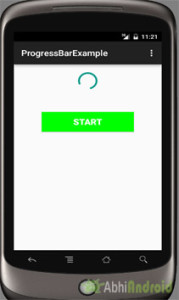
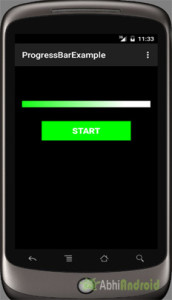
There are 3 ways to solve this question:
- How to adjust the progressbar color declaratively
- How to adjust the progressbar color programmatically, but choose the color from various predetermined colors declared before compile-time
- How to adjust the progressbar color programmatically, and also create the color programatically.
In particular there is a lot of confusion around #2 and #3, as seen in comments to amfcosta’s answer. That answer will yield unpredictable color results anytime you’d like to set the progressbar to anything except primary colors, as it only modifies the background color, and the actual progress bar «clip» area will still be a yellow overlay with reduced opacity. For example, using that method to set the background to dark purple will result in a progress bar «clip» color of some crazy pinkish color resulting from dark purple and yellow mixing via reduced alpha.
So anyhow, #1 is answered perfectly by Ryan and Štarke answers most of #3, but for those looking for a complete solution to #2 and #3:
How to adjust the progressbar color programmatically, but choose the color from a predetermined color declared in XML
res/drawable/my_progressbar.xml:
Create this file but change the colors in my_progress and my_secondsProgress:
(NOTE: This is just a copy of the actual XML file defining the default android SDK ProgressBar, but I’ve changed the IDs and Colors. The original is named progress_horizontal)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layer-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:id="@+id/my_progress_background">
<shape>
<corners android:radius="5dip" />
<gradient
android:startColor="#ff9d9e9d"
android:centerColor="#ff5a5d5a"
android:centerY="0.75"
android:endColor="#ff747674"
android:angle="270"
/>
</shape>
</item>
<item android:id="@+id/my_secondaryProgress">
<clip>
<shape>
<corners android:radius="5dip" />
<gradient
android:startColor="#80ff171d"
android:centerColor="#80ff1315"
android:centerY="0.75"
android:endColor="#a0ff0208"
android:angle="270"
/>
</shape>
</clip>
</item>
<item android:id="@+id/my_progress">
<clip>
<shape>
<corners android:radius="5dip" />
<gradient
android:startColor="#7d2afdff"
android:centerColor="#ff2afdff"
android:centerY="0.75"
android:endColor="#ff22b9ba"
android:angle="270"
/>
</shape>
</clip>
</item>
In your Java:
final Drawable drawable;
int sdk = android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT;
if(sdk < 16) {
drawable = ctx.getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.my_progressbar);
} else {
drawable = ContextCompat.getDrawable(ctx, R.drawable.my_progressbar);
}
progressBar.setProgressDrawable(drawable)
How to adjust the progressbar color programmatically, and also create the color programatically
EDIT: I found the time to solve this properly. My former answer left this a bit ambiguous.
A ProgressBar is composed as 3 Drawables in a LayerDrawable.
- Layer 1 is the background
- Layer 2 is the secondary progress color
- Layer 3 is the main progress bar color
In the example below I’ll change the color of the main progress bar to cyan.
//Create new ClipDrawable to replace the old one
float pxCornerRadius = viewUtils.convertDpToPixel(5);
final float[] roundedCorners = new float[] { pxCornerRadius, pxCornerRadius, pxCornerRadius, pxCornerRadius, pxCornerRadius, pxCornerRadius, pxCornerRadius, pxCornerRadius };
ShapeDrawable shpDrawable = new ShapeDrawable(new RoundRectShape(roundedCorners, null, null));
shpDrawable.getPaint().setColor(Color.CYAN);
final ClipDrawable newProgressClip = new ClipDrawable(shpDrawable, Gravity.LEFT, ClipDrawable.HORIZONTAL);
//Replace the existing ClipDrawable with this new one
final LayerDrawable layers = (LayerDrawable) progressBar.getProgressDrawable();
layers.setDrawableByLayerId(R.id.my_progress, newProgressClip);
That example set it to a solid color. You may set it to a gradient color by replacing
shpDrawable.getPaint().setColor(Color.CYAN);
with
Shader shader = new LinearGradient(0, 0, 0, progressBar.getHeight(), Color.WHITE, Color.BLACK, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP);
shpDrawable.getPaint().setShader(shader);
Cheers.
-Lance
Asked
13 years, 1 month ago
Viewed
754k times
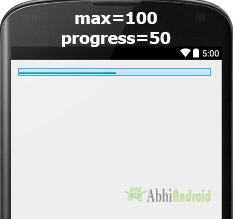
I’m using an horizontal progress bar in my Android application, and I want to change its progress color (which is Yellow by default). How can I do it using code (not XML)?
Mahozad
15.3k11 gold badges101 silver badges119 bronze badges
asked Jan 7, 2010 at 14:13
4
For a horizontal ProgressBar, you can use a ColorFilter, too, like this:
progressBar.getProgressDrawable().setColorFilter(
Color.RED, android.graphics.PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
Note: This modifies the appearance of all progress bars in your app. To only modify one specific progress bar, do this:
Drawable progressDrawable = progressBar.getProgressDrawable().mutate();
progressDrawable.setColorFilter(Color.RED, android.graphics.PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
progressBar.setProgressDrawable(progressDrawable);
If progressBar is indeterminate then use getIndeterminateDrawable() instead of getProgressDrawable().
Since Lollipop (API 21) you can set a progress tint:
progressBar.setProgressTintList(ColorStateList.valueOf(Color.RED));
answered Apr 4, 2013 at 11:25
Torben KohlmeierTorben Kohlmeier
6,6231 gold badge15 silver badges15 bronze badges
16
This is not programmatically but I think it could help a lot of people anyway.
I tried a lot and the most efficient way was to add this lines to my ProgressBar in the .xml File:
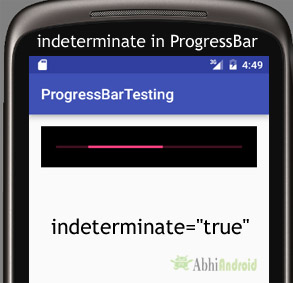
android:indeterminate="true"
android:indeterminateTintMode="src_atop"
android:indeterminateTint="@color/secondary"
So in the end this code did it for me:
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressBar"
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleLarge"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="50dp"
android:visibility="visible"
android:indeterminate="true"
android:indeterminateTintMode="src_atop"
android:indeterminateTint="@color/secondary">
This solution works for API 21+
Vadim Kotov
7,9648 gold badges48 silver badges62 bronze badges
answered Jul 11, 2015 at 16:04
FFirmenichFFirmenich
5,4511 gold badge17 silver badges28 bronze badges
6
I’m sorry that it’s not the answer, but what’s driving the requirement setting it from code ?
And .setProgressDrawable should work if it’s defined correctly
<layer-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:id="@android:id/background">
<shape>
<corners android:radius="5dip" />
<gradient
android:startColor="#ff9d9e9d"
android:centerColor="#ff5a5d5a"
android:centerY="0.75"
android:endColor="#ff747674"
android:angle="270"
/>
</shape>
</item>
<item android:id="@android:id/secondaryProgress">
<clip>
<shape>
<corners android:radius="5dip" />
<gradient
android:startColor="#80ffd300"
android:centerColor="#80ffb600"
android:centerY="0.75"
android:endColor="#a0ffcb00"
android:angle="270"
/>
</shape>
</clip>
</item>
<item android:id="@android:id/progress">
<clip>
<shape>
<corners
android:radius="5dip" />
<gradient
android:startColor="@color/progress_start"
android:endColor="@color/progress_end"
android:angle="270"
/>
</shape>
</clip>
</item>
</layer-list>
WarrenFaith
57.3k25 gold badges134 silver badges148 bronze badges
answered Jan 7, 2010 at 15:00
Alex VolovoyAlex Volovoy
67.5k13 gold badges73 silver badges54 bronze badges
11
For my indeterminate progressbar (spinner) I just set a color filter on the drawable. Works great and just one line.
Example where setting color to red:
ProgressBar spinner = new android.widget.ProgressBar(
context,
null,
android.R.attr.progressBarStyle);
spinner.getIndeterminateDrawable().setColorFilter(0xFFFF0000, android.graphics.PorterDuff.Mode.MULTIPLY);
answered Jun 7, 2012 at 9:14
jhavatarjhavatar
3,2061 gold badge17 silver badges11 bronze badges
5
This is an old question, but using theme is not mentioned here. If your default theme is using AppCompat, your ProgressBar‘s color will be colorAccent you have defined.
Changing colorAccent will also change your ProgressBar‘s color, but there changes also reflects at multiple places. So, if you want a different color just for a specific PregressBar you can do that by applying theme to that ProgressBar :
-
Extend your default theme and override
colorAccent<style name="AppTheme.WhiteAccent"> <item name="colorAccent">@color/white</item> <!-- Whatever color you want--> </style> -
And in
ProgressBaradd theandroid:themeattribute:android:theme="@style/AppTheme.WhiteAccent"
So it will look something like this:
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/loading"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme.WhiteAccent" />
So you are just changing a colorAccent for your particular ProgressBar.
Note: Using style will not work. You need to use android:theme only.
You can find more use of theme here: https://plus.google.com/u/0/+AndroidDevelopers/posts/JXHKyhsWHAH
answered Jul 9, 2016 at 13:08
kirtan403kirtan403
7,1476 gold badges52 silver badges95 bronze badges
9
All API
if use all API just create the theme in style
style.xml
<resources>
//...
<style name="progressBarBlue" parent="@style/Theme.AppCompat">
<item name="colorAccent">@color/blue</item>
</style>
</resources>
and use in progress
<ProgressBar
...
android:theme="@style/progressBarBlue" />
API level 21 and higher
if used in API level 21 and higher just use this code:
<ProgressBar
//...
android:indeterminate="true"
android:indeterminateTintMode="src_atop"
android:indeterminateTint="@color/secondary"/>
answered Sep 24, 2018 at 14:03
Rasoul MiriRasoul Miri
10.2k1 gold badge64 silver badges75 bronze badges
1
This works for me. It also works for lower version too. Add this to your syles.xml
<style name="ProgressBarTheme" parent="ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Light">
<item name="colorAccent">@color/colorPrimary</item>
</style>
And use it like this in xml
<ProgressBar
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:theme="@style/ProgressBarTheme"
/>
answered Sep 25, 2019 at 5:39
3
This worked for me :
<ProgressBar
android:indeterminateTint="#d60909"
... />
answered Jul 6, 2017 at 5:40
MOH3NMOH3N
8859 silver badges14 bronze badges
1
as per some of the suggestions, you CAN specify a shape and clipdrawable with a colour, then set it. I have this working programatically. This is how I do it..
First make sure you import the drawable library..
import android.graphics.drawable.*;
Then use the code similar to below;
ProgressBar pg = (ProgressBar)row.findViewById(R.id.progress);
final float[] roundedCorners = new float[] { 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5 };
pgDrawable = new ShapeDrawable(new RoundRectShape(roundedCorners, null,null));
String MyColor = "#FF00FF";
pgDrawable.getPaint().setColor(Color.parseColor(MyColor));
ClipDrawable progress = new ClipDrawable(pgDrawable, Gravity.LEFT, ClipDrawable.HORIZONTAL);
pg.setProgressDrawable(progress);
pg.setBackgroundDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(android.R.drawable.progress_horizontal));
pg.setProgress(45);
answered Mar 6, 2011 at 9:46
PaulieGPaulieG
3413 silver badges2 bronze badges
6
if Indeterminate:
((ProgressBar)findViewById(R.id.progressBar))
.getIndeterminateDrawable()
.setColorFilter(Color.RED, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
answered Mar 22, 2015 at 17:24
the.knifethe.knife
4094 silver badges3 bronze badges
1
android:progressTint="#ffffff"
answered Sep 14, 2016 at 13:32
PaulPaul
7741 gold badge9 silver badges15 bronze badges
0
Nowadays in 2016 I found some pre-Lollipop devices don’t honour the colorAccent setting, so my final solution for all APIs is now the following:
// fixes pre-Lollipop progressBar indeterminateDrawable tinting
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
Drawable wrapDrawable = DrawableCompat.wrap(mProgressBar.getIndeterminateDrawable());
DrawableCompat.setTint(wrapDrawable, ContextCompat.getColor(getContext(), android.R.color.holo_green_light));
mProgressBar.setIndeterminateDrawable(DrawableCompat.unwrap(wrapDrawable));
} else {
mProgressBar.getIndeterminateDrawable().setColorFilter(ContextCompat.getColor(getContext(), android.R.color.holo_green_light), PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
}
For bonus points, it doesn’t use any deprecated code. Try it!
answered Sep 14, 2016 at 10:31
2
For SDK ver 21 and above
android:indeterminateTint="@color/orange"
in XML Works for me, is easy enough.
answered Apr 21, 2017 at 12:38
MughilMughil
6856 silver badges8 bronze badges
1
Trust me, the easiest solution is just paste this inside progressBar :
android:indeterminateTint="@android:color/white"
answered Nov 8, 2021 at 15:42
A.I.ShakilA.I.Shakil
7354 silver badges18 bronze badges
THis is what i did. Worked.
ProgressBar:
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressBar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="4"
android:indeterminateDrawable="@drawable/progressdrawable"
/>
progressdrawable.xml:
Here use gradient to change colour as you like. And android:toDegrees=»X» increse the value of X and progressbar rotate fast. Decrease and it rotate slow.Customize according to your needs.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<rotate xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:duration="4000"
android:fromDegrees="0"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:toDegrees="360" >
<shape
android:innerRadius="20dp"
android:shape="ring"
android:thickness="4dp"
android:useLevel="false" >
<size
android:height="48dp"
android:width="48dp" />
<gradient
android:centerColor="#80ec7e2a"
android:centerY="0.5"
android:endColor="#ffec7e2a"
android:startColor="#00ec7e2a"
android:type="sweep"
android:useLevel="false" />
</shape>
</rotate>
sample:
answered Jan 31, 2018 at 6:44
1
Add in ProgressBar inside of Xml
For SDK ver 21 and above
android:indeterminateTint="@color/red"
answered Jun 23, 2021 at 3:04
Mark NashatMark Nashat
5907 silver badges8 bronze badges
2
Hit the same problem while working on modifying the look/feel of the default progress bar. Here is some more info that will hopefully help people 
- The name of the xml file must only contain characters:
a-z0-9_.(ie. no capitals!) - To reference your «drawable» it is
R.drawable.filename - To override the default look, you use
myProgressBar.setProgressDrawable(...), however you need can’t just refer to your custom layout asR.drawable.filename, you need to retrieve it as aDrawable:Resources res = getResources(); myProgressBar.setProgressDrawable(res.getDrawable(R.drawable.filename); - You need to set style before setting progress/secondary progress/max (setting it afterwards for me resulted in an ’empty’ progress bar)
answered Feb 28, 2011 at 12:41
pykopyko
3,3595 gold badges25 silver badges31 bronze badges
You can try to change your Styles, Themes, or using android:indeterminateTint=»@color/yourColor» anywhere you want, but there’s just one way o doing that will work on any Android SKD version:
If you progress bar is not indeterminate, please use:
progressBar.getProgressDrawable().setColorFilter(ContextCompat.getColor(context, R.color.yourColor), PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN );
If you progress bar is indeterminate, please use:
progressBar.getIndeterminateDrawable().setColorFilter(ContextCompat.getColor(getContext(), R.color.yourColor), PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN );
It’s sad that Android is such a mess!
answered Dec 4, 2017 at 16:53
1
How I did it in horizontal ProgressBar:
LayerDrawable layerDrawable = (LayerDrawable) progressBar.getProgressDrawable();
Drawable progressDrawable = layerDrawable.findDrawableByLayerId(android.R.id.progress);
progressDrawable.setColorFilter(color, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
answered Dec 16, 2015 at 11:36
mieszk3mieszk3
2663 silver badges9 bronze badges
2
There’s probably one thing that hasn’t been referred to in this answer:
If your theme is inheriting from Theme.AppCompat, ProgressBar will assume the color you defined as "colorAccent" in your theme.
So, using..
<item name="colorAccent">@color/custom_color</item>
..will tint the color of the ProgressBar automagically to the @color/custom_color .
answered Jan 21, 2016 at 18:53
1
Simplest Solution if you want to change the colour in the layout xml file, use the below code and use indeterminateTint property for your desired color.
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressBar"
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:indeterminate="true"
android:indeterminateTintMode="src_atop"
android:indeterminateTint="#ddbd4e"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
answered Nov 25, 2017 at 4:27
Naveed AhmadNaveed Ahmad
6,5672 gold badges58 silver badges83 bronze badges
0
The most simple way of changing the foreground and background colour of a progress bar is
<ProgressBar
style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal"
android:id="@+id/pb_main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="8dp"
android:progress="30"
android:progressTint="#82e9de"
android:progressBackgroundTint="#82e9de"
/>
just add
android:progressTint="#82e9de" //for foreground colour
android:progressBackgroundTint="#82e9de" //for background colour
answered Apr 18, 2020 at 6:50
1
This solution worked for me :
<style name="Progressbar.White" parent="AppTheme">
<item name="colorControlActivated">@color/white</item>
</style>
<ProgressBar
android:layout_width="@dimen/d_40"
android:layout_height="@dimen/d_40"
android:indeterminate="true"
android:theme="@style/Progressbar.White"/>
Hiroyuki Nuri
5,21815 gold badges71 silver badges124 bronze badges
answered Aug 1, 2017 at 13:55
S.JavedS.Javed
3303 silver badges7 bronze badges
0
For default ( indeterminate )
add
android:indeterminateTint="@color/white"
for determinate
android:progressTint="@color/color_1"
//OR
progressBar.getProgressDrawable().setColorFilter( PorterDuffColorFilter(Color.RED,android.graphics.PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN));
answered Oct 7, 2021 at 9:19
NasibNasib
1,0181 gold badge11 silver badges22 bronze badges
To change horizontal ProgressBar color (in kotlin):
fun tintHorizontalProgress(progress: ProgressBar, @ColorInt color: Int = ContextCompat.getColor(progress.context, R.color.colorPrimary)){
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
progress.progressTintList = ColorStateList.valueOf(color)
} else{
val layerDrawable = progress.progressDrawable as? LayerDrawable
val progressDrawable = layerDrawable?.findDrawableByLayerId(android.R.id.progress)
progressDrawable?.setColorFilter(color, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_ATOP)
}
}
To change indeterminate ProgressBar color:
fun tintIndeterminateProgress(progress: ProgressBar, @ColorInt color: Int = ContextCompat.getColor(progress.context, R.color.colorPrimary)){
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
progress.indeterminateTintList = ColorStateList.valueOf(color)
} else {
(progress.indeterminateDrawable as? LayerDrawable)?.apply {
if (numberOfLayers >= 2) {
setId(0, android.R.id.progress)
setId(1, android.R.id.secondaryProgress)
val progressDrawable = findDrawableByLayerId(android.R.id.progress).mutate()
progressDrawable.setColorFilter(color, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_ATOP)
}
}
}
}
And it finally normally tint pre-lollipop progressBars
answered Apr 5, 2019 at 14:19
JohnJohn
1,38014 silver badges15 bronze badges
0
One more little thing, the theme solution does work if you inherit a base theme, so for app compact your theme should be:
<style name="AppTheme.Custom" parent="@style/Theme.AppCompat">
<item name="colorAccent">@color/custom</item>
</style>
And then set this in the progress bar theme
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressCircle_progressBar"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme.Custom"
android:indeterminate="true"/>
answered May 23, 2017 at 19:27
CalinCalin
6,5815 gold badges47 silver badges79 bronze badges
0
Simply use:
DrawableCompat.setTint(progressBar.getIndeterminateDrawable(),yourColor)
answered May 3, 2020 at 14:15
1
simply use:
PorterDuff.Mode mode = PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN;
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT <= Build.VERSION_CODES.GINGERBREAD_MR1) {
mode = PorterDuff.Mode.MULTIPLY;
}
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
progressBar.setProgressTintList(ColorStateList.valueOf(Color.RED));
progressBar.setProgressBackgroundTintList(ColorStateList.valueOf(Color.RED));
} else {
Drawable progressDrawable;
progressDrawable = (progressBar.isIndeterminate() ? progressBar.getIndeterminateDrawable() : progressBar.getProgressDrawable()).mutate();
progressDrawable.setColorFilter(context.getResources().getColor(Color.RED), mode);
progressBar.setProgressDrawable(progressDrawable);
}
answered Aug 10, 2019 at 15:57
Mohammad FneishMohammad Fneish
7391 gold badge8 silver badges19 bronze badges
Horizontal progress bar custom material style :
To change color of background and progress of horizontal progress bar.
