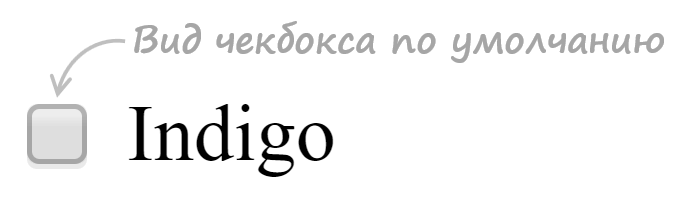I builded another fork of @klewis’ code sample to demonstrate some playing with pure css and gradients by using :before/:after pseudo elements and a hidden radio input button.
HTML:
sample radio buttons:
<div style="background:lightgrey;">
<span class="radio-item">
<input type="radio" id="ritema" name="ritem" class="true" value="ropt1" checked="checked">
<label for="ritema">True</label>
</span>
<span class="radio-item">
<input type="radio" id="ritemb" name="ritem" class="false" value="ropt2">
<label for="ritemb">False</label>
</span>
</div>
:
CSS:
.radio-item input[type='radio'] {
visibility: hidden;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
margin: 0 5px 0 5px;
padding: 0;
}
.radio-item input[type=radio]:before {
position: relative;
margin: 4px -25px -4px 0;
display: inline-block;
visibility: visible;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
border: 2px inset rgba(150,150,150,0.75);
background: radial-gradient(ellipse at top left, rgb(255,255,255) 0%, rgb(250,250,250) 5%, rgb(230,230,230) 95%, rgb(225,225,225) 100%);
content: "";
}
.radio-item input[type=radio]:checked:after {
position: relative;
top: 0;
left: 9px;
display: inline-block;
visibility: visible;
border-radius: 6px;
width: 12px;
height: 12px;
background: radial-gradient(ellipse at top left, rgb(245,255,200) 0%, rgb(225,250,100) 5%, rgb(75,175,0) 95%, rgb(25,100,0) 100%);
content: "";
}
.radio-item input[type=radio].true:checked:after {
background: radial-gradient(ellipse at top left, rgb(245,255,200) 0%, rgb(225,250,100) 5%, rgb(75,175,0) 95%, rgb(25,100,0) 100%);
}
.radio-item input[type=radio].false:checked:after {
background: radial-gradient(ellipse at top left, rgb(255,225,200) 0%, rgb(250,200,150) 5%, rgb(200,25,0) 95%, rgb(100,25,0) 100%);
}
.radio-item label {
display: inline-block;
height: 25px;
line-height: 25px;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
preview:
https://www.codeply.com/p/y47T4ylfib
В этой статье подробно разберём процесс кастомной стилизации чекбоксов и радиокнопок с помощью CSS.
Как осуществляется создание кастомного чекбокса или переключателя
Данный процесс осуществляется посредством скрытия стандартного элемента и создания с помощью CSS другого «поддельного», такого как мы хотим.
Но как же это будет работать, если стандартный input скрыть? Это можно выполнить благодаря тому, что в HTML переключить состояние checked можно не только с помощью самого элемента input, но и посредством связанного с ним label.
В HTML связывание label с input выполняется одним из 2 способов:
1. Посредством помещения элемента input в label:
<label> <input type="checkbox" name="happy" value="yes">Happy </label>
2. Посредством задания элементу input атрибута id, а label – for с таким же значением как у id.
<input type="checkbox" id="happy" name="happy" value="yes"> <label for="happy">Happy</label>
В этой статье мы подробно разберём шаги по кастомизации checkbox и radio, в которых label с input свяжем по 2 варианту. Создание «поддельного» чекбокса выполним с использованием псевдоэлемента ::before, который поместим в label. При этом никакие дополнительные элементы в разметку добавлять не будем.
Создание стильного чекбокса
Процесс замены стандартного вида чекбокса на кастомный осуществим посредством выполнения следующей последовательности шагов.
Шаг 1. Создадим разметку.
