Download Article
Download Article
- Installing AutoHotkey
- Creating a Script
- Creating a Hotkey
- Creating a Hotstring
- Launching Apps or Websites
|
|
|
|
This wikiHow teaches you how to use AutoHotkey on a Windows computer. AutoHotkey is a free Windows scripting language that allows you to program different actions with various keyboard shortcuts. The following steps will show you how to install AutoHotkey as well as program a few basic scripts to enter text, run programs, and open websites using simple keyboard shortcuts.
-
1
Go to https://autohotkey.com in a web browser. Using your preferred web browser, go to official AutoHotkey website.
-
2
Click Download. It’s the green button in the center of the page.
Advertisement
-
3
Click Download AutoHotkey Installer. It’s the blue button at the top of the page. This will start the download of the AutoHotkey installer.
-
4
Run the installation file. Double-click the installation file you just downloaded to start the installer.
- By default, all your downloaded files can be found in your Downloads folder.
-
5
Click Express Installation. It’s the first option in the AutoHotkey Setup wizard. This will install AutoHotkey on your computer with the default configuration.
- When it’s finished installing you can click «Run AutoHotkey» to launch some of the documentation about AutoHotkey.
Advertisement
-
1
Right-click your desktop. When you right-click on any blank part of your desktop, this opens a drop-down menu.
-
2
Hover the mouse over New. When you place the mouse cursor over «New» you will see a list of programs you can create a new file for.
-
3
Click AutoHotkey Script. This will create a new AutoHotkey script on your desktop. It will have an image of a white page with a red «H» on it.
-
4
Rename the AutoHotkey file. By default, the new document will be named «NewAutoHotkeyScript.ahk» and it will be highlighted, allowing you type a new name for your script.
- Be sure not to erase the file extension of «.ahk» at the end. Your file must end with the «.ahk» file extension or else it won’t work with AutoHotkey.
-
5
Right-click your new script. This will open a drop-down menu with additional options for the file.
-
6
Click Edit Script. It’s the third option from the top. This will launch the AutoHotkey script in Notepad. This is where you will write the programming to create your first AutoHotkey script.
- There is some code and text already inserted into the first few lines of every new AHK script, you can ignore this and leave it alone for now.
Advertisement
-
1
On a new line, type the code for the keyboard shortcut you want to assign. For example, if you want to assign a command that does something when you press the key combination of Ctrl+E, you would type ^e. Each lowercase letter represents its own key, while special keys have their own symbols:
- + = ⇧ Shift
- ^ = Ctrl
- ! = Alt
- # = ⊞ Win (Windows key)
- Click here for a complete list of key commands.
-
2
Type two colons after the keys you assigned. Any key or key combination you typed needs to be followed by ::. So in our example, the first line of our code would look like:
-
3
Press ↵ Enter to go to the next line and press Tab ↹ to indent. You’ll type the command for what will happen with then hotkey is pressed on the line below the two colons. You can indent the line by pressing «Tab» or by typing several spaces
- You don’t have to indent the command line but it will keep your code organized and easy to read if you have errors later.
-
4
Type Send, and then type a message. The Send command will automatically type a message when a Hotkey is triggered. Anything you type after the comma will be typed automatically when you press the assigned Hotkey. For our example, if you wanted to include the message «wikiHow is awesome!» your code would look like:
- Special characters, like the exclamation mark, must be enclosed in braces { } so it isn’t confused with the symbol for the «Alt» key.
^e:: Send, wikiHow is awesome{!}
-
5
Press ↵ Enter to go the next line and type Return. The Return command denotes the end of a command and stops the code from going to the lines below.[1]
Your finished code should look like:^e:: Send, wikiHow is awesome{!} Return
-
6
Save your script. Click «File» in the menu bar at the top of Notepad and click «Save» in the drop-down menu. This will save the code you’ve added to the script file.
- You can close Notepad once your work has been saved.
-
7
Run the script. Double-click the script file on your desktop to run the script. You’ll see a green AutoHotkey icon appear in your system tray on the bottom-right of your screen. This indicates that an AutoHotkey script is active.