<style name="MyProgressBar" parent="@style/Widget.AppCompat.ProgressBar.Horizontal">
<item name="android:progressBackgroundTint">#69f0ae</item>
<item name="android:progressTint">#b71c1c</item>
<item name="android:minWidth">200dp</item>
</style>
Apply it to progress bar by setting style attribute, for custom material styles and custom progress bar check http://www.zoftino.com/android-progressbar-and-custom-progressbar-examples
answered Sep 21, 2017 at 14:53
Arnav RaoArnav Rao
6,5122 gold badges32 silver badges31 bronze badges
1
Use the android.support.v4.graphics.drawable.DrawableCompat:
Drawable progressDrawable = progressBar.getIndeterminateDrawable();
if (progressDrawable != null) {
Drawable mutateDrawable = progressDrawable.mutate();
DrawableCompat.setTint(mutateDrawable, primaryColor);
progressBar.setProgressDrawable(mutateDrawable);
}
answered Mar 15, 2018 at 13:35
Alécio CarvalhoAlécio Carvalho
13.3k5 gold badges67 silver badges73 bronze badges
Asked
13 years, 1 month ago
Viewed
754k times
I’m using an horizontal progress bar in my Android application, and I want to change its progress color (which is Yellow by default). How can I do it using code (not XML)?
Mahozad
15.3k11 gold badges101 silver badges119 bronze badges
asked Jan 7, 2010 at 14:13
4
For a horizontal ProgressBar, you can use a ColorFilter, too, like this:
progressBar.getProgressDrawable().setColorFilter(
Color.RED, android.graphics.PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
Note: This modifies the appearance of all progress bars in your app. To only modify one specific progress bar, do this:
Drawable progressDrawable = progressBar.getProgressDrawable().mutate();
progressDrawable.setColorFilter(Color.RED, android.graphics.PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
progressBar.setProgressDrawable(progressDrawable);
If progressBar is indeterminate then use getIndeterminateDrawable() instead of getProgressDrawable().
Since Lollipop (API 21) you can set a progress tint:
progressBar.setProgressTintList(ColorStateList.valueOf(Color.RED));
answered Apr 4, 2013 at 11:25
Torben KohlmeierTorben Kohlmeier
6,6231 gold badge15 silver badges15 bronze badges
16
This is not programmatically but I think it could help a lot of people anyway.
I tried a lot and the most efficient way was to add this lines to my ProgressBar in the .xml File:
android:indeterminate="true"
android:indeterminateTintMode="src_atop"
android:indeterminateTint="@color/secondary"
So in the end this code did it for me:
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressBar"
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleLarge"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="50dp"
android:visibility="visible"
android:indeterminate="true"
android:indeterminateTintMode="src_atop"
android:indeterminateTint="@color/secondary">
This solution works for API 21+
Vadim Kotov
7,9648 gold badges48 silver badges62 bronze badges
answered Jul 11, 2015 at 16:04
FFirmenichFFirmenich
5,4511 gold badge17 silver badges28 bronze badges
6
I’m sorry that it’s not the answer, but what’s driving the requirement setting it from code ?
And .setProgressDrawable should work if it’s defined correctly
<layer-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:id="@android:id/background">
<shape>
<corners android:radius="5dip" />
<gradient
android:startColor="#ff9d9e9d"
android:centerColor="#ff5a5d5a"
android:centerY="0.75"
android:endColor="#ff747674"
android:angle="270"
/>
</shape>
</item>
<item android:id="@android:id/secondaryProgress">
<clip>
<shape>
<corners android:radius="5dip" />
<gradient
android:startColor="#80ffd300"
android:centerColor="#80ffb600"
android:centerY="0.75"
android:endColor="#a0ffcb00"
android:angle="270"
/>
</shape>
</clip>
</item>
<item android:id="@android:id/progress">
<clip>
<shape>
<corners
android:radius="5dip" />
<gradient
android:startColor="@color/progress_start"
android:endColor="@color/progress_end"
android:angle="270"
/>
</shape>
</clip>
</item>
</layer-list>
WarrenFaith
57.3k25 gold badges134 silver badges148 bronze badges
answered Jan 7, 2010 at 15:00
Alex VolovoyAlex Volovoy
67.5k13 gold badges73 silver badges54 bronze badges
11
For my indeterminate progressbar (spinner) I just set a color filter on the drawable. Works great and just one line.
Example where setting color to red:
ProgressBar spinner = new android.widget.ProgressBar(
context,
null,
android.R.attr.progressBarStyle);
spinner.getIndeterminateDrawable().setColorFilter(0xFFFF0000, android.graphics.PorterDuff.Mode.MULTIPLY);
answered Jun 7, 2012 at 9:14
jhavatarjhavatar
3,2061 gold badge17 silver badges11 bronze badges
5
This is an old question, but using theme is not mentioned here. If your default theme is using AppCompat, your ProgressBar‘s color will be colorAccent you have defined.
Changing colorAccent will also change your ProgressBar‘s color, but there changes also reflects at multiple places. So, if you want a different color just for a specific PregressBar you can do that by applying theme to that ProgressBar :
-
Extend your default theme and override
colorAccent<style name="AppTheme.WhiteAccent"> <item name="colorAccent">@color/white</item> <!-- Whatever color you want--> </style> -
And in
ProgressBaradd theandroid:themeattribute:android:theme="@style/AppTheme.WhiteAccent"
So it will look something like this:
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/loading"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme.WhiteAccent" />
So you are just changing a colorAccent for your particular ProgressBar.
Note: Using style will not work. You need to use android:theme only.
You can find more use of theme here: https://plus.google.com/u/0/+AndroidDevelopers/posts/JXHKyhsWHAH
answered Jul 9, 2016 at 13:08
kirtan403kirtan403
7,1476 gold badges52 silver badges95 bronze badges
9
All API
if use all API just create the theme in style
style.xml
<resources>
//...
<style name="progressBarBlue" parent="@style/Theme.AppCompat">
<item name="colorAccent">@color/blue</item>
</style>
</resources>
and use in progress
<ProgressBar
...
android:theme="@style/progressBarBlue" />
API level 21 and higher
if used in API level 21 and higher just use this code:
<ProgressBar
//...
android:indeterminate="true"
android:indeterminateTintMode="src_atop"
android:indeterminateTint="@color/secondary"/>
answered Sep 24, 2018 at 14:03
Rasoul MiriRasoul Miri
10.2k1 gold badge64 silver badges75 bronze badges
1
This works for me. It also works for lower version too. Add this to your syles.xml
<style name="ProgressBarTheme" parent="ThemeOverlay.AppCompat.Light">
<item name="colorAccent">@color/colorPrimary</item>
</style>
And use it like this in xml
<ProgressBar
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:theme="@style/ProgressBarTheme"
/>
answered Sep 25, 2019 at 5:39
3
This worked for me :
<ProgressBar
android:indeterminateTint="#d60909"
... />
answered Jul 6, 2017 at 5:40
MOH3NMOH3N
8859 silver badges14 bronze badges
1
as per some of the suggestions, you CAN specify a shape and clipdrawable with a colour, then set it. I have this working programatically. This is how I do it..
First make sure you import the drawable library..
import android.graphics.drawable.*;
Then use the code similar to below;
ProgressBar pg = (ProgressBar)row.findViewById(R.id.progress);
final float[] roundedCorners = new float[] { 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5 };
pgDrawable = new ShapeDrawable(new RoundRectShape(roundedCorners, null,null));
String MyColor = "#FF00FF";
pgDrawable.getPaint().setColor(Color.parseColor(MyColor));
ClipDrawable progress = new ClipDrawable(pgDrawable, Gravity.LEFT, ClipDrawable.HORIZONTAL);
pg.setProgressDrawable(progress);
pg.setBackgroundDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(android.R.drawable.progress_horizontal));
pg.setProgress(45);
answered Mar 6, 2011 at 9:46
PaulieGPaulieG
3413 silver badges2 bronze badges
6
if Indeterminate:
((ProgressBar)findViewById(R.id.progressBar))
.getIndeterminateDrawable()
.setColorFilter(Color.RED, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
answered Mar 22, 2015 at 17:24
the.knifethe.knife
4094 silver badges3 bronze badges
1
android:progressTint="#ffffff"
answered Sep 14, 2016 at 13:32
PaulPaul
7741 gold badge9 silver badges15 bronze badges
0
Nowadays in 2016 I found some pre-Lollipop devices don’t honour the colorAccent setting, so my final solution for all APIs is now the following:
// fixes pre-Lollipop progressBar indeterminateDrawable tinting
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
Drawable wrapDrawable = DrawableCompat.wrap(mProgressBar.getIndeterminateDrawable());
DrawableCompat.setTint(wrapDrawable, ContextCompat.getColor(getContext(), android.R.color.holo_green_light));
mProgressBar.setIndeterminateDrawable(DrawableCompat.unwrap(wrapDrawable));
} else {
mProgressBar.getIndeterminateDrawable().setColorFilter(ContextCompat.getColor(getContext(), android.R.color.holo_green_light), PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
}
For bonus points, it doesn’t use any deprecated code. Try it!
answered Sep 14, 2016 at 10:31
2
For SDK ver 21 and above
android:indeterminateTint="@color/orange"
in XML Works for me, is easy enough.
answered Apr 21, 2017 at 12:38
MughilMughil
6856 silver badges8 bronze badges
1
Trust me, the easiest solution is just paste this inside progressBar :
android:indeterminateTint="@android:color/white"
answered Nov 8, 2021 at 15:42
A.I.ShakilA.I.Shakil
7354 silver badges18 bronze badges
THis is what i did. Worked.
ProgressBar:
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressBar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="4"
android:indeterminateDrawable="@drawable/progressdrawable"
/>
progressdrawable.xml:
Here use gradient to change colour as you like. And android:toDegrees=»X» increse the value of X and progressbar rotate fast. Decrease and it rotate slow.Customize according to your needs.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<rotate xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:duration="4000"
android:fromDegrees="0"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:toDegrees="360" >
<shape
android:innerRadius="20dp"
android:shape="ring"
android:thickness="4dp"
android:useLevel="false" >
<size
android:height="48dp"
android:width="48dp" />
<gradient
android:centerColor="#80ec7e2a"
android:centerY="0.5"
android:endColor="#ffec7e2a"
android:startColor="#00ec7e2a"
android:type="sweep"
android:useLevel="false" />
</shape>
</rotate>
sample:
answered Jan 31, 2018 at 6:44
1
Add in ProgressBar inside of Xml
For SDK ver 21 and above
android:indeterminateTint="@color/red"
answered Jun 23, 2021 at 3:04
Mark NashatMark Nashat
5907 silver badges8 bronze badges
2
Hit the same problem while working on modifying the look/feel of the default progress bar. Here is some more info that will hopefully help people 
- The name of the xml file must only contain characters:
a-z0-9_.(ie. no capitals!) - To reference your «drawable» it is
R.drawable.filename - To override the default look, you use
myProgressBar.setProgressDrawable(...), however you need can’t just refer to your custom layout asR.drawable.filename, you need to retrieve it as aDrawable:Resources res = getResources(); myProgressBar.setProgressDrawable(res.getDrawable(R.drawable.filename); - You need to set style before setting progress/secondary progress/max (setting it afterwards for me resulted in an ’empty’ progress bar)
answered Feb 28, 2011 at 12:41
pykopyko
3,3595 gold badges25 silver badges31 bronze badges
You can try to change your Styles, Themes, or using android:indeterminateTint=»@color/yourColor» anywhere you want, but there’s just one way o doing that will work on any Android SKD version:
If you progress bar is not indeterminate, please use:
progressBar.getProgressDrawable().setColorFilter(ContextCompat.getColor(context, R.color.yourColor), PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN );
If you progress bar is indeterminate, please use:
progressBar.getIndeterminateDrawable().setColorFilter(ContextCompat.getColor(getContext(), R.color.yourColor), PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN );
It’s sad that Android is such a mess!
answered Dec 4, 2017 at 16:53
1
How I did it in horizontal ProgressBar:
LayerDrawable layerDrawable = (LayerDrawable) progressBar.getProgressDrawable();
Drawable progressDrawable = layerDrawable.findDrawableByLayerId(android.R.id.progress);
progressDrawable.setColorFilter(color, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
answered Dec 16, 2015 at 11:36
mieszk3mieszk3
2663 silver badges9 bronze badges
2
There’s probably one thing that hasn’t been referred to in this answer:
If your theme is inheriting from Theme.AppCompat, ProgressBar will assume the color you defined as "colorAccent" in your theme.
So, using..
<item name="colorAccent">@color/custom_color</item>
..will tint the color of the ProgressBar automagically to the @color/custom_color .
answered Jan 21, 2016 at 18:53
1
Simplest Solution if you want to change the colour in the layout xml file, use the below code and use indeterminateTint property for your desired color.
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressBar"
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:indeterminate="true"
android:indeterminateTintMode="src_atop"
android:indeterminateTint="#ddbd4e"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
answered Nov 25, 2017 at 4:27
Naveed AhmadNaveed Ahmad
6,5672 gold badges58 silver badges83 bronze badges
0
The most simple way of changing the foreground and background colour of a progress bar is
<ProgressBar
style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal"
android:id="@+id/pb_main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="8dp"
android:progress="30"
android:progressTint="#82e9de"
android:progressBackgroundTint="#82e9de"
/>
just add
android:progressTint="#82e9de" //for foreground colour
android:progressBackgroundTint="#82e9de" //for background colour
answered Apr 18, 2020 at 6:50
1
This solution worked for me :
<style name="Progressbar.White" parent="AppTheme">
<item name="colorControlActivated">@color/white</item>
</style>
<ProgressBar
android:layout_width="@dimen/d_40"
android:layout_height="@dimen/d_40"
android:indeterminate="true"
android:theme="@style/Progressbar.White"/>
Hiroyuki Nuri
5,21815 gold badges71 silver badges124 bronze badges
answered Aug 1, 2017 at 13:55
S.JavedS.Javed
3303 silver badges7 bronze badges
0
For default ( indeterminate )
add
android:indeterminateTint="@color/white"
for determinate
android:progressTint="@color/color_1"
//OR
progressBar.getProgressDrawable().setColorFilter( PorterDuffColorFilter(Color.RED,android.graphics.PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN));
answered Oct 7, 2021 at 9:19
NasibNasib
1,0181 gold badge11 silver badges22 bronze badges
To change horizontal ProgressBar color (in kotlin):
fun tintHorizontalProgress(progress: ProgressBar, @ColorInt color: Int = ContextCompat.getColor(progress.context, R.color.colorPrimary)){
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
progress.progressTintList = ColorStateList.valueOf(color)
} else{
val layerDrawable = progress.progressDrawable as? LayerDrawable
val progressDrawable = layerDrawable?.findDrawableByLayerId(android.R.id.progress)
progressDrawable?.setColorFilter(color, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_ATOP)
}
}
To change indeterminate ProgressBar color:
fun tintIndeterminateProgress(progress: ProgressBar, @ColorInt color: Int = ContextCompat.getColor(progress.context, R.color.colorPrimary)){
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
progress.indeterminateTintList = ColorStateList.valueOf(color)
} else {
(progress.indeterminateDrawable as? LayerDrawable)?.apply {
if (numberOfLayers >= 2) {
setId(0, android.R.id.progress)
setId(1, android.R.id.secondaryProgress)
val progressDrawable = findDrawableByLayerId(android.R.id.progress).mutate()
progressDrawable.setColorFilter(color, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_ATOP)
}
}
}
}
And it finally normally tint pre-lollipop progressBars
answered Apr 5, 2019 at 14:19
JohnJohn
1,38014 silver badges15 bronze badges
0
One more little thing, the theme solution does work if you inherit a base theme, so for app compact your theme should be:
<style name="AppTheme.Custom" parent="@style/Theme.AppCompat">
<item name="colorAccent">@color/custom</item>
</style>
And then set this in the progress bar theme
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressCircle_progressBar"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme.Custom"
android:indeterminate="true"/>
answered May 23, 2017 at 19:27
CalinCalin
6,5815 gold badges47 silver badges79 bronze badges
0
Simply use:
DrawableCompat.setTint(progressBar.getIndeterminateDrawable(),yourColor)
answered May 3, 2020 at 14:15
1
simply use:
PorterDuff.Mode mode = PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN;
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT <= Build.VERSION_CODES.GINGERBREAD_MR1) {
mode = PorterDuff.Mode.MULTIPLY;
}
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
progressBar.setProgressTintList(ColorStateList.valueOf(Color.RED));
progressBar.setProgressBackgroundTintList(ColorStateList.valueOf(Color.RED));
} else {
Drawable progressDrawable;
progressDrawable = (progressBar.isIndeterminate() ? progressBar.getIndeterminateDrawable() : progressBar.getProgressDrawable()).mutate();
progressDrawable.setColorFilter(context.getResources().getColor(Color.RED), mode);
progressBar.setProgressDrawable(progressDrawable);
}
answered Aug 10, 2019 at 15:57
Mohammad FneishMohammad Fneish
7391 gold badge8 silver badges19 bronze badges
Horizontal progress bar custom material style :
To change color of background and progress of horizontal progress bar.