<input type="checkbox" class="custom-checkbox" id="happy" name="happy" value="yes"> <label for="happy">Happy</label>
При создании разметки очень важно соблюдать последовательность расположения элементов. Это необходимо, потому что в зависимости от того, как они расположены мы будем составлять выражения для выбора элементов в CSS и назначать им стили.
В этом примере элемент label расположен после input. Связь label с input осуществляется посредством соответствия значения for элемента label с id элемента input.
В примере к элементу input добавлен класс custom-checkbox. Данный класс мы будем использовать при составлении селекторов и тем самым с помощью него определять элементы к которым следует добавить стилизованный чекбокс вместо обычного. Т.е. его присутствие или отсутствие будет определять с каким чекбоксом (со стандартным или поддельным) будет выводится элемент input с type="checkbox".
Шаг 2. Напишем стили для скрытия стандартного элемента input.
.custom-checkbox {
position: absolute;
z-index: -1;
opacity: 0;
}
Мы не будем использовать display: none, а установим ему стили, с помощью которых уберём его из потока (position: absolute), поместим его ниже существующих элементов (z-index: -1), а также сделаем его полностью прозрачным (opacity: 0). Зачем это нужно? Это нам необходимо для того, чтобы мы могли получить состояние фокуса, а затем стилизовать «подделный» checkbox или radio, когда он будет находиться в нём.
Шаг 3. Создадим поддельный чекбокс.
.custom-checkbox+label {
display: inline-flex;
align-items: center;
user-select: none;
}
.custom-checkbox+label::before {
content: '';
display: inline-block;
width: 1em;
height: 1em;
flex-shrink: 0;
flex-grow: 0;
border: 1px solid #adb5bd;
border-radius: 0.25em;
margin-right: 0.5em;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: center center;
background-size: 50% 50%;
}
Создание «поддельного» чекбокса выполним с помощью псевдоэлемента ::before. Посредством CSS зададим ему размеры (в данном случае 1emx1em), а затем нарисуем его с помощью border: 1px solid #adb5bd. Свойства начинающие со слова background будут определять положение самого флажка (когда checkbox будет в состоянии checked).
Первое правило необходимо для вертикального центрирования флажка и надписи к нему. Это действие в примере выполнено через CSS Flexbox.
Шаг 4. Создадим стили при нахождении элемента в состоянии checked.
.custom-checkbox:checked+label::before {
border-color: #0b76ef;
background-color: #0b76ef;
background-image: url("data:image/svg+xml,%3csvg xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg' viewBox='0 0 8 8'%3e%3cpath fill='%23fff' d='M6.564.75l-3.59 3.612-1.538-1.55L0 4.26 2.974 7.25 8 2.193z'/%3e%3c/svg%3e");
}
В этом коде при получении элементом состояния checked применим к псевдоэлементу ::before находящемуся в label стили, посредством которых установим цвет границы, цвет фону и фоновую картинку (флажок) в формате svg.
Шаг 5. Добавим код для стилизации чекбокса при нахождении его в состояниях hover, active, focus и disabled.
/* стили при наведении курсора на checkbox */
.custom-checkbox:not(:disabled):not(:checked)+label:hover::before {
border-color: #b3d7ff;
}
/* стили для активного состояния чекбокса (при нажатии на него) */
.custom-checkbox:not(:disabled):active+label::before {
background-color: #b3d7ff;
border-color: #b3d7ff;
}
/* стили для чекбокса, находящегося в фокусе */
.custom-checkbox:focus+label::before {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 0.2rem rgba(0, 123, 255, 0.25);
}
/* стили для чекбокса, находящегося в фокусе и не находящегося в состоянии checked */
.custom-checkbox:focus:not(:checked)+label::before {
border-color: #80bdff;
}
/* стили для чекбокса, находящегося в состоянии disabled */
.custom-checkbox:disabled+label::before {
background-color: #e9ecef;
}
Открыть пример
Разработка кастомного переключателя
Стилизация переключателя (input с type="radio") выполняется аналогично, т.е. посредством тех же шагов которые мы применяли при кастомизации чекбокса.