-
8
Test your Hotkey. Open a new word processing app or any app you can type text and press your Hotkey combo. In our example, if you press Ctrl+E you’ll see the text «wikiHow is awesome!» instantly appear.
Advertisement
-
1
Open your script or create a new one. You can open the script you were working on earlier and add a new command to it or create a new script from scratch.
- Right-click the script and select «Edit Script» to edit the previous script.
- Right-click the desktop and go to «New,» then select «Auto Hotkey Script.»
-
2
Go to a new line and type two colons. A Hotstring command starts with :: at the beginning.
- A Hotstring can take a word or phrase you type and replace it with a different word or phrase.
-
3
Type the letters, word, or phrase you want to replace. For example, you can create a Hotstring so that every time you type the acronym «btw» it would automatically change it to «By the way,» so you didn’t have to type it all out. In that example, so far your code would look like:
-
4
Type two more colons again. This will separate the end of the message you want to replace from the words or you want to replace it with. Using our example, the code would look like:
-
5
Type the message you want to replace it with. The message you type after the second pair of colons will automatically replace the first message in between the two sets of colons. In our example, the code would look like:
- Hotstrings don’t need a «Return» command and the end because they are self-contained on one line of a script
-
6
Save and run the script to test it out. Just like before, save your work by clicking «File» and «Save»—then double-click the script to run it. Then open any app or program you can type in to test it out. When you type the letters «btw» onto any page, it should immediately be replaced with «By the way,» in the text field.
Advertisement
-
1
Open your script or create a new one. You can open the script you were working on earlier and add a new command to it or create a new script from scratch.
- Right-click the script and select «Edit Script» to edit the previous script.
- Right-click the desktop and go to «New,» then select «Auto Hotkey Script.»
-
2
On a new line, type the code for the Hotkeys you want to assign. For example, if you wanted to open the wikiHow website whenever you pressed they keys Wind+W, you would type the code #w because «#» is the symbol for the Windows key and «w» is the code for the W key. In that example, the code would look like:
- Click here for a complete list of key symbols if you want to use a different key combination for your Hotkey.
-
3
Type the two colons, then go to the next line and indent. Immediately after typing the code for the keyboard shortcut, type two colons :: and then press ↵ Enter to go to the next line. Indent the line using several spaces or the Tab ↹ key.
- You don’t have to indent the command line but it will keep your code organized and easy to read if you have errors later.
-
4
Type Run,. The Run command can be used to launch any program, application or website. Type Run, with the comma at the end and Auto Hotkey will look for the name or location of any program or website listed after the comma. In our example, the code so far would look like:
-
5
Type the full location of any program on your computer or type any website’s full URL. For example, if you wanted your Hotkey to launch Internet Explorer, you would type C:Program Filesinternet exploreriexplore.exe after the Run command. In our example, since we want to launch the wikiHow website, our code would look like:
#w:: Run, https://wikihow.com
-
6
Press ↵ Enter to go the next line and type Return. The Return command denotes the end of a command and stops the code from going to the lines below. In our example. your finished code should look like:
#w:: Run, https://wikihow.com Return
-
7
Save and run the script to test it out. Just like before, save your work by clicking «File» and «Save»—then double-click the script to run it. If you followed our example, whenever you press the key combination of ⊞ Win+W, the wikiHow website will open in your default browser!
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
References
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Install AutoHotkey from https://www.autohotkey.com.
2. Right-click the desktop and click New.
3. Click AutoHotkey Script.
4. Right-click the script icon and select Edit Script.
5. Enter the code for the keyboard shortcut followed by two colons.
6. Press Enter.
7. Type «Send» followed by the word(s) or command.
8. Press Enter.
9. Type «Return» and save the file.
10. Double-click the script to run it.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 49,448 times.
Is this article up to date?