<style name="MyProgressBar" parent="@style/Widget.AppCompat.ProgressBar.Horizontal">
<item name="android:progressBackgroundTint">#69f0ae</item>
<item name="android:progressTint">#b71c1c</item>
<item name="android:minWidth">200dp</item>
</style>
Apply it to progress bar by setting style attribute, for custom material styles and custom progress bar check http://www.zoftino.com/android-progressbar-and-custom-progressbar-examples
answered Sep 21, 2017 at 14:53
Arnav RaoArnav Rao
6,5122 gold badges32 silver badges31 bronze badges
1
Use the android.support.v4.graphics.drawable.DrawableCompat:
Drawable progressDrawable = progressBar.getIndeterminateDrawable();
if (progressDrawable != null) {
Drawable mutateDrawable = progressDrawable.mutate();
DrawableCompat.setTint(mutateDrawable, primaryColor);
progressBar.setProgressDrawable(mutateDrawable);
}
answered Mar 15, 2018 at 13:35
Alécio CarvalhoAlécio Carvalho
13.3k5 gold badges67 silver badges73 bronze badges
Improve Article
Save Article
Improve Article
Save Article
In this article, we will see how we can add color to a ProgressBar in android. Android ProgressBar is a user interface control that indicates the progress of an operation. For example, downloading a file, uploading a file on the internet we can see the ProgressBar estimate the time remaining in operation. Note in this article we will be using Java and XML to set the color.
Step by Step Implementation
Step 1: Create a New Project
- To create a new project in Android Studio please refer to How to Create/Start a New Project in Android Studio.
- Note that select Java as the programming language.
Step 2: Create a custom ProgressBar
- Go to the app > res > drawable > right-click > New > Drawable Resource File and name the file as progress_bg.
- Inside the XML file add a rotate tag with some attributes(see code)
- Inside rotate tag create a shape tag within which create the size and gradient tag
- Attributes of these tags are given in the code below.
- Below is the code for the progress_bg.xml file.
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<rotate
android:fromDegrees="0"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:toDegrees="360">
<shape
android:innerRadiusRatio="3"
android:shape="ring"
android:thicknessRatio="8"
android:useLevel="false">
<size
android:width="76dip"
android:height="76dip" />
<gradient
android:angle="0"
android:endColor="#00ffffff"
android:startColor="#447a29"
android:type="sweep"
android:useLevel="false" />
</shape>
</rotate>
Step 3: Working with the activity_main.xml file
- Go to the activity_main.xml file and refer to the following code.
- Open the activity_main.xml file and in the ProgressBar tag and set the drawable in indeterminateDrawable attribute.
- Below is the code for the activity_main.xml file.
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="20dp">
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/ProgressBar01"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:indeterminate="true"
android:indeterminateDrawable="@drawable/progress_bg"
android:progress="0" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/show_button"
android:layout_width="191dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/ProgressBar01"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="80dp"
android:text="Progress Bar" />
</RelativeLayout>
Step 4: Working with the MainActivity.java file
- Go to the MainActivity.java file and refer to the following code.
- Below is the code for the MainActivity.java file. Comments are added inside the code to understand the code in more detail.
Java
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.ProgressBar;
import android.widget.TextView;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Handler handler = new Handler();
public static Button button;
public static TextView textView;
public static ImageView img1, img2;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final ProgressBar progressBar = findViewById(R.id.ProgressBar01);
progressBar.getProgress();
}
}
Output:
Основы
Стилизация
Индикатор с текстом
Программное создание индикатора
Основы
Компонент ProgressBar (Индикатор прогресса) применяется в тех случаях, когда пользователю нужно показать, что программа не зависла, а выполняет продолжительную работу.
Находится в категории Widgets.
Студия предлагает несколько видов индикаторов: ProgressBar и ProgressBar (Horizontal). В свою очередь компонент имеет несколько модификаций и их отличия заложены в стилях, если посмотреть XML-описание компонентов. Стили постоянно меняются, поэтому проще выбрать атрибут style и посмотреть предлагаемые варианты из выпадающего списка на текущий момент.
Методы для работы с ProgressBar:
- setProgress() — устанавливает заданное значение индикатора прогресса;
- getProgress() — возвращает текущее значение индикатора прогресса;
- incrementProgressBy() — устанавливает величину дискретизации приращения значения индикатора;
- setMax() — устанавливает максимальное значение величины прогресса.
Круговые индикаторы Normal, Small и Large можно просто разместить на экране, и они будут бесконечно выводить анимацию вращения без единой строчки кода.
Как правило, «бесконечный» индикатор выводят в нужный момент, а когда задача выполнена, то его скрывают. Видимость можно установить через XML и программно.
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressBar"
android:visibility="invisible"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
В коде используется метод setVisibility()
ProgressBar progressBar = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.progressBar);
progressBar.setVisibility(ProgressBar.VISIBLE);
// запускаем длительную операцию
progressBar.setVisibility(ProgressBar.INVISIBLE);
Сейчас проекты в студии используют Material Design, поэтому цвет индикатора будет соответствовать ресурсу colorAccent.
Можно переопределить цвет, если вы хотите отказаться от этой связи с colorAccent, задав свой стиль.
<style name="CircularProgress" parent="Theme.AppCompat.Light">
<item name="colorAccent">@android:color/holo_green_light</item>
</style>
Подключаем через тему.
<ProgressBar
...
android:theme="@style/CircularProgress" />
Другая настройка связана с Tint — оттенками цвета (Android 5.0).
<ProgressBar
android:indeterminateTintMode="src_in"
android:indeterminateTint="@color/my_color"/>
Стилизация
Если вам не нравится внешний вид стандартных индикаторов, то можете придумать свой. Есть два варианта для реализации этой цели. В первом случае можно подготовить готовый png-файл (spin_custom.png) и поместить его в ресурс, например, в папку res/drawable.
Затем в этой же папке создаём xml-файл spinner_png.xml с таким содержанием:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<animated-rotate xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:drawable="@drawable/spin_custom"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%" />
Теперь в разметке активности можно определять ProgressBar так:
<ProgressBar
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:indeterminateDrawable="@drawable/spinner_png"
android:indeterminateOnly="true" />
Если запустить проект, то увидим такой индикатор:
В реальности индикатор выглядит немного корявым, подёргиваясь на экране. Кроме того, изображение можно улучшить, уменьшив количество цветов и сократив размер файла.
Второй вариант выглядит предпочтительней. На этот раз мы обойдёмся без графических файлов, а будем использовать только XML-разметку. В этой же папке поместим файл spinner_ring.xml следующего содержания:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<animated-rotate xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%" >
<shape
android:innerRadiusRatio="4"
android:shape="ring"
android:thicknessRatio="5.333"
android:useLevel="false" >
<size
android:height="18dip"
android:width="18dip" />
<gradient
android:centerColor="#886688cc"
android:centerY="0.50"
android:endColor="#ff6688cc"
android:startColor="#006688cc"
android:type="sweep"
android:useLevel="false" />
</shape>
</animated-rotate>
Теперь в разметке активности пропишем строки:
<ProgressBar
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dip"
android:indeterminateDrawable="@drawable/spinner_ring"
android:indeterminateOnly="true" />
Получим следующий результат:
Индикатор с текстом
К сожалению, индикатор не выводит текст во время работы, что не очень удобно. Можно создать свой ProgressBar из TextView или создать свой компонент на основе ProgressBar. Другой простой способ — наложить текстовый блок прямо на индикатор, используя RelativeLayout. Пример для пояснения.
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/rl_progress_bar_set"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/btn_start"
android:visibility="visible" >
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/pb_horizontal"
style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:max="100" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_progress_horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBottom="@id/pb_horizontal"
android:background="@android:color/transparent"
android:gravity="center" />
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_below="@id/pb_horizontal"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp" >
<ProgressBar
style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Large"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:background="@android:color/background_dark" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_progress_circle"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:background="@android:color/transparent"
android:gravity="center"
android:textColor="@android:color/white" />
</RelativeLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_start"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="15dp"
android:onClick="onClick"
android:text="Поехали"
android:textSize="25dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
Код, чтобы увидеть работу индикатора. При каждом щелчке кнопки значение индикаторов увеличиваются на 10 процентов.
package ru.alexanderklimov.test;
import ...
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private int progress = 0;
private ProgressBar pbHorizontal;
private TextView tvProgressHorizontal;
private TextView tvProgressCircle;
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
pbHorizontal = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.pb_horizontal);
tvProgressHorizontal = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_progress_horizontal);
tvProgressCircle = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv_progress_circle);
}
public void onClick(View v) {
progress = progress + 10;
postProgress(progress);
}
private void postProgress(int progress) {
String strProgress = String.valueOf(progress) + " %";
pbHorizontal.setProgress(progress);
if (progress == 0) {
pbHorizontal.setSecondaryProgress(0);
} else {
pbHorizontal.setSecondaryProgress(progress + 5);
}
tvProgressHorizontal.setText(strProgress);
tvProgressCircle.setText(strProgress);
}
}
Индикаторы прогресса также можно использовать в заголовках приложения у старых устройств, а также в ActionBar и ToolBar у новых устройств.
Компонент постоянно дорабатывается. Например, в Android 8 появились новые методы isAnimating(), getMin(), setMin().
Анимация ObjectAnimator
Можно подключить готовую анимацию для визуализации компонента.
private static final TimeInterpolator GAUGE_ANIMATION_INTERPOLATOR = new DecelerateInterpolator(2);
private static final int MAX_LEVEL = 100;
private static final long GAUGE_ANIMATION_DURATION = 5000;
private ProgressBar mProgressBar;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mProgressBar = findViewById(R.id.progressBar);
}
// По щелчку кнопки
public void onClick(View view) {
ObjectAnimator animator = ObjectAnimator.ofInt(mProgressBar, "progress", 0, MAX_LEVEL);
animator.setInterpolator(GAUGE_ANIMATION_INTERPOLATOR);
animator.setDuration(GAUGE_ANIMATION_DURATION);
animator.start();
}
Дополнительное чтение
Меняем стандартный индикатор через drawable — простой и быстрый способ.
Material ProgressBar — статья про создание собственного индикатора в стиле Material Design
Indeterminate — серия статей на тему создания индикаторов прогресса, ссылка на первую часть.
How to create your own progressBar in Android. – Medium
Make an android custom view, publish and open source.
Библиотеки
skydoves/ProgressView: A polished and flexible ProgressView, fully customizable with animations.
GitHub — nipun-birla/BoxLoaderView
GitHub — VladimirWrites/Lemniscate: An easy way to make your progress view nice and sleek.
yuriy-budiyev/circular-progress-bar: Circular progress bar
timqi/SectorProgressView: a simple progress prompt or chart widget of android using circle and a sector
kofigyan/StateProgressBar: Android library to realize the various states and transitions in a ProgressBar.
JustZak/DilatingDotsProgressBar: A customizable indeterminate progress bar
DreaminginCodeZH/MaterialProgressBar: Material Design ProgressBar with consistent appearance
castorflex/SmoothProgressBar
Todd-Davies/ProgressWheel
passsy/android-HoloCircularProgressBar
daimajia/NumberProgressBar
lsjwzh/MaterialLoadingProgressBar
amanjeetsingh150/CoolProgressViews: Android library with collection of cool progress views.
Подборка индикаторов
glomadrian/loading-balls: A highly configurable library to do loading progress with animated balls — анимация для длительных операций.
droidchef/tinglingsquares: A delightful progress animation
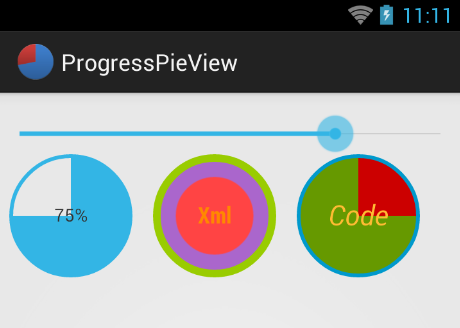
Индикатор прогресса в виде пирога. Домашняя страница FilipPudak/ProgressPieView
cdeange/RopeProgressBar: Android ProgressBar that «bends» under its own weight. Inspired by http://drbl.in/nwih
biodunalfet/SlidingSquaresLoader: A simple progress loader
Реклама
void
addChildrenForAccessibility(ArrayList<View> outChildren)
Adds the children of this View relevant for accessibility to the given list
as output.
void
addExtraDataToAccessibilityNodeInfo(AccessibilityNodeInfo info, String extraDataKey, Bundle arguments)
Adds extra data to an AccessibilityNodeInfo based on an explicit request for the
additional data.
void
addFocusables(ArrayList<View> views, int direction)
Add any focusable views that are descendants of this view (possibly
including this view if it is focusable itself) to views.
void
addFocusables(ArrayList<View> views, int direction, int focusableMode)
Adds any focusable views that are descendants of this view (possibly
including this view if it is focusable itself) to views.
void
addKeyboardNavigationClusters(Collection<View> views, int direction)
Adds any keyboard navigation cluster roots that are descendants of this view (possibly
including this view if it is a cluster root itself) to views.
void
addOnAttachStateChangeListener(View.OnAttachStateChangeListener listener)
Add a listener for attach state changes.
void
addOnLayoutChangeListener(View.OnLayoutChangeListener listener)
Add a listener that will be called when the bounds of the view change due to
layout processing.
void
addOnUnhandledKeyEventListener(View.OnUnhandledKeyEventListener listener)
Adds a listener which will receive unhandled KeyEvents.
void
addTouchables(ArrayList<View> views)
Add any touchable views that are descendants of this view (possibly
including this view if it is touchable itself) to views.
ViewPropertyAnimator
animate()
This method returns a ViewPropertyAnimator object, which can be used to animate
specific properties on this View.
void
announceForAccessibility(CharSequence text)
Convenience method for sending a AccessibilityEvent#TYPE_ANNOUNCEMENT
AccessibilityEvent to suggest that an accessibility service announce the
specified text to its users.
void
autofill(AutofillValue value)
Automatically fills the content of this view with the value.
void
autofill(SparseArray<AutofillValue> values)
Automatically fills the content of the virtual children within this view.
boolean
awakenScrollBars(int startDelay, boolean invalidate)
Trigger the scrollbars to draw.
boolean
awakenScrollBars(int startDelay)
Trigger the scrollbars to draw.
boolean
awakenScrollBars()
Trigger the scrollbars to draw.
void
bringToFront()
Change the view’s z order in the tree, so it’s on top of other sibling
views.
void
buildDrawingCache(boolean autoScale)
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The view drawing cache was largely made obsolete with the introduction of
hardware-accelerated rendering in API 11. With hardware-acceleration, intermediate cache
layers are largely unnecessary and can easily result in a net loss in performance due to the
cost of creating and updating the layer. In the rare cases where caching layers are useful,
such as for alpha animations, setLayerType(int, android.graphics.Paint) handles this with hardware
rendering. For software-rendered snapshots of a small part of the View hierarchy or
individual Views it is recommended to create a Canvas from either a Bitmap or
Picture and call draw(android.graphics.Canvas) on the View. However these
software-rendered usages are discouraged and have compatibility issues with hardware-only
rendering features such as Config.HARDWARE
bitmaps, real-time shadows, and outline clipping. For screenshots of the UI for feedback
reports or unit testing the PixelCopy API is recommended.
void
buildDrawingCache()
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The view drawing cache was largely made obsolete with the introduction of
hardware-accelerated rendering in API 11. With hardware-acceleration, intermediate cache
layers are largely unnecessary and can easily result in a net loss in performance due to the
cost of creating and updating the layer. In the rare cases where caching layers are useful,
such as for alpha animations, setLayerType(int, android.graphics.Paint) handles this with hardware
rendering. For software-rendered snapshots of a small part of the View hierarchy or
individual Views it is recommended to create a Canvas from either a Bitmap or
Picture and call draw(android.graphics.Canvas) on the View. However these
software-rendered usages are discouraged and have compatibility issues with hardware-only
rendering features such as Config.HARDWARE
bitmaps, real-time shadows, and outline clipping. For screenshots of the UI for feedback
reports or unit testing the PixelCopy API is recommended.
void
buildLayer()
Forces this view’s layer to be created and this view to be rendered
into its layer.
boolean
callOnClick()
Directly call any attached OnClickListener.
boolean
canResolveLayoutDirection()
Check if layout direction resolution can be done.
boolean
canResolveTextAlignment()
Check if text alignment resolution can be done.
boolean
canResolveTextDirection()
Check if text direction resolution can be done.
boolean
canScrollHorizontally(int direction)
Check if this view can be scrolled horizontally in a certain direction.
boolean
canScrollVertically(int direction)
Check if this view can be scrolled vertically in a certain direction.
final
void
cancelDragAndDrop()
Cancels an ongoing drag and drop operation.
void
cancelLongPress()
Cancels a pending long press.
final
void
cancelPendingInputEvents()
Cancel any deferred high-level input events that were previously posted to the event queue.
boolean
checkInputConnectionProxy(View view)
Called by the InputMethodManager
when a view who is not the current
input connection target is trying to make a call on the manager.
void
clearAnimation()
Cancels any animations for this view.
void
clearFocus()
Called when this view wants to give up focus.
void
clearViewTranslationCallback()
Clear the ViewTranslationCallback from this view.
static
int
combineMeasuredStates(int curState, int newState)
Merge two states as returned by getMeasuredState().
int
computeHorizontalScrollExtent()
Compute the horizontal extent of the horizontal scrollbar’s thumb
within the horizontal range.
int
computeHorizontalScrollOffset()
Compute the horizontal offset of the horizontal scrollbar’s thumb
within the horizontal range.
int
computeHorizontalScrollRange()
Compute the horizontal range that the horizontal scrollbar
represents.
void
computeScroll()
Called by a parent to request that a child update its values for mScrollX
and mScrollY if necessary.
WindowInsets
computeSystemWindowInsets(WindowInsets in, Rect outLocalInsets)
Compute insets that should be consumed by this view and the ones that should propagate
to those under it.
int
computeVerticalScrollExtent()
Compute the vertical extent of the vertical scrollbar’s thumb
within the vertical range.
int
computeVerticalScrollOffset()
Compute the vertical offset of the vertical scrollbar’s thumb
within the horizontal range.
int
computeVerticalScrollRange()
Compute the vertical range that the vertical scrollbar represents.