Итоговый набор стилей для кастомного оформления input с type="radio":
<style>
/* для элемента input c type="radio" */
.custom-radio {
position: absolute;
z-index: -1;
opacity: 0;
}
/* для элемента label связанного с .custom-radio */
.custom-radio+label {
display: inline-flex;
align-items: center;
user-select: none;
}
/* создание в label псевдоэлемента before со следующими стилями */
.custom-radio+label::before {
content: '';
display: inline-block;
width: 1em;
height: 1em;
flex-shrink: 0;
flex-grow: 0;
border: 1px solid #adb5bd;
border-radius: 50%;
margin-right: 0.5em;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: center center;
background-size: 50% 50%;
}
/* стили при наведении курсора на радио */
.custom-radio:not(:disabled):not(:checked)+label:hover::before {
border-color: #b3d7ff;
}
/* стили для активной радиокнопки (при нажатии на неё) */
.custom-radio:not(:disabled):active+label::before {
background-color: #b3d7ff;
border-color: #b3d7ff;
}
/* стили для радиокнопки, находящейся в фокусе */
.custom-radio:focus+label::before {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 0.2rem rgba(0, 123, 255, 0.25);
}
/* стили для радиокнопки, находящейся в фокусе и не находящейся в состоянии checked */
.custom-radio:focus:not(:checked)+label::before {
border-color: #80bdff;
}
/* стили для радиокнопки, находящейся в состоянии checked */
.custom-radio:checked+label::before {
border-color: #0b76ef;
background-color: #0b76ef;
background-image: url("data:image/svg+xml,%3csvg xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg' viewBox='-4 -4 8 8'%3e%3ccircle r='3' fill='%23fff'/%3e%3c/svg%3e");
}
/* стили для радиокнопки, находящейся в состоянии disabled */
.custom-radio:disabled+label::before {
background-color: #e9ecef;
}
</style>
<input class="custom-radio" name="color" type="radio" id="color-green" value="green">
<label for="color-green">Green</label>
Открыть пример
Ещё примеры по кастомизации checkbox и label
В этом разделе представлены следующие примеры:
- оформление чекбокса, когда input расположен в label
- оформление переключателя, когда input расположен в label
1. Стилизация checkbox, когда input расположен в label.
HTML разметка:
<label class="custom-checkbox"> <input type="checkbox" value="value-1"> <span>Indigo</span> </label>
CSS код:
/* для элемента input c type="checkbox" */
.custom-checkbox>input {
position: absolute;
z-index: -1;
opacity: 0;
}
/* для элемента label, связанного с .custom-checkbox */
.custom-checkbox>span {
display: inline-flex;
align-items: center;
user-select: none;
}
/* создание в label псевдоэлемента before со следующими стилями */
.custom-checkbox>span::before {
content: '';
display: inline-block;
width: 1em;
height: 1em;
flex-shrink: 0;
flex-grow: 0;
border: 1px solid #adb5bd;
border-radius: 0.25em;
margin-right: 0.5em;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: center center;
background-size: 50% 50%;
}
/* стили при наведении курсора на checkbox */
.custom-checkbox>input:not(:disabled):not(:checked)+span:hover::before {
border-color: #b3d7ff;
}
/* стили для активного чекбокса (при нажатии на него) */
.custom-checkbox>input:not(:disabled):active+span::before {
background-color: #b3d7ff;
border-color: #b3d7ff;
}
/* стили для чекбокса, находящегося в фокусе */
.custom-checkbox>input:focus+span::before {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 0.2rem rgba(0, 123, 255, 0.25);
}
/* стили для чекбокса, находящегося в фокусе и не находящегося в состоянии checked */
.custom-checkbox>input:focus:not(:checked)+span::before {
border-color: #80bdff;
}
/* стили для чекбокса, находящегося в состоянии checked */
.custom-checkbox>input:checked+span::before {
border-color: #0b76ef;
background-color: #0b76ef;
background-image: url("data:image/svg+xml,%3csvg xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg' viewBox='0 0 8 8'%3e%3cpath fill='%23fff' d='M6.564.75l-3.59 3.612-1.538-1.55L0 4.26 2.974 7.25 8 2.193z'/%3e%3c/svg%3e");
}
/* стили для чекбокса, находящегося в состоянии disabled */
.custom-checkbox>input:disabled+span::before {
background-color: #e9ecef;
}
Открыть пример
2. Стилизация radio, когда input расположен в label.