Download Article
Download Article
- Installing AutoHotkey
- Creating a Script
- Creating a Hotkey
- Creating a Hotstring
- Launching Apps or Websites
|
|
|
|
This wikiHow teaches you how to use AutoHotkey on a Windows computer. AutoHotkey is a free Windows scripting language that allows you to program different actions with various keyboard shortcuts. The following steps will show you how to install AutoHotkey as well as program a few basic scripts to enter text, run programs, and open websites using simple keyboard shortcuts.
-
1
Go to https://autohotkey.com in a web browser. Using your preferred web browser, go to official AutoHotkey website.
-
2
Click Download. It’s the green button in the center of the page.
Advertisement
-
3
Click Download AutoHotkey Installer. It’s the blue button at the top of the page. This will start the download of the AutoHotkey installer.
-
4
Run the installation file. Double-click the installation file you just downloaded to start the installer.
- By default, all your downloaded files can be found in your Downloads folder.
-
5
Click Express Installation. It’s the first option in the AutoHotkey Setup wizard. This will install AutoHotkey on your computer with the default configuration.
- When it’s finished installing you can click «Run AutoHotkey» to launch some of the documentation about AutoHotkey.
Advertisement
-
1
Right-click your desktop. When you right-click on any blank part of your desktop, this opens a drop-down menu.
-
2
Hover the mouse over New. When you place the mouse cursor over «New» you will see a list of programs you can create a new file for.
-
3
Click AutoHotkey Script. This will create a new AutoHotkey script on your desktop. It will have an image of a white page with a red «H» on it.
-
4
Rename the AutoHotkey file. By default, the new document will be named «NewAutoHotkeyScript.ahk» and it will be highlighted, allowing you type a new name for your script.
- Be sure not to erase the file extension of «.ahk» at the end. Your file must end with the «.ahk» file extension or else it won’t work with AutoHotkey.
-
5
Right-click your new script. This will open a drop-down menu with additional options for the file.
-
6
Click Edit Script. It’s the third option from the top. This will launch the AutoHotkey script in Notepad. This is where you will write the programming to create your first AutoHotkey script.
- There is some code and text already inserted into the first few lines of every new AHK script, you can ignore this and leave it alone for now.
Advertisement
-
1
On a new line, type the code for the keyboard shortcut you want to assign. For example, if you want to assign a command that does something when you press the key combination of Ctrl+E, you would type ^e. Each lowercase letter represents its own key, while special keys have their own symbols:
- + = ⇧ Shift
- ^ = Ctrl
- ! = Alt
- # = ⊞ Win (Windows key)
- Click here for a complete list of key commands.
-
2
Type two colons after the keys you assigned. Any key or key combination you typed needs to be followed by ::. So in our example, the first line of our code would look like:
-
3
Press ↵ Enter to go to the next line and press Tab ↹ to indent. You’ll type the command for what will happen with then hotkey is pressed on the line below the two colons. You can indent the line by pressing «Tab» or by typing several spaces
- You don’t have to indent the command line but it will keep your code organized and easy to read if you have errors later.
-
4
Type Send, and then type a message. The Send command will automatically type a message when a Hotkey is triggered. Anything you type after the comma will be typed automatically when you press the assigned Hotkey. For our example, if you wanted to include the message «wikiHow is awesome!» your code would look like:
- Special characters, like the exclamation mark, must be enclosed in braces { } so it isn’t confused with the symbol for the «Alt» key.
^e:: Send, wikiHow is awesome{!}
-
5
Press ↵ Enter to go the next line and type Return. The Return command denotes the end of a command and stops the code from going to the lines below.[1]
Your finished code should look like:^e:: Send, wikiHow is awesome{!} Return
-
6
Save your script. Click «File» in the menu bar at the top of Notepad and click «Save» in the drop-down menu. This will save the code you’ve added to the script file.
- You can close Notepad once your work has been saved.
-
7
Run the script. Double-click the script file on your desktop to run the script. You’ll see a green AutoHotkey icon appear in your system tray on the bottom-right of your screen. This indicates that an AutoHotkey script is active.