AccessibilityNodeInfo
createAccessibilityNodeInfo()
Returns an AccessibilityNodeInfo representing this view from the
point of view of an AccessibilityService.
void
createContextMenu(ContextMenu menu)
Show the context menu for this view.
void
destroyDrawingCache()
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The view drawing cache was largely made obsolete with the introduction of
hardware-accelerated rendering in API 11. With hardware-acceleration, intermediate cache
layers are largely unnecessary and can easily result in a net loss in performance due to the
cost of creating and updating the layer. In the rare cases where caching layers are useful,
such as for alpha animations, setLayerType(int, android.graphics.Paint) handles this with hardware
rendering. For software-rendered snapshots of a small part of the View hierarchy or
individual Views it is recommended to create a Canvas from either a Bitmap or
Picture and call draw(android.graphics.Canvas) on the View. However these
software-rendered usages are discouraged and have compatibility issues with hardware-only
rendering features such as Config.HARDWARE
bitmaps, real-time shadows, and outline clipping. For screenshots of the UI for feedback
reports or unit testing the PixelCopy API is recommended.
WindowInsets
dispatchApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets)
Request to apply the given window insets to this view or another view in its subtree.
boolean
dispatchCapturedPointerEvent(MotionEvent event)
Pass a captured pointer event down to the focused view.
void
dispatchConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig)
Dispatch a notification about a resource configuration change down
the view hierarchy.
void
dispatchCreateViewTranslationRequest(Map<AutofillId, long[]> viewIds, int[] supportedFormats, TranslationCapability capability, List<ViewTranslationRequest> requests)
Dispatch to collect the ViewTranslationRequests for translation purpose by traversing
the hierarchy when the app requests ui translation.
void
dispatchDisplayHint(int hint)
Dispatch a hint about whether this view is displayed.
boolean
dispatchDragEvent(DragEvent event)
Detects if this View is enabled and has a drag event listener.
void
dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas)
Called by draw to draw the child views.
void
dispatchDrawableHotspotChanged(float x, float y)
Dispatches drawableHotspotChanged to all of this View’s children.
void
dispatchFinishTemporaryDetach()
Dispatch onFinishTemporaryDetach() to this View and its direct children if this is
a container View.
boolean
dispatchGenericFocusedEvent(MotionEvent event)
Dispatch a generic motion event to the currently focused view.
boolean
dispatchGenericMotionEvent(MotionEvent event)
Dispatch a generic motion event.
boolean
dispatchGenericPointerEvent(MotionEvent event)
Dispatch a generic motion event to the view under the first pointer.
boolean
dispatchHoverEvent(MotionEvent event)
Dispatch a hover event.
boolean
dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event)
Dispatch a key event to the next view on the focus path.
boolean
dispatchKeyEventPreIme(KeyEvent event)
Dispatch a key event before it is processed by any input method
associated with the view hierarchy.
boolean
dispatchKeyShortcutEvent(KeyEvent event)
Dispatches a key shortcut event.
boolean
dispatchNestedFling(float velocityX, float velocityY, boolean consumed)
Dispatch a fling to a nested scrolling parent.
boolean
dispatchNestedPreFling(float velocityX, float velocityY)
Dispatch a fling to a nested scrolling parent before it is processed by this view.
boolean
dispatchNestedPrePerformAccessibilityAction(int action, Bundle arguments)
Report an accessibility action to this view’s parents for delegated processing.
boolean
dispatchNestedPreScroll(int dx, int dy, int[] consumed, int[] offsetInWindow)
Dispatch one step of a nested scroll in progress before this view consumes any portion of it.
boolean
dispatchNestedScroll(int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, int[] offsetInWindow)
Dispatch one step of a nested scroll in progress.
void
dispatchPointerCaptureChanged(boolean hasCapture)
boolean
dispatchPopulateAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event)
Dispatches an AccessibilityEvent to the View first and then
to its children for adding their text content to the event.
void
dispatchProvideAutofillStructure(ViewStructure structure, int flags)
Dispatches creation of a ViewStructures for autofill purposes down the hierarchy,
when an Assist structure is being created as part of an autofill request.
void
dispatchProvideStructure(ViewStructure structure)
Dispatch creation of ViewStructure down the hierarchy.
void
dispatchRestoreInstanceState(SparseArray<Parcelable> container)
Called by restoreHierarchyState(android.util.SparseArray) to retrieve the
state for this view and its children.
void
dispatchSaveInstanceState(SparseArray<Parcelable> container)
Called by saveHierarchyState(android.util.SparseArray) to store the state for
this view and its children.
void
dispatchScrollCaptureSearch(Rect localVisibleRect, Point windowOffset, Consumer<ScrollCaptureTarget> targets)
Dispatch a scroll capture search request down the view hierarchy.
void
dispatchSetActivated(boolean activated)
Dispatch setActivated to all of this View’s children.
void
dispatchSetPressed(boolean pressed)
Dispatch setPressed to all of this View’s children.
void
dispatchSetSelected(boolean selected)
Dispatch setSelected to all of this View’s children.
void
dispatchStartTemporaryDetach()
Dispatch onStartTemporaryDetach() to this View and its direct children if this is
a container View.
void
dispatchSystemUiVisibilityChanged(int visibility)
This method was deprecated
in API level 30.
Use WindowInsets#isVisible(int) to find out about system bar visibilities
by setting a OnApplyWindowInsetsListener on this view.
boolean
dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
Pass the touch screen motion event down to the target view, or this
view if it is the target.
boolean
dispatchTrackballEvent(MotionEvent event)
Pass a trackball motion event down to the focused view.
boolean
dispatchUnhandledMove(View focused, int direction)
This method is the last chance for the focused view and its ancestors to
respond to an arrow key.
void
dispatchVisibilityChanged(View changedView, int visibility)
Dispatch a view visibility change down the view hierarchy.
void
dispatchWindowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus)
Called when the window containing this view gains or loses window focus.
void
dispatchWindowInsetsAnimationEnd(WindowInsetsAnimation animation)
Dispatches WindowInsetsAnimation.Callback#onEnd(WindowInsetsAnimation)
when Window Insets animation ends.
void
dispatchWindowInsetsAnimationPrepare(WindowInsetsAnimation animation)
Dispatches WindowInsetsAnimation.Callback#onPrepare(WindowInsetsAnimation)
when Window Insets animation is being prepared.
WindowInsets
dispatchWindowInsetsAnimationProgress(WindowInsets insets, List<WindowInsetsAnimation> runningAnimations)
Dispatches WindowInsetsAnimation.Callback#onProgress(WindowInsets, List)
when Window Insets animation makes progress.
WindowInsetsAnimation.Bounds
dispatchWindowInsetsAnimationStart(WindowInsetsAnimation animation, WindowInsetsAnimation.Bounds bounds)
Dispatches WindowInsetsAnimation.Callback#onStart(WindowInsetsAnimation, Bounds)
when Window Insets animation is started.
void
dispatchWindowSystemUiVisiblityChanged(int visible)
This method was deprecated
in API level 30.
SystemUiVisibility flags are deprecated. Use WindowInsetsController
instead.
void
dispatchWindowVisibilityChanged(int visibility)
Dispatch a window visibility change down the view hierarchy.
void
draw(Canvas canvas)
Manually render this view (and all of its children) to the given Canvas.
void
drawableHotspotChanged(float x, float y)
This function is called whenever the view hotspot changes and needs to
be propagated to drawables or child views managed by the view.
void
drawableStateChanged()
This function is called whenever the state of the view changes in such
a way that it impacts the state of drawables being shown.
View
findFocus()
Find the view in the hierarchy rooted at this view that currently has
focus.
final
OnBackInvokedDispatcher
findOnBackInvokedDispatcher()
Walk up the View hierarchy to find the nearest OnBackInvokedDispatcher.
final
<T extends View>
T
findViewById(int id)
Finds the first descendant view with the given ID, the view itself if
the ID matches getId(), or null if the ID is invalid
(< 0) or there is no matching view in the hierarchy.
final
<T extends View>
T
findViewWithTag(Object tag)
Look for a child view with the given tag.
void
findViewsWithText(ArrayList<View> outViews, CharSequence searched, int flags)
Finds the Views that contain given text.
boolean
fitSystemWindows(Rect insets)
This method was deprecated
in API level 20.
As of API 20 use dispatchApplyWindowInsets(android.view.WindowInsets) to apply
insets to views. Views should override onApplyWindowInsets(android.view.WindowInsets) or use
setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(android.view.View.OnApplyWindowInsetsListener)
to implement handling their own insets.
View
focusSearch(int direction)
Find the nearest view in the specified direction that can take focus.
void
forceHasOverlappingRendering(boolean hasOverlappingRendering)
Sets the behavior for overlapping rendering for this view (see hasOverlappingRendering() for more details on this behavior).
void
forceLayout()
Forces this view to be laid out during the next layout pass.
boolean
gatherTransparentRegion(Region region)
This is used by the ViewRoot to perform an optimization when
the view hierarchy contains one or several SurfaceView.
void
generateDisplayHash(String hashAlgorithm, Rect bounds, Executor executor, DisplayHashResultCallback callback)
Called to generate a DisplayHash for this view.
static
int
generateViewId()
Generate a value suitable for use in setId(int).
CharSequence
getAccessibilityClassName()
Return the class name of this object to be used for accessibility purposes.
View.AccessibilityDelegate
getAccessibilityDelegate()
Returns the delegate for implementing accessibility support via
composition.
int
getAccessibilityLiveRegion()
Gets the live region mode for this View.
AccessibilityNodeProvider
getAccessibilityNodeProvider()
Gets the provider for managing a virtual view hierarchy rooted at this View
and reported to AccessibilityServices
that explore the window content.
CharSequence
getAccessibilityPaneTitle()
Get the title of the pane for purposes of accessibility.
int
getAccessibilityTraversalAfter()
Gets the id of a view after which this one is visited in accessibility traversal.
int
getAccessibilityTraversalBefore()
Gets the id of a view before which this one is visited in accessibility traversal.
float
getAlpha()
The opacity of the view.
Animation
getAnimation()
Get the animation currently associated with this view.
Matrix
getAnimationMatrix()
Return the current transformation matrix of the view.
IBinder
getApplicationWindowToken()
Retrieve a unique token identifying the top-level «real» window of
the window that this view is attached to.
int[]
getAttributeResolutionStack(int attribute)
Returns the ordered list of resource ID that are considered when resolving attribute values
for this View.
Map<Integer, Integer>
getAttributeSourceResourceMap()
Returns the mapping of attribute resource ID to source resource ID where the attribute value
was set.
String[]
getAutofillHints()
Gets the hints that help an AutofillService determine how
to autofill the view with the user’s data.
final
AutofillId
getAutofillId()
Gets the unique, logical identifier of this view in the activity, for autofill purposes.
int
getAutofillType()
Describes the autofill type of this view, so an
AutofillService can create the proper AutofillValue
when autofilling the view.
AutofillValue
getAutofillValue()
Gets the View‘s current autofill value.
Drawable
getBackground()
Gets the background drawable
BlendMode
getBackgroundTintBlendMode()
Return the blending mode used to apply the tint to the background
drawable, if specified.
ColorStateList
getBackgroundTintList()
Return the tint applied to the background drawable, if specified.
PorterDuff.Mode
getBackgroundTintMode()
Return the blending mode used to apply the tint to the background
drawable, if specified.
int
getBaseline()
Return the offset of the widget’s text baseline from the widget’s top
boundary.
final
int
getBottom()
Bottom position of this view relative to its parent.
float
getBottomFadingEdgeStrength()
Returns the strength, or intensity, of the bottom faded edge.
int
getBottomPaddingOffset()
Amount by which to extend the bottom fading region.
float
getCameraDistance()
Gets the distance along the Z axis from the camera to this view.
boolean
getClipBounds(Rect outRect)
Populates an output rectangle with the clip bounds of the view,
returning true if successful or false if the view’s
clip bounds are null.
Rect
getClipBounds()
Returns a copy of the current clipBounds.
final
boolean
getClipToOutline()
Returns whether the Outline should be used to clip the contents of the View.
final
ContentCaptureSession
getContentCaptureSession()
Gets the session used to notify content capture events.
CharSequence
getContentDescription()
Returns the View‘s content description.
final
Context
getContext()
Returns the context the view is running in, through which it can
access the current theme, resources, etc.
ContextMenu.ContextMenuInfo
getContextMenuInfo()
Views should implement this if they have extra information to associate
with the context menu.
final
boolean
getDefaultFocusHighlightEnabled()
Returns whether this View should use a default focus highlight when it gets focused but
doesn’t have R.attr.state_focused defined in its background.
static
int
getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec)
Utility to return a default size.
Display
getDisplay()
Gets the logical display to which the view’s window has been attached.
final
int[]
getDrawableState()
Return an array of resource IDs of the drawable states representing the
current state of the view.
Bitmap
getDrawingCache()
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The view drawing cache was largely made obsolete with the introduction of
hardware-accelerated rendering in API 11. With hardware-acceleration, intermediate cache
layers are largely unnecessary and can easily result in a net loss in performance due to the
cost of creating and updating the layer. In the rare cases where caching layers are useful,
such as for alpha animations, setLayerType(int, android.graphics.Paint) handles this with hardware
rendering. For software-rendered snapshots of a small part of the View hierarchy or
individual Views it is recommended to create a Canvas from either a Bitmap or
Picture and call draw(android.graphics.Canvas) on the View. However these
software-rendered usages are discouraged and have compatibility issues with hardware-only
rendering features such as Config.HARDWARE
bitmaps, real-time shadows, and outline clipping. For screenshots of the UI for feedback
reports or unit testing the PixelCopy API is recommended.
Bitmap
getDrawingCache(boolean autoScale)
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The view drawing cache was largely made obsolete with the introduction of
hardware-accelerated rendering in API 11. With hardware-acceleration, intermediate cache
layers are largely unnecessary and can easily result in a net loss in performance due to the
cost of creating and updating the layer. In the rare cases where caching layers are useful,
such as for alpha animations, setLayerType(int, android.graphics.Paint) handles this with hardware
rendering. For software-rendered snapshots of a small part of the View hierarchy or
individual Views it is recommended to create a Canvas from either a Bitmap or
Picture and call draw(android.graphics.Canvas) on the View. However these
software-rendered usages are discouraged and have compatibility issues with hardware-only
rendering features such as Config.HARDWARE
bitmaps, real-time shadows, and outline clipping. For screenshots of the UI for feedback
reports or unit testing the PixelCopy API is recommended.
int
getDrawingCacheBackgroundColor()
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The view drawing cache was largely made obsolete with the introduction of
hardware-accelerated rendering in API 11. With hardware-acceleration, intermediate cache
layers are largely unnecessary and can easily result in a net loss in performance due to the
cost of creating and updating the layer. In the rare cases where caching layers are useful,
such as for alpha animations, setLayerType(int, android.graphics.Paint) handles this with hardware
rendering. For software-rendered snapshots of a small part of the View hierarchy or
individual Views it is recommended to create a Canvas from either a Bitmap or
Picture and call draw(android.graphics.Canvas) on the View. However these
software-rendered usages are discouraged and have compatibility issues with hardware-only
rendering features such as Config.HARDWARE
bitmaps, real-time shadows, and outline clipping. For screenshots of the UI for feedback
reports or unit testing the PixelCopy API is recommended.
int
getDrawingCacheQuality()
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The view drawing cache was largely made obsolete with the introduction of
hardware-accelerated rendering in API 11. With hardware-acceleration, intermediate cache
layers are largely unnecessary and can easily result in a net loss in performance due to the
cost of creating and updating the layer. In the rare cases where caching layers are useful,
such as for alpha animations, setLayerType(int, android.graphics.Paint) handles this with hardware
rendering. For software-rendered snapshots of a small part of the View hierarchy or
individual Views it is recommended to create a Canvas from either a Bitmap or
Picture and call draw(android.graphics.Canvas) on the View. However these
software-rendered usages are discouraged and have compatibility issues with hardware-only
rendering features such as Config.HARDWARE
bitmaps, real-time shadows, and outline clipping. For screenshots of the UI for feedback
reports or unit testing the PixelCopy API is recommended.
void
getDrawingRect(Rect outRect)
Return the visible drawing bounds of your view.
long
getDrawingTime()
Return the time at which the drawing of the view hierarchy started.
float
getElevation()
The base elevation of this view relative to its parent, in pixels.
int
getExplicitStyle()
Returns the resource ID for the style specified using style="..." in the
AttributeSet‘s backing XML element or Resources#ID_NULL otherwise if not
specified or otherwise not applicable.
boolean
getFilterTouchesWhenObscured()
Gets whether the framework should discard touches when the view’s
window is obscured by another visible window at the touched location.
boolean
getFitsSystemWindows()
Check for state of setFitsSystemWindows(boolean).
int
getFocusable()
Returns the focusable setting for this view.
ArrayList<View>
getFocusables(int direction)
Find and return all focusable views that are descendants of this view,
possibly including this view if it is focusable itself.
void
getFocusedRect(Rect r)
When a view has focus and the user navigates away from it, the next view is searched for
starting from the rectangle filled in by this method.
Drawable
getForeground()
Returns the drawable used as the foreground of this View.
int
getForegroundGravity()
Describes how the foreground is positioned.
BlendMode
getForegroundTintBlendMode()
Return the blending mode used to apply the tint to the foreground
drawable, if specified.
ColorStateList
getForegroundTintList()
Return the tint applied to the foreground drawable, if specified.
PorterDuff.Mode
getForegroundTintMode()
Return the blending mode used to apply the tint to the foreground
drawable, if specified.
final
boolean
getGlobalVisibleRect(Rect r)
Sets r to the coordinates of the non-clipped area of this view in
the coordinate space of the view’s root view.
boolean
getGlobalVisibleRect(Rect r, Point globalOffset)
Sets r to the coordinates of the non-clipped area of this view in
the coordinate space of the view’s root view.
Handler
getHandler()
float
getHandwritingBoundsOffsetBottom()
Return the amount of offset applied to the bottom edge of this view’s handwriting bounds, in
the unit of pixel.
float
getHandwritingBoundsOffsetLeft()
Return the amount of offset applied to the left edge of this view’s handwriting bounds,
in the unit of pixel.
float
getHandwritingBoundsOffsetRight()
Return the amount of offset applied to the right edge of this view’s handwriting bounds, in
the unit of pixel.
float
getHandwritingBoundsOffsetTop()
Return the amount of offset applied to the top edge of this view’s handwriting bounds,
in the unit of pixel.