HTML разметка:
<label class="custom-radio"> <input type="radio" name="color" value="indigo"> <span>Indigo</span> </label>
CSS код:
/* для элемента input c type="radio" */
.custom-radio>input {
position: absolute;
z-index: -1;
opacity: 0;
}
/* для элемента label связанного с .custom-radio */
.custom-radio>span {
display: inline-flex;
align-items: center;
user-select: none;
}
/* создание в label псевдоэлемента before со следующими стилями */
.custom-radio>span::before {
content: '';
display: inline-block;
width: 1em;
height: 1em;
flex-shrink: 0;
flex-grow: 0;
border: 1px solid #adb5bd;
border-radius: 50%;
margin-right: 0.5em;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: center center;
background-size: 50% 50%;
}
/* стили при наведении курсора на радио */
.custom-radio>input:not(:disabled):not(:checked)+span:hover::before {
border-color: #b3d7ff;
}
/* стили для активной радиокнопки (при нажатии на неё) */
.custom-radio>input:not(:disabled):active+span::before {
background-color: #b3d7ff;
border-color: #b3d7ff;
}
/* стили для радиокнопки, находящейся в фокусе */
.custom-radio>input:focus+span::before {
box-shadow: 0 0 0 0.2rem rgba(0, 123, 255, 0.25);
}
/* стили для радиокнопки, находящейся в фокусе и не находящейся в состоянии checked */
.custom-radio>input:focus:not(:checked)+span::before {
border-color: #80bdff;
}
/* стили для радиокнопки, находящейся в состоянии checked */
.custom-radio>input:checked+span::before {
border-color: #0b76ef;
background-color: #0b76ef;
background-image: url("data:image/svg+xml,%3csvg xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg' viewBox='-4 -4 8 8'%3e%3ccircle r='3' fill='%23fff'/%3e%3c/svg%3e");
}
/* стили для радиокнопки, находящейся в состоянии disabled */
.custom-radio>input:disabled+span::before {
background-color: #e9ecef;
}
Открыть пример
Improve Article
Save Article
Improve Article
Save Article
In this article, we are going to discuss how to change the color of the radio button using the accent-color CSS property.
The accent-color property in CSS specifies the color of user interface elements/controls like checkboxes, radio buttons, range, and progress elements. As per this article, we are using this accent-color property to change the color of the radio button from a default color. The syntax and its property values are given below
Syntax:
accent-color : auto | color | initial | inherit;
Property values:
- auto: The browser will set the accent color for the control elements.
- color: It will specify the color for an accent color in RGB representation, hex representation, and also with the color name.
- initial: Sets the accent-color property to the default value.
- inherit: Inherits the property from the parent component.
Note: Depending on the browser the color set by auto property value varies.
Example 1: In the below code, we have created a radio button and specified the color of the radio button using the accent-color property.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
#specifyColor {
accent-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h3> Red colored radio button </h3>
<input type="radio" id="specifyColor"
name="radio1" value="GFG">
<label for="specifyColor">GFG</label>
</center>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Example 2: In this example program, we have used various kinds of accent-color properties by specifying the color in different forms like the name of color directly, using RGB color value, hex color code, etc. to change the color of radio buttons.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
input[type=radio]#Yellow {
accent-color: pink;
}
input[type=radio]#Green {
accent-color: rgb(0, 255, 0);
}
input[type=radio]#auto {
accent-color: auto;
}
input[type=radio]#Red {
accent-color: #FF0000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h3> Radio button color change </h3>
</center>
<input type="radio" id="Yellow" name="colors" value="Yellow">
<label for="Yellow">Yellow</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="Green" name="colors" value="Green">
<label for="Green">Green using RGB</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="auto" name="colors" value="auto">
<label for="auto">auto-color set by browser</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="Red" name="colors" value="Red">
<label for="Red">Red color using hex representation
</label><br>
</body>
</html>
Output:
I builded another fork of @klewis’ code sample to demonstrate some playing with pure css and gradients by using :before/:after pseudo elements and a hidden radio input button.