-
8
Test your Hotkey. Open a new word processing app or any app you can type text and press your Hotkey combo. In our example, if you press Ctrl+E you’ll see the text «wikiHow is awesome!» instantly appear.
Advertisement
-
1
Open your script or create a new one. You can open the script you were working on earlier and add a new command to it or create a new script from scratch.
- Right-click the script and select «Edit Script» to edit the previous script.
- Right-click the desktop and go to «New,» then select «Auto Hotkey Script.»
-
2
Go to a new line and type two colons. A Hotstring command starts with :: at the beginning.
- A Hotstring can take a word or phrase you type and replace it with a different word or phrase.
-
3
Type the letters, word, or phrase you want to replace. For example, you can create a Hotstring so that every time you type the acronym «btw» it would automatically change it to «By the way,» so you didn’t have to type it all out. In that example, so far your code would look like:
-
4
Type two more colons again. This will separate the end of the message you want to replace from the words or you want to replace it with. Using our example, the code would look like:
-
5
Type the message you want to replace it with. The message you type after the second pair of colons will automatically replace the first message in between the two sets of colons. In our example, the code would look like:
- Hotstrings don’t need a «Return» command and the end because they are self-contained on one line of a script
-
6
Save and run the script to test it out. Just like before, save your work by clicking «File» and «Save»—then double-click the script to run it. Then open any app or program you can type in to test it out. When you type the letters «btw» onto any page, it should immediately be replaced with «By the way,» in the text field.
Advertisement
-
1
Open your script or create a new one. You can open the script you were working on earlier and add a new command to it or create a new script from scratch.
- Right-click the script and select «Edit Script» to edit the previous script.
- Right-click the desktop and go to «New,» then select «Auto Hotkey Script.»
-
2
On a new line, type the code for the Hotkeys you want to assign. For example, if you wanted to open the wikiHow website whenever you pressed they keys Wind+W, you would type the code #w because «#» is the symbol for the Windows key and «w» is the code for the W key. In that example, the code would look like:
- Click here for a complete list of key symbols if you want to use a different key combination for your Hotkey.
-
3
Type the two colons, then go to the next line and indent. Immediately after typing the code for the keyboard shortcut, type two colons :: and then press ↵ Enter to go to the next line. Indent the line using several spaces or the Tab ↹ key.
- You don’t have to indent the command line but it will keep your code organized and easy to read if you have errors later.
-
4
Type Run,. The Run command can be used to launch any program, application or website. Type Run, with the comma at the end and Auto Hotkey will look for the name or location of any program or website listed after the comma. In our example, the code so far would look like:
-
5
Type the full location of any program on your computer or type any website’s full URL. For example, if you wanted your Hotkey to launch Internet Explorer, you would type C:Program Filesinternet exploreriexplore.exe after the Run command. In our example, since we want to launch the wikiHow website, our code would look like:
#w:: Run, https://wikihow.com
-
6
Press ↵ Enter to go the next line and type Return. The Return command denotes the end of a command and stops the code from going to the lines below. In our example. your finished code should look like:
#w:: Run, https://wikihow.com Return
-
7
Save and run the script to test it out. Just like before, save your work by clicking «File» and «Save»—then double-click the script to run it. If you followed our example, whenever you press the key combination of ⊞ Win+W, the wikiHow website will open in your default browser!
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
References
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Install AutoHotkey from https://www.autohotkey.com.
2. Right-click the desktop and click New.
3. Click AutoHotkey Script.
4. Right-click the script icon and select Edit Script.
5. Enter the code for the keyboard shortcut followed by two colons.
6. Press Enter.
7. Type «Send» followed by the word(s) or command.
8. Press Enter.
9. Type «Return» and save the file.
10. Double-click the script to run it.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 49,448 times.
Is this article up to date?
Все разделы
Нужна помощь?
Краткое обучение (начать здесь)
Оказавшись на этой странице, вероятно, вы собираетесь начать осваивать язык автоматизации Autohotkey.