HandwritingDelegateConfiguration
getHandwritingDelegateConfiguration()
If this view has been configured as a handwriting initiation delegate, returns the delegate
configuration.
final
boolean
getHasOverlappingRendering()
Returns the value for overlapping rendering that is used internally.
final
int
getHeight()
Return the height of your view.
void
getHitRect(Rect outRect)
Hit rectangle in parent’s coordinates
int
getHorizontalFadingEdgeLength()
Returns the size of the horizontal faded edges used to indicate that more
content in this view is visible.
int
getHorizontalScrollbarHeight()
Returns the height of the horizontal scrollbar.
Drawable
getHorizontalScrollbarThumbDrawable()
Returns the currently configured Drawable for the thumb of the horizontal scroll bar if it
exists, null otherwise.
Drawable
getHorizontalScrollbarTrackDrawable()
Returns the currently configured Drawable for the track of the horizontal scroll bar if it
exists, null otherwise.
int
getId()
Returns this view’s identifier.
int
getImportantForAccessibility()
Gets the mode for determining whether this View is important for accessibility.
int
getImportantForAutofill()
Gets the mode for determining whether this view is important for autofill.
int
getImportantForContentCapture()
Gets the mode for determining whether this view is important for content capture.
boolean
getKeepScreenOn()
Returns whether the screen should remain on, corresponding to the current
value of KEEP_SCREEN_ON.
KeyEvent.DispatcherState
getKeyDispatcherState()
Return the global KeyEvent.DispatcherState
for this view’s window.
int
getLabelFor()
Gets the id of a view for which this view serves as a label for
accessibility purposes.
int
getLayerType()
Indicates what type of layer is currently associated with this view.
int
getLayoutDirection()
Returns the resolved layout direction for this view.
ViewGroup.LayoutParams
getLayoutParams()
Get the LayoutParams associated with this view.
final
int
getLeft()
Left position of this view relative to its parent.
float
getLeftFadingEdgeStrength()
Returns the strength, or intensity, of the left faded edge.
int
getLeftPaddingOffset()
Amount by which to extend the left fading region.
final
boolean
getLocalVisibleRect(Rect r)
Sets r to the coordinates of the non-clipped area of this view
relative to the top left corner of the view.
void
getLocationInSurface(int[] location)
Gets the coordinates of this view in the coordinate space of the
Surface that contains the view.
void
getLocationInWindow(int[] outLocation)
Gets the coordinates of this view in the coordinate space of the window
that contains the view, irrespective of system decorations.
void
getLocationOnScreen(int[] outLocation)
Gets the coordinates of this view in the coordinate space of the device
screen, irrespective of system decorations and whether the system is in
multi-window mode.
Matrix
getMatrix()
The transform matrix of this view, which is calculated based on the current
rotation, scale, and pivot properties.
final
int
getMeasuredHeight()
Like getMeasuredHeightAndState(), but only returns the
raw height component (that is the result is masked by
MEASURED_SIZE_MASK).
final
int
getMeasuredHeightAndState()
Return the full height measurement information for this view as computed
by the most recent call to measure(int, int).
final
int
getMeasuredState()
Return only the state bits of getMeasuredWidthAndState()
and getMeasuredHeightAndState(), combined into one integer.
final
int
getMeasuredWidth()
Like getMeasuredWidthAndState(), but only returns the
raw width component (that is the result is masked by
MEASURED_SIZE_MASK).
final
int
getMeasuredWidthAndState()
Return the full width measurement information for this view as computed
by the most recent call to measure(int, int).
int
getMinimumHeight()
Returns the minimum height of the view.
int
getMinimumWidth()
Returns the minimum width of the view.
int
getNextClusterForwardId()
Gets the id of the root of the next keyboard navigation cluster.
int
getNextFocusDownId()
Gets the id of the view to use when the next focus is FOCUS_DOWN.
int
getNextFocusForwardId()
Gets the id of the view to use when the next focus is FOCUS_FORWARD.
int
getNextFocusLeftId()
Gets the id of the view to use when the next focus is FOCUS_LEFT.
int
getNextFocusRightId()
Gets the id of the view to use when the next focus is FOCUS_RIGHT.
int
getNextFocusUpId()
Gets the id of the view to use when the next focus is FOCUS_UP.
View.OnFocusChangeListener
getOnFocusChangeListener()
Returns the focus-change callback registered for this view.
int
getOutlineAmbientShadowColor()
ViewOutlineProvider
getOutlineProvider()
Returns the current ViewOutlineProvider of the view, which generates the Outline
that defines the shape of the shadow it casts, and enables outline clipping.
int
getOutlineSpotShadowColor()
int
getOverScrollMode()
Returns the over-scroll mode for this view.
ViewOverlay
getOverlay()
Returns the overlay for this view, creating it if it does not yet exist.
int
getPaddingBottom()
Returns the bottom padding of this view.
int
getPaddingEnd()
Returns the end padding of this view depending on its resolved layout direction.
int
getPaddingLeft()
Returns the left padding of this view.
int
getPaddingRight()
Returns the right padding of this view.
int
getPaddingStart()
Returns the start padding of this view depending on its resolved layout direction.
int
getPaddingTop()
Returns the top padding of this view.
final
ViewParent
getParent()
Gets the parent of this view.
ViewParent
getParentForAccessibility()
Gets the parent for accessibility purposes.
float
getPivotX()
The x location of the point around which the view is rotated
and scaled.
float
getPivotY()
The y location of the point around which the view is rotated
and scaled.
PointerIcon
getPointerIcon()
Gets the pointer icon for the current view.
final
List<Rect>
getPreferKeepClearRects()
String[]
getReceiveContentMimeTypes()
Returns the MIME types accepted by performReceiveContent(ContentInfo) for this view, as
configured via setOnReceiveContentListener(String[], OnReceiveContentListener).
Resources
getResources()
Returns the resources associated with this view.
final
boolean
getRevealOnFocusHint()
Returns this view’s preference for reveal behavior when it gains focus.
final
int
getRight()
Right position of this view relative to its parent.
float
getRightFadingEdgeStrength()
Returns the strength, or intensity, of the right faded edge.
int
getRightPaddingOffset()
Amount by which to extend the right fading region.
AttachedSurfaceControl
getRootSurfaceControl()
The AttachedSurfaceControl itself is not a View, it is just the interface to the
windowing-system object that contains the entire view hierarchy.
View
getRootView()
Finds the topmost view in the current view hierarchy.
WindowInsets
getRootWindowInsets()
Provide original WindowInsets that are dispatched to the view hierarchy.
float
getRotation()
The degrees that the view is rotated around the pivot point.
float
getRotationX()
The degrees that the view is rotated around the horizontal axis through the pivot point.
float
getRotationY()
The degrees that the view is rotated around the vertical axis through the pivot point.
float
getScaleX()
The amount that the view is scaled in x around the pivot point, as a proportion of
the view’s unscaled width.
float
getScaleY()
The amount that the view is scaled in y around the pivot point, as a proportion of
the view’s unscaled height.
int
getScrollBarDefaultDelayBeforeFade()
Returns the delay before scrollbars fade.
int
getScrollBarFadeDuration()
Returns the scrollbar fade duration.
int
getScrollBarSize()
Returns the scrollbar size.
int
getScrollBarStyle()
Returns the current scrollbar style.
int
getScrollCaptureHint()
Returns the current scroll capture hint for this view.
int
getScrollIndicators()
Returns a bitmask representing the enabled scroll indicators.
final
int
getScrollX()
Return the scrolled left position of this view.
final
int
getScrollY()
Return the scrolled top position of this view.
int
getSolidColor()
Override this if your view is known to always be drawn on top of a solid color background,
and needs to draw fading edges.
int
getSourceLayoutResId()
A View can be inflated from an XML layout.
final
CharSequence
getStateDescription()
Returns the View‘s state description.
StateListAnimator
getStateListAnimator()
Returns the current StateListAnimator if exists.
int
getSuggestedMinimumHeight()
Returns the suggested minimum height that the view should use.
int
getSuggestedMinimumWidth()
Returns the suggested minimum width that the view should use.
List<Rect>
getSystemGestureExclusionRects()
Retrieve the list of areas within this view’s post-layout coordinate space where the system
should not intercept touch or other pointing device gestures.
int
getSystemUiVisibility()
This method was deprecated
in API level 30.
SystemUiVisibility flags are deprecated. Use WindowInsetsController
instead.
Object
getTag()
Returns this view’s tag.
Object
getTag(int key)
Returns the tag associated with this view and the specified key.
int
getTextAlignment()
Return the resolved text alignment.
int
getTextDirection()
Return the resolved text direction.
CharSequence
getTooltipText()
Returns the view’s tooltip text.
final
int
getTop()
Top position of this view relative to its parent.
float
getTopFadingEdgeStrength()
Returns the strength, or intensity, of the top faded edge.
int
getTopPaddingOffset()
Amount by which to extend the top fading region.
TouchDelegate
getTouchDelegate()
Gets the TouchDelegate for this View.
ArrayList<View>
getTouchables()
Find and return all touchable views that are descendants of this view,
possibly including this view if it is touchable itself.
float
getTransitionAlpha()
This property is intended only for use by the Fade transition, which animates
it to produce a visual translucency that does not side-effect (or get affected
by) the real alpha property.
String
getTransitionName()
Returns the name of the View to be used to identify Views in Transitions.
float
getTranslationX()
The horizontal location of this view relative to its left position.
float
getTranslationY()
The vertical location of this view relative to its top position.
float
getTranslationZ()
The depth location of this view relative to its elevation.
long
getUniqueDrawingId()
Get the identifier used for this view by the drawing system.
int
getVerticalFadingEdgeLength()
Returns the size of the vertical faded edges used to indicate that more
content in this view is visible.
int
getVerticalScrollbarPosition()
Drawable
getVerticalScrollbarThumbDrawable()
Returns the currently configured Drawable for the thumb of the vertical scroll bar if it
exists, null otherwise.
Drawable
getVerticalScrollbarTrackDrawable()
Returns the currently configured Drawable for the track of the vertical scroll bar if it
exists, null otherwise.
int
getVerticalScrollbarWidth()
Returns the width of the vertical scrollbar.
ViewTranslationResponse
getViewTranslationResponse()
Returns the ViewTranslationResponse associated with this view.
ViewTreeObserver
getViewTreeObserver()
Returns the ViewTreeObserver for this view’s hierarchy.
int
getVisibility()
Returns the visibility status for this view.
final
int
getWidth()
Return the width of your view.
int
getWindowAttachCount()
WindowId
getWindowId()
Retrieve the WindowId for the window this view is
currently attached to.
WindowInsetsController
getWindowInsetsController()
Retrieves the single WindowInsetsController of the window this view is attached to.
int
getWindowSystemUiVisibility()
This method was deprecated
in API level 30.
SystemUiVisibility flags are deprecated. Use WindowInsetsController
instead.
IBinder
getWindowToken()
Retrieve a unique token identifying the window this view is attached to.
int
getWindowVisibility()
Returns the current visibility of the window this view is attached to
(either GONE, INVISIBLE, or VISIBLE).
void
getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(Rect outRect)
Retrieve the overall visible display size in which the window this view is
attached to has been positioned in.
float
getX()
The visual x position of this view, in pixels.
float
getY()
The visual y position of this view, in pixels.
float
getZ()
The visual z position of this view, in pixels.
boolean
hasExplicitFocusable()
Returns true if this view is focusable or if it contains a reachable View
for which hasExplicitFocusable() returns true.
boolean
hasFocus()
Returns true if this view has focus itself, or is the ancestor of the
view that has focus.
boolean
hasFocusable()
Returns true if this view is focusable or if it contains a reachable View
for which hasFocusable() returns true.
boolean
hasNestedScrollingParent()
Returns true if this view has a nested scrolling parent.
boolean
hasOnClickListeners()
Return whether this view has an attached OnClickListener.
boolean
hasOnLongClickListeners()
Return whether this view has an attached OnLongClickListener.
boolean
hasOverlappingRendering()
Returns whether this View has content which overlaps.
boolean
hasPointerCapture()
Checks pointer capture status.
boolean
hasTransientState()
Indicates whether the view is currently tracking transient state that the
app should not need to concern itself with saving and restoring, but that
the framework should take special note to preserve when possible.
boolean
hasWindowFocus()
Returns true if this view is in a window that currently has window focus.
static
View
inflate(Context context, int resource, ViewGroup root)
Inflate a view from an XML resource.
void
invalidate()
Invalidate the whole view.
void
invalidate(Rect dirty)
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The switch to hardware accelerated rendering in API 14 reduced
the importance of the dirty rectangle. In API 21 the given rectangle is
ignored entirely in favor of an internally-calculated area instead.
Because of this, clients are encouraged to just call invalidate().
void
invalidate(int l, int t, int r, int b)
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The switch to hardware accelerated rendering in API 14 reduced
the importance of the dirty rectangle. In API 21 the given rectangle is
ignored entirely in favor of an internally-calculated area instead.
Because of this, clients are encouraged to just call invalidate().
void
invalidateDrawable(Drawable drawable)
Invalidates the specified Drawable.
void
invalidateOutline()
Called to rebuild this View’s Outline from its outline provider
boolean
isAccessibilityDataPrivate()
Whether this view should restrict accessibility service access only to services that have the
AccessibilityServiceInfo.isAccessibilityTool() property
set to true.
boolean
isAccessibilityFocused()
Returns whether this View is accessibility focused.
boolean
isAccessibilityHeading()
Gets whether this view is a heading for accessibility purposes.
boolean
isActivated()
Indicates the activation state of this view.
boolean
isAttachedToWindow()
Returns true if this view is currently attached to a window.
boolean
isAutoHandwritingEnabled()
Return whether the View allows automatic handwriting initiation.
boolean
isClickable()
Indicates whether this view reacts to click events or not.
boolean
isContextClickable()
Indicates whether this view reacts to context clicks or not.
boolean
isCredential()
Gets the mode for determining whether this view is a credential.
boolean
isDirty()
True if this view has changed since the last time being drawn.
boolean
isDrawingCacheEnabled()
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The view drawing cache was largely made obsolete with the introduction of
hardware-accelerated rendering in API 11. With hardware-acceleration, intermediate cache
layers are largely unnecessary and can easily result in a net loss in performance due to the
cost of creating and updating the layer. In the rare cases where caching layers are useful,
such as for alpha animations, setLayerType(int, android.graphics.Paint) handles this with hardware
rendering. For software-rendered snapshots of a small part of the View hierarchy or
individual Views it is recommended to create a Canvas from either a Bitmap or
Picture and call draw(android.graphics.Canvas) on the View. However these
software-rendered usages are discouraged and have compatibility issues with hardware-only
rendering features such as Config.HARDWARE
bitmaps, real-time shadows, and outline clipping. For screenshots of the UI for feedback
reports or unit testing the PixelCopy API is recommended.
boolean
isDuplicateParentStateEnabled()
Indicates whether this duplicates its drawable state from its parent.
boolean
isEnabled()
Returns the enabled status for this view.
final
boolean
isFocusable()
Returns whether this View is currently able to take focus.
final
boolean
isFocusableInTouchMode()
When a view is focusable, it may not want to take focus when in touch mode.
boolean
isFocused()
Returns true if this view has focus
final
boolean
isFocusedByDefault()
Returns whether this View should receive focus when the focus is restored for the view
hierarchy containing this view.
boolean
isForceDarkAllowed()
See setForceDarkAllowed(boolean)
boolean
isHapticFeedbackEnabled()
boolean
isHardwareAccelerated()
Indicates whether this view is attached to a hardware accelerated
window or not.
boolean
isHorizontalFadingEdgeEnabled()
Indicate whether the horizontal edges are faded when the view is
scrolled horizontally.
boolean
isHorizontalScrollBarEnabled()
Indicate whether the horizontal scrollbar should be drawn or not.
boolean
isHovered()
Returns true if the view is currently hovered.
boolean
isImportantForAccessibility()
Computes whether this view should be exposed for accessibility.
final
boolean
isImportantForAutofill()
Hints the Android System whether the AssistStructure.ViewNode
associated with this view is considered important for autofill purposes.
final
boolean
isImportantForContentCapture()
Hints the Android System whether this view is considered important for content capture, based
on the value explicitly set by setImportantForContentCapture(int) and heuristics
when it’s IMPORTANT_FOR_CONTENT_CAPTURE_AUTO.
boolean
isInEditMode()
Indicates whether this View is currently in edit mode.
boolean
isInLayout()
Returns whether the view hierarchy is currently undergoing a layout pass.
boolean
isInTouchMode()
Returns the touch mode state associated with this view.
final
boolean
isKeyboardNavigationCluster()
Returns whether this View is a root of a keyboard navigation cluster.
boolean
isLaidOut()
Returns true if this view has been through at least one layout since it
was last attached to or detached from a window.
boolean
isLayoutDirectionResolved()
boolean
isLayoutRequested()
Indicates whether or not this view’s layout will be requested during
the next hierarchy layout pass.
boolean
isLongClickable()
Indicates whether this view reacts to long click events or not.
boolean
isNestedScrollingEnabled()
Returns true if nested scrolling is enabled for this view.
boolean
isOpaque()
Indicates whether this View is opaque.
boolean
isPaddingOffsetRequired()
If the View draws content inside its padding and enables fading edges,
it needs to support padding offsets.
boolean
isPaddingRelative()
Return if the padding has been set through relative values
setPaddingRelative(int, int, int, int) or through
boolean
isPivotSet()
Returns whether or not a pivot has been set by a call to setPivotX(float) or
setPivotY(float).
final
boolean
isPreferKeepClear()
Retrieve the preference for this view to be kept clear.
boolean
isPressed()
Indicates whether the view is currently in pressed state.
boolean
isSaveEnabled()
Indicates whether this view will save its state (that is,
whether its onSaveInstanceState() method will be called).
boolean
isSaveFromParentEnabled()
Indicates whether the entire hierarchy under this view will save its
state when a state saving traversal occurs from its parent.
boolean
isScreenReaderFocusable()
Returns whether the view should be treated as a focusable unit by screen reader
accessibility tools.
boolean
isScrollContainer()
Indicates whether this view is one of the set of scrollable containers in
its window.
boolean
isScrollbarFadingEnabled()
Returns true if scrollbars will fade when this view is not scrolling
boolean
isSelected()
Indicates the selection state of this view.
final
boolean
isShowingLayoutBounds()
Returns true when the View is attached and the system developer setting to show
the layout bounds is enabled or false otherwise.
boolean
isShown()
Returns the visibility of this view and all of its ancestors
boolean
isSoundEffectsEnabled()
final
boolean
isTemporarilyDetached()
Tells whether the View is in the state between onStartTemporaryDetach()
and onFinishTemporaryDetach().
boolean
isTextAlignmentResolved()
boolean
isTextDirectionResolved()
boolean
isVerticalFadingEdgeEnabled()
Indicate whether the vertical edges are faded when the view is
scrolled horizontally.
boolean
isVerticalScrollBarEnabled()
Indicate whether the vertical scrollbar should be drawn or not.
boolean
isVisibleToUserForAutofill(int virtualId)
Computes whether this virtual autofill view is visible to the user.
void
jumpDrawablesToCurrentState()
Call Drawable.jumpToCurrentState()
on all Drawable objects associated with this view.