HTML:
sample radio buttons:
<div style="background:lightgrey;">
<span class="radio-item">
<input type="radio" id="ritema" name="ritem" class="true" value="ropt1" checked="checked">
<label for="ritema">True</label>
</span>
<span class="radio-item">
<input type="radio" id="ritemb" name="ritem" class="false" value="ropt2">
<label for="ritemb">False</label>
</span>
</div>
:
CSS:
.radio-item input[type='radio'] {
visibility: hidden;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
margin: 0 5px 0 5px;
padding: 0;
}
.radio-item input[type=radio]:before {
position: relative;
margin: 4px -25px -4px 0;
display: inline-block;
visibility: visible;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
border: 2px inset rgba(150,150,150,0.75);
background: radial-gradient(ellipse at top left, rgb(255,255,255) 0%, rgb(250,250,250) 5%, rgb(230,230,230) 95%, rgb(225,225,225) 100%);
content: "";
}
.radio-item input[type=radio]:checked:after {
position: relative;
top: 0;
left: 9px;
display: inline-block;
visibility: visible;
border-radius: 6px;
width: 12px;
height: 12px;
background: radial-gradient(ellipse at top left, rgb(245,255,200) 0%, rgb(225,250,100) 5%, rgb(75,175,0) 95%, rgb(25,100,0) 100%);
content: "";
}
.radio-item input[type=radio].true:checked:after {
background: radial-gradient(ellipse at top left, rgb(245,255,200) 0%, rgb(225,250,100) 5%, rgb(75,175,0) 95%, rgb(25,100,0) 100%);
}
.radio-item input[type=radio].false:checked:after {
background: radial-gradient(ellipse at top left, rgb(255,225,200) 0%, rgb(250,200,150) 5%, rgb(200,25,0) 95%, rgb(100,25,0) 100%);
}
.radio-item label {
display: inline-block;
height: 25px;
line-height: 25px;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
preview:
https://www.codeply.com/p/y47T4ylfib
I builded another fork of @klewis’ code sample to demonstrate some playing with pure css and gradients by using :before/:after pseudo elements and a hidden radio input button.
HTML:
sample radio buttons:
<div style="background:lightgrey;">
<span class="radio-item">
<input type="radio" id="ritema" name="ritem" class="true" value="ropt1" checked="checked">
<label for="ritema">True</label>
</span>
<span class="radio-item">
<input type="radio" id="ritemb" name="ritem" class="false" value="ropt2">
<label for="ritemb">False</label>
</span>
</div>
:
CSS:
.radio-item input[type='radio'] {
visibility: hidden;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
margin: 0 5px 0 5px;
padding: 0;
}
.radio-item input[type=radio]:before {
position: relative;
margin: 4px -25px -4px 0;
display: inline-block;
visibility: visible;
width: 20px;
height: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
border: 2px inset rgba(150,150,150,0.75);
background: radial-gradient(ellipse at top left, rgb(255,255,255) 0%, rgb(250,250,250) 5%, rgb(230,230,230) 95%, rgb(225,225,225) 100%);
content: "";
}
.radio-item input[type=radio]:checked:after {
position: relative;
top: 0;
left: 9px;
display: inline-block;
visibility: visible;
border-radius: 6px;
width: 12px;
height: 12px;
background: radial-gradient(ellipse at top left, rgb(245,255,200) 0%, rgb(225,250,100) 5%, rgb(75,175,0) 95%, rgb(25,100,0) 100%);
content: "";
}
.radio-item input[type=radio].true:checked:after {
background: radial-gradient(ellipse at top left, rgb(245,255,200) 0%, rgb(225,250,100) 5%, rgb(75,175,0) 95%, rgb(25,100,0) 100%);
}
.radio-item input[type=radio].false:checked:after {
background: radial-gradient(ellipse at top left, rgb(255,225,200) 0%, rgb(250,200,150) 5%, rgb(200,25,0) 95%, rgb(100,25,0) 100%);
}
.radio-item label {
display: inline-block;
height: 25px;
line-height: 25px;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
preview:
https://www.codeply.com/p/y47T4ylfib
There are two approaches to styling checkboxes and radio buttons with CSS. For a simple way to match the colour of the standard controls to your site’s design, you can use the accent-color property. For complete control over the design of checkboxes and radio buttons, you can use the appearance property to disable their standard styling and implement your own.