В этой статье описана установка программы, ее базовые возможности и примеры кода. Наберитесь терпения, запасайтесь чаем и приступаем 
Все интересующие вопросы вы можете задать в нашей группе Вконтакте.
Autohotkey в играх
Обратите внимание, что макросы запрещены во многих играх. За использование Autohotkey ваш аккаунт может быть забанен!
Кроме этого, многие современные игры имеют активный античит, препятствующий программной эмуляции нажатий. Это значит, что нажатия, воспроизводимые скриптом могут игнорироваться.
Мы не содействуем читерству, и если античит блокирует работу Autohotkey в определенной игре- не будем помогать вам обойти защиту!
Стоит так же учитывать, что Autohotkey разработан для взаимодействия со средой Explorer’a и его окон. Такие команды как PixelSearch, PixelGetColor и ImageSearch вероятнее всего не будут работать в полноэкранных 3D приложениях.
Чаще всего Autohotkey воспринимает окна с отрисовкой 3D как черный квадрат (цвет 0x000000). Иногда проблема решается переводом игры в оконный режим, но корректная работа все равно не гарантируется и единого решения НЕТ.
Установка Autohotkey и редактора Notepad++
Перед началом работы неплохо бы скачать Autohotkey с оффициального сайта.
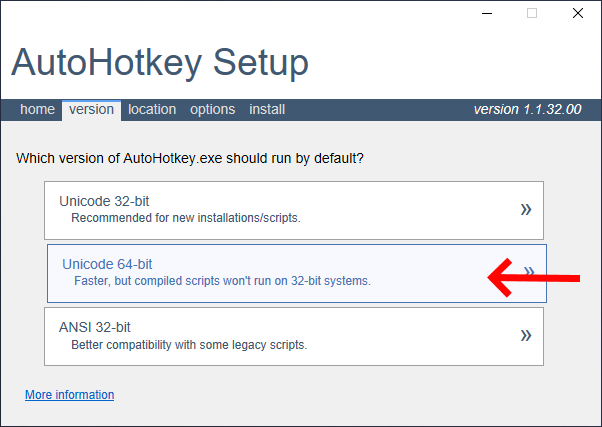
После запуска инсталятора выбираем Unicode версию программы, иначе получим иероглифы вместо русских букв. Лучше выбрать разрядность, соответствующую вашей ОС. Но стоит помнить что скрипты, скомпилированные x64 версией не запустятся на 32-разрядных ОС.
Для редактирования скриптов можно использовать любой текстовый редактор, включая «Блокнот». Но для удобства работы с кодом лучше использовать Notepad++, который так же скачиваем с оффициального сайта и устанавливаем.
После установки вам понадобится файл подсветки синтаксиса Autohotkey userDefineLang_AHK.xml. Сохраняем его в любое удобное место.
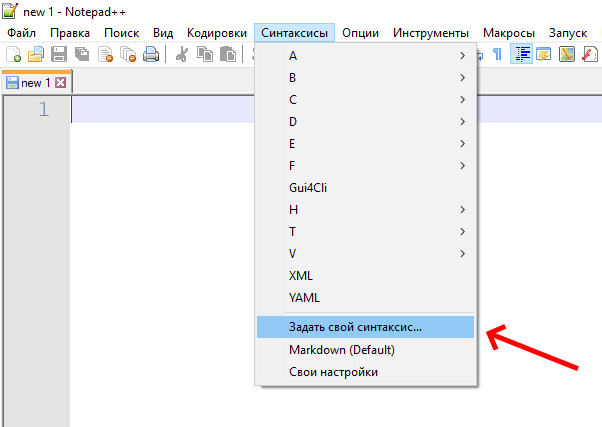
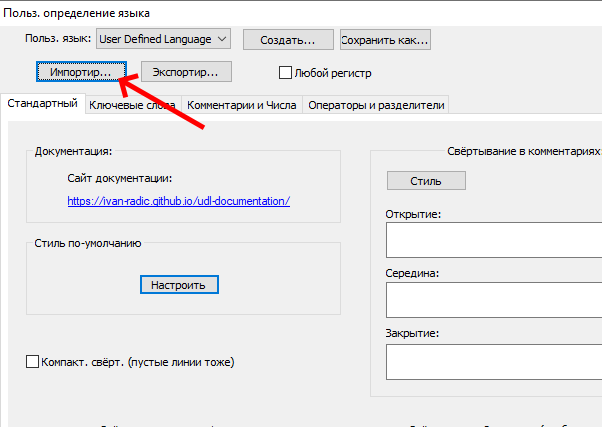
Теперь запускаем Notepad++, в меню «Синтксисы» выбираем «Задать свой синтаксис…». В открывшемся окне жмем «Импортировать» и выбираем скачанный файл.