View
keyboardNavigationClusterSearch(View currentCluster, int direction)
Find the nearest keyboard navigation cluster in the specified direction.
void
layout(int l, int t, int r, int b)
Assign a size and position to a view and all of its
descendants
This is the second phase of the layout mechanism.
final
void
measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
This is called to find out how big a view should be.
static
int[]
mergeDrawableStates(int[] baseState, int[] additionalState)
Merge your own state values in additionalState into the base
state values baseState that were returned by
onCreateDrawableState(int).
void
offsetLeftAndRight(int offset)
Offset this view’s horizontal location by the specified amount of pixels.
void
offsetTopAndBottom(int offset)
Offset this view’s vertical location by the specified number of pixels.
void
onAnimationEnd()
Invoked by a parent ViewGroup to notify the end of the animation
currently associated with this view.
void
onAnimationStart()
Invoked by a parent ViewGroup to notify the start of the animation
currently associated with this view.
WindowInsets
onApplyWindowInsets(WindowInsets insets)
Called when the view should apply WindowInsets according to its internal policy.
void
onAttachedToWindow()
This is called when the view is attached to a window.
void
onCancelPendingInputEvents()
Called as the result of a call to cancelPendingInputEvents() on this view or
a parent view.
boolean
onCapturedPointerEvent(MotionEvent event)
Implement this method to handle captured pointer events
boolean
onCheckIsTextEditor()
Check whether the called view is a text editor, in which case it
would make sense to automatically display a soft input window for
it.
void
onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig)
Called when the current configuration of the resources being used
by the application have changed.
void
onCreateContextMenu(ContextMenu menu)
Views should implement this if the view itself is going to add items to
the context menu.
int[]
onCreateDrawableState(int extraSpace)
Generate the new Drawable state for
this view.
InputConnection
onCreateInputConnection(EditorInfo outAttrs)
Create a new InputConnection for an InputMethod to interact
with the view.
void
onCreateViewTranslationRequest(int[] supportedFormats, Consumer<ViewTranslationRequest> requestsCollector)
Collects a ViewTranslationRequest which represents the content to be translated in
the view.
void
onCreateVirtualViewTranslationRequests(long[] virtualIds, int[] supportedFormats, Consumer<ViewTranslationRequest> requestsCollector)
Collects ViewTranslationRequests which represents the content to be translated
for the virtual views in the host view.
void
onDetachedFromWindow()
This is called when the view is detached from a window.
void
onDisplayHint(int hint)
Gives this view a hint about whether is displayed or not.
boolean
onDragEvent(DragEvent event)
Handles drag events sent by the system following a call to
startDragAndDrop().
void
onDraw(Canvas canvas)
Implement this to do your drawing.
void
onDrawForeground(Canvas canvas)
Draw any foreground content for this view.
final
void
onDrawScrollBars(Canvas canvas)
Request the drawing of the horizontal and the vertical scrollbar.
boolean
onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(MotionEvent event)
Filter the touch event to apply security policies.
void
onFinishInflate()
Finalize inflating a view from XML.
void
onFinishTemporaryDetach()
Called after onStartTemporaryDetach() when the container is done
changing the view.
void
onFocusChanged(boolean gainFocus, int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect)
Called by the view system when the focus state of this view changes.
boolean
onGenericMotionEvent(MotionEvent event)
Implement this method to handle generic motion events.
void
onHoverChanged(boolean hovered)
Implement this method to handle hover state changes.
boolean
onHoverEvent(MotionEvent event)
Implement this method to handle hover events.
void
onInitializeAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event)
Initializes an AccessibilityEvent with information about
this View which is the event source.
void
onInitializeAccessibilityNodeInfo(AccessibilityNodeInfo info)
Initializes an AccessibilityNodeInfo with information about this view.
boolean
onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event)
Default implementation of KeyEvent.Callback.onKeyDown(): perform press of the view
when KeyEvent#KEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER or KeyEvent#KEYCODE_ENTER
is released, if the view is enabled and clickable.
boolean
onKeyLongPress(int keyCode, KeyEvent event)
Default implementation of KeyEvent.Callback.onKeyLongPress(): always returns false (doesn’t handle
the event).
boolean
onKeyMultiple(int keyCode, int repeatCount, KeyEvent event)
Default implementation of KeyEvent.Callback.onKeyMultiple(): always returns false (doesn’t handle
the event).
boolean
onKeyPreIme(int keyCode, KeyEvent event)
Handle a key event before it is processed by any input method
associated with the view hierarchy.
boolean
onKeyShortcut(int keyCode, KeyEvent event)
Called on the focused view when a key shortcut event is not handled.
boolean
onKeyUp(int keyCode, KeyEvent event)
Default implementation of KeyEvent.Callback.onKeyUp(): perform clicking of the view
when KeyEvent#KEYCODE_DPAD_CENTER, KeyEvent#KEYCODE_ENTER
or KeyEvent#KEYCODE_SPACE is released.
void
onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom)
Called from layout when this view should
assign a size and position to each of its children.
void
onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
Measure the view and its content to determine the measured width and the
measured height.
void
onOverScrolled(int scrollX, int scrollY, boolean clampedX, boolean clampedY)
Called by overScrollBy(int, int, int, int, int, int, int, int, boolean) to
respond to the results of an over-scroll operation.
void
onPointerCaptureChange(boolean hasCapture)
Called when the window has just acquired or lost pointer capture.
void
onPopulateAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event)
Called from dispatchPopulateAccessibilityEvent(android.view.accessibility.AccessibilityEvent)
giving a chance to this View to populate the accessibility event with its
text content.
void
onProvideAutofillStructure(ViewStructure structure, int flags)
Populates a ViewStructure to fullfil an autofill request.
void
onProvideAutofillVirtualStructure(ViewStructure structure, int flags)
Populates a ViewStructure containing virtual children to fullfil an autofill
request.
void
onProvideContentCaptureStructure(ViewStructure structure, int flags)
Populates a ViewStructure for content capture.
void
onProvideStructure(ViewStructure structure)
Called when assist structure is being retrieved from a view as part of
Activity.onProvideAssistData.
void
onProvideVirtualStructure(ViewStructure structure)
Called when assist structure is being retrieved from a view as part of
Activity.onProvideAssistData to
generate additional virtual structure under this view.
ContentInfo
onReceiveContent(ContentInfo payload)
Implements the default behavior for receiving content for this type of view.
PointerIcon
onResolvePointerIcon(MotionEvent event, int pointerIndex)
Returns the pointer icon for the motion event, or null if it doesn’t specify the icon.
void
onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state)
Hook allowing a view to re-apply a representation of its internal state that had previously
been generated by onSaveInstanceState().
void
onRtlPropertiesChanged(int layoutDirection)
Called when any RTL property (layout direction or text direction or text alignment) has
been changed.
Parcelable
onSaveInstanceState()
Hook allowing a view to generate a representation of its internal state
that can later be used to create a new instance with that same state.
void
onScreenStateChanged(int screenState)
This method is called whenever the state of the screen this view is
attached to changes.
void
onScrollCaptureSearch(Rect localVisibleRect, Point windowOffset, Consumer<ScrollCaptureTarget> targets)
Called when scroll capture is requested, to search for appropriate content to scroll.
void
onScrollChanged(int l, int t, int oldl, int oldt)
This is called in response to an internal scroll in this view (i.e., the
view scrolled its own contents).
boolean
onSetAlpha(int alpha)
Invoked if there is a Transform that involves alpha.
void
onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh)
This is called during layout when the size of this view has changed.
void
onStartTemporaryDetach()
This is called when a container is going to temporarily detach a child, with
ViewGroup.detachViewFromParent.
boolean
onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
Implement this method to handle touch screen motion events.
boolean
onTrackballEvent(MotionEvent event)
Implement this method to handle trackball motion events.
void
onViewTranslationResponse(ViewTranslationResponse response)
Called when the content from View#onCreateViewTranslationRequest had been translated
by the TranslationService.
void
onVirtualViewTranslationResponses(LongSparseArray<ViewTranslationResponse> response)
Called when the content from View#onCreateVirtualViewTranslationRequests had been
translated by the TranslationService.
void
onVisibilityAggregated(boolean isVisible)
Called when the user-visibility of this View is potentially affected by a change
to this view itself, an ancestor view or the window this view is attached to.
void
onVisibilityChanged(View changedView, int visibility)
Called when the visibility of the view or an ancestor of the view has
changed.
void
onWindowFocusChanged(boolean hasWindowFocus)
Called when the window containing this view gains or loses focus.
void
onWindowSystemUiVisibilityChanged(int visible)
This method was deprecated
in API level 30.
SystemUiVisibility flags are deprecated. Use WindowInsetsController
instead.
void
onWindowVisibilityChanged(int visibility)
Called when the window containing has change its visibility
(between GONE, INVISIBLE, and VISIBLE).
boolean
overScrollBy(int deltaX, int deltaY, int scrollX, int scrollY, int scrollRangeX, int scrollRangeY, int maxOverScrollX, int maxOverScrollY, boolean isTouchEvent)
Scroll the view with standard behavior for scrolling beyond the normal
content boundaries.
boolean
performAccessibilityAction(int action, Bundle arguments)
Performs the specified accessibility action on the view.
boolean
performClick()
Call this view’s OnClickListener, if it is defined.
boolean
performContextClick(float x, float y)
Call this view’s OnContextClickListener, if it is defined.
boolean
performContextClick()
Call this view’s OnContextClickListener, if it is defined.
boolean
performHapticFeedback(int feedbackConstant)
BZZZTT!!1!
Provide haptic feedback to the user for this view.
boolean
performHapticFeedback(int feedbackConstant, int flags)
BZZZTT!!1!
Like performHapticFeedback(int), with additional options.
boolean
performLongClick(float x, float y)
Calls this view’s OnLongClickListener, if it is defined.
boolean
performLongClick()
Calls this view’s OnLongClickListener, if it is defined.
ContentInfo
performReceiveContent(ContentInfo payload)
Receives the given content.
void
playSoundEffect(int soundConstant)
Play a sound effect for this view.
boolean
post(Runnable action)
Causes the Runnable to be added to the message queue.
boolean
postDelayed(Runnable action, long delayMillis)
Causes the Runnable to be added to the message queue, to be run
after the specified amount of time elapses.
void
postInvalidate()
Cause an invalidate to happen on a subsequent cycle through the event loop.
void
postInvalidate(int left, int top, int right, int bottom)
Cause an invalidate of the specified area to happen on a subsequent cycle
through the event loop.
void
postInvalidateDelayed(long delayMilliseconds, int left, int top, int right, int bottom)
Cause an invalidate of the specified area to happen on a subsequent cycle
through the event loop.
void
postInvalidateDelayed(long delayMilliseconds)
Cause an invalidate to happen on a subsequent cycle through the event
loop.
void
postInvalidateOnAnimation(int left, int top, int right, int bottom)
Cause an invalidate of the specified area to happen on the next animation
time step, typically the next display frame.
void
postInvalidateOnAnimation()
Cause an invalidate to happen on the next animation time step, typically the
next display frame.
void
postOnAnimation(Runnable action)
Causes the Runnable to execute on the next animation time step.
void
postOnAnimationDelayed(Runnable action, long delayMillis)
Causes the Runnable to execute on the next animation time step,
after the specified amount of time elapses.
void
refreshDrawableState()
Call this to force a view to update its drawable state.
void
releasePointerCapture()
Releases the pointer capture.
boolean
removeCallbacks(Runnable action)
Removes the specified Runnable from the message queue.
void
removeOnAttachStateChangeListener(View.OnAttachStateChangeListener listener)
Remove a listener for attach state changes.
void
removeOnLayoutChangeListener(View.OnLayoutChangeListener listener)
Remove a listener for layout changes.
void
removeOnUnhandledKeyEventListener(View.OnUnhandledKeyEventListener listener)
Removes a listener which will receive unhandled KeyEvents.
void
requestApplyInsets()
Ask that a new dispatch of onApplyWindowInsets(android.view.WindowInsets) be performed.
void
requestFitSystemWindows()
This method was deprecated
in API level 20.
Use requestApplyInsets() for newer platform versions.
final
boolean
requestFocus(int direction)
Call this to try to give focus to a specific view or to one of its
descendants and give it a hint about what direction focus is heading.
final
boolean
requestFocus()
Call this to try to give focus to a specific view or to one of its
descendants.
boolean
requestFocus(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect)
Call this to try to give focus to a specific view or to one of its descendants
and give it hints about the direction and a specific rectangle that the focus
is coming from.
final
boolean
requestFocusFromTouch()
Call this to try to give focus to a specific view or to one of its descendants.
void
requestLayout()
Call this when something has changed which has invalidated the
layout of this view.
void
requestPointerCapture()
Requests pointer capture mode.
boolean
requestRectangleOnScreen(Rect rectangle)
Request that a rectangle of this view be visible on the screen,
scrolling if necessary just enough.
boolean
requestRectangleOnScreen(Rect rectangle, boolean immediate)
Request that a rectangle of this view be visible on the screen,
scrolling if necessary just enough.
final
void
requestUnbufferedDispatch(int source)
Request unbuffered dispatch of the given event source class to this view.
final
void
requestUnbufferedDispatch(MotionEvent event)
Request unbuffered dispatch of the given stream of MotionEvents to this View.
final
<T extends View>
T
requireViewById(int id)
Finds the first descendant view with the given ID, the view itself if the ID matches
getId(), or throws an IllegalArgumentException if the ID is invalid or there is no
matching view in the hierarchy.
void
resetPivot()
Clears any pivot previously set by a call to setPivotX(float) or
setPivotY(float).
static
int
resolveSize(int size, int measureSpec)
Version of resolveSizeAndState(int, int, int)
returning only the MEASURED_SIZE_MASK bits of the result.
static
int
resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState)
Utility to reconcile a desired size and state, with constraints imposed
by a MeasureSpec.
boolean
restoreDefaultFocus()
Gives focus to the default-focus view in the view hierarchy that has this view as a root.
void
restoreHierarchyState(SparseArray<Parcelable> container)
Restore this view hierarchy’s frozen state from the given container.
final
void
saveAttributeDataForStyleable(Context context, int[] styleable, AttributeSet attrs, TypedArray t, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes)
Stores debugging information about attributes.
void
saveHierarchyState(SparseArray<Parcelable> container)
Store this view hierarchy’s frozen state into the given container.
void
scheduleDrawable(Drawable who, Runnable what, long when)
Schedules an action on a drawable to occur at a specified time.
void
scrollBy(int x, int y)
Move the scrolled position of your view.
void
scrollTo(int x, int y)
Set the scrolled position of your view.
void
sendAccessibilityEvent(int eventType)
Sends an accessibility event of the given type.
void
sendAccessibilityEventUnchecked(AccessibilityEvent event)
This method behaves exactly as sendAccessibilityEvent(int) but
takes as an argument an empty AccessibilityEvent and does not
perform a check whether accessibility is enabled.
void
setAccessibilityDataPrivate(int accessibilityDataPrivate)
Specifies whether this view should only allow interactions from
AccessibilityServices with the
AccessibilityServiceInfo.isAccessibilityTool() property
set to true.
void
setAccessibilityDelegate(View.AccessibilityDelegate delegate)
Sets a delegate for implementing accessibility support via composition
(as opposed to inheritance).
void
setAccessibilityHeading(boolean isHeading)
Set if view is a heading for a section of content for accessibility purposes.
void
setAccessibilityLiveRegion(int mode)
Sets the live region mode for this view.
void
setAccessibilityPaneTitle(CharSequence accessibilityPaneTitle)
Visually distinct portion of a window with window-like semantics are considered panes for
accessibility purposes.
void
setAccessibilityTraversalAfter(int afterId)
Sets the id of a view after which this one is visited in accessibility traversal.
void
setAccessibilityTraversalBefore(int beforeId)
Sets the id of a view before which this one is visited in accessibility traversal.
void
setActivated(boolean activated)
Changes the activated state of this view.
void
setAllowClickWhenDisabled(boolean clickableWhenDisabled)
Enables or disables click events for this view when disabled.
void
setAlpha(float alpha)
Sets the opacity of the view to a value from 0 to 1, where 0 means the view is
completely transparent and 1 means the view is completely opaque.
void
setAnimation(Animation animation)
Sets the next animation to play for this view.
void
setAnimationMatrix(Matrix matrix)
Changes the transformation matrix on the view.
void
setAutoHandwritingEnabled(boolean enabled)
Set whether this view enables automatic handwriting initiation.
void
setAutofillHints(String... autofillHints)
Sets the hints that help an AutofillService determine how
to autofill the view with the user’s data.
void
setAutofillId(AutofillId id)
Sets the unique, logical identifier of this view in the activity, for autofill purposes.
void
setBackground(Drawable background)
Set the background to a given Drawable, or remove the background.
void
setBackgroundColor(int color)
Sets the background color for this view.
void
setBackgroundDrawable(Drawable background)
This method was deprecated
in API level 16.
use setBackground(android.graphics.drawable.Drawable) instead
void
setBackgroundResource(int resid)
Set the background to a given resource.
void
setBackgroundTintBlendMode(BlendMode blendMode)
Specifies the blending mode used to apply the tint specified by
setBackgroundTintList(android.content.res.ColorStateList)} to the background
drawable.
void
setBackgroundTintList(ColorStateList tint)
Applies a tint to the background drawable.
void
setBackgroundTintMode(PorterDuff.Mode tintMode)
Specifies the blending mode used to apply the tint specified by
setBackgroundTintList(android.content.res.ColorStateList)} to the background
drawable.
final
void
setBottom(int bottom)
Sets the bottom position of this view relative to its parent.
void
setCameraDistance(float distance)
Sets the distance along the Z axis (orthogonal to the X/Y plane on which
views are drawn) from the camera to this view.
void
setClickable(boolean clickable)
Enables or disables click events for this view.
void
setClipBounds(Rect clipBounds)
Sets a rectangular area on this view to which the view will be clipped
when it is drawn.
void
setClipToOutline(boolean clipToOutline)
Sets whether the View’s Outline should be used to clip the contents of the View.
void
setContentCaptureSession(ContentCaptureSession contentCaptureSession)
Sets the (optional) ContentCaptureSession associated with this view.
void
setContentDescription(CharSequence contentDescription)
Sets the View‘s content description.