Setting an accent colour
The accent-color property sets the colour used by checkboxes and radio buttons, as well as range fields and progress indicators. The accent colour is inherited, so only needs to be set at the root of the document:
|
|
The accent-color property is currently supported by Firefox, Chrome, and Edge, and will be supported in the next version of Safari. These checkboxes and radio buttons are styled using accent-color:
A fully custom design
The design of checkboxes and radio buttons styled using the accent-color property varies between browsers and operating systems, and may not work well with the rest of your site’s design. As an alternative, you can use the appearance property to disable the standard styling and implement a fully custom design, as these checkboxes and radio buttons do:
Creating the boxes
Firstly we style the default state of the controls (enabled, but not active, focused, or checked):
|
|
Lines 2 and 3 disable the standard styling by setting the appearance property to none (the -webkit-appearance property is needed for Safari).
Lines 4 and 5 set the size of the controls. While we would usually use relative units to scale user interface controls based on the text size, for checkboxes and radio buttons this can lead to controls that are too small or excessively large, so we instead use a reasonable fixed size. Note that we are assuming the use of border box sizing, so these dimensions include the border width.
Lines 6 and 7 align the controls with their label text. The vertical-align property isn’t precise enough on its own, so we combine it with a margin on the top of half the line height (here 1.5em) minus half the widget height, which centres the controls within the line. We also add some margin on the right to create more space between the control and its label.
Lines 8, 9, and 14 set the borders of the controls. Checkboxes are given slightly rounded corners, while radio buttons are made circular. Line 10 sets the background, including the positioning of the images that we will add later.
Active and focused states
Next we style the active and focused states, which are essential for visitors who use the keyboard to interact with sites:
|
|
The change in border colour clearly indicates the active or focused element, so we can disable the default outline. Note that we add :not(:disabled) to the :active selector as otherwise disabled controls would show as active while the mouse is held down on them.
Disabled state
Next we style the disabled state by greying out the controls:
|
|
Checked state
Finally we style the checked state using background images:
|
|
You can download checkbox.svg (148 bytes) and radio.svg (137 bytes) for use on your own site.
The finished code
Combining all of the above leads to the finished code:
|
|
Sharing styling with other input controls
Other input controls usually share elements of their design — such as borders and active, focus, and disabled styling — with checkboxes and radio buttons:
In this case, the shared styling can be set for all controls (lines 1 to 18), reducing the amount of additional styling needed for checkboxes and radio buttons (lines 20 to 39):
|
|

Меня недавно попросили рассказать, как поменять фон у радиокнопки через CSS. Задача это не тривиальная, поскольку обычными путями фон радиокнопки не изменить. Однако, есть обходные пути, о которых я в этой статье и поведаю.
Привожу HTML-код:
<input class="r_button" type="radio" name="name" id="r_1" />
<label for="r_1">Описание радиокнопки</label>
<input class="r_button" type="radio" name="name" id="r_2" />
<label for="r_2">Описание радиокнопки</label>
Отмечу важную вещь, что обязательно должен быть атрибут id у радиокнопки, плюс for на этот id у тега label. Без этого ничего работать не будет.