После перезапуска программы в меню «Синтаксисы» появится Autohotkey, а файлы с расширением .ahk будут сразу открываться с подсветкой синтаксиса.
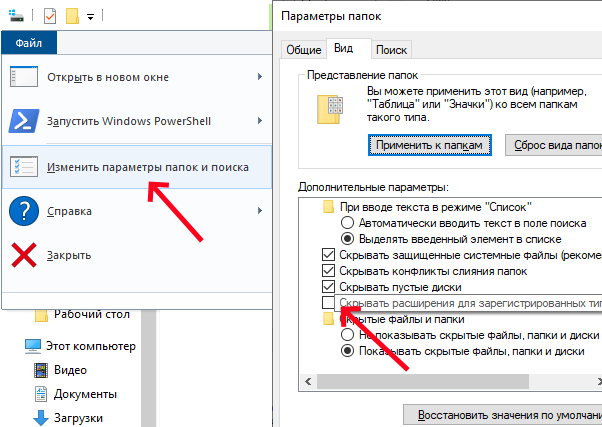
Рекомендую сразу включить отображение расширений файлов в системе. Для этого откройте любое окно проводника, в верхнем меню «Файл» выберите пункт «Параметры папок и поиска». В открывшемся окне во вкладке «Вид» снимите галочку «Скрывать расширения для зарегистрированных типов файлов».
Создание первого скрипта
После того, как среда Autohotkey и текстовый редактор установлены, можно приступать к созданию первого скрипта.
Скрипты являются обычными текстовыми файлами, имеющими расширение .ahk. Запускаются как любое приложение, двойным кликом мыши.
Чтобы отредактировать скрипт, нажмите на нем ПКМ > Открыть с помощью > Notepad++.
Вы можете создать обычный текстовый документ и переименовать его, изменив расширение с «.txt» на «.ahk», или сразу создать пустой скрипт, нажав ПКМ / Создать > / AutoHotkey Script. Не забудьте установить Notepad++ в качестве редактора по умолчанию для .ahk файлов.
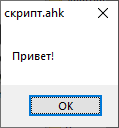
Создайте скрипт со следующим кодом и запустите его. Если вы увидели окно с приветствием- все установлено правильно и можно продолжать.
MsgBox, Привет!
Порядок исполнения команд
Обратите внимание! Данный пункт крайне важен для понимания работы программы.
В момент запуска скрипта, команды начинают выполняться по очереди сверху вниз. Выполнение новой команды не будет начато до тех пор, пока не окончена предыдущая.
Так интерпретатор будет последовательно исполнять код, пока не встретит Return. Эта команда прерывает текущий поток. С его помощью обозначаются пределы макрокоманды, а так же возвращаются значения из функций.
MsgBox, Эта команда выполнится
Return
MsgBox, А эта нет, ведь поток был прерван
Если по мере выполнения кода встречается цикл- он выполняется до тех пор, пока истинно его условие, или он не будет разорван командой Break. Как выглядят циклы мы разберем чуть ниже, не торопитесь 
Комментарии в коде и отладка
Когда нужно оставить в коде строчку с пояснением- на помощь приходит комментарий, по умолчанию он отделяется точкой с запятой. Вся строка после ; игнорируется интерпретатором. Обратите внимание, что в Autohotkey нет многострочных комментариев! Каждая строка экранируется отдельно.