void
setContextClickable(boolean contextClickable)
Enables or disables context clicking for this view.
void
setDefaultFocusHighlightEnabled(boolean defaultFocusHighlightEnabled)
Sets whether this View should use a default focus highlight when it gets focused but doesn’t
have R.attr.state_focused defined in its background.
void
setDrawingCacheBackgroundColor(int color)
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The view drawing cache was largely made obsolete with the introduction of
hardware-accelerated rendering in API 11. With hardware-acceleration, intermediate cache
layers are largely unnecessary and can easily result in a net loss in performance due to the
cost of creating and updating the layer. In the rare cases where caching layers are useful,
such as for alpha animations, setLayerType(int, android.graphics.Paint) handles this with hardware
rendering. For software-rendered snapshots of a small part of the View hierarchy or
individual Views it is recommended to create a Canvas from either a Bitmap or
Picture and call draw(android.graphics.Canvas) on the View. However these
software-rendered usages are discouraged and have compatibility issues with hardware-only
rendering features such as Config.HARDWARE
bitmaps, real-time shadows, and outline clipping. For screenshots of the UI for feedback
reports or unit testing the PixelCopy API is recommended.
void
setDrawingCacheEnabled(boolean enabled)
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The view drawing cache was largely made obsolete with the introduction of
hardware-accelerated rendering in API 11. With hardware-acceleration, intermediate cache
layers are largely unnecessary and can easily result in a net loss in performance due to the
cost of creating and updating the layer. In the rare cases where caching layers are useful,
such as for alpha animations, setLayerType(int, android.graphics.Paint) handles this with hardware
rendering. For software-rendered snapshots of a small part of the View hierarchy or
individual Views it is recommended to create a Canvas from either a Bitmap or
Picture and call draw(android.graphics.Canvas) on the View. However these
software-rendered usages are discouraged and have compatibility issues with hardware-only
rendering features such as Config.HARDWARE
bitmaps, real-time shadows, and outline clipping. For screenshots of the UI for feedback
reports or unit testing the PixelCopy API is recommended.
void
setDrawingCacheQuality(int quality)
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The view drawing cache was largely made obsolete with the introduction of
hardware-accelerated rendering in API 11. With hardware-acceleration, intermediate cache
layers are largely unnecessary and can easily result in a net loss in performance due to the
cost of creating and updating the layer. In the rare cases where caching layers are useful,
such as for alpha animations, setLayerType(int, android.graphics.Paint) handles this with hardware
rendering. For software-rendered snapshots of a small part of the View hierarchy or
individual Views it is recommended to create a Canvas from either a Bitmap or
Picture and call draw(android.graphics.Canvas) on the View. However these
software-rendered usages are discouraged and have compatibility issues with hardware-only
rendering features such as Config.HARDWARE
bitmaps, real-time shadows, and outline clipping. For screenshots of the UI for feedback
reports or unit testing the PixelCopy API is recommended.
void
setDuplicateParentStateEnabled(boolean enabled)
Enables or disables the duplication of the parent’s state into this view.
void
setElevation(float elevation)
Sets the base elevation of this view, in pixels.
void
setEnabled(boolean enabled)
Set the enabled state of this view.
void
setFadingEdgeLength(int length)
Set the size of the faded edge used to indicate that more content in this
view is available.
void
setFilterTouchesWhenObscured(boolean enabled)
Sets whether the framework should discard touches when the view’s
window is obscured by another visible window at the touched location.
void
setFitsSystemWindows(boolean fitSystemWindows)
Sets whether or not this view should account for system screen decorations
such as the status bar and inset its content; that is, controlling whether
the default implementation of fitSystemWindows(android.graphics.Rect) will be
executed.
void
setFocusable(boolean focusable)
Set whether this view can receive the focus.
void
setFocusable(int focusable)
Sets whether this view can receive focus.
void
setFocusableInTouchMode(boolean focusableInTouchMode)
Set whether this view can receive focus while in touch mode.
void
setFocusedByDefault(boolean isFocusedByDefault)
Sets whether this View should receive focus when the focus is restored for the view
hierarchy containing this view.
void
setForceDarkAllowed(boolean allow)
Sets whether or not to allow force dark to apply to this view.
void
setForeground(Drawable foreground)
Supply a Drawable that is to be rendered on top of all of the content in the view.
void
setForegroundGravity(int gravity)
Describes how the foreground is positioned.
void
setForegroundTintBlendMode(BlendMode blendMode)
Specifies the blending mode used to apply the tint specified by
setForegroundTintList(android.content.res.ColorStateList)} to the background
drawable.
void
setForegroundTintList(ColorStateList tint)
Applies a tint to the foreground drawable.
void
setForegroundTintMode(PorterDuff.Mode tintMode)
Specifies the blending mode used to apply the tint specified by
setForegroundTintList(android.content.res.ColorStateList)} to the background
drawable.
void
setHandwritingBoundsOffsets(float offsetLeft, float offsetTop, float offsetRight, float offsetBottom)
Set the amount of offset applied to this view’s stylus handwriting bounds.
void
setHandwritingDelegateConfiguration(HandwritingDelegateConfiguration configuration)
Configures this view to act as a handwriting initiation delegate.
void
setHapticFeedbackEnabled(boolean hapticFeedbackEnabled)
Set whether this view should have haptic feedback for events such as
long presses.
void
setHasTransientState(boolean hasTransientState)
Set whether this view is currently tracking transient state that the
framework should attempt to preserve when possible.
void
setHorizontalFadingEdgeEnabled(boolean horizontalFadingEdgeEnabled)
Define whether the horizontal edges should be faded when this view
is scrolled horizontally.
void
setHorizontalScrollBarEnabled(boolean horizontalScrollBarEnabled)
Define whether the horizontal scrollbar should be drawn or not.
void
setHorizontalScrollbarThumbDrawable(Drawable drawable)
Defines the horizontal thumb drawable
void
setHorizontalScrollbarTrackDrawable(Drawable drawable)
Defines the horizontal track drawable
void
setHovered(boolean hovered)
Sets whether the view is currently hovered.
void
setId(int id)
Sets the identifier for this view.
void
setImportantForAccessibility(int mode)
Sets how to determine whether this view is important for accessibility
which is if it fires accessibility events and if it is reported to
accessibility services that query the screen.
void
setImportantForAutofill(int mode)
Sets the mode for determining whether this view is considered important for autofill.
void
setImportantForContentCapture(int mode)
Sets the mode for determining whether this view is considered important for content capture.
void
setIsCredential(boolean isCredential)
Gets the mode for determining whether this view is a credential.
void
setKeepScreenOn(boolean keepScreenOn)
Controls whether the screen should remain on, modifying the
value of KEEP_SCREEN_ON.
void
setKeyboardNavigationCluster(boolean isCluster)
Set whether this view is a root of a keyboard navigation cluster.
void
setLabelFor(int id)
Sets the id of a view for which this view serves as a label for
accessibility purposes.
void
setLayerPaint(Paint paint)
Updates the Paint object used with the current layer (used only if the current
layer type is not set to LAYER_TYPE_NONE).
void
setLayerType(int layerType, Paint paint)
Specifies the type of layer backing this view.
void
setLayoutDirection(int layoutDirection)
Set the layout direction for this view.
void
setLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams params)
Set the layout parameters associated with this view.
final
void
setLeft(int left)
Sets the left position of this view relative to its parent.
final
void
setLeftTopRightBottom(int left, int top, int right, int bottom)
Assign a size and position to this view.
void
setLongClickable(boolean longClickable)
Enables or disables long click events for this view.
final
void
setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight)
This method must be called by onMeasure(int, int) to store the
measured width and measured height.
void
setMinimumHeight(int minHeight)
Sets the minimum height of the view.
void
setMinimumWidth(int minWidth)
Sets the minimum width of the view.
void
setNestedScrollingEnabled(boolean enabled)
Enable or disable nested scrolling for this view.
void
setNextClusterForwardId(int nextClusterForwardId)
Sets the id of the view to use as the root of the next keyboard navigation cluster.
void
setNextFocusDownId(int nextFocusDownId)
Sets the id of the view to use when the next focus is FOCUS_DOWN.
void
setNextFocusForwardId(int nextFocusForwardId)
Sets the id of the view to use when the next focus is FOCUS_FORWARD.
void
setNextFocusLeftId(int nextFocusLeftId)
Sets the id of the view to use when the next focus is FOCUS_LEFT.
void
setNextFocusRightId(int nextFocusRightId)
Sets the id of the view to use when the next focus is FOCUS_RIGHT.
void
setNextFocusUpId(int nextFocusUpId)
Sets the id of the view to use when the next focus is FOCUS_UP.
void
setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(View.OnApplyWindowInsetsListener listener)
Set an OnApplyWindowInsetsListener to take over the policy for applying
window insets to this view.
void
setOnCapturedPointerListener(View.OnCapturedPointerListener l)
Set a listener to receive callbacks when the pointer capture state of a view changes.
void
setOnClickListener(View.OnClickListener l)
Register a callback to be invoked when this view is clicked.
void
setOnContextClickListener(View.OnContextClickListener l)
Register a callback to be invoked when this view is context clicked.
void
setOnCreateContextMenuListener(View.OnCreateContextMenuListener l)
Register a callback to be invoked when the context menu for this view is
being built.
void
setOnDragListener(View.OnDragListener l)
Register a drag event listener callback object for this View.
void
setOnFocusChangeListener(View.OnFocusChangeListener l)
Register a callback to be invoked when focus of this view changed.
void
setOnGenericMotionListener(View.OnGenericMotionListener l)
Register a callback to be invoked when a generic motion event is sent to this view.
void
setOnHoverListener(View.OnHoverListener l)
Register a callback to be invoked when a hover event is sent to this view.
void
setOnKeyListener(View.OnKeyListener l)
Register a callback to be invoked when a hardware key is pressed in this view.
void
setOnLongClickListener(View.OnLongClickListener l)
Register a callback to be invoked when this view is clicked and held.
void
setOnReceiveContentListener(String[] mimeTypes, OnReceiveContentListener listener)
Sets the listener to be used to handle insertion of
content into this view.
void
setOnScrollChangeListener(View.OnScrollChangeListener l)
Register a callback to be invoked when the scroll X or Y positions of
this view change.
void
setOnSystemUiVisibilityChangeListener(View.OnSystemUiVisibilityChangeListener l)
This method was deprecated
in API level 30.
Use WindowInsets#isVisible(int) to find out about system bar visibilities
by setting a OnApplyWindowInsetsListener on this view.
void
setOnTouchListener(View.OnTouchListener l)
Register a callback to be invoked when a touch event is sent to this view.
void
setOutlineAmbientShadowColor(int color)
Sets the color of the ambient shadow that is drawn when the view has a positive Z or
elevation value.
void
setOutlineProvider(ViewOutlineProvider provider)
Sets the ViewOutlineProvider of the view, which generates the Outline that defines
the shape of the shadow it casts, and enables outline clipping.
void
setOutlineSpotShadowColor(int color)
Sets the color of the spot shadow that is drawn when the view has a positive Z or
elevation value.
void
setOverScrollMode(int overScrollMode)
Set the over-scroll mode for this view.
void
setPadding(int left, int top, int right, int bottom)
Sets the padding.
void
setPaddingRelative(int start, int top, int end, int bottom)
Sets the relative padding.
void
setPivotX(float pivotX)
Sets the x location of the point around which the view is
rotated and scaled.
void
setPivotY(float pivotY)
Sets the y location of the point around which the view is rotated
and scaled.
void
setPointerIcon(PointerIcon pointerIcon)
Set the pointer icon for the current view.
final
void
setPreferKeepClear(boolean preferKeepClear)
Set a preference to keep the bounds of this view clear from floating windows above this
view’s window.
final
void
setPreferKeepClearRects(List<Rect> rects)
Set a preference to keep the provided rects clear from floating windows above this
view’s window.
void
setPressed(boolean pressed)
Sets the pressed state for this view.
void
setRenderEffect(RenderEffect renderEffect)
Configure the RenderEffect to apply to this View.
final
void
setRevealOnFocusHint(boolean revealOnFocus)
Sets this view’s preference for reveal behavior when it gains focus.
final
void
setRight(int right)
Sets the right position of this view relative to its parent.
void
setRotation(float rotation)
Sets the degrees that the view is rotated around the pivot point.
void
setRotationX(float rotationX)
Sets the degrees that the view is rotated around the horizontal axis through the pivot point.
void
setRotationY(float rotationY)
Sets the degrees that the view is rotated around the vertical axis through the pivot point.
void
setSaveEnabled(boolean enabled)
Controls whether the saving of this view’s state is
enabled (that is, whether its onSaveInstanceState() method
will be called).
void
setSaveFromParentEnabled(boolean enabled)
Controls whether the entire hierarchy under this view will save its
state when a state saving traversal occurs from its parent.
void
setScaleX(float scaleX)
Sets the amount that the view is scaled in x around the pivot point, as a proportion of
the view’s unscaled width.
void
setScaleY(float scaleY)
Sets the amount that the view is scaled in Y around the pivot point, as a proportion of
the view’s unscaled width.
void
setScreenReaderFocusable(boolean screenReaderFocusable)
Sets whether this View should be a focusable element for screen readers
and include non-focusable Views from its subtree when providing feedback.
void
setScrollBarDefaultDelayBeforeFade(int scrollBarDefaultDelayBeforeFade)
Define the delay before scrollbars fade.
void
setScrollBarFadeDuration(int scrollBarFadeDuration)
Define the scrollbar fade duration.
void
setScrollBarSize(int scrollBarSize)
Define the scrollbar size.
void
setScrollBarStyle(int style)
Specify the style of the scrollbars.
final
void
setScrollCaptureCallback(ScrollCaptureCallback callback)
Sets the callback to receive scroll capture requests.
void
setScrollCaptureHint(int hint)
Sets the scroll capture hint for this View.
void
setScrollContainer(boolean isScrollContainer)
Change whether this view is one of the set of scrollable containers in
its window.
void
setScrollIndicators(int indicators, int mask)
Sets the state of the scroll indicators specified by the mask.
void
setScrollIndicators(int indicators)
Sets the state of all scroll indicators.
void
setScrollX(int value)
Set the horizontal scrolled position of your view.
void
setScrollY(int value)
Set the vertical scrolled position of your view.
void
setScrollbarFadingEnabled(boolean fadeScrollbars)
Define whether scrollbars will fade when the view is not scrolling.
void
setSelected(boolean selected)
Changes the selection state of this view.
void
setSoundEffectsEnabled(boolean soundEffectsEnabled)
Set whether this view should have sound effects enabled for events such as
clicking and touching.
void
setStateDescription(CharSequence stateDescription)
Sets the View‘s state description.
void
setStateListAnimator(StateListAnimator stateListAnimator)
Attaches the provided StateListAnimator to this View.
void
setSystemGestureExclusionRects(List<Rect> rects)
Sets a list of areas within this view’s post-layout coordinate space where the system
should not intercept touch or other pointing device gestures.
void
setSystemUiVisibility(int visibility)
This method was deprecated
in API level 30.
SystemUiVisibility flags are deprecated. Use WindowInsetsController
instead.
void
setTag(int key, Object tag)
Sets a tag associated with this view and a key.
void
setTag(Object tag)
Sets the tag associated with this view.
void
setTextAlignment(int textAlignment)
Set the text alignment.
void
setTextDirection(int textDirection)
Set the text direction.
void
setTooltipText(CharSequence tooltipText)
Sets the tooltip text which will be displayed in a small popup next to the view.
final
void
setTop(int top)
Sets the top position of this view relative to its parent.
void
setTouchDelegate(TouchDelegate delegate)
Sets the TouchDelegate for this View.
void
setTransitionAlpha(float alpha)
This property is intended only for use by the Fade transition, which animates it
to produce a visual translucency that does not side-effect (or get affected by)
the real alpha property.
final
void
setTransitionName(String transitionName)
Sets the name of the View to be used to identify Views in Transitions.
void
setTransitionVisibility(int visibility)
Changes the visibility of this View without triggering any other changes.
void
setTranslationX(float translationX)
Sets the horizontal location of this view relative to its left position.
void
setTranslationY(float translationY)
Sets the vertical location of this view relative to its top position.
void
setTranslationZ(float translationZ)
Sets the depth location of this view relative to its elevation.
void
setVerticalFadingEdgeEnabled(boolean verticalFadingEdgeEnabled)
Define whether the vertical edges should be faded when this view
is scrolled vertically.
void
setVerticalScrollBarEnabled(boolean verticalScrollBarEnabled)
Define whether the vertical scrollbar should be drawn or not.
void
setVerticalScrollbarPosition(int position)
Set the position of the vertical scroll bar.
void
setVerticalScrollbarThumbDrawable(Drawable drawable)
Defines the vertical scrollbar thumb drawable
void
setVerticalScrollbarTrackDrawable(Drawable drawable)
Defines the vertical scrollbar track drawable
void
setViewTranslationCallback(ViewTranslationCallback callback)
Sets a ViewTranslationCallback that is used to display/hide the translated
information.
void
setVisibility(int visibility)
Set the visibility state of this view.
void
setWillNotCacheDrawing(boolean willNotCacheDrawing)
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The view drawing cache was largely made obsolete with the introduction of
hardware-accelerated rendering in API 11. With hardware-acceleration, intermediate cache
layers are largely unnecessary and can easily result in a net loss in performance due to the
cost of creating and updating the layer. In the rare cases where caching layers are useful,
such as for alpha animations, setLayerType(int, android.graphics.Paint) handles this with hardware
rendering. For software-rendered snapshots of a small part of the View hierarchy or
individual Views it is recommended to create a Canvas from either a Bitmap or
Picture and call draw(android.graphics.Canvas) on the View. However these
software-rendered usages are discouraged and have compatibility issues with hardware-only
rendering features such as Config.HARDWARE
bitmaps, real-time shadows, and outline clipping. For screenshots of the UI for feedback
reports or unit testing the PixelCopy API is recommended.
void
setWillNotDraw(boolean willNotDraw)
If this view doesn’t do any drawing on its own, set this flag to
allow further optimizations.
void
setWindowInsetsAnimationCallback(WindowInsetsAnimation.Callback callback)
Sets a WindowInsetsAnimation.Callback to be notified about animations of windows that
cause insets.
void
setX(float x)
Sets the visual x position of this view, in pixels.
void
setY(float y)
Sets the visual y position of this view, in pixels.
void
setZ(float z)
Sets the visual z position of this view, in pixels.
boolean
showContextMenu()
Shows the context menu for this view.
boolean
showContextMenu(float x, float y)
Shows the context menu for this view anchored to the specified
view-relative coordinate.
