boolean | 验证 ISO 类型的日期格式。 |
| dateDE() | Boolean | 验证德式的日期格式(29.04.1994 或 1.1.2006)。 |
| number() | Boolean | 验证十进制数字(包括小数的)。 |
| digits() | Boolean | 验证整数。 |
| creditcard() | Boolean | 验证信用卡号。 |
| accept(extension) | Boolean | 验证相同后缀名的字符串。 |
| equalTo(other) | Boolean | 验证两个输入框的内容是否相同。 |
| phoneUS() | Boolean | 验证美式的电话号码。 |
validate () is optional
| 描述 | 代码 |
|---|---|
| debug:进行调试模式(表单不提交)。 |
$(".selector").validate
({
debug:true
})
|
| 把调试设置为默认。 |
$.validator.setDefaults({
debug:true
})
|
| submitHandler:通过验证后运行的函数,里面要加上表单提交的函数,否则表单不会提交。 |
$(".selector").validate({
submitHandler:function(form) {
$(form).ajaxSubmit();
}
})
|
| ignore:对某些元素不进行验证。 |
$("#myform").validate({
ignore:".ignore"
})
|
| rules:自定义规则,key:value 的形式,key 是要验证的元素,value 可以是字符串或对象。 |
$(".selector").validate({
rules:{
name:"required",
email:{
required:true,
email:true
}
}
})
|
| messages:自定义的提示信息,key:value 的形式,key 是要验证的元素,value 可以是字符串或函数。 |
$(".selector").validate({
rules:{
name:"required",
email:{
required:true,
email:true
}
},
messages:{
name:"Name不能为空",
email:{
required:"E-mail不能为空",
email:"E-mail地址不正确"
}
}
})
|
| groups:对一组元素的验证,用一个错误提示,用 errorPlacement 控制把出错信息放在哪里。 |
$("#myform").validate({
groups:{
username:"fname
lname"
},
errorPlacement:function(error,element) {
if (element.attr("name") == "fname" || element.attr("name") == "lname")
error.insertAfter("#lastname");
else
error.insertAfter(element);
},
debug:true
})
|
| OnSubmit:类型 Boolean,默认 true,指定是否提交时验证。 |
$(".selector").validate({
onsubmit:false
})
|
| onfocusout:类型 Boolean,默认 true,指定是否在获取焦点时验证。 |
$(".selector").validate({
onfocusout:false
})
|
| onkeyup:类型 Boolean,默认 true,指定是否在敲击键盘时验证。 |
$(".selector").validate({
onkeyup:false
})
|
| onclick:类型 Boolean,默认 true,指定是否在鼠标点击时验证(一般验证 checkbox、radiobox)。 |
$(".selector").validate({
onclick:false
})
|
| focusInvalid:类型 Boolean,默认 true。提交表单后,未通过验证的表单(第一个或提交之前获得焦点的未通过验证的表单)会获得焦点。 |
$(".selector").validate({
focusInvalid:false
})
|
| focusCleanup:类型 Boolean,默认 false。当未通过验证的元素获得焦点时,移除错误提示(避免和 focusInvalid 一起使用)。 |
$(".selector").validate({
focusCleanup:true
})
|
| errorClass:类型 String,默认 «error»。指定错误提示的 css 类名,可以自定义错误提示的样式。 |
$(".selector").validate({
errorClass:"invalid"
})
|
| errorElement:类型 String,默认 «label»。指定使用什么标签标记错误。 |
$(".selector").validate
errorElement:"em"
})
|
| wrapper:类型 String,指定使用什么标签再把上边的 errorELement 包起来。 |
$(".selector").validate({
wrapper:"li"
})
|
| errorLabelContainer:类型 Selector,把错误信息统一放在一个容器里面。 |
$("#myform").validate({
errorLabelContainer:"#messageBox",
wrapper:"li",
submitHandler:function() {
alert("Submitted!")
}
})
|
| showErrors:跟一个函数,可以显示总共有多少个未通过验证的元素。 |
$(".selector").validate({
showErrors:function(errorMap,errorList) {
$("#summary").html("Your form contains " + this.numberOfInvalids() + " errors,see details below.");
this.defaultShowErrors();
}
})
|
| errorPlacement:跟一个函数,可以自定义错误放到哪里。 |
$("#myform").validate({
errorPlacement:function(error,element) {
error.appendTo(element.parent("td").next("td"));
},
debug:true
})
|
| success:要验证的元素通过验证后的动作,如果跟一个字符串,会当作一个 css 类,也可跟一个函数。 |
$("#myform").validate({
success:"valid",
submitHandler:function() {
alert("Submitted!")
}
})
|
| highlight:可以给未通过验证的元素加效果、闪烁等。 |
addMethod (name, method, message) method
Parameters name is the name of the add method.
Parameter method is a function that takes three parameters (value, element, param).
value is the value of the element, element is the element itself, param is the parameter.
We can use addMethod to add except the built-in authentication method Validation method. For example, there is a field, only to lose a letter, the range is af, written as follows:
$ .validator.addMethod ( "Af", function (value, element, params) {
if (value.length> 1) {
return false;
}
if (value> = params [0] && value <= params [1]) {
return true;
} Else {
return false;
}
}, "Must be a letter, and af");
If there is a form field id = «username», written in the rules:
username: {
af: [ "a", "f"]
}
AddMethod first parameter is the name of the authentication method to add, then is af.
addMethod third parameter, a custom error message, suggesting here is: «must be a letter, and af».
addMethod second parameter is a function, this is more important, the wording of the decision to use this method of verification.
If only one parameter, write directly, such as af: «a», then this is a unique parameter, if more than one parameter is written in [], separated by commas.
meta String mode
$ ( "# Myform"). Validate ({
meta: "validate",
submitHandler: function () {
alert ( "Submitted!")}
})
<Script type = "text / javascript"
src = "js / jquery.metadata.js"> </ script>
<Script type = "text / javascript"
src = "js / jquery.validate.js"> </ script>
<Form id = "myform">
<Input type = "text"
name = "email" class = "{validate: {required: true, email: true}}" />
<Input type = "submit"
value = "Submit" />
</ Form>
Examples Demo
Fictional examples
- Error message container
- Custom message as a data element
- radio (radio buttons), checkbox (check button) and select (drop-down box)
- Interactive form (Form) and plug (AJAX submission)
- Custom methods and message display
- Dynamic Forms
- Use jQuery UI Themeroller custom form style
- TinyMCE — a lightweight browser-based WYSIWYG editor
- File input box
- jQuery Mobile Forms Authentication
Examples of real-world
- Milk registration form
- Marketo registration form
- Housing sale folding panel form
- Remote CAPTCHA (PIN) verification