MsgBox, Тест ;А это комментарий в коде, он обычно поясняет происходящее
Для отладки кода (проверки условий, просмотра значений переменных и т.д.) проще всего использовать команды MsgBox и ToolTip. Первая выводит информацию в виде окна и ждет подтверждения, вторая показывает всплывающую подсказку и не прерывает выполнение кода.
Горячие клавиши
Основным назначением Autohotkey является назначение горячих клавиш. Они представляют собой сочетания клавиш и кнопок мыши, при нажатии которых выполняется заданная последовательность команд (макрокоманда, она же- макрос).
Запись горячей клавиши может иметь однострочный и многострочный вид, в зависимости от необходимого количества команд.
^1::MsgBox, вы нажали Ctrl+1 ;Однострочная запись
;Многострочная запись
^2::
MsgBox, Вы нажали Ctrl+2
Sleep, 3000
MsgBox, И дождались появления второго окна через 3 сек.
Return
Перед двоеточием указывается клавиша или сочетание клавиш, вызывающие действие. Больше о горячих клавишах можно узнать здесь. Так же, наверняка, вам пригодится список клавиш и кнопок мыши.
Строки автозамены
Строки автозамены имеют тот же принцип, что и горячие клавиши, но заменяют не сочетание клавиш, а фрагмент строки. Чаще всего используются для развертывания аббревиатур.
;При вводе «кхл», развернет сокращение
::кхл::Континентальная хоккейная лига
;Поддерживает многострочную запись и вызов любых команд
::ихний::
MsgBox, вы допустили ужасную грамматическую ошибку. Ваш компьютер будет выключен.
Shutdown, 1
Return
Все возможности строк автозамены, такие как чувствительность к регистру, замена части слова, задержка нажатий- ищите в соответствующей Статье.
Эмуляция нажатий
Для эмуляции нажатий и ввода текста используется команда Send.
Она имеет несколько вариаций: Send, SendPlay, SendInput и SendRaw. Подробно про их отличия можно прочитать по ссылке выше.
;Ввод строки по нажатию 1
1::Send, Здравствуйте, чем могу вам помочь?{Enter}Текст с новой строки
;Обратите внимание на !, без скобок он равносилен нажатию Alt
2::Send, Благодарим за визит{!}
;Выполнит комбинацию Ctrl+Shift+Esc, запустив диспетчер задач
3::Send, ^+{Esc}
;Зажмет Alt и несколько раз нажмет Tab, переключая окна
4::
Send, {Alt down}
Loop, 5
{
Send, {Tab}
Sleep, 500
}
Send, {Alt up}
Return
Переменные и выражения
Для хранения и обработки информации служат переменные. Во вступительном гайде мы рассмотрим лишь три основных вида: логический, числовой и текстовый. Переменные в Autohotkey динамически изменяют свой тип в зависимости от последнего присвоенного значения.
Имя переменной не должно превышать 254 знаков, может состоять из букв, цифр и знаков # _ @ $ ? [ ]. Вопреки традициям других языков, в хоткее имена переменных могут начинаться с цифр и даже содержать кириллицу.
Логический (булевый) тип предназначен для хранения 1 или 0 (true или false). Чаше всего используется в условиях, где есть всего два варианта выбора, а так же в функциях, для обозначения успешности или провала операции.
bool_val := true
;Здесь мы при нажатии 1 инвертируем значение переменной
1::
MsgBox, bool_val содержал значение %bool_val%
bool_val := !bool_val
Return
Числовой тип, как не сложно догадаться, применяется для операций с числами. Поддерживается большинство арифметических операций, а так же десятичные дроби.
numeric_val := 0
;Здесь мы при нажатии 1 добавляем 10 к значению переменной
1::
MsgBox, numeric_val содержал значение %numeric_val%
numeric_val := numeric_val + 10
Return
Строковый тип хранит отдельные символы или фрагменты текста. Работа со строками немного отличается от цифровых и булевых переменных- для них есть целый ряд специальных строковых функций.
string:=»Валера»
string.=» — гений кодинга»
StringReplace, string, string, ни
string := SubStr(string, 1, 12)
MsgBox, %string%
Логическое ветвление
Наверняка вы уже задумались, как выполнять действие только при соблюдении конкретного условия? На помощь приходит ветвление с логическими операторами if и else.