И CSS-код:
.r_button {
display: none;
}
.r_button + label {
background: url("radio.png") no-repeat scroll 0 0;
cursor: pointer;
padding-left: 25px;
}
.r_button:checked + label {
background: url("radio_active.png") no-repeat scroll 0 0;
}
Сразу скажу, что «+» означает, что стиль должен быть применён к label, следующему после .r_button.
Теперь поясню, как это работает. Мы скрываем вообще радиокнопку, то есть она не показывается. Зато у label мы ставим поле слева, плюс слева ставим фон неактивной радиокнопки. Однако, мы с Вами поставили for у label. Следовательно, по клику на метке, у нас радиокнопка включается. Следовательно, срабатывает селектор «.r_button:checked + label«, который меняет у нас фон label.
Как только идёт переключение на другую кнопку, сразу возвращаемся к неактивному фону.
Вот таким хитрым образом можно поменять фон у радиокнопки через CSS, а также сделать свой вид «активности«.
Отмечу, что данный способ работает во всех современных браузерах, за исключением IE8 и ниже. Для них придётся писать отдельный файл стилей, в которых оставить стандартные радиокнопки.
-
Создано 13.03.2013 04:34:00
-
Михаил Русаков
Копирование материалов разрешается только с указанием автора (Михаил Русаков) и индексируемой прямой ссылкой на сайт (http://myrusakov.ru)!
Добавляйтесь ко мне в друзья ВКонтакте: http://vk.com/myrusakov.
Если Вы хотите дать оценку мне и моей работе, то напишите её в моей группе: http://vk.com/rusakovmy.
Если Вы не хотите пропустить новые материалы на сайте,
то Вы можете подписаться на обновления: Подписаться на обновления
Если у Вас остались какие-либо вопросы, либо у Вас есть желание высказаться по поводу этой статьи, то Вы можете оставить свой комментарий внизу страницы.
Если Вам понравился сайт, то разместите ссылку на него (у себя на сайте, на форуме, в контакте):
-
Кнопка:
Она выглядит вот так:
-
Текстовая ссылка:
Она выглядит вот так: Как создать свой сайт
- BB-код ссылки для форумов (например, можете поставить её в подписи):
Несколько примеров изменения вида радио кнопок на чистом CSS. Единственное неудобство метода в том, что приходится указывать уникальные id.
1
Стандартные элементы
Понадобятся всего два изображения, которые можно объединить в спрайт. Состояния заблокированного элемента и при наведении можно сделать CSS фильтрами.
<div class="form_radio">
<input id="radio-1" type="radio" name="radio" value="1" checked>
<label for="radio-1">Radio button 1</label>
</div>
<div class="form_radio">
<input id="radio-2" type="radio" name="radio" value="2">
<label for="radio-2">Radio button 2</label>
</div>
<div class="form_radio">
<input id="radio-3" type="radio" name="radio" value="3">
<label for="radio-3">Radio button 3</label>
</div>
<div class="form_radio">
<input id="radio-4" type="radio" name="radio" value="4" disabled>
<label for="radio-4">Radio disabled</label>
</div>HTML
.form_radio {
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
.form_radio input[type=radio] {
display: none;
}
.form_radio label {
display: inline-block;
cursor: pointer;
position: relative;
padding-left: 25px;
margin-right: 0;
line-height: 18px;
user-select: none;
}
.form_radio label:before {
content: "";
display: inline-block;
width: 17px;
height: 18px;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
bottom: 1px;
background: url(/img/radio-1.png) 0 0 no-repeat;
}
/* Checked */
.form_radio input[type=radio]:checked + label:before {
background: url(/img/radio-2.png) 0 0 no-repeat;
}
/* Hover */
.form_radio label:hover:before {
filter: brightness(120%);
}
/* Disabled */
.form_radio input[type=radio]:disabled + label:before {