ActionMode
startActionMode(ActionMode.Callback callback, int type)
Start an action mode with the given type.
ActionMode
startActionMode(ActionMode.Callback callback)
Start an action mode with the default type ActionMode#TYPE_PRIMARY.
void
startAnimation(Animation animation)
Start the specified animation now.
final
boolean
startDrag(ClipData data, View.DragShadowBuilder shadowBuilder, Object myLocalState, int flags)
This method was deprecated
in API level 24.
Use startDragAndDrop() for newer platform versions.
final
boolean
startDragAndDrop(ClipData data, View.DragShadowBuilder shadowBuilder, Object myLocalState, int flags)
Starts a drag and drop operation.
boolean
startNestedScroll(int axes)
Begin a nestable scroll operation along the given axes.
void
stopNestedScroll()
Stop a nested scroll in progress.
String
toString()
Returns a string representation of the object.
void
transformMatrixToGlobal(Matrix matrix)
Modifies the input matrix such that it maps view-local coordinates to
on-screen coordinates.
void
transformMatrixToLocal(Matrix matrix)
Modifies the input matrix such that it maps on-screen coordinates to
view-local coordinates.
void
unscheduleDrawable(Drawable who, Runnable what)
Cancels a scheduled action on a drawable.
void
unscheduleDrawable(Drawable who)
Unschedule any events associated with the given Drawable.
final
void
updateDragShadow(View.DragShadowBuilder shadowBuilder)
Updates the drag shadow for the ongoing drag and drop operation.
boolean
verifyDrawable(Drawable who)
If your view subclass is displaying its own Drawable objects, it should
override this function and return true for any Drawable it is
displaying.
boolean
willNotCacheDrawing()
This method was deprecated
in API level 28.
The view drawing cache was largely made obsolete with the introduction of
hardware-accelerated rendering in API 11. With hardware-acceleration, intermediate cache
layers are largely unnecessary and can easily result in a net loss in performance due to the
cost of creating and updating the layer. In the rare cases where caching layers are useful,
such as for alpha animations, setLayerType(int, android.graphics.Paint) handles this with hardware
rendering. For software-rendered snapshots of a small part of the View hierarchy or
individual Views it is recommended to create a Canvas from either a Bitmap or
Picture and call draw(android.graphics.Canvas) on the View. However these
software-rendered usages are discouraged and have compatibility issues with hardware-only
rendering features such as Config.HARDWARE
bitmaps, real-time shadows, and outline clipping. For screenshots of the UI for feedback
reports or unit testing the PixelCopy API is recommended.
boolean
willNotDraw()
Returns whether or not this View draws on its own.
How to modify horizontal progress bar theme and create with new color.
In this tutorial we are creating 5 different type of horizontal progress bars each with different color theme using getProgressDrawable().setColorFilter(Color.BLUE, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN); method. This method helps us the choose any color from android color directory and also apply any color code. So here is the complete step by step tutorial for How to change horizontal progress bar color in android programmatically.
How to change horizontal progress bar color in android programmatically.
Code for MainActivity.java file.
package com.horizontalprogressbarcolorchange_android_examples.com;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.widget.ProgressBar;
import android.graphics.PorterDuff;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
ProgressBar progressbar1,progressbar2,progressbar3,progressbar4,progressbar5;
int intValue = 0;
Handler handler = new Handler();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
progressbar1 = (ProgressBar)findViewById(R.id.progressBar1);
progressbar2 = (ProgressBar)findViewById(R.id.progressBar2);
progressbar3 = (ProgressBar)findViewById(R.id.progressBar3);
progressbar4 = (ProgressBar)findViewById(R.id.progressBar4);
progressbar5 = (ProgressBar)findViewById(R.id.progressBar5);
// Adding colors on progress bar
progressbar1.getProgressDrawable().setColorFilter(Color.BLUE, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
progressbar2.getProgressDrawable().setColorFilter(Color.CYAN, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
progressbar3.getProgressDrawable().setColorFilter(Color.GREEN, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
progressbar4.getProgressDrawable().setColorFilter(Color.RED, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
progressbar5.getProgressDrawable().setColorFilter(Color.YELLOW, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while(intValue < 100)
{
intValue++;
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
progressbar1.setProgress(intValue);
progressbar2.setProgress(intValue);
progressbar3.setProgress(intValue);
progressbar4.setProgress(intValue);
progressbar5.setProgress(intValue);
}
});try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
}
Code for activity_main.xml layout file.
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context="com.horizontalprogressbarcolorchange_android_examples.com.MainActivity" > <ProgressBar android:id="@+id/progressBar1" style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_marginTop="91dp" android:minHeight="60dp" android:minWidth="220dp" /> <ProgressBar android:id="@+id/progressBar2" style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_marginTop="120dp" android:minHeight="60dp" android:minWidth="220dp" /> <ProgressBar android:id="@+id/progressBar3" style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_marginTop="150dp" android:minHeight="60dp" android:minWidth="220dp" /> <ProgressBar android:id="@+id/progressBar4" style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_marginTop="180dp" android:minHeight="60dp" android:minWidth="220dp" /> <ProgressBar android:id="@+id/progressBar5" style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_marginTop="210dp" android:minHeight="60dp" android:minWidth="220dp" /> </RelativeLayout>
Screenshots :
Click here to download How to change horizontal progress bar color in android programmatically project with source code.
In Android, ProgressBar is used to display the status of work being done like analyzing status of work or downloading a file etc. In Android, by default a progress bar will be displayed as a spinning wheel but If we want it to be displayed as a horizontal bar then we need to use style attribute as horizontal. It mainly use the “android.widget.ProgressBar” class.
Important Note: A progress bar can also be made indeterminate. In this mode a progress bar shows a cyclic animation without an indication of progress. This mode is used in application when we don’t know the amount of work to be done.
To add a progress bar to a layout (xml) file, you can use the <ProgressBar> element. By default, a progress bar is a spinning wheel (an indeterminate indicator). To change to a horizontal progress bar, apply the progress bar’s horizontal style.
ProgressBar code:
<ProgressBar android:id="@+id/simpleProgressBar" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
Horizontal ProgressBar code:
<ProgressBar android:id="@+id/simpleProgressBar" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" style="@style/Widget.AppCompat.ProgressBar.Horizontal"/>
Table Of Contents
- 1 Important Methods Used In ProgressBar:
- 2 Attributes of ProgressBar In Android:
- 3 ProgressBar Example In Android Studio:
- 4 Horizontal ProgressBar Example In Android Studio:
- 5 Related Topic – ProgressDialog In Android
Important Methods Used In ProgressBar:
1. getMax() – returns the maximum value of progress bar
We can get the maximum value of the progress bar in java class. This method returns a integer value. Below is the code to get the maximum value from a Progress bar.
ProgressBar simpleProgressBar=(ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.simpleProgressBar); // initiate the progress bar int maxValue=simpleProgressBar.getMax(); // get maximum value of the progress bar
2. getProgress() – returns current progress value
We can get the current progress value from a progress bar in java class. This method also returns a integer value. Below is the code to get current progress value from a Progress bar.
ProgressBar simpleProgressBar=(ProgressBar)findViewById(R.id.simpleProgressBar); // initiate the progress bar int progressValue=simpleProgressBar.getProgress(); // get progress value from the progress bar
Attributes of ProgressBar In Android:
Now let’s discuss important attributes that helps us to configure a Progress bar in xml file (layout).
1. id: id is an attribute used to uniquely identify a Progress bar.
<ProgressBar android:id="@+id/simpleProgressBar" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" style="@style/Widget.AppCompat.ProgressBar.Horizontal"/>
2. max: max is an attribute used in android to define maximum value of the progress can take. It must be an integer value like 100, 200 etc.
Below we set 100 maximum value for a progress bar.
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/simpleProgressBar"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
style="@style/Widget.AppCompat.ProgressBar.Horizontal"
android:max="100" /><!--set 100 maximum value for the progress bar-->
Set Max Value of ProgressBar In Java Class :
ProgressBar simpleProgressBar=(ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.simpleProgressBar); // initiate the progress bar simpleProgressBar.setMax(100); // 100 maximum value for the progress bar
3. progress: progress is an attribute used in android to define the default progress value between 0 and max. It must be an integer value.
Below we set the 100 max value and then set 50 default progress.
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/simpleProgressBar"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:max="100"
style="@style/Widget.AppCompat.ProgressBar.Horizontal"
android:progress="50"/><!--// 50 default progress value-->
Setting Progress Value of ProgressBar In Java Class :
ProgressBar simpleProgressBar=(ProgressBar)findViewById(R.id.simpleProgressBar); // initiate the progress bar simpleProgressBar.setMax(100); // 100 maximum value for the progress value simpleProgressBar.setProgress(50); // 50 default progress value for the progress bar
4. progressDrawable: progress drawable is an attribute used in Android to set the custom drawable for the progress mode.
Below we set a custom gradient drawable for the progress mode of a progress bar. Before you try below code make sure to download a progress icon from the web and add in your drawable folder.
Step 1: Add this code in activity_main.xml or main.xml inside layout.
<ProgressBar android:id="@+id/simpleProgressBar" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:max="100" android:progress="60" android:layout_marginTop="100dp" style="@style/Widget.AppCompat.ProgressBar.Horizontal" android:progressDrawable="@drawable/custom_progress"/><!--custom progress drawable for progress mode-->
Step 2: Create a new drawable resource xml in drawable folder and name it custom_progress. Here add the below code which creates gradient effect in progressbar.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layer-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<item>
<shape>
<gradient
android:endColor="#fff"
android:startColor="#1f1"
android:useLevel="true" />
</shape>
</item>
</layer-list>
5. background: background attribute is used to set the background of a Progress bar. We can set a color or a drawable in the background of a Progress bar.
Below we set the black color for the background of a Progress bar.
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/simpleProgressBar"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:max="100"
android:progress="50"
style="@style/Widget.AppCompat.ProgressBar.Horizontal"
android:background="#000"/><!-- black background color for progress bar-->
6. indeterminate: indeterminate attribute is used in Android to enable the indeterminate mode. In this mode a progress bar shows a cyclic animation without an indication of progress. This mode is used in application when we don’t know the amount of work to be done. In this mode the actual working will not be shown.
In below code we set the indeterminate to true.
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/simpleProgressBar"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:max="100"
android:progress="50"
android:background="#000"
android:padding="20dp" style="@style/Widget.AppCompat.ProgressBar.Horizontal"
android:indeterminate="true"/><!--true value for indeterminate-->
Setting indeterminate of ProgressBar In Java class:
ProgressBar simpleProgressBar=(ProgressBar)findViewById(R.id.simpleProgressBar); // initiate the progress bar simpleProgressBar.setBackgroundColor(Color.BLACK); // black background color for the progress bar
7. padding: padding attribute is used to set the padding from left, right, top or bottom of ProgressBar.
- paddingRight: set the padding from the right side of the Progress bar.
- paddingLeft: set the padding from the left side of the Progress bar.
- paddingTop: set the padding from the top side of the Progress bar.
- paddingBottom: set the padding from the bottom side of the Progress bar.
- Padding: set the padding from the all side’s of the Progress bar.
Below we set the 20dp padding from all the side’s of the Progress bar.
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/simpleProgressBar"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:max="100"
android:progress="50"
android:background="#000"
style="@style/Widget.AppCompat.ProgressBar.Horizontal"
android:padding="20dp"/><!--// 20dp padding from all the sides of the progress bar-->
ProgressBar Example In Android Studio:
In the first example of ProgressBar we displayed a default spinning wheel progress bar and a start button whenever a user click on the button the progress bar is displayed. Below is the final output, download code and step by step explanation:
Download Code ?
Step 1: Create a new project and name it ProgressBarExample.
Select File -> New -> New Project… then Fill the forms and click "Finish" button.
Step 2: Open res -> layout -> activity_main.xml (or) main.xml and add following code:
In this step we open an xml file and add the code for displaying a progress bar and set its visibility to invisible and one start button.
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/simpleProgressBar"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:visibility="invisible"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/startButton"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Start"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="100dp"
android:padding="10dp"
android:background="#0f0"
android:textColor="#fff"/>
</RelativeLayout>
Step 3: Now Open src -> package -> MainActivity.java
In this step we open MainActivity where we add the code to initiate the progress bar & button and then perform click event on button which display the progress bar.
package example.gb.progressbarexample;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ProgressBar;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// initiate progress bar and start button
final ProgressBar simpleProgressBar = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.simpleProgressBar);
Button startButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.startButton);
// perform click event on button
startButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// visible the progress bar
simpleProgressBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
});
}
}
Output:
Now start the AVD in Emulator and run the App. Click on the start button and Progress Bar will be displayed on screen.
Horizontal ProgressBar Example In Android Studio:
In the second example we display a horizontal progress bar with drawable background and a start button. Here whenever a user clicks on button a thread is used to start the progress. Below is the final output, download code and step by step explanation:
Download Code ?
Step 1: Create a new project and name it ProgressBarExample.
Select File -> New -> New Project… then Fill the forms and click "Finish" button.
Step 2: Open res -> layout -> activity_main.xml (or) main.xml and add following code:
In this step we open an xml file and add the code for displaying a horizontal progress bar by using style property, drawable progress xml and one start button.
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#000"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/simpleProgressBar"
style="@style/Widget.AppCompat.ProgressBar.Horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="70dp"
android:max="100"
android:progress="0"
android:progressDrawable="@drawable/custom_progress" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/startButton"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="120dp"
android:background="#0f0"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="Start"
android:textColor="#fff"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textStyle="bold" />
</RelativeLayout>
Step 3: Create an xml file in drawable -> custom_progress.xml
In this step we create a custom drawable xml for the progress bar. In this xml we create a layer list in which we create an item and then set the gradient colors for our custom progress bar.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layer-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<item>
<shape>
<gradient
android:endColor="#fff"
android:startColor="#1f1"
android:useLevel="true" />
</shape>
</item>
</layer-list>
Step 4: Open app -> package -> MainActivity.java
In this step we open MainActivity and add the code to initiate the progress bar, button and then perform click event on button. After that we start the progressing in a progress bar using a thread.
package example.gb.progressbarexample;
import android.app.Dialog;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.provider.Settings;
import android.support.v7.app.AlertDialog;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ProgressBar;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
int progress = 0;
ProgressBar simpleProgressBar;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// initiate progress bar and start button
simpleProgressBar = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.simpleProgressBar);
Button startButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.startButton);
// perform click event on button
startButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// call a function
setProgressValue(progress);
}
});
}
private void setProgressValue(final int progress) {
// set the progress
simpleProgressBar.setProgress(progress);
// thread is used to change the progress value
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
setProgressValue(progress + 10);
}
});
thread.start();
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will
// automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long
// as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml.
int id = item.getItemId();
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
if (id == R.id.action_settings) {
return true;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
Output:
Now run the App in AVD, click on start button and you will see horizontal progressbar.
Related Topic – ProgressDialog In Android
Android Progress Dialog is a UI which shows the progress of a task like you want user to wait until the previous lined up task is completed and for that purpose you can use progress dialog. Read our Progressdialog tutorial with example.
Continue Reading:
- RatingBar Tutorial With Example in Android
- SeekBar Tutorial With Example in Android
- VideoView Tutorial With Example in Android
- Adapter Tutorial With Example in Android
- TextSwitcher Tutorial With Example in Android
Published September 24, 2021
In this Android kotlin example we will learn how to set the color to the Progressbar programmatically. Progressbar is a widget which will used to show the progress status of the work in the android application. we always set the colors of the widget inside xml files, but how we can set the color to the Progressbar dynamically.
There are two ways to set the color to the progressbar by programmatically
progressBar.progressTintList
progressBar2.progressDrawable.colorFilter
Set color by progressBar.progressTintList
progressBar.progressTintList= ColorStateList.valueOf(Color.GREEN)
set color by progressBar2.progressDrawable.colorFilter
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.Q) {
progressBar2.progressDrawable.colorFilter =
BlendModeColorFilter(Color.BLUE, BlendMode.SRC_IN)
}else {
progressBar2.progressDrawable
.setColorFilter(Color.BLUE, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN)
}
Let’s create android example to set color for the progressbar dynamically
Step 1: Create Android application
Step 2: Update xml file with below code, this xml file contains two progressbar, one textview and one button
<androidx.appcompat.widget.LinearLayoutCompat
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/constraintLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<com.google.android.material.textview.MaterialTextView
android:id="@+id/txt_progress"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="24dp"
android:textAppearance=
"@style/TextAppearance.MaterialComponents.Headline6"
android:text="0" />
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressBar"
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="16dp"/>
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progressBar2"
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_marginStart="16dp"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="16dp" />
<com.google.android.material.button.MaterialButton
android:id="@+id/btn_event"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:text="Start"
android:textColor="#FFF"
android:backgroundTint="#000" />
</androidx.appcompat.widget.LinearLayoutCompat>
Step 3: Inflate views in activity screen
package com.rrtutors.kotlinexample2021
import android.content.res.ColorStateList
import android.graphics.BlendMode
import android.graphics.BlendModeColorFilter
import android.graphics.Color
import android.graphics.PorterDuff
import android.os.Build
import android.os.Bundle
import android.os.Handler
import android.os.Looper
import android.util.Log
import android.widget.ProgressBar
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import com.google.android.material.button.MaterialButton
import com.google.android.material.textview.MaterialTextView
import java.lang.Thread.sleep
class ProgressbarActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
lateinit var txt_progress:MaterialTextView
lateinit var progressBar:ProgressBar
lateinit var progressBar2:ProgressBar
lateinit var btn_event:MaterialButton
var progres:Int=0;
lateinit var thread:Thread;
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_progressbar)
txt_progress=findViewById(R.id.txt_progress);
progressBar=findViewById(R.id.progressBar);
progressBar2=findViewById(R.id.progressBar2);
btn_event=findViewById(R.id.btn_event);
progressBar.progress=10;
progressBar2.progress=10;
progressBar.progressTintList= ColorStateList.valueOf(Color.GREEN)
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.Q) {
progressBar2.progressDrawable.colorFilter =
BlendModeColorFilter(Color.BLUE, BlendMode.SRC_IN)
}else {
progressBar2.progressDrawable
.setColorFilter(Color.BLUE, PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN)
}
btn_event.setOnClickListener {
thread= Thread(Runnable {
while (progres < 100){
progres=progres+1;
Log.v("Progress","Progress "+progres);
runOnUiThread {
progressBar.progress = progres
progressBar2.progress = progres
txt_progress.text = "$progres %"
progressBar.progressTintList= ColorStateList.valueOf(Color.RED)
}
}
})
thread.start();
}
}
}
Step 4: Now run the application
Conclusion: In this example we learned how to inflate views from xml file and set color to the progressbar programmatically.
Circular seekbar android