Так же существуют и другие команды, представляющие собой условие.
Пожалуй, самым простым применением условия является назначение двух чередующихся действий на одну и ту же горячую клавишу. В этом примере введена переменная, которая принимает противоположное значение при каждом новом вызове ГК.
ckeck := false
^1::
if(ckeck)
MsgBox, Сейчас условие верно!
else
MsgBox, Условие не верно
ckeck := !ckeck
Return
Еще одним примером может служить определение времени суток:
if(A_Hour < 6)
state = ночь
else if(A_Hour < 10)
state = утро
else if(A_Hour < 17)
state = день
else
state = вечер
MsgBox, Сейчас %state%`, %A_Hour% часов
Блок кода {}
Блок кода обозначается фигурными скобками и объединяет несколько комад или функций.
Он нужен чтобы указать интерпретатору, что несколько команд нужно выполнить вместе.
Чаще всего блок {} используется для группировки команд внутри условий или циклов.
;Здесь MsgBox и Send будут выполнены только если MyVar равна 5
if(MyVar == 5)
{
MsgBox, MyVar равна 5!
Send, Абсолютно равна
}
;А здесь скобок нет и Send будет выполнен в любом случае
if(MyVar == 5)
MsgBox, MyVar равна 5!
Send, Абсолютно равна
Циклы
Для повторения определенного участка кода несколько раз используются циклы. В Autohotkey их несколько видов, самым простым из которых является Loop.
;Пять повторений одного участка кода
^1::
Loop, 5
MsgBox, Это %A_Index% интерация цикла из 5
return
;Отображение тултипа пока нажата ЛКМ
~LButton::
while(GetKeyState(«LButton»))
{
ToolTip, А теперь отпустите ЛКМ
Sleep, 100
}
ToolTip
return
Запуск программ, открытие ссылок
Для запуска EXE приложений, открытия окон проводника или браузера используется команда Run.
;Запуск программы
Run, %A_ProgramFiles%Some_ProgramProgram.exe
;Открытие веб страницы
Run, https://ahk-wiki.ru
Команды и функции
В Autohotkey есть две основных структуры: команды и функции.
Обе предназначены для выполнения какого-либо действия, но отличаются способом записи.
У многих команд есть функция-двойник, выполняющая ту же операцию.
В отличае от функций, команды нельзя комбинировать или использовать одну команду как аргумент другой.
Команды не используют скобки вокруг параметров, вы можете легко отличить их от функций:
;Пример команды
Command, параметр1, параметр2, параметр3
;Пример функции
Function(параметр1, параметр2, параметр3)
Обратите внимание, что:
;Внутри функций можно производить вычисления:
SubStr(37 * 12, 1, 2)
;Переменные в функции передаются без знаков %%:
SubStr(A_Now, 7, 2)
;Результат выполнения одной функции может быть параметром другой:
SubStr(A_AhkPath, InStr(A_AhkPath, «AutoHotkey»))
;Текст в функциях должен быть обернут в кавычки:
SubStr(«I’m scripting, awesome!», 16)
;Функции могут возвращать результат
;Здесь MyVar будет присвоен результат выполнения функции
MyVar := SubStr(«I’m scripting, awesome!», 16)
Заключение
В этой статье приведены самые базовые возможности программы. Полный список функций можно найти на Главной странице справочника.
Рекомендуем последовательно пройти по описанию всех команд для примерного понимания их назначения перед тем, как начинать писать свой первый скрипт 
Перед тем, как приступить к написанию кода, необходимо составить алгоритм. Распишите по шагам, что должна делать ваша программа. Так будет гораздо проще искать команды, необходимые для выполнения каждого из шагов.