filter: grayscale(100%);
}CSS
2
Radio в виде кнопок
<div class="form_radio_btn">
<input id="radio-1" type="radio" name="radio" value="1" checked>
<label for="radio-1">Radio button 1</label>
</div>
<div class="form_radio_btn">
<input id="radio-2" type="radio" name="radio" value="2">
<label for="radio-2">Radio button 2</label>
</div>
<div class="form_radio_btn">
<input id="radio-3" type="radio" name="radio" value="3">
<label for="radio-3">Radio button 3</label>
</div>
<div class="form_radio_btn">
<input id="radio-4" type="radio" name="radio" value="4" disabled>
<label for="radio-4">Disabled</label>
</div>HTML
.form_radio_btn {
display: inline-block;
margin-right: 10px;
}
.form_radio_btn input[type=radio] {
display: none;
}
.form_radio_btn label {
display: inline-block;
cursor: pointer;
padding: 0px 15px;
line-height: 34px;
border: 1px solid #999;
border-radius: 6px;
user-select: none;
}
/* Checked */
.form_radio_btn input[type=radio]:checked + label {
background: #ffe0a6;
}
/* Hover */
.form_radio_btn label:hover {
color: #666;
}
/* Disabled */
.form_radio_btn input[type=radio]:disabled + label {
background: #efefef;
color: #666;
}CSS
3
Группа кнопок
<div class="form_radio_group">
<div class="form_radio_group-item">
<input id="radio-1" type="radio" name="radio" value="1" checked>
<label for="radio-1">Radio button 1</label>
</div>
<div class="form_radio_group-item">
<input id="radio-2" type="radio" name="radio" value="2">
<label for="radio-2">Radio button 2</label>
</div>
<div class="form_radio_group-item">
<input id="radio-3" type="radio" name="radio" value="3">
<label for="radio-3">Radio button 3</label>
</div>
<div class="form_radio_group-item">
<input id="radio-4" type="radio" name="radio" value="4" disabled>
<label for="radio-4">Disabled</label>
</div>
</div>HTML
.form_radio_group {
display: inline-block;
overflow: hidden;
}
.form_radio_group-item {
display: inline-block;
float: left;
}
.form_radio_group input[type=radio] {
display: none;
}
.form_radio_group label {
display: inline-block;
cursor: pointer;
padding: 0px 15px;
line-height: 34px;
border: 1px solid #999;
border-right: none;
user-select: none;
}
.form_radio_group .form_radio_group-item:first-child label {
border-radius: 6px 0 0 6px;
}
.form_radio_group .form_radio_group-item:last-child label {
border-radius: 0 6px 6px 0;
border-right: 1px solid #999;
}
/* Checked */
.form_radio_group input[type=radio]:checked + label {
background: #ffe0a6;
}
/* Hover */
.form_radio_group label:hover {
color: #666;
}
/* Disabled */
.form_radio_group input[type=radio]:disabled + label {
background: #efefef;
color: #666;
}CSS
4
Переключатель
<div class="form_toggle">
<div class="form_toggle-item item-1">
<input id="fid-1" type="radio" name="radio" value="off" checked>
<label for="fid-1">OFF</label>
</div>
<div class="form_toggle-item item-2">
<input id="fid-2" type="radio" name="radio" value="on">
<label for="fid-2">ON</label>
</div>
</div>
HTML
.form_toggle {
display: inline-block;
overflow: hidden;
}
.form_toggle-item {
float: left;
display: inline-block;
}
.form_toggle-item input[type=radio] {
display: none;
}
.form_toggle-item label {
display: inline-block;
padding: 0px 15px;
line-height: 34px;
border: 1px solid #999;
border-right: none;
cursor: pointer;
user-select: none;
}
.form_toggle .item-1 label {
border-radius: 6px 0 0 6px;
}
.form_toggle .item-2 label {
border-radius: 0 6px 6px 0;
border-right: 1px solid #999;
}
/* Checked */
.form_toggle .item-1 input[type=radio]:checked + label {
background: #ffc5c5;
}
.form_toggle .item-2 input[type=radio]:checked + label {
background: #bbffbb;
}